Abstract
Objective:
The objective of this study is to investigate the efficacy and safety of early ultrafiltration in patients with acute decompensated heart failure.
Methods:
A systematic search was conducted on PubMed, Cochrane Library, and EMbase databases from inception to April 2023 to identify randomized controlled trials that compared the efficacy and safety of early ultrafiltration and conventional diuretics in patients with acute decompensated heart failure. Two investigators independently screened all eligible studies and extracted relevant data. The primary outcomes of interest were changes in body weight and creatinine levels, as well as the rate of readmission and mortality within 30 days. Meta-analysis was conducted using RevMan 5.4 software.
Results:
This meta-analysis included eight studies and found that early ultrafiltration was effective in reducing body weight in patients with acute decompensated heart failure (RR = 1.45, 95% CI: 0.54–2.35, P = 0.002), but it also increased serum creatinine (RR = 0.1, 95% CI: 0.03–0.17, P = 0.003). However, it did not reduce the 30-day rehospitalization rate or mortality rate (30-day rehospitalization rate: RR = 0.84, 95% CI: 0.62–1.14, P = 0.28; Mortality: RR = 0.90, 95% CI: 0.57–1.44, P = 0.67).
Conclusion:
Although early ultrafiltration is more effective in reducing body weight in patients with acute decompensated heart failure, it is associated with an increase in serum creatinine levels and does not reduce the rate of readmission or mortality within 30 days.
Systematic Review Registration:
identifier: CRD42023416152.
1. Introduction
Heart failure (HF) is a critical aspect of cardiovascular disease, with device therapy, including ultrafiltration therapy, emerging as a viable option in recent years. Ultrafiltration is a treatment method that involves the passage of water and small to medium weight solutes through a semi-permeable membrane, thereby reducing the volume load (1). Both Chinese and European guidelines recommend ultrafiltration for heart failure patients with significant volume overload and poor response to conventional diuretics to quickly relieve symptoms of heart failure and fluid retention (2). The ACC/AHA guidelines are more active in recommending ultrafiltration therapy and do not emphasize diuretic resistance (3). They also consider significant fluid retention as an indication of ultrafiltration. The selection of the optimal timing for ultrafiltration is still a topic of discussion. This study aims to examine the effectiveness and safety of early ultrafiltration for patients with acute decompensated heart failure through a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Inclusion and exclusion criteria
2.1.1. Study types
Randomized controlled trials.
2.1.2. Subjects
This study included patients of any race, nationality, gender, and stage of disease who had been clinically diagnosed with acute decompensated heart failure.
2.1.3. Interventions
The study compared the effectiveness of two treatment methods: early ultrafiltration and traditional diuretics.
2.1.4. Outcome measures
The primary outcome measures were changes in body weight and creatinine, rates of rehospitalization within 30 days, and mortality.
2.1.5. Exclusion criteria
(1) ultrafiltration therapy was not administered within 24 h after admission; (2) animal experiments, case reports and repeated published studies; (3) studies with incomplete or unextractable data; (4) non-English literature.
2.2. Literature search
A systematic search was conducted on PubMed, Cochrane Library, and EMbase databases using the following search terms: ((cardi* or heart* or myocard*) and (fail* or incompet* or insufficien* or decomp*)) and (Ultrafiltration or ultrafiltration or UF). The search was limited to the period from the inception of the databases to April 2023.
2.3. Literature screening and data extraction
The literature was screened and data was extracted and cross-checked by two independent researchers. Any disagreements were resolved through discussion. The screening process involved reading the title first and then excluding any obviously irrelevant literature. After this, the full text of remaining articles was read to determine if they were relevant. In cases where additional information was needed, the original authors were contacted by mail or telephone. The extracted data included the first author, year of publication, country, number of cases, sex, age, comorbidities, changes in body weight and creatinine, rate of readmission within 30 days, and mortality.
2.4. Assessment of the risk of bias of the included studies
The included studies were evaluated for risk of bias by two independent researchers and their results were cross-checked. The Cochrane Risk of Bias tool was used for this assessment.
2.5. Statistical analysis
Meta-analysis was performed using Rev Man 5.4 software. RR was used as the effect index for count data, while MD was used as the effect index for measurement data. The point estimate and 95% CI were reported for each effect size. Heterogeneity among the included studies was assessed using a χ2 test (test level α = 0.1) and quantitatively determined by combining with I2. After excluding the influence of obvious clinical heterogeneity, a random-effects model was used for the meta-analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Literature screening process and results
A total of 894 relevant literatures were retrieved and underwent a layer-by-layer screening process. Ultimately, 8 studies (4–11) were included. The literature screening process and results are illustrated in Figure 1.
Figure 1
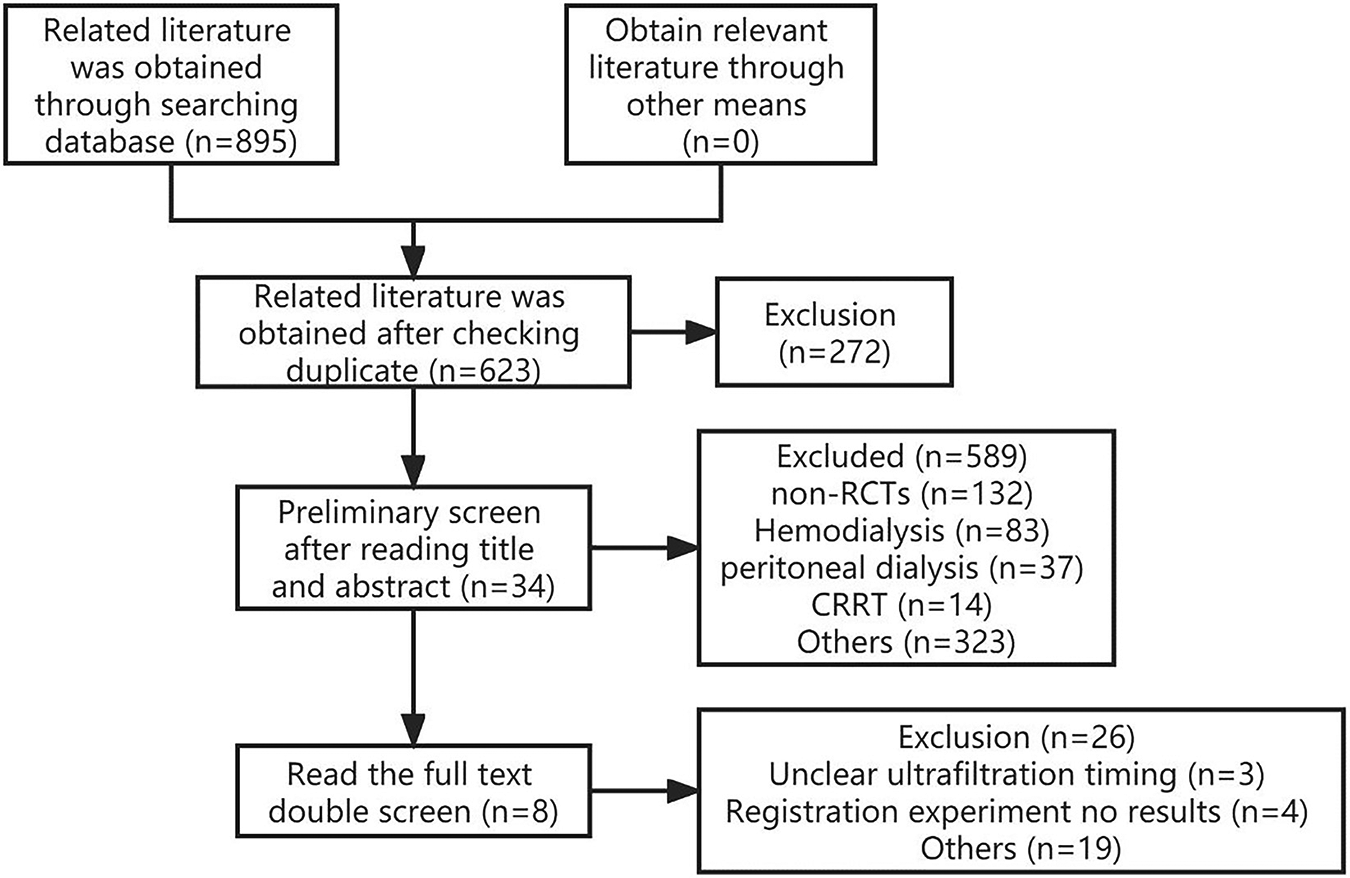
Literature screening process and results.
3.2. Basic characteristics of included studies and results of bias risk assessment
The basic characteristics of the included studies are shown in Table 1, and the risk of bias assessment results of the included studies are shown in Figure 2.
Table 1
| Study | Country | Cases | Male % | Age (year) | Hypertension % | DM % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rogers et al. (4) | USA | 19 | 78/60 | 64 ± 15/54 ± 16 | 78/40 | 78/50 |
| Costanzo et al. (5) | USA | 221 | 69.1/73 | 67 ± 13/67 ± 13 | 88.2/83 | 61.8/64 |
| Marenzi et al. (6) | Italy | 56 | 83/81 | 73 ± 9/75 ± 8 | 66/48 | 45/59 |
| Giglioli et al. (7) | Italy | 30 | 87/87 | 72.4 ± 14.1/65.8 ± 18.4 | 20/60 | 40/60 |
| Hu et al. (8) | China | 100 | 55/55 | 70.6 ± 10.44/73.52 ± 9.83 | 80/80 | 65/63.3 |
| Hanna et al. (9) | USA | 36 | 84.2/76 | 60 ± 9.1/59 ± 15.5 | 42.1/52.9 | 36.8/29.4 |
| Bart et al. (10) | USA | 188 | 72/78 | 66 (57–78)/69 (61–78) | – | 67/65 |
| Costanzo et al. (11) | USA | 200 | 70/68 | 62 ± 15/63 ± 14 | 74/74 | 50/49 |
Basic characteristics of the included studies.
Figure 2
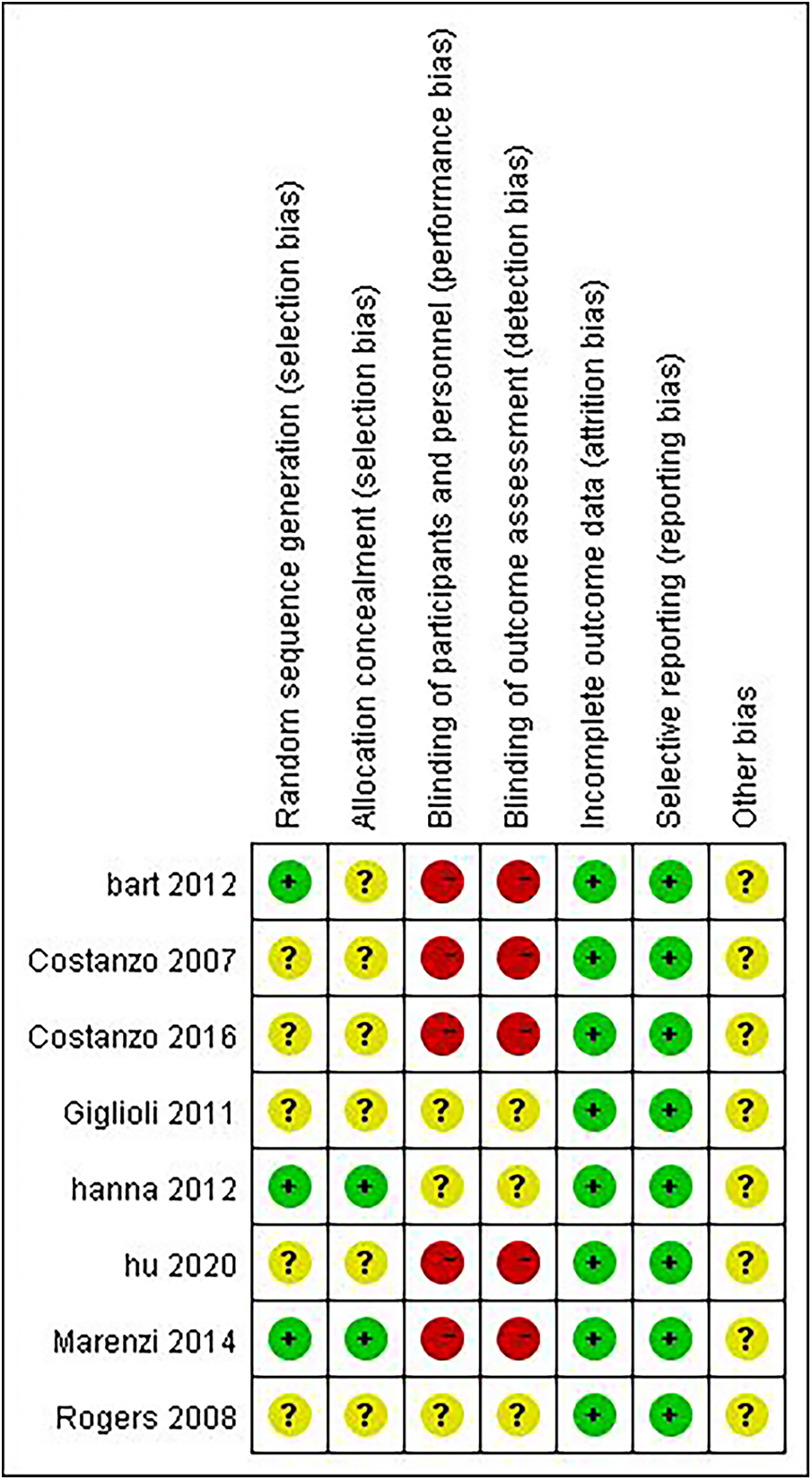
Results of bias risk assessment of the included studies.
3.3. Results of meta-analysis
Results of meta-analysis are presented in Table 2 and Figures 3–6. This meta-analysis found that early ultrafiltration was effective in reducing body weight in patients with acute decompensated heart failure (RR = 1.45, 95% CI: 0.54–2.35, P = 0.002), but it also increased serum creatinine (RR = 0.1, 95% CI: 0.03–0.17, P = 0.003). However, it did not reduce the 30-day rehospitalization rate or mortality rate (30-day rehospitalization rate: RR = 0.84, 95% CI: 0.62–1.14, P = 0.28; Mortality: RR = 0.90, 95% CI: 0.57–1.44, P = 0.67).
Table 2
| Name | Statistical method | Effect measure | Analysis model | Mean 1 | SD 1 | Total 1 | Mean 2 | SD 2 | Total 2 | Effect Estimate | CI Start | CI End | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UF VS UC | |||||||||||||
| Body weight | IV | Mean difference | Random | 251 | 277 | 1.445983 | 0.538299 | 2.353666 | 100 | ||||
| Bartet al. (10) | 5.67 | 4.84 | 92 | 5.45 | 6.46 | 94 | 0.22 | −1.41816 | 1.858159 | 20.7398 | |||
| Costanzo et al. (11) | 5 | 3.16 | 83 | 3.1 | 3.51 | 84 | 1.9 | 0.887292 | 2.912708 | 35.59658 | |||
| Hu et al. (8) | 2.94 | 3.76 | 40 | 0.64 | 0.91 | 60 | 2.3 | 1.112253 | 3.487747 | 30.518 | |||
| Marenzi et al. (6) | 7 | 12.5 | 27 | 8 | 17 | 29 | −1 | −8.779 | 6.778997 | 1.333117 | |||
| Rogers et al. (4) | 2.2 | 2.6 | 9 | 1.9 | 2.7 | 10 | 0.3 | −2.08449 | 2.684489 | 11.8125 | |||
| Creatinine | IV | Mean difference | Fixed | 378 | 407 | 0.101736 | 0.033457 | 0.170015 | 100 | ||||
| Bart et al. (10) | 0.23 | 0.44 | 92 | −0.04 | 0.35 | 94 | 0.27 | 0.155589 | 0.384411 | 35.61537 | |||
| Costanzo et al. (11) | 0.1 | 0.42 | 69 | 0.07 | 0.35 | 75 | 0.03 | −0.09687 | 0.156867 | 28.96539 | |||
| Costanzo et al. (5) | 0.13 | 0.88 | 107 | 0.05 | 0.3 | 107 | 0.08 | −0.09616 | 0.256163 | 15.02268 | |||
| Giglioli et al. (7) | −0.55 | 0.75 | 15 | 0.07 | 0.63 | 15 | −0.62 | −1.11568 | −0.12432 | 1.897448 | |||
| Hanna et al. (9) | 0.2 | 0.75 | 19 | 0 | 0.75 | 17 | 0.2 | −0.29075 | 0.690749 | 1.935779 | |||
| Hu et al. (8) | −0.01 | 0.92 | 40 | −0.02 | 0.9 | 60 | 0.01 | −0.35489 | 0.37489 | 3.501465 | |||
| Marenzi et al. (6) | 0.1 | 0.66 | 27 | 0 | 0.7 | 29 | 0.1 | −0.25621 | 0.456206 | 3.674272 | |||
| Rogers et al. (4) | −0.01 | 0.31 | 9 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 10 | −0.12 | −0.34285 | 0.102849 | 9.387598 | |||
| Readmission | MH | Risk ratio | Random | 369 | 393 | 0.844839 | 0.62359 | 1.144588 | 100 | ||||
| Bart et al. (10) | 0 | 0 | 90 | 0 | 0 | 93 | 0.990278 | 0.604827 | 1.621374 | 37.93041 | |||
| Costanzo et al. (11) | 0 | 0 | 88 | 0 | 0 | 86 | 0.895833 | 0.41801 | 1.919853 | 15.86952 | |||
| Costanzo et al. (5) | 0 | 0 | 105 | 0 | 0 | 108 | 0.467532 | 0.232735 | 0.939209 | 18.94885 | |||
| Hanna et al. (9) | 0 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 0 | 17 | 1.192982 | 0.519144 | 2.741451 | 13.31923 | |||
| Hu et al. (8) | 0 | 0 | 40 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 0.875 | 0.37702 | 2.03073 | 13.00796 | |||
| Marenzi et al. (6) | 0 | 0 | 27 | 0 | 0 | 29 | 0.357143 | 0.015169 | 8.408812 | 0.92403 | |||
| Mortality | MH | Risk ratio | Random | 290 | 311 | 0.904188 | 0.569691 | 1.435088 | 100 | ||||
| Bart et al. (10) | 0 | 0 | 94 | 0 | 0 | 94 | 1.230769 | 0.627477 | 2.414101 | 47.01773 | |||
| Costanzo et al. (5) | 0 | 0 | 110 | 0 | 0 | 111 | 0.201802 | 0.009799 | 4.155886 | 2.332004 | |||
| Hanna et al. (9) | 0 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 0 | 17 | 0.894737 | 0.263702 | 3.035833 | 14.29688 | |||
| Hu et al. (8) | 0 | 0 | 40 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 0.495935 | 0.020706 | 11.87848 | 2.115471 | |||
| Marenzi et al. (6) | 0 | 0 | 27 | 0 | 0 | 29 | 0.683502 | 0.310368 | 1.505227 | 34.23791 | |||
Changes in body weight, changes in creatinine, readmission rates within 30 days and mortality.
Figure 3
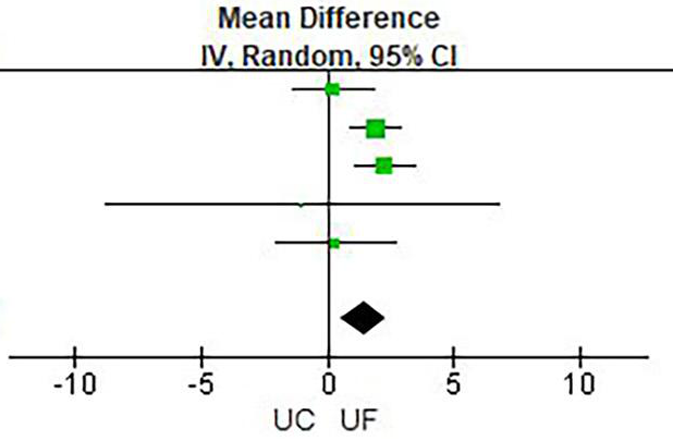
Weight change.
Figure 4
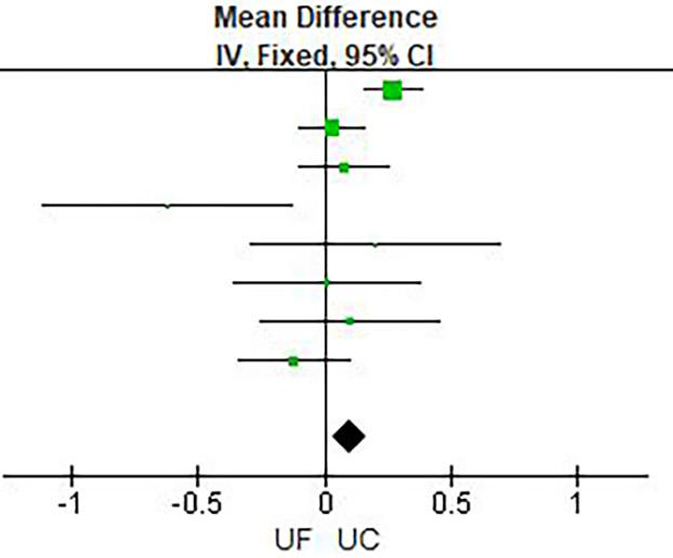
Creatinine change.
Figure 5
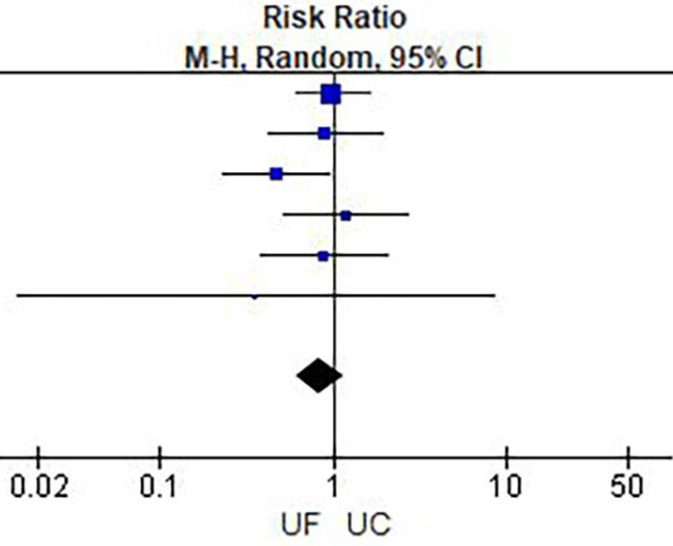
Rehospitalization rate within 30 days.
Figure 6
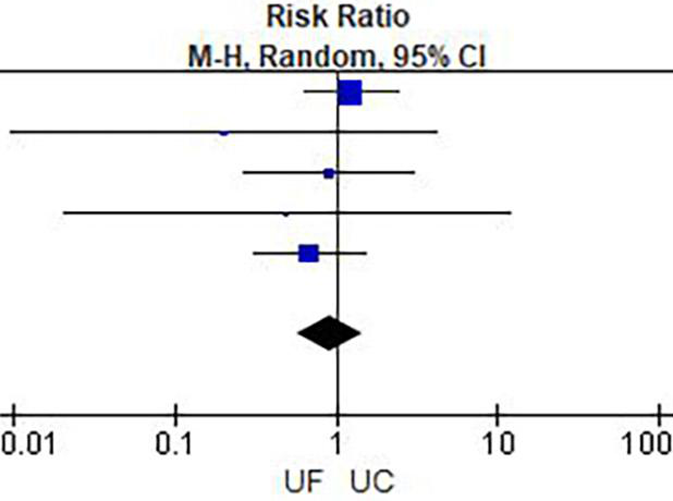
Mortality.
4. Discussion
The study revealed that early ultrafiltration was more effective in reducing body weight in patients with acute decompensated heart failure. However, it caused an increase in creatinine and did not reduce the rate of readmission or mortality within 30 days.
It should be noted that, diuretics have a poor dose-effect relationship and cannot accurately predict urine volume. Many clinical trials have shown that ultrafiltration therapy is safe and effective (12). Ultrafiltration therapy has distinct advantages in managing fluid overload. It facilitates the removal of body fluids, excretes a higher amount of total sodium, and has favorable hemodynamic effects. Additionally, this therapy does not cause electrolyte disturbances or activate the neuroendocrine system. Moreover, it can restore the diuretic effect in some patients who have not responded to other diuretic treatments (13). Extracorporeal ultrafiltration can be utilized for mechanical dehydration, with the amount and speed of dehydration being determined based on the patient’s fluid load. Typically, the initial blood pump flow during treatment is set between 20 and 30 ml/min. It is important to note that a higher flow rate can increase the cardiac load and should not exceed 50 ml/min. The ultrafiltration speed is usually set at 200 to 300 ml/h, with a maximum limit of 500 ml/h. This speed can be adjusted according to the patient’s treatment response and vital signs. It is generally recommended that the total amount of ultrafiltration should not exceed 5,000 ml within a 24-h period. However, if the patient’s blood excitation dynamics are stable, the amount of ultrafiltration fluid can be increased based on the patient’s actual condition. However, ultrafiltration may lead to renal hypoperfusion, which can negatively impact renal function. Patarroyo et al. (14) demonstrated that while early ultrafiltration improved hemodynamics, it was linked to an increased risk of subsequent CRRT and higher in-hospital mortality rates. Other studies (15–17) have also indicated that worsening renal function in heart failure patients is associated with a poor prognosis.
According to the Heart Failure Registry study, it was found that out of 2,067 patients with heart failure, 21% of them developed diuretic resistance while undergoing treatment (18). Recent studies (19, 20) suggest starting ultrafiltration therapy early in patients with CHF, even before diuretic therapy becomes ineffective. This is particularly beneficial for patients with severe dyspnea symptoms of left heart failure, as ultrafiltration can effectively and regularly remove excess body fluid and improve symptoms rapidly (21), providing more reliable results than diuretics. Additionally, early use of ultrafiltration can buy time for further treatment. However, in cases of refractory heart failure or severe cardiorenal syndrome, ultrafiltration may not be effective as a “rescue” treatment. The RAPID-CHF test initiated ultrafiltration treatment within 24 h of admission for patients with acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF). The average volume of fluid removed through ultrafiltration in a 24-h period was 4,650 ml, compared to 2,838 ml in the diuretic group. This indicates that ultrafiltration was more effective than diuretic treatment in terms of fluid clearance (19). The UNLOAD study, which is the largest randomized controlled trial on ultrafiltration therapy for ADHF, divided 200 patients into an early ultrafiltration group and a routine diuresis group. The results showed that patients in the early ultrafiltration group experienced greater weight reduction, a lower rate of re-hospitalization within 90 days, similar relief of dyspnea compared to the routine diuresis group, and a lower incidence of hypokalemia (11). Previous meta-analyses (22) have compared ultrafiltration with diuresis in patients with heart failure and have shown that ultrafiltration is more effective in reducing volume load and rehospitalization rate, but it does not reduce the incidence of adverse events and mortality. This study’s innovation lies in the timing of early ultrafiltration, which aims to determine the efficacy and safety of this approach in patients with acute decompensated heart failure. This study has some limitations that should be considered. Firstly, the sample size of 8 studies included in this research was relatively small, which may have limited the power of the evidence provided. Secondly, there was heterogeneity among the results of the different studies included, which could be due to various confounding factors, such as differences in sample sizes.
Based on current evidence, early ultrafiltration appears to be more effective in reducing body weight in patients with acute decompensated heart failure. However, it is important to note that this treatment may increase serum creatinine levels and does not necessarily reduce the rate of readmission or mortality within 30 days. It is important to acknowledge that the conclusions drawn from the available studies are limited by both the quantity and quality of the research. As such, further high-quality studies are needed to verify these findings.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
SC and HW contributed equally to this paper. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Zhi-wei Yang, MD, for giving consultations about the work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1.
Ronco C Ricci Z Bellomo R Bedogni F . Extracorporeal ultrafiltration for the treatment of overhydration and congestive heart failure. Cardiology. (2001) 96:155–68. 10.1159/000047399
2.
Ponikowski P Voors A Anker S Bueno H Cleland J Coats A et al 2016 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Revista espanola de cardiologia (English ed). (2016) 69(12):1167. 10.1016/j.rec.2016.11.005
3.
Yancy C Jessup M Bozkurt B Butler J Casey D Drazner M et al 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American college of cardiology foundation/American heart association task force on practice guidelines. Circulation. (2013) 128(16):e240–27. 10.1161/CIR.0b013e31829e8776
4.
Rogers HL Marshall J Bock J Dowling TC Feller E Robinson S et al A randomized, controlled trial of the renal effects of ultrafiltration as compared to furosemide in patients with acute decompensated heart failure. J Card Fail. (2008) 14(1):1–5. 10.1016/j.cardfail.2007.09.007
5.
Costanzo MR Negoianu D Jaski BE Bart BA Heywood JT Anand IS et al Aquapheresis versus intravenous diuretics and hospitalizations for heart failure. JACC Heart Fail. (2016) 4(2):95–105. 10.1016/j.jchf.2015.08.005
6.
Marenzi G Muratori M Cosentino ER Rinaldi ER Donghi V Milazzo V et al Continuous ultrafiltration for congestive heart failure: the CUORE trial. J Card Fail. (2014) 20(5):378.e371–79.
7.
Giglioli C Landi D Cecchi E Chiostri M Gensini GF Valente S et al Effects of ULTRAfiltration vs. DIureticS on clinical, biohumoral and haemodynamic variables in patients with deCOmpensated heart failure: the ULTRADISCO study. Eur J Heart Fail. (2011) 13(3):337–46. 10.1093/eurjhf/hfq207
8.
Hu J Wan Q Zhang Y Zhou J Li M Jiang L et al Efficacy and safety of early ultrafiltration in patients with acute decompensated heart failure with volume overload: a prospective, randomized, controlled clinical trial. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2020) 20(1):447. 10.1186/s12872-020-01733-5
9.
Hanna MA Tang WH Teo BW O'Neill JO Weinstein DM Lau SM et al Extracorporeal ultrafiltration vs. conventional diuretic therapy in advanced decompensated heart failure. Congest Heart Fail. (2012) 18(1):54–63. 10.1111/j.1751-7133.2011.00231.x
10.
Bart BA Goldsmith SR Lee KL Givertz MM O'Connor CM Bull DA et al Ultrafiltration in decompensated heart failure with cardiorenal syndrome. N Engl J Med. (2012) 367(24):2296–304. 10.1056/NEJMoa1210357
11.
Costanzo MR Guglin ME Saltzberg MT Jessup ML Bart BA Teerlink JR et al Ultrafiltration versus intravenous diuretics for patients hospitalized for acute decompensated heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2007) 49(6):675–83. 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.07.073
12.
Teo L Lim C Neo C Teo L Ng S Chan L et al Ultrafiltration in patients with decompensated heart failure and diuretic resistance: an Asian centre's experience. Singapore Med J. (2016) 57(7):378–83. 10.11622/smedj.2016014
13.
Marenzi G Grazi S Giraldi F Lauri G Perego G Guazzi M et al Interrelation of humoral factors, hemodynamics, and fluid and salt metabolism in congestive heart failure: effects of extracorporeal ultrafiltration. Am J Med. (1993) 94(1):49–56. 10.1016/0002-9343(93)90119-A
14.
Patarroyo M Wehbe E Hanna M Taylor DO Starling RC Demirjian S et al Cardiorenal outcomes after slow continuous ultrafiltration therapy in refractory patients with advanced decompensated heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2012) 60(19):1906–12. 10.1016/j.jacc.2012.08.957
15.
Butler J Forman D Abraham W Gottlieb S Loh E Massie B et al Relationship between heart failure treatment and development of worsening renal function among hospitalized patients. Am Heart J. (2004) 147(2):331–8. 10.1016/j.ahj.2003.08.012
16.
Forman D Butler J Wang Y Abraham W O'Connor C Gottlieb S et al Incidence, predictors at admission, and impact of worsening renal function among patients hospitalized with heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2004) 43(1):61–7. 10.1016/j.jacc.2003.07.031
17.
Owan T Hodge D Herges R Jacobsen S Roger V Redfield M . Secular trends in renal dysfunction and outcomes in hospitalized heart failure patients. J Card Fail. (2006) 12(4):257–62. 10.1016/j.cardfail.2006.02.007
18.
Trullàs J Casado J Morales-Rull J Formiga F Conde-Martel A Quirós R et al Prevalence and outcome of diuretic resistance in heart failure. Intern Emerg Med. (2019) 14(4):529–37. 10.1007/s11739-018-02019-7
19.
Bart B Boyle A Bank A Anand I Olivari M Kraemer M et al Ultrafiltration versus usual care for hospitalized patients with heart failure: the Relief for Acutely Fluid-Overloaded Patients with Decompensated Congestive Heart Failure (RAPID-CHF) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2005) 46(11):2043–46. 10.1016/j.jacc.2005.05.098
20.
Costanzo M Saltzberg M Jessup M Teerlink J Sobotka P . Ultrafiltration is associated with fewer rehospitalizations than continuous diuretic infusion in patients with decompensated heart failure: results from UNLOAD. J Card Fail. (2010) 16(4):277–84. 10.1016/j.cardfail.2009.12.009
21.
Xiangli S Lan L Libiya Z Jun M Shubin J . Efficacy and safety of ultrafiltration in patients with heart failure: a single-center experience. Adv Ther. (2022) 39(10):4523–32. 10.1007/s12325-022-02227-w
22.
Wang M Zheng Y Jin H . Ultrafiltration for patients with acute decompensated heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). (2021) 100(50):e28029. 10.1097/MD.0000000000028029
Summary
Keywords
efficacy, safety, early ultrafiltration, acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF), meta-analysis
Citation
Chen S, Wang H and Ning B (2023) Efficacy and safety of early ultrafiltration in patients with acute decompensated heart failure: a meta-analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 10:1234092. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1234092
Received
03 June 2023
Accepted
19 September 2023
Published
18 October 2023
Volume
10 - 2023
Edited by
Filippo Valbusa, Sacro Cuore Don Calabria Hospital (IRCCS), Italy
Reviewed by
Vojko Kanic, Maribor University Medical Centre, Slovenia Takeshi Kitai, Kobe City Medical Center General Hospital, Japan
Updates
Copyright
© 2023 Chen, Wang and Ning.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Bin Ning fysyynb0301@163.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.