- The First Affiliated Hospital, Institute of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Center for Clinical Research in Diabetes, Hengyang Medical School, University of South China, Hengyang, Hunan, China
Vascular calcification (VC) is a pathological condition closely associated with a range of cardiovascular diseases, including atherosclerosis (AS), hypertension, vascular injury, and diabetic angiopathy. Programmed cell death, encompassing apoptosis, autophagy, pyroptosis and ferroptosis, plays a pivotal role in the progression of VC. These cellular processes are intricately regulated by multiple signaling pathways, such as the Wnt/β-catenin and NF-κB pathways, among others. A deeper understanding of the roles and underlying mechanisms of programmed cell death in VC could offer valuable insights for the development of innovative therapeutic strategies targeting cardiovascular diseases.
1 Definition, epidemiology, and treatment of VC
Vascular calcification (VC) is a pathological process characterized by the deposition and crystallization of calcium within the blood vessel walls, leading to vascular hardening and structural damage (1). This condition is frequently observed as a complication in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and chronic kidney disease (CKD), and is often associated with concurrent pathological processes such as chronic inflammation and collagen proliferation (2, 3). Pathological investigations have established that VC development is closely linked to inflammatory responses, tissue repair mechanisms, and metabolic dysregulation (4). In the context of atherosclerosis (AS), VC significantly influences plaque stability. While minimal calcification may predispose plaques to rupture, extensive calcification can enhance plaque rigidity and stability (5). Epidemiological evidence indicates that VC serves as an independent risk factor for cardiovascular events and mortality in adults. The prevalence of VC demonstrates an age-dependent increase, with additional risk factors including hypercholesterolemia, hypertension, obesity, smoking, physical inactivity, and genetic predisposition (6, 7). Current clinical management of VC encompasses pharmacological interventions, interventional procedures, and surgical approaches (8). Pharmacological treatments typically involve cholesterol-lowering agents, antihypertensive medications, diuretics, and calcium channel blockers. Interventional strategies primarily include balloon angioplasty and arterial bypass grafting (9). Surgical intervention is generally reserved for cases of severe VC resulting in significant vascular stenosis and ischemia (10). Complementary non-pharmacological interventions, including dietary modification, regular exercise, and smoking cessation, have been shown to alleviate symptoms and decelerate disease progression. Given the clinical significance of VC, elucidation of its underlying mechanisms is crucial for the development of novel therapeutic strategies to mitigate its progression and associated complications.
2 Cell types that participate in VC
The pathogenesis of VC involves multiple cellular components within the vascular wall, including vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), endothelial cells (ECs), and macrophages, each playing distinct roles in this pathological process. Under physiological conditions, VSMCs maintain a contractile phenotype characterized by significant plasticity. However, under pathological stimuli, these cells can undergo phenotypic transition into osteoblast-like cells, initiating calcium deposition within the cellular matrix and contributing to VC progression. Notably, VSMC apoptosis precedes calcification formation and intensifies with disease progression. The apoptotic bodies derived from VSMCs possess calcium-concentrating capabilities, further facilitating calcification (11). ECs contribute to VC through endothelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), acquiring multipotent differentiation capacity. Through activation of TGF-β and Wnt signaling pathways, these transformed ECs can differentiate into osteoblast-like cells. Under pathological conditions such as chronic inflammation and hyperglycemia, ECs release extracellular vesicle (EV) containing calcium ions and bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP2), which serve as nucleation sites for calcification initiation and progression (12).CKD elevated phosphate levels not only directly promote VC but also stimulate ECs to secrete tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase. This enzyme catalyzes the degradation of extracellular pyrophosphate into phosphate ions, thereby eliminating its natural vascular protective effect (1). Macrophages exhibit dual roles in VC pathogenesis, with their phenotypic polarization determining their functional impact. M1 macrophages significantly promote VC through the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines that enhance VSMCs osteogenic differentiation. Conversely, M2 macrophages exert inhibitory effects via anti-inflammatory factor secretion and phagocytic clearance of apoptotic cells. Furthermore, macrophages contribute to VC through multiple mechanisms: (1) secretion of various cytokines and osteogenic factors that promote vascular cell differentiation; (2) release of microvesicles (MVs) that serve as calcium phosphate nucleation sites; and (3) potential differentiation into osteoclast-like cells that may counteract VC development (13). The complex interplay between these cellular components and their phenotypic states underscores the multifaceted nature of VC pathogenesis. Elucidating the precise roles and regulatory mechanisms of these cellular participants is crucial for developing targeted therapeutic strategies against VC (Figure 1).
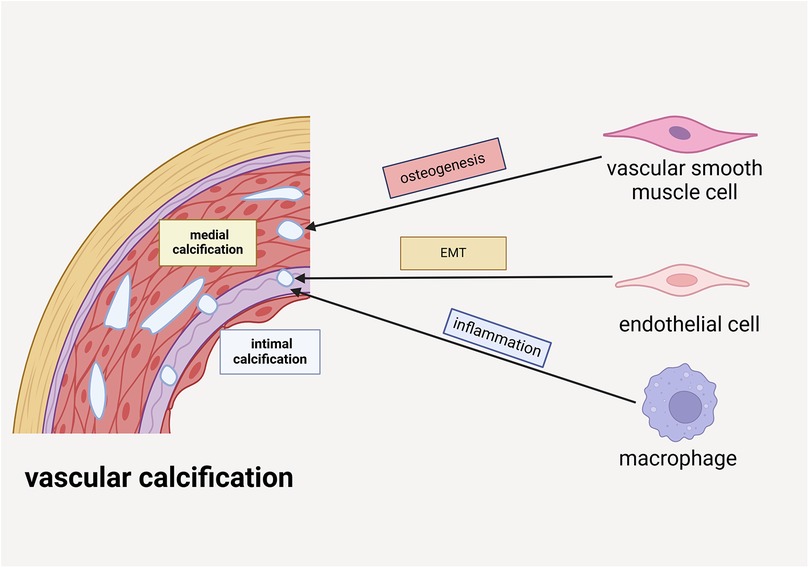
Figure 1. VSMCs, ECs and macrophages are involved in the formation of vascular calcification. VSMCs participate in medial calcification by undergoing osteogenic differentiation. ECs are implicated in intimal calcification through the process of EMT. Additionally, macrophages contribute to intimal calcification by driving inflammatory mechanisms.
3 Programmed cell death plays a critical role in VC
Emerging evidence has identified apoptosis, autophagy, and pyroptosis as the principal forms of programmed cell death implicated in the pathogenesis of VC, with VSMCs and ECs serving as the primary cellular mediators (14, 15). Among these, apoptosis represents the most extensively studied form of programmed cell death in VSMCs during VC development. Apoptotic cells release matrix vesicles enriched with calcium and phosphate, which serve as direct mediators of extracellular matrix mineralization (16). In contrast to the pro-calcific effects of apoptosis, autophagy acts as a protective mechanism against VC through its catabolic function. This process prevents the accumulation of senescent cells and calcifying vesicles, thereby exerting an inhibitory effect on vascular mineralization (17). Pyroptosis, characterized by its inflammatory nature, is triggered through death receptor activation and contributes to VC progression through the release of calcifying extracellular vesicles containing calcium and phosphate ions (18, 19). Recent investigations have revealed that ferroptosis, an iron-dependent form of cell death, promotes VC through mechanisms involving oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation. These processes induce cellular damage, leading to abnormal calcium and phosphate ion deposition within the vascular wall (20). Despite these advances, the precise molecular mechanisms underlying these distinct cell death pathways and their intricate interplay in VC pathogenesis remain to be fully elucidated, warranting further comprehensive investigation.
3.1 Apoptosis and vascular calcification
Apoptosis represents a fundamental physiological process of programmed cell death that plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and tissue integrity. This process is mediated through two distinct pathways: the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. The intrinsic pathway is initiated by intracellular apoptotic signals that induce mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization, leading to the release of cytochrome c into the cytosol. This event subsequently triggers a cascade of enzymatic reactions involving various cytokines and caspases, ultimately resulting in apoptotic cell death. In contrast, the extrinsic pathway is activated through the recognition of extracellular death signals by specific cell surface receptors, initiating a downstream signaling cascade. Both pathways converge on the activation of executioner caspases, particularly caspases-3 and -7, which mediate the characteristic morphological changes of apoptosis. These changes include cellular fragmentation into membrane-bound apoptotic bodies, which are subsequently recognized and phagocytosed by macrophages. Under pathological conditions, particularly in the context of vascular calcification, apoptotic bodies released by VSMCs have been shown to significantly promote the calcification process (19).
3.1.1 Inhibition of VSMCs apoptosis can effectively improve VC
Accumulating evidence demonstrates that pharmacological interventions targeting apoptosis can effectively attenuate VC. Traditional Chinese medicine compounds have shown promising anti-calcification effects through apoptosis modulation. Shenqi has been found to inhibit diabetic VC by suppressing the Hippo-YAP signaling pathway, thereby reducing VSMCs apoptosis and inflammation while providing vascular protection (21). Baicalin, a bioactive flavonoid extracted from Scutellaria baicalensis, significantly inhibits β-glycerophosphate-induced VSMCs apoptosis and osteogenic differentiation, consequently suppressing VC progression (22). Shuxuetong exhibits dual protective effects by inhibiting dexamethasone-induced oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis, consequently preventing both vascular calcification and osteoporosis (23). Dendrobium officinale polysaccharides demonstrate therapeutic potential through Heme Oxygenase-1 (HMOX-1) activation, effectively inhibiting high-phosphate-induced VSMCs apoptosis and inflammation, while significantly ameliorating VC in CKD mouse models (24). Ginsenoside Rb1, a major active component of Panax ginseng, exerts cardiovascular protective effects by inhibiting VSMCs apoptosis and VC under high-phosphate conditions through upregulation of the Gas6/pAkt pathway (25). Experimental studies have identified several cytokines with anti-apoptotic and anti-calcification properties. Growth Differentiation Factor 11 emerges as a potential therapeutic cytokine, effectively inhibiting both VSMCs apoptosis and osteogenic differentiation (26). Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 demonstrates protective effects by suppressing oxidative stress-induced apoptosis and VC through inhibition of the C/EBP Homologous Protein (CHOP) and caspase-12 signaling pathways (27). Protein-based interventions have also shown significant anti-calcification effects. Activation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) effectively reduces apoptosis and osteogenic gene expression in VSMCs under high-phosphate conditions, thereby inhibiting VSMCs osteogenesis and VC progression (28). Overexpression of sclerostin protein significantly reduces calcium deposition in VSMCs under calcifying conditions through apoptosis inhibition, representing a novel therapeutic direction for VC treatment (29). Polypeptide N-acetylgalactosamine transferase 3 exerts its anti-calcification effects by reducing apoptosis through inhibition of oxidative stress and the TNFR1/NF-κB signaling pathway in high-phosphate conditions (30).
3.1.2 Promoting apoptosis exacerbates VC
Emerging research has elucidated complex molecular mechanisms through which various biochemical factors promote VC via apoptosis induction in VSMCs. Calcium ions and aldosterone synergistically interact through the AIF-1/NF-κB signaling pathway, exacerbating both apoptosis and inflammation in VSMCs under uremic conditions, thereby accelerating VC progression (31). Parathyroid hormone contributes to VC pathogenesis by inducing oxidative stress through dual signaling pathways: the PERK-CHOP and IRE1-JNK cascades, which collectively promote VSMCs apoptosis and calcification (32). Beyond hormonal influences, various exogenous and endogenous substances have been implicated in VC progression through apoptosis modulation.Nano-Sized Hydroxyapatite has been shown to promote VSMCs apoptosis and osteogenic differentiation via activation of the JNK/c-JUN signaling pathway, thereby aggravating VC (33). 25-Hydroxycholesterol, an oxysterol derived from enzymatic cholesterol oxidation, plays a significant role in cellular signaling by promoting apoptosis and exacerbating VC through activation of the ATF4/CHOP signaling pathway (34). Metabolic factors also contribute significantly to VC pathogenesis. Glucose variability participates in VC development through oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis, potentially involving multiple molecular mediators including Wnt1, galectin-3, and BMP-2 in this process (35). Furthermore, saturated fatty acids have been demonstrated to promote VSMCs apoptosis in VC by suppressing SIRT6 expression, revealing a novel mechanism linking lipid metabolism to VC (36).
3.1.3 Endothelial cell apoptosis is involved in the process of VC
ECs serve as critical regulators of vascular homeostasis, maintaining essential functions including vasodilation regulation, thrombosis inhibition, and vascular wall integrity preservation. However, ECs apoptosis can compromise vascular barrier function, thereby exacerbating VC. Homocysteine, a sulfur-containing amino acid derived from methionine and cysteine metabolism, has been implicated in vascular pathology. Professor Liu's research team demonstrated that elevated homocysteine concentrations significantly enhance ECs apoptosis rates and promote VC progression (37). ECs-derived microvesicles, particularly exosomes, play a significant role in VC through intercellular communication. Research has revealed that exosomes released by ECs under hyperglycemic conditions can induce VSMCs calcification and senescence (38). Comparative studies have shown that CKD patients exhibit significantly higher levels of endothelial-derived EVs in circulation compared to healthy individuals, suggesting that ECs are the primary source of circulating EVs in CKD. These EVs exhibit dual pathological effects: promoting VSMCs calcification in vitro and inducing endothelial dysfunction, characterized by increased apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells and impaired angiogenesis. These effects are mediated through the upregulation of miR-223 levels within EVs (39). Furthermore, ECs exposed to the uremic toxin indoxyl sulfate release MVs with elevated calcium content. These calcium-rich MVs promote VC by modulating the expression of inflammatory genes in VSMCs, revealing another mechanism linking uremic toxins to vascular pathology (40).
3.1.4 MicroRNAs play important roles in VSMCs apoptosis and then participate in VC
Emerging evidence highlights the dual regulatory roles of microRNAs in VC through modulation of VSMC apoptosis. Certain microRNAs have been identified as promoters of VC by enhancing VSMCs apoptosis. Specifically, miR-155 overexpression exacerbates VC by inducing VSMCs apoptosis through the Akt-FOXO3a signaling pathway (41). Conversely, several microRNAs demonstrate protective effects against VC by suppressing apoptosis.MiR-146-5p exerts anti-apoptotic effects by targeting tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 and simultaneously inhibiting VSMCs osteogenic differentiation (42). Further research has identified additional microRNAs with protective roles in VC pathogenesis. MiR-140-5p overexpression significantly inhibits β-glycerophosphate-induced VSMC apoptosis by targeting Toll-like receptor 4 (43). In diabetic models, miR-128-3p activates the Wnt pathway while suppressing ISL1 expression, thereby inhibiting both VSMCs apoptosis and osteogenic differentiation (44). Notably, the therapeutic potential of exosomal microRNAs has also been demonstrated. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes containing miR-381-3p protect against VC by inhibiting VSMC apoptosis and osteogenesis through suppression of nuclear factor of activated T cells 5 (NFAT5) expression (45). These findings collectively underscore the pivotal role of cellular apoptosis in VC pathogenesis, with microRNAs serving as critical regulators that influence disease progression through modulation of apoptotic pathways in VSMCs.
3.2 Autophagy and vascular calcification
Autophagy is a fundamental cellular process that plays a vital role in maintaining normal cellular functions. It involves the encapsulation of damaged organelles and proteins by autophagosomes, which are subsequently degraded and recycled through lysosomal activity (46). Recent studies have demonstrated that autophagy is essential for preserving the normal contractile phenotype of VSMCs, thereby preventing their transition to a synthetic phenotype and reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases (47). In healthy cells, autophagy selectively removes damaged or redundant mitochondria, underscoring its critical role in maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis (48). Interestingly, during the calcification process of VSMCs, key autophagy-related genes such as Microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3-I (LC3-I), p62, and Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 3 (IGFBP3) are significantly upregulated, suggesting a direct involvement of autophagy in VC (49). However, when lysosomal function in VSMCs is impaired and autophagy is inhibited, the progression of VC is markedly exacerbated (50).
3.2.1 AMPK-mediated autophagy regulates VC
It is widely acknowledged that the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-related signaling pathway plays a pivotal role in regulating the initiation and progression of autophagy. Extensive research has demonstrated that AMPK-mediated activation of autophagy significantly contributes to the inhibition of VC (51). Metformin, a first-line medication for diabetes management, has been shown by several studies to reverse VSMC calcification through the AMPK-eNOS-NO and AMPK-RANKL signaling pathways, underscoring its potential in vascular protection (52, 53). Additionally, other therapeutic agents, such as policosanol, have been reported to suppress VC via the AMPK signaling pathway (54). Furthermore, melatonin has been found to enhance autophagy in VSMCs by upregulating the AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 signaling pathway, thereby effectively ameliorating β-glycerophosphate (β-GP)-induced calcification (55). Investigating the regulatory role of AMPK in autophagy may provide novel strategies for the prevention and treatment of VC in the future.
3.2.2 RNA participates in vascular calcification by regulating autophagy
RNA not only plays a regulatory role in apoptosis but is also actively involved in the modulation of autophagy. Professor Liu's discovered that the expression of long non-coding RNA (LncRNA) SNHG1 is significantly downregulated in VSMCs under high glucose conditions. Further investigations revealed that SNHG1 regulates autophagy by promoting the expression of Blhe40 mRNA, which in turn modulates atg10, thereby exerting a protective effect on VSMCs (56). In addition to LncRNAs, microRNAs also play a crucial role in the regulation of autophagy. For example, under high phosphorus conditions, miR-30b has been shown to regulate autophagy by targeting BECN1 (57). Overexpression of miR-30b enhances autophagy in VSMCs and inhibits VC through modulation of the mTOR signaling pathway (58). Similarly, under high glucose conditions, the expression of miR-32 in exosomes secreted by macrophages is significantly upregulated. miR-32 suppresses autophagy in VSMCs and promotes VC by targeting Mef2d (59).
3.2.3 Autophagy can improve VC by inhibiting apoptosis
Autophagy is essential for maintaining the normal function and phenotype of VSMCs by clearing damaged organelles and misfolded proteins (14). Currently, a growing number of studies indicate that certain drugs protect VSMCs by enhancing autophagy and reducing cell apoptosis. For instance, Iron citrate can inhibit calcium deposition in VSMCs under high phosphorus conditions through the GAS 6/AXL signaling pathway, promoting autophagy and suppressing cell apoptosis (60). Rosuvastatin effectively inhibits Platelet-Derived Growth Factor(PDGF)-induced VSMCs apoptosis by activating autophagy and suppressing P38 expression, thus providing effective protection for VSMCs (61). However, knocking down Heat Shock Protein Family B Member 1(HSPB1) in VSMCs reduces the expression of autophagy-related proteins, significantly enhancing cell apoptosis (62).
3.3 Pyroptosis and vascular calcification
Upon recognition of extracellular signals, cells assemble and activate inflammasomes, a process that serves as the initiating event of pyroptosis. Following activation, inflammasomes modify Cysteine Aspartate-Specific Protease-1 (CASPASE-1), which in turn cleaves Gasdermin D (GSDMD), a key pyroptosis effector protein. The cleaved GSDMD is then inserted into the cell membrane, forming pores that disrupt membrane integrity, ultimately resulting in cell rupture and death (19).
3.3.1 Inhibiting pyroptosis can effectively suppress VC
Pang et al. demonstrated that pyroptosis plays a significant role in VC, and its inhibition effectively attenuates calcification. Irisin, an exercise-induced hormone-like protein, is known to contribute to cardiovascular health protection. Their study revealed that irisin activates autophagy to suppress NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain-associated protein 3 (NLRP3)-mediated pyroptosis, thereby preventing VC (63). Additionally, VX-765, a selective caspase-1 inhibitor, has been shown to effectively suppress pyroptosis in VSMCs under high-phosphate conditions, significantly reducing aortic calcification (64). Calcium deposition in atherosclerotic plaques is also a component of VC, and pyroptosis exacerbates plaque destabilization and increases plaque area. Growing evidence suggests that inhibiting pyroptosis can effectively mitigate plaque formation. Zhang et al. demonstrated through animal experiments that polydatin reduces plaque burden and stabilizes plaques by activating autophagy and inhibiting NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis (65). Similarly, apigenin has been found to inhibit macrophage pyroptosis by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation and oxidative stress, thereby reducing atherosclerotic plaque area (66). Cui et al. reported that fucoxanthin suppresses pyroptosis by modulating the PI3K/AKT and TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathways, effectively attenuating atherosclerotic plaque formation (67). Salvianolic acid A has been shown to inhibit high-glucose-induced endothelial cell pyroptosis by downregulating the PKM2/PKR signaling pathway, thereby improving plaque stability in diabetic mice and providing vascular protection (68). Furthermore, exosomes secreted by cells can also effectively inhibit pyroptosis. For example, miR-199a-5p in macrophage-derived exosomes inhibits endothelial cell pyroptosis by downregulating SMARCA4 expression, leading to a significant reduction in atherosclerotic plaque area (69).
3.3.2 Promoting pyroptosis can exacerbate VC
Studies have demonstrated that the promotion of pyroptosis can significantly exacerbate calcium deposition in atherosclerotic plaques. Genetic material, particularly RNA, plays a pivotal role in driving pyroptosis and facilitating plaque formation. lncRNA Gaplinc has been shown to promote EC pyroptosis by binding to the transcription factor Sp1. Knockout of Gaplinc significantly inhibits EC pyroptosis induced by oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) (70). Similarly, Linc00657 enhances EC pyroptosis under ox-LDL conditions by sequestering miR-106b-5p, leading to upregulated expression of thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) and subsequent enlargement of plaque area (71). Emerging evidence indicates that proteins and enzymes also contribute to atherosclerotic plaque formation by promoting pyroptosis. For example, Cathepsin B facilitates the nuclear translocation of NF-κB, thereby inducing cell pyroptosis. Furthermore, tissue protease B has been shown to significantly accelerate plaque formation, while its inhibition results in a marked reduction in plaque burden (72). Additionally, the expression of IQ motif-containing GTPase-activating protein 1 (IQGAP1) is notably elevated in atherosclerotic plaques. IQGAP1 protein activates NLRP3-mediated EC pyroptosis by upregulating the cGAS-STING pathway, thereby exacerbating plaque formation (73).
3.4 Ferroptosis and vascular calcification
Ferroptosis, a distinct form of regulated cell death, is characterized by the accumulation of iron, Reactive Oxygen Species(ROS), and phospholipids containing unsaturated fatty acids. This process is driven by the peroxidation of intracellular phospholipids, which ultimately leads to cell death. Emerging evidence in recent years has increasingly demonstrated the significant involvement of ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases and its crucial role in immune surveillance mechanisms (5).
3.4.1 Inhibiting VSMCs ferroptosis effectively suppresses VC
Emerging studies have established a significant association between ferroptosis and VC. Notably, Ye et al. demonstrated that ferroptosis plays a crucial role in high phosphate- and calcium-induced VC. Their findings revealed that inhibition of key ferroptosis regulators, including solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11) and glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), markedly exacerbates VC progression (74). Palmitic acid, a saturated fatty acid ubiquitously present in animal and plant fats, has been implicated in cardiovascular risk when consumed in excess. Mechanistically, palmitic acid promotes VSMCs osteogenic differentiation and enhances periostin expression in the extracellular matrix. These changes are associated with downregulation of SLC7A11 and GPX4, thereby increasing VSMCs susceptibility to ferroptosis. Importantly, metformin has been shown to effectively counteract PA-induced VC and VSMCs ferroptosis (75). Furthermore, the cytokine fra-1 (FOSL1) exhibits upregulated expression in VSMCs under high phosphate and calcium conditions. Genetic knockout studies have demonstrated that FOSL1 deletion increases SLC7A11 expression, subsequently inhibiting reactive oxygen species generation and calcification processes, suggesting FOSL1's involvement in VC through ferroptosis regulation (20). The role of ferroptosis extends to AS development, where excessive iron promotes macrophage lipid uptake and foam cell formation. Experimental evidence indicates that ferroptosis contributes to atherosclerotic plaque formation through multiple mechanisms. For instance, cigarette tar has been shown to increase plaque area by activating NF-κB, which upregulates hepcidin while downregulating the ferroptosis regulators SLC7A11 and GPX4, ultimately promoting macrophage ferroptosis and plaque expansion (76) Similarly, hyperuricemia significantly downregulates SLC7A11 and GPX4 expression in plaques, promoting macrophage ferroptosis and aggregation, which contributes to increased plaque area (77). Additionally, Jak2VF-induced red blood cells have been found to promote ROS and lipid peroxidation accumulation, driving macrophage ferroptosis and expanding the necrotic core area of atherosclerotic plaques (78).
3.4.2 Inhibiting ECs ferroptosis can effectively suppresses VC
Iron overload plays a significant role in cardiovascular pathology by promoting ROS generation, which damages ECs and contributes to atherosclerotic plaque formation. N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac), a nine-carbon monosaccharide, has recently emerged as a critical factor in cardiovascular diseases. Mechanistically, Neu5Ac promotes ferroptosis and induces inflammatory damage in ECs through downregulation of the ferroptosis regulator solute carrier family 3 member 2 (SLC3A2), ultimately leading to increased plaque area and exacerbation of necrotic cores (79). Therapeutic interventions targeting EC ferroptosis have shown promising results in preventing plaque progression. Hydroxysafflor yellow A (HSYA), a valuable pharmaceutical compound extracted from Carthamus tinctorius L. (safflower) of the Asteraceae family, demonstrates significant anti-atherosclerotic effects. HSYA inhibits miR-429 expression, resulting in upregulation of SLC7A11 and subsequent suppression of ECs ferroptosis, effectively reducing atherosclerotic plaque formation (80). Another promising therapeutic agent is icariin, a bioactive flavonoid glycoside derived from Epimedium species. Icariin exerts cardiovascular protective effects by activating autophagy pathways, thereby inhibiting EC ferroptosis and reducing plaque area (81). Endocrine regulation also plays a crucial role in modulating EC ferroptosis. Estradiol has been shown to upregulate nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) and GPX4 expression, effectively inhibiting EC ferroptosis and improving lipid accumulation in atherosclerotic plaques in menopausal mouse models (82). Furthermore, Hu et al. demonstrated that vitamin D receptor overexpression protects against atherosclerosis by inhibiting EC ferroptosis through AMPK signaling pathway, resulting in reduced plaque area and lipid deposition (83) (Figure 2).
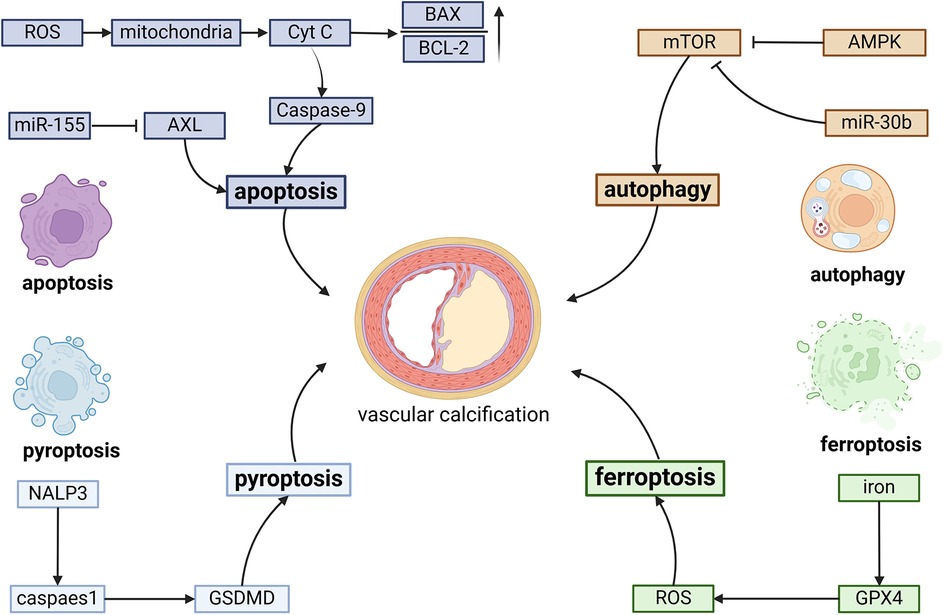
Figure 2. The fundamental molecular pathways involved in programmed cell death during vascular calcification include several key processes. Apoptosis is triggered by caspase-9 activation, an elevated BAX/Bcl-2 ratio, and suppression of AKT signaling. Autophagy is promoted through the inhibition of mTOR, regulated by AMPK and miR-30b. Pyroptosis is initiated by the NLRP3 inflammasome, which activates GSDMD. Excessive iron accumulation can trigger ferroptosis through the excessive generation of ROS.
4 Conclusion
Cardiovascular diseases continue to represent the predominant cause of global mortality, with VC significantly contributing to the increased incidence of cardiovascular complications. Consequently, investigating the underlying mechanisms of VC holds substantial importance for public health. Our comprehensive review demonstrates that programmed cell death serves as a fundamental pathophysiological mechanism in VC progression. Specifically, apoptosis, autophagy, pyroptosis, and ferroptosis exert distinct regulatory effects on VC pathogenesis. These findings underscore the critical importance of elucidating the complex interplay between various forms of programmed cell death and VC, which may provide valuable insights for developing therapeutic strategies against VC.
Author contributions
JZ: Writing – original draft. ZL: Writing – review & editing. XZ: Writing – review & editing. JL: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. grants: 82270939 to Jianghua Liu).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Villa-Bellosta R. Vascular calcification: key roles of phosphate and pyrophosphate. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22(24):13536. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413536
2. Yahagi K, Kolodgie FD, Lutter C, Mori H, Romero ME, Finn AV, et al. Pathology of human coronary and carotid artery atherosclerosis and vascular calcification in diabetes mellitus. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2017) 37(2):191–204. doi: 10.1161/atvbaha.116.306256
3. Yamada S, Giachelli CM. Vascular calcification in CKD-MBD: roles for phosphate, FGF23, and Klotho. Bone. (2017) 100:87–93. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2016.11.012
4. Cai X, Tintut Y, Demer LL. A potential new link between inflammation and vascular calcification. J Am Heart Assoc. (2023) 12(1):e028358. doi: 10.1161/jaha.122.028358
5. Drüeke TB, Massy ZA. Vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease: contribution of ferroptosis? Kidney Int. (2022) 102(6):1209–11. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2022.08.031
6. Rhee EJ. The influence of obesity and metabolic health on vascular health. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). (2022) 37(1):1–8. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2022.101
7. Hao Q-Y, Gao J-W, Yuan Z-M, Gao M, Wang J-F, Schiele F, et al. Remnant cholesterol and the risk of coronary artery calcium progression: insights from the CARDIA and MESA study. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. (2022) 15(7):e014116. doi: 10.1161/circimaging.122.014116
8. Singh A, Tandon S, Tandon C. An update on vascular calcification and potential therapeutics. Mol Biol Rep. (2021) 48(1):887–96. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-06086-y
9. Xu C, Smith ER, Tiong MK, Ruderman I, Toussaint ND. Interventions to attenuate vascular calcification progression in chronic kidney disease: a systematic review of clinical trials. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2022) 33(5):1011–32. doi: 10.1681/asn.2021101327
10. Yoo J-H, Kim J-G, Chung K, Lee SH, Oh H-C, Park S-H, et al. Vascular calcification in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty: frequency and effects on the surgery. Clin Orthop Surg. (2020) 12(2):171–7. doi: 10.4055/cios19125
11. Durham AL, Speer MY, Scatena M, Giachelli CM, Shanahan CM. Role of smooth muscle cells in vascular calcification: implications in atherosclerosis and arterial stiffness. Cardiovasc Res. (2018) 114(4):590–600. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvy010
12. Jiang H, Li L, Zhang L, Zang G, Sun Z, Wang Z. Role of endothelial cells in vascular calcification. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 9:895005. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.895005
13. Li Y, Sun Z, Zhang L, Yan J, Shao C, Jing L, et al. Role of macrophages in the progression and regression of vascular calcification. Front Pharmacol. (2020) 11:661. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00661
14. Zhou X, Xu S-N, Yuan S-T, Lei X, Sun X, Xing L, et al. Multiple functions of autophagy in vascular calcification. Cell Biosci. (2021) 11(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s13578-021-00639-9
15. Wang SS, Wang C, Chen H. MicroRNAs are critical in regulating smooth muscle cell mineralization and apoptosis during vascular calcification. J Cell Mol Med. (2020) 24(23):13564–72. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16005
16. Zhu Y, Han X-Q, Sun X-J, Yang R, Ma W-Q, Liu N-F. Lactate accelerates vascular calcification through NR4A1-regulated mitochondrial fission and BNIP3-related mitophagy. Apoptosis. (2020) 25(5-6):321–40. doi: 10.1007/s10495-020-01592-7
17. Li L, Liu W, Mao Q, Zhou D, Ai K, Zheng W, et al. Klotho ameliorates vascular calcification via promoting autophagy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:7192507. doi: 10.1155/2022/7192507
18. Jefferies BJ, Evans E, Bundred J, Hodson J, Whiting JL, Forde C, et al. Vascular calcification does not predict anastomotic leak or conduit necrosis following oesophagectomy. World J Gastrointest Surg. (2019) 11(7):308–21. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v11.i7.308
19. Li M, Wang Z-W, Fang L-J, Cheng S-Q, Wang X, Liu N-F. Programmed cell death in atherosclerosis and vascular calcification. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13(5):467. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04923-5
20. Shao S, Liu Y, Hong W, Mo Y, Shu F, Jiang L, et al. Influence of FOSL1 inhibition on vascular calcification and ROS generation through ferroptosis via P53-SLC7A11 axis. Biomedicines. (2023) 11(2):635. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020635
21. Yang C, Xie Z, Liu H, Wang X, Zhang Z, Du L, et al. Efficacy and mechanism of Shenqi compound in inhibiting diabetic vascular calcification. Mol Med. (2023) 29(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s10020-023-00767-7
22. Sulistyowati E, Hsu J-H, Lee S-J, Huang S-E, Sihotang WY, Wu B-N, et al. Potential actions of baicalein for preventing vascular calcification of smooth muscle cells in vitro and in vivo. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23(10):5673. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105673
23. Xu Z, Liu X, Li Y, Gao H, He T, Zhang C, et al. Shuxuetong injection simultaneously ameliorates dexamethasone-driven vascular calcification and osteoporosis. Exp Ther Med. (2021) 21(3):197. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.9630
24. Jiang W, Ruan W, Wang Z. Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide inhibits vascular calcification via anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects in chronic kidney disease. FASEB J. (2022) 36(9):e22504. doi: 10.1096/fj.202200353RRR
25. Nanao-Hamai M, Son B-K, Komuro A, Asari Y, Hashizume T, Takayama K-i, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 inhibits vascular calcification as a selective androgen receptor modulator. Eur J Pharmacol. (2019) 859:172546. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172546
26. Sheng Y, Zhang C, Liu Y, Xu B, Jin T, Ye T, et al. GDF11 is a novel protective factor against vascular calcification. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. (2022) 80(6):852–60. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000001357
27. Shi Y, Wang S, Peng H, Lv Y, Li W, Cheng S, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 21 attenuates vascular calcification by alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress mediated apoptosis in rats. Int J Biol Sci. (2019) 15(1):138–47. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.28873
28. Jin D, Lin L, Xie Y, Jia M, Qiu H, Xun K. NRF2-suppressed vascular calcification by regulating the antioxidant pathway in chronic kidney disease. FASEB J. (2022) 36(1):e22098. doi: 10.1096/fj.202100625RR
29. González-Salvatierra S, García-Fontana C, Lacal J, Andújar-Vera F, Martínez-Heredia L, Sanabria-de la Torre R, et al. Cardioprotective function of sclerostin by reducing calcium deposition, proliferation, and apoptosis in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2023) 22(1):12933-023-02043-8. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-02043-8
30. Wang Y-k, Li S-j, Zhou L-l, Li D, Guo L-w. GALNT3 protects against vascular calcification by reducing oxidative stress and apoptosis of smooth muscle cells. Eur J Pharmacol. (2023) 939:175447. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175447
31. Hao J, Tang J, Zhang L, Li X, Hao L. The crosstalk between calcium ions and aldosterone contributes to inflammation, apoptosis, and calcification of VSMC via the AIF-1/NF-kappaB pathway in uremia. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2020) 2020:3431597. doi: 10.1155/2020/3431597
32. Duang S, Zhang M, Liu C, Dong Q. Parathyroid hormone-induced vascular smooth muscle cells calcification by endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Physiol Pharmacol. (2022) 73(5):597–604. doi: 10.26402/jpp.2022.5.03
33. Liu Q, Xiang P, Chen M, Luo Y, Zhao Y, Zhu J, et al. Nano-sized hydroxyapatite induces apoptosis and osteogenic differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells via JNK/c-JUN pathway. Int J Nanomedicine. (2021) 16:3633–48. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S303714
34. Dong Q, Chen Y, Liu W, Liu X, Chen A, Yang X, et al. 25-Hydroxycholesterol Promotes vascular calcification via activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Eur J Pharmacol. (2020) 880:173165. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173165
35. Zhang L, Sun H, Liu S, Gao J, Xia J. Glycemic variability is associated with vascular calcification by the markers of endoplasmic reticulum stress-related apoptosis, Wnt1, galectin-3 and BMP-2. Diabetol Metab Syndr. (2019) 11:67. doi: 10.1186/s13098-019-0464-4
36. Tao Y, Wu Y, Jiang C, Wang Q, Geng X, Chen L, et al. Saturated fatty acid promotes calcification via suppressing SIRT6 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Hypertens. (2023) 41(3):393–401. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000003342
37. Fang K, Chen Z, Liu M, Peng J, Wu P. Apoptosis and calcification of vascular endothelial cell under hyperhomocysteinemia. Med Oncol. (2015) 32(1):403. doi: 10.1007/s12032-014-0403-z
38. Li S, Zhan J-K, Wang Y-J, Lin X, Zhong J-Y, Wang Y, et al. Exosomes from hyperglycemia-stimulated vascular endothelial cells contain versican that regulate calcification/senescence in vascular smooth muscle cells. Cell Biosci. (2019) 9(1):1–15. doi: 10.1186/s13578-018-0263-x
39. Cavallari C, Dellepiane S, Fonsato V, Medica D, Marengo M, Migliori M, et al. Online hemodiafiltration inhibits inflammation-related endothelial dysfunction and vascular calcification of uremic patients modulating miR-223 expression in plasma extracellular vesicles. The Journal of Immunology. (2019) 202(8):2372–83. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800747
40. Alique M, Bodega G, Corchete E, García-Menéndez E, de Sequera P, Luque R, et al. Microvesicles from indoxyl sulfate-treated endothelial cells induce vascular calcification in vitro. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. (2020) 18:953–66. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.04.006
41. Li Y, Sun W, Saaoud F, Wang Y, Wang Q, Hodge J, et al. Mir155 modulates vascular calcification by regulating Akt-FOXO3a signalling and apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cell Mol Med. (2021) 25(1):535–48. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16107
42. Yang J, Zhou X, Lu J, Li M. miR-146-5p restrains calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells by suppressing TRAF6. Open Med (Wars). (2022) 17(1):1515–27. doi: 10.1515/med-2022-0471
43. Zhang F, Li J, Gu C, Zhang H. MiR-140-5p upregulation suppressed beta-glycerophosphate-induced vascular smooth muscle cell calcification via targeting TLR4. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. (2022) 44(3):295–305. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2022.2043896
44. Wang X, Zhang X, Li F, Ji Q. MiR-128-3p accelerates cardiovascular calcification and insulin resistance through ISL1-dependent wnt pathway in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234(4):4997–5010. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27300
45. Liu Y, Guo Y, Bao S, Huang H, Liu W, Guo W, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-381-3p alleviates vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease by targeting NFAT5. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13(3):278. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04703-1
46. Mizushima N, Komatsu M. Autophagy: renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. (2011) 147(4):728–41. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.10.026
47. Salabei JK, Hill BG. Implications of autophagy for vascular smooth muscle cell function and plasticity. Free Radic Biol Med. (2013) 65:693–703. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.08.003
48. Wang P, Zhang N, Wu B, Wu S, Zhang Y, Sun Y. The role of mitochondria in vascular calcification. J Transl Intern Med. (2020) 8(2):80–90. doi: 10.2478/jtim-2020-0013
49. Frauscher B, Kirsch AH, Schabhüttl C, Schweighofer K, Kétszeri M, Pollheimer M, et al. Autophagy protects from uremic vascular media calcification. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:1866. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01866
50. Liu Q, Luo Y, Zhao Y, Xiang P, Zhu J, Jing W, et al. Nano-hydroxyapatite accelerates vascular calcification via lysosome impairment and autophagy dysfunction in smooth muscle cells. Bioact Mater. (2022) 8:478–93. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.06.004
51. Lu Y, Yuan T, Min X, Yuan Z, Cai Z. AMPK: potential therapeutic target for vascular calcification. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2021) 8:670222. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.670222
52. Cao X, Li H, Tao H, Wu N, Yu L, Zhang D, et al. Metformin inhibits vascular calcification in female rat aortic smooth muscle cells via the AMPK-eNOS-NO pathway. Endocrinology. (2013) 154(10):3680–9. doi: 10.1210/en.2013-1002
53. Lee J, Hong S-W, Kim M-J, Kwon H, Park SE, Rhee E-J, et al. Metformin, resveratrol, and exendin-4 inhibit high phosphate-induced vascular calcification via AMPK-RANKL signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2020) 530(2):374–80. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.07.136
54. Kim K, Kim C, Cho K, Jang W. Policosanol attenuates pi-induced calcification via AMPK-mediated INSIGs expression in rat VSMCs. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. (2021) 48(10):1336–45. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.13530
55. Chen WR, Yang JQ, Liu F, Shen XQ, Zhou YJ. Melatonin attenuates vascular calcification by activating autophagy via an AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 signaling pathway. Exp Cell Res. (2020) 389(1):111883. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.111883
56. Li S, Ni Y, Li C, Xiang Q, Zhao Y, Xu H, et al. Long noncoding RNA SNHG1 alleviates high glucose-induced vascular smooth muscle cells calcification/senescence by post-transcriptionally regulating Bhlhe40 and autophagy via Atg10. J Physiol Biochem. (2022) 79(1):83–105. doi: 10.1007/s13105-022-00924-2
57. Wang J, Sun Y-T, Xu T-H, Sun W, Tian B-Y, Sheng Z-T, et al. MicroRNA-30b regulates high phosphorus level-induced autophagy in vascular smooth muscle cells by targeting BECN1. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2017) 42(2):530–6. doi: 10.1159/000477602
58. Xu T, Qiu X, Sheng Z, Han Y, Wang J, Tian B, et al. Restoration of microRNA-30b expression alleviates vascular calcification through the mTOR signaling pathway and autophagy. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234(8):14306–18. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28130
59. Cao J, Chen C, Chen Q, Gao Y, Zhao Z, Yuan Q, et al. Extracellular vesicle miR-32 derived from macrophage promotes arterial calcification in mice with type 2 diabetes via inhibiting VSMC autophagy. J Transl Med. (2022) 20(1):307. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03502-8
60. Ciceri P, Falleni M, Tosi D, Martinelli C, Cannizzo S, Marchetti G, et al. Therapeutic effect of iron citrate in blocking calcium deposition in high Pi-calcified VSMC: role of autophagy and apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20(23):5925. doi: 10.3390/ijms20235925
61. Jo J-H, Park H-S, Lee D-H, Han J-H, Heo K-S, Myung C-S. Rosuvastatin inhibits the apoptosis of platelet-derived growth factor–stimulated vascular smooth muscle cells by inhibiting p38 via autophagy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (2021) 378(1):10–9. doi: 10.1124/jpet.121.000539
62. Chen K, Hou C, Xu L, Peng H, He C, Liu J, et al. HSPB1 regulates autophagy and apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells in arteriosclerosis obliterans. Cardiovasc Ther. (2022) 2022:1–11. doi: 10.1155/2022/3889419
63. Pang Q, Wang P, Pan Y, Dong X, Zhou T, Song X, et al. Irisin protects against vascular calcification by activating autophagy and inhibiting NLRP3-mediated vascular smooth muscle cell pyroptosis in chronic kidney disease. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13(3):283. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04735-7
64. Duan Y, Peng Z, Zhong S, Zhou P, Huang H, Li J, et al. VX-765 ameliorates CKD VSMC calcification by regulating STAT3 activation. Eur J Pharmacol. (2023) 945:175610. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175610
65. Zhang X, Wang Z, Li X, Chen J, Yu Z, Li X, et al. Polydatin protects against atherosclerosis by activating autophagy and inhibiting pyroptosis mediated by the NLRP3 inflammasome. J Ethnopharmacol. (2023) 309:116304. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116304
66. Weng X, Luo X, Dai X, Lv Y, Zhang S, Bai X, et al. Apigenin inhibits macrophage pyroptosis through regulation of oxidative stress and the NF-kappaB pathway and ameliorates atherosclerosis. Phytother Res. (2023) 37(11):5300–14. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7962
67. Cui S, Wu H, He Q, Wang L, Yi X, Feng G, et al. Fucoxanthin alleviated atherosclerosis by regulating PI3K/AKT and TLR4/NFkappaB mediated pyroptosis in endothelial cells. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 120:110370. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110370
68. Zhu J, Chen H, Le Y, Guo J, Liu Z, Dou X, et al. Salvianolic acid A regulates pyroptosis of endothelial cells via directly targeting PKM2 and ameliorates diabetic atherosclerosis. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:1009229. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1009229
69. Liang W, Chen J, Zheng H, Lin A, Li J, Wu W, et al. MiR-199a-5p-containing macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles inhibit SMARCA4 and alleviate atherosclerosis by reducing endothelial cell pyroptosis. Cell Biol Toxicol. (2023) 39(3):591–605. doi: 10.1007/s10565-022-09732-2
70. Tang Y, Yan J-H, Ge Z-W, Fei A-H, Zhang Y-C. LncRNA gaplinc promotes the pyroptosis of vascular endothelial cells through SP1 binding to enhance NLRP3 transcription in atherosclerosis. Cell Signal. (2022) 99:110420. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2022.110420
71. Liang Y, Xu X-D, Xu X, Cai Y-B, Zhu Z-X, Zhu L, et al. Linc00657 promoted pyroptosis in THP-1-derived macrophages and exacerbated atherosclerosis via the miR-106b-5p/TXNIP/NLRP3 axis. Int J Biol Macromol. (2023) 253(Pt 4):126953. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.126953
72. Li H, Zhao Q, Liu D, Zhou B, Liao F, Chen L. Cathepsin B aggravates atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice by modulating vascular smooth muscle cell pyroptosis through NF-kappaB/NLRP3 signaling pathway. PLoS One. (2024) 19(1):e0294514. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294514
73. An C, Sun F, Liu C, Huang S, Xu T, Zhang C, et al. IQGAP1 Promotes mitochondrial damage and activation of the mtDNA sensor cGAS-STING pathway to induce endothelial cell pyroptosis leading to atherosclerosis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 123:110795. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110795
74. Ye Y, Chen A, Li L, Liang Q, Wang S, Dong Q, et al. Repression of the antiporter SLC7A11/glutathione/glutathione peroxidase 4 axis drives ferroptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells to facilitate vascular calcification. Kidney Int. (2022) 102(6):1259–75. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2022.07.034
75. Ma W-Q, Sun X-J, Zhu Y, Liu N-F. Metformin attenuates hyperlipidaemia-associated vascular calcification through anti-ferroptotic effects. Free Radic Biol Med. (2021) 165:229–42. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.01.033
76. Bao X, Luo X, Bai X, Lv Y, Weng X, Zhang S, et al. Cigarette tar mediates macrophage ferroptosis in atherosclerosis through the hepcidin/FPN/SLC7A11 signaling pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. (2023) 201:76–88. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.03.006
77. Yu W, Liu W, Xie D, Wang Q, Xu C, Zhao H, et al. High level of uric acid promotes atherosclerosis by targeting NRF2-mediated autophagy dysfunction and ferroptosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:9304383. doi: 10.1155/2022/9304383
78. Liu W, Östberg N, Yalcinkaya M, Dou H, Endo-Umeda K, Tang Y, et al. Erythroid lineage Jak2V617F expression promotes atherosclerosis through erythrophagocytosis and macrophage ferroptosis. J Clin Invest. (2022) 132(13):155724. doi: 10.1172/JCI155724
79. Xiang P, Chen Q, Chen L, Lei J, Yuan Z, Hu H, et al. Metabolite Neu5Ac triggers SLC3A2 degradation promoting vascular endothelial ferroptosis and aggravates atherosclerosis progression in ApoE(-/-)mice. Theranostics. (2023) 13(14):4993–5016. doi: 10.7150/thno.87968
80. Rong J, Li C, Zhang Q, Zheng G, Fan W, Pan Z, et al. Hydroxysafflor yellow a inhibits endothelial cell ferroptosis in diabetic atherosclerosis mice by regulating miR-429/SLC7A11. Pharm Biol. (2023) 61(1):404–15. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2023.2225543
81. Wang X, Zhang M, Mao C, Zhang C, Ma W, Tang J, et al. Icariin alleviates ferroptosis-related atherosclerosis by promoting autophagy in xo-LDL-induced vascular endothelial cell injury and atherosclerotic mice. Phytother Res. (2023) 37(9):3951–63. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7854
82. Lv Y, Zhang S, Weng X, Huang J, Zhao H, Dai X, et al. Estrogen deficiency accelerates postmenopausal atherosclerosis by inducing endothelial cell ferroptosis through inhibiting NRF2/GPX4 pathway. FASEB J. (2023) 37(6):e22992. doi: 10.1096/fj.202300083R
83. Hu Y, Gu X, Zhang Y, Ma W, Sun L, Wang C, et al. Adrenomedullin, transcriptionally regulated by vitamin D receptors, alleviates atherosclerosis in mice through suppressing AMPK-mediated endothelial ferroptosis. Environ Toxicol. (2024) 39(1):199–211. doi: 10.1002/tox.23958
Glossary
Keywords: vascular calcification, programmed cell death, signaling pathways, diabetic angiopathy, atherosclerosis
Citation: Zheng J, Lin Z, Zhong X and Liu J (2025) The relationship between programmed cell death and vascular calcification. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1549857. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1549857
Received: 22 December 2024; Accepted: 25 June 2025;
Published: 10 July 2025.
Edited by:
Masanori Aikawa, Brigham and Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School, United StatesReviewed by:
Eileen M. Redmond, University of Rochester, United StatesCopyright: © 2025 Zheng, Lin, Zhong and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianghua Liu, MjAxODAxMDAwMkB1c2MuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jie Zheng†
Jie Zheng† Xiaolin Zhong
Xiaolin Zhong Jianghua Liu
Jianghua Liu