Abstract
Pyroptosis is an inflammatory form of programmed cell death, distinct from apoptosis, necroptosis, and ferroptosis, and is primarily mediated by gasdermin proteins and inflammatory caspases. Recent advances highlight the central role of pyroptosis in the pathogenesis and progression of a spectrum of cardiovascular diseases, including myocardial infarction, myocarditis, heart failure, atherosclerosis, hypertension, and cardiac arrhythmias. Activation of inflammasomes and the subsequent cleavage of gasdermins drive cell membrane pore formation, leading to the release of interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-18 (IL-18), and other pro-inflammatory mediators, amplifying tissue injury and sterile inflammation. Both experimental and clinical evidence reveal that targeting key molecules in the pyroptotic pathway, such as NLRP3 inflammasome, caspase-1, and gasdermin D, can attenuate myocardial injury, inhibit adverse cardiac remodeling, and stabilise atherosclerotic plaques. This review systematically summarises the current understanding of the molecular mechanisms of pyroptosis in cardiovascular pathology, details its disease-specific roles, and discusses translational and therapeutic perspectives. Modulating pyroptosis may provide new opportunities for the diagnosis, risk stratification, and treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
1 Introduction
Despite major advances in cardiovascular medicine, inflammation-driven cell death remains a fundamental challenge in the pathogenesis and progression of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). While traditional forms of cell death such as apoptosis and necrosis have been extensively studied, the discovery of pyroptosis has unveiled a new dimension in inflammatory tissue injury. Pyroptosis is an inflammatory form of regulated cell death distinguished by gasdermin-mediated plasma membrane pore formation, cell swelling, and release of pro-inflammatory intracellular contents (1, 2). It is typically triggered by the activation of cytosolic pattern-recognition receptors (inflammasomes) in response to danger signals, leading to caspase-1 (canonical pathway) or caspase-4/5/11 (non-canonical pathway) activation and cleavage of gasdermin family effectors (3–6).
Pyroptosis has been shown to impact the development and progression of various CVDs, including myocardial infarction (MI), myocarditis, heart failure (HF), atherosclerosis, hypertension, and arrhythmias (7, 8). However, key questions persist regarding the triggers of pyroptosis in cardiac and vascular tissues, the interplay between different inflammasome pathways, and the clinical value of targeting pyroptosis as a therapeutic strategy. Additionally, the molecular distinction between pyroptosis and other cell death modalities in the cardiovascular context is not fully resolved. Addressing these gaps, this review summarises recent advances in our understanding of the molecular mechanisms of pyroptosis in cardiovascular pathology, highlighting key disease models and potential clinical implications. Notably, this review offers several novel insights beyond previous works. First, we integrate recent findings on non-canonical pyroptosis mediated by gasdermin E (GSDME), particularly in immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced myocarditis—an emerging and clinically relevant form of inflammatory cardiotoxicity. Second, we explore the contribution of pyroptosis to atrial arrhythmogenesis, including its impact on structural and electrical remodeling in atrial fibrillation, which remains under-recognized. Third, we provide a mechanistic overview of pyroptosis within broader inflammatory signaling frameworks such as PANoptosis and the cGAS–STING pathway. Finally, we discuss the clinical translation of pyroptosis-related biomarkers and therapies, highlighting current limitations and future opportunities. These elements collectively distinguish our review as a forward-looking synthesis that bridges molecular insights with potential clinical applications.
2 Myocardial infarction and ischaemic injury
2.1 Pathophysiological evidence
MI triggers an intense inflammatory reaction in the myocardium, and pyroptotic cell death has been strongly implicated in this process (9). In experimental models of myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury, cardiomyocyte pyroptosis is detected soon after reperfusion, contributing to infarct expansion and cardiac dysfunction (10). Genetic ablation of key pyroptosis mediators confers cardioprotection: mice lacking gasdermin D (GSDMD) have significantly reduced infarct sizes, less cardiomyocyte death, and improved post-MI cardiac function compared to wild-type mice (10–12). In a seminal study, GSDMD knockout in mice attenuated myocardial injury after coronary ligation, with fewer infiltrating neutrophils and macrophages in the infarct and reduced release of IL-1β (11). Correspondingly, pharmacological inhibition of caspase-1 with specific inhibitors (e.g., VX-765) during reperfusion limits infarct size and preserves left ventricular function in rodents (13). These findings indicate that the inflammasome-caspase-1-GSDMD pathway is activated by ischaemic injury and contributes to cardiomyocyte loss beyond apoptosis or necrosis (7). Mechanistically, I/R releases DAMPs including ATP, HMGB1, reactive oxygen species (ROS) that activate inflammasomes (especially NLRP3) in cardiomyocytes, macrophages, and infiltrating neutrophils (14, 15). The resulting pyroptotic cell death amplifies inflammation, creating a feed-forward cycle of injury. Clinically, patients with AMI have elevated circulating markers of pyroptosis. A study reported that plasma GSDMD levels are significantly higher in acute MI patients than in controls, correlating with infarct biomarkers and inflammatory cytokines (16). These human data support that pyroptosis is not merely a laboratory phenomenon but is active in human MI pathophysiology.
2.2 Molecular mechanisms
MI engages both canonical and non-canonical pyroptotic pathways. The canonical pathway is driven by inflammasome activation (chiefly NLRP3) and caspase-1 (17). In mouse models, myocardial I/R rapidly activates NLRP3 and caspase-1 in the heart, leading to IL-1β/IL-18 maturation and GSDMD cleavage in cardiomyocytes and resident immune cells (10). GSDMD N-terminal fragments form membrane pores, inducing osmotic lysis of cells and spillage of pro-inflammatory contents. Neutrophils have been shown to undergo pyroptosis in infarcted hearts, which exacerbates tissue injury; interestingly, neutrophil-derived proteases can also cleave GSDMD and contribute to IL-1β release (11). The non-canonical pathway involves caspase-11 (in mice; caspase-4/5 in humans) sensing intracellular LPS, which has relevance in sterile MI through gut microbial translocation or endogenous oxidised lipids acting similarly to activate caspase-11 (10, 18). Caspase-11 can induce pyroptosis by directly cleaving GSDMD and indirectly via NLRP3 activation. Indeed, one study showed that caspase-11 deficiency reduced infarct size, suggesting that non-canonical inflammasome activation contributes to myocardial I/R injury (10). Upstream, multiple inflammasome sensors may be involved: NLRP3 is the most studied and responds to mitochondrial ROS, Ca2+ flux, and ion imbalances during reperfusion (19, 20), but AIM2 (activated by DNA from necrotic cells) may also drive caspase-1 in MI, as suggested by elevated DNA-sensing pathway activation in infarct tissue (19, 21). Downstream, IL-1β and IL-18 released from pyroptotic cells act on surviving myocardium and infiltrating cells to augment inflammation and apoptotic pathways. IL-18, in particular, has been identified as a mediator of post-MI adverse remodeling; high serum IL-18 in MI patients predicts worse outcomes, linking pyroptosis to later HF (19). Thus, MI involves a complex interplay: ischaemia triggers inflammasome assembly (via NLRP3 and possibly others), caspase-1/-11 activation cleaves GSDMD, and pyroptosis of cardiomyocytes, neutrophils, and macrophages ensues, aggravating myocardial injury.
2.3 Clinical and therapeutic insights
Recognising pyroptosis as a driver of myocardial damage has spurred interest in anti-inflammatory therapies for MI. The IL-1β neutralising antibody canakinumab, tested in the CANTOS trial in post-MI patients, significantly reduced recurrent cardiovascular events, providing proof-of-concept that targeting inflammasome outputs benefits patients (22, 23). Although canakinumab's mechanism is broad IL-1β inhibition, its success underscores the pathological role of IL-1β (largely produced by inflammasome-pyroptosis activity) in post-infarction inflammation (24). Similarly, low-dose colchicine, an unspecific inflammasome inhibitor, lowered the risk of ischaemic events after MI in the COLCOT trial (25), hinting that suppressing inflammasome-driven inflammation (and by extension pyroptosis) is cardioprotective. These clinical trials align with animal studies where direct inhibition of inflammasome components or GSDMD has been beneficial. Selective NLRP3 inhibitors (like MCC950) have shown efficacy in reducing infarct size in preclinical MI models (porcine and murine) (26). Caspase-1 inhibitors (e.g., VX-765) improved cardiac function and reduced long-term remodeling when given at reperfusion in rodents (27–30). Such agents are now being explored for clinical use. Importantly, these interventions did not appear to compromise host defense acutely in sterile MI, suggesting a therapeutic window where modulating pyroptosis is beneficial. Beyond reducing acute injury, pyroptosis markers might serve as diagnostic or prognostic biomarkers in MI. As noted, circulating GSDMD or ASC specks have been proposed as indices of inflammasome activation (16), potentially aiding risk stratification. Moving forward, ongoing research aims to refine strategies to inhibit detrimental cardiac pyroptosis—for instance, using small-molecule gasdermin inhibitors or interfering with pyroptotic pore formation—to improve MI outcomes while avoiding undue immunosuppression. In summary, pyroptosis is a critical mediator of myocardial injury in infarction, and its modulation holds promise as a novel cardioprotective strategy.
3 Myocarditis
3.1 Evidence of involvement
Myocarditis, an inflammatory disease of the heart muscle often triggered by viral infection, has recently been linked to pyroptotic cell death as part of its pathogenic immune response. In Coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3)–induced viral myocarditis, myocardial tissues show activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and increased caspase-1 activity, suggesting pyroptosis in infected cardiomyocytes and infiltrating immune cells (31, 32). A landmark study demonstrated that cathepsin B released during CVB3 infection can activate the NLRP3 inflammasome, leading to caspase-1–dependent pyroptosis and worsening myocardial injury. In mice, pharmacologic inhibition or genetic deletion of cathepsin B markedly reduced caspase-1 activation and IL-1β release in the heart, thereby attenuating myocarditis severity (31, 33). This indicates that Recent evidence implicates is a key mechanism by which enteroviral infection causes cardiomyocyte death and inflammation. Furthermore, IL-1β and IL-18 levels are elevated in myocarditis, implicating inflammasome activation; indeed, myocardial biopsies from myocarditis patients have shown increased NLRP3 and IL-1β expression (32). Beyond infectious causes, immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy used in cancer can induce fulminant autoimmune myocarditis (34). Recent evidence implicates pyroptosis in ICI myocarditis: a 2024 study found that gasdermin E (GSDME) –mediated pyroptosis (rather than GSDMD) is extensively activated in ICI-related myocarditis, both in a mouse model and in patient heart samples (35). Mice lacking GSDME were protected from ICI myocarditis, with less immune cell infiltration and improved survival, demonstrating a direct pathogenic role for pyroptosis in this setting. Together, these findings across viral and immune-mediated myocarditis establish that pyroptosis contributes to cardiomyocyte loss and inflammatory amplification in the myocarditic heart.
3.2 Molecular mechanisms
In viral myocarditis, the interplay between viral pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and host sensors drives pyroptosis (36). Enteroviruses like CVB3 cause cardiomyocyte damage that releases cathepsin B from lysosomes; cathepsin B in the cytosol can trigger NLRP3 inflammasome assembly, perhaps by promoting mitochondrial dysfunction and reactive oxygen species. NLRP3 then activates caspase-1, leading to GSDMD pore formation and pyroptosis of infected cells. This not only kills cardiomyocytes, exacerbating ventricular dysfunction but also unleashes IL-1β/IL-18 which recruit and activate immune cells, fueling a vicious cycle of myocardium-targeted inflammation. Supporting this, interventions like IL-1 blockade or NLRP3 inhibition ameliorate experimental myocarditis (32). Another mechanism involves alarmins from necrotic cells: e.g., DNA from damaged cardiomyocytes can activate AIM2 inflammasomes in macrophages, potentially contributing to pyroptosis and cytokine release in myocarditis. In ICI-induced myocarditis, hyperactivated T cells produce excessive IFN-γ, triggering caspase-3 activation in cardiomyocytes, which cleaves GSDME to execute pyroptosis via pore formation (37–39). GSDME-mediated mitochondrial DNA release activates the cGAS-STING pathway, amplifying IFN and inflammatory responses through a feed-forward loop (35, 40, 41). This highlights non-canonical pyroptosis pathways (caspase-3/GSDME) in disease pathogenesis. Elevated IL-1β drives myocardial inflammation, with IL-1 neutralization improving outcomes, while IL-18 contributes to systemic symptoms (42). Pyroptosis coexists with apoptosis and necroptosis, forming PANoptosis in fulminant myocarditis (31, 43). Inflammasome activation and gasdermin pore formation remain central to myocardial injury, underscoring their therapeutic targeting potential.
Recent studies have demonstrated that viral myocarditis involves PANoptosis-dependent cell death pathways, wherein pyroptosis, apoptosis, and necroptosis are activated in a coordinated manner (43). Upon viral infection—particularly with coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3)—cytosolic viral sensors such as Z-DNA-binding protein 1 (ZBP1) and RIG-I are upregulated in cardiomyocytes. These sensors promote the formation of the PANoptosome complex, a multiprotein platform that orchestrates the activation of caspase-1 (pyroptosis via GSDMD), caspase-3 (apoptosis), and RIPK3/MLKL (necroptosis) (44). Among these, GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis plays a central role not only by causing membrane rupture but also by facilitating the release of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) into the cytosol (35). This mtDNA activates the cGAS–STING pathway, leading to type I interferon signaling and amplifying innate immune responses (45). This mechanistic interplay between pyroptosis, other cell death pathways, and cGAS–STING signaling forms a feed-forward inflammatory loop that drives myocardial injury in viral myocarditis (Figure 1).
Figure 1
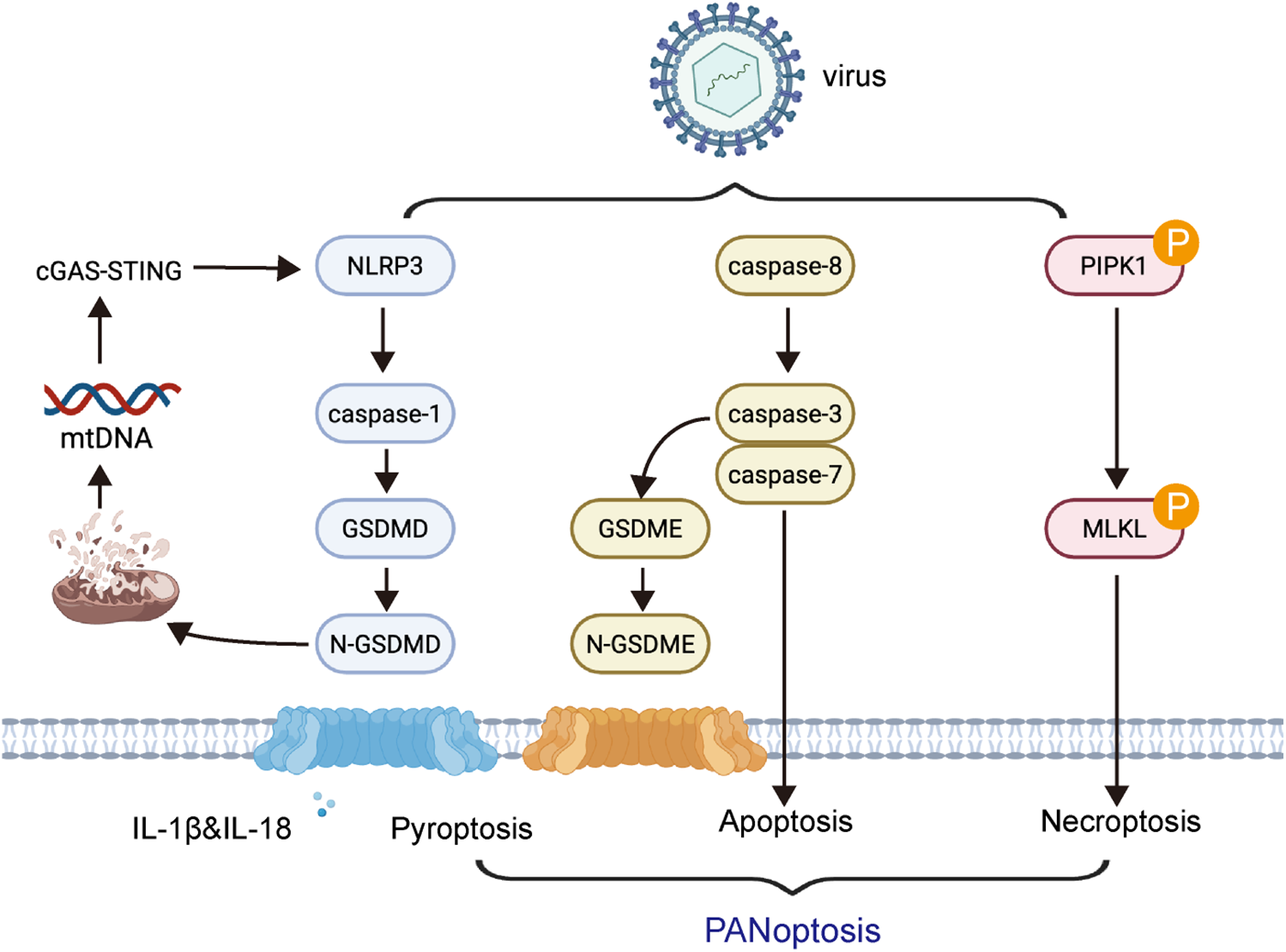
Mechanistic interplay of pyroptosis with other cell death pathways and immune signaling in myocarditis. Upon viral infection such as coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3), intracellular viral sensors including ZBP1 and RIG-I are activated in cardiomyocytes. These sensors initiate the assembly of the PANoptosome, which orchestrates the simultaneous activation of pyroptosis (via caspase-1 and GSDMD), apoptosis (via caspase-3), and necroptosis (via RIPK3 and MLKL). Gasdermin D (GSDMD)-mediated membrane pore formation facilitates the release of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) into the cytosol, which triggers the cGAS–STING signaling pathway.
3.3 Clinical implications
Understanding the role of pyroptosis in myocarditis opens avenues for targeted therapy and better biomarkers. Clinically, myocarditis ranges from mild to life-threatening, and current treatments are mainly supportive or immunosuppressive (for giant-cell or immune myocarditis). The evidence that IL-1 plays a causal role (via pyroptosis) has spurred trials of anakinra (an IL-1 receptor antagonist) in acute myocarditis (46). Case reports and small series have noted rapid improvement in severe myocarditis with anakinra, aligning with pyroptosis's pathogenic role. Likewise, NLRP3 inhibitors or caspase-1 inhibitors might attenuate myocardial inflammation—experimental IL-37 therapy (a cytokine that broadly suppresses inflammasome activity) dramatically reduced cardiac inflammation and improved survival in CVB3 myocarditis mice, highlighting inflammasome inhibition as a potential strategy (32, 47). For ICI-myocarditis, recognizing pyroptosis involvement suggests that adding inflammasome or gasdermin inhibitors to immunosuppressive regimens might better protect the heart while allowing some anti-tumor immunity to continue (35). Indeed, in the preclinical study, a small-molecule GSDME inhibitor reduced cardiac damage without entirely abrogating the immune response. In terms of diagnosis, endomyocardial biopsy showing active caspase-1 or GSDMD pores could help confirm myocarditis and distinguish it from ischaemic injury (35, 48). Additionally, circulating IL-18 or even cardiac troponin combined with IL-1 could improve diagnostic specificity for myocarditis if validated. An important translational insight is that therapies targeting pyroptosis (e.g., NLRP3 inhibitors like dapansutrile) are already in trials for other inflammatory diseases and could be repurposed for myocarditis. Overall, pyroptosis represents a novel therapeutic target in myocarditis: by dampening the inflammasome-gasdermin axis, one might quell the hyperinflammatory myocardial milieu, reduce tissue destruction, and preserve cardiac function in affected patients.
4 Heart failure and cardiac remodeling
4.1 Pyroptosis in heart failure pathophysiology
HF, whether secondary to ischaemic injury or chronic pressure/volume overload, is characterised by the progressive loss of cardiomyocytes, fibrotic remodeling, and ongoing inflammation (49, 50). Recent studies reveal that pyroptosis significantly contributes to cardiomyocyte loss and adverse cardiac remodeling in HF (51–53). In non-ischaemic dilated cardiomyopathy, myocardial tissues display increased NLRP3, cleaved caspase-1, and GSDMD expression compared to controls, consistent with persistent pyroptotic activity (52). Animal models further confirm this: NLRP3 activation in cardiomyocytes drives pyroptosis and promotes HF progression, while genetic silencing of NLRP3 or pharmacologic inhibition of caspase-1 improves ventricular function and reduces fibrosis (10). Pressure overload, as seen in hypertension or aortic stenosis, is another key cause of HF in which pyroptosis plays a pathogenic role. In mouse models with transaortic constriction (TAC), cardiomyocyte membrane rupture and IL-1β release—a hallmark of pyroptosis—have been observed. Inhibition of caspase-1 or knockout of NLRP3 protects against hypertrophy and cardiac dysfunction, whereas NLRP3 overexpression exacerbates hypertrophy under stress (54). These findings underscore that chronic cardiac stress leads to inflammasome activation and pyroptotic cardiomyocyte death, thus advancing HF. Clinically, chronic HF patients, particularly those with prior MI or diabetic cardiomyopathy, exhibit elevated circulating IL-1β and IL-18. Myocardial biopsies from end-stage HF have demonstrated active caspase-1 and inflammasome components, supporting the notion of ongoing, low-level pyroptosis that contributes to HF progression by persistent cell death and sterile myocardial inflammation.
4.2 Mechanistic insights
Multiple triggers induce pyroptosis in chronic HF. In pressure overload-induced HF, myocardial stretch and neurohormonal activation (angiotensin II, catecholamines) promote oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in cardiomyocytes—potent activators of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Once activated, the NLRP3/caspase-1 pathway induces release of IL-1β and IL-18, both with critical effects in HF: IL-1β impairs contractility and stimulates fibroblast activation, while IL-18 promotes myocyte hypertrophy and amplifies inflammation. Elevated IL-18 levels have been found in hypertrophic and failing hearts; mice lacking IL-18 are less susceptible to pressure-overload-induced hypertrophy, implicating pyroptosis-derived IL-18 in pathological hypertrophy (55). In metabolic or diabetic cardiomyopathy, factors such as high glucose, free fatty acids, and ceramides can also activate inflammasomes in cardiac cells (56, 57). For example, hyperglycaemia-induced ROS activate NLRP3, leading to cardiomyocyte pyroptosis and contractile dysfunction. Moreover, non-myocyte cardiac cells—including macrophages and fibroblasts—can also undergo inflammasome activation, contributing to adverse remodeling. Activated fibroblasts release IL-1, further weakening myocardial tissue. Pyroptosis in endothelial and smooth muscle cells of the cardiac microvasculature may worsen HF by compromising microcirculation and inducing cytokine production, though this is less well studied.
At the molecular level, a feed-forward loop often operates in HF: initial cell death from infarction or stress releases DAMPs (e.g., ATP, DNA), which in turn activate inflammasomes in neighbouring cells, promoting further pyroptosis and DAMP release (58). This perpetuates a chronic inflammatory state in the failing heart. Additionally, pyroptosis and apoptosis are interconnected. Caspase-8, traditionally apoptotic, can promote IL-1 production via NLRP3, while caspase-3 can cleave GSDME to trigger secondary pyroptosis—especially relevant in advanced HF with ischaemic episodes. Thus, once cell death pathways are activated in HF, pyroptosis can become a major mechanism of cell loss.
4.3 Therapeutic perspectives
The role of pyroptosis in HF highlights promising therapeutic targets. Several interventions have been investigated in preclinical and early clinical studies. Anti-IL-1 therapies have shown benefit: in acute decompensated HF, anakinra improved exercise tolerance and reduced inflammation, likely reflecting reduced pyroptosis-driven cytokine production (59). Colchicine, a broad anti-inflammatory agent, is being tested for its potential to limit cardiac remodeling by inhibiting inflammasome activity (60). Targeted drugs, such as dapansutrile (an NLRP3 inhibitor), have demonstrated reduction in inflammatory markers and improved diastolic function in HF with preserved ejection fraction (61). Direct inhibition of GSDMD offers another avenue—selective inhibitors can block pore formation, preventing pyroptosis regardless of upstream triggers (62). Preclinical studies show that GSDMD inhibition can reduce fibrosis and improve ejection fraction in HF models without major immunosuppression.
Pyroptosis pathway components may also serve as biomarkers in HF. Elevated IL-18 correlates with poor prognosis and ventricular dysfunction and could help identify patients with high inflammasome activity. ASC specks, oligomers derived from inflammasomes, have been detected in the circulation in inflammatory conditions and might indicate active cardiac inflammasomes if found in HF patients (63). Importantly, some inflammation is necessary for myocardial repair, so future therapies must carefully target pathological, not adaptive, pyroptosis. Research into cardioprotective factors such as irisin—a myokine upregulated by exercise—shows potential in inhibiting cardiac NLRP3 inflammasomes and pyroptosis, suggesting that metabolic interventions could also modulate pyroptosis.
In summary, pyroptosis is a significant driver of inflammation and cell loss in HF. Targeting this pathway could slow HF progression, improve cardiac function, and inform both prognosis and therapy in clinical practice.
5 Atherosclerosis
5.1 Role in atherosclerotic plaque development
Atherosclerosis is fundamentally an inflammatory disease of the arteries. Recent research has established pyroptosis as a critical mechanism linking cholesterol-induced metabolic stress to arterial inflammation and plaque development (64–67). During early atherogenesis, cholesterol crystals and oxidised LDL within the arterial wall serve as danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), activating the NLRP3 inflammasome in macrophages (64, 68). This triggers caspase-1 activation and the release of IL-1β and IL-18, key cytokines that amplify local inflammation and recruit additional immune cells. Duewell et al. first showed that cholesterol crystals stimulate NLRP3-dependent IL-1β release, directly promoting atherosclerosis (69). Pyroptotic macrophage death within plaques contributes to the formation of necrotic cores—regions filled with debris and extracellular lipid—which destabilise plaque structure. Studies have detected active GSDMD and increased IL-1β secretion in atherosclerotic lesions, supporting the presence of ongoing macrophage pyroptosis within plaques (67, 70, 71). The significance of IL-1β from pyroptosis is underscored by genetic studies: ApoE-deficient mice lacking IL-1β show a marked reduction in lesion size, demonstrating the pivotal role of IL-1β in plaque growth (70). Conversely, deficiency of the IL-1 receptor antagonist accelerates atherosclerosis, emphasising that unchecked IL-1 signalling, much of it stemming from pyroptosis, exacerbates disease (72). IL-18, although its role is more nuanced, also appears to foster plaque progression and instability. Thus, pyroptosis fuels a vicious cycle within plaques: as macrophages ingest excess lipids and become foam cells, sustained cholesterol overload activates inflammasomes, leading to pyroptotic foam cell death and the release of cellular contents (lipids, enzymes, cytokines) that intensify inflammation and necrotic core expansion.
5.2 Mechanisms and cell types
Multiple cell types within atherosclerotic lesions can undergo pyroptosis, with macrophages being the most prominent. Foam cells—lipid-laden macrophages—struggle with cholesterol clearance, resulting in cholesterol crystal accumulation and persistent NLRP3 activation. The pyroptotic death of these macrophages not only releases IL-1β, but also acts on endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). In VSMCs, IL-1β and IL-18 induce adhesion molecules and chemokines, attracting more monocytes into plaques (73). IL-1β can also suppress collagen synthesis in VSMCs, potentially thinning the fibrous cap and increasing the risk of plaque rupture. While IL-1β deficiency reduces plaque burden, it is also associated with thicker fibrous caps, hinting that IL-1β influences plaque composition and stability (73). VSMCs themselves can activate inflammasomes under oxidative or metabolic stress; VSMC pyroptosis has been linked to vascular calcification in advanced plaques, partly through the release of matrix vesicles. Endothelial cells are also susceptible: exposure to disturbed flow or oxidised LDL can trigger inflammasome activation and local IL-1β release, promoting endothelial pyroptosis, dysfunction, and increased permeability to lipids (74). Notably, there is crosstalk between apoptotic and pyroptotic pathways in plaques. Macrophages initially undergoing apoptosis due to ER stress may progress to pyroptosis if caspase-1 is activated—a process called apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD (ASC)-mediated pyroptosis. This leads to abundant inflammasome activation in cholesterol- and cell debris-rich lesions.
A hallmark of advanced plaques is the necrotic core, comprising remnants of numerous pyroptotic macrophages. This region is highly pro-thrombotic and destabilises plaques, making them prone to rupture and clinical events. Pyroptosis is believed to enlarge the necrotic core by causing rapid foam cell lysis and the release of prothrombotic factors such as tissue factor. Additionally, IL-18 from pyroptotic cells can induce apoptosis in surrounding VSMCs, further weakening plaque structure. In contrast, controlled, non-inflammatory apoptosis of macrophages can benefit early plaque regression; however, pyroptosis shifts this balance toward inflammation and instability. In essence, pyroptosis transforms relatively stable lipid storage into highly inflammatory, rupture-prone plaques.
5.3 Clinical and translational insights
Recognition of the inflammasome–pyroptosis–IL-1β axis has shaped new therapeutic strategies. The CANTOS trial using canakinumab, an IL-1β inhibitor, was the first to demonstrate that blocking this cytokine can significantly reduce major cardiovascular events in patients with prior MI and elevated inflammation (22, 73). This finding strongly implicates inflammasome-driven IL-1β—mainly from plaque macrophages—in atherogenesis and its complications. While canakinumab targets IL-1β broadly and not specifically pyroptosis, its success has spurred interest in upstream interventions. Colchicine, which suppresses inflammasome assembly and activity, has also shown efficacy in reducing cardiovascular events in patients with chronic coronary disease and post-MI (75). Experimental NLRP3 inhibitors, such as MCC950, have shown promise in preclinical models: in hyperlipidaemic mice, MCC950 reduces plaque size and complexity, at least partly by preventing macrophage pyroptosis and necrotic core formation (70). This suggests that therapies targeting NLRP3 may stabilise plaques by preserving macrophage viability or shifting cell death toward less inflammatory mechanisms. Therapies that enhance cholesterol efflux (e.g., HDL mimetics) may also reduce pyroptosis by alleviating cholesterol crystal burden in foam cells.
Biomarker development is ongoing. Elevated IL-18 levels are associated with higher cardiovascular risk and may help identify patients likely to benefit from anti-IL-1 or anti-inflammatory therapy (76). Measurement of GSDMD or caspase-1 activity in blood cells might serve as indicators of systemic inflammasome activation in atherosclerosis, though this remains investigational. Importantly, not all inflammasome activity is harmful: some studies suggest that complete NLRP3 deficiency does not always decrease atherosclerosis, possibly due to compensation by alternative inflammatory pathways. Thus, patient selection and combination therapy may be necessary. Another relevant consideration is the role of infectious agents. Pathogens such as periodontal bacteria have been linked to NLRP3 activation in arteries, implying that infection control may indirectly reduce pyroptosis within plaques (77).
In conclusion, pyroptosis is a central process in the formation and destabilisation of atherosclerotic lesions. Targeting the inflammasome–pyroptosis pathway—via inhibition of upstream triggers, key proteins (NLRP3, caspase-1, GSDMD), or downstream cytokines (IL-1β, IL-18)—represents a promising strategy to prevent or treat atherosclerotic CVDs.
6 Hypertension
6.1 Inflammatory paradigm and pyroptosis in hypertension
Hypertension is the most prevalent modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality worldwide, classically defined by a persistent elevation in systolic and/or diastolic blood pressure (78). Accumulating evidence has established chronic low-grade inflammation as a central contributor to the development and maintenance of hypertension, with increased infiltration of immune cells and elevated pro-inflammatory cytokines detectable in both hypertensive patients and animal models (53, 79). Among these, IL-1β and IL-18 are consistently elevated in essential hypertension and act as key mediators of vascular inflammation and end-organ damage (53). Recent studies have confirmed overactivation of the inflammasome and pyroptotic pathways in the cardiovascular and renal complications associated with hypertension. For example, downregulation or pharmacological inhibition of key inflammasome components (such as NLRP3 or caspase-1) markedly attenuates blood pressure elevation in various hypertensive animal models (80). Meanwhile, research with two PH rat models and hypoxic human pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells (hPASMCs) indicates that pyroptosis contributes to pulmonary vascular fibrosis in pulmonary hypertension, with caspase-1 activation and STAT1-mediated PD-L1 upregulation in smooth muscle cells playing key roles in disease progression (81). Thus, elucidating the role of pyroptosis in hypertension pathogenesis not only provides mechanistic insight but also offers novel therapeutic opportunities.
6.2 Molecular mechanisms linking hypertensive stimuli to pyroptosis
Common hypertensive stimuli—including elevated angiotensin II (Ang II) and high dietary salt—elicit excessive production of ROS. ROS triggers dissociation of thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP), which subsequently binds and activates the NLRP3 inflammasome (82). Sustained activation of this Ang II/ROS/TXNIP/NLRP3 axis in hypertensive states drives pyroptotic cell death and robust local inflammation in target organs such as the heart, vasculature, kidney, and brain (82). In vitro studies demonstrate that Ang II exposure induces NLRP3 activation and IL-1β production in tubular epithelial cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner, which can be mitigated by ROS scavenging or NLRP3 knockdown (83). These data collectively support the concept that pyroptosis is a key intermediary between classic hypertensive insults and subsequent target organ damage (82).
6.3 Pyroptosis in cardiovascular and renal target organ damage
Renal involvement is a hallmark of hypertension-related end-organ damage. Ang II and high salt exposure induce mitochondrial dysfunction and excessive ROS production in renal tubular epithelial cells, activating NLRP3 and promoting pyroptotic cell death (83). In murine models, NLRP3 knockout protects against tubular injury and proteinuria during chronic Ang II infusion, confirming the pathogenic role of the inflammasome in hypertensive nephropathy (83). Salt-sensitive hypertension models (such as 1 K/DOCA/salt mice and Dahl salt-sensitive rats) display marked activation of renal NLRP3 inflammasome and IL-1β production, which are attenuated by genetic or pharmacological inhibition of NLRP3 (e.g., MCC950) (80, 84). Notably, blockade of IL-1 signalling with anakinra in such models significantly reduces blood pressure and renal fibrosis, further substantiating the role of IL-1β as a mediator of hypertensive renal injury (85).
6.4 Central nervous system inflammasome activation
Emerging evidence indicates that the central nervous system, particularly key regulatory nuclei within the hypothalamus, is susceptible to inflammasome activation in hypertension. Rodent studies show that high-salt diets induce activation of microglia and NLRP3 inflammasome in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN), promoting neuroinflammation and heightened sympathetic outflow (86). Selective blockade of NLRP3 within the PVN dampens local inflammatory responses, attenuates sympathetic excitation, and delays blood pressure elevation (86). While these findings are mainly limited to animal studies, they provide mechanistic insight into the contribution of central neuro-inflammation to hypertension and suggest new potential targets for intervention.
6.5 Translational and therapeutic perspectives
Given the central role of pyroptosis in hypertensive target organ damage, targeting the inflammasome–pyroptosis axis represents a promising therapeutic avenue. Preclinical studies have demonstrated that pharmacological inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome (e.g., MCC950) effectively reduces blood pressure and attenuates cardiac and renal injury in a variety of hypertensive models (80). Similarly, IL-1 receptor antagonists such as anakinra confer blood pressure-lowering and organ-protective effects (85). While broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory agents like colchicine have shown efficacy in reducing cardiovascular events in coronary artery disease, their ability to inhibit inflammasome assembly provides a rationale for their ongoing evaluation in hypertension (25, 87). Notably, monoclonal antibodies targeting IL-1β (such as canakinumab) have reduced recurrent cardiovascular events in large clinical trials, despite having little direct effect on blood pressure, suggesting that inflammasome inhibition may improve hypertension-related outcomes even in the absence of antihypertensive effects per se (22).
In summary, the evidence to date underscores pyroptosis as a pivotal link between classical hypertensive stimuli and downstream end-organ damage. Targeting this pathway holds promise for the dual aims of blood pressure reduction and organ protection, ushering in a potential paradigm shift towards integrated “anti-hypertensive plus anti-inflammatory” therapy. Future clinical trials will be essential to define the safety, efficacy, and optimal patient populations for such strategies in the management of hypertension.
7 Cardiac arrhythmias
Atrial fibrillation (AF), the most common sustained arrhythmia, is increasingly recognised as a condition with a strong inflammatory component, where inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis plays a pivotal role in both electrical and structural atrial remodeling. Seminal work by Yao et al. demonstrated that NLRP3 inflammasome activation in atrial cardiomyocytes directly promotes AF by fostering ectopic firing, atrial fibrosis, and creating a substrate for sustained arrhythmia (88). Consistently, atrial biopsies from patients with chronic AF reveal increased expression of the active caspase-1 p20 subunit and higher levels of IL-1β and IL-18 in both tissue and serum compared to individuals in sinus rhythm, correlating with AF burden and persistence (9, 89). Mechanistic insights reveal that NLRP3 activation in atrial myocytes impairs calcium handling through CaMKII signaling and disrupts connexin-mediated conduction, thus promoting electrical remodeling and reentry circuits (90). GSDMD–mediated pyroptosis has been directly linked to arrhythmogenesis: enforced expression of the GSDMD N-terminal fragment in murine atria increased AF susceptibility, promoted IL-1β release, and triggered macrophage recruitment (91). Furthermore, epicardial adipose tissue-derived IL-1β, especially in post-cardiac surgery patients, has been causally implicated in triggering postoperative AF through promoting local inflammation and atrial fibrosis (92). Clinical studies further confirm that AF patients typically present with elevated inflammasome cytokines. Elevated IL-1β and IL-18 predict AF persistence or recurrence after ablation, and inflammatory markers such as CRP and IL-6 are associated with increased risk of AF, especially following cardiac surgery (89, 93). Importantly, factors such as oxidative stress, obesity, diabetes, aging, and gut dysbiosis can all prime or activate the NLRP3 inflammasome in atrial tissue, highlighting a convergence of metabolic and inflammatory risk (94–97).
GSDMD plays a pivotal pathogenic role in the development of atrial fibrillation (AF). On one hand, it forms membrane pores in atrial cardiomyocytes, facilitating the release of interleukin-1β (IL-1β), thereby triggering local inflammatory responses, promoting atrial fibrosis, and recruiting macrophage infiltration (93, 98). On the other hand, NT-GSDMD anchors to the mitochondrial membrane, compromising its structural integrity and leading to mitochondrial dysfunction with excessive release of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Mitochondria-derived ROS disrupt intracellular calcium homeostasis, enhance sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release, and increase the likelihood of ectopic electrical activity (99, 100). In addition, ROS activate the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway, which upregulates potassium channels (e.g., Kv1.5), shortens action potential duration in atrial myocytes, and contributes to atrial electrical remodeling. Moreover, mitochondrial damage results in the release of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), which activates the cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS)-stimulator of interferon genes (STING) pathway, further amplifying inflammatory responses (93). Collectively, these events promote atrial fibrosis, immune cell infiltration, and electrical instability, thereby providing a pathological substrate for the initiation and maintenance of atrial fibrillation (Figure 2).
Figure 2
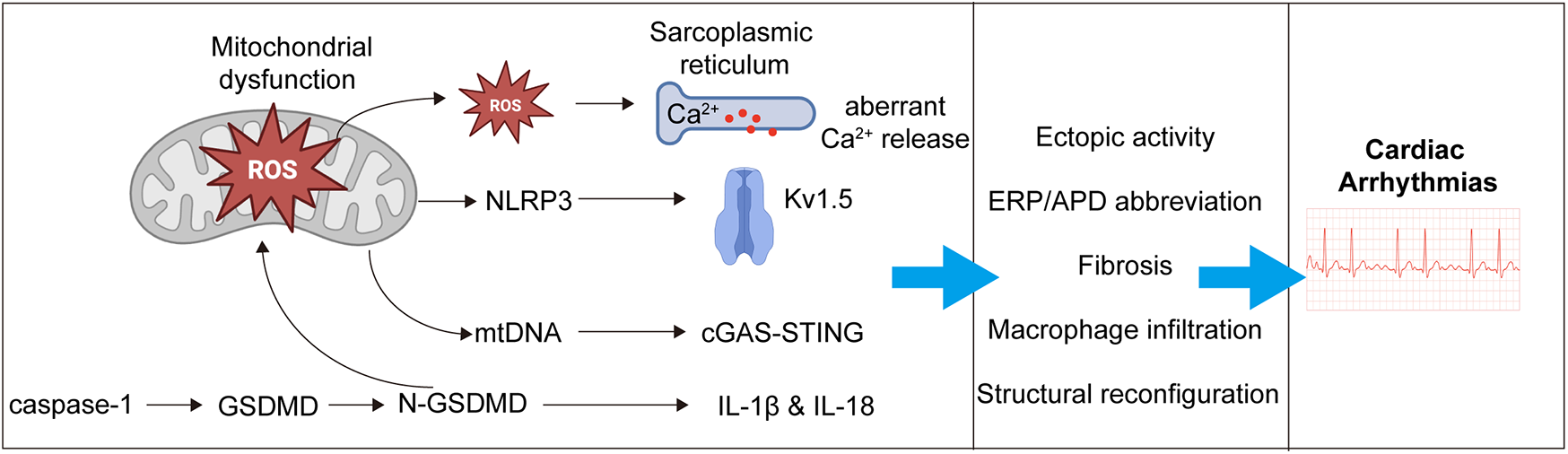
Mechanistic pathways linking pyroptosis to the development of atrial fibrillation. Activated gasdermin D (GSDMD) promotes the development of AF through both membrane pore formation and mitochondrial injury. Upon cleavage, the N-terminal fragment (NT-GSDMD) forms pores in the plasma membrane of atrial cardiomyocytes, facilitating the release of interleukin-1β (IL-1β), which triggers local inflammation, macrophage infiltration, and atrial fibrosis. Simultaneously, NT-GSDMD translocates to the mitochondrial membrane, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction and overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS). These ROS disrupt intracellular calcium homeostasis, enhance sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) calcium release, and increase the risk of ectopic electrical activity. ROS also activate the NLRP3 inflammasome, upregulating potassium channels (e.g., Kv1.5), shortening action potential duration, and promoting atrial electrical remodeling. Additionally, mitochondrial damage causes the release of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), which activates the cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS)–stimulator of interferon genes (STING) pathway, further amplifying the inflammatory response. Together, these events drive structural remodeling, immune cell infiltration, and electrical instability, creating a pro-arrhythmic substrate for the initiation and maintenance of AF.
SCHEMATIC ILLUSTRATION
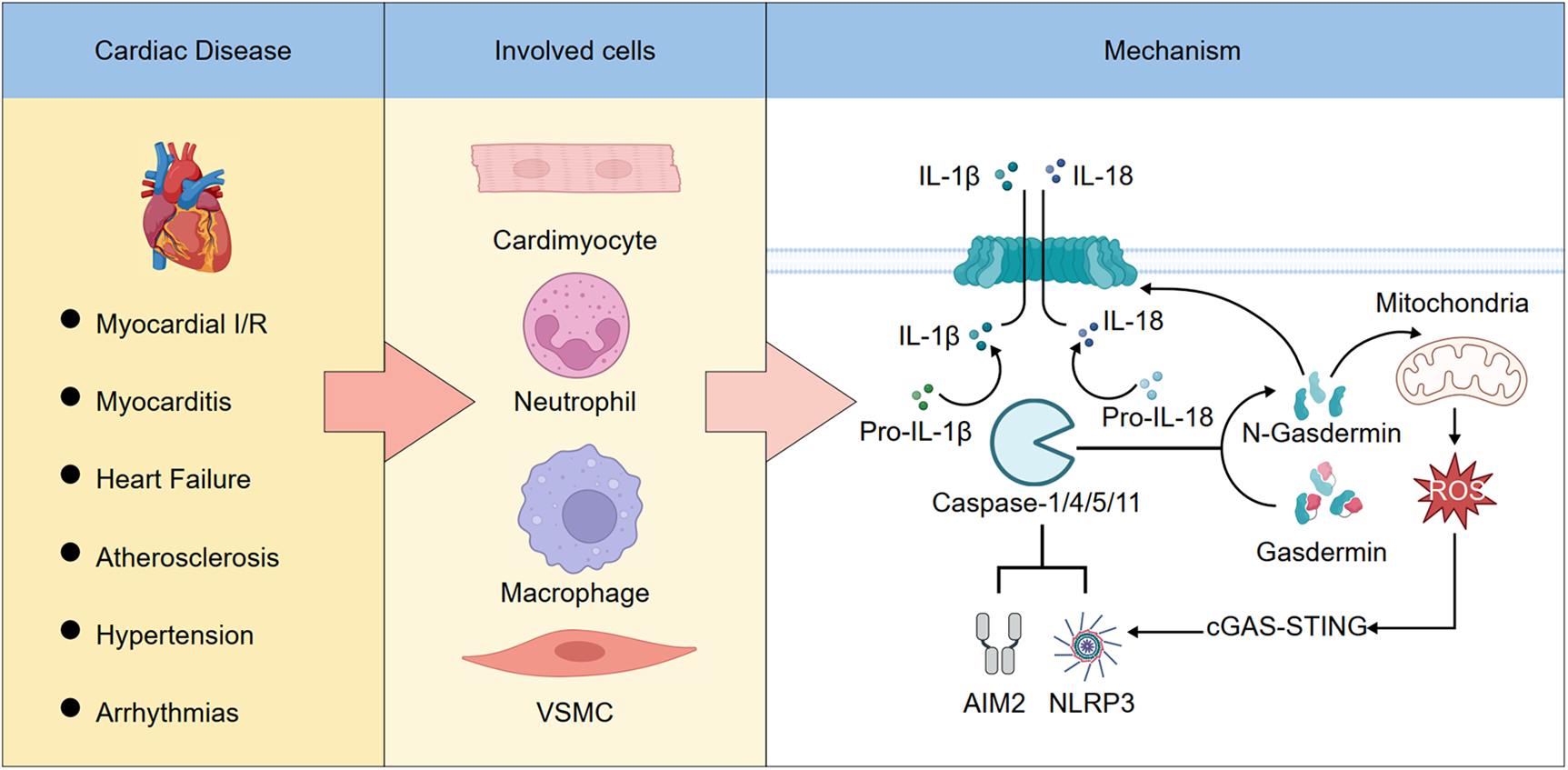
The role and mechanism of pyroptosis in cardiovascular diseases. (Left) Pyroptosis plays a pivotal role in various cardiovascular diseases. (Middle) It occurs in multiple cardiac cell types. (Right) Activation of the NLRP3 or AIM2 inflammasomes leads to the cleavage and activation of caspase-1, -4, -5, or -11. These activated caspases then process pro-inflammatory cytokines pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18 into their mature forms, IL-1β and IL-18. In addition, caspase-1/4/5/11 cleave gasdermin D (GSDMD), releasing its N-terminal fragment, which forms pores in the plasma membrane and mitochondria. Pore formation on the plasma membrane allows IL-1β and IL-18 to be released into the extracellular space, leading to pyroptotic cell death. Mitochondrial pore formation increases the release of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which further amplifies inflammasome activation, forming a feed-forward loop.
7.1 Translational and therapeutic perspective
These insights into inflammasome–pyroptosis pathways offer promising therapeutic implications for arrhythmia management. Pharmacological inhibition of NLRP3 with compounds such as MCC950 has been shown to prevent electrical remodeling and reduce AF inducibility in animal models (88, 101, 102). In the clinical setting, anti-inflammatory agents like colchicine have demonstrated efficacy in reducing the incidence and recurrence of post-operative and post-ablation AF, as confirmed by meta-analyses (103, 104). Other interventions, including IL-1β blockers (e.g., canakinumab), statins, and RAAS inhibitors, have shown variable but generally protective effects, likely mediated through attenuation of upstream inflammatory or oxidative stress signaling (105–107). Notably, IL-1 blockade after AF cardioversion may reduce recurrence, though larger trials are needed (108). Lifestyle interventions such as weight loss, improved glycaemic control, and exercise may also blunt atrial inflammasome activation and thus reduce AF risk, supporting a holistic management paradigm. In patients with HF or HFpEF, targeting inflammasome signaling can also lower AF vulnerability and arrhythmic remodeling (102, 109). Collectively, mounting evidence indicates that inflammation, particularly via the NLRP3–caspase-1–GSDMD/IL-1β/IL-18 axis, is a central driver of both electrical and structural remodeling in AF. Targeting these pathways—pharmacologically or through upstream risk modification—represents a promising adjunct to conventional rhythm and rate control strategies, particularly in patients with high inflammatory burden or comorbid metabolic disease.
8 Conclusion
Multiple forms of cell death—including pyroptosis, apoptosis, necroptosis, and ferroptosis—contribute to the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases through distinct molecular mechanisms and cellular processes (110–116), as summarized in Table 1. Pyroptosis represents a pivotal inflammatory cell death pathway that bridges innate immune activation with irreversible cardiac and vascular injury. Increasing evidence highlights its substantial involvement in the initiation and progression of diverse CVDs, including MI, myocarditis, HF, atherosclerosis, hypertension, and arrhythmias. By amplifying local and systemic inflammation through gasdermin-mediated membrane rupture and cytokine release, pyroptosis drives adverse tissue remodelling and clinical deterioration. Recent experimental and early translational studies suggest that targeting key components of the pyroptotic machinery—such as NLRP3, caspases, and gasdermins—may attenuate organ damage and improve outcomes in CVDs. This is summarized in the Schematic Illustration, which outlines the role and mechanism of pyroptosis in cardiovascular diseases. Nonetheless, significant challenges remain, including the need for precise biomarkers, improved understanding of disease- and cell-specific roles, and the development of selective, safe inhibitors suitable for clinical application. Further research into the temporal and spatial regulation of pyroptosis and its interplay with other death modalities will be essential for translating these insights into effective therapies. Ultimately, modulating pyroptosis holds promise as a novel avenue for CVDs intervention and risk stratification.
Recent studies have highlighted pyroptosis-related molecules—particularly gasdermin D (GSDMD), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and interleukin-18 (IL-18)—as potential biomarkers for cardiovascular diseases (111). Circulating GSDMD levels are elevated in patients with acute myocardial infarction and heart failure, correlating with infarct size and inflammatory cytokine profiles. Although ELISA kits for GSDMD, IL-1β, and IL-18 are available with some achieving clinical-grade sensitivity, large-scale, multicenter validation remains lacking (110). While IL-1β and IL-18 are broadly elevated across various inflammatory conditions, limiting their specificity for cardiovascular pathology, GSDMD's proximal role in the pyroptotic cascade may offer improved diagnostic precision (35). However, assay standardization and reference range establishment are urgently needed (34). Moreover, the dynamic temporal patterns of these biomarkers throughout disease onset, progression, and resolution are not yet fully characterized. Future prospective studies should aim to elucidate their diagnostic and prognostic utility and assess their integration with established cardiac biomarkers, such as troponins and B-type natriuretic peptide, to enhance cardiovascular risk stratification.
Table 1
| Cell death type | Key molecules | Morphological features | Inflammatory | Role in CVDs | Therapeutic targets |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pyroptosis | Caspase-1/4/5/11, GSDMD, GSDME, NLRP3 | Cell swelling, membrane pore formation, lysis | Yes | Myocarditis, Myocardial infarction, Heart failure, Atherosclerosis, Arrhythmia | NLRP3 inhibitors (e.g., MCC950), caspase-1 inhibitors (e.g., VX-765), GSDMD blockers |
| Apoptosis | Caspase-3/7, Bcl-2 Bax | Cell shrinkage, chromatin condensation, membrane blebbing | No | Ischemia-reperfusion injury, Heart failure | Caspase inhibitors |
| Necroptosis | RIPK1/RIPK3, MLKL | Organelle swelling, membrane rupture | Yes | Ischemia/reperfusion injury, Heart failure, Diabetic cardiomyopathy | RIPK1 inhibitors (e.g., Nec-1) MLKL inhibitors |
| Ferroptosis | GPX4, ACSL4, lipid ROS Fe2+ | Iron-dependent lipid peroxidation, mitochondrial shrinkage | Yes | Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy, Heart failure, Atherosclerosis | Ferrostatins, iron chelators, GPX4 activators |
Comparative characteristics of pyroptosis, apoptosis, necroptosis, and ferroptosis in cardiovascular diseases.
Although extensive preclinical studies have demonstrated the pathogenic role of pyroptosis in cardiovascular diseases such as myocarditis, heart failure, and atrial fibrillation, the clinical translation of anti-pyroptotic therapies remains challenging. Key pathway inhibitors—including MCC950 (targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome) and VX-765 (a caspase-1 inhibitor)—have shown therapeutic potential in animal models but are limited by suboptimal pharmacokinetics, poor tissue specificity, and risks of immunosuppression and infection during long-term use. A study shows that while these agents can improve cardiac function and attenuate remodeling, their narrow therapeutic windows and potential to impair host immunity constrain their clinical applicability (117). Moreover, the degree of pyroptosis activation varies across patient populations and disease stages, underscoring the need for reliable biomarkers to guide patient stratification and individualized therapy. A recent review highlighted that circulating or tissue levels of IL-1β, IL-18, and cleaved GSDMD may serve as valuable diagnostic and prognostic indicators (44). Notably, pyroptosis often acts in concert with apoptosis and necroptosis via the PANoptosis pathway, indicating that single-target therapies may be insufficient to halt inflammation-driven tissue injury. Current strategies increasingly emphasize combination regimens that integrate anti-pyroptotic agents with anti-fibrotic or immunomodulatory therapies to enhance efficacy (44, 118). Importantly, the timing of intervention is critical—early-phase blockade may effectively reverse pathological remodeling, whereas late-stage inhibition may be less beneficial or even detrimental. Furthermore, obstacles such as limited access to cardiac tissue, a lack of standardized clinical endpoints, and insufficient mechanistic validation continue to impede the clinical development of anti-pyroptosis therapies.
Statements
Author contributions
YN: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LW: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Formal analysis, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the project funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [82371795 to CZ], [82300461 to YZ], Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province of China [2022CFB241 to CZ].
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Correction Note
A correction has been made to this article. Details can be found at: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1680298.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
AF, atrial fibrillation; CVB3, coxsackievirus B3; CVDs, cardiovascular diseases; DAMPs, danger-associated molecular patterns; GSDMD, gasdermin D; GSDME, gasdermin E; HF, heart failure; ICI, immune checkpoint inhibitor; MI, myocardial infarction; PAMPs, pathogen-associated molecular patterns; PVN, paraventricular nucleus; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TAC, transaortic constriction; TXNIP, thioredoxin-interacting protein; VSMCs, vascular smooth muscle cells.
References
1.
Yu P Zhang X Liu N Tang L Peng C Chen X . Pyroptosis: mechanisms and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2021) 6(1):128. 10.1038/s41392-021-00507-5
2.
Vasudevan SO Behl B Rathinam VA . Pyroptosis-induced inflammation and tissue damage. Semin Immunol. (2023) 69:101781. 10.1016/j.smim.2023.101781
3.
Shi J Gao W Shao F . Pyroptosis: gasdermin-mediated programmed necrotic cell death. Trends Biochem Sci. (2017) 42(4):245–54. 10.1016/j.tibs.2016.10.004
4.
Evavold CL Kagan JC . How inflammasomes inform adaptive immunity. J Mol Biol. (2018) 430(2):217–37. 10.1016/j.jmb.2017.09.019
5.
Wang Y Yin B Li D Wang G Han X Sun X . GSDME mediates caspase-3-dependent pyroptosis in gastric cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2018) 495(1):1418–25. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.11.156
6.
Kesavardhana S Malireddi RKS Kanneganti T-D . Caspases in cell death, inflammation, and pyroptosis. Annu Rev Immunol. (2020) 38:567–95. 10.1146/annurev-immunol-073119-095439
7.
Mauro AG Bonaventura A Mezzaroma E Quader M Toldo S . NLRP3 inflammasome in acute myocardial infarction. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. (2019) 74(3):175–87. 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000717
8.
Liu P Zhang Z Chen H Chen Q . Pyroptosis: mechanisms and links with diabetic cardiomyopathy. Ageing Res Rev. (2024) 94:102182. 10.1016/j.arr.2023.102182
9.
Chen X Tian P-C Wang K Wang M Wang K . Pyroptosis: role and mechanisms in cardiovascular disease. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 9:897815. 10.3389/fcvm.2022.897815
10.
Shi H Gao Y Dong Z Yang J Gao R Li X et al GSDMD-mediated cardiomyocyte pyroptosis promotes myocardial I/R injury. Circ Res. (2021) 129(3):383–96. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.318629
11.
Jiang K Tu Z Chen K Xu Y Chen F Xu S et al Gasdermin D inhibition confers antineutrophil-mediated cardioprotection in acute myocardial infarction. J Clin Invest. (2022) 132(1):e151268. 10.1172/JCI151268
12.
Ye X Zhang P Zhang Y Luan J Xu C Wu Z et al GSDMD contributes to myocardial reperfusion injury by regulating pyroptosis. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:893914. 10.3389/fimmu.2022.893914
13.
Zhou W Yang Y Feng Z Zhang Y Chen Y Yu T et al Inhibition of caspase-1-dependent pyroptosis alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury during cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) in type 2 diabetic rats. Sci Rep. (2024) 14(1):19420. 10.1038/s41598-024-70477-5
14.
Heger LA Schommer N Van Bruggen S Sheehy CE Chan W Wagner DD . Neutrophil NLRP3 promotes cardiac injury following acute myocardial infarction through IL-1β production, VWF release and NET deposition in the myocardium. Sci Rep. (2024) 14(1):14524. 10.1038/s41598-024-64710-4
15.
Qiu Y . The role of pyroptosis in coronary heart disease. Anatol J Cardiol. (2024) 28(7):318–28. 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2024.4001
16.
Weng Y Ye B Lin J Lin S Zhong L Huang W et al Elevated circulating levels of gasdermin D are related to acute myocardial infarction and pyrogptosis. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2022) 22(1):554. 10.1186/s12872-022-02998-8
17.
Shen S Wang Z Sun H Ma L . Role of NLRP3 inflammasome in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and ventricular remodeling. Med Sci Monit. (2022) 28:e934255. 10.12659/MSM.934255
18.
Zhaolin Z Guohua L Shiyuan W Zuo W . Role of pyroptosis in cardiovascular disease. Cell Prolif. (2019) 52(2):e12563. 10.1111/cpr.12563
19.
Toldo S Abbate A . The NLRP3 inflammasome in acute myocardial infarction. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2018) 15(4):203–14. 10.1038/nrcardio.2017.161
20.
Yarovinsky TO Su M Chen C Xiang Y Tang WH Hwa J . Pyroptosis in cardiovascular diseases: pumping gasdermin on the fire. Semin Immunol. (2023) 69:101809. 10.1016/j.smim.2023.101809
21.
Onódi Z Ruppert M Kucsera D Sayour AA Toth VE Koncsos G et al AIM2-driven Inflammasome activation in heart failure. Cardiovasc Res. (2021) 117(13):2639–51. 10.1093/cvr/cvab202
22.
Ridker PM Everett BM Thuren T MacFadyen JG Chang WH Ballantyne C et al Antiinflammatory therapy with canakinumab for atherosclerotic disease. N Engl J Med. (2017) 377(12):1119–31. 10.1056/NEJMoa1707914
23.
Abbate A Wohlford GF Del Buono MG Chiabrando JG Markley R Turlington J et al Interleukin-1 blockade with anakinra and heart failure following ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: results from a pooled analysis of the VCUART clinical trials. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. (2022) 8(5):503–10. 10.1093/ehjcvp/pvab075
24.
Abbate A Toldo S Marchetti C Kron J Van Tassell BW Dinarello CA . Interleukin-1 and the inflammasome as therapeutic targets in cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. (2020) 126(9):1260–80. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.315937
25.
Tardif J-C Kouz S Waters DD Bertrand OF Diaz R Maggioni AP et al Efficacy and safety of low-dose colchicine after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. (2019) 381(26):2497–505. 10.1056/NEJMoa1912388
26.
Van Hout GP Bosch L Ellenbroek GH De Haan JJ Van Solinge WW Cooper MA et al The selective NLRP3-inflammasome inhibitor MCC950 reduces infarct size and preserves cardiac function in a pig model of myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. (2017) 38(11):828–36. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw247
27.
Do Carmo H Arjun S Petrucci O Yellon DM Davidson SM . The caspase 1 inhibitor VX-765 protects the isolated rat heart via the RISK pathway. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. (2018) 32(2):165–8. 10.1007/s10557-018-6781-2
28.
Ye X Lin Z-j Hong G-h Wang Z-m Dou R-t Lin J-y et al Pyroptosis inhibitors MCC950 and VX-765 mitigate myocardial injury by alleviating oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in acute myocardial hypoxia. Exp Cell Res. (2024) 438(2):114061. 10.1016/j.yexcr.2024.114061
29.
Liu W Shen J Li Y Wu J Luo X Yu Y et al Pyroptosis inhibition improves the symptom of acute myocardial infarction. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12(10):852. 10.1038/s41419-021-04143-3
30.
Audia JP Yang X-M Crockett ES Housley N Haq EU O’Donnell K et al Caspase-1 inhibition by VX-765 administered at reperfusion in P2Y12 receptor antagonist-treated rats provides long-term reduction in myocardial infarct size and preservation of ventricular function. Basic Res Cardiol. (2018) 113(5):32. 10.1007/s00395-018-0692-z
31.
Wang Y Jia L Shen J Wang Y Fu Z Su S-a et al Cathepsin B aggravates coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis through activating the inflammasome and promoting pyroptosis. PLoS Pathog. (2018) 14(1):e1006872. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006872
32.
Sun L Yuan H Zhao G . IL-37 alleviates coxsackievirus B3-induced viral myocarditis via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis. Sci Rep. (2022) 12(1):20077. 10.1038/s41598-022-22617-y
33.
Nadkarni R Chu WC Lee CQ Mohamud Y Yap L Toh GA et al Viral proteases activate the CARD8 inflammasome in the human cardiovascular system. J Exp Med. (2022) 219(10):e20212117. 10.1084/jem.20212117
34.
Chen YF Cheng LL Shen YH Zhang H Wang XJ Xu YC et al Investigate the role of neutrophil extracellular traps in immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated myocarditis with programmed death protein-1 inhibitors involvement. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. (2023) 103(42):3384–93. 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20230901-00357
35.
Sun S-J Jiao X-D Chen Z-G Cao Q Zhu J-H Shen Q-R et al Gasdermin-E-mediated pyroptosis drives immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated myocarditis via cGAS-STING activation. Nat Commun. (2024) 15(1):6640. 10.1038/s41467-024-50996-5
36.
Yao J Sterling K Wang Z Zhang Y Song W . The role of inflammasomes in human diseases and their potential as therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2024) 9(1):10. 10.1038/s41392-023-01687-y
37.
Nielsen DL Juhl CB Nielsen OH Chen IM Herrmann J . Immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced cardiotoxicity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. (2024) 10(10):1390–9. 10.1001/jamaoncol.2024.3065
38.
Matzen E Bartels LE Løgstrup B Horskær S Stilling C Donskov F . Immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced myocarditis in cancer patients: a case report and review of reported cases. Cardio-oncol. (2021) 7(1):27. 10.1186/s40959-021-00114-x
39.
Wong C-K Lam T-H Liao S-Y Lau Y-M Tse H-F So BYF . Immunopathogenesis of immune checkpoint inhibitor induced myocarditis: insights from experimental models and treatment implications. Biomedicines. (2023) 11(1):107. 10.3390/biomedicines11010107
40.
Han J Dai S Zhong L Shi X Fan X Zhong X et al GSDMD (Gasdermin D) mediates pathological cardiac hypertrophy and generates a feed-forward amplification cascade via mitochondria-STING (stimulator of interferon genes) axis. Hypertension. (2022) 79:2505–18. 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.122.20004
41.
Liu J Zhou J Luan Y Li X Meng X Liao W et al cGAS-STING, inflammasomes and pyroptosis: an overview of crosstalk mechanism of activation and regulation. Cell Commun Signal. (2024) 22(1):22. 10.1186/s12964-023-01466-w
42.
Won T Gilotra NA Wood MK Hughes DM Talor MV Lovell J et al Increased interleukin 18-dependent immune responses are associated with myopericarditis after COVID-19 mRNA vaccination. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:851620. 10.3389/fimmu.2022.851620
43.
Xiang Q Geng Z-X Yi X Wei X Zhu X-H Jiang D-S et al PANoptosis: a novel target for cardiovascular diseases. Trends Pharmacol Sci. (2024) 45(8):739–56. 10.1016/j.tips.2024.06.002
44.
Wu S Ding D Wang D . Regulated cell death pathways in pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Rev Cardiovasc Med. (2024) 25(10):366. 10.31083/j.rcm2510366
45.
Zhang H Lin J Shen Y Pan J Wang C Cheng L . Protective effect of crocin on immune checkpoint inhibitors-related myocarditis through inhibiting NLRP3 mediated pyroptosis in cardiomyocytes via NF-kappaB pathway. J Inflamm Res. (2022) 15:1653–66. 10.2147/JIR.S348464
46.
Kerneis M Cohen F Combes A Amoura Z Pare C Brugier D et al Rationale and design of the ARAMIS trial: anakinra versus placebo, a double blind randomized controlled trial for the treatment of acute myocarditis. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. (2023) 116(10):460–6. 10.1016/j.acvd.2023.07.004
47.
Chin C-G Chen Y-C Lin F-J Lin Y-K Lu Y-Y Cheng T-Y et al Targeting NLRP3 signaling reduces myocarditis-induced arrhythmogenesis and cardiac remodeling. J Biomed Sci. (2024) 31(1):42. 10.1186/s12929-024-01032-7
48.
Wang Y Qin Y Wang T Chen Y Lang X Zheng J et al Pyroptosis induced by enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus B3 infection affects viral replication and host response. Sci Rep. (2018) 8(1):2887. 10.1038/s41598-018-20958-1
49.
González A Schelbert EB Díez J Butler J . Myocardial interstitial fibrosis in heart failure: biological and translational perspectives. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2018) 71(15):1696–706. 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.02.021
50.
Bacmeister L Schwarzl M Warnke S Stoffers B Blankenberg S Westermann D et al Inflammation and fibrosis in murine models of heart failure. Basic Res Cardiol. (2019) 114(3):19. 10.1007/s00395-019-0722-5
51.
Chai R Xue W Shi S Zhou Y Du Y Li Y et al Cardiac remodeling in heart failure: role of pyroptosis and its therapeutic implications. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 9:870924. 10.3389/fcvm.2022.870924
52.
Zeng C Duan F Hu J Luo B Huang B Lou X et al NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis contributes to the pathogenesis of non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. Redox Biol. (2020) 34:101523. 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101523
53.
De Miguel C Pelegrín P Baroja-Mazo A Cuevas S . Emerging role of the inflammasome and pyroptosis in hypertension. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22(3):1064. 10.3390/ijms22031064
54.
Yue R Zheng Z Luo Y Wang X Lv M Qin D et al NLRP3-mediated Pyroptosis aggravates pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy, fibrosis, and dysfunction in mice: cardioprotective role of irisin. Cell Death Discov. (2021) 7(1):50. 10.1038/s41420-021-00434-y
55.
Carbone S Lee PJH Mauro AG Mezzaroma E Buzzetti R Van Tassell B et al Interleukin-18 mediates cardiac dysfunction induced by western diet independent of obesity and hyperglycemia in the mouse. Nutr Diabetes. (2017) 7(4):e258. 10.1038/nutd.2017.1
56.
Lu Y Lu Y Meng J Wang Z . Pyroptosis and its regulation in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Front Physiol. (2022) 12:791848. 10.3389/fphys.2021.791848
57.
Naryzhnaya NV Maslov LN Popov SV Mukhomezyanov AV Ryabov VV Kurbatov BK et al Pyroptosis is a drug target for prevention of adverse cardiac remodeling: the crosstalk between pyroptosis, apoptosis, and autophagy. J Biomed Res. (2022) 36(6):375–89. 10.7555/JBR.36.20220123
58.
Wang J Deng B Liu Q Huang Y Chen W Li J et al Pyroptosis and ferroptosis induced by mixed lineage kinase 3 (MLK3) signaling in cardiomyocytes are essential for myocardial fibrosis in response to pressure overload. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11(7):574. 10.1038/s41419-020-02777-3
59.
Abbate A Trankle CR Buckley LF Lipinski MJ Appleton D Kadariya D et al Interleukin-1 blockade inhibits the acute inflammatory response in patients with ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction. J Am Heart Assoc. (2020) 9(5):e014941. 10.1161/JAHA.119.0149
60.
Sun X Duan J Gong C Feng Y Hu J Gu R et al Colchicine ameliorates dilated cardiomyopathy via SIRT2-mediated suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. J Am Heart Assoc. (2022) 11(13):e025266. 10.1161/JAHA.122.02526
61.
Wohlford GF Van Tassell BW Billingsley HE Kadariya D Canada JM Carbone S et al Phase 1B, randomized, double-blinded, dose escalation, single-center, repeat dose safety and pharmacodynamics study of the oral NLRP3 inhibitor dapansutrile in subjects with NYHA II-III systolic heart failure. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. (2021) 77(1):49–60. 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000931
62.
Zhuang Z Gu J Li B Yang L . Inhibition of gasdermin D palmitoylation by disulfiram is crucial for the treatment of myocardial infarction. Transl Res. (2024) 264:66–75. 10.1016/j.trsl.2023.09.007
63.
Kogel A Baumann L Maeder C Büttner P Thiele H Kneuer JM et al NLRP3 inflammasome-induced pyroptosis and serum ASC specks are increased in patients with cardiogenic shock. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2024) 327(4):H869–79. 10.1152/ajpheart.00231.2024
64.
Watanabe-Kusunoki K Li C Bandeira Honda TS Zhao D Kusunoki Y Ku J et al Gasdermin D drives focal crystalline thrombotic microangiopathy by accelerating immunothrombosis and necroinflammation. Blood. (2024) 144(3):308–22. 10.1182/blood.2023021949
65.
Burger F Baptista D Roth A da Silva RF Montecucco F Mach F et al NLRP3 inflammasome activation controls vascular smooth muscle cells phenotypic switch in atherosclerosis. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23(1):340. 10.3390/ijms23010340
66.
Fan X Han J Zhong L Zheng W Shao R Zhang Y et al Macrophage-derived GSDMD plays an essential role in atherosclerosis and cross talk between macrophages via the mitochondria-STING-IRF3/NF-κB axis. Arterioscler, Thromb, Vasc Biol. (2024) 44(6):1365–78. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.123.320612
67.
Huang B Zou Z Li Y Chen H Lai K Yuan Y et al Gasdermin D-mediated pyroptosis promotes the development of atherosclerosis. Lab Invest. (2024) 104(4):100337. 10.1016/j.labinv.2024.100337
68.
Jin Y Fu J . Novel insights into the NLRP 3 inflammasome in atherosclerosis. J Am Heart Assoc. (2019) 8(12):e012219. 10.1161/JAHA.119.012219
69.
Duewell P Kono H Rayner KJ Sirois CM Vladimer G Bauernfeind FG et al NLRP3 inflammasomes are required for atherogenesis and activated by cholesterol crystals. Nature. (2010) 464(7293):1357–61. 10.1038/nature08938
70.
Zeng W Wu D Sun Y Suo Y Yu Q Zeng M et al The selective NLRP3 inhibitor MCC950 hinders atherosclerosis development by attenuating inflammation and pyroptosis in macrophages. Sci Rep. (2021) 11(1):19305. 10.1038/s41598-021-98437-3
71.
Zeng X Liu D Huo X Wu Y Liu C Sun Q . Pyroptosis in NLRP3 inflammasome-related atherosclerosis. Cell Stress. (2022) 6(10):79–88. 10.15698/cst2022.10.272
72.
Kirii H Niwa T Yamada Y Wada H Saito K Iwakura Y et al Lack of interleukin-1beta decreases the severity of atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice. Arterioscler, Thromb, Vasc Biol. (2003) 23(4):656–60. 10.1161/01.ATV.0000064374.15232.C3
73.
Li Y Niu X Xu H Li Q Meng L He M et al VX-765 attenuates atherosclerosis in ApoE deficient mice by modulating VSMCs pyroptosis. Exp Cell Res. (2020) 389(1):111847. 10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.111847
74.
Zhaolin Z Jiaojiao C Peng W Yami L Tingting Z Jun T et al OxLDL induces vascular endothelial cell pyroptosis through miR-125a-5p/TET2 pathway. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234(5):7475–91. 10.1002/jcp.27509
75.
Nidorf SM Fiolet ATL Mosterd A Eikelboom JW Schut A Opstal TSJ et al Colchicine in patients with chronic coronary disease. N Engl J Med. (2020) 383(19):1838–47. 10.1056/NEJMoa2021372
76.
Mallat Z Corbaz A Scoazec A Besnard S Lesèche G Chvatchko Y et al Expression of interleukin-18 in human atherosclerotic plaques and relation to plaque instability. Circulation. (2001) 104(14):1598–603. 10.1161/hc3901.096721
77.
Gong T Chen Q Mao H Zhang Y Ren H Xu M et al Outer membrane vesicles of Porphyromonas gingivalis trigger NLRP3 inflammasome and induce neuroinflammation, tau phosphorylation, and memory dysfunction in mice. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2022) 12:925435. 10.3389/fcimb.2022.925435
78.
Messerli FH Williams B Ritz E . Essential hypertension. Lancet. (2007) 370(9587):591–603. 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61299-9
79.
Dörffel Y . Preactivated monocytes from hypertensive patients as a factor for atherosclerosis?Atherosclerosis. (2001) 157(1):151–60. 10.1016/S0021-9150(00)00674-2
80.
Krishnan SM Ling YH Huuskes BM Ferens DM Saini N Chan CT et al Pharmacological inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome reduces blood pressure, renal damage, and dysfunction in salt-sensitive hypertension. Cardiovasc Res. (2019) 115(4):776–87. 10.1093/cvr/cvy252
81.
Zhang M Xin W Yu Y Yang X Ma C Zhang H et al Programmed death-ligand 1 triggers PASMCs pyroptosis and pulmonary vascular fibrosis in pulmonary hypertension. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2020) 138:23–33. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2019.10.008
82.
Zhou R Tardivel A Thorens B Choi I Tschopp J . Thioredoxin-interacting protein links oxidative stress to inflammasome activation. Nat Immunol. (2010) 11(2):136–40. 10.1038/ni.1831
83.
Wen Y Liu Y Tang T Lv L Liu H Ma K et al NLRP3 inflammasome activation is involved in Ang II-induced kidney damage via mitochondrial dysfunction. Oncotarget. (2016) 7(34):54290–302. 10.18632/oncotarget.11091
84.
Krishnan SM Dowling JK Ling YH Diep H Chan CT Ferens D et al Inflammasome activity is essential for one kidney/deoxycorticosterone acetate/salt-induced hypertension in mice. Br J Pharmacol. (2016) 173(4):752–65. 10.1111/bph.13230
85.
Ling YH Krishnan SM Chan CT Diep H Ferens D Chin-Dusting J et al Anakinra reduces blood pressure and renal fibrosis in one kidney/DOCA/salt-induced hypertension. Pharmacol Res. (2017) 116:77–86. 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.12.015
86.
Wang M-L Kang Y-M Li X-G Su Q Li H-B Liu K-L et al Central blockade of NLRP3 reduces blood pressure via regulating inflammation microenvironment and neurohormonal excitation in salt-induced prehypertensive rats. J Neuroinflammation. (2018) 15(1):95. 10.1186/s12974-018-1131-7
87.
Wu D Chen Y Sun Y Gao Q Li H Yang Z et al Target of MCC950 in inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation: a literature review. Inflammation. (2020) 43(1):17–23. 10.1007/s10753-019-01098-8
88.
Yao C Veleva T Scott L Cao S Li L Chen G et al Enhanced cardiomyocyte NLRP3 inflammasome signaling promotes atrial fibrillation. Circulation. (2018) 138(20):2227–42. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.035202
89.
Ajoolabady A Nattel S Lip GYH Ren J . Inflammasome signaling in atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2022) 79(23):2349–66. 10.1016/j.jacc.2022.03.379
90.
Heijman J Muna AP Veleva T Molina CE Sutanto H Tekook M et al Atrial myocyte NLRP3/CaMKII nexus forms a substrate for postoperative atrial fibrillation. Circ Res. (2020) 127(8):1036–55. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316710
91.
Yuan Y Martsch P Chen X Martinez E Li L Song J et al Atrial cardiomyocyte-restricted cleavage of gasdermin D promotes atrial arrhythmogenesis. Eur Heart J. (2025) 46(13):1250–62. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaf024
92.
Cabaro S Conte M Moschetta D Petraglia L Valerio V Romano S et al Epicardial adipose tissue-derived IL-1β triggers postoperative atrial fibrillation. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2022) 10:893729. 10.3389/fcell.2022.893729
93.
Weymann A Popov A-F Sabashnikov A Ali-Hasan-Al-Saegh S Ryazanov M Tse G et al Baseline and postoperative levels of C-reactive protein and interleukins as inflammatory predictors of atrial fibrillation following cardiac surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Kardiol Pol. (2018) 76(2):440–51. 10.5603/KP.a2017.0242
94.
Yang X An N Zhong C Guan M Jiang Y Li X et al Enhanced cardiomyocyte reactive oxygen species signaling promotes ibrutinib-induced atrial fibrillation. Redox Biol. (2020) 30:101432. 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101432
95.
Scott L Fender AC Saljic A Li L Chen X Wang X et al NLRP3 inflammasome is a key driver of obesity-induced atrial arrhythmias. Cardiovasc Res. (2021) 117(7):1746–59. 10.1093/cvr/cvab024
96.
Zhou X Liu H Feng F Kang GJ Liu M Guo Y et al Macrophage IL-1β mediates atrial fibrillation risk in diabetic mice. JCI Insight. (2024) 9(15):e171102. 10.1172/jci.insight.171102
97.
Zhang Y Zhang S Li B Luo Y Gong Y Jin X et al Gut microbiota dysbiosis promotes age-related atrial fibrillation by lipopolysaccharide and glucose-induced activation of NLRP3-inflammasome. Cardiovasc Res. (2022) 118(3):785–97. 10.1093/cvr/cvab114
98.
Yan B Liu T Yao C Liu X Du Q Pan L . LncRNA XIST shuttled by adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles suppresses myocardial pyroptosis in atrial fibrillation by disrupting miR-214-3p-mediated Arl2 inhibition. Lab Invest. (2021) 101(11):1427–38. 10.1038/s41374-021-00635-0
99.
Ping Z Fangfang T Yuliang Z Xinyong C Lang H Fan H et al Oxidative stress and pyroptosis in doxorubicin-induced heart failure and atrial fibrillation. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2023) 2023:4938287. 10.1155/2023/4938287
100.
Luo Y Zhang Y Han X Yuan Y Zhou Y Gao Y et al Akkermansia muciniphila prevents cold-related atrial fibrillation in rats by modulation of TMAO induced cardiac pyroptosis. EBioMedicine. (2022) 82:104087. 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104087
101.
Jiang X Yang F Ou D Huang L Li H Lang M . MCC950 ameliorates ventricular arrhythmia vulnerability induced by heart failure. Bioengineered. (2022) 13(4):8593–604. 10.1080/21655979.2022.2053813
102.
Yang H Zhu J Fu H Shuai W . Dapansutrile ameliorates atrial inflammation and vulnerability to atrial fibrillation in HFpEF rats. Heart Lung Circ. (2024) 33(1):65–77. 10.1016/j.hlc.2023.09.017
103.
Varghese B Feldman DI Chew C Valilis E Blumenthal RS Sharma G et al Inflammation, atrial fibrillation, and the potential role for colchicine therapy. Heart Rhythm O2. (2021) 2(3):298–303. 10.1016/j.hroo.2021.03.011
104.
Ge P Fu Y Su Q Jin M Guo L Miao C et al Colchicine for prevention of post-operative atrial fibrillation: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 9:1032116. 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1032116
105.
Niskala A Heijman J Dobrev D Jespersen T Saljic A . Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome signalling for the management of atrial fibrillation. Br J Pharmacol. (2024) 181(24):4939–57. 10.1111/bph.16470
106.
Peng H Yang Y Zhao Y Xiao H . The effect of statins on the recurrence rate of atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation: a meta-analysis. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. (2018) 41(11):1420–7. 10.1111/pace.13485
107.
Zhao J Chen M Zhuo C Huang Y Zheng L Wang Q . The effect of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors on the recurrence of atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation. Int Heart J. (2020) 61(6):1174–82. 10.1536/ihj.20-346
108.
Krisai P Blum S Schnabel RB Sticherling C Kühne M von Felten S et al Canakinumab after electrical cardioversion in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. (2020) 13(7):e008197. 10.1161/CIRCEP.119.008197
109.
Camm AJ Naccarelli GV Mittal S Crijns HJGM Hohnloser SH Ma C-S et al The increasing role of rhythm control in patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2022) 79(19):1932–48. 10.1016/j.jacc.2022.03.337
110.
Lv C Hu C Zhu C Wan X Chen C Ji X et al Empagliflozin alleviates the development of autoimmune myocarditis via inhibiting NF-kappaB-dependent cardiomyocyte pyroptosis. Biomed Pharmacother. (2024) 170:115963. 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115963
111.
Jia C Chen H Zhang J Zhou K Zhuge Y Niu C et al Role of pyroptosis in cardiovascular diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. (2019) 67:311–8. 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.12.028
112.
Zeng C Wang R Tan H . Role of pyroptosis in cardiovascular diseases and its therapeutic implications. Int J Biol Sci. (2019) 15(7):1345–57. 10.7150/ijbs.33568
113.
Wang Y Zhang Z Li H Wang M Qiu Y Lu L . miR-29b-3p regulates cardiomyocytes pyroptosis in CVB3-induced myocarditis through targeting DNMT3A. Cell Mol Biol Lett. (2024) 29(1):55. 10.1186/s11658-024-00576-8
114.
Li GZ Liu JY Zhou H . Ferroptosis: a novel therapeutic target for diabetic cardiomyopathy. World J Diabetes. (2025) 16(6):104665. 10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.104665
115.
Wang S Yu Z Ye L Xiao D Wang P Wang Y et al Ferritinophagy in cardiovascular diseases: mechanisms and potential therapy. Mol Cell Biochem. (2025). 10.1007/s11010-025-05301-3
116.
Xiong Y Zhang Z Liu S Shen L Zheng L Ding L et al Lupeol alleviates autoimmune myocarditis by suppressing macrophage pyroptosis and polarization via PPARalpha/LACC1/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Phytomedicine. (2024) 123:155193. 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155193
117.
Li X You J Dai F Wang S Yang FH Wang X et al TAK1 activation by NLRP3 deficiency confers cardioprotection against pressure overload-induced cardiomyocyte pyroptosis and hypertrophy. JACC: Basic Trans Sci. (2023) 8(12):1555–73. 10.1016/j.jacbts.2023.05.008
118.
Wei J Peng MY Wang SN Lu HX . CXCL4:nLRP3-mediated pyroptosis product that regulates cardiac fibrosis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 133:112096. 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112096
Summary
Keywords
pyroptosis, cardiovascular diseases, myocardial infarction, myocarditis, heart failure, atherosclerosis, hypertension, arrhythmia
Citation
Niu Y, Wang L, Zhang Y, Zou Y and Zhou C (2025) Pyroptosis in cardiovascular diseases: roles, mechanisms, and clinical implications. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1629016. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1629016
Received
15 May 2025
Accepted
17 July 2025
Published
04 August 2025
Corrected
11 September 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
DeLisa Fairweather, Mayo Clinic Florida, United States
Reviewed by
Zhengwu Sun, Dalian Municipal Central Hospital, China
Jieyun You, Tongji University School of Medicine, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Niu, Wang, Zhang, Zou and Zhou.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Cheng Zhou zhoucheng_xhxw@163.comYanqiang Zou zouyanqiang123@yeah.net
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.