Abstract
Oncogenes are typically overexpressed in tumor tissues and often linked to poor prognosis. However, recent advancements in bioinformatics have revealed that many highly expressed genes in tumors are associated with better patient outcomes. These genes, which act as tumor suppressors, are referred to as “paradoxical genes.” Analyzing The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) confirmed the widespread presence of paradoxical genes, and KEGG analysis revealed their role in regulating tumor metabolism. Mechanistically, discrepancies between gene and protein expression-affected by pre- and post-transcriptional modifications-may drive this phenomenon. Mechanisms like upstream open reading frames and alternative splicing contribute to these inconsistencies. Many paradoxical genes modulate the tumor immune microenvironment, exerting tumor-suppressive effects. Further analysis shows that the stage- and tumor-specific expression of these genes, along with their environmental sensitivity, influence their dual roles in various signaling pathways. These findings highlight the importance of paradoxical genes in resisting tumor progression and maintaining cellular homeostasis, offering new avenues for targeted cancer therapy.
Graphical Abstract
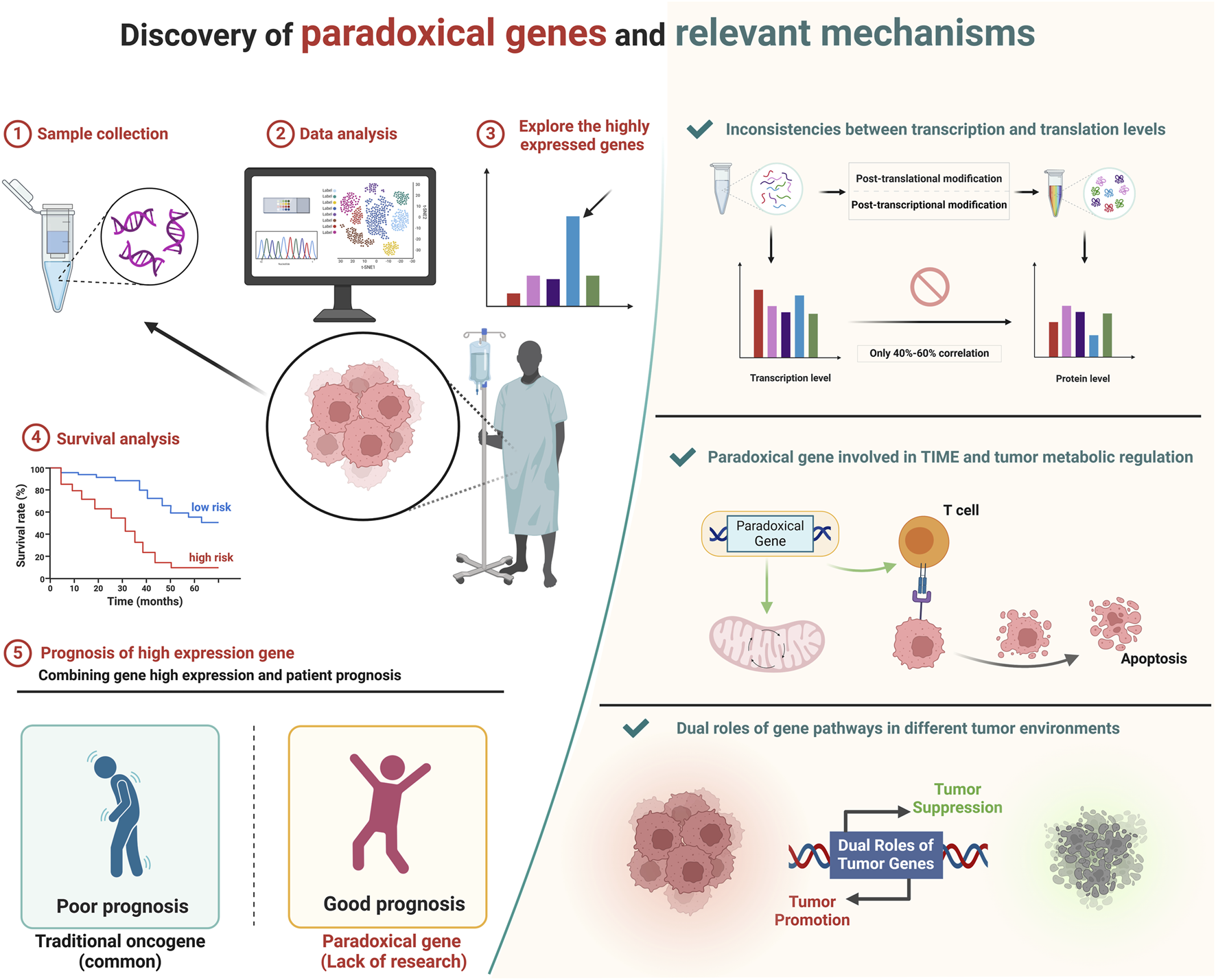
Typically, oncogenes show higher expression in tumors and are linked to poor prognoses. However, some highly expressed genes in tumors are associated with better outcomes and act as tumor suppressors, termed paradoxical genes. We explored these genes using bioinformatics, revealing their significant roles in regulating tumor metabolism and immune microenvironments, offering new insights for targeted cancer therapy. Created in BioRender. ZHAO, X. (2025) https://BioRender.com/b00e214.
1 Introduction
Traditionally, bioinformatics analyses often utilize the differential gene abundance between tumor and normal tissues to screen for target genes (Golub et al., 1999). Typically, genes with significantly higher abundance in tumors than normal tissues are classified as oncogenes and become focal points of research (Bishop, 1991; Croce, 2008). However, a new understanding has emerged with the proliferation of comprehensive databases such as TCGA. Researchers increasingly recognize that not all genes are highly expressed in tumors act as promoters of cancer (Cao et al., 2021; Yan et al., 2019; Boor et al., 2020; Martinez-Turtos et al., 2022). In fact, some genes show high abundance in tumor tissues but are associated with good patients prognosis (Cao et al., 2021; Yan et al., 2019; Boor et al., 2020; Martinez-Turtos et al., 2022). This finding challenges the traditional understanding of tumor biology. Although public databases provide evidence that genes which are highly expressed in tumor tissues and serve tumor suppressor roles are prevalent, they have not been broadly recognized or systematically analyzed by the scientific community. Our work pioneers the classification and definition of these genes as “paradoxical genes,” and it delves deeply into the reasons and context for the existence of these paradoxical genes.
The discrepancy between mRNA and protein levels may be a reason for the emergence of paradoxical genes (Vogel and Marcotte, 2012). This difference is mainly due to post-transcriptional and -translational modifications, which are crucial in the dynamic regulation of gene expression (Vogel and Marcotte, 2012). Post-transcriptional modifications include processes such as alternative splicing, enabling a single gene to generate multiple mRNA variants, thereby expanding the diversity of the proteome (Vogel and Marcotte, 2012; Wahl et al., 2009). The upstream open reading frames (uORFs) can significantly regulate the translation of the main open reading frame (ORF) (Barbosa et al., 2013; Johnstone et al., 2016). Concurrently, post-translational modifications such as phosphorylation and ubiquitination further diversify protein functions and regulation (Hershko and Ciechanover, 1998; Hunter, 2007). However, within the context of TCGA, the focus is solely on the measurement of mRNA abundance (Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, 2008; Author anonymous, 2012; Weinstein et al., 2013). This is typically quantified using RNA sequencing data, which provides detailed information on the levels of mRNA present in a given sample (Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, 2008; Author anonymous, 2012; Weinstein et al., 2013). Inconsistencies between gene and protein levels can potentially distort patient prognosis results, contributing to the emergence of paradoxical genes (Akbani et al., 2014).
The tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) is critical for suppressing tumor progression, through its complex network of immune cells, stromal cells, signaling molecules, and extracellular matrix components (Joyce and Fearon, 2015; Fridman et al., 2012; Quail and Joyce, 2013). This dynamic environment can promote or inhibit tumor growth, depending on the balance of pro- and anti-tumor factors (Schreiber et al., 2011). Key players include cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), natural killer (NK) cells, dendritic cells, B cells, proinflammatory cytokines, and chemokines (Schreiber et al., 2011; Smyth et al., 2002; Palucka and Banchereau, 2012; Nelson, 2010; Müller et al., 2009; Topalian et al., 2015). There is currently evidence that some Paradoxical genes are involved in regulating TIME and inhibiting tumor progression (Cao et al., 2021; Yan et al., 2019; Boor et al., 2020; Martinez-Turtos et al., 2022). The regulatory influence of paradoxical genes on TIME elucidates the mechanism underlying their tumor suppressor effects.
The expression of genes and pathways exhibits context-dependent effects, also known as context specificity, which refer to the phenomenon where the function or behavior of a gene varies depending on the specific context in which it operates (Feil and Fraga, 2012; Huang, 2009; Beyer et al., 2007). In the context of cancer, the role of a gene can vary significantly depending on factors such as the type of cancer, the tissue in which the tumor originates, and the stage of the cancer (Vogelstein and Kinzler, 2004; Hanahan and Weinberg, 2011; Stratton et al., 2009). For instance, genes associated with signaling pathways like TGFβ, NOTCH, and NF-κB demonstrate differential expression across various tumor tissues. The TGFβ pathway presents a dual role, acting as a tumor suppressor in early stages and a promoter in advanced stages, with the expression varying significantly in breast, pancreatic, and colorectal cancers (Massagué, 2008). Similarly, the NOTCH signaling pathway, critical for cell fate determination and differentiation, shows oncogenic as well as tumor-suppressive functions, depending on the cancer type, as observed in breast cancer (BRCA), T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and lung cancer (Stylianou et al., 2006; Weng et al., 2004; Kopan and Ilagan, 2009). Often, the NF-κB pathway, a key regulator of inflammation and immune responses, is dysregulated in BRCA, multiple myeloma, and colorectal cancer, where it facilitates cell proliferation, survival, and chronic inflammation (Karin, 2006; Annunziata et al., 2007; Greten et al., 2004). The specific roles and expression patterns of these similar pathways in different tumor environments are also one of the reasons for the widespread existence of paradoxical genes.
In this article, by exploring the mechanism of paradoxical genes formation, we seek to broaden the current understanding of tumor biology and provide new ideas for tumor treatment and research.
2 Paradoxical genes emerge as a key focus in bioinformatics research
When genes highly expressed in cancer compared to normal tissues, are identified through bioinformatics analyses, it often implies that these genes may act as drivers of oncogenesis, serve as diagnostic or prognostic biomarkers, or act as predictive markers for treatment response (Niu et al., 2022; Liu Y. et al., 2021). Indeed, the relationship between gene expression and cancer prognosis can be complex and sometimes counterintuitive (Hanahan and Weinberg, 2011). Contrary to what might be expected, high expression of certain genes in tumors can be associated with a more favorable prognosis (Hanahan and Weinberg, 2011). This paradoxical finding highlights the complexity of cancer biology, revealing that genes may play multifaceted roles in tumorigenesis and cancer progression (Hanahan and Weinberg, 2011). For instance, some genes highly expressed in tumors could participate in immune response activation, DNA repair mechanisms, or cellular differentiation processes, potentially inhibiting tumor growth or spread, thereby improving patient outcomes (Blagih et al., 2020; Williams and Schumacher, 2016; Kalluri and Weinberg, 2009). Researchers face a challenge of dissecting the dual roles that some genes, acting as oncogenes in certain contexts while serving protective or suppressive functions in others (Hanahan and Weinberg, 2011).
2.1 Paradoxical genes exhibit differential and uneven expression across various tumors
In recent years, our understanding of the molecular underpinnings of cancer has been revolutionized by the integration of genomic databases such as TCGA into cancer research (Tomczak et al., 2015). TCGA provides an extensive compilation of genetic mutations, gene expression data, and epigenetic alterations across thousands of tumors, spanning over 30 human tumor types (Weinstein et al., 2013; Tomczak et al., 2015). Through our analysis of the TCGA database, our team has determined that the role of paradoxical genes cannot be overlooked. We conducted a detailed analysis of the distribution of paradoxical genes across various tumor types, ranking them by the number of highly expressed genes within each tumor category (Figure 1A). We observed that this type of gene is ubiquitously present across various cancers. Notably, BRCA, bladder urothelial carcinoma, and kidney renal clear cell carcinoma (KIRC) exhibit the highest expression levels of these tumor suppressor genes. In contrast, kidney chromophobe (KICH), esophageal carcinoma (ESCA), and prostate adenocarcinoma (PRAD) have significantly lower expression of these genes.
FIGURE 1
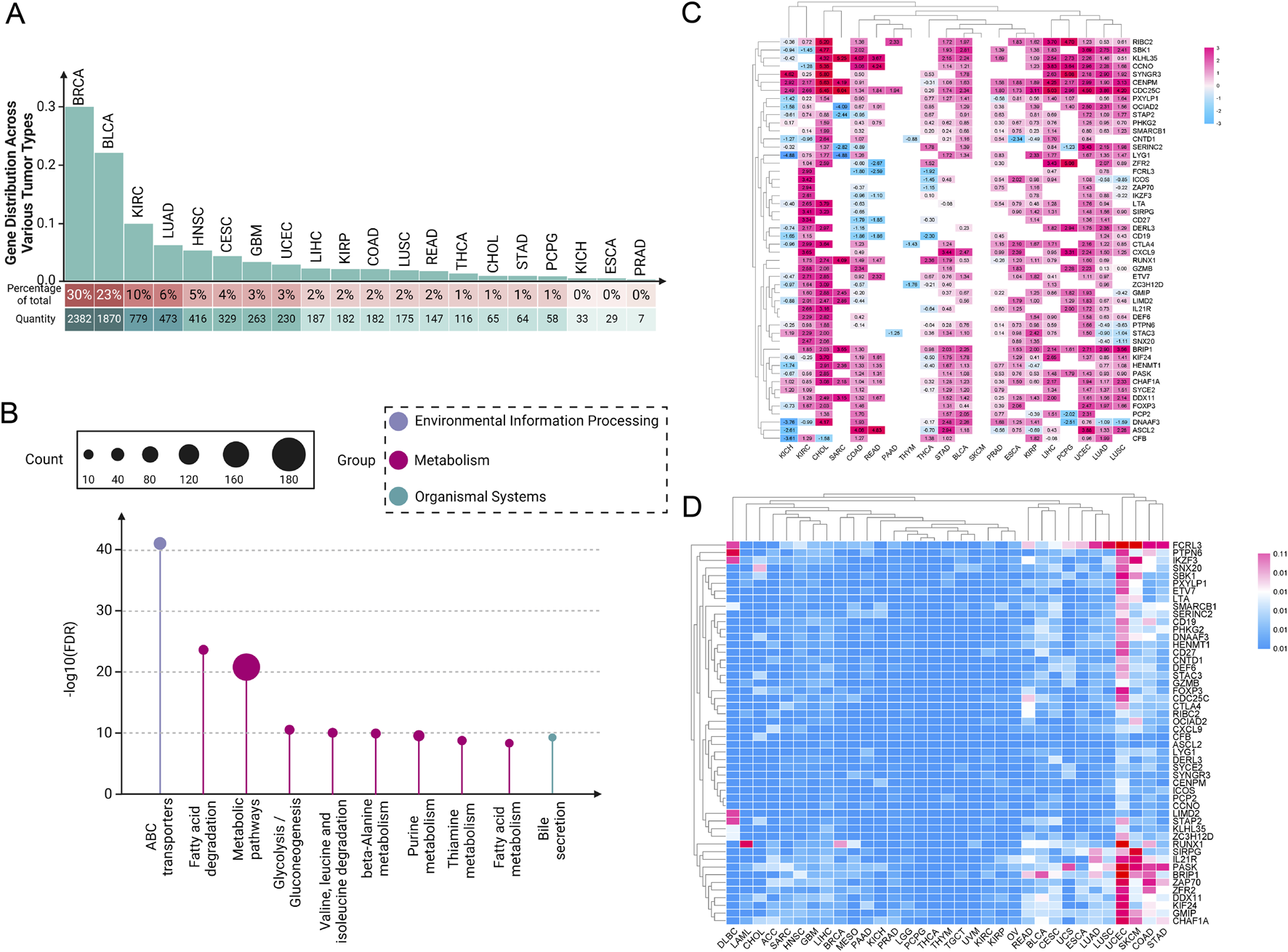
Pan-cancer analysis of paradoxical genes. (A) Expression of paradoxical genes in various tumors. The proportion of paradoxical genes in tumors is rounded to the nearest whole number; (B) KEGG analysis of 254 paradoxical genes; (C) Heat map depicting expression intensity of 50 paradoxical genes across various tumors; (D) SNV of paradoxical genes.
This disparity suggests a complex regulatory mechanism involved in the expression of paradoxical genes, which the tumor microenvironment (TME) and specific oncogenic pathways could influence. The high expression levels of paradoxical genes in BRCA, BLCA, and KIRC suggest that these cancers possibly utilize these genes to balance between tumor suppression and oncogenic activity, potentially as a response to oncogenic stress or other cellular pressures. In contrast, the reduced expression of paradoxical genes in KICH, ESCA, and PRAD might indicate a loss of this balancing mechanism, possibly contributing to more aggressive tumor behavior. These findings provide a crucial direction for future research into the mechanisms regulating paradoxical genes and their role in cancer progression.
2.2 Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes analysis of paradoxical genes: insights into their relationship with tumor metabolism
To investigate the functional mechanisms of paradoxical genes further, we initially screened 254 paradoxical genes for a KEGG analysis (Figure 1B). A common characteristic among these genes is their high expression in at least three tumor cell groups, correlating with improved patient prognosis. Our KEGG analysis revealed that these genes are extensively involved in various metabolism-related pathways, suggesting it as a primary mechanism through which paradoxical genes influence tumor prognosis.
Notably, liver X receptor (LXR) genes, including LXRα and LXRβ, are a few examples of this phenomenon (Han et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2023). LXRs are nuclear receptors involved in lipid metabolism, inflammation, and cholesterol homeostasis (Zelcer and Tontonoz, 2006). In the context of cancer, LXRs have demonstrated a dual role in tumor prognosis, influenced by their regulatory impact on metabolic pathways and immune responses in the tumor microenvironment (Han et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2023). LXR genes can play a role in inhibiting tumor progression (Zhang et al., 2014; Nguyen-Vu et al., 2013). This is primarily mediated through their anti-inflammatory effects within the tumor microenvironment. High expression of LXR genes causes upregulation of cholesterol efflux transporters such as ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) and ABCG1, which facilitate cholesterol efflux and reduce lipid accumulation within macrophages, thus attenuating the inflammatory response associated with tumor progression (Joseph et al., 2003; Wang et al., 2006). Furthermore, LXR activation has been linked to the suppression of inflammatory cytokine production by immune cells, leading to a less conducive environment for tumor growth (Joseph et al., 2003; Fessler, 2016; Chawla et al., 2001). A study demonstrated that LXRs activation disrupts BRCA cell proliferation by downregulating the expression of genes involved in cell growth and proliferation, particularly those regulated by the E2F family of transcription factors (Nguyen-Vu et al., 2013). The activation of LXRs leads to the downregulation of key genes involved in the cell cycle, DNA replication, and other critical processes for cancer cell division (Nguyen-Vu et al., 2013). This effect is partly mediated through the regulation of E2F2, highlighting a potential mechanism by which LXRs inhibit proliferation in cancer cells (Nguyen-Vu et al., 2013).
Conversely, LXRs can promote tumor growth through several mechanisms. Their activation leads to upregulation of genes involved in lipid biosynthesis, such as SREBP-1c (Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Protein 1c) (Okazaki et al., 2010; Jeong et al., 2021). SREBP-1c is a crucial transcription factor that enhances the expression of genes required for fatty acid and triglyceride synthesis (Okazaki et al., 2010; Jeong et al., 2021). In many cancers, particularly those with high lipid requirements like breast cancer, this can contribute to tumor cell proliferation and survival by ensuring a steady supply of essential lipids that are critical for membrane synthesis, energy storage, and signaling (Santos and Schulze, 2012; Menendez and Lupu, 2007; Swinnen et al., 2006; Zadra et al., 2013; Fukuchi et al., 2004; Vedin et al., 2009). Our research (Figure 1A) demonstrated that paradoxical genes are prevalently expressed in breast cancer, which also supports the notion that the modulation of these genes, particularly their regulation of tumor lipid metabolism, is fundamental to their anticancer effects.
In our previous investigation of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), we further examined the dual role of LXR (Wu et al., 2019). Our findings suggest that LXR functions as a balance gene, where both heightened and diminished expression levels can exert inhibitory effects on ccRCC progression (Wu et al., 2019). Specifically, both LXR agonists and inverse agonists inhibits cell proliferation and colony formation. The LXR agonist LXR623 downregulates low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) and upregulated ABCA1, causing a decline in intracellular cholesterol and induced apoptosis (Wu et al., 2019). Conversely, the LXR inverse agonist SR9243 downregulates key FA synthesis proteins, including sterol regulatory SREBP-1c, FA synthase, and stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1(SCD1), leading to decreased FA content and apoptosis in ccRCC(Wu et al., 2019). This phenomenon illustrates that alterations in cancer metabolism are a pivotal factor in mediating the regulatory effects of paradoxical genes on tumor prognosis.
2.3 Expression intensity and single nucleotide variations (SNV) analysis of paradoxical genes across different tumors
Subsequently, we screened out 50 paradoxical genes for pan-cancer analysis (Figure 1C). Their common feature is that they are highly expressed in ≥4 groups of tumor cells, and are associated with better patient prognosis. The expression intensity of these genes was analyzed in 20 different tumor tissues, and we found widespread overexpression, including, but not limited to, KIRC, cholangiocarcinoma (CHOL), stomach adenocarcinoma (STAD), BLCA, PRAD, ESCA, and liver hepatocellular carcinoma (LIHC), highlighting their potential as pan-cancer prognostic markers. Interestingly, subsequent analysis of SNVs in these genes showed that mutations are infrequent, a characteristic not generally observed in traditional oncogenes (Figure 1D). This observation further supports the hypothesis that the prognostic effect of paradoxical genes is mediated through mechanisms distinct from those employed by oncogenes, potentially driving tumor evolution towards less aggressive and more treatable forms. Nonetheless, there are currently very few reports on the occurrence of highly expressed tumor suppressor genes in tumors. Uncovering previously underappreciated complexities in the relationship between gene expression and cancer prognosis is critical.
3 The relationship between gene abundance and protein abundance: is there always a direct correlation?
The central dogma of molecular biology, formulated by Francis Crick, describes the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein through the processes of transcription and translation (Crick, 1970). While it is generally hypothesized that higher mRNA levels correlate with higher protein levels, this relationship is influenced by several factors (Vogel and Marcotte, 2012; Schwanhäusser et al., 2011; Tian et al., 2004). Post-transcriptional regulation can modify mRNA stability and translation efficiency, as well as the sequence features of the mRNA itself, such as upstream ORFs, can affect how efficiently it is translated (Barbosa et al., 2013; Sonenberg and Hinnebusch, 2009). Protein stability and degradation processes further modulate the levels of functional protein in the cell (Ciechanover and Kwon, 2015; Sherman and Goldberg, 2001). Although studies have typically shown a positive correlation between mRNA and protein levels, the variability suggests that multiple mechanisms, including translation efficiency and protein stability, are significant in determining final protein levels in biological systems (Schwanhäusser et al., 2011; Liu et al., 2016). Several studies have reported average correlation coefficients around 40%–60%, indicating that mRNA levels indicate protein abundance but are far from perfectly predictive due to various biological and methodological confounders (Vogel and Marcotte, 2012; Perl et al., 2017; Kosti et al., 2016) (Figure 2). This makes studies involving the gene level resulting from bioinformatics analysis somewhat one-sided.
FIGURE 2
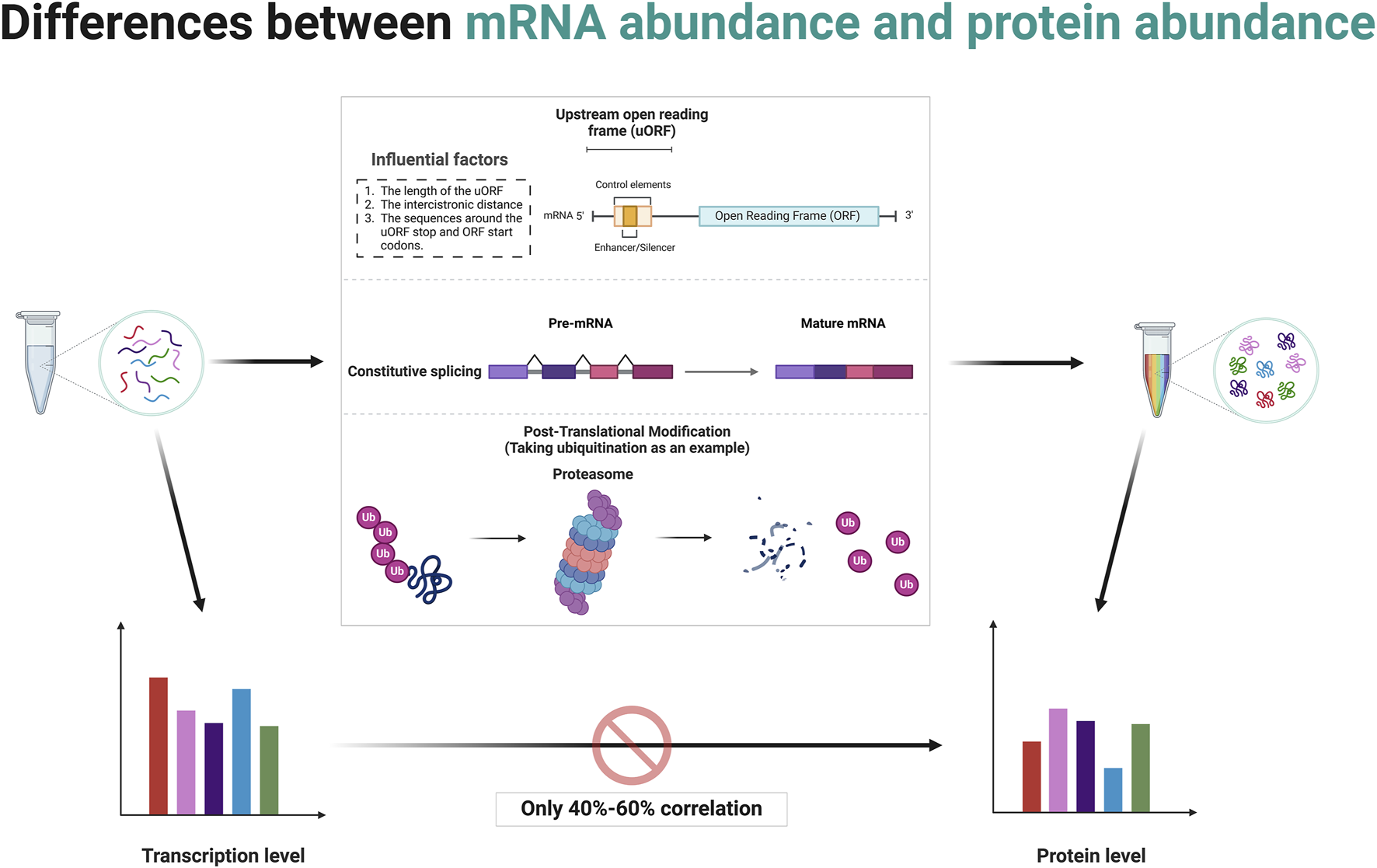
Post-transcriptional and post-translational modifications contribute to discrepancies between mRNA abundance and protein abundance. Created in BioRender. ZHAO, X. (2025) https://BioRender.com/q14t025.
3.1 The insights from the effect of upstream open reading frames
The concept of mRNA translation primarily involves coding mRNA into proteins by ribosomes, a process central to gene expression (Kozak, 1999; Jackson et al., 2010). Typically, this decoding focuses on the ORF that starts with a start codon (usually AUG) and ends with a stop codon (Jackson et al., 2010; Kozak, 2001). The discovery and study of uORFs have expanded our understanding of translational regulation and its complexities (Barbosa et al., 2013; Calvo et al., 2009; Wethmar, 2014). uORFs are alternative ORFs located upstream of the in the 5′untranslated region (5′UTR) of main coding sequence of an mRNA (Calvo et al., 2009). These uORFs can play a significant role in the regulation of translation of the main ORF (Barbosa et al., 2013; McGillivray et al., 2018).
uORFs are initiated when a ribosome recognizes and binds to a start codon (usually AUG, but sometimes a near-cognate codon) at the 5′UTR of an mRNA (Silva et al., 2019). The presence of a uORF upstream of the main coding sequence can alter ribosomal scanning and initiation dynamics, consequently affecting the translation of the downstream ORF (Hinnebusch et al., 2016; Morris and Geballe, 2000). After a uORF is translated, ribosomes can either dissociate from the mRNA or resume scanning for another start codon (Kozak, 2005). Several factors affect the ability of ribosomes to re-initiate translation at the downstream main ORF depends on, including the length of the uORF, the distance between the cistrons (the gap between the uORF and the main ORF), and the sequence context around the stop codon of the uORF and the start codon of the main ORF (Jackson et al., 2010; Ivanov et al., 2010; Kozak, 1987) (Figure 2). Often, efficient re-initiation is contingent upon the ribosomal retention of initiation factors during the uORF translation. The impact of a uORF on the main ORF translation can vary dramatically depending on its sequence and context (Pavitt, 2005). Some uORFs exhibit features that stall ribosomal function or slow translation, potentially enhancing or inhibiting the translation of the main ORF (Caliskan et al., 2015). For instance, Phan et al. elucidate how conserved uORFs in the 5′UTR of Polo-like kinase 4 (PLK4) mRNA play a crucial role in controlling the translation of PLK4, thereby regulating the duplication of centriole in primordial germ cells (PGCs) and preserving genomic integrity (Phan et al., 2022). This translational control mechanism prevents excessive PLK4 synthesis, vital for preventing centriole amplification and associated mitotic errors, highlighting a specific requirement for uORF in regulating the balance of PLK4 levels during germ cell development (Phan et al., 2022). A recent study by Cieśla et al. reveals that the regulation of SF3B1 protein levels through ALKBH5-driven N6-methyladenosine demethylation in the 5′UTR influences its translation, driving splicing mechanisms that impact DNA repair and epigenetic regulation (Cieśla et al., 2023). These studies demonstrate the critical role of post-transcriptional modifications in the expression of final protein.
3.2 The insights from alternative splicing
Alternative splicing is a post-transcriptional regulatory mechanism that contributes significantly to proteomic diversity and gene expression regulation in eukaryotic organisms (Nilsen and Graveley, 2010; Wang et al., 2008; Black, 2003; Barash et al., 2010). It involves the selective inclusion or exclusion of pre-mRNA segments (exons) during the RNA splicing process, resulting in multiple distinct mRNA transcripts from a single gene (Chen and Manley, 2009; Kornblihtt et al., 2013) (Figure 2). This process can affect the quantity as well as the functionality of the encoded proteins (Kornblihtt et al., 2013). When determining RNA abundance using technologies like RNA-seq, reads mapping to a gene are typically aggregated to estimate the overall abundance of the gene (Wang et al., 2009; Mortazavi et al., 2008). This standard approach does not differentiate between the various transcripts produced by alternative splicing (Ozsolak and Milos, 2011; Trapnell et al., 2009). Consequently, even if the total mRNA of a gene remains constant, changes in the splicing patterns can lead to proteins with significantly altered types and functions (Black, 2003; Kalsotra and Cooper, 2011). This is a critical factor to consider in gene expression analysis because while the quantitative measure (total RNA transcripts) might not show variation, the qualitative changes (different splice variants) can have profound biological ramifications (Nilsen and Graveley, 2010; Barash et al., 2010). Meanwhile, specific conditions or stimuli might induce changes in splicing patterns without altering the overall mRNA levels (Wang et al., 2008; David and Manley, 2010). Such differential splicing events can produce protein variants with differing, sometimes opposing, functions (Wang et al., 2008; David and Manley, 2010). Some splice variants may include or exclude sequences with regulatory elements affecting translation efficiency, such as internal ribosome entry sites or uORFs (Barbosa et al., 2013; Sonenberg and Hinnebusch, 2009).
In a recent study, researchers demonstrated the significant role of alternative splicing in the regulation of chromatin dynamics, particularly through the manipulation of histone deacetylase (HDAC)7 splicing downstream of T cell signaling pathways (Agosto et al., 2023). Notably, the longer HDAC7 isoform, induced by the RNA-binding protein CUGBP Elav-like family member 2, enhances the expression of key T cell surface proteins such as CD3, CD28, and CD69, highlighting the broad implications of alternative splicing on histone modification and gene regulatory mechanisms in T cells (Agosto et al., 2023). Particularly in studies related to diseases such as cancer, where splicing patterns can be drastically altered, researchers must consider the total expression level of a gene as well as the expression levels of individual splice variants.
3.3 The insights from post-translational regulation
Differences in protein abundance and gene abundance are largely caused by post-translational modifications (PTMs). PTMs like ubiquitination and phosphorylation can target proteins for degradation, leading to lower protein levels despite high mRNA expression (Hershko and Ciechanover, 1998; Hunter, 2007; Cohen, 2000; Ciechanover, 2005; Deshaies and Ferrell, 2001). Conversely, protein levels rise when modifications protect proteins from degradation. PTMs also modulate protein activity, producing active or inactive forms that do not directly correlate with mRNA levels (Figure 2). For instance, phosphorylated proteins often exhibit functions or stabilities different from their non-phosphorylated counterparts (Hunter, 2007; Olsen et al., 2006; Manning et al., 2002). Modifications such as phosphorylation, methylation, and acetylation also impact protein-protein interactions, altering binding affinities and affecting signaling pathways and cellular processes independent of gene expression (Ross et al., 2023; Nishi et al., 2014; Duan and Walther, 2015). The regulatory mechanism of post-translational modifications is comprehensively summarized in Table 1.
TABLE 1
| PTM | Mechanism | Regulation direction | Biological effects | Clinical significance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phosphorylation | Addition of phosphate groups to amino acids (Ser, Thr, Tyr) | Activate or inhibit | Regulates enzyme activity, signal transduction, cell cycle, apoptosis | Targeting phosphorylation pathways is a strategy in cancer therapy | Hunter (2007), Singh et al. (2017) |
| Ubiquitination | Attachment of ubiquitin to lysine residues | Usually leads to degradation | Controls protein turnover, modulates signaling pathways, cellular stress responses | Central in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, and cancer therapies | Popovic et al. (2014) |
| Acetylation | Addition of acetyl groups to lysine residues | Can activate or stabilize proteins | Influences gene expression, enzyme activity, protein stability, and metabolic regulation | Targeted by HDAC inhibitors in cancer treatment | Shvedunova and Akhtar (2022), Drazic et al. (2016), He et al. (2023) |
| Methylation | Addition of methyl groups to lysine or arginine | Can activate or repress | Affects protein interaction, stability, DNA binding, and transcriptional regulation | Targeted by drugs that modify methylation dynamics (inhibitors of methyltransferases and demethylases) | Greer and Shi (2012), Dawson and Kouzarides (2012), Klose and Zhang (2007) |
| Sumoylation | Addition of SUMO proteins to lysine residues | Typically inhibits | Regulates nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional activity, DNA repair | Implicated in cancer and heart disease | Flotho and Melchior (2013), Geiss-Friedlander and Melchior (2007), Chang and Yeh (2020) |
| Prenylation | Attachment of lipid groups (farnesyl or geranylgeranyl) to cysteine residues at the C-terminus of proteins | Generally activates | Facilitates membrane attachment, affects protein localization and function in signaling | Targeted in anti-cancer therapies, especially in Ras-related cancers | Jung and Bachmann (2023), Baranyi et al. (2020) |
Overview of post-translational modifications in protein regulation.
PTM, post-translational modifications; HDAC, histone deacetylase; SUMO, small ubiquitin-like modifier; Ser, serine; Thr, threonine; Tyr, tyrosine.
Integrative multi-omics analysis highlights the significant impact of PTMs on the differences in protein and gene levels, particularly during the human cell cycle (Parkes and Niranjan, 2019). While mRNA and translation data explain some variations in protein abundance, the remaining inconsistencies are primarily due to PTMs, which adjust protein levels post-synthesis (Parkes and Niranjan, 2019). In a study focusing on triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), researchers identified tumor endothelial marker 8 (TEM8) as a key indicator of breast tumor-initiating cells (Xu et al., 2021). The study also highlighted the binding of estrogen receptor α to the promoter region of the ubiquitin E3 enzyme ankyrin repeat and SOCS box containing 10 (ASB10). It also activates ASB10 transcription, and ASB10 interacts with TEM8, thereby affecting the ubiquitination of TEM8 and ultimately affecting the TEM8 protein level (Xu et al., 2021). Thus, Indirect evidence indicates that variations in TEM8 mRNA and protein expression across BRCA subtypes may be attributed to post-translational modifications (Xu et al., 2021).
4 Regulation of tumor immune microenvironment by paradoxical genes
The process of TIME begins with the recognition of tumor-specific antigens by antigen-presenting cells, like dendritic cells, which capture and present these neoantigens to naïve T cells in lymph nodes, thereby initiating T-cell activation (Mellman et al., 2011). This activation triggers a series of immune responses, including the release of chemokines that attract more effector immune cells (such as CTLs, NK cells, and macrophages) to the tumor site, effectively infiltrating the tumor (Joyce and Fearon, 2015). Within the TIME, a pivotal change occurs as effector T cells reprogram immunosuppressive cells and alter the metabolic environment, diminishing the suppressive function of regulatory immune cells such as regulatory T cells (Tregs), myeloid-derived suppressor cells (Ho et al., 2015). This culminates in the direct cytotoxic attack on tumor cells by CTLs and NK cells, utilizing mechanisms like perforin and granzyme release to induce tumor cell apoptosis (Trapani and Smyth, 2002). Furthermore, some activated T cells differentiate into memory T cells, providing long-term surveillance and a rapid response mechanism against tumor recurrence (Sallusto et al., 2004) (Figure 3).
FIGURE 3
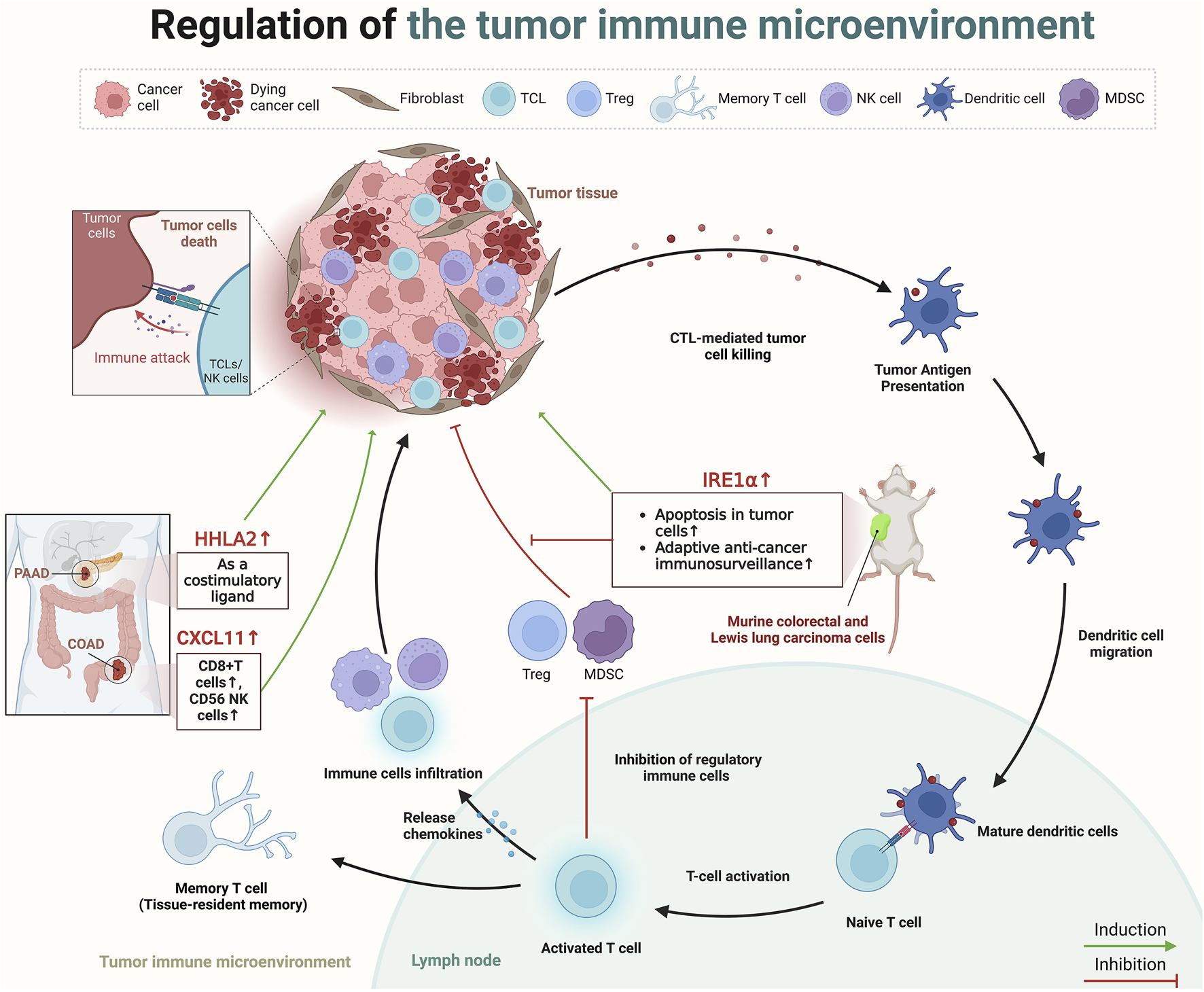
The role of paradoxical genes in regulating the TIME. Created in BioRender. ZHAO, X. (2025) https://BioRender.com/k01e299.
Recently, several scholars have dedicated their research efforts to understanding how paradoxical genes influence prognosis through the regulation of the TIME. Cao et al. analyzed data from TCGA and the gene expression omnibus, revealing that the expression of C-X-C motif chemokine ligand (CXCL)11 was elevated in colon cancer tissues compared to healthy tissues, and higher levels of CXCL11 correlated with improved survival outcomes (Cao et al., 2021). Furthermore, assessment of three independent datasets, including TCGA and two single-cell RNA sequencing datasets from Gene Expression Omnibus, in addition to immunohistochemistry data from a COAD patient cohort demonstrated that this tumor suppressor effect possibly due to its association with an increased presence of antitumor immune cells (CD8+ T cells, and CD56 NK cells), underscored CXCL11’s role in modulating the TIME (4). Furthermore, HERV-H LTR-associating 2 (HHLA2), a newly identified member of the B7 immune checkpoint family, is also a typical paradoxical gene (Yan et al., 2019). HHLA2 is minimally expressed in normal pancreatic tissues but shows significant upregulation from precancerous stages to invasive pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), according to immunohistochemistry analyses on tissue microarrays (Yan et al., 2019). In 77.17% of PDAC cases, the expression of HHLA2 is strongly associated with an improved post-surgical prognosis, indicating functions of HHLA2 as a costimulatory ligand in pancreatic cancer, activating CD8+ T cell proliferation and improving patient prognosis (Yan et al., 2019). A subsequent study also presented a similar point; immunohistochemical analysis on tissue micro-arrays from surgically resected tumors of 122 pancreatic and 72 ampullary cancer patients revealed HHLA2 expression in 67% of pancreatic and 93% of ampullary tumors, associating enhanced expression with improved post-surgical outcomes, including delayed cancer recurrence and improved cancer-specific survival (Boor et al., 2020). Similarly, the study by Martinez-Turtos et al. highlights that overexpression of inositol-requiring enzyme 1α (IRE1α) in murine colorectal and Lewis lung carcinoma cells in syngeneic immunocompetent mice, leads to a tumor-suppressive phenotype (Martinez-Turtos et al., 2022). This anti-tumoral effect is attributed to the RNAse activity of IRE1α, which induces apoptosis in tumor cells, enhances adaptive anti-cancer immunosurveillance through XBP1 mRNA splicing, and regulates IRE1-dependent degradation of RNA (RIDD) (Martinez-Turtos et al., 2022). However, in addition to the tumor suppressive role of IRE1α, its tumor-promoting role is also evident in preclinical models of various cancers, including TNBC, PDAC, and colon cancer (Harnoss et al., 2020; Garcia-Carbonero et al., 2018; Xie et al., 2019). This duality suggests that the impact of Paradoxical genes on cancer prognosis may be multifaceted and not solely affected by the TIME (Figure 3).
5 Dual roles of paradoxical genes and associated signaling pathways in tumors
Certain genes and their associated signaling pathways exhibit bidirectional effects on tumor prognosis, transitioning between inhibiting and promoting tumor progression. This dualistic behavior is also one of the key factor contributing to the emergence of paradoxical genes (Hanahan and Weinberg, 2011; Sadikovic et al., 2008). This biphasic regulatory effect can depend on various factors, including tumor stage, tumor-specific expression, and TME (Hanahan and Weinberg, 2011; Plaks et al., 2015; Gerlinger et al., 2012; Marusyk et al., 2012; Bray, 2016). The impact of gene expression can vary by cancer type and the tissue of origin (Stratton et al., 2009). Genes beneficial in one type of cancer might be deleterious in another (Vogelstein and Kinzler, 2004; Hanahan and Weinberg, 2011; Sadikovic et al., 2008). The role of E-cadherin in tumor suppression is well-established in BRCA due to its function in maintaining cell-cell adhesion and inhibiting metastasis (Padmanaban et al., 2019). However, in other cases, such as gastric cancer, the expression of can be associated with different outcomes based on additional factors like the presence of specific mutations or the overall state of cellular adhesion molecules (Becker et al., 1994). We focuses on signaling pathways with biphasic regulatory effects, including the TGFβ, NOTCH, and NF-κB pathways (Figure 4). Genes associated with these pathways are key contributors to the development of paradoxical genes, which exhibit peculiar behaviors during gene expression and regulation.
FIGURE 4
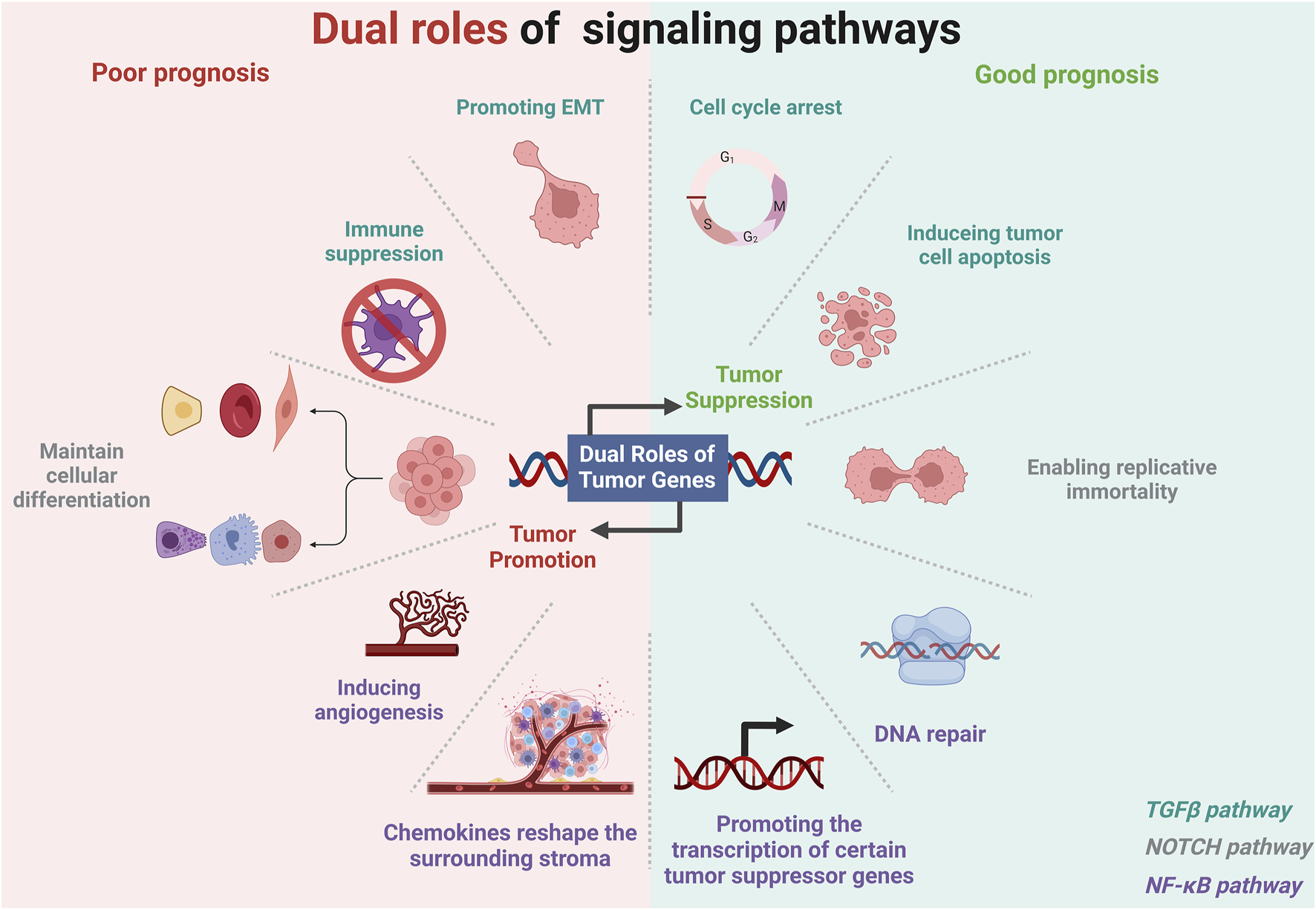
Dual roles of gene pathways in different tumor environments. Created in BioRender. ZHAO, X. (2025) https://BioRender.com/f74o594.
6 Stage-specific expression of paradoxical genes: insights from the transforming growth factor-β signaling pathways
The expression of tumor suppressor genes exhibits significant variability across different cancer stages, contributing to the phenomenon of paradoxical genes (Sherr and McCormick, 2002). For instance, in the early stages of cancer, key genes like TP53 and RB1 play a crucial role in maintaining cellular integrity by regulating DNA damage repair and controlling cell cycle progression (Sherr and McCormick, 2002). However, as the tumor evolves, these genes often become inactivated due to mutations, deletions, or epigenetic modifications, leading to unchecked cell proliferation and advancement to more aggressive stages (Li et al., 1997; Cantley and Neel, 1999). PTEN, which regulates the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, is commonly altered in cancers such as prostate and breast cancer, thereby facilitating tumor growth and survival (Li et al., 1997; Cantley and Neel, 1999; Salmena et al., 2008). In later stages, the suppression of tumor suppressor genes can precipitate metastasis and resistance to treatment, severely worsening the prognosis (Valastyan and Weinberg, 2011; Gottesman, 2002; Hanahan and Weinberg, 2000). Notably, the TGF-β pathway is recognized for its dual role in oncogenesis, acting as a tumor suppressor in initial stages while potentially fostering cancer progression in advanced stages (Massagué, 2008). Within this pathway, SMAD family members, including SMAD2 and SMAD4, are pivotal in relaying TGF-β signals that suppress cell division (Derynck and Zhang, 2003).
The TGFβ pathway suppresses tumors in the early stages of tumor development mainly by maintaining cellular homeostasis (including cell cycle arrest and apoptosis) and preventing uncontrolled cell proliferation (Colak and Ten Dijke, 2017). TGFβ regulates the cell cycle by inhibiting the transition from the G1 phase to the S phase, thereby preventing DNA replication and cell division, which is facilitated through the upregulation of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitors, which deactivate CDKs essential for cell cycle progression (Derynck, 1994; Decker et al., 2021). TGFβ also induces apoptosis, or programmed cell death through the activation of death-associated proteins and modulation of apoptosis-related genes, eliminating cells with potentially harmful mutations (Zhao et al., 2018; Schulte-Hermann et al., 1992). It also maintains cellular differentiation and proper morphology, thereby inhibiting the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), a critical process in cancer metastasis (Hao et al., 2019). Furthermore, TGFβ exerts anti-inflammatory effects within the cellular environment, regulating immune cell activity and cytokine production to suppress chronic inflammation, thus preventing tumor growth (Viel et al., 2016; Coussens and Werb, 2002).
In advanced cancer, TGF-β primarily acts as a tumor promoter. TGFβ promotes the EMT, a critical process for metastasis, by regulating transcription factors like Snail, Slug, and Twist that modify adhesion and migration properties of the cell (Peng et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2013; Ang et al., 2023). Simultaneously, TGF-β exerts systemic immune suppression and inhibits host immunosurveillance and also regulates the infiltration of inflammatory/immune cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts in the TME, causing direct changes in tumor cells (Yang et al., 2010). Neutralizing TGF-β enhances CD8+ T-cell- and NK-cell-mediated anti-tumor immune responses and increases the neutrophil-attracting chemokine production, leading to the recruitment and activation of neutrophils with an antitumor phenotype (Yang et al., 2010). It also interacts with cancer-associated fibroblasts and mesenchymal stem cells within the TME to remodel the extracellular matrix, increasing tumor stiffness and spreading cancer (Arima et al., 2023) (Figure 4).
The development of inhibitors that target TGFβ signaling is a promising treatment approach for cancers where TGFβ promotes tumor growth and metastasis (Derynck and Akhurst, 2007; Herbertz et al., 2015). These inhibitors generally block TGFβ receptors, preventing the downstream signaling cascades that lead to oncogenic effects (Herbertz et al., 2015). SB-431542 was initially identified as a potent and specific inhibitor of the activin receptor-like kinase (ALK)4, ALK5, and ALK7 type I receptors of the TGF-β superfamily, effectively and selectively inhibiting activin and TGF-β signaling without impacting BMP signaling or other divergent pathways like extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), or p38 mitogen activated protein kinase (Inman et al., 2002). In recent years, galunisertib (LY2157299 monohydrate), a selective, small molecule that can be taken orally to inhibit TGF-β receptor I kinase, exhibits antitumor activity across various cancer models, including breast, colon, lung, and HCC, by specifically downregulating SMAD2 phosphorylation and inhibiting the canonical TGF-β pathway (Herbertz et al., 2015). This drug is currently being evaluated in clinical trials in an intermittent dosing regimen (14 days on/14 days off, on a 28-day cycle) as part of monotherapy or in combination with other antitumor treatments to balance efficacy and safety, targeting cancers with high unmet medical needs like glioblastoma, pancreatic cancer, and HCC (Herbertz et al., 2015; Akhurst and Hata, 2012; Nadal et al., 2023). Clinical trials investigating combinations of TGFβ inhibitors with programmed cell death protein 1(PD-1)/programmed death-ligand 1(PD-L1) inhibitors are exploring this approach, showing promising results in improving anti-tumor immunity and patient outcomes (Wrzesinski et al., 2007). Hence, understanding the tumor stage and the specific role of TGFβ is crucial to determining when and how to target this pathway effectively. Personalizing treatment based on the genetic and molecular profiles of individual tumors could optimize the efficacy of TGFβ inhibitors and minimize adverse effects.
7 Tumor-specific expression of paradoxical genes: insights from the NOTCH signaling pathway
The NOTCH signaling pathway is a crucial cell communication mechanism that influences various biological processes, such as differentiation, proliferation, apoptosis, and stem cell maintenance (Bray, 2016). This pathway involves NOTCH receptors (NOTCH1-4) interacting with delta-like (DLL1, DLL3, DLL4) or Jagged (JAG1, JAG2) ligands on adjacent cells, initiating proteolytic cleavages that release the NOTCH intracellular domain (NICD) (Bray, 2016). This domain moves to the nucleus, where it converts recombination signal binding protein for immunoglobulin kappa J region from a repressor to an activator, with mastermind-like proteins, initiating transcription of target genes families like HES and HEY (Bray, 2016). The finely tuned regulation of this pathway, which includes endocytic trafficking and post-translational modifications, is essential for maintaining cellular and tissue homeostasis (Fortini, 2009). The dual nature of NOTCH signalling in cancer biology—acting as a tumor suppressor in some contexts while promoting tumor progression in others—underscores the complexity of its signaling pathways and their diverse effects on cancer etiology and progression (Valdez and Xin, 2013) (Figure 4).
In specific cancers like those of skin and liver, NOTCH signaling is essential for maintaining cellular differentiation and tissue architecture (Panelos and Massi, 2009; Kawaguchi and Kaneko, 2021). Specifically, in squamous cell carcinoma, increased NOTCH signaling is associated with reduced tumor formation and progression (Panelos et al., 2008). Impaired NOTCH signaling, as demonstrated by the expression of the pan-NOTCH inhibitor dominant negative mastermind-like (DNMAML)1 in conditional transgenic mice, leads to hyperplastic epidermis and spontaneous development of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) and actinic keratoses, suggesting a protective role of canonical NOTCH signaling against cutaneous SCC (Proweller et al., 2006). Meanwhile, NOTCH1 signaling significantly inhibits the growth of HCC by inducing cell cycle arrest at the G (0)/G (1) phase and promoting apoptosis, by downregulating key cell cycle proteins and upregulating p21 and p53, while also suppressing antiapoptotic B-cell lymphoma 2(Bcl-2) expression (Giovannini et al., 2016; Giovannini et al., 2014; Kim et al., 2017; Qi et al., 2003; Viatour et al., 2011). However, the role of NOTCH signaling is paradoxically reversed in other types of cancers. In T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) and certain breast cancers, NOTCH activation enhances cell proliferation, survival, and stemness, thereby promoting tumor growth and survival (Weng et al., 2004; Reedijk et al., 2005). Besides, the NOTCH signaling pathway also presents a biological dual nature widely in various cancers (Table 2).
TABLE 2
| Effect on tumors | Cancer type | Predominant NOTCH receptor | Role of notch signaling pathway | Signaling pathways involved | Mechanism of action | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Promotion | Breast cancer | NOTCH1, NOTCH2, NOTCH3 | Promotes cell proliferation, survival, stemness, and contributes to treatment resistance and metastasis in breast cancer | JAG1-NOTCH1, NOTCH1-PTEN-ERK1/2, HER2, PKCα-JAG1-NOTCH, Notch3, FYN-STAT5-NOTCH2 | Enhances proliferation, stem cell survival, and metastasis; modulates resistance to treatments; promotes aggressive tumor traits | Reedijk et al. (2005), Baker et al. (2018), Pandya et al. (2016), Saran et al. (2023), Leontovich et al. (2018), Lee et al. (2018) |
| Colon cancer | NOTCH1, NOTCH3 | Activates pathways that facilitate tumor cell survival and maintain stem cells | Wnt/β-catenin, Hedgehog | Enhances tumor cell survival, supports stem cell maintenance, and represses secretory cell differentiation | Ishiguro et al. (2017), Bertrand et al. (2012), Brzozowa-Zasada (2022) | |
| T lymphoblastic neoplasms | NOTCH1 | Activates oncogenic pathways in T-cell neoplasms, contributes to chromosomal translocations, and influences transcriptional regulation in T-cell leukemia | Chromosomal translocations involving TAN-1 (NOTCH1), convergence with transcription factors like Ikaros | Induces oncogenic transformations in T-cell neoplasms, facilitates leukemia progression, and influences transcriptional regulation | Ellisen et al. (1991), Bellavia et al. (2007) | |
| T-ALL | NOTCH1, NOTCH3 | Serves as a biomarker and strengthens NOTCH signaling in T-ALL, indicating aggressive disease and supporting leukemia maintenance | Related to NOTCH signaling pathways, specifically NOTCH3/Jagged1 signaling | Serves as a biomarker indicating aggressive disease, reinforces Notch signaling, and promotes disease progression and maintenance | Bardelli et al. (2021), Pelullo et al. (2014) | |
| NSCLC | NOTCH1, NOTCH3 | Activates EGFR and other pathways, contributes to metastasis and stemness, and is associated with poor prognosis in NSCLC | EGFR, RFC4/Notch1 signaling, Notch3 overexpression | Enhances NSCLC metastasis, stemness, and tumor progression; correlates with poor prognosis | Pancewicz-Wojtkiewicz (2016), Liu et al. (2021b), Ye et al. (2013) | |
| CCRCC | NOTCH1, NOTCH3 | Influences renal cancer cell proliferation and increases metastasis risk and tumor growth | Cell cycle regulation and HIF-2α, PI3K/Akt signaling | NOTCH3 regulates cell cycle progression and HIF-2α; NOTCH1 linked to increased metastasis risk and promotes tumor growth via PI3K/Akt | Han et al. (2020), Ai et al. (2012), Xu et al. (2012) | |
| Glioma | NOTCH1, NOTCH3 | Regulates several pathways to promote tumor growth, stemness, and invasion in gliomas | EGFR/c-myc, TGFβ/Hippo/Notch | Enhances glioma cell invasion, self-renewal, and growth; interacts with multiple pathways to promote tumor development | Zhao et al. (2017), Xing et al. (2015), Pierfelice et al. (2011), Yi et al. (2019) | |
| Prostate cancer | NOTCH1, NOTCH3 | Influences tumor growth and progression in prostate cancer by altering cellular behaviors and gene expression | Changes in NOTCH expression during development and tumorigenesis | Supports tumor growth and development through modulation of signaling pathways | Carvalho et al. (2014), Shou et al. (2001) | |
| Both | HNSCC | NOTCH1 | Influences tumor cell plasticity and contributes to HNSCC progression and suppression | EGFR, γ-secretase, Mutational landscape | Modulates tumor cell behavior and survival through interactions with EGFR and γ-secretase; linked to survival outcomes | Kałafut et al. (2021), Li et al. (2007), Stransky et al. (2011), Wirth et al. (2018) |
| Suppression | HCC | NOTCH1, NOTCH3 | Inhibits HCC growth through cell cycle arrest, apoptosis induction, and modulation of key molecular pathways | Hippo, Wnt/β-catenin, JNK, Cyclin G1, MDM2, miR-221 | Induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis; suppresses tumor growth by modulating signaling pathways | Giovannini et al. (2016), Giovannini et al. (2014), Kim et al. (2017), Qi et al. (2003), Viatour et al. (2011), Sui et al. (2017) |
| Cervical cancer | NOTCH1 | Downregulation of Notch1 signaling is required for sustained HPV-E6/E7 expression in cervical cancer | HPV-E6/E7 expression, Notch1 signaling | Sustains HPV-E6/E7 expression and facilitates malignant transformation by specifically modulating Notch1 signaling | Talora et al. (2002) | |
| Neuroblastoma | NOTCH1, NOTCH2 | Induces growth arrest in neuroblastoma cells by activating NOTCH signaling | Delta-Notch, Phox2B mutations | Induces cell cycle arrest and inhibits neuroblastoma cell growth through activation of Notch signaling | Zage et al. (2012), van Limpt et al. (2005) |
Summary of the tumor-promoting or tumor-inhibiting effects of the NOTCH signaling pathway in various cancers.
T-ALL, T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; CCRCC, clear cell renal cell carcinoma; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; HNSCC, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; TGF, transforming growth factor; HPV, human papillomavirus; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; HIF, hypoxia-inducible factor; PKCα, protein kinase C α Phox2B, paired-like homeobox 2B; RFC4, replication factor C subunit 4; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase.
8 The impact of environmental sensitivity on the formation of paradoxical genes
The environmental sensitivity of suppressor genes refers to the fact that the expression and function of these genes are affected by the TME, including factors such as hypoxia and acidity, which in turn affects cancer progression and cellular behavior (Gatenby and Gillies, 2004; Webb et al., 2011). Additionally, immune cells within this microenvironment release a variety of cytokines and growth factors that significantly impact cancer dynamics (Coussens and Werb, 2002; Grivennikov et al., 2010; de Visser et al., 2006). Specifically, certain immune-derived factors may suppress tumor cells, while others might activate signaling pathways that induce tumor cells (Coussens and Werb, 2002; Grivennikov et al., 2010; de Visser et al., 2006). These regulatory effects of environmental sensitivity on tumor suppressor genes undoubtedly contributed to the emergence of paradoxical genes.
8.1 Insights from hypoxia
Hypoxia within the TME critically influences the progression of cancer by modulating tumor suppressor genes, primarily via the stabilization of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) such as HIF-1α and HIF-2α (Semenza, 2003; Keith et al., 2011). Under low oxygen conditions, these transcription factors translocate to the nucleus, activating genes that drive angiogenesis, metabolism, cell survival, and invasion (Semenza, 2003). The suppression of the VHL gene under hypoxic conditions leads to unregulated HIF activity, promoting the secretion of angiogenic factors like vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor, which are instrumental in tumor growth and proliferation (Semenza, 2003). Hypoxia plays a significant role in the regulation of tumor suppressor genes. For instance, Chen et al. discovered that Hypoxia-inducible HIF-1α directly interacts with Mdm2, enhancing the in vivo association between p53 and HIF-1 alpha and acting as a mediator in their indirect interaction, which is crucial for the stabilization and activation of p53 in response to hypoxic stress (Chen et al., 2003). Furthermore, they found that HIF-1 alpha inhibits the Mdm2-mediated ubiquitination and nuclear export of p53, thereby protecting p53 from degradation and facilitating its role in transcriptional activation under hypoxic conditions (Chen et al., 2003). Additionally, PTEN, a crucial regulator of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, is downregulated by microRNAs like miR-21, which are themselves upregulated under hypoxic conditions. This indicates that hypoxia indirectly plays a significant role in the regulation of PTEN through the modulation of microRNA levels (Cascio et al., 2010; Kulshreshtha et al., 2007; Meng et al., 2007).
Hypoxic stress within solid tumors profoundly influences epigenetic regulation, particularly affecting DNA methylation and histone modifications (Shahrzad et al., 2007; Krieg et al., 2010). For instance, Watson et al. investigated the effects of chronic hypoxia in prostate cells and identified significant epigenetic changes, including increased global DNA methylation and H3K9 histone acetylation, associated with an altered cellular phenotype characterized by enhanced apoptotic resistance, cellular senescence, and increased invasiveness (Watson et al., 2009). These findings suggest that chronic hypoxia induces genome-wide adjustments in DNA methylation and histone modifications, potentially promoting and maintaining a hypoxic-adapted cellular phenotype that may contribute to tumor development (Watson et al., 2009). Meanwhile, Krieg et al. demonstrated that HIF-1α regulates the histone demethylase JMJD1A, which enhances the expression of hypoxia-responsive genes and promotes tumor growth (Krieg et al., 2010). This study highlights the critical role of HIF-1α in modifying histone enzymes under hypoxic conditions, thereby contributing to the dynamic regulation of gene expression in cancer cells (Krieg et al., 2010). These epigenetic modifications could further facilitate the emergence of paradoxical genes by modulating the expression diversity of tumor suppressor genes.
These molecular alterations under hypoxic stress lead to severe consequences, including enhanced angiogenesis, facilitating metastatic spread, altered cellular metabolism favoring cancer cell survival in low oxygen conditions, and increased resistance to conventional therapies (Semenza, 2003; Harris, 2002; Semenza, 2010). Targeting these adaptations has led to novel therapeutic strategies aimed at the hypoxic niche—such as the development of inhibitors that block HIFs, strategies to restore the functions of inactivated tumor suppressor pathways, and the use of hypoxia-activated prodrugs (Semenza, 2003; Wilson and Hay, 2011; Brown and Wilson, 2004; Wigerup et al., 2016). Additionally, addressing the downstream effects of tumor suppressor gene suppression, such as the use of PI3K inhibitors in cases of PTEN loss, offers a refined approach to disrupt the survival mechanisms employed by tumor cells in the hypoxic TME (Sansal and Sellers, 2004; Janku et al., 2018). These approaches leverage the modulation of tumor suppressor genes within the hypoxic tumor microenvironment to enhance the efficacy of cancer treatment.
8.2 Insights from acidosis
Acidosis within the TME significantly also impacts the cancer cell behavior (Webb et al., 2011; Damaghi et al., 2013). This condition stems from metabolic alterations in tumor cells, notably the high rates of glycolysis leading to excessive lactic acid production, even in the presence of oxygen (Webb et al., 2011; Gillies et al., 2008). This metabolic shift results in an accumulation of lactic acid, leading to a marked decrease in pH within the surrounding tissue (Gillies and Gatenby, 2007). Meanwhile, Riemann et al. demonstrated that an acidic tumor microenvironment induces reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation which then activate mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) signaling in cancer cells (Riemann et al., 2011). This activation leads to phosphorylation of the transcription factor CREB via p38, altering transcriptional activity and potentially sustaining tumorigenic changes even after cells return to a normal environment (Riemann et al., 2011). Additionally, the acidic environment can further lead to epigenetic changes, affecting DNA methylation and histone modifications, potentially leading to the silencing of tumor suppressor genes or the activation of oncogenes (Thorne et al., 2009; Kulis and Esteller, 2010). These insights highlight the regulatory influence of pH factors on tumor prognosis and related signaling pathways, thereby creating conditions that are favorable for the emergence of paradoxical genes.
8.3 Insights from immune signaling pathways modulation
Immune modulation can have profound effects on the expression and function of tumor suppressor genes (Oeckinghaus et al., 2011). A key player in this regulatory network is the NF-κB signaling pathway, which orchestrates responses that can either inhibit or promote tumor progression based on the surrounding cellular context (Karin et al., 2002; Baud and Karin, 2009). NF-κB promotes oncogenesis by upregulating the expression of genes that promote cell proliferation and inhibit programmed cell death. Key targets include genes encoding anti-apoptotic proteins, such as Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma-extra large (Bcl-xL), and inhibitor of apoptosis proteins, cell cycle regulators (such as cyclin D1 and c-Myc), and growth factors that together foster an environment conducive to the survival and proliferation of cancer cells (Annunziata et al., 2007; Karin et al., 2002; Baud and Karin, 2009). This role of NF-κB has been extensively documented in cancers like multiple myeloma, where it contributes directly to the survival and proliferation of malignant cells under chemotherapeutic stress (Annunziata et al., 2007). Additionally, NF-κB is a critical regulator of the TME by stimulating the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines such as TNF-α, interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-8. These molecules aid in reshaping the surrounding stroma, promoting angiogenesis, and facilitating tumor cell invasion and metastasis (Karin, 2006). Furthermore, NF-κB helps recruit and activate various immune cells within the TME that support tumor growth rather than combat it, thus contributing to tumor progression and the suppression of effective anti-tumor immune responses (Karin, 2006). NF-κB also contributes to the ability of tumor cells to evade immune surveillance. It modulates the expression of molecules affecting the immune response, such as major histocompatibility complex molecules and PD-L1, a ligand for the PD-1 receptor on T cells, which inhibits T cell function. NF-κB promotes an immunosuppressive microenvironment by enhancing the expression of PD-L1 on tumor cells, allowing tumor cells to escape detection and destruction by the immune system (Greten and Karin, 2004).
The NF-κB also plays key role as a suppressor of tumor development under certain contexts (Perkins, 2012). This suppression is primarily evident during the early stages of cancer and involves mechanisms that maintain cellular homeostasis and inhibit malignant transformations (Perkins, 2012). NF-κB contributes to genomic stability maintenance by regulating the expression of genes involved in DNA repair and cell cycle checkpoints. This function prevents the accumulation of genetic mutations that could otherwise lead to oncogenesis (Volcic et al., 2012). NF-κB can also induce cellular senescence, a permanent cell cycle arrest that functions as a barrier against the proliferation of potentially cancerous cells. This dual role of promoting DNA repair and senescence helps to suppress early tumor development and progression (Janssens and Tschopp, 2006). In specific cellular contexts, NF-κB can activate the transcription of certain tumor suppressor genes. For example, NF-κB induces the expression of GADD45β, a stress-response gene that plays a crucial role in DNA repair and cell cycle regulation (Jarome et al., 2015; Al Tarrass et al., 2024; De Smaele et al., 2001). By activating such genes, NF-κB contributes to the activation of mechanisms that can curb uncontrolled cell growth and promote apoptotic pathways in cells that have undergone malignant transformation (De Smaele et al., 2001) (Figure 4).
The ubiquitous role of the NF-κB signaling pathway in cancer makes it a significant target for therapeutic intervention (Karin, 2006). Current therapeutic modalities focus on NF-κB aim to mitigate its tumor-promoting actions while preserving or enhancing its tumor-suppressive capabilities (Karin and Greten, 2005). Therapeutic agents that inhibit NF-κB can potentially reduce tumor-associated inflammation and diminish the supportive TME that fosters cancer cell survival and metastasis (Moreau et al., 2011). For instance, the use of proteasome inhibitors such as bortezomib, which prevents the degradation of IκB (inhibitor of NF-κB), thus inhibiting NF-κB activation, has been found effective in treating multiple myeloma by reducing NF-κB mediated survival signals (Moreau et al., 2011). Additionally, strategies to modulate the role of NF-κB in immune suppression are being explored; modulation of NF-κB is being studied in the context of enhancing the effectiveness of immunotherapies, such as checkpoint inhibitors (Lim et al., 2016). By suppressing NF-κB-induced PD-L1 expression on tumor cells, these therapies can enhance T-cell activity against tumors, through a dual approach by directly inhibiting tumor cell survival mechanisms while boosting anti-tumor immunity (Lim et al., 2016). These examples illustrate the importance of the therapeutic targeting of NF-κB is significant due to its ability to alter the TME, reduce tumor resistance to conventional therapies, and improve the outcomes of immunotherapeutic approaches (Karin, 2006; Greten and Karin, 2004; Gilmore and Herscovitch, 2006).
9 Conclusion
Traditionally, tumor suppressor genes such as TP53, retinoblastoma 1, and PTEN are well-known for their roles in regulating vital cellular processes, including DNA repair, cell cycle progression, and apoptosis (Salmena et al., 2008; Vogelstein et al., 2000; Kaelin, 1997). The TP53 gene, often described as the “guardian of the genome,” is implicated in nearly half of the occurrence of all human cancers due to its critical functions in DNA repair and cell cycle regulation (Vogelstein et al., 2000). Similarly, RB1 controls the G1/S transition in the cell cycle, and PTEN counteracts the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway to influence cell survival (Salmena et al., 2008; Kaelin, 1997). Typically, the loss of function in these genes, whether through mutations, deletions, or epigenetic alterations, lead to the uncontrolled cell growth that characterizes cancer (Salmena et al., 2008; Vogelstein et al., 2000; Kaelin, 1997).
Contrary to long-standing scientific beliefs that these genes are rarely overexpressed in tumor tissues, recent advancements and the continuous enrichment of gene network databases, including TCGA have confirmed that the potential overexpression of tumor suppressor genes in such tissues. This phenomenon may be influenced by variations in tumor mutational burden and the interplay between compensatory regulatory mechanisms and the tumor microenvironment. Tumors with high tumor mutational burden often exhibit increased genomic instability, which can lead to the upregulation of tumor suppressor genes as part of a compensatory response. This has been consistently demonstrated in database studies as well as in basic experimental research. This phenomenon has been consistently demonstrated through both database analyses and fundamental experimental studies. While many studies focus primarily on gene expression at the transcriptional level, neglecting the corresponding expression at the protein level can result in unbalanced and potentially biased interpretations of biological effects. Nonetheless, given that non-coding genes vastly outnumber coding genes, this imbalance is likely only a secondary factor contributing to the existence of contradictory genes. Moreover, as previously discussed, substantial evidence supports the notion that variations in pathway expression across distinct tissue environments underscore the presence of contradictory genes. Of particular relevance is the stage-specific expression of these genes. Notably, the overexpression of tumor suppressor genes frequently occurs during the early stages of tumorigenesis, functioning as part of the cellular response to oncogenic stress (Sakaguchi et al., 2003; Ohuchida et al., 2006; Braig et al., 2005; Brambilla et al., 1999). For instance, S100A11 has been identified as a paradoxical gene (Sakaguchi et al., 2003). Sakaguchi et al. demonstrated that S100C/A11 is a critical mediator of calcium-induced growth inhibition in human epidermal keratinocytes by facilitating the phosphorylation-induced nuclear translocation of S100C/A11, thereby halting cell growth (Sakaguchi et al., 2003). However, Ohuchida et al. investigated the expression of the tumor suppressor gene S100A11 across various stages of pancreatic carcinogenesis (Ohuchida et al., 2006). Their research revealed overexpression of S100A11 in the early stages of pancreatic cancer development, such as in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms and pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (Ohuchida et al., 2006). However, its expression diminishes as the disease progresses advances (Ohuchida et al., 2006). Similarly, the overexpression of the tumor suppressor gene p16INK4a has been documented in early-stage tumors, where it has a crucial role in inducing cellular senescence and halting the proliferation of potentially cancerous cells (Braig et al., 2005; Brambilla et al., 1999). Similar studies not only confirm the existence of paradoxical genes but also emphasize their potential antagonistic effects on tumor progression during tumorigenesis. Paradoxical genes strive to maintain cellular homeostasis. As discussed in our previous work, this antagonistic effect may be linked to alterations in tumor metabolism, TIME, and related signaling pathways, suggesting a potential self-protective mechanism of the body against tumors. We propose that this might represent a form of intrinsic tumor suppression. This overexpression may arise from mechanisms such as subclonal heterogeneity or attempts to balance rapid proliferation and genomic instability. However, once this antagonistic equilibrium is disrupted, paradoxical genes may no longer be able to counteract the progression, leading to their diminished expression and the subsequent unchecked advancement of the tumor towards increased malignancy. Therefore, enhancing the expression of these tumor suppressor genes at early stages could offer promising potential for effective tumor treatment.
In summary, this review introduces the innovative concept of paradoxical genes, highlights the crucial role of tumor suppressor genes in targeted cancer therapy, and provides a theoretical framework for treating cancer by exploiting the balanced interplay between oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes.
Statements
Author contributions
DL: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. LL: Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. XC: Supervision, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. GW: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing–original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This project is supported by the Horizontal Project Department Fund of the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University (No. 2022CR015), and the Liaoning Provincial Education Department (No. JYTMS20230577).
Acknowledgments
We extend our gratitude to BioRender.com for providing drawing support. Additionally, we express appreciation for the data made available by databases like TCGA.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Glossary
- ABCA1
ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter A1
- ALK
Activin Receptor-Like Kinase
- ASB10
Ankyrin Repeat and SOCS Box Containing 10
- Bcl-2
B-Cell Lymphoma 2
- Bcl-xL
B-Cell Lymphoma-extra Large
- BLCA
Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma
- BRCA
Breast Cancer
- ccRCC
Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- CDK
Cyclin-Dependent Kinase
- CELF2
CUGBP Elav-Like Family Member 2
- CHOL
Cholangiocarcinoma
- COAD
Colon Adenocarcinoma
- CTLs
Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes
- CXCL
C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand
- CXCR
C-X-C Motif Chemokine Receptor
- DEA
Differential Expression Analysis
- DLL
Delta-Like
- DNMAML
Dominant Negative Mastermind-Like
- EGFR
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor
- EMT
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
- ERK
Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase
- ESCA
Esophageal Carcinoma
- FA
Fatty Acid
- FDA
Food and Drug Administration
- GO
Gene Ontology
- GTEx
Genotype-Tissue Expression
- GADD45β
Growth Arrest and DNA Damage-Inducible β
- HDAC
Histone Deacetylase
- HHLA2
HERV-H LTR-Associating 2
- HGP
Human Genome Project
- HIF
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor
- HNSCC
Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- HPV
Human Papillomavirus
- IAPs
Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins
- ICGC
International Cancer Genome Consortium
- IRES
Internal Ribosome Entry Sites
- IκB
Inhibitor of NF-κB
- IPMN
Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms
- IRE
Inositol-Requiring Enzyme
- JNK
c-Jun N-terminal Kinase
- KEGG
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- KICH
Kidney Chromophobe
- KIRC
Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma
- LDLR
Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor
- LIHC
Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- LXR
Liver X Receptor
- MDSCs
Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells
- MHC
Major Histocompatibility Complex
- NF-κB
Nuclear Factor Kappa Light Chain Enhancer of Activated B Cells
- NICD
Notch Intracellular Domain
- NK
Natural Killer
- NGS
Next-Generation Sequencing
- ORF
Open Reading Frame
- PD-1
Programmed Cell Death Protein 1
- PD-L1
Programmed Death-Ligand 1
- PDAC
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
- Phox2B
Paired-Like Homeobox 2B
- PI3K
Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase
- PKCα
Protein Kinase C α
- PLK4
Polo-Like Kinase 4
- PRAD
Prostate Adenocarcinoma
- PTMs
Post-Translational Modifications
- QC
Quality Control
- RB1
Retinoblastoma 1
- RFC4
Replication Factor C Subunit 4
- RIDD
Regulated IRE1-Dependent Decay of RNA
- SCC
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- SCD1
Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase 1
- SNPs
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms
- SREBP-1c
Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Protein 1c
- SUMO
Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier
- T-ALL
T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- TCGA
The Cancer Genome Atlas
- TGFβ
Transforming Growth Factor β
- TEM8
Tumor Endothelial Marker 8
- Thr
Threonine
- TIME
Tumor Immune Microenvironment
- TNBC
Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Tyr
Tyrosine
- uORFs
Upstream Open Reading Frames
References
1
Author anonymous (2012). Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature490 (7418), 61–70. 10.1038/nature11412
2
Agosto L. M. Mallory M. J. Ferretti M. B. Blake D. Krick K. S. Gazzara M. R. et al (2023). Alternative splicing of HDAC7 regulates its interaction with 14-3-3 proteins to alter histone marks and target gene expression. Cell Rep.42 (3), 112273. 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112273
3
Ai Q. Ma X. Huang Q. Liu S. Shi T. Zhang C. et al (2012). High-level expression of Notch1 increased the risk of metastasis in T1 stage clear cell renal cell carcinoma. PLoS One7 (4), e35022. 10.1371/journal.pone.0035022
4
Akbani R. Ng P. K. Werner H. M. Shahmoradgoli M. Zhang F. Ju Z. et al (2014). A pan-cancer proteomic perspective on the Cancer Genome Atlas. Nat. Commun.5, 3887. 10.1038/ncomms4887
5
Akhurst R. J. Hata A. (2012). Targeting the TGFβ signalling pathway in disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.11 (10), 790–811. 10.1038/nrd3810
6
Al Tarrass M. Belmudes L. Koça D. Azemard V. Liu H. Al T. T. et al (2024). Large-scale phosphoproteomics reveals activation of the MAPK/GADD45β/P38 axis and cell cycle inhibition in response to BMP9 and BMP10 stimulation in endothelial cells. Cell Commun. Signal22 (1), 158. 10.1186/s12964-024-01486-0
7
Ang H. L. Mohan C. D. Shanmugam M. K. Leong H. C. Makvandi P. Rangappa K. S. et al (2023). Mechanism of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer and its regulation by natural compounds. Med. Res. Rev.43 (4), 1141–1200. 10.1002/med.21948
8
Annunziata C. M. Davis R. E. Demchenko Y. Bellamy W. Gabrea A. Zhan F. et al (2007). Frequent engagement of the classical and alternative NF-kappaB pathways by diverse genetic abnormalities in multiple myeloma. Cancer Cell12 (2), 115–130. 10.1016/j.ccr.2007.07.004
9
Arima Y. Matsueda S. Saya H. (2023). Significance of cancer-associated fibroblasts in the interactions of cancer cells with the tumor microenvironment of heterogeneous tumor tissue. Cancers (Basel)15 (9), 2536. 10.3390/cancers15092536
10
Baker A. Wyatt D. Bocchetta M. Li J. Filipovic A. Green A. et al (2018). Notch-1-PTEN-ERK1/2 signaling axis promotes HER2+ breast cancer cell proliferation and stem cell survival. Oncogene37 (33), 4489–4504. 10.1038/s41388-018-0251-y
11
Baranyi M. Buday L. Hegedűs B. (2020). K-Ras prenylation as a potential anticancer target. Cancer Metastasis Rev.39 (4), 1127–1141. 10.1007/s10555-020-09902-w
12
Barash Y. Calarco J. A. Gao W. Pan Q. Wang X. Shai O. et al (2010). Deciphering the splicing code. Nature465 (7294), 53–59. 10.1038/nature09000
13
Barbosa C. Peixeiro I. Romão L. (2013). Gene expression regulation by upstream open reading frames and human disease. PLoS Genet.9 (8), e1003529. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003529
14
Bardelli V. Arniani S. Pierini V. Di Giacomo D. Pierini T. Gorello P. et al (2021). T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: biomarkers and their clinical usefulness. Genes (Basel)12 (8), 1118. 10.3390/genes12081118
15
Baud V. Karin M. (2009). Is NF-kappaB a good target for cancer therapy? Hopes and pitfalls. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.8 (1), 33–40. 10.1038/nrd2781
16
Becker K. F. Atkinson M. J. Reich U. Becker I. Nekarda H. Siewert J. R. et al (1994). E-cadherin gene mutations provide clues to diffuse type gastric carcinomas. Cancer Res.54 (14), 3845–3852.
17
Bellavia D. Mecarozzi M. Campese A. F. Grazioli P. Gulino A. Screpanti I. (2007). Notch and Ikaros: not only converging players in T cell leukemia. Cell Cycle6 (22), 2730–2734. 10.4161/cc.6.22.4894
18
Bertrand F. E. Angus C. W. Partis W. J. Sigounas G. (2012). Developmental pathways in colon cancer: crosstalk between WNT, BMP, Hedgehog and Notch. Cell Cycle11 (23), 4344–4351. 10.4161/cc.22134
19
Beyer A. Bandyopadhyay S. Ideker T. (2007). Integrating physical and genetic maps: from genomes to interaction networks. Nat. Rev. Genet.8 (9), 699–710. 10.1038/nrg2144
20
Bishop J. M. (1991). Molecular themes in oncogenesis. Cell64 (2), 235–248. 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90636-d
21
Black D. L. (2003). Mechanisms of alternative pre-messenger RNA splicing. Annu. Rev. Biochem.72, 291–336. 10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161720
22
Blagih J. Buck M. D. Vousden K. H. (2020). p53, cancer and the immune response. J. Cell Sci.133 (5), jcs237453. 10.1242/jcs.237453
23
Boor P. P. C. Sideras K. Biermann K. Hosein Aziz M. Levink I. J. M. Mancham S. et al (2020). HHLA2 is expressed in pancreatic and ampullary cancers and increased expression is associated with better post-surgical prognosis. Br. J. Cancer122 (8), 1211–1218. 10.1038/s41416-020-0755-4
24
Braig M. Lee S. Loddenkemper C. Rudolph C. Peters A. H. Schlegelberger B. et al (2005). Oncogene-induced senescence as an initial barrier in lymphoma development. Nature436 (7051), 660–665. 10.1038/nature03841
25
Brambilla E. Gazzeri S. Moro D. Lantuejoul S. Veyrenc S. Brambilla C. (1999). Alterations of Rb pathway (Rb-p16INK4-cyclin D1) in preinvasive bronchial lesions. Clin. Cancer Res.5 (2), 243–250.
26
Bray S. J. (2016). Notch signalling in context. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.17 (11), 722–735. 10.1038/nrm.2016.94
27
Brown J. M. Wilson W. R. (2004). Exploiting tumour hypoxia in cancer treatment. Nat. Rev. Cancer4 (6), 437–447. 10.1038/nrc1367
28
Brzozowa-Zasada M. (2022). Prognostic significance of Notch3 immunoreactivity patterns in Caucasian colon adenocarcinoma patients. Prz. Gastroenterol.17 (2), 162–168. 10.5114/pg.2022.116389
29
Caliskan N. Peske F. Rodnina M. V. (2015). Changed in translation: mRNA recoding by -1 programmed ribosomal frameshifting. Trends Biochem. Sci.40 (5), 265–274. 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.03.006
30
Calvo S. E. Pagliarini D. J. Mootha V. K. (2009). Upstream open reading frames cause widespread reduction of protein expression and are polymorphic among humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.106 (18), 7507–7512. 10.1073/pnas.0810916106
31
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network (2008). Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Nature455 (7216), 1061–1068. 10.1038/nature07385
32
Cantley L. C. Neel B. G. (1999). New insights into tumor suppression: PTEN suppresses tumor formation by restraining the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.96 (8), 4240–4245. 10.1073/pnas.96.8.4240
33
Cao Y. Jiao N. Sun T. Ma Y. Zhang X. Chen H. et al (2021). CXCL11 correlates with antitumor immunity and an improved prognosis in colon cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol.9, 646252. 10.3389/fcell.2021.646252
34
Carvalho F. L. Simons B. W. Eberhart C. G. Berman D. M. (2014). Notch signaling in prostate cancer: a moving target. Prostate74 (9), 933–945. 10.1002/pros.22811
35
Cascio S. D'Andrea A. Ferla R. Surmacz E. Gulotta E. Amodeo V. et al (2010). miR-20b modulates VEGF expression by targeting HIF-1 alpha and STAT3 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J. Cell Physiol.224 (1), 242–249. 10.1002/jcp.22126
36
Chang H. M. Yeh E. T. H. (2020). SUMO: from bench to bedside. Physiol. Rev.100 (4), 1599–1619. 10.1152/physrev.00025.2019
37
Chawla A. Repa J. J. Evans R. M. Mangelsdorf D. J. (2001). Nuclear receptors and lipid physiology: opening the X-files. Science.294 (5548), 1866–1870. 10.1126/science.294.5548.1866
38
Chen D. Li M. Luo J. Gu W. (2003). Direct interactions between HIF-1 alpha and Mdm2 modulate p53 function. J. Biol. Chem.278 (16), 13595–13598. 10.1074/jbc.C200694200
39
Chen M. Manley J. L. (2009). Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation: insights from molecular and genomics approaches. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.10 (11), 741–754. 10.1038/nrm2777
40
Ciechanover A. (2005). Proteolysis: from the lysosome to ubiquitin and the proteasome. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.6 (1), 79–87. 10.1038/nrm1552
41
Ciechanover A. Kwon Y. T. (2015). Degradation of misfolded proteins in neurodegenerative diseases: therapeutic targets and strategies. Exp. Mol. Med.47 (3), e147. 10.1038/emm.2014.117
42
Cieśla M. Ngoc P. C. T. Muthukumar S. Todisco G. Madej M. Fritz H. et al (2023). m(6)A-driven SF3B1 translation control steers splicing to direct genome integrity and leukemogenesis. Mol. Cell83 (7), 1165–1179.e11. 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.02.024
43
Cohen P. (2000). The regulation of protein function by multisite phosphorylation--a 25 year update. Trends Biochem. Sci.25 (12), 596–601. 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)01712-6
44
Colak S. Ten Dijke P. (2017). Targeting TGF-β signaling in cancer. Trends Cancer3 (1), 56–71. 10.1016/j.trecan.2016.11.008
45
Coussens L. M. Werb Z. (2002). Inflammation and cancer. Nature420 (6917), 860–867. 10.1038/nature01322
46
Crick F. (1970). Central dogma of molecular biology. Nature227 (5258), 561–563. 10.1038/227561a0
47
Croce C. M. (2008). Oncogenes and cancer. N. Engl. J. Med.358 (5), 502–511. 10.1056/NEJMra072367
48
Damaghi M. Wojtkowiak J. W. Gillies R. J. (2013). pH sensing and regulation in cancer. Front. Physiol.4, 370. 10.3389/fphys.2013.00370
49
David C. J. Manley J. L. (2010). Alternative pre-mRNA splicing regulation in cancer: pathways and programs unhinged. Genes Dev.24 (21), 2343–2364. 10.1101/gad.1973010
50
Dawson M. A. Kouzarides T. (2012). Cancer epigenetics: from mechanism to therapy. Cell150 (1), 12–27. 10.1016/j.cell.2012.06.013
51
Decker J. T. Ma J. A. Shea L. D. Jeruss J. S. (2021). Implications of TGFβ signaling and CDK inhibition for the treatment of breast cancer. Cancers (Basel)13 (21), 5343. 10.3390/cancers13215343
52
Derynck R. (1994). TGF-beta-receptor-mediated signaling. Trends Biochem. Sci.19 (12), 548–553. 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90059-0
53
Derynck R. Akhurst R. J. (2007). Differentiation plasticity regulated by TGF-beta family proteins in development and disease. Nat. Cell Biol.9 (9), 1000–1004. 10.1038/ncb434
54
Derynck R. Zhang Y. E. (2003). Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature425 (6958), 577–584. 10.1038/nature02006
55
Deshaies R. J. Ferrell J. E. Jr (2001). Multisite phosphorylation and the countdown to S phase. Cell107 (7), 819–822. 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00620-1
56
De Smaele E. Zazzeroni F. Papa S. Nguyen D. U. Jin R. Jones J. et al (2001). Induction of gadd45beta by NF-kappaB downregulates pro-apoptotic JNK signalling. Nature414 (6861), 308–313. 10.1038/35104560
57
de Visser K. E. Eichten A. Coussens L. M. (2006). Paradoxical roles of the immune system during cancer development. Nat. Rev. Cancer6 (1), 24–37. 10.1038/nrc1782
58
Drazic A. Myklebust L. M. Ree R. Arnesen T. (2016). The world of protein acetylation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta1864 (10), 1372–1401. 10.1016/j.bbapap.2016.06.007
59
Duan G. Walther D. (2015). The roles of post-translational modifications in the context of protein interaction networks. PLoS Comput. Biol.11 (2), e1004049. 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004049
60
Ellisen L. W. Bird J. West D. C. Soreng A. L. Reynolds T. C. Smith S. D. et al (1991). TAN-1, the human homolog of the Drosophila notch gene, is broken by chromosomal translocations in T lymphoblastic neoplasms. Cell66 (4), 649–661. 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90111-b
61
Feil R. Fraga M. F. (2012). Epigenetics and the environment: emerging patterns and implications. Nat. Rev. Genet.13 (2), 97–109. 10.1038/nrg3142
62
Fessler M. B. (2016). The intracellular cholesterol landscape: dynamic integrator of the immune response. Trends Immunol.37 (12), 819–830. 10.1016/j.it.2016.09.001
63
Flotho A. Melchior F. (2013). Sumoylation: a regulatory protein modification in health and disease. Annu. Rev. Biochem.82, 357–385. 10.1146/annurev-biochem-061909-093311
64
Fortini M. E. (2009). Notch signaling: the core pathway and its posttranslational regulation. Dev. Cell16 (5), 633–647. 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.03.010
65
Fridman W. H. Pagès F. Sautès-Fridman C. Galon J. (2012). The immune contexture in human tumours: impact on clinical outcome. Nat. Rev. Cancer12 (4), 298–306. 10.1038/nrc3245
66
Fukuchi J. Kokontis J. M. Hiipakka R. A. Chuu C. P. Liao S. (2004). Antiproliferative effect of liver X receptor agonists on LNCaP human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res.64 (21), 7686–7689. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2332
67
Garcia-Carbonero N. Li W. Cabeza-Morales M. Martinez-Useros J. Garcia-Foncillas J. (2018). New hope for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma treatment targeting endoplasmic reticulum stress response: a systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci.19 (9), 2468. 10.3390/ijms19092468
68
Gatenby R. A. Gillies R. J. (2004). Why do cancers have high aerobic glycolysis?Nat. Rev. Cancer4 (11), 891–899. 10.1038/nrc1478
69
Geiss-Friedlander R. Melchior F. (2007). Concepts in sumoylation: a decade on. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.8 (12), 947–956. 10.1038/nrm2293
70
Gerlinger M. Rowan A. J. Horswell S. Math M. Larkin J. Endesfelder D. et al (2012). Intratumor heterogeneity and branched evolution revealed by multiregion sequencing. N. Engl. J. Med.366 (10), 883–892. 10.1056/NEJMoa1113205
71
Gillies R. J. Gatenby R. A. (2007). Hypoxia and adaptive landscapes in the evolution of carcinogenesis. Cancer Metastasis Rev.26 (2), 311–317. 10.1007/s10555-007-9065-z
72
Gillies R. J. Robey I. Gatenby R. A. (2008). Causes and consequences of increased glucose metabolism of cancers. J. Nucl. Med.49 (Suppl. 2), 24S-42S–42s. 10.2967/jnumed.107.047258
73
Gilmore T. D. Herscovitch M. (2006). Inhibitors of NF-kappaB signaling: 785 and counting. Oncogene25 (51), 6887–6899. 10.1038/sj.onc.1209982
74
Giovannini C. Bolondi L. Gramantieri L. (2016). Targeting Notch3 in hepatocellular carcinoma: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci.18 (1), 56. 10.3390/ijms18010056
75
Giovannini C. Minguzzi M. Baglioni M. Fornari F. Giannone F. Ravaioli M. et al (2014). Suppression of p53 by Notch3 is mediated by Cyclin G1 and sustained by MDM2 and miR-221 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget5 (21), 10607–10620. 10.18632/oncotarget.2523
76
Golub T. R. Slonim D. K. Tamayo P. Huard C. Gaasenbeek M. Mesirov J. P. et al (1999). Molecular classification of cancer: class discovery and class prediction by gene expression monitoring. Science286 (5439), 531–537. 10.1126/science.286.5439.531
77
Gottesman M. M. (2002). Mechanisms of cancer drug resistance. Annu. Rev. Med.53, 615–627. 10.1146/annurev.med.53.082901.103929
78
Greer E. L. Shi Y. (2012). Histone methylation: a dynamic mark in health, disease and inheritance. Nat. Rev. Genet.13 (5), 343–357. 10.1038/nrg3173
79
Greten F. R. Eckmann L. Greten T. F. Park J. M. Li Z. W. Egan L. J. et al (2004). IKKbeta links inflammation and tumorigenesis in a mouse model of colitis-associated cancer. Cell118 (3), 285–296. 10.1016/j.cell.2004.07.013
80
Greten F. R. Karin M. (2004). The IKK/NF-kappaB activation pathway-a target for prevention and treatment of cancer. Cancer Lett.206 (2), 193–199. 10.1016/j.canlet.2003.08.029
81
Grivennikov S. I. Greten F. R. Karin M. (2010). Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell140 (6), 883–899. 10.1016/j.cell.2010.01.025
82
Han N. Yuan M. Yan L. Tang H. (2023). Emerging insights into liver X receptor α in the tumorigenesis and therapeutics of human cancers. Biomolecules13 (8), 1184. 10.3390/biom13081184
83
Han Q. Han F. Fan Y. Lian B. Xiao J. Sun W. et al (2020). Notch3 is involved in the proliferation of renal cancer cells via regulation of cell cycle progression and HIF-2α. Oncol. Lett.20 (6), 379. 10.3892/ol.2020.12242
84
Hanahan D. Weinberg R. A. (2000). The hallmarks of cancer. Cell100 (1), 57–70. 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81683-9
85
Hanahan D. Weinberg R. A. (2011). Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell144 (5), 646–674. 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013
86
Hao Y. Baker D. Ten Dijke P. (2019). TGF-β-Mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci.20 (11), 2767. 10.3390/ijms20112767
87
Harnoss J. M. Le Thomas A. Reichelt M. Guttman O. Wu T. D. Marsters S. A. et al (2020). IRE1α disruption in triple-negative breast cancer cooperates with antiangiogenic therapy by reversing ER stress adaptation and remodeling the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res.80 (11), 2368–2379. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-3108
88
Harris A. L. (2002). Hypoxia--a key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nat. Rev. Cancer2 (1), 38–47. 10.1038/nrc704
89
He W. Li Q. Li X. (2023). Acetyl-CoA regulates lipid metabolism and histone acetylation modification in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer1878 (1), 188837. 10.1016/j.bbcan.2022.188837
90
Herbertz S. Sawyer J. S. Stauber A. J. Gueorguieva I. Driscoll K. E. Estrem S. T. et al (2015). Clinical development of galunisertib (LY2157299 monohydrate), a small molecule inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathway. Drug Des. Devel Ther.9, 4479–4499. 10.2147/DDDT.S86621
91
Hershko A. Ciechanover A. (1998). The ubiquitin system. Annu. Rev. Biochem.67, 425–479. 10.1146/annurev.biochem.67.1.425
92
Hinnebusch A. G. Ivanov I. P. Sonenberg N. (2016). Translational control by 5'-untranslated regions of eukaryotic mRNAs. Science352 (6292), 1413–1416. 10.1126/science.aad9868
93
Ho P. C. Bihuniak J. D. Macintyre A. N. Staron M. Liu X. Amezquita R. et al (2015). Phosphoenolpyruvate is a metabolic checkpoint of anti-tumor T cell responses. Cell162 (6), 1217–1228. 10.1016/j.cell.2015.08.012
94
Huang S. (2009). Reprogramming cell fates: reconciling rarity with robustness. Bioessays.31 (5), 546–560. 10.1002/bies.200800189
95
Hunter T. (2007). The age of crosstalk: phosphorylation, ubiquitination, and beyond. Mol. Cell28 (5), 730–738. 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.11.019
96
Inman G. J. Nicolás F. J. Callahan J. F. Harling J. D. Gaster L. M. Reith A. D. et al (2002). SB-431542 is a potent and specific inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta superfamily type I activin receptor-like kinase (ALK) receptors ALK4, ALK5, and ALK7. Mol. Pharmacol.62 (1), 65–74. 10.1124/mol.62.1.65
97
Ishiguro H. Okubo T. Kuwabara Y. Kimura M. Mitsui A. Sugito N. et al (2017). NOTCH1 activates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in colon cancer. Oncotarget8 (36), 60378–60389. 10.18632/oncotarget.19534
98
Ivanov I. P. Loughran G. Sachs M. S. Atkins J. F. (2010). Initiation context modulates autoregulation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 1 (eIF1). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.107 (42), 18056–18060. 10.1073/pnas.1009269107
99
Jackson R. J. Hellen C. U. Pestova T. V. (2010). The mechanism of eukaryotic translation initiation and principles of its regulation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.11 (2), 113–127. 10.1038/nrm2838
100
Janku F. Yap T. A. Meric-Bernstam F. (2018). Targeting the PI3K pathway in cancer: are we making headway?Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol.15 (5), 273–291. 10.1038/nrclinonc.2018.28
101
Janssens S. Tschopp J. (2006). Signals from within: the DNA-damage-induced NF-kappaB response. Cell Death Differ.13 (5), 773–784. 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401843
102
Jarome T. J. Butler A. A. Nichols J. N. Pacheco N. L. Lubin F. D. (2015). NF-κB mediates Gadd45β expression and DNA demethylation in the hippocampus during fear memory formation. Front. Mol. Neurosci.8, 54. 10.3389/fnmol.2015.00054
103
Jeong D. W. Lee S. Chun Y. S. (2021). How cancer cells remodel lipid metabolism: strategies targeting transcription factors. Lipids Health Dis.20 (1), 163. 10.1186/s12944-021-01593-8
104
Johnstone T. G. Bazzini A. A. Giraldez A. J. (2016). Upstream ORFs are prevalent translational repressors in vertebrates. Embo J.35 (7), 706–723. 10.15252/embj.201592759
105
Joseph S. B. Castrillo A. Laffitte B. A. Mangelsdorf D. J. Tontonoz P. (2003). Reciprocal regulation of inflammation and lipid metabolism by liver X receptors. Nat. Med.9 (2), 213–219. 10.1038/nm820
106
Joyce J. A. Fearon D. T. (2015). T cell exclusion, immune privilege, and the tumor microenvironment. Science.348 (6230), 74–80. 10.1126/science.aaa6204
107
Jung D. Bachmann H. S. (2023). Regulation of protein prenylation. Biomed. Pharmacother.164, 114915. 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114915
108
Kaelin W. G. Jr (1997). Alterations in G1/S cell-cycle control contributing to carcinogenesis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci.833, 29–33. 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1997.tb48589.x
109
Kałafut J. Czerwonka A. Anameriç A. Przybyszewska-Podstawka A. Misiorek J. O. Rivero-Müller A. et al (2021). Shooting at moving and hidden targets-tumour cell plasticity and the notch signalling pathway in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Cancers (Basel)13 (24), 6219. 10.3390/cancers13246219
110
Kalluri R. Weinberg R. A. (2009). The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Invest119 (6), 1420–1428. 10.1172/JCI39104
111
Kalsotra A. Cooper T. A. (2011). Functional consequences of developmentally regulated alternative splicing. Nat. Rev. Genet.12 (10), 715–729. 10.1038/nrg3052
112
Karin M. (2006). Nuclear factor-kappaB in cancer development and progression. Nature441 (7092), 431–436. 10.1038/nature04870
113
Karin M. Cao Y. Greten F. R. Li Z. W. (2002). NF-kappaB in cancer: from innocent bystander to major culprit. Nat. Rev. Cancer2 (4), 301–310. 10.1038/nrc780
114
Karin M. Greten F. R. (2005). NF-kappaB: linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nat. Rev. Immunol.5 (10), 749–759. 10.1038/nri1703
115
Kawaguchi K. Kaneko S. (2021). Notch signaling and liver cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.1287, 69–80. 10.1007/978-3-030-55031-8_6
116
Keith B. Johnson R. S. Simon M. C. (2011). HIF1α and HIF2α: sibling rivalry in hypoxic tumour growth and progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer12 (1), 9–22. 10.1038/nrc3183
117
Kim W. Khan S. K. Yang Y. (2017). Interacting network of Hippo, Wnt/β-catenin and Notch signaling represses liver tumor formation. BMB Rep.50 (1), 1–2. 10.5483/bmbrep.2017.50.1.196
118
Klose R. J. Zhang Y. (2007). Regulation of histone methylation by demethylimination and demethylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.8 (4), 307–318. 10.1038/nrm2143
119
Kopan R. Ilagan M. X. (2009). The canonical Notch signaling pathway: unfolding the activation mechanism. Cell137 (2), 216–233. 10.1016/j.cell.2009.03.045
120
Kornblihtt A. R. Schor I. E. Alló M. Dujardin G. Petrillo E. Muñoz M. J. (2013). Alternative splicing: a pivotal step between eukaryotic transcription and translation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.14 (3), 153–165. 10.1038/nrm3525
121
Kosti I. Jain N. Aran D. Butte A. J. Sirota M. (2016). Cross-tissue analysis of gene and protein expression in normal and cancer tissues. Sci. Rep.6, 24799. 10.1038/srep24799
122
Kozak M. (1987). Effects of intercistronic length on the efficiency of reinitiation by eucaryotic ribosomes. Mol. Cell Biol.7 (10), 3438–3445. 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3438
123
Kozak M. (1999). Initiation of translation in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Gene234 (2), 187–208. 10.1016/s0378-1119(99)00210-3
124
Kozak M. (2001). Constraints on reinitiation of translation in mammals. Nucleic Acids Res.29 (24), 5226–5232. 10.1093/nar/29.24.5226
125
Kozak M. (2005). Regulation of translation via mRNA structure in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Gene361, 13–37. 10.1016/j.gene.2005.06.037
126
Krieg A. J. Rankin E. B. Chan D. Razorenova O. Fernandez S. Giaccia A. J. (2010). Regulation of the histone demethylase JMJD1A by hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha enhances hypoxic gene expression and tumor growth. Mol. Cell Biol.30 (1), 344–353. 10.1128/MCB.00444-09
127
Kulis M. Esteller M. (2010). DNA methylation and cancer. Adv. Genet.70, 27–56. 10.1016/B978-0-12-380866-0.60002-2
128
Kulshreshtha R. Ferracin M. Wojcik S. E. Garzon R. Alder H. Agosto-Perez F. J. et al (2007). A microRNA signature of hypoxia. Mol. Cell Biol.27 (5), 1859–1867. 10.1128/MCB.01395-06
129
Lee G. H. Yoo K. C. An Y. Lee H. J. Lee M. Uddin N. et al (2018). FYN promotes mesenchymal phenotypes of basal type breast cancer cells through STAT5/NOTCH2 signaling node. Oncogene37 (14), 1857–1868. 10.1038/s41388-017-0114-y
130
Leontovich A. A. Jalalirad M. Salisbury J. L. Mills L. Haddox C. Schroeder M. et al (2018). NOTCH3 expression is linked to breast cancer seeding and distant metastasis. Breast Cancer Res.20 (1), 105. 10.1186/s13058-018-1020-0
131
Li J. Yen C. Liaw D. Podsypanina K. Bose S. Wang S. I. et al (1997). PTEN, a putative protein tyrosine phosphatase gene mutated in human brain, breast, and prostate cancer. Science.275 (5308), 1943–1947. 10.1126/science.275.5308.1943
132
Li T. Wen H. Brayton C. Das P. Smithson L. A. Fauq A. et al (2007). Epidermal growth factor receptor and notch pathways participate in the tumor suppressor function of gamma-secretase. J. Biol. Chem.282 (44), 32264–32273. 10.1074/jbc.M703649200
133
Lim S. O. Li C. W. Xia W. Cha J. H. Chan L. C. Wu Y. et al (2016). Deubiquitination and stabilization of PD-L1 by CSN5. Cancer Cell30 (6), 925–939. 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.10.010
134
Liu L. Tao T. Liu S. Yang X. Chen X. Liang J. et al (2021b). An RFC4/Notch1 signaling feedback loop promotes NSCLC metastasis and stemness. Nat. Commun.12 (1), 2693. 10.1038/s41467-021-22971-x
135
Liu Y. Beyer A. Aebersold R. (2016). On the dependency of cellular protein levels on mRNA abundance. Cell165 (3), 535–550. 10.1016/j.cell.2016.03.014
136
Liu Y. Teng L. Fu S. Wang G. Li Z. Ding C. et al (2021a). Highly heterogeneous-related genes of triple-negative breast cancer: potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers. BMC Cancer21 (1), 644. 10.1186/s12885-021-08318-1
137
Manning G. Whyte D. B. Martinez R. Hunter T. Sudarsanam S. (2002). The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science.298 (5600), 1912–1934. 10.1126/science.1075762
138
Martinez-Turtos A. Paul R. Grima-Reyes M. Issaoui H. Krug A. Mhaidly R. et al (2022). IRE1α overexpression in malignant cells limits tumor progression by inducing an anti-cancer immune response. Oncoimmunology11 (1), 2116844. 10.1080/2162402X.2022.2116844
139
Marusyk A. Almendro V. Polyak K. (2012). Intra-tumour heterogeneity: a looking glass for cancer?Nat. Rev. Cancer12 (5), 323–334. 10.1038/nrc3261
140
Massagué J. (2008). TGFbeta in cancer. Cell.134 (2), 215–230. 10.1016/j.cell.2008.07.001
141
McGillivray P. Ault R. Pawashe M. Kitchen R. Balasubramanian S. Gerstein M. (2018). A comprehensive catalog of predicted functional upstream open reading frames in humans. Nucleic Acids Res.46 (7), 3326–3338. 10.1093/nar/gky188
142
Mellman I. Coukos G. Dranoff G. (2011). Cancer immunotherapy comes of age. Nature480 (7378), 480–489. 10.1038/nature10673
143
Menendez J. A. Lupu R. (2007). Fatty acid synthase and the lipogenic phenotype in cancer pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer7 (10), 763–777. 10.1038/nrc2222
144
Meng F. Henson R. Wehbe-Janek H. Ghoshal K. Jacob S. T. Patel T. (2007). MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology133 (2), 647–658. 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.05.022
145
Moreau P. Avet-Loiseau H. Facon T. Attal M. Tiab M. Hulin C. et al (2011). Bortezomib plus dexamethasone versus reduced-dose bortezomib, thalidomide plus dexamethasone as induction treatment before autologous stem cell transplantation in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Blood118 (22), 5752–5758. quiz 982. 10.1182/blood-2011-05-355081
146
Morris D. R. Geballe A. P. (2000). Upstream open reading frames as regulators of mRNA translation. Mol. Cell Biol.20 (23), 8635–8642. 10.1128/mcb.20.23.8635-8642.2000
147
Mortazavi A. Williams B. A. McCue K. Schaeffer L. Wold B. (2008). Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat. Methods5 (7), 621–628. 10.1038/nmeth.1226
148
Müller I. Munder M. Kropf P. Hänsch G. M. (2009). Polymorphonuclear neutrophils and T lymphocytes: strange bedfellows or brothers in arms?Trends Immunol.30 (11), 522–530. 10.1016/j.it.2009.07.007
149
Nadal E. Saleh M. Aix S. P. Ochoa-de-Olza M. Patel S. P. Antonia S. et al (2023). A phase Ib/II study of galunisertib in combination with nivolumab in solid tumors and non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer23 (1), 708. 10.1186/s12885-023-11153-1
150
Nelson B. H. (2010). CD20+ B cells: the other tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. J. Immunol.185 (9), 4977–4982. 10.4049/jimmunol.1001323
151
Nguyen-Vu T. Vedin L. L. Liu K. Jonsson P. Lin J. Z. Candelaria N. R. et al (2013). Liver × receptor ligands disrupt breast cancer cell proliferation through an E2F-mediated mechanism. Breast Cancer Res.15 (3), R51. 10.1186/bcr3443
152
Nilsen T. W. Graveley B. R. (2010). Expansion of the eukaryotic proteome by alternative splicing. Nature463 (7280), 457–463. 10.1038/nature08909
153
Nishi H. Shaytan A. Panchenko A. R. (2014). Physicochemical mechanisms of protein regulation by phosphorylation. Front. Genet.5, 270. 10.3389/fgene.2014.00270
154
Niu X. Ren L. Hu A. Zhang S. Qi H. (2022). Identification of potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for gastric cancer based on bioinformatic analysis. Front. Genet.13, 862105. 10.3389/fgene.2022.862105
155
Oeckinghaus A. Hayden M. S. Ghosh S. (2011). Crosstalk in NF-κB signaling pathways. Nat. Immunol.12 (8), 695–708. 10.1038/ni.2065
156
Ohuchida K. Mizumoto K. Ohhashi S. Yamaguchi H. Konomi H. Nagai E. et al (2006). S100A11, a putative tumor suppressor gene, is overexpressed in pancreatic carcinogenesis. Clin. Cancer Res.12 (18), 5417–5422. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0222
157
Okazaki H. Goldstein J. L. Brown M. S. Liang G. (2010). LXR-SREBP-1c-phospholipid transfer protein axis controls very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) particle size. J. Biol. Chem.285 (9), 6801–6810. 10.1074/jbc.M109.079459
158
Olsen J. V. Blagoev B. Gnad F. Macek B. Kumar C. Mortensen P. et al (2006). Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks. Cell127 (3), 635–648. 10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026
159
Ozsolak F. Milos P. M. (2011). RNA sequencing: advances, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Genet.12 (2), 87–98. 10.1038/nrg2934
160
Padmanaban V. Krol I. Suhail Y. Szczerba B. M. Aceto N. Bader J. S. et al (2019). E-cadherin is required for metastasis in multiple models of breast cancer. Nature573 (7774), 439–444. 10.1038/s41586-019-1526-3
161
Palucka K. Banchereau J. (2012). Cancer immunotherapy via dendritic cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer12 (4), 265–277. 10.1038/nrc3258
162
Pancewicz-Wojtkiewicz J. (2016). Epidermal growth factor receptor and notch signaling in non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Med.5 (12), 3572–3578. 10.1002/cam4.944
163
Pandya K. Wyatt D. Gallagher B. Shah D. Baker A. Bloodworth J. et al (2016). PKCα attenuates jagged-1-mediated notch signaling in ErbB-2-positive breast cancer to reverse trastuzumab resistance. Clin. Cancer Res.22 (1), 175–186. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0179
164
Panelos J. Massi D. (2009). Emerging role of Notch signaling in epidermal differentiation and skin cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther.8 (21), 1986–1993. 10.4161/cbt.8.21.9921
165
Panelos J. Tarantini F. Paglierani M. Di Serio C. Maio V. Pellerito S. et al (2008). Photoexposition discriminates Notch 1 expression in human cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Mod. Pathol.21 (3), 316–325. 10.1038/modpathol.3801007
166
Parkes G. M. Niranjan M. (2019). Uncovering extensive post-translation regulation during human cell cycle progression by integrative multi-'omics analysis. BMC Bioinforma.20 (1), 536. 10.1186/s12859-019-3150-5
167
Pavitt G. D. (2005). eIF2B, a mediator of general and gene-specific translational control. Biochem. Soc. Trans.33 (Pt 6), 1487–1492. 10.1042/BST20051487
168
Pelullo M. Quaranta R. Talora C. Checquolo S. Cialfi S. Felli M. P. et al (2014). Notch3/Jagged1 circuitry reinforces notch signaling and sustains T-ALL. Neoplasia16 (12), 1007–1017. 10.1016/j.neo.2014.10.004
169
Peng D. Fu M. Wang M. Wei Y. Wei X. (2022). Targeting TGF-β signal transduction for fibrosis and cancer therapy. Mol. Cancer21 (1), 104. 10.1186/s12943-022-01569-x
170
Perkins N. D. (2012). The diverse and complex roles of NF-κB subunits in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer12 (2), 121–132. 10.1038/nrc3204
171
Perl K. Ushakov K. Pozniak Y. Yizhar-Barnea O. Bhonker Y. Shivatzki S. et al (2017). Reduced changes in protein compared to mRNA levels across non-proliferating tissues. BMC Genomics18 (1), 305. 10.1186/s12864-017-3683-9
172
Phan T. P. Boatwright C. A. Drown C. G. Skinner M. W. Strong M. A. Jordan P. W. et al (2022). Upstream open reading frames control PLK4 translation and centriole duplication in primordial germ cells. Genes Dev.36 (11-12), 718–736. 10.1101/gad.349604.122
173
Pierfelice T. J. Schreck K. C. Dang L. Asnaghi L. Gaiano N. Eberhart C. G. (2011). Notch3 activation promotes invasive glioma formation in a tissue site-specific manner. Cancer Res.71 (3), 1115–1125. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0690
174
Plaks V. Kong N. Werb Z. (2015). The cancer stem cell niche: how essential is the niche in regulating stemness of tumor cells?Cell Stem Cell16 (3), 225–238. 10.1016/j.stem.2015.02.015
175
Popovic D. Vucic D. Dikic I. (2014). Ubiquitination in disease pathogenesis and treatment. Nat. Med.20 (11), 1242–1253. 10.1038/nm.3739
176
Proweller A. Tu L. Lepore J. J. Cheng L. Lu M. M. Seykora J. et al (2006). Impaired notch signaling promotes de novo squamous cell carcinoma formation. Cancer Res.66 (15), 7438–7444. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0793
177
Qi R. An H. Yu Y. Zhang M. Liu S. Xu H. et al (2003). Notch1 signaling inhibits growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma through induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Cancer Res.63 (23), 8323–8329.
178
Quail D. F. Joyce J. A. (2013). Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat. Med.19 (11), 1423–1437. 10.1038/nm.3394
179
Reedijk M. Odorcic S. Chang L. Zhang H. Miller N. McCready D. R. et al (2005). High-level coexpression of JAG1 and NOTCH1 is observed in human breast cancer and is associated with poor overall survival. Cancer Res.65 (18), 8530–8537. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1069
180
Riemann A. Schneider B. Ihling A. Nowak M. Sauvant C. Thews O. et al (2011). Acidic environment leads to ROS-induced MAPK signaling in cancer cells. PLoS One6 (7), e22445. 10.1371/journal.pone.0022445
181
Ross K. E. Zhang G. Akcora C. Lin Y. Fang B. Koomen J. et al (2023). Network models of protein phosphorylation, acetylation, and ubiquitination connect metabolic and cell signaling pathways in lung cancer. PLoS Comput. Biol.19 (3), e1010690. 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010690
182
Sadikovic B. Al-Romaih K. Squire J. A. Zielenska M. (2008). Cause and consequences of genetic and epigenetic alterations in human cancer. Curr. Genomics9 (6), 394–408. 10.2174/138920208785699580
183
Sakaguchi M. Miyazaki M. Takaishi M. Sakaguchi Y. Makino E. Kataoka N. et al (2003). S100C/A11 is a key mediator of Ca(2+)-induced growth inhibition of human epidermal keratinocytes. J. Cell Biol.163 (4), 825–835. 10.1083/jcb.200304017
184
Sallusto F. Geginat J. Lanzavecchia A. (2004). Central memory and effector memory T cell subsets: function, generation, and maintenance. Annu. Rev. Immunol.22, 745–763. 10.1146/annurev.immunol.22.012703.104702
185
Salmena L. Carracedo A. Pandolfi P. P. (2008). Tenets of PTEN tumor suppression. Cell133 (3), 403–414. 10.1016/j.cell.2008.04.013
186
Sansal I. Sellers W. R. (2004). The biology and clinical relevance of the PTEN tumor suppressor pathway. J. Clin. Oncol.22 (14), 2954–2963. 10.1200/JCO.2004.02.141
187
Santos C. R. Schulze A. (2012). Lipid metabolism in cancer. Febs J.279 (15), 2610–2623. 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08644.x
188
Saran U. Chandrasekaran B. Tyagi A. Shukla V. Singh A. Sharma A. K. et al (2023). A small molecule inhibitor of Notch1 modulates stemness and suppresses breast cancer cell growth. Front. Pharmacol.14, 1150774. 10.3389/fphar.2023.1150774
189
Schreiber R. D. Old L. J. Smyth M. J. (2011). Cancer immunoediting: integrating immunity's roles in cancer suppression and promotion. Science331 (6024), 1565–1570. 10.1126/science.1203486
190
Schulte-Hermann R. Bursch W. Kraupp-Grasl B. Oberhammer F. Wagner A. (1992). Programmed cell death and its protective role with particular reference to apoptosis. Toxicol. Lett.64-65, 569–574. Spec No. 10.1016/0378-4274(92)90233-a
191
Schwanhäusser B. Busse D. Li N. Dittmar G. Schuchhardt J. Wolf J. et al (2011). Global quantification of mammalian gene expression control. Nature473 (7347), 337–342. 10.1038/nature10098
192
Semenza G. L. (2003). Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer3 (10), 721–732. 10.1038/nrc1187
193
Semenza G. L. (2010). Oxygen homeostasis. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med.2 (3), 336–361. 10.1002/wsbm.69
194
Shahrzad S. Bertrand K. Minhas K. Coomber B. L. (2007). Induction of DNA hypomethylation by tumor hypoxia. Epigenetics2 (2), 119–125. 10.4161/epi.2.2.4613
195
Sherman M. Y. Goldberg A. L. (2001). Cellular defenses against unfolded proteins: a cell biologist thinks about neurodegenerative diseases. Neuron29 (1), 15–32. 10.1016/s0896-6273(01)00177-5
196
Sherr C. J. McCormick F. (2002). The RB and p53 pathways in cancer. Cancer Cell2 (2), 103–112. 10.1016/s1535-6108(02)00102-2
197
Shou J. Ross S. Koeppen H. de Sauvage F. J. Gao W. Q. (2001). Dynamics of notch expression during murine prostate development and tumorigenesis. Cancer Res.61 (19), 7291–7297.
198
Shvedunova M. Akhtar A. (2022). Modulation of cellular processes by histone and non-histone protein acetylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.23 (5), 329–349. 10.1038/s41580-021-00441-y
199
Silva J. Fernandes R. Romão L. (2019). Translational regulation by upstream open reading frames and human diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.1157, 99–116. 10.1007/978-3-030-19966-1_5
200
Singh V. Ram M. Kumar R. Prasad R. Roy B. K. Singh K. K. (2017). Phosphorylation: implications in cancer. Protein J.36 (1), 1–6. 10.1007/s10930-017-9696-z
201
Smyth M. J. Hayakawa Y. Takeda K. Yagita H. (2002). New aspects of natural-killer-cell surveillance and therapy of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer2 (11), 850–861. 10.1038/nrc928
202
Sonenberg N. Hinnebusch A. G. (2009). Regulation of translation initiation in eukaryotes: mechanisms and biological targets. Cell136 (4), 731–745. 10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.042
203
Stransky N. Egloff A. M. Tward A. D. Kostic A. D. Cibulskis K. Sivachenko A. et al (2011). The mutational landscape of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Science333 (6046), 1157–1160. 10.1126/science.1208130
204
Stratton M. R. Campbell P. J. Futreal P. A. (2009). The cancer genome. Nature458 (7239), 719–724. 10.1038/nature07943
205
Stylianou S. Clarke R. B. Brennan K. (2006). Aberrant activation of notch signaling in human breast cancer. Cancer Res.66 (3), 1517–1525. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3054
206
Sui C. Zhuang C. Sun D. Yang L. Zhang L. Song L. (2017). Notch1 regulates the JNK signaling pathway and increases apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget8 (28), 45837–45847. 10.18632/oncotarget.17434
207
Swinnen J. V. Brusselmans K. Verhoeven G. (2006). Increased lipogenesis in cancer cells: new players, novel targets. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care9 (4), 358–365. 10.1097/01.mco.0000232894.28674.30
208
Talora C. Sgroi D. C. Crum C. P. Dotto G. P. (2002). Specific down-modulation of Notch1 signaling in cervical cancer cells is required for sustained HPV-E6/E7 expression and late steps of malignant transformation. Genes Dev.16 (17), 2252–2263. 10.1101/gad.988902
209
Thorne J. L. Campbell M. J. Turner B. M. (2009). Transcription factors, chromatin and cancer. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol.41 (1), 164–175. 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.08.029
210
Tian Q. Stepaniants S. B. Mao M. Weng L. Feetham M. C. Doyle M. J. et al (2004). Integrated genomic and proteomic analyses of gene expression in Mammalian cells. Mol. Cell Proteomics3 (10), 960–969. 10.1074/mcp.M400055-MCP200
211
Tomczak K. Czerwińska P. Wiznerowicz M. (2015). The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA): an immeasurable source of knowledge. Contemp. Oncol. Pozn.19 (1a), A68–A77. 10.5114/wo.2014.47136
212
Topalian S. L. Drake C. G. Pardoll D. M. (2015). Immune checkpoint blockade: a common denominator approach to cancer therapy. Cancer Cell27 (4), 450–461. 10.1016/j.ccell.2015.03.001
213
Trapani J. A. Smyth M. J. (2002). Functional significance of the perforin/granzyme cell death pathway. Nat. Rev. Immunol.2 (10), 735–747. 10.1038/nri911
214
Trapnell C. Pachter L. Salzberg S. L. (2009). TopHat: discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics25 (9), 1105–1111. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp120
215
Valastyan S. Weinberg R. A. (2011). Tumor metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell147 (2), 275–292. 10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.024
216
Valdez J. M. Xin L. (2013). The dual nature of Notch in tissue homeostasis and carcinogenesis. Cell Cycle12 (4), 541. 10.4161/cc.23671
217
van Limpt V. Chan A. Schramm A. Eggert A. Versteeg R. (2005). Phox2B mutations and the Delta-Notch pathway in neuroblastoma. Cancer Lett.228 (1-2), 59–63. 10.1016/j.canlet.2005.02.050
218
Vedin L. L. Lewandowski S. A. Parini P. Gustafsson J. A. Steffensen K. R. (2009). The oxysterol receptor LXR inhibits proliferation of human breast cancer cells. Carcinogenesis30 (4), 575–579. 10.1093/carcin/bgp029
219
Viatour P. Ehmer U. Saddic L. A. Dorrell C. Andersen J. B. Lin C. et al (2011). Notch signaling inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma following inactivation of the RB pathway. J. Exp. Med.208 (10), 1963–1976. 10.1084/jem.20110198
220
Viel S. Marçais A. Guimaraes F. S. Loftus R. Rabilloud J. Grau M. et al (2016). TGF-β inhibits the activation and functions of NK cells by repressing the mTOR pathway. Sci. Signal9 (415), ra19. 10.1126/scisignal.aad1884
221
Vogel C. Marcotte E. M. (2012). Insights into the regulation of protein abundance from proteomic and transcriptomic analyses. Nat. Rev. Genet.13 (4), 227–232. 10.1038/nrg3185
222
Vogelstein B. Kinzler K. W. (2004). Cancer genes and the pathways they control. Nat. Med.10 (8), 789–799. 10.1038/nm1087
223
Vogelstein B. Lane D. Levine A. J. (2000). Surfing the p53 network. Nature408 (6810), 307–310. 10.1038/35042675
224
Volcic M. Karl S. Baumann B. Salles D. Daniel P. Fulda S. et al (2012). NF-κB regulates DNA double-strand break repair in conjunction with BRCA1-CtIP complexes. Nucleic Acids Res.40 (1), 181–195. 10.1093/nar/gkr687
225
Wahl M. C. Will C. L. Lührmann R. (2009). The spliceosome: design principles of a dynamic RNP machine. Cell136 (4), 701–718. 10.1016/j.cell.2009.02.009
226
Wang E. T. Sandberg R. Luo S. Khrebtukova I. Zhang L. Mayr C. et al (2008). Alternative isoform regulation in human tissue transcriptomes. Nature456 (7221), 470–476. 10.1038/nature07509
227
Wang N. Ranalletta M. Matsuura F. Peng F. Tall A. R. (2006). LXR-induced redistribution of ABCG1 to plasma membrane in macrophages enhances cholesterol mass efflux to HDL. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol.26 (6), 1310–1316. 10.1161/01.ATV.0000218998.75963.02
228
Wang Q. Zhang W. Qi X. Li J. Liu Y. Li Q. et al (2023). The mechanism of liver X receptor regulates the balance of glycoFAsynthesis and cholesterol synthesis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Transl. Med.13 (5), e1248. 10.1002/ctm2.1248
229
Wang Y. Shi J. Chai K. Ying X. Zhou B. P. (2013). The role of Snail in EMT and tumorigenesis. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets13 (9), 963–972. 10.2174/15680096113136660102
230
Wang Z. Gerstein M. Snyder M. (2009). RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat. Rev. Genet.10 (1), 57–63. 10.1038/nrg2484
231
Watson J. A. Watson C. J. McCrohan A. M. Woodfine K. Tosetto M. McDaid J. et al (2009). Generation of an epigenetic signature by chronic hypoxia in prostate cells. Hum. Mol. Genet.18 (19), 3594–3604. 10.1093/hmg/ddp307
232
Webb B. A. Chimenti M. Jacobson M. P. Barber D. L. (2011). Dysregulated pH: a perfect storm for cancer progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer11 (9), 671–677. 10.1038/nrc3110
233
Weinstein J. N. Collisson E. A. Mills G. B. Shaw K. R. Ozenberger B. A. Ellrott K. et al (2013). The cancer genome Atlas pan-cancer analysis project. Nat. Genet.45 (10), 1113–1120. 10.1038/ng.2764
234
Weng A. P. Ferrando A. A. Lee W. Morris J. P. Silverman L. B. Sanchez-Irizarry C. et al (2004). Activating mutations of NOTCH1 in human T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Science306 (5694), 269–271. 10.1126/science.1102160
235
Wethmar K. (2014). The regulatory potential of upstream open reading frames in eukaryotic gene expression. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA5 (6), 765–778. 10.1002/wrna.1245
236
Wigerup C. Påhlman S. Bexell D. (2016). Therapeutic targeting of hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors in cancer. Pharmacol. Ther.164, 152–169. 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.04.009
237
Williams A. B. Schumacher B. (2016). p53 in the DNA-Damage-Repair Process. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med.6 (5), a026070. 10.1101/cshperspect.a026070
238
Wilson W. R. Hay M. P. (2011). Targeting hypoxia in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer11 (6), 393–410. 10.1038/nrc3064
239
Wirth M. Jira D. Ott A. Piontek G. Pickhard A. (2018). High NOTCH1 mRNA expression is associated with better survival in HNSCC. Int. J. Mol. Sci.19 (3), 830. 10.3390/ijms19030830
240
Wrzesinski S. H. Wan Y. Y. Flavell R. A. (2007). Transforming growth factor-beta and the immune response: implications for anticancer therapy. Clin. Cancer Res.13 (18 Pt 1), 5262–5270. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1157
241
Wu G. Wang Q. Xu Y. Li J. Zhang H. Qi G. et al (2019). Targeting the transcription factor receptor LXR to treat clear cell renal cell carcinoma: agonist or inverse agonist?Cell Death Dis.10 (6), 416. 10.1038/s41419-019-1654-6
242
Xie Y. Liu C. Qin Y. Chen J. Fang J. (2019). Knockdown of IRE1ɑ suppresses metastatic potential of colon cancer cells through inhibiting FN1-Src/FAK-GTPases signaling. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol.114, 105572. 10.1016/j.biocel.2019.105572
243
Xing Z. Y. Sun L. G. Guo W. J. (2015). Elevated expression of Notch-1 and EGFR induced apoptosis in glioblastoma multiforme patients. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg.131, 54–58. 10.1016/j.clineuro.2015.01.018
244
Xu J. Yang X. Deng Q. Yang C. Wang D. Jiang G. et al (2021). TEM8 marks neovasculogenic tumor-initiating cells in triple-negative breast cancer. Nat. Commun.12 (1), 4413. 10.1038/s41467-021-24703-7
245
Xu L. Zhu Y. Xu J. Wu K. Li J. Xu W. et al (2012). Notch1 activation promotes renal cell carcinoma growth via PI3K/Akt signaling. Cancer Sci.103 (7), 1253–1258. 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2012.02291.x
246
Yan H. Qiu W. Koehne de Gonzalez A. K. Wei J. S. Tu M. Xi C. H. et al (2019). HHLA2 is a novel immune checkpoint protein in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and predicts post-surgical survival. Cancer Lett.442, 333–340. 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.11.007
247
Yang L. Pang Y. Moses H. L. (2010). TGF-beta and immune cells: an important regulatory axis in the tumor microenvironment and progression. Trends Immunol.31 (6), 220–227. 10.1016/j.it.2010.04.002
248
Ye Y. Z. Zhang Z. H. Fan X. Y. Xu X. L. Chen M. L. Chang B. W. et al (2013). Notch3 overexpression associates with poor prognosis in human non-small-cell lung cancer. Med. Oncol.30 (2), 595. 10.1007/s12032-013-0595-7
249
Yi L. Zhou X. Li T. Liu P. Hai L. Tong L. et al (2019). Notch1 signaling pathway promotes invasion, self-renewal and growth of glioma initiating cells via modulating chemokine system CXCL12/CXCR4. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res.38 (1), 339. 10.1186/s13046-019-1319-4
250
Zadra G. Photopoulos C. Loda M. (2013). The fat side of prostate cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta1831 (10), 1518–1532. 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.03.010
251
Zage P. E. Nolo R. Fang W. Stewart J. Garcia-Manero G. Zweidler-McKay P. A. (2012). Notch pathway activation induces neuroblastoma tumor cell growth arrest. Pediatr. Blood Cancer58 (5), 682–689. 10.1002/pbc.23202
252
Zelcer N. Tontonoz P. (2006). Liver X receptors as integrators of metabolic and inflammatory signaling. J. Clin. Invest116 (3), 607–614. 10.1172/JCI27883
253
Zhang W. Jiang H. Zhang J. Zhang Y. Liu A. Zhao Y. et al (2014). Liver X receptor activation induces apoptosis of melanoma cell through caspase pathway. Cancer Cell Int.14 (1), 16. 10.1186/1475-2867-14-16
254
Zhao K. Wang Q. Wang Y. Huang K. Yang C. Li Y. et al (2017). EGFR/c-myc axis regulates TGFβ/Hippo/Notch pathway via epigenetic silencing miR-524 in gliomas. Cancer Lett.406, 12–21. 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.07.022
255
Zhao M. Mishra L. Deng C. X. (2018). The role of TGF-β/SMAD4 signaling in cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci.14 (2), 111–123. 10.7150/ijbs.23230
Summary
Keywords
paradoxical genes, bioinformatics, tumor metabolism, discordant gene-protein abundance, tumor immune microenvironment, signaling pathway
Citation
Liu D, Liu L, Che X and Wu G (2025) Discovery of paradoxical genes: reevaluating the prognostic impact of overexpressed genes in cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 13:1525345. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1525345
Received
09 November 2024
Accepted
07 January 2025
Published
22 January 2025
Volume
13 - 2025
Edited by
Marzia Di Donato, University of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli, Italy
Reviewed by
Magdalena Julita Orzechowska, Medical University of Lodz, Poland
Liang Xu, Second Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, China
Weiyu Bai, Yunnan University, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Liu, Liu, Che and Wu.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guangzhen Wu, wuguangzhen@firsthosp-dmu.com; Xiangyu Che, chexiangyu@firsthosp-dmu.com
‡These authors have contributed equally to this work
ORCID: Guangzhen Wu, orcid.org/0000-0002-2300-8465; Xiangyu Che, orcid.org/0000-0003-4646-1390
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.