Abstract
Malignant tumors of the urinary system, such as kidney cancer, bladder cancer, and prostate cancer, remain a significant challenge despite the various treatment options available. Identifying therapeutic targets for urological tumors is crucial due to the potential for recurrence and metastasis. Recent research has highlighted the importance of RNA modifications in post-transcriptional regulation, impacting various biological functions in urological tumors, including tumorigenesis, progression, metastasis, and drug resistance. However, the specific mechanisms underlying these interactions are not fully understood. This review will focus on exploring the regulatory role of RNA modifications like m1A, m5C, and m7G in urological tumors, shedding light on the pathways and molecular mechanisms involved. This analysis aims to provide new insights for the treatment of urological tumors.
Introduction
Malignant tumors of the urinary system predominantly consist of kidney cancer, bladder cancer, and prostate cancer (Günther et al., 1970). In 2024, the United States reported 299,010 new cases of prostate cancer, with 35,250 deaths, ranking it as the most common urinary system tumor. Additionally, there were 83,190 new cases of bladder cancer and 81,610 new cases of kidney cancer, with corresponding mortality rates of 12,290 and 9,450, respectively (Siegel et al., 2024). Generally, surgery remains the primary treatment for urinary system tumors, often resulting in a favorable prognosis (Kumar et al., 2018). However, for patients with advanced tumors who are no longer eligible for surgery, identifying the mechanisms influencing tumor progression and discovering new therapeutic targets can significantly enhance patient prognosis.
As research on RNA modification progresses, over 100 types of RNA modifications have been identified (Boccaletto et al., 2022). These modifications target both mRNAs and non-coding RNAs, with ribosomal RNAs and transporter RNAs showing the highest frequency of modifications (Roundtree et al., 2017; Ontiveros et al., 2019; Li and Mason, 2014). The 5′cap structure is ubiquitous in mRNA (nearly 100% of mRNAs have this modification), but the proportion of internal m7G (occurring within the chain) is approximately 0.01%–0.1%. It accounts for about 0.1%–0.3% of mRNA modifications, is sparsely distributed, but is more significant in non-coding RNAs (such as tRNA), accounting for about 10%–20% (Sakai et al., 2016). For m1A modification, each rRNA molecule typically has only 1-2 m1A sites, with a modification ratio close to 100%, yet its rate for mRNA modification is less than one percent (Oerum et al., 2017). Furthermore, studies have revealed that m5C occurs at a modification rate of approximately 5%–10% in tRNA, and is generally sparsely distributed in mRNA but enriched in the coding sequence (CDS) and 3′untranslated region (3′UTR), playing a crucial role in regulating mRNA stability and translation efficiency (Sun et al., 2023). In RNA modification, the key enzymes include “writers,” “erasers,” and “readers,” whose corresponding roles are to catalyze the addition of chemical modifications to RNA molecules, remove RNA modifications (reversing the action of writers), and recognize and bind to specific modifications, thereby triggering downstream effects (Haruehanroengra et al., 2020). RNA modifications have diverse molecular functions that can impact RNA shearing, stability, protein translation efficiency, and intermolecular interactions. Aberrant expression and altered activity of RNA-modifying enzymes can lead to diseases such as inflammation and tumors (Chen et al., 2021; Luo et al., 2021).
RNA modifications are prevalent in various types of RNAs, including mRNAs and non-coding RNAs like microRNAs (miRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs) (Zhang et al., 2023a; Luo et al., 2023; He et al., 2023). Notably, tRNAs and rRNAs undergo frequent modifications, primarily impacting protein translation efficiency and fidelity enhancement (Agris, 2008). Specifically, rRNA modifications are concentrated at decoding sites, regions near the peptidyl transfer center (PTC), and other functional sites, influencing protein synthesis efficiency (Deca et al., 2002; Natchia et al., 2017). On the other hand, tRNA modifications predominantly affect codons, thereby regulating protein turnover (Chan et al., 2015; Chionh et al., 2016; Gkatza et al., 2019). Fluctuations in the external environment and internal molecular disturbances can disrupt the dynamic equilibrium of RNA modifications, serving as a compensatory mechanism for cells to adapt to environmental changes (Sonenberg and Hinnebusch, 2009; Dominissini et al., 2012; Blanco et al., 2016; Chan et al., 2010). This suggests a potential role of RNA modification in tumor development. In recent years, advancements in RNA modification detection technology have revealed that N1-methyladenosine (m1A), 5-methylcytidine (m5C), and N7-methylguanosine (m7G) can impact tumor proliferation, invasion, migration, and drug resistance (Xue et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2023a; Luo et al., 2022). m5C, m1A, and m7G modifications are important epitranscriptomic modifications that have demonstrated critical roles in various fields such as virology, cancer, developmental biology, and immune regulation in recent years. With the advancement of detection technologies and in-depth functional studies, the dynamic regulatory mechanisms and physiological and pathological functions of these modifications are gradually being revealed. Research has found that m5C modifications are widely present in mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, and viral RNA, and exhibit dynamic changes across different tissues and cell types (Huang et al., 2019a). In tumor immunity, metabolic disorders, and aging-related diseases, m1A modification enzymes (such as TRMT6/TRMT61A, ALKBH3) may serve as potential intervention targets (Miao et al., 2025). m7G modification is highly expressed in various cancers (such as gastric cancer, oral squamous cell carcinoma, colorectal cancer, and thyroid cancer) and promotes tumor proliferation, metastasis, and metabolic reprogramming by regulating key genes (such as SDHAF4, NEK1, ICAM-1, and TNF-α) (Xu et al., 2025; Cai et al., 2025).
This review examines the influence of RNA modifications, specifically m1A, m5C, and m7G, on urological tumors. It delves into the pathways and molecular mechanisms linked to RNA modifications that could impact urological tumors. Additionally, it discusses the significance of RNA-modifying enzymes in urological tumors and their potential as targets for novel treatment approaches.
5-methylcytosine
m5C overview
The m5C modification is a highly conserved and prevalent RNA modification that can be found on a wide range of RNAs (Figure 1) (Zhao et al., 2024a). For example, m5C modifications are commonly found in the variable loop and anticodon loop of tRNAs, influencing tRNA stability and translation efficiency (Schaefer et al., 2010). In the rRNAs of eukaryotes (such as yeast and humans), m5C modifications are catalyzed by the NSUN methyltransferase family, affecting ribosome assembly and translation fidelity (Zheng et al., 2023a). m5C modifications have been detected in the coding regions and untranslated regions (UTRs) of mRNAs, potentially regulating mRNA stability, nuclear export, and translation efficiency (Yang et al., 2017). A limited number of studies suggest that snoRNAs or precursor miRNAs may possess m5C modifications, though their functions remain unclear (Blanco et al., 2011). Early detection methods for RNA modifications were primarily chromatographic, limiting detection to modifications with high abundance like those found in tRNAs and non-coding RNAs (Boccaletto et al., 2018). However, with the development of purification techniques based on poly-A tails, a variety of modifications on mRNAs, including m6A and m5C, have been discovered (Dubin and Taylor, 1975). Currently, detection of m5C is primarily done using the sodium bisulfite method or immunoprecipitation with m5C-specific antibodies (García-Vílchez et al., 2019). RNA bisulfite sequencing is a valuable tool for quickly and accurately detecting 5-methylcytosine modifications on RNA, particularly for highly expressed RNAs such as tRNAs and rRNAs (Dai et al., 2024; Blanco et al., 2014). Despite its utility, the identification of m5C modification sites remains a topic of debate (Huang et al., 2019a). Research has revealed over 10,275 m5C modification sites on mRNAs and tRNAs in animal cells, with a notable concentration in the untranslated region and Argonaute binding region (Squires et al., 2012). Conversely, some studies suggest that RNA methylation modifications are rare in mouse embryonic stem cells and challenging to detect in mRNAs (Legrand et al., 2017). Recent studies have focused on achieving single-base resolution and quantification of modification scores using biochemical methods to identify RNA modification sites. This approach shows promise for achieving base-resolution localization of low-abundance RNA modifications in mRNAs (Zhang et al., 2024). Therefore, there is still a need for further improvements in the technical methods for sequencing and localizing RNA methylation modifications to achieve more precise single-base region localization.
FIGURE 1
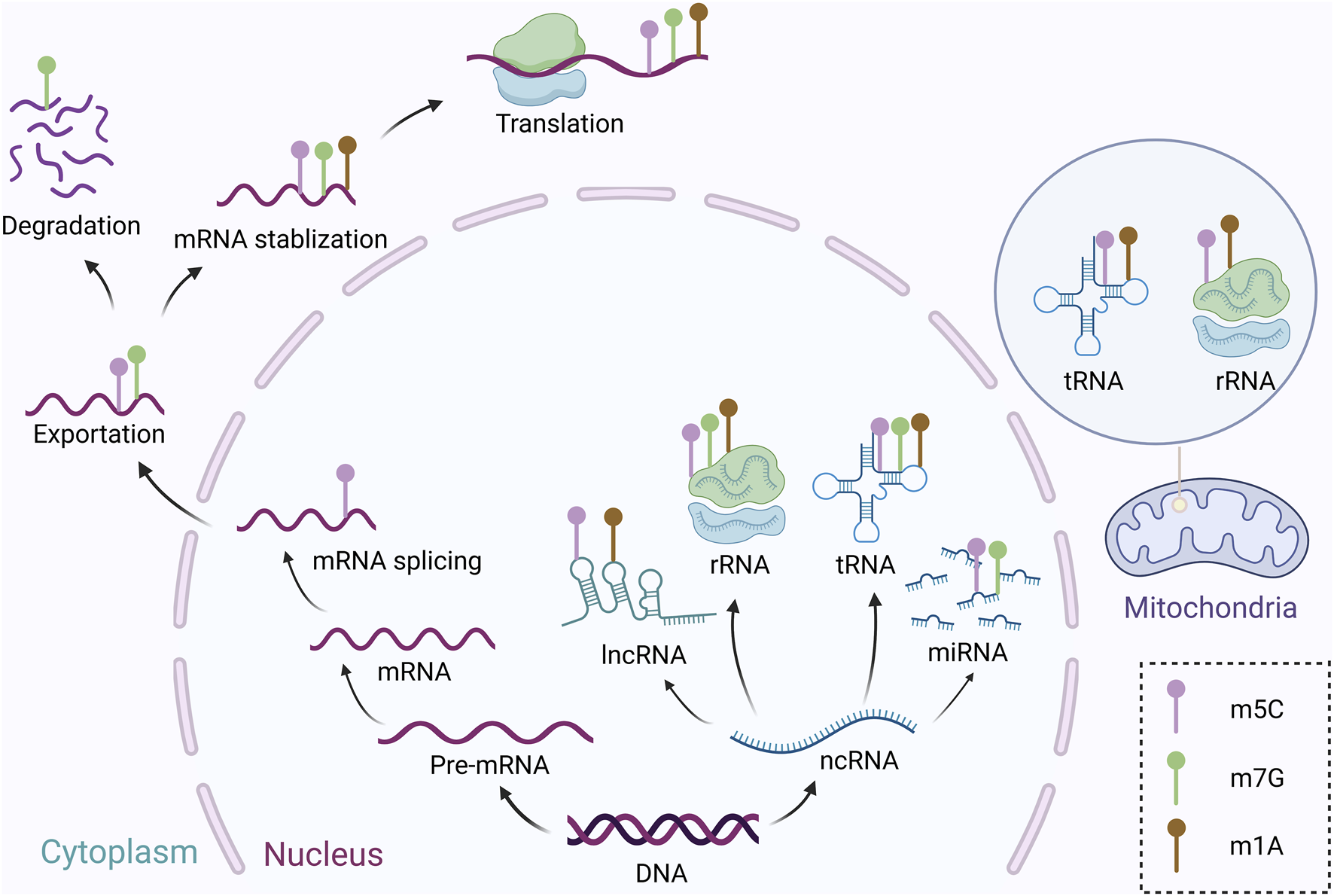
The roles of m5C, m1A, and m7G in cellular processes. Purple stands for m5C, and this modification mainly plays roles in mRNA splicing, exportation, stabilization, and translation, and is also involved in ncRNA—lncRNA, miRNA, tRNA, and rRNA, and in mitochondrial activity, it also affects the function of tRNA and rRNA. Brown represents m1A modification, which is primarily associated with mRNA stabilization and translations, and also affects lncRNA, rRNA, and tRNA in the cell nucleus, as well as rRNA and tRNA in the mitochondria. Green indicates m7G, this modification participates in mRNA exportation, degradation, stabilization, and translation, as well as ncRNAs such as miRNA, rRNA, and tRNA.
Regulation of coding RNAs and non-coding RNAs by m5C
Although m5C is not as widely enriched in RNA modification as m6A, the regulatory role of m5C for both coding and non-coding RNAs has been gradually discovered with the development of epigenetics (Table 1). This modification has been found to affect the biological processes of cells. In thyroid cancer, a high m5C modification state has been observed, leading to increased tRNA stability, intracellular leucine transport, and ultimately enhancing the translation efficiency of certain proto-oncogenes (Li et al., 2023a). Studies have also shown that a decrease in m5C levels of tRNAs can result in tRNAGly coencoder dysfunction and reduced protein translation efficiency (Blaze et al., 2021). M5C modification of tRNA at sites 48, 49, and 50 in mammalian mitochondria enhances tRNA stability and supports phosphonate oxidation during cell differentiation (Van Haute et al., 2019). The tRNAs that undergo m5C modification exhibit enhanced stability and translation efficiency. In the event of DNA damage, there is an upregulation of rRNA and non-coding RNAs, with RNA modification (m5C) contributing to R-loop stability and involvement in transcriptionally linked homologous recombination (Chen et al., 2020a). The smooth assembly of mitochondrial ribosomes in mammals relies on the coordinated maturation of both the large subunit (LSU) and the small subunit (SSU), with 12S rRNA methylation ensuring that only mature LSUs and SSUs can be assembled correctly (Metodiev et al., 2014). This process serves as a crucial factor in ribosome assembly. In cholangiocarcinoma, the functional LncRNA (NKILA) undergoes m5C modification upon interaction with YBX1, leading to its stabilization and promoting tumor progression (Zheng et al., 2022). Similarly, m5C modification enhances circ_0102913 expression, contributing to malignancy in colon cancer through the miR-571/RAC2 axis (Hou et al., 2024). Detecting methylation modifications in less abundant miRNAs poses challenges due to sample purification and the presence of interfering highly abundant RNAs (Richter et al., 2022; Schaefer et al., 2017). Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) nucleoside analysis and liquid-solid two-step hybridization (LSTH) were utilized to identify m5C modifications in miR-21-5p, Let-7a/e-5p, and miR-10a-5p, revealing modifications at each site to be less than 1% (Lü et al., 2024). This underscores the need for further development in detection techniques to enhance the sensitivity and specificity for identifying low abundance RNA modifications. For coding RNAs, m5C modifications primarily enhance mRNA stability and protein translation efficiency. YBX1, a reader of m5C, promotes target mRNA stability by recognizing the indole loop of W65 in the cold shock structural domain of the target mRNA, leading to the recruitment of ELAVL1 (Chen et al., 2019a). Additionally, PEBP1P2 interacts directly with 5-methylcytosine (m5C)-containing PEBP1 mRNA and facilitates the stabilization of PEBP1 mRNA by recruiting the YBX1/ELAVL1 complex (Yang et al., 2022a). NSUN6, an m5C writer, has been shown to drive target genes to undergo m5C modifications that impact translation termination, potentially playing a role in quality control of translation termination fidelity (Selmi et al., 2021). However, the precise mechanism remains unclear.
TABLE 1
| RNA modifications | Disease type | Biological function | Molecular mechanism | Expression | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m5C | Thyroid cancer | Increase intracellular leucine transport | Stablize tRNA | Upregulated | Yang et al. (2017) |
| Depression | Regulate glutamatergic neurotransmission | Reduced protein translation efficiency | Downregulated | Blanco et al. (2011) | |
| - | Support phosphonate oxidation | Stablize tRNA | Upregulated | Boccaletto et al. (2018) | |
| - | Mitochondrial ribosome maturation | rRNA assembles | Upregulated | García-Vílchez et al. (2019) | |
| Cholangiocarcinoma | Promote tumor progression | Stablize LncRNA (NKILA) | Upregulated | Dai et al. (2024) | |
| Colorectal cancer | Promote proliferation, invasion and migration | Stablize circRNA (circ_0102913) | Upregulated | Blanco et al. (2014) | |
| Bladder cancer | Promote tumor progression | Stablize mRNA | Upregulated | Zhang et al. (2024) | |
| Renal cell carcinoma | Promote migration, invasion and metastasis formation | Stablize mRNA (PEBP1) | Downregulated | Li et al. (2023a) | |
| m1A | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Promote cholesterol synthesis | Stablize tRNA, Promote protein translation | Upregulated | Zhu et al. (2022) |
| Urothelial carcinoma of the bladder | Participate in the unfolded protein response | Stablize tRNA | - | Alshaker et al. (2019) | |
| Adoptive transfer colitis model | Inhibit T cell activation | Promote translation efficiency | Downregulated | Kar et al. (2016) | |
| Yeast | Carbohydrate metabolism, translation, and ribosome synthesis | Maintain rRNA an optimal 60S conformation | - | Wang et al. (2023b) | |
| Escherichia coli | Regulate protein synthesis and cell growth | Maintain 16S rRNA modification | - | Sun et al. (2022) | |
| - | Inhibit the expression of P53 | Mediated 28S rRNA modification | - | Sun et al. (2020b) | |
| Oplastic transformation of oral Mucosa | Promote MYC and PD-L1 protein synthesis | Stablize tRNA | Upregulated | Zhang et al. (2023b) | |
| Melanoma | Inhibits the malignant transformation of cancers | Promote mRNA stability and translational efficacy (SP100A) | Downregulated | Dunn (1961) | |
| Mammalian cells | Promote ciliogenesis in mammalian cells | Inhibits mRNA stability and translational efficacy (Aurora A) | - | Liu et al. (2024a), Zhou et al. (2019) | |
| m7G | Bladder cancer | Promote proliferation, migration and angiogenesis | Promote translation efficiency (VEGFA) | Upregulated | Monshaugen et al. (2024) |
| Bladder cancer | Promote proliferation and migration | Promote translation efficiency (TROP2), Stablize miRNA (miR-760) | Upregulated | Shimada et al. (2012), Malbec et al. (2019) | |
| Lung cancer | Promote proliferation and migration | Promote mRNA translation efficiency | Upregulated | Koike et al. (2012), Ohira and Suzuki (2016) | |
| Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | Regulate cell cycle, epidermal growth factor receptor and tumor drug resistance | Stablize tRNA, Promote mRNA translation | Upregulated | Ueda et al. (2018), Cheng et al. (2022) | |
| Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | Promote tumor progression and metastasis | Promote mRNA translation efficiency | Upregulated | Boulias and Greer (2019), Furuichi (2015) | |
| Osteosarcoma | Promote proliferation, migration and invasion capacities, Modulate chemotherapy resistance | Promote mRNA translation efficiency, Stablize miRNA (miR-26a-5p) | Upregulated | Zhu et al. (2018), Shoombuatong et al. (2022) | |
| Acute myeloid leukemia | Promote cell proliferation and inhibit apoptosis | Stablize tRNA | Upregulated | Zhang et al. (2022) | |
| Regulate cell migration | Disrupt primary miRNA transcript (pri-miRNA) | - | Zhang et al. (2019) |
Molecular mechanism and biological functions of RNA modifications.
Effect of m5C modification on the signal transduction pathways
An abnormal increase in NSUN2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma was found to promote increased m5C abundance. Additionally, the protein LIN28B was shown to promote GRB2 mRNA stabilisation in an m5C-dependent manner, leading to activation of the PI3K/AKT and ERK/MAPK signalling pathways (Su et al., 2021). Similarly, m5C modifications were found to be significantly higher in hepatocellular carcinomas compared to adjacent normal tissues. Transcriptomic analyses revealed that hypermethylation modifications activated phosphokinase signalling pathways such as the PI3K and Ras pathways (Song et al., 2023; Xiang et al., 2020). According to bioinformatics analysis, DNMT1, the key enzyme of m5C, is closely associated with immune infiltration in liver cancer. The growth factor β (TGF-β)/EMT pathway may be activated to facilitate tumor invasion and metastasis (Gu et al., 2021). In rheumatoid arthritis, NSUN2 is upregulated to drive inflammatory progression through the SFRP1/Wnt/β-catenin signaling axis, a process that can be counteracted by the m5C demethylase FTO (Huang et al., 2024). Following TRDMT1 (m5C methyltransferase) knockout and sequencing of both wild-type and HEK293 cells using RNA-Seq and RNA-bisseq, GO analysis of differentially expressed genes revealed a notable enrichment of the Notch signaling pathway (Xue et al., 2019). In non-small cell lung cancer, LINC02159 binds to the Aly/REF output factor (ALYREF) to promote YAP1 mRNA stability in an m5C-dependent manner, thereby activating Hippo and β-catenin signaling pathways (Yang et al., 2023a). The above explanation indicates that m5C can upregulate numerous signaling pathways, thereby regulating cellular biological functions such as tumor cell proliferation, apoptosis inhibition, invasion, migration, and angiogenesis. Overall, m5C methylation modification is prevalent in various diseases and enhances disease progression by influencing the activity of multiple signaling pathways (Table 2).
TABLE 2
| RNA modifications | target RNA | Disease type | Pathway | Pathway status | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m5C | mRNA | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | PI3K/AKT, ERK/MAPK | Activation | Van Haute et al. (2019) |
| mRNA, tRNA, rRNA | Hepatocellular carcinomas | PI3K/AKT, Ras, TGF-β | Activation | Chen et al. (2020a), Metodiev et al. (2014), Zheng et al. (2022) | |
| mRNA | Rheumatoid arthritis | Wnt/β-catenin | Activation | Hou et al. (2024) | |
| mRNA | Non-small cell lung cancer | Hippo, β-catenin | Activation | Schaefer et al. (2017) | |
| m1A | tRNA, rRNA | Gastrointestinal tumors, Hepatocellular carcinoma | PI3K/AKT | Activation | Wu et al. (2022), Li et al. (2016) |
| tRNA | Advanced hepatocellular carcinoma | Hedgehog | Activation | Chen et al. (2020b) | |
| rRNA | P53 | Inhibition | Sun et al. (2020b) | ||
| m7G | mRNA, rRNA | Ameloblastoma, Transplantation of endothelial progenitor cells | MAPK | Activation | Ueda et al. (1991), Zhao et al. (2021) |
| tRNA | Pancreatic Cancer | MEK/ERK | Activation | Chen et al. (2023b) | |
| mRNA, tRNA | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | PI3K/AKT/mTOR | Activation | Boulias and Greer (2019) | |
| tRNA | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | WNT/β-catenin | Activation | Ma et al. (2021) | |
| tRNA | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma | EGFR | Activation | Ueda et al. (2018), Cheng et al. (2022) |
RNA modification regulates multiple disease pathways.
The m5C writers
m5C modifying enzymes can be categorized into writers, erasers, and readers, which are responsible for modifying various types of RNA (Table 3). m5C modified writers consist mainly of the NOL1/NOP2/SUN (NSUN) domain protein family, DNA Methyltransferase (DNMT), and TRNA Aspartic Acid Methyltransferase 1 (TRDMT1) (Buj et al., 2004; Motorin et al., 2010). Studies have shown that multiple types of RNA can undergo m5C modification (Figure 1). The main function of m5C is to maintain RNA stability and retard degradation, with S-adenosylmethionine (S-adenosylmethionine) as a methyl donor to form a methylation modification on cytosine. Different cellular regions are mediated by different modifying enzymes, and in the nucleus NSUN2, NSUN5, NSUN6, NSUN7, and NOP2 are responsible for the methylation modification of mRNAs and some non-coding RNAs (Bourgeois et al., 2015; Xu et al., 2020; Heiss et al., 2019; Yang et al., 2021; Aguilo et al., 2016; Surovtseva and Shadel, 2013). In mitochondria, NSUN2, NSUN3, and NSUN4 play a key role in tRNA and 12S rRNA methylation, facilitating mitochondrial ribosome assembly (Nakano et al., 2016; Kawarada et al., 2017; Van Haute et al., 2016; Lenarčič et al., 2021; Cipullo et al., 2021). While some methyltransferases modify the same RNA types, they target different modification sites. For instance, NSUN1/NOP2 and NSUN5 target m5C 4447 and m5C 3782 on 28S rRNA, respectively (Bourgeois et al., 2015; Heiss et al., 2019; Janin et al., 2019). Moreover, NSUN6 and DNMT2 modify m5C72 and m5C38 on tRNA, respectively (Schaefer et al., 2010; Yang et al., 2021; Tuorto et al., 2012; Goll et al., 2006; Shanmugam et al., 2015). NSUN2, the most extensively studied methyltransferase, acts on mRNA (Yang et al., 2017; Xu et al., 2020; Cai et al., 2016; Xing et al., 2015; Li et al., 2017a), tRNA (Van Haute et al., 2019), miRNA (Yuan et al., 2014; Yang et al., 2015), and lncRNA (Sun et al., 2020a; Li et al., 2018). NSUN3 is an intra-mitochondrial methyltransferase that facilitates the S-adenosylmethionine (AdoMet) dependent methylation initiation of mt-tRNA, leading to the biogenesis of 5-formylcytidine (f5C) 34 and ultimately promoting protein synthesis (Nakano et al., 2016; Kawarada et al., 2017; Van Haute et al., 2016). NSUN4 is involved in the m5C modification of rRNA (Metodiev et al., 2014; Lenarčič et al., 2021; Cipullo et al., 2021; Cheng et al., 2021; Yakubovskaya et al., 2012; Cámara et al., 2011) and mRNA (Yang et al., 2022b), which enhances ribosome conformational stability, assembly maturation, and protein translation. In humans, NSUN5 primarily methylates the m5C 3782 site of rRNA, contributing to protein stability (Heiss et al., 2019; Janin et al., 2019). NSUN6 is responsible for modifying the m5C 72 sites of tRNACys/Thr in the cytoplasm (Yang et al., 2021) and methylating certain mRNA 3′UTR regions (Yang et al., 2021). Lastly, NSUN7 is responsible for the m5C modification of enhancer RNAs (eRNAs), promoting eRNA stability and enhancing transcription (Aguilo et al., 2016).
TABLE 3
The type of RNA modified by the RNA modifying enzyme corresponds to the modification.
The m5C erasers
While m5C writers have been extensively studied, research on m5C erasers has been more limited. Current research indicates that m5C erasers primarily consist of Tet family (Tet1-3) members and ALKBH1. Tet family enzymes not only facilitate DNA methylation modifications, but also catalyze 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmrC) activity in RNA (Fu et al., 2014). In mammals, RNA m5C is oxidized to produce 5-hydroxymethylcytidine and 5-formylcytidine (Huber et al., 2015). Tet1 plays a role in clearing m5C modifications at hybrid sites during DNA damage repair, thereby promoting homologous recombination (Yang et al., 2022c). Furthermore, Tet1 has been shown to decrease the m5C levels of RelB mRNA and stabilize its mRNA expression (Lin et al., 2024). Tet2 has been found to significantly reduce tRNA m5C levels in vitro, leading to enhanced translation levels (Shen et al., 2021). Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase homologue 1 (ALKBH1), primarily involved in demethylation, exhibits substrate diversity and suggests a diverse biological function (Zhang and Wang, 2021).
The m5C readers
As research progressed, various m5C-related readers were gradually identified, including ALYREF, YBX1, LIN28B, YTHDF2, RAD52, and FMRP proteins. The first m5C reader identified was Aly/REF export factor (ALYREF) (Yang et al., 2017), known for its role in promoting mRNA stability and export, closely linked to amino acid metabolism and immune regulation (Meng et al., 2024; Nulali et al., 2024; Eckwahl et al., 2020). YBX1, another well-studied m5C reader, primarily utilizes the cold shock domain (CSD) to bind to target mRNA and facilitate m5C modification (Su et al., 2021; Chen et al., 2019c; Yang et al., 2019). YBX1 functions as an RNA-binding protein, interacting with target RNA to enhance stability and translation, influencing biological processes such as cell autophagy, lipid synthesis (Wang et al., 2023a; Wu et al., 2023), ferroptosis (Chen et al., 2024), and angiogenesis (Li et al., 2024a). Research indicates that YBX1 binds to E2F1 mRNA, forming a positive feedback loop to stabilize and enhance its expression, highlighting the context-dependent regulatory mechanism of YBX1 (Liu et al., 2023a; Liu et al., 2024a). Moreover, YBX1 predominantly interacts with the CDS or 3′UTR regions of target mRNAs, impacting their stability (Liu et al., 2024b; Yu et al., 2023; Zheng et al., 2023b; Huang et al., 2019b). Lin-28 homolog B (LIN28B), recruited by NSUN2, enhances the stability of multiple pathway-related mRNAs, impacting esophageal cancer progression (Su et al., 2021). Despite weaker binding to m5C compared to m6A, YTHDF2 can recognize m5C sites through the Trp432 conserved domain, facilitating rRNA maturation and processing (Dai et al., 2020). RAD52 and FMRP promote mRNA m5C modification at DNA damage sites in a TRDMT1-dependent manner, promoting homologous recombination (Yang et al., 2022c; Chen et al., 2020a).
m5C writers modification regulates urinary system tumors
The research on RNA modification has revealed the significant impact of m5C modification on urinary system tumors (Table 4). Analysis of NOP2-related data in ccRCC from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) indicates that NOP2 is highly expressed in renal cancer, showing a significant correlation with poor prognosis. Furthermore, there is an observed relationship between NOP2 expression and MSI, TMB, TNB, and immunity (Wang et al., 2021a). Consistent with the aforementioned bioinformatics analysis findings, NOP2, NSUN4, and NSUN6 exhibit differential high expression levels in renal cancer samples. Additionally, both risk scores and clinicopathological correlations have the potential to serve as valuable prognostic indicators for clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) (Li et al., 2021). Furthermore, bioinformatics analysis suggests that NSUN5, a gene prominently expressed in renal cancer, could potentially influence immunity and drug resistance. Recent studies have shown that the suppression of NSUN5 leads to a decrease in cell proliferation, invasion, and migration, while simultaneously increasing levels of apoptosis. The mechanism underlying this phenomenon involves the upregulation of apoptosis-related proteins and activation of the p53 signaling pathway (Li et al., 2023b).
TABLE 4
| Gene symbol | Enzyme | Cancer type | Role | Main target | Expression | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m5C | ||||||
| NOP2 | Writer | Renal cell cancer | Oncogene | Regulate MSI, TMB, TNB and immunity | Upregulated | Aguilo et al. (2016), Yang et al. (2022b) |
| NSUN4 | Writer | Renal cell cancer | Oncogene | Regulate PI3K-AKT pathway | Upregulated | Aguilo et al. (2016) |
| NSUN6 | Writer | Renal cell cancer | Tumour suppressor | Regulate PI3K-AKT pathway | Downregulated | Aguilo et al. (2016) |
| NSUN5 | Writer | Renal cell cancer | Oncogene | Inhibits the P53 pathway | Upregulated | Fu et al. (2014) |
| NSUN2, ALYREF | Writer, Reader | Bladder cancer | Oncogene | Enhance oncogenic mRNA splicing and stability | Upregulated | Huber et al. (2015) |
| NSUN2, YBX1 | Writer, Reader | Bladder cancer | Oncogene | Stabilize HDGF3 mRNA | Upregulated | Yang et al. (2022c) |
| NSUN2, YBX1 | Writer, Reader | Prostate cancer | Oncogene | Stabilize AR mRNA | Upregulated | Zhang and Wang (2021) |
| NSUN5 | Writer | Prostate cancer | Oncogene | Stabilize ACC1 mRNA and increases nuclear export | Upregulated | Nulali et al. (2024) |
| m1A | ||||||
| TRMT6/61A | Writer | Bladder cancer | Oncogene | Target tRF-3B and ATF6 | Upregulated | Wang et al. (2021a), Oerum et al. (2018) |
| ALKBH3 | Eraser | Bladder cancer | Oncogene | Target tweak/Fn14/VEGF | Upregulated | Bhatta et al. (2021) |
| ALKBH3 | Eraser | Prostate cancer | Oncogene | Target MMP9 and AKT | Upregulated | Murakami et al. (2018), Liu et al. (2016) |
| m7G | ||||||
| METTL1 | Writer | Bladder cancer | Oncogene | Target miR-760, EGFR/EFEMP1 and TROP2 | Upregulated | Shimada et al. (2012), Malbec et al. (2019), Cruz and Joseph (2022) |
| METTL1 | Writer | Prostate cancer | Oncogene | Target tRNA and CDK14 | Upregulated | Pandolfini et al. (2019), Peter et al. (2017) |
| eIF4E | Reader | Renal cell cancer | Oncogene | Target activation of multiple oncogenes | Upregulated | Yang et al. (2017), Meng et al. (2024),Nulali et al. (2024) |
| eIF4E | Reader | Bladder cancer | Oncogene | Target mTOR pathway | Upregulated | Culjkovic et al. (2007), Matsuo et al. (1997), Haimov et al. (2018) |
| eIF4E | Reader | Prostate cancer | Oncogene | Target PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Ras/MAPK pathway | Upregulated | Amaya Ramirez et al. (2018), Ruscica et al. (2019), Jafarnejad et al. (2018) |
The role of RNA-modifying enzymes in urinary system tumors.
Bladder cancer research has shown that NSUN2 co-exists with Aly/REF export factor (ALYREF), contributing to bladder cancer proliferation, invasion, and poor prognosis. Specifically, m5C-mediated ALYREF recognizes RABL6 and TK1 mRNA m5C modification through its K171 domain, enhancing mRNA splicing and stability to increase bladder cancer malignancy (Wang et al., 2023b). Additionally, NSUN2 collaborates with YBX1 to stabilize HDGF3 mRNA by recruiting ELAVL1 and targeting the m5C modification site in the HDGF 3′untranslated region, ultimately promoting bladder cancer progression. Higher expression of m5C key enzymes NUSN2 and YBX1 has been associated with a negative prognosis (Chen et al., 2019a).
The expression of NOP2 is increased in prostate cancer tissue (Sun et al., 2022), potentially promoting the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and influencing prostate metastasis (Sun et al., 2020b). However, the specific mechanism by which NOP2 mediates m5C regulation in prostate cancer remains unclear. Studies suggest that NSUN2 and androgen receptor (AR) can establish a positive feedback loop in prostate cancer, accelerating disease progression. NSUN2 helps maintain the stability of AR-related mRNA through m5C modification, while ARV7 boosts NSUN2 expression at the transcriptional level (Zhu et al., 2022). NSUN3 and NSUN4 have received less attention in prostate cancer research, but they may play a role in chemotherapy resistance and tumor advancement (Alshaker et al., 2019), potentially serving as risk factors for prostate cancer (Kar et al., 2016). NSUN5 is closely associated with abnormal lipid metabolism in prostate cancer. Research indicates that NSUN5 facilitates the phosphorylation and m5C modification of the Ser327 site on acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC1) mRNA. This process recruits ALYREF to bind to ACC1 mRNA, ultimately enhancing its stability and nuclear export. These findings suggest that NSUN5 could be a promising therapeutic target for prostate cancer (Zhang et al., 2023b).
Collectively, these findings expose that m5C-related writers are important for both the regulation and development of urologic tumors and that these key enzymes may be therapeutic targets for urologic tumor therapy.
m5C readers modification regulates urinary system tumors
ALYREF is highly expressed in bladder cancer and is associated with a poor prognosis (Wang et al., 2023b; Pan et al., 2024). Through its K171 domain, ALYREF recognizes RABL6 and TK1 mRNA m5C modification, promoting their mRNA splicing and stability to increase bladder cancer malignancy (Wang et al., 2023b). Additionally, hypoxia-inducible factor 1A transcriptionally activates ALYREF expression, which then binds to the 3′-untranslated regions of PKM2 mRNA, leading to elevated PKM2 expression. Consequently, PKM2 mediates glycolysis to promote tumor proliferation (Wang et al., 2021b). Another m5C reader, YBX1, is also highly expressed in bladder cancer and is linked to a negative prognosis. Mechanistically, YBX1 recruits ELAVL1 to interact with the m5C site in the 3′untranslated region of HDGF mRNA via the W65 residue in its cold shock domain (Chen et al., 2019c).
In prostate cancer, ACC1 mRNA in the m5C modified state interacts with ALYREF to enhance its stability and facilitate nuclear export, resulting in lipid accumulation and progression of prostate cancer (Zhang et al., 2023b). Prostate cancer-related m5C prognostic model shows that abnormal YBX1 expression affects patient prognosis and immune infiltration (Yu et al., 2022). YBX1 stabilizes ARV7 mRNA in an m5C-dependent manner and forms a positive feedback loop with NSUN2 to promote prostate progression (Zhu et al., 2022).
According to current research findings, ALYREF and YBX1, as m5C readers, play a crucial role in regulating the proliferation, invasion, migration, lipid metabolism, and immune microenvironment of urinary system tumors. Abnormal expression of these proteins is closely associated with prognosis.
1-methylcytosine
m1A overview
Although m1A modification is not as extensive as m6A modification, research from the 1960s has shown its presence in coding RNA and non-coding RNA, such as tRNA, rRNA, and LncRNA (Dunn, 1961; Zhou et al., 2019). This modification alters RNA base pairing, impacting RNA stability and protein translation efficiency, thus regulating molecular biological functions (Wu et al., 2022; Li et al., 2016; Zhou et al., 2016; Kuang et al., 2022). While mRNA m1A modification sites have been less studied, tRNA and rRNA modification sites are more commonly investigated. Advancements in m1A sequencing technology allow for more accurate and precise identification of m1A modification sites. Previous research utilizing m1A antibodies for immunoprecipitation, followed by m1A-ID-seq, has revealed a diverse range of modification sites on both coding and non-coding RNAs. Specifically, mRNA m1A sites have been identified, with a notable enrichment in the 5′untranslated region (Li et al., 2016). However, follow-up analysis showed that previous studies may have had defects such as duplication of detection sites, annotation errors and inaccurate sequencing results, which showed that modification of m1A on mRNA is rare (Schwartz, 2018). Similarly., it was still shown that m1A modification on mRNA is not predominantly enriched in the 5′UTR, and their detection of m1A using m1A antibody at single-nucleotide resolution found that it could be a false-positive result produced by the antibody’s interactions with the m7G-cap, which again gives the idea that m1A modification on mRNA is rare (Grozhik et al., 2019; Khoddami et al., 2019). In the last 2 years, there have been further advances in the study of m1A modification, with the newly developed fluorescence-based RT evolution platform revealing hundreds of m1 - A sites in human multitailed RNAs, as well as modifications of the m1A modification in nascent mitochondrial RNAs (mt-RNAs) (Zhang et al., 2024). As RNA modification detection techniques are improved, more potential sites for m1A modification will be identified, likewise more false modification sites will be excluded.
Regulation of coding RNAs and non-coding RNAs by m1A
As described earlier, m1A modifications are primarily found in tRNAs, rRNAs, and a small number of mRNAs (Table 1). In eukaryotes, the RNA processing enzyme 8 targets position 645 of 25S rRNA for m1A modification, impacting carbohydrate metabolism and translation (Yang et al., 2023b; Li et al., 2022a; Yip et al., 2013; Peifer et al., 2013; Sharma et al., 2018). Moreover, in humans, the nuclear methyl protein (NML) catalyzes methylation at site 1,322 of 28S rRNA (Peifer et al., 2013). The TRMT61B-mediated m1A modification at position 947 of mitochondrial rRNA plays a crucial role in regulating mitochondria-encoded proteins (Bar-Yaacov et al., 2016). Furthermore, NML-mediated methylation modification of m1A in 28S rRNA enhances the translation of target proteins while suppressing the expression of P53 (Waku et al., 2016). For tRNA, m1A modification promotes partial tRNA methylation in hepatocellular carcinoma, leading to increased translation of PPARδ and impacting cholesterol synthesis (Wang et al., 2021c). Additionally, TRMT6-mediated m1A modification of tRNA negatively regulates gene silencing of tRF-3s (Su et al., 2022). The high m1A modification status of tRNAs in T cells enhances the translation efficiency of MYC-associated proteins (Liu et al., 2022; Li et al., 2024b). In summary, m1A modification promotes tRNA stability and correct folding of tRNA structure. As for mRNA, m1A modification primarily occurs in nuclear mRNA in the 5′UTR (near the translation start codon) and in mitochondrial mRNA in the CDS and 3′UTR (Li et al., 2016; Dominissini et al., 2016). Generally, m1A is situated near translation initiation sites to regulate translation initiation and enhance translation efficiency (Safra et al., 2017). For instance, m1A at the SP100 mRNA initiation site promotes its translation process (G et al., 2024). However, when m1A modification is found in the mRNA 5′UTR and CDS region, it may disrupt base complementary pairing, thereby inhibiting the translation process (Li et al., 2016; Wu et al., 2022; Kuang et al., 2022). Although the modification of non-coding RNAs (LncRNAs, miRNAs, and circRNAs) by m1A is currently less studied, the shared key enzymes with m6A suggest potential expansion in future research.
Effect of m1A modification on the signal transduction pathways
Current studies have shown that in gastrointestinal tumors, m1A modification may play a regulatory role in the PI3K/AKT pathway, with specific mechanisms requiring further investigation (Zhao et al., 2019; Shi et al., 2020). In patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma, higher levels of m1A modification of tRNAs have been associated with increased PPARδ translation efficiency, leading to elevated cholesterol synthesis and activation of the Hedgehog pathway (Yang et al., 2023b). Additionally, during T cell pre-activation, TRMT6 upregulates tRNA m1A58 modification, enhancing the synthesis of MYC-related proteins (Yip et al., 2013). Knockdown of MNL has been found to promote RPL11 expression through m1A modification, resulting in inhibition of the ubiquitinating enzyme MDM2 and subsequent activation of the P53 pathway (Waku et al., 2016). These findings highlight the current research focus on the impact of RNA m1A modifications on signaling pathways (Table 2).
The m1A writers
m1A modifying enzymes can be categorized into writers, erasers, and readers, which are responsible for modifying various types of RNA (Table 3). Like other types of RNA modifications, m1A modifications have a set of key enzymes including writers, erasers, and readers, of which the writers consist of TRMT6, TRMT61A, TRMT61B, TRMT10C, and NML (Safra et al., 2017; El Yacoubi et al., 2012; Ozanick et al., 2005; Vilardo et al., 2018; Ozanick et al., 2005). Although m1A modification is less prevalent than m6A, it can occur in various types of RNA (Figure 1). Currently known m1A-modified writers mainly belong to the tRNA methyltransferase protein family members, of which the TRMT6/TRMT61A complex is mainly responsible for the formation of stable m1A modifications in tRNAs at the neck-loop region (Li et al., 2017b)and regulation of some mRNAs (Chujo and Suzuki, 2012). Trmt61B is mainly responsible for m1A modification at site 58 in tRNA (Leu (UUR)), tRNA (Lys) and tRNA (Ser(UCN)) within mitochondria (Safra et al., 2017). In addition, it has been found that m1A modification at site 947 of 16S rRNA in mitochondria is also regulated by TRMT61B (Sun et al., 2022). Discrimination of individual base modifications for m1A is lacking, and TRMT10C was developed in mitochondria to specifically catalyze the m1A site, whose catalytic process is tightly regulated (Safra et al., 2017). In addition, TRMT10C in mitochondria is responsible for m1A modification of the mt-tRNA 9 site, which is essential for proper tRNA folding and mitochondrial maturation (Vilardo et al., 2018; Bhatta et al., 2021). Mechanistically, TRMT10C and SDR5C1 form a complex that binds to tRNA conserved sequences thereby promoting m1A modification at this locus (Murakami et al., 2018). NML (also known as yeast homologues RRP8) facilitates 60S ribosomal subunit formation by m1A modification of 28S rRNAs (Sharma et al., 2018; Waku et al., 2016).
The m1A erasers
The current m1A-associated erasers mainly include AlkB family proteins (ALKBH1 and ALKBH3) and FTO. Although ALKBH1 does not affect mitochondrial structure, its m1A modification of mitochondrial tRNA regulates respiration and protein translation (; Liu et al., 2016) and stimulates the mitochondrial unfolded protein response (Wagner et al., 2019). Furthermore, ALKBH1 in mitochondria dynamically regulates m1A modification of tRNA, decreases tRNA stability and promotes tRNA cleavage (Rashad et al., 2020). Recent studies have shown that m1A modification of mRNA by ALKBH1 promotes colon cancer progression and poor prognosis, which mechanistically may be due to its modification of METTL3 mRNA (Chen et al., 2023a). Possesses a tRNA-binding structural domain similar to ALKBH1, so ALKBH3 also functions to modify tRNAm1A to promote ribosome assembly (Chen et al., 2019c). Similarly, ALKBH3 can regulate mRNA stability and protein translation through m1A modification, which is achieved by binding different regions of the mRNA (Kuang et al., 2022; G et al., 2024; Seo and Kleiner, 2020; Woo and Chambers, 2019). ALKBH3 also eliminates DNA/RNA deregulated methylation modifications, thereby completing the DNA damage repair process (Aas et al., 2003; Ougla et al., 2004). FTO has been widely studied in the modification of m6A, but in the modification of m1A, its substrate selection is more limited, such as the circular structure in tRNA rather than the linear structure, thereby inhibiting the translation process (Wei et al., 2018).
The m1A readers
YTH structural domain family proteins (YTHDF1-3 and YTHDC1) act as readers of m1A to recognize multiple RNA methylation modifications (Dai et al., 2018). It was shown that YTHDF1 not only promotes the mRNA translation process through m1A dynamic modification (Dunn, 1961; Dai et al., 2018), but also reduces the translation efficiency by forming a complex in concert with eRF1 (Wu et al., 2023), which might be due to the Watson-Crick destructive properties generated by its binding to different m1A modification sites (Safra et al., 2017; Li et al., 2017b). In addition, YTHDF2 and YTHDF3 can interact with some mRNAs to destabilize transcripts through m1A modification. In addition, YTHDF2 and YTHDF3 can interact with some mRNAs to destabilize transcripts through m1A modification (Seo and Kleiner, 2020; Zheng et al., 2020), and Trp432, a conserved residue in YTHDF2, is an important site for recognizing m1A modification (Dai et al., 2018). YTHDC1 is involved in the repair of RNA damage-induced DNA breaks (RDIBs) through m1A modification (Tsao et al., 2024).
m1A writers modification regulates urinary system tumors
The impact of m1A modification on bladder cancer is gradually being uncovered (Table 4). Research has indicated that increased m1A modification in bladder cancer is closely linked to the abnormal expression of TRMT6/61A, which controls the target mRNA unfolded protein response (UPR) and bladder cancer advancement through tRF-3B (Li et al., 2022a). Specifically, the removal of TRMT6/TRMT61A resulted in decreased mRNA levels of the conventional transcription factor UPR ATF6-associated targets, leading to a reduction in bladder cancer cell proliferation and stress resistance (Monshaugen et al., 2024). Since the role of m1A writers in urologic tumors has not been extensively discussed, further comprehensive studies are necessary.
m1A erasers modification regulates urinary system tumors
ALKBH3 has been thoroughly researched in the field of bladder cancer. Silencing ALKBH3 results in the halting of tumor cell cycle progression by influencing NOX-2 to increase ROS activity. Moreover, ALKBH3 plays a role in regulating VEGF expression by affecting Tweak and Fn14. However, the exact mechanism by which ALKBH3 controls m1A modification is still not fully understood (Shimada et al., 2012).
ALKBH3 is recognized as a marker for prostate cancer, with its elevated levels being closely linked to the aggressiveness of the cancer and its ability to inhibit apoptosis (Koike et al., 2012; Ueda et al., 2018). Due to the absence of a reliable enzymatic assay for ALKBH3, a novel electrochemical signaling assay was created to study its m1A modification. This assay operates on the principle that the alkyl group of the Fc-DNA probe is eliminated, resulting in the formation of a 3′flat end on the DNA, ultimately leading to a reduction in the signal produced by Fc (Cheng et al., 2022).
N7-methylguanosine
m7G overview
Similar to m5C and m1A, m7G is a common modification of RNA, with methylation of the guanine N7 site, which regulates RNA structure by altering molecular charge changes (Boulias and Greer, 2019). The m7G modification can occur within a variety of RNAs, including mRNA 5′capsids (Furuichi, 2015) and some precursor tRNAs, protecting them from stable maturation (Ohira and Suzuki, 2016). This modification functionally regulates mRNA splicing, stabilization and protein synthesis and translation (Furuichi, 2015). In addition, m7G modifications are widely found not only within mRNAs and tRNAs, but also in rRNAs, miRNAs, and lncRNAs, which are responsible for RNA processing, stabilization, and translocation (Zhu et al., 2018; Pandolfini et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2022; Lu et al., 2023; Dai et al., 2021; Volpon et al., 2016). In the early days, m7G-MeRIP sequencing (MeRIP-seq) was utilized to analyze the m7G modification sites of transcriptomic mRNAs and tRNAs (Zhang et al., 2019). With the development of sequencing technology, it was found by immunoprecipitation sequencing (m7G miCLIP-seq) that the m7G modification is mainly located in the 5′UTR region of mRNAs, and the modification significantly accumulates in the CDS and 3′UTR regions under stress (Malbec et al., 2019). A novel predictor, THRONE, was validated to more accurately predict m7G modification site (Shoombuatong et al., 2022).
Regulation of coding RNAs and non-coding RNAs by m7G
m7G plays a role in regulating mRNA stability and translation processes (Table 1), with its most probable binding mode against the mRNA cap structure involving the stacking of Trp-102 and hydrogen bond pairing of Glu-105 (Ueda et al., 1991). METTL1 has been shown to enhance VEGFA mRNA translation in a manner dependent on m7G methylation, thereby facilitating tumor progression (Zhao et al., 2021). METTL1 plays a role in promoting CDK11 and ATF5 mRNA stability in an m7G manner, impacting tumor progression (Chen et al., 2023b; Ma et al., 2021). Additionally, RNA modification does not act independently; the METTL3/METTL1-mediated m6A/m7G dual RNA modification boosts TROP2 translation, leading to the promotion of bladder carcinogenesis (Chen et al., 2023b). Furthermore, a codon-frequency-dependent mechanism of m7G-tRNA decoding catalyzed by METTL1 is known to facilitate mRNA translation in various types of tumors (Ma et al., 2021; Dai et al., 2021; Huang et al., 2023; Chen et al., 2022a; Han et al., 2022; Orellana et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2023c; García-Vílchez et al., 2023; Zhao et al., 2024b; Huang et al., 2022). The structural basis of METTL1-mediated tRNA modification involves the αC region of METTL1 becoming helical and stabilizing the tRNA along with the α6 helix. Additionally, phosphorylation of the N-terminal S27 of METTL1 impacts its catalytic activity (Li et al., 2023c). While sequencing results have identified m7G modifications in rRNAs, further research is needed to determine the specific sites of these modifications and their spatial structural changes (Bujnicki and Rychlewski, 2001). miRNAs can be regulated by m7G modifications, which can inhibit the expression of target mRNAs. Research has shown that METTL1-mediated modification of miRNAs by m7G can disrupt the secondary structure of precursor miRNAs. This was observed through borohydride reduction sequencing and RNA immunoprecipitation (Pandolfini et al., 2019). In the context of bladder cancer, METTL1 is involved in m7G modification of miR-760, leading to the suppression of ATF3 mRNA expression (Xie et al., 2022). Additionally, METTL1 plays a role in mediating m7G modification of miR-26a-5p, indirectly inhibiting FTH1 mRNA expression and translational efficiency (He et al., 2024).
Effect of m7G modification on the signal transduction pathways
Inhibition of m7G modification by knockdown of METTL1 reduces MAPK pathway activity, ultimately inhibiting the proliferative phenotype (Deng et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2024). Likewise, NCBP2-mediated m7G modification promotes c-JUN mRNA translation, activating the MEK/ERK pathway (Xie et al., 2023). Knockdown of METTL1 decreases the level of m7G modification of tRNAs, resulting in the downregulation of oncogenic transcripts and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway (Chen et al., 2022a). In nasopharyngeal carcinoma, METTL1 enhances the efficiency of target mRNA codon recognition during translation by modifying tRNAs with m7G, thereby activating the WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway (Chen et al., 2022b). Quaking proteins (QKIs) recognize internal mRNA m7G modifications and downregulate key targets within the Hippo pathway (Zhao et al., 2023). The modification of tRNA m7G by METTL1 leads to the upregulation of genes associated with the EGFR pathway, a transcript linked to oncogenesis, thereby facilitating cancer advancement and resistance to drugs (Dai et al., 2021; Huang et al., 2023). In summary, RNA m7G modifications play a crucial role in regulating signaling pathways and promoting tumor progression (Table 2).
The m7G writers
m7G modifying enzymes can be categorized into writers, erasers, and readers, which are responsible for modifying various types of RNA (Table 3). The METTL1/WDR4 complex, a well-researched m7G methyltransferase, has homologs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae known as Trm8 and Trm82. These homologs are essential in S. cerevisiae for tRNA m7G modification (Figure 1) (Alexandrov et al., 2002). METTL1/WDR4 is responsible for m7G modification of various RNAs, impacting a range of biological functions. The complex directly modifies mRNA m7G, leading to increased mRNA output and translation efficiency. For example, VEGFA and Sptbn2 mRNA m7G modification by METTL1/WDR4 enhances their stability and translation efficiency (Zhao et al., 2021; Li et al., 2023d). METTL1/WDR4 indirectly promotes partial mRNA translation efficiency through high-frequency m7G tRNA decoding codons, impacting stem cell self-renewal, tumor progression, and drug resistance (Ma et al., 2021; Dai et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2023c; Lin et al., 2018). Additionally, METTL1 can individually mediate primary miRNA m7G modifications that influence the stability of let-7e-5p miRNA, miR-760, and miR-26a-5p (Pandolfini et al., 2019; Xie et al., 2022; He et al., 2024). RNMT plays a crucial role in maintaining mRNA cap methylation and, in conjunction with the cofactor RAM, enhances mRNA stabilization and translational efficiency; however, its monomer exhibits a weak affinity for mRNAs (Gonatopoulos-Pournatzis et al., 2011; Trotman et al., 2017; Bueren-Calabuig et al., 2019). The human WBSCR22/TRMT112 complex, similar to its yeast counterpart, is primarily involved in m7G modification of 18s rRNA and ribosome maturation (Figaro et al., 2012; Õunap et al., 2013; Zorbas et al., 2015; Taforeau et al., 2013; Joshi et al., 2005; Carroll and Borden, 2013; Culjkovic et al., 2007; Matsuo et al., 1997; Haimov et al., 2018; Cruz and Joseph, 2022; Peter et al., 2017; Weber et al., 2020; Amaya Ramirez et al., 2018; Ruscica et al., 2019).
The m7G readers
The study revealed that the m7G-modified readers of mRNAs primarily consist of eIF family members eIF4E1 (eIF4E), eIF4E2 (4EHP), and eIF4E3 (Joshi et al., 2005). The translation initiation factor eIF4E identifies the 7-methylguanosine (m7G) cap structure in the 5′-UTR of mRNA, facilitating mRNA binding to ribosomes and enhancing mRNA transport from the nucleus to the cytoplasm (Carroll and Borden, 2013; Culjkovic et al., 2007). It was noted that the eIF4E monomer alone does not facilitate mRNA translation activity; instead, it must form a complex with eIF4G to recognize the mRNA m7G modification, a process reliant on a curved eight-stranded antiparallel beta sheet (Matsuo et al., 1997; Haimov et al., 2018; Cruz and Joseph, 2022). Early 4EHP was initially identified as a translational repressor that could interact with GIGYF1/2 to collectively regulate mRNA degradation and translation repression (Peter et al., 2017; Weber et al., 2020). Mechanistically, GIGYF proteins recruit CCR4-NOT to conserved mRNA sequences to facilitate mRNA decay and translational repression (Amaya Ramirez et al., 2018; Ruscica et al., 2019). Additionally, 4EHP mediates miRNAs to achieve translational repression through the competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) theory (Jafarnejad et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2021). It has been demonstrated that 4EHP and GIGYF can form a translational repression complex with other proteins (Villaescusa et al., 2009; Peter et al., 2019). Additionally, 4EHP has been found to interact with coactivators such as TRS and ARIH1 to enhance the translation process (von Stechow et al., 2015; Jeong et al., 2019; Christie and Igreja, 2023). Compared to eIF4E1, eIF4E3 exhibits stronger inhibition of mRNA translation, export, and tumor suppressor factors (Volpon et al., 2013). eIF4E3 utilizes its residue structure to interact with m7G modification through electrostatic and van der Waals forces (Osborne et al., 2013). The m7G-related reader NCBP2 plays a critical role in identifying m7G modifications for mRNA stabilization and translation processes (Xie et al., 2023). Dysregulation of NCBP2 has been observed in various tumors and is linked to immune responses (Li et al., 2022b; Zhou et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2023b).
m7G writers modification regulates urinary system tumors
Reports of m7G modification in urinary system tumors are relatively limited and have far-reaching research significance (Table 4). In the context of bladder cancer, METTL1 has been shown to promote proliferation, invasion, and migration by modifying tRNAs in an m7G-dependent manner, which enhances the translational efficiency of EGFR/EFEMP1 and TROP2 (Chen et al., 2023b; Ying et al., 2021). Furthermore, METTL1 can also modify miR-760 in an m7G-dependent manner to suppress ATF3 mRNA expression, thereby contributing to the progression of bladder cancer (Bujnicki and Rychlewski, 2001). In prostate cancer, METTL1 plays a role in regulating the levels of interferons and immune factors in the immune microenvironment through m7G modification. Specifically, this modification regulates the production of new small non-coding RNAs derived from 5′tRNA fragments (García-Vílchez et al., 2023). The abnormal increase in CDK14 levels in prostate cancer is linked to METTL1-mediated modification of its mRNA expression in an m7G manner, resulting in enhanced CDK14 mRNA stability (Zhang et al., 2023c).
m7G readers modification regulates urinary system tumors
Disturbed expression of eIF4E in renal cancer may be associated with poor prognosis (Ichiyanagi et al., 2018). Research has shown that eIF4E mediates enhanced translation of proto-oncogenes (Yang et al., 2023c), promotes proliferation and invasion of renal cancer (Li et al., 2017c), and is closely associated with sunitinib resistance (Chen et al., 2020b). However, despite being a classical translation initiation factor, eIF4E has not been extensively discussed in its role of regulating downstream proto-oncogenes through the m7G mechanism.
Phosphorylation modification of the eIF4E protein has been found to promote the progression of bladder cancer (Jana et al., 2021). Conversely, inhibiting eIF4E phosphorylation has been shown to decrease bladder tumor cell activity and proliferation (Kyou Kwon et al., 2014; Chi et al., 2015). Furthermore, eIF4E may play a role in resistance to Pirarubicin by affecting autophagy (Li et al., 2015).
The role of eIF4E in prostate cancer is influenced by factors such as phosphorylation modification and miRNA (D'Abronzo and Ghosh, 2018; Furic et al., 2010; Xu et al., 2021). Dysregulation of eIF4E has been shown to affect proliferation, invasion, migration, and chemotherapy resistance in prostate cancer (Kwegyir-Afful et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2020). Mechanistically, eIF4E facilitates m7G modification of specific mRNA 5′end structures, impacting key pathways in prostate cancer development like PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Ras/MAPK, ultimately regulating the progression of prostate tumors [405]. While eIF4E is extensively studied among m7G-related readers in urologic tumors, the regulation of other molecules in urologic tumors requires further exploration and investigation.
Conclusion
While m6A is a commonly studied RNA modification (Boccaletto et al., 2022; Chen et al., 2019b), other modifications such as m5C, m1A, and m7G have also been linked to tumor proliferation, invasion, migration, drug resistance, and metabolism (Xue et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2023a; Luo et al., 2022). This review examines the effects of m5C, m1A, and m7G modifications on both coding and non-coding RNAs. It discusses their roles as writers, readers, and erasers in regulating tumor-related signaling pathways, and explores their modulation in the context of urinary tract tumors.
The study of RNA modification is closely tied to advancements in specific antibodies, enhanced sequencing techniques, and more precise algorithms. In the past, due to limitations in sequencing technology, only mass spectrometry could be used to detect RNA modifications that were highly abundant (Boccaletto et al., 2018). However, as the purity of mRNA poly-A samples improved, the study of coding RNA modifications has gained significant attention (Dubin and Taylor, 1975). Various RNA modification sequencing methods and corresponding algorithms each have unique characteristics. Currently, the detection of m5C primarily relies on the sodium bisulfite method or immunoprecipitation with m5C-specific antibodies (García-Vílchez et al., 2019). Immunoprecipitation with specific antibodies can be used to identify enrichment sites of m1A and m7G on RNA (; Zhang et al., 2019). However, sequencing technology has limitations and controversies. For instance, the number of m5C modification sites in animal cells and mouse embryonic stem cells showed significant differences in sequencing results (Squires et al., 2012; Schaefer et al., 2017). Similarly, early sequencing results suggested that m1A was predominantly enriched in the mRNA 5′untranslated region (), but subsequent findings indicated rare m1A enrichment on mRNA (Schwartz, 2018), possibly due to false positive results from m1A antibody detection at single nucleotide resolution (Grozhik et al., 2019; Khoddami et al., 2019). Immunoprecipitation sequencing (m7G miCLIP-seq) revealed changes in m7G modification sites on mRNA under different conditions (Malbec et al., 2019). The development of new prediction tools like THRONE can enhance the accuracy of predicting RNA m7G modifications (Shoombuatong et al., 2022). To achieve more precise enrichment site identification and understand modification mechanisms, further advancements in sequencing technology and algorithm adjustments are necessary.
Both coding and non-coding RNAs can undergo modifications such as m5C, m1A, and m7G to either stabilize the RNA or enhance translation levels. For instance, modifications like m5C, m1A, and m7G in tRNAs play a role in bolstering their structural integrity and improving protein translation efficiency, impacting proto-oncogene oncogenicity (Li et al., 2023a), cellular differentiation processes (Van Haute et al., 2019), cholesterol synthesis (Wang et al., 2021c), the immune microenvironment (Liu et al., 2022; Li et al., 2024b), and ROS levels (Li et al., 2023c). Interestingly, recent findings suggest that reducing m5C levels in tRNAs may lead to dysfunction in tRNAGly coencoder and decreased protein translation efficiency, contradicting previous observations (Blaze et al., 2021). The m5C and m1A modifications of rRNA play a crucial role in ribosome assembly and protein translation (Metodiev et al., 2014; Waku et al., 2016), impacting intracellular sugar metabolism (Peifer et al., 2013; Sharma et al., 2018) and p53 pathway activity (Waku et al., 2016). Further research is needed to investigate the significance of m7GrRNA modification sites and spatial structure changes (Bujnicki and Rychlewski, 2001). While LC-MS/MS nucleoside analysis and LSTH have identified fewer m5C-modified sites on miRNAs (Lü et al., 2024), studies have shown that m5C modification of LncRNAs (NKILA) and miRNAs (miR-571) can enhance their stability, promoting the progression of cholangiocarcinomas and colon cancers (Zheng et al., 2022; Hou et al., 2024). METTL1-mediated m7G modification of miR-760 and miR-26a-5p has been shown to increase miRNA stability (Xie et al., 2022; He et al., 2024). Furthermore, this modification disrupts the secondary structure of precursor miRNAs, as evidenced by borohydride-reduced sequencing and RNA immunoprecipitation assays (Pandolfini et al., 2019). Generally, m5C, m1A, and m7G modifications are known to enhance mRNA stability and translational efficiency (Chen et al., 2019a; Yang et al., 2022a; Safra et al., 2017; Ueda et al., 1991; Zhao et al., 2021; Chen et al., 2023b; Ma et al., 2021). However, enrichment of specific modification sites can lead to translation termination or reduced mRNA stability. For instance, NSUN6-mediated m5C modification of target genes can trigger translation termination, potentially contributing to quality control of translation fidelity (Selmi et al., 2021). Moreover, when m1A modification occurs in the 5′UTR and CDS regions of mRNA, it may impede translation by disrupting base complementary pairing (Wu et al., 2022; Kuang et al., 2022). In conclusion, the diverse effects of RNA modifications are influenced by the specific sites of modification and resultant changes in RNA and protein structures, highlighting the need for in-depth mechanistic studies.
The regulation of urological tumors by key modifying enzymes of m5C, m1A, and m7G (writers, erasers, and readers) is a significant area of study. Aberrant expression of a variety of RNA modifying enzymes in urological tumors is closely linked to poor prognosis (Chen et al., 2019c; Li et al., 2021; Sun et al., 2022; Koike et al., 2012; Ueda et al., 2018; Ichiyanagi et al., 2018). These RNA modifications play crucial roles in the proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, migration, immune escape, and drug resistance of urological tumors (Li et al., 2023b; Alshaker et al., 2019; Monshaugen et al., 2024; Yang et al., 2023c; Li et al., 2017c; Chen et al., 2020b). As such, these key enzymes hold promise as both diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets for urological tumors. The development of targeted drugs aimed at these key enzymes is expected to play a vital role in the treatment of urological tumors.
Statements
Author contributions
WX: Writing – original draft. YZ: Methodology, Writing – original draft. GZ: Writing – review and editing. ZL: Validation, Writing – review and editing. JL: Investigation, Writing – review and editing. XF: Investigation, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was funded partly by the joint fund of Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (Doctoral Scientific Research Initiation Project, grant number 2023-BSBA-340, JL).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Department of Urology, Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University for their inspiration and support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Aas P. A. Otterlei M. Falnes P. O. Vågbø C. B. Skorpen F. Akbari M. et al (2003). Human and bacterial oxidative demethylases repair alkylation damage in both RNA and DNA. Nature421, 859–863. 10.1038/nature01363
2
Agris P. F. (2008). Bringing order to translation: the contributions of transfer RNA anticodon-domain modifications. EMBO Rep.9, 629–635. 10.1038/embor.2008.104
3
Aguilo F. Li S. Balasubramaniyan N. Sancho A. Benko S. Zhang F. et al (2016). Deposition of 5-methylcytosine on enhancer RNAs enables the coactivator function of PGC-1α. Cell. Rep.14 (3), 479–492. 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.12.043
4
Alexandrov A. Martzen M. R. Phizicky E. M. (2002). Two proteins that form a complex are required for 7-methylguanosine modification of yeast tRNA. RNA8 (10), 1253–1266. 10.1017/s1355838202024019
5
Alshaker H. Wang Q. Brewer D. Pchejetski D. (2019). Transcriptome-wide effects of sphingosine kinases knockdown in metastatic prostate and breast cancer cells: implications for therapeutic targeting. Front. Pharmacol.10, 303. 10.3389/fphar.2019.00303
6
Amaya Ramirez C. C. Hubbe P. Mandel N. Béthune J. (2018). 4EHP-independent repression of endogenous mRNAs by the RNA-Binding protein GIGYF2. Nucleic Acids Res.46 (11), 5792–5808. 10.1093/nar/gky198
7
Bar-Yaacov D. Frumkin I. Yashiro Y. Chujo T. Ishigami Y. Chemla Y. et al (2016). Mitochondrial 16S rRNA is methylated by tRNA methyltransferase TRMT61B in all vertebrates. PLoS Biol.14 (9), e1002557. 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002557
8
Bhatta A. Dienemann C. Cramer P. Hillen H. S. (2021). Structural basis of RNA processing by human mitochondrial RNase P. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.28 (9), 713–723. 10.1038/s41594-021-00637-y
9
Blanco S. Bandiera R. Popis M. Hussain S. Lombard P. Aleksic J. et al (2016). Stem cell function and stress response are controlled by protein synthesis. Nature534, 335–340. 10.1038/nature18282
10
Blanco S. Dietmann S. Flores J. V. Hussain S. Kutter C. Humphreys P. et al (2014). Aberrant methylation of tRNAs links cellular stress to neuro-developmental disorders. EMBO J.33, 2020–2039. 10.15252/embj.201489282
11
Blanco S. Kurowski A. Nichols J. Watt F. M. Benitah S. A. Frye M. (2011). The RNA-Methyltransferase misu (NSun2) poises epidermal stem cells to differentiate. PLoS Genet.7 (12), e1002403. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002403
12
Blaze J. Navickas A. Phillips H. L. Heissel S. Plaza-Jennings A. Miglani S. et al (2021). Neuronal Nsun2 deficiency produces tRNA epitranscriptomic alterations and proteomic shifts impacting synaptic signaling and behavior. Nat. Commun.12 (1), 4913. 10.1038/s41467-021-24969-x
13
Boccaletto P. Machnicka M. A. Purta E. Piatkowski P. Baginski B. Wirecki T. K. et al (2018). MODOMICS: a database of RNA modification pathways. 2017 update. Nucleic acids Res.46, D303–D307. 10.1093/nar/gkx1030
14
Boccaletto P. Stefaniak F. Ray A. Cappannini A. Mukherjee S. Purta E. et al (2022). MODOMICS: a database of RNA modification pathways. 2021 update. Nucleic Acids Res.50, D231–D235. 10.1093/nar/gkab1083
15
Boulias K. Greer E. L. (2019). Put the pedal to the METTL1: adding internal m(7)G increases mRNA translation efficiency and augments miRNA processing. Mol. Cell.74, 1105–1107. 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.06.004
16
Bourgeois G. Ney M. Gaspar I. Aigueperse C. Schaefer M. Kellner S. et al (2015). Eukaryotic rRNA modification by yeast 5-Methylcytosine-Methyltransferases and human proliferation-associated antigen p120. PLoS ONE10 (7), e0133321. 10.1371/journal.pone.0133321
17
Bueren-Calabuig J. A. G Bage M. Cowling V. H. Pisliakov A. V. (2019). Mechanism of allosteric activation of human mRNA cap methyltransferase (RNMT) by RAM: insights from accelerated molecular dynamics simulations. Nucleic Acids Res.47, 8675–8692. 10.1093/nar/gkz613
18
Bujnicki J. M. Feder M. Ayres C. L. Redman K. L. (2004). Sequence-structure-function studies of tRNA:m5C methyltransferase Trm4p and its relationship to DNA:m5C and RNA:m5U methyltransferases. Nucleic Acids Res.32, 2453–2463. 10.1093/nar/gkh564
19
Bujnicki J. M. Rychlewski L. (2001). Sequence analysis and structure prediction of aminoglycoside-resistance 16S rRNA:m7G methyltransferases. Acta Microbiol. Pol.50 (1), 7–17.
20
Cai S. Mi S. Chen J. Shao L. Yang X. Xue M. (2025). METTL1-mediated m7G modification promotes colorectal cancer metastasis via stabilization of ICAM-1. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 10.1007/s11010-025-05293-0
21
Cai X. Hu Y. Tang H. Hu H. Pang L. Xing J. et al (2016). RNA methyltransferase NSUN2 promotes stress-induced HUVEC senescence. Oncotarget7 (15), 19099–19110. 10.18632/oncotarget.8087
22
Cámara Y. Asin-Cayuela J. Park C. Metodiev M. Shi Y. Ruzzenente B. et al (2011). MTERF4 regulates translation by targeting the methyltransferase NSUN4 to the Mammalian mitochondrial ribosome. Cell. Metab.13 (5), 527–539. 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.04.002
23
Carroll M. Borden K. L. (2013). The oncogene eIF4E: using biochemical insights to target cancer. J. Interferon Cytokine Res.33, 227–238. 10.1089/jir.2012.0142
24
Chan C. T. Deng W. Li F. DeMott M. S. Babu I. R. Begley T. J. et al (2015). Highly predictive reprogramming of tRNA modifications is linked to selective expression of codon-biased genes. Chem. Res. Toxicol.28, 978–988. 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.5b00004
25
Chan C. T. Dyavaiah M. DeMott M. S. Taghizadeh K. Dedon P. C. Begley T. J. (2010). A quantitative systems approach reveals dynamic control of tRNA modifications during cellular stress. PLoS Genet.6, e1001247. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001247
26
Chen B. Jiang W. Huang Y. Zhang J. Yu P. Wu L. et al (2022b). N7-methylguanosine tRNA modification promotes tumorigenesis and chemoresistance through WNT/β-catenin pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncogene41 (15), 2239–2253. 10.1038/s41388-022-02250-9
27
Chen C. Chao Y. Zhang C. Hu W. Huang Y. Lv Y. et al (2023b). TROP2 translation mediated by dual m6A/m7G RNA modifications promotes bladder cancer development. Cancer Lett.566, 216246. 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216246
28
Chen H. Yang H. Zhu X. Yadav T. Ouyang J. Truesdell S. S. et al (2020a). m5 C modification of mRNA serves a DNA damage code to promote homologous recombination. Nat. Commun.11, 2834. 10.1038/s41467-020-16722-7
29
Chen J. Li K. Chen J. Wang X. Ling R. Cheng M. et al (2022a). Aberrant translation regulated by METTL1/WDR4-mediated tRNA N7-methylguanosine modification drives head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression. Cancer Commun. (Lond)42 (3), 223–244. 10.1002/cac2.12273
30
Chen K. Song B. Tang Y. Wei Z. Xu Q. Su J. et al (2021). RMDisease: a database of genetic variants that affect RNA modifications, with implications for epitranscriptome pathogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res.49, D1396–d1404. 10.1093/nar/gkaa790
31
Chen R. X. Chen X. Xia L. P. Zhang J. X. Pan Z. Z. Ma X. D. et al (2019b). N6-methyladenosine modification of circNSUN2 facilitates cytoplasmic export and stabilizes HMGA2 to promote colorectal liver metastasis. Nat. Commun.10 (1), 4695. 10.1038/s41467-019-12651-2
32
Chen S. Cui L. Hu Q. Shen Y. Jiang Y. Zhao J. (2020b). Preclinical evidence that MNK/eIF4E inhibition by cercosporamide enhances the response to antiangiogenic TKI and mTOR inhibitor in renal cell carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.530 (1), 142–148. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.06.133
33
Chen S. J. Zhang J. Zhou T. Rao S. S. Li Q. Xiao L. Y. et al (2024). Epigenetically upregulated NSUN2 confers ferroptosis resistance in endometrial cancer via m5C modification of SLC7A11 mRNA. Redox Biol.69, 102975. 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102975
34
Chen W. Wang H. Mi S. Shao L. Xu Z. Xue M. (2023a). ALKBH1-mediated m1 A demethylation of METTL3 mRNA promotes the metastasis of colorectal cancer by downregulating SMAD7 expression. Mol. Oncol.17 (2), 344–364. 10.1002/1878-0261.13366
35
Chen X. Sun B. F. Yang Y. Han Y. N. Yuan X. et al (2019a). 5-Methylcytosine promotes pathogenesis of bladder cancer through stabilizing mRNAs. Nat. Cell. Biol.21, 978–990. 10.1038/s41556-019-0361-y
36
Chen Z. Qi M. Shen B. Luo G. Wu Y. Li J. et al (2019c). Transfer RNA demethylase ALKBH3 promotes cancer progression via induction of tRNA-derived small RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res.47 (5), 2533–2545. 10.1093/nar/gky1250
37
Cheng J. Berninghausen O. Beckmann R. (2021). A distinct assembly pathway of the human 39S late pre-mitoribosome. Nat. Commun.12 (1), 4544. 10.1038/s41467-021-24818-x
38
Cheng W. Ma J. Tao Q. Adeel K. Xiang L. Liu D. et al (2022). Demethylation of m1A assisted degradation of the signal probe for rapid electrochemical detection of ALKBH3 activity with practical applications. Talanta240, 123151. 10.1016/j.talanta.2021.123151
39
Chi B. H. Kim S. J. Seo H. K. Lee S. J. Kwon J. K. et al (2015). P70S6K and Elf4E dual inhibition is essential to control bladder tumor growth and progression in orthotopic mouse non-muscle invasive bladder tumor model. J. Korean Med. Sci.30 (3), 308–316. 10.3346/jkms.2015.30.3.308
40
Chionh Y. H. McBee M. Babu I. R. Hia F. Lin W. Zhao W. et al (2016). tRNA-mediated codon-biased translation in mycobacterial hypoxic persistence. Nat. Commun.7, 13302. 10.1038/ncomms13302
41
Cho E. S. Ruminski A. M. Aloni S. Liu Y. S. Guo J. Urban J. J. (2016). Graphene oxide/metal nanocrystal multilaminates as the atomic limit for safe and selective hydrogen storage. Nat. Commun.7, 10804. 10.1038/ncomms10804
42
Christie M. Igreja C. (2023). eIF4E-homologous protein (4EHP): a multifarious cap-binding protein. FEBS J.290 (2), 266–285. 10.1111/febs.16275
43
Chujo T. Suzuki T. (2012). Trmt61B is a methyltransferase responsible for 1-methyladenosine at position 58 of human mitochondrial tRNAs. Rna18, 2269–2276. 10.1261/rna.035600.112
44
Cipullo M. Pearce S. F. Lopez Sanchez I. G. Gopalakrishna S. Krüger A. Schober F. et al (2021). Human GTPBP5 is involved in the late stage of mitoribosome large subunit assembly. Nucleic Acids Res.49 (1), 354–370. 10.1093/nar/gkaa1131
45
Cruz A. Joseph S. (2022). Interaction of the influenza A virus NS1 protein with the 5'-m7G-mRNA·eIF4E·eIF4G1 complex. Biochemistry61 (14), 1485–1494. 10.1021/acs.biochem.2c00019
46
Culjkovic B. Topisirovic I. Borden K. L. (2007). Controlling gene expression through RNA regulons: the role of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF4E. Cell. Cycle6, 65–69. 10.4161/cc.6.1.3688
47
D'Abronzo L. S. Ghosh P. M. (2018). eIF4E phosphorylation in prostate cancer. Neoplasia20 (6), 563–573. 10.1016/j.neo.2018.04.003
48
Dai Q. Ye C. Irkliyenko I. Wang Y. Sun H. L. Gao Y. et al (2024). Ultrafast bisulfite sequencing detection of 5-methylcytosine in DNA and RNA. Nat. Biotechnol.42, 1559–1570. 10.1038/s41587-023-02034-w
49
Dai X. Gonzalez G. Li L. Li J. You C. Miao W. et al (2020). YTHDF2 binds to 5-Methylcytosine in RNA and modulates the maturation of ribosomal RNA. Anal. Chem.92 (1), 1346–1354. 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04505
50
Dai X. Wang T. Gonzalez G. Wang Y. (2018). Identification of YTH domain-containing proteins as the readers for N1-Methyladenosine in RNA. Anal. Chem.90 (11), 6380–6384. 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b01703
51
Dai Z. Liu H. Liao J. Huang C. Ren X. Zhu W. et al (2021). N(7)-methylguanosine tRNA modification enhances oncogenic mRNA translation and promotes intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma progression. Mol. Cell.81, 3339–3355.e8. 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.07.003
52
Decatur W. A. Fournier M. J. (2002). rRNA modifications and ribosome function. Trends Biochem. Sci.27, 344–351. 10.1016/s0968-0004(02)02109-6
53
Deng Y. Zhou Z. Lin S. Yu B. (2020). METTL1 limits differentiation and functioning of EPCs derived from human-induced pluripotent stem cells through a MAPK/ERK pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.527 (3), 791–798. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.04.115
54
Dominissini D. Moshitch-Moshkovitz S. Schwartz S. Salmon-Divon M. Ungar L. Osenberg S. et al (2012). Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature485, 201–206. 10.1038/nature11112
55
Dominissini D. Nachtergaele S. Moshitch-Moshkovitz S. Peer E. Kol N. Ben-Haim M. S. et al (2016). The dynamic N(1)-methyladenosine methylome in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature530 (7591), 441–446. 10.1038/nature16998
56
Dubin D. T. Taylor R. H. (1975). The methylation state of poly A-containing messenger RNA from cultured hamster cells. Nucleic acids Res.2, 1653–1668. 10.1093/nar/2.10.1653
57
Dunn D. B. (1961). The occurrence of 1-methyladenine in ribonucleic acid. Biochim. Biophys. Acta46, 198–200. 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90668-0
58
Eckwahl M. Xu R. Michalkiewicz J. Zhang W. Patel P. Cai Z. et al (2020). 5-Methylcytosine RNA modifications promote retrovirus replication in an ALYREF reader protein-dependent manner. J. Virol.94 (13), e00544–e00620. 10.1128/JVI.00544-20
59
El Yacoubi B. Bailly M. de Crécy-Lagard V. (2012). Biosynthesis and function of posttranscriptional modifcations of transfer RNAs. Annu. Rev. Genet.46, 69–95. 10.1146/annurev-genet-110711-155641
60
Figaro S. Wacheul L. Schillewaert S. Graille M. Huvelle E. Mongeard R. et al (2012). Trm112 is required for Bud23-mediated methylation of the 18S rRNA at position G1575. Mol. Cell. Biol.32 (12), 2254–2267. 10.1128/MCB.06623-11
61
Frye M. Watt F. M. (2006). The RNA methyltransferase misu (NSun2) mediates Myc-induced proliferation and is upregulated in tumors. Curr. Biol.16 (10), 971–981. 10.1016/j.cub.2006.04.027
62
Fu L. Guerrero C. R. Zhong N. Amato N. J. Liu Y. Liu S. et al (2014). Tet-mediated formation of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in RNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc.136 (33), 11582–11585. 10.1021/ja505305z
63
Furic L. Rong L. Larsson O. Koumakpayi I. H. Yoshida K. Brueschke A. et al (2010). eIF4E phosphorylation promotes tumorigenesis and is associated with prostate cancer progression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.107 (32), 14134–14139. 10.1073/pnas.1005320107
64
Furuichi Y. (2015). Discovery of m(7)G-cap in eukaryotic mRNAs. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci.91 (8), 394–409. 10.2183/pjab.91.394
65
García-Vílchez R. Añazco-Guenkova A. M. Dietmann S. López J. Morón-Calvente V. D'Ambrosi S. et al (2023). METTL1 promotes tumorigenesis through tRNA-derived fragment biogenesis in prostate cancer. Mol. Cancer22 (1), 119. 10.1186/s12943-023-01809-8
66
García-Vílchez R. Sevilla A. Blanco S. (2019). Post-transcriptional regulation by cytosine-5 methylation of RNA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech.1862 (3), 240–252. 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2018.12.003
67
Gkatza N. A. Castro C. Harvey R. F. Heiss M. Popis M. C. Blanco S. et al (2019). Cytosine-5 RNA methylation links protein synthesis to cell metabolism. PLoS Biol.17, e3000297. 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000297
68
Goll M. G. Kirpekar F. Maggert K. A. Yoder J. A. Hsieh C. L. Zhang X. et al (2006). Methylation of tRNAAsp by the DNA methyltransferase homolog Dnmt2. Science311 (5759), 395–398. 10.1126/science.1120976
69
Gonatopoulos-Pournatzis T. Dunn S. Bounds R. Cowling V. H. (2011). RAM/Fam103a1 is required for mRNA cap methylation. Mol. Cell.44, 585–596. 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.08.041
70
Grozhik A. V. Olarerin-George A. O. Sindelar M. Li X. Gross S. S. Jaffrey S. R. (2019). Antibody cross-reactivity accounts for widespread appearance of m1A in 5′UTRs. Nat. Commun.10, 5126. 10.1038/s41467-019-13146-w
71
Gu X. Zhou H. Chu Q. Zheng Q. Wang J. Zhu H. (2021). Uncovering the association between m5C regulator-mediated methylation modification patterns and tumour microenvironment infiltration characteristics in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol.9, 727935. 10.3389/fcell.2021.727935
72
Gu X. Zhuang A. Yu J. Yang L. Ge S. Ruan J. et al (2024). Histone lactylation-boosted ALKBH3 potentiates tumor progression and diminished promyelocytic leukemia protein nuclear condensates by m1A demethylation of SP100A. Nucleic Acids Res.52 (5), 2273–2289. 10.1093/nar/gkad1193
73
Günther J. Lohse R. Wehnert J. (1970). Vorschlag einer einheitlichen Stadieneinteilung für Geschwülste der Harnorgane und des männlichen Genitale nach dem TNM-System. I. Teil Geschwülste der Nieren und der Harnblase [Proposal for a unified stage classification for tumors of the urinary organs and the male genitals according to the TNM system. I. Tumors of the kidneys and the urinary bladder]. Z Urol. Nephrol.63 (9), 675–680.
74
Haimov O. Sehrawat U. Tamarkin-Ben H. A. Bahat A. Uzonyi A. Will A. et al (2018). Dynamic interaction of eukaryotic initiation factor 4G1 (eIF4G1) with eIF4E and eIF1 underlies scanning-dependent and -Independent translation. Mol. Cell. Biol.38 (18), e00139–18. 10.1128/MCB.00139-18
75
Haltom A. R. Lee T. V. Harvey B. M. Leonardi J. Chen Y. J. Hong Y. et al (2014). The protein O-glucosyltransferase rumi modifies eyes shut to promote rhabdomere separation in drosophila. PLoS Genet.10 (11), e1004795. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004795
76
Han H. Yang C. Ma J. Zhang S. Zheng S. Ling R. et al (2022). N7-methylguanosine tRNA modification promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tumorigenesis via the RPTOR/ULK1/autophagy axis. Nat. Commun.13 (1), 1478. 10.1038/s41467-022-29125-7
77
Haruehanroengra P. Zheng Y. Y. Zhou Y. Huang Y. Sheng J. (2020). RNA modifications and cancer. RNA Biol.17 (11), 1560–1575. 10.1080/15476286.2020.1722449
78
He M. Wang Y. Xie J. Pu J. Shen Z. Wang A. et al (2024). M7G modification of FTH1 and pri-miR-26a regulates ferroptosis and chemotherapy resistance in osteosarcoma. Oncogene43 (5), 341–353. 10.1038/s41388-023-02882-5
79
He W. Zhang H. Cheng H. Wen J. Li D. (2023). PIK3CD correlates with prognosis, epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor immune infiltration in breast carcinoma. Discov. Oncol.14 (1), 187. 10.1007/s12672-023-00805-0
80
Heissenberger C. Liendl L. Nagelreiter F. Gonskikh Y. Yang G. Stelzer E. M. et al (2019). Loss of the ribosomal RNA methyltransferase NSUN5 impairs global protein synthesis and normal growth. Nucleic Acids Res.47 (22), 11807–11825. 10.1093/nar/gkz1043
81
Hou C. Liu J. Liu J. Yao D. Liang F. Qin C. et al (2024). 5-methylcytosine-mediated upregulation of circular RNA 0102913 augments malignant properties of colorectal cancer cells through a microRNA-571/Rac family small GTPase 2 axis. Gene901, 148162. 10.1016/j.gene.2024.148162
82
Huang M. Long J. Yao Z. Zhao Y. Zhao Y. Liao J. et al (2023). METTL1-Mediated m7G tRNA modification promotes lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res.83 (1), 89–102. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-0963
83
Huang S. Zhang X. Guan B. Sun P. Hong C. T. Peng J. et al (2019b). A novel circular RNA hsa_circ_0008035 contributes to gastric cancer tumorigenesis through targeting the miR-375/YBX1 axis. Am. J. Transl. Res.11 (4), 2455–2462.
84
Huang T. Chen W. Liu J. Gu N. Zhang R. (2019a). Genome-wide identification of mRNA 5-methylcytosine in mammals. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.26 (5), 380–388. 10.1038/s41594-019-0218-x
85
Huang Y. Ma J. Yang C. Wei P. Han H. et al (2022). METTL1 promotes neuroblastoma development through m7G tRNA modification and selective oncogenic gene translation. Biomark. Res.10 (1), 68. 10.1186/s40364-022-00414-z
86
Huang Y. Xu P. Liao F. Ca H. Wang X. Wang X. et al (2024). Fat mass and obesity-associated protein inhibit the pathology of rheumatoid arthritis through the NSUN2/SFRP1/Wnt/β-catenin signal axis. J. Pharm. Pharmacol.76 (3), 283–294. 10.1093/jpp/rgae003
87
Huber S. M. van Delft P. Mendil L. Bachman M. Smollett K. Werner F. et al (2015). Formation and abundance of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in RNA. Chembiochem16 (5), 752–755. 10.1002/cbic.201500013
88
Ichiyanagi O. Naito S. Ito H. Kabasawa T. Narisawa T. Kanno H. et al (2018). Levels of 4EBP1/eIF4E activation in renal cell carcinoma could differentially predict its early and late recurrence. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer16 (5), e1029–e1058. 10.1016/j.clgc.2018.06.002
89
Jafarnejad S. M. Chapat C. Matta-Camacho E. Gelbart I. A. Hesketh G. G. Arguello M. et al (2018). Translational control of ERK signaling through miRNA/4EHP-directed silencing. Elife7, e35034. 10.7554/eLife.35034
90
Jana S. Deo R. Hough R. P. Liu Y. Horn J. L. Wright J. L. et al (2021). mRNA translation is a therapeutic vulnerability necessary for bladder epithelial transformation. JCI Insight6 (11), e144920. 10.1172/jci.insight.144920
91
Janin M. Ortiz-Barahona V. de Moura M. C. Martínez-Cardús A. Llinàs-Arias P. Soler M. et al (2019). Epigenetic loss of RNA-Methyltransferase NSUN5 in glioma targets ribosomes to drive a stress adaptive translational program. Acta Neuropathol.138 (6), 1053–1074. 10.1007/s00401-019-02062-4
92
Jeong S. J. Park S. Nguyen L. T. Hwang J. Lee E. Y. Giong H. K. et al (2019). A threonyl-tRNA synthetase-mediated translation initiation machinery. Nat. Commun.10, 1357. 10.1038/s41467-019-09086-0
93
Joshi B. Lee K. Maeder D. L. Jagus R. (2005). Phylogenetic analysis of eIF4E-family members. BMC Evol. Biol.5, 48. 10.1186/1471-2148-5-48
94
Kar S. P. Beesley J. Amin Al O. A. Michailidou K. Tyrer J. Kote-Jarai Z. et al (2016). Genome-wide meta-analyses of breast, ovarian, and prostate cancer association studies identify multiple new susceptibility loci shared by at least two cancer types. Cancer Discov.6 (9), 1052–1067. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-1227
95
Kawarada L. Suzuki T. Ohira T. Hirata S. Miyauchi K. Suzuki T. (2017). ALKBH1 is an RNA dioxygenase responsible for cytoplasmic and mitochondrial tRNA modifications. Nucleic Acids Res.45 (12), 7401–7415. 10.1093/nar/gkx354
96
Khoddami V. Yerra A. Mosbruger T. L. Fleming A. M. Burrows C. J. Cairns B. R. (2019). Transcriptome-wide profiling of multiple RNA modifications simultaneously at singlebase resolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.116, 6784–6789. 10.1073/pnas.1817334116
97
Koike K. Ueda Y. Hase H. Kitae K. Fusamae Y. Masai S. et al (2012). anti-tumor effect of AlkB homolog 3 knockdown in hormone-independent prostate cancer cells. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets12 (7), 847–856. 10.2174/156800912802429283
98
Kuang W. Jin H. Yang F. Chen X. Liu J. Li T. et al (2022). ALKBH3-dependent m1A demethylation of Aurora A mRNA inhibits ciliogenesis. Cell. Discov.8 (1), 25. 10.1038/s41421-022-00385-3
99
Kumar A. Kumari N. Gupta V. Prasad R. (2018). Renal cell carcinoma: molecular aspects. Indian J. Clin. Biochem.33 (3), 246–254. 10.1007/s12291-017-0713-y
100
Kwegyir-Afful A. K. Bruno R. D. Purushottamachar P. Murigi F. N. Njar V. C. (2016). Galeterone and VNPT55 disrupt Mnk-eIF4E to inhibit prostate cancer cell migration and invasion. FEBS J.283 (21), 3898–3918. 10.1111/febs.13895
101
Kyou Kwon J. Kim S. J. Hoon Kim J. Mee Lee K. Ho Chang I. (2014). Dual inhibition by S6K1 and Elf4E is essential for controlling cellular growth and invasion in bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol.32 (1), 51.e27–51.e5.1E35. 10.1016/j.urolonc.2013.08.005
102
Legrand C. Tuorto F. Hartmann M. Liebers R. Jacob D. Helm M. et al (2017). Statistically robust methylation calling for whole-transcriptome bisulfite sequencing reveals distinct methylation patterns for mouse RNAs. Genome Res.27, 1589–1596. 10.1101/gr.210666.116
103
Lenarčič T. Jaskolowski M. Leibundgut M. Scaiola A. Schönhut T. Saurer M. et al (2021). Stepwise maturation of the peptidyl transferase region of human mitoribosomes. Nat. Commun.12 (1), 3671. 10.1038/s41467-021-23811-8
104
Li G. Chong T. Xiang X. Yang J. Li H. (2017c). Downregulation of microRNA-15a suppresses the proliferation and invasion of renal cell carcinoma via direct targeting of eIF4E. Oncol. Rep.38 (4), 1995–2002. 10.3892/or.2017.5901
105
Li H. Jiang H. Huang Z. Chen Z. Chen N. (2021). Prognostic value of an m5C RNA methylation regulator-related signature for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Manag. Res.13, 6673–6687. 10.2147/CMAR.S323072
106
Li J. Wang L. Hahn Q. Nowak R. P. Viennet T. Orellana E. A. et al (2023c). Structural basis of regulated m7G tRNA modification by METTL1-WDR4. Nature613 (7943), 391–397. 10.1038/s41586-022-05566-4
107
Li K. Chen X. Liu C. Gu P. Li Z. Wu S. et al (2015). Pirarubicin induces an autophagic cytoprotective response through suppression of the Mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway in human bladder cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.460 (2), 380–385. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.03.042
108
Li L. Li M. Zheng J. Li Z. Chen X. (2023b). Knocking Down NSUN5 inhibits the development of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by inhibiting the p53 pathway. Aging (Albany NY)15 (11), 4757–4773. 10.18632/aging.204761
109
Li P. Wang W. Zhou R. Ding Y. Li X. (2023a). The m5 C methyltransferase NSUN2 promotes codon-dependent oncogenic translation by stabilising tRNA in Anaplastic thyroid cancer. Clin. Transl. Med.13 (11), e1466. 10.1002/ctm2.1466
110
Li Q. Li X. Tang H. Jiang B. Dou Y. Gorospe M. et al (2017a). NSUN2-mediated m5C methylation and METTL3/METTL14-mediated m6A methylation cooperatively enhance p21 translation. J. Cell. Biochem.118 (9), 2587–2598. 10.1002/jcb.25957
111
Li Q. Liu H. Li L. Guo H. Xie Z. Kong X. et al (2023d). Mettl1-mediated internal m7G methylation of Sptbn2 mRNA elicits neurogenesis and anti-alzheimer's disease. Cell. Biosci.13 (1), 183. 10.1186/s13578-023-01131-2
112
Li S. Feng T. Liu Y. Yang Q. Song A. Wang S. et al (2024b). m1A inhibition fuels oncolytic virus-elicited antitumor immunity via downregulating MYC/PD-L1 signaling. Int. J. Oral Sci.16 (1), 36. 10.1038/s41368-024-00304-0
113
Li S. Mason C. E. (2014). The pivotal regulatory landscape of RNA modifications. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet.15, 127–150. 10.1146/annurev-genom-090413-025405
114
Li X. Xiong X. Wang K. Wang L. Shu X. Ma S. et al (2016). Transcriptome-wide mapping reveals reversible and dynamic N(1)-methyladenosine methylome. Nat. Chem. Biol.12 (5), 311–316. 10.1038/nchembio.2040
115
Li X. Xiong X. Zhang M. Wang K. Chen Y. Zhou J. et al (2017b). Base-resolution mapping reveals distinct m(1)A methylome in nuclear- and mitochondrial-encoded transcripts. Mol. Cell.68, 993–1005.e9. 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.019
116
Li X. Y. Zhao Z. J. Wang J. B. Shao Y. H. Liu H. You J. X. et al (2022b). m7G methylation-related genes as biomarkers for predicting overall survival outcomes for hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol.10, 849756. 10.3389/fbioe.2022.849756
117
Li Y. Li J. Luo M. Zhou C. Shi X. Yang W. et al (2018). Novel long noncoding RNA NMR promotes tumor progression via NSUN2 and BPTF in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett.430, 57–66. 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.05.013
118
Li Y. J. Guo Q. Ye M. S. Cai G. Xiao W. F. Deng S. et al (2024a). YBX1 promotes type H vessel-dependent bone formation in an m5C-dependent manner. JCI Insight9 (4), e172345. 10.1172/jci.insight.172345
119
Li J. Zhang H. Wang H. (2022a). N1-methyladenosine modification in cancer biology: current status and future perspectives. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J.20, 6578–6585. 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.11.045
120
Lin S. Liu Q. Lelyveld V. S. Choe J. Szostak J. W. Gregory R. I. (2018). Mettl1/Wdr4-Mediated m7G tRNA methylome is required for normal mRNA translation and embryonic stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. Mol. Cell.71 (2), 244–255.e5. 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.06.001
121
Lin Y. Liu M. Deng P. Zhang J. (2024). TET1 mediated m5C modification of RelB aggravates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced neuroinflammation through regulating microglia polarization. Cell. Signal120, 111210. 10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111210
122
Liu F. Clark W. Luo G. Wang X. Fu Y. Wei J. et al (2016). ALKBH1-Mediated tRNA demethylation regulates translation. Cell.167 (3), 816–828.e16. 10.1016/j.cell.2016.09.038
123
Liu K. Xu P. Lv J. Ge H. Yan Z. Huang S. et al (2023a). Peritoneal high-fat environment promotes peritoneal metastasis of gastric cancer cells through activation of NSUN2-mediated ORAI2 m5C modification. Oncogene42 (24), 1980–1993. 10.1038/s41388-023-02707-5
124
Liu L. Chen Y. Zhang T. Cui G. Wang W. Zhang G. et al (2024b). YBX1 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via m5C‐Dependent SMOX mRNA stabilization. Adv. Sci. (Weinh)11, e2302379. 10.1002/advs.202302379
125
Liu W. Wang Y. Ulivi P. Tavolari S. Rizvi S. A. A. Capobianco E. et al (2023b). A signature of five 7-methylguanosine-related genes is a prognostic marker for lung squamous cell carcinoma. J. Thorac. Dis.15 (11), 6265–6278. 10.21037/jtd-23-1504
126
Liu X. Vaidya A. M. Sun D. Zhang Y. Ayat N. Schilb A. et al (2020). Role of eIF4E on epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion, and chemoresistance of prostate cancer cells. Cancer Commun. (Lond).40 (2-3), 126–131. 10.1002/cac2.12011
127
Liu X. Wei Q. Yang C. Zhao H. Xu J. Mobet Y. et al (2024a). RNA m5C modification upregulates E2F1 expression in a manner dependent on YBX1 phase separation and promotes tumor progression in ovarian cancer. Exp. Mol. Med.56 (3), 600–615. 10.1038/s12276-024-01184-4
128
Liu Y. Zhou J. Li X. Zhang X. Shi J. Wang X. et al (2022). tRNA-m1A modification promotes T cell expansion via efficient MYC protein synthesis. Nat. Immunol.23 (10), 1433–1444. 10.1038/s41590-022-01301-3
129
Lü C. Xu H. Gao P. Huang A. Qu M. He W. et al (2024). Abundance of modifications in mature miRNAs revealed by LC-MS/MS method coupled with a two-step hybridization purification strategy. Anal. Chem.96 (18), 6870–6874. 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c01326
130
Lu J. Yang P. Yu L. Xie N. Wu Y. Li B. (2023). Identification of m7G-Related LncRNA signature for predicting prognosis and evaluating tumor immune infiltration in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Diagn. (Basel)13 (10), 1697. 10.3390/diagnostics13101697
131
Luo Q. Huang C. Chen M. (2023). Comprehensive analysis of N1-methylandenosine regulators and m1A-related mRNAs and lncRNAs as prognostic factors in bladder cancer. Gene.887, 147735. 10.1016/j.gene.2023.147735
132
Luo X. Li H. Liang J. Zhao Q. Xie Y. Ren J. et al (2021). RMVar: an updated database of functional variants involved in RNA modifications. Nucleic Acids Res.49, D1405–D1412. 10.1093/nar/gkaa811
133
Luo Y. Yao Y. Wu P. Zi X. Sun N. He J. (2022). The potential role of N7-methylguanosine (m7G) in cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol.15 (1), 63. 10.1186/s13045-022-01285-5
134
Ma J. Han H. Huang Y. Yang C. Zheng S. Cai T. et al (2021). METTL1/WDR4-mediated m7G tRNA modifications and m7G codon usage promote mRNA translation and lung cancer progression. Mol. Ther.29 (12), 3422–3435. 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.08.005
135
Malbec L. Zhang T. Chen Y. S. Zhang Y. Sun B. F. Shi B. Y. et al (2019). Dynamic methylome of internal mRNA N(7)-methylguanosine and its regulatory role in translation. Cell. Res.29 (11), 927–941. 10.1038/s41422-019-0230-z
136
Matsuo H. Li H. McGuire A. M. Fletcher C. M. Gingras A. C. Sonenberg N. et al (1997). Structure of translation factor eIF4E bound to m7GDP and interaction with 4E-binding protein. Nat. Struct. Biol.4 (9), 717–724. 10.1038/nsb0997-717
137
Meng Q. Xie Y. Sun K. He L. Wu H. Zhang Q. et al (2024). ALYREF-JunD-SLC7A5 axis promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression through epitranscriptome-metabolism reprogramming and immune evasion. Cell. Death Discov.10 (1), 97. 10.1038/s41420-024-01862-2
138
Metodiev M. D. Spåhr H. Loguercio P. P. Meharg C. Becker C. Altmueller J. et al (2014). NSUN4 is a dual function mitochondrial protein required for both methylation of 12S rRNA and coordination of mitoribosomal assembly. PLoS Genet.10 (2), e1004110. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004110
139
Miao S. Li H. Song X. Liu Y. Wang G. Kan C. et al (2025). tRNA m1A modification regulates cholesterol biosynthesis to promote antitumor immunity of CD8+ T cells. J. Exp. Med.222 (3), e20240559. 10.1084/jem.20240559
140
Monshaugen I. Luna L. Rhodes J. Kristiansen F. I. S. Lång A. Bøe S. O. et al (2024). Depletion of the m1A writer TRMT6/TRMT61A reduces proliferation and resistance against cellular stress in bladder cancer. Front. Oncol.13, 1334112. 10.3389/fonc.2023.1334112
141
Motorin Y. Lyko F. Helm M. (2010). 5-methylcytosine in RNA: detection, enzymatic formation and biological functions. Nucleic Acids Res.38, 1415–1430. 10.1093/nar/gkp1117
142
Murakami S. Suzuki T. Yokoyama W. Yagi S. Matsumura K. Nakajima Y. et al (2018). Nucleomethylin deficiency impairs embryonic erythropoiesis. J. Biochem.163 (5), 413–423. 10.1093/jb/mvx086
143
Nakano S. Suzuki T. Kawarada L. Iwata H. Asano K. Suzuki T. (2016). NSUN3 methylase initiates 5-formylcytidine biogenesis in human mitochondrial tRNA(Met). Nat. Chem. Biol.12 (7), 546–551. 10.1038/nchembio.2099
144
Natchiar S. K. Myasnikov A. G. Kratzat H. Hazemann I. Klaholz B. P. (2017). Visualization of chemical modifications in the human 80S ribosome structure. Nature551, 472–477. 10.1038/nature24482
145
Nulali J. Zhang K. Long M. Wan Y. Liu Y. Zhang Q. et al (2024). ALYREF-Mediated RNA 5-Methylcytosine modification promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via stabilizing EGFR mRNA and pSTAT3 activation. Int. J. Biol. Sci.20 (1), 331–346. 10.7150/ijbs.82316
146
Oerum S. Dégut C. Barraud P. Tisné C. (2017). m1A post-transcriptional modification in tRNAs. Biomolecules7 (1), 20. 10.3390/biom7010020
147
Oerum S. Roovers M. Rambo R. P. Kopec J. Bailey H. J. Fitzpatrick F. et al (2018). Structural insight into the human mitochondrial tRNA purine N1-methyltransferase and ribonuclease P complexes. J. Biol. Chem.293, 12862–12876. 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001286
148
Ohira T. Suzuki T. (2016). Precursors of tRNAs are stabilized by methylguanosine cap structures. Nat. Chem. Biol.12 (8), 648–655. 10.1038/nchembio.2117
149
Ontiveros R. J. Stoute J. Liu K. F. (2019). The chemical diversity of RNA modifications. Biochem. J.476, 1227–1245. 10.1042/BCJ20180445
150
Orellana E. A. Liu Q. Yankova E. Pirouz M. De Braekeleer E. Zhang W. et al (2021). METTL1-mediated m7G modification of Arg-TCT tRNA drives oncogenic transformation. Mol. Cell.81 (16), 3323–3338.e14. 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.06.031
151
Osborne M. J. Volpon L. Kornblatt J. A. Culjkovic-Kraljacic B. Baguet A. Borden K. L. (2013). eIF4E3 acts as a tumor suppressor by utilizing an atypical mode of methyl-7-guanosine cap recognition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.110 (10), 3877–3882. 10.1073/pnas.1216862110
152
Ougland R. Lando D. Jonson I. Dahl J. A. Moen M. N. Nordstrand L. M. et al (2012). ALKBH1 is a histone H2A dioxygenase involved in neural differentiation. Stem Cells30 (12), 2672–2682. 10.1002/stem.1228
153
Ougland R. Zhang C. M. Liiv A. Johansen R. F. Seeberg E. Hou Y. M. et al (2004). AlkB restores the biological function of mRNA and tRNA inactivated by chemical methylation. Mol. Cell.16, 107–116. 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.09.002
154
Õunap K. Käsper L. Kurg A. Kurg R. (2013). The human WBSCR22 protein is involved in the biogenesis of the 40S ribosomal subunits in Mammalian cells. PLoS ONE8 (9), e75686. 10.1371/journal.pone.0075686
155
Ozanick S. Krecic A. Andersland J. Anderson J. T. (2005). The bipartite structure of the tRNA m1A58 methyltransferase from S. cerevisiae is conserved in humans. Rna11, 1281–1290. 10.1261/rna.5040605
156
Pan W. Liu X. Liu S. (2024). ALYREF m5C RNA methylation reader predicts bladder cancer prognosis by regulating the tumor immune microenvironment. Med. Baltim.103 (14), e37590. 10.1097/MD.0000000000037590
157
Pandolfini L. Barbieri I. Bannister A. J. Hendrick A. Andrews B. Webster N. et al (2019). METTL1 promotes let-7 MicroRNA processing via m7G methylation. Mol. Cell.74 (6), 1278–1290.e9. 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.03.040
158
Peifer C. Sharma S. Watzinger P. Lamberth S. Kötter P. Entian K. D. (2013). Yeast Rrp8p, a novel methyltransferase responsible for m1A 645 base modification of 25S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res.41 (2), 1151–1163. 10.1093/nar/gks1102
159
Peter D. Ruscica V. Bawankar P. Weber R. Helms S. Valkov E. et al (2019). Molecular basis for GIGYF-Me31B complex assembly in 4EHP-mediated translational repression. Genes. Dev.33 (19-20), 1355–1360. 10.1101/gad.329219.119
160
Peter D. Weber R. Sandmeir F. Wohlbold L. Helms S. Bawankar P. et al (2017). GIGYF1/2 proteins use auxiliary sequences to selectively bind to 4EHP and repress target mRNA expression. Genes. Dev.31 (11), 1147–1161. 10.1101/gad.299420.117
161
Rashad S. Han X. Sato K. Mishima E. Abe T. Tominaga T. et al (2020). The stress specific impact of ALKBH1 on tRNA cleavage and tiRNA generation. RNA Biol.17, 1092–1103. 10.1080/15476286.2020.1779492
162
Richter F. Plehn J. E. Bessler L. Hertler J. Jörg M. Cirzi C. et al (2022). RNA marker modifications reveal the necessity for rigorous preparation protocols to avoid artifacts in epitranscriptomic analysis. Nucleic Acids Res.50 (8), 4201–4215. 10.1093/nar/gkab1150
163
Roundtree I. A. Evans M. E. Pan T. He C. (2017). Dynamic RNA modifications in gene expression regulation. Cell.169, 1187–1200. 10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.045
164
Ruscica V. Bawankar P. Peter D. Helms S. Igreja C. Izaurralde E. (2019). Direct role for the drosophila GIGYF protein in 4EHP-mediated mRNA repression. Nucleic Acids Res.47 (13), 7035–7048. 10.1093/nar/gkz429
165
Safra M. Sas-Chen A. Nir R. Winkler R. Nachshon A. Bar-Yaacov D. et al (2017). The m1A landscape on cytosolic and mitochondrial mRNA at single-base resolution. Nature551, 251–255. 10.1038/nature24456
166
Sakai Y. Miyauchi K. Kimura S. Suzuki T. (2016). Biogenesis and growth phase-dependent alteration of 5-methoxycarbonylmethoxyuridine in tRNA anticodons. Nucleic Acids Res.44 (2), 509–523. 10.1093/nar/gkv1470
167
Schaefer M. Kapoor U. Jantsch M. F. (2017). Understanding RNA modifications: the promises and technological bottlenecks of the 'epitranscriptome'. Open Biol.7 (5), 170077. 10.1098/rsob.170077
168
Schaefer M. Pollex T. Hanna K. Tuorto F. Meusburger M. Helm M. et al (2010). RNA methylation by Dnmt2 protects transfer RNAs against stress-induced cleavage. Genes. Dev.24 (15), 1590–1595. 10.1101/gad.586710
169
Schosserer M. Minois N. Angerer T. B. Amring M. Dellago H. Harreither E. et al (2015). Methylation of ribosomal RNA by NSUN5 is a conserved mechanism modulating organismal lifespan. Nat. Commun.6, 6158. 10.1038/ncomms7158
170
Schwartz S. (2018). m1A within cytoplasmic mRNAs at single nucleotide resolution: a reconciled transcriptome-wide map. RNA24 (11), 1427–1436. 10.1261/rna.067348.118
171
Selmi T. Hussain S. Dietmann S. Heiß M. Borland K. Flad S. et al (2021). Sequence- and structure-specific cytosine-5 mRNA methylation by NSUN6. Nucleic Acids Res.49 (2), 1006–1022. 10.1093/nar/gkaa1193
172
Seo K. W. Kleiner R. E. (2020). YTHDF2 recognition of N(1)-methyladenosine (m(1)A)- modified RNA is associated with transcript destabilization. ACS Chem. Biol.15, 132–139. 10.1021/acschembio.9b00655
173
Shanmugam R. Fierer J. Kaiser S. Helm M. Jurkowski T. P. Jeltsch A. (2015). Cytosine methylation of tRNA-Asp by DNMT2 has a role in translation of proteins containing poly-Asp sequences. Cell. Discov.1, 15010. 10.1038/celldisc.2015.10
174
Sharma S. Hartmann J. D. Watzinger P. Klepper A. Peifer C. Kötter P. et al (2018). A single N1-methyladenosine on the large ribosomal subunit rRNA impacts locally its structure and the translation of key metabolic enzymes. Sci. Rep.8 (1), 11904. 10.1038/s41598-018-30383-z
175
Shen H. Ontiveros R. J. Owens M. C. Liu M. Y. Ghanty U. Kohli R. M. et al (2021). TET-Mediated 5-methylcytosine oxidation in tRNA promotes translation. J. Biol. Chem.296, 100087. 10.1074/jbc.RA120.014226
176
Shi Q. Xue C. Yuan X. He Y. Yu Z. (2020). Gene signatures and prognostic values of m1A-related regulatory genes in hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep.10 (1), 15083. 10.1038/s41598-020-72178-1
177
Shimada K. Fujii T. Tsujikawa K. Anai S. Fujimoto K. Konishi N. (2012). ALKBH3 contributes to survival and angiogenesis of human urothelial carcinoma cells through NADPH oxidase and tweak/Fn14/VEGF signals. Clin. Cancer Res.18 (19), 5247–5255. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0955
178
Shoombuatong W. Basith S. Pitti T. Lee G. Manavalan B. (2022). THRONE: a new approach for accurate prediction of human RNA N7-Methylguanosine sites. J. Mol. Biol.434 (11), 167549. 10.1016/j.jmb.2022.167549
179
Siegel R. L. Giaquinto A. N. Jemal A. (2024). Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin.74 (1), 12–49. 10.3322/caac.21820
180
Smoczynski J. Yared M. J. Meynier V. Barraud P. Tisné C. (2024). Advances in the structural and functional understanding of m1A RNA modification. Acc. Chem. Res.10.1021/acs.accounts.3c00568
181
Sonenberg N. Hinnebusch A. G. (2009). Regulation of translation initiation in eukaryotes: mechanisms and biological targets. Cell.136 (4), 731–745. 10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.042
182
Song D. An K. Zhai W. Feng L. Xu Y. Sun R. et al (2023). NSUN2-mediated mRNA m5C modification regulates the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Genomics Proteomics Bioinforma.21 (4), 823–833. 10.1016/j.gpb.2022.09.007
183
Squires J. E. Patel H. R. Nousch M. Sibbritt T. Humphreys D. T. Parker B. J. et al (2012). Widespread occurrence of 5-methylcytosine in human coding and non-coding RNA. Nucleic Acids Res.40, 5023–5033. 10.1093/nar/gks144
184
Su J. Wu G. Ye Y. Zhang J. Zeng L. Huang X. et al (2021). NSUN2-mediated RNA 5-methylcytosine promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via LIN28B-dependent GRB2 mRNA stabilization. Oncogene40 (39), 5814–5828. 10.1038/s41388-021-01978-0
185
Su Z. Monshaugen I. Wilson B. Wang F. Klungland A. Ougland R. et al (2022). TRMT6/61A-dependent base methylation of tRNA-derived fragments regulates gene-silencing activity and the unfolded protein response in bladder cancer. Nat. Commun.13 (1), 2165. 10.1038/s41467-022-29790-8
186
Sun F. Wu K. Yao Z. Mu X. Zheng Z. Sun M. et al (2020b). Long noncoding RNA LINC00963 induces NOP2 expression by sponging tumor suppressor miR-542-3p to promote metastasis in prostate cancer. Aging (Albany NY)12 (12), 11500–11516. 10.18632/aging.103236
187
Sun G. Ma S. Zheng Z. Wang X. Chen S. Chang T. et al (2022). Multi-omics analysis of expression and prognostic value of NSUN members in prostate cancer. Front. Oncol.12, 965571. 10.3389/fonc.2022.965571
188
Sun H. Li K. Liu C. Yi C. (2023). Regulation and functions of non-m6A mRNA modifications. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol.24 (10), 714–731. 10.1038/s41580-023-00622-x
189
Sun Z. Xue S. Zhang M. Xu H. Hu X. Chen S. et al (2020a). Aberrant NSUN2-mediated m5C modification of H19 lncRNA is associated with poor differentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene39 (45), 6906–6919. 10.1038/s41388-020-01475-w
190
Surovtseva Y. V. Shadel G. S. (2013). Transcription-independent role for human mitochondrial RNA polymerase in mitochondrial ribosome biogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res.41 (4), 2479–2488. 10.1093/nar/gks1447
191
Suzuki T. (2021). The expanding world of tRNA modifications and their disease relevance. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol.22 (6), 375–392. 10.1038/s41580-021-00342-0
192
Suzuki Y. Noma A. Suzuki T. Ishitani R. Nureki O. (2009). Structural basis of tRNA modification with CO2 fixation and methylation by wybutosine synthesizing enzyme TYW4. Nucleic Acids Res.37 (9), 2910–2925. 10.1093/nar/gkp158
193
Taforeau L. Zorbas C. Langhendries J. L. Mullineux S. T. Stamatopoulou V. Mullier R. et al (2013). The complexity of human ribosome biogenesis revealed by systematic nucleolar screening of Pre-rRNA processing factors. Mol. Cell.51 (4), 539–551. 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.08.011
194
Trotman J. B. Giltmier A. J. Mukherjee C. Schoenberg D. R. (2017). RNA guanine-7 methyltransferase catalyzes the methylation of cytoplasmically recapped RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res.45, 10726–10739. 10.1093/nar/gkx801
195
Tsao N. Olabode J. Rodell R. Sun H. Brickner J. R. Tsai M. S. et al (2024). YTHDC1 cooperates with the THO complex to prevent RNA damage-induced DNA breaks. Prepr. Biorxiv.2024, 2024.03.14.585107. 10.1101/2024.03.14.585107
196
Tuorto F. Liebers R. Musch T. Schaefer M. Hofmann S. Kellner S. et al (2012). RNA cytosine methylation by Dnmt2 and NSun2 promotes tRNA stability and protein synthesis. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.19 (9), 900–905. 10.1038/nsmb.2357
197
Ueda H. Iyo H. Doi M. Inoue M. Ishida T. Morioka H. et al (1991). Combination of trp and glu residues for recognition of mRNA cap structure. Analysis of m7G base recognition site of human cap binding protein (IF-4E) by site-directed mutagenesis. FEBS Lett.280 (2), 207–210. 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80294-d
198
Ueda M. Shimizu T. Mabuchi M. Horiike K. Kitae K. Hase H. et al (2018). Novel metabolically stable PCA-1/ALKBH3 inhibitor has potent antiproliferative effects on DU145 cells in vivo. Anticancer Res.38 (1), 211–218. 10.21873/anticanres.12210
199
Uno M. Honjoh S. Matsuda M. Hoshikawa H. Kishimoto S. Yamamoto T. et al (2013). A fasting-responsive signaling pathway that extends life span in C. elegans. Cell. Rep.3 (1), 79–91. 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.12.018
200
Van Haute L. Dietmann S. Kremer L. Hussain S. Pearce S. F. Powell C. A. et al (2016). Deficient methylation and formylation of mt-tRNA(Met) wobble cytosine in a patient carrying mutations in NSUN3. Nat. Commun.7, 12039. 10.1038/ncomms12039
201
Van Haute L. Lee S. Y. McCann B. J. Powell C. A. Bansal D. Vasiliauskaitė L. et al (2019). NSUN2 introduces 5-methylcytosines in Mammalian mitochondrial tRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res.47 (16), 8720–8733. 10.1093/nar/gkz559
202
van Tran N. Ernst F. G. M. Hawley B. R. Zorbas C. Ulryck N. Hackert P. et al (2019). The human 18S rRNA m6A methyltransferase METTL5 is stabilized by TRMT112. Nucleic Acids Res.47 (15), 7719–7733. 10.1093/nar/gkz619
203
Vilardo E. Nachbagauer C. Buzet A. Taschner A. Holzmann J. Rossmanith W. (2012). A subcomplex of human mitochondrial RNase P is a bifunctional methyltransferase-extensive moonlighting in mitochondrial tRNA biogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res.40 (22), 11583–11593. 10.1093/nar/gks910
204
Vilardo E. Nachbagauer C. Buzet A. Taschner A. Holzmann J. Rossmanith W. (2018). A subcomplex of human mitochondrial RNase P is a bifunctional methyltransferase - extensive moonlighting in mitochondrial tRNA biogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res.46 (20), 11126–11127. 10.1093/nar/gky931
205
Villaescusa J. C. Buratti C. Penkov D. Mathiasen L. Planagumà J. Ferretti E. et al (2009). Cytoplasmic Prep1 interacts with 4EHP inhibiting Hoxb4 translation. PLoS One4 (4), e5213. 10.1371/journal.pone.0005213
206
Volpon L. Culjkovic-Kraljacic B. Osborne M. J. Ramteke A. Sun Q. Niesman A. et al (2016). Importin 8 mediates m7G cap-sensitive nuclear import of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF4E. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.113, 5263–5268. 10.1073/pnas.1524291113
207
Volpon L. Osborne M. J. Culjkovic-Kraljacic B. Borden K. L. (2013). eIF4E3, a new actor in mRNA metabolism and tumor suppression. Cell. Cycle12 (8), 1159–1160. 10.4161/cc.24566
208
von Stechow L. Typas D. Carreras Puigvert J. Oort L. Siddappa R. Pines A. et al (2015). The E3 ubiquitin ligase ARIH1 protects against genotoxic stress by initiating a 4EHP-mediated mRNA translation arrest. Mol. Cell. Biol.35, 1254–1268. 10.1128/MCB.01152-14
209
Wagner A. Hofmeister O. Rolland S. G. Maiser A. Aasumets K. Schmitt S. et al (2019). Mitochondrial Alkbh1 localizes to mtRNA granules and its knockdown induces the mitochondrial UPR in humans and C. elegans. J. Cell. Sci.132, jcs223891. 10.1242/jcs.223891
210
Waku T. Nakajima Y. Yokoyama W. Nomura N. Kako K. Kobayashi A. et al (2016). NML-Mediated rRNA base methylation links ribosomal subunit formation to cell proliferation in a p53-dependent manner. J. Cell. Sci.129 (12), 2382–2393. 10.1242/jcs.183723
211
Wang G. Qu F. Liu S. Zhou J. Wang Y. (2021a). Nucleolar protein NOP2 could serve as a potential prognostic predictor for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Bioengineered12 (1), 4841–4855. 10.1080/21655979.2021.1960130
212
Wang J. Z. Zhu W. Han J. Yang X. Zhou R. Lu H. C. et al (2021b). The role of the HIF-1α/ALYREF/PKM2 axis in glycolysis and tumorigenesis of bladder cancer. Cancer Commun. (Lond).41 (7), 560–575. 10.1002/cac2.12158
213
Wang N. Chen R. X. Deng M. H. Wei W. S. Zhou Z. H. Ning K. et al (2023b). m5C-dependent cross-regulation between nuclear reader ALYREF and writer NSUN2 promotes urothelial bladder cancer malignancy through facilitating RABL6/TK1 mRNAs splicing and stabilization. Cell. Death Dis.14 (2), 139. 10.1038/s41419-023-05661-y
214
Wang Y. Wang J. Li X. Xiong X. Zhou Z. et al (2021c). N1-methyladenosine methylation in tRNA drives liver tumourigenesis by regulating cholesterol metabolism. Nat. Commun.12 (1), 6314. 10.1038/s41467-021-26718-6
215
Wang Y. Wei J. Feng L. Li O. Huang L. Zhou S. et al (2023a). Aberrant m5C hypermethylation mediates intrinsic resistance to gefitinib through NSUN2/YBX1/QSOX1 axis in EGFR-Mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol. Cancer22 (1), 81. 10.1186/s12943-023-01780-4
216
Wang Y. Xiong G. Cai W. Tao Q. (2024). METTL1 facilitates ameloblastoma invasive growth via MAPK signaling pathway. Gene905, 148234. 10.1016/j.gene.2024.148234
217
Wang Z. Yu P. Zou Y. Ma J. Han H. Wei W. et al (2023c). METTL1/WDR4-mediated tRNA m7G modification and mRNA translation control promote oncogenesis and doxorubicin resistance. Oncogene42 (23), 1900–1912. 10.1038/s41388-023-02695-6
218
Weber R. Chung M. Y. Keskeny C. Zinnall U. Landthaler M. Valkov E. et al (2020). 4EHP and GIGYF1/2 mediate translation-coupled messenger RNA decay. Cell. Rep.33 (2), 108262. 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108262
219
Wei J. Liu F. Lu Z. Fei Q. Ai Y. He P. C. et al (2018). Differential m6A, m6Am, and m1A demethylation mediated by FTO in the cell nucleus and cytoplasm. Mol. Cell.71 (6), 973–985.e5. 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.08.011
220
Woo H. H. Chambers S. K. (2019). Human ALKBH3-induced m(1)A demethylation increases the CSF-1 mRNA stability in breast and ovarian cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech.1862, 35–46. 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2018.10.008
221
Wu R. Feng S. Li F. Shu G. Wang L. Gao P. et al (2023). Transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of autophagy and adipogenesis by YBX1. Cell. Death Dis.14 (1), 29. 10.1038/s41419-023-05564-y
222
Wu Y. Chen Z. Xie G. Zhang H. Wang Z. Zhou J. et al (2022). RNA m1A methylation regulates glycolysis of cancer cells through modulating ATP5D. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.119 (28), e2119038119. 10.1073/pnas.2119038119
223
Xiang S. Ma Y. Shen J. Zhao Y. Wu X. Li M. et al (2020). m5C RNA methylation primarily affects the ErbB and PI3K-Akt signaling pathways in gastrointestinal cancer. Front. Mol. Biosci.7, 599340. 10.3389/fmolb.2020.599340
224
Xie G. Lu Y. He J. Yang X. Zhou J. Yi C. et al (2024). Small molecule-inducible and photoactivatable cellular RNA N1-Methyladenosine editing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.63 (26), e202320029. 10.1002/anie.202320029
225
Xie H. Wang M. Yu H. Ding L. Wang R. et al (2022). METTL1 drives tumor progression of bladder cancer via degrading ATF3 mRNA in an m7G-modified miR-760-dependent manner. Cell. Death Discov.8 (1), 458. 10.1038/s41420-022-01236-6
226
Xie J. Mo T. Li R. Zhang H. Liang G. Ma T. et al (2023). The m7G reader NCBP2 promotes pancreatic cancer progression by upregulating MAPK/ERK signaling. Cancers (Basel)15 (22), 5454. 10.3390/cancers15225454
227
Xing J. Yi J. Cai X. Tang H. Liu Z. Zhang X. et al (2015). NSun2 promotes cell growth via elevating cyclin-dependent kinase 1 translation. Mol. Cell. Biol.35 (23), 4043–4052. 10.1128/MCB.00742-15
228
Xu G. Meng Y. Wang L. Dong B. Peng F. Liu S. et al (2021). miRNA-214-5p inhibits prostate cancer cell proliferation by targeting SOX4. World J. Surg. Oncol.19 (1), 338. 10.1186/s12957-021-02449-2
229
Xu X. Huang Z. Han H. Yu Z. Ye L. Zhao Z. et al (2025). N7-methylguanosine tRNA modification promotes gastric cancer progression by activating SDHAF4-dependent mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. Cancer Lett.615, 217566. 10.1016/j.canlet.2025.217566
230
Xu X. Zhang Y. Zhang J. Zhang X. (2020). NSun2 promotes cell migration through methylating autotaxin mRNA. J. Biol. Chem.295 (52), 18134–18147. 10.1074/jbc.RA119.012009
231
Xu X. Zhao Y. Ying Y. Zhu H. Luo J. Mou T. et al (2023). m7G-related genes-NCBP2 and EIF4E3 determine immune contexture in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by regulating CCL4/CCL5 expression. Mol. Carcinog.62 (8), 1091–1106. 10.1002/mc.23548
232
Xue M. Mi S. Zhang Z. Wang H. Chen W. Wei W. et al (2023). MFAP2, upregulated by m1A methylation, promotes colorectal cancer invasiveness via CLK3. Cancer Med.12 (7), 8403–8414. 10.1002/cam4.5561
233
Xue S. Xu H. Sun Z. Shen H. Chen S. Ouyang J. et al (2019). Depletion of TRDMT1 affects 5-methylcytosine modification of mRNA and inhibits HEK293 cell proliferation and migration. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.520 (1), 60–66. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.09.098
234
Yakubovskaya E. Guja K. E. Mejia E. Castano S. Hambardjieva E. Choi W. S. et al (2012). Structure of the essential MTERF4:NSUN4 protein complex reveals how an MTERF protein collaborates to facilitate rRNA modification. Structure20 (11), 1940–1947. 10.1016/j.str.2012.08.027
235
Yang H. Wang Y. Xiang Y. Yadav T. Ouyang J. Phoon L. et al (2022c). FMRP promotes transcription-coupled homologous recombination via facilitating TET1-mediated m5C RNA modification demethylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.119 (12), e2116251119. 10.1073/pnas.2116251119
236
Yang J. Li G. Huang Y. Liu Y. (2023c). Decreasing expression of Prohibitin-2 lowers the oncogenicity of renal cell carcinoma cells by suppressing eIF4E-mediated oncogene translation via MNK inhibition. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol.466, 116458. 10.1016/j.taap.2023.116458
237
Yang J. Wang Y. Huang Z. Jiang Y. Pan X. Dong X. et al (2023b). Roles of rRNA N-methyladenosine modification in the function of ribosomes. Cell. Biochem. Funct.41 (8), 1106–1114. 10.1002/cbf.3891
238
Yang L. Ma Y. Han W. Li W. Cui L. Zhao X. et al (2015). Proteinase-activated receptor 2 promotes cancer cell migration through RNA methylation-mediated repression of miR-125b. J. Biol. Chem.290 (44), 26627–26637. 10.1074/jbc.M115.667717
239
Yang L. Ren Z. Yan S. Zhao L. Liu J. Zhao L. et al (2022b). Nsun4 and Mettl3 mediated translational reprogramming of Sox9 promotes BMSC chondrogenic differentiation. Commun. Biol.5, 495. 10.1038/s42003-022-03420-x
240
Yang L. Yin H. Chen Y. Pan C. Hang H. Lu Y. et al (2022a). Low expression of PEBP1P2 promotes metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by post-transcriptional regulation of PEBP1 and KLF13 mRNA. Exp. Hematol. Oncol.11 (1), 87. 10.1186/s40164-022-00346-2
241
Yang Q. Wang M. Xu J. Yu D. Li Y. Chen Y. et al (2023a). LINC02159 promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression via ALYREF/YAP1 signaling. Mol. Cancer22 (1), 122. 10.1186/s12943-023-01814-x
242
Yang R. Liang X. Wang H. Guo M. Shen H. Shi Y. et al (2021). The RNA methyltransferase NSUN6 suppresses pancreatic cancer development by regulating cell proliferation. EBioMedicine63, 103195. 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.103195
243
Yang X. Yang Y. Sun B. F. Chen Y. S. Xu J. W. Lai W. Y. et al (2017). 5-methylcytosine promotes mRNA export - NSUN2 as the methyltransferase and ALYREF as an m5C reader. Cell. Res.27 (5), 606–625. 10.1038/cr.2017.55
244
Yang Y. Wang L. Han X. Yang W. L. Zhang M. Ma H. L. et al (2019). RNA 5-methylcytosine facilitates the maternal-to-zygotic transition by preventing maternal mRNA decay. Mol. Cell.75, 1188–1202.e11. 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.06.033
245
Ying X. Liu B. Yuan Z. Huang Y. Chen C. Jiang X. et al (2021). METTL1-m7 G-EGFR/EFEMP1 axis promotes the bladder cancer development. Clin. Transl. Med.11 (12), e675. 10.1002/ctm2.675
246
Yip W. S. Vincent N. G. Baserga S. J. (2013). Ribonucleoproteins in archaeal pre-rRNA processing and modification. Archaea2013, 614735. 10.1155/2013/614735
247
Yu G. Bao J. Zhan M. Wang J. Li X. Gu X. et al (2022). Comprehensive analysis of m5C methylation regulatory genes and tumor microenvironment in prostate cancer. Front. Immunol.13, 914577. 10.3389/fimmu.2022.914577
248
Yu T. Zhang Q. Yu S. K. Nie F. Q. Zhang M. L. Wang Q. et al (2023). THOC3 interacts with YBX1 to promote lung squamous cell carcinoma progression through PFKFB4 mRNA modification. Cell. Death Dis.14 (7), 475. 10.1038/s41419-023-06008-3
249
Yuan S. Tang H. Xing J. Fan X. Cai X. Li Q. et al (2014). Methylation by NSun2 represses the levels and function of microRNA 125b. Mol. Cell. Biol.34 (19), 3630–3641. 10.1128/MCB.00243-14
250
Zhang C. Yi X. Hou M. Li Q. Li X. Lu L. et al (2023a). The landscape of m1A modification and its posttranscriptional regulatory functions in primary neurons. Elife12, e85324. 10.7554/eLife.85324
251
Zhang C. Zhou D. Wang Z. Ju Z. He J. Zhao G. et al (2022). Risk model and immune signature of m7G-Related lncRNA based on lung adenocarcinoma. Front. Genet.13, 907754. 10.3389/fgene.2022.907754
252
Zhang L. S. Dai Q. He C. (2024). Base-resolution sequencing methods for whole-transcriptome quantification of mRNA modifications. Acc. Chem. Res.57 (1), 47–58. 10.1021/acs.accounts.3c00532
253
Zhang L. S. Liu C. Ma H. Dai Q. Sun H. L. Luo G. et al (2019). Transcriptome-wide mapping of internal N(7)-methylguanosine methylome in Mammalian mRNA. Mol. Cell.74 (6), 1304–1316.e8. 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.03.036
254
Zhang M. Kan D. Zhang B. Chen X. Wang C. Chen S. et al (2023c). P300/SP1 complex mediating elevated METTL1 regulates CDK14 mRNA stability via internal m7G modification in CRPC. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res.42 (1), 215. 10.1186/s13046-023-02777-z
255
Zhang X. Chapat C. Wang P. Choi J. H. Li Q. Luo J. et al (2021). microRNA-induced translational control of antiviral immunity by the cap-binding protein 4EHP. Mol. Cell.81 (6), 1187–1199.e5. 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.01.030
256
Zhang Y. Chen X. N. Zhang H. Wen J. K. Gao H. T. Shi B. et al (2023b). CDK13 promotes lipid deposition and prostate cancer progression by stimulating NSUN5-mediated m5C modification of ACC1 mRNA. Cell. Death Differ.30 (12), 2462–2476. 10.1038/s41418-023-01223-z
257
Zhang Y. Wang C. (2021). Demethyltransferase AlkBH1 substrate diversity and relationship to human diseases. Mol. Biol. Rep.48 (5), 4747–4756. 10.1007/s11033-021-06421-x
258
Zhao P. Xia L. Chen D. Xu W. Guo H. Xu Y. et al (2024b). METTL1 mediated tRNA m7G modification promotes leukaemogenesis of AML via tRNA regulated translational control. Exp. Hematol. Oncol.13 (1), 8. 10.1186/s40164-024-00477-8
259
Zhao Y. Kong L. Pei Z. Li F. Li C. Sun X. et al (2021). m7G methyltransferase METTL1 promotes post-ischemic angiogenesis via promoting VEGFA mRNA translation. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol.9, 642080. 10.3389/fcell.2021.642080
260
Zhao Y. Xing C. Peng H. (2024a). ALYREF (aly/REF export factor): a potential biomarker for predicting cancer occurrence and therapeutic efficacy. Life Sci.338, 122372. 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.122372
261
Zhao Y. Zhao Q. Kaboli P. J. Shen J. Li M. Wu X. et al (2019). m1A regulated genes modulate PI3K/AKT/mTOR and ErbB pathways in gastrointestinal cancer. Transl. Oncol.12 (10), 1323–1333. 10.1016/j.tranon.2019.06.007
262
Zhao Z. Qing Y. Dong L. Han L. Wu D. Li Y. et al (2023). QKI shuttles internal m7G-modified transcripts into stress granules and modulates mRNA metabolism. Cell.186 (15), 3208–3226.e27. 10.1016/j.cell.2023.05.047
263
Zheng H. Zhu M. Li W. Zhou Z. Wan X. (2022). m5 C and m6 A modification of long noncoding NKILA accelerates cholangiocarcinoma progression via the miR-582-3p-YAP1 axis. Liver Int.42 (5), 1144–1157. 10.1111/liv.15240
264
Zheng L. Duan Y. Li M. Wei J. Xue C. Chen S. et al (2023a). Deciphering the vital roles and mechanism of m5C modification on RNA in cancers. Am. J. Cancer Res.13 (12), 6125–6146.
265
Zheng Q. Gan H. Yang F. Yao Y. Hao F. Hong L. et al (2020). Cytoplasmic m(1)A reader YTHDF3 inhibits trophoblast invasion by downregulation of m(1)A-methylated IGF1R. Cell. Discov.6, 12. 10.1038/s41421-020-0144-4
266
Zheng W. Mu H. Chen J. Wang C. Hou L. (2023b). Circ_0002762 regulates oncoprotein YBX1 in cervical cancer via mir-375 to regulate the malignancy of cancer cells. Protein Pept. Lett.30 (2), 162–172. 10.2174/0929866530666230104155209
267
Zhou H. Kimsey I. J. Nikolova E. N. Sathyamoorthy B. Grazioli G. McSally J. et al (2016). m(1)A and m(1)G disrupt A-RNA structure through the intrinsic instability of hoogsteen base pairs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.23, 803–810. 10.1038/nsmb.3270
268
Zhou H. Rauch S. Dai Q. Cui X. Zhang Z. Nachtergaele S. et al (2019). Evolution of a reverse transcriptase to map N(1)-methyladenosine in human messenger RNA. Nat. Methods16, 1281–1288. 10.1038/s41592-019-0550-4
269
Zhou K. Yang J. Li X. Xiong W. Zhang P. Zhang X. (2022). N7-Methylguanosine regulatory genes profoundly affect the prognosis, progression, and antitumor immune response of hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Surg.9, 893977. 10.3389/fsurg.2022.893977
270
Zhu C. Yan Q. Weng C. Hou X. Mao H. Liu D. et al (2018). Erroneous ribosomal RNAs promote the generation of antisense ribosomal siRNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.115, 10082–10087. 10.1073/pnas.1800974115
271
Zhu W. Wan F. Xu W. Liu Z. Wang J. Zhang H. et al (2022). Positive epigenetic regulation loop between AR and NSUN2 promotes prostate cancer progression. Clin. Transl. Med.12 (9), e1028. 10.1002/ctm2.1028
272
Zorbas C. Nicolas E. Wacheul L. Huvelle E. Heurgué-Hamard V. Lafontaine D. L. (2015). The human 18S rRNA base methyltransferases DIMT1L and WBSCR22-TRMT112 but not rRNA modification are required for ribosome biogenesis. Mol. Biol. Cell.26 (11), 2080–2095. 10.1091/mbc.E15-02-0073
Summary
Keywords
RNA modification, m5C, m1A, m7G, urological tumours
Citation
Xue W, Zhao Y, Zhang G, Li Z, Li J and Fei X (2025) The role of m5C, m1A and m7G modifications in tumors of urinary system. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 13:1549588. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1549588
Received
21 December 2024
Accepted
16 July 2025
Published
30 July 2025
Volume
13 - 2025
Edited by
Hailin Wang, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), China
Reviewed by
Sujata Jana, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, United States
Xiaoju Zhang, METiS Therapeutics, United States
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Xue, Zhao, Zhang, Li, Li and Fei.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jixin Li, drlijixin@163.com; Xiang Fei, 18940250513@163.com
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.