- 1Department of Hematology, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Jiangxi Medical College, Nanchang University, Jiangxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Hematological Diseases (2024SSY06052), Nanchang, Jiangxi, China
- 2Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jiangxi Medical College, Nanchang University, Nanchang, Jiangxi, China
- 3Department of Hematology, Jishou University First Affiliated Hospital, Jishou, China
- 4Department of Pathology, Eye Hospital affiliated with Nanchang University, Nanchang, China
Background: Cholesterol is an essential molecule for tumor cell growth and proliferation, and dysregulated cholesterol metabolism has been widely implicated in cancer pathogenesis. However, the specific role and underlying molecular mechanisms of cholesterol metabolism alterations in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) remain poorly understood.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed clinical data from 200 DLBCL patients and 185 healthy controls, focusing on lipid and lipoprotein levels, including triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), apolipoprotein A1 (ApoA1), apolipoprotein B (ApoB), and apolipoprotein E (ApoE). Univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazard models were used to evaluate the prognostic value of these markers, and Kaplan-Meier analysis assessed their associations with overall survival (OS). Bioinformatics analysis predicted associations between lipid markers and cholesterol metabolism. Cellular experiments further investigated the expression of cholesterol metabolism-related proteins and the effect of the cholesterol-depleting agent Methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MβCD) on DLBCL cells.
Results: We confirmed significant alterations in metabolic markers (such as TC and ApoA1) between the healthy control group and patients, which were significantly associated with patient prognosis and overall OS. Bioinformatics analysis revealed a strong correlation between these markers and elevated CD36 expression. In addition, DLBCL cells exhibited increased expression of cholesterol uptake and synthesis proteins (CD36, SREBP2, and HMGCR) and decreased expression of efflux proteins (APOA1, NR1H2 and ABCG1), consistent with cholesterol metabolic reprogramming. Treatment with MβCD disrupted CD36 expression and cholesterol metabolism, leading to reduced DLBCL cell survival.
Conclusion: These findings underscore the pivotal role of cholesterol metabolic reprogramming in DLBCL progression. CD36 and related metabolic markers represent promising therapeutic targets, opening novel avenues for the treatment of this malignancy.
1 Introduction
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) in adults, characterized by significant clinical and prognostic heterogeneity. Despite advances in treatments such as immunotherapy, CAR-T therapy, and transplantation, which have improved outcomes for many patients, approximately 30%–40% of DLBCL cases still show treatment resistance or relapse (Klener and Klanova, 2020). Current prognostic markers, including chromosomal aberrations and gene mutations, have been pivotal in guiding therapeutic decisions (Reddy et al., 2017; Lenz and Staudt, 2010). However, further enhancement of patient survival outcomes requires the identification of additional factors influencing DLBCL treatment and prognosis. Emergingevidence highlights the critical role of metabolic reprogramming, particularly alterations in cholesterol metabolism and cancer progression. Cholesterol, an essential molecule for maintaining cell membrane integrity and signaling, has been widely implicated in the pathogenesis of various cancers (Huang et al., 2020). Dysregulation of cholesterol metabolism supports tumor cell growth and proliferation and promotes immune evasion by altering the tumor microenvironment (Snaebjornsson et al., 2020; Ma et al., 2019).
However, the mechanisms by which cholesterol metabolism influences DLBCL remain poorly understood. Previous studies have shown that high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels are inversely associated with the risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (Lim et al., 2007), whereas low serum apolipoprotein A1 (APOA1) levels are significantly correlated with poor prognosis in DLBCL patients (Huang et al., 2024). These findings suggest that cholesterol metabolism could serve as a potential therapeutic target for DLBCL. Nevertheless, the specific role of cholesterol metabolism in DLBCL pathogenesis and progression requires further investigation.
In this study, a retrospective analysis of clinical parameters from 200 DLBCL patients and 185 healthy controls was conducted to systematically investigate the correlation between cholesterol metabolism and DLBCL prognosis. The focus was on evaluating changes in serum lipid levels before and after treatment, including triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), HDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), lipoprotein A (Lp(a)), ApoA1, apolipoprotein B (ApoB) and apolipoprotein E (ApoE). By integrating bioinformatics analysis with in vitro experiments, it was found that alterations in lipid metabolites are closely associated with cholesterol metabolic reprogramming, a key feature of DLBCL. Lipid metabolic markers significantly impact patient prognosis. Furthermore, CD36 and cholesterol metabolism-related markers were identified as potential therapeutic targets, providing new insights for DLBCL treatment.
This study combines clinical cases analysis with bioinformatics and fundamental research to elucidate the role of cholesterol metabolism in DLBCL pathogenesis and explore the therapeutic potential of targeting cholesterol metabolic pathways in this malignancy.
2 Methods
2.1 Patients
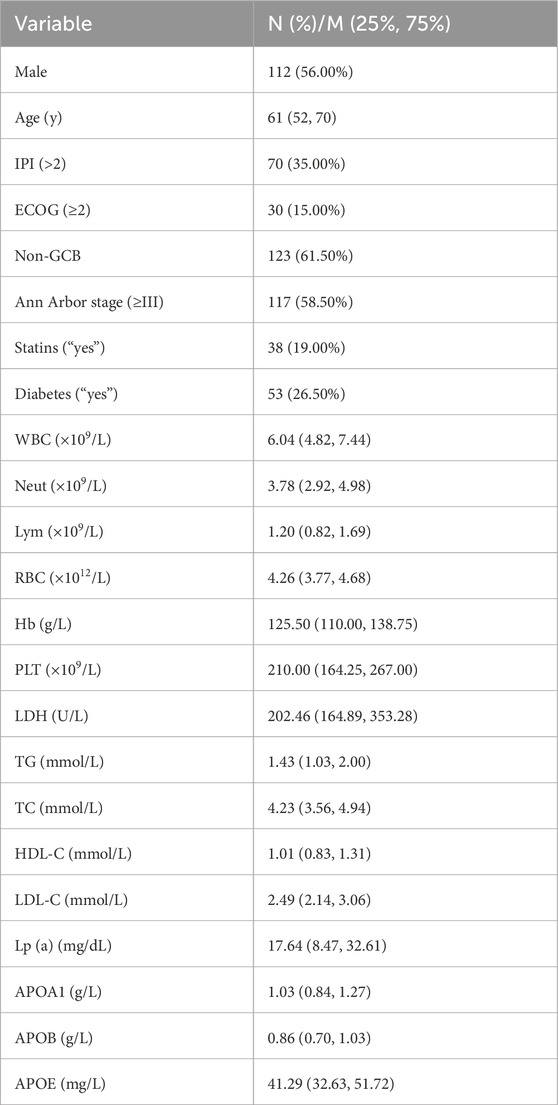
According to the diagnostic criteria established by the World Health Organization (WHO), 200 patients diagnosed with DLBCL at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University between October 2010 and December 2023 (112 males and 88 females; median age, 61 years) were included in the DLBCL group for retrospective analysis. Additionally, 185 age- and gender-matched healthy individuals were recruited from the health examination center of the same hospital to serve as the control group. The demographic characteristics of the patients are provided in Table 1. All data in this study were obtained in compliance with the ethical principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Jiangxi, China.
The inclusion criteria for DLBCL patients in this study were as follows: 1) cases diagnosed as DLBCL based on the 2016 WHO criteria (Zhou et al., 2018); 2) newly diagnosed DLBCL patients who had not previously received any anticancer treatment; 3) patients who received at least one cycle of standard treatment after admission; and 4) availability of complete treatment and follow-up records. The exclusion criterion was as follow: presence of other malignancies.
A post hoc power analysis was performed using Schoenfeld’s formula, which estimated a statistical power of 79% to detect a hazard ratio (HR) of 0.40, given 48 events, a prevalence of 25.5% in the low-cholesterol group, and a two-sided α level of 0.05.
2.2 Data acquisition and processing
In this study, cholesterol metabolism-related genes were identified through a literature review and validated using KEGG enrichment analysis via the website http://sangerbox.com/home.html. Data from 87 healthy controls and 76 DLBCL patients’ blood samples from the GSE83632 dataset in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/) were extracted using www.aclbi.com, and a heatmap of cholesterol metabolism gene expression was created using the “pheatmap” package in R. Data from 223 DLBCL patients in the GSE83371 dataset were also retrieved from the GEO database, and the optimal cutoff value for CD36 was determined using X-tile software (Yale University, CT, United States). The prognostic efficacy of CD36 was evaluated through Kaplan-Meier analysis with a two-sided statistical test. Immunohistochemical results of CD36 in three normal lymph nodes and three cases of NHL were obtained from https://www.proteinatlas.org/.
2.3 Cell lines and culture
In this study, the normal lymphocyte cell line GM12878 and DLBCL cell lines WSU-DLCL-4, OCI-LY3, SU-DHL-4, and DB were purchased from Cellverse Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China). Of these, GM12878, WSU-DLCL-4, SU-DHL-4, and DB cell lines were cultured in RPMI 1640 complete medium, whereas the OCI-LY3 cell line was cultured in IMDM complete medium. All cells were maintained in a humidified incubator at 5% CO2. Cell line identity was confirmed through short tandem repeat (STR) profiling, and tests were performed to ensure the absence of fungal and mycoplasma contamination.
2.4 Cell viability assay
To assess cell viability, cells were seeded into 96-well plates and treated with the specified drugs for 24, 48, or 72 h. Subsequently, Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8; Dojindo, Kumamoto, Japan) was added, and absorbance was measured at 450 nm using a microplate reader (Thermo Fisher Scientific, United States).
2.5 RT-PCR
Total cellular RNA was extracted using the TRIzol™ reagent (Takara, Japan). RNA from cells treated with MβCD was harvested 48 h post-treatment. Reverse transcription was performed using a commercial kit (AE311-02, TransGen Biotech, China). For RT-PCR analysis, the synthesized cDNA served as template, and PCR amplification was carried out using 2×Taq PCR MasterMix (G3326-15, ServiceBio, Wuhan, China).
2.6 Western blotting
Cells were seeded in culture flasks and treated with the specified drugs for 48 h before collection. Total proteins were extracted using cell lysis buffer (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, United States) and quantified using a bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assay kit (ServiceBio, China). Equal amounts of proteins were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes (Millipore, Billerica, MA, United States). The PVDF membranes were blocked with 5% (0.05 g/mL) skim milk and incubated with primary antibodies (Supplementary Table S1) at 4°C overnight. After washing, the membranes were incubated with secondary antibodies (Supplementary Table S1) for 60 min, and signals were detected using an ECL luminescence reagent (ShareBio, China).
2.7 Transfection
The siRNA sequences targeting CD36 were designed and synthesized by Tsingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (China). The sequences are as follows: siCD36-1: Sense: 5′-CGACAUGAUUAAUGGUACAdTdT-3′; Antisense: 3′-dTdTGCUGUACUAAUUACCAUGU-5′. siCD36-2: Sense: 5′-GGACCAUUGGUGAUGAGAAdTdT-3′; Antisense: 3′-dTdTCCUGGUAACCACUACUCUU-5′. The transfection of siRNA was performed using the Suspended Cell Nucleic Acid Transfection Reagent (#21032, BIOG, China). RNA was extracted at 24 h post-transfection, and protein was harvested at 48 h for subsequent validation.
2.8 Statistical analysis
In this study, all statistical analyses were conducted using IBM SPSS version 25.0 (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, United States), GraphPad Prism version 9.5.1 (GraphPad Software, CA, United States), and the R programming language (R Core Team, Vienna, Austria). Comparisons of categorical variables were made using the chi-square test, while continuous variables were analyzed using the t-test (for normal distribution) or non-parametric tests (for non-normal distribution) based on data distribution. After stratifying eight lipid indicators using X-tile software (Yale University, CT, United States), prognostic efficacy was evaluated using the Kaplan-Meier analysis with a two-sided statistical test. Additionally, univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses were performed to determine the statistical relationships between independent variables and survival rates, with multivariate analysis incorporating variables showing significance in univariate analysis. The Cox proportional hazards regression model was used to assess the impact of lipids as independent risk factors, expressed as hazard ratios (HR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI).
3 Results
3.1 The difference of serum lipid between DLBCL patients and healthy controls
Based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria, a total of 200 DLBCL patients were recruited for this study, and their baseline characteristics and serum lipid levels are detailed in Table 1. Among them, 112 were male (56%) and 88 were female (44%), with a median age of 61 years (range, 14–83 years). The healthy control group consisted of 185 individuals matched for age and gender with the DLBCL cohort (Supplementary Figure S1A,B). Comparison of lipid levels between the DLBCL group and the healthy control group revealed that DLBCL patients had significantly lower levels of TC, HDL-C, LDL-C, Lp(a), ApoA1, and ApoB compared to healthy controls (p < 0.05), while ApoE levels were significantly higher in DLBCL patients (p < 0.05, Figure 1). These results suggest that significant alterations in serum lipid levels are closely associated with the development and progression of DLBCL.
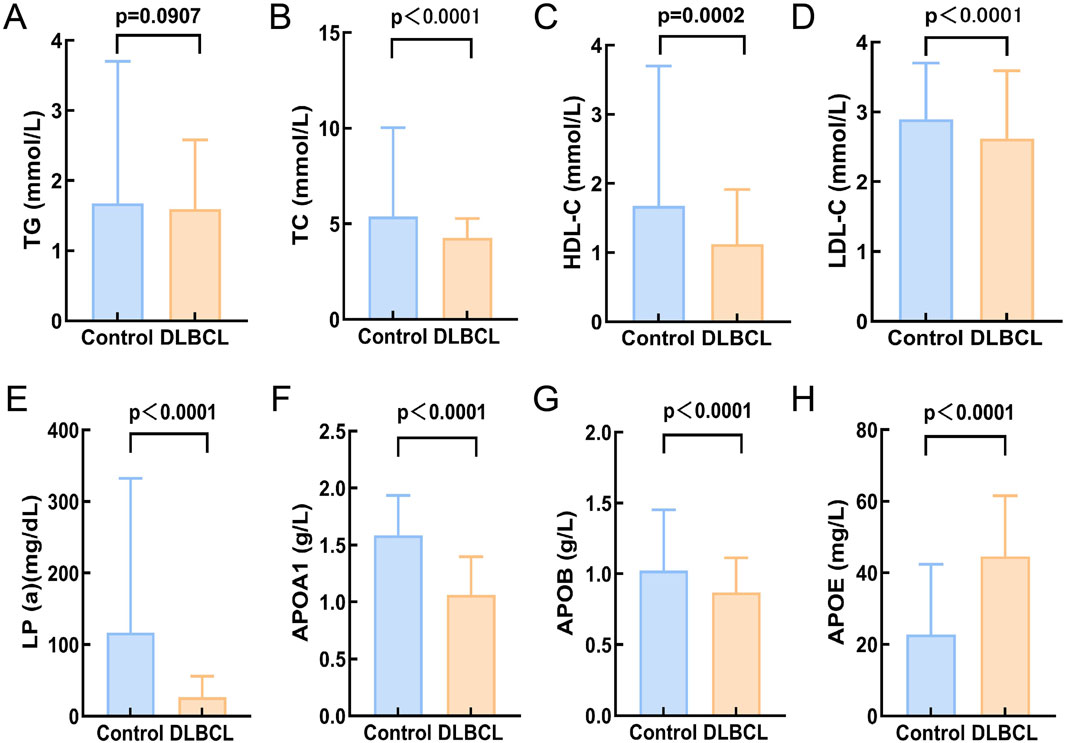
Figure 1. Comparison of serum lipid levels between DLBCLpatients and healthy controls. (A) There was no significant difference in TG levels between helthy control and DLBCL (p > 0.05); (B-G):The expression levels of TC, HDL-C, LDL-C, Lp(a), APOA1, and APOB in DLBCL were significantly lower compared to the healthy control group (p < 0.05); (H)The expression level of APOE in the DLBCL was significantly higher than that in healthy control group (p > 0.05). Abbreviations: TG, Triglyceride; TC, Total Cholesterol; HDL-C, High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol; LDL-C, Low Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol; Lp(a), Lipoprotein A; APOA1, Apolipoprotein A1; APOB, Apolipoprotein B; APOE, Apolipoprotein E.
3.2 Serum lipid level in relation to DLBCL staging and IPI score
The Ann Arbor staging system is widely used for staging malignant lymphomas, including Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), and plays a critical role in guiding treatment decisions and prognostic evaluations. The International Prognostic Index (IPI) score is another essential tool for assessing the prognosis of NHL patients. In this study, we evaluated all patients using the IPI scoring criteria and the Ann Arbor staging system and analyzed the relationship between serum lipid levels and these two parameters. The results revealed that low levels of HDL-C and APOA1 were significantly associated with higher IPI scores (p < 0.05, Supplementary Figure S1C,D). Additionally, HDL-C, APOA1, and TC levels were correlated with Ann Arbor staging, with lower levels corresponding to higher Ann Arbor stages (III-IV) (p < 0.05, Supplementary Figure S1E-G). These findings indicate that HDL-C, APOA1, and TC levels are significantly associated with disease staging in DLBCL and have important prognostic value.
3.3 Relationship between serum lipid levels and outcome
This study included 200 DLBCL patients who received at least one cycle of chemotherapy, and their treatment outcomes were evaluated following the completion of therapy. Of these, 158 patients achieved complete or partial remission (CR/PR). To further explore the relationship between serum lipid levels at diagnosis and treatment efficacy, paired comparisons of serum lipid levels before and after treatment were conducted in patients who achieved complete or partial remission. The results demonstrated that post-treatment levels of TG, TC, LDL-C, ApoA1, ApoB, and APOE were significantly increased (p < 0.05, Figure 2), while HDL-C and Lp(a) levels showed no significant changes (p > 0.05, Figure 2). Conversely, no significant changes in serum lipid levels were observed in the 14 non-CR/PR patients, which may partly explain their lack of therapeutic efficacy (p > 0.05, Supplementary Figure S2).
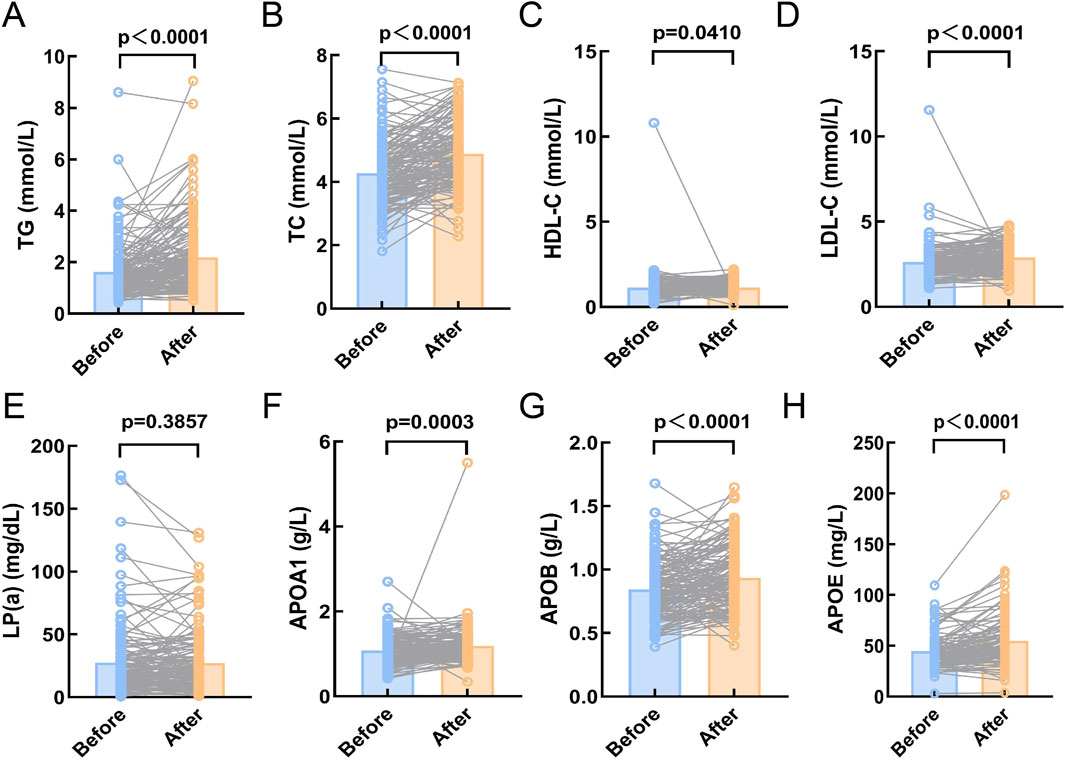
Figure 2. Compare the serum lipid levels of DLBCL patients in CR/PR before and after chemotherapy. (A-H): The expression levels of TG, TC, HDL-C, LDL-C, APOA1, APOB, and APOE were significantly higher after chemotherapy compared to before chemotherapy (p < 0.05). (E): There was no significant difference in the expression level of Lp(a) before and after chemotherapy (p > 0.05). Abbreviations: TG, Triglyceride; TC, Total Cholesterol; HDL-C, High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol; LDL-C, Low Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol; Lp(a), Lipoprotein A; APOA1, Apolipoprotein A1; APOB, Apolipoprotein B; APOE, Apolipoprotein E.
3.4 Serum lipid levels are significantly associated with prognosis
The relationship between survival outcomes and serum lipid levels was analyzed in 200 DLBCL patients. Optimal cutoff values for overall survival (OS) were determined using the X-tile program for TG, TC, HDL-C, LDL-C, Lp(a), ApoA1, ApoB, and APOE, which were 0.9 mmol/L, 3.56 mmol/L, 0.94 mmol/L, 2.17 mmol/L, 20.03 mg/dL, 0.81 g/L, 0.61 g/L, and 32.11 mg/L, respectively (Supplementary Figure S3). Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed that DLBCL patients with higher levels of TC, HDL-C, LDL-C, Lp(a), and ApoA1 had significantly prolonged OS compared to those with lower lipid levels (p < 0.05, Figure 3).
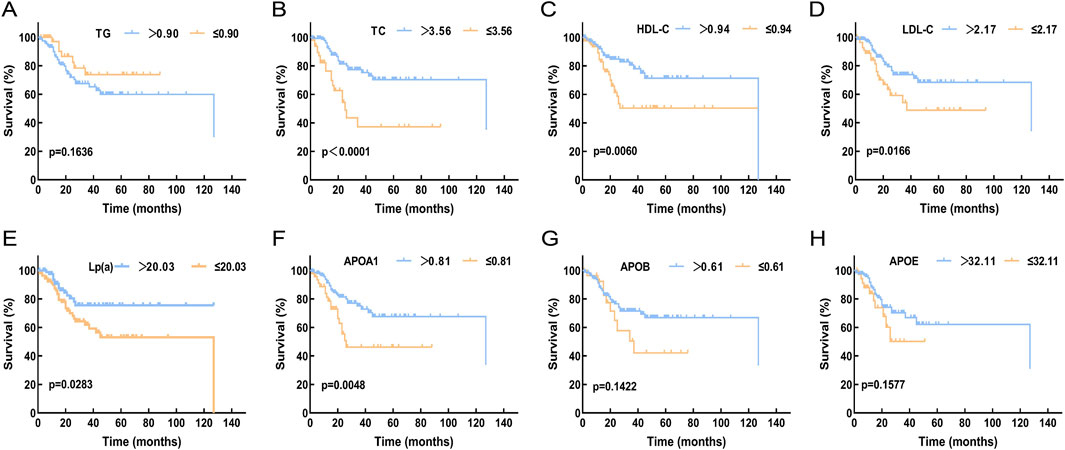
Figure 3. Compare the relationship between the expression levels of serum lipid levels and prognosis in DLBCL patients. (A) The expression level of TG showed no significant correlation with OS (p > 0.05). (B-F): High expression levels of TC, HDL-C, LDL-C, Lp(a), and APOA1 were associated with better OS (p < 0.05). (G,H): The expression levels of APOB and APOE showed no significant correlation with OS (p > 0.05). Abbreviations: TG, Triglyceride; TC, Total Cholesterol; HDL-C, High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol; LDL-C, Low Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol; Lp(a), Lipoprotein A; APOA1, Apolipoprotein A1; APOB, Apolipoprotein B; APOE, Apolipoprotein E.
3.5 Univariate and multivariate cox regression analyses of prognostic factors
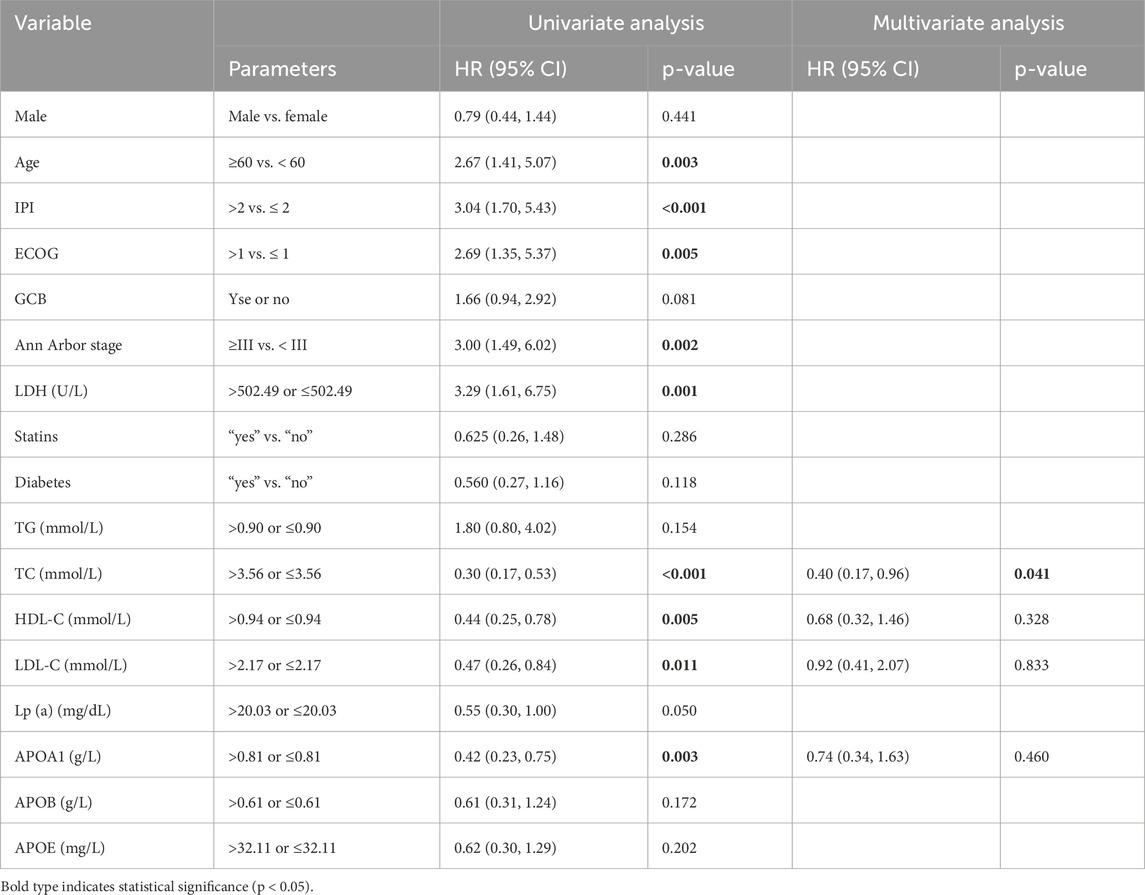
To identify potential prognostic factors, univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses were performed for OS (Table 2). Univariate analysis revealed that age, IPI score, ECOG score, Ann Arbor stage, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), TC, HDL-C, LDL-C, and ApoA1 were significantly associated with OS (p < 0.05). In the multivariate analysis, after excluding known prognostic factors (such as age, IPI score, ECOG score, Ann Arbor stage, and LDH), serum lipid index that were associated with OS in the univariate analysis were incorporated into the Cox proportional hazards regression model. The results demonstrated that TC was an independent prognostic factor for DLBCL (p < 0.05).
3.6 The role of cholesterol metabolism in DLBCL
KEGG analysis revealed that these genes are closely associated with cholesterol metabolism (Figure 4A). We analyzed the differential expression of these genes between healthy controls and DLBCL patients using blood sample data from 87 healthy controls and 76 DLBCL patients sourced from the GEO database. It is evident that the expression of CD36, a key mediator of de novo cholesterol synthesis, is significantly elevated in DLBCL compared to healthy controls (Figures 4B,C). Additionally, we extracted sequencing and survival data from 223 DLBCL patients in the GEO database. The optimal cutoff value for overall survival (OS) was determined using the X-tile program (Figure 4D). Our analysis demonstrated that high expression of CD36, a key mediator of cholesterol synthesis, was significantly associated with poor prognosis (p < 0.05, Figure 4E). Furthermore, immunohistochemical analysis from the ProteinAtlas database confirmed that CD36 expression was markedly elevated in NHL compared to normal lymph nodes (p < 0.05, Figure 4F). Collectively, these findings suggest that cholesterol metabolism may play a crucial role in promoting tumor growth in DLBCL.
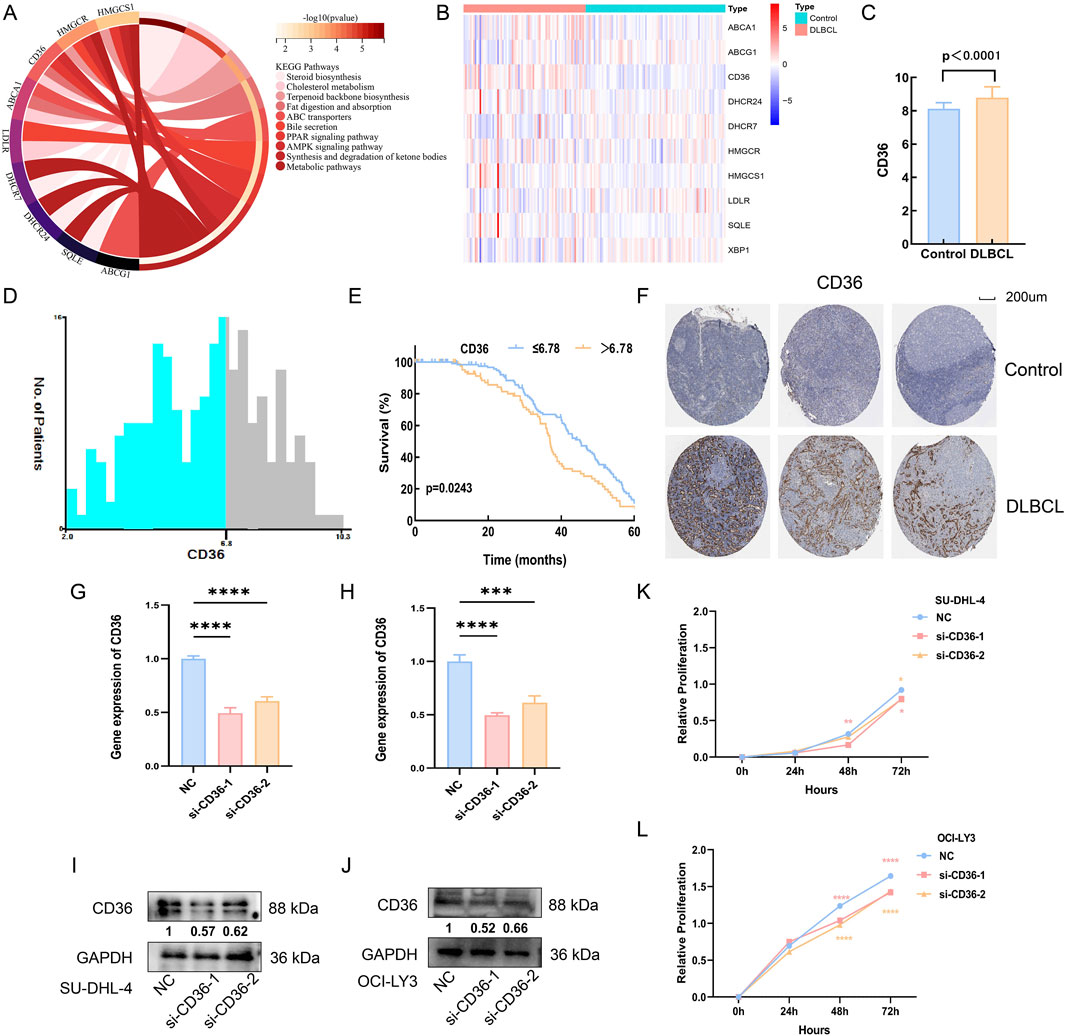
Figure 4. The role of cholesterol metabolism in DLBCL. (A) KEGG enrichment analysis of cholesterol metabolism-related genes; (B) Heatmap analysis of the differential expression of cholesterol metabolism genes in the blood of healthy controls and DLBCL patients; (C) CD36 expression is higher in DLBCL patients compared to healthy controls (p < 0.05); (D,E): X-tile analysis identifies 6.78 as the optimal cutoff value for CD36, and patients with high CD36 expression in DLBCL have a poorer prognosis (p < 0.05); (F) Immunohistochemistry indicates that CD36 expression is higher in non-Hodgkin lymphoma compared to normal lymph nodes (p < 0.05). (G,H): CD36 mRNA expression levels in SU-DHL-4 and OCI-LY3 cells, respectively, after transfection with CD36-specific siRNA. (I,J): CD36 protein expression levels in SU-DHL-4 and OCI-LY3 cells, respectively, following transfection with CD36-targeting siRNA. (K,L): Proliferation levels of SU-DHL-4 and OCI-LY3 cells, respectively, after transfection with CD36 siRNA.
Next, to further elucidate the functional role of CD36 in DLBCL cell proliferation, we transfected SU-DHL-4 and OCI-LY3 cell lines with CD36-specific siRNA. Efficient knockdown was confirmed at both the mRNA and protein levels via RT-qPCR and Western blot analysis, respectively (p < 0.05; Figures 4G–J). Subsequent CCK-8 assays revealed that CD36 knockdown significantly impaired the proliferative capacity of DLBCL cells (p < 0.05; Figures 4K,L). These results indicate that CD36 may facilitate tumor growth in DLBCL through modulation of cholesterol metabolism pathways, offering experimental support for its potential utility as a therapeutic target.
3.7 Effects of Methy-β-cyclodextrin on proliferation of DLBCL cells
To further investigate the role of cholesterol metabolism in DLBCL, the expression levels of cholesterol metabolism-related proteins were examined in a normal lymphocyte cell line (GM12878) and DLBCL cell lines (WSU-DLBCL-2, OCI-LY3, SU-DCL-4, and DB). RT-PCR and Western blot (WB) results showed that the expression of cholesterol synthesis-related proteins CD36, SREBP2 and HMGCR was significantly higher in WSU-DLBCL-2, OCI-LY3, and SU-DCL-4 cells compared to GM12878, while the expression of cholesterol efflux-related proteins NR1H2, APOA1 and ABCG1 was significantly lower (Figures 5A,B). These results validated the phenomenon of increased cholesterol synthesis and reduced efflux in DLBCL cells, confirming cholesterol metabolic reprogramming in DLBCL at the cellular level. Furthermore, the effects of the cholesterol inhibitor Methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MβCD) on DLBCL cell growth were explored. The impact of MβCD at different doses and time points on SU-DCL-4 and OCI-LY3 cells was assessed, and the proliferation of both cell lines was significantly inhibited in a dose- and time-dependent manner (Figures 5C,D).
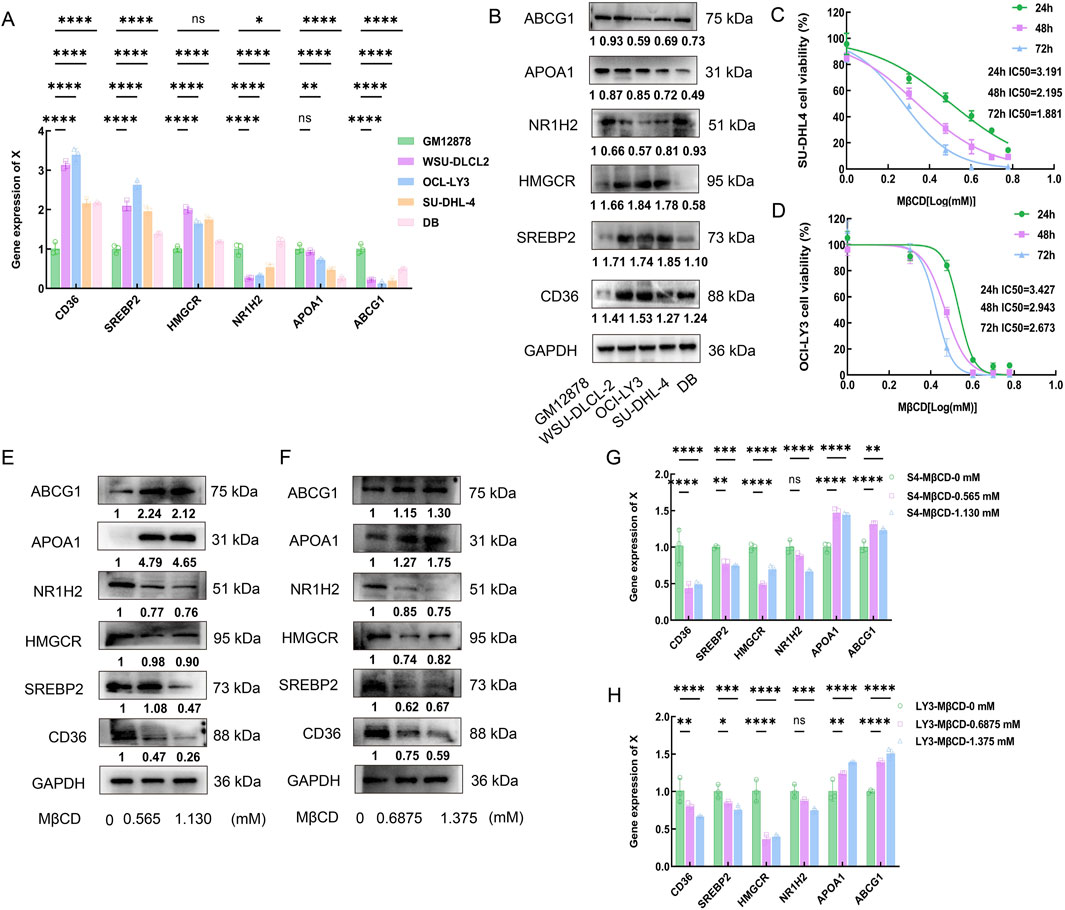
Figure 5. Effects of Methy-β-cyclodextrin on proliferation of DLBCL cells. (A,B): RT-PCR and Western blot (WB) results show the expression levels of CD36, SREBP2, HMGCR, NR1H2, APOA1 and ABCG1 in the normal lymphocyte cell line GM12878 and DLBCL cell lines (WSU-DLCL-2, OCI-LY3, SU-DHL-4, and DB). (C,D): CCK-8 assay was used to evaluate the time- and dose-dependent effects of MβCD on SU-DHL-4 and OCI-LY3 cell lines, and the IC50 values were calculated. SU-DHL-4 and OCI-LY3 cell lines were exposed to MβCD (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 mmol/L) for 24, 48, and 72 h. Cell viability was measured using the CCK-8 assay, and the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values were determined. (E-H): SU-DHL-4 and OCI-LY3 cell lines were treated with Methyl-β-cyclodextrin for 48 h. Western blot and RT-PCR results demonstrated that the expression levels of CD36, SREBP2 and HMGCR decreased in both cell lines, while the expression levels of APOA1 and ABCG1 increased. MβCD:Methyl-β-cyclodextrin.
The half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of MβCD was calculated at different time points through triplicate experiments, and concentrations equivalent to 1/4 and 1/2 of the average IC50 value at 48 h were selected to further validate the effects of MβCD on cholesterol synthesis- and efflux-related proteins in DLBCL cells. The experimental results showed that, after MβCD treatment, the expression levels of CD36, SREBP2 and HMGCR were significantly reduced, whereas the expression levels of APOA1 and ABCG1 were significantly increased (Figures 5E–H). These findings suggest that MβCD may effectively inhibit DLBCL cell growth through a dual mechanism of suppressing cholesterol synthesis and promoting cholesterol efflux.
4 Discussion
At the clinical level, a retrospective analysis of 200 DLBCL patients and 185 healthy controls from the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University revealed significant differences in serum lipid levels between DLBCL patients and healthy controls. DLBCL patients exhibited significantly lower levels of TC, HDL-C, LDL-C, Lp(a), APOA1, and ApoB compared to healthy controls (p < 0.05), while ApoE levels were significantly higher in DLBCL patients (p < 0.05). Among these, HDL-C, APOA1, and TC levels were significantly associated with disease staging in DLBCL patients and held important prognostic value. Patients with higher levels of TC, HDL-C, LDL-C, Lp(a), and APOA1 had better prognoses (p < 0.05). Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses demonstrated that pre-treatment TC levels were an independent prognostic factor for OS, providing a new direction for stratified treatment of DLBCL. It is noteworthy that this study also evaluated potential confounders known to influence lipid metabolism, such as a history of diabetes and statin use. Univariate analysis indicated that neither factor was a significant predictor for OS in this cohort (p > 0.05). We speculate that this result may be related to the relatively small sample size and somewhat limited statistical power, which may have hindered the detection of potential subtle effects. Future studies with expanded cohorts are warranted to further elucidate the potential impact of diabetes and statin medication on the survival outcomes of DLBCL patients.
Bioinformatics analysis suggested that these alterations in lipid levels were closely related to cholesterol metabolism and often accompanied by high expression of CD36 and low expression of APOA1. At the mechanistic level, cell experiments confirmed that the expression of proteins and enzymes promoting cholesterol absorption and synthesis (CD36, SREBP2 and HMGCR) was elevated in DLBCL cell lines, while the expression of proteins promoting cholesterol efflux (NR1H2, APOA1 and ABCG1) was reduced, collectively driving the proliferation of DLBCL tumor cells. Following intervention with the cholesterol inhibitor MβCD, the expression of cholesterol synthesis-related proteins (CD36, SREBP2 and HMGCR) decreased, while the expression of cholesterol efflux-related proteins (APOA1 and ABCG1) increased, leading to significant inhibition of tumor cell growth. These results indicate that cholesterol and its metabolites are potential therapeutic targets for DLBCL.
The relationship between serum cholesterol levels and prognosis is complex and heterogeneous across different cancer types. A large meta-analysis involving 24,655 cancer patients demonstrated that low levels of TC and HDL-C were associated with poorer OS, suggesting that TC and HDL-C may act as protective factors in cancer patients (Zhou et al., 2018). However, in breast cancer, elevated TC levels have been linked to an adverse prognosis, potentially due to the increased risk of metastasis associated with high cholesterol levels (Nelson, 2018). Previous clinical studies on DLBCL identified TC and HDL-C as favorable prognostic factors (Wang et al., 2023; Gao et al., 2018), a finding consistent with the results of this study. Nevertheless, the specific regulatory mechanisms of cholesterol metabolism in DLBCL remain unclear, warranting further in-depth investigation.
Lipid metabolism undergoes significant reprogramming in cancer, with cholesterol metabolic reprogramming being one of the most common forms of lipid reprogramming (Faubert et al., 2020; Cheng et al., 2018). The processes of cholesterol synthesis, absorption, storage, and efflux play crucial roles in tumor growth (Xu et al., 2020). As a key component of cell membranes, cholesterol is a fundamental building block of the phospholipid bilayer, primarily maintaining membrane stability and regulating its fluidity (de Boer et al., 2018). During tumor development, cholesterol is essential for cell proliferation and membrane biosynthesis (Silvente-Poirot and Poirot, 2012). Cells acquire cholesterol through two primary pathways: The first involves receptor-mediated endocytosis of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles via the LDL receptor (LDL-R), facilitating cholesterol uptake from the blood into cells (Bilot et al., 2020). In addition, the transmembrane glycoprotein CD36, which acts as a receptor for fatty acids and cholesteryl esters, enhances cellular cholesterol uptake by directly binding to LDL particles and promoting their adsorption and internalization at the cell surface (Ulug and Nergiz-Unal, 2021). This mechanism partially accounts for the observed decrease in serum cholesterol levels and concomitant increase in intracellular cholesterol content in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). The second pathway involves the transport of the precursor acetyl-CoA into cells by CD36, where de novo cholesterol synthesis occurs through biochemical reactions catalyzed by rate-limiting enzymes such as 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase (HMGCR) and squalene monooxygenase (SQLE), along with the master regulator of cholesterol synthesis, SREBP2 (Steck and Lange, 2010).
Studies have shown that CD36 is upregulated in various cancers, including acute myeloid leukemia, breast cancer, colorectal cancer, and gastric cancer. Both in vitro and in vivo experiments have confirmed that CD36 regulates tumor growth, metastasis, and drug resistance through multiple molecular mechanisms (Wang et al., 2020; Farge et al., 2023). In this study, CD36 expression was significantly elevated and associated with poor prognosis in DLBCL. Functionally, siRNA-mediated knockdown of CD36 markedly suppressed the proliferation of DLBCL cells, underscoring its crucial role in promoting tumor growth. Compared to normal lymphocyte cell lines, the expression of key regulatory factors for de novo cholesterol synthesis, such as SREBP2 and the rate-limiting enzyme HMGCR, was significantly higher in DLBCL cell lines. This suggests that CD36 may drive cholesterol metabolic reprogramming in DLBCL by regulating de novo cholesterol synthesis in tumor cells, altering their metabolic patterns and acting as a critical driver of cholesterol metabolism in DLBCL.
The efflux of intracellular cholesterol primarily relies on receptor-mediated transport proteins that facilitate the movement of cholesterol from inside the cell to the extracellular space or cell membrane (Juhl et al., 2022). Intracellular cholesterol is transported to the extracellular space by ABCA1 and ABCG1, where it binds to HDL to form mature HDL particles, participating in reverse cholesterol transportIntracellular cholesterol is transported to the extracellular space by ABCA1 and ABCG1, where it binds to HDL to form mature HDL particles, participating in reverse cholesterol transport (Yu and Tang, 2019). NR1H2 (also known as LXRβ, liver X receptor beta) promotes cholesterol efflux by activating the expression of ATP-binding cassette transporters, such as ABCA1 and ABCG1 (Nelson et al., 2017). Studies have shown that these genes regulating cholesterol efflux play important roles in the progression of various cancers by modulating lipid metabolism, inflammation, and immune evasion (Savic et al., 2016; Xinyi and Gong, 2024). In this study, NR1H2 and ABCG1 expression levels were significantly higher in DLBCL compared to healthy controls, consistent with the aforementioned findings. This further supports the potential role of cholesterol efflux mechanisms in DLBCL.
Additionally, APOA1 is involved in intracellular cholesterol efflux. As the primary protein component of HDL-C, APOA1 binds to ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters, accepting excess cholesterol from cells and facilitating its reverse transport to the liver for metabolism, thereby maintaining cholesterol homeostasis (Luo et al., 2020). Moreover, APOA1 possesses anti-inflammatory properties, modulates immune responses, and inhibits tumor cell proliferation and metastasis by reducing intracellular cholesterol levels (Georgila et al., 2019). Although serum APOA1 levels were not identified as independent prognostic factors for OS in the clinical analysis of this study, low expression was significantly associated with poor prognosis. Additionally, the statistically significant differences in APOA1 levels before and after treatment in patients achieving CR and PR confirmed that downregulation of APOA1 expression promotes DLBCL progression by reducing cholesterol efflux in tumor cells.
The limitations of this study include: First, the clinical sample size is relatively small, requiring further expansion to validate the predictive value of serum cholesterol as an independent prognostic marker for DLBCL. Second, the absence of in vivo models (e.g., mouse xenografts) to verify the efficacy and toxicity of MβCD highlights the need for further exploration of its clinical translational potential.
In summary, this study confirms cholesterol metabolic reprogramming in DLBCL, suggesting that targeting cholesterol and its metabolites may represent a novel therapeutic strategy. However, its clinical application requires further validation through multicenter, prospective studies. Current research primarily focuses on the correlation between serum lipid levels and DLBCL prognosis, while in-depth exploration of cholesterol metabolism mechanisms remains limited. Future studies should focus on elucidating the specific mechanisms of cholesterol and its related metabolites in DLBCL and developing targeted therapies to improve patient outcomes. Additionally, the reliability and utility of serum cholesterol levels as prognostic indicators must be validated through broader clinical research.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the studies on humans or animals in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements because only commercially available established cell lines were used.
Author contributions
LZ: Project administration, Writing – original draft. WC: Data curation, Writing – review and editing. DL: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review and editing. ZP: Resources, Writing – review and editing. JM: Resources, Writing – review and editing. QL: Data curation, Writing – review and editing. TY: Data curation, Writing – review and editing. YW: Data curation, Writing – review and editing. ZL: Data curation, Writing – review and editing. CH: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. NY: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. DL: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. LY: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review and editing, Project administration.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82460044, 82260043), the Jiangxi Provincial Nature Science Foundation (20232ACB206016, 20204BCJ22030) and the Main academic disciplines and technical leaders training program leading talents project of Jiangxi Province (20225BCJ22001).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcell.2025.1585521/full#supplementary-material
References
Bilotta, M. T., Petillo, S., Santoni, A., and Cippitelli, M. (2020). Liver X receptors: regulators of cholesterol metabolism, inflammation, autoimmunity, and cancer. Front. Immunol. 11, 584303. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.584303
Cheng, C., Geng, F., Cheng, X., and Guo, D. (2018). Lipid metabolism reprogramming and its potential targets in cancer. Cancer Commun. 38, 27–14. doi:10.1186/s40880-018-0301-4
de Boer, J. F., Kuipers, F., and Groen, A. K. (2018). Cholesterol transport revisited: a new turbo mechanism to drive cholesterol excretion. Trends Endocrinol. and Metabolism 29, 123–133. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2017.11.006
Farge, T., Nakhle, J., Lagarde, D., Cognet, G., Polley, N., Castellano, R., et al. (2023). CD36 drives metastasis and relapse in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Res. 83, 2824–2838. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-3682
Faubert, B., Solmonson, A., and DeBerardinis, R. J. (2020). Metabolic reprogramming and cancer progression. Science 368, eaaw5473. doi:10.1126/science.aaw5473
Gao, R., Liang, J. H., Wang, L., Zhu, H. Y., Wu, W., Cao, L., et al. (2018). Low serum cholesterol levels predict inferior prognosis and improve NCCN-IPI scoring in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Int. J. Cancer 143, 1884–1895. doi:10.1002/ijc.31590
Georgila, K., Vyrla, D., and Drakos, E. (2019). Apolipoprotein AI (ApoA-I), immunity, inflammation and cancer. Cancers 11, 1097. doi:10.3390/cancers11081097
Huang, B., Song, B., and Xu, C. (2020). Cholesterol metabolism in cancer: mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Metab. 2, 132–141. doi:10.1038/s42255-020-0174-0
Huang, X., Wang, Y., Huang, Z., Chen, X., Lin, Q., Huang, H., et al. (2024). Low serum apolipoprotein A1 level predicts poor prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the real world: a retrospective study. BMC cancer 24, 62. doi:10.1186/s12885-024-11818-5
Juhl, A. D., and Wüstner, D. (2022). Pathways and mechanisms of cellular cholesterol Efflux—Insight from imaging. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 10, 834408. doi:10.3389/fcell.2022.834408
Klener, P., and Klanova, M. (2020). Drug resistance in Non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 2081. doi:10.3390/ijms21062081
Lenz, G., and Staudt, L. M. (2010). Aggressive lymphomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 362, 1417–1429. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0807082
Lim, U., Gayles, T., Katki, H. A., Stolzenberg-Solomon, R., Weinstein, S. J., Pietinen, P., et al. (2007). Serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and risk of non-hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer Res. 67, 5569–5574. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0212
Luo, J., Yang, H., and Song, B.-L. (2020). Mechanisms and regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 21, 225–245. doi:10.1038/s41580-019-0190-7
Ma, X., Bi, E., Lu, Y., Su, P., Huang, C., Liu, L., et al. (2019). Cholesterol induces CD8+ T cell exhaustion in the tumor microenvironment. Cell Metab. 30, 143–156. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2019.04.002
Nelson, E. R. (2018). The significance of cholesterol and its metabolite, 27-hydroxycholesterol in breast cancer. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 466, 73–80. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2017.09.021
Nelson, J. K., Koenis, D. S., Scheij, S., Cook, E. C. L., Moeton, M., Santos, A., et al. (2017). EEPD1 is a novel LXR target gene in macrophages which regulates ABCA1 abundance and cholesterol efflux. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, Vasc. Biol. 37, 423–432. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.308434
Reddy, A., Zhang, J., Davis, N. S., Moffitt, A. B., Love, C. L., Waldrop, A., et al. (2017). Genetic and functional drivers of diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cell 171, 481–494. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.027
Savic, D., Ramaker, R. C., Roberts, B. S., Dean, E. C., Burwell, T. C., Meadows, S. K., et al. (2016). Distinct gene regulatory programs define the inhibitory effects of liver X receptors and PPARG on cancer cell proliferation. Genome Med. 8, 74–16. doi:10.1186/s13073-016-0328-6
Silvente-Poirot, S., and Poirot, M. (2012). Cholesterol metabolism and cancer: the good, the bad and the ugly. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 12, 673–676. doi:10.1016/j.coph.2012.10.004
Snaebjornsson, M. T., Janaki-Raman, S., and Schulze, A. (2020). Greasing the wheels of the cancer machine: the role of lipid metabolism in cancer. Cell Metab. 31, 62–76. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2019.11.010
Steck, T. L., and Lange, Y. (2010). Cell cholesterol homeostasis: mediation by active cholesterol. Trends Cell Biol. 20, 680–687. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2010.08.007
Ulug, E., and Nergiz-Unal, R. (2021). Dietary fatty acids and CD36-mediated cholesterol homeostasis: potential mechanisms. Nutr. Res. Rev. 34, 64–77. doi:10.1017/S0954422420000128
Wang, H., Franco, F., Tsui, Y.-C., Xie, X., Trefny, M. P., Zappasodi, R., et al. (2020). CD36-mediated metabolic adaptation supports regulatory T cell survival and function in tumors. Nat. Immunol. 21, 298–308. doi:10.1038/s41590-019-0589-5
Wang, F., Lu, L., Chen, H., Yue, Y., Sun, Y., Yan, F., et al. (2023). Altered serum lipid levels are associated with prognosis of diffuse large B cell lymphoma and influenced by utility of rituximab. Ann. Hematol. 102, 393–402. doi:10.1007/s00277-023-05092-x
Xinyi, X., and Gong, Y. (2024). The role of ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member 1 in tumor progression. Cancer Med. 13, e7285. doi:10.1002/cam4.7285
Xu, H., Zhou, S., Tang, Q., Xia, H., and Bi, F. (2020). Cholesterol metabolism: new functions and therapeutic approaches in cancer. Biochimica Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Reviews Cancer 1874, 188394. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188394
Yu, X.-H., and Tang, C.-K. (2019). ABCA1, ABCG1, and cholesterol homeostasis, HDL metabolism and diseases, 95–107. Springer2022.
Keywords: diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, cholesterol metabolism, prognosis, survival, serumlipids
Citation: Zhou L, Cheng W, Luo D, Peng Z, Mei J, Luo Q, Yu T, Wang Y, Lei Z, Huang C, Yan N, Luo D and Yu L (2025) Cholesterol metabolic reprogramming drives the onset of DLBCL and represents a promising therapeutic target. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 13:1585521. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1585521
Received: 28 February 2025; Accepted: 01 September 2025;
Published: 17 September 2025.
Edited by:
Gang Wang, Zhejiang Shuren University, ChinaReviewed by:
Zixin Hu, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, ChinaZhixiong Li, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center (SYSUCC), China
Jiagui Song, Peking University Third Hospital, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhou, Cheng, Luo, Peng, Mei, Luo, Yu, Wang, Lei, Huang, Yan, Luo and Yu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Li Yu, bmRlZnkwMjAyMUBuY3UuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Lili Zhou
Lili Zhou Wei Cheng
Wei Cheng Dan Luo3
Dan Luo3 Jiaqi Mei
Jiaqi Mei Qingqing Luo
Qingqing Luo Tiantian Yu
Tiantian Yu Zhixiang Lei
Zhixiang Lei Chunhong Huang
Chunhong Huang