- 1Emergency Department Outpatient Chemotherapy Center, Yunnan Cancer Hospital, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Peking University Cancer Hospital Yunnan, Kunming, Yunnan, China
- 2Department of Nuclear Medicine, Yunnan Cancer Hospital, The Third Affiliated of Kunming Medical University, Peking University Cancer Hospital Yunnan, Kunming, Yunnan, China
As a major global health challenge with rising incidence and poor prognosis, head and continues to impose a significant clinical burden due to its aggressive biological behavior and frequent therapeutic resistance. Within this context, the atypical Hippo signaling pathway emerges as a crucial regulatory network, integrating diverse components including core kinases (TAO kinases, MAP4K family, NDR1/2 kinases), cell polarity determinants (CRUMBS, SCRIBBLE), junctional adhesion molecules (AMOT family), phosphorylation mediators (14-3-3 proteins), and tumor suppressors (NF2, RASSF family). This multifaceted system governs fundamental cellular processes spanning proliferation, apoptosis, migratory capacity, and immune microenvironment modulation. Notably, post-translational modifications (ubiquitination, acetylation, SUMOylation) of pathway components dynamically regulate the stability and activity of downstream effectors YAP/TAZ, whose sustained activation through molecular aberrations drives tumor progression and treatment resistance in head and neck malignancies.The pathway’s extensive crosstalk with Wnt signaling, NF-κB cascades, and estrogen receptor networks creates context-dependent regulatory plasticity that contributes to tumor heterogeneity. Current therapeutic innovation focuses on molecular diagnostics and precision targeting approaches, including direct YAP/TAZ-TEAD complex inhibitors, upstream receptor modulators, and rational combinations with immune checkpoint blockade. Future investigations should employ multi-omics profiling to delineate tumor subtype-specific regulatory architectures while advancing novel drug delivery platforms. These efforts promise to translate mechanistic insights into multi-targeted therapeutic strategies capable of overcoming resistance mechanisms and improving survival outcomes for this therapeutically challenging malignancy.
1 Introduction
Head and neck cancer is a prevalent malignancy with poor prognosis worldwide, posing significant clinical challenges due to its anatomical complexity and difficulties in early diagnosis (Chowl, 2020). In recent years, with continuous advancements in molecular biology research, the Hippo signaling pathway has garnered substantial attention for its critical roles in regulating organ size, tissue regeneration, and tumorigenesis (Moya and halder, 2019; Dey et al., 2020). The classical Hippo pathway primarily relies on the cascade reactions of MST1/2 and LATS1/2 kinases, which restrict cell proliferation by inhibiting the nuclear translocation of the transcriptional co-activators YAP/TAZ. However, recent studies have revealed that, in addition to the classical pathway, the non-classical Hippo pathway also modulates cell fate through a complex signaling network, with its regulatory components and mechanisms exhibiting remarkable diversity and hierarchical organization.
The non-classical Hippo pathway not only comprises core kinase components—such as TAO kinases (TAOK1/2/3) (Fang et al., 2020), MAP4K family kinases (Chen et al., 2019), and NDR1/2 kinases (Ye et al., 2020)—which regulate cell proliferation, apoptosis, and migration via pathways independent of the classical MST1/2-LATS1/2 axis, but also involves a series of proteins closely associated with cell polarity, junctions, and adhesion, including CRUMBS (Thompson et al., 2013), SCRIBBLE (Buckley and st johnston, 2022), and AMOT family proteins (Wang et al., 2022). In addition, the 14-3-3 protein, serving as a critical phosphorylation adaptor, plays an essential role in maintaining intracellular protein localization and signal transduction (Hermann et al., 2021). Simultaneously, tumor suppressors such as NF2 (Merlin) and members of the RASSF family establish a defensive barrier for the non-classical Hippo pathway by modulating upstream kinase activities and stabilizing the cytoskeleton (Fu et al., 2022; Djos et al., 2012). Furthermore, post-translational modifications of proteins in the non-classical Hippo pathway—such as the ubiquitination, acetylation, and SUMOylation of MST1/2, ΔNp63, TEAD family members, RASSF1A, Beclin 1, and MOB proteins—significantly affect downstream signaling and YAP/TAZ activity, thereby playing crucial roles in the regulation of cell proliferation, apoptosis, and autophagy, and are closely linked to drug resistance and invasiveness in head and neck cancer (Sannigrahi et al., 2015; Lin et al., 2024; Fang et al., 2018). More complex still, extensive crosstalk exists between the non-classical Hippo pathway and the Wnt, NF-κB, and estrogen receptor (ER) signaling pathways; these interactive networks jointly regulate cell fate, immune responses, metabolic reprogramming, and the formation of the tumor microenvironment (Zhao et al., 2023; Britschgi et al., 2017; Ma et al., 2021). For example, VGLL4, a downstream transcriptional co-regulator within the non-classical Hippo pathway, competitively binds TEAD, thereby not only inhibiting YAP/TAZ-mediated gene expression but also synergistically suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling, which in turn impedes tumor cell proliferation and metastasis (Jiao et al., 2017). Additionally, the interplay between the NF-κB pathway and ER signaling with the Hippo pathway further influences the biological behavior and drug resistance of head and neck cancer, representing a promising breakthrough for future precision therapies (Ma et al., 2021).
This review aims to systematically examine the various components of the non-classical Hippo pathway and their post-translational regulatory mechanisms, as well as to explore the crosstalk between this pathway and other signaling pathways, including Wnt, NF-κB, and ER, in the context of head and neck cancer development. By comprehensively analyzing current research progress, we hope to provide new theoretical insights and practical guidance for early diagnosis, prognostic assessment, and precision treatment of head and neck cancer.
2 Overview of the Hippo signaling pathway
2.1 Overview of the classical Hippo pathway
The classical Hippo signaling pathway is primarily composed of a highly conserved kinase cascade, with core components including the MST1/2 kinases, their adaptor protein SAV1, the downstream LATS1/2 kinases, and the regulatory protein MOB1 (Wu et al., 2003). This cascade transmits signals via sequential phosphorylation: MST1/2 kinases activate SAV1 and MOB1, which in turn activate the LATS1/2 kinases (Huang et al., 2005). Once activated, LATS1/2 phosphorylate the transcriptional coactivators YAP and TAZ, inducing conformational changes that expose masked nuclear localization signals (NLS), thereby promoting their cytoplasmic retention or leading to subsequent ubiquitination and degradation (Dong et al., 2007) (Supplementary Figure S1). Consequently, the classical Hippo pathway plays a critical inhibitory role in cell proliferation, apoptosis, and tissue size control, with its dysregulation often closely associated with tumorigenesis and cancer progression.
2.2 Definition and characteristics of the non-classical Hippo pathway
The non-classical Hippo pathway refers to regulatory mechanisms that modulate cell fate independently of the traditional MST1/2–LATS1/2 kinase axis. These pathways exhibit a more diversified regulatory approach with the participation of alternative signaling cascades, incorporating factors such as mechanical stress, inflammatory signals, metabolic status, and other extracellular environmental changes. For example, under certain circumstances, cells can directly regulate the subcellular localization of YAP/TAZ via mechanical tension or cell-contact signals without engaging the complete MST1/2–LATS1/2 cascade (Cho and Jiang, 2021). Additionally, inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α or the NF-κB pathway can modulate the output of the Hippo pathway through cross-regulatory mechanisms (Wang et al., 2020). This non-classical mode of regulation reflects the complexity and multi-layered nature of the signaling network, offering enhanced flexibility for cellular adaptation to a dynamic environment, while also providing new insights into the mechanisms of signal dysregulation during tumorigenesis (Ma et al., 2021; Chen, 2019).
3 The relationship between non-classical Hippo pathway components and head and neck cancer
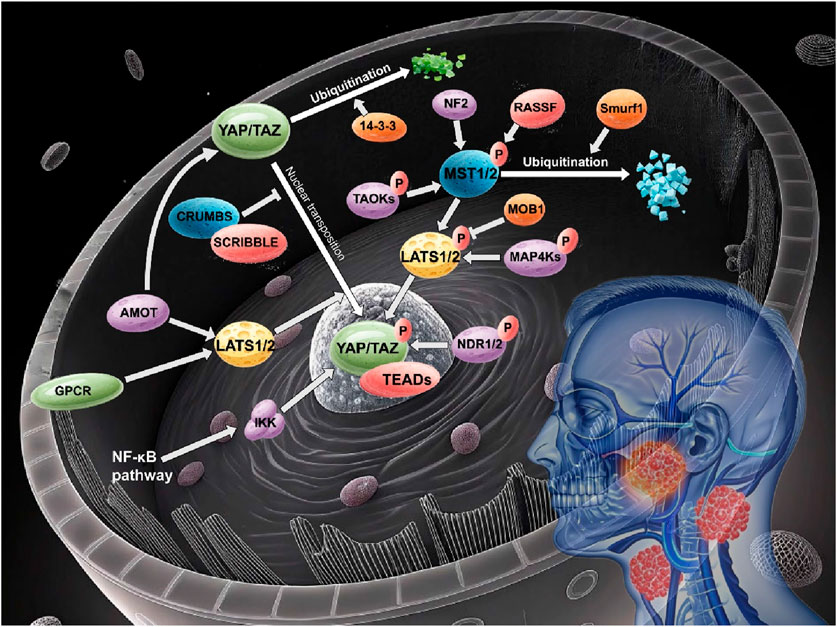
The non-classical Hippo signaling pathway has emerged as a critical contributor to the pathogenesis of head and neck cancer, with its distinct regulatory components and complex cross-talk mechanisms influencing tumor proliferation, invasion, and chemoresistance (Figure 1).
3.1 Non-classical Hippo pathway core kinase components
3.1.1 TAO kinases (TAOK1/2/3)
TAO kinases (TAOK1/2/3), belonging to the STE20 kinase family, serve as crucial upstream regulators of the Hippo signaling pathway. Current studies indicate that TAO kinases can phosphorylate and activate MST1/2, thereby indirectly promoting LATS1/2 activation. This cascade leads to the phosphorylation of YAP/TAZ, resulting in conformational changes that expose masked nuclear localization signals (NLS), thus causing cytoplasmic retention or ubiquitin-mediated degradation of YAP/TAZ (Fang et al., 2020; Kapfhamer et al., 2012; Boggiano et al., 2011). Additionally, some studies suggest that TAO kinases (e.g., TAOK3) may further enhance LATS1/2 kinase activity by directly phosphorylating hydrophobic motifs within LATS1/2 (Fang et al., 2020; Boggiano et al., 2011). This regulatory mechanism is essential for maintaining proper cell proliferation, apoptosis, and tissue homeostasis, while also significantly impacting tumorigenesis.
It has been reported that head and neck squamous cell carcinoma samples often exhibit high expression levels of TAO kinase family members. This aberrant expression may reduce LATS1/2 activity or disrupt the normal phosphorylation cascade, leading to persistent dephosphorylation and excessive nuclear localization of YAP/TAZ, which in turn activates downstream pro-growth and pro-invasive target genes (Faraji et al., 2022; Shin and Kim, 2020). For example, the EGFR signaling pathway is frequently abnormally active in head and neck cancer; its effects may be partly mediated by interfering with MOB1-dependent LATS1/2 activation in synergy with TAO kinase upregulation, collectively promoting YAP/TAZ activation (Ando et al., 2021). Moreover, in other tumor types such as lung, breast, and colon cancers, TAO kinases along with MAP4K family kinases have been shown to exhibit certain tumor-specific roles. Notably, high TAOK3 expression in breast cancer has been associated with the HER2-positive subtype, potentially facilitating tumor metastasis through activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway (Boggiano et al., 2011).
3.1.2 MAP4K family kinases
MAP4K family kinases are also pivotal components of the Hippo signaling pathway. Research has demonstrated that MAP4K family members (e.g., MAP4K1/2/3 and MAP4K4/6/7) can cooperate with MST1/2 by directly phosphorylating key residues on LATS1/2—such as hydrophobic motifs and activation loops—thus promoting LATS1/2 autophosphorylation and full activation (Meng et al., 2015; Li et al., 2015). This redundant and complementary activation mechanism ensures the stringent regulation of YAP/TAZ under various cellular conditions. In addition, MAP4Ks may also influence YAP/TAZ stability and subcellular localization via non-classical pathways (e.g., through modulation of AMPK or mTOR signaling) (Meng et al., 2015; Gao et al., 2016).
The role of MAP4K family kinases in head and neck cancer is gradually gaining attention. Some studies have indicated that members such as MAP4K4 in head and neck cancer may enhance tumor cell migration and chemoresistance by activating the JNK signaling pathway (Meng et al., 2015; Li et al., 2015). Furthermore, in oral squamous cell carcinoma, downregulation of LATS1/2 expression is closely associated with enhanced nuclear localization of YAP/TAZ, and MAP4K family kinases may act as alternative kinases in this context, maintaining partial Hippo signaling that affects tumor stem cell self-renewal and metastasis (Faraji et al., 2022). In other tumor types, MAP4K4 has been implicated in promoting tumor cell invasion and resistance in pancreatic cancer and melanoma through activation of the JNK and RhoA signaling pathways (Li et al., 2015; Gao et al., 2016).
3.1.3 NDR1/2 kinases
NDR1/2 kinases belong to the NDR/LATS kinase family. In the classical Hippo signaling pathway, MST1/2 kinases phosphorylate and activate LATS1/2, which in turn maintain YAP/TAZ in a phosphorylated state, thereby preventing their nuclear translocation and subsequent pro-proliferative effects. However, recent studies have revealed that NDR1/2 kinases not only contribute to classical signal transduction but also play key roles in the non-classical regulation of the Hippo pathway.
In non-classical regulatory mechanisms, NDR1/2 kinases can act in concert with upstream kinases (such as MST1/2) or, in certain contexts, independently regulate the phosphorylation status of YAP/TAZ. For example, by directly phosphorylating specific residues on YAP/TAZ, NDR1/2 can modulate their subcellular localization and transcriptional activity, thereby influencing cell proliferation, apoptosis, and cell cycle progression (Hergovich, 2016; Hergovich, 2013). In addition, NDR1/2 play important roles in cell cycle regulation by modulating the stability of cell cycle inhibitors (such as p21), thus affecting the G1/S transition and maintaining cellular growth homeostasis (Cornils et al., 2011).
Studies on solid tumors have shown that NDR1/2 kinases exhibit complex functions. For instance, in glioblastoma, NDR1 has been reported to phosphorylate YAP, thereby suppressing its oncogenic activity and exerting a tumor-suppressive effect (Chen et al., 2021); in colorectal cancer, loss of NDR1/2 correlates with YAP dephosphorylation, leading to uncontrolled cell proliferation and carcinogenesis (Zhang et al., 2015); in prostate cancer, NDR1 appears to inhibit tumor metastasis through crosstalk with the Wnt pathway (Xuan et al., 2024), although its impact on tumor immunity manifests as a pro-tumorigenic effect (Fu et al., 2024). Although direct studies on NDR1/2 in head and neck cancer are relatively limited, research has implicated the loss of the tumor suppressor NDRG2 in the development of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) via modulation of PI3K/AKT-mediated dephosphorylation of PTEN at S380/S382/T383 (STT) (Tamura et al., 2017). Given that head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is often characterized by aberrant activation of YAP/TAZ, NDR1/2 kinases may also have significant regulatory roles in this tumor type, where their dysregulation could disrupt Hippo signaling and thereby promote tumor cell proliferation, invasion, and drug resistance.
3.2 Non-classical Hippo pathway cell polarity components
Cell polarity and adhesion proteins are fundamental to maintaining normal epithelial cell functions and are essential prerequisites for proper activation of the Hippo signaling pathway. Polarity proteins such as CRUMBS and SCRIBBLE not only determine the apical-basal polarity of cells but also regulate membrane architecture and cell–cell adhesion, indirectly restricting the nuclear translocation of YAP/TAZ and thereby preventing excessive cell proliferation and abnormal tissue growth.
3.2.1 CRUMBS protein
CRUMBS proteins form a complex with intracellular partners (such as Pals1 and Patj) to establish and maintain the apical polarity of cells (Muthuswamy and Xue, 2012; Stephens et al., 2018). The proper localization of this complex is instrumental in anchoring the adaptor protein Expanded (Ex) at the apical membrane, thereby facilitating activation of the Hippo signaling cascade (MST1/2→LATS1/2) which leads to the phosphorylation and cytoplasmic retention of YAP/TAZ (Bulgakova and Knust, 2009; Eaton and Martin-belmonte, 2014). Studies have demonstrated that loss or downregulation of CRUMBS proteins results in mislocalization of Ex, insufficient LATS1/2 kinase activity, and consequent excessive dephosphorylation and nuclear accumulation of YAP/TAZ. This aberrant activation triggers pro-proliferative and anti-apoptotic gene expression, promoting tumorigenesis (Huang and Muthuswamy, 2010). In epithelial-derived tumors such as head and neck cancer, downregulation of CRUMBS family members (e.g., CRB3) is closely associated with loss of cell polarity, epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), and aberrant activation of YAP/TAZ, potentially driving tumor invasion and metastasis (Faraji et al., 2022; Chen et al., 2010).
3.2.2 SCRIBBLE protein
SCRIBBLE is another critical regulator of cell polarity that, together with Dlg and Lgl in a multi-protein complex, maintains basal polarity and overall structural integrity of cells (Margolis, 2018; Kumichel and Knust, 2014). In addition to stabilizing epithelial cells via regulation of cell–cell adhesion (e.g., through interaction with E-cadherin), SCRIBBLE can interact directly or indirectly with core components of the Hippo pathway (such as MST1/2 and LATS1/2) to promote the phosphorylation and cytoplasmic retention of YAP/TAZ (Charrier et al., 2015). In head and neck cancer, particularly in HPV-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, the HPV E6 protein frequently targets SCRIBBLE through its PDZ-binding motif, leading to its ubiquitination, degradation, and functional loss (Bazzoun et al., 2013). Loss of SCRIBBLE function disrupts cell polarity balance, facilitating the nuclear entry of YAP/TAZ, which subsequently activates downstream pro-tumorigenic transcriptional programs and promotes tumor growth and invasion (Kumichel and Knust, 2014; Bazzoun et al., 2013; Zhan et al., 2008).
3.3 Non-classical Hippo pathway cell junction and adhesion protein components
The Angiomotin (AMOT) protein family comprises cell junction-associated proteins that are closely linked to adherens and tight junctions. Members of this family (including AMOT, AMOTL1, and AMOTL2) possess conserved domains such as coiled-coil structures and C-terminal PDZ-binding motifs, which allow them to directly interact with the WW domains of YAP/TAZ (Zhao et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2011). This physical association anchors YAP/TAZ in the cytoplasm or at cell junctions, thereby preventing their nuclear entry and inhibiting their function as transcriptional co-activators. In addition, AMOT proteins can function as scaffolds to facilitate the activation of LATS1/2 kinases, enhancing the phosphorylation of YAP/TAZ and further promoting their binding to 14-3-3 proteins (Zhao et al., 2011). Experimental data indicate that when the expression or function of AMOT family proteins is downregulated, YAP/TAZ become dephosphorylated more readily and translocate to the nucleus, where they activate pro-proliferative and anti-apoptotic genes, thereby driving tumorigenesis and progression (Paramasivam et al., 2011).
In head and neck cancer and other epithelial-derived solid tumors, aberrant regulation of the AMOT family proteins is considered a major factor contributing to the persistent activation of YAP/TAZ. For example, the SRSF3/AMOTL1 splicing axis has been reported to promote the tumorigenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by regulating the nuclear translocation of YAP1 (Xu et al., 2023). In head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, reduced expression of AMOT family proteins (such as AMOTL2) decreases their recruitment and stabilization of LATS1/2 kinases, thereby enhancing YAP nuclear translocation by suppressing LATS-dependent YAP phosphorylation (Zou et al., 2024), which is closely associated with YAP/TAZ nuclear accumulation and activation of oncogenic genes (An et al., 2023). Moreover, in other cancers such as breast and liver cancer, studies have demonstrated that the loss or degradation of AMOT family proteins correlates with aberrant activation of YAP/TAZ, thereby promoting tumor progression (Zhao et al., 2011; Paramasivam et al., 2011).
3.4 Non-classical Hippo pathway phosphorylation adaptor protein components
Upon activation of the Hippo pathway, LATS1/2 kinases phosphorylate key residues on YAP/TAZ (for instance, Ser127 on YAP and the corresponding site on TAZ), generating binding sites recognized by 14-3-3 proteins (An et al., 2023; Chan et al., 2011). The binding of 14-3-3 proteins not only masks the nuclear localization signals of YAP/TAZ but also promotes their stable retention in the cytoplasm, thereby preventing their nuclear translocation and transcriptional co-activation function. Further studies have revealed that this interaction also renders YAP/TAZ more susceptible to ubiquitination and degradation mediated by SCFβ-TrCP, thus exerting a negative regulatory effect on cell proliferation and survival (An et al., 2023; Chan et al., 2011).
14-3-3 proteins play crucial roles in the initiation, progression, and treatment of head and neck cancer. Among them, 14-3-3σ and 14-3-3ζ have been the focus of extensive research. 14-3-3σ regulates the chemotherapeutic sensitivity of tongue cancer through the GSK3β/β-catenin/ZEB1 pathway, and its methylation status as well as intratumoral heterogeneity are closely associated with the development of oral cancer (Peng et al., 2015). Moreover, the expression level of 14-3-3σ may serve as a potential biomarker for predicting the initial response of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) to chemoradiotherapy (Huang et al., 2020). In addition, 14-3-3ζ is widely aberrantly expressed in various head and neck cancers, including oral and laryngeal cancers, and is involved in regulating cancer cell apoptosis, senescence, and drug resistance (Matta et al., 2012). Abnormal expression and impaired function of 14-3-3ζ in some head and neck cancer cells weaken its ability to sequester phosphorylated YAP/TAZ, thus facilitating their nuclear translocation and promoting cell proliferation, invasion, and chemoresistance (Macha et al., 2010). Studies have shown that guggulsterone can induce apoptosis in head and neck cancer cells by targeting 14-3-3ζ, and that siRNA-mediated downregulation of 14-3-3ζ enhances the efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents (Macha et al., 2010). Moreover, the protein interaction network of 14-3-3ζ underscores its key role in oral cancer (Matta et al., 2016), while the loss of USP18 suppress lung cancer metastasis by reducing the stability of 14-3-3ζ (Chen et al., 2022).
3.5 Non-classical Hippo pathway tumor suppressors
In the non-classical Hippo pathway, several tumor suppressors play critical roles in maintaining cellular homeostasis by modulating cell proliferation, apoptosis, and polarity. These factors ensure that oncogenic signals remain in check, and their inactivation or loss often contributes to uncontrolled cell growth and tumor progression.
3.5.1 NF2 (Merlin)
NF2, also known as Merlin, is a key upstream tumor suppressor within the non-classical Hippo pathway. Its primary functions include the regulation of cell proliferation, apoptosis, and the maintenance of cell polarity (Harvey et al., 2003). NF2 forms complexes with molecules such as WWC1 and FRMD6, thereby promoting the activation of MST1/2 kinases. This activation subsequently enhances the phosphorylation of YAP/TAZ by LATS1/2, leading to the cytoplasmic retention of these pro-proliferative transcriptional co-activators and ultimately inhibiting aberrant tumor cell growth (Hong et al., 2020; Wu et al., 2024). Moreover, as a member of the ERM protein family, NF2 modulates the functions of E-cadherin, receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), and β-catenin, integrating extracellular mechanical cues and cytoskeletal signals to maintain cell–cell adhesion and polarity stability (Cao et al., 2020; Nita and Moroishi, 2024). In head and neck cancer, mutations or reduced expression of the NF2 gene often result in abnormal nuclear translocation of YAP/TAZ, thereby activating oncogenic gene expression and correlating with increased tumor invasiveness and poor patient prognosis (Nouri et al., 2024).
3.5.2 RASSF family members
Members of the RASSF family (such as RASSF1A and RASSF5/NORE1A) also play important tumor suppressive roles in the non-classical Hippo pathway. RASSF1A directly interacts with MST1/2 kinases, preventing dephosphorylation by the PP2A phosphatase, thus maintaining MST1/2 activity and promoting the propagation of apoptotic signals (Bae et al., 2017; Oh et al., 2006). Additionally, RASSF1A can directly bind to microtubules, stabilizing their dynamics and thereby inhibiting cell migration and tumor metastasis (Dallol et al., 2004). RASSF5 (NORE1A), acting downstream of Ras, activates MST1/2 to induce cell cycle arrest and Fas-dependent apoptosis (Shivakumar et al., 2002; Graves et al., 2001). Furthermore, through its conserved SARAH domain, RASSF family members form heterodimers with MST1/2 to modulate other non-classical apoptotic signaling pathways, such as the JNK/SAPK pathway, which further suppresses tumor cell proliferation (Hwang et al., 2007). In head and neck cancer, RASSF family members are frequently inactivated due to promoter methylation or gene mutations, a loss of function that is closely associated with decreased MST1/2 activity and aberrant activation of YAP/TAZ, ultimately leading to uncontrolled cell proliferation and tumor metastasis (Dhanaraman et al., 2020; Iwasa et al., 2015).
The non-canonical Hippo pathway orchestrates head and neck carcinogenesis through a diverse array of molecular components, as discussed above (Figure 1). Core kinases (TAO, MAP4K, NDR1/2), polarity regulators (CRUMBS/SCRIBBLE), junction proteins (AMOT family), and tumor suppressors (NF2, RASSF family) collectively maintain cellular homeostasis via phosphorylation-dependent signaling and cytoskeletal interactions. Meanwhile, post-translational modifications—ubiquitination, acetylation, and SUMOylation—fine-tune effector stability and activity, with dysregulation driving YAP/TAZ hyperactivation and tumor progression (Table 1).
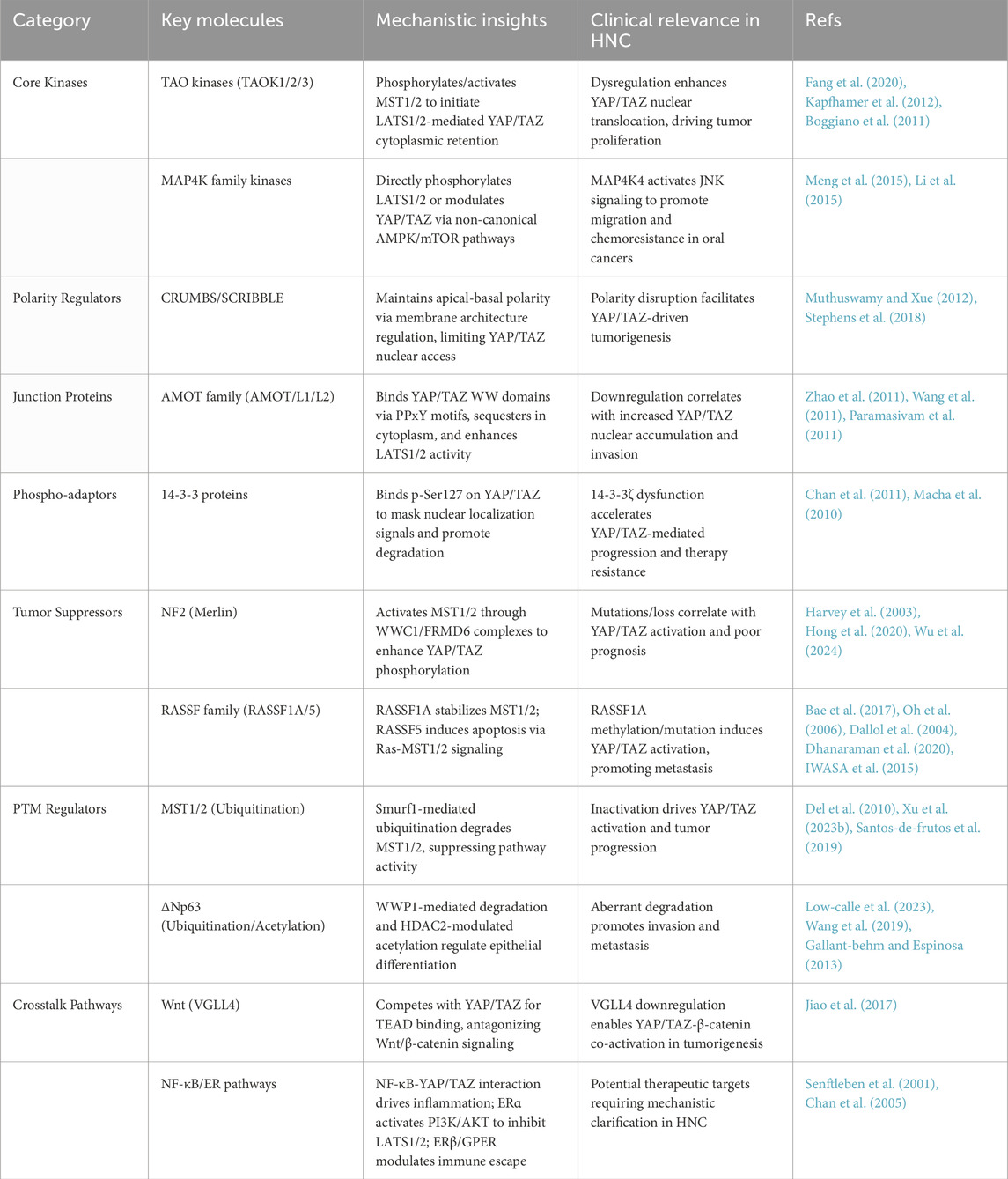
Table 1. Functional classification of non-canonical hippo pathway components in head and neck cancer.
3.6 Hippo pathway dysregulation drives HNSCC initiation and therapy resistance
Genomic analyses of HNSCC from TCGA have revealed frequent inactivating mutations of FAT1 (29%), amplifications of WWTR1 (TAZ, 14%) and YAP1 (8%), all of which associate with persistent YAP/TAZ activation and poor clinical outcome (Chowl, 2020; Moya and Halder, 2019; Dey et al., 2020; Fang et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2019)]. Transcriptomic profiling corroborates these findings, showing that elevated YAP1 and WWTR1 mRNA levels in tumor specimens correlate with advanced clinical stage, higher metastatic risk, and shorter overall survival (Moya and Halder, 2019) (Hermann et al., 2021); immunohistochemistry further confirms that nuclear YAP positivity is enriched in late-stage, chemoresistant cases (Hermann et al., 2021). Functionally, overexpression of YAP1 in HNSCC cell lines (FaDu, SCC-25) markedly enhances proliferation, migration, and cisplatin resistance, whereas knockdown of YAP1 or TAZ restores drug sensitivity and induces apoptosis (Moya and Halder, 2019; Boggiano et al., 2011) (Moya and Halder, 2019; Boggiano et al., 2011). In murine xenograft models, YAP1 depletion in FaDu cells slows tumor growth by ∼50% and reduces pulmonary metastases, and treatment with Verteporfin (a YAP–TEAD inhibitor) further suppresses tumor progression and diminishes resistant lesions (Boggiano et al., 2011). Moreover, hyperactive EGFR signaling drives MOB1 tyrosine phosphorylation to inhibit LATS1/2, thereby promoting YAP nuclear accumulation and induction of resistance-related genes; combined inhibition of EGFR and YAP signaling synergistically attenuates tumor growth and reverses therapeutic resistance (Fu et al., 2022).
4 Targeting post-translational modifications of Hippo pathway proteins
4.1 Ubiquitination regulation of MST1/2
As key kinases in the non-classical Hippo pathway, the activity of MST1/2 is critical for maintaining the balance between cell proliferation and apoptosis. Studies have demonstrated that the E3 ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 can ubiquitinate MST1/2 at the K285/K282 residues, thereby promoting their degradation and diminishing their tumor-suppressive functions (Xu Y. et al., 2023). In addition, RASSF1A can indirectly stabilize MST1/2 activity by preventing PP2A-mediated dephosphorylation; however, if RASSF1A itself is degraded via ubiquitination, the loss of MST1/2 signaling is further exacerbated (Del et al., 2010). In head and neck cancer, reduced MST1/2 activity is closely associated with sustained activation of YAP/TAZ, which in turn drives cell proliferation and invasion (Shin and Kim, 2020; Santos-de-frutos et al., 2019; Ando et al., 2022).
4.2 Post-translational modifications of the TEAD family
TEAD transcription factors, as key downstream effectors of the Hippo pathway, depend not only on their interaction with YAP/TAZ but also on post-translational modifications for proper function. Studies have shown that palmitoylation of TEAD proteins occurs on conserved cysteine residues, enhancing the stability of TEAD-YAP/TAZ binding and thereby promoting the transcription of oncogenic genes (Lin et al., 2017). In parallel, ubiquitination mediated by E3 ubiquitin ligases (such as RNF146) may influence TEAD stability and nuclear localization, thereby modulating its transcriptional activity (Landin-Malt et al., 2016). Abnormal activation of TEAD function in head and neck cancer is closely linked to YAP/TAZ-driven proliferation and migration (Zhao et al., 2007; Zhao et al., 2008; Huh et al., 2019; Noland et al., 2016).
4.3 Ubiquitination regulation of RASSF1A
As a tumor suppressor within the non-classical Hippo pathway, RASSF1A maintains MST1/2 kinase activity through interaction via its SARAH domain (Guo et al., 2011). However, RASSF1A can be ubiquitinated by ITCH and the CUL4A-DDB1 complex, leading to its degradation. This degradation releases its positive regulatory effect on MST1/2, allowing YAP/TAZ to escape inhibition (García-gutiérrez et al., 2020; Jiang et al., 2011). Promoter methylation-mediated inactivation of RASSF1A is common, and aberrations in the ubiquitination pathway further disrupt Hippo signaling, thereby promoting tumor development (Del et al., 2010; Rabizadeh et al., 2004).
4.4 Ubiquitination regulation of Beclin 1
Beclin 1, an important regulator of autophagy, is subject to control by ubiquitination. For instance, TRAF6-mediated K63-linked ubiquitination promotes Beclin 1 oligomerization, which activates the autophagy-related protein ULK1 and enhances autophagic activity (Zalckvar et al., 2009; Shi and Kehrl, 2010). Conversely, the deubiquitinating enzymes USP10 and USP13 reduce Beclin 1 ubiquitination levels, thereby inhibiting autophagy (Liu et al., 2011). In certain tumors, including head and neck cancer, dysregulated autophagy is closely associated with cancer cell survival, migration, and drug resistance, suggesting that abnormalities in the ubiquitination status of Beclin 1 may significantly influence cancer cell fate (Li et al., 2017; Ashkenazi et al., 2017).
4.5 Ubiquitination regulation of MOB proteins
MOB1, a coactivator in the Hippo pathway, promotes the phosphorylation of YAP/TAZ through interactions with MST1/2 and LATS1/2. Its stability is also regulated by ubiquitination (Ando et al., 2021). E3 ubiquitin ligases, such as praja2, can ubiquitinate MOB1, thereby reducing its stability within the cell and indirectly weakening the inhibitory effect of the Hippo pathway on YAP/TAZ. This regulatory mechanism potentially contributes to the aberrant activation of YAP/TAZ observed in head and neck cancer (Liu and Deng, 2019; Yang et al., 2024).
5 Cross-regulation between the Hippo pathway and other signaling pathways in head and neck cancer
In recent years, accumulating evidence has revealed that the transcriptional co-regulators of the non-classical Hippo signaling pathway encompass not only the classical YAP/TAZ-TEAD regulatory mode but also integrate inputs from non-classical Wnt, NF-κB, and estrogen receptor (ER) signaling pathways. These pathways regulate the activity of YAP, TAZ, and other related transcription factors through their distinct molecular mechanisms, thereby influencing cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and the formation of the tumor microenvironment. Consequently, they play critical roles in the initiation and progression of solid tumors, including head and neck cancer.
5.1 Crosstalk between the Wnt signaling pathway and the Hippo pathway
The Wnt signaling pathway (e.g., Wnt5a, Wnt4) activates downstream kinases such as RhoA/ROCK via its receptors (e.g., ROR2 and FZD2), thereby regulating cytoskeletal reorganization and cell polarity. This process significantly influences the activation status of the Hippo pathway (Wang and Martin, 2017). Studies have shown that activation of Wnt signaling can inhibit LATS1/2 kinase activity, resulting in decreased phosphorylation of YAP/TAZ. The ensuing dephosphorylation enables their nuclear translocation and enhances their binding to TEAD, which in turn initiates the transcription of pro-proliferative genes (Kriz and Korinek, 2018; Wei et al., 2018). VGLL4, a key transcriptional co-regulator within the non-classical Hippo pathway, competitively binds TEAD family proteins via its two conserved Tondu domains, thereby blocking the interaction between YAP/TAZ and TEAD. This interference not only prevents YAP/TAZ nuclear entry but also diminishes TEAD-mediated transcriptional activity, effectively maintaining the balance between cell proliferation and apoptosis. Moreover, VGLL4 negatively regulates TCF4-mediated transcription under the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, thereby achieving coordinated cross-pathway regulation (Jiao et al., 2017). In head and neck cancer, this Hippo-Wnt crosstalk is particularly critical; downregulation of VGLL4 is common in certain head and neck squamous cell carcinomas, leading to the co-activation of YAP/TAZ and β-catenin, which in turn promotes cancer cell proliferation and invasion.
5.2 Crosstalk between the NF-κB pathway and the Hippo pathway
The NF-κB signaling pathway is a key regulator of inflammatory responses, cell survival, and immune modulation, with its activation primarily dependent on IκB degradation mediated by the IKK complex (Tam et al., 2012). Studies have indicated that YAP/TAZ are not only downstream effectors of the Hippo pathway but can also modulate NF-κB activity through interactions with the IKK complex (Senftleben et al., 2001; Hayden and Ghosh, 2008). Under certain inflammatory and stress conditions, activation of the NF-κB pathway can upregulate key proteins associated with the Hippo pathway, such as MST1/2, thereby forming a negative feedback regulatory loop. Conversely, inactivation of the Hippo pathway (resulting in YAP/TAZ nuclear translocation) can enhance the expression of NF-κB target genes (e.g., pro-inflammatory factors IL-6 and TNF-α), thereby promoting the establishment of the tumor microenvironment (Chan et al., 2005; Hayden and Ghosh, 2008). In head and neck cancer, where chronic inflammation is common, the crosstalk between NF-κB and the Hippo pathway contributes to cancer cell proliferation, migration, and immune evasion, providing a molecular basis for tumor progression and drug resistance.
5.3 Crosstalk between the estrogen receptor (ER) pathway and the Hippo pathway
The estrogen receptor signaling pathway primarily regulates cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival through ERα and related receptors (e.g., GPER). In certain breast cancer studies, the interaction between ER signaling and the Hippo pathway has been preliminarily elucidated: activation of ERα can indirectly inhibit LATS1/2 activity via upregulation of the PI3K/AKT pathway, thereby promoting the dephosphorylation and nuclear accumulation of YAP/TAZ (Klinge, 2001; Filardo et al., 2000). Moreover, non-classical estrogen signaling mediated by GPER has been found to activate YAP/TAZ, and by enhancing the expression of downstream effector genes such as CTGF, it promotes cell migration and invasion (Gutierrez et al., 2005; Kim et al., 2020; Chimento et al., 2022). Although head and neck cancer is not typically classified as a hormone-dependent tumor, some studies suggest that ERβ and GPER may also participate in the regulation of the Hippo pathway in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, thereby affecting tumor growth and immune evasion (Cheng et al., 2011; Wu and Yang, 2018). This cross-regulation mechanism provides a novel avenue for exploring potential therapeutic targets within the non-classical ER-Hippo signaling axis in head and neck cancer.
5.4 Crosstalk between the ΔNp63 and the Hippo pathway
ΔNp63, a transcription factor closely related to epithelial differentiation, is regulated at the level of protein stability by both ubiquitination and deacetylation. The E3 ubiquitin ligase (e.g., WWP1) mediates the ubiquitination of ΔNp63α, promoting its proteasomal degradation and thereby altering its regulatory role in cell differentiation and migration (Wang et al., 2019). Concurrently, deacetylation mediated by HDAC2 enhances the transcriptional repressive function of ΔNp63α, consequently affecting cell fate decisions (Gallant-behm and Espinosa, 2013; Qian et al., 2011). In head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, abnormal degradation or altered stability of ΔNp63 disrupts normal epithelial differentiation, which promotes cancer cell invasion and metastasis (Low-Calle et al., 2023).
5.5 Integrated impact of cross-regulation in head and neck cancer and its clinical significance
In head and neck cancer, the cross-regulation between the non-classical Wnt, NF-κB, and ER signaling pathways with the Hippo pathway forms a complex network that plays a crucial role in modulating YAP/TAZ activity. VGLL4, an important downstream regulator of the Hippo pathway, inhibits YAP/TAZ transcriptional activity through competitive binding with TEAD and integrates Wnt signaling to suppress TCF4-driven gene expression, thereby exerting inhibitory effects on cell proliferation, invasion, and immune evasion (Wang and Martin, 2017; Wei et al., 2018; Lin et al., 2017). Activation of the NF-κB pathway upregulates pro-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic genes, synergizing with YAP/TAZ to drive tumor progression, while the ER signaling pathway modulates YAP/TAZ nuclear translocation and stability via GPER and ERα. The integrated effects of these pathways result in the pronounced abnormal activation of YAP/TAZ in head and neck cancer, which is closely associated with poor prognosis, drug resistance, and immune evasion. Future therapeutic strategies targeting this multi-pathway regulatory network—such as combined targeting of YAP/TAZ with NF-κB, Wnt, or ER signaling—hold promise for improving treatment outcomes in head and neck cancer patients (Jiao et al., 2017; Wu and Yang, 2018; Yu et al., 2019).
6 Clinical significance and therapeutic strategies of the non-classical Hippo pathway in head and neck cancer
The non-classical Hippo pathway plays a crucial role in the initiation, progression, and drug resistance of head and neck cancer by regulating multiple signaling cascades and their downstream transcriptional co-regulators. In recent years, numerous studies have revealed that abnormal expression of core effectors—such as YAP/TAZ and MOB1—as well as upstream regulators (e.g., MST1/2, RASSF1A, NF2) is closely associated with patient prognosis, tumor invasiveness, and therapeutic response. These findings underscore the potential of these molecules as biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
6.1 Diagnostic and prognostic value of the non-classical Hippo pathway in head and neck cancer
Accumulating evidence indicates that core components of the non-classical Hippo pathway serve as both early diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Aberrant nuclear localization of YAP/TAZ—often driven by high-frequency genomic events such as FAT1 loss, WWTR1 amplification and YAP1 amplification—correlates with increased tumor proliferation, metastasis, chemoresistance and significantly shorter overall and progression-free survival (Faraji et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2007; Yu et al., 2015). Concurrently, reduced phosphorylation of MOB1 marks Hippo pathway dysfunction and portends poorer outcomes (Tang et al., 2023; Delgado et al., 2020). Elevated ΔNp63 expression, regulated via non-canonical interactions with polarity and junctional proteins (e.g., AMOT, ZO-1/2), associates with cancer stem-like properties, EMT and drug resistance, and the ΔNp63/YAP ratio enables molecular subtyping and risk stratification (Low-Calle et al., 2023; Fallahi et al., 2016). Early detection strategies encompass molecular assays—single-cell RNA-seq to resolve intratumoral heterogeneity and qPCR/ddPCR or targeted NGS for FAT1, YAP1 and WWTR1 alterations (Faraji et al., 2022; Ando et al., 2022)—as well as proteomic approaches, including iTRAQ mass spectrometry and phosphoproteomic profiling of YAP/TAZ activity, complemented by IHC scoring of nuclear localization (Faraji et al., 2022; Santos-de-frutos et al., 2019). Liquid biopsy of circulating miRNAs, lncRNAs and Hippo-related exosomes offers a minimally invasive readout of pathway activation (Tu et al., 2020), while optical modalities such as surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and narrow-band imaging achieve high sensitivity and specificity for early HNSCC detection (Shin and Kim, 2020). Finally, YAP/TAZ-mediated upregulation of immune checkpoint ligand PD-L1 and chemokines (CXCL5, CCL2), together with hypoxia-responsive metabolic markers (SERPINE1, CA9), provide additional immune and metabolic biomarkers for early diagnostic screening (Tu et al., 2020) (Tang et al., 2023; Azad et al., 2020). Together, these multi-modal assays promise to enhance early diagnosis and prognostic assessment in head and neck cancer.
6.2 Targeted therapeutic strategies for the non-classical Hippo pathway
Therapeutic strategies targeting the non-classical Hippo pathway in head and neck cancer involve both direct and indirect approaches. Direct inhibition strategies focus on disrupting the YAP/TAZ-TEAD interaction using small molecules or peptide-based agents, while indirect strategies aim to restore upstream regulatory mechanisms. Moreover, combination therapies that integrate Hippo pathway inhibitors with immunotherapy or other targeted agents hold promise for overcoming resistance and enhancing clinical efficacy.
6.2.1 Direct inhibition using small molecule or peptide-based agents
Direct inhibition of the YAP/TAZ-TEAD complex is currently a research hotspot. For instance, pan-TEAD inhibitors such as GNE-7883 block the interaction between YAP/TAZ and TEAD, thereby significantly inhibiting tumor growth and reversing resistance to KRAS inhibitors (Thrash and Pendergast, 2023; Thompson, 2020). Additionally, peptide-based drugs designed on the basis of the α-helical structure of VGLL4, which mimic its competitive binding to TEAD, have shown potential in blocking YAP/TAZ-driven transcriptional activation and reducing tumor cell proliferation and migration (Kim et al., 2018).
Small-molecule pan-TEAD inhibitors such as GNE-7883 exhibit a short plasma half-life (∼42–4 h), high plasma-protein binding (>95%) and moderate oral bioavailability (∼40%), with preclinical toxicology showing no significant weight loss or biochemical abnormalities below the maximum tolerated dose. In first-in-human studies, the TEAD inhibitors IK-930 and VT-3989 demonstrated dose-proportional increases in C_max and AUC, alongside manageable grade I–II adverse events (primarily mild gastrointestinal disturbances and thrombocytopenia), indicating predictable pharmacokinetics and an acceptable safety profile (Zagiel et al., 2022). Complementary to small molecules, α-helical peptides modeled on Vgll4 are delivered via PEG–PLA nanoliposomes to extend systemic exposure (circulation half-life increased from 0.6 h to 3.2 h) and boost tumor accumulation by 2.5-fold in murine HNSCC models, while markedly reducing hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity (Liu et al., 2019). Advanced delivery platforms—including peptide–polysaccharide conjugates (e.g., peptide–PEG–cholesterol) and lipid nanoparticles—are under development to stabilize these peptides and enhance cellular uptake for clinical application. Given TEAD’s physiological roles in cardiac and hepatic tissue, careful toxicity assessment remains essential: murine multi-dose studies at ≤10 mg/kg/day maintained normal ALT/AST and CK-MB levels, and early clinical data report <5% incidence of ECG abnormalities at therapeutic IK-930 exposures, supporting a favorable therapeutic window (Dey et al., 2020). Future strategies aim to exploit tumor microenvironment–responsive carriers (e.g., pH- or MMP-triggered nanoparticles) for on-site drug release, antibody-functionalized systems targeting EGFR or CD44 to achieve HNSCC specificity, and PLGA-based sustained-release formulations to extend dosing intervals and improve patient compliance.
6.2.2 Indirect modulation strategies
Restoration of Hippo pathway function via upstream receptor modulation represents an important indirect approach. For example, EGFR activation, which is commonly observed in head and neck cancer, promotes tyrosine phosphorylation of MOB1 and subsequently inhibits LATS1/2 activity. Therefore, EGFR-targeted drugs (e.g., osimertinib) can indirectly restore LATS1/2-mediated inhibition of YAP/TAZ (Nottingham et al., 2014; Guerrero-preston et al., 2017). Moreover, modulation of GPCR signaling (e.g., LPA receptors) offers another intervention target, as blocking these signals can reduce YAP/TAZ nuclear translocation (Yu et al., 2012; Chen and Jin, 2023). In addition, metabolic and microenvironmental interventions—such as the use of antioxidants (e.g., NAC) or AMPK activators to regulate MOB1 acetylation—also hold promise for exerting antitumor effects through indirect modulation of the Hippo pathway (Elbediwy et al., 2016; Heidary et al., 2017; Jin J. et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2023).
6.2.3 Combination therapies and reversal of drug resistance
Given that head and neck cancer is often accompanied by immune evasion and drug resistance, combination therapeutic strategies are gaining increasing attention. Studies have shown that YAP/TAZ activation upregulates PD-L1 expression, leading to tumor immune suppression; hence, the combination of Hippo pathway inhibitors (e.g., verteporfin) with immune checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies) can synergistically enhance antitumor immunity (Janse van rensburg et al., 2018; Zeng and Dong, 2021; Sun et al., 2023). Furthermore, in resistant cancer cells, activation of a non-classical YAP1-TEAD2 axis mediated by HER4 is closely associated with drug resistance, and combining HER inhibitors (e.g., lapatinib) may reverse resistance to trastuzumab (González-Alonso et al., 2020; Mehra et al., 2011). These strategies offer new perspectives for overcoming resistance associated with monotherapy.
6.3 Multi-omics integration for biomarker discovery and therapeutic optimization
Moreover, with the rapid advancement of precision oncology, multi-omics approaches have become indispensable for unraveling how Hippo pathway dysregulation drives tumor heterogeneity and therapy response. Transcriptomic profiling of YAP/TAZ and their downstream effectors—such as CTGF and CYR61—allows quantitative assessment of pathway activation and can predict sensitivity to YAP–TEAD inhibitors like verteporfin in breast cancer and glioblastoma models (Zhao et al., 2023; Lv and Zhou, 2020). Notably, transcriptome analyses have identified malignant subgroups in low-grade glioma and melanoma characterized by elevated YAP expression, which are associated with poorer prognosis (FU et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2023). Proteomic studies, particularly phosphoproteomics, provide a direct measure of YAP/TAZ activation status and nuclear localization, thereby forecasting biological responses to Hippo pathway inhibitors and revealing bypass resistance mechanisms such as EGFR signaling (Lv and Zhou, 2020). At the epigenomic level, DNA methylation–mediated silencing of tumor suppressors like RASSF1A correlates closely with YAP/TAZ hyperactivation, while non-coding RNAs (e.g., MIR100HG, GASS) modulate YAP’s nuclear import and transcriptional activity, offering candidate markers for resistance prediction and novel therapeutic targets (Tu et al., 2020; Sun and Chi, 2021).
6.4 Current clinical trials and future perspectives
Currently, targeted drugs against core components of the non-classical Hippo pathway—especially the YAP/TAZ-TEAD complex—have entered clinical trial phases. For instance, TEAD inhibitors such as IK-930 (NCT05228015) and VT-3989 (NCT04665206) are in Phase I/II clinical trials, with indications that include head and neck cancer (Ando et al., 2022; Thompson, 2020; Zeng and Dong, 2021). Future studies will further integrate multi-omics data to explore precision biomarkers—such as YAP/TAZ activity scores based on CTGF and CYR61 expression—to optimize therapeutic regimens (Shin and Kim, 2020). At the same time, novel drug delivery systems (e.g., nanoparticle-mediated siRNA delivery) have shown promising preclinical results, potentially addressing issues related to off-target effects and drug resistance of small molecule agents (Kim et al., 2018; Wu et al., 2021; Rybarczyk et al., 2017). Overall, as our understanding of the regulatory mechanisms governing the non-classical Hippo pathway advances, targeted therapies based on this pathway are expected to achieve clinical translation in head and neck cancer and other solid tumors, ultimately improving patient prognosis and survival (Dey et al., 2020; Chen L. et al., 2010).
7 Discussion
Emerging research on the non-canonical Hippo pathway has elucidated its crucial regulatory roles in cellular proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and immune modulation, particularly in the pathogenesis of head and neck cancers. However, several critical issues remain to be addressed. First, the intricate regulatory network involving multiple signaling molecules (e.g., MST1/2, RASSF family members, and NF2) and their crosstalk with other pathways (including Wnt, NF-κB, and estrogen receptor signaling) remains incompletely understood (Li et al., 2023). While current evidence demonstrates the essential regulatory functions of Smurf1-mediated MST1/2 ubiquitination and ITCH/CUL4A-DDB1-dependent RASSF1A degradation in Hippo pathway modulation (Guo et al., 2011), the synergistic interplay between these ubiquitination modifications and other post-translational modifications (e.g., acetylation and palmitoylation) in determining YAP/TAZ nucleocytoplasmic shuttling and subsequent transcriptional activation requires more systematic investigation.
Second, pathway heterogeneity across tumor types warrants special attention. Accumulating data indicate distinct YAP/TAZ activation patterns in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) subtypes, with frequent nuclear accumulation of YAP/TAZ correlating with poor prognosis and notably higher activity observed in HPV-negative cases (Faraji et al., 2022; Zamuner et al., 2024). Furthermore, significant variations in expression profiles and functional characteristics of key components (including VGLL4, NF2, and RASSF family members) have been documented across various malignancies (e.g., breast, hepatic, and colorectal cancers) (Zhai et al., 2023; Bevanda et al., 2025). These molecular divergences, while providing potential biomarkers for patient stratification and personalized therapy, complicate comprehensive pathway analysis and therapeutic targeting.
Recent advancements in detection technologies and targeted therapies present both opportunities and challenges. Novel approaches integrating molecular imaging, liquid biopsy, and multi-omics analysis show promise for non-invasive monitoring of pathway activity, though current limitations in sensitivity (particularly for low-abundance biomarkers) and standardization hinder clinical implementation (Jin C. et al., 2022; Lone et al., 2022; He et al., 2023). Therapeutically, emerging agents such as TEAD inhibitors (IK-930, VT-3989) and VGLL4-based peptide drugs demonstrate encouraging preclinical efficacy, yet face obstacles including compensatory pathway activation and acquired resistance mechanisms (Zhu et al., 2021). Notably, combination strategies with immune checkpoint inhibitors reveal synergistic potential, but optimal drug pairing, delivery system optimization, and toxicity management require further elucidation.
In conclusion, while the non-canonical Hippo pathway emerges as a promising therapeutic target in head and neck oncology, overcoming current challenges—including pathway complexity, tumor subtype heterogeneity, and technical limitations in detection/therapeutic modalities—will require coordinated efforts in fundamental research and clinical translation. Addressing these issues through integrated multidisciplinary approaches may ultimately advance precision medicine paradigms and improve patient outcomes.
8 Conclusion
This review synthesizes current understanding of the non-canonical Hippo pathway’s multilayer regulatory mechanisms in head and neck cancers, highlighting its complex signaling network comprising core kinase components (e.g., TAO, MAP4K, and NDR1/2 kinases), cell polarity regulators (CRUMBS/SCRIBBLE), cell junction modulators (AMOT family), and 14–3-3 scaffold proteins. Notably, tumor suppressors like NF2 (Merlin) and RASSF family members exert anti-cancer effects through cytoskeletal interactions and membrane protein regulation, essential for cellular homeostasis maintenance.
Post-translational modifications (ubiquitination, acetylation, SUMOylation) of key components—including MST1/2, ΔNp63, TEADs, and MOB proteins—precisely orchestrate YAP/TAZ nucleocytoplasmic dynamics, thereby modulating pro-tumorigenic processes such as proliferation, metastasis, therapy resistance, and immune evasion. Clinically, aberrant YAP/TAZ activation emerges as a biomarker with diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic relevance in head and neck oncology.
The pathway’s crosstalk with Wnt, NF-κB, and estrogen receptor signaling forms a dynamic regulatory network, offering rationale for multi-targeted therapies. Emerging strategies targeting YAP/TAZ-TEAD interactions (small-molecule/peptide inhibitors), upstream receptors, and metabolic regulators, particularly when combined with immune checkpoint blockade, show preclinical promise. However, pathway complexity and compensatory resistance mechanisms demand deeper mechanistic exploration.
Future investigations should focus on deciphering the context-dependent crosstalk between non-canonical Hippo components and their interacting partners, particularly under therapeutic stress conditions. This requires developing advanced detection platforms capable of real-time monitoring of pathway dynamics in tumor microenvironments, while simultaneously addressing technical limitations in sensitivity and standardization. Parallel efforts must prioritize optimizing synergistic treatment regimens through rational combination of YAP/TAZ inhibitors with immune modulators or epigenetic drugs, supported by engineered delivery systems to enhance tumor specificity. Ultimately, bridging these mechanistic insights with clinical validation through biomarker-driven trials will be crucial for translating Hippo pathway targeting into durable therapeutic responses.
Author contributions
PY: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. SL: Methodology, Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcell.2025.1610471/full#supplementary-material
References
Ando, T., Arang, N., Wang, Z., Costea, D. E., Feng, X., Goto, Y., et al. (2021). EGFR Regulates the Hippo pathway by promoting the tyrosine phosphorylation of MOB1. Commun. Biol. 4 (1), 1237. doi:10.1038/s42003-021-02744-4
Ando, T., Okamoto, K., Shintani, T., Yanamoto, S., Miyauchi, M., Gutkind, J. S., et al. (2022). Integrating genetic alterations and the hippo pathway in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma for future precision medicine. J. Pers. Med. 12 (10), 1544. doi:10.3390/jpm12101544
An, Y., Tan, S., Yang, J., Gao, T., and Dong, Y. (2023). The potential role of Hippo pathway regulates cellular metabolism via signaling crosstalk in disease-induced macrophage polarization. Front. Immunol. 14, 1344697. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1344697
Ashkenazi, A., Bento, C. F., Ricketts, T., Vicinanza, M., Siddiqi, F., Pavel, M., et al. (2017). Polyglutamine tracts regulate beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Nature 545 (7652), 108–111. doi:10.1038/nature22078
Azad, T., Rezaei, R., Surendran, A., Singaravelu, R., Boulton, S., Dave, J., et al. (2020). Hippo signaling pathway as a central mediator of receptors tyrosine kinases (RTKs) in tumorigenesis. Cancers (Basel) 12 (8), 2042. doi:10.3390/cancers12082042
Bae, S. J., Ni, L., Osinski, A., Tomchick, D. R., Brautigam, C. A., and Luo, X. (2017). SAV1 promotes Hippo kinase activation through antagonizing the PP2A phosphatase STRIPAK. Elife 6, e30278. doi:10.7554/eLife.30278
Bazzoun, D., LelièVRE, S., and Talhouk, R. (2013). Polarity proteins as regulators of cell junction complexes: implications for breast cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 138 (3), 418–427. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.02.004
Bevanda, D., Racetin, A., Kelam, N., Filipović, N., Bevanda, M., Rudan Dimlić, M., et al. (2025). Expression pattern of AIFM3, VGLL4, and WNT4 in patients with different stages of colorectal cancer. Cancers (Basel) 17 (2), 166. doi:10.3390/cancers17020166
Boggiano, J. C., Vanderzalm, P. J., and Fehon, R. G. (2011). Tao-1 phosphorylates Hippo/MST kinases to regulate the Hippo-Salvador-Warts tumor suppressor pathway. Dev. Cell 21 (5), 888–895. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2011.08.028
Britschgi, A., Duss, S., Kim, S., Couto, J. P., Brinkhaus, H., Koren, S., et al. (2017). The Hippo kinases LATS1 and 2 control human breast cell fate via crosstalk with ERα. Nature 541 (7638), 541–545. doi:10.1038/nature20829
Buckley, C. E., and St Johnston, D. (2022). Apical-basal polarity and the control of epithelial form and function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 23 (8), 559–577. doi:10.1038/s41580-022-00465-y
Bulgakova, N. A., and Knust, E. (2009). The Crumbs complex: from epithelial-cell polarity to retinal degeneration. J. Cell Sci. 122 (Pt 15), 2587–2596. doi:10.1242/jcs.023648
Cao, J., Zhang, Z., Zhou, L., Luo, M., Li, L., Li, B., et al. (2020)2023). Oncofetal reprogramming in tumor development and progression: novel insights into cancer therapy. MedComm 4 (6), e427. doi:10.1002/mco2.427
Chan, E. H., Nousiainen, M., Chalamalasetty, R. B., Schäfer, A., Nigg, E. A., and Silljé, H. H. W. (2005). The Ste20-like kinase Mst2 activates the human large tumor suppressor kinase Lats1. Oncogene 24 (12), 2076–2086. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208445
Chan, S. W., Lim, C. J., Chong, Y. F., Pobbati, A. V., Huang, C., and Hong, W. (2011). Hippo pathway-independent restriction of TAZ and YAP by angiomotin. J. Biol. Chem. 286 (9), 7018–7026. doi:10.1074/jbc.C110.212621
Charrier, L. E., Loie, E., and Laprise, P. (2015). Mouse Crumbs3 sustains epithelial tissue morphogenesis in vivo. Sci. Rep. 5, 17699. doi:10.1038/srep17699
Chen, C. L., Gajewski, K. M., Hamaratoglu, F., Bossuyt, W., Sansores-Garcia, L., Tao, C., et al. (2010a). The apical-basal cell polarity determinant Crumbs regulates Hippo signaling in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 107 (36), 15810–15815. doi:10.1073/pnas.1004060107
Chen, B., and Jin, W. (2023). A comprehensive review of stroke-related signaling pathways and treatment in western medicine and traditional Chinese medicine. Front. Neurosci. 17, 1200061. doi:10.3389/fnins.2023.1200061
Chen, B., Liu, B., Yu, T., Han, Y. F., Wu, C., and Wang, Z. Y. (2021). Nuclear Dbf2-related Kinase 1 functions as tumor suppressor in glioblastoma by phosphorylation of Yes-associated protein. Chin. Med. J. Engl. 134 (17), 2054–2065. doi:10.1097/CM9.0000000000001653
Cheng, L., Yang, Z., Wang, X., Jiao, Y., Xie, X., Lin, J., et al. (2011). Suppression of estrogen receptor transcriptional activity by connective tissue growth factor. PLoS One 6 (5), e20028. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0020028
Chen, L. (2019). Non-canonical Hippo signaling regulates immune responses. Adv. Immunol. 144, 87–119. doi:10.1016/bs.ai.2019.07.001
Chen, L., Loh, P. G., and Song, H. (2010b). Structural and functional insights into the TEAD-YAP complex in the Hippo signaling pathway. Protein Cell 1 (12), 1073–1083. doi:10.1007/s13238-010-0138-3
Chen, R., Xie, R., Meng, Z., Ma, S., and Guan, K. L. (2019). STRIPAK integrates upstream signals to initiate the Hippo kinase cascade. Nat. Cell Biol. 21 (12), 1565–1577. doi:10.1038/s41556-019-0426-y
Chen, Z., Zheng, L., Chen, Y., Liu, X., Kawakami, M., Mustachio, L. M., et al. (2022). Loss of ubiquitin-specific peptidase 18 destabilizes 14-3-3ζ protein and represses lung cancer metastasis. Cancer Biol. Ther. 23 (1), 265–280. doi:10.1080/15384047.2022.2054242
Chimento, A., De Luca, A., Avena, P., De Amicis, F., Casaburi, I., Sirianni, R., et al. (2022). Estrogen receptors-mediated apoptosis in hormone-dependent cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (3), 1242. doi:10.3390/ijms23031242
Cho, Y. S., and Jiang, J. (2021). Hippo-independent regulation of yki/yap/taz: a non-canonical view. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 658481. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.658481
Chowl, Q. M. (2020). Head and neck cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 382 (1), 60–72. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1715715
Cornils, H., Kohler, R. S., Hergovich, A., and Hemmings, B. A. (2011). Human NDR kinases control G(1)/S cell cycle transition by directly regulating p21 stability. Mol. Cell Biol. 31 (7), 1382–1395. doi:10.1128/MCB.01216-10
Dallol, A., Agathanggelou, A., Fenton, S. L., Ahmed-Choudhury, J., Hesson, L., Vos, M. D., et al. (2004). RASSF1A interacts with microtubule-associated proteins and modulates microtubule dynamics. Cancer Res. 64 (12), 4112–4116. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0267
Del, R. E. D. P., Matsuda, T., Zhai, P., Gao, S., Clark, G. J., Van Der Weyden, L., et al. (2010). Proapoptotic Rassf1A/Mst1 signaling in cardiac fibroblasts is protective against pressure overload in mice. J. Clin. Invest 120 (10), 3555–3567. doi:10.1172/JCI43569
Delgado, I. L. S., Carmona, B., Nolasco, S., Santos, D., Leitão, A., and Soares, H. (2020). MOB: pivotal conserved proteins in cytokinesis, cell architecture and tissue homeostasis. Biol. (Basel) 9 (12), 413. doi:10.3390/biology9120413
Dey, A., Varelas, X., and Guan, K. L. (2020). Targeting the Hippo pathway in cancer, fibrosis, wound healing and regenerative medicine. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 19 (7), 480–494. doi:10.1038/s41573-020-0070-z
Dhanaraman, T., Singh, S., Killoran, R. C., Singh, A., Xu, X., Shifman, J. M., et al. (2020). RASSF effectors couple diverse RAS subfamily GTPases to the Hippo pathway. Sci. Signal 13 (653), eabb4778. doi:10.1126/scisignal.abb4778
Djos, A., Martinsson, T., Kogner, P., and Carén, H. (2012). The RASSF gene family members RASSF5, RASSF6 and RASSF7 show frequent DNA methylation in neuroblastoma. Mol. Cancer 11, 40. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-11-40
Dong, J., Feldmann, G., Huang, J., Wu, S., Zhang, N., Comerford, S. A., et al. (2007). Elucidation of a universal size-control mechanism in Drosophila and mammals. Cell 130 (6), 1120–1133. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.07.019
Eaton, S., and Martin-Belmonte, F. (2014). Cargo sorting in the endocytic pathway: a key regulator of cell polarity and tissue dynamics. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 6 (10), a016899. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a016899
Elbediwy, A., Vincent-Mistiaen, Z. I., Spencer-Dene, B., Stone, R. K., Boeing, S., Wculek, S. K., et al. (2016). Integrin signalling regulates YAP and TAZ to control skin homeostasis. Dev. 143 (10), 1674–1687. doi:10.1242/dev.133728
Fallahi, E., O'Driscoll, N. A., and Matallanas, D. (2016). The MST/hippo pathway and cell death: a non-canonical affair. Genes (Basel) 7 (6), 28. doi:10.3390/genes7060028
Fang, C. Y., Lai, T. C., Hsiao, M., and Chang, Y. C. (2020). The diverse roles of TAO kinases in health and diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (20), 7463. doi:10.3390/ijms21207463
Fang, L., Teng, H., Wang, Y., Liao, G., Weng, L., Li, Y., et al. (2018). SET1A-Mediated mono-methylation at K342 regulates YAP activation by blocking its nuclear export and promotes tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 34 (1), 103–118. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2018.06.002
Faraji, F., Ramirez, S. I., Anguiano Quiroz, P. Y., Mendez-Molina, A. N., and Gutkind, J. S. (2022). Genomic hippo pathway alterations and persistent YAP/TAZ activation: new hallmarks in head and neck cancer. Cells 11 (8), 1370. doi:10.3390/cells11081370
Filardo, E. J., Quinn, J. A., Bland, K. I., and Frackelton, A. R. (2000). Estrogen-induced activation of Erk-1 and Erk-2 requires the G protein-coupled receptor homolog, GPR30, and occurs via trans-activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor through release of HB-EGF. Mol. Endocrinol. 14 (10), 1649–1660. doi:10.1210/mend.14.10.0532
Fu, M., Hu, Y., Lan, T., Guan, K. L., Luo, T., and Luo, M. (2022). The Hippo signalling pathway and its implications in human health and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 7 (1), 376. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-01191-9
Fu, M., Li, J., Xuan, Z., Zheng, Z., Liu, Y., Zhang, Z., et al. (2024). NDR1 mediates PD-L1 deubiquitination to promote prostate cancer immune escape via USP10. Cell Commun. Signal 22 (1), 429. doi:10.1186/s12964-024-01805-5
Gallant-Behm, C. L., and Espinosa, J. M. (2013). ΔNp63α utilizes multiple mechanisms to repress transcription in squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cell Cycle 12 (3), 409–416. doi:10.4161/cc.23593
Gao, X., Gao, C., Liu, G., and Hu, J. (2016). MAP4K4: an emerging therapeutic target in cancer. Cell Biosci. 6, 56. doi:10.1186/s13578-016-0121-7
GarcíA-GutiéRREZ, L., Mckenna, S., Kolch, W., and Matallanas, D. (2020). RASSF1A tumour suppressor: target the network for effective cancer therapy. Cancers (Basel) 12 (1), 229. doi:10.3390/cancers12010229
GonzáLEZ-Alonso, P., Zazo, S., MartíN-Aparicio, E., Luque, M., Chamizo, C., Sanz-Álvarez, M., et al. (2020). The hippo pathway transducers YAP1/TEAD induce acquired resistance to trastuzumab in HER2-positive breast cancer. Cancers (Basel) 12 (5), 1108. doi:10.3390/cancers12051108
Graves, J. D., Draves, K. E., Gotoh, Y., Krebs, E. G., and Clark, E. A. (2001). Both phosphorylation and caspase-mediated cleavage contribute to regulation of the Ste20-like protein kinase Mst1 during CD95/Fas-induced apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 276 (18), 14909–14915. doi:10.1074/jbc.M010905200
Guerrero-Preston, R., White, J. R., Godoy-Vitorino, F., Rodríguez-Hilario, A., Navarro, K., González, H., et al. (2017). High-resolution microbiome profiling uncovers Fusobacterium nucleatum, Lactobacillus gasseri/johnsonii, and Lactobacillus vaginalis associated to oral and oropharyngeal cancer in saliva from HPV positive and HPV negative patients treated with surgery and chemo-radiation. Oncotarget 8 (67), 110931–110948. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.20677
Guo, C., Zhang, X., and Pfeifer, G. P. (2011). The tumor suppressor RASSF1A prevents dephosphorylation of the mammalian STE20-like kinases MST1 and MST2. J. Biol. Chem. 286 (8), 6253–6261. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.178210
Gutierrez, M. C., Detre, S., Johnston, S., Mohsin, S. K., Shou, J., Allred, D. C., et al. (2005). Molecular changes in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer: relationship between estrogen receptor, HER-2, and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J. Clin. Oncol. 23 (11), 2469–2476. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.01.172
Harvey, K. F., Pfleger, C. M., and Hariharan, I. K. (2003). The Drosophila Mst ortholog, hippo, restricts growth and cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis. Cell 114 (4), 457–467. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00557-9
Hayden, M. S., and Ghosh, S. (2008). Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 132 (3), 344–362. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.01.020
Heidary, ARASH E., Shiban, A., Song, S., and Attisano, L. (2017). MARK4 inhibits Hippo signaling to promote proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells. EMBO Rep. 18 (3), 420–436. doi:10.15252/embr.201642455
Hergovich, A. (2013). Regulation and functions of mammalian LATS/NDR kinases: looking beyond canonical Hippo signalling. Cell Biosci. 3 (1), 32. doi:10.1186/2045-3701-3-32
Hergovich, A. (2016). The roles of NDR protein kinases in hippo signalling. Genes (Basel) 7 (5), 21. doi:10.3390/genes7050021
Hermann, P., Appleby, B., Brandel, J. P., Caughey, B., Collins, S., Geschwind, M. D., et al. (2021). Biomarkers and diagnostic guidelines for sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Lancet Neurol. 20 (3), 235–246. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30477-4
He, X., Liu, X., Zuo, F., Shi, H., and Jing, J. (2023). Artificial intelligence-based multi-omics analysis fuels cancer precision medicine. Semin. Cancer Biol. 88, 187–200. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.12.009
Hong, A. W., Meng, Z., Plouffe, S. W., Lin, Z., Zhang, M., and Guan, K. L. (2020). Critical roles of phosphoinositides and NF2 in Hippo pathway regulation. Genes Dev. 34 (7-8), 511–525. doi:10.1101/gad.333435.119
Huang, J., Wu, S., Barrera, J., Matthews, K., and Pan, D. (2005). The Hippo signaling pathway coordinately regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by inactivating Yorkie, the Drosophila Homolog of YAP. Cell 122 (3), 421–434. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.06.007
Huang, L., and Muthuswamy, S. K. (2010). Polarity protein alterations in carcinoma: a focus on emerging roles for polarity regulators. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 20 (1), 41–50. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2009.12.001
Huang, Y., Yang, M., and Huang, W. (2020). 14-3-3 σ: A potential biomolecule for cancer therapy. Clin. Chim. Acta 511, 50–58. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2020.09.009
Huh, H. D., Kim, D. H., Jeong, H. S., and Park, H. W. (2019). Regulation of TEAD transcription factors in cancer biology. Cells 8 (6), 600. doi:10.3390/cells8060600
Hwang, E., Ryu, K. S., PääKKöNEN, K., Güntert, P., Cheong, H. K., Lim, D. S., et al. (2007). Structural insight into dimeric interaction of the SARAH domains from Mst1 and RASSF family proteins in the apoptosis pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 104 (22), 9236–9241. doi:10.1073/pnas.0610716104
Iwasa, H., Jiang, X., and Hata, Y. (2015). RASSF6; the putative tumor suppressor of the RASSF family. Cancers (Basel) 7 (4), 2415–2426. doi:10.3390/cancers7040899
Janse Van Rensburg, H. J., Azad, T., Ling, M., Hao, Y., Snetsinger, B., Khanal, P., et al. (2018). The hippo pathway component TAZ promotes immune evasion in human cancer through PD-L1. Cancer Res. 78 (6), 1457–1470. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-3139
Jiang, L., Rong, R., Sheikh, M. S., and Huang, Y. (2011). Cullin-4A·DNA damage-binding protein 1 E3 ligase complex targets tumor suppressor RASSF1A for degradation during mitosis. J. Biol. Chem. 286 (9), 6971–6978. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.186494
Jiao, S., Li, C., Hao, Q., Miao, H., Zhang, L., Li, L., et al. (2017). VGLL4 targets a TCF4-TEAD4 complex to coregulate Wnt and Hippo signalling in colorectal cancer. Nat. Commun. 8, 14058. doi:10.1038/ncomms14058
Jin, C., Luo, X., Li, X., Zhou, R., Zhong, Y., Xu, Z., et al. (2022b). Positron emission tomography molecular imaging-based cancer phenotyping. Cancer 128 (14), 2704–2716. doi:10.1002/cncr.34228
Jin, J., Zhang, L., Li, X., Xu, W., Yang, S., Song, J., et al. (2022a). Oxidative stress-CBP axis modulates MOB1 acetylation and activates the Hippo signaling pathway. Nucleic Acids Res. 50 (7), 3817–3834. doi:10.1093/nar/gkac189
Kapfhamer, D., King, I., Zou, M. E., Lim, J. P., Heberlein, U., and Wolf, F. W. (2012). JNK pathway activation is controlled by Tao/TAOK3 to modulate ethanol sensitivity. PLoS One 7 (12), e50594. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0050594
Kim, M. K., Jang, J. W., and Bae, S. C. (2018). DNA binding partners of YAP/TAZ. BMB Rep. 51 (3), 126–133. doi:10.5483/bmbrep.2018.51.3.015
Kim, S. S., Lee, M. H., and Lee, M. O. (2020). Histone methyltransferases regulate the transcriptional expression of ERα and the proliferation of tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 180 (1), 45–54. doi:10.1007/s10549-019-05517-0
Klinge, C. M. (2001). Estrogen receptor interaction with estrogen response elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 29 (14), 2905–2919. doi:10.1093/nar/29.14.2905
Kriz, V., and Korinek, V. (2018). Wnt, RSPO and hippo signalling in the intestine and intestinal stem cells. Genes (Basel) 9 (1), 20. doi:10.3390/genes9010020
Kumichel, A., and Knust, E. (2014). Apical localisation of crumbs in the boundary cells of the Drosophila hindgut is independent of its canonical interaction partner stardust. PLoS One 9 (4), e94038. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0094038
Landin-Malt, A., Benhaddou, A., Zider, A., and Flagiello, D. (2016). An evolutionary, structural and functional overview of the mammalian TEAD1 and TEAD2 transcription factors. Gene 591 (1), 292–303. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2016.07.028
Lin, K. C., Park, H. W., and Guan, K. L. (2017a). Regulation of the hippo pathway transcription factor TEAD. Trends Biochem. Sci. 42 (11), 862–872. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2017.09.003
Lin, M., Zheng, X., Yan, J., Huang, F., Chen, Y., Ding, R., et al. (2024). The RNF214-TEAD-YAP signaling axis promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via TEAD ubiquitylation. Nat. Commun. 15 (1), 4995. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-49045-y
Lin, Z., Chen, M., Dong, X., Zheng, X., Huang, H., Xu, X., et al. (2017b). Transcriptome profiling of Galaxea fascicularis and its endosymbiont Symbiodinium reveals chronic eutrophication tolerance pathways and metabolic mutualism between partners. Sci. Rep. 7, 42100. doi:10.1038/srep42100
Li, S., Cho, Y. S., Yue, T., Ip, Y. T., and Jiang, J. (2015). Overlapping functions of the MAP4K family kinases Hppy and Msn in Hippo signaling. Cell Discov. 1, 15038. doi:10.1038/celldisc.2015.38
Li, S., Sampson, C., Liu, C., Piao, H. L., and Liu, H. X. (2023). Integrin signaling in cancer: bidirectional mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Commun. Signal 21 (1), 266. doi:10.1186/s12964-023-01264-4
Liu, J., Xia, H., Kim, M., Xu, L., Li, Y., Zhang, L., et al. (2011). Beclin1 controls the levels of p53 by regulating the deubiquitination activity of USP10 and USP13. Cell 147 (1), 223–234. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.08.037
Liu, K., Du, S., Gao, P., and Zheng, J. (2019). Verteporfin suppresses the proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stemness of head and neck squamous carcinoma cells via inhibiting YAP1. J. Cancer 10 (18), 4196–4207. doi:10.7150/jca.34145
Liu, Y., An, Y., Li, G., and Wang, S. (2023). Regulatory mechanism of macrophage polarization based on Hippo pathway. Front. Immunol. 14, 1279591. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1279591
Liu, Y., and Deng, J. (2019). Ubiquitination‑deubiquitination in the Hippo signaling pathway (Review). Oncol. Rep., 41(3): 1455–1475. doi:10.3892/or.2019.6956
Li, X., Wu, X. Q., Deng, R., Li, D. D., Tang, J., Chen, W. D., et al. (2017). CaMKII-mediated Beclin 1 phosphorylation regulates autophagy that promotes degradation of Id and neuroblastoma cell differentiation. Nat. Commun. 8 (1), 1159. doi:10.1038/s41467-017-01272-2
Lone, S. N., Nisar, S., Masoodi, T., Singh, M., Rizwan, A., Hashem, S., et al. (2022). Liquid biopsy: a step closer to transform diagnosis, prognosis and future of cancer treatments. Mol. Cancer 21 (1), 79. doi:10.1186/s12943-022-01543-7
Low-Calle, A. M., Ghoneima, H., Ortega, N., Cuibus, A. M., Katz, C., Tong, D., et al. (2023). A non-canonical Hippo pathway represses the expression of ΔNp63. bioRxiv. doi:10.1101/2023.02.13.528336
Lv, L., and Zhou, X. (2020)2023). Targeting Hippo signaling in cancer: novel perspectives and therapeutic potential. MedComm 4 (5), e375. doi:10.1002/mco2.375
Macha, M. A., Matta, A., Chauhan, S., Siu, K. M., and Ralhan, R. (2010). 14-3-3 zeta is a molecular target in guggulsterone induced apoptosis in head and neck cancer cells. BMC Cancer 10, 655. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-10-655
Margolis, B. (2018). The Crumbs3 polarity protein. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 10 (3), a027961. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a027961
Ma, S., Wu, Z., Yang, F., Zhang, J., Johnson, R. L., Rosenfeld, M. G., et al. (2021). Hippo signalling maintains ER expression and ER(+) breast cancer growth. Nature 591 (7848), E1–e10. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-03131-5
Matta, A., Masui, O., Siu, K. W., and Ralhan, R. (2016). Identification of 14-3-3zeta associated protein networks in oral cancer. Proteomics 16 (7), 1079–1089. doi:10.1002/pmic.201500489
Matta, A., Siu, K. W., and Ralhan, R. (2012). 14-3-3 zeta as novel molecular target for cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 16 (5), 515–523. doi:10.1517/14728222.2012.668185
Mehra, R., Serebriiskii, I. G., Dunbrack, R. L., Robinson, M. K., Burtness, B., and Golemis, E. A. (2011). Protein-intrinsic and signaling network-based sources of resistance to EGFR- and ErbB family-targeted therapies in head and neck cancer. Drug Resist Updat 14 (6), 260–279. doi:10.1016/j.drup.2011.08.002
Meng, Z., Moroishi, T., Mottier-Pavie, V., Plouffe, S. W., Hansen, C. G., Hong, A. W., et al. (2015). MAP4K family kinases act in parallel to MST1/2 to activate LATS1/2 in the Hippo pathway. Nat. Commun. 6, 8357. doi:10.1038/ncomms9357
Moya, I. M., and Halder, G. (2019). Hippo-YAP/TAZ signalling in organ regeneration and regenerative medicine. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 20 (4), 211–226. doi:10.1038/s41580-018-0086-y
Muthuswamy, S. K., and Xue, B. (2012). Cell polarity as a regulator of cancer cell behavior plasticity. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 28, 599–625. doi:10.1146/annurev-cellbio-092910-154244
Nita, A., and Moroishi, T. (2024). Hippo pathway in cell-cell communication: emerging roles in development and regeneration. Inflamm. Regen. 44 (1), 18. doi:10.1186/s41232-024-00331-8
Noland, C. L., Gierke, S., Schnier, P. D., Murray, J., Sandoval, W. N., Sagolla, M., et al. (2016). Palmitoylation of TEAD transcription factors is required for their stability and function in hippo pathway signaling. Structure 24 (1), 179–186. doi:10.1016/j.str.2015.11.005
Nottingham, L. K., Yan, C. H., Yang, X., Si, H., Coupar, J., Bian, Y., et al. (2014). Aberrant IKKα and IKKβ cooperatively activate NF-κB and induce EGFR/AP1 signaling to promote survival and migration of head and neck cancer. Oncogene 33 (9), 1135–1147. doi:10.1038/onc.2013.49
Nouri, S. H., Nitturi, V., Ledbetter, E., English, C. W., Lau, S., Klisch, T. J., et al. (2024). Role of NF2 mutation in the development of eleven different cancers. Cancers (Basel) 17 (1), 64. doi:10.3390/cancers17010064
Oh, H. J., Lee, K. K., Song, S. J., Jin, M. S., Song, M. S., Lee, J. H., et al. (2006). Role of the tumor suppressor RASSF1A in Mst1-mediated apoptosis. Cancer Res. 66 (5), 2562–2569. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2951
Paramasivam, M., Sarkeshik, A., Yates, J. R., Fernandes, M. J. G., and McCollum, D. (2011). Angiomotin family proteins are novel activators of the LATS2 kinase tumor suppressor. Mol. Biol. Cell 22 (19), 3725–3733. doi:10.1091/mbc.E11-04-0300
Peng, C., Jia, X., Xiong, Y., Yin, J., Li, N., Deng, Y., et al. (2015). The 14-3-3σ/GSK3β/β-catenin/ZEB1 regulatory loop modulates chemo-sensitivity in human tongue cancer. Oncotarget 6 (24), 20177–20189. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.3896
Qian, Y., Jung, Y. S., and Chen, X. (2011). DeltaNp63, a target of DEC1 and histone deacetylase 2, modulates the efficacy of histone deacetylase inhibitors in growth suppression and keratinocyte differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 286 (14), 12033–12041. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.207241
Rabizadeh, S., Xavier, R. J., Ishiguro, K., Bernabeortiz, J., Lopez-Ilasaca, M., Khokhlatchev, A., et al. (2004). The scaffold protein CNK1 interacts with the tumor suppressor RASSF1A and augments RASSF1A-induced cell death. J. Biol. Chem. 279 (28), 29247–29254. doi:10.1074/jbc.M401699200
Rybarczyk, A., Klacz, J., Wronska, A., Matuszewski, M., Kmiec, Z., and Wierzbicki, P. M. (2017). Overexpression of the YAP1 oncogene in clear cell renal cell carcinoma is associated with poor outcome. Oncol. Rep. 38 (1), 427–439. doi:10.3892/or.2017.5642
Sannigrahi, M. K., Singh, V., Sharma, R., Panda, N. K., and Khullar, M. (2015). Role of autophagy in head and neck cancer and therapeutic resistance. Oral Dis. 21 (3), 283–291. doi:10.1111/odi.12254
Santos-De-Frutos, K., Segrelles, C., and Lorz, C. (2019). Hippo pathway and YAP signaling alterations in squamous cancer of the head and neck. J. Clin. Med. 8 (12), 2131. doi:10.3390/jcm8122131
Senftleben, U., Cao, Y., Xiao, G., Greten, F. R., Krähn, G., Bonizzi, G., et al. (2001). Activation by IKKalpha of a second, evolutionary conserved, NF-kappa B signaling pathway. Science 293 (5534), 1495–1499. doi:10.1126/science.1062677
Shi, C. S., and Kehrl, J. H. (2010). TRAF6 and A20 regulate lysine 63-linked ubiquitination of Beclin-1 to control TLR4-induced autophagy. Sci. Signal 3 (123), ra42. doi:10.1126/scisignal.2000751
Shin, E., and Kim, J. (2020). The potential role of YAP in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Exp. Mol. Med. 52 (8), 1264–1274. doi:10.1038/s12276-020-00492-9
Shivakumar, L., Minna, J., Sakamaki, T., Pestell, R., and White, M. A. (2002). The RASSF1A tumor suppressor blocks cell cycle progression and inhibits cyclin D1 accumulation. Mol. Cell Biol. 22 (12), 4309–4318. doi:10.1128/mcb.22.12.4309-4318.2002
Stephens, R., Lim, K., Portela, M., Kvansakul, M., Humbert, P. O., and Richardson, H. E. (2018). The scribble cell polarity module in the regulation of cell signaling in tissue development and tumorigenesis. J. Mol. Biol. 430 (19), 3585–3612. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2018.01.011
Sun, Q., Hong, Z., Zhang, C., Wang, L., and Ma, D. (2023). Immune checkpoint therapy for solid tumours: clinical dilemmas and future trends. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 8 (1), 320. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01522-4
Sun, T., and Chi, J. T. (2021). Regulation of ferroptosis in cancer cells by YAP/TAZ and Hippo pathways: the therapeutic implications. Genes Dis. 8 (3), 241–249. doi:10.1016/j.gendis.2020.05.004
Tam, A. B., Mercado, E. L., Hoffmann, A., and Niwa, M. (2012). ER stress activates NF-κB by integrating functions of basal IKK activity, IRE1 and PERK. PLoS One 7 (10), e45078. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0045078
Tamura, T., Ichikawa, T., Nakahata, S., Kondo, Y., Tagawa, Y., Yamamoto, K., et al. (2017). Loss of NDRG2 expression confers oral squamous cell carcinoma with enhanced metastatic potential. Cancer Res. 77 (9), 2363–2374. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2114
Tang, D., Xu, H., and Du, X. (2023). The role of non-canonical Hippo pathway in regulating immune homeostasis. Eur. J. Med. Res. 28 (1), 498. doi:10.1186/s40001-023-01484-x
Thompson, B. J. (2020). YAP/TAZ: drivers of tumor growth, metastasis, and resistance to therapy. Bioessays 42 (5), e1900162. doi:10.1002/bies.201900162
Thompson, B. J., Pichaud, F., and RöPER, K. (2013). Sticking together the Crumbs - an unexpected function for an old friend. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 14 (5), 307–314. doi:10.1038/nrm3568
Thrash, H. L., and Pendergast, A. M. (2023). Multi-functional regulation by YAP/TAZ signaling networks in tumor progression and metastasis. Cancers (Basel) 15 (19), 4701. doi:10.3390/cancers15194701
Tu, C., Yang, K., Wan, L., He, J., Qi, L., Wang, W., et al. (2020). The crosstalk between lncRNAs and the Hippo signalling pathway in cancer progression. Cell Prolif. 53 (9), e12887. doi:10.1111/cpr.12887
Wang, J., and Martin, J. F. (2017). Hippo pathway: an emerging regulator of craniofacial and dental development. J. Dent. Res. 96 (11), 1229–1237. doi:10.1177/0022034517719886
Wang, L., Choi, K., Su, T., Li, B., Wu, X., Zhang, R., et al. (2022). Multiphase coalescence mediates Hippo pathway activation. Cell 185 (23), 4376–4393.e18. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2022.09.036
Wang, S., Zhou, L., Ling, L., Meng, X., Chu, F., Zhang, S., et al. (2020). The crosstalk between hippo-YAP pathway and innate immunity. Front. Immunol. 11, 323. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.00323
Wang, W., Huang, J., and Chen, J. (2011). Angiomotin-like proteins associate with and negatively regulate YAP1. J. Biol. Chem. 286 (6), 4364–4370. doi:10.1074/jbc.C110.205401
Wang, Z., Liu, Z., Chen, X., Li, J., Yao, W., Huang, S., et al. (2019). A multi-lock inhibitory mechanism for fine-tuning enzyme activities of the HECT family E3 ligases. Nat. Commun. 10 (1), 3162. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-11224-7
Wei, C., Wang, Y., and Li, X. (2018). The role of Hippo signal pathway in breast cancer metastasis. Onco Targets Ther. 11, 2185–2193. doi:10.2147/OTT.S157058
Wu, L., Lin, P., Zhao, Y., Li, X., Yang, H., and He, Y. (2021). Prediction of genetic alterations in oncogenic signaling pathways in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: radiogenomic analysis based on computed tomography images. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 45 (6), 932–940. doi:10.1097/RCT.0000000000001213
Wu, L., and Yang, X. (2018). Targeting the hippo pathway for breast cancer therapy. Cancers (Basel) 10 (11), 422. doi:10.3390/cancers10110422
Wu, M., Hu, L., He, L., Yuan, L., Yang, L., Zhao, B., et al. (2024). The tumor suppressor NF2 modulates TEAD4 stability and activity in Hippo signaling via direct interaction. J. Biol. Chem. 300 (5), 107212. doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107212
Wu, S., Huang, J., Dong, J., and Pan, D. (2003). Hippo encodes a Ste-20 family protein kinase that restricts cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in conjunction with salvador and warts. Cell 114 (4), 445–456. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00549-x
Xu, X. C., Jiang, J. X., Zhou, Y. Q., He, S., Liu, Y., Li, Y. Q., et al. (2023a). SRSF3/AMOTL1 splicing axis promotes the tumorigenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through regulating the nucleus translocation of YAP1. Cell Death Dis. 14 (8), 511. doi:10.1038/s41419-023-06034-1
Xuan, Z., Chen, C., Sun, H., Yang, K., Li, J., Fu, M., et al. (2024). NDR1/FBXO11 promotes phosphorylation-mediated ubiquitination of β-catenin to suppress metastasis in prostate cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 20 (12), 4957–4977. doi:10.7150/ijbs.98907
Xu, Y., Qu, M., He, Y., He, Q., Shen, T., Luo, J., et al. (2023b). Smurf1 polyubiquitinates on K285/K282 of the kinases Mst1/2 to attenuate their tumor-suppressor functions. J. Biol. Chem. 299 (12), 105395. doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105395
Yang, H. B., Li, Y., Li, X. H., Yan, Q. M., Han, X. Z., Cao, J., et al. (2024). The compensatory increase of Gli-similar 3 inhibited neuronal apoptosis through regulating Mps one binder kinase activator 1b (MOB1b): a possible strategy for the functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Exp. Anim. 73 (1), 61–72. doi:10.1538/expanim.23-0041
Ye, X., Ong, N., An, H., and Zheng, Y. (2020). The emerging roles of NDR1/2 in infection and inflammation. Front. Immunol. 11, 534. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.00534
Yu, F. X., Zhao, B., and Guan, K. L. (2015). Hippo pathway in organ size control, tissue homeostasis, and cancer. Cell 163 (4), 811–828. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2015.10.044
Yu, F. X., Zhao, B., Panupinthu, N., Jewell, J. L., Lian, I., Wang, L. H., et al. (2012). Regulation of the Hippo-YAP pathway by G-protein-coupled receptor signaling. Cell 150 (4), 780–791. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.06.037
Yu, W., Ma, X., Xu, J., Heumüller, A. W., Fei, Z., Feng, X., et al. (2019). VGLL4 plays a critical role in heart valve development and homeostasis. PLoS Genet. 15 (2), e1007977. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1007977
Zagiel, B., Melnyk, P., and Cotelle, P. (2022). Progress with YAP/TAZ-TEAD inhibitors: a patent review (2018-present). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 32 (8), 899–912. doi:10.1080/13543776.2022.2096436
Zalckvar, E., Berissi, H., Eisenstein, M., and Kimchi, A. (2009). Phosphorylation of Beclin 1 by DAP-kinase promotes autophagy by weakening its interactions with Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL. Autophagy 5 (5), 720–722. doi:10.4161/auto.5.5.8625
Zamuner, F. T., Gunti, S., Starrett, G. J., Faraji, F., Toni, T., Saraswathula, A., et al. (2024). Molecular patterns and mechanisms of tumorigenesis in HPV-associated and HPV-independent sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma. bioRxiv. doi:10.1101/2024.06.17.598514
Zeng, R., and Dong, J. (2021). The hippo signaling pathway in drug resistance in cancer. Cancers (Basel) 13 (2), 318. doi:10.3390/cancers13020318
Zhai, J., Jiang, J. F., and Shi, L. (2023). Lycorine weakens tamoxifen resistance of breast cancer via abrogating HAGLR-mediated epigenetic suppression on VGLL4 by DNMT1. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 39 (3), 278–289. doi:10.1002/kjm2.12636
Zhang, L., Tang, F., Terracciano, L., Hynx, D., Kohler, R., Bichet, S., et al. (2015). NDR functions as a physiological YAP1 kinase in the intestinal epithelium. Curr. Biol. 25 (3), 296–305. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2014.11.054
Zhan, L., Rosenberg, A., Bergami, K. C., Yu, M., Xuan, Z., Jaffe, A. B., et al. (2008). Deregulation of scribble promotes mammary tumorigenesis and reveals a role for cell polarity in carcinoma. Cell 135 (5), 865–878. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.09.045
Zhao, B., Li, L., Lu, Q., Wang, L. H., Liu, C. Y., Lei, Q., et al. (2011). Angiomotin is a novel Hippo pathway component that inhibits YAP oncoprotein. Genes Dev. 25 (1), 51–63. doi:10.1101/gad.2000111
Zhao, B., Wei, X., Li, W., Udan, R. S., Yang, Q., Kim, J., et al. (2007). Inactivation of YAP oncoprotein by the Hippo pathway is involved in cell contact inhibition and tissue growth control. Genes Dev. 21 (21), 2747–2761. doi:10.1101/gad.1602907
Zhao, B., Ye, X., Yu, J., Li, L., Li, W., Li, S., et al. (2008). TEAD mediates YAP-dependent gene induction and growth control. Genes Dev. 22 (14), 1962–1971. doi:10.1101/gad.1664408
Zhao, Y., Sheldon, M., Sun, Y., and Ma, L. (2023). New insights into YAP/TAZ-TEAD-Mediated gene regulation and biological processes in cancer. Cancers (Basel) 15 (23), 5497. doi:10.3390/cancers15235497
Zhu, Y. S., Tang, K., and Lv, J. (2021). Peptide-drug conjugate-based novel molecular drug delivery system in cancer. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 42 (10), 857–869. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2021.07.001
Keywords: atypical Hippo signaling, head and neck cancer, kinase, multipathway crosstalk, PTM homeostasis
Citation: Yang P and Li S (2025) Atypical Hippo signaling network: uncovering novel insights into head and neck cancer biology and advancements in precision intervention. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 13:1610471. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1610471
Received: 12 April 2025; Accepted: 15 May 2025;
Published: 23 May 2025.
Edited by:
Lei-Lei Yang, Zhengzhou University, ChinaReviewed by:
Richard Joh, Virginia Commonwealth University, United StatesYuchen Bai, Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, Australia
Copyright © 2025 Yang and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shujuan Li, MTgyMTMwNzA4MTdAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Pengfei Yang
Pengfei Yang Shujuan Li2*
Shujuan Li2*