Abstract
Progesterone (P4) is essential for pregnancy establishment and maintenance. Clinically, P4 is widely used to regulate the menstrual cycle, maintain pregnancy, and treat luteal phase deficiency. However, P4 administration protocols, particularly regarding routes, dosage, and timing remain poorly defined. Although excessive P4 impairs embryo implantation and decidualization in mice, the underlying mechanism remains unclear. Our data show that decidualization in day 8 pregnant mice and artificial decidualization in day 8 pseudopregnant mice are impaired by 4 mg or 8 mg/mouse P4. The mRNA levels of Prl8a2 and Prl3c1, markers of in vitro decidualization are significantly downregulated by 10 or 20 μM P4. The uterine fluorescent signal of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) and protein levels of tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO) are increased after ovariectomized mice are treated with excessive P4. Treatment of uterine stromal cells with excessive P4 also significantly upregulates the protein levels of IDO1 and TDO, and kynurenine (Kyn) secretion. Epacadostat (IDO1 antagonist) or RU486 (progesterone receptor antagonist) effectively block P4-induced Kyn elevation. The mRNA levels of Prl8a2 and Prl3c1 and the protein levels of BMP2 are significantly inhibited by Kyn. The high-dose of P4 activates the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and its downstream targets CYP1A1 and CYP1B1. Under in vitro decidualization, the mRNA levels of Prl8a2 and Prl3c1 are inhibited by 2-OH-E2 and 4-OH-E2, the catalytic products of CYP1A1 and CYP1B1, respectively. CH-223191, a specific AhR antagonist, effectively counteracts the effects of Kyn on Cyp1a1, Cyp1b1, and Prl8a2 expression. Additionally, nucleolar size in stromal cells is increased both in vivo and in vitro following excessive P4 treatment. Our findings suggest that excessive P4 impairs mouse decidualization via the Kyn-AhR pathway.
1 Introduction
Embryo implantation and decidualization are pivotal steps for a successful pregnancy. Decidualization involves the conversion of endometrial fibroblastic stromal cells into specialized decidual cells, which establish a nutrient and immunologically privileged environment for fetal development (Gellersen and Brosens, 2014). Deficiency in embryo implantation and decidualization can lead to adverse pregnancy outcomes, including delayed embryo development, preeclampsia, miscarriage, and preterm birth (Cheng et al., 2023). Ovarian estrogen (E2) and progesterone (P4) closely regulate this process in mice and humans (Paria et al., 2000). P4 is essential for embryo implantation in all studied species (Wetendorf and DeMayo, 2012). In mice, pregnancy maintenance until parturition relies on continuous P4 secretion from the corpus luteum (Maurya et al., 2021). P4 primarily functions through progesterone receptors (PR), including PR-A and PR-B. Mice lacking both PR-A and PR-B (Pgr−/−) exhibit ovarian and uterine defects (Lydon et al., 1995; Lydon et al., 1996).
In clinical practice, P4 is widely used for the conservative management of luteal phase deficiency (LPD) and for treating threatened and recurrent abortion (Soules et al., 1977; Daya et al., 1988). LPD is a pregnancy disorder associated with infertility and spontaneous abortion, and the potential etiologies include inadequate P4 duration, inadequate P4 levels, or endometrial P4 resistance (Jones, 1976). Nevertheless, little agreement exists on LPD diagnosis and treatment (Karamardian and Grimes, 1992). Although P4 has a significant positive impact on reproductive outcomes in assisted reproduction, the scientific debate remains open regarding P4 administration protocols, particularly concerning routes of administration, dosage, timing, and potential interactions with other drugs (Garg et al., 2024). A previous study showed that P4 supplementation in natural frozen embryo transfer cycles does not increase the pregnancy rate (Eftekhar et al., 2013). A prospective study also demonstrates that P4 has no any significant positive impact on pregnancy outcomes in cases of threatened miscarriage (Boza et al., 2016). Women experiencing recurrent miscarriage exhibit reduced endometrial P4 levels. However, it remains unclear whether reduced P4 levels can predict or contribute to adverse pregnancy outcomes (McLindon et al., 2023). Concerns exist about progestin use in pregnancy, particularly the potential risk of genital anomalies (e.g., hypospadias in males, female virilization) and non-genital malformations (Carmichael et al., 2005). For clinicians, supplementing P4 for all possible LPD patients is an empirical practice. P4 as luteal phase support may carry the risk of overconsumption and has adverse effects on pregnancy outcomes. Consequently, it is indispensable to further examine whether excessive P4 has any influence on pregnancy outcomes.
Tryptophan (Trp), an essential amino acid, is necessary during pregnancy (Badawy, 2015; Badawy et al., 2016; Hoang et al., 2023; Xue et al., 2023). Trp is mainly metabolized through kynurenine (Kyn) pathway, which is closely associated with various diseases through its metabolites (Stone and Darlington, 2002). Indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) and tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase (TDO), two key enzymes, regulate the first and rate-limiting step of the Kyn pathway (Austin et al., 2010). IDO and TDO are implicated in various diseases, including inflammation, cancer, diabetes, and mental disorders (Ye et al., 2019). The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), a ligand-activated transcription factor, is involved in the metabolism of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and estrogens through regulating cytochrome P450 enzymes CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 upon activation by Kyn (Yin et al., 2016; Pacheco and Elizondo, 2023). Furthermore,CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 participate in the metabolism of estrogen and generate 2-hydroxyestradiol (2-OH-E2) and 4-hydroxyestradiol (4-OH-E2), respectively (Lee et al., 2003). P4 regulates TDO2 expression in endometrium and breast tissue, contributing to both normal tissue function and tumor growth (Li et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2020; Hutchinson et al., 2022). Furthermore, activation of the IDO/TDO/Kyn/AhR pathway plays a crucial role in promoting tumor growth (Pacheco and Elizondo, 2023).
In this study, we examined whether excessive P4 has any effects on Kyn-AhR pathway during early pregnancy. Our data showed that excessive P4 activates Kyn-AhR pathway that suppresses mouse decidualization.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Animal treatments
All animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of South China Agricultural University. Adult CD1 mice (6–8 weeks old) were maintained in a temperature- and light-regulated environment with a 14 h light/10 h dark photoperiod. Pregnant and pseudopregnant female mice were obtained by mating with fertile or vasectomized male mice, respectively. The day when the vaginal plug was detected was defined as day 1 of pregnancy (D1) or pseudopregnancy.
The P4 doses used in this experiment were based on our previous study (Liang et al., 2018). To investigate effects of excessive P4 on early pregnancy, pregnant mice were subcutaneously injected with 2, 4, or 8 mg of P4 (P0130, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) in 100 μL of sesame oil (S9057, Macklin, Shanghai, China) at 9:00 AM daily from days 3–7. Control mice received 100 μL of sesame oil. On day 8, the mice were sacrificed to collect uteri for further analysis.
To further examine effects of P4, ovariectomized mice rested for 2 weeks were subcutaneously injected with 2, 4, or 8 mg of P4 in 100 μL of sesame oil for 1, 3, or 7 consecutive days. Control mice received 100 μL of sesame oil. Mice were sacrificed 24 h after the last injection to collect uteri for further analysis.
2.2 Artificial decidualization
Artificial decidualization was induced as previously described (Liang et al., 2018). Briefly, on day 4 of pseudopregnancy, 10 μL of sesame oil was injected into one uterine horn to induce decidualization, and the contralateral horn served as a control. Female mice undergoing artificial decidualization were subcutaneously injected with 4 mg P4 daily from days 5–7, while controls received 100 μL of sesame oil. On day 8 of pseudopregnancy, mice were sacrificed to collect uteri for further analysis.
2.3 Cell isolation, culture and treatments
Mouse endometrial stromal cells were isolated and cultured as previously described (Li et al., 2023a). Briefly, the uteri of day 4 pseudopregnant mice were longitudinally incised and digested with HBSS (PB180321, Procell, Wuhan, China) containing 1% trypsin (0,458, VWR, Radnor, PA) and 6 mg/mL dispase (82,003,500, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO). After the uteri were rinsed in HBSS to remove luminal epithelial cells, the remaining tissue was further digested with 0.15 mg/mL collagenase I (2,691,550, Gibco, Grand Island, NY). The collected stromal cells were cultured in DMEM/F12 medium (D2906, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) supplemented with 10% FBS (164,210, Procell, Wuhan, China).
Mouse stromal cells were induced for in vitro decidualization using 10 nM E2 (HY-B0141, MedChemExpress, NJ, USA) and 1 μM P4 as previously described (Chen et al., 2023). The P4 doses for the in vitro experiments were based on previous studies (Liang et al., 2018; Suthaporn et al., 2021). To investigate the effects of excessive P4 on decidualization, stromal cells under in vitro decidualization were treated with different doses of P4 and analyzed the mRNA levels of Prl8a2 and Prl3c1, markers of mouse in vitro decidualization. To examine effects of Kyn on decidualization, stromal cells under in vitro decidualization were treated with different concentrations of L-kynurenine (HY-104026; MedChemExpress, NJ, USA).
2.4 Kynurenine assay
Kynurenine amount was measured as previously described (Chen et al., 2024a). Briefly, the cultured medium was collected from cultured stromal cells and centrifuged at 5,000×g for 10 min to remove cellular debris. Total 360 μL supernatant was mixed with 180 μL of 30% trichloroacetic acid (TCA; T6399, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) and incubated at 50 °C for 30 min. After the mixture was centrifuged at 3,000 × g for 10 min, the supernatant was thoroughly mixed with an equal volume of Ehrlich reagent (2% p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde, D109644, Aladdin, Shanghai, China) and incubated for 12–30 min. The absorbance was measured at 492 nm to calculate the concentration using a standard curve of L-kynurenine.
2.5 RNA extraction and real-time PCR
qPCR was performed as previously described (Li et al., 2024). Total RNAs were extracted from mouse uterine tissue or mouse stromal cells using TRIzol (AG21101, Accurate Biology, Changsha, China). cDNA was synthesized from RNA using the HiScript II Q RT SuperMix kit (R222-01-AB, Vazyme, Nanjing, China). qPCR was performed using the SYBR Premix (Q311-02-AA, Vazyme, Nanjing, China). The data were analyzed using the 2−ΔΔCt method and normalized to mouse Rpl7. The primer sequences were listed in Table 1.
TABLE 1
| Primer sequences | |
|---|---|
| Mouse -Cyp1a1- sense | CAGAAGGTGATGGCAGAG |
| Mouse -Cyp1a1- antisense | ACGGAGGACAGGAATGAA |
| Mouse -Cyp1b1- sense | CTGGACTTGGAGGATGTG |
| Mouse -Cyp1b1- antisense | GCTGGAGAATCGCATTGA |
| Mouse-Prl8a2-sense | AGCCAGAAATCACTGCCACT |
| Mouse-Prl8a2-antisense | TGATCCATGCACCCATAAAA |
| Mouse-Prl3c1-sense | GCCACACGATATGACCGGAA |
| Mouse-Prl3c1-antisense | GGTTTGGCACATCTTGGTGTT |
| Mouse-Rpl7-sense | GCAGATGTACCGCACTGAGATTC |
| Mouse-Rpl7-antisense | ACCTTTGGGCTTACTCCATTGATA |
Primer sequences used in this study.
2.6 Western blot
Western blot was performed as previously described (Chen et al., 2024b). After tissues or cultured cells were lysed with RIPA (R0010, Solarbio, Beijing, China), the protein concentration was determined by the BCA method (23,225, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA). The samples were separated via SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and transferred onto a PVDF membrane (Immobilon®-P, IPVH00010, Millipore, Billerica, MA). After blocked with 5% nonfat milk (A600669, Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China), the PVDF membranes were incubated with each primary antibody and secondary antibody (1:5,000). The signal was detected using the ECL chemiluminescence kit (Millipore). The primary antibodies utilized in this study include IDO1 (51,851, Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA), TDO (ab259359, Abcam, Cambridge, United Kingdom), BMP2 (A0231, ABclonal, Wuhan, China), SNAIL (3879T, Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA), AhR (A00225-4, Boster, Wuhan, China), CYP1A1 (GTX55582, GeneTex), CYP1B1 (GTX104424, GeneTex), and α-TUBULIN (2144S, Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA), GAPDH (SC-32233, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX), Histone H3 (ab176842, Abcam, Cambridge, United Kingdom).
2.7 Immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence was performed as previously described (Li et al., 2023b). Briefly, paraffin sections were dewaxed and rehydrated. Antigen retrieval was achieved with citrate buffer (pH 6.0) or Tris/EDTA buffer (pH 9.0). Cell membranes were permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 (T0694, Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China) in PBS. After non-specific binding was blocked with horse serum (ZLI-9024, ZSGB-BIO, Beijing, China) for 1 h, sections were incubated with each primary antibody overnight at 4 °C and Alexa 488-conjugated secondary antibody (169,549, Jackson ImmunoResearch, West Grove, PA) at 37 °C for 30 min. Nuclei were counterstained with propidium iodide (PI, P4170, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) or 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, D9542, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO). Fluorescence signals were captured using a Nikon C2 confocal microscope. The primary antibodies used in this study include IDO1 (66,528-1, Proteintech, Wuhan, China), Phospho-AhR (PA5-36025, Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA), AhR (A00225-4, Boster, Wuhan, China) and Nucleolin (14,574, Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA).
2.8 Cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts
The nuclear and cytoplasmic extractions were conducted as previously described (Deng et al., 2014). Cultured cells were washed twice with pre-chilled PBS, incubated with Buffer B (5 mM EDTA in PBS) on ice for 5 min and scraped off from culture plates. After centrifuged at 1,000 g for 5 min at 4 °C, the pellet was resuspended in Buffer A (10 mM HEPES, 10 mM KCl, 0.1 mM EDTA with fresh added dithiothreitol and phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride) and shaked at 4 °C for 20 min, mixed with 2.5% Nonidet P-40 and vortexed for 10 s. Following centrifugation at 15,000 g for 5 min at 4 °C, the supernatant was collected as cytoplasmic protein. The remaining pellet was resuspended in Buffer C (20 mM HEPES, 0.4 M NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, freshly added DTT and PMSF), vortexed, and centrifuged at 18,000 g for 5 min at 4 °C, and collected the supernatant as nuclear protein.
2.9 Statistical analysis
Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. The two-tailed Student’s t-test was used to compare two groups. For more than two groups, one-way ANOVA was conducted with post hoc tests: LSD (if equal variances were assumed based on Levene’s test) or Games-Howell (if variances were unequal). Statistical significance was set at *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.
3 Results
3.1 Excessive P4 impairs decidualization in mice
To examine effects of excessive P4 on decidualization, pregnant mice were subcutaneously injected with 4 mg or 8 mg of P4 in 100 μL sesame oil daily from days 3–7 of pregnancy. Compared with controls, the decidual weight of implantation site on day 8 was significantly reduced by 4 mg or 8 mg P4 treatments (Figure 1A). Alkaline phosphatase is a marker of mouse decidualization (Yee and Kennedy, 1988). The staining density of alkaline phosphatase activity in day 8 pregnant uterus was also significantly decreased by 4 mg or 8 mg P4 (Figure 1B). Under artificial decidualization, the decidual weight on day 8 pseudopregnant mice was significantly reduced by 4 mg P4 treatments from days 5–7 (Figure 1C). Prl8a2 and Prl3c1 serve as markers for mouse in vitro decidualization (Rasmussen et al., 1997). Under in vitro decidualization, Prl8a2 mRNA was significantly downregulated by 20 μM P4, while no significant changes were observed by 0.16, 0.8, or 4 μM P4 treatment for 2 days (Figure 1D). Meanwhile, Prl3c1 mRNA levels were significantly reduced by 10 μM or 20 μM P4 (Figure 1D).
FIGURE 1
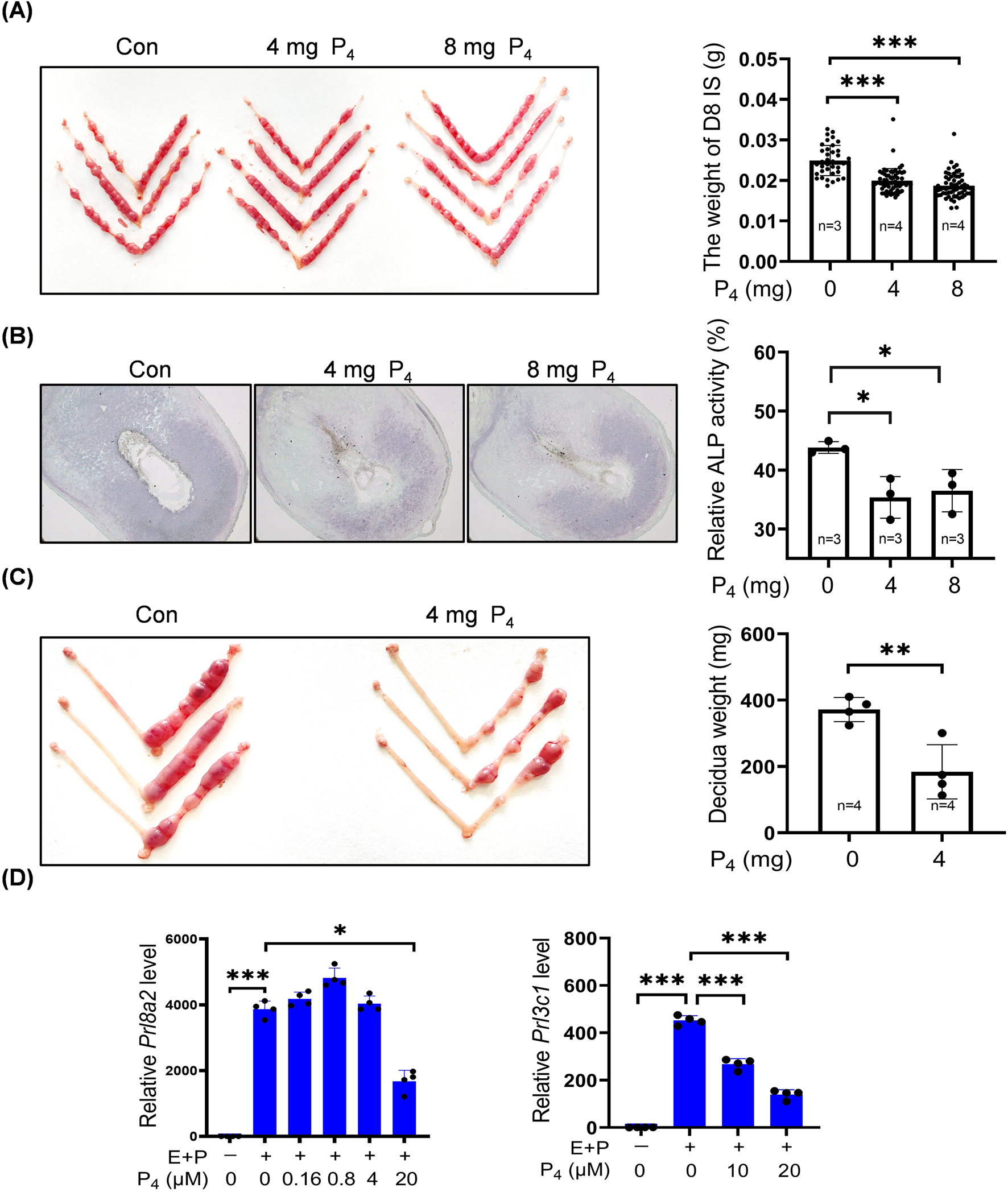
Excessive P4 impairs mouse decidualization. (A) Representative images and the decidual weights of implantation site on day 8 of pregnancy after pregnant mice were daily treated with P4 (4 mg or 8 mg) from days 3–7. (B) Alkaline phosphatase staining of day 8 uteri after pregnant mice were treated daily with P4 (4 mg or 8 mg) from days 3–7. (C) Representative images and the decidual weights of day 8 pseudopregnant uteri after pseudopregnant mice under artificial decidualization were treated daily with 4 mg P4 from days 5–7. (D) Effects of P4 treatment on Prl8a2 and Prl3c1 mRNA levels under in vitro decidualization for 2 days. The qPCR values were normalized to the Rpl7 mRNA level. All images are the representative of at least three biologically independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
3.2 P4 activates the IDO1/TDO-Kyn pathway
Trp is crucial during pregnancy and mainly metabolized via Kyn pathway (Badawy, 2015; Badawy et al., 2016; Hoang et al., 2023; Xue et al., 2023). TDO, IDO1 and IDO2 are the key rate-limiting enzymes in Kyn pathway and essential for pregnancy (Munn et al., 1998). Because excess P4 is detrimental for pregnancy, we wondered whether Kyn pathway was affected by excess P4. When ovariectomized mice were treated with 4 mg or 8 mg P4 for 7 days, uterine Kyn levels were significantly increased (Figure 2A). IDO1 immunofluorescence signals in the uterine luminal epithelium were clearly increased after ovariectomized mice were treated with 4 mg or 8 mg P4 for 24 h, while 2 mg P4 had no obvious effect (Figure 2C). Uterine TDO protein levels were also upregulated by 2 mg or 4 mg P4, but not by 8 mg P4 (Figure 2D).
FIGURE 2
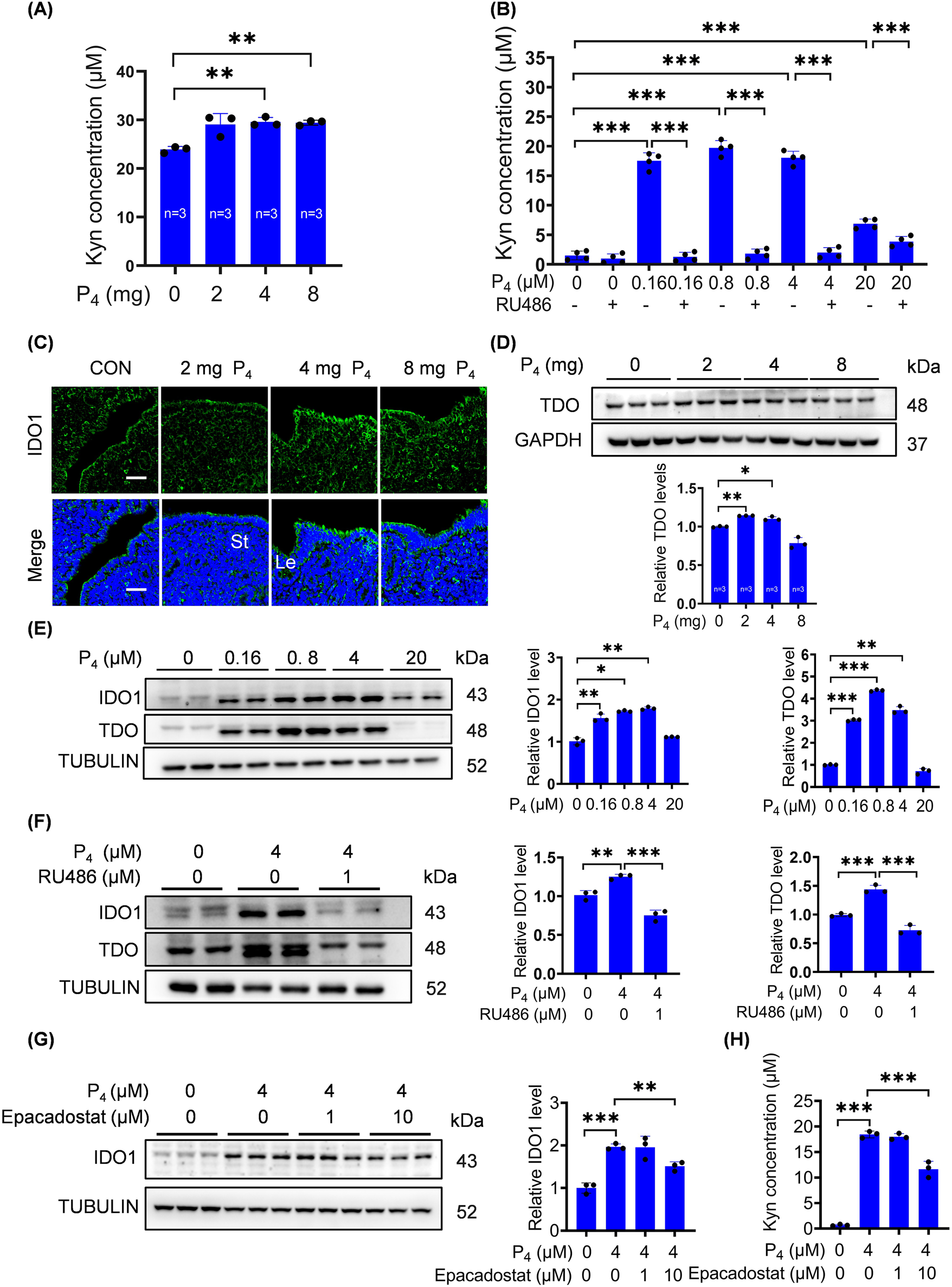
P4 activates the IDO1/TDO-Kyn pathway. (A) Kyn levels in uterine tissues after ovariectomized mice were subcutaneously injected with 2 mg, 4 mg, or 8 mg P4 per mouse for 7 consecutive days. (B) Kyn levels in culture medium after stromal cells were treated with P4 with or without RU486 for 2 days. (C) Uterine IDO1 immunofluorescence after ovariectomized mice were treated with P4 (2 mg, 4 mg, 8 mg) for 24 h. Nuclei were counter-stained with DAPI. Le, luminal epithelia; St, stroma. Scale bar, 50 μm. n = 3 mice per group. (D) Uterine TDO protein levels after ovariectomized mice were treated with P4 for 24 h. (E) Western blot analysis of IDO1 and TDO protein levels in stromal cells treated with P4 for 3 days. (F) IDO1 and TDO protein levels in stromal cells treated with 4 μM P4 with or without RU486 for 2 days. (G) IDO1 protein levels in stromal cells treated with 4 μM P4 with or without Epacadostat for 2 days. (H) Kyn levels in the culture medium after stromal cells were treated with 4 μM P4 with or without Epacadostat for 2 days. All images are the representative of at least three biologically independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
After stromal cells were treated with 0.16, 0.8, 4, or 20 μM P4 for 2 days, Kyn secretion was significantly increased, which was abrogated by RU486, an antagonist of progesterone receptor (Figure 2B). IDO1 and TDO protein levels were also significantly increased after stromal cells were treated with 0.16, 0.8, or 4 μM P4 for 3 days (Figure 2E). P4-induced increases in IDO1 and TDO protein levels were blocked by RU486 treatments (Figure 2F). Epacadostat, a selective inhibitor of IDO1, effectively suppressed P4-induced increases in IDO1 protein levels and Kyn secretion (Figures 2G,H).
3.3 Kyn impairs decidualization of mouse stromal cells and activates AhR
Because high-dose P4 increases Kyn levels, we explored whether Kyn had any effects on decidualization. Under in vitro decidualization, Prl8a2 mRNA levels were significantly downregulated in a dose-dependent manner by 0.25, 0.5, or 1 mM Kyn (Figure 3A). Meanwhile, Prl3c1 mRNA levels were upregulated by 0.5 mM Kyn, but downregulated by 1 mM Kyn (Figure 3A). BMP2 is essential for decidualization (Wang and Dey, 2006). BMP2 protein levels were downregulated after stromal cells were treated with 0.2, or 1 mM Kyn, whereas 0.04 mM Kyn had no detectable change on BMP2 protein levels for 2 days (Figure 3B). SNAIL, a key player during the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, is decreased during decidualization (Zhang et al., 2013; Serrano-Gomez et al., 2016). SNAIL protein levels were significantly upregulated after stromal cells were treated with 0.2, or 1 mM Kyn rather than 0.04 mM Kyn for 2 days (Figure 3B).
FIGURE 3
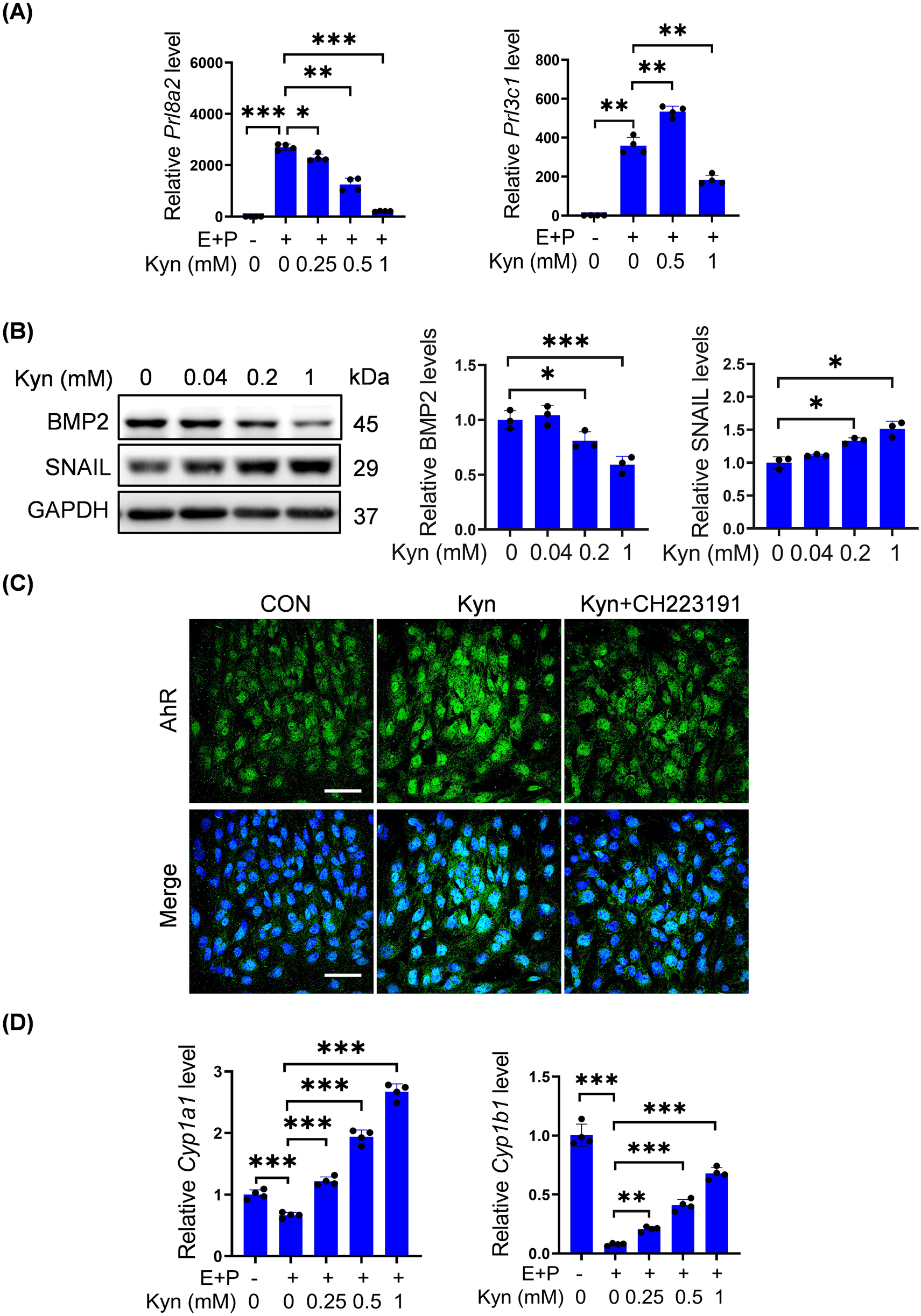
Kyn impairs decidualization of mouse stromal cells and activates AhR. (A)Prl8a2 and Prl3c1 mRNA levels after stromal cells were treated with Kyn for 2 days under in vitro decidualization. (B) Western blot analysis and quantification of BMP2 and SNAIL protein levels in stromal cells treated with Kyn for 2 days. (C) AhR fluorescence in stromal cells treated with 1 mM Kyn with or without 10 μM CH223191 for 24 h. Nuclei were counter-stained with DAPI. Scale bar, 50 μm. (D) The mRNA levels of Cyp1a1 and Cyp1b1 after stromal cells were treated with Kyn for 2 days under in vitro decidualization. All images are the representative of at least three biologically independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
Kyn is an effective AhR agonist (DiNatale et al., 2010). Treatment of stromal cells with 1 mM Kyn increased the fluorescence intensity of nuclear AhR, which was abrogated by CH-223191, a specific AhR antagonist (Figure 3C). CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 are downstream targets of AhR (Denison and Whitlock, 1995; Nebert and Dalton, 2006; MacPherson et al., 2013). Under in vitro decidualization, Cyp1a1 and Cyp1b1 mRNA levels were significantly downregulated, but upregulated in a dose-dependent manner by 0.25, 0.5, or 1 mM Kyn (Figure 3D).
3.4 P4 activates the AhR-CYP1A1/CYP1B1 signaling pathway
We further explored whether excessive P4 could directly activate the AhR pathway. When ovariectomized mice were treated with 2 or 4 mg P4, p-AhR immunofluorescence in stromal cells was enhanced (Figure 4A). The mRNA levels of Cyp1a1 and Cyp1b1 were significantly increased after ovariectomized mice were treated with 2, 4, or 8 mg P4 for 7 days (Figure 4B). Furthermore, CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 protein levels in uterine tissues of ovariectomized mice significantly increased after 4 mg or 8 mg P4 treatment (Figure 4C). After stromal cells were treated with 2.5, 5, 10, or 20 μM P4 for 2 days, nuclear AhR protein levels were clearly elevated (Figure 4D). In addition, nuclear AhR fluorescence in stromal cells was enhanced after treatment with 0.8, 4, or 20 μM P4 for 48 h (Figure 4E).
FIGURE 4
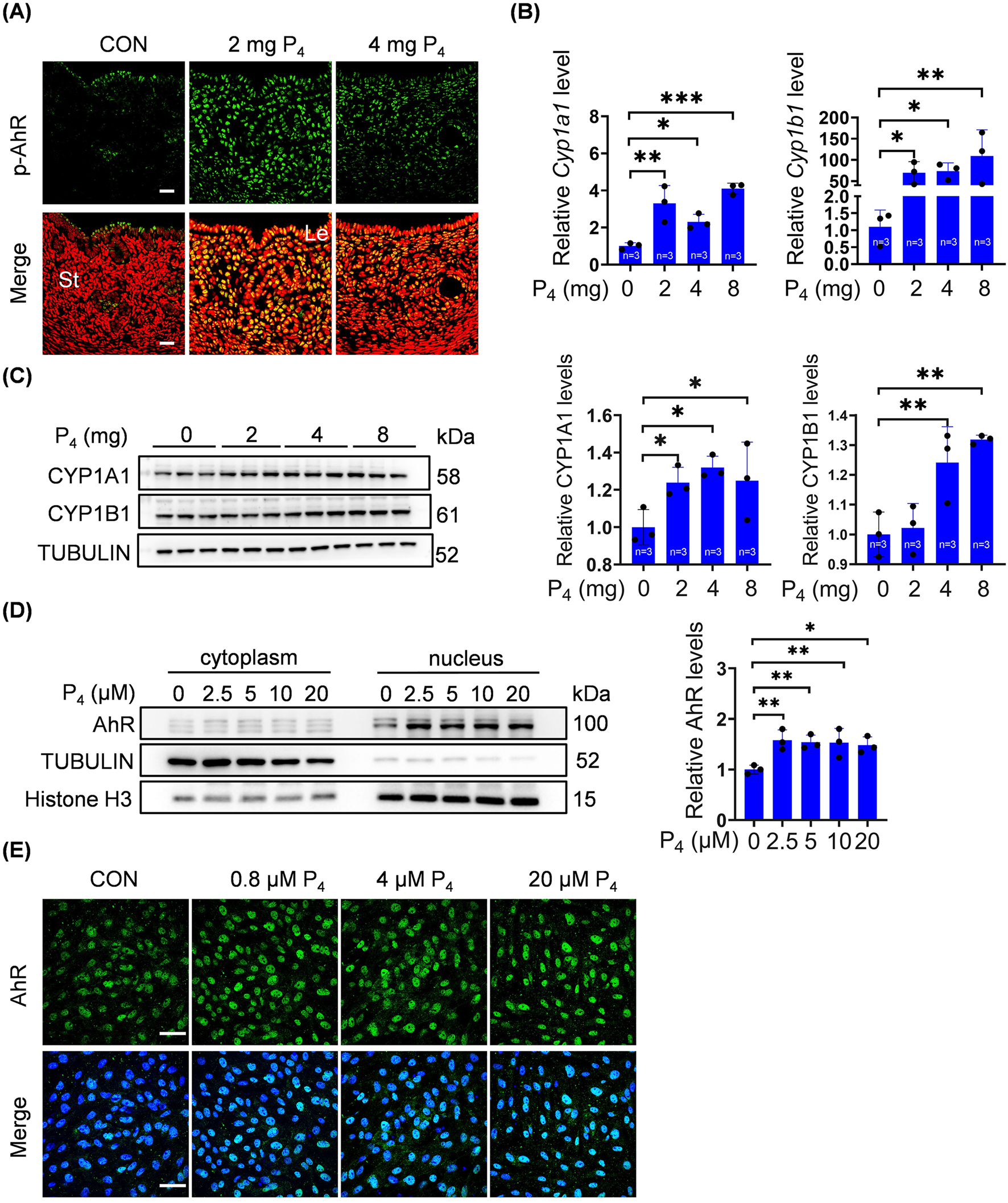
P4 activates AhR pathway. (A) Uterine phosphorylated AhR immunofluorescence after ovariectomized mice were treated with 2 mg or 4 mg P4 for 7 days. Nuclei were counter-stained with PI. Le, luminal epithelia; St, stroma. Scale bar, 20 μm. n = 3 mice per group. (B) Uterine mRNA levels of Cyp1a1 and Cyp1b1 after ovariectomized mice were treated with 2, 4 or 8 mg P4 for 7 days. (C) Western blot analysis and quantification of uterine CYP1A1 (3 days injection) and CYP1B1 (7 days injection) protein levels after ovariectomized mice were treated with 2, 4 or 8 mg P4. (D) Western blot analysis of AhR protein level in nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions, and quantification of AhR in nuclear fractions after stromal cells were treated with P4 for 48 h (E) AhR immunofluorescence in stromal cells treated with 0.8, 4, or 20 μM P4 for 48 h. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Scale bar: 50 μm. All images are the representative of at least three biologically independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
3.5 Kyn inhibits stromal decidualization through activating AhR
Under in vitro decidualization, Kyn significantly suppressed Prl8a2 mRNA levels, but upregulated Cyp1a1 and Cyp1b1 mRNA levels, which were reversed by CH-223191, a specific AhR antagonist (Figures 5A,B). CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 are cytochrome P450 enzymes that catalyze the formation of non-toxic 2-OH-E2 and genotoxic 4-OH-E2 from E2 (Mao et al., 2023). Under in vitro decidualization, Prl8a2 and Prl3c1 mRNA levels were downregulated by 10 μM 2-OH-E2 and 10 μM 4-OH-E2, respectively (Figures 5C,D).
FIGURE 5
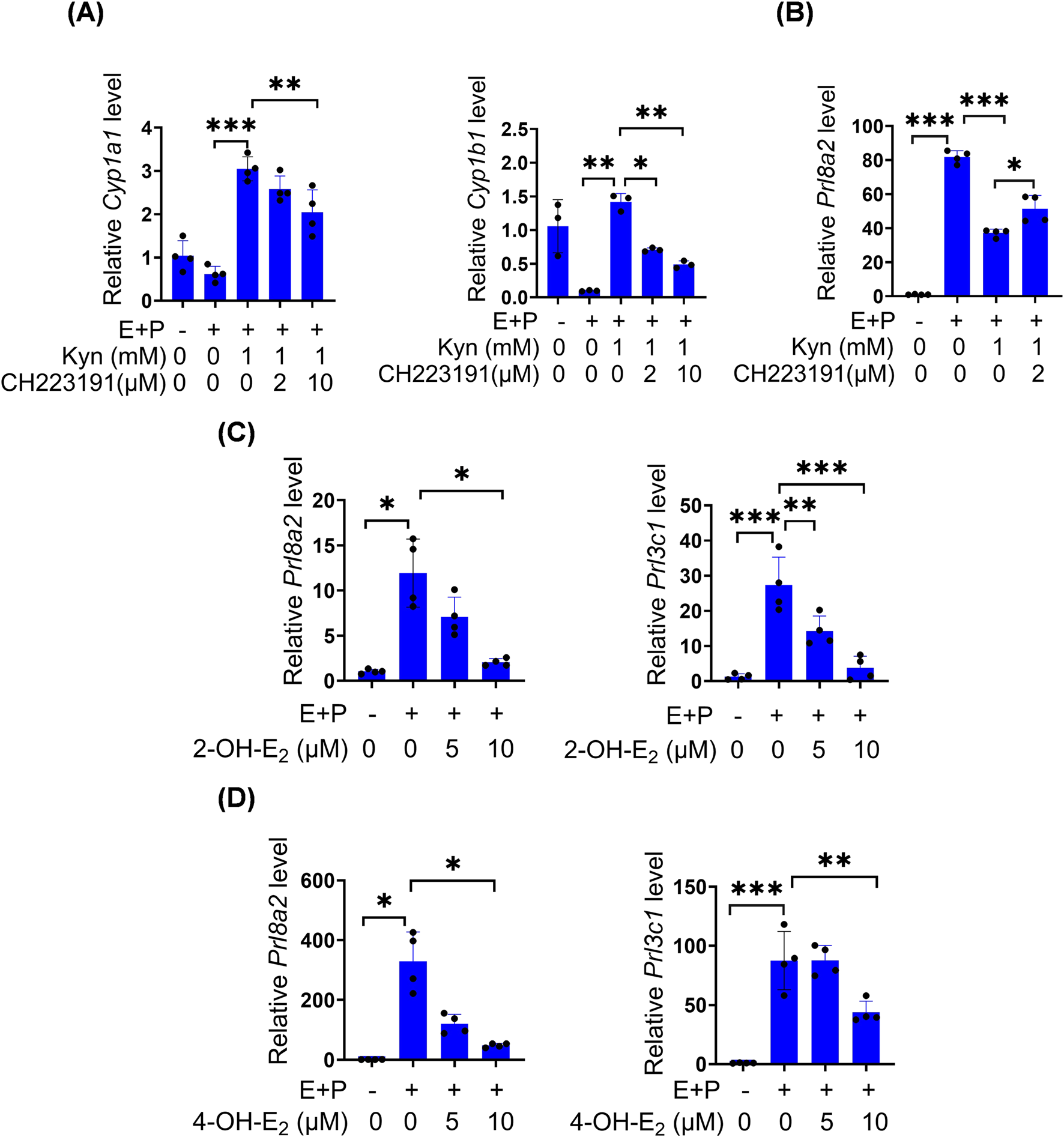
Kyn inhibits mouse stromal cell decidualization through activating AhR. (A) The mRNA levels of Cyp1a1 and Cyp1b1 after stromal cells under in vitro decidualization were treated with Kyn for 48 h with or without AhR inhibitor CH223191. (B) Prl8a2 mRNA level after stromal cells under in vitro decidualization were treated with Kyn for 24 h with or without CH223191. (C) The mRNA levels of Prl8a2 and Prl3c1 after stromal cells were treated with 2-OH-E2 for 12 h under in vitro decidualization. (D) The mRNA levels of Prl8a2 and Prl3c1 after stromal cells were treated with 4-OH-E2 for 24 h under in vitro decidualization. All images are the representative of at least three biologically independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
3.6 Effects of excessive P4 on nucleolus
The nucleolus plays a crucial role in ribosome biogenesis. The morphology, size, and activity of nucleolus are closely linked, exhibiting diverse reorganization patterns under stress (Yang et al., 2018). AhR modulates nucleolar activity and enhances protein synthesis (Lafita-Navarro et al., 2018). Given that excess P4 was detrimental to pregnancy and could activate the AhR pathway, we investigated excess P4 effects on nucleoleus. Nucleolin (NCL), constituting approximately 10% of total nucleolar protein, serves as a nucleolar marker (Lo et al., 2006). After ovariectomized mice were subcutaneously injected with 2 mg or 8 mg P4 for 7 days, the size and NCL intensity of nucleolus in the uterine stromal cells were obviously increased, while there were no clear changes for NCL immunofluorescence in luminal and glandular epithelium (Figure 6A). When stromal cells were treated with 0.5, 5, or 20 μM P4 for 24 h, the size of nucleolar NCL immunofluorescence was also increased (Figure 6B).
FIGURE 6
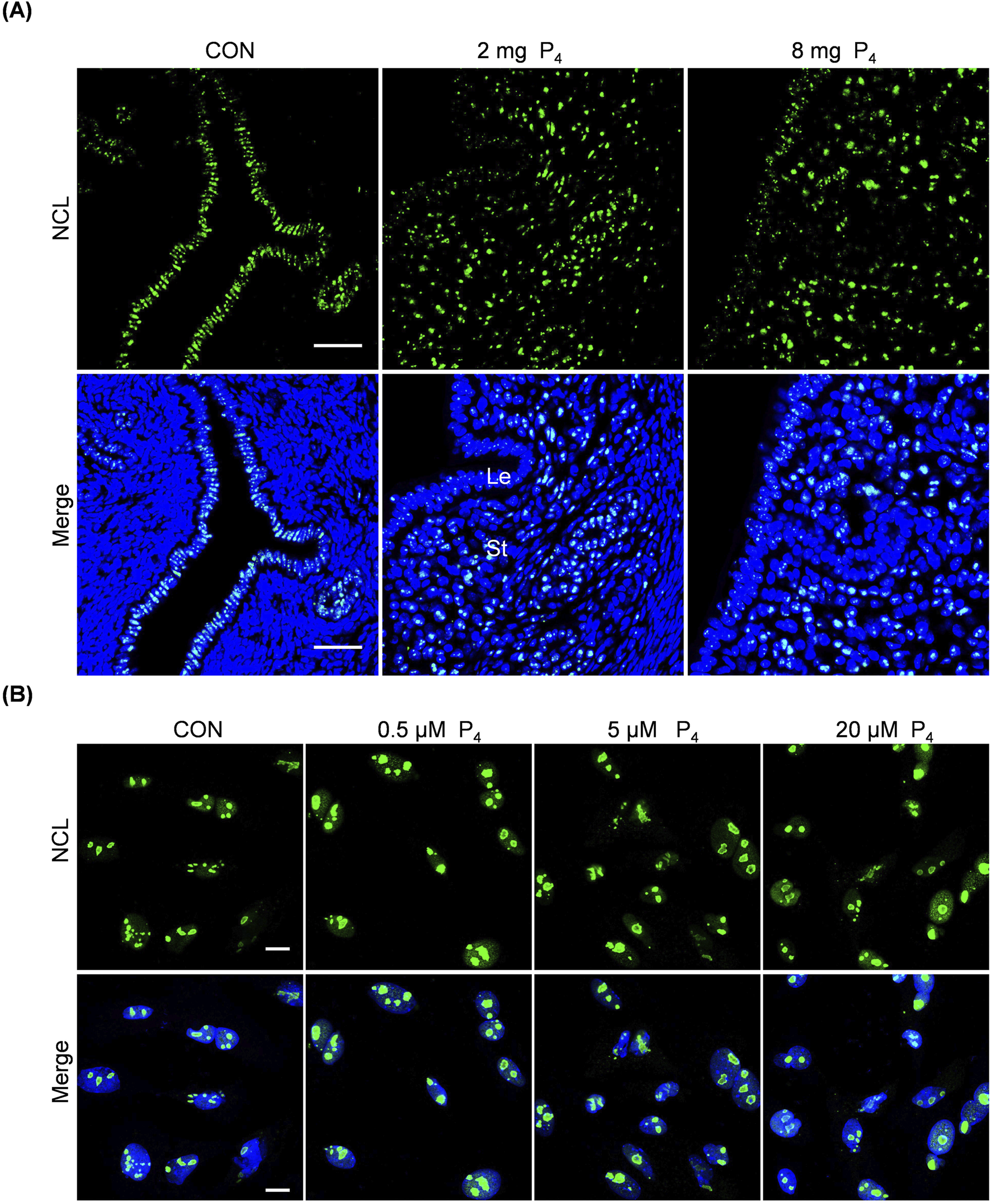
Effects of excessive P4 on nucleolus. (A) Uterine NCL immunofluorescence after ovariectomized mice were subcutaneously injected with 2 or 8 mg P4 for 7 days. Nuclei were counter-stained with DAPI. Le, luminal epithelia; St, stroma. Scale bar, 50 μm. n = 3 mice per group. (B) NCL immunofluorescence after stromal cells were treated with 0.5,5 or 20 μM P4 for 24 h. Nuclei were counter-stained with DAPI. Scale bar, 20 μm. All images are the representative of at least three biologically independent experiments.
4 Discussion
P4 is essential for establishing and maintaining pregnancy (Bhurke et al., 2016). However, the potential adverse effects of excessive P4 on pregnancy outcomes are frequently overlooked. In this study, we found that excessive P4 impaired mouse decidualization both in vivo and in vitro, potentially through changing tryptophan metabolism and activating AhR pathway.
Numerous studies have reported that excessive P4 adversely affects pregnancy outcomes. High P4 exposure from the end of menstruation to oocyte maturation is associated with a decreased probability of pregnancy (Kyrou et al., 2011). P4 levels ≥1.7 ng/mL before oocyte retrieval significantly reduce endometrial receptivity (Liu et al., 2015). Endometrial gene expression profiles are altered when P4 levels exceed 1.5 ng/mL at the end of the follicular phase (Labarta et al., 2011). Elevated P4 levels on the day of hCG administration during initial fresh cycles correlate with poor pregnancy outcomes in fresh embryo transfers but not in subsequent frozen-thawed embryo transfers (Venetis et al., 2013). Our previous study also demonstrated that excessive P4 impairs mouse embryo implantation and decidualization (Liang et al., 2018).
Trp, an essential amino acid for protein biosynthesis and a precursor of serotonin, has been detected in the ovary, uterus, fallopian tubes, placenta, and ovarian follicular fluid (Doherty et al., 2011; Li et al., 2014). During pregnancy, Trp enhances maternal and fetal protein synthesis, participates in 5-hydroxytryptamine synthesis, provides neuroprotection through kynurenic acid, and suppresses fetal rejection reactions (Xu et al., 2017). Excess Trp must be metabolized early in pregnancy to avoid adverse effects. In mammals, over 95% of free Trp is metabolized through the Kyn pathway, which is closely linked to pregnancy (Stone and Darlington, 2002). Plasma and uterine Trp levels decrease, while Kyn levels increase in human, mouse, and cattle pregnancy (Minatogawa et al., 2003; Schrocksnadel et al., 2006; Groebner et al., 2011). High levels of Trp in culture media inhibit embryo development to the blastocyst stage in vitro (McKiernan et al., 1995). Dynamic Trp metabolism serves as a regulatory mechanism to control oxidative stress during pregnancy (Xu et al., 2017). Our previous study demonstrated that Trp deficiency in feed impairs mouse decidualization via the Kyn pathway (Chen et al., 2024a).
IDO1/2 and TDO2 are key rate-limiting enzymes in the Kyn pathway of Trp metabolism (Campesato et al., 2020). IDO1 and TDO2 are intimately associated with the decidualization process (Suzuki et al., 2001; Kudo et al., 2004). IDO1 in mouse placenta is important for preventing the immune rejection of fetal allografts (Sedlmayr et al., 2014). TDO2 can facilitate decidualization in mice (Tatsumi et al., 2000; Li et al., 2014), whereas overexpression of both IDO1 and IDO2 inhibits mouse in vitro decidualization (Li et al., 2015a; Li et al., 2015b). IDO1 is possibly involved in endometriosis pathogenesis (Mei et al., 2012). In this study, treatment with excessive P4 led to upregulation of IDO1 and TDO protein levels and increased Kyn levels in the mouse uterus and cultured stromal cells. Additionally, high Kyn concentrations inhibited mouse in vitro decidualization, suggesting that excessive P4 may impair decidualization by activating IDO1 and TDO. P4 is able to stimulate IDO1 and IDO2 expression in mouse uterine stromal cells (Li et al., 2015a; Li et al., 2015b). TDO expression is induced by decidualization (Tatsumi et al., 2000). Based on these evidences, it seems that overactivated IDO1 should be detrimental for decidualization.
Kyn, as an endogenous ligand of AhR, activates AhR in mouse stromal cells and induced the expression of downstream genes CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 in our study. AhR is essential for ovarian function, optimizing the fertilization environment, nurturing embryos, maintaining pregnancy, and regulating reproductive lifespan and fertility (Hernandez-Ochoa et al., 2009). AhR is expressed in the pre-implantation mouse uterus (Kitajima et al., 2004). AhR mediates the reproductive toxicity induced by polychlorinated biphenyl congener 126 in rats (Klenov et al., 2021). In early pregnancy, Kyn-AhR enhances NK cell cytotoxicity, contributing to recurrent spontaneous abortion (Yang et al., 2021). Additionally, activation of the Trp/Kyn/AhR pathway promotes the growth of uterine leiomyomas (Zuberi et al., 2023). In our study, AhR was also activated by excessive P4, suggesting that overactivated AhR suppresses decidualization.
CYP1A1 and CYP1B1, members of the cytochrome P450 enzyme family, catalyze the formation of 2-OH-E2 and 4-OH-E2 from E2, respectively (Hanna et al., 2000; Lee et al., 2003). CYP1B1 is highly expressed in E2 target tissues such as breast, ovary, and uterus (Hakkola et al., 1997). 4-OH-E2 generates free radicals through redox cycling with semiquinone and quinone forms, leading to cellular damage and contributing to breast and endometrial cancer development (Tsuchiya et al., 2005). During mouse delayed implantation, 2-OH-E2 and 4-OH-E2 show no difference in inducing implantation compared to E2 (Hoversland et al., 1982). However, in rats, 4-OH-E2 is less effective than E2 but more effective than 2-OH-E2 in initiating implantation (Kantor et al., 1985). Our results demonstrated that both 2-OH-E2 and 4-OH-E2 inhibit stromal cell decidualization.
Furthermore, based on our NCL immunofluorescence, the nucleolar size was obviously increased both in uterine endometrial stromal cells and cultured stromal cells following excessive P4 treatment. These findings suggest that excessive P4 may affect endometrial function by altering nucleolar structure and function. The nucleolus, a prominent membraneless structure within the nucleus, plays a crucial role in ribosome formation. This complex process encompasses the transcription of ribosomal DNA (rDNA), the processing of ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and the subsequent assembly of rRNA with ribosomal proteins to generate functional ribosomes (Bassler and Hurt, 2019; Lafontaine et al., 2021). Any disruptions during ribosome biogenesis can induce nucleolar stress, which is marked by changes in nucleolar structure and functionality (Lafita-Navarro and Conacci-Sorrell, 2023). Larger and more nucleoli are frequently observed in tumor cells compared to normal cells, making abnormal nucleolar size and number important indicators for cancer prognosis (Derenzini et al., 2000; Lo et al., 2006). AhR regulates nucleolar activity and protein synthesis (Lafita-Navarro et al., 2018). P4 and MPA increase Nucleolin protein levels, which is associated with the proliferative potential of the cells (Yokoyama et al., 1998). Future research could further explore how P4 affects embryo implantation and decidualization by influencing the expression of nucleolar-associated proteins.
During decidualization, P4 classically affects the endometrium via two well-characterized receptors, PR-A and PR-B (Lydon et al., 1996). However, the effects of P4 are also mediated by progesterone receptor membrane component 1 (PGRMC1) (Kaluka et al., 2015). PGRMC1 expression is also tightly regulated at the maternal-fetal interface in humans and rodents (Pru and Clark, 2013). Uterine ablation of PGRMC1 leads to reduced fertility in female mice and the development of endometrial cysts (McCallum et al., 2016). Additionally, P4 weakly binds to the nuclear glucocorticoid receptor (GR), which may represent a key mechanism underlying its anti-inflammatory effects in reproductive tissues (Shah et al., 2019). Deficiency in uterine GR signaling results in an exaggerated inflammatory response during induced decidualization, including altered immune cell recruitment (Whirledge et al., 2015). Although this study shows that excessive P4 disrupts the Kyn-AhR axis during decidualization, it is still possible that excessive P4 may impair decidualization through GR signaling or PGRMC1.
5 Conclusion
In summary, our results demonstrate that excessive P4 impairs mouse decidualization via activating Kyn-AhR pathway, highlighting the potential mechanisms underlying reproductive disorders and adverse pregnancy outcomes associated with abnormal P4 levels.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of South China Agricultural University. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
H-NL: Validation, Methodology, Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. H-YY: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Methodology. Z-MW: Methodology, Investigation, Data curation, Writing – original draft. J-ML: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Investigation. T-TZ: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. Z-MY: Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization, Supervision, Project administration.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32171114 and 31871511).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
AhR, Aryl hydrocarbon receptor; E2, Estrogen; IDO, Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; Kyn, Kynurenine; LPD, Luteal phase deficiency; NCL, Nucleolin; Prl3c1, Prolactin family 3, subfamily C, member 1; Prl8a2, Prolactin family 8, subfamily A, member 2; Progesterone, P4; PR, Progesterone receptor; PI, Propidium iodide; Trp, Tryptophan; TDO, Tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase; 2-OH-E2, 2-hydroxyestradiol; 4-OH-E2, 4-hydroxyestradiol; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.
References
1
Austin C. J. Mailu B. M. Maghzal G. J. Sanchez-Perez A. Rahlfs S. Zocher K. et al (2010). Biochemical characteristics and inhibitor selectivity of mouse indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-2. Amino Acids39, 565–578. 10.1007/s00726-010-0475-9
2
Badawy A. A. (2015). Tryptophan metabolism, disposition and utilization in pregnancy. Biosci. Rep.35, e00261. 10.1042/BSR20150197
3
Badawy A. A. Namboodiri A. M. Moffett J. R. (2016). The end of the road for the tryptophan depletion concept in pregnancy and infection. Clin. Sci. (Lond)130, 1327–1333. 10.1042/CS20160153
4
Bassler J. Hurt E. (2019). Eukaryotic ribosome assembly. Annu. Rev. Biochem.88, 281–306. 10.1146/annurev-biochem-013118-110817
5
Bhurke A. S. Bagchi I. C. Bagchi M. K. (2016). Progesterone-regulated endometrial factors controlling implantation. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol.75, 237–245. 10.1111/aji.12473
6
Boza A. Api M. Kayatas S. Ceyhan M. Boza B. (2016). Is progestogen supplementation necessary to prevent abortion?J. Obstet. Gynaecol.36, 1076–1079. 10.1080/01443615.2016.1205556
7
Campesato L. F. Budhu S. Tchaicha J. Weng C. H. Gigoux M. Cohen I. J. et al (2020). Blockade of the AHR restricts a Treg-macrophage suppressive axis induced by L-Kynurenine. Nat. Commun.11, 4011. 10.1038/s41467-020-17750-z
8
Carmichael S. L. Shaw G. M. Laurent C. Croughan M. S. Olney R. S. Lammer E. J. (2005). Maternal progestin intake and risk of hypospadias. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med.159, 957–962. 10.1001/archpedi.159.10.957
9
Chen S. T. Shi W. W. Lin Y. Q. Yang Z. S. Wang Y. Li M. Y. et al (2023). Embryo-derive TNF promotes decidualization via fibroblast activation. Elife12, e82970. 10.7554/eLife.82970
10
Chen S. T. Ran F. Shi W. W. Liu C. K. Wang P. C. Luo H. N. et al (2024a). Tryptophan in the mouse diet is essential for embryo implantation and decidualization. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne)15, 1356914. 10.3389/fendo.2024.1356914
11
Chen S. T. Shi W. W. Ran F. Liu C. K. Luo H. N. Wu L. J. et al (2024b). The activation of cGAS-STING pathway causes abnormal uterine receptivity in aged mice. Aging Cell23, e14303. 10.1111/acel.14303
12
Cheng J. Sha Z. Li J. Li B. Luo X. Zhang Z. et al (2023). Progress on the role of estrogen and progesterone signaling in mouse embryo implantation and decidualization. Reprod. Sci.30, 1746–1757. 10.1007/s43032-023-01169-0
13
Daya S. Ward S. Burrows E. (1988). Progesterone profiles in luteal phase defect cycles and outcome of progesterone treatment in patients with recurrent spontaneous abortion. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol.158, 225–232. 10.1016/0002-9378(88)90127-5
14
Deng W. B. Liang X. H. Liu J. L. Yang Z. M. (2014). Regulation and function of deiodinases during decidualization in female mice. Endocrinology155, 2704–2717. 10.1210/en.2014-1015
15
Denison M. S. Whitlock J. P. Jr. (1995). Xenobiotic-inducible transcription of cytochrome P450 genes. J. Biol. Chem.270, 18175–18178. 10.1074/jbc.270.31.18175
16
Derenzini M. Trere D. Pession A. Govoni M. Sirri V. Chieco P. (2000). Nucleolar size indicates the rapidity of cell proliferation in cancer tissues. J. Pathol.191, 181–186. 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(200006)191:2<181::AID-PATH607>3.0.CO;2-V
17
DiNatale B. C. Murray I. A. Schroeder J. C. Flaveny C. A. Lahoti T. S. Laurenzana E. M. et al (2010). Kynurenic acid is a potent endogenous aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand that synergistically induces interleukin-6 in the presence of inflammatory signaling. Toxicol. Sci.115, 89–97. 10.1093/toxsci/kfq024
18
Doherty L. F. Kwon H. E. Taylor H. S. (2011). Regulation of tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase by HOXA10 enhances embryo viability through serotonin signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab.300, E86–E93. 10.1152/ajpendo.00439.2010
19
Eftekhar M. Rahsepar M. Rahmani E. (2013). Effect of progesterone supplementation on natural frozen-thawed embryo transfer cycles: a randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Fertil. Steril.7, 13–20.
20
Garg A. Zielinska A. P. Yeung A. C. Abdelmalak R. Chen R. Hossain A. et al (2024). Luteal phase support in assisted reproductive technology. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol.2, 149–167. 10.1038/s41574-023-00921-5
21
Gellersen B. Brosens J. J. (2014). Cyclic decidualization of the human endometrium in reproductive health and failure. Endocr. Rev.35, 851–905. 10.1210/er.2014-1045
22
Groebner A. E. Schulke K. Schefold J. C. Fusch G. Sinowatz F. Reichenbach H. D. et al (2011). Immunological mechanisms to establish embryo tolerance in early bovine pregnancy. Reprod. Fertil. Dev.23, 619–632. 10.1071/RD10230
23
Hakkola J. Pasanen M. Pelkonen O. Hukkanen J. Evisalmi S. Anttila S. et al (1997). Expression of CYP1B1 in human adult and fetal tissues and differential inducibility of CYP1B1 and CYP1A1 by Ah receptor ligands in human placenta and cultured cells. Carcinogenesis18, 391–397. 10.1093/carcin/18.2.391
24
Hanna I. H. Dawling S. Roodi N. Guengerich F. P. Parl F. F. (2000). Cytochrome P450 1B1 (CYP1B1) pharmacogenetics: association of polymorphisms with functional differences in estrogen hydroxylation activity. Cancer Res.60, 3440–3444.
25
Hernandez-Ochoa I. Karman B. N. Flaws J. A. (2009). The role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in the female reproductive system. Biochem. Pharmacol.77, 547–559. 10.1016/j.bcp.2008.09.037
26
Hoang V. H. Trang N. T. K. Minh T. C. Long L. T. B. Lan T. H. Hue N. T. et al (2023). Design, synthesis and evaluation the bioactivities of novel 1,3-dimethyl-6-amino-1H-indazole derivatives as anticancer agents. Bioorg Med. Chem.90, 117377. 10.1016/j.bmc.2023.117377
27
Hoversland R. C. Dey S. K. Johnson D. C. (1982). Catechol estradiol induced implantation in the mouse. Life Sci.30, 1801–1804. 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90316-2
28
Hutchinson A. P. Yin P. Neale I. Coon J. S. t. Kujawa S. A. Liu S. et al (2022). Tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase-2 in uterine leiomyoma: dysregulation by MED12 mutation status. Reprod. Sci.29, 743–749. 10.1007/s43032-022-00852-y
29
Jones G. S. (1976). The luteal phase defect. Fertil. Steril.27, 351–356. 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)41769-3
30
Kaluka D. Batabyal D. Chiang B. Y. Poulos T. L. Yeh S. R. (2015). Spectroscopic and mutagenesis studies of human PGRMC1. Biochemistry54, 1638–1647. 10.1021/bi501177e
31
Kantor B. S. Dey S. K. Johnson D. C. (1985). Catechol oestrogen induced initiation of implantation in the delayed implanting rat. Acta Endocrinol. (Copenh)109, 418–422. 10.1530/acta.0.1090418
32
Karamardian L. M. Grimes D. A. (1992). Luteal phase deficiency: effect of treatment on pregnancy rates. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol.167, 1391–1398. 10.1016/s0002-9378(11)91724-4
33
Kitajima M. Khan K. N. Fujishita A. Masuzaki H. Koji T. Ishimaru T. (2004). Expression of the arylhydrocarbon receptor in the peri-implantation period of the mouse uterus and the impact of dioxin on mouse implantation. Arch. Histol. Cytol.67, 465–474. 10.1679/aohc.67.465
34
Klenov V. Flor S. Ganesan S. Adur M. Eti N. Iqbal K. et al (2021). The Aryl hydrocarbon receptor mediates reproductive toxicity of polychlorinated biphenyl congener 126 in rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol.426, 115639. 10.1016/j.taap.2021.115639
35
Kudo Y. Hara T. Katsuki T. Toyofuku A. Katsura Y. Takikawa O. et al (2004). Mechanisms regulating the expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase during decidualization of human endometrium. Hum. Reprod.19, 1222–1230. 10.1093/humrep/deh218
36
Kyrou D. Kolibianakis E. M. Fatemi H. M. Camus M. Tournaye H. Tarlatzis B. C. et al (2011). High exposure to progesterone between the end of menstruation and the day of triggering final oocyte maturation is associated with a decreased probability of pregnancy in patients treated by in vitro fertilization and intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Fertil. Steril.96, 884–888. 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2011.07.1101
37
Labarta E. Martinez-Conejero J. A. Alama P. Horcajadas J. A. Pellicer A. Simon C. et al (2011). Endometrial receptivity is affected in women with high circulating progesterone levels at the end of the follicular phase: a functional genomics analysis. Hum. Reprod.26, 1813–1825. 10.1093/humrep/der126
38
Lafita-Navarro M. C. Conacci-Sorrell M. (2023). Nucleolar stress: from development to cancer. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol.136, 64–74. 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.04.001
39
Lafita-Navarro M. C. Kim M. Borenstein-Auerbach N. Venkateswaran N. Hao Y. H. Ray R. et al (2018). The aryl hydrocarbon receptor regulates nucleolar activity and protein synthesis in MYC-expressing cells. Genes Dev.32, 1303–1308. 10.1101/gad.313007.118
40
Lafontaine D. L. J. Riback J. A. Bascetin R. Brangwynne C. P. (2021). The nucleolus as a multiphase liquid condensate. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.22, 165–182. 10.1038/s41580-020-0272-6
41
Lee A. J. Cai M. X. Thomas P. E. Conney A. H. Zhu B. T. (2003). Characterization of the oxidative metabolites of 17beta-estradiol and estrone formed by 15 selectively expressed human cytochrome p450 isoforms. Endocrinology144, 3382–3398. 10.1210/en.2003-0192
42
Li D. D. Gao Y. J. Tian X. C. Yang Z. Q. Cao H. Zhang Q. L. et al (2014). Differential expression and regulation of Tdo2 during mouse decidualization. J. Endocrinol.220, 73–83. 10.1530/JOE-13-0429
43
Li D. D. Liu X. Y. Guo C. H. Yue L. Yang Z. Q. Cao H. et al (2015a). Differential expression and regulation of Ido2 in the mouse uterus during peri-implantation period. Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim.51, 264–272. 10.1007/s11626-014-9833-3
44
Li D. D. Yin Y. H. Wu J. Y. Yang Z. Q. Cao H. Zhang Q. L. et al (2015b). Effects of Ido1 on mouse decidualization. Mol. Biol. Mosk.49, 649–657. 10.7868/S002689841503012X
45
Li B. Yan Y. P. He Y. Y. Liang C. Li M. Y. Wang Y. et al (2023a). IHH, SHH, and primary cilia mediate epithelial-stromal cross-talk during decidualization in mice. Sci. Signal16, eadd0645. 10.1126/scisignal.add0645
46
Li Y. Chen S. T. He Y. Y. Li B. Yang C. Yang Z. S. et al (2023b). The regulation and function of acetylated high-mobility group box 1 during implantation and decidualization. Front. Immunol.14, 1024706. 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1024706
47
Li M. Y. Wu Y. Tang H. L. Wang Y. Li B. He Y. Y. et al (2024). Embryo-derived cathepsin B promotes implantation and decidualization by activating pyroptosis. Adv. Sci. (Weinh)11, e2402299. 10.1002/advs.202402299
48
Liang Y. X. Liu L. Jin Z. Y. Liang X. H. Fu Y. S. Gu X. W. et al (2018). The high concentration of progesterone is harmful for endometrial receptivity and decidualization. Sci. Rep.8, 712. 10.1038/s41598-017-18643-w
49
Liu L. Sailan S. Li T. Mariee N. Laird S. Jiang Z. et al (2015). The effect of a high progesterone concentration before oocyte retrieval on the peri-implantation endometrium. Reprod. Biomed. Online31, 739–746. 10.1016/j.rbmo.2015.09.003
50
Liu Q. Zhai J. Kong X. Wang X. Wang Z. Fang Y. et al (2020). Comprehensive analysis of the expression and prognosis for TDO2 in breast cancer. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics17, 153–168. 10.1016/j.omto.2020.03.013
51
Lo S. J. Lee C. C. Lai H. J. (2006). The nucleolus: reviewing oldies to have new understandings. Cell Res.16, 530–538. 10.1038/sj.cr.7310070
52
Lydon J. P. DeMayo F. J. Funk C. R. Mani S. K. Hughes A. R. Montgomery C. A. Jr. et al (1995). Mice lacking progesterone receptor exhibit pleiotropic reproductive abnormalities. Genes Dev.9, 2266–2278. 10.1101/gad.9.18.2266
53
Lydon J. P. DeMayo F. J. Conneely O. M. O'Malley B. W. (1996). Reproductive phenotpes of the progesterone receptor null mutant mouse. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.56, 67–77. 10.1016/0960-0760(95)00254-5
54
MacPherson L. Tamblyn L. Rajendra S. Bralha F. McPherson J. P. Matthews J. (2013). 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (TiPARP, ARTD14) is a mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase and repressor of aryl hydrocarbon receptor transactivation. Nucleic Acids Res.41, 1604–1621. 10.1093/nar/gks1337
55
Mao X. Li H. Zheng J. (2023). Effects of xenobiotics on CYP1 enzyme-mediated biotransformation and bioactivation of estradiol. Drug Metab. Rev.55, 1–49. 10.1080/03602532.2023.2177671
56
Maurya V. K. DeMayo F. J. Lydon J. P. (2021). Illuminating the “black box” of progesterone-dependent embryo implantation using engineered mice. Front. Cell Dev. Biol.9, 640907. 10.3389/fcell.2021.640907
57
McCallum M. L. Pru C. A. Niikura Y. Yee S. P. Lydon J. P. Peluso J. J. et al (2016). Conditional ablation of progesterone receptor membrane component 1 results in subfertility in the female and development of endometrial cysts. Endocrinology157, 3309–3319. 10.1210/en.2016-1081
58
McKiernan S. H. Clayton M. K. Bavister B. D. (1995). Analysis of stimulatory and inhibitory amino acids for development of hamster one-cell embryos in vitro. Mol. Reprod. Dev.42, 188–199. 10.1002/mrd.1080420208
59
McLindon L. A. James G. Beckmann M. M. Bertolone J. Mahomed K. Vane M. et al (2023). Progesterone for women with threatened miscarriage (STOP trial): a placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. Hum. Reprod.38, 560–568. 10.1093/humrep/dead029
60
Mei J. Jin L. P. Ding D. Li M. Q. Li D. J. Zhu X. Y. (2012). Inhibition of Ido1 suppresses cyclooxygenase-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression and decreases proliferation, adhesion and invasion of endometrial stromal cells. Mol. Hum. Reprod.18, 467–476. 10.1093/molehr/gas021
61
Minatogawa Y. Suzuki S. Ando Y. Tone S. Takikawa O. (2003). Tryptophan pyrrole ring cleavage enzymes in placenta. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.527, 425–434. 10.1007/978-1-4615-0135-0_50
62
Munn D. H. Zhou M. Attwood J. T. Bondarev I. Conway S. J. Marshall B. et al (1998). Prevention of allogeneic fetal rejection by tryptophan catabolism. Science281, 1191–1193. 10.1126/science.281.5380.1191
63
Nebert D. W. Dalton T. P. (2006). The role of cytochrome P450 enzymes in endogenous signalling pathways and environmental carcinogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer6, 947–960. 10.1038/nrc2015
64
Pacheco J. H. L. Elizondo G. (2023). Interplay between Estrogen, Kynurenine, and AHR Pathways: an immunosuppressive axis with therapeutic potential for breast cancer treatment. Biochem. Pharmacol.217, 115804. 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115804
65
Paria B. C. Lim H. Das S. K. Reese J. Dey S. K. (2000). Molecular signaling in uterine receptivity for implantation. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol.11, 67–76. 10.1006/scdb.2000.0153
66
Pru J. K. Clark N. C. (2013). PGRMC1 and PGRMC2 in uterine physiology and disease. Front. Neurosci.7, 168. 10.3389/fnins.2013.00168
67
Rasmussen C. A. Orwig K. E. Vellucci S. Soares M. J. (1997). Dual expression of prolactin-related protein in decidua and trophoblast tissues during pregnancy in rats. Biol. Reprod.56, 647–654. 10.1095/biolreprod56.3.647
68
Schrocksnadel K. Wirleitner B. Winkler C. Fuchs D. (2006). Monitoring tryptophan metabolism in chronic immune activation. Clin. Chim. Acta364, 82–90. 10.1016/j.cca.2005.06.013
69
Sedlmayr P. Blaschitz A. Stocker R. (2014). The role of placental tryptophan catabolism. Front. Immunol.5, 230. 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00230
70
Serrano-Gomez S. J. Maziveyi M. Alahari S. K. (2016). Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition through epigenetic and post-translational modifications. Mol. Cancer15, 18. 10.1186/s12943-016-0502-x
71
Shah N. M. Lai P. F. Imami N. Johnson M. R. (2019). Progesterone-Related immune modulation of pregnancy and labor. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne)10, 198. 10.3389/fendo.2019.00198
72
Soules M. R. Wiebe R. H. Aksel S. Hammond C. B. (1977). The diagnosis and therapy of luteal phase deficiency. Fertil. Steril.28, 1033–1037. 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)42850-5
73
Stone T. W. Darlington L. G. (2002). Endogenous kynurenines as targets for drug discovery and development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.1, 609–620. 10.1038/nrd870
74
Suthaporn S. Jayaprakasan K. Thornton J. G. Walker K. F. Castellanos M. May S. et al (2021). Evaluating the influence of progesterone concentration and time of exposure on in vitro endometrial decidualisation. Mol. Cell Endocrinol.528, 111242. 10.1016/j.mce.2021.111242
75
Suzuki S. Tone S. Takikawa O. Kubo T. Kohno I. Minatogawa Y. (2001). Expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase in early concepti. Biochem. J.355, 425–429. 10.1042/0264-6021:3550425
76
Tatsumi K. Higuchi T. Fujiwara H. Nakayama T. Egawa H. Itoh K. et al (2000). Induction of tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase in the mouse endometrium during implantation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.274, 166–170. 10.1006/bbrc.2000.3115
77
Tsuchiya Y. Nakajima M. Yokoi T. (2005). Cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism of estrogens and its regulation in human. Cancer Lett.227, 115–124. 10.1016/j.canlet.2004.10.007
78
Venetis C. A. Kolibianakis E. M. Bosdou J. K. Tarlatzis B. C. (2013). Progesterone elevation and probability of pregnancy after IVF: a systematic review and meta-analysis of over 60 000 cycles. Hum. Reprod. Update19, 433–457. 10.1093/humupd/dmt014
79
Wang H. Dey S. K. (2006). Roadmap to embryo implantation: clues from mouse models. Nat. Rev. Genet.7, 185–199. 10.1038/nrg1808
80
Wetendorf M. DeMayo F. J. (2012). The progesterone receptor regulates implantation, decidualization, and glandular development via a complex paracrine signaling network. Mol. Cell Endocrinol.357, 108–118. 10.1016/j.mce.2011.10.028
81
Whirledge S. D. Oakley R. H. Myers P. H. Lydon J. P. DeMayo F. Cidlowski J. A. (2015). Uterine glucocorticoid receptors are critical for fertility in mice through control of embryo implantation and decidualization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.112, 15166–15171. 10.1073/pnas.1508056112
82
Xu K. Liu H. Bai M. Gao J. Wu X. Yin Y. (2017). Redox properties of tryptophan metabolism and the concept of tryptophan use in pregnancy. Int. J. Mol. Sci.18, 1595. 10.3390/ijms18071595
83
Xue C. Li G. Zheng Q. Gu X. Shi Q. Su Y. et al (2023). Tryptophan metabolism in health and disease. Cell Metab.35, 1304–1326. 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.06.004
84
Yang K. Yang J. Yi J. (2018). Nucleolar Stress: hallmarks, sensing mechanism and diseases. Cell Stress2, 125–140. 10.15698/cst2018.06.139
85
Yang S. L. Tan H. X. Niu T. T. Li D. J. Wang H. Y. Li M. Q. (2021). Kynurenine promotes the cytotoxicity of NK cells through aryl hydrocarbon receptor in early pregnancy. J. Reprod. Immunol.143, 103270. 10.1016/j.jri.2020.103270
86
Ye Z. Yue L. Shi J. Shao M. Wu T. (2019). Role of Ido and TDO in cancers and related diseases and the therapeutic implications. J. Cancer10, 2771–2782. 10.7150/jca.31727
87
Yee G. M. Kennedy T. G. (1988). Stimulatory effects of prostaglandins upon endometrial alkaline phosphatase activity during the decidual cell reaction in the rat. Biol. Reprod.38, 1129–1136. 10.1095/biolreprod38.5.1129
88
Yin J. Sheng B. Qiu Y. Yang K. Xiao W. Yang H. (2016). Role of AhR in positive regulation of cell proliferation and survival. Cell Prolif.49, 554–560. 10.1111/cpr.12282
89
Yokoyama Y. Takahashi Y. Hashimoto M. Shinohara A. Lian Z. Tamaya T. (1998). Effects of sex steroids on silver stained proteins of nucleolar organizer regions (Ag-NOR) in the rabbit uterus. Biotech. Histochem73, 202–210. 10.3109/10520299809141111
90
Zhang X. H. Liang X. Liang X. H. Wang T. S. Qi Q. R. Deng W. B. et al (2013). The mesenchymal-epithelial transition during in vitro decidualization. Reprod. Sci.20, 354–360. 10.1177/1933719112472738
91
Zuberi A. Huang Y. Dotts A. J. Wei H. Coon J. S. t. Liu S. et al (2023). MED12 mutation activates the tryptophan/kynurenine/AHR pathway to promote growth of uterine leiomyomas. JCI Insight8, e171305. 10.1172/jci.insight.171305
Summary
Keywords
decidualization, progesterone, IDO1, TDO, KYN, AhR, nucleolin
Citation
Luo H-N, Yang H-Y, Wang Z-M, Luo J-M, Zhang T-T and Yang Z-M (2025) Excessive progesterone impairs mouse decidualization via the Kyn-AhR pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 13:1622998. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1622998
Received
05 May 2025
Accepted
08 September 2025
Published
22 September 2025
Volume
13 - 2025
Edited by
Víctor Carriel, University of Granada, Spain
Reviewed by
Zhenshan Yang, Lund University, Sweden
Yali Hu, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, China
Medhi Wangpaichitr, Miami VA Healthcare System, Veterans Health Administration, United States Department of Veterans Affairs, United States
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Luo, Yang, Wang, Luo, Zhang and Yang.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zeng-Ming Yang, yangzm@gzu.edu.cn
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.