- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Fengcheng Hospital of Fengxian District, Shanghai, China
- 2Clinical Medical College, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China
- 3Key Laboratory of Systems Health Science of Zhejiang Province, School of Life Science, Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, China
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) represents a major global health burden, with resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) posing a significant barrier to effective immunotherapy. Emerging evidence implicates non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs)—including microRNAs (miRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs)—as pivotal regulators of this resistance. In this review, we discuss how ncRNAs contribute to OSCC immunotherapy resistance by modulating immune checkpoint expression, suppressing anti-tumor T cell function while promoting immunosuppressive Tregs, reprogramming the tumor microenvironment (TME) via metabolic remodeling and myeloid cell regulation, and enhancing intrinsic tumor resistance through epigenetic alterations and cancer stem cell activation. These multifaceted roles highlight the therapeutic potential of targeting ncRNAs. Strategies involve inhibiting oncogenic ncRNAs or restoring tumor-suppressive counterparts, facilitated by advanced delivery methods like nanoparticles or exosomes. Combining ncRNA-based therapies with ICIs offers a promising approach to overcome resistance. Key challenges remain, including precise functional annotation, efficient and specific delivery, experimental validation, biomarker identification, and the design of optimized clinical trials—potentially guided by artificial intelligence and multi-omics approaches. Ultimately, targeting the complex ncRNA networks may offer transformative improvements in immunotherapy outcomes for OSCC patients.
1 Introduction
Oral cancer constitutes a major global health challenge, with oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) being the predominant histological type, accounting for approximately 90% of cases (Chai et al., 2020; Kujan et al., 2020). In 2022 alone, there were an estimated 389,485 new cases and 188,230 deaths worldwide (Bray et al., 2024). Despite advances in treatment modalities, the overall prognosis for oral cancer patients remains suboptimal. The average 5-year survival rate hovers around 50%–60% (Lu et al., 2024), a figure that has seen little significant improvement over recent decades (Shao et al., 2025).
The advent of immunotherapy, particularly immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), has marked a significant shift in cancer treatment, including for OSCC (Ma and Kim, 2024). ICIs, such as antibodies targeting programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) or its ligand PD-L1, and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4), function by releasing the brakes on the host immune system, enabling T cells to recognize and attack tumor cells (Mivehchi et al., 2025). The expression of PD-L1 in tumor samples has shown potential as a prognostic and predictive biomarker, supporting the use of ICIs in OSCC management. However, immunotherapy benefits only a subset of OSCC patients. A substantial proportion of patients exhibit primary resistance (lack of initial response) or develop acquired resistance after an initial period of response (Chen F. et al., 2023). The overall response rates to ICI monotherapy in OSCC 10%–20%, benefiting only a fraction of patients (Ries et al., 2024). This limited efficacy highlights significant gaps in our understanding of the complex interactions between the tumor, its microenvironment, and the host immune system that dictate treatment success or failure (He et al., 2025). The heterogeneity of OSCC and the intricate mechanisms enabling tumor cells to evade immune surveillance are major obstacles (Wickenhauser et al., 2021). Therefore, elucidating the mechanisms underlying immune escape and immunotherapy resistance is paramount to developing strategies that can broaden the applicability and enhance the durability of immunotherapeutic responses in oral cancer patients (Li S. et al., 2024).
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are recognized as crucial functional molecules involved in virtually all aspects of cellular biology, with their dysregulation linked to various human diseases, including cancer (Anastasiadou et al., 2018). Aberrant ncRNA expression can drive tumorigenesis, promote metastasis, and contribute to therapy resistance by acting as oncogenic ncRNAs (oncomiRs, onco-lncRNAs) (Zhu P. et al., 2023). They participate in modulating immune checkpoint pathways and shaping the tumor microenvironment (TME) (Denaro et al., 2019). In the context of oral cancer, dysregulated expression of various miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs has been linked to disease initiation, progression, metastasis, and resistance to therapies like chemotherapy (Liu H. et al., 2022). This convergence of ncRNA involvement in both cancer biology and immune regulation strongly suggests their pivotal role in mediating the immune escape mechanisms observed in the oral cancer TME (Dey et al., 2023). Understanding these roles is critical, as ncRNAs represent a largely untapped source of potential diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets to overcome immunotherapy limitations (Li R. et al., 2024; Fan et al., 2025).
This review systematically delineates the mechanisms by which ncRNAs, particularly miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs, mediate immunotherapy resistance in OSCC, with a focus on their regulation of key immune processes within the OSCC TME. We highlight the intricate molecular mechanisms by which ncRNAs modulate immune checkpoint expression, reshape the immune landscape, and promote a suppressive TME. In parallel, we discuss emerging therapeutic strategies that target these ncRNAs, including both inhibitory and restorative approaches, and explore their potential when combined with ICIs. Finally, we address the key challenges that hinder the clinical translation of ncRNA-based diagnostics and therapeutics, while outlining promising directions for future research aimed at overcoming these barriers.
2 Core mechanisms of ncRNA-Mediated immunotherapy resistance
ncRNAs are broadly classified based on size, with small ncRNAs (<200 nucleotides) including microRNAs (miRNAs), small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), and Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs), and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) comprising transcripts >200 nucleotides (Mehler and Mattick, 2007). Circular RNAs (circRNAs), characterized by a covalently closed loop structure, represent another major class (Kos et al., 1986). ncRNAs exert their regulatory functions through diverse and intricate mechanisms (Chen K. et al., 2023). miRNAs typically function post-transcriptionally by binding to target messenger RNAs (mRNAs), primarily within the 3′ untranslated region (UTR), leading to mRNA degradation or translational repression (Moore, 2005). LncRNAs exhibit remarkable functional versatility; they can act as molecular scaffolds assembling protein complexes, as guides recruiting chromatin-modifying enzymes (like Polycomb Repressive Complex 2, PRC2) to specific genomic loci for epigenetic regulation (Balas et al., 2021), as decoys sequestering proteins or miRNAs, and as competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) that “sponge” miRNAs, thereby regulating the expression of other miRNA targets (Salmena et al., 2011). CircRNAs, owing to their stability, primarily function as potent miRNA sponges but can also interact with proteins and regulate transcription or splicing (Memczak et al., 2013).
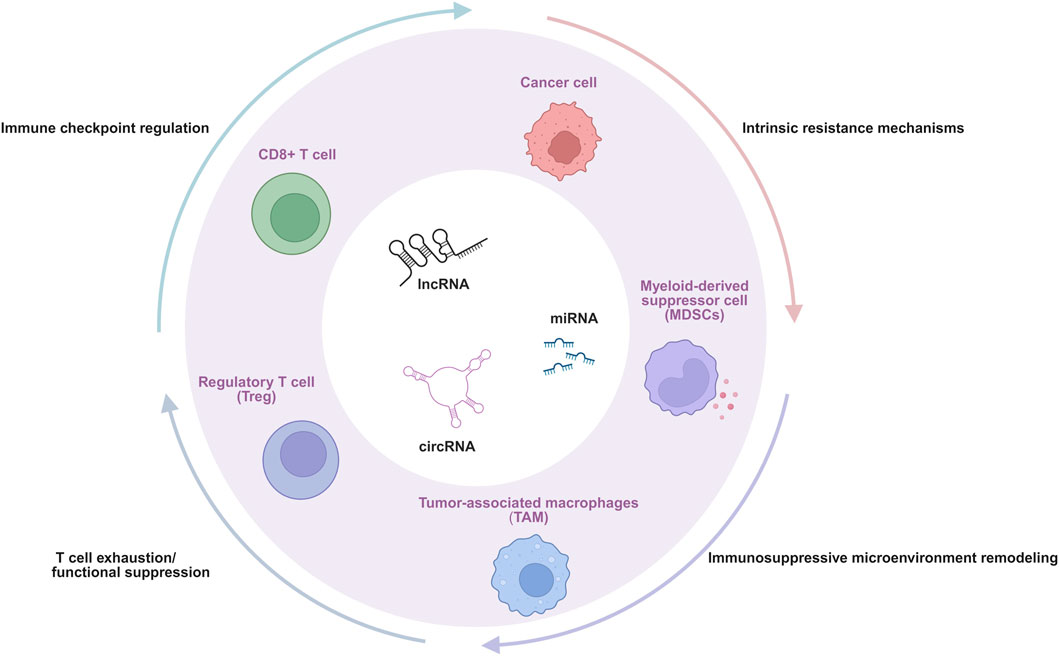
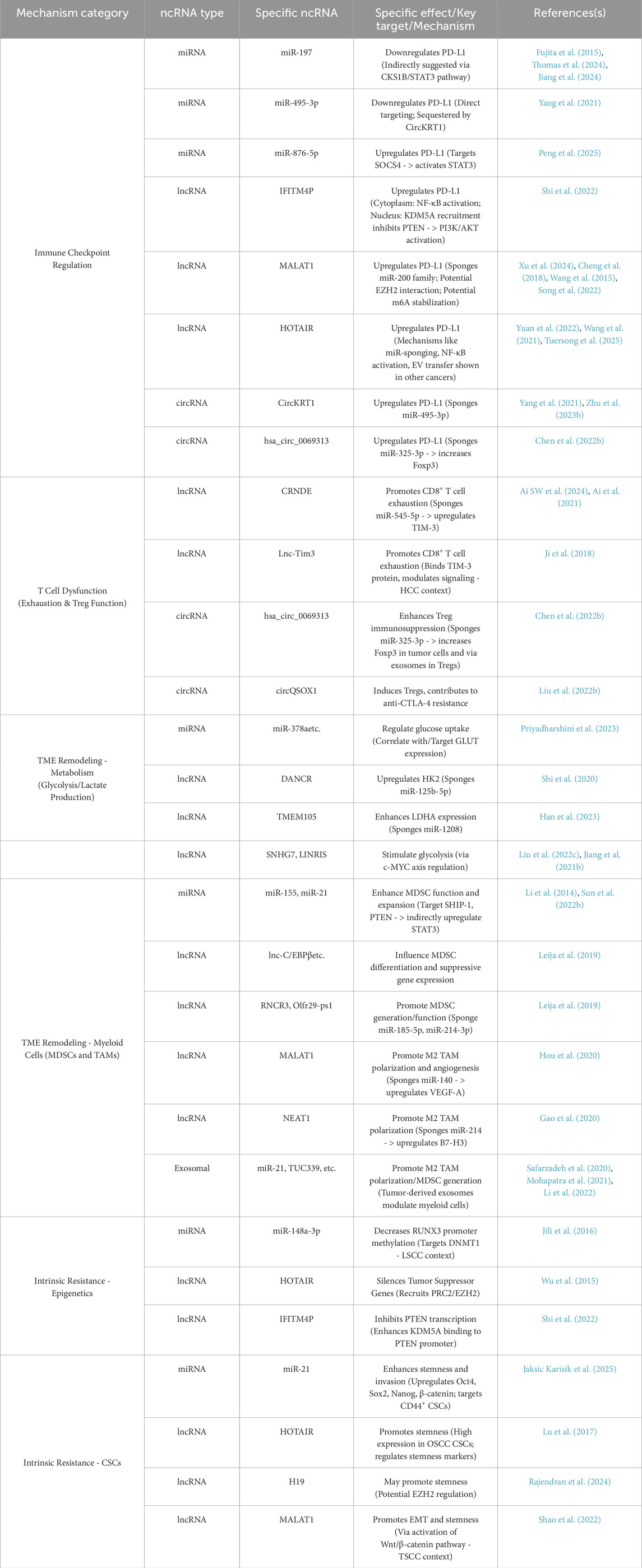
Given the indispensable role of ncRNAs in gene expression regulatory networks and their broad impact on various tumor biological behaviors, their involvement in the complex process of immune escape in oral cancer is receiving increasing attention (Memczak et al., 2013; Chen et al., 2017; O'Connell et al., 2010). ncRNAs do not function via a single pathway; instead, they weave a multi-level, multi-faceted regulatory network, intricately manipulating the interaction between tumor cells and the immune system, ultimately leading to the failure of immune surveillance and tumor progression (Denaro et al., 2019; O'Connell et al., 2010). Although numerous pathways are involved, current research evidence and therapeutic relevance increasingly point to four interconnected and crucial core mechanisms that constitute the main pillars of ncRNA-mediated immune escape in oral cancer. These four core mechanisms are: (Chai et al., 2020): the direct regulation of key immune checkpoint molecules, which affects T cell activation and tumor immune visibility (Saadi et al., 2022; Kujan et al., 2020) the induction of T cell exhaustion and functional suppression, alongside the promotion of regulatory T cells (Tregs) (Li et al., 2025; Afra et al., 2024); (Bray et al., 2024) the profound remodeling of the immunosuppressive TME, including influencing metabolic reprogramming and myeloid cell populations; and (Lu et al., 2024) the enhancement of intrinsic resistance mechanisms within tumor cells. These interconnected processes collectively enable tumor immune evasion (Figure 1). Following we will dissect in detail how various types of ncRNAs (miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs) specifically mediate immune escape in oral cancer through these four core mechanisms (Table 1).
2.1 ncRNA regulation of immune checkpoint pathways
The PD-1/PD-L1 pathways are critical negative regulators of T cell activation and function, acting as crucial “brakes” on the immune system to maintain self-tolerance (Freeman et al., 2000; Pardoll, 2012; Tivol et al., 1995). PD-L1, often upregulated on tumor cells or immune cells within the TME, binds to PD-1 on activated T cells, suppressing their proliferation, cytokine production, and cytotoxic activity (Pauken and Wherry, 2015; Wherry et al., 2007). While ICIs targeting PD-1/PD-L1 pathways have revolutionized cancer therapy, resistance remains a major challenge (Sharma et al., 2017). Tumor cells commonly evade immune surveillance by exploiting the PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint pathway. Emerging evidence indicates that ncRNAs are key players in regulating the expression and function of these checkpoint molecules, offering potential explanations for resistance and new therapeutic targets (Chen B. et al., 2022).
2.1.1 Specific miRNAs regulating checkpoints in OSCC
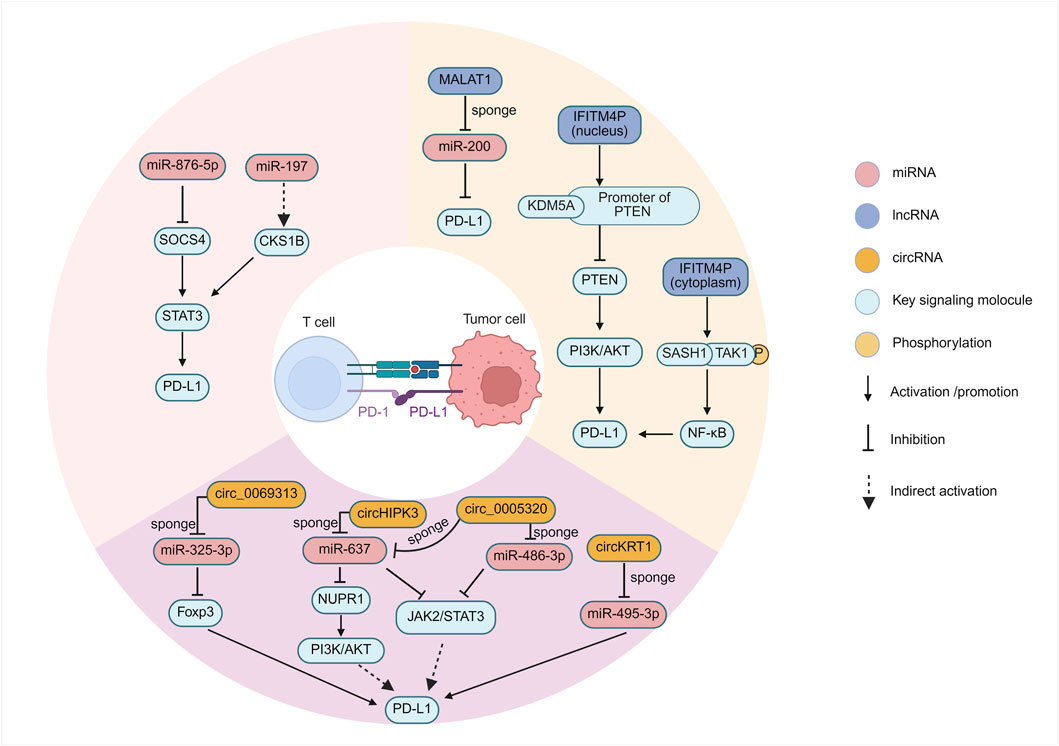
miRNAs are potent regulators of immune checkpoint expression (Vaxevanis et al., 2024). Research involving OSCC patient samples has revealed an inverse correlation between the expression levels of miR-197 and PD-L1 protein (Ahn et al., 2017). Although the direct binding of miR-197 to the PD-L1 3′UTR in OSCC cells requires further validation, studies in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) suggest a potential regulatory pathway involving miR-197, CKS1B (CDC28 protein kinase regulatory subunit 1B), and STAT3 (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3), where miR-197 downregulation leads to increased CKS1B/STAT3 activity and subsequent PD-L1 upregulation (Fujita et al., 2015). Given that STAT3 signaling is relevant in OSCC (Thomas et al., 2024; Jiang et al., 2024), this pathway provides a plausible, albeit indirectly supported, mechanism for miR-197-mediated PD-L1 regulation in OSCC (Figure 2). The implication is that loss of miR-197 expression could contribute to immune evasion by relieving the suppression of PD-L1.
In OSCC, functional assays including dual-luciferase reporter assays have confirmed that miR-495-3p directly targets PD-L1 mRNA, and its downregulation or functional sequestration in OSCC contributes to increased PD-L1 expression (Yang et al., 2021). Crucially, this regulation was shown to be part of a larger ceRNA network involving a circular RNA, CircKRT1, which acts as a sponge for miR-495-3p (Yang et al., 2021). This finding provides a clear example of how miRNA directly mediates the suppression of PD-L1 in OSCC and how this suppression can be counteracted by other ncRNAs.
Furthermore, a study in OSCC identified upregulated miR-876-5p expression, which significantly correlated with tumor recurrence and poor clinical prognosis. Functionally, miR-876-5p was shown to promote OSCC cell proliferation, migration, stemness, and chemoresistance. Mechanistically, miR-876-5p directly targets the tumor suppressor SOCS4 (Suppressor of cytokine signaling 4), leading to sustained activation of the STAT3 pathway and subsequent upregulation of PD-L1, thereby facilitating tumor immune escape (Peng et al., 2025). This study establishes a clear connection between miR-876-5p and various malignant phenotypes as well as immune evasion through the SOCS4/STAT3/PD-L1 axis in OSCC. This underscores the potential for miRNAs to act as critical nodes integrating distinct oncogenic mechanisms, suggesting that targeting miR-876-5p could concurrently counteract multiple malignant characteristics of OSCC.
Several other miRNAs have been implicated in regulating PD-L1 in various cancer types, including miR-138-5p, miR-513, miR-570, miR-34a, and miR-200 (Chen et al., 2016; Deng et al., 2023; Song N. et al., 2020; Zhao et al., 2016; Chen et al., 2014; Kishta et al., 2025). However, their specific roles and direct interactions with PD-L1 mRNA within the OSCC context have not yet been definitively established based on the available data. While miRNAs like miR-21 are frequently upregulated in OSCC and associated with poor prognosis and cancer stem cell properties (Jaksic Karisik et al., 2025), and others like miR-375, miR-92b-3p, and miR-486-5p are downregulated and associated with recurrence (Yan et al., 2017), their direct regulatory impact on PD-1, PD-L1, or CTLA-4 expression in OSCC remains largely uninvestigated.
The available evidence indicates that miRNAs provide a significant layer of post-transcriptional control over immune checkpoint expression, particularly PD-L1, within OSCC cells. The downregulation or sequestration of specific tumor-suppressive miRNAs, such as miR-197 and miR-495-3p, appears to directly contribute to the upregulation of PD-L1 on OSCC cells. This mechanism represents a direct route by which miRNA dysregulation can facilitate immune evasion. Since PD-L1 binding to PD-1 on T cells suppresses anti-tumor immunity (Hirai et al., 2017), the loss of miRNA-mediated inhibition of PD-L1 allows tumor cells to enhance this immunosuppressive signaling.
2.1.2 lncRNA networks regulating checkpoints in OSCC
In the context of various cancers, lncRNAs have been demonstrated to participate in the regulation of immune checkpoint pathways, providing a framework for potential mechanisms in OSCC. For example, multiple lncRNAs have been shown to modulate PD-L1 expression by acting as microRNA sponges. In pancreatic cancer, LINC00473 promotes PD-L1 expression by sponging miR-195-5p (Zhou et al., 2019), while in hepatocellular carcinoma, PCED1B-AS1 upregulates PD-L1 via miR-194-5p (Fan et al., 2021). Similarly, the lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 regulates PD-L1 by sponging miR-15a in prostate cancer and miR-506 in hepatocellular carcinoma (Chen et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2020), and it also affects the miR-30a/USP22 axis in colorectal cancer, which has implications in cancer progression though direct regulation of PD-L1 protein stability via this specific axis requires further clarification (Xian et al., 2021). Beyond these mechanisms, Some lncRNAs indirectly regulate checkpoints by influencing signaling pathways. CASC11 affects PD-L1 by activating NF-κB and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling through the EIF4A3/E2F1 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma (Song H. et al., 2020), while HOTTIP induces IL-6 production, activating the IL-6/JAK/STAT3/PD-L1 pathway in neutrophils within the ovarian cancer microenvironment (Shang et al., 2019). Furthermore, lncRNAs employ epigenetic mechanisms, such as HOTAIR potentially participating in PRC2-mediated silencing (Balas et al., 2021), and LncMX1–215 inhibiting PD-L1 and Galectin-9 expression by interfering with GCN5-mediated H3K27 acetylation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (Ma et al., 2020). Even more directly, lncRNAs like Lnc-Tim3 can bind to immune checkpoint proteins (e.g., TIM-3), interfere with their downstream molecular interactions, and consequently affect T cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma (Ji et al., 2018). These examples from other cancers highlight plausible, yet unconfirmed, regulatory axes that warrant investigation within the OSCC-specific context.
In the field of OSCC, research investigating the lncRNA-mediated regulation of immune checkpoints has also yielded notable advances (Figure 2). During the progression from oral leukoplakia, a premalignant lesion, to OSCC, the long non-coding RNA IFITM4P was found to be significantly upregulated and promotes PD-L1 expression through a unique dual mechanism dependent on its subcellular localization (Shi et al., 2022). In the cytoplasm, IFITM4P functions as a molecular scaffold, facilitating the interaction between SASH1 and TAK1, leading to TAK1 phosphorylation at Thr187. This subsequently activates the NF-κB signaling pathway, evidenced by p65 phosphorylation at Ser536, which in turn induces PD-L1 gene transcription. By contrast, within the nucleus, IFITM4P enhances the binding of the histone demethylase KDM5A to the promoter of the tumor suppressor gene PTEN, thereby inhibiting PTEN transcription (Shi et al., 2022). The resulting loss or inactivation of PTEN function is known to activate the PI3K/AKT pathway, which subsequently leads to the indirect upregulation of PD-L1 expression. This discovery not only reveals the pro-oncogenic role of IFITM4P in oral carcinogenesis but also elegantly demonstrates how the same lncRNA can utilize distinct molecular mechanisms—signal transduction modulation in the cytoplasm and epigenetic regulation in the nucleus—to synergistically upregulate the key immune checkpoint molecule PD-L1. The complexity and precision of this regulatory mechanism highlight the central role of lncRNAs in cellular regulatory networks. Intriguingly, in mouse models, tumors exhibiting high IFITM4P expression demonstrated enhanced sensitivity to anti-PD-1 antibody therapy (Shi et al., 2022), suggesting that IFITM4P could serve as a potential biomarker for predicting ICI efficacy, despite its function in promoting PD-L1 expression.
LncRNA MALAT1, a well-documented oncogenic driver upregulated in OSCC and other malignancies, promotes tumor progression through multifaceted mechanisms including PD-L1 mediated immune evasion (Chang and Hu, 2018; Xiao et al., 2020). Its overexpression correlates strongly with advanced disease stages, metastatic propensity, and dismal clinical outcomes (Fu et al., 2020). Mechanistically, its regulation of PD-L1 is complex, with several potential pathways elucidated in other cancers that may also be relevant to OSCC: (I) ceRNA activity by sponging miR-200 family members that normally suppress PD-L1 translation, MALAT1 derepresses PD-L1 production, enabling cancer cells to evade T cell surveillance in lung cancer (Xu et al., 2024); (II) MALAT1 interacts with epigenetic regulatory complexes. Specifically, its association with EZH2, the catalytic subunit of the PRC2 complex, has been demonstrated in cancers such as pancreatic cancer (Cheng et al., 2018) and castration-resistant prostate cancer (Wang et al., 2015). This interaction suggests that MALAT1 might influence PD-L1 expression by guiding epigenetic modifications or by serving as a regulatory protein scaffold, although the precise mechanism in OSCC requires further investigation; (III) At the epitranscriptomic level, the N6-methyladenosine (m6A) writer protein METTL3 has been shown in pancreatic cancer to enhance MALAT1 stability. This modification indirectly increases PD-L1 levels by increasing the abundance of the MALAT1 transcript (Song et al., 2022). Although direct evidence for some of these pathways in OSCC is still emerging, these convergent mechanisms, validated across different cancers, collectively suggest that MALAT1 is a potential regulator of immunosuppressive signaling in OSCC.
HOX transcript antisense intergenic RNA (HOTAIR) is another lncRNA frequently overexpressed in numerous cancers, including OSCC, where its high levels are associated with advanced stage, metastasis, poor prognosis, and the promotion of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) (Chen et al., 2021). However, the mechanisms by which HOTAIR upregulates PD-L1 have been elucidated primarily in other tumor types, and their applicability to OSCC requires specific investigation. HOTAIR employs several mechanisms to upregulate PD-L1 expression and promote immune evasion in cancer. One prominent mechanism involves acting as a ceRNA or microRNA sponge. In laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma, HOTAIR sponges hsa-miR-30a-5p, thereby relieving the inhibition of its target GRP78 (HSPA5), which subsequently leads to increased PD-L1 protein levels (Yuan et al., 2022). Although not yet confirmed in OSCC, this suggests a plausible regulatory axis. Another key mechanism is the activation of signaling pathways that control PD-L1 transcription. In glioma, HOTAIR has been shown to activate the NF-κB pathway, potentially by suppressing upstream inhibitors like UBXN1, leading to increased NF-κB nuclear translocation and subsequent binding to the PD-L1 promoter to drive its expression (Wang et al., 2021). Furthermore, HOTAIR can be transferred between cells via extracellular vesicles (EVs), as observed in esophageal cancer, where EV-delivered HOTAIR modulates the TME and upregulates PD-L1 in recipient cells, contributing to chemoresistance and immune escape (Tuersong et al., 2025). While HOTAIR is well-known for recruiting the PRC2 complex for epigenetic silencing, its direct regulation of PD-L1 appears to rely more on these post-transcriptional and signaling-based mechanisms found in other cancers, highlighting the need for studies to validate these pathways specifically within the OSCC context.
The involvement of lncRNAs adds significant complexity to the regulation of immune checkpoints in OSCC. They function as crucial integrators, connecting diverse upstream cellular signals—ranging from inflammatory responses triggered by the microenvironment (e.g., LPS/TLR4 activating IFITM4P (Ji et al., 2024)) to aberrant activation of developmental pathways like Wnt/β-catenin driving EMT (Shao et al., 2022)—to downstream effectors, including potentially the expression levels of immune checkpoint molecules like PD-L1. This positions lncRNAs as central mediators translating the cellular state and environmental cues into specific immune evasion phenotypes.
2.1.3 CircRNAs regulating checkpoints in OSCC
Specific circRNAs have been identified that directly regulate the expression of PD-L1 in OSCC, consequently contributing to tumor immune evasion (Figure 2). CircKRT1 is significantly upregulated in OSCC tissues and cell lines, such as Cal-27, SCC-25, SCC-9, and HSC-3 (78). Functional studies have demonstrated that circKRT1 acts as a sponge for miR-495-3p, sequestering this miRNA and thus relieving its inhibitory effect on the target PD-L1 mRNA, which leads to the upregulation of PD-L1 protein expression. Elevated PD-L1 levels subsequently inhibit the anti-tumor activity of CD8+ T cells, promote OSCC cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and the EMT process, ultimately facilitating immune escape and accelerating tumor progression. Clinical data also indicate that high expression of circKRT1 is closely associated with poor prognosis in OSCC patients (Yang et al., 2021).
Another extensively studied circRNA, hsa_circ_0069313 (also designated as circ_0069313), is also highly expressed in OSCC tissues and cells, and its expression level is significantly associated with advanced clinical stage and poor prognosis (Chen Y. et al., 2022). The mechanism of this circRNA involves a dual role in promoting immune evasion. First, hsa_circ_0069313 competitively binds to miR-325-3p, thereby preventing the miRNA-mediated degradation of Forkhead box P3 (Foxp3) mRNA, resulting in increased Foxp3 protein levels within OSCC cells themselves (Chen Y. et al., 2022). Increased Foxp3 subsequently upregulates the expression of the immune checkpoint protein PD-L1 on the surface of cancer cells (Mulder et al., 2025; Xu et al., 2023). This completes a key immunosuppressive cascade: the elevated PD-L1 on tumor cells engages with its receptor, PD-1, on activated cytotoxic CD8+ T cells. This interaction recruits the phosphatase SHP-2 to the PD-1 cytoplasmic domain, which in turn dampens the T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling cascade. The ultimate consequence is the induction of T-cell exhaustion, a state of dysfunction characterized by reduced proliferation, impaired cytokine production (e.g., IFN-γ, TNF-α), and diminished cytotoxic capacity, thereby allowing the tumor to escape immune-mediated destruction (Celis-Gutierrez et al., 2019). This is consistent with clinical findings where high hsa_circ_0069313 levels negatively correlate with CD8+ T cell infiltration scores in OSCC tissues (Chen Y. et al., 2022). Second, hsa_circ_0069313 can also be packaged into exosomes secreted by OSCC cells and subsequently delivered to Tregs within TME. Inside Tregs, exosome-derived hsa_circ_0069313 continues to function as a sponge for miR-325-3p, stabilizing Foxp3 expression (Chen Y. et al., 2022). This stabilization is critical, as foundational studies have established Foxp3 as the master regulatory gene that programs the entire immunosuppressive lineage and function of Tregs (Fontenot et al., 2003; Hori et al., 2003). This fundamental program, driven by sustained Foxp3 expression, includes the upregulation of characteristic molecules like CD25, GITR, and the inhibitory receptor CTLA-4 (Fontenot et al., 2003). Functionally, it renders Tregs hyporesponsive to TCR stimulation while empowering them to actively suppress the proliferation of other effector T cells through mechanisms requiring cell-to-cell contact (Fontenot et al., 2003; Hori et al., 2003). By reinforcing this core suppressive program in Tregs within the tumor microenvironment, the exosome-delivered circRNA enhances their capacity to inhibit anti-tumor effector cells. This dual action—enhancing PD-L1 on tumor cells and reinforcing the suppressive machinery of Tregs—establishes hsa_circ_0069313 as a critical driver of immunosuppression in OSCC. In addition to the circRNAs mentioned above that directly regulate PD-L1, some circRNAs dysregulated in OSCC, while not yet directly proven to regulate PD-L1, are implicated in modulating key signaling pathways, such as the PI3K/AKT and JAK/STAT pathways, which are known to be closely involved in PD-L1 regulation (Sanchez et al., 2024; Wu et al., 2024). These suggest that circRNAs might indirectly influence the immune checkpoint status in OSCC. CircHIPK3, which is highly expressed in OSCC, reportedly activates the PI3K/AKT pathway via the miR-637/NUPR1 axis, a critical pathway for PD-L1 expression regulation (Jiang W. et al., 2021). Similarly, the highly expressed circ_0005320 can activate the JAK2/STAT3 pathway by sponging miR-486-3p and miR-637; STAT3 signaling is also a key inducer of PD-L1 transcription which is mentioned above (Zheng et al., 2022). Nevertheless, these potential indirect regulatory links still require more direct experimental evidence for confirmation.
Collectively, based on the available research data, the study of direct regulation of immune checkpoints, particularly PD-L1, by circRNAs in OSCC is still in its relatively early stages. The number of clearly reported and thoroughly investigated examples is limited, and the observed mechanisms predominantly involve the miRNA sponge effect. This current situation may reflect the maturity of this research field, while also suggesting that the miRNA sponge mechanism could be a primary mode of circRNA-mediated PD-L1 regulation in OSCC.
2.2 T Cell exhaustion and functional suppression
2.2.1 CD8+ T Cell exhaustion
Cytotoxic CD8+ T lymphocytes (CTLs) are critical for eliminating cancer cells (Zabeti and Vahidi, 2024). However, within the TME, chronic antigen exposure and immunosuppressive signals can drive CTLs into a state of exhaustion (Chen et al., 2025; Zarour, 2016). Persistent antigen stimulation leads to sustained high expression of PD-1 on the T cell surface (Freeman et al., 2006), while the interaction between PD-1 and PD-L1, represents a critical pathway for inducing T cell exhaustion (Sasaki et al., 2024). As previously mentioned, miR-495-3p directly targets the PD-L1 mRNA. The downregulation or trapping of this miRNA in OSCC results in increased expression of PD-L1 (Yang et al., 2021). In non-small cell lung cancer, circRNA-002178 acts as a ceRNA sponge for specific miRNAs, subsequently upregulating the expression of both PD-1 and PD-L1 (Li Z. et al., 2024). Furthermore, in nasopharyngeal carcinoma, circBART2.2 upregulates PD-L1 expression and induces T cell apoptosis (Li Z. et al., 2024). These findings indicate that ncRNAs are involved in CTL-mediated immunosuppression associated with PD-1/PD-L1 interaction.
T cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain containing-3 (TIM-3) is another critical marker of T cell exhaustion, often co-expressed with PD-1 on the most functionally defective tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) (Sakuishi et al., 2010). In OSCC, the expression level of the lncRNA CRNDE is significantly elevated within tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells and shows a negative correlation with interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) production (Ai SW et al., 2024). Further mechanistic investigation revealed that CRNDE functions as a ceRNA by competitively binding to miR-545-5p, which relieves the suppressive effect of miR-545-5p on TIM-3 (encoded by the HAVCR2 gene) mRNA. This results in upregulated TIM-3 protein expression, which consequently promotes CD8+ T cell exhaustion and diminishes their anti-tumor cytotoxic capabilities (Ai et al., 2021). This CRNDE/miR-545-5p/TIM-3 axis provides concrete molecular evidence for lncRNA-mediated regulation of T cell exhaustion in OSCC through ceRNA network interactions. Additionally, in hepatocellular carcinoma, the lncRNA Lnc-Tim3 was found to be highly expressed in exhausted CD8+ T cells. It can directly bind to the TIM-3 receptor, preventing the interaction between TIM-3 and Bat3, and inhibiting the downstream Lck/NFAT1/AP-1 signaling pathway. Concurrently, it promotes Bat3 nuclear translocation, enhancing the p300-dependent transcriptional activation of anti-apoptotic genes (such as MDM2 and Bcl-2) by p53 and RelA, thereby exacerbating the state of T cell exhaustion (Ji et al., 2018). Therefore, modulating miRNAs targeting TIM-3 or associated lncRNAs holds therapeutic potential for reversing T cell exhaustion (Zabeti and Vahidi, 2024).
Lymphocyte-activation gene 3 (LAG-3) is an inhibitory receptor expressed on the surface of various lymphocytes; it negatively regulates T cell activation and effector function through binding to Major Histocompatibility Complex class II (MHC-II) molecules (Wuerdemann et al., 2020). LAG-3 is frequently co-expressed with PD-1 on exhausted T cells and synergistically drives their state of exhaustion (Sakuishi et al., 2010). Studies have shown that the combined action of LAG-3 and PD-1 can drive the expression of the exhaustion-associated transcription factor TOX. Furthermore, effective enhancement of anti-tumor immunity upon blockade of both LAG-3 and PD-1 requires autocrine interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) signaling (Andrews et al., 2024). Clinical trials have also confirmed that combined blockade of PD-1 and LAG-3 (e.g., nivolumab plus relatlimab) demonstrates superior efficacy compared to monotherapy blockade in tumors such as melanoma (Andrews et al., 2024). In oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC), LAG-3 expression on TILs is significantly associated with CD8+ T cell infiltration, particularly in HPV-positive cases (Wuerdemann et al., 2020). Although specific reports on the direct regulation of LAG-3 expression by ncRNAs in OSCC are currently lacking, considering the synergistic action of LAG-3 and PD-1, ncRNAs that regulate either pathway individually or both simultaneously are likely to significantly impact the state of T cell exhaustion.
In other disease models, miRNAs such as miR-31 and miR-155 have been demonstrated to be involved in the regulation of pathways associated with T cell exhaustion (Li and Wang, 2022). CircRNAs also play significant roles. Exosome-derived circUSP7 induces CD8+ T cell dysfunction and resistance to anti-PD-1 therapy through the regulation of the miR-934/SHP2 axis. Moreover, the expression and function of circRNAs themselves can potentially be modulated by RNA modifications, such as m6A, which may in turn affect T cell activation and proliferation (Li Z. et al., 2024).
2.2.2 Treg expansion and immunosuppression
In OSCC, increased infiltration of Treg cells is generally associated with poor prognosis, and they are key contributors to the formation of an immunosuppressive microenvironment and the development of immunotherapy resistance (Mohd Faizal et al., 2025). Treg cells, typically characterized by the expression of CD4, CD25, and the transcription factor FOXP3, represent one of the major immunosuppressive cell populations within TME (Ghods et al., 2021). Multiple ncRNAs have been found to directly or indirectly regulate the expression of FOXP3. MiR-125b inhibits FOXP3 expression by targeting the 3′ untranslated region (3′ UTR) of its mRNA (Wang et al., 2018). Conversely, miR-4281 can bind to the human FOXP3 promoter region and upregulate its protein expression (Zhang et al., 2018). In gastric cancer, both the MKL1/miR-34a/FOXP3 axis and miR-133a-3p suppress FOXP3 expression (Wang et al., 2024). In esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), lncRNA MEG3 indirectly upregulates FOXP3 expression by inhibiting the ubiquitination of p53, an upstream regulator of miR-149-3p, thereby enhancing the immunosuppressive activity of Tregs (Xu et al., 2021). In hepatocellular carcinoma, lnc-EGFR promotes immune evasion by stabilizing the EGFR protein, which enhances the downstream AP-1/NF-AT1 signaling pathway and drives Treg differentiation (Jiang et al., 2017). In OSCC, circRNA has_circ_0069313 has been found to promote tumor immune evasion through the miR-325-3p/Foxp3 axis, a mechanism impacting both OSCC cells and Tregs (Chen Y. et al., 2022). This multi-layered and intricate regulatory network underscores the crucial role of ncRNAs in maintaining the immunosuppressive state within TME.
Specific ncRNAs have been directly linked to Treg-mediated immunotherapy resistance. CircQSOX1-mediated Treg induction contributes to resistance against anti-CTLA-4 therapy (Liu Z. et al., 2022), whereas circ_0069313 promotes immune evasion in OSCC by influencing Tregs (Chen Y. et al., 2022). This suggests that assessing the expression levels of specific ncRNAs within Tregs could aid in predicting patient responses to certain immune checkpoint inhibitors. Furthermore, targeting these pivotal ncRNA molecules may represent a novel strategy to overcome Treg-mediated immunosuppression and therapeutic resistance.
2.3 Remodeling of the immunosuppressive microenvironment
2.3.1 Metabolic reprogramming
Metabolic reprogramming is one of the ten hallmarks of cancer (Meng et al., 2024). To meet the energy and biosynthetic demands associated with rapid proliferation, tumor cells exhibit significant metabolic shifts. Most notably, they preferentially engage in glycolysis even under aerobic conditions, resulting in substantial lactate accumulation (Mao et al., 2024). This microenvironment is typically characterized by high lactate levels, low pH, hypoxia, and competition for nutrients. These factors collectively suppress the function of effector T cells while promoting the activity of inhibitory cells, including Tregs and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), consequently leading to immunosuppression and resistance to immunotherapy (Zhang X. et al., 2024). As key regulators of gene expression, ncRNAs play pivotal roles in driving and sustaining tumor metabolic reprogramming. In OSCC, specific ncRNAs have been demonstrated to directly engage with and remodel glycolysis by targeting key metabolic molecules. The m6A-modified circFOXK2 has been shown to enhance the stability of glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) mRNA, thereby promoting carcinogenesis in OSCC (Cui Y. et al., 2023). Another study identified that the upregulated circMDM2 in OSCC promotes cell proliferation and glycolysis by modulating the miR-532-3p/HK2 axis (Zheng et al., 2020). These findings directly link specific circRNAs to core aspects of glycolysis in OSCC.
Multiple miRNAs have been found to regulate the expression of glucose transporters (GLUTs), consequently influencing glucose uptake and the glycolytic rate in OSCC. For instance, miR-378a, miR-182-5p, miR-340, miR-150-5p, and miR-200c have been reported to correlate with GLUT1 expression, whereas miR-23a-3p is associated with GLUT3 (Priyadharshini et al., 2023). Dysregulation of these miRNAs leads to aberrant GLUT expression, subsequently impacting the glycolytic activity of OSCC cells and tumor progression. Moreover, lncRNAs can regulate key enzymes within the glycolytic pathway—such as hexokinase 2 (HK2), lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA), and pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2)—through diverse mechanisms. LncRNA HITT inhibits the oligomerization of PKM2, thereby suppressing lactate production (Zhao et al., 2022); lncRNA DANCR upregulates HK2 by sponging miR-125b-5p (Shi et al., 2020); and lncRNA TMEM105 enhances LDHA expression by acting as a sponge for miR-1208 (Han et al., 2023). These regulatory actions directly impact glycolytic flux and lactate generation.
ncRNAs can regulate key metabolic transcription factors, such as hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and c-Myc, both of which are crucial drivers of the Warburg effect (Alamoudi, 2025). LncRNA SNHG7 stimulates glycolysis via the SRSF1/c-MYC axis (Liu J. et al., 2022), while lncRNA LINRIS maintains glycolysis by stabilizing the IGF2BP2 protein, leading to upregulated c-Myc expression (Jiang T. et al., 2021). Furthermore, ncRNAs can influence key signaling pathways governing cellular metabolism, including the AMPK, mTOR, and Hippo/YAP pathways. LncRNA MACC1-AS1 influences glycolysis by activating the AMPK pathway (Zhao Y. et al., 2018), while knockdown of lncRNA MALAT1 suppresses phosphorylation within the mTOR pathway, thereby inhibiting the Warburg effect (Malakar et al., 2019).
Through these multifaceted regulatory mechanisms, ncRNAs drive metabolic reprogramming in OSCC, characterized by elevated glycolysis and lactate accumulation, shaping an immunosuppressive TME, which directly suppresses the activity of anti-tumor immune cells, particularly T cells, inducing their dysfunction or exhaustion, thereby establishing a key foundation for immunotherapy resistance.
2.3.2 Myeloid cell-mediated barrier
Myeloid cells, particularly MDSCs and tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), represent major immunosuppressive populations within TME (Mo et al., 2023). Through diverse mechanisms, myeloid cells suppress T cell responses, promote tumor progression and immune evasion, thereby constituting a formidable barrier to effective immunotherapy (Huang et al., 2025). ncRNAs play crucial roles in regulating the differentiation, recruitment, polarization, and function of these myeloid cells.
MDSCs constitute a heterogeneous population of immature myeloid cells characterized by potent immunosuppressive capabilities (Sun Y. et al., 2022). Within the TME of OSCC, MDSCs suppress T cell proliferation and function through the production of factors such as arginase 1 (ARG1), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and reactive oxygen species (ROS), while also inducing Treg generation (Li C. et al., 2024). ncRNAs regulate the generation, recruitment, and function of MDSCs through intricate networks. miR-17-5p and miR-20a, by targeting STAT3, can downregulate the suppressive functions of MDSCs, including ROS production (Liang et al., 2022). Similarly, miR-6991-3p targets STAT3, thereby inhibiting MDSC expansion (Sun et al., 2019). Conversely, miR-155 and miR-21 enhance MDSC function and expansion by indirectly upregulating STAT3, achieved through targeting SHIP-1 (Li et al., 2014) and PTEN (Sun Q. et al., 2022), respectively. miR-449c influences the expansion of monocytic MDSCs (M-MDSCs) through the regulation of STAT6 (Han et al., 2020). LncRNAs such as lnc-C/EBPβ, lnc-CHOP, and RUNXOR influence MDSC differentiation and the expression of suppressive genes (Arg-1, iNOS, NOX2) through direct binding to, or indirect regulation of, key transcription factors including C/EBPβ, CHOP, and RUNX1 (Leija et al., 2019). Furthermore, lncRNAs such as RNCR3 and Olfr29-ps1 function by sponging specific miRNAs (miR-185-5p and miR-214-3p), thereby relieving the inhibitory effects of these miRNAs on downstream pro-MDSC generation/function genes, including CHOP and MyD88 (Leija et al., 2019). Moreover, evidence has also demonstrated that tumor cell-derived exosomes can transfer ncRNAs to monocytes, promoting their differentiation into MDSC-like cells and augmenting their immunosuppressive capabilities (Safarzadeh et al., 2020).
As one of the most abundant immune cell populations in the TME, TAMs typically exhibit an M2-like polarization state. They possess functions including the promotion of tumor angiogenesis, matrix remodeling, immunosuppression, and tumor metastasis (Peltanova et al., 2019). The polarization state of macrophages (pro-inflammatory M1 versus anti-inflammatory/pro-tumoral M2) is governed by diverse signals within the TME, with ncRNAs acting as critical regulators in this process (Zhou et al., 2022). MiRNAs such as miR-155 and miR-142-3p typically promote M1 polarization, exerting anti-tumor effects; conversely, miR-21, miR-29a-3p, miR-145, and miR-301a-3p tend to drive M2 polarization, contributing to pro-tumor functions (Mohapatra et al., 2021). LncRNAs also play significant roles: lncRNA MALAT1 promotes M2 polarization and angiogenesis by sponging miR-140, leading to the upregulation of VEGF-A (Hou et al., 2020). Similarly, lncRNA NEAT1 induces M2 polarization by sponging miR-214, resulting in increased B7-H3 expression (Gao et al., 2020). Tumor cells can also deliver specific miRNAs (e.g., miR-21, miR-29a-3p) or lncRNAs (e.g., TUC339, RPPH1) to macrophages via exosomes, thereby promoting their polarization towards an M2 phenotype (Mohapatra et al., 2021). Reciprocally, TAMs can transfer ncRNAs back to tumor cells via exosomes, influencing tumor cell proliferation, invasion, and drug resistance (Li et al., 2022). This bidirectional communication via exosomal ncRNAs constitutes a crucial mechanism underlying the co-evolution of tumor and immune cells within the TME.
In summary, ncRNAs exert fine-tuned control over the generation, recruitment, and functional status of two critical myeloid suppressor cell populations—MDSCs and TAMs—by modulating key transcription factors, signaling pathways, and acting as miRNA sponges. Notably, the exosome-mediated transfer of ncRNAs represents a significant pathway through which tumor cells actively sculpt the immunosuppressive microenvironment. This myeloid cell barrier, meticulously orchestrated by ncRNAs, effectively suppresses anti-tumor T cell responses and represents a major cause of immunotherapy resistance in OSCC.
2.4 Intrinsic resistance mechanisms in tumor cells
In addition to mediating resistance through effects on immune cells and TME, ncRNAs can also directly regulate the intrinsic biological characteristics of tumor cells, thereby conferring inherent resistance to immunotherapy. These mechanisms primarily involve epigenetic remodeling and the maintenance of cancer stem cell (CSC) characteristics.
2.4.1 Epigenetic remodeling
In contrast to genetic mutations that directly change nucleotide sequences, epigenetic modifications—encompassing DNA methylation, histone modifications, and ncRNA-mediated regulation—modulate gene expression patterns without modifying the DNA sequence. These modifications represent one of the key mechanisms underlying tumorigenesis, progression, and the development of therapeutic resistance (Bais, 2019). Aberrant epigenetic patterns are prevalent in OSCC, exemplified by the hypermethylation of promoter regions in tumor suppressor genes (TSGs), leading to their silencing, or by abnormal histone modifications that result in oncogene activation (Kim et al., 2019; Adimulam et al., 2021). There is intricate crosstalk between ncRNAs and epigenetic modifications, which collectively shape the resistant phenotype of tumor cells (Huang and Aghaei-Zarch, 2024).
Certain ncRNAs, especially miRNAs, can directly target and regulate the expression of key epigenetic modifying enzymes, including DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs), histone deacetylases (HDACs), histone methyltransferases (HMTs), and lysine demethylases (KDMs) (Bure et al., 2022; Gazdzicka et al., 2020). In laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma, miR-148a-3p targets DNMT1, thereby decreasing the methylation level of the tumor suppressor gene RUNX3 (Jili et al., 2016). Furthermore, acting as scaffolds or guides in epigenetic regulation, lncRNAs can associate with chromatin-modifying complexes, such as the Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2) containing EZH2, or with other epigenetic enzymes like DNMTs, HDACs, Histone acetyltransferases, and KDMs. By recruiting these complexes/enzymes to specific genomic loci, lncRNAs mediate local histone modifications or DNA methylation, consequently regulating target gene transcription (Lei et al., 2021). The lncRNA HOTAIR, implicated in various cancers including OSCC, suppresses the expression of downstream tumor suppressor genes by recruiting EZH2 and mediating H3K27 trimethylation (Wu et al., 2015). In OSCC, the lncRNA IFITM4P inhibits PTEN transcription by enhancing the binding of KDM5A to the PTEN promoter (Shi et al., 2022).
Conversely, the expression of numerous ncRNA genes is regulated by epigenetic mechanisms, including DNA methylation or histone modifications. In OSCC, the promoter regions of tumor-suppressive miRNAs like miR-137 and miR-193a are frequently silenced via hypermethylation (Kozaki et al., 2008). In contrast, the lncRNA H19 exhibits hypomethylation and elevated expression in OSCC (Rajendran et al., 2024). This bidirectional interplay between ncRNAs and epigenetic machinery establishes a complex regulatory network. Targeting these pivotal ncRNAs or related epigenetic pathways could potentially reverse adverse epigenetic states, reinstate the expression of immune-associated genes, and consequently improve sensitivity to immunotherapy.
2.4.2 Cancer stem cell properties
CSCs represent a small subpopulation within tumors characterized by self-renewal capacity and multipotent differentiation potential. These cells are believed to be the driving force behind tumor initiation, progression, metastasis, recurrence, and resistance to various therapies, including chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and immunotherapy (Chen and Wang, 2019). In OSCC, distinct CSC populations have been identified based on the expression of specific markers, including CD44, ALDH1, CD133, and Bmi-1 (Siqueira et al., 2023). ncRNAs play significant roles in regulating key characteristics of CSCs, and a growing body of research in OSCC has identified specific ncRNA molecules that directly govern the CSC phenotype.
Specific examples of ncRNA regulation in OSCC CSCs include the let-7 family, which inhibits CSC characteristics by targeting factors like Lin28B, ARID3B, and HMGA2, leading to the negative regulation of Oct4, Sox2, and Nanog expression (Hsieh et al., 2020). The miR-200 family inhibits CSC traits by targeting the EMT-associated transcription factors ZEB1/ZEB2, leading to the indirect suppression of the stemness factor Bmi-1 (Hsieh et al., 2020). Conversely, miR-21 enhances stemness maintenance and invasion in CD44+ OSCC CSCs by upregulating the expression of Oct4, Sox2, Nanog, and β-catenin (Jaksic Karisik et al., 2025). The lncRNA HOTAIR is highly expressed in OSCC CSCs, and its knockdown inhibits sphere formation ability, reduces ALDH1 activity, and downregulates the expression of stemness markers (Lu et al., 2017). LncRNA H19 might also contribute to stemness maintenance, potentially through mechanisms involving the regulation of EZH2 in OSCC(150). Furthermore, lncRNA MALAT1 promotes EMT and stemness-associated characteristics in tongue squamous cell carcinoma via activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway (Shao et al., 2022). ncRNAs can also impact the therapeutic resistance of CSCs by regulating components like ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters, anti-apoptotic proteins (such as Bcl-2), and DNA repair pathways. For example, miR-21 suppresses apoptosis in CD44+ OSCC CSCs by modulating the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio (Jaksic Karisik et al., 2025). These examples clearly illustrate the central role of lncRNAs within the OSCC CSC regulatory network.
CSCs can evade immune recognition through the downregulation of Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)/Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) molecules (Zhang et al., 2023). With respect to the regulation of CSC immune evasion, while specific ncRNAs directly controlling MHC expression in CSCs may not be explicitly detailed in the available literature, their extensive regulatory influence over stemness factors (e.g., Sox2, Oct4) and epigenetic mechanisms (which potentially affect MHC expression) suggests their involvement in CSC immune escape pathways. For instance, stemness-maintaining factors like miR-21 or HOTAIR could indirectly contribute to the downregulation of MHC molecules.
Thus, ncRNAs are crucial regulators involved in maintaining the OSCC CSC population and upholding its malignant features. Targeting these critical ncRNAs within CSCs holds the potential not only to directly diminish CSC stemness and therapeutic resistance but also to restore their immunogenicity, rendering them more susceptible to immune system recognition and clearance. Consequently, this approach presents a novel therapeutic strategy for overcoming immunotherapy resistance and preventing tumor recurrence.
3 Therapeutic strategies targeting ncRNAs for OSCC immunotherapy
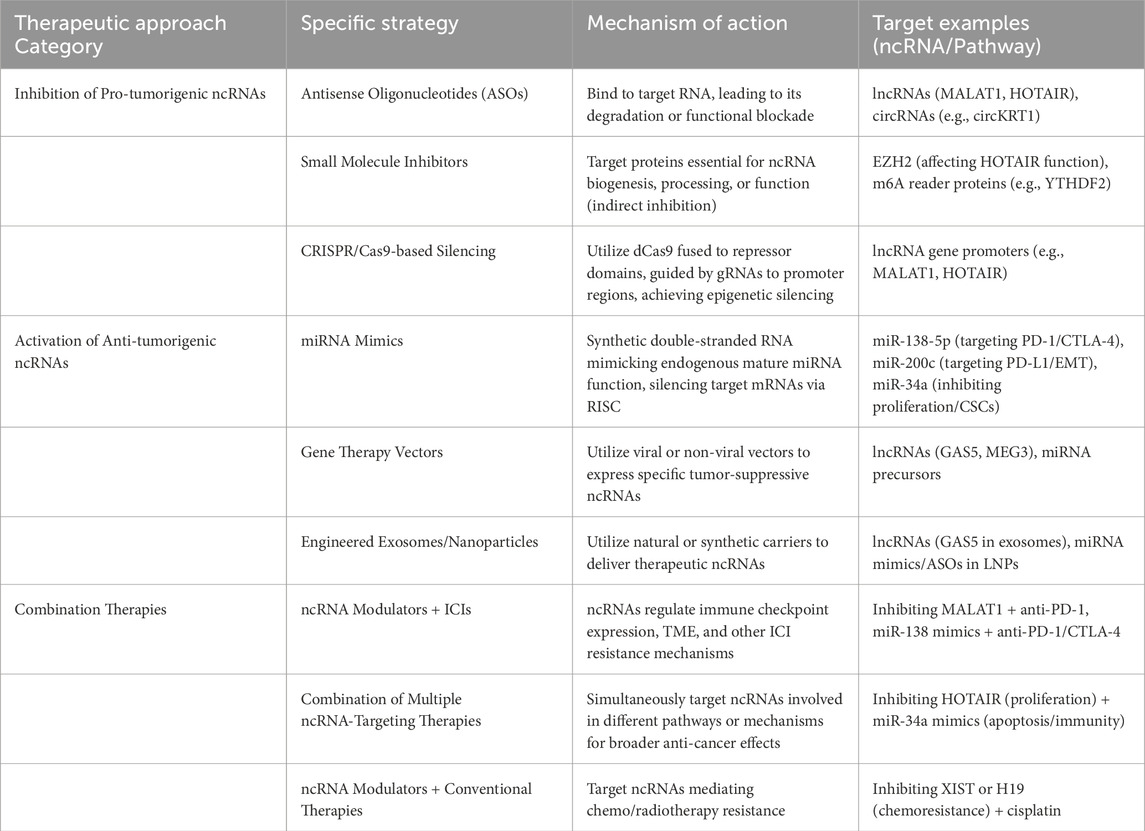
The growing understanding of ncRNAs as critical drivers of immune evasion and therapy resistance in OSCC has spurred interest in developing therapeutic strategies that directly target these molecules (Hashemi et al., 2024). These approaches aim to inhibit the function of pro-tumorigenic ncRNAs or restore the activity of anti-tumorigenic ncRNAs, in order to endogenous anti-tumor immunity or overcoming resistance to existing treatments like ICIs. The summary of therapeutic strategies targeting ncRNAs is listed in Table 2.
3.1 Inhibitory approaches for pro-tumorigenic ncRNAs
Many ncRNAs, particularly certain lncRNAs and miRNAs (oncomiRs), are upregulated in OSCC and promote tumor growth, metastasis, and immune escape by, for example, enhancing PD-L1 expression, driving M2 TAM polarization, or suppressing T cell function (Irimie et al., 2017). Inhibiting these oncogenic ncRNAs presents a rational therapeutic strategy, but how to effectively and specifically deliver therapeutic drugs to tumor cells remains a huge challenge.
3.1.1 Antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs)
ASOs are short, synthetic strands of nucleic acid designed to bind with high specificity to a target RNA molecule through Watson-Crick base pairing. This binding can lead to the degradation of the target RNA or sterically block its function (e.g., preventing interaction with proteins or miRNA binding sites) (Zhang et al., 2019). ASOs can be designed to target specific lncRNAs (like MALAT1 or HOTAIR) or circRNAs (Hua et al., 2025). MALAT1 can sponge miR-125b to increase STAT3 expression (Chang and Hu, 2018), miR-101 to influence EZH2 activity (Ding et al., 2021), and miR-224-5p to modulate KDM2A levels in OSCC (Li et al., 2023). ASOs designed to target MALAT1 have entered preclinical and clinical development for various cancers (Neveu et al., 2024). FLM-7523 (formerly FTX-001), an ASO targeting MALAT1, is reported to be ready for clinical investigation (Neveu et al., 2024). However, the clinical translation of ASOs faces challenges, including ensuring efficient in vivo delivery to solid tumors like OSCC, minimizing potential off-target effects, and managing possible immunotoxicity. To date, their development for OSCC remains firmly in the preclinical stage (Lv et al., 2025).
3.1.2 Small molecule inhibitors
While directly targeting RNA structures with small molecules is challenging, indirect inhibition is possible. Small molecules can target proteins essential for the biogenesis, processing, or function of specific ncRNAs. Inhibitors of EZH2 (a component of PRC2) could attenuate the downstream effects of HOTAIR-mediated gene silencing (Ahmad et al., 2024), or lead to the de-repression of tumor-suppressive miRNAs like miR-34a in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (Li et al., 2021), thereby initiating a cascade of anti-tumor and immunomodulatory effects. In OSCC, HOTAIR binds to EZH2 and induces epigenetic silencing by enhancing H3K27me3 modification levels at the E-cadherin promoter region (Wu et al., 2015). This mechanism suggests that EZH2 inhibitors may restore the expression of tumor suppressor genes such as E-cadherin by blocking the formation of the HOTAIR-PRC2 complex, thereby inhibiting tumor invasion and metastasis. Similarly, inhibitors targeting m6A reader proteins like YTHDF2 are being developed; these could potentially stabilize beneficial m6A-modified RNAs or destabilize oncogenic ones (including mRNAs or ncRNAs regulated by YTHDF2), thereby modulating immune responses (Xiao et al., 2024). While the direct regulation of specific ncRNAs by YTHDF2 in OSCC is an emerging field of investigation, lncRNAs themselves can be m6A-modified, and YTHDF2 could therefore influence their function (Ju et al., 2025). The primary limitation of this indirect strategy is specificity, as these protein targets often have broad cellular functions, which can lead to significant systemic toxicity and this approach is still exploratory and preclinical for OSCC.
3.1.3 CRISPR/Cas9-based silencing
The CRISPR/Cas9 system can be adapted for targeted gene silencing without inducing DNA breaks. Using a catalytically inactive or “dead” Cas9 (dCas9) fused to transcriptional repressor domains (e.g., KRAB domain, or histone modifiers like HDAC1 (Liu J. et al., 2021)), guided by specific guide RNAs (gRNAs), allows for the targeted epigenetic silencing of gene promoters (Rajanathadurai et al., 2024). This approach holds promise for achieving durable silencing of specific oncogenic lncRNA genes, such as MALAT1 or HOTAIR, by altering local chromatin structure. As previously discussed, MALAT1 is a key promoter of OSCC proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. Preclinical investigations and theoretical considerations suggest that CRISPR-mediated knockout or CRISPRi-mediated transcriptional repression of MALAT1 could possibly inhibit OSCC progression (Panda et al., 2025). The precision of CRISPRi might be particularly advantageous for abundant lncRNAs like MALAT1, which may have structural roles in addition to gene regulation (Gutschner et al., 2013); reducing its transcript levels via CRISPRi could mitigate oncogenic effects without completely ablating other potential cellular functions, thereby minimizing toxicity. Although CRISPR exhibits high precision in targeted gene knockout, the clinical translation of CRISPR-based therapies faces substantial hurdles. The safe and efficient in vivo delivery of the entire CRISPR machinery (e.g., Cas9 protein and guide RNAs) to tumor cells remains a major bottleneck, alongside unresolved concerns about long-term safety and off-target effects (Singh et al., 2025). Therefore, this approach is currently confined to preclinical research for OSCC.
3.2 Activation strategies for anti-tumorigenic ncRNAs
Conversely, many ncRNAs, particularly miRNAs like miR-34a, miR-138, and the miR-200 family, function as tumor suppressors, inhibiting proliferation, metastasis, CSC properties, and promoting anti-tumor immunity by targeting oncogenes or immune checkpoints. Their expression is often lost or downregulated during oral cancer progression. Restoring the function of these beneficial ncRNAs is another key therapeutic strategy.
3.2.1 miRNA mimics
These are synthetic double-stranded RNA molecules designed to mimic the function of endogenous mature miRNAs. Once delivered into cells, they are processed and incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) to silence target mRNAs (Ariyoshi et al., 2015; Kawamata et al., 2009). In OSCC,miR-34a is frequently downregulated; however, restoring its levels using mimics has been demonstrated in preclinical models to inhibit OSCC cell proliferation, induce G1 phase arrest, and suppress metastasis and EMT (Li et al., 2021; Li et al., 2015; Ren et al., 2023). However, due to the lack of safe and efficient delivery systems, the clinical development of miRNA mimics has been challenging. A prominent example is the Phase 1 trial of the miR-34a mimic MRX34, which was halted due to severe immune-related adverse events in patients. This trial failure underscores a critical translational hurdle: the toxicity often associated not with the mimic itself, but with the nanoparticle delivery systems required to protect it from degradation in vivo (Hong et al., 2020; Beg et al., 2017).
3.2.2 ncRNA delivery systems
Safe and effective delivery is the cornerstone of ncRNA therapeutics. Viral vectors (e.g., lentivirus, adenovirus) or non-viral vectors (e.g., nanovesicles) (Qi et al., 2022) can be engineered to express specific tumor-suppressive ncRNAs, such as lncRNAs like GAS5 or MEG3, or precursors of beneficial miRNAs (Meng et al., 2021), aiming for sustained expression within target cells. Concurrently, leveraging natural or synthetic delivery vehicles is a major focus. Exosomes, which are natural intercellular messengers, can be engineered to carry specific therapeutic ncRNAs (e.g., lncRNA GAS5) (Gezer et al., 2014; Song et al., 2024). In OSCC, tumor cells naturally secrete exosomes containing specific ncRNA profiles that can influence the TME. The lncRNA MEG3 in OSCC cells has been shown to regulate the content of exosomal miR-421, which in turn promotes angiogenesis in endothelial cells (Huang et al., 2024). Similarly, OSCC-derived exosomes carrying hsa_circ_0069313 can modulate Treg cell function (Zhu M. et al., 2023). This natural role of exosomes in OSCC ncRNA biology provides a strong rationale for their use as therapeutic delivery vehicles. However, significant challenges hinder their clinical use. As discussed in recent studies, key translational hurdles include standardizing isolation methods to ensure purity, improving the stability and efficiency of drug encapsulation, and modifying exosome surfaces for better tumor-targeting specificity (Abd-Rabou et al., 2024). These standardization and manufacturing issues must be resolved before exosomes can be reliably used as therapeutic carriers in OSCC. Furthermore, lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) represent a clinically validated platform for RNA delivery, as demonstrated by mRNA vaccines and siRNA therapeutics (Cui S. et al., 2023). While OSCC-specific clinical data for LNP-ncRNA therapeutics are scarce, preclinical studies in other cancers, such as the delivery of miR-101 using nanorods, have demonstrated increased intracellular ncRNA levels and enhanced therapeutic effects (Xin et al., 2019), highlighting the potential for OSCC. Another promising, though entirely preclinical, strategy involves loading ncRNA therapeutics onto biocompatible scaffolds for controlled, localized release. This approach could be particularly useful for preventing local recurrence after surgery. Recent studies have shown that nanofibrous scaffolds can create a supportive microenvironment for cell-based therapies to repair tissue damage, such as after myocardial infarction (Aglan et al., 2024). This principle could be adapted for OSCC, where a scaffold loaded with miRNA mimics or ASOs could be placed in the tumor bed post-resection to modulate the local immune environment and eliminate residual cancer cells, which may effectively eliminate the recurrence caused by incomplete removal of tumor cells during surgery.
3.3 Rationale and potential of combination therapies
Given the complexity of OSCC biology and the multifactorial nature of immune escape and therapy resistance, combination therapies are likely essential for achieving significant clinical benefit. Targeting ncRNAs offers compelling opportunities for synergistic combinations.
3.3.1 Synergistic ncRNA targeting
Combining different ncRNA-based therapies could provide broader pathway coverage. For example, simultaneously inhibiting an oncogenic lncRNA that promotes proliferation (e.g., HOTAIR (154)) and delivering a tumor-suppressive miRNA mimic that enhances apoptosis or immune recognition (e.g., miR-34a (Li et al., 2015)) might yield greater efficacy.
Perhaps the most immediate potential lies in combining ncRNA modulators with ICIs (e.g., anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies) (Kujan et al., 2020). Since ncRNAs regulate checkpoint expression (e.g., MALAT1/miR-200/PD-L1 (Xu et al., 2024), miR-138/PD-1/CTLA-4 (Wei et al., 2016)) and other resistance mechanisms within the TME (e.g., M2 TAM polarization, T cell exhaustion, metabolic barriers) (Zhang B. et al., 2024), targeting these ncRNAs could potentially reverse resistance and re-sensitize tumors to ICI therapy (Zhou et al., 2023). For instance, inhibiting YTHDF2 showed synergistic effects with anti-PD-L1 (166), and delivering miR-138 mimics could enhance immune checkpoint blockade by targeting multiple checkpoints simultaneously (Liu W. et al., 2021).
3.3.2 Combination with conventional therapies
ncRNAs are deeply involved in regulating sensitivity and resistance to chemotherapy and radiotherapy (Gao et al., 2024). Identifying and targeting the specific ncRNAs that mediate resistance to agents commonly used in OSCC (e.g., cisplatin, 5-FU) could significantly improve the efficacy of these standard treatments. For example, targeting lncRNAs like XIST (Liu H. et al., 2022) or H19 (Yue et al., 2021) implicated in chemoresistance could be beneficial.
The rationale for combining ncRNA modulation with ICIs is particularly strong, addressing the critical clinical challenge of immunotherapy resistance (Vianello et al., 2024; Yang et al., 2023). By targeting ncRNAs that regulate pathways critical for ICI function, ncRNA-based therapies present a promising strategy to improve immunotherapy success rates for OSCC.
4 Challenges and future directions
Despite the immense potential of ncRNAs as therapeutic targets in oral cancer, significant hurdles remain before these can be effectively translated into clinical practice. Addressing these challenges requires continued innovation in technology, delivery systems, and clinical trial design.
4.1 Overcoming technical hurdles
4.1.1 Mapping ncRNA expression and function with precision
The OSCC TME is highly heterogeneous, comprising diverse cell types interacting in complex spatial arrangements (Sutera et al., 2025). Traditional bulk RNA sequencing averages signals across all cells, masking crucial cell-type-specific expression patterns and functions of ncRNAs (Wei et al., 2024). To truly understand how ncRNAs orchestrate immune escape in specific cellular contexts (e.g., ncRNA expression in M2 vs. M1 TAMs, or in exhausted vs. effector T cells), higher resolution techniques are essential. Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) allows for the profiling of ncRNA expression at the individual cell level, revealing cellular heterogeneity (Guo et al., 2024). Spatial transcriptomics (ST) goes a step further by mapping gene (including ncRNA) expression within the intact tissue architecture, providing insights into the spatial organization of cells and their interactions within specific niches or “ecosystems” that influence immune responses and immunotherapy outcomes (Abdulrahman et al., 2025). Applying these technologies to OSCC tissues, particularly before and after immunotherapy, will be critical for identifying context-dependent ncRNA functions and relevant therapeutic targets.
4.1.2 Improving in vivo delivery systems
Efficient and safe delivery of RNA therapeutics to the target cells in vivo remains a major bottleneck (Hastings and Krainer, 2023). Naked RNA molecules are rapidly degraded and poorly taken up by cells. While delivery systems like LNPs have achieved clinical success for mRNA vaccines (Meng et al., 2025), optimizing them for ncRNA delivery (ASOs, mimics, CRISPR components) specifically to the OSCC TME presents unique challenges. Key requirements include:(I)Developing strategies to direct nanoparticles specifically to tumor cells or distinct immune cell populations (e.g., TAMs, T cells) within the TME, minimizing off-tumor accumulation (Chen et al., 2024). This might involve incorporating targeting ligands (antibodies, aptamers) onto the nanoparticle surface. (II)Ensuring efficient encapsulation of the ncRNA payload, protection from degradation in circulation, effective cellular uptake, and crucially, escape from endosomes to reach the cytoplasm or nucleus where ncRNAs function (Meng et al., 2025). (III)Minimizing immunogenicity and toxicity associated with the delivery vehicle itself (Schock Vaiani et al., 2025). The clinical trial failure of the miR-34a mimic MRX34 due to severe immune-related adverse events underscores the critical importance of safe delivery platforms (Beg et al., 2017). Ongoing research focuses on optimizing LNP lipid composition (e.g., ionizable lipids, helper lipids, PEG-lipids), particle size, and surface charge to enhance delivery and safety (Meng et al., 2025). Engineered exosomes are also being explored as natural delivery vehicles (Ma et al., 2025).
4.1.3 Functional validation
While transcriptomic studies can identify correlations between ncRNA expression and clinical outcomes or immune phenotypes, rigorous functional validation is essential to establish causality and confirm therapeutic targets. This requires robust in vitro and in vivo models that accurately recapitulate the OSCC TME. CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing technology is invaluable for precisely deleting or modifying ncRNA genes in relevant cell types (tumor cells, immune cells) within these models to directly assess their functional impact on tumor growth, metastasis, and immune response (Rajanathadurai et al., 2024). Furthermore, a deeper understanding of the relationship between ncRNA sequence, structure, and function is needed to design more effective therapeutic interventions.
4.2 Bridging the translational gap
4.2.1 Biomarker development and validation
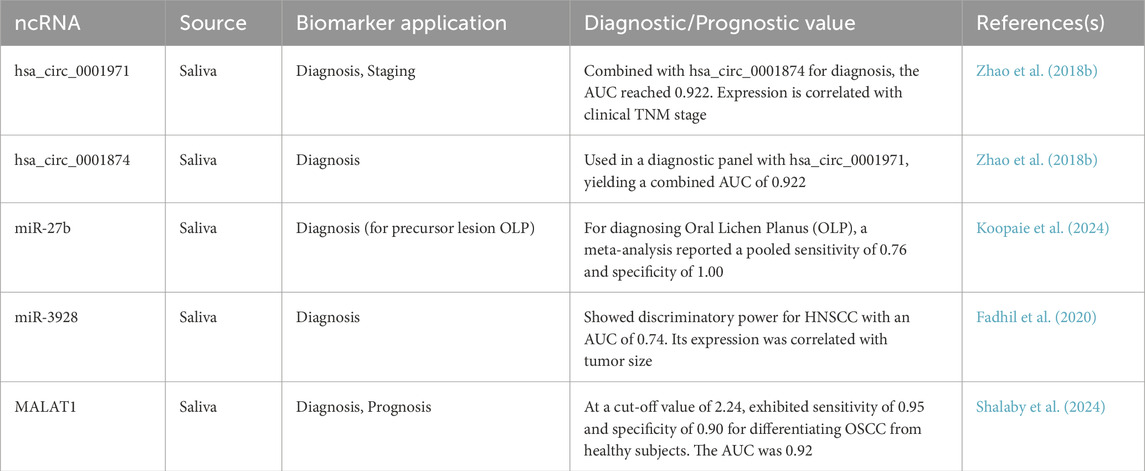
ncRNAs hold significant promise as biomarkers for OSCC, potentially improving early detection, prognosis, and treatment selection (Balakittnen et al., 2023). Detecting ncRNAs in easily accessible body fluids offers a non-invasive approach. Saliva is particularly significant for OSCC due to its direct contact with the oral cavity (Kalmatte et al., 2023). Studies have identified specific miRNAs (e.g., miR-3928, miR-27b, miR-137), lncRNAs (e.g., MALAT1), and circRNAs (e.g., hsa_circ_0001971) that are differentially expressed in the saliva of OSCC patients compared to healthy controls or individuals with potentially malignant disorders (Das et al., 2025). For instance, salivary hsa_circ_0001971 is significantly upregulated in OSCC patients and its expression is correlated with the clinical TNM stage (P = 0.019), as shown in Table 3 (Zhao SY. et al., 2018). A study combining hsa_circ_0001971 with another circRNA, hsa_circ_0001874, for OSCC diagnosis yielded a high area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.922, demonstrating significant diagnostic potential (Zhao SY. et al., 2018). Similarly, salivary miR-27b has been identified as a potential biomarker, with one meta-analysis reporting a pooled sensitivity of 0.76 and specificity of 1.00 for its use in diagnosing Oral Lichen Planus (OLP), a precursor to OSCC (Koopaie et al., 2024). In a study on Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC), of which OSCC is the most common type, salivary miR-3928 was found to be significantly downregulated in patients. This miRNA showed good discriminatory power with an AUC of 0.74 and its expression was correlated with tumor size (p = 0.02) (Fadhil et al., 2020). Additionally, as a lncRNA significantly upregulated in the saliva of OSCC patients, MALAT1 demonstrated excellent performance in a diagnostic accuracy study, with a sensitivity of 95%, a specificity of 90%, and an AUC of 92.2% (Shalaby et al., 2024). These salivary ncRNAs show potential for early diagnosis and correlation with disease stage (Das et al., 2025). Circulating ncRNAs in blood (plasma or serum) are also being investigated (Ito et al., 2023). However, large-scale, prospective clinical validation studies are crucial to confirm the sensitivity, specificity, and clinical utility of these potential biomarkers before they can be implemented in practice. Moreover, a critical goal is to identify ncRNA signatures that can predict a patient’s response to specific therapies, particularly immunotherapy (Sun and He, 2024). Identifying patients likely to respond or develop resistance to ICIs based on their ncRNA profiles could enable better patient stratification and personalized treatment strategies, avoiding unnecessary toxicity and cost for non-responders.
4.2.2 Clinical trial design
Translating promising preclinical findings into effective therapies requires well-designed clinical trials. The current landscape for OSCC trials often involves small, single-center, non-randomized studies, although immunotherapy trials are increasing (Zeng et al., 2024). Specific interventional trials evaluating ncRNA-based therapeutics for OSCC are still very limited. Future trials must prioritize safety, establish optimal dosing and delivery strategies, and incorporate predictive biomarkers for patient selection (Ito et al., 2023). Learning from past setbacks, like the MRX34 trial, is essential for designing safer and more effective next-generation ncRNA therapies. Collaboration and standardized reporting are needed to advance the field.
4.2.3 Artificial intelligence (AI) and multi-omics integration
The complexity of ncRNA regulatory networks, TME interactions, metabolic influences, and patient heterogeneity necessitates sophisticated analytical approaches (Tao et al., 2025). AI and machine learning (ML) algorithms are powerful tools for integrating large, high-dimensional datasets from multiple “omics” layers (genomics, transcriptomics including ncRNAs, proteomics, metabolomics, spatial omics) with clinical data (Lopes et al., 2025; Singh et al., 2024). This integrated approach can help uncover complex patterns and interactions that are missed by analyzing single data types (Spooner et al., 2025). It can also identify robust ncRNA-based biomarker signatures for diagnosis, prognosis, and prediction of immunotherapy response and enable the development of predictive models to guide personalized treatment decisions (Tao et al., 2025). Additionally, it generates new hypotheses about ncRNA function and regulatory networks within the OSCC TME. The application of AI/ML to multi-omics data, including ncRNA profiles, represents a crucial path forward for realizing the potential of precision oncology in oral cancer.
5 Conclusion
Immunotherapy resistance remains a critical barrier to improving outcomes for patients with OSCC. This review has synthesized the compelling evidence establishing ncRNAs—encompassing miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs—as pivotal regulators orchestrating this resistance. We have detailed how these molecules intricately modulate anti-tumor immunity and tumor biology through diverse and often interconnected mechanisms. These include the fine-tuning of crucial immune checkpoint pathways like PD-1/PD-L1, the induction of T cell exhaustion and promotion of regulatory T cell suppression, the profound remodeling of the tumor microenvironment via metabolic reprogramming and myeloid cell manipulation, and the direct influence on intrinsic tumor cell properties such as epigenetic states and cancer stem cell characteristics.
The deep involvement of ncRNAs in these fundamental processes positions them as highly attractive therapeutic targets and potential biomarkers. Strategies aimed at inhibiting oncogenic ncRNAs or restoring tumor-suppressive ones offer novel avenues to combat OSCC progression and treatment failure. The prospect of combining ncRNA-targeted therapies with existing treatments, particularly immune checkpoint inhibitors, provides a rational and promising approach to synergistically enhance anti-tumor responses and overcome resistance mechanisms.
However, significant hurdles must be overcome to translate this potential into clinical reality. Further research, leveraging advanced single-cell and spatial technologies, is crucial to fully map the complex ncRNA regulatory networks within the heterogeneous OSCC microenvironment. Paramount challenges include the development and optimization of safe, efficient, and precisely targeted delivery systems for ncRNA therapeutics in vivo, alongside the rigorous validation of specific ncRNAs as reliable predictive biomarkers for treatment response. Future efforts focused on addressing these challenges through continued mechanistic investigation, technological innovation, and well-designed translational studies will be essential to ultimately harness the power of ncRNA modulation for more effective and personalized therapeutic strategies against oral cancer.
Author contributions
ZL: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. YZ: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. XW: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Supervision. YL: Supervision, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2024YFA1108100); The National Natural Science Foundation of China (32271347); Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LZ23C050001); The Research Funds of Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, UCAS (2023HIAS-Y022); The Social Sector Science and Technology Development Fund of Fengxian District Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai (FK20221422).
Acknowledgments
Figure illustrated using BioRender (https://BioRender.com).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abd-Rabou, A. A., Kishta, M. S., Yakout, S. M., Youssef, A. M., Abdallah, A. N., and Ahmed, H. H. (2024). Copper/Tin nanocomposites-loaded exosomes induce apoptosis and cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 phase in skin cancer cell line. Chem. Biodivers. 21 (8), e202400486. doi:10.1002/cbdv.202400486
Abdulrahman, Z., Slieker, R. C., McGuire, D., Welters, M. J. P., van Poelgeest, M. I. E., and van der Burg, S. H. (2025). Single-cell spatial transcriptomics unravels cell states and ecosystems associated with clinical response to immunotherapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 13 (3), e011308. doi:10.1136/jitc-2024-011308
Adimulam, T., Arumugam, T., Foolchand, A., Ghazi, T., and Chuturgoon, A. A. (2021). The effect of organoselenium compounds on histone deacetylase inhibition and their potential for cancer therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (23), 12952. doi:10.3390/ijms222312952
Afra, F., Eftekhar, S. P., Farid, A. S., and Ala, M. (2024). Non-coding RNAs in cancer immunotherapy: a solution to overcome immune resistance? Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 209, 215–240. doi:10.1016/bs.pmbts.2024.02.003
Aglan, H. A., Ahmed, H. H., Beherei, H. H., Abdel-Hady, B. M., Ekram, B., and Kishta, M. S. (2024). Generation of cardiomyocytes from stem cells cultured on nanofibrous scaffold: experimental approach for attenuation of myocardial infarction. Tissue Cell 89, 102461. doi:10.1016/j.tice.2024.102461
Ahmad, F., Sudesh, R., Ahmed, A. T., Arumugam, M., Mathkor, D. M., and Haque, S. (2024). The multifaceted functions of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR in neuropathologies and its potential as a prognostic marker and therapeutic biotarget. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 26, e11. doi:10.1017/erm.2024.11
Ahn, H., Yang, J. M., Kim, H., Chung, J. H., Ahn, S. H., Jeong, W. J., et al. (2017). Clinicopathologic implications of the miR-197/PD-L1 axis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 8 (39), 66178–66194. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.19842
Ai, Y., Wu, S., Gao, H., Wei, H., Tang, Z., Li, X., et al. (2021). Repression of CRNDE enhances the anti-tumour activity of CD8 + T cells against oral squamous cell carcinoma through regulating miR-545-5p and TIM-3. J. Cell Mol. Med. 25 (23), 10857–10868. doi:10.1111/jcmm.16909
Ai Sw, Y., Gao, H., Wei, H., Tang, Z., Li, X., and Zou, C. (2024). RETRACTION: repression of CRNDE enhances the anti-tumour activity of CD8 + T cells against oral squamous cell carcinoma through regulating Mir-545-5p and TIM-3. J. Cell Mol. Med. 28 (15), e18566. doi:10.1111/jcmm.18566
Alamoudi, A. A. (2025). The role of non-coding RNAs in MYC-Mediated metabolic regulation: feedback loops and interactions. Noncoding RNA 11 (2), 27. doi:10.3390/ncrna11020027
Anastasiadou, E., Jacob, L. S., and Slack, F. J. (2018). Non-coding RNA networks in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 18 (1), 5–18. doi:10.1038/nrc.2017.99
Andrews, L. P., Butler, S. C., Cui, J., Cillo, A. R., Cardello, C., Liu, C., et al. (2024). LAG-3 and PD-1 synergize on CD8(+) T cells to drive T cell exhaustion and hinder autocrine IFN-gamma-dependent anti-tumor immunity. Cell 187 (16), 4355–4372.e22. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2024.07.016
Ariyoshi, J., Momokawa, D., Eimori, N., Kobori, A., Murakami, A., and Yamayoshi, A. (2015). Development of novel antisense oligonucleotides for the functional regulation of RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) by promoting the release of microRNA from RISC. Bioconjug Chem. 26 (12), 2454–2460. doi:10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.5b00501
Bais, M. V. (2019). Impact of epigenetic regulation on head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J. Dent. Res. 98 (3), 268–276. doi:10.1177/0022034518816947
Balakittnen, J., Weeramange, C. E., Wallace, D. F., Duijf, P. H. G., Cristino, A. S., Kenny, L., et al. (2023). Noncoding RNAs in oral cancer. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 14 (3), e1754. doi:10.1002/wrna.1754
Balas, M. M., Hartwick, E. W., Barrington, C., Roberts, J. T., Wu, S. K., Bettcher, R., et al. (2021). Establishing RNA-RNA interactions remodels lncRNA structure and promotes PRC2 activity. Sci. Adv. 7 (16), eabc9191. doi:10.1126/sciadv.abc9191
Beg, M. S., Brenner, A. J., Sachdev, J., Borad, M., Kang, Y. K., Stoudemire, J., et al. (2017). Phase I study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, administered twice weekly in patients with advanced solid tumors. Invest New Drugs 35 (2), 180–188. doi:10.1007/s10637-016-0407-y
Bray, F., Laversanne, M., Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R. L., Soerjomataram, I., et al. (2024). Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 74 (3), 229–263. doi:10.3322/caac.21834
Bure, I. V., Nemtsova, M. V., and Kuznetsova, E. B. (2022). Histone modifications and non-coding RNAs: mutual epigenetic regulation and role in pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (10), 5801. doi:10.3390/ijms23105801
Celis-Gutierrez, J., Blattmann, P., Zhai, Y., Jarmuzynski, N., Ruminski, K., Gregoire, C., et al. (2019). Quantitative interactomics in primary T cells provides a rationale for concomitant PD-1 and BTLA coinhibitor blockade in cancer immunotherapy. Cell Rep. 27 (11), 3315–3330.e7. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2019.05.041
Chai, A. W. Y., Lim, K. P., and Cheong, S. C. (2020). Translational genomics and recent advances in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Semin. Cancer Biol. 61, 71–83. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.09.011
Chang, S. M., and Hu, W. W. (2018). Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma development via microRNA-125b/STAT3 axis. J. Cell Physiol. 233 (4), 3384–3396. doi:10.1002/jcp.26185
Chen, D., and Wang, C. Y. (2019). Targeting cancer stem cells in squamous cell carcinoma. Precis. Clin. Med. 2 (3), 152–165. doi:10.1093/pcmedi/pbz016
Chen, L., Gibbons, D. L., Goswami, S., Cortez, M. A., Ahn, Y. H., Byers, L. A., et al. (2014). Metastasis is regulated via microRNA-200/ZEB1 axis control of tumour cell PD-L1 expression and intratumoral immunosuppression. Nat. Commun. 5, 5241. doi:10.1038/ncomms6241
Chen, J., Jiang, C. C., Jin, L., and Zhang, X. D. (2016). Regulation of PD-L1: a novel role of pro-survival signalling in cancer. Ann. Oncol. 27 (3), 409–416. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdv615
Chen, Y. G., Satpathy, A. T., and Chang, H. Y. (2017). Gene regulation in the immune system by long noncoding RNAs. Nat. Immunol. 18 (9), 962–972. doi:10.1038/ni.3771
Chen, Q. H., Li, B., Liu, D. G., Zhang, B., Yang, X., and Tu, Y. L. (2020). LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 sponges miR-15a to promote immune evasion and malignant progression of prostate cancer via up-regulating PD-L1. Cancer Cell Int. 20, 394. doi:10.1186/s12935-020-01481-8
Chen, L., Qian, X., Wang, Z., and Zhou, X. (2021). The HOTAIR lncRNA: a remarkable oncogenic promoter in human cancer metastasis. Oncol. Lett. 21 (4), 302. doi:10.3892/ol.2021.12563
Chen, B., Dragomir, M. P., Yang, C., Li, Q., Horst, D., and Calin, G. A. (2022a). Targeting non-coding RNAs to overcome cancer therapy resistance. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 7 (1), 121. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-00975-3
Chen, Y., Li, Z., Liang, J., Liu, J., Hao, J., Wan, Q., et al. (2022b). CircRNA has_circ_0069313 induced OSCC immunity escape by miR-325-3p-Foxp3 axes in both OSCC cells and Treg cells. Aging (Albany NY) 14 (10), 4376–4389. doi:10.18632/aging.204068
Chen, F., Zhao, D., Huang, Y., Wen, X., and Feng, S. (2023a). Synergetic impact of combined navoximod with cisplatin mitigates chemo-immune resistance via blockading IDO1(+) CAFs-secreted Kyn/AhR/IL-6 and pol zeta-prevented CIN in human oral squamous cell carcinoma. Life Sci. 335, 122239. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2023.122239
Chen, K., Zhu, X., Wang, J., Zhao, Z., Hao, L., Guo, X., et al. (2023b). MFPred: prediction of ncRNA families based on multi-feature fusion. Brief. Bioinform 24 (5), bbad303. doi:10.1093/bib/bbad303
Chen, S., He, Y., Huang, X., Shen, Y., Zou, Q., Yang, G., et al. (2024). Photosensitive and dual-targeted chromium nanoparticle delivering small interfering RNA YTHDF1 for molecular-targeted immunotherapy in liver cancer. J. Nanobiotechnology 22 (1), 348. doi:10.1186/s12951-024-02612-3
Chen, W. L., Chang, Y. L., Lin, S. F., Protzer, U., Isogawa, M., Yang, H. C., et al. (2025). Differential regulation of calcium-NFAT signaling pathway by Akt isoforms: unraveling effector dynamics and exhaustion of cytotoxic T lymphocytes in tumor microenvironment. J. Immunother. Cancer 13 (3), e009827. doi:10.1136/jitc-2024-009827
Cheng, Y., Imanirad, P., Jutooru, I., Hedrick, E., Jin, U. H., Rodrigues Hoffman, A., et al. (2018). Role of metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript-1 (MALAT-1) in pancreatic cancer. PLoS One 13 (2), e0192264. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0192264
Cui, Y., Liu, J., Liu, L., Ma, X., Gui, Y., Liu, H., et al. (2023a). m(6)A-modified circFOXK2 targets GLUT1 to accelerate oral squamous cell carcinoma aerobic glycolysis. Cancer Gene Ther. 30 (1), 163–171. doi:10.1038/s41417-022-00526-6
Cui, S., Liu, H., and Cui, G. (2023b). Nanoparticles as drug delivery systems in the treatment of oral squamous cell carcinoma: current status and recent progression. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1176422. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1176422
Das, S., Basak, S., and Sarkar, S. (2025). Decoding salivary ncRNAomes as novel biomarkers for oral cancer detection and prognosis. Noncoding RNA 11 (2), 28. doi:10.3390/ncrna11020028
Denaro, N., Merlano, M. C., and Lo Nigro, C. (2019). Long noncoding RNAs as regulators of cancer immunity. Mol. Oncol. 13 (1), 61–73. doi:10.1002/1878-0261.12413
Deng, S., Wang, M., Wang, C., Zeng, Y., Qin, X., Tan, Y., et al. (2023). p53 downregulates PD-L1 expression via miR-34a to inhibit the growth of triple-negative breast cancer cells: a potential clinical immunotherapeutic target. Mol. Biol. Rep. 50 (1), 577–587. doi:10.1007/s11033-022-08047-z
Dey, S., Biswas, B., Manoj Appadan, A., Shah, J., Pal, J. K., Basu, S., et al. (2023). Non-Coding RNAs in oral cancer: emerging roles and clinical applications. Cancers (Basel) 15 (15), 3752. doi:10.3390/cancers15153752
Ding, Y. F., Wen, Y. C., Chuang, C. Y., Lin, C. W., Yang, Y. C., Liu, Y. F., et al. (2021). Combined impacts of genetic variants of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 and the environmental carcinogen on the susceptibility to and progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 11, 684941. doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.684941
Fadhil, R. S., Wei, M. Q., Nikolarakos, D., Good, D., and Nair, R. G. (2020). Salivary microRNA miR-let-7a-5p and miR-3928 could be used as potential diagnostic bio-markers for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One 15 (3), e0221779. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0221779
Fan, F., Chen, K., Lu, X., Li, A., Liu, C., and Wu, B. (2021). Dual targeting of PD-L1 and PD-L2 by PCED1B-AS1 via sponging hsa-miR-194-5p induces immunosuppression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Int. 15 (2), 444–458. doi:10.1007/s12072-020-10101-6
Fan, L., Na, J., Shi, T., and Liao, Y. (2025). Hepatoblastoma: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies. Curr. Oncol. 32 (3), 149. doi:10.3390/curroncol32030149
Fontenot, J. D., Gavin, M. A., and Rudensky, A. Y. (2003). Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat. Immunol. 4 (4), 330–336. doi:10.1038/ni904
Freeman, G. J., Long, A. J., Iwai, Y., Bourque, K., Chernova, T., Nishimura, H., et al. (2000). Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte activation. J. Exp. Med. 192 (7), 1027–1034. doi:10.1084/jem.192.7.1027
Freeman, G. J., Wherry, E. J., Ahmed, R., and Sharpe, A. H. (2006). Reinvigorating exhausted HIV-specific T cells via PD-1-PD-1 ligand blockade. J. Exp. Med. 203 (10), 2223–2227. doi:10.1084/jem.20061800
Fu, S., Wang, Y., Li, H., Chen, L., and Liu, Q. (2020). Regulatory networks of LncRNA MALAT-1 in cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 12, 10181–10198. doi:10.2147/CMAR.S276022
Fujita, Y., Yagishita, S., Hagiwara, K., Yoshioka, Y., Kosaka, N., Takeshita, F., et al. (2015). The clinical relevance of the miR-197/CKS1B/STAT3-mediated PD-L1 network in chemoresistant non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol. Ther. 23 (4), 717–727. doi:10.1038/mt.2015.10
Gao, Y., Fang, P., Li, W. J., Zhang, J., Wang, G. P., Jiang, D. F., et al. (2020). LncRNA NEAT1 sponges miR-214 to regulate M2 macrophage polarization by regulation of B7-H3 in multiple myeloma. Mol. Immunol. 117, 20–28. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2019.10.026
Gao, Z., Luan, X., Wang, X., Han, T., Li, X., Li, Z., et al. (2024). DNA damage response-related ncRNAs as regulators of therapy resistance in cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1390300. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1390300
Gazdzicka, J., Golabek, K., Strzelczyk, J. K., and Ostrowska, Z. (2020). Epigenetic modifications in head and neck cancer. Biochem. Genet. 58 (2), 213–244. doi:10.1007/s10528-019-09941-1
Gezer, U., Ozgur, E., Cetinkaya, M., Isin, M., and Dalay, N. (2014). Long non-coding RNAs with low expression levels in cells are enriched in secreted exosomes. Cell Biol. Int. 38 (9), 1076–1079. doi:10.1002/cbin.10301
Ghods, A., Mehdipour, F., Shariat, M., Talei, A. R., and Ghaderi, A. (2021). Regulatory T cells express Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 2 with the highest intensity among CD4(+) T cells in the draining lymph nodes of breast cancer. Mol. Immunol. 137, 52–56. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2021.06.013
Guo, H., Zhang, L., Cui, X., Cheng, L., Zhao, T., and Wang, Y. (2024). SCancerRNA: expression at the single-cell level and interaction resource of non-coding RNA biomarkers for cancers. Genomics Proteomics Bioinforma. 22 (3), qzae023. doi:10.1093/gpbjnl/qzae023
Gutschner, T., Hammerle, M., and Diederichs, S. (2013). MALAT1 -- a paradigm for long noncoding RNA function in cancer. J. Mol. Med. Berl. 91 (7), 791–801. doi:10.1007/s00109-013-1028-y
Han, X., Luan, T., Sun, Y., Yan, W., Wang, D., and Zeng, X. (2020). MicroRNA 449c mediates the generation of monocytic Myeloid-derived suppressor cells by targeting STAT6. Mol. Cells 43 (9), 793–803. doi:10.14348/molcells.2020.2307
Han, J., Chen, X., Wang, J., and Liu, B. (2023). Glycolysis-related lncRNA TMEM105 upregulates LDHA to facilitate breast cancer liver metastasis via sponging miR-1208. Cell Death Dis. 14 (2), 80. doi:10.1038/s41419-023-05628-z
Hashemi, M., Khoushab, S., Aghmiuni, M. H., Anaraki, S. N., Alimohammadi, M., Taheriazam, A., et al. (2024). Non-coding RNAs in oral cancer: emerging biomarkers and therapeutic frontier. Heliyon 10 (21), e40096. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40096
Hastings, M. L., and Krainer, A. R. (2023). RNA therapeutics. RNA 29 (4), 393–395. doi:10.1261/rna.079626.123
He, L., Wan, M., Yang, X., and Meng, H. (2025). Distant metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma: immune escape mechanism and new perspectives on treatment. Discov. Oncol. 16 (1), 257. doi:10.1007/s12672-025-01997-3
Hirai, M., Kitahara, H., Kobayashi, Y., Kato, K., Bou-Gharios, G., Nakamura, H., et al. (2017). Regulation of PD-L1 expression in a high-grade invasive human oral squamous cell carcinoma microenvironment. Int. J. Oncol. 50 (1), 41–48. doi:10.3892/ijo.2016.3785
Hong, D. S., Kang, Y. K., Borad, M., Sachdev, J., Ejadi, S., Lim, H. Y., et al. (2020). Phase 1 study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 122 (11), 1630–1637. doi:10.1038/s41416-020-0802-1
Hori, S., Nomura, T., and Sakaguchi, S. (2003). Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science 299 (5609), 1057–1061. doi:10.1126/science.1079490
Hou, Z. H., Xu, X. W., Fu, X. Y., Zhou, L. D., Liu, S. P., and Tan, D. M. (2020). Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes angiogenesis and immunosuppressive properties of HCC cells by sponging miR-140. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 318 (3), C649–C663. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00510.2018
Hsieh, P. L., Liao, Y. W., Pichler, M., and Yu, C. C. (2020). MicroRNAs as theranostics targets in oral carcinoma stem cells. Cancers (Basel) 12 (2), 340. doi:10.3390/cancers12020340
Hua, J., Wang, Z., Cheng, X., Dai, J., and Zhao, P. (2025). Circular RNAs modulate cancer drug resistance: advances and challenges. Cancer Drug Resist 8, 17. doi:10.20517/cdr.2024.195
Huang, C., and Aghaei-Zarch, S. M. (2024). From molecular pathogenesis to therapy: unraveling non-coding RNAs/DNMT3A axis in human cancers. Biochem. Pharmacol. 222, 116107. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116107
Huang, C. Y., Chou, S. T., Hsu, Y. M., Chao, W. J., Wu, G. H., Hsiao, J. R., et al. (2024). MEG3-Mediated oral squamous-cell-carcinoma-derived exosomal miR-421 activates angiogenesis by targeting HS2ST1 in vascular endothelial cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (14), 7576. doi:10.3390/ijms25147576
Huang, L., Zhang, C., Jiang, A., Lin, A., Zhu, L., Mou, W., et al. (2025). T-cell senescence in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Immunol. Res. 13 (5), 618–632. doi:10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-24-0894
Irimie, A. I., Braicu, C., Sonea, L., Zimta, A. A., Cojocneanu-Petric, R., Tonchev, K., et al. (2017). A looking-Glass of Non-coding RNAs in oral cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18 (12), 2620. doi:10.3390/ijms18122620
Ito, M., Miyata, Y., and Okada, M. (2023). Current clinical trials with non-coding RNA-based therapeutics in malignant diseases: a systematic review. Transl. Oncol. 31, 101634. doi:10.1016/j.tranon.2023.101634
Jaksic Karisik, M., Lazarevic, M., Mitic, D., Milosevic Markovic, M., Riberti, N., Jelovac, D., et al. (2025). MicroRNA-21 as a regulator of cancer stem cell properties in oral cancer. Cells 14 (2), 91. doi:10.3390/cells14020091
Ji, J., Yin, Y., Ju, H., Xu, X., Liu, W., Fu, Q., et al. (2018). Long non-coding RNA Lnc-Tim3 exacerbates CD8 T cell exhaustion via binding to Tim-3 and inducing nuclear translocation of Bat3 in HCC. Cell Death Dis. 9 (5), 478. doi:10.1038/s41419-018-0528-7
Ji, L., Liang, S., Cheng, Y., Gao, R., Yan, W., Pang, F., et al. (2024). Identification of a novel necroptosis-related LncRNA signature for prognostic prediction and immune response in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 40 (3-4), 319–342. doi:10.3233/CBM-230407
Jiang, R., Tang, J., Chen, Y., Deng, L., Ji, J., Xie, Y., et al. (2017). The long noncoding RNA lnc-EGFR stimulates T-regulatory cells differentiation thus promoting hepatocellular carcinoma immune evasion. Nat. Commun. 8, 15129. doi:10.1038/ncomms15129
Jiang, W., Zhang, C., Zhang, X., Sun, L., Li, J., and Zuo, J. (2021a). CircRNA HIPK3 promotes the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma through upregulation of the NUPR1/PI3K/AKT pathway by sponging miR-637. Ann. Transl. Med. 9 (10), 860. doi:10.21037/atm-21-1908
Jiang, T., Zheng, L., Li, X., Liu, J., Song, H., Xu, Y., et al. (2021b). Quiescin Sulfhydryl oxidase 2 overexpression predicts poor prognosis and tumor progression in patients with colorectal cancer: a Study based on data mining and clinical verification. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 678770. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.678770
Jiang, X., Liang, X., Li, S., Yang, Y., Xu, X., Gu, W., et al. (2024). The LINC00319 binding to STAT3 promotes the cell proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT process in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 761, 110170. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2024.110170
Jili, S., Eryong, L., Lijuan, L., and Chao, Z. (2016). RUNX3 inhibits laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma malignancy under the regulation of miR-148a-3p/DNMT1 axis. Cell Biochem. Funct. 34 (8), 597–605. doi:10.1002/cbf.3233
Ju, Y., Lv, Y., Liu, X., Lu, J., Shi, Y., Guo, H., et al. (2025). Role of long non-coding RNAs in the regulation of ferroptosis in tumors. Front. Immunol. 16, 1568567. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2025.1568567
Kalmatte, A., Rekha, P. D., and Ratnacaram, C. K. (2023). Emerging cell cycle related non-coding RNA biomarkers from saliva and blood for oral squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Biol. Rep. 50 (11), 9479–9496. doi:10.1007/s11033-023-08791-w
Kawamata, T., Seitz, H., and Tomari, Y. (2009). Structural determinants of miRNAs for RISC loading and slicer-independent unwinding. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 16 (9), 953–960. doi:10.1038/nsmb.1630
Kim, S. Y., Han, Y. K., Song, J. M., Lee, C. H., Kang, K., Yi, J. M., et al. (2019). Aberrantly hypermethylated tumor suppressor genes were identified in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). Clin. Epigenetics 11 (1), 116. doi:10.1186/s13148-019-0715-0
Kishta, M. S., Khamis, A., Am, H., Elshaar, A. H., and Gul, D. (2025). Exploring the tumor-suppressive role of miRNA-200c in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: potential and mechanisms of exosome-mediated delivery for therapeutic applications. Transl. Oncol. 51, 102216. doi:10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102216
Koopaie, M., Akhbari, P., Fatahzadeh, M., and Kolahdooz, S. (2024). Identification of common salivary miRNA in oral lichen planus and oral squamous cell carcinoma: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health 24 (1), 1177. doi:10.1186/s12903-024-04986-0
Kos, A., Dijkema, R., Arnberg, A. C., van der Meide, P. H., and Schellekens, H. (1986). The hepatitis delta (delta) virus possesses a circular RNA. Nature 323 (6088), 558–560. doi:10.1038/323558a0
Kozaki, K., Imoto, I., Mogi, S., Omura, K., and Inazawa, J. (2008). Exploration of tumor-suppressive microRNAs silenced by DNA hypermethylation in oral cancer. Cancer Res. 68 (7), 2094–2105. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5194
Kujan, O., van Schaijik, B., and Farah, C. S. (2020). Immune checkpoint inhibitors in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma and oral potentially malignant disorders: a systematic review. Cancers (Basel) 12 (7), 1937. doi:10.3390/cancers12071937
Lei, C. S., Kung, H. J., and Shih, J. W. (2021). Long non-coding RNAs as functional codes for oral cancer: translational potential, progress and promises. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (9), 4903. doi:10.3390/ijms22094903
Leija, M. G., Gonzalez Ramirez, J., Sandoval Basilio, J., Serafin Higuera, I., Isiordia Espinoza, M., Gonzalez Gonzalez, R., et al. (2019). Long non-coding RNAs: regulators of the activity of Myeloid-Derived suppressor cells. Front. Immunol. 10, 1734. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.01734
Li, K., and Wang, Z. (2022). Non-coding RNAs: key players in T cell exhaustion. Front. Immunol. 13, 959729. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.959729
Li, L., Zhang, J., Diao, W., Wang, D., Wei, Y., Zhang, C. Y., et al. (2014). MicroRNA-155 and MicroRNA-21 promote the expansion of functional myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J. Immunol. 192 (3), 1034–1043. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1301309
Li, T., Li, L., Li, D., Wang, S., and Sun, J. (2015). MiR-34a inhibits oral cancer progression partially by repression of interleukin-6-receptor. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 8 (2), 1364–1373. Available online at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25973020/.
Li, W. J., Wang, Y., Liu, R., Kasinski, A. L., Shen, H., Slack, F. J., et al. (2021). MicroRNA-34a: potent tumor suppressor, cancer stem cell inhibitor, and potential anticancer therapeutic. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 640587. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.640587
Li, W., Wang, X., Li, C., Chen, T., and Yang, Q. (2022). Exosomal non-coding RNAs: emerging roles in bilateral communication between cancer cells and macrophages. Mol. Ther. 30 (3), 1036–1053. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.12.002
Li, J., Momen-Heravi, F., Wu, X., and He, K. (2023). Mechanism of METTL14 and m6A modification of lncRNA MALAT1 in the proliferation of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Oral Dis. 29 (5), 2012–2026. doi:10.1111/odi.14220
Li, S., Feng, T., Liu, Y., Yang, Q., Song, A., Wang, S., et al. (2024a). m(1)A inhibition fuels oncolytic virus-elicited antitumor immunity via downregulating MYC/PD-L1 signaling. Int. J. Oral Sci. 16 (1), 36. doi:10.1038/s41368-024-00304-0
Li, R., Ji, Y., Ye, R., Tang, G., Wang, W., Chen, C., et al. (2024b). Potential therapies for non-coding RNAs in breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 14, 1452666. doi:10.3389/fonc.2024.1452666
Li, Z., Yin, S., Yang, K., Zhang, B., Wu, X., Zhang, M., et al. (2024c). CircRNA regulation of T cells in cancer: unraveling potential targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (12), 6383. doi:10.3390/ijms25126383
Li, C., Dong, X., and Li, B. (2024d). Tumor microenvironment in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 15, 1485174. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1485174
Li, D., Shi, Y., Yu, S., Zhang, B., Huang, Z., Ling, F., et al. (2025). NK cellular derived nanovesicles in tumor immunity. Mol. Immunol. 182, 54–61. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2025.03.018
Liang, L., Xu, X., Li, J., and Yang, C. (2022). Interaction between microRNAs and Myeloid-Derived suppressor cells in tumor microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 13, 883683. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.883683
Liu, J., Sun, M., Cho, K. B., Gao, X., and Guo, B. (2021a). A CRISPR-Cas9 repressor for epigenetic silencing of KRAS. Pharmacol. Res. 164, 105304. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105304
Liu, W., Zheng, X., Wang, J., He, Q., Li, J., Zhang, Z., et al. (2021b). MicroRNA-138 regulates T-Cell function by targeting PD-1 in patients with hepatitis B virus-related liver diseases. Lab. Med. 52 (5), 439–451. doi:10.1093/labmed/lmaa110
Liu, H., Wang, D., Kan, S., Hao, M., Chang, L., Lu, P., et al. (2022a). The role of lncRNAs and XIST in oral cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 10, 826650. doi:10.3389/fcell.2022.826650
Liu, Z., Zheng, N., Li, J., Li, C., Zheng, D., Jiang, X., et al. (2022b). N6-methyladenosine-modified circular RNA QSOX1 promotes colorectal cancer resistance to anti-CTLA-4 therapy through induction of intratumoral regulatory T cells. Drug Resist Updat 65, 100886. doi:10.1016/j.drup.2022.100886
Liu, J., Yuan, J. F., and Wang, Y. Z. (2022c). METTL3-stabilized lncRNA SNHG7 accelerates glycolysis in prostate cancer via SRSF1/c-Myc axis. Exp. Cell Res. 416 (1), 113149. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2022.113149
Lopes, M. B., Coletti, R., Duranton, F., Glorieux, G., Jaimes Campos, M. A., Klein, J., et al. (2025). The omics-driven machine learning path to cost-effective precision medicine in chronic kidney disease. Proteomics 25, e202400108. doi:10.1002/pmic.202400108
Lu, M. Y., Liao, Y. W., Chen, P. Y., Hsieh, P. L., Fang, C. Y., Wu, C. Y., et al. (2017). Targeting LncRNA HOTAIR suppresses cancer stemness and metastasis in oral carcinomas stem cells through modulation of EMT. Oncotarget 8 (58), 98542–98552. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.21614
Lu, N., Jiang, Q., Xu, T., Gao, Q., Wang, Y., Huang, Z., et al. (2024). LncOCMRL1 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma growth and metastasis via the RRM2/EMT pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 43 (1), 267. doi:10.1186/s13046-024-03190-w
Lv, X., Sun, X., Gao, Y., Song, X., Hu, X., Gong, L., et al. (2025). Targeting RNA splicing modulation: new perspectives for anticancer strategy? J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 44 (1), 32. doi:10.1186/s13046-025-03279-w
Ma, L., and Kim, M. O. (2024). Advances in preventive and therapeutic strategies for oral cancer: a short review. J. Cancer Prev. 29 (4), 113–119. doi:10.15430/JCP.24.027
Ma, H., Chang, H., Yang, W., Lu, Y., Hu, J., and Jin, S. (2020). A novel IFNα-induced long noncoding RNA negatively regulates immunosuppression by interrupting H3K27 acetylation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 19 (1), 4. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1123-y
Ma, C., Tang, W., Wang, J., Yang, S., Hou, J., Guo, M., et al. (2025). Application of engineered exosomes in tumor therapy. Am. J. Transl. Res. 17 (2), 736–747. doi:10.62347/KIXF4662
Malakar, P., Stein, I., Saragovi, A., Winkler, R., Stern-Ginossar, N., Berger, M., et al. (2019). Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 regulates cancer glucose metabolism by enhancing mTOR-Mediated translation of TCF7L2. Cancer Res. 79 (10), 2480–2493. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-1432
Mao, Y., Xia, Z., Xia, W., and Jiang, P. (2024). Metabolic reprogramming, sensing, and cancer therapy. Cell Rep. 43 (12), 115064. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2024.115064
Mehler, M. F., and Mattick, J. S. (2007). Noncoding RNAs and RNA editing in brain development, functional diversification, and neurological disease. Physiol. Rev. 87 (3), 799–823. doi:10.1152/physrev.00036.2006
Memczak, S., Jens, M., Elefsinioti, A., Torti, F., Krueger, J., Rybak, A., et al. (2013). Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 495 (7441), 333–338. doi:10.1038/nature11928
Meng, X., Lou, Q. Y., Yang, W. Y., Wang, Y. R., Chen, R., Wang, L., et al. (2021). The role of non-coding RNAs in drug resistance of oral squamous cell carcinoma and therapeutic potential. Cancer Commun. (Lond) 41 (10), 981–1006. doi:10.1002/cac2.12194
Meng, X., Zheng, Y., Zhang, L., Liu, P., Liu, Z., and He, Y. (2024). Single-Cell analyses reveal the metabolic heterogeneity and plasticity of the tumor microenvironment during head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression. Cancer Res. 84 (15), 2468–2483. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-1344
Meng, S., Hara, T., Miura, Y., Arao, Y., Saito, Y., Inoue, K., et al. (2025). In vivo engineered CAR-T cell therapy: lessons built from COVID-19 mRNA vaccines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 26 (7), 3119. doi:10.3390/ijms26073119
Mivehchi, H., Eskandari-Yaghbastlo, A., Ghazanfarpour, M., Ziaei, S., Mesgari, H., Faghihinia, F., et al. (2025). Microenvironment-based immunotherapy in oral cancer: a comprehensive review. Med. Oncol. 42 (5), 140. doi:10.1007/s12032-025-02694-5
Mo, W., Liu, S., Zhao, X., Wei, F., Li, Y., Sheng, X., et al. (2023). ROS scavenging nanozyme modulates immunosuppression for sensitized cancer immunotherapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater 12 (21), e2300191. doi:10.1002/adhm.202300191
Mohapatra, S., Pioppini, C., Ozpolat, B., and Calin, G. A. (2021). Non-coding RNAs regulation of macrophage polarization in cancer. Mol. Cancer 20 (1), 24. doi:10.1186/s12943-021-01313-x
Mohd Faizal, N. F., Shai, S., Savaliya, B. P., Karen-Ng, L. P., Kumari, R., Kumar, R., et al. (2025). A narrative review of prognostic gene signatures in oral squamous cell carcinoma using LASSO cox regression. Biomedicines 13 (1), 134. doi:10.3390/biomedicines13010134
Moore, M. J. (2005). From birth to death: the complex lives of eukaryotic mRNAs. Science 309 (5740), 1514–1518. doi:10.1126/science.1111443
Mulder, F. J., de Ruiter, E. J., Gielgens, T., Farshadpour, F., de Bree, R., van den Hout, M., et al. (2025). Frequent PD-L1 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma of non-smokers and non-drinkers, and association of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes with favorable prognosis. Transl. Oncol. 55, 102357. doi:10.1016/j.tranon.2025.102357
Neveu, M.-A., Revenko, A., Kim, T.-W., Luo, X., Kim, Y., Schmidt, J., et al. (2024). “Preclinical development of FTX-001: first-in-class inhibitor of the long non-coding RNA MALAT1,” in EACR 2024 Annual congress.
O'Connell, R. M., Rao, D. S., Chaudhuri, A. A., and Baltimore, D. (2010). Physiological and pathological roles for microRNAs in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 10 (2), 111–122. doi:10.1038/nri2708
Panda, A., Kumar, H., Bhattacharjee, T., Maheswaran, T., Dash, K. C., and Mohanty, A. (2025). The role of long non-coding RNAs HOTTIP, HOTAIR, and MALAT1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Bangladesh J. Med. Sci., 34–38. doi:10.3329/bjms.v24i10.79173
Pardoll, D. M. (2012). The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 12 (4), 252–264. doi:10.1038/nrc3239
Pauken, K. E., and Wherry, E. J. (2015). Overcoming T cell exhaustion in infection and cancer. Trends Immunol. 36 (4), 265–276. doi:10.1016/j.it.2015.02.008
Peltanova, B., Raudenska, M., and Masarik, M. (2019). Effect of tumor microenvironment on pathogenesis of the head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 63. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-0983-5
Peng, H. Y., Huang, Y. L., Wu, P. H., Li, L. J., Peng, B. Y., Wu, C. Y., et al. (2025). The miR-876-5p/SOCS4/STAT3 pathway induced the expression of PD-L1 and suppressed antitumor immune responses. Cancer Cell Int. 25 (1), 114. doi:10.1186/s12935-025-03704-2
Priyadharshini, P., Yuwanati, M., Sekaran, S., and M, S. (2023). miRNA associated with glucose transporters in oral squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review. Cureus 15 (9), e46057. doi:10.7759/cureus.46057
Qi, Y., Ding, L., Zhang, S., Yao, S., Ong, J., Li, Y., et al. (2022). A plant immune protein enables broad antitumor response by rescuing microRNA deficiency. Cell 185 (11), 1888–1904.e24. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2022.04.030
Rajanathadurai, J., Perumal, E., and Sindya, J. (2024). Advances in targeting cancer epigenetics using CRISPR-dCas9 technology: a comprehensive review and future prospects. Funct. Integr. Genomics 24 (5), 164. doi:10.1007/s10142-024-01455-3
Rajendran, P., Sekar, R., Abdallah, B. M., Fathima, Jh S., Ali, E. M., Jayaraman, S., et al. (2024). Epigenetic modulation of long noncoding RNA H19 in oral squamous cell carcinoma-A narrative review. Noncoding RNA Res. 9 (2), 602–611. doi:10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.01.020
Ren, Y., Pan, K., Wang, Y., Zhang, S., Wang, Y., Zhou, X., et al. (2023). circFANCA accelerates the malignant process of OSCC by modulating miR-34a/PA28γ signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 665, 45–54. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.04.084
Ries, J., Trumet, L., Hahn, A., Kunater, L., Lutz, R., Geppert, C., et al. (2024). The immune checkpoint BTLA in oral cancer: expression analysis and its correlation to other immune modulators. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (12), 6601. doi:10.3390/ijms25126601
Saadi, W., Fatmi, A., Pallardo, F. V., Garcia-Gimenez, J. L., and Mena-Molla, S. (2022). Long non-coding RNAs as epigenetic regulators of immune checkpoints in cancer immunity. Cancers (Basel) 15 (1), 184. doi:10.3390/cancers15010184
Safarzadeh, E., Asadzadeh, Z., Safaei, S., Hatefi, A., Derakhshani, A., Giovannelli, F., et al. (2020). MicroRNAs and lncRNAs-A new layer of myeloid-derived suppressor cells regulation. Front. Immunol. 11, 572323. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.572323
Sakuishi, K., Apetoh, L., Sullivan, J. M., Blazar, B. R., Kuchroo, V. K., and Anderson, A. C. (2010). Targeting Tim-3 and PD-1 pathways to reverse T cell exhaustion and restore anti-tumor immunity. J. Exp. Med. 207 (10), 2187–2194. doi:10.1084/jem.20100643
Salmena, L., Poliseno, L., Tay, Y., Kats, L., and Pandolfi, P. P. (2011). A ceRNA hypothesis: the rosetta stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 146 (3), 353–358. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.014
Sanchez, J. C., Pierpont, T. M., Argueta-Zamora, D., Wilson, K., August, A., and Cerione, R. A. (2024). PTEN loss in glioma cell lines leads to increased extracellular vesicles biogenesis and PD-L1 cargo in a PI3K-dependent manner. bioRxiv., 2023.07.26.550575. doi:10.1101/2023.07.26.550575
Sasaki, H., Umezawa, N., Itakura, T., Iwai, H., and Yasuda, S. (2024). Pathogenicity of functionally activated PD-1+CD8+ cells and counterattacks by muscular PD-L1 through IFNγ in myositis. J. Autoimmun. 142, 103131. doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2023.103131
Schock Vaiani, J., Broekgaarden, M., Coll, J. L., Sancey, L., and Busser, B. (2025). In vivo vectorization and delivery systems for gene therapies and RNA-Based therapeutics in oncology. Nanoscale 17 (10), 5501–5525. doi:10.1039/d4nr05371k
Shalaby, R., Ibrahim, S., Kotb, A. A. W., Baz, S., Hafed, L., Shaker, O., et al. (2024). MALAT1 as a potential salivary biomarker in oral squamous cell carcinoma through targeting miRNA-124. Oral Dis. 30 (4), 2075–2083. doi:10.1111/odi.14730
Shang, A., Wang, W., Gu, C., Chen, C., Zeng, B., Yang, Y., et al. (2019). Long non-coding RNA HOTTIP enhances IL-6 expression to potentiate immune escape of ovarian cancer cells by upregulating the expression of PD-L1 in neutrophils. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 38 (1), 411. doi:10.1186/s13046-019-1394-6
Shao, Z., Wang, X., Li, Y., Hu, Y., and Li, K. (2022). The role of long noncoding RNAs as regulators of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition process in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Front. Mol. Biosci. 9, 942636. doi:10.3389/fmolb.2022.942636
Shao, Y., Du, Y., Chen, Z., Xiang, L., Tu, S., Feng, Y., et al. (2025). Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated adipogenic transformation: a key driver of oral squamous cell carcinoma progression. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 16 (1), 12. doi:10.1186/s13287-025-04132-9
Sharma, P., Hu-Lieskovan, S., Wargo, J. A., and Ribas, A. (2017). Primary, adaptive, and acquired resistance to cancer immunotherapy. Cell 168 (4), 707–723. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2017.01.017
Shi, H., Li, K., Feng, J., Liu, G., Feng, Y., and Zhang, X. (2020). LncRNA-DANCR interferes with miR-125b-5p/HK2 axis to desensitize Colon cancer cells to Cisplatin vis activating anaerobic glycolysis. Front. Oncol. 10, 1034. doi:10.3389/fonc.2020.01034
Shi, L., Yang, Y., Li, M., Li, C., Zhou, Z., Tang, G., et al. (2022). LncRNA IFITM4P promotes immune escape by up-regulating PD-L1 via dual mechanism in oral carcinogenesis. Mol. Ther. 30 (4), 1564–1577. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.01.003
Singh, A. V., Bhardwaj, P., Laux, P., Pradeep, P., Busse, M., Luch, A., et al. (2024). AI and ML-based risk assessment of chemicals: predicting carcinogenic risk from chemical-induced genomic instability. Front. Toxicol. 6, 1461587. doi:10.3389/ftox.2024.1461587
Singh, S., Raj, D., Mathur, A., Mani, N., and Kumar, D. (2025). Current approaches in CRISPR-Cas systems for hereditary diseases. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 210, 205–229. doi:10.1016/bs.pmbts.2024.07.015
Siqueira, J. M., Heguedusch, D., Rodini, C. O., Nunes, F. D., and Rodrigues, M. (2023). Mechanisms involved in cancer stem cell resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Drug Resist 6 (1), 116–137. doi:10.20517/cdr.2022.107
Song, N., Li, P., Song, P., Li, Y., Zhou, S., Su, Q., et al. (2020a). MicroRNA-138-5p suppresses non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting PD-L1/PD-1 to regulate tumor microenvironment. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 8, 540. doi:10.3389/fcell.2020.00540
Song, H., Liu, Y., Li, X., Chen, S., Xie, R., Chen, D., et al. (2020b). Long noncoding RNA CASC11 promotes hepatocarcinogenesis and HCC progression through EIF4A3-mediated E2F1 activation. Clin. Transl. Med. 10 (7), e220. doi:10.1002/ctm2.220
Song, Z., Wang, X., Chen, F., Chen, Q., Liu, W., Yang, X., et al. (2022). LncRNA MALAT1 regulates METTL3-mediated PD-L1 expression and immune infiltrates in pancreatic cancer. Front. Oncol. 12, 1004212. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.1004212
Song, X., Duan, L., and Dong, Y. (2024). Diagnostic accuracy of exosomal long noncoding RNAs in diagnosis of NSCLC: a meta-analysis. Mol. Diagn Ther. 28 (4), 455–468. doi:10.1007/s40291-024-00715-z
Spooner, A., Moridani, M. K., Toplis, B., Behary, J., Safarchi, A., Maher, S., et al. (2025). Benchmarking ensemble machine learning algorithms for multi-class, multi-omics data integration in clinical outcome prediction. Brief. Bioinform 26 (2), bbaf116. doi:10.1093/bib/bbaf116
Sun, G., and He, L. (2024). A new paradigm for cancer immunotherapy: targeting immunogenic cell death-related noncoding RNA. Front. Immunol. 15, 1498781. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1498781
Sun, J. P., Ge, Q. X., Ren, Z., Sun, X. F., and Xie, S. P. (2019). MiR-6991-3p is identified as a novel suppressor in the expansion and activation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in hepatoma-bearing mice. Onco Targets Ther. 12, 309–317. doi:10.2147/OTT.S185422
Sun, Y., Han, X., Shang, C., Wang, Y., Xu, B., Jiang, S., et al. (2022a). The downregulation of type I IFN signaling in G-MDSCs under tumor conditions promotes their development towards an immunosuppressive phenotype. Cell Death Dis. 13 (1), 36. doi:10.1038/s41419-021-04487-w
Sun, Q., Xiao, L., Cui, Z., Yang, Y., Ma, J., Huang, Z., et al. (2022b). 3,3'-Diindolylmethane improves antitumor immune responses of PD-1 blockade via inhibiting myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Chin. Med. 17 (1), 81. doi:10.1186/s13020-022-00638-z
Sutera, S., Furchi, O. A., and Pentenero, M. (2025). Exploring cancer-associated fibroblasts in OSCC and OPMDs: microenvironment insights. Scoping review. Oral Dis. 31, 1982–1990. doi:10.1111/odi.15275
Tao, W., Sun, Q., Xu, B., and Wang, R. (2025). Towards the prediction of responses to cancer immunotherapy: a multi-omics review. Life (Basel) 15 (2), 283. doi:10.3390/life15020283
Thomas, P., Selvakumar, S. C., Preethi, K. A., and Sekar, D. (2024). Expression profiling of signal transducer and activator of transcription3 in oral squamous cell carcinoma in south Indian population. Minerva Dent. Oral Sci. 73 (1), 37–44. doi:10.23736/S2724-6329.23.04840-4
Tivol, E. A., Borriello, F., Schweitzer, A. N., Lynch, W. P., Bluestone, J. A., and Sharpe, A. H. (1995). Loss of CTLA-4 leads to massive lymphoproliferation and fatal multiorgan tissue destruction, revealing a critical negative regulatory role of CTLA-4. Immunity 3 (5), 541–547. doi:10.1016/1074-7613(95)90125-6
Tuersong, T., Shataer, M., Chen, Y., Chen, G., Li, X., Lei, L., et al. (2025). Extracellular vesicle-LncRNA HOTAIR modulates esophageal cancer chemoresistance and immune microenvironment via miR-375/CDH2 pathway. J. Cell Commun. Signal 19 (2), e70014. doi:10.1002/ccs3.70014
Vaxevanis, C., Bachmann, M., and Seliger, B. (2024). Immune modulatory microRNAs in tumors, their clinical relevance in diagnosis and therapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 12 (8), e009774. doi:10.1136/jitc-2024-009774
Vianello, C., Monti, E., Leoni, I., Galvani, G., Giovannini, C., Piscaglia, F., et al. (2024). Noncoding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: potential applications in combined therapeutic strategies and promising candidates of treatment response. Cancers (Basel) 16 (4), 766. doi:10.3390/cancers16040766
Wang, D., Ding, L., Wang, L., Zhao, Y., Sun, Z., Karnes, R. J., et al. (2015). LncRNA MALAT1 enhances oncogenic activities of EZH2 in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Oncotarget 6 (38), 41045–41055. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.5728
Wang, S., Wu, J., Ren, J., Vlantis, A. C., Li, M. Y., Liu, S. Y. W., et al. (2018). MicroRNA-125b interacts with Foxp3 to induce autophagy in thyroid cancer. Mol. Ther. 26 (9), 2295–2303. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.06.015
Wang, Y., Yi, K., Liu, X., Tan, Y., Jin, W., Li, Y., et al. (2021). HOTAIR Up-Regulation activates NF-κB to induce immunoescape in gliomas. Front. Immunol. 12, 785463. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.785463
Wang, W., Ding, M., Wang, Q., Song, Y., Huo, K., Chen, X., et al. (2024). Advances in Foxp3+ regulatory T cells (Foxp3+ Treg) and key factors in digestive malignancies. Front. Immunol. 15, 1404974. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1404974
Wei, J., Nduom, E. K., Kong, L. Y., Hashimoto, Y., Xu, S., Gabrusiewicz, K., et al. (2016). MiR-138 exerts anti-glioma efficacy by targeting immune checkpoints. Neuro Oncol. 18 (5), 639–648. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nov292
Wei, Y., Lei, J., Peng, Y., Chang, H., Luo, T., Tang, Y., et al. (2024). Expression characteristics and potential function of non-coding RNA in mouse cortical cells. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 17, 1365978. doi:10.3389/fnmol.2024.1365978
Wherry, E. J., Ha, S. J., Kaech, S. M., Haining, W. N., Sarkar, S., Kalia, V., et al. (2007). Molecular signature of CD8+ T cell exhaustion during chronic viral infection. Immunity. 27 (4), 670–684. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2007.09.006
Wickenhauser, C., Bethmann, D., Kappler, M., Eckert, A. W., Steven, A., Bukur, J., et al. (2021). Tumor microenvironment, HLA class I and APM expression in HPV-Negative oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancers (Basel) 13 (4), 620. doi:10.3390/cancers13040620
Wu, Y., Zhang, L., Zhang, L., Wang, Y., Li, H., Ren, X., et al. (2015). Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes tumor cell invasion and metastasis by recruiting EZH2 and repressing E-cadherin in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 46 (6), 2586–2594. doi:10.3892/ijo.2015.2976
Wu, H., Lai, W., Wang, Q., Zhou, Q., Zhang, R., and Zhao, Y. (2024). Gypenoside induces apoptosis by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and enhances T-cell antitumor immunity by inhibiting PD-L1 in gastric cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1243353. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1243353
Wuerdemann, N., Putz, K., Eckel, H., Jain, R., Wittekindt, C., Huebbers, C. U., et al. (2020). LAG-3, TIM-3 and VISTA expression on tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma-potential biomarkers for targeted therapy concepts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (1), 379. doi:10.3390/ijms22010379
Xian, D., Niu, L., Zeng, J., and Wang, L. (2021). LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 secreted by tumor cell-derived exosomes mediates immune escape in colorectal cancer by regulating PD-L1 ubiquitination via MiR-30a-5p/USP22. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 653808. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.653808
Xiao, L., Wang, W., Zhao, J., Xu, H., Li, S., and Yang, X. (2020). lncRNA MALAT1 promotes cell proliferation and invasion by regulating the miR-101/EZH2 axis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 20 (5), 164. doi:10.3892/ol.2020.12024
Xiao, S., Ma, S., Sun, B., Pu, W., Duan, S., Han, J., et al. (2024). The tumor-intrinsic role of the m(6)A reader YTHDF2 in regulating immune evasion. Sci. Immunol. 9 (95), eadl2171. doi:10.1126/sciimmunol.adl2171
Xin, X., Du, X., Xiao, Q., Azevedo, H. S., He, W., and Yin, L. (2019). Drug nanorod-mediated intracellular delivery of microRNA-101 for self-sensitization via autophagy inhibition. Nanomicro Lett. 11 (1), 82. doi:10.1007/s40820-019-0310-0
Xu, Q. R., Tang, J., Liao, H. Y., Yu, B. T., He, X. Y., Zheng, Y. Z., et al. (2021). Long non-coding RNA MEG3 mediates the miR-149-3p/FOXP3 axis by reducing p53 ubiquitination to exert a suppressive effect on regulatory T cell differentiation and immune escape in esophageal cancer. J. Transl. Med. 19 (1), 264. doi:10.1186/s12967-021-02907-1
Xu, S. B., Wang, M. Y., Shi, X. Z., Wang, Q., Yu, M., Zhang, W., et al. (2023). Influence of PD-1/PD-L1 on immune microenvironment in oral leukoplakia and oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Dis. 29 (8), 3268–3277. doi:10.1111/odi.14332
Xu, D., Wang, W., Wang, D., Ding, J., Zhou, Y., and Zhang, W. (2024). Long noncoding RNA MALAT-1: a versatile regulator in cancer progression, metastasis, immunity, and therapeutic resistance. Noncoding RNA Res. 9 (2), 388–406. doi:10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.01.015
Yan, Y., Wang, X., Veno, M. T., Bakholdt, V., Sorensen, J. A., Krogdahl, A., et al. (2017). Circulating miRNAs as biomarkers for oral squamous cell carcinoma recurrence in operated patients. Oncotarget 8 (5), 8206–8214. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.14143
Yang, Z., Chen, W., Wang, Y., Qin, M., and Ji, Y. (2021). CircKRT1 drives tumor progression and immune evasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma by sponging miR-495-3p to regulate PDL1 expression. Cell Biol. Int. 45 (7), 1423–1435. doi:10.1002/cbin.11581
Yang, F., Li, J., Ge, Q., Zhang, Y., Zhang, M., Zhou, J., et al. (2023). Non-coding RNAs: emerging roles in the characterization of immune microenvironment and immunotherapy of prostate cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 214, 115669. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115669
Yuan, X., Shen, Q., and Ma, W. (2022). Long noncoding RNA hotair promotes the progression and immune escape in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma through MicroRNA-30a/GRP78/PD-L1 axis. J. Immunol. Res. 2022, 5141426. doi:10.1155/2022/5141426
Yue, J., Wu, Y., Qiu, L., Zhao, R., Jiang, M., and Zhang, H. (2021). LncRNAs link cancer stemness to therapy resistance. Am. J. Cancer Res. 11 (4), 1051–1068. Available online at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33948345/.
Zabeti, T. A., and Vahidi, S. (2024). Unraveling the interplay of CD8 + T cells and microRNA signaling in cancer: implications for immune dysfunction and therapeutic approaches. J. Transl. Med. 22 (1), 1131. doi:10.1186/s12967-024-05963-5
Zarour, H. M. (2016). Reversing T-cell dysfunction and exhaustion in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 22 (8), 1856–1864. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1849
Zeng, Y., Luo, J., Zi, M., Jiang, S., Ge, W., Yu, Y., et al. (2024). Comprehensive analysis of clinicopathological characteristics in oral squamous cell carcinoma arising from oral submucous fibrosis: a retrospective study. Discov. Oncol. 15 (1), 455. doi:10.1007/s12672-024-01351-z
Zhang, Y., Liu, W., Chen, Y., Liu, J., Wu, K., Su, L., et al. (2018). A cellular MicroRNA facilitates regulatory T lymphocyte development by targeting the FOXP3 promoter TATA-Box motif. J. Immunol. 200 (3), 1053–1063. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1700196
Zhang, L., Meng, X., Zhu, X. W., Yang, D. C., Chen, R., Jiang, Y., et al. (2019). Long non-coding RNAs in oral squamous cell carcinoma: biologic function, mechanisms and clinical implications. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 102. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1021-3
Zhang, J., Zhao, X., Ma, X., Yuan, Z., and Hu, M. (2020). KCNQ1OT1 contributes to sorafenib resistance and programmed death-ligand-1-mediated immune escape via sponging miR-506 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 46 (5), 1794–1804. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2020.4710
Zhang, S., Yang, R., Ouyang, Y., Shen, Y., Hu, L., and Xu, C. (2023). Cancer stem cells: a target for overcoming therapeutic resistance and relapse. Cancer Biol. Med. 20 (12), 985–1020. doi:10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2023.0333
Zhang, X., Zhang, Y., Liu, Q., Zeng, A., and Song, L. (2024a). Glycolysis-associated lncRNAs in cancer energy metabolism and immune microenvironment: a magic key. Front. Immunol. 15, 1456636. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1456636
Zhang, B., Liu, J., Mo, Y., Zhang, K., Huang, B., and Shang, D. (2024b). CD8(+) T cell exhaustion and its regulatory mechanisms in the tumor microenvironment: key to the success of immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 15, 1476904. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1476904
Zhao, L., Yu, H., Yi, S., Peng, X., Su, P., Xiao, Z., et al. (2016). The tumor suppressor miR-138-5p targets PD-L1 in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 7 (29), 45370–45384. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.9659
Zhao, Y., Liu, Y., Lin, L., Huang, Q., He, W., Zhang, S., et al. (2018a). The lncRNA MACC1-AS1 promotes gastric cancer cell metabolic plasticity via AMPK/Lin28 mediated mRNA stability of MACC1. Mol. Cancer 17 (1), 69. doi:10.1186/s12943-018-0820-2
Zhao, S. Y., Wang, J., Ouyang, S. B., Huang, Z. K., and Liao, L. (2018b). Salivary Circular RNAs Hsa_Circ_0001874 and Hsa_Circ_0001971 as novel biomarkers for the diagnosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 47 (6), 2511–2521. doi:10.1159/000491624
Zhao, K., Wang, X., Zhao, D., Lin, Q., Zhang, Y., and Hu, Y. (2022). “lncRNA HITT inhibits lactate production by repressing PKM2 oligomerization to reduce tumor growth and macrophage polarization,”, 2022. Washington, DC: Research Wash D C. doi:10.34133/2022/9854904
Zheng, Z., Ma, X., and Li, H. (2020). Circular RNA circMDM2 accelerates the glycolysis of oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting miR-532-3p/HK2. J. Cell Mol. Med. 24 (13), 7531–7537. doi:10.1111/jcmm.15380
Zheng, X., Du, F., Gong, X., and Xu, P. (2022). Circ_0005320 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma tumorigenesis by sponging microRNA-486-3p and microRNA-637. Bioengineered 13 (1), 440–454. doi:10.1080/21655979.2021.2009317
Zhou, W. Y., Zhang, M. M., Liu, C., Kang, Y., Wang, J. O., and Yang, X. H. (2019). Long noncoding RNA LINC00473 drives the progression of pancreatic cancer via upregulating programmed death-ligand 1 by sponging microRNA-195-5p. J. Cell Physiol. 234 (12), 23176–23189. doi:10.1002/jcp.28884
Zhou, Z., Wang, Z., Gao, J., Lin, Z., Wang, Y., Shan, P., et al. (2022). Noncoding RNA-mediated macrophage and cancer cell crosstalk in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 25, 98–120. doi:10.1016/j.omto.2022.03.002
Zhou, H., Jia, W., Lu, L., and Han, R. (2023). MicroRNAs with multiple targets of immune checkpoints, as a potential sensitizer for immune checkpoint inhibitors in breast cancer treatment. Cancers (Basel) 15 (3), 824. doi:10.3390/cancers15030824
Zhu, P., Liu, B., and Fan, Z. (2023a). Noncoding RNAs in tumorigenesis and tumor therapy. Fundam. Res. 3 (5), 692–706. doi:10.1016/j.fmre.2023.05.014
Keywords: oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), non-coding RNA (ncRNA), immunotherapy resistance, tumor microenvironment, targeting strategies
Citation: Liang Z, Zhao Y, Wang X and Li Y (2025) The role and targeting strategies of non-coding RNAs in immunotherapy resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 13:1642417. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1642417
Received: 06 June 2025; Accepted: 14 October 2025;
Published: 27 October 2025.
Edited by:
Remya Raja, Mayo Clinic Arizona, United StatesReviewed by:
R. C. Koumar, Yenepoya University, IndiaMohamed Kishta, National Research Centre, Egypt
Copyright © 2025 Liang, Zhao, Wang and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xin Wang, d3hAdWNhcy5hYy5jbg==; Yuehe Li, bHVlc2hAMTI2LmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Zhinan Liang
Zhinan Liang Yicheng Zhao3†
Yicheng Zhao3† Xin Wang
Xin Wang