- 1Department of Urology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
- 2Department of Urology, Guangzhou Institute of Cancer Research, the Affiliated Cancer Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
- 3Department of Urology, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
- 4Department of Radiotherapy, Guangzhou Institute of Cancer Research, The Affiliated Cancer Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
- 5Department of Urology, The Fourth Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
- 6First Clinical Medical College, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
- 7Department of Urology, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Major Obstetric Diseases, Guangdong Provincial Clinical Research Center for Obstetrics and Gynecology, The Third Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
A Correction on
ELOVL2 mediated stabilization of AR contributes to enzalutamide resistance in prostate cancer
by Cen J, Guo J, Zeng X, Song X, Ge S, Chen M, Li Q, Yu Y, Lv D and Zhao S (2025). Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 13:1598400. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1598400
In the published article, there was an error in the legend for Figure 3E. Due to an oversight, the IC50 value for LNCaP-NC was incorrectly reported as:
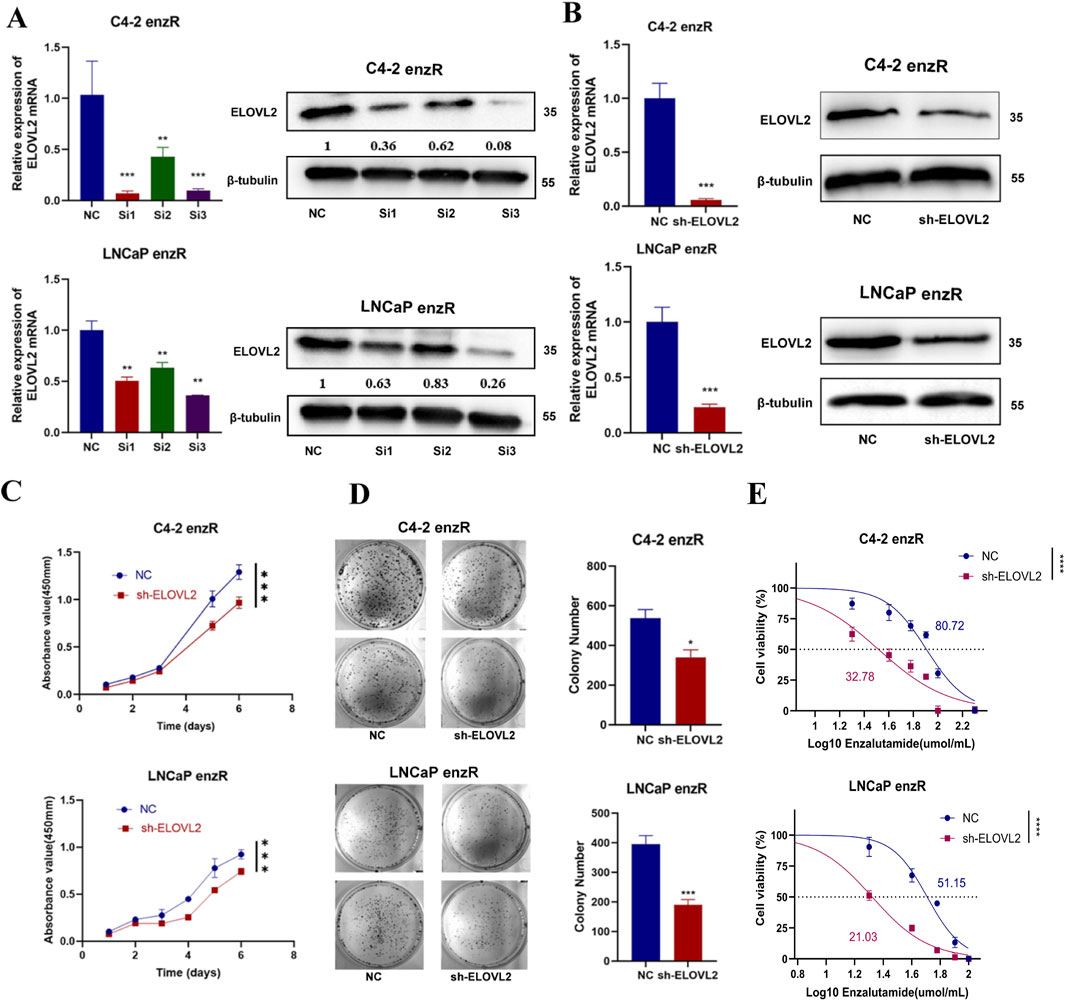
Figure 3. ELOVL2 inhibition suppresses growth and restores enzalutamide sensitivity in resistant PCa cells. (A)Validation of ELOVL2 knockdown efficiency using three independent small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) by qRT-PCR and Western blot analysis. siRNA#3 showed the most potent knockdown effect and was selected for subsequent experiments. (B) Stable ELOVL2 knockdown using lentiviral shRNA (derived from siRNA#3 sequence). Knockdown efficiency was confirmed by qRT-PCR and Western blot. (C) Cell proliferation assessed by CCK-8 assay in C4-2-enzR and LNCaP-enzR cells following ELOVL2 knockdown. Data represent mean ± SD (n = 5), ***p < 0.001. (D) Colony formation assay demonstrating the proliferative capacity of C4-2-enzR and LNCaP-enzR cells after ELOVL2 inhibition. Colonies were counted after 14 days (mean ± SD, n = 3), *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001. (E) Dose-response curves and calculated half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values for enzalutamide in ELOVL2-depleted cells. ELOVL2 knockdown significantly reduced IC50 values in both C4-2-enzR (32.78 µM, 95% CI: 27.95–37.54; ****p < 0.0001) and LNCaP-enzR (21.03 µM, 95% CI: 19.62–22.36; ****p < 0.0001) cells compared to control (C4-2-NC: 80.72 µM, 95% CI: 75.26–86.48; LNCaP-NC: 51.15 µM, 95% CI: 47.92–54.33).
“LNCaP-NC: 21.03 µM, 95% CI: 19.62–22.36.”
The corrected legend appears below.
“LNCaP-NC: 51.15 µM, 95% CI: 47.92–54.33.”
The authors apologize for this error and confirm that it does not affect the scientific conclusions of the article. The original article has been updated accordingly.
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 3E as presented. The visualization results for Figure 3E were correctly submitted and approved during the first round of revisions. However, due to an oversight on our part, this figure was inadvertently omitted in the second revised version. The corrected Figure 3E and its accompanying caption—Figure 3 ELOVL2 inhibition suppresses growth and restores enzalutamide sensitivity in resistant PCa cells—are provided below.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: ELOVL2, enzalutamide resistance, androgen receptor, prostate cancer, CRPC
Citation: Cen J, Guo J, Zeng X, Song X, Ge S, Chen M, Li Q, Yu Y, Lv D and Zhao S (2025) Correction: ELOVL2 mediated stabilization of AR contributes to enzalutamide resistance in prostate cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 13:1646699. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1646699
Received: 13 June 2025; Accepted: 16 June 2025;
Published: 25 June 2025.
Edited and reviewed by:
Sehbanul Islam, University of Pennsylvania, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Cen, Guo, Zeng, Song, Ge, Chen, Li, Yu, Lv and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yuzhong Yu, eXl6MTM1MzQ2MjA0OUAxMjYuY29t; Daojun Lv, ZGFvanVubHY4OEBnemhtdS5lZHUuY24=; Shanchao Zhao, bHVsdWx1bHVAc211LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work contribute to this work and share the first authorship
 Jinpeng Cen
Jinpeng Cen Jiading Guo2†
Jiading Guo2† Shengdong Ge
Shengdong Ge Shanchao Zhao
Shanchao Zhao