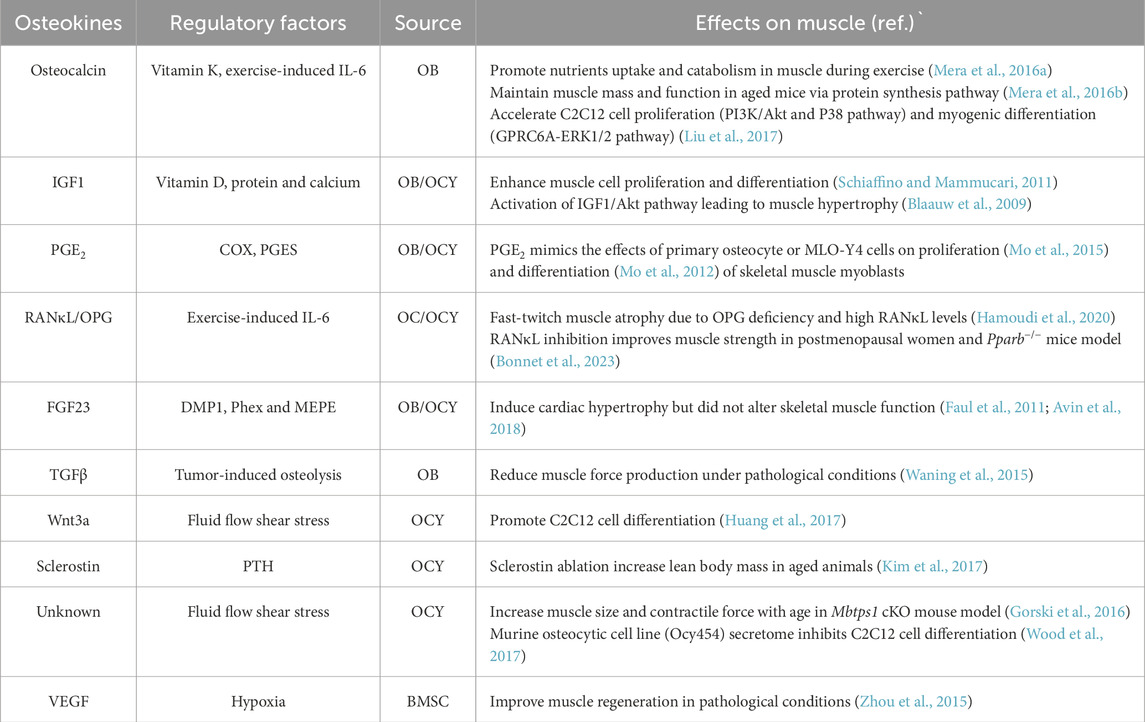
- 1College of Life Sciences, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, Inner Mongolia, China
- 2Inner Mongolia Key Laboratory of Biomanufacturing Techenology, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, Inner Mongolia, China
- 3Key Laboratory for Space Bioscience and Biotechnology, School of Life Sciences, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, China
The intricate interactions between bone and muscle are central to musculoskeletal health. It was historically assumed that bone and muscle interact through mechanical coupling, that is, skeletal muscles attach to bone and facilitate movement of the bone via muscular contraction. However, recent studies have recognized bone and muscle as endocrine organs, capable of producing and releasing osteokines and extracellular vesicles (EVs) that influence each other’s functions, thereby introducing a novel concept known as “bone-muscle crosstalk”. The influence of muscle on bone has been extensively studied, little has reported regarding the muscle regulation by bone. Emerging studies indicate that the transmission of signaling molecules from bone to muscle is partially mediated by hemichannels and gap junctions formed by connexin 43 (Cx43) in osteoblasts and osteocytes. This review aims to summarize the latest findings on bone-muscle crosstalk, with a particular emphasis on the roles of osteokines and EVs derived from bone. Furthermore, it highlights the channel functions of Cx43 in the release of secretory factors through this crosstalk mechanism. The continued research into bone–muscle crosstalk is expected to identify new therapeutic targets for the twin diseases of osteoporosis and sarcopenia.
1 Introduction
In the musculoskeletal system, bone and muscle are closely correlated across the life cycle. They share the common mesodermal precursors during embryogenesis. In case of exercise and disuse, changes in bone and muscle mass are also tightly linked. With aging, there is a simultaneous decline in both bone and muscle mass. Traditionally, this relationship has been understood primarily in terms of mechanical coupling, where bone serve as a scaffold for muscle attachment, and muscle applies load to bone (Zhao et al., 2024). The physical linkage is undoubtedly necessary to support locomotion and the shape/forms of animals. However, the synergy between bone and muscle goes beyond mechanical, as evidenced by the discovery of the endocrine functions of these two tissues (Lee et al., 2007; Kurek et al., 1997; Karsenty and Olson, 2016). Both bone and muscle can produce soluble factors that exert either positive or negative effects on each other (Welc et al., 2025). This intricate reciprocity is central to maintain musculoskeletal health.
Bone is a highly vascularized organ, with osteocytes residing in lacunae that are in close proximity to blood vessels via lacunocanalicular networks. The release of osteokines into the bloodstream appears to be the most prominent mechanism of communication between bone and muscle (Lara-Castillo and Johnson, 2020). Likewise, several myokines produced by muscle also are known to circulate (Zhao et al., 2024). Recent research has identified extracellular vesicles (EVs), which are shed cellular components, as an additional mechanism facilitating crosstalk between bone and muscle (Ma et al., 2023). EVs are lipid bilayer-bound particles that encapsulate various biomolecules, including mRNAs, miRNAs, and proteins, reflecting the cellular state. These shed EVs can exert local effects in an autocrine manner or be transported into circulation to influence distant organs (He C. et al., 2020). Furthermore, due to their anatomical proximity, another potential mechanism of bone-muscle communication involves the diffusion of molecules across the periosteum. An early study by Lai et al. (2014) demonstrated that the semi-permeable periosteum permits the diffusion of molecules smaller than 40 kDa. This suggests that small osteokines can easily reach the adjacent muscle by passive diffusion, and those molecules with greater than 40 kDa are likely to be delivered via the circulation or as EVs cargo.
The adult skeleton predominantly consists of three cell types: osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteocytes. Osteocytes, which account for over 90% of the total bone cell population, establish an extensive lacunar-canalicular network facilitating intercellular communication among these cell types (He et al., 2025). One mechanism of cell-cell communication is mediated via gap junctions, which are membrane-spanning channels formed by the docking of two hemichannels (Zhao et al., 2022). In addition to direct intercellular communication through gap junctions, hemichannels facilitate interactions between osteocytes and the pericellular environment. Both types of connexin-based channels exhibit selective permeability, allowing the diffusion of molecules smaller than 1.2 kDa (Zhang et al., 2025). Connexin43 (Cx43) is the most prevalently expressed connexin subtype in osteoblasts and osteocytes. Previous research has demonstrated that Cx43 in bone plays a crucial role in skeletal muscle development, as evidenced by the impaired formation of skeletal muscle in mice lacking Cx43 in osteoblasts/osteocytes (Shen et al., 2015). Our group has recently elucidated the distinct functions of Cx43 hemichannels and gap junctions in osteocytes, which regulate skeletal muscle function (Li et al., 2021; Li et al., 2022). These findings underscore the potential roles of Cx43 in mediating signal transmission from bone to muscle.
Osteoporosis and sarcopenia are major clinical concerns in the aging population, and these two conditions often occur concurrently in many patients. However, the current therapeutic approach for the twin disease mostly targets the one rather than both tissues simultaneously (Kirk et al., 2020a). A treatment paradigm shift may be underway with increasing recognition of the close ties between bone and muscle. Herein, we summarize the latest progress of the role of bone-derived factors and Cx43 in bone-muscle crosstalk. Such knowledge is crucial for the discovery of potential therapeutic targets that may lead to more integrated treatment strategies for the musculoskeletal disorders.
2 Bone as an endocrine organ
In addition to provide structural support for the internal organs, bone serves as a substantial reservoir for osteogenic growth factors, such as insulin-like growth factors (IGFS), bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) and transforming growth factor β (TGFβ), etc (He et al., 2025). These factors play a critical role in the continuous bone remodeling through bone formation by osteoblasts and bone resorption by osteoclasts. Osteocytes, which are embedded within the bone matrix, are also considered indispensable orchestrators of osteoblast and osteoclast functions (Zhang et al., 2025). Recent evidence from multiple research groups supports the notion that bone functions as an endocrine organ. This is primarily due to its highly vascularized nature and its ability to secrete osteokines into the bloodstream, which can influence the function of distant tissues, including muscle.
Of the major cell types in skeleton, osteoblasts constitute only 5% of total bone cells compared to 1% of osteoclasts, and the remaining more than 90% are osteocytes (Zhang and Chen, 2024). Osteocytes, residing within lacunae, extend their dendritic processes to form a lacunocanalicular system that connects with the vasculature in the bone matrix. Considering the substantial mass of osteocytes and their dendritic processes within the skeleton, these cells likely serve as the primary source of circulating factors derived from bone. Various imaging techniques have demonstrated the connectivity between dendritic processes, adjacent osteocytes, and the vasculature. A study conducted by Beno and colleagues (Beno et al., 2006) revealed that the injection of small dyes or molecules, up to 70 kDa in size, into the tail vein of a mouse traverses the lacunocanalicular network within a few minutes. This observation suggests that canalicular fluid permeates into the circulation, allowing osteocyte-secreted factors to potentially influence distant target tissues. To the best of our knowledge, the initial evidence supporting the role of the osteocyte as an endocrine cell was the discovery that fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23), which is highly expressed in osteocytes, regulates phosphorus homeostasis in the kidneys (Feng et al., 2006). The list of bone-derived factors continues to expand, with significant examples including osteocalcin, prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1), receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa β ligand (RANKL), osteoprotegerin (OPG), Wnt proteins, Dickkopf-1 (DKK1), sclerostin, fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23), and transforming growth factor β (TGFβ), as elaborated below (Table 1).
3 Bone-muscle crosstalk and involvement of bone factors
The intricate relationship between bone and muscle is established during fetal development, as both tissues originate from common progenitor cells and undergo organogenesis regulated by a complex gene network (Dong et al., 2024). Historically, the emphasis on the mechanical coupling between these two tissues may have stemmed from embryological studies. In the developing embryo, muscle forces significantly influence skeletal growth and bone morphology, while skeletal adaptations in early postnatal life are primarily driven by changes in mechanical stimuli (Deng et al., 2024). However, a more comprehensive understanding of bone-muscle interaction beyond mechanical coupling to include a wide array of signaling factors exchanged between the two tissues. Also, the consequences of bone-to-muscle signaling mainly include alterations in skeletal muscle mass and muscle function (Figure 1).
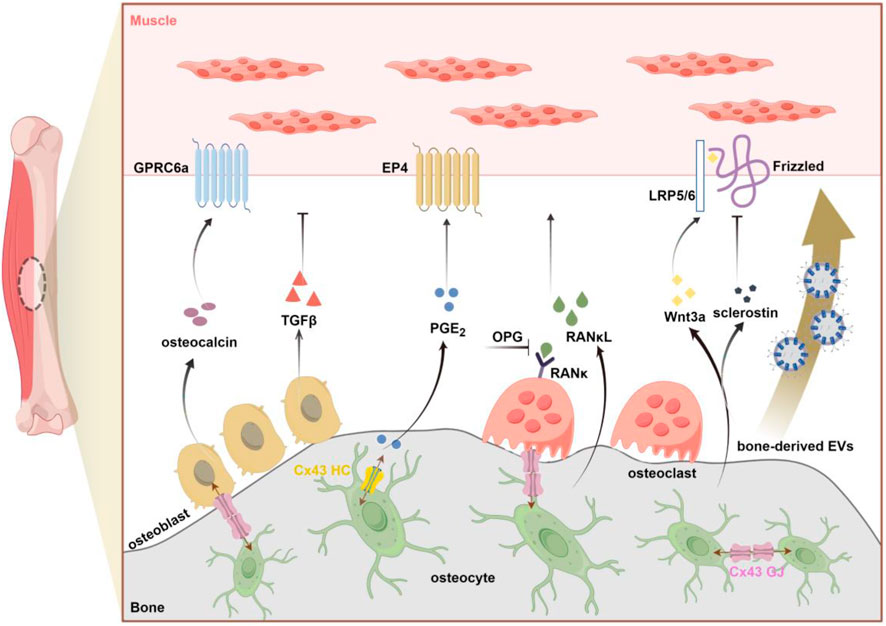
Figure 1. Schematic overview of bone-derived factors (osteokines and EVS) involved in bone-to-muscle communication (by figdraw.com). Primary factors released from bone that affect muscle including: osteocalcin, TGFβ (Transforming growth factorβ), PGE2 (Prostaglandin E2), RANκL (Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor Kappa β Ligand), OPG (osteoprotegerin), Wnt3a, sclerostin. Emerging evidence also supports the potential role of bone-derived EVs in signal transmission from bone to muscle. As the key gateway to the passasge of signaling molecules, Cx43-formed GJ and HC in osteocytes can regulate bone-muscle crosstalk through the release of small molecules such as PGE2. GPRC6a, G protein-coupled receptor; EP4, E-type prostanoid receptor4; LRP5/6, lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5/6; Cx43, connexin43; GJ, gap junction; HC, hemichannel.
3.1 Role of bone-derived osteokines
3.1.1 Osteocalcin
Osteocalcin, also referred to as carboxyglutamic acid or BGLAP, is a protein secreted by mature osteoblasts and osteocytes. Osteocalcin undergoes post-translational modification at three specific glutamate residues (in positions 17, 21, and 24), by γ-glutamyl carboxylase with vitamin K as a cofactor (Kirk et al., 2025). Due to the high affinity of osteocalcin for hydroxyapatite crystals following its γ-carboxylation, most secreted osteocalcin is deposited in the mineralized bone matrix (Battafarano et al., 2020). It can be released into the circulation through decarboxylation at low pH levels. Osteocalcin has been shown to affect distant adipocytes and pancreatic β-cells by binding to the Gprc6a receptor. Beyond its role in the regulation of energy metabolism (Lee et al., 2007), glucose metabolism (Kanazawa, 2015), and ectopic calcification (Bonewald, 2019) in rodent models, osteocalcin also affects muscle physiology. The study by Karsenty and colleagues demonstrated a significant reduction in muscle mass in Gprc6a−/− mice. Conversely, Esp−/− mice, which lack a phosphatase that inhibits osteocalcin function, exhibit increased muscle mass. Furthermore, osteocalcin supplementation enhances exercise capacity in young mice and mitigates age-related declines in muscle strength. Aerobic exercise increases circulating osteocalcin levels and osteocalcin signaling in muscle tissue, leading to the secretion of the myokine IL-6 (Mera et al., 2016a). The mechanism by which exercise affect osteocalcin and interleukin-6 (IL-6) involves the exercise-induced release of the myokine IL-6, which acts on osteoblasts. This interaction results in increased secretion of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-Β ligand (RANκL) by osteoclasts, facilitating the remodeling of the bone matrix. Consequently, osteocalcin is liberated from the bone matrix into the circulation, where it reaches muscle tissue and binds to its receptor, Gprc6a, thereby modulating muscle function (Chowdhury et al., 2020). These findings provide robust evidence supporting the beneficial role of osteocalcin in the regulation of muscle mass and function.
3.1.2 Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2)
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) is an eicosanoid compound derived from arachidonic acid that can be generated by a reaction catalyzed via cyclooxygenase (COX) and terminal PGE2 synthases (PGES) (Cheng et al., 2021). This soluble factor can be released by bone cells and participates in the regulation of various physiological responses, including inflammation, tissue repair, and regeneration. A recent study by Palla et al. demonstrated the beneficial roles of PGE2 signaling in the rejuvenation of aged muscle mass and strength (Palla et al., 2021). The study found that elevated levels of 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-PGDH), an enzyme responsible for the degradation of PGE2, in aged muscle contribute to muscle atrophy and decreased muscle strength. Moreover, the physiological restoration of PGE2 levels through the inhibition of 15-PGDH was shown to enhance mitochondrial function, thereby increasing muscle mass and function. Notably, a comparison with muscle cells revealed that osteocytes produce PGE2 at levels 100 to 1000 times higher (Welc et al., 2025). This substantial production of PGE2 by osteocytes plays a crucial role in supporting muscle regeneration and the repair of injured muscle tissue (Ho et al., 2017). Moreover, multiple investigations conducted by Brotto’s research group have demonstrated that PGE2 serves as a potent stimulator of myogenesis and enhances primary muscle function in ex vivo studies (Mo et al., 2015; Mo et al., 2012). An earlier in vivo investigation by Wang et al. (Wang et al., 2005) revealed that PGE2, released from mechanically stimulated osteocytes, was detectable in the circulatory system. These findings suggest that bone, particularly osteocytes, can modulate muscle function through the secretion of PGE2. Nonetheless, the mechanism by which PGE2 produced by osteocytes reaches muscle cells remains unclear, given its short half-life in circulation.
3.1.3 Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1)
Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1) is recognized as a crucial anabolic factor in both embryonic and postnatal skeletal muscle development. IGF-1, produced by osteoblasts, may be either secreted freely or deposited into the bone matrix, from which it is released through osteoclast-mediated bone resorption (Wildemann et al., 2007). Osteocyte-derived IGF-1 signaling serves as a critical component of mechanotransduction in bone. The upregulation of IGF-1 expression in osteocytes represents one of the earliest responses of bone to mechanical loading. In addition, nutritional factors including vitamin D, protein and calcium can also upregulate IGF-1 to synergistically regulate the muscle anabolism (Kirk et al., 2020b). As a key regulator of muscle mass during development, IGF-1 has been demonstrated to enhance both the proliferation and differentiation of myogenic cells (Schiaffino and Mammucari, 2011). In adult skeletal muscle, the activation of Akt, a downstream effector of IGF-1 signaling, induces a significant hypertrophic response, characterized by an increase in absolute force without alterations in specific force (Blaauw et al., 2009; Regan et al., 2017). Similarly, Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 (BMP2) signaling has been shown to sustain and promote adult muscle mass. Notably, BMP2-induced muscle hypertrophy is largely reflected by an increase in absolute muscle force, with specific muscle force remaining unchanged or slightly reduced compared to control mice (Winbanks et al., 2013; Sartori et al., 2014). However, the role of IGF-1 in bone-muscle communication warrants further investigation.
3.1.4 Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa β ligand (RANκL)
Osteocytes are the primary source of RANκL, an osteokine that plays a crucial role in osteoclast activity and formation. The deletion of RANκL results in significant bone loss, including tooth loss and the absence of osteoclasts in mice (Kong et al., 1999). The receptor for RANκL, known as RANκ, is expressed in both osteoclasts and fully differentiated myotubes. The interaction between RANκL and RANκ induces osteoclast activation and osteoclastogenesis via NF-κB signaling. Activation of RANκ can inhibit myogenic differentiation and activate the ubiquitin–proteasome system, ultimately leading to muscle atrophy (Kirk et al., 2025; Langen et al., 2001). Osteoprotegerin (OPG), a decoy receptor for RANκL, exerts an inhibitory effect on osteoclast differentiation. A study on glucocorticoid-induced osteoporotic rats showed that treadmill training significantly decreased RANκL expression and increased OPG levels, suggesting that the RANκ/RANκL/OPG signaling is modulated by exercise (Pichler et al., 2013). In addition, elevated circulating IL-6 levels during exercise can also signal to osteoblasts to produce RANκL. Recent evidence suggests a role for RANκL in bone-muscle crosstalk. The OPG knockout mouse exhibits reduced bone mass and fast-twitch muscle atrophy due to elevated RANκL levels (Hamoudi et al., 2020). Furthermore, improvements in bone biomechanical properties and fast-twitch muscle mass have been observed with the administration of an anti-RANκL antibody. In 2024, Gostage and colleagues (Gostage et al., 2024) demonstrated that the ablation of RANκL (RANκL−/−) or OPG (Opg−/−) in mice resulted in deleterious effects on both bone and muscle. Conversely, beneficial effects were observed when these mice were treated with anti-RANκL or OPG-Fc. Clinical data further suggest that a three-year treatment regimen with the anti-RANκL antibody denosumab can enhance lean muscle mass and strength in women (Bonnet et al., 2023). Notably, the effects of anti-RANκL therapy appear to be specifically targeted towards fast-twitch skeletal muscle. Consequently, the RANκ-RANκL-OPG pathway is regarded as a therapeutic target for osteoporosis and sarcopenia.
3.1.5 Regulators of Wnt/β-catenin pathway
The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway plays an essential role in regulating the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts during embryonic development, maintaining bone homeostasis during postnatal growth, and facilitating bone accrual in response to mechanical loading (Huang et al., 2017). Various components of this pathway serve as key regulators, enabling osteocytes to transmit mechanical loading signals to cells on the bone surface. Mechanical loading can activate the Wnt/β-catenin pathway through its interaction with the prostaglandin pathway, resulting in an increase in positive regulators of bone formation, such as Wnt proteins, and a decrease in negative regulators, including Dkk-1 and sclerostin (Kitase et al., 2010). Although these factors primarily originate from bone and exert local effects, such as Wnt 3a and sclerostin, are also detectable in serum, suggesting their potential role in bone-muscle crosstalk regulation. Wnt 3a is secreted by osteocytes, and its expression level is significantly elevated in MLO-Y4 cells subjected to fluid flow shear stress (Huang et al., 2017). Research conducted by Brotto’s group has demonstrated that osteocyte-derived Wnt3a promotes the myogenic differentiation of C2C12 mouse myoblasts and human muscle cells by upregulating myogenin and MyoD. Conversely, sclerostin acts as an inhibitor of Wnt 3a, thereby hindering myoblast differentiation (Huang et al., 2017; Jähn et al., 2012). Despite the current understanding of the roles of Wnt proteins and sclerostin in bone-muscle crosstalk, in vivo evidence remains insufficient. In addition to the skeleton, sclerostin is also found in serum and its circulating levels associated with whole-body metabolism, are affected by sex hormones, and respond to intermittent parathyroid hormone (PTH) (Chen et al., 2022). Notably, a study utilizing a breast cancer mouse model demonstrated that the administration of an anti-sclerostin antibody effectively prevented bone destruction and enhanced skeletal muscle function, in contrast to the outcomes observed in vehicle-treated mice (Hesse et al., 2019). It has been established that Dkk-1 in bone is predominantly secreted by osteoblasts rather than osteocytes (Ke et al., 2012). Mice deficient in Dkk-1 exhibit high bone mass despite elevated levels of circulating sclerostin. However, the potential impact of Dkk-1 on muscle remains unclear. These findings prompt several unresolved questions, such as the mechanism by which osteocyte-derived Wnt3a affects muscle function—whether through an endocrine pathway, via extracellular vesicles, or through an alternative mechanism.
3.1.6 Fibroblast growth factor 23(FGF23)
Contrary to the hypertrophic response induced by bone-derived factors, certain osteokines have been demonstrated to adversely affect muscle mass and function. Since its identification in 2000, fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) has been recognized as an osteocyte-produced hormone that plays a crucial role in renal phosphate handling and the synthesis of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (1,25D), the most biologically active form of vitamin D (Shimada et al., 2004; Riminucci et al., 2003). The secretion of FGF23 is co-regulated by other osteocyte-derived factors, including dentin matrix protein 1 (Dmp1), phosphate-regulating neutral endopeptidase X-linked (Phex), and matrix extracellular phosphoglycoprotein (MEPE) (Delgado-Calle and Bellido, 2022). In the absence of Phex or Dmp1, an increase in systemic FGF23 levels in osteocytes results in enhanced phosphate excretion by the kidneys, leading to conditions such as rickets and osteomalacia. Recent studies suggest that FGF23 plays a critical role in regulating phosphate homeostasis in response to exercise, with osteocyte responsiveness to the exercise-induced myokine β-aminoisobutyric acid (BAIBA) influencing this process during aging, as reviewed by Welc and colleagues (Welc et al., 2025).
The activation of canonical FGF23 signaling necessitates interaction with the essential co-receptor α-klotho, whereas non-canonical FGF23 signaling operates independently of α-klotho (Kirk et al., 2025). Both FGF23 and α-klotho have been demonstrated to inhibit the myogenic differentiation of cultured human skeletal muscle cells by downregulating IGF1 signaling. Furthermore, FGF23 induces premature senescence in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived from human skeletal muscle via the p53-p21 pathway, independently of α-klotho, without impacting satellite cell function (Sato et al., 2016). In a rickets/osteomalacia model, administration of an FGF23 neutralizing antibody in mice resulted in elevated serum phosphate levels and enhanced muscle function (Regan et al., 2017; Waning and Guise, 2014). Additionally, skeletal muscle function was impaired in Dmp1-deficient mice, although cardiac force production remained unaffected (Wacker et al., 2016). These findings suggest that osteocyte-derived FGF23 may serve as a potential mediator in bone-to-muscle communication, warranting further investigation into its precise role.
3.1.7 Transforming growth factorβ (TGFβ)
Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TGFβ) is produced by a variety of tissues throughout the body, with the skeletal system serving as the predominant source. This cytokine is primarily synthesized by bone-forming osteoblasts and is stored in the mineralized matrix in a latent form. The activation and release of TGFβ occur in response to low pH conditions during osteoclast-mediated bone resorption or mechanical stretching (Wang et al., 2022). Beyond its interactions with osteoclasts and osteoblasts, TGFβ also plays a critical role in remodeling the osteocyte lacunocanalicular network. The deletion of TGFβ in osteocytes has been associated with increased bone fragility (Schurman et al., 2021). A study by Waning and colleagues (Waning et al., 2015) has demonstrated that TGFβ is integral to bone-muscle communication. Specifically, bone degradation resulting from cancer metastasis leads to elevated TGFβ release from the bone matrix, which subsequently contributes to muscle weakness by impairing calcium-induced muscle force production. Interventions utilizing the bone-targeting bisphosphonate zoledronic acid or the TGFβ receptor I kinase inhibitor SD-208, aimed at inhibiting TGFβ signaling, have shown promise in ameliorating skeletal muscle wasting and weakness. These findings underscore the detrimental effects of osteoclast-mediated TGFβ release on skeletal muscle health.
3.1.8 Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), produced by bone, is an endothelial cell survival factor that coordinates the processes of angiogenesis and osteogenesis. It plays a central role in bone homeostasis, repair, and the pathobiological processes affecting these functions (Chen et al., 2023). Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) function as progenitor cells within the bone marrow niche and have the capacity to differentiate into various cell types, including osteoblasts and myoblasts (Han et al., 2025; Zhu et al., 2021). The unique ability of BMSCs to modulate the immune system and facilitate tissue repair distinguishes them from other stem cell types, indicating that BMSCs may be ideal candidates for use in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Notably, BMSCs derived from patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) exhibit reduced stem cell capacity and produce fewer trophic factors, with these deficiencies correlating with disease progression (Zhou et al., 2015). Research has demonstrated that the paracrine release of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) by BMSCs in the bone marrow enhances muscle regeneration (Sassoli et al., 2012). These findings suggest a potential role for BMSC-derived VEGF in bone-muscle crosstalk. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying this potential interaction between muscle and bone remain largely unexplored.
3.2 Role of bone-derived extracellular vesicles
In addition to the conventional factors previously discussed, extracellular vesicles (EVs) are increasingly recognized as novel contributors to bone-muscle crosstalk (Figure 1). EVs, a class of membrane-bound particles released by nearly all cell types, convey information in the form of proteins, mRNAs, and miRNAs (Kirk et al., 2025; Van Niel et al., 2018). These vesicles can be categorized based on their size, synthesis, and secretion mechanisms. Currently, the most extensively characterized EVs are exosomes (20–140 nm) and microvesicles (100 nm-1 μm) (Huang et al., 2022). EVs, along with their molecular cargo, traverse the circulatory system and interact with distant target cells, influencing their differentiation and/or function. The interactions between EVs and their target cells primarily occur through mechanisms such as endocytosis, receptor-ligand binding, fusion with the plasma membrane, and antigen presentation (Kirk et al., 2025). In the context of bone-muscle crosstalk, EVs may play a role by facilitating the exchange of myokines, osteokines, and organelles (Ma et al., 2023; Murray and Krasnodembskaya, 2019).
At present, specific cell surface markers for the identification or enrichment of extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from bone cells, such as osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteocytes, remain unidentified. While E11/gp38 and Phex have been proposed as potential markers for osteocyte-derived EVs, they lack specificity. The use of DMP1 and sclerostin as surface markers for osteocyte-derived EVs is contentious, despite their expression in early-stage and mature osteocytes, respectively. Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) may serve as an identifier for osteoblast-derived EVs, whereas potential surface markers for osteoclast-derived EVs include DC-STAMP, OSCAR, and the calcitonin receptor. Further research is necessary to delineate the markers that can effectively distinguish subpopulations of circulating EVs originating from various bone cell types (Qin and Dallas, 2019).
Previous research has identified a subset of differentially expressed extracellular vesicle microRNAs (EV-miRNAs) between young and aging BMSCs. Among these, muscle-targeting miRNAs such as miR-24, miR-328-3p, miR-365, and miR-374 are downregulated, whereas miR-15b, miR-17, miR-20a, miR-186, miR-221, miR-31a-5p, and miR-99b are upregulated (He C. et al., 2020). Sun et al. (2008) demonstrated that the absence of miR-24 inhibits myogenic differentiation in C2C12 cells, while its ectopic expression counteracts the anti-myogenic effects induced by TGFβ1. Additionally, the pro-osteogenic miRNAs miR-365 and miR-374 have been reported to promote cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by inhibiting autophagy through the Skp-2-mTOR (Wu et al., 2017) and VEGF (Lee et al., 2017) pathways, respectively. A study involving 93 elderly patients clinically diagnosed with sarcopenia found that the circulating levels of miR-328 were significantly lower in individuals with sarcopenia compared to those without the condition (He N. et al., 2020), potentially due to miR-328's activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway via targeting axin-1 (Liu D. et al., 2018). Moreover, miR-328 is highly expressed in apoptotic bodies derived from BMSCs, which exhibit impaired osteogenic differentiation and self-renewal in an apoptotic-deficient mouse model (MRL/lpr-Casp3−/−) (Liu D. et al., 2018). These findings suggest that miR-328 may play a role in mediating bone-muscle crosstalk during aging.
The overexpression of miR-15b has been documented to inhibit myoblast differentiation via SET-domain containing 3 (SETD3), a methyltransferase implicated in the regulation of myogenesis (Zhao et al., 2019). Research has indicated that members of the miR-17–92 cluster, specifically miR-17 and miR-20a, can enhance the proliferation of C2C12 myoblasts while concurrently inhibiting myogenic differentiation (Qiu et al., 2016). Additionally, the knockdown of miR-17 has been shown to positively affect the microstructure of trabecular bone (Fang et al., 2016). However, it remains unclear whether miR-17 and miR-20a function as a cluster encapsulated within extracellular vesicles (EVs) to impact the phenotypes of bone and muscle during aging. As a negative regulator of bone formation, the ectopic overexpression of miR-221 has been demonstrated to impede myotube formation (Gan et al., 2020; Liu B. et al., 2018). In vitro studies have revealed that miR-186 exerts an inhibitory effect on myogenin-dependent differentiation (Antoniou et al., 2014). miR-31a-5p is upregulated in extracellular vesicles derived from aged bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs), promoting osteoclastogenesis, adipogenesis, and bone resorption (Xu et al., 2018). Additionally, the age-related increase in miR-31a-5p inhibits the dystrophin response to mechanical loading, thereby heightening muscle susceptibility to disuse-induced injury (Hughes et al., 2018). In primary human myotubes, the overexpression of miR-99b results in decreased protein synthesis by inhibiting the regulatory-associated protein of mTOR (RPTOR) (Zacharewicz et al., 2020). As for bone, Franceschetti et al. (Franceschetti et al., 2014) demonstrated that the inhibition of miR-99b reduces both the size and number of osteoclasts during osteoclastogenesis. These findings suggest that miR-99b may serve as a novel therapeutic target for addressing osteo-sarcopenia in the elderly.
4 The channel functions of Cx43 in bone-muscle communication
Connexins (Cx) are expressed in bone and skeletal muscle, with Cx43 being the most prevalent connexin in these tissues (Deng et al., 2022). Structurally, Cx43 consists of four transmembrane domains, two extracellular loops, one intracellular loop, and cytosolic amino-terminal and carboxy-terminal regions (Plotkin et al., 2017). Connexons are formed through the oligomerization of six connexin proteins. These structures, also known as hemichannels, facilitate communication between bone cells and the extracellular environment. When two hemichannels from adjacent cells dock together, they form gap junction channels that enable intercellular communication. These connexin-based channels are selectively permeable to molecules smaller than 1.2 kDa due to their relatively low substrate selectivity. Substantial evidence highlights the critical roles of Cx43 in the development and maintenance of bone and skeletal muscle.
Since the proposal in 2006 that bone functions as an endocrine organ, there has been a growing interest in elucidating the crosstalk between bone and muscle. In this context, a seminal study by Shen et al. (Shen et al., 2015) was the first to employ in vivo experiments to elucidate the pivotal role of connexin 43 (Cx43) in modulating bone-muscle communication. Mice with a targeted deletion of Cx43, achieved through the expression of Cre recombinase in osteoblast progenitors (Col α1-Cre; Cx43fl/fl), exhibited impaired muscle development, characterized by a significant reduction in both muscle mass and grip strength. This reduction in muscle mass contributes to a lower overall body weight, a phenomenon not observed in Cx43-deficient mice with deletions in mature osteoblasts/osteocytes or in osteocytes alone (Plotkin et al., 2008; Bivi et al., 2012). Notably, the administration of the bone-derived factor undercarboxylated osteocalcin (glu-OC) partially ameliorates the compromised muscle function. The observed phenotypes in mice suggest that Cx43 expression in osteoblast precursors is crucial for optimal skeletal muscle development and underscores the significant role of osteocalcin in bone-muscle communication. Similar to connexins, pannexins in bone cells also form hemichannels within the cell membrane; however, there is currently no evidence supporting their ability to form gap junction channels that connect adjacent cells (Plotkin et al., 2017; Luo et al., 2024). Pannexin1 (Panx1) is the predominant pannexin subtype expressed across all bone cells, and female mice with osteocytic Panx1 deletion (Panx1Δot) exhibit increased muscle mass without alterations in muscle strength (Aguilar-Perez et al., 2019). However, the roles of pannexin channels in bone-muscle crosstalk remain insufficiently explored.
The knockout of Cx43 in osteoblasts and osteocytes results in impaired muscle development; however, Cx43 deficiency concurrently disrupts the function of both gap junctions and hemichannels. Consequently, it remains unclear which of these channel types is responsible for the observed muscle phenotypes. To address this, our research group has previously developed two transgenic mouse models to investigate the distinct roles of Cx43 hemichannels and gap junctions specifically in osteocytes. Utilizing a 10 kb-DMP1 promoter, the transgenic mice, R76W and Δ130-136, overexpress dominant-negative Cx43 mutants in osteocytes (Xu et al., 2015). In the R76W point mutant model, where the amino acid arginine-76 (R) is substituted with tyrosine (W), Cx43 is able to form functional hemichannels but not gap junctions. Conversely, in the Δ130–136 mutant, characterized by the deletion of amino acids at positions 130–136, Cx43 is unable to form either hemichannels or gap junctions. The fast-twitch muscle phenotypes observed in Δ130–136 mice are analogous to those in osteoblast/osteocyte-specific Cx43 conditional knockout (cKO) mice driven by the 2.3-kb Col1a1 promoter (Shen et al., 2015), indicating that Cx43 deficiency in osteocytes impairs hemichannel function, thereby affecting muscle development. In contrast, the obstruction of Cx43 gap junctions results in diminished muscle contractile force and myogenesis. Relative to wild-type (WT) mice, these two transgenic mouse models exhibited reduced levels of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) in both the circulatory system and primary osteocyte-conditioned media (Li et al., 2021). As previously discussed, PGE2 released by osteocytes via Cx43 hemichannels has been demonstrated to facilitate myogenic differentiation and enhance muscle function. In alignment with these observations, our recent investigation has shown that the intraperitoneal administration of PGE2 partially ameliorates the deficits in muscle mass and function observed in Cx43 transgenic mice. Furthermore, the diminished PGE2 levels in osteocytes, resulting from compromised Cx43 hemichannels, contribute to increased collagen deposition in aged skeletal muscle, a process mediated by the activation of the TGFβ/Smad2/3 signaling pathway (Li et al., 2022). In summary, Cx43 hemichannels and PGE2 in osteocytes are likely to play a pivotal role in the communication between bone and muscle (Figure 1).
5 Conclusion and future directions
Recent advances in our understanding of bone-muscle crosstalk have been significant. This progress can be attributed to the identification of bone as an endocrine organ and the discovery of osteokines, cytokines released by bone that facilitate communication with skeletal muscle. In this review, we examine the roles of bone-derived factors and the potential mechanisms underlying Cx43-mediated crosstalk between bone and muscle. However, there are still many unanswered questions in the field.
Firstly, more unknown bone factors remain to be further identified. An example is that mice with osteocyte-specific deletion of Mbtps1, a membrane-bound transcription factor, exhibit an age-related increase in muscle mass and contractile force in the slow-twitch soleus muscle (SOL) (Gorski et al., 2016). This indicates that osteocytes are likely to produce an unidentified muscle factor that is negatively regulated with aging, which is associated with the production of other negative factors such as RANκL and sclerostin. Furthermore, Connexin 43 (Cx43), as a fundamental component of functionally specific gap junctions and hemichannels, facilitates cellular communication through the release of small molecules. Recently, Cx43 has also garnered attention for its channel-independent cellular regulatory and signaling functions mediated through its specialized C-terminus. Several studies have demonstrated that Cx43 acts as a scaffold protein, and its interactions with cytoskeletal proteins play a crucial role in regulating cell growth, differentiation, and migration (Strauss and Gourdie, 2020; Casanellas et al., 2022). Nevertheless, the extent to which the non-channel functions of Cx43 regulate bone-muscle crosstalk remains largely unclear, presenting potential avenues for future research. Additionally, the burgeoning interest in the roles of extracellular vesicles (EVs) in cellular communication has gained significant attention. EVs encapsulate a diverse array of bioactive molecules, such as proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, which facilitate the exchange of information between both local and distant organs. Notably, the presence of Cx43 in EVs has been documented, where it enhances EV-cell communication (Xiong et al., 2024). The relationship between Cx43 and extracellular vesicles (EVs) in bone-muscle crosstalk warrants further investigation. Elucidating the complex regulatory networks that mediate the interaction between bone and muscle is crucial to develop small molecule drugs that target Cx43 hemichannels or EVs preparations loaded with bone-derived miR-328 for the combined treatment of osteosarcopenia.
Author contributions
GL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Writing – original draft. MQ: Investigation, Writing – original draft. YW: Investigation, Writing – original draft. SL: Investigation, Writing – original draft. HX: Investigation, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region of China (Grant No. 2023QN03027), Inner Mongolia Agricultural University High-level/Outstanding Doctoral Introduction Talents Research Start-up Project (Grant No. NDYB 2021-23), Innovation Team of Higher Education Institutions in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (Grant No. NMGIRT2219) and Innovation Training Program (Grant No. 202410129050).
Acknowledgements
Figure 1 in the manuscript was created by Figdraw 2.0.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aguilar-Perez, A., Pacheco-Costa, R., Atkinson, E. G., Deosthale, P., Davis, H. M., Essex, A. L., et al. (2019). Age- and sex-dependent role of osteocytic pannexin1 on bone and muscle mass and strength. Sci. Rep. 9 (1), 13903. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-50444-1
Antoniou, A., Mastroyiannopoulos, N. P., Uney, J. B., and Phylactou, L. A. (2014). miR-186 inhibits muscle cell differentiation through my-ogenin regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 289 (7), 3923–3935. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.507343
Avin, K. G., Vallejo, J. A., Chen, N. X., Wang, K., Touchberry, C. D., Brotto, M., et al. (2018). Fibroblast growth factor 23 does not directly influence skeletal muscle cell proliferation and differentiation or ex vivo muscle contractility. Am. J. Physiol-Endoc M. 315 (4), E594–E604. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00343.2017
Battafarano, G., Rossi, M., Marampon, F., Minisola, S., and Del Fattore, A. (2020). Bone control of muscle function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (4), 1178. doi:10.3390/ijms21041178
Beno, T., Yoon, Y. J., Cowin, S. C., and Fritton, S. P. (2006). Estimation of bone permeability using accurate microstructural measurements. J. Biomech. 39, 2378–2387. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2005.08.005
Bivi, N., Condon, K. W., Allen, M. R., Farlow, N., Passeri, G., Brun, L. R., et al. (2012). Cell autonomous requirement of connexin 43 for osteocyte survival: consequences for endocortical resorption and periosteal bone formation. J. Bone Min. Res. 27 (2), 374–389. doi:10.1002/jbmr.548
Blaauw, B., Canato, M., Agatea, L., Toniolo, L., Mammucari, C., Masiero, E., et al. (2009). Inducible activation of Akt increases skeletal muscle mass and force without satellite cell activation. FASEB J. 23 (11), 3896–3905. doi:10.1096/fj.09-131870
Bonewald, L. (2019). Use it or lose it to age: a review of bone and muscle communication. Bone 120, 212–218. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2018.11.002
Bonnet, N., Bourgoin, L., Biver, E., Douni, E., and Ferrari, S. (2023). RANKL inhibition improves muscle strength and insulin sensitivity and restores bone mass. J. Clin. Invest 129 (8), 3214–3223. doi:10.1172/JCI125915
Casanellas, I., Lagunas, A., Vida, Y., Pérez-Inestrosa, E., Rodríguez-Pereira, C., Magalhaes, J., et al. (2022). Nanoscale ligand density modulates gap junction intercellular communication of cell condensates during chondrogenesis. Nanomedicine (Lond) 17, 775–791. doi:10.2217/nnm-2021-0399
Chen, L., Gao, G., Shen, L., Yue, H., Zhang, G., and Zhang, Z. (2022). Serum sclerostin and its association with bone turnover marker in metabolic bone diseases. Dis. Markers 2022, 7902046. doi:10.1155/2022/7902046
Chen, Q., Wang, Z., Yang, C., Li, B., Ren, X., Liu, C., et al. (2023). High resolution intravital photoacoustic microscopy reveals VEGF-induced bone regeneration in mouse tibia. Bone 167, 116631. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2022.116631
Cheng, H., Huang, H., Guo, Z., Chang, Y., and Li, Z. (2021). Role of prostaglandin E2 in tissue repair and regeneration. Theranostics 11, 8836–8854. doi:10.7150/thno.63396
Chowdhury, S., Schulz, L., Palmisano, B., Singh, P., Berger, J. M., Yadav, V. K., et al. (2020). Muscle-derived interleukin 6 increases exercise capacity by signaling in osteoblasts. J. Clin. Invest 130 (6), 2888–2902. doi:10.1172/JCI133572
Delgado-Calle, J., and Bellido, T. (2022). The osteocyte as a signaling cell. Physiol. Rev. 102 (1), 379–410. doi:10.1152/physrev.00043.2020
Deng, Z., Li, Y., Wang, C., Chen, S., Cai, Z., Zheng, S., et al. (2022). Connexin43 in musculoskeletal system: new targets for development and disease progression. Aging Dis. 13, 1715–1732. doi:10.14336/AD.2022.0421
Deng, A. F., Wang, F. X., Wang, S. C., Zhang, Y. Z., Bai, L., and Su, J. C. (2024). Bone-organ axes: bidirectional crosstalk. Mil. Med. Res. 11, 37. doi:10.1186/s40779-024-00540-9
Dong, Y., Yuan, H., Ma, G., and Cao, H. (2024). Bone-muscle crosstalk under physiological and pathological conditions. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 81, 310. doi:10.1007/s00018-024-05331-y
Fang, T., Wu, Q., Zhou, L., Mu, S., and Fu, Q. (2016). miR-106b-5p and miR-17-5p suppress osteogenic differentiation by targeting smad5 and inhibit bone formation. Exp. Cell Res. 347 (1), 74–82. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.07.010
Faul, C., Amaral, A. P., Oskouei, B., Hu, M. C., Sloan, A., Isakova, T., et al. (2011). FGF23 induces left ventricular hypertrophy. J. Clin. Invest 121 (11), 4393–4408. doi:10.1172/JCI46122
Feng, J. Q., Ward, L. M., Liu, S., Lu, Y., Xie, Y., Yuan, B., et al. (2006). Loss of dmp1 causes rickets and osteomalacia and identifies a role for osteocytes in mineral metabolism. Nat. Genet. 38 (11), 1310–1315. doi:10.1038/ng1905
Franceschetti, T., Dole, N. S., Kessler, C. B., Lee, S. K., and Delany, A. M. (2014). Pathway analysis of microRNA expression profile during murine osteoclastogenesis. PloS one 9 (9), e107262. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0107262
Gan, K., Dong, G., Wang, N., and Zhu, J. (2020). miR-221-3p and miR-222-3p downregulation promoted osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchyme stem cells through IGF-1/Erk pathway under high glucose condition. Diabetes Res. Clin. P. R. 167, 108121. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108121
Gorski, J. P., Huffman, N. T., Vallejo, J., Brotto, L., Chittur, S. V., Breggia, A., et al. (2016). Deletion of MBTPS1 (pcsk8, s1p, ski-1) gene in osteocytes stimulates soleus muscle regeneration and increased size and contractile force with age. J. Biol. Chem. 291 (9), 4308–4322. doi:10.1074/jbc.M115.686626
Gostage, J., Kostenuik, P., Goljanek-Whysall, K., Bellantuono, I., McCloskey, E., and Bonnet, N. (2024). Extra-osseous roles of the RANK-RANKL-OPG axis with a focus on skeletal muscle. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 22 (6), 632–650. doi:10.1007/s11914-024-00890-2
Hamoudi, D., Bouredji, Z., Marcadet, L., Yagita, H., Landry, L. B., Argaw, A., et al. (2020). Muscle weakness and selective muscle atrophy in osteoprotegerin-deficient mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 29 (3), 483–494. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddz312
Han, X., Liao, R., Li, X., Zhang, C., Huo, S., Qin, L., et al. (2025). Mesenchymal stem cells in treating human diseases: molecular mechanisms and clinical studies. Signal Transduct. Tar 10, 262. doi:10.1038/s41392-025-02313-9
He, C., He, W., Hou, J., Chen, K., Huang, M., Yang, M., et al. (2020). Bone and muscle crosstalk in aging. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 8, 585644. doi:10.3389/fcell.2020.585644
He, N., Zhang, Y. L., Zhang, Y., Feng, B., Zheng, Z., Wang, D., et al. (2020). Circulating MicroRNAs in plasma decrease in response to sarcopenia in the elderly. Front. Genet. 11, 167. doi:10.3389/fgene.2020.00167
He, T., Qin, L., Chen, S., Huo, S., Li, J., Zhang, F., et al. (2025). Bone-derived factors mediate crosstalk between skeletal and extra-skeletal organs. Bone Res. 13, 49. doi:10.1038/s41413-025-00424-1
Hesse, E., Schröder, S., Brandt, D., Pamperin, J., Saito, H., and Taipaleenmäki, H. (2019). Sclerostin inhibition alleviates breast cancer–induced bone metastases and muscle weakness. JCI insight 4 (9), e125543. doi:10.1172/jci.insight.125543
Ho, A. T. V., Palla, A. R., Blake, M. R., Yucel, N. D., Wang, Y. X., Magnusson, K. E. G., et al. (2017). Prostaglandin E2 is essential for efficacious skeletal muscle stem-cell function, augmenting regeneration and strength. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 114 (26), 6675–6684. doi:10.1073/pnas.1705420114
Huang, J., Romero-Suarez, S., Lara, N., Mo, C., Kaja, S., Brotto, L., et al. (2017). Crosstalk between MLO-Y4 osteocytes and C2C12 muscle cells is mediated by the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. JBMR Plus 1 (2), 86–100. doi:10.1002/jbm4.10015
Huang, X., Lan, Y., Shen, J., Chen, Z., and Xie, Z. (2022). Extracellular vesicles in bone homeostasis: emerging mediators of osteoimmune interactions and promising therapeutic targets. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 18, 4088–4100. doi:10.7150/ijbs.69816
Hughes, D. C., Marcotte, G. R., Baehr, L. M., West, D. W., Marshall, A. G., Ebert, S. M., et al. (2018). Alterations in the muscle force transfer apparatus in aged rats during unloading and reloading: impact of microRNA-31. J. Physio 596 (14), 2883–2900. doi:10.1113/JP275833
Jähn, K., Lara-Castillo, N., Brotto, L., Mo, C., Johnson, M. L., Brotto, M., et al. (2012). Skeletal muscle secreted factors prevent glucocorticoid-induced osteocyte apoptosis through activation of β-catenin. Eur. Cells Mater 24, 197–210. doi:10.22203/ecm.v024a14
Kanazawa, I. (2015). Osteocalcin as a hormone regulating glucose metabolism. World J. Diabetes 6 (18), 1345–1354. doi:10.4239/wjd.v6.i18.1345
Karsenty, G., and Olson, E. N. (2016). Bone and muscle endocrine functions: unexpected paradigms of inter-organ communication. Cell 164 (6), 1248–1256. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2016.02.043
Ke, H. Z., Richards, W. G., Li, X., and Ominsky, M. S. (2012). Sclerostin and dickkopf-1 as therapeutic targets in bone diseases. Endocr. Rev. 33 (5), 747–783. doi:10.1210/er.2011-1060
Kim, S. P., Frey, J. L., Li, Z., Kushwaha, P., Zoch, M. L., Tomlinson, R. E., et al. (2017). Sclerostin influences body composition by regulating catabolic and anabolic metabolism in adipocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 114 (52), E11238–E11247. doi:10.1073/pnas.1707876115
Kirk, B., Zanker, J., and Duque, G. (2020a). Osteosarcopenia: epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment—facts and numbers. J. Cachexia Sarcopeni 11 (3), 609–618. doi:10.1002/jcsm.12567
Kirk, B., Feehan, J., Lombardi, G., and Duque, G. (2020b). Muscle, bone, and fat crosstalk: the biological role of myokines, osteokines, and adipokines. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 18, 388–400. doi:10.1007/s11914-020-00599-y
Kirk, B., Lombardi, G., and Duque, G. (2025). Bone and muscle crosstalk in ageing and disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 21, 375–390. doi:10.1038/s41574-025-01088-x
Kitase, Y., Barragan, L., Qing, H., Kondoh, S., Jiang, J. X., Johnson, M. L., et al. (2010). Mechanical induction of PGE2 in osteocytes blocks glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis through both the beta-catenin and PKA pathways. J. Bone Min. Res. 25 (12), 2657–2668. doi:10.1002/jbmr.168
Kong, Y. Y., Yoshida, H., Sarosi, I., Tan, H. L., Timms, E., Capparelli, C., et al. (1999). Opgl is a key regulator of osteoclastogenesis, lymphocyte development and lymph-node organogenesis. Nature 397 (6717), 315–323. doi:10.1038/16852
Kurek, J. B., Bower, J. J., Romanella, M., Koentgen, F., Murphy, M., and Austin, L. (1997). The role of leukemia inhibitory factor in skeletal muscle regeneration. Muscle Nerve 20 (7), 815–822. doi:10.1002/(sici)1097-4598(199707)20:7<815::aid-mus5>3.0.co;2-a
Lai, X., Price, C., Lu, X. L., and Wang, L. (2014). Imaging and quantifying solute transport across periosteum: implications for muscle-bone crosstalk. Bone 66, 82–89. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2014.06.002
Langen, R. C., Schols, A. M., Kelders, M. C., Wouters, E. F., and Janssen-Heininger, Y. M. (2001). Inflammatory cytokines inhibit myogenic differentiation through activation of nuclear factor-kappaB. FASEB J. 15 (7), 1169–1180. doi:10.1096/fj.00-0463
Lara-Castillo, N., and Johnson, M. L. (2020). Bone-muscle mutual interactions. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 18 (4), 408–421. doi:10.1007/s11914-020-00602-6
Lee, N. K., Sowa, H., Hinoi, E., Ferron, M., Ahn, J. D., Confavreux, C., et al. (2007). Endocrine regulation of energy metabolism by the skeleton. Cell 130 (3), 456–469. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.047
Lee, J. S., Song, D. W., Park, J. H., Kim, J. O., Cho, C., and Kim, D. H. (2017). miR-374 promotes myocardial hypertrophy by negatively regulating vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 signaling. BMB Rep. 50 (4), 208–213. doi:10.5483/bmbrep.2017.50.4.165
Li, G., Zhang, L., Ning, K., Yang, B., Acosta, F. M., Shang, P., et al. (2021). Osteocytic connexin43 channels regulate bone-muscle crosstalk. Cells 10 (2), 237. doi:10.3390/cells10020237
Li, G., Zhang, L., Lu, Z., Yang, B., Yang, H., Shang, P., et al. (2022). Connexin 43 channels in osteocytes are necessary for bone mass and skeletal muscle function in aged male mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (21), 13506. doi:10.3390/ijms232113506
Liu, S., Gao, F., Wen, L., Ouyang, M., Wang, Y., Wang, Q., et al. (2017). Osteocalcin induces proliferation via positive activation of the PI3K/AKT, p38 MAPK pathways and promotes differentiation through activation of the GPRC6a-Erk1/2 pathway in C2C12 myoblast cells. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 43 (3), 1100–1112. doi:10.1159/000481752
Liu, D., Kou, X., Chen, C., Liu, S., Liu, Y., Yu, W., et al. (2018). Circulating apoptotic bodies maintain mes-enchymal stem cell homeostasis and ameliorate osteopenia via transferring multiple cellular factors. Cell Res. 28 (9), 918–933. doi:10.1038/s41422-018-0070-2
Liu, B., Shi, Y., He, H., Cai, M., Xiao, W., Yang, X., et al. (2018). miR-221 modulates skeletal muscle satellite cells proliferation and differentiation. Vitro Cell Dev-Anl 54 (2), 147–155. doi:10.1007/s11626-017-0210-x
Luo, Y., Zheng, S., Xiao, W., Zhang, H., and Li, Y. (2024). Pannexins in the musculoskeletal system: new targets for development and disease progression. Bone Res. 12, 26. doi:10.1038/s41413-024-00334-8
Ma, S., Xing, X., Huang, H., Gao, X., Xu, X., Yang, J., et al. (2023). Skeletal muscle-derived extracellular vesicles transport glycolytic enzymes to mediate muscle-to-bone crosstalk. Cell Metab. 35, 2028–2043.e7. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2023.10.013
Mera, P., Laue, K., Ferron, M., Confavreux, C., Wei, J., Galan-Diez, M., et al. (2016a). Osteocalcin signaling in myofibers is necessary and sufficient for optimum adaptation to exercise. Cell Metab. 23 (6), 218–1092. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2016.12.003
Mera, P., Laue, K., Wei, J., Berger, J. M., and Karsenty, G. (2016b). Osteocalcin is necessary and sufficient to maintain muscle mass in older mice. Mol. Metab. 5 (10), 1042–1047. doi:10.1016/j.molmet.2016.07.002
Mo, C., Romero-Suarez, S., Bonewald, L., Johnson, M., and Brotto, M. (2012). Prostaglandin E2 from clinical applications to its potential role in bone-muscle crosstalk and myogenic differentiation. Recent Pat. Biotechno 6 (3), 223–229. doi:10.2174/1872208311206030223
Mo, C., Zhao, R., Vallejo, J., Igwe, O., Bonewald, L., Wetmore, L., et al. (2015). Prostaglandin E2 promotes proliferation of skeletal muscle myoblasts via EP4 receptor activation. Cell cycle 14 (10), 1507–1516. doi:10.1080/15384101.2015.1026520
Murray, L. M., and Krasnodembskaya, A. D. (2019). Concise review: intercellular communication via organelle transfer in the biology and therapeutic applications of stem cells. Stem cells 37, 14–25. doi:10.1002/stem.2922
Palla, A. R., Ravichandran, M., Wang, Y. X., Alexandrova, L., Yang, A. V., Kraft, P., et al. (2021). Inhibition of prostaglandin-degrading enzyme 15-PGDH rejuvenates aged muscle mass and strength. Science 371 (6528), eabc8059. doi:10.1126/science.abc8059
Pichler, K., Loreto, C., Leonardi, R., Reuber, T., Weinberg, A. M., and Musumeci, G. (2013). RANKL is downregulated in bone cells by physical activity (treadmill and vibration stimulation training) in rat with glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Histol. Histopathol. 28 (9), 1185–1196. doi:10.14670/HH-28.1185
Plotkin, L. I., Lezcano, V., Thostenson, J., Weinstein, R. S., Manolagas, S. C., and Bellido, T. (2008). Connexin 43 is required for the anti-apoptotic effect of bisphosphonates on osteocytes and osteoblasts in vivo. J. Bone Min. Res. 23 (11), 1712–1721. doi:10.1359/jbmr.080617
Plotkin, L. I., Davis, H. M., Cisterna, B. A., and Saez, J. C. (2017). Connexins and pannexins in bone and skeletal muscle. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 15 (4), 326–334. doi:10.1007/s11914-017-0374-z
Qin, W., and Dallas, S. L. (2019). Exosomes and extracellular RNA in muscle and bone aging and crosstalk. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 17, 548–559. doi:10.1007/s11914-019-00537-7
Qiu, H., Liu, N., Luo, L., Zhong, J., Tang, Z., Kang, K., et al. (2016). MicroRNA-17-92 regulates myoblast proliferation and differentiation by targeting the ENH1/Id1 signaling axis. Cell Death Differ. 23 (10), 1658–1669. doi:10.1038/cdd.2016.56
Regan, J. N., Trivedi, T., Guise, T. A., and Waning, D. L. (2017). The role of TGFβ in bone-muscle crosstalk. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 15 (1), 18–23. doi:10.1007/s11914-017-0344-5
Riminucci, M., Collins, M. T., Fedarko, N. S., Cherman, N., Corsi, A., White, K. E., et al. (2003). FGF-23 in fibrous dysplasia of bone and its relationship to renal phosphate wasting. J. Clin. Invest 112 (5), 683–692. doi:10.1172/JCI18399
Sartori, R., Gregorevic, P., and Sandri, M. (2014). TGFβ and BMP signaling in skeletal muscle: potential significance for muscle-related disease. Trends Endocrin Met. 25 (9), 464–471. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2014.06.002
Sassoli, C., Pini, A., Chellini, F., Mazzanti, B., Nistri, S., Nosi, D., et al. (2012). Bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells stimulate skeletal myoblast proliferation through the paracrine release of VEGF. PloS one 7, e37512. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0037512
Sato, C., Iso, Y., Mizukami, T., Otabe, K., Sasai, M., Kurata, M., et al. (2016). Fibroblast growth factor-23 induces cellular senescence in human mesenchymal stem cells from skeletal muscle. BBRC 470 (3), 657–662. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.01.086
Schiaffino, S., and Mammucari, C. (2011). Regulation of skeletal muscle growth by the IGF1-AKT/PKB pathway: insights from genetic models. Skelet. muscle 1, 4–14. doi:10.1186/2044-5040-1-4
Schurman, C. A., Verbruggen, S. W., and Alliston, T. (2021). Disrupted osteocyte connectivity and pericellular fluid flow in bone with aging and defective TGF-β signaling. P Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 118, e2023999118. doi:10.1073/pnas.2023999118
Shen, H., Grimston, S., Civitelli, R., and Thomopoulos, S. (2015). Deletion of connexin43 in osteoblasts/osteocytes leads to impaired muscle formation in mice. J. Bone Min. Res. 30 (4), 596–605. doi:10.1002/jbmr.2389
Shimada, T., Kakitani, M., Yamazaki, Y., Hasegawa, H., Takeuchi, Y., Fujita, T., et al. (2004). Targeted ablation of FGF23 demonstrates an essential physiological role of FGF23 in phosphate and vitamin D metabolism. J. Clin. Invest 113 (4), 561–568. doi:10.1172/JCI19081
Strauss, R. E., and Gourdie, R. G. (2020). Cx43 and the actin cytoskeleton: novel roles and implications for cell-cell junction-based barrier function regulation. Biomolecules 10, 1656. doi:10.3390/biom10121656
Sun, Q., Zhang, Y., Yang, G., Chen, X., Zhang, Y., Cao, G., et al. (2008). Transforming growth factor-β-regulated miR-24 promotes skeletal muscle differentiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 36, 2690–2699. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn032
Van Niel, G., d'Angelo, G., and Raposo, G. (2018). Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Bio 19, 213–228. doi:10.1038/nrm.2017.125
Wacker, M. J., Touchberry, C. D., Silswal, N., Brotto, L., Elmore, C. J., Bonewald, L. F., et al. (2016). Skeletal muscle, but not cardiovascular function, is altered in a mouse model of autosomal recessive hypophosphatemic rickets. Front. Physiol. 7, 173. doi:10.3389/fphys.2016.00173
Wang, L., Wang, Y., Han, Y., Henderson, S. C., Majeska, R. J., Weinbaum, S., et al. (2005). In situ measurement of solute transport in the bone lacunar-canalicular system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 102 (33), 11911–11916. doi:10.1073/pnas.0505193102
Wang, L., You, X., Zhang, L., Zhang, C., and Zou, W. (2022). Mechanical regulation of bone remodeling. Bone Res. 10, 16. doi:10.1038/s41413-022-00190-4
Waning, D. L., and Guise, T. A. (2014). Molecular mechanisms of bone metastasis and associated muscle weakness. Clin. Cancer Res. 20 (12), 3071–3077. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1590
Waning, D. L., Mohammad, K. S., Reiken, S., Xie, W., Andersson, D. C., John, S., et al. (2015). Excess TGF-β mediates muscle weakness associated with bone metastases in mice. Nat. Med. 21 (11), 1262–1271. doi:10.1038/nm.3961
Welc, S. S., Brotto, M., White, K. E., and Bonewald, L. F. (2025). Aging: a struggle for beneficial to overcome negative factors made by muscle and bone. Mech. Ageing Dev. 224, 112039. doi:10.1016/j.mad.2025.112039
Wildemann, B., Kadow-Romacker, A., Haas, N., and Schmidmaier, G. (2007). Quantification of various growth factors in different demineralized bone matrix preparations. J. Biomed. Mater Res. A 81 (2), 437–442. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.31085
Winbanks, C. E., Chen, J. L., Qian, H., Liu, Y., Bernardo, B. C., Beyer, C., et al. (2013). The bone morphogenetic protein axis is a positive regulator of skeletal muscle mass. J. Cell Biol. 203 (2), 345–357. doi:10.1083/jcb.201211134
Wood, C. L., Pajevic, P. D., and Gooi, J. H. (2017). Osteocyte secreted factors inhibit skeletal muscle differentiation. Bone Rep. 6, 74–80. doi:10.1016/j.bonr.2017.02.007
Wu, H., Wang, Y., Wang, X., Li, R., and Yin, D. (2017). MicroRNA-365 accelerates cardiac hypertrophy by inhibiting autophagy via the modulation of Skp2 expression. Biochem. Bioph Res. Co. 484, 304–310. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.01.108
Xiong, X., Chen, W., Chen, C., Wu, Q., and He, C. (2024). Analysis of the function and therapeutic strategy of connexin 43 from its subcellular localization. Biochimie 218, 1–7. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2023.08.011
Xu, H., Gu, S., Riquelme, M. A., Burra, S., Callaway, D., Cheng, H., et al. (2015). Connexin 43 channels are essential for normal bone structure and osteocyte viability. J. Bone Min. Res. 30, 436–448. doi:10.1002/jbmr.2374
Xu, R., Shen, X., Si, Y., Fu, Y., Zhu, W., Xiao, T., et al. (2018). Micro RNA-31a-5p from aging BMSCs links bone formation and resorption in the aged bone marrow microenvironment. Aging cell 17 (4), e12794. doi:10.1111/acel.12794
Zacharewicz, E., Kalanon, M., Murphy, R. M., Russell, A. P., and Lamon, S. (2020). MicroRNA-99b-5p downregulates protein synthesis in human primary myotubes. Am. J. Physiol-Cell P. H. 319 (2), C432–C440. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00172.2020
Zhang, Y., and Chen, Q. (2024). Novel insights into osteocyte and inter-organ/tissue crosstalk. Front. Endocrinol. 14, 1308408. doi:10.3389/fendo.2023.1308408
Zhang, J., Acosta, F. M., Wang, X., Zhao, D., Zhang, L., Hua, R., et al. (2025). Osteocyte connexin hemichannels and prostaglandin E2 release dictate bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cell commitment. P Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 122, e2412144122. doi:10.1073/pnas.2412144122
Zhao, M., Xie, J., Shu, W., Wang, H., Bi, J., Jiang, W., et al. (2019). miR-15b and miR-322 inhibit setd3 expression to repress muscle cell differentiation. Cell Death Dis. 10 (3), 183. doi:10.1038/s41419-019-1432-5
Zhao, D., Riquelme, M. A., Guda, T., Tu, C., Xu, H., Gu, S., et al. (2022). Connexin hemichannels with prostaglandin release in anabolic function of bone to mechanical loading. Elife 11, e74365. doi:10.7554/eLife.74365
Zhao, Q., Chen, Y., and Mao, G. (2024). Muscle-bone crosstalk: involvement of myokines in the regulation of osteoporosis. Eur. Cells Mater 48, 115–136. doi:10.22203/eCM.v048a07
Zhou, J., Yi, J., and Bonewald, L. (2015). Muscle-bone crosstalk in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 13, 274–279. doi:10.1007/s11914-015-0281-0
Zhu, Y., Ge, J., Huang, C., Liu, H., and Jiang, H. (2021). Application of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for aging frailty: from mechanisms to therapeutics. Theranostics 11, 5675–5685. doi:10.7150/thno.46436
Glossary
EVs Extracellular Vesicles
Cx43 Connexin43
IGFS Insulin-like Growth Factors
BMPs Bone Morphogenetic Proteins
TGFβ Transforming Growth Factor β
FGF23 Fibroblast Growth Factor 23
IGF1 Insulin-like Growth Factor 1
RANκL Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor kappa β Ligand
OPG Osteoprotegerin
Dkk1 Dickkopf-1
OB Oteoblast
OCY Osteocyte
OC Osteoclast
BGLAP Bone γ -Carboxyglutamic Acid Protein
GPRC6a G Protein-Coupled Receptor 6a
IL-6 Interleukin-6
15-PGDH 15-Hydroxyprostaglandin Dehydrogenase
BMP2 Bone Morphogenetic Protein2
RANκ Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor Kappa β
MyoD Myogenic Differentiation
DMP1 Dentin Matrix Protein 1
PHEX Phosphate-regulating neutral Endopeptidase X-linked
MEPE Matrix Extracellular Phosphoglycoprotein
BAIBA β-aminoisobutyric Acid
MSCs Mesenchymal Stem Cells
DC-STAMP Dendritic cell-specific transmembrane protei
OSCAR Osteoclast Associated Receptor
BMSCs Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells
miRNA Micro RNA
SKP2 S-phase Kinase-associated Protein 2
mTOR Mammalian Target of Rapamycin
VEGF Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor
SETD3 SET-domain containing 3
RPTOR Regulatory-associated protein of mTOR
GJ Gap Junction
HC Hemichannel
EP4 E-type Prostanoid Receptor 4
LRP5/6 Lipoprotein Receptor-related Protein 5/6
glu-OC Undercarboxylated Osteocalcin
Panx1 Pannexin1
WT Wild type
cKO Conditional knockout
α-klotho α-Klotho Protein
BMSCs Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
COX Cyclooxygenase
PGES PGE synthases
PTH Parathyroid hormone
VEGF Vascular endothelial growth factor.
Keywords: bone, muscle, osteokines, extracellular vesicles, crosstalk, connexin43
Citation: Li G, Qi M, Wang Y, Liang S and Xu H (2025) Molecular communication from bone to skeletal muscle: an overview. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 13:1715009. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1715009
Received: 28 September 2025; Accepted: 20 October 2025;
Published: 07 November 2025.
Edited by:
Silvia Masciarelli, Sapienza University of Rome, ItalyReviewed by:
Tailin He, Southern University of Science and Technology, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Li, Qi, Wang, Liang and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guobin Li, Z3VvYmlubEAxMjYuY29t; Huiyun Xu, Y2VsbGRvbkBud3B1LmVkdS5jbg==
 Guobin Li
Guobin Li Mingyan Qi1
Mingyan Qi1 Yuzhen Wang
Yuzhen Wang Shibin Liang
Shibin Liang Huiyun Xu
Huiyun Xu