Abstract
Jitter in Internet Protocol (IP) networks refers to the variation in packet arrival times, which can cause delays or disruptions in real-time communications like voice or video calls. Managing jitter is crucial for applications requiring consistent data flow, such as voice over internet protocol, online gaming, and video conferencing, to maintain quality and reliability. Dahmouni et al. derived an analytical model for jitter in an important paper cited by many authors. But some of the fundamental equations in Dahmouni et al. do not appear correct. We correct the equations and study some analytical properties of jitter. Among others, we show that jitter can be expressed as , where denotes the rate of service times, denotes the rate of transit times and denotes the rate of inter-arrival times. We provide a Maple code to check correctness of our equations.
1 Introduction
According to Dahmouni et al. (2012a), “IP network planning and design is mostly based on the average delay or loss constraints which can often be easily calculated. Jitter, on the other hand, is much more difficult to evaluate, but it is particularly important to manage the QoS of realtime and interactive services such as VoIP and streaming video”. Dahmouni et al. (2012a) derived an important analytical model for jitter. Their results have been so important that their paper has been cited by many authors, see, for example, (Ye et al., 2023; Masli et al., 2022; Chang et al., 2024; Dbira et al., 2016; Dahmouni et al., 2012b; Sreedevi and Rama Rao, 2020; El Amri and Meddeb, 2021; Gore et al., 2022; Husen et al., 2021; Mustapha et al., 2020).
However, some of the fundamental equations (see Equations 8–11 of Dahmouni et al. (2012a)) derived in Dahmouni et al. (2012a) do not appear correct. The aim of this letter is to correct the equations. In the process, we derive an exact expression for jitter when the service times, transit times and inter-arrival times are exponentially distributed (Section 2). We also study some analytical properties of the expression (Section 2). The correctness of our derivation is verified by a Maple code given in Section 3. Some conclusions are provided in Section 4.
2 Analytical derivation
Let , and denote the probability density functions of service, transit and inter-arrival times, respectively. According to Equation 7 of Dahmouni et al. (2012a), the most general formula for jitter is
Equations 9–11 of Dahmouni et al. (2012a) derive an expression for Equation 1 when , and . Actually, Dahmouni et al. (2012a) stated the following: “Note that this expression (referring to Equation 1) is entirely general. We now assume that the distributions are exponential, namely that
From these, we can compute Equation 7 and get.from which we get …”. The expression given by Equations 2–4 reduces to .
Proposition 1 in Dahmouni et al. (2012a) supposes that , corresponding to an M/M/1 queue, although there is no mention of an M/M/1 queue in Dahmouni et al. (2012a). The condition is mentioned only in Proposition 1 and it is not clear if applies to any result outside of the proposition. The derivations leading to Equations 2–4 do not refer to Proposition 1 and do not appear to suppose any restriction between , and . Yet, Equations 2–4 reduces to . We now show that is incorrect unless .
The reminder of this section gives an exact expression for Equation 1 and studies its analytical properties when , and . Note that we can writesay. Some simple calculations show thatand
Substituting Equations 6–10 into Equation 5 and simplifying, we obtain
If , corresponding to an M/M/1 queue, then Equation 11 reduces to , the expression given in Dahmouni et al. (2012a). Equation 11 can be useful for general queues not just an M/M/1 queue.
Some properties of Equation 11 areand
Let . We can then write Equation 11 as
Note thatand
The partial derivatives of Equation 12 with respect to and areand
Moreover,
Setting (Equation 13) to zero, we obtain . Setting (Equation 14) to zero, we obtain .
Plots of the jitter in Equation 12 versus and are shown in Figures 1, 2. We see that jitter is a decreasing function of for , an increasing function of for and reaches a minimum with respect to when . The minimum of jitter at is , which is a decreasing function of . We also see that jitter is a decreasing function of for , an increasing function of for and reaches a minimum with respect to when . The minimum of jitter at is , which is a decreasing function of . Further, there is a singularity at .
FIGURE 1

Plot of Equation 12 versus and .
FIGURE 2
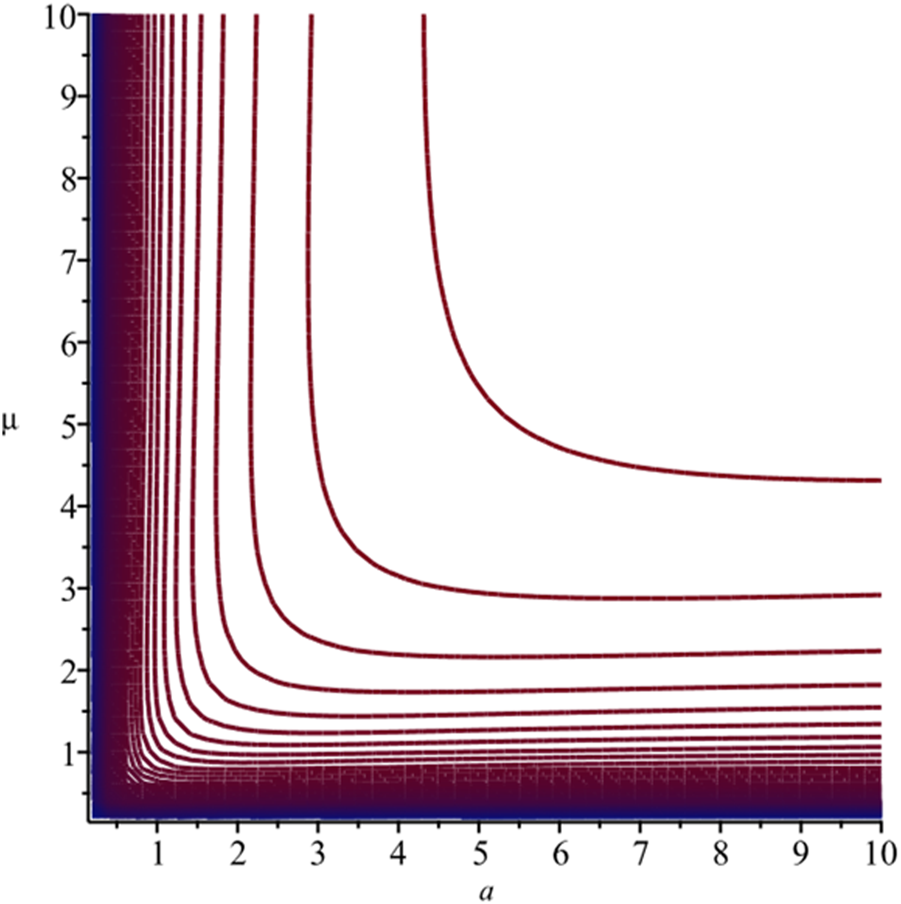
Contours of Equation 12 versus and .
3 Derivation using maple
The execution of the following code in Maple gives the same answer as in Equation 11.
assume(mu>0);
assume(lambda>0);
assume(eta>0);
t1:=int(mu*exp(-mu*s)*abs(s-y)*exp(-eta*y), s = 0 … infinity);
tt1:=int(t1*lambda*exp(-lambda*y), y = 0 … infinity);
t2:=int(abs(s-x)*eta*exp(-eta*x), x = 0 … y);
t3:=int(mu*exp(-mu*s)*t2, s = 0 … infinity);
t4:=int(lambda*exp(-lambda*y)*t3, y = 0 … infinity);
final:=simplify(t4+tt1);
4 Conclusion
We have derived an exact expression for jitter when the service times, transit times and inter-arrival times are exponentially distributed. The correctness of this expression has been checked by a Maple code.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
SN: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. AB: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
Both authors would like to thank the referee and the editor for careful reading and comments which greatly improved the paper.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Chang S. Wu S. Huang N. Zhang Y. Y. Zhu Y. J. Wang C. et al (2024). Delay jitter analysis for VLC under indoor industrial internet of things scenarios. IEEE Photonics J.16, 1–15. 10.1109/jphot.2024.3456115
2
Dahmouni H. Girard A. Ouzineb M. Sanso B. (2012b). The impact of jitter on traffic flow optimization in communication networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag.9, 279–292. 10.1109/tnsm.2012.051712.110148
3
Dahmouni H. Girard A. Sanso B. (2012a). An analytical model for jitter in IP networks. Ann. Telecommun.67, 81–90. 10.1007/s12243-011-0254-y
4
Dbira H. Girard A. Sanso B. (2016). Calculation of packet jitter for non-poisson traffic. Ann. Telecommun.71, 223–237. 10.1007/s12243-016-0492-0
5
El Amri A. Meddeb A. (2021). Optimal server selection for competitive service providers in network virtualization context. Telecommun. Syst.77, 451–467. 10.1007/s11235-021-00764-3
6
Gore R. N. Lisova E. Åkerberg J. Bjorkman M. (2022). Network calculus approach for packet delay variation analysis of multi-hop wired networks. Appl. Sci.12, 11207. article id 11207. 10.3390/app122111207
7
Husen A. Chaudary M. H. Ahmad F. Alam M. I. Sohail A. Asif M. (2021). Improving scheduling performance in congested networks. PeerJ Comput. Sci.7, e754. article id e754. 10.7717/peerj-cs.754
8
Masli A. A. Ahmed F. Y. H. Mansoor A. M. (2022). QoS-Aware scheduling algorithm enabling video services in LTE networks. Computers11, 77. article id 77. 10.3390/computers11050077
9
Mustapha O. Z. Hu Y. F. Sheriff R. Abd-Alhameed R. A. Ali M. (2020). Evaluation of bandwidth resource allocation using dynamic LSP and LDP in MPLS for wireless networks. Int. J. Comput. Digital Syst.9, 147–158.
10
Sreedevi A. G. Rama Rao T. (2020). SINR based association algorithm for indoor device-to-device communication networks. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl.13, 1921–1930. 10.1007/s12083-020-00951-0
11
Ye Z. Gang S. Guizani M. (2023). ILBPS: an integrated optimization approach based on adaptive load-balancing and heuristic path selection in SDN. IEEE Internet Things J.11, 6144–6157.
Summary
Keywords
integration, maple, singularity, IP, jitter
Citation
Nadarajah S and Ba A (2025) On the analytical model for jitter. Front. Commun. Netw. 6:1602095. doi: 10.3389/frcmn.2025.1602095
Received
01 April 2025
Accepted
30 June 2025
Published
24 July 2025
Volume
6 - 2025
Edited by
Gangwei Wang, Hebei University of Economics and Business, China
Reviewed by
Wuyunzhaola Borjigin, Inner Mongolia University of Finance and Economics, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Nadarajah and Ba.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Saralees Nadarajah, mbbsssn2@manchester.ac.uk
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.