- CNOOC Safety Technology Services Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China
Edge computing has emerged as a vital paradigm for processing data near its source, significantly reducing latency and improving data privacy. Simultaneously, large language models (LLMs) such as GPT-4 and BERT have showcased impressive capabilities in data analysis, natural language processing, and decision-making. This survey explores the intersection of these two domains, specifically focusing on the adaptation and optimization of LLMs for data analysis tasks in edge computing environments. We examine the challenges faced by resource-constrained edge devices, including limited computational power, energy efficiency, and network reliability. Additionally, we discuss how recent advancements in model compression, distributed learning, and edge-friendly architectures are addressing these challenges. Through a comprehensive review of the current research, we analyze the applications, challenges, and future directions of deploying LLMs in edge computing. This analysis aims to facilitate intelligent data analysis across various industries, including healthcare, smart cities, and the internet of things.
1 Introduction
Edge computing has emerged as a powerful paradigm for processing and analyzing data near its source. It effectively addresses limitations such as latency and bandwidth constraints, which are particularly critical in real-time applications (Zhou et al., 2024a; Syu et al., 2023). By distributing computational resources across a network of edge devices, it enables rapid, local processing, minimizing dependency on centralized cloud infrastructures. This shift is particularly important in latency-sensitive applications like autonomous vehicles and smart cities, where instantaneous data processing is essential (Deng et al., 2020).
Simultaneously, deep learning, particularly with large language models (LLMs), has achieved remarkable advancements in natural language processing (NLP) and data analysis, revolutionizing the way machines understand and produce human language (Gangadhar et al., 2023). Models like BERT (Devlin et al., 2019) and GPT-4 (Brown et al., 2020) have exhibited remarkable proficiency in various applications, encompassing language translation, text summarization, sentiment assessment, and intricate data analysis. These advancements have significantly improved the performance of various applications, from virtual assistants to advanced data analytics platforms.
However, deploying these models in edge environments presents a set of technical challenges that must be addressed to fully harness their potential. The high computational demands and substantial memory consumption of LLMs present significant challenges for their implementation on edge devices, which are typically characterized by limited processing capabilities and storage resources. Additionally, the need for frequent model updates to ensure accuracy and relevance intensifies these challenges, as the operational constraints of edge devices may not accommodate the continuous retraining required for LLMs. As a result, directly deploying these models in edge environments is often impractical without significant optimizations (Han et al., 2015). This situation underscores the necessity to explore innovative techniques that can reduce the resource consumption of LLMs while preserving their performance and effectiveness.
The integration of LLMs with edge computing presents both a significant opportunity and a series of technical challenges. On one hand, deploying LLMs on edge devices can facilitate intelligent real-time data processing without relying on centralized cloud infrastructure, which is particularly crucial for applications that prioritize data privacy and security (Zhou et al., 2022a). By processing sensitive data locally, organizations can mitigate the risks associated with data breaches and ensure compliance with privacy regulations. On the other hand, the inherent limitations of edge devices in terms of processing power and storage capacity necessitate the development of strategies focused on model compression and adaptation. Such strategies are essential to reduce the overall resource consumption of LLMs, making them viable for deployment in edge environments (Sun and Ansari, 2019; Chi et al., 2024). Ultimately, addressing these challenges will be key to unlocking the full potential of LLMs in edge computing applications.
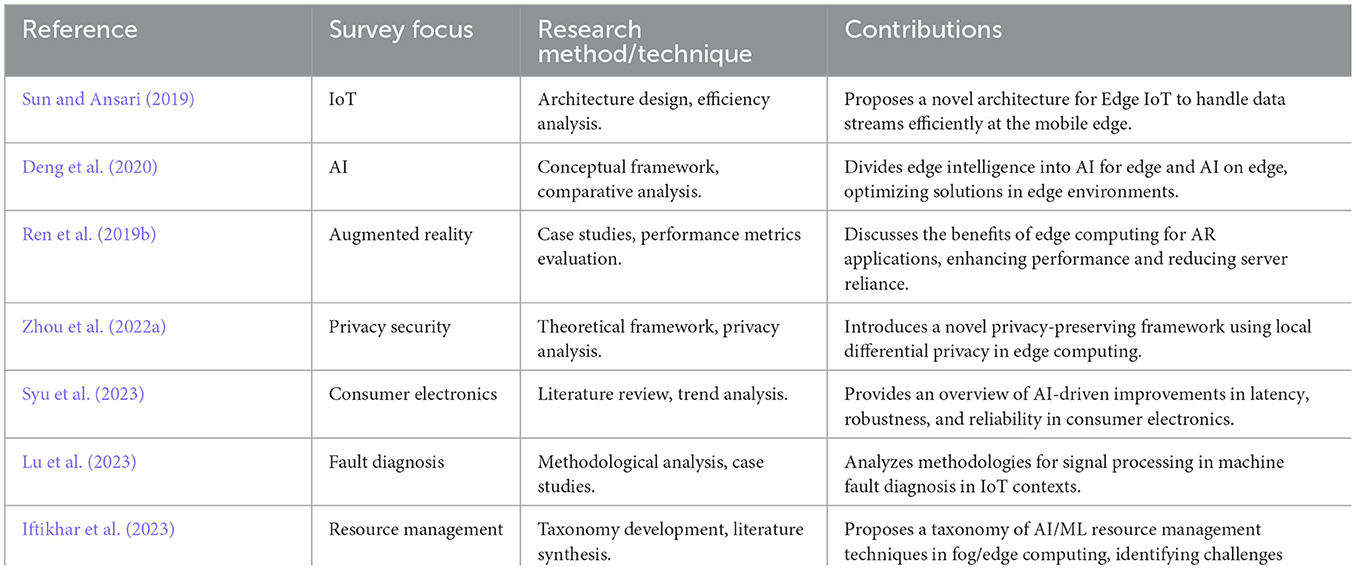
As shown in Table 1, this table presents an overview of relevant publications focused on various aspects of edge computing and its applications. Based on this foundation, this paper offers a comprehensive analysis of the applications, challenges, and future directions of intelligent data analysis in edge computing using LLMs. This analysis highlights the key obstacles associated with deploying LLMs on resource-constrained edge devices, explores innovative strategies for adapting LLMs to edge environments, and showcases their practical applications across diverse sectors such as healthcare, IoT, and industrial automation.
This survey offers the following contributions:
• We provide a comprehensive review of edge computing and LLM fundamentals, highlighting the distinct advantages and limitations they present for various data analysis tasks.
• We identify and discuss the primary challenges in deploying LLMs on resource-constrained edge devices, covering areas such as resource limitations, energy efficiency, privacy, and latency requirements.
• We examine state-of-the-art techniques for making LLMs compatible with edge deployment, including model compression, federated learning, and optimized frameworks.
• We review practical applications of LLMs in edge computing across various domains, including healthcare, IoT, industrial automation, and consumer electronics, demonstrating the utility of LLMs for edge-based data analysis.
• We outline emerging trends and future directions in LLM and edge integration, including advancements in Transformer architectures, privacy-preserving techniques, and hardware developments that could shape the future of edge-based intelligent systems.
The subsequent sections of this paper are structured in the following manner. Section 2 offers background information on edge computing and LLM architectures, emphasizing their essential characteristics pertinent to edge-based applications. Section 3 examines the specific applications of LLMs in edge computing for data analysis, while Section 4 discusses the challenges of implementing LLMs in edge computing, including resource constraints, energy efficiency, privacy, and latency requirements. Section 5 explores various techniques for edge-compatible LLM deployment, such as model compression, federated learning, and optimized frameworks. Section 6 explores potential avenues for future research. Section 7 wraps up the paper by highlighting essential observations and suggesting areas for further investigation.
2 Background
2.1 Edge computing fundamentals
Edge computing is a decentralized computing model that facilitates data processing closer to the data source, rather than relying on centralized cloud servers (Cicconetti et al., 2021). This innovative approach effectively addresses several challenges associated with traditional cloud computing, particularly in environments where speed, efficiency, and security are paramount (Shi et al., 2016; Deng et al., 2020). By performing computations locally on devices such as sensors, gateways, and mobile devices, edge computing significantly reduces latency and bandwidth requirements (Ren et al., 2019a), which are often limitations of cloud-based systems. This significant reduction in latency is crucial for applications that demand real-time responses, such as autonomous vehicles, healthcare monitoring, and smart city infrastructure (Lu et al., 2023; Iftikhar et al., 2023).
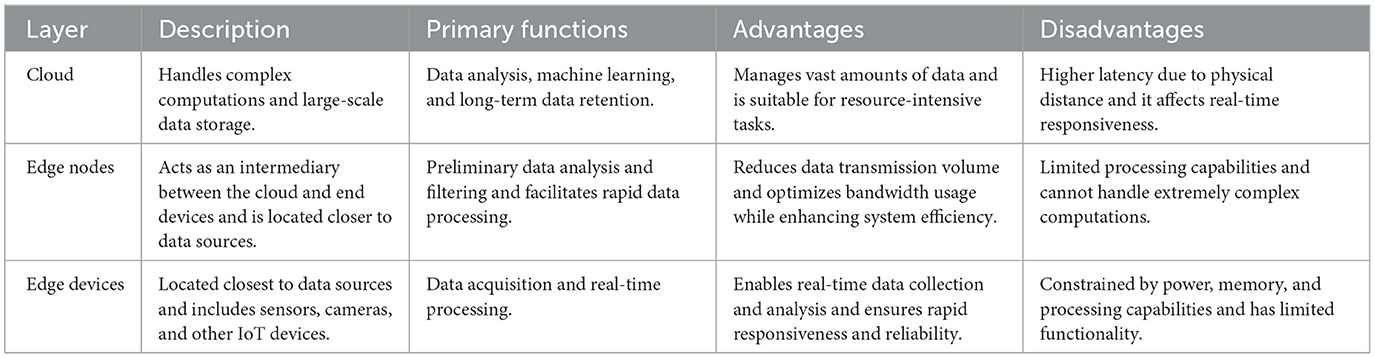
By processing data at the edge, applications can enhance operational efficiency, enabling them to make faster decisions based on real-time data analysis without the delays associated with transferring data to and from centralized servers. The architecture of edge computing generally consists of three distinct layers (Khan et al., 2019), each serving a specific purpose in the data processing workflow, as shown in Table 2.
The first layer, known as the cloud, is responsible for handling complex computations and large-scale data storage. This layer can process and store vast amounts of data, making it well-suited for demanding activities such as data analysis, machine learning, and long-term data storage (Sandhu, 2022). However, its physical distance from the data sources often results in higher latency (Memari et al., 2022), which can hinder the performance of applications that require immediate responses.
The second layer, referred to as edge nodes or fog nodes, serves as an intermediary between the cloud and the end devices. Positioned closer to the data sources, edge nodes provide moderate processing capabilities that enable quicker data handling in latency-sensitive applications (Pelle et al., 2021). By performing preliminary data analysis and filtering at this layer, edge nodes can reduce the volume of data that needs to be sent to the cloud, thus optimizing bandwidth usage and enhancing overall system efficiency. This layer plays a crucial role in scenarios where timely decision-making is essential, such as in smart manufacturing or real-time monitoring systems (Nain et al., 2022).
The third layer comprises edge devices, which are located closest to the data source. These devices include sensors, cameras, and other IoT devices that possess limited computing power and primarily focus on data acquisition and real-time processing tasks (Shi et al., 2016). Edge devices are typically constrained by factors including energy, memory, and computational capacities, making efficient data handling critical for ensuring responsiveness and reliability. Despite these limitations, edge devices are vital for collecting real-time data, enabling immediate analysis and actions that are essential in various applications, including autonomous vehicles, healthcare monitoring, and smart city infrastructure.
Together, these three layers create a cohesive edge computing architecture that enhances data processing efficiency, reduces latency, and supports a wide range of applications. By distributing computing resources across these layers, edge computing not only addresses the limitations of traditional cloud computing but also empowers organizations to leverage real-time data for improved decision-making and operational effectiveness. This capability not only improves the user experience but also optimizes resource utilization by minimizing the need for extensive data transfers and reducing the load on network infrastructure (Yu et al., 2018). Consequently, edge computing enhances performance and provides a robust solution for the evolving needs of various data analysis tasks, facilitating more secure and efficient data management practices.
2.2 The evolution and advancements of language models
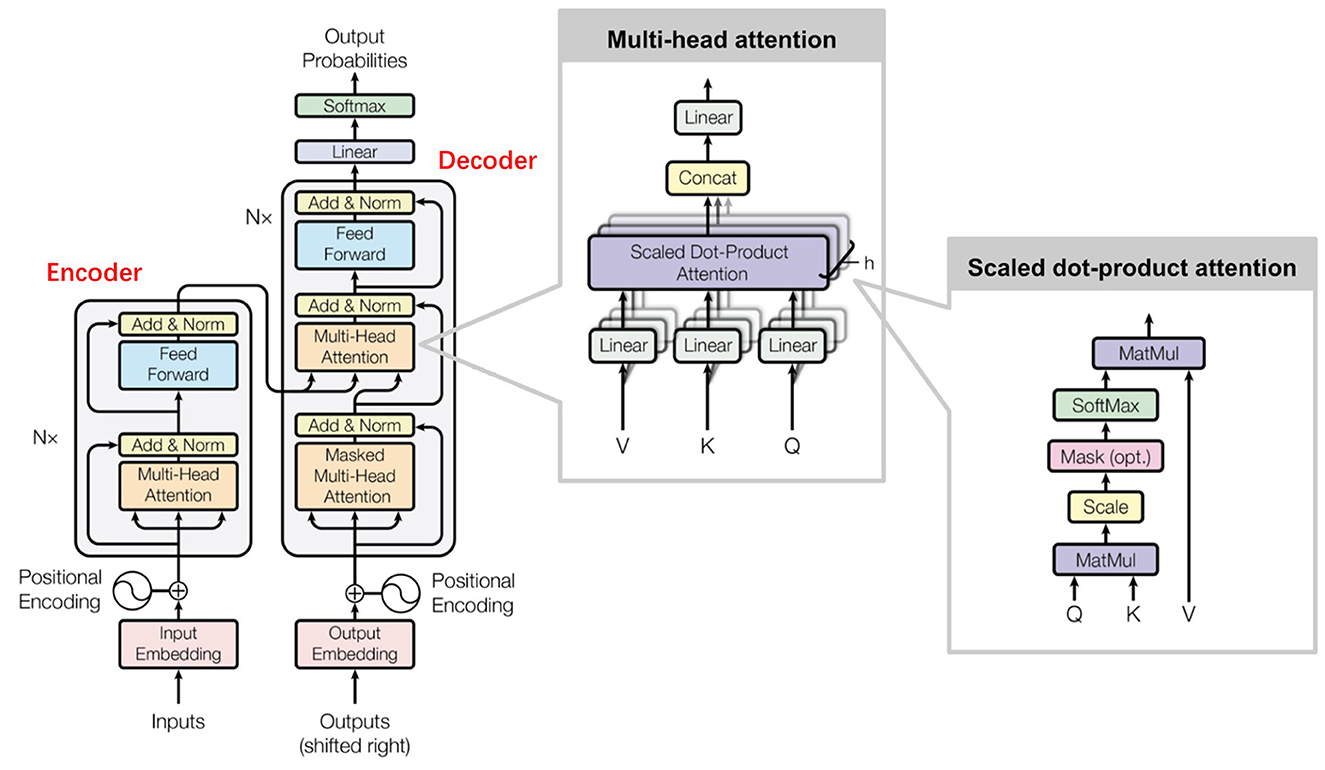
LLMs exemplified by notable architectures such as BERT (Devlin et al., 2019) and GPT-4 (Brown et al., 2020), have profoundly influenced the field of NLP by enhancing the capability of machines to comprehend and generate human-like text. A fundamental underpinning of these models is the Transformer architecture, which employs self-attention mechanisms to effectively capture dependencies and contextual relationships within textual data (Vaswani et al., 2017). As shown in Figure 1, Transformer architecture is characterized by its layered structure, comprised of multiple encoders and decoders, each integrating self-attention and feedforward neural networks (Raffel et al., 2020).
Prior to the advent of the Transformer, models like Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), Long Short-Term Memory networks (LSTMs), and Gated Recurrent Units (GRUs) have been predominant in sequence modeling tasks. RNNs were specifically designed to process sequential input by retaining a hidden state that reflects information from previous time steps (Gu et al., 2021). However, they encountered significant limitations in capturing long-range dependencies due to the vanishing gradient problem, which made it difficult for the model to learn relationships between distant words (Ribeiro et al., 2020). To address this, LSTMs were introduced, incorporating gating mechanisms that regulate the passage of information, allowing them to preserve relevant context over prolonged sequences (Gu et al., 2020). While LSTMs improved upon RNNs by mitigating issues related to long-term dependencies, they still suffered from inefficiencies in computational speed and the inability to fully leverage parallel processing due to their inherently sequential nature. GRUs further simplified the architecture of LSTMs by combining the forget and input gates into a singular update gate, thus reducing the complexity and enhancing performance on various sequence tasks (Savadi Hosseini and Ghaderi, 2020). Nonetheless, RNNs, LSTMs, and GRUs were still constrained by their sequential processing limitations, which hindered their scalability and posed challenges in handling large datasets efficiently.
In contrast, Transformer architecture fundamentally revolutionizes the approach to modeling sequence data by enabling the self-attention mechanism (Raffel et al., 2020), which allows the model to evaluate the significance of each word relative to all other words in the input simultaneously, irrespective of their positional distance. This capability not only facilitates the capture of complex relationships and context with remarkable accuracy but also significantly enhances computational efficiency through parallelization (Zeng et al., 2022). By processing entire sequences at once, Transformers can dramatically reduce training times and handle larger datasets more effectively, thereby overcoming the limitations imposed by earlier models.
The self-attention mechanism represents a pivotal innovation, empowering Transformers to dynamically assess and weigh the relevance of different words, thus ensuring that the contextual meaning is preserved across various tasks (Yang et al., 2023). As a result, LLMs built on the Transformer architecture have proven to be highly effective in diverse NLP applications, including translation (Brown et al., 2020), summarization, and question answering (Yao and Wan, 2020). However, despite these advantages, it is important to note that LLMs are inherently computationally intensive, often requiring substantial memory and processing power that can be a barrier to implementation in resource-constrained environments (Han et al., 2015).
2.3 Intersection of LLMs and edge computing
The convergence of edge computing and LLMs creates new possibilities for intelligent, real-time data processing right at the source of the data. This development is especially significant for applications that prioritize privacy and time sensitivity, such as those found in healthcare and industrial automation (Sun and Ansari, 2019; Li D. et al., 2023). By deploying LLMs on edge devices, applications can leverage advanced NLP capabilities to conduct localized data analysis. This not only minimizes reliance on cloud infrastructure but also significantly enhances data privacy and operational efficiency (Barua et al., 2020). The ability to process data closer to where it is generated allows for quicker decision-making and reduces latency, which is critical in scenarios where timely responses are essential. Furthermore, this localized approach ensures that sensitive information remains on-site, thereby mitigating the risks associated with data transmission (Cao et al., 2020).
The deployment of LLMs on edge devices presents considerable challenges primarily due to the substantial computational and memory requirements inherent to these models (Yang et al., 2024). As the demand for intelligent applications grows, particularly in environments constrained by hardware limitations, addressing these challenges becomes crucial (Kong et al., 2022). To make LLMs practical for edge environments, researchers are actively exploring a variety of optimization techniques aimed at reducing both the model size and the computational demands, all while striving to maintain acceptable performance levels.
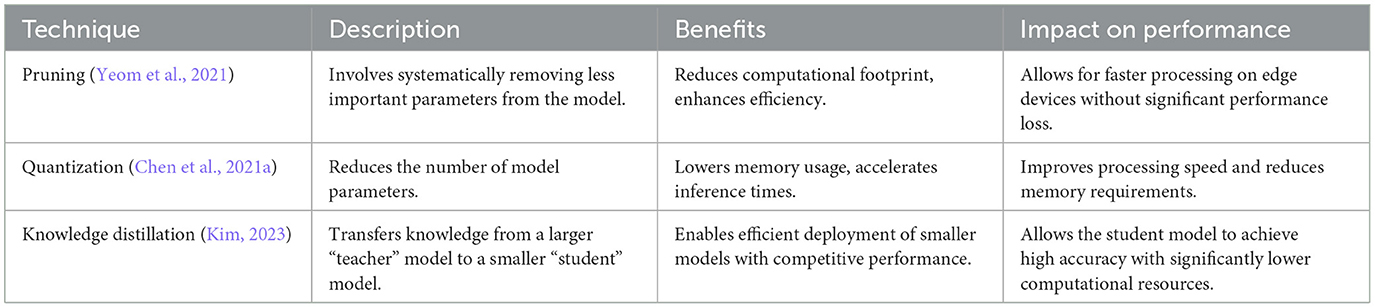
One promising approach is model compression, which encompasses several methods such as pruning, quantization, and knowledge distillation. Pruning involves systematically removing less important parameters from the model, resulting in a reduced computational footprint that allows for faster processing on edge devices (Yeom et al., 2021). By streamlining the model in this way, developers can enhance its efficiency without significantly compromising its capabilities. Additionally, quantization techniques are crucial as they reduce the number of parameters in the model, which in turn decreases memory usage and speeds up inference times (Kim et al., 2023). Furthermore, knowledge distillation—a technique that conveys insights from a larger, more intricate model commonly called the “teacher” to a smaller, more streamlined model referred to as the “student”—provides an alternative method for facilitating efficient deployment on edge devices. Through this method, the student learns to perform tasks by mimicking the teacher, allowing it to achieve competitive performance with a fraction of the computational resources (Gou et al., 2021). As shown in Table 3, these optimization techniques represent significant advancements in the field, making it possible to leverage the sophisticated capabilities of LLMs in edge computing environments, thereby broadening their applicability across various industries and use cases.
Federated learning represents a promising approach for enhancing edge applications, particularly as it enables distributed training across multiple devices without the need to transmit raw data to a central server (Kairouz et al., 2021; Liu G. et al., 2021). This decentralized method is particularly beneficial for applications that prioritize data privacy, allowing sensitive information to remain on the local device while still contributing to the improvement of machine learning models. By facilitating cooperative learning without compromising user privacy, federated learning seeks to harness the collective intelligence of multiple devices, ultimately resulting in more robust and accurate models.
In summary, the integration of LLMs with edge computing presents substantial opportunities for real-time, privacy-sensitive data analysis across a wide range of applications, from healthcare to smart cities and industrial automation. This convergence allows for the processing of data closer to its source, which not only enhances response times but also mitigates the risks associated with data transmission to centralized servers. However, to fully realize this vision, it is imperative to address several critical challenges that have emerged in the current literature. One significant challenge is the computational constraints inherent in edge devices, which often have limited processing power and memory compared to traditional cloud-based systems. This limitation can hinder the deployment of complex LLMs, necessitating the development of more lightweight models or innovative techniques that can efficiently leverage available resources. Additionally, ensuring robust data privacy is paramount, as edge computing environments often handle sensitive information that must be protected from unauthorized access. This requires the implementation of advanced encryption methods and privacy-preserving techniques to safeguard user data while still allowing for effective analysis. Moreover, optimizing LLMs for efficient performance on edge devices is crucial. This involves not only reducing the model size and complexity but also adapting algorithms to ensure they can operate effectively within the constraints of edge infrastructures.
By tackling these interconnected issues, we can unlock the transformative potential of LLMs in edge environments, paving the way for the development of smarter, more responsive systems. Such advancements will cater to the evolving needs of users, providing them with timely insights and services while maintaining a strong emphasis on privacy and security.
3 Applications of LLMs for data analysis in edge computing
LLMs hold considerable potential for data analysis in edge computing due to their capability to process and analyze data locally, providing real-time insights and enhanced data privacy. In this section, we discuss several critical application areas: healthcare and wearable devices, IoT and smart cities, industrial automation, and consumer applications, as shown in Figure 2.
3.1 Healthcare and wearable devices
In the realm of healthcare, edge computing significantly enhances the capacity for real-time analysis of patient data collected through wearable devices, thereby improving responsiveness and minimizing latency. The deployment of LLMs on edge devices enables the analysis of substantial volumes of textual data derived from medical records and wearable health monitors. This capability is instrumental in facilitating early anomaly detection and comprehensive trend analysis, which are critical for timely medical interventions (Esteva et al., 2019; Dias and Paulo Silva Cunha, 2018). By processing data locally on edge devices, sensitive patient information remains secure, effectively reducing the necessity for cloud transmission and, consequently, preserving data privacy (Zhou B. et al., 2022).
Wearable devices that incorporate LLMs are adept at continuously monitoring vital signs, thus providing ongoing health assessments (Kim et al., 2024). For instance, a wearable device may issue alerts to healthcare providers regarding irregularities in a patient's vital signs, as determined through the analytical capabilities of LLMs. This proactive approach to medical intervention not only enhances patient care but also exemplifies the potential for continuous health monitoring without reliance on centralized data processing (Babu et al., 2024).
Furthermore, the integration of edge computing within the domain of wearable health technology fosters significant advancements in academic research. Researchers can leverage the real-time data collected from edge devices to conduct extensive analyses of health trends across diverse populations. This data-driven approach enables the identification of potential health risks and the formulation of more effective preventive measures and treatment protocols (García-Méndez and de Arriba-Pérez, 2024). Such insights are invaluable for the advancement of personalized medicine, as they allow for tailored healthcare solutions that address the unique needs of individual patients. The implications of edge computing extend beyond individual patient care to influence broader public health strategies (Jo et al., 2023). By analyzing aggregated data from wearable devices, researchers can derive insights that inform health policy decisions and resource allocation, ultimately contributing to improved health outcomes at the population level. This paradigm shift toward decentralized data processing not only enhances the efficiency and security of healthcare delivery but also paves the way for innovative research methodologies that capitalize on the wealth of data generated by wearable technologies (Shiranthika et al., 2023).
In conclusion, the application of edge computing in the healthcare wearable sector not only enhances the efficiency and security of data processing but also propels academic research forward, offering new perspectives and tools for advancing health management. As technology continues to evolve, edge computing is poised to play an increasingly pivotal role in the future of healthcare, facilitating more precise and effective patient care while supporting the ongoing quest for knowledge in medical research.
3.2 IoT and smart cities
In the context of smart city applications, edge computing plays a pivotal role in managing the vast amounts of data generated by IoT sensors across various domains, including traffic management, environmental monitoring, autonomous driving, and public safety. The deployment of LLMs on edge devices enables the analysis of diverse data streams, such as sensor reports, social media posts, and other real-time data inputs, thereby providing actionable insights that are crucial for city planners and emergency responders (Jan et al., 2021; Li X. et al., 2022).
For instance, real-time traffic data analysis conducted by LLMs on edge devices can significantly optimize traffic light timing (de Zarzà et al., 2023), which in turn reduces congestion and enhances fuel efficiency. By processing data locally, these systems can react swiftly to changing traffic conditions, allowing for dynamic adjustments that promote smoother traffic flow and minimize delays. This capability not only improves the overall transportation experience for citizens but also contributes to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions associated with idling vehicles.
In the realm of environmental monitoring, LLMs can locally process air quality data collected from various sensors deployed throughout the city. When pollution levels exceed predefined safe thresholds, these edge-based systems can issue immediate alerts to both authorities and the public, facilitating timely interventions to protect public health (Alahi et al., 2023). Such proactive measures are essential in maintaining compliance with health standards and mitigating the adverse effects of pollution on urban populations.
The advantages of edge computing in smart city applications extend beyond immediate responsiveness; they also encompass a reduction in dependency on centralized cloud infrastructure. By enabling data processing at the edge, cities can ensure that data-driven responses can be initiated without the delays often associated with cloud-based systems (Khan et al., 2020; Lv et al., 2021). This decentralized approach enhances the resilience of urban infrastructure, particularly in emergency situations where rapid decision-making is critical. Furthermore, the integration of edge computing within smart city frameworks fosters significant opportunities for academic research. Researchers can utilize the rich datasets generated by IoT sensors and edge devices to conduct comprehensive studies on urban dynamics, environmental impacts, and public safety trends. This data-driven research paradigm enables the identification of patterns and correlations that can inform policy decisions and urban planning strategies, ultimately leading to more sustainable and livable cities (Liu Q. et al., 2021).
3.3 Industrial automation and predictive maintenance
In industrial settings, predictive maintenance is of paramount importance for ensuring equipment reliability and optimizing operational efficiency. The integration of LLMs with edge computing technologies facilitates on-site analysis of a variety of data sources, including text-based maintenance logs, sensor data, and equipment performance reports. This capability enables organizations to predict potential failures before they manifest, thereby enhancing the overall reliability of industrial operations (Zonta et al., 2020).
By processing data at the edge, companies can substantially reduce latency associated with data transmission to centralized cloud systems. This reduction in latency is critical, as it allows for the timely initiation of preventive measures, which in turn minimizes costly downtimes and enhances productivity (Pang et al., 2021). For instance, an LLM deployed on an edge device can continuously analyze vibration patterns and temperature fluctuations from manufacturing equipment. When anomalies are detected, the system can generate immediate alerts for preventive maintenance, enabling operators to address issues proactively rather than reactively. This localized processing capability not only enhances operational safety but also substantially reduces the likelihood of unexpected shutdowns, which can have severe financial implications for manufacturing operations.
Moreover, the advantages of edge computing in predictive maintenance extend to the realm of data security and privacy (Qiu et al., 2020; Zhang J. et al., 2018). By conducting analyses locally, sensitive operational data is less exposed to external threats associated with cloud transmission, thereby enhancing the overall security posture of industrial facilities. This is particularly important in industries where proprietary processes and trade secrets are involved, as edge computing mitigates the risks of data breaches and intellectual property theft (Zhou et al., 2024b).
The integration of edge computing and LLMs also opens new avenues for academic research within the field of industrial automation. Researchers can leverage the vast amounts of data generated by industrial equipment to develop advanced predictive models that improve maintenance strategies. By utilizing machine learning methods and data analytics, researchers can identify patterns and correlations that guide best practices in predictive maintenance, ultimately enhancing the effectiveness and efficiency of operational frameworks.
3.4 Consumer applications
In consumer applications, the integration of LLMs embedded in edge devices has become increasingly prevalent, particularly in smart home assistants, smartphones, and personal wearables. These devices leverage LLMs to process user commands locally, significantly enhancing response times and preserving user privacy by minimizing reliance on cloud processing (Syu et al., 2023). This local processing capability not only facilitates quicker interactions but also mitigates concerns related to data security and privacy, as sensitive information remains on the device rather than being transmitted to remote servers.
For instance, smart home systems equipped with LLMs can analyze and predict energy usage patterns, enabling users to optimize their energy consumption based on real-time insights (Yu et al., 2021; Iqbal et al., 2023). By monitoring factors such as appliance usage and user behavior, these systems can provide tailored recommendations that promote energy efficiency and cost savings. This capability is particularly relevant in an era where energy conservation is of paramount importance, as it empowers consumers to make informed decisions regarding their energy consumption habits.
Moreover, edge-deployed LLMs enhance security in smart home environments by analyzing data from various sensors to detect unusual patterns. For example, they can monitor for unexpected motion or unusual access times, alerting users immediately to potential security threats (Siriwardhana et al., 2021). This proactive approach to home security not only provides peace of mind for users but also demonstrates the potential for LLMs to contribute to safer living environments through real-time monitoring and alerting mechanisms.
The advantages of edge computing in consumer applications extend beyond improved response times and enhanced privacy. The localized processing of data allows for greater resilience in the face of connectivity issues, as devices can continue to function effectively even when offline or in low-bandwidth situations (Li J. et al., 2023). This characteristic is particularly valuable in resource-constrained environments, where consistent internet access may not be guaranteed.
In summary, the integration of LLMs with edge computing in consumer applications offers substantial benefits, including reduced latency, enhanced privacy, and decreased dependency on cloud infrastructure. These applications underscore the transformative potential of edge-compatible LLMs in providing real-time, privacy-conscious data insights, thereby enriching user experiences across various domains. As research in this field progresses, it will undoubtedly yield innovative solutions that further enhance the capabilities and societal acceptance of AI-driven consumer technologies.
4 Challenges of implementing LLMs in edge computing
Deploying LLMs in edge computing environments presents significant challenges due to the resource-constrained nature of edge devices (Boumendil et al., 2025). These challenges include resource constraints, energy efficiency, data privacy and security, as well as latency and real-time requirements, as shown in Table 4. Resource constraints arise from the limited computational and memory capabilities of edge devices compared to robust cloud servers, making it difficult to effectively utilize large models. Additionally, the energy demands of LLMs pose challenges in battery-powered edge devices, necessitating optimizations to minimize power consumption. Data privacy concerns are amplified in scenarios involving sensitive information, where centralized processing introduces risks that must be mitigated. Finally, the inherent computational intensity of traditional LLMs often results in high latency, which is incompatible with the near-instantaneous processing required in critical applications such as autonomous driving and real-time diagnostics. To address these challenges, solutions such as model compression techniques, secure local processing methods, and latency reduction strategies are essential for ensuring the successful integration of LLMs into resource-constrained edge environments (Cheng et al., 2024).
4.1 Resource constraints
One of the fundamental challenges associated with the deployment of LLMs on edge devices lies in the constraints imposed by limited computational and memory resources (Shi et al., 2016; Sun and Ansari, 2019). In contrast to robust cloud servers that possess the capacity to manage large model sizes and perform complex calculations, edge devices are typically characterized by their insufficient memory and processing power. This inadequacy limits their ability to store and execute LLMs directly, thereby presenting a significant barrier to the practical application of such models in real-world scenarios.
For example, models like GPT-3, which contain billions of parameters, necessitate high-performance hardware such as GPUs or TPUs to function effectively (Brown et al., 2020). These advanced processing units are instrumental in handling the extensive computational demands associated with both the training and inference stages of LLMs. However, such high-performance hardware is frequently absent in edge environments, where devices are designed to be small, energy-efficient, and cost-effective. This disparity between the resource requirements of state-of-the-art LLMs and the capabilities of edge devices leads to challenges in executing these models without significant degradation in performance.
The limitations in computational power and memory capacity are further compounded by the diverse nature of edge environments, which may include mobile devices, IoT sensors, and embedded systems. Each of these platforms comes with its own set of constraints, making it essential for researchers to explore alternative strategies for model deployment (Wang S. et al., 2019). One potential avenue is to develop model compression techniques, such as quantization and pruning (Chen et al., 2021a; Liang et al., 2021), which aim to reduce the size of models while retaining their essential functionalities. Additionally, approaches such as knowledge distillation can be employed to create smaller (Matsubara et al., 2020; Ji et al., 2024), more efficient surrogate models that approximate the performance of larger LLMs while being suitable for deployment on edge devices.
Overall, addressing these computational and memory limitations is paramount for the successful integration of LLMs into edge devices, thereby enabling the delivery of advanced language processing capabilities in a variety of resource-constrained environments.
4.2 Energy efficiency
Energy efficiency poses a substantial challenge in the deployment of LLMs on edge devices, which are inherently constrained by their battery-powered design and limited availability of energy resources. The increasing proliferation of edge devices, encompassing a diverse range of applications such as mobile phones, smart home systems, and IoT devices, necessitates the optimization of LLMs to ensure minimal power consumption while maintaining the required level of computational efficacy (Shuvo et al., 2022). This requirement is particularly critical given the growing demand for sophisticated NLP capabilities in scenarios where low power use is paramount.
Standard architectures for LLMs, including well-known models such as BERT and GPT, are particularly notable for their substantial energy consumption during both the training and inference phases. During these phases, particularly when dealing with extensive datasets and complex tasks, these models can require significant computational power and energy resources to operate effectively. This characteristic starkly contrasts with the low-power requirements typically associated with edge environments, where devices are designed to function under strict energy constraints without sacrificing performance (Devlin et al., 2019). The challenge here is twofold: not only must the models operate efficiently, but they must also be capable of delivering acceptable performance levels despite the limitations of edge devices. Larger models, characterized by billions of parameters, tend to demand exponentially increasing amounts of computational resources, which translates to higher energy usage (Strubell et al., 2020; Wang H. et al., 2019). This relationship underscores the urgency for developing model adaptation techniques aimed at achieving performance equivalence while significantly reducing energy expenditure. Such techniques are not merely advantageous but essential for effectively integrating the capabilities of LLMs within energy-constrained contexts, allowing for the deployment of advanced NLP applications in a variety of settings without detrimental impacts on device operation.
To address these energy efficiency challenges, several strategies can be employed. One prominent approach is model compression, which encompasses techniques such as pruning, quantization, and knowledge distillation. Pruning involves removing redundant parameters from the model, thereby reducing its size and, consequently, its computational demands (Kim, 2023). Quantization refers to the process of approximating the model weights using lower precision formats, which can further decrease memory usage and accelerate inference speed (Zhang et al., 2025). In contrast, knowledge distillation involves training a smaller, more efficient model (referred to as the student) to imitate the behavior of a larger, more complex model (the teacher) (Wang et al., 2024). This process yields a streamlined version that maintains a significant portion of the original model's performance while utilizing fewer resources.
4.3 Data privacy and security
Data privacy emerges as a critical concern in the deployment of LLMs at the edge, particularly in applications that involve handling sensitive information such as healthcare records, financial transactions, and personal data (Kairouz et al., 2021). Traditional centralized models typically necessitate the transfer of data to cloud servers for processing, which introduces substantial privacy risks. These risks arise from several factors, including potential data interception during transmission, vulnerabilities associated with centralized storage systems, and the possibility of unauthorized access to sensitive information (Zhou et al., 2022b). Consequently, such centralized architectures may compromise user confidentiality and trust, raising ethical and regulatory concerns.
In contrast, edge computing offers a paradigm that can significantly mitigate these privacy-related challenges by ensuring that data remains closer to its source. By processing data locally on edge devices, the exposure of sensitive information is inherently reduced, thereby reducing the likelihood of data breaches and unauthorized access. This localized data processing approach enables organizations to leverage powerful LLMs while adhering to privacy regulations and maintaining user trust (Ali et al., 2021). However, the transition to edge computing does not eliminate the need for robust privacy protections; rather, it necessitates the implementation of secure local processing techniques. Effective encryption methods must be employed to safeguard data both at rest and in transit, ensuring that even if data does reside on edge devices, it remains protected from potential adversaries (Alwarafy et al., 2021). Additionally, incorporating differential privacy techniques can further enhance data security by adding noise to the data during processing, making it increasingly challenging for attackers to infer sensitive information without significantly impacting the model's performance (Du et al., 2020). Edge environments often consist of a diverse array of devices, each with varying levels of security capabilities, which complicates the development of standardized privacy protocols. Therefore, it is essential to adopt a multifaceted approach that considers the unique attributes and constraints of different edge devices. This may include utilizing lightweight privacy-preserving algorithms that are compatible with the limited computational resources typical of edge devices while ensuring compliance with relevant legal and ethical standards.
The integration of federated learning into edge computing architectures presents a promising solution to enhance data privacy (Nguyen et al., 2021b). Federated learning facilitates the training of models across various edge devices without the necessity of sharing raw data. Instead, only model updates–devoid of sensitive information—are sent to a central server for aggregation. This approach preserves user privacy while allowing for the ongoing enhancement of LLMs (Abreha et al., 2022; Xia et al., 2021). While the deployment of LLMs at the edge offers significant advantages in terms of data privacy, it also presents unique challenges related to secure local processing. A comprehensive strategy that incorporates encryption, differential privacy, lightweight algorithms, and federated learning is essential for mitigating privacy risks while ensuring the effective use of LLMs in sensitive applications.
4.4 Latency and real-time requirements
Low latency is a critical requirement for edge applications across various sectors (Ke et al., 2023), including autonomous driving, augmented reality (Zhang et al., 2020), and real-time diagnostics, where even minor delays in response times can lead to significant consequences, potentially jeopardizing safety and operational efficiency (Kang et al., 2017). In these contexts, traditional LLMs pose challenges due to their inherent computational intensity, which often results in elevated latency levels that are incompatible with the stringent demands of edge applications that necessitate near-instantaneous processing capabilities.
For instance, in the realm of autonomous driving, the ability to process sensory data and make real-time decisions is paramount (Roszyk et al., 2022); any delay can result in critical failures, such as the inability to react promptly to dynamic road conditions or obstacles (Lin et al., 2018). Similarly, augmented reality applications rely on real-time data processing to provide users with seamless and interactive experiences, where lag can disrupt the immersive quality of the application (Chen et al., 2018; Zhang W. et al., 2018). In the field of real-time diagnostics, the timely analysis of medical data can be a matter of life and death (Köhl and Hermanns, 2023), underscoring the importance of minimizing latency.
To effectively utilize LLMs for real-time processing of speech or image data, a range of optimizations is essential to minimize processing time while maintaining accuracy. Various techniques are being investigated to tackle latency issues, including model partitioning and early exit strategies. Model partitioning involves distributing the model across multiple devices, enabling parallel processing that significantly reduces latency (Kang et al., 2017). Meanwhile, early exit mechanisms allow the model to generate predictions at intermediate layers once a high level of confidence is reached, thereby decreasing computation time for simpler tasks (Teerapittayanon et al., 2016). These strategies are crucial for meeting the real-time demands of edge applications, allowing LLMs to deliver timely responses without sacrificing performance.
5 Recent advances for edge-compatible LLMs
Given the computational and storage constraints of edge devices, deploying LLMs necessitates the implementation of various techniques aimed at minimizing model size, energy consumption, and latency. These constraints are critical considerations, as edge devices often operate under limited processing power and memory capacity, which can significantly impact the performance of LLMs. Therefore, it is essential to adopt strategies that not only reduce the resource footprint of these models but also ensure their effectiveness in real-world applications.
This section discusses three major approaches for making LLMs compatible with edge devices. First, model compression techniques, such as pruning, quantization, and knowledge distillation, play a crucial role in reducing the size and complexity of LLMs without substantially sacrificing their performance. These methods allow for the deployment of smaller models that can operate efficiently within the constraints of edge environments. Second, federated and distributed learning frameworks offer innovative solutions for training LLMs across decentralized data sources while preserving data privacy. By enabling collaborative learning without the need to centralize sensitive information, these approaches not only enhance security but also improve the robustness of the models through diverse data exposure. Lastly, optimized architectures and frameworks, particularly those that are edge-friendly, are crucial for ensuring that LLMs can operate effectively in resource-constrained environments. These architectures focus on balancing performance and efficiency, allowing for rapid inference times and reduced energy consumption, which are essential for applications that require real-time processing.
5.1 Model compression techniques
Model compression is essential to fit LLMs within the resource-constrained environments of edge devices. Compression methods aim to reduce model size and computational demands while retaining performance. Three popular compression techniques are pruning, quantization, and knowledge distillation (Han et al., 2015; Sanh et al., 2019). Pruning involves removing the less important connections within the model to reduce its size without a significant drop in performance (Han et al., 2015). Quantization reduces the precision of the model weights, decreasing memory requirements and improving computational efficiency (Jacob et al., 2018). Knowledge distillation enables a student model to learn from a teacher model, retaining key features of the original model but in a more compact form (Sanh et al., 2019). These techniques, illustrated in Figure 3, have shown promise in adapting LLMs to edge devices, but further advances are needed to effectively balance model performance with hardware limitations.
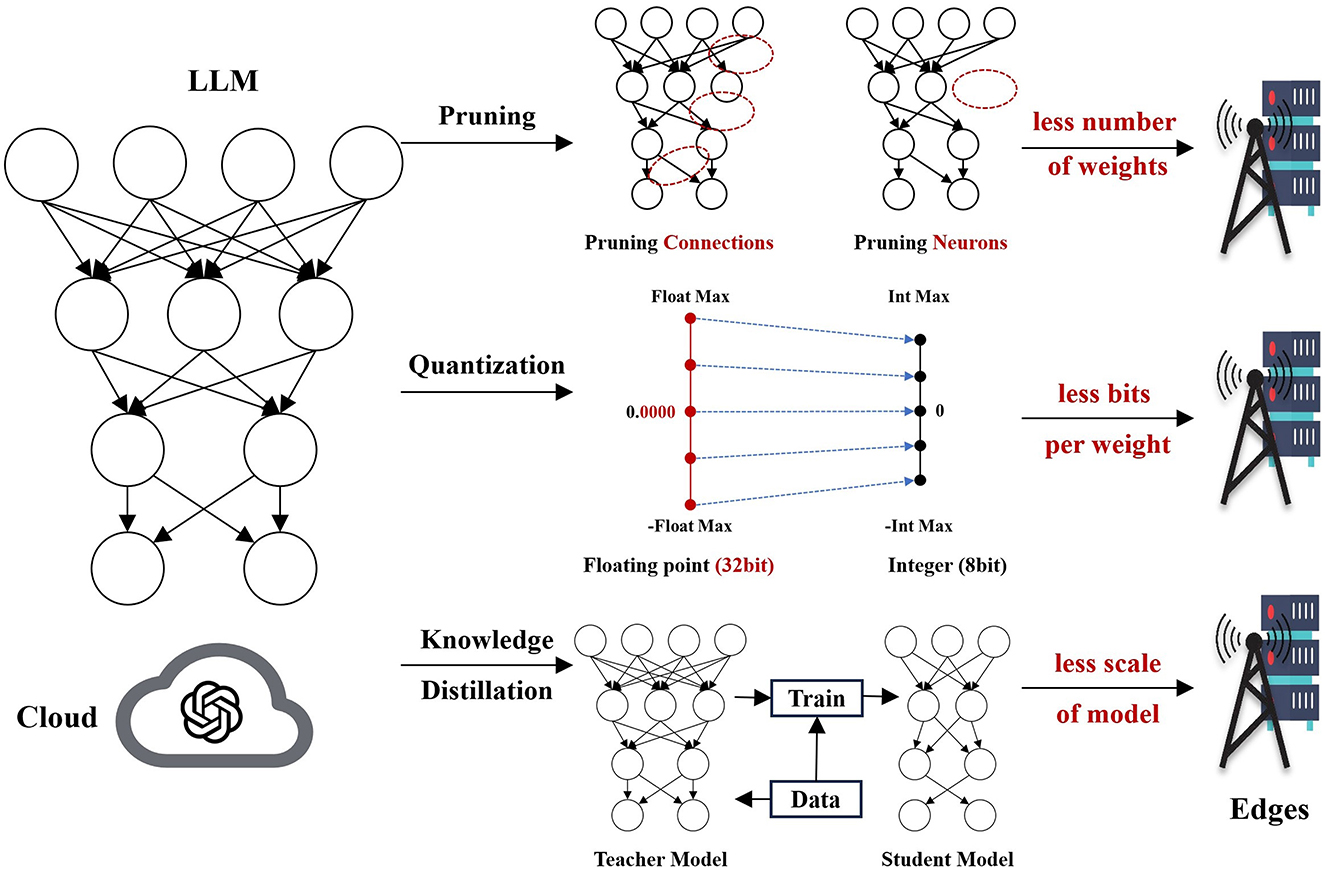
Figure 3. Illustration of model compression techniques for edge deployment: pruning, quantization, and knowledge distillation.
5.1.1 Pruning
Pruning is a pivotal technique in the field of model compression that focuses on enhancing the efficiency of neural networks by removing redundant connections (Wang et al., 2021). This is accomplished by systematically removing low-weight parameters, leading to a substantial decrease in both memory requirements and computational costs. Pruning techniques can be generally divided into two categories: structured and unstructured methods. Structured pruning entails the removal of entire neurons, channels, or layers, while unstructured pruning focuses on the elimination of individual weights (Gale et al., 2019).
Recent advancements in pruning techniques have highlighted two primary approaches: structured and unstructured pruning (Vahidian et al., 2021). Structured pruning focuses on the removal of entire neurons, channels, or layers, thereby maintaining the overall architecture of the network while significantly enhancing its efficiency (Anwar et al., 2017). On the other hand, unstructured pruning targets individual weights, allowing for a finer level of granularity in the pruning process. While unstructured pruning often achieves higher compression rates, it can lead to irregular sparsity patterns that may not be as easily optimized for hardware acceleration (Vahidian et al., 2021). In contrast, structured pruning tends to produce more regular sparsity patterns, making it more compatible with various hardware architectures (Xu et al., 2025), such as GPUs and TPUs, which can exploit these structures for improved performance. The integration of pruning with neural architecture search (NAS) has gained traction, enabling the automatic discovery of optimal architectures that are inherently more efficient (Ding et al., 2022). Additionally, the development of dynamic pruning methods, which adaptively prune weights during training based on their importance, has shown promise in maintaining model performance while achieving significant reductions in size (Hu et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2018). Another notable trend is the use of pruning in conjunction with quantization techniques, which further compress models by reducing the precision of the weights (Chowdhury et al., 2021), leading to even greater efficiency.
5.1.2 Quantization
Quantization is a pivotal technique in the optimization of neural networks, specifically designed to enhance computational efficiency and reduce memory usage. This process involves decreasing the precision of model weights, allowing them to be represented with fewer bits—commonly using 8-bit integers in place of the traditional 32-bit floating-point representations (Jacob et al., 2018). By reducing the bit-width of weights, quantization not only conserves memory but also accelerates computational operations, making quantized models particularly well-suited for deployment on edge devices that often have stringent resource constraints. In recent years, the field of quantization has witnessed significant advancements, especially in the context of LLMs.
One notable trend is the integration of quantization with retraining strategies, where models are fine-tuned after quantization to recover any potential loss in accuracy (Wu et al., 2020). This approach has proven effective in mitigating the impact of reduced precision, ensuring that the quantized models remain robust and reliable for real-world applications. Another area of focus has been the development of adaptive quantization methods, which dynamically adjust the quantization strategy based on the distribution of weight values within the model (Zhou et al., 2018). This technique allows for more efficient representation of weights, optimizing both performance and resource utilization. Additionally, researchers have explored the potential of mixed-precision quantization, where different layers of a neural network are quantized to varying degrees of precision based on their sensitivity to quantization errors (Chen et al., 2021b). This tailored approach can lead to enhanced performance while still achieving significant reductions in model size (Liu X. et al., 2021). The rise of quantization-aware training has also emerged as a key area of research. This technique involves incorporating quantization effects into the training process itself, allowing the model to learn to be robust against the quantization noise it will encounter during inference (Nagel et al., 2022). This proactive strategy has shown promise in preserving accuracy while maximizing the benefits of quantization (Sakr et al., 2022).
5.1.3 Knowledge distillation
Knowledge distillation is a powerful technique in the field of deep learning. The primary objective of this process is to train the student to replicate the outputs of the teacher, effectively allowing it to inherit the performance characteristics of the more sophisticated model while maintaining a significantly reduced size (Gou et al., 2021).
One prominent example of knowledge distillation is DistilBERT (Sanh et al., 2019), which is a distilled variant of the well-known BERT model. DistilBERT achieves remarkable efficiency by retaining approximately 97% of BERT's language understanding capabilities while being roughly half the size of the original model. This compression is particularly advantageous for applications requiring deployment on edge devices, where computational resources and memory are often limited (Gou et al., 2021). One notable direction is the exploration of multi-teacher distillation, where the student model is trained to learn from multiple teacher models simultaneously (Liu et al., 2020). This approach can enhance the student's performance by leveraging diverse knowledge representations, thus improving generalization capabilities across various tasks (Yuan et al., 2021). Another significant development is the integration of knowledge distillation with other model compression techniques, such as pruning and quantization (Kim, 2023). By combining these methods, researchers have been able to create even more compact models that not only maintain high levels of accuracy but also achieve lower latency and energy consumption during inference (Bao et al., 2019).
Additionally, there has been a growing interest in the application of knowledge distillation beyond traditional supervised learning settings. For instance, distillation techniques are being adapted for use in semi-supervised (Li et al., 2019; Guo et al., 2022) and unsupervised learning scenarios (Han et al., 2022), allowing student models to benefit from the knowledge encoded in teacher models trained on large, unlabeled datasets. Advancements in the design of loss functions used during the distillation process have also emerged. Researchers are investigating new ways to optimize the training objective, focusing on enhancing the alignment between the teacher's and student's outputs (Liu P. et al., 2021), which can lead to improved performance of the distilled models.
5.2 Federated and distributed learning for edge applications
Federated and distributed learning techniques enable the training and updating of LLMs across multiple edge devices without requiring raw data to be transferred to a central server. These methods are especially beneficial in privacy-sensitive applications, such as healthcare and finance, as they allow data to remain local to the device (Kairouz et al., 2021; Ye et al., 2023).
5.2.1 Federated learning
Federated learning is an innovative distributed machine learning paradigm that enables multiple edge devices to collaboratively train a shared model while keeping their data localized. In this approach, each device computes local model updates based on its unique dataset, which are subsequently aggregated to form a global model (Kairouz et al., 2021). This methodology significantly mitigates the need for centralized data storage, thereby enhancing data privacy and security, as sensitive information remains on the individual devices rather than being transmitted to a central server. Federated learning has gained considerable attention, particularly in contexts where data privacy is paramount, such as healthcare, finance, and personal mobile applications. One of the critical challenges associated with federated learning is the heterogeneity of data across devices, which often leads to non-IID (independent and identically distributed) data distributions (McMahan et al., 2017). This variability can complicate the training process, as models trained on diverse data may not converge effectively.
To address these challenges, researchers have been developing various techniques aimed at improving communication efficiency and model synchronization (Zhou et al., 2023). One prominent method is federated averaging, which optimally aggregates the model updates from different devices (Nguyen et al., 2021a). This technique helps to balance the contributions from devices with varying amounts of data, ensuring that the global model reflects the knowledge from all participating devices. Another noteworthy advancement is the concept of adaptive federated learning, which dynamically adjusts the training process based on the characteristics of the participating devices and their data (Wang S. et al., 2019). This approach can include mechanisms to prioritize updates from devices with more representative or higher-quality data, thereby enhancing the overall performance of the federated model.
Recent studies have explored the integration of federated learning with other emerging technologies, such as differential privacy (Wei et al., 2020) and secure multi-party computation (Byrd and Polychroniadou, 2021). These integrations aim to further bolster the privacy and security guarantees of federated learning systems, making them more robust against potential adversarial attacks. Additionally, advancements in communication protocols have been a focal point of research, with efforts aimed at reducing the bandwidth required for model updates (Qin et al., 2021). Techniques such as model compression and quantization are being employed to minimize the size of the updates transmitted between devices and the central server, thus improving the overall efficiency of the federated learning process.
5.2.2 Distributed learning
Distributed learning represents a significant evolution in machine learning paradigms, extending the principles of federated learning to encompass a broader range of computational resources, including both edge devices and cloud servers. This approach capitalizes on the strengths of edge devices for real-time data processing, while simultaneously leveraging the substantial computational power of cloud servers for more resource-intensive tasks. By dynamically distributing model components across various devices and servers, distributed learning effectively balances latency and computational efficiency, making it particularly suitable for applications that require rapid response times and substantial processing capabilities (Kang et al., 2017).
One notable technique is split learning, which involves partitioning a neural network into segments that can be processed on different devices. In this framework, the initial layers of the model may run on edge devices, which handle local data and perform preliminary processing. The subsequent layers are executed on cloud servers, where the more complex computations take place (Vepakomma et al., 2018). This separation not only reduces the computational burden on edge devices but also minimizes the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to the cloud, thereby enhancing privacy and reducing communication costs (Zhang et al., 2024).
Recent advancements have also focused on optimizing the training process in distributed learning scenarios. Techniques such as adaptive resource allocation (Li J.-Y. et al., 2023) and dynamic task scheduling (de Zarzà et al., 2023) are being explored to ensure that computational resources are utilized effectively. By intelligently assigning tasks based on the current workload and capabilities of each device, distributed learning systems can achieve improved performance and responsiveness. Moreover, the integration of distributed learning with edge computing and the IoT has opened new avenues for real-time data analytics and decision-making (Saha et al., 2021). For instance, in smart cities, distributed learning can enable the analysis of data generated by various sensors and devices to optimize traffic management, energy consumption, and public safety measures. This real-time processing capability is crucial for applications that require immediate insights and actions based on rapidly changing data.
5.3 Optimized architectures and frameworks for edge deployment
Optimized architectures and frameworks have been specifically developed to facilitate the deployment of LLMs on edge devices. These solutions focus on creating lightweight and efficient models that significantly reduce the computational demands traditionally associated with LLMs. By optimizing both the architecture and the underlying frameworks, these tailored systems ensure that edge devices can effectively perform a wide range of NLP tasks without sacrificing performance or functionality. This advancement not only enhances the usability of LLMs in resource-constrained environments but also broadens their applicability in scenarios requiring real-time processing and low-latency responses.
5.3.1 Lightweight model architectures
Lightweight model architectures are vital in NLP, especially for LLMs. They seek to optimize complexity and resource usage without sacrificing performance, driven by the need to deploy advanced models on resource-limited devices like smartphones and edge computing platforms.
One notable example of a lightweight architecture is ALBERT, which introduces several innovative modifications to the original BERT architecture (Lan et al., 2019). By sharing parameters across different layers, ALBERT significantly reduces memory requirements without compromising the model's ability to understand and generate human-like text. This parameter-sharing technique not only enhances efficiency but also facilitates faster training and inference times, making it a compelling choice for applications that require rapid processing. Another significant development in lightweight model architectures is MobileBERT. This model incorporates bottleneck structures and various optimizations specifically designed to enable BERT to function effectively on mobile and edge devices (Sun et al., 2020). By leveraging these architectural innovations, MobileBERT achieves a balance between model size and performance, allowing it to deliver high-quality natural language understanding capabilities in environments where computational resources are limited.
The exploration of hybrid architectures that integrate lightweight models with more complex systems has also gained traction. These hybrid approaches allow for the efficient handling of various tasks by dynamically allocating resources based on the particular demands of each task, optimizing both performance and efficiency (Sun et al., 2022; Bayoudh, 2024).
5.3.2 Edge-AI frameworks
Edge-AI frameworks have become instrumental in enabling the deployment of LLMs on edge devices, addressing the challenges posed by limited computational resources and varying hardware capabilities (Ignatov et al., 2018). Notable examples of such frameworks include TensorFlow Lite, ONNX Runtime, and PyTorch Mobile, all provide tools to enhance LLM implementation in resource-limited edge computing environments (Danopoulos et al., 2021).
TensorFlow Lite is a lightweight version of TensorFlow specifically tailored for mobile and edge applications. It provides robust support for model conversion and optimization techniques, such as quantization (Pandey and Asati, 2023). Quantization reduces the precision of model weights and activations, leading to a significant decrease in model size and an increase in inference speed without a substantial loss in accuracy. TensorFlow Lite also includes acceleration capabilities for various hardware architectures, enabling efficient execution on mobile CPUs and GPUs (Adi and Casson, 2021). This adaptability makes it particularly suitable for applications that require real-time processing, such as voice assistants and interactive chatbots.
ONNX Runtime is designed to facilitate cross-platform compatibility for optimized model execution. It supports models developed in various frameworks, allowing developers to leverage the strengths of different tools while maintaining a consistent runtime environment (Kim et al., 2022). ONNX Runtime incorporates several optimization techniques, including graph optimization and kernel fusion, which enhance the performance of models during inference (Niu et al., 2021). This framework is particularly beneficial for deploying LLMs across diverse hardware platforms, ensuring that models can be executed efficiently, whether on edge devices, cloud servers, or hybrid environments.
PyTorch Mobile has proven to be a robust solution for implementing machine learning models on edge devices. It allows developers to convert PyTorch models into a format optimized for mobile environments, ensuring that they can run efficiently on both Android and iOS platforms (Deng, 2019). PyTorch Mobile supports a variety of optimizations, including quantization and pruning, to reduce model size and improve inference speed. Additionally, it provides tools for dynamic model updates (Li M. et al., 2022), enabling applications to adapt to new data or requirements without necessitating a complete redeployment.
Recent advancements in these frameworks have further expanded their capabilities. For instance, TensorFlow Lite, ONNX Runtime, and PyTorch Mobile have integrated support for hardware-specific optimizations that take advantage of the unique features of different processors, such as ARM and NVIDIA GPUs. These optimizations allow models to run more efficiently, maximizing the performance of edge devices while minimizing energy consumption. Additionally, the emergence of new model compression methods, has been incorporated into these frameworks (Pandey and Asati, 2023). Pruning involves removing less significant weights from a model, resulting in a sparser representation that requires fewer resources for inference. Knowledge distillation enables the creation of smaller student models that can mimic the performance of larger teacher models, making it easier to deploy high-performing models on edge devices.
In summary, the advancement of model compression techniques, including pruning, quantization, and knowledge distillation, plays a pivotal role in enhancing the deployment of LLMs on edge devices. These techniques enable the reduction of model size and complexity, allowing for efficient utilization of limited computational resources inherent in edge environments. Pruning effectively removes redundant parameters from models, thereby streamlining their structure without significantly compromising performance. Quantization reduces the precision of the model weights, which not only decreases memory usage but also accelerates inference times. Knowledge distillation, on the other hand, involves training a smaller, more efficient model to replicate the behavior of a larger model, thus maintaining performance while ensuring that the model is lightweight and suitable for edge deployment.
Additionally, federated and distributed learning frameworks offer innovative solutions for training models across decentralized data sources while preserving data privacy. These approaches allow for collaborative learning without the need to transfer sensitive information to a central server, thus enhancing security and compliance with privacy regulations.
Furthermore, the development of optimized architectures and frameworks, such as lightweight model architectures and edge-AI frameworks, is essential for facilitating efficient model deployment in edge computing scenarios. Lightweight architectures are specifically designed to operate within the constraints of edge devices, ensuring that models can deliver high performance with minimal resource consumption.
By addressing these interconnected challenges and leveraging these advanced techniques, we can unlock the full potential of LLMs in edge computing, paving the way for smarter, more responsive systems. These advancements will not only meet the evolving needs of users but also ensure that privacy and security are maintained throughout the data analysis process.
6 Future directions
The field of LLMs in edge computing is dynamic and constantly evolving. To fully leverage LLMs for edge applications, researchers are focusing on several future directions, including ultra-efficient Transformer architectures, adaptive deployment models, edge-specific hardware, enhanced privacy, multi-modal LLMs, and hybrid edge-cloud systems. This section discusses these emerging areas.
6.1 Ultra-efficient transformer architectures for edge
Developing ultra-efficient Transformer architectures is vital for deploying LLMs in edge environments with limited resources. Current models, such as MobileBERT and TinyBERT, achieve significant efficiency gains by reducing the parameter count and computational complexity (Sun et al., 2020). MobileBERT, for example, is a compact, task-agnostic model that uses bottleneck structures and parameter sharing across layers, enabling high performance in edge scenarios with constrained processing capabilities. By reducing the model size and adapting it for specific tasks, MobileBERT represents a viable approach for deploying Transformers on edge devices where real-time processing is essential.
Further research into efficient model architectures, such as sparse Transformers and lightweight attention mechanisms, could yield even more optimized models for edge deployment. Sparse Transformers reduce memory and processing requirements by using selective attention, focusing computational resources only on relevant data (Jaszczur et al., 2021). Techniques like these allow models to operate with minimal resources, making them suitable for applications requiring continuous processing, such as wearable health monitors and environmental sensors. As the need for efficient edge-compatible LLMs grows, more research will likely focus on refining these architectures to achieve better performance without sacrificing accuracy.
The future of edge-based LLMs may also involve adaptive Transformers that adjust their complexity based on input characteristics. By enabling models to dynamically allocate computational resources, adaptive Transformers optimize processing power and latency, which is important for edge applications that need quick responses amid varying resource availability. These innovations are expected to enhance the accessibility and utility of LLMs across various edge computing scenarios.
6.2 Adaptive and context-aware model deployment
To enhance flexibility in edge computing, future LLMs will likely feature adaptive deployment mechanisms, allowing models to adjust to their operating context. Context-aware models can dynamically allocate resources based on device capabilities, user needs, or network conditions, optimizing processing efficiency and power consumption (Neseem et al., 2023). For instance, early-exit strategies enable models to terminate processing once they reach an acceptable confidence level, saving computational resources and reducing latency. This approach is particularly beneficial for edge environments where device capabilities vary significantly.
Another promising approach is on-device model compression, where edge devices themselves can prune or quantize models in real-time based on task requirements. This adaptability is especially useful for consumer devices such as smartphones, where power and memory limitations fluctuate depending on user activity and battery status. Research into self-optimizing models that adjust based on operational data could further improve LLM performance in edge settings, allowing devices to perform complex analytics even in low-power modes.
The continued development of context-aware models could also lead to smarter load balancing between edge and cloud resources. By dynamically offloading certain tasks to cloud resources based on network conditions and processing demands, adaptive deployment strategies can enhance responsiveness and resource management. As edge computing applications grow more complex, adaptable LLMs will become essential for delivering real-time insights without straining device resources.
6.3 Hardware-accelerated edge AI
Hardware advancements specifically designed for edge AI will play a crucial role in supporting complex LLMs on resource-constrained devices. AI accelerators like FPGAs, edge Tensor Processing Units (TPUs), Neural Network Processing Units (NPUs), and neuromorphic processors are being developed to execute LLM inference tasks with lower power consumption and higher efficiency compared to traditional CPUs (Krestinskaya et al., 2019).
Edge TPUs are tailored to perform high-speed inferences on deep learning models, offering a solution for real-time applications that require continuous processing while preserving power efficiency (Akin et al., 2022; Shuvo et al., 2022). NPUs represent another class of specialized hardware that is increasingly being utilized in edge computing. NPUs are specifically designed to accelerate deep learning tasks by optimizing the execution of neural networks (Jang et al., 2021). They offer significant advantages in terms of throughput and energy efficiency, making them particularly suitable for real-time applications in mobile devices and IoT. By enabling high-speed computations and supporting parallel processing of neural network layers, NPUs facilitate the deployment of complex LLMs directly on edge devices, thereby enhancing responsiveness and preserving user privacy (Heo et al., 2024; Xu et al., 2024).
Neuromorphic computing represents a promising direction for supporting LLMs in edge environments. Neuromorphic processors use spiking neural networks to perform computations, which can significantly reduce power usage compared to traditional deep learning hardware. This technology holds great potential for applications such as autonomous drones and mobile health monitors, where low-latency, energy-efficient processing is critical (Schuman et al., 2022).
In addition to traditional AI accelerators, the field of quantum computing is emerging as a revolutionary force that could reshape the landscape of machine learning and edge AI (Liang et al., 2023). Quantum processors utilize the principles of quantum mechanics to execute computations at unprecedented speeds, potentially enabling the processing of complex models that are currently impractical with classical hardware. While still in its nascent stages, quantum computing holds the promise of improving the training and inference capabilities of LLMs, especially for tasks that demand significant computational resources (Aizpurua et al., 2024). Researchers are investigating hybrid methods that integrate classical and quantum processing. This approach would allow edge devices to offload demanding computations to quantum processors while maintaining real-time responsiveness for less intensive tasks.
As hardware development progresses, the integration of specialized AI accelerators in edge devices will enhance the performance and efficiency of LLMs, enabling more sophisticated applications. Continued research and innovation in this area will help overcome one of the key barriers to deploying LLMs on the edge: the high computational demand of complex models.
6.4 Data privacy and federated security models
Data privacy remains a top priority as LLMs handle increasingly sensitive information in edge environments. Methods such as differential privacy, homomorphic encryption, and secure multi-party computation offer means to safeguard data while preserving its usability (Phan et al., 2017). Differential privacy ensures that individual data points are anonymized, allowing LLMs to analyze data collectively without revealing personal information. Homomorphic encryption, meanwhile, enables computations on encrypted data, which is invaluable for applications where data must remain secure throughout the processing lifecycle.
Federated learning has emerged as a powerful tool for training models on decentralized data sources while preserving user privacy (Kairouz et al., 2021). However, traditional federated learning approaches face challenges in terms of communication efficiency and handling non-IID data. Advances in hierarchical federated learning and split learning, where portions of the model are trained locally and others centrally, offer solutions to these challenges by reducing communication overhead and ensuring robust model updates across devices (Vepakomma et al., 2018). Future research will likely focus on refining these methods to make federated learning more adaptable for complex LLMs and diverse edge applications.
As privacy-preserving technologies evolve, integrating them into edge-compatible LLMs will allow for safer, more responsible deployment in sensitive domains like healthcare, finance, and smart cities. Ensuring that LLMs operate within ethical and regulatory boundaries will be essential for broadening their adoption in edge computing.
6.5 Multi-modal LLMs for edge applications
The development of multi-modal LLMs that can process diverse data types, including text, images, and audio, is a key future direction for edge applications. Multi-modal capabilities allow models to provide more comprehensive insights by analyzing various data streams simultaneously, which is particularly useful in autonomous systems and IoT applications (Radford et al., 2021). For example, a multi-modal LLM in a smart vehicle could analyze visual data from cameras and textual data from sensors to enhance object detection and navigation (Xie et al., 2022).
Edge devices equipped with multi-modal LLMs can also improve situational awareness in smart cities, processing real-time data from transport infrastructure, air quality sensors, and emergency alerts. By deploying multi-modal LLMs on the edge, systems can respond more quickly and intelligently to real-world events without relying on cloud-based processing. Such real-time, multi-modal analytics is vital for applications where latency could impact safety or operational effectiveness.
Future research in multi-modal LLMs will focus on developing lightweight architectures that integrate multiple data types without excessive computational demand. These advancements will expand the range of edge applications, enabling devices to handle complex tasks in real-time while conserving resources.
6.6 Hybrid edge-cloud architectures and collaborative intelligence
Hybrid edge-cloud architectures address the constraints of fully decentralized edge computing by optimizing resource distribution between the edge and the cloud (Kang et al., 2017). Additionally, methods such as differential privacy, homomorphic encryption, and secure multi-party computation enable data protection without sacrificing functionality. This collaborative intelligence framework allows for dynamic adjustments in workload distribution, improving performance in applications that require a mix of local and remote processing.
Collaborative edge-cloud architectures are particularly beneficial for applications such as smart cities and industrial IoT, where devices need both rapid, localized responses and access to extensive computational resources. For instance, edge devices in a smart factory might analyze sensor data to detect defects in real-time, while more complex, large-scale analytics are processed in the cloud to optimize production processes. By leveraging both edge and cloud resources, hybrid architectures can provide a flexible and scalable solution for deploying LLMs across distributed environments.
Hybrid systems will likely involve more advanced orchestration algorithms that optimize resource allocation based on real-time conditions, such as network latency, device availability, and task complexity. These systems promise to make LLMs more scalable and adaptable, facilitating a new generation of intelligent, responsive edge applications.
The future of LLMs in edge computing will be driven by advancements in model efficiency, adaptive deployment, specialized hardware, privacy, multi-modal capabilities, and hybrid architectures. Together, these innovations will expand the capabilities of edge-based LLMs, enabling them to process data in real time, protect user privacy, and respond flexibly to diverse operational requirements. The continued exploration of these areas will be crucial for realizing the full potential of LLMs in edge computing.
7 Conclusion
The convergence of LLMs and edge computing signifies a groundbreaking advancement in the field of data analysis, with the potential to redefine operational frameworks across a multitude of industries. This integration offers a transformative opportunity to enhance real-time insights, bolster data privacy, and enable autonomous decision-making, addressing critical demands in an increasingly data-driven world. By decentralizing computational capabilities and bringing them closer to the source of data generation, the deployment of LLMs on edge devices addresses key challenges such as latency, scalability, and security, while simultaneously paving the way for a new era of intelligent, localized data processing.
The deployment of LLMs on edge devices is accompanied by significant challenges. Resource constraints remain a primary obstacle, as edge devices typically have limited computational power, memory, and energy efficiency compared to centralized cloud systems. Addressing these constraints requires the development of lightweight models through techniques such as model compression, pruning, quantization, and knowledge distillation, which reduce model size while preserving performance. Additionally, ensuring data privacy and security in distributed edge environments is critical, as edge devices are often more vulnerable to targeted attacks. Robust security mechanisms, adaptive frameworks, and real-time threat mitigation strategies are essential to protect sensitive data and maintain trust. Another challenge lies in the variability and unpredictability of edge environments, which can affect the performance and reliability of deployed models. Adaptive learning techniques, continuous model updates, and mechanisms for dynamic optimization are necessary to ensure that LLMs remain effective and relevant in changing operational contexts.
The convergence of LLMs and edge computing represents not just a technological innovation but a paradigm shift in how data is processed, analyzed, and utilized across industries. By addressing the unique challenges of edge deployments and leveraging cutting-edge techniques such as model compression, federated learning, and collaborative frameworks, this integration offers transformative benefits. The ability to derive actionable insights in real time, while preserving data privacy and enabling autonomous decision-making, has far-reaching implications for a wide range of sectors.
Author contributions
XW: Conceptualization, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZX: Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft. XS: Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
XW, ZX, and XS were employed by CNOOC Safety Technology Services Co., Ltd.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abreha, H. G., Hayajneh, M., and Serhani, M. A. (2022). Federated learning in edge computing: a systematic survey. Sensors 22:450. doi: 10.3390/s22020450
Adi, S. E., and Casson, A. J. (2021). “Design and optimization of a tensorflow lite deep learning neural network for human activity recognition on a smartphone,” in 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC) (Mexico: IEEE), 7028–7031.
Aizpurua, B., Jahromi, S. S., Singh, S., and Orus, R. (2024). Quantum large language models via tensor network disentanglers. arXiv [preprint] arXiv:2410.17397. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2410.17397
Akin, B., Gupta, S., Long, Y., Spiridonov, A., Wang, Z., White, M., et al. (2022). “Searching for efficient neural architectures for on-device ml on edge TPUS,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (New Orleans, LA: IEEE), 2667–2676.
Alahi, M. E. E., Sukkuea, A., Tina, F. W., Nag, A., Kurdthongmee, W., Suwannarat, K., et al. (2023). Integration of iot-enabled technologies and artificial intelligence (ai) for smart city scenario: recent advancements and future trends. Sensors 23:5206. doi: 10.3390/s23115206
Ali, B., Gregory, M. A., and Li, S. (2021). Multi-access edge computing architecture, data security and privacy: A review. IEEE Access 9, 18706–18721. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3053233
Alwarafy, A., Al-Thelaya, K. A., Abdallah, M., Schneider, J., and Hamdi, M. (2021). A survey on security and privacy issues in edge-computing-assisted internet of things. IEEE Internet Things J. 8, 4004–4022. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3015432
Anwar, S., Hwang, K., and Sung, W. (2017). Structured pruning of deep convolutional neural networks. ACM J. Emerg. Technol. Comp. Syst. 13, 1–18. doi: 10.1145/3005348
Babu, M., Lautman, Z., Lin, X., Sobota, M. H., and Snyder, M. P. (2024). Wearable devices: implications for precision medicine and the future of health care. Annu. Rev. Med. 75, 401–415. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-052422-020437
Bao, Z., Liu, J., and Zhang, W. (2019). “Using distillation to improve network performance after pruning and quantization,” in Proceedings of the 2019 2nd International Conference on Machine Learning and Machine Intelligence, MLMI '19 (New York, NY: Association for Computing Machinery), 3–6.
Barua, A., Dong, C., Al-Turjman, F., and Yang, X. (2020). Edge computing-based localization technique to detecting behavior of dementia. IEEE Access 8, 82108–82119. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2988935
Bayoudh, K. (2024). A survey of multimodal hybrid deep learning for computer vision: Architectures, applications, trends, and challenges. Inform. Fusion 105:102217. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2023.102217
Boumendil, A., Bechkit, W., and Benatchba, K. (2025). On-device deep learning: survey on techniques improving energy efficiency of DNNS. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 36, 7806–7821. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2024.3430028
Brown, T., Mann, B., Ryder, N., Subbiah, M., Kaplan, J., Dhariwal, P., et al. (2020). Language models are few-shot learners. arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.14165. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2005.14165
Byrd, D., and Polychroniadou, A. (2021). “Differentially private secure multi-party computation for federated learning in financial applications,” in Proceedings of the First ACM International Conference on AI in Finance, ICAIF '20 (New York, NY: Association for Computing Machinery).
Cao, K., Liu, Y., Meng, G., and Sun, Q. (2020). An overview on edge computing research. IEEE Access 8, 85714–85728. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2991734
Chen, K., Li, T., Kim, H.-S., Culler, D. E., and Katz, R. H. (2018). “Marvel: Enabling mobile augmented reality with low energy and low latency,” in Proceedings of the 16th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, SenSys '18 (New York, NY: Association for Computing Machinery).
Chen, W., Qiu, H., Zhuang, J., Zhang, C., Hu, Y., Lu, Q., et al. (2021a). Quantization of deep neural networks for accurate edge computing. ACM J. Emerg. Technol. Comp. Syst. (JETC) 17:4. doi: 10.1145/3451211
Chen, W., Wang, P., and Cheng, J. (2021b). “Towards mixed-precision quantization of neural networks via constrained optimization,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (Montreal, QC: IEEE), 5350–5359. doi: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00530
Cheng, L., Gu, Y., Liu, Q., Yang, L., Liu, C., and Wang, Y. (2024). Advancements in accelerating deep neural network inference on aiot devices: A survey. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Comput. 9, 830–847. doi: 10.1109/TSUSC.2024.3353176
Chi, J., Zhou, X., Xiao, F., Lim, Y., and Qiu, T. (2024). Task offloading via prioritized experience-based double dueling dqn in edge-assisted IIoT. IEEE Trans. Mobile Comp. 23, 14575–14591. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2024.3452502
Chowdhury, S. S., Garg, I., and Roy, K. (2021). “Spatio-temporal pruning and quantization for low-latency spiking neural networks,” in 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) (Shenzhen: IEEE), 1–9.
Cicconetti, C., Conti, M., and Passarella, A. (2021). A decentralized framework for serverless edge computing in the internet of things. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Managem.18, 2166–2180. doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2020.3023305
Danopoulos, D., Kachris, C., and Soudris, D. (2021). Utilizing cloud FPGAs towards the open neural network standard. Sustain. Comp.: Inform. Syst. 30:100520. doi: 10.1016/j.suscom.2021.100520
de Zarzà, I., de Curtò, J., Roig, G., and Calafate, C. T. (2023). LLM Multimodal Traffic Accident Forecasting. Sensors 23:9225. doi: 10.3390/s23229225
Deng, S., Zhao, H., Fang, W., Yin, J., Dustdar, S., and Zomaya, A. Y. (2020). Edge intelligence: The confluence of edge computing and artificial intelligence. IEEE Intern. Things J. 7, 7457–7469. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2984887
Deng, Y. (2019). “Deep learning on mobile devices: a review,” in Mobile Multimedia/Image Processing, Security, and Applications 2019, eds. S. S. Agaian, V. K. Asari, and S. P. DelMarco (New York: SPIE).
Devlin, J., Chang, M.-W., Lee, K., and Toutanova, K. (2019). “BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding,” in Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (New York: Association for Computational Linguistics), 4171–4186.
Dias, D., and Paulo Silva Cunha, J. (2018). Wearable health devices—vital sign monitoring, systems and technologies. Sensors 18:2414. doi: 10.3390/s18082414
Ding, Y., Wu, Y., Huang, C., Tang, S., Wu, F., Yang, Y., et al. (2022). Nap: Neural architecture search with pruning. Neurocomputing 477, 85–95. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.12.002
Du, M., Wang, K., Xia, Z., and Zhang, Y. (2020). Differential privacy preserving of training model in wireless big data with edge computing. IEEE Trans. Big Data 6, 283–295. doi: 10.1109/TBDATA.2018.2829886
Esteva, A., Robicquet, A., Ramsundar, B., Kuleshov, V., DePristo, M., Chou, K., et al. (2019). A guide to deep learning in healthcare. Nat. Med. 25, 24–29. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0316-z
Gale, T., Elsen, E., and Hooker, S. (2019). The state of sparsity in deep neural networks. arXiv [preprint] arXiv:1902.09574. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1902.09574
Gangadhar, C., Moutteyan, M., Vallabhuni, R. R., Vijayan, V. P., Sharma, N., and Theivadas, R. (2023). Analysis of optimization algorithms for stability and convergence for natural language processing using deep learning algorithms. Measurement: Sens. 27:100784. doi: 10.1016/j.measen.2023.100784
García-Méndez, S., and de Arriba-Pérez, F. (2024). Large language models and healthcare alliance: potential and challenges of two representative use cases. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 52, 1928–1931. doi: 10.1007/s10439-024-03454-8
Gou, J., Yu, B., Maybank, S. J., and Tao, D. (2021). Knowledge distillation: a survey. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 129, 1789–1819. doi: 10.1007/s11263-021-01453-z
Gu, A., Gulcehre, C., Paine, T., Hoffman, M., and Pascanu, R. (2020). “Improving the gating mechanism of recurrent neural networks,” in Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning (New York: Proceedings of Machine Learning Research), 3800–3809.
Gu, A., Johnson, I., Goel, K., Saab, K., Dao, T., Rudra, A., et al. (2021). “Combining recurrent, convolutional, and continuous-time models with linear state space layers,” in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, eds. M. Ranzato, A. Beygelzimer, Y. Dauphin, P. Liang and J. W. Vaughan (New York: Curran Associates, Inc), 572–585.
Guo, Q., Mu, Y., Chen, J., Wang, T., Yu, Y., and Luo, P. (2022). “Scale-equivalent distillation for semi-supervised object detection,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (New Orleans, LA: IEEE), 14522–14531.
Han, S., Mao, H., and Dally, W. J. (2015). Deep compression: compressing deep neural networks with pruning, trained quantization, and huffman coding. arXiv [preprint] arXiv:1510.00149. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1510.00149
Han, S., Park, S., Wu, F., Kim, S., Wu, C., Xie, X., et al. (2022). “FEDX: Unsupervised federated learning with cross knowledge distillation,” in Computer Vision-ECCV 2022, S. Avidan, G. Brostow, M. Cissé, G. Farinella, and T. Hassner (Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland), 691–707.
Heo, G., Lee, S., Cho, J., Choi, H., Lee, S., Ham, H., et al. (2024). “NeuPIMS: NPU-PIM heterogeneous acceleration for batched llm inferencing,” in Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Architectural Support for Programming Languages and Operating Systems (New York: ACM), 722–737.
Hu, J., Lin, P., Zhang, H., Lan, Z., Chen, W., Xie, K., et al. (2023). A dynamic pruning method on multiple sparse structures in deep neural networks. IEEE Access 11, 38448–38457. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3267469
Iftikhar, S., Gill, S. S., Song, C., Xu, M., Aslanpour, M. S., Toosi, A. N., et al. (2023). Ai-based fog and edge computing: a systematic review, taxonomy and future directions. Intern. Things 21:100674. doi: 10.1016/j.iot.2022.100674
Ignatov, A., Timofte, R., and Van Gool, L. (2018). “AI benchmark: running deep neural networks on android smartphones,” in Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Workshops (Munich). doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-11021-5_19
Iqbal, F., Altaf, A., Waris, Z., Aray, D. G., Flores, M. A. L., Díez, I., et al. (2023). Blockchain-modeled edge-computing-based smart home monitoring system with energy usage prediction. Sensors 23:5263. doi: 10.3390/s23115263
Jacob, B., Kligys, S., Chen, B., Zhu, M., Tang, M., Howard, A., et al. (2018). “Quantization and training of neural networks for efficient integer-arithmetic-only inference,” in Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (Salt Lake City, UT: IEEE), 2704–2713. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00286
Jan, M. A., He, X., Song, H., and Babar, M. (2021). Machine learning and big data analytics for iot-enabled smart cities. Mobile Netw. Appl. 26, 156–158. doi: 10.1007/s11036-020-01702-4
Jang, J.-W., Lee, S., Kim, D., Park, H., Ardestani, A. S., Choi, Y., et al. (2021). “Sparsity-aware and re-configurable NPU architecture for samsung flagship mobile SoC,” in 2021 ACM/IEEE 48th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA) (Valencia: IEEE), 15–28.
Jaszczur, S., Chowdhery, A., Mohiuddin, A., Kaiser, L., Gajewski, W., Michalewski, H., et al. (2021). Sparse is enough in scaling transformers. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 9895–9907. Available online at: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2021/hash/51f15efdd170e6043fa02a74882f0470-Abstract.html
Ji, J., Shu, Z., Li, H., Lai, K. X., Lu, M., Jiang, G., et al. (2024). Edge-computing-based knowledge distillation and multitask learning for partial discharge recognition. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 73, 1–11. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2024.3351239
Jo, E., Epstein, D. A., Jung, H., and Kim, Y.-H. (2023). “Understanding the benefits and challenges of deploying conversational ai leveraging large language models for public health intervention,” in Proceedings of the 2023 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (New York, NY: Association for Computing Machinery).
Kairouz, P., and McMahan, H. B. (2021). Advances and open problems in federated learning. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 14, 1–210. doi: 10.1561/9781680837896
Kang, Y., Hauswald, J., Gao, C., Rovinski, A., Mudge, T. N., Mars, J., et al. (2017). “Neurosurgeon: Collaborative intelligence between the cloud and mobile edge,” in ACM SIGARCH Computer Architecture News (New York: ACM), 615–629.
Ke, Z., Zhou, X., Jiang, D., Yan, H., and Qiu, T. (2023). “CollabVr: Reprojection-based edge-client collaborative rendering for real-time high-quality mobile virtual reality,” in 2023 IEEE Real-Time Systems Symposium (RTSS) (Taipei: IEEE), 304–316.
Khan, L. U., Yaqoob, I., Tran, N. H., Kazmi, S. M. A., Dang, T. N., and Hong, C. S. (2020). Edge-computing-enabled smart cities: a comprehensive survey. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 7, 10200–10232. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2987070
Khan, W. Z., Ahmed, E., Hakak, S., Yaqoob, I., and Ahmed, A. (2019). Edge computing: A survey. Future Generation Computer Systems 97:219–235. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2019.02.050
Kim, J. (2023). Quantization robust pruning with knowledge distillation. IEEE Access 11, 26419–26426. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3257864
Kim, J., Lee, J. H., Kim, S., Park, J., Yoo, K. M., Kwon, S. J., et al. (2023). “Memory-efficient fine-tuning of compressed large language models via sub-4-bit integer quantization,” in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, eds. A. Oh, T. Naumann, A. Globerson, K. Saenko, M. Hardt, and S. Levine (New York: Curran Associates, Inc), 36187–36207.
Kim, S. Y., Lee, J., Kim, C. H., Lee, W. J., and Kim, S. W. (2022). “Extending the onnx runtime framework for the processing-in-memory execution,” in 2022 International Conference on Electronics, Information, and Communication (ICEIC) (Jeju: IEEE), 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ICEIC54506.2022.9748444
Kim, Y., Xu, X., McDuff, D., Breazeal, C., and Park, H. W. (2024). Health-llm: Large language models for health prediction via wearable sensor data. arXiv [preprint] arXiv:2401.06866.
Köhl, M. A., and Hermanns, H. (2023). Model-based diagnosis of real-time systems: Robustness against varying latency, clock drift, and out-of-order observations. ACM Trans. Embed. Comput. Syst. 22:1–48. doi: 10.1145/3597209
Kong, L., Tan, J., Huang, J., Chen, G., Wang, S., Jin, X., et al. (2022). Edge-computing-driven internet of things: A survey. ACM Computing Surveys 55(8):1–41. doi: 10.1145/3555308
Krestinskaya, O., James, A. P., and Chua, L. (2019). Neuromemristive circuits for edge computing: a review. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 31, 4–23. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2899262
Lan, Z., Chen, M., Goodman, S., Gimpel, K., Sharma, P., and Soricut, R. (2019). “Albert: a lite bert for self-supervised learning of language representations,” in Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) (Addis Ababa: openreview.net). Available online at: https://openreview.net/forum?id=H1eA7AEtvS
Li, B., Sainath, T. N., Pang, R., and Wu, Z. (2019). “Semi-supervised training for end-to-end models via weak distillation,” in ICASSP 2019 - 2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (Brighton: IEEE), 837–2841.
Li, D., Lai, J., Wang, R., Li, X., Vijayakumar, P., Gupta, B. B., et al. (2023). Ubiquitous intelligent federated learning privacy-preserving scheme under edge computing. Future Generat. Comp. Syst. 144, 205–218. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2023.03.010
Li, J., Liang, W., Xu, W., Xu, Z., Li, Y., and Jia, X. (2023). Service home identification of multiple-source iot applications in edge computing. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comp. 16, 1417–1430. doi: 10.1109/TSC.2022.3176576
Li, J.-Y., Du, K.-J., Zhan, Z.-H., Wang, H., and Zhang, J. (2023). Distributed differential evolution with adaptive resource allocation. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 53(5):2791–2804. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2022.3153964
Li, M., Zhao, M., Luo, T., Yang, Y., and Peng, S.-L. (2022). A compact parallel pruning scheme for deep learning model and its mobile instrument deployment. Mathematics 10:2126. doi: 10.3390/math10122126
Li, X., Liu, H., Wang, W., Zheng, Y., Lv, H., and Lv, Z. (2022). Big data analysis of the internet of things in the digital twins of smart city based on deep learning. Future Generat. Comp. Syst. 128, 167–177. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2021.10.006
Liang, T., Glossner, J., Wang, L., Shi, S., and Zhang, X. (2021). Pruning and quantization for deep neural network acceleration: a survey. Neurocomputing 461, 370–403. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.07.045
Liang, Z., Cheng, J., Yang, R., Ren, H., Song, Z., Wu, D., et al. (2023). Unleashing the potential of llms for quantum computing: A study in quantum architecture design. arXiv [preprint] arXiv:2307.08191. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2307.08191
Lin, S.-C., Zhang, Y., Hsu, C.-H., Skach, M., Haque, M. E., Tang, L., et al. (2018). The architectural implications of autonomous driving: Constraints and acceleration. SIGPLAN Not., 53, 751–766. doi: 10.1145/3296957.3173191
Liu, G., Wang, C., Ma, X., and Yang, Y. (2021). Keep your data locally: Federated-learning-based data privacy preservation in edge computing. IEEE Netw. 35, 60–66. doi: 10.1109/MNET.011.2000215
Liu, P., Zhang, Z., Meng, Z., and Gao, N. (2021). Monocular depth estimation with joint attention feature distillation and wavelet-based loss function. Sensors 21:54. doi: 10.3390/s21010054
Liu, Q., Gu, J., Yang, J., Li, Y., Sha, D., Xu, M., et al. (2021). Cloud, Edge, and Mobile Computing for Smart Cities. Singapore: Springer Singapore, 757–795.
Liu, X., Ye, M., Zhou, D., and Liu, Q. (2021). Post-training quantization with multiple points: Mixed precision without mixed precision. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intellig. 35, 8697–8705. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v35i10.17054
Liu, Y., Zhang, W., and Wang, J. (2020). Adaptive multi-teacher multi-level knowledge distillation. Neurocomputing 415, 106–113. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.07.048
Liu, Z., Xu, J., Peng, X., and Xiong, R. (2018). “Frequency-domain dynamic pruning for convolutional neural networks,” in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, eds. S. Bengio, H. Wallach, H. Larochelle, K. Grauman, N. Cesa-Bianchi, and R. Garnett (New York: Curran Associates, Inc).
Lu, S., Lu, J., An, K., Wang, X., and He, Q. (2023). Edge computing on iot for machine signal processing and fault diagnosis: a review. IEEE Intern. Things J. 10, 11093–11116. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3239944
Lv, Z., Chen, D., Lou, R., and Wang, Q. (2021). Retracted: Intelligent edge computing based on machine learning for smart city. Future Generat. Comp. Syst. 115, 90–99. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2020.08.037
Matsubara, Y., Callegaro, D., Baidya, S., Levorato, M., and Singh, S. (2020). Head network distillation: splitting distilled deep neural networks for resource-constrained edge computing systems. IEEE Access 8, 212177–212193. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3039714
McMahan, H. B., Moore, E., Ramage, D., Hampson, S., and Aguera y Arcas, B. (2017). “Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data,” in Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS) (New York: PMLR), 1273–1282.
Memari, P., Mohammadi, S. S., Jolai, F., and Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R. (2022). A latency-aware task scheduling algorithm for allocating virtual machines in a cost-effective and time-sensitive fog-cloud architecture. J. Supercomput. 78, 93–122. doi: 10.1007/s11227-021-03868-4
Nagel, M., Fournarakis, M., Bondarenko, Y., and Blankevoort, T. (2022). “Overcoming oscillations in quantization-aware training,” in Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning, eds. K. Chaudhuri, S. Jegelka, L. Song, C. Szepesvari, G. Niu, and S. Sabato (New York: PMLR), 16318–16330.
Nain, G., Pattanaik, K., and Sharma, G. (2022). Towards edge computing in intelligent manufacturing: Past, present and future. J. Manufact. Syst. 62, 588–611. doi: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2022.01.010
Neseem, M., Agiza, A., and Reda, S. (2023). “ADAMTL: Adaptive input-dependent inference for efficient multi-task learning,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (Vancouver, BC: IEEE), 4730–4739.
Nguyen, D. C., Ding, M., Pathirana, P. N., Seneviratne, A., Li, J., and Poor, H. V. (2021a). Federated learning for internet of things: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 23, 1622–1658. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3075439
Nguyen, D. C., Ding, M., Pham, Q.-V., Pathirana, P. N., Le, L. B., Seneviratne, A., et al. (2021b). Federated learning meets blockchain in edge computing: Opportunities and challenges. IEEE Intern, Things J. 8, 12806–12825. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3072611
Niu, W., Guan, J., Wang, Y., Agrawal, G., and Ren, B. (2021). “DNNFusion: accelerating deep neural networks execution with advanced operator fusion,” in Proceedings of the 42nd ACM SIGPLAN International Conference on Programming Language Design and Implementation, PLDI 2021 (New York, NY: Association for Computing Machinery), 883–898.
Pandey, J., and Asati, A. R. (2023). Lightweight convolutional neural network architecture implementation using TensorFlow lite. Int. J. Inform. Technol. 15, 2489–2498. doi: 10.1007/s41870-023-01320-9
Pang, G., Shen, C., Cao, L., and Hengel, A. V. D. (2021). Deep learning for anomaly detection: A review. ACM Comp. Surv. (CSUR) 54, 1–38. doi: 10.1145/3439950
Pelle, I., Czentye, J., Dóka, J., Kern, A., Gerő, B. P., and Sonkoly, B. (2021). Operating latency sensitive applications on public serverless edge cloud platforms. IEEE Intern. Things J. 8, 7954–7972. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3042428
Phan, N., Wang, Y., Wu, X., and Dou, D. (2017). “Differential privacy preservation for deep auto-encoders: An application of human behavior prediction,” in Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (Philadelphia: AAAI), 1309–1316.
Qin, Z., Li, G. Y., and Ye, H. (2021). Federated learning and wireless communications. IEEE Wireless Commun. 28, 134–140. doi: 10.1109/MWC.011.2000501
Qiu, T., Chi, J., Zhou, X., Ning, Z., Atiquzzaman, M., and Wu, D. O. (2020). Edge computing in industrial internet of things: Architecture, advances and challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 22, 2462–2488. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2020.3009103
Radford, A., Kim, J. W., Hallacy, C., Ramesh, A., Goh, G., Agarwal, S., et al. (2021). Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. Proc. Int. Conf. Mach. Learn. (ICML) 38, 8748–8763. Available online at: https://proceedings.mlr.press/v139/radford21a
Raffel, C., Shazeer, N., Roberts, A., Lee, K., Narang, S., Matena, M., et al. (2020). Exploring the limits of transfer learning with a unified text-to-text transformer. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 21, 1–67. Available online at: http://jmlr.org/papers/v21/20-074.html
Ren, J., He, Y., Huang, G., Yu, G., Cai, Y., and Zhang, Z. (2019b). An edge-computing based architecture for mobile augmented reality. IEEE Network 33, 162–169. doi: 10.1109/MNET.2018.1800132
Ren, J., Yu, G., He, Y., and Li, G. Y. (2019a). Collaborative cloud and edge computing for latency minimization. IEEE Trans. Vehicular Technol. 68, 5031–5044. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2904244
Ribeiro, A. H., Tiels, K., Aguirre, L. A., and Schön, T. (2020). “Beyond exploding and vanishing gradients: analysing rnn training using attractors and smoothness,” in Proceedings of the Twenty Third International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, eds. S. Chiappa, and R. Calandra (New York: Proceedings of Machine Learning Research).
Roszyk, K., Nowicki, M. R., and Skrzypczyńki, P. (2022). Adopting the yolov4 architecture for low-latency multispectral pedestrian detection in autonomous driving. Sensors 22:1082. doi: 10.3390/s22031082
Saha, R., Chakraborty, A., Misra, S., Das, S. K., and Chatterjee, C. (2021). Dlsense: Distributed learning-based smart virtual sensing for precision agriculture. IEEE Sens. J. 21, 17556–17563. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3048593
Sakr, C., Dai, S., Venkatesan, R., Zimmer, B., Dally, W., and Khailany, B. (2022). “Optimal clipping and magnitude-aware differentiation for improved quantization-aware training,” in Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning, eds. K. Chaudhuri, S. Jegelka, L. Song, C. Szepesvari, G. Niu, and S. Sabato (New York: PMLR), 19123–19138.
Sandhu, A. K. (2022). Big data with cloud computing: Discussions and challenges. Big Data Mining Analyt. 5, 32–40. doi: 10.26599/BDMA.2021.9020016
Sanh, V., Debut, L., Chaumond, J., and Wolf, T. (2019). Distilbert, a distilled version of bert: Smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter. arXiv [preprint] arXiv:1910.01108. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1910.01108
Savadi Hosseini, M., and Ghaderi, F. (2020). A hybrid deep learning architecture using 3d cnns and grus for human action recognition. Int. J. Eng. 33, 959–965. doi: 10.5829/ije.2020.33.05b.29
Schuman, C. D., Kulkarni, S. R., Parsa, M., Mitchell, J. P., Date, P., and Kay, B. (2022). Opportunities for neuromorphic computing algorithms and applications. Nat, Comp. Sci. 2, 10–19. doi: 10.1038/s43588-021-00184-y
Shi, W., Cao, J., Zhang, Q., Li, Y., and Xu, L. (2016). Edge computing: vision and challenges. IEEE Intern. Things J. 3, 637–646. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2016.2579198
Shiranthika, C., Saeedi, P., and Bajić, I. V. (2023). Decentralized learning in healthcare: A review of emerging techniques. IEEE Access 11, 54188–54209. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3281832
Shuvo, M. M. H., Islam, S. K., Cheng, J., and Morshed, B. I. (2022). Efficient acceleration of deep learning inference on resource-constrained edge devices: a review. Proc. IEEE 111, 42–91. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2022.3226481
Siriwardhana, Y., Porambage, P., Liyanage, M., and Ylianttila, M. (2021). A survey on mobile augmented reality with 5G mobile edge computing: architectures, applications, and technical aspects. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 23, 1160–1192. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3061981
Strubell, E., Ganesh, A., and McCallum, A. (2020). Energy and policy considerations for modern deep learning research. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intellig. 34, 13693–13696. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v34i09.7123
Sun, G., Chen, D., Zhu, G., and Li, Q. (2022). Lightweight hybrid materials and structures for energy absorption: a state-of-the-art review and outlook. Thin-Walled Struct. 172:108760. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2021.108760
Sun, L., and Ansari, N. (2019). Edgeiot: Mobile edge computing for the internet of things. IEEE Commun. Magaz. 54, 22–29. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2016.1600492CM
Sun, Z., Yu, H., Song, X., Liu, R., Yang, Y., and Zhou, D. (2020). Mobilebert: A compact task-agnostic bert for resource-limited devices. arXiv [preprint] arXiv:2004.02984. doi: 10.18653/v1/2020.acl-main.195
Syu, J.-H., Lin, J. C.-W., Srivastava, G., and Yu, K. (2023). A comprehensive survey on artificial intelligence empowered edge computing on consumer electronics. IEEE Trans.Consumer Electron. 69, 1023–1034. doi: 10.1109/TCE.2023.3318150
Teerapittayanon, S., McDanel, B., and Kung, H.-T. (2016). “BranchyNET: Fast inference via early exiting from deep neural networks,” in Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR) (Cancun: IEEE), 2464–2469.
Vahidian, S., Morafah, M., and Lin, B. (2021). “Personalized federated learning by structured and unstructured pruning under data heterogeneity,” in 2021 IEEE 41st International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems Workshops (ICDCSW) (Washington, DC: IEEE), 27–34. doi: 10.1109/ICDCSW53096.2021.00012
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A. N., et al. (2017). “Attention is all you need,” in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (Long Beach, CA: Curran Associates, Inc.), 5998–6008.
Vepakomma, P., Gupta, O., Swedish, A., and Raskar, R. (2018). Split learning for health: Distributed deep learning without sharing raw patient data. arXiv [Preprint]. arXiv:1812.00564. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1812.00564
Wang, H., Lei, Z., Zhang, X., Zhou, B., and Peng, J. (2019). A review of deep learning for renewable energy forecasting. Energy Convers. Managem. 198:111799. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2019.111799
Wang, S., Tuor, T., Salonidis, T., Leung, K. K., Makaya, C., He, T., et al. (2019). Adaptive federated learning in resource constrained edge computing systems. IEEE J. Select. Areas Commun. 37, 1205–1221. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2019.2904348
Wang, Y., Yu, Z., Wu, J., Wang, C., Zhou, Q., and Hu, J. (2024). Adaptive knowledge distillation-based lightweight intelligent fault diagnosis framework in iot edge computing. IEEE Intern.Things J. 11, 23156–23169. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3387328
Wang, Z., Li, C., and Wang, X. (2021). “Convolutional neural network pruning with structural redundancy reduction,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (Nashville, TN: IEEE), 14913–14922.
Wei, K., Li, J., Ding, M., Ma, C., Yang, H. H., Farokhi, F., et al. (2020). Federated learning with differential privacy: Algorithms and performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Inform. Forens. Security 15, 3454–3469. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2020.2988575
Wu, Z., Nagarajan, T., Kumar, A., Davis, L. S., Hariharan, B., and Farhadi, A. (2020). “Blockdrop: Dynamic inference paths in residual networks,” in Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (Salt Lake City: IEEE), 8817–8826.
Xia, Q., Ye, W., Tao, Z., Wu, J., and Li, Q. (2021). A survey of federated learning for edge computing: Research problems and solutions. High-Confidence Comp. 1:100008. doi: 10.1016/j.hcc.2021.100008
Xie, Q., Zhou, X., Qiu, T., Zhang, Q., and Qu, W. (2022). Soft actor–critic-based multilevel cooperative perception for connected autonomous vehicles. IEEE Intern. Things J. 9, 21370–21381. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3179739
Xu, D., Zhang, H., Yang, L., Liu, R., Xu, M., and Liu, X. (2024). “WIP: Efficient LLM prefilling with mobile NPU,” in Proceedings of the Workshop on Edge and Mobile Foundation Models, 33–35.
Xu, K., Wang, Z., Chen, C., Geng, X., Lin, J., Yang, X., et al. (2025). “LPVIT: Low-power semi-structured pruning for vision transformers,” in eds. Computer Vision-ECCV 2024, A. Leonardis, E. Ricci, S. Roth, O. Russakovsky, T. Sattler, and G. Varol (Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland), 269–287.
Yang, J., Jin, H., Tang, R., Han, X., Feng, Q., Jiang, H., et al. (2024). Harnessing the power of llms in practice: a survey on chatgpt and beyond. ACM Trans. Knowl. Discov. Data 18, 1–32. doi: 10.1145/3649506
Yang, Y., Li, M., Huang, S., Lu, H., Tu, W., and Wan, W. (2023). “Multi-scale spatial-spectral attention guided fusion network for pansharpening,” in Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, MM '23 (New York, NY: Association for Computing Machinery), 3346–3354.
Yao, S., and Wan, X. (2020). “Multimodal transformer for multimodal machine translation,” in Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, eds. D. Jurafsky, J. Chai, N. Schluter, and J. Tetreault (New York: Association for Computational Linguistics), 4346–4350.
Ye, M., Fang, X., Du, B., Yuen, P. C., and Tao, D. (2023). Heterogeneous federated learning: State-of-the-art and research challenges. ACM Com. Surv. 56, 1–44. doi: 10.1145/3625558
Yeom, S.-K., Seegerer, P., Lapuschkin, S., Binder, A., Wiedemann, S., Müller, K.-R., et al. (2021). Pruning by explaining: A novel criterion for deep neural network pruning. Pattern Recognit. 115:107899. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2021.107899
Yu, B., Zhang, X., You, I., and Khan, U. S. (2021). Efficient computation offloading in edge computing enabled smart home. IEEE Access 9, 48631–48639. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3066789
Yu, W., Liang, F., He, X., Hatcher, W. G., Lu, C., Lin, J., et al. (2018). A survey on the edge computing for the internet of things. IEEE Access 6, 6900–6919. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2778504
Yuan, F., Shou, L., Pei, J., Lin, W., Gong, M., Fu, Y., et al. (2021). Reinforced multi-teacher selection for knowledge distillation. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intellig. 35, 14284–14291. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v35i16.17680
Zeng, Z., Liu, C., Tang, Z., Li, K., and Li, K. (2022). Acctfm: An effective intra-layer model parallelization strategy for training large-scale transformer-based models. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 33, 4326–4338. doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2022.3187815
Zhang, C., Zhang, W., Wu, Q., Fan, P., Fan, Q., Wang, J., et al. (2025). Distributed deep reinforcement learning based gradient quantization for federated learning enabled vehicle edge computing. IEEE Intern. Things J. 12, 4899–4913. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3447036
Zhang, C., Zheng, R., Cui, Y., Li, C., and Wu, J. (2020). “Delay-sensitive computation partitioning for mobile augmented reality applications,” in 2020 IEEE/ACM 28th International Symposium on Quality of Service (IWQoS) (Hang Zhou: IEEE), 1–10.
Zhang, J., Chen, B., Zhao, Y., Cheng, X., and Hu, F. (2018). Data security and privacy-preserving in edge computing paradigm: Survey and open issues. IEEE Access 6, 18209–18237. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2820162
Zhang, S., Zhou, X., Qiu, T., and Wu, D. O. (2024). Quantum-inspired robust networking model with multiverse co-evolution for scale-free iot. IEEE Trans. Mobile Comp. 23, 14085–14098. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2024.3439511
Zhang, W., Han, B., and Hui, P. (2018). “Jaguar: Low latency mobile augmented reality with flexible tracking,” in Proceedings of the 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, MM '18 (New York, NY: Association for Computing Machinery), 355–363.
Zhou, B., Yang, G., Shi, Z., and Ma, S. (2022). Natural language processing for smart healthcare. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 17, 4–18. doi: 10.1109/RBME.2022.3210270
Zhou, H., Yang, G., Dai, H., and Liu, G. (2022a). Pflf: Privacy-preserving federated learning framework for edge computing. IEEE Trans. Inform. Forens. Secur. 17, 1905–1918. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2022.3174394
Zhou, H., Yang, G., Huang, Y., Dai, H., and Xiang, Y. (2022b). Privacy-preserving and verifiable federated learning framework for edge computing. IEEE Trans. Inform. Forens. Secur. 18, 565–580. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2022.3227435
Zhou, X., Ge, S., Liu, P., and Qiu, T. (2024a). Dag-based dependent tasks offloading in mec-enabled iot with soft cooperation. IEEE Trans. Mobile Comp. 23, 6908–6920. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2023.3328333
Zhou, X., Ge, S., Qiu, T., Li, K., and Atiquzzaman, M. (2023). Energy-efficient service migration for multi-user heterogeneous dense cellular networks. IEEE Trans. Mobile Comp. 22, 890–905. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2021.3087198
Zhou, X., Ke, Z., and Qiu, T. (2024b). Recommendation-driven multi-cell cooperative caching: A multi-agent reinforcement learning approach. IEEE Trans. Mobile Comp. 23, 4764–4776. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2023.3297213
Zhou, Y., Moosavi-Dezfooli, S.-M., Cheung, N.-M., and Frossard, P. (2018). “Adaptive quantization for deep neural network,” in Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (Washington, DC: AAAI), 32.
Keywords: edge computing, large language models, intelligent data analysis, resource-constrained devices, edge-friendly architectures
Citation: Wang X, Xu Z and Sui X (2025) Intelligent data analysis in edge computing with large language models: applications, challenges, and future directions. Front. Comput. Sci. 7:1538277. doi: 10.3389/fcomp.2025.1538277
Received: 02 December 2024; Accepted: 17 April 2025;
Published: 14 May 2025.
Edited by:
Xiaotong Wu, Nanjing Normal University, ChinaReviewed by:
Chaokun Zhang, Tianjin University, ChinaRajeev Ratna Vallabhuni, Bayview Asset Management, LLC, United States
Xiaoding Wang, Fujian Normal University, China
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Xu and Sui. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xuanzheng Wang, d2FuZ3h6aDIwQGNub29jLmNvbS5jbg==
 Xuanzheng Wang*
Xuanzheng Wang* Zhipeng Xu
Zhipeng Xu