- 1Riphah Institute of Languages and Literature, Riphah International University, Lahore, Pakistan
- 2Department of Humanities, COMSATS University Islamabad, Lahore Campus, Lahore, Pakistan
- 3Department of Language and Literature, The University of Lahore, Lahore, Pakistan
- 4Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Near East University, Nicosia, Cyprus
This study investigates the dynamics of user feedback for two prominent mobile language learning applications, Babbel and Duolingo, through the lenses of Dynamic Systems Theory (DST) and Sociocultural Theory (SCT). By employing a mixed-methods approach that integrates sentiment analysis, network analysis, and linguistic features analysis, a dataset of 190 user reviews for each application collected from app review platforms has been analysed. The research reveals distinct sentiment clusters, network metrics, and user engagement patterns, highlighting how sociocultural factors and user experiences shape perceptions of app functionality and effectiveness. Findings indicate that Duolingo users predominantly appreciate the gamified elements and simplicity of lessons, while Babbel users emphasize structured methodologies and cultural context. The application of network analysis using Gephi software elucidates the interconnectedness of user sentiments, identifying influential nodes and feedback trends that inform app design and development. This study contributes to the field of applied linguistics by demonstrating the potential of user feedback to enhance the usability and pedagogical efficacy of language learning technologies, ultimately advocating for a more learner-centered approach in the design of educational tools. The insights garnered from this research not only bridge the gap between linguistic theory and technological application but also underscore the importance of integrating user perspectives in the continuous evolution of language learning platforms.
Introduction
The concept of Mobile Language Learning Applications (MLLAs) is the latest innovation in language education that has greater relevance in applied linguistics where the accompaniments of theory play a practical role in addressing manifold issues in the context of the real world. The embedding of these rich applications into language learning recognizes the differences between learners and the learning environment, thus providing support for different types of learning profiles. These tools enrich learning not only in individual and group work in the classroom but also outside typical learning arrangements. Indeed, as Nami (2019) explains, language learning applications are a significant part of educational applications since the demand for individualized and accessible language learning is obvious. Yildiz (2020) also supports the researcher’s claim by pointing out that educational applications remain among the most popular in terms of download, meaning that these applications have an essential impact on the transformation of modern language education. As such, the MLLAs are well positioned to become pivotal in improving language learning within and out of the classroom, thus fitting neatly into the applied linguistics field of the optimization of language acquisition processes (Deroey, 2007).
An advantage of MLLAs is that they may be integrated into language practice and interaction at any time and in any place which is true learner independence, a principle which is salient in mostly applied linguistics. According to Loewen et al. (2019), it helps exploit the versatility that ensures that learners are always in contact with language constantly practising what they are taught in class, independently. The construction of these apps in an asynchronous pattern enables learners to incorporate the use of language into their daily schedule, which is the best model of Language acquisition wherein the input and practice occur as often as possible (Aslam et al., 2022). This approach supports the Input Hypothesis as postulated in the Natural Approach by Krashen and describes comprehensible input as crucial for learning a second language.
Furthermore, game-based learning and gamification integrated into MLLAs share the same characteristics for engagement and motivation to language learning as provided by applied linguistics. Learner participation is described by Kukulska-Hulme and Viberg (2017) and Berns et al. (2016) to be influenced by motivating aspects of enablers enabling skills, primarily rewards and challenges. These applications solve the affective filter hypothesis which states that learners acquire language more effectively when the anxiety level is low because of the use of interactive applications that take the stress out of learning a language out of the language learning process. In his review of the Mobile Game-Based Language Learning Applications (MGBLLAs), Gamlo (2019) notes that these learning aids motivate the development of the basic skills of listening, speaking, reading, and writing as students seek to complete preset goals. Such features increase intrinsic motivation, which is one of the major driving forces for effective and long-term language acquisition.
According to the principles of applied linguistics, the factors of usability and design of language learning tools are widely researched. In their study, Al-Sabbagh et al. (2019) support that simplicity in ergonomic interface designs guarantees continued learner attention and interest. Non-sustainable applications can interfere with the learning process, increasing the affective filter and learners’ motivation. Consequently, the focus should be made on UX as developers are to consider the usability and accessibility of products intended for users. Efficient MLLAs should be easy to use, aesthetically pleasant, and designed for multilevel learners, including students with disabilities based on user difficulty level.
Consequently, MLLAs have become an effective tool for a shifting paradigm in language education, which is focused on flexibility, game attributes, and interaction (Agrawal and Moparthi, 2021; Usama et al., 2019). These tools are compatible with the principles of adaptive learning: learning with these tools helps the learners become more autonomous, remain Motivated and contain meaningful uses of the language consistently. The future developments of Artificial Intelligence and Adaptive Learning could, to an even greater extent, magnify the pedagogical usefulness of MLLAs and therefore be an invaluable tool for teaching languages all around the world. Mobile communication technology must therefore be seen as having the capacity to revolutionize the practice of MLLAs within the concept of accessibility, instruction and effectiveness such is the applied linguistics’ goal to link theory and practice for better language acquisition in context (Aljabri et al., 2021).
Rationale of the study
When it comes to the creation of mobile applications, especially language learning apps, the process of its development has to inevitably include the reception of feedback from its users as one of the means to update the system and upgrade it. In the context of applied linguistics, user feedback is a principled and direct source of information regarding learner attitudes, difficulties and practice. According to Zheng and Wang (2023), users are capable of offering first-hand information on the trends as well as the experiences of users and hence are a direct window to the application developers as the language learning applications require. Furthermore, consumers’ reviews provide much more detailed information regarding usage conditions, possible failures, and recommendations for improvement than comparative data and, therefore, help developers enhance their products’ performance (Panichella et al., 2015). However, this feedback is unstructured feedback which makes it hard to pull out useful insights from it. To answer this, methods that try to automate text classification can be used for the analysis of feedback (Hadi and Fard, 2021; Barunaha, 2023).
From an applied linguistics point of view, incorporating the feedback of the users in the development of app design adheres to the principle of learner-autonomous learning proposed by learner-autonomous learning. Implementing feedback also increases the perspective of user trust and satisfaction, making them feel like the owners of the content (Honeycutt et al., 2020). Evaluation mechanisms enable learners to state their attitude and experience, which by using techniques from the sentiment analysis of the provided feedback, reveal the efficiency of the language-learning process. As Bano et al. (2017) have noted, performing the analysis will make it easier to assess learner attitudes and improve app design and dissemination to boost the efficiency of teaching while synchronizing technological values within instructional objectives.
This study is justified by the lack of knowledge on the part of applied linguistics concerning the workings of user feedback in the particular context of mobile language-learning applications. Although user reviews provide valuable and credible input for enhancing platform functionality, such data source is not fully harnessed because of the unstructured nature of feedback (Du et al., 2021; Umarani et al., 2021). To fill this gap, this research uses machine learning approaches and graph visualization to conduct sentiment analysis on feedback provided by the users. This approach not only reshapes and categorizes user feedback, but also reveals how the applications can be better fine-tuned to meet the needs of modern learners. Through the synthesis of linguistic research findings with technological advancement, this work seeks to offer a systematic solution to improvement of the mobile language learning applications user experience in the application of language learning, thereby narrowing the gap in applied linguistics as the learner feedback and language learning strategies (Gass and Mackey, 2013).
Significance of study
The significance of this study lies in the fact that it relies on an analysis of the reviews of two of the most popular language-learning applications: Babbel and Duolingo based on applied linguistics by conducting sentiment analysis as well as linguistic features analysis. When putting the feedback in positive negative, and neutral contexts, this research exposes important trends concerning the learner preferences, difficulties they meet, or their satisfaction levels (Fouadi et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2020). These recommendations are valuable for app developers seeking to optimize application parameters for accumulating relevant evidence about the impact of application parameters on usability and learning, in particular.
From an Adaptive Learning perspective, this research fits well with the operational imperative of the field to enhance language learning using technology. It shows how learners’ feedback may be used to design educational tools so that they meet learners’ language and learning profiles (Gao et al., 2018). The employment of sentiment analysis provides a way to classify learner attitudes and perceptions in a comprehensible structured approach, which ultimately strives to tackle specific issues such as interface usability, effective instructional application and motivational factors or features which determine successful learning of a language (Holmes and Wilson, 2022).
In addition, this work adds to the limited literature on educational technology by showing how methods of data analysis, including sentiment analysis, can evaluate the usability and benefit of features such as interactivity and user engagement in language-learning applications. In doing this, the research maps theory-derived insights from applied linguistics onto technological approaches and methodologies and highlights the enabling role of user feedback in enhancing the design of better, more motivating and effective LEPs (Klímová, 2018; Singh, 2023). Such integration of research focuses not only on the improvement of language education alone but also on the learning process of using technologies in the actual environment (Lakshmi, 2023).
Research objectives:
1. To analyze sentiment dynamics in user feedback for Babbel and Duolingo, focusing on how emotional responses influence user engagement and satisfaction.
2. To compare feedback structures between Babbel and Duolingo, identifying differences in sentiment clustering, user interactions, and influential nodes within their networks.
3. To examine linguistic features in user reviews, exploring how lexical choices, grammatical patterns, and sentiment intensity shape user perceptions of each platform.
4. To investigate the role of gamification and structured learning in driving user motivation and engagement for beginner and intermediate learners.
5. To provide actionable insights for improving platform design and user satisfaction by leveraging findings from sentiment, linguistic, and network analyses.
Research questions:
1. How do user sentiments about Babbel and Duolingo differ in terms of positive, negative, and neutral feedback, and what emotional patterns can be identified?
2. What are the key structural differences in the sentiment networks of Babbel and Duolingo, and how do these affect user engagement and satisfaction?
3. How do linguistic features such as lexical choices, grammatical patterns, and sentiment intensity reflect user experiences and perceptions of the two platforms?
4. In what ways do Babbel’s structured lessons and Duolingo’s gamification contribute to user engagement, and how do these approaches address the needs of beginner and intermediate learners?
5. What strategies can be implemented to address the criticisms of repetitiveness and lack of depth in Duolingo, and high cost and limited personalization in Babbel?
Literature review
Mobile learning training has thus become an important research topic, especially in the field of applied linguistics, because it points to the incorporation of mobile technology into language teaching and learning. Mobile-Assisted Language Learning (MALL), more accurately explained by Miangah and Nezarat (2012) as the utilization of mobile devices for learning and acquisition of languages in a flexible and context-sensitive manner, presents the most benefits in labs and usage aspects that have informal learning potential and are mostly applied individually. It proves helpful for students failing to succeed in traditional environment-based instruction, as an alternative asynchronous approach fits the various and dynamic needs of language learners in modern society (Panah et al., 2021).
In the following section, a vast number of studies emphasize the effectiveness of the MALL, especially in the area of learners’ motivation, which remains one of the core factors for language learning (Yang et al., 2021; Zakaria, 2023). Mobile applications enhance learning for students with learning difficulties with conventional methods as described by Kacetl and Klímová (2019) as shown in the following: similarly, Poláková and Klímová (2022) make use of mobile applications as mediators, reveal that they actualize the learning process and the process, empower learners. This focus on learner agency is fully supported by applied linguistics since it is critical for the language learning process. In more recent work, Mihaylova et al. (2020) associate MALL with the enhancement of cognitive abilities inclusive of memory especially in learners of advanced age; thus plays a role over age also. Furthermore, MALL takes into consideration motivational and affective factors of language learning and these two are central to the process of learning a second language (SL) (Nami, 2019).
At the same time, MALL has various pitfalls that have to be solved within the framework of the applied ling, which can make it work more challenging: the following challenges that have been described by Grimshaw et al. (2017) acted as barriers towards the use of MALL in formal education as follows; Mobile learning environments, therefore, may not be easily manageable by the ESL learners as highlighted by Hashim et al. (2017) hence the call for properly substantiated approaches towards the use of MALL in teaching practices. Meeting these challenges entails integrating technology with principles of applied linguistics to make MALL suitable for teachers and learners.
The knowledge of user preferences and application usage in the MALL context is important to leverage the benefit (Pathak and Piyush, 2023). Mobile technology makes the expansion of learners’ vocabulary and their language proficiency easier, as Nehe et al. (2023) showed; MALL increases learner participation and engagement, which are critical for achieving better learning outcomes, according to Metruk (2021). Such resources as MALL should be used in context-related learning considerations to enhance understanding by having learners apply skills in real-life situations in courses. These ideas are consonant with applied linguistics’ focus on how best to furnish purposeful and contextually appropriate learning experiences.
The corpus analysis and text classification have become critical for evaluating the user feedback within MALL and improving the learners’ experience (Shadiev et al., 2019; Zhao, 2024). This Natural Language Processing (NLP) technique categorizes and analyses text data such as user reviews, it helps in monitoring work satisfaction, identifying problems and subsequently enhancing program performance. Considering the context of language learning, Bano et al. (2017) state that sentiment analysis is useful in identifying learner’s attitudes to particular aspects of an application and, thus, helping application developers improve educational apps. SVM and LSTM networks for deep learning have enhanced the sophistication of the sentiment analysis work, Hadi and Fard (2021) and Dashtipour et al. (2018). These advancements are in tandem with applied linguistics interest in technology-supported language education.
Apart from language learning, sentiment analysis has successfully been incorporated in many areas as seen above, flexibility. For example, Barik et al. (2023) used sentiment analysis to understand variables from customer data feedback for product development and managing market messages. For the mental health domain, Oyebode et al. (2020) conducted sentiment analysis to feedback from using mental health apps while Ho et al. (2019) gave direction to app developers based on usability issues encountered. The following applications show the readiness of sentiment analysis as a decision-making tool appropriate to be adopted in the field of language learning to address issues of user experience.
MALL stands for Meaningful and Authentic Language Learning, which is in tandem with the applied linguistic principles of learner autonomy, situated learning, and learner-centeredness. New possibilities remain such as the integration of sentiment analysis for capturing learner feedback to improve the design of the apps, as well as the ongoing technological challenge of providing user support (Pham et al., 2020). When infused into situations such as the ones described in this paper, the MALL framework can transform language learning to better fit the needs of learners, especially in providing language learning support in the form of flexible, interactive and effective technological assistance (Rajput and Gupta, 2022).
Mobile applications aim to facilitate language learning, a hugely debated in the field of Applied Linguistics (Roberts et al., 2018). The studies have indicated that the context of learning within technology can affect learners’ engagement and motivation (Vygotsky, 1978). In addition, opinions from the post-testing reviews on learners’ emotions and affective states can be profound in identifying deficits and assets of language-learning apps such as Duolingo and Babbel. Traditional attitude mining has been employed for understanding the affective reactions towards educational resources (Gass and Mackey, 2013), however, its role in the context of app-based pragmatic language learning is quite limited.
In Applied Linguistics, a learner’s attitude is highly important as such internal variables as motivation and frustration may influence language acquisition. In this current research, sentiment analysis is complemented with linguistic features, including lexical resources, modality, and negation to analyze users’ feedback on teaching tools and learning applications such as Duolingo and Babbel (Rosell-Aguilar, 2017).
Theoretical framework
As the theoretical framework of this study, Dynamic Systems Theory (Larsen-Freeman, 2015) and Sociocultural Theory (Vygotsky, 1978) are applied, as they offer an adequate, complex understanding of language learning processes in the context of the use of mobile devices. DST approach to learning language is complex and does not follow a linear process, and depends on the quad factors of emotion, cognition, development, and sociocultural. Sentiment analysis captures the dynamics of such processes by pointing out users’ emotional reactions, dynamics between motivation, engagement, and personalized learning environment design (Zhang et al., 2018).
SCT is founded on the belief that learners are unique and communicate with different apps in various ways, thus, interaction in environments and features defines the experience. Focusing on learners’ feedback on the use of social and cultural factors and personal interests, this research supports the cultural-contextual approach to the design of MALL.
Methodology
This study reviewed user feedback using a mixed-methods approach to compare how Babbel and Duolingo mobile language learning apps are being used. We looked at user feelings, language used, and how users interacted to understand their experiences.
Data collection and preprocessing
Using Scrapestorm, the researchers managed to scrape and review user feedback up to 190 users per app from easily accessible app review platforms. Babbel had a limited number of reviews, so Duolingo reviews were matched in order to make sure the results were comparable. Information is gathered over 3 months to achieve both a good volume of data and relevance in time. The researchers used OpenRefine to clean up the data by taking out duplicate, unnecessary, and inconsistent entries from the dataset. After cleaning the reviews, they were grouped into positive, neutral, and negative feelings and added to CSV reports that include data to help with later analyses.
Sentiment and linguistic feature analysis
NLP was used to examine user feedback and pick out the feelings behind the comments, showing how each feature either added to or removed from people’s emotional experience. Through an analysis of words, sentence arrangements, how messages are linked, and the expression of emotion, patterns in user writing were discovered. Duolingo was praised mostly for its motivating phrases, but Babbel was commended for organizing instruction and covering a lot of material.
Network construction and analysis
Users’ reviews were used to make user feedback networks by creating nodes from individual reviews, with edges drawn based on the cosine similarity between TF-IDF vectors (threshold being 0.3). The graph representation stored as adjacency matrices was imported into Gephi (version 10.0) and plotted using ForceAtlas2, Fruchterman-Reingold, Yifan Hu Proportional, and Random Layout layouts. A key finding from the visualizations was sentiment grouping, important resource distribution, and feedback being exchanged.
The researchers used the NetworkX Python library (version 2.8.4) to perform quantitative analyses of the network and its dynamics, relying on degree centrality, modularity, the clustering coefficient, and network density. Babbel’s data clustered groups of accounts, while Duolingo’s data spread reviews evenly rather than forming groups.
Results and analysis
This study explored the affective dimension of user engagement with Babbel and Duolingo by applying Dynamic Systems Theory (DST) and Sociocultural Theory (SCT) as interpretive frameworks. DST allowed the feedback networks to be understood as adaptive systems where user sentiments evolve and influence overall community dynamics. SCT provided a lens to examine how shared cultural and social contexts shape user attitudes and preferences toward each platform.
User reviews were collected, categorized by sentiment (positive, neutral, negative), and preprocessed for analysis. Sentiment networks were constructed using textual similarity and visualized in Gephi to reveal structural patterns such as centrality, clustering, and feedback dispersion. Quantitative network metrics reinforced these visual insights: modularity scores (e.g., 0.906 for Duolingo) confirmed strong sentiment clustering, clustering coefficients (e.g., 0.534) reflected moderate local cohesion, and low densities (e.g., 0.025) indicated selective but meaningful connectivity. The following is a detailed analysis of both the apps (Figure 1).
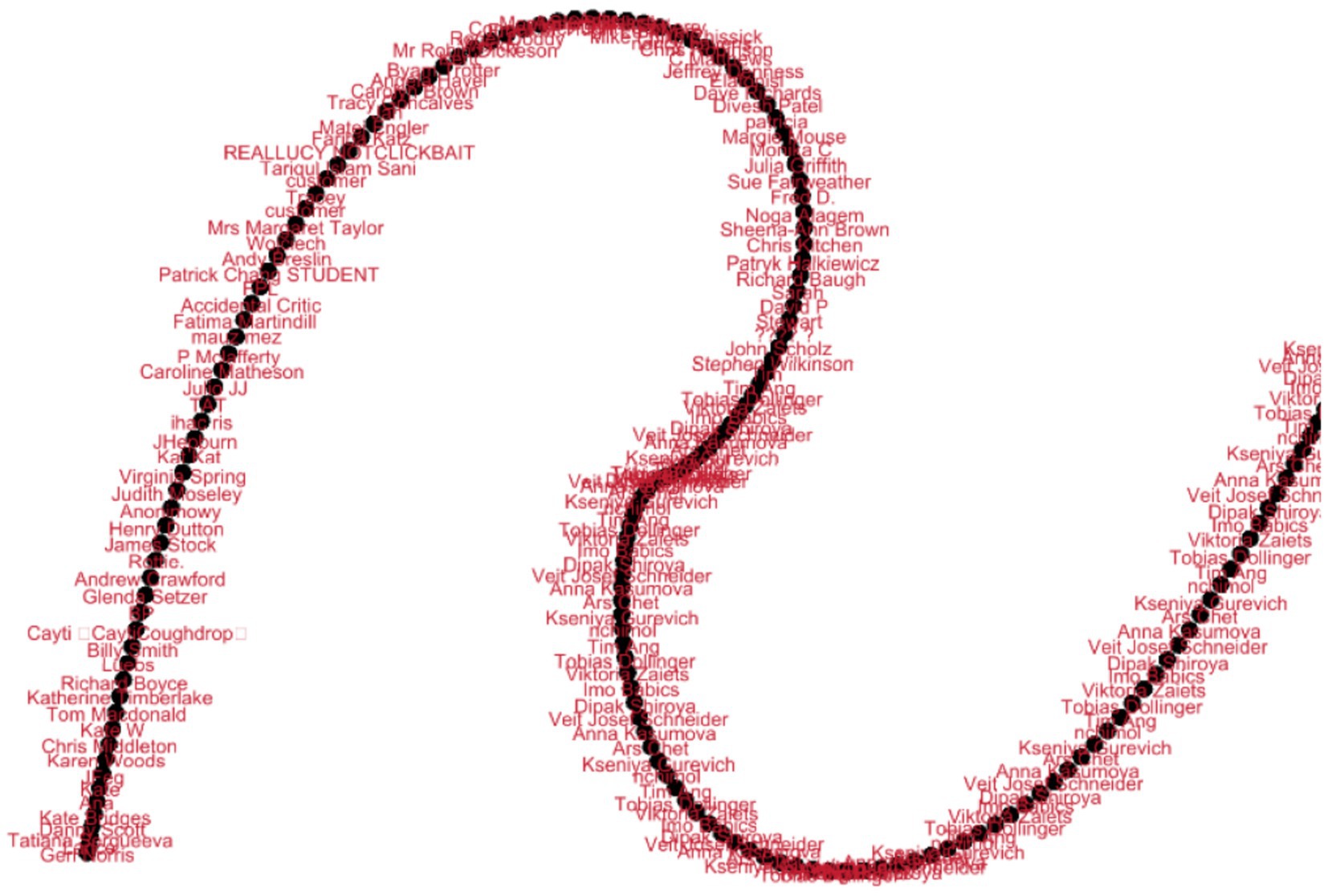
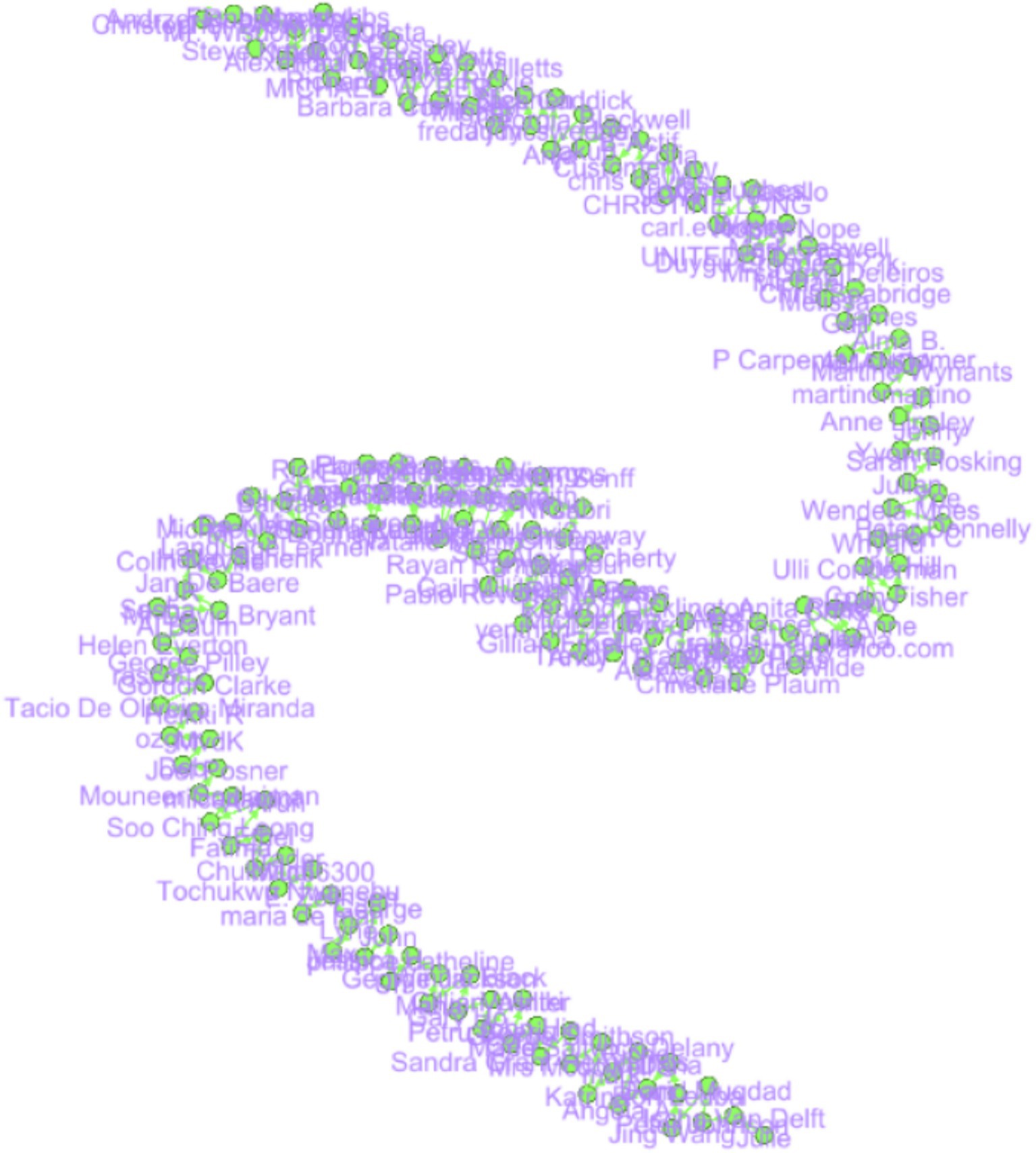
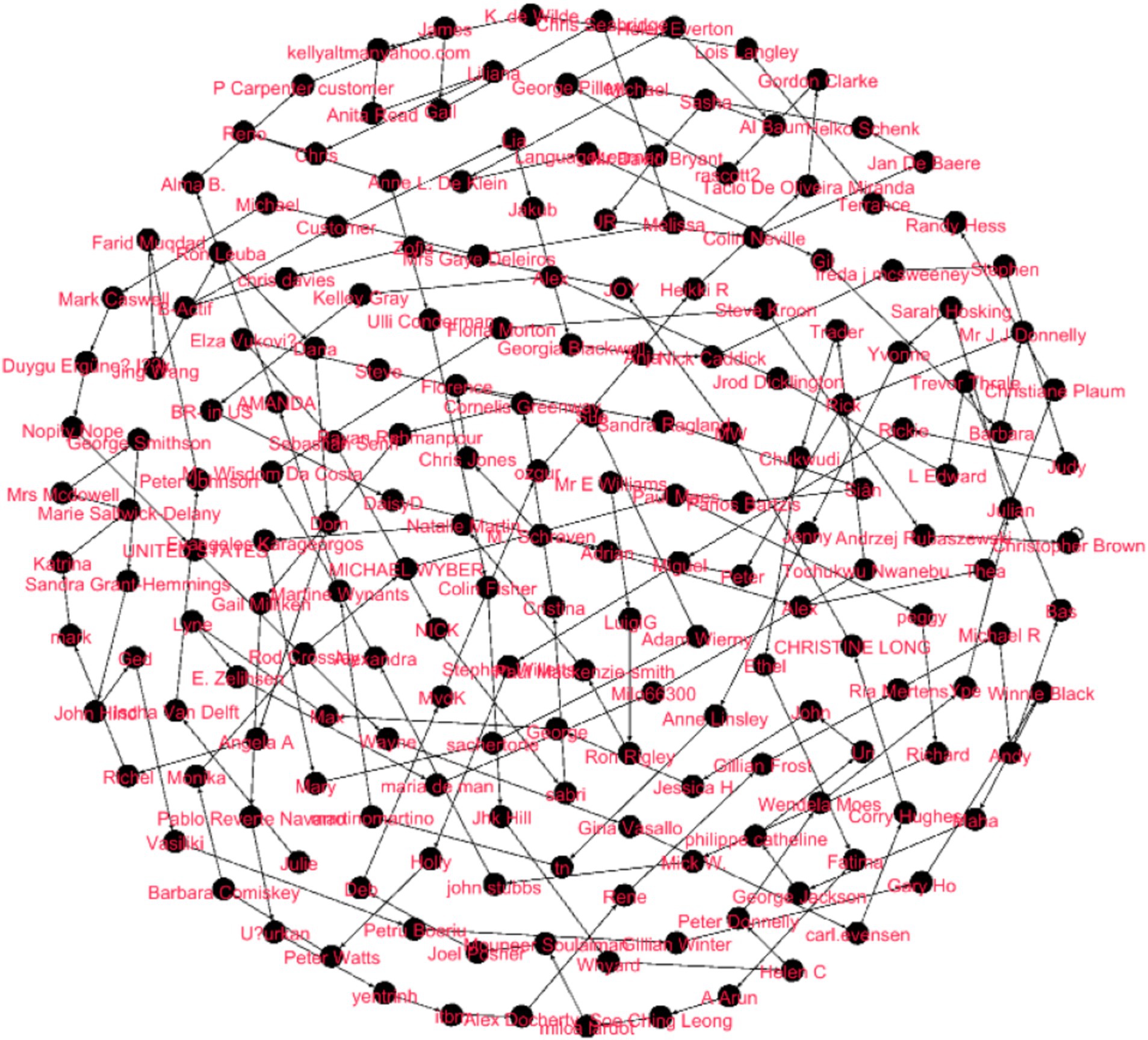
Figure 1. Network graph of Duolingo user reviews based on textual similarity (this ForceAtlas2 layout reveals clusters of user feedback, with central mediators connecting distinct subgroups. For detailed network metrics supporting this visualization, see the network metrics overview for the Duolingo feedback section).
Duolingo sentimental analysis
The Force Atlas2 graph above demonstrates a closed feedback loop with node clustering indicating the level of similarity of feedback provided to students. Cognoscenti nearer to each other have similar viewpoints, while nodes farther apart have divergent views. The nodes located in the middle of the graph, named “Patrick Chang” and “Mrs Margaret Taylor,” can provide feedback that would concern other subgroups and can be significant, or, in other words, these persons might be “mediators” in the given social network. The edges signify considerable feedback alignment for the high density and lack of isolated nodes, where all the participants provide the feedback loop within the network. Some of the nodes, such as “Katherine Cornflake” and Ger Norris, are probably feedback connectors, which are nodes that connect two different feedback clusters (Figure 2).
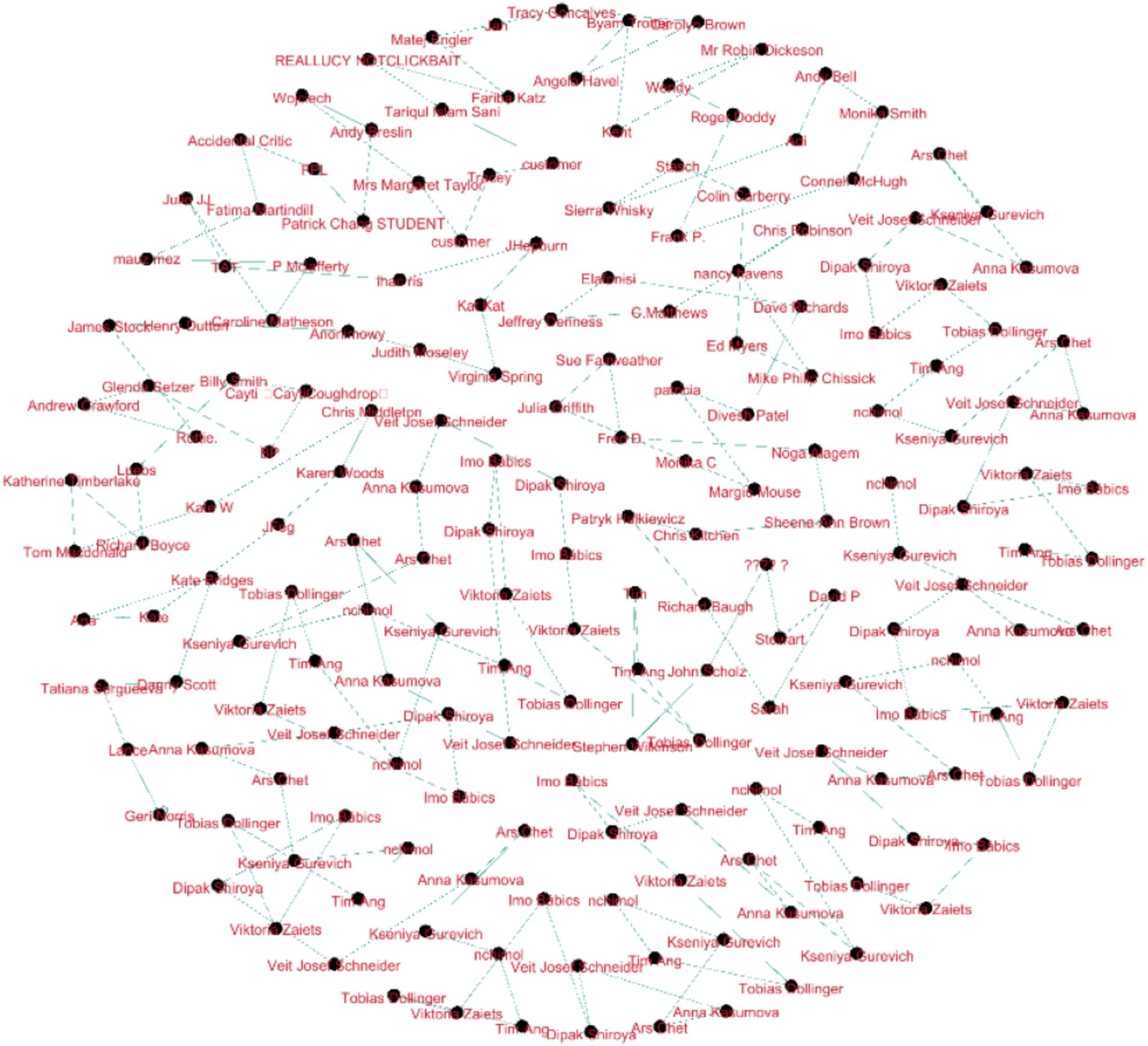
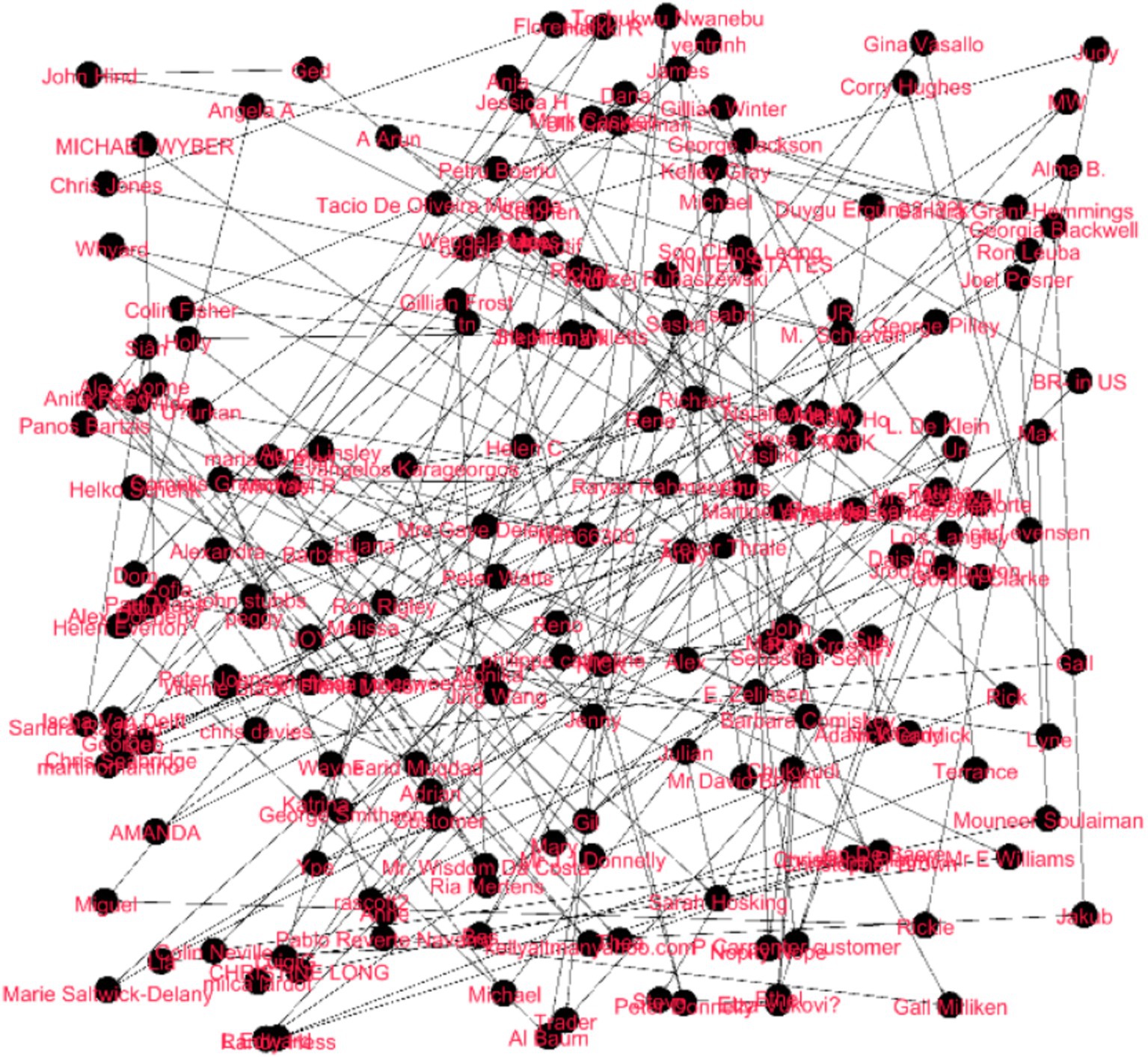
Figure 2. Fruchterman-Reingold network graph for Duolingo sentiment analysis (the graph highlights clear feedback clusters and influential nodes within the network. For comprehensive quantitative metrics, refer to the network metrics overview for the Duolingo feedback section).
This is a nice Fruchterman-Reingold graphical representation of the feedback network with little node overlap and clear connection lines. Having feedback with nodes closer together represented more similarity, as a result of pair contents, the subgroups like “Tobias Dollinger,” “Viktor Zaiets,” and “Veit Jose Schneider” are at the bottom, while “Matej Engler” and “REALLUCY” are at the top. The main nodes can be named “Patrick Chang” and “Mrs. Margaret Taylor”; they are the members who bridge different subgroups. The nodes’ connectivity is dense, and there is little suggestion of highly isolated nodes, indicating a coherent feedback community, in which elevated connection density is concentrative in denser clusters.
This graph uses the Fruchterman Reingold layout, which focuses on evenly distributing nodes across the space while maintaining relationships between them (Figure 3).
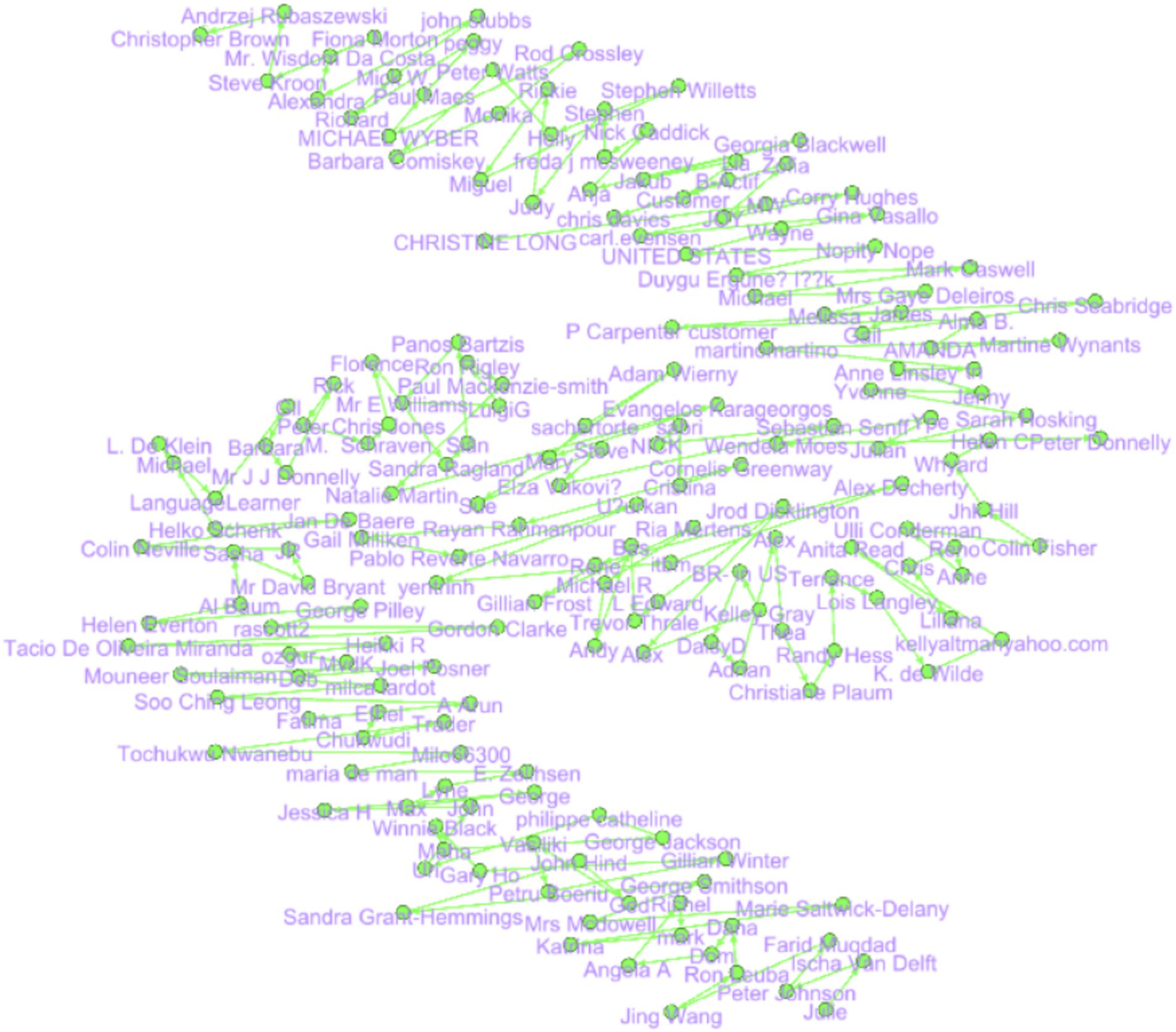
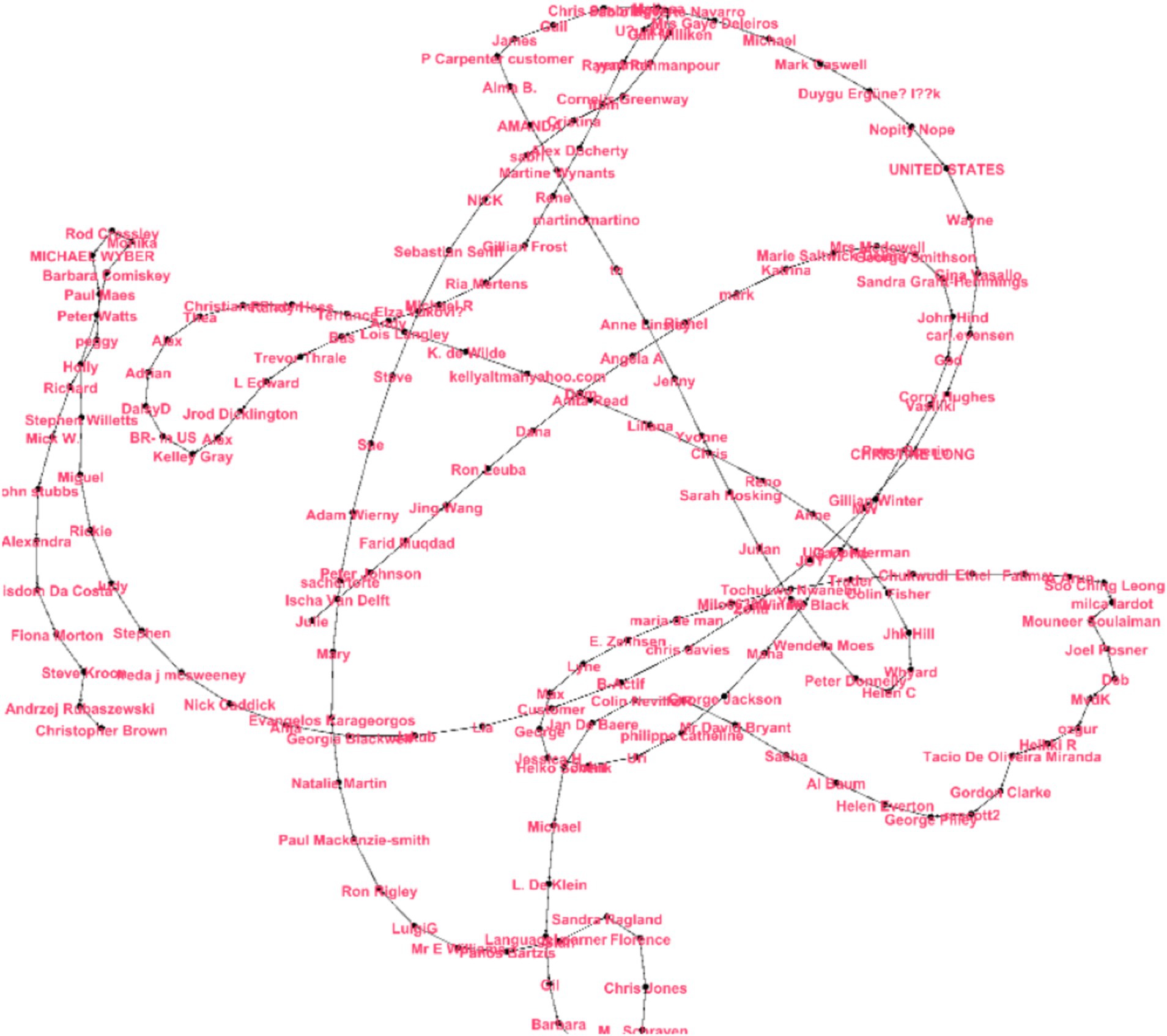
Figure 3. Layout label adjust graph displaying user reviews with clear, non-overlapping labels, facilitating traceability of individual feedback. Central connectors bridging subgroups are evident. For supporting network metrics, see the network metrics overview for the Duolingo feedback section.
The goal of the LayoutLabel Adjust is to have all nodes labeled without overlapping, and using connections, it is easy to trace students. Neither label clarity nor node positions are inherently a priority, yet the letter “C” at the bottom left is clustered with “Sandra Grant-Hemmings” and “Soo Ching Leong.” Moreover, at the extreme top, “Christopher Brown.” There could be central figures like “CHRISTINE LONG” as well as “Mr. Wisdom Da Costa” who links different groups of users. The disadvantage of this layout is the fact that it is less orientated towards grouping or connections than other layouts, but it has a rather simple and clear view of single nodes as well as their bonds (Figure 4).

Figure 4. Random Expansion layout illustrating user feedback connections despite random node placement. Central nodes suggest key contributors within the network. Refer to the network metrics overview for the Duolingo Feedback section for quantitative analysis.
In Random Expansion, layout nodes are positioned randomly in the space so that node size and position do not represent the relationship between nodes. Although there is no actual cluster formation or increased structuring here, as you can see, a denser middle area of the nodes, such as “Carolyn Brown” and “Dipak Shiroya,” depicts better connectedness, which indicates that these students’ feedback is more universal. It seems that “Tobias Dollinger” is more of an outsider, as well as “REALUCY NOT CLICKBAIT,” which can mean some different feedback. While random, edge visibility creates relations between nodes, central nodes possibly imply the members providing essential feedback within the network (Figure 5).

Figure 5. Yifan Hu Proportional layout showing proportional modularity within the feedback network, differentiating group-level consensus from individual opinions. See the network metrics overview for the Duolingo feedback section for relevant metrics.
The cliques of the Yifan Hu Proportional layout represent a proportional modularity within the network of the students’ feedback responses. Potential super-mention users such as “CHRISTINE LONG” and “Michael R” represent central individuals with many feedback connections to other subgroups. Two nodes that are most probably more unique or less connected feedbacks are “Farid Muqdad” and “Jing Wang” figured out in the peripheral part of the mentioned diagram. What is circumscribed in the central part looks like a dense cluster of edges, the peripheral setting suggests that the edges are considerably weaker. This layout concerns two types of feedback, general for a group level and more generalized for the overall level structures, separating more general opinions and more individualistic ones (Figure 6).

Figure 6. Yifan Hu’s network graph for Duolingo sentiment analysis. This layout emphasizes the proportional relationships and cluster formations among user feedback. For detailed quantitative metrics, consult the network metrics overview for the Duolingo feedback section.
Analysis of the Yifan Hu layout shows that there is a core presenting a dense negative feedback loop that has multiple subgroups in which individuals such as Ksenyia Gurevich and Veit Jose Schneider play connectivity hub roles. These central nodes probably have popular or positive reviews. Peripheral nodes, for example, “Ger Norris,” are more unique or less connected in feedback. The closeness of the nodes mentioned inside the central box means that the feedback relations are strong, and the weak connection mentioned in the outer nodes means comparatively weaker feedback relations. The diagram shows the position of an individual and collective, focusing on the overall structure of the network combined with certain subclusters that reveal the general cohesiveness and individual feedback in the group.
Network metrics overview for Duolingo feedback
The network analysis of Duolingo user reviews reveals a cohesive and interactive feedback community. Quantitative metrics substantiate this observation:
• The modularity coefficient is 0.906, indicating strong community structure with well-defined clusters of similar feedback.
• The clustering coefficient is 0.534, reflecting moderate local cohesiveness among user groups.
• The network density is 0.025, demonstrating selective yet meaningful connections that preserve clarity and prevent excessive complexity.
Together, these metrics highlight the presence of tightly knit clusters and influential mediator nodes that drive the dynamics of user feedback across the platform (Figure 7).
Babbel sentiment analysis
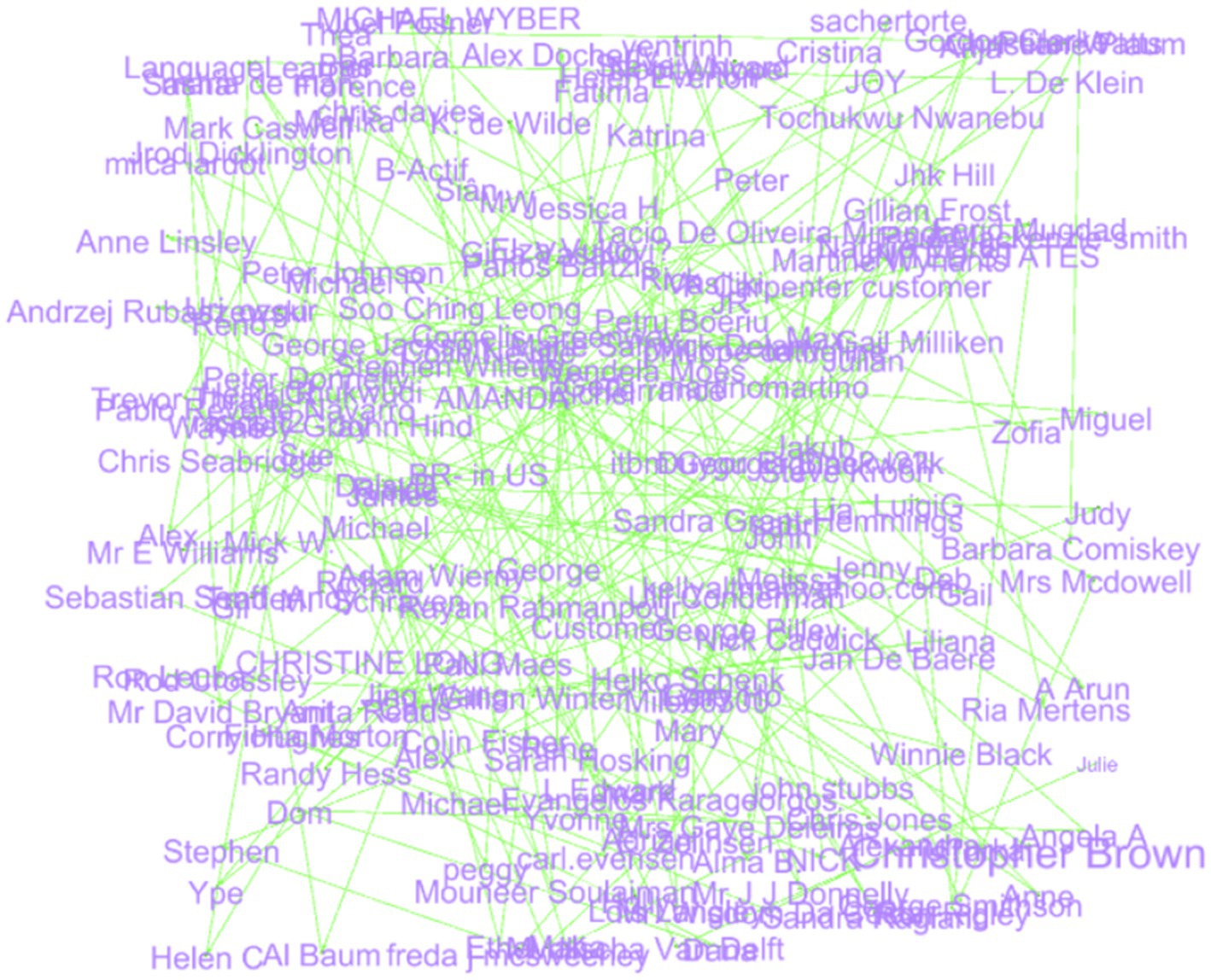
After applying the Force Atlas2, the layout suggests a closed loop of feedback, arranged in a spiraling, serpentine pattern in which nodes are grouped depending on feedback or opinions they share. Some of the nodes at the curve, for example, CHRISTINE LONG and Nick Caddick, seem to interconnect more than one subgroup or affect overall feedback. The cohesiveness in a central area shows that feedback is similar, while nodes, such as “Isabel De Delft,” are peripheral or different. The linking nodes, for instance, Soo Ching Leong, are the core of different clusters of feedback. In general, it is seen that this layout serves both influential central nodes and middle participants as well as relatively unique peripheral feedback (Figure 8).
The Fruchterman Reingold layout shows a round feedback network where the larger concentration of nodes is uniformly positioned, which is good and balanced. Hubs such as “CHRISTINE LONG” and “Mr Wisdom Da Costa” are seen as important advocates with multiple connections, indicating that the impressions shared get experienced by many. Rising to the category level, subclusters like “Ria Mertens” and “Trevor Thrale” identify groups of customers with similar comments; conversely, “Farid Muqdad” single nodes are restricted to unique or less common comments. The topology is dense with a few weak peripheral nodes, so that the details of the connection point to the high amount of sharing feedback, and most likely, the central nodes make up some general feedback pattern (Figure 9).
This general layout graph represents a feedback construct in which the majority of nodes connect with many of the other nodes, which points to a lot of feedback similarity. Other nodes, such as “CHRISTINE LONG” and “Mr. Wisdom Da Costa,” contain a variety of people and are quite typical representations of the conventional observations. Next, peripheral nodes are less associated with specific shared content and include John Hind and BR in the US. The graph does not accentuate clusters, yet the closest neighborhood consisting of five nodes, where one subgraph is around “Sarlab Aziz” and the other near “Angela A,” is most densely connected. In summary, the graph illustrates both the influencer identification and feedback dispersion in the services’ social network (Figure 10).
The Noverlap layout aligns all nodes so that there is maximal distance between them and all connections are immediately distinguishable from one another. If the layout does not cluster people based on their relations, as it is aimed at being readable, it still shows the curved, snakelike structure, where some nodes, like CHRISTINE LONG or Nick Caddick, can be considered central as they are connected with many others. Outliers like “Sandra Grant Hemmings” and “Jing Wang” are other varieties of peripheral node data. Such edges convey the level of feedback relationship and the short edges show a stronger relationship between nodes. In general, clarity is achieved in layout, though it does not negate the fundamental architecture of the feedback network (Figure 11).
The Random Layout graph randomly positions nodes but does not group them, or accent on structures, or connections, while still representing that connections exist between all individuals. However, the high number of edges, or rather the high density of the chart, reveals the strong interconnectedness of the feedback and, indeed, “users” like CHRISTINE LONG or Randy Hess seem to be even more connected than others, implying the probable influence of these users as feedback multipliers. Despite the layout making it somewhat difficult to determine clusters and the relationship strength, the graph helps to determine the degree of feedback relationships (Figure 12).
In the Yifan Hu layout nodes are distributed evenly and are smoothly curved; on the other hand, there is clear emphasis both on local clusters and on the context of the entire network. Many positive comments are posted by potential customers, and the central nodes, such as “CHRISTINE LONG” or “kellyatlam” unite different communities. It suggests that peripheral nodes who are the panellists like “Miguel” or “Joel Posner” give somewhat isolated or distinctive impressions. The connections within the core areas suggest a strong feedback alignment, and the fewer connections at the periphery, and the fewer connections of less share suggest more specific views. In general, the specified layout reveals a good example of a connected feedback system and central topical nodes and opinion clusters. This analysis provided a clear understanding of how user sentiments are shared, the strength of those relationships, and the overall structure of feedback on both platforms.
Network metrics overview for Babbel feedback
The Babbel feedback network exhibits cohesive user participation characterized by:
• A modularity coefficient of 0.89, demonstrating strong community structure with well-defined clusters.
• A clustering coefficient of 0.52, indicating moderate local clustering among user feedback groups.
• A network density of 0.03, reflecting selective yet meaningful connectivity, preserving network clarity.
These metrics complement the qualitative network visualizations, highlighting influential nodes and feedback dynamics that shape Babbel’s user experience.
Duolingo user sentiment linguistic analysis
Duolingo’s user reviews predominantly reflect positive sentiments, with phrases like “fun,” “engaging,” and “easy to use” frequently appearing. Linguistic analysis reveals that satisfaction is often emphasized through intensifiers (e.g., “very helpful,” “absolutely love”) and modal verbs (e.g., “I can now,” “I can understand”), signaling a sense of accomplishment and progression. Users praised Duolingo’s gamification strategies, which maintained consistent engagement and motivation, especially for beginner-level learners. For instance, one user noted, “Duolingo is a fun way to learn English. It’s easy to use, and I can already understand basic conversations!”
However, negative reviews expressed dissatisfaction with the limited depth of content and repetitiveness of lessons, often employing negation and hedging language (e.g., “not enough,” “could be better”). For example, one user lamented, “The app does not help advance beyond basic skills. The lessons get repetitive and do not challenge me enough.” This feedback aligns with the need for a broader pedagogical focus on higher-level language acquisition.
Babbel user sentiment linguistic analysis
In Babbel reviews, users also conveyed strong positive emotions, with frequent mentions of its “structured,” “comprehensive,” and “detailed” lessons. This linguistic emphasis indicates satisfaction with the platform’s focus on grammar and real-world application, exemplified by one user’s comment: “Babbel’s lessons are very well-structured and comprehensive. I feel like I’m learning real grammar!”
However, negative sentiments toward Babbel often centered around its pricing model and lack of personalization. Users criticized the high subscription costs and the generic nature of some lessons, as reflected in statements like, “Babbel is too expensive, and the lessons do not feel personalized enough. It does not seem to cater to my specific learning needs.” These critiques suggest a need to address perceived value and enhance personalized learning experiences.
Linguistic features and sentiment patterns
Positive comments noted on both apps were often related to the convenience of the application, the activity, and the motivation of the application. The words “interactive,” “fun,” and “useful” were used with adverbs that drove the focus back to the user. However, negative feedback identified problems like redundancy, insufficient depth, as well as high prices, using modal verbs (for example, should include, could be), and negative phrases (for example, not enough, too simplistic). These linguistic patterns give developers ideas on how to improve usage patterns among people who use their creations.
The comparative analysis of Babbel and Duolingo
Using DST and SCT, this study evaluates how users feel and what they prefer with Babbel and Duolingo. DST explores how learning in apps can keep evolving and shifts according to users’ growing experiences. In SCT, it is argued that learning and thinking are shaped by people’s social and cultural experiences.
Most users appreciate Babbel because its grammar lessons are organized and cover a lot which is in line with DST’s thinking about integrated learning systems. Still, many complaints about Babbel focus on its priciness and missing personal features, things SCT considers valuable for effective social learning. Unlike other platforms, Duolingo is noted for its fun, motivating design which echoes SCT’s focus on socializing and keeping students interested. Even so, issues with the same content repeated and not enough depth connect to DST’s request for adaptable and personal learning paths.
Looking carefully at the language, we see that Duolingo comments often talk about motivation and achievement, while Babbel comments highlight the content structure and say something about the costs and if it fits each user.
More analysis of the network suggests that Babbel’s feedback gathers in a central hub, meaning users in this community are closely connected and organized by topic. Because Duolingo covers a lot of different people, its feedback is not as well organized as it could be for advanced users.
To make sure users are happier, Duolingo can broaden its advanced content and minimize disruptive ads, and both can focus more on adding socio-cultural features, such as allowing users to interact with each other and join a community. While grammatically based learning fits DST and SCT, Babbel should work to balance ease of use with flexibility and depth of study. Both apps must respond to a range of learner needs with sociocultural changes.
Structural differences in feedback networks
The feedback networks of Babbel and Duolingo show that these learning platforms have radically dissimilar operational processes. In this study, Babbel adopts a localized and clustered structure characterized by leading prominent nodes such as “Christine Long” and “Michael Wyber.” These key nodes play a feedback reporting platform where information flows from one group to another or between different clusters. This dynamic co-positions with SCT whereby the Babbel ecosystem is formed and framed by social power relations and mediated by key opinion leaders. Involving such influences in product development might improve products because it can identify specific users’ segments and predominant needs. For instance, while giving feedback in clusters, Babbel highlights structured lessons and detailed content meaning that people in clusters prefer highly niche experiences.
On the other hand, Duolingo’s feedback network is relatively decentralized and has no highly influential central nodes. These trends show that the site is much more aligned and coherent, and the nature of feedback is more balanced throughout the platform. In DST terms, Duolingo’s network functions as a stable system in which differences help reduce susceptibility to negative tones. Analyzing the text of Duolingo’s customer feedback reaches the same conclusion in terms of its stability as the lexical profile of Duolingo and, therefore, the words “fun,” “engaging,” and “easy-to-use” were mentioned repeatedly. The decision does not have one focus, meaning that alterations to the site can be carried out across the board, affecting most users.
Linguistic features and sentiment analysis
A comparison of user feedback for both platforms makes it possible to identify patterns of language usage that are characteristic of network organization and dynamics. Reactions to Babbel consist of very positive adjectives combined with structuring elements such as “well-structured and very detailed,” or “comprehensive and groaningly occupying.” The contents of this language can be traced to the user’s gratitude for grammar and the practicality of lessons that Babbel has to offer, which also resonates with SCT’s mediated meaningful activity. Praise is often generalized and positive, while negative feedback is frequently about cost: keywords are often hedged and modalised like “too expensive,” and “could be cheaper.”
The Duolingo reviews, therefore, are tilted in a gamified motivational manner, with positives stressing “fun,” “motivating,” and “interactive.” Positive words such as Intensifiers and Modal verbs such as; “absolutely love,” and “can now,” depict the sustainability of the engagement that the application has exhibited. Negative feedback in contrast however often judges content depth using such terms as “not enough” or “too repetitious,” which is a sign that users are pegging their expectation levels to the intellectually limited and not the high-end learning capabilities that may be inherent in them. This linguistic pattern justifies the fact that as Duolingo continues to grow, it needs to fill content gaps while remaining popular.
Comparing how feedback networks and linguistic design components of Babbel and Duolingo has stark insights for platform design. The connectivity of the segmented and clustered network shows that Babbel adheres to the Sociocultural Theory (SCT) that focuses on social mediation and focused efforts for engagement. As well as, searching for key opinion leaders, and creating selective experiences of usage for different clusters of users, Babbel can reach a variety of requirements and increase the retention rates. DST complements this localized effect by demonstrating that Babbel’s feedback system allows for dynamic change following fluctuations in user attitude localized in specific subgroups.
On the other hand, the feedback in Duolingo is spread out across an expansive network, indicating the users’ feedback provides a common overall view which again is not as focused on certain individuals. Such an equal distribution of feedback makes the system more scalable and less sensitive to opinion dynamics at the cost of requiring global and structural changes rather than point-like interventions. There are more accurate feedback channels in Duolingo that could be implemented, for instance, real-time sentiment analysis to accommodate user’s special needs as well as seek enhancements for the program. The linguistic analysis points to quite specific improvements that should be introduced: providing more detail to the explanations of when the material becomes more complex and retaining the game-based interface.
Future directions
To exploit these insights, Babbel should focus attention on the nodes that are currently influential in their network and work towards the formation of denser learning groups as well as towards better reacting towards the localized feedback. The use of personalization and utilization feedback gathered from peripheral nodes would be fruitful to satisfy everyone’s varying requirements, enhance people’s satisfaction, and increase retention rates. Such systems could further strengthen and improve Babbel’s capacity to modify its offering in response to the users’ sentiments in real time hence developing and maintaining relevance.
For Duolingo the content network shows good internal cohesion, it is also important for Duolingo to maintain a balanced structure of its network. More feedback sources support investigating problems in detail and improving them while amplifying qualitative data analysis aids in reaching that goal. Solving content depth issues for higher proficiency learners and avoiding constant lesson review and re-teaching is significant. Further, incorporating actual feedback brought with the help of the network, analysis tools can help Duolingo be more agile in its approach to maintaining the key features of its appeal both its infinitely accessible approach and the game-like nature of its platform.
Pedagogical implications
Concerning the implications for language teaching, the findings offer practical suggestions to language teachers and curriculum developers. Applying similar logic based on SCT, for Duolingo, incorporating fun and game approaches and incorporating the game-like elements into the classroom practice can maintain the motivation among the beginners. Thus, Babbel is ideal for learners of mid-intermediate level as it is based on grammar knowledge which may mean that teachers should use more structured lesson plans while on the search for opportunities to make their lessons as individual as possible for every learner. DST acknowledges the bus concept of delivering teaching and learning in dynamic and constantly evolving learner-centred ways that are supported by the outlined pedagogical strategies.
Conclusion
This study compared the Babbel and Duolingo applications utilising sentiment analysis, network metrics and linguistic features analysis with the help of Dynamic Systems Theory (DST) and Sociocultural Theory (SCT) as applied linguistics frameworks. These insights reveal the strengths of Babbel specifically in terms of the clearly defined units, grammar and vocabulary, intermediate level solidifying its stance in continuous communicative lessons marked by a segmented feedback network where opinion leaders regulate the sentiments (Wang, 2023). Nevertheless, issues such as costs and lack of customization present certain problems which can only be solved by specific lecturers to improve users’ satisfaction and loyalty. Such a game-based approach opens Duolingo to a vast audience and beginners, in particular, which can be observed through its tightly knit and balanced feedback structure. Though this structure helps reduce dependence on certain influencers, it also shows that content lacks depth for the advanced learners and there are problems repeating lessons, which need system changes.
It is found that both platforms need a real-time feedback handling mechanism to balance the changing user requirements (Wardhana and Sibaroni, 2021). Babbel should pay special attention to the responses from individual user groups and use its localized feedback clusters to ensure specific user expectations are met, at the same time Duolingo should work on expanding the depth of the content and the variety of lessons offered without sacrificing the game-like nature of the application. Thus, if each of the platforms resolves the stated contradictions and applies the determined strengths accordingly, it is possible to enhance the existing services, satisfy the customers, and ensure the leaders’ positions in the online language-learning market. Thus, this study presents how both user-centric approaches and dynamic and sociocultural parameters need to be effectively integrated into the learning technologies for different learners.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
HT: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SC: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. MJ: Data curation, Software, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. AH: Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Agrawal, M., and Moparthi, N. (2021). A comprehensive survey on aspect-based word embedding models and sentiment analysis classification approaches. Recent Trends Int. Computing 2021, 33–39. doi: 10.3233/apc210175
Aljabri, M., Chrouf, S., Alzahrani, N., Alghamdi, L., Alfehaid, R., Alqarawi, R., et al. (2021). Sentiment analysis of Arabic tweets regarding distance learning in Saudi Arabia during the COVID-19 pandemic. Sensors 21:5431. doi: 10.3390/s21165431
Al-Sabbagh, K., Bradley, L., and Bartram, L. (2019). Mobile language learning applications for Arabic speaking migrants – a usability perspective. Lang. Learn. High. Educ. 9, 71–95. doi: 10.1515/cercles-2019-0004
Aslam, N., Xia, K., Rustam, F., Lee, E., and Ashraf, I. (2022). Self voting classification model for online meeting app review sentiment analysis and topic modeling. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 8:e1141. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.1141
Bano, M., Zowghi, D., and Kearney, M. (2017). Feature-based sentiment analysis for evaluating the mobile pedagogical affordances of apps. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 281–291.
Barik, K., Misra, S., Ray, A., and Anthony, B. (2023). Lstm-dgwo-based sentiment analysis framework for analyzing online customer reviews. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2023:6348831. doi: 10.1155/2023/6348831
Barunaha, A. (2023). Real-time sentiment analysis of social media content for brand improvement and topic tracking. London: Atlantis Press, 26–31.
Berns, A., Montes, J., Palomo-Duarte, M., and Dodero, J. (2016). Motivation, students’ needs, and learning outcomes: a hybrid game-based app for enhanced language learning. Springerplus 5:2971. doi: 10.1186/s40064-016-2971-1
Dashtipour, K., Gogate, M., Adeel, A., Ieracitano, C., Larijani, H., and Hussain, A. (2018). Exploiting deep learning for Persian sentiment analysis. Cham: Springer, 597–604.
Deroey, K. (2007). Douglas Biber: university language: a corpus-based study of spoken and written registers. Appl. Linguistics 28, 624–627. doi: 10.1093/applin/amm039
Du, M., Li, X., and Luo, L. (2021). A training-optimization-based method for constructing domain-specific sentiment lexicon. Complexity 2021:6152494. doi: 10.1155/2021/6152494
Fouadi, H., Moubtahij, H., Lamtougui, H., and Yahyaouy, A. (2022). Sentiment analysis of Arabic comments using machine learning and deep learning models. Indian J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 13, 598–606. doi: 10.21817/indjcse/2022/v13i3/221303003
Gamlo, N. (2019). The impact of mobile game-based language learning apps on EFL learners’ motivation. Engl. Lang. Teach. 12:49. doi: 10.5539/elt.v12n4p49
Gao, C., Zeng, J., Lyu, M., and King, I. (2018). “Online app review analysis for identifying emerging issues,” in Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Software Engineering, 48–58.
Gass, S. M., and Mackey, A. (2013). The routledge handbook of second language acquisition. London: Routledge.
Grimshaw, J., Cardoso, W., and Collins, L. (2017). Teacher perspectives on the integration of mobile-assisted language learning. Irvine, CA: Research Publishing, 135–139.
Hadi, M., and Fard, F. (2021). Evaluating pre-trained models for user feedback analysis in software engineering: a study on classification of app-reviews. Empirical Software Eng. 28:88. doi: 10.48550/arxiv.2104.05861
Hashim, H., Yunus, M., Embi, M., and Ozir, N. (2017). Mobile-assisted language learning (mall) for ESL learners: a review of affordances and constraints. Sains Humanika 9, 1–5. doi: 10.11113/sh.v9n1-5.1175
Ho, J., Tumkaya, T., Aryal, S., Choi, H., and Claridge-Chang, A. (2019). Moving beyond P values: data analysis with estimation graphics. Nature methods 16, 565–566.
Honeycutt, D., Nourani, M., and Ragan, E. (2020). Soliciting human-in-the-loop user feedback for interactive machine learning reduces user trust and impressions of model accuracy. Proc. AAAI Conf. Hum. Comput. Crowdsourcing 8, 63–72. doi: 10.1609/hcomp.v8i1.7464
Kacetl, J., and Klímová, B. (2019). Use of smartphone applications in English language learning—a challenge for foreign language education. Educ. Sci. 9:179. doi: 10.3390/educsci9030179
Klímová, B. (2018). Learning a foreign language: a review on recent findings about its effect on the enhancement of cognitive functions among healthy older individuals. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 12:305. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2018.00305
Kukulska-Hulme, A., and Viberg, O. (2017). Mobile collaborative language learning: state of the art. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 49, 207–218. doi: 10.1111/bjet.12580
Lakshmi, E. (2023). Advances in sentiment analysis in deep learning models and techniques. Int. J. Recent Innov. Trends Comput. Commun. 11, 474–482. doi: 10.17762/ijritcc.v11i9.8831
Larsen-Freeman, D. (2015). Research into practice: grammar learning and teaching. Lang. Teach. 48, 263–280. doi: 10.1017/S0261444814000408
Loewen, S., Crowther, D., Isbell, D., Kim, K., Maloney, J., Miller, Z., et al. (2019). Mobile-assisted language learning: a Duolingo case study. ReCALL 31, 293–311. doi: 10.1017/s0958344019000065
Metruk, R. (2021). The use of smartphone English language learning apps in the process of learning English: Slovak efl students’ perspectives. Sustain. For. 13:8205. doi: 10.3390/su13158205
Miangah, T., and Nezarat, A. (2012). Mobile-assisted language learning. Int. J. Distrib. Parallel Syst. 3, 309–319. doi: 10.5121/ijdps.2012.3126
Mihaylova, M., Gorin, S., Reber, T., and Rothen, N. (2020). A meta-analysis on mobile-assisted language learning applications: benefits and risks. Psychologica Belgica 62:252. doi: 10.31219/osf.io/ux93y
Nami, F. (2019). Educational smartphone apps for language learning in higher education: students’ choices and perceptions. Australas. J. Educ. Technol. 36, 82–95. doi: 10.14742/ajet.5350
Nehe, B., Mualimah, E., Bastaman, W., Arini, I., and Purwantiningsih, S. (2023). Exploring English learners’ experiences of using mobile language learning applications. JTP 25, 76–90. doi: 10.21009/jtp.v25i1.34883
Oyebode, O., Alqahtani, F., and Orji, R. (2020). Using machine learning and thematic analysis methods to evaluate mental health apps based on user reviews. IEEE Access 8, 111141–111158. doi: 10.1109/access.2020.3002176
Panah, E., Babar, M., Shakib, S., and Ghanad, A. (2021). Analysis of mobile apps for learning grammar through mobile-assisted language learning approach. Asian Tesol J. 1, 46–67. doi: 10.35307/asiantj.v1i1.21
Panichella, S., Sorbo, A., Guzmán, E., Visaggio, C., Canfora, G., and Gall, H. (2015). “How can I improve my app? Classifying user reviews for software maintenance and evolution,” in 2015 IEEE International Conference on Software Maintenance and Evolution (ICSME), 281–290. IEEE.
Pathak, U., and Piyush, E. (2023). Sentiment analysis: methods, applications, and future directions. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 11, 1453–1458. doi: 10.22214/ijraset.2023.49165
Pham, T., Vo, D., Li, F., Baker, K., Han, B., Lindsay, L., et al. (2020). Natural language processing for analysis of student online sentiment in a postgraduate program. Pac. J. Technol. Enhanc. Learn. 2, 15–30. doi: 10.24135/pjtel.v2i2.4
Poláková, P., and Klímová, B. (2022). Vocabulary mobile learning application in blended English language learning. Front. Psychol. 13:869055. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.869055
Rajput, L., and Gupta, S. (2022). Sentiment analysis using latent Dirichlet allocation for aspect term extraction. JCMM 1, 30–35. doi: 10.57159/gadl.jcmm.1.2.22026
Roberts, C., Sage, A., Geryk, L., Sleath, B., and Carpenter, D. (2018). Adolescent preferences and design recommendations for an asthma self-management app: mixed-methods study. JMIR Formative Res. 2:e10055. doi: 10.2196/10055
Rosell-Aguilar, F. (2017). State of the app: a taxonomy and framework for evaluating language learning mobile applications. CALICO J. 34:243. doi: 10.1558/cj.27623
Shadiev, R., Liu, T., and Hwang, W. (2019). Review of research on mobile-assisted language learning in familiar, authentic environments. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 51, 709–720. doi: 10.1111/bjet.12839
Singh, N. (2023). Sentiment analysis using machine learning. Adv. Distributed Comput. Artif. Int. J. 12:e26785. doi: 10.14201/adcaij.26785
Umarani, V., Julian, A., and Deepa, J. (2021). Sentiment analysis using various machine learning and deep learning techniques. J. Niger. Soc. Phys. Sci. 2021, 385–394. doi: 10.46481/jnsps.2021.308
Usama, M., Xiao, W., Ahmad, B., Hassan, M., and Alelaiwi, A. (2019). Deep learning-based weighted feature fusion approach for sentiment analysis. IEEE Access 7, 140252–140260. doi: 10.1109/access.2019.2940051
Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind in society: The development of higher psychological processes. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Wang, G. (2023). Analysis of sentiment analysis model based on deep learning. Appl. Comput. Eng. 5, 750–756. doi: 10.54254/2755-2721/5/20230694
Wardhana, J., and Sibaroni, Y. (2021). Aspect level sentiment analysis on zoom cloud meetings app review using lda. J. Resti 5, 631–638. doi: 10.29207/resti.v5i4.3143
Yang, T., Gao, C., Zang, J., Lo, D., and Lyu, M. (2021). “Tour: dynamic topic and sentiment analysis of user reviews for assisting app release,” in Companion Proceedings of the Web Conference 2021, 708–712.
Yildiz, S. (2020). Use of mobile device language learning applications by Turkish-speaking adults: a survey study. Abant İzzet Baysal Üniversitesi Eğitim Fakültesi Dergisi 20, 1442–1458. doi: 10.17240/aibuefd.2020.660171
Zakaria, Z. (2023). Sentiment analysis to measure public trust in the government due to the increase in fuel prices using naive Bayes and support vector machine. IJAIR 5, 54–62. doi: 10.25139/ijair.v5i2.7167
Zhang, L., Wang, S., and Liu, B. (2018). Deep learning for sentiment analysis: a survey. WIREs Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 8:1253. doi: 10.1002/widm.1253
Zhang, Y., Zhao, Z., Wang, P., Li, X., Lu, R., and Song, D. (2020). Scenarios: a dyadic conversational database for interactive sentiment analysis. IEEE Access 8, 90652–90664. doi: 10.1109/access.2020.2994147
Zhao, H. (2024). A survey on multimodal aspect-based sentiment analysis. IEEE Access 12, 12039–12052. doi: 10.1109/access.2024.3354844
Keywords: mobile language learning applications (MLLAs), sentiment analysis, user feedback, Babbel, Duolingo
Citation: Tabssam HA, Chattha SA, Javeed MF and Hayat A (2025) Sentiment analysis of user reviews: exploring Duolingo and Babbel in English language learning. Front. Comput. Sci. 7:1569058. doi: 10.3389/fcomp.2025.1569058
Edited by:
Mohamed Wiem Mkaouer, University of Michigan–Flint, United StatesReviewed by:
Liudmyla Gryzun, Simon Kuznets Kharkiv National University of Economics, UkraineSabina Rossi, Ca’ Foscari University of Venice, Italy
Anwar Ghammam, Oakland University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Tabssam, Chattha, Javeed and Hayat. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Husnat Ahmed Tabssam, aHVzbmF0LmFobWVkQHJpcGhhaC5lZHUucGs=
 Husnat Ahmed Tabssam
Husnat Ahmed Tabssam Saima Akhtar Chattha2
Saima Akhtar Chattha2