- Department of Computer Sciences, College of Computer Engineering & Sciences, Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University, Al-Kharj, Saudi Arabia
Introduction: This research addresses the security weaknesses in SOAP-based web services, with a particular focus on authentication vulnerabilities resulting from XML-based attacks, such as Signature Wrapping or Replay Attacks. With an emphasis on the fact that an increasing number of cloud services are utilizing SOAP, this study aims to develop a formally verified model that can more effectively identify and address these vulnerabilities.
Method: We propose and execute a TulaFale-based verification framework that formally models SOAP authentication scenarios by introducing the standard constructs, UsernameToken, Timestamp, and X.509 digital certificates. These scripts are transformed into the applied pi-calculus and verified using the ProVerif verification tool to check for properties such as authentication, confidentiality, and message integrity.
Results: By examining XML web services security problems and consulting with security professionals, a number of key risks were identified and discussed. The research contributes to developing a comprehensive language design for cloud security and vulnerabilities using Blanchet’s ProVerif. A controlled experimental testbed was set up to emulate client–server SOAP communication streams and to evaluate the model’s effectiveness in identifying an XML-based attack performed on the web services security framework. The framework was experimentally examined for verification time and scalability for concurrency, and for accuracy of identification. The results confirmed our success in identifying attack patterns and confirming secure message exchanges built to the standards set by WS-Security.
Discussion: The proposed approach addresses and allows for the addition of automated, formal verification to realistic SOAP deployments. By modeling and verifying a security protocol before the deployment, developers can be confident that their implementation is resilient against protocol-level vulnerabilities, improving the trust in the security of web services deployed within cloud applications.
1 Introduction
The popular use of cloud computing has greatly increased data access and scalability, but it has also brought with it essential authentication-related security issues. Proper authentication mechanisms must be in place to avoid unauthorized access and protect against possible data breaches. Alquwayzani et al. (2024) emphasize that security weaknesses in cloud computing, especially in web services, expose sensitive information to cyberattacks. Among the different communication protocols utilized by cloud-based applications, the Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) is still popularly used owing to its robust security and reliability features. Its use of XML-based messaging, however, presents performance overhead and heightened vulnerability to advanced cyberattacks (Sakshi, 2023). Cloud misconfigurations can also cause catastrophic data breaches, hence the need for robust authentication protocols. In medicine, the migration of Electronic Health Records (EHRs) to the cloud has raised issues about patient privacy, yet again justifying the implementation of robust authentication controls (Alquwayzani et al., 2024).
The reliance of SOAPs on XML makes it vulnerable to different XML-based attacks, including attacks such as XML External Entity (XXE), XML Injection, and XML Signature Wrapping (XSW) that exploit the message framework to avoid controls of authentication (Modak et al., 2021). These susceptibilities can lead to data violations, unauthorized access, and disturbances in service. Several studies have emphasized that vulnerabilities in XML injection permit attackers to mediate with application logic, access sensitive data, or perform unauthorized actions. Available mechanisms in security, such as WS-Security, give digital signatures and encryption to protect SOAP messages. These, however, may not be sufficient to counter XML-specific threats on their own. For example, XSW attacks maintain digital signatures but alter the message structure to provide unauthorized access (Modak et al., 2021). Similarly, XML-based Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks take advantage of SOAP’s XML parsing mechanisms, causing service interruption (Krishnamoorthy and Umarani, 2021a). A recent study discovered that XSW vulnerabilities in Germany’s Personal Health Record system could be used to circumvent authentication, which proves the actual-world relevance of these threats (Saxena et al., 2021). Current research highlights the threats of XXE attacks, where XML parsers resolving external entities may inadvertently leak sensitive information or run malicious code. An attacker may create XML payloads that reference external files, causing unauthorized data exposure or service disruptions. A study in the International Journal of Innovative Technology and Research verifies that blocking external entity resolution is the best mitigation technique (Saxena et al., 2021). One of the recent studies on the shortcomings of WS-Security in countering Denial-of-Service (DoS) and injection-based attacks presents an overview of current security patterns and pinpoints shortcomings in current countermeasures, such as the inadequacy of WS-Security in countering certain threats like DoS and injection attacks. The authors strongly promote stronger and stronger security patterns capable of fending off such flaws (Washizaki et al., 2021).
While numerous improvements are being made to the security of web services, several issues are still open for discussion. Firstly, WS-Security is a web service security standard that provides basic authentication and encryption features, but does not address XML-specific security issues like XML Injection, XXE, or XSW attacks. Even systems that claim to use WS-Security standards are not secure due to the known attacks. On the other hand, however, ProVerif is one of the formal verification tools that has been successfully employed to look into general security protocols, but it is still lacking when it comes to SOAP-based authentication models. The gap in the research that attempts to merge formal verification methods with SOAP security techniques prevents a meaningful approach to proving the authentication system’s integrity and security before it is put into use. Some studies have been done to incorporate AI technologies in an attempt to secure against cyberattacks through SOAP, but the results so far are inadequate to claim the use of AI to secure APIs, but not for SOAP proposals. However, with the increasing number of attacks made using AI, there is an urgent necessity for intelligent security frameworks designed for SOAP cloud environments (Krishnamoorthy and Umarani, 2021b; Saxena et al., 2021).
Finally, the trade-off between security and performance in SOAP-based web services is another overlooked area. Most existing security models focus on improving authentication and encryption without considering the computational overhead introduced by these mechanisms. Research is needed to develop authentication frameworks that enhance security while maintaining optimal performance in cloud-based applications. This study aims to address these research gaps by analyzing the security vulnerabilities associated with SOAP-based web services and proposing an enhanced authentication framework to mitigate XML-based threats. With the increasing adoption of cloud computing and web service integration, ensuring robust security measures is essential to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and service disruptions. The research specifically focuses on identifying and addressing security challenges posed by XML-based attack vectors, such as XML Injection, XML External Entity (XXE) attacks, XML Signature Wrapping (XSW), and XML-based Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks. These attacks exploit weaknesses in SOAP over HTTP, posing significant threats to data integrity, confidentiality, and availability.
To address these vulnerabilities, the research designs a secure authentication framework for SOAP-based web services. The model uses TulaFale, a proprietary security protocol specification language integrated with ProVerif, to formally verify the security policies and the authentication mechanisms. In addition, the framework employs WS-Security Enhancements (WSE) to improve the confidentiality and integrity of messages while reducing XML-specific security risks. The objective of this study is to discover and model formally the structural authentication vulnerabilities in the web services that work on the Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP); these include those vulnerabilities caused by XML-based attacks such as Signature Wrapping attacks and Replay attacks. To construct a secure authentication framework, uses WS-Security components such as Username Token, Timestamp, and X.509 certificates, and operates within a simulated SOAP environment, thus being able to justify the name claimed. To subject the framework for proposed verification using formal weapons such as TulaFale and ProVerif, on the reasonable assurance that properties of authentication, confidentiality, and integrity of the message are retained. To further assess its efficacy in identifying protocol-level vulnerability from empirical test scenarios and formal security analysis. To recommend a design that will integrate WS-Security Enhancements (WSE) into SOAP services; this will lay the groundwork for future deployment and observe its performance empirically.
2 Literature review
In the world of ever-developing web services, two major paradigms have emerged: SOAP and REST. SOAP is a protocol-based means of transferring data using XML messaging, with very strict standards like WSDL. SOAP emphasizes security and reliability, hence its suitability for applications requiring very strong transactional support from the server. On the other hand, REST is an architecture that makes use of standard web query protocols and data formats, such as JSON, for stateless communication. REST has become popular in such cases where lightweight and rapid interaction is demanded owing to its simplicity, scalability, and efficiency. Testing the performance characteristics of these two approaches is important for optimizing system design and ensuring seamless communication over diverse platforms, especially in mobile environments and multimedia conferencing applications (Alquwayzani et al., 2024).
As web service technology develops, the need for integration and security becomes a critical challenge. These challenges have been tackled lately in various ways. For example, in a recent study, a system was proposed that integrates wireless sensor networks (WSNs) with web services through the NATO System Enabled Capability (NSEC) framework, which improves energy consumption and network lifetime. Also, another study discussed security principles for implementing RESTful APIs in Python frameworks and noted the need for strong security applications to safeguard the application. All these studies bring the issue of harsh network capabilities and security severe to modern web services (Tabasum et al., 2023; Kornienko et al., 2021). On the other hand, SOAP-based communication is still highly used for web services, but their servers are constantly under security threats. This calls for effective user authentication. The use of SOAP as a Social Authentication Protocol pointed out the need for strong authentication verification to guard against unauthorized access (Linker and Basin, 2024). A previous study investigated the use of Kerberos authentication in SOAP messaging and proved its usefulness in securely verifying users and reducing identity spoofing. Still, authentication alone is not enough because SOAP is among the most vulnerable protocols to XML attacks (Ajvazi and Halili, 2022).
Conventional SOAP authentication mechanisms, like username-password and token-based authentication mechanisms, are generally ineffective against advanced XML-based attacks. To enhance SOAP security, the WS-Security standard has been adopted, offering features such as message integrity and confidentiality (Garg and Garg, 2024). Vulnerability remains, especially regarding XML rewriting attacks. Several studies proposed a SOAP model in the WS-Security framework for the detection and prevention of such attacks. A token-based biometric-enhanced key derivation scheme for wireless network authentication highlighted the requirement of strong authentication mechanisms in cloud computing. These studies show the need for ongoing innovation in authentication approaches to address evolving threats in SOAP-based services and provide long-term security resilience (Mohana, 2018; Cui et al., 2023; Parast et al., 2022). Attacks in the XML language parser system can potentially result in the exposure of sensitive information and unauthorized access to systems. XXE attacks are often overlooked but are equally as damaging as traditional cyberattacks. Data is vulnerable if an XML interface is vulnerable, as it can be compromised in numerous ways. A security concern put advanced consideration into the study of the prevention mechanisms of the XXE attack and concentrated on the safe configuration of XML parsers (Hulloowan and Bekaroo, 2024; Gupta et al., 2023). In the same way, a study pointed out the need to properly set up parsers to protect against these weaknesses (Shahid et al., 2022) and also defended that a secure XML parsing design pattern should be implemented for XML content not to be malicious. Since guessing XML tags is practically unrestricted, these studies reinforce the claim that safe XML parsing should be implemented all the time. Furthermore, the other part of the security aspects, which includes vulnerability methods in web services, particularly SOAP and WSDL protocols, was explained. The authors also noted that common XML services are prone to normal attacks, such as XML injection, XPath injection, and SQL injection, because ordinary XML is in a free text file, making it easy to exploit. To address these issues, the authors defend the implementation of XML Signature and XML Encryption as basic protection methods. Also, the noticed shift to using JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) instead of XML is indisputable as far as not assisting in the protection. The research delves into the use of internet brake systems and presents a report on the need to concentrate more on protecting details and public web services from sabotage alongside thorough control for advanced attacks (Jagruti et al., 2018).
A recent study proposed a hybrid method for enhancing the protection of SOAP messages that combined RSA with 4,096-bit AES encryption and XOR operation for greater computational efficiency (Chaudhary et al., 2024). A combination of applied pi-calculus and formal TulaFale, a scripting language for SOAP, increases the security of SOAP messages by enabling the specification and validation of security attributes associated with them. This extension to the Pi language supports XML syntax design and cryptographic functions, which allow for accurate SOAP messages and WS-Security header validation in the context of automated tooling. This allows for the accurate identification of certain types of exploits, such as XML rewriting attacks, thus increasing the dependability of the protocols used for web services security. The use of these techniques can greatly improve the level of security trust for critical system applications (Bhargavan et al., 2004).
Applied pi-calculus further secures authentication protocols with a strict methodology for checking security properties. It has been used to verify protocols such as TLS 1.3, remote attestation, and compositional reasoning about the security of protocols (Wu et al., 2023; Reaz and Wunder, 2024; Blanchet, 2022). At the same time, TulaFale, when integrated with the Tamarin Prover, has been applied to prove authentication, confidentiality, and integrity in security protocols, proving its utility in real-world applications like the Permission Voucher Protocol and other vital authentication mechanisms (Lanckriet et al., 2023) verification tools such as TulaFale have greatly enhanced protocol security, their success relies on correct implementation and ongoing evolution to counter new threats. Subsequent research needs to improve these methodologies to meet emerging security issues in web services. TulaFale, along with the Tamarin Prover, has been crucial in ensuring security protocols by authenticating, keeping information confidential, and ensuring integrity. Research emphasizes its power, including the examination of the Permission Voucher Protocol, which remained robust against tampering with messages and impersonation (Lanckriet et al., 2023). Further, the I/O specifications framework for compiling Tamarin models has enabled verifications of real-world systems such as WireGuard’s key exchange protocol and various cryptographic authentication schemes (Horne et al., 2023). Resolution-based protocol verification applies explicit approaches to assure the accuracy and security of cryptographic applications and network connections. By utilizing resolution theorem proving, it computerizes verifications, and addresses challenges such as boundless state areas and difficult interaction with protocols. A primary application is Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) verification, which authenticates address mapping before using it, helps to prevent misuse of the network, and improves security (Arquint et al., 2023). Validating distributed protocols can take advantage of decidable modeling, allowing automatic checks of inductive invariants. Tools like Ivy improve effective verification even in complex distributed systems by simplifying invariant analysis (Vijayvargiya et al., 2020), strengthening the reliability and security of network protocols.
Resolution-based verification, as used by tools such as ProVerif, is superior to fuzzing and combinatorial testing in detecting vulnerabilities in SOAP-based communication in several ways. Through the application of Horn clauses and resolution algorithms, ProVerif securely and systematically verifies security properties and identifies possible attacks more thoroughly than heuristic-based methods (Padon, 2022). Unlike fuzzing approaches that could potentially ignore some edge cases, resolution-based approaches analyze all protocol states, thereby providing a thorough security assessment (Le and Pham, 2024). Although fuzzing tools such as SOAPFuzzer can identify zero-day vulnerabilities via traffic analysis, they do not possess the richness of formal verification (Ding and Xu, 2025). Similarly, combinatorial testing, although beneficial in identifying vulnerabilities via mutation-based testing, is very much dependent on test case quality and might not be able to cover the protocol completely (Chen et al., 2014).
This work extends previous research by formally verifying weaknesses in SOAP authentication using formal verification techniques. Although previous work has examined authentication protocols, their verifications were typically not rigorous or automated against dynamically changing threats. The contribution of this work is to apply TulaFale, a dedicated tool for verifying the security properties of web services, to formally examine and verify SOAP authentication protocols. With TulaFale incorporated, the present study extends reliability in authentication by reducing risk levels of security threats and misconfigurations. The model extends SOAP security with an effective verification model that offers an enhanced approach to ensuring resilient authentication against anticipated future cyberattacks. Additionally, the study offers an efficient and scalable technique for responding to web service security issues in the future.
3 Proposed model
Addressing authentication issues related to SOAP protocols is crucial due to the increasing reliance on web services and the need for secure communication. Weak or flawed authentication mechanisms in SOAP can lead to unauthorized access, data breaches, and compromised system integrity. By addressing these issues, organizations can protect data confidentiality, promote trust in web services, and comply with regulatory requirements. The research in this area aims to enhance security, privacy, and trustworthiness, ensuring the integrity of data exchanged and protecting sensitive information.
To address the authentication issues related to SOAP protocol based on XML attacks, the TulaFale script can be adapted for modeling such distinctions in the protocol. The tool instantly and automatically identifies the errors and the revenue explanations of the messages delivered throughout the attacks. Such faults are distinctive errors in cryptographic procedures in web services code. The practical effect of such flaws is complicated, as flaws were detected in the preliminary code before installation. Nonetheless, it is practical to eliminate such impairments as well as tools for systematically ruling them out. In this regard, the traditional top-level begins to establish and explore messages 1 and 2 of the example procedure based on the established definitions reflecting the WS-Security and SOAP specifications.
In the standard top-level specification, Messages 1 and 2 of the authentication protocol using the WS-Security and SOAP definitions were constructed. Figure 1 demonstrates how the client assembled Message 1 (msg1) using the mkMsg1 predicate. This message includes a username token, which was encrypted and digitally signed for confidentiality and authenticity. Figure 2 illustrates the message’s authorization on the server-side, using the server’s signature principles to validate the generated signature, and extract2 the root session identifiers (i.e., S, id1), timestamp (t1), and bindings (b1) of the message, and acknowledge that it is both valid (i.e., an authorized session) and fresh (i.e., from previous interaction). Figure 3 illustrates how the client validates consensus upon receipt of Message 2 (msg2): it validates that the response is fresh and unpredictable (based on the previous exchange), thereby reducing replay attacks. Figure 4 illustrates how the server assembles msg2 based on the validated inputs, where the authentication sequence’s response message is securely assembled from the user’s bindings, as referenced in valid session contexts.

Figure 1. Client-side construction of Message 1 (msg1) using the mkMsg1 predicate. This step includes the encryption of the username token and generation of a digital signature in accordance with WS-Security.
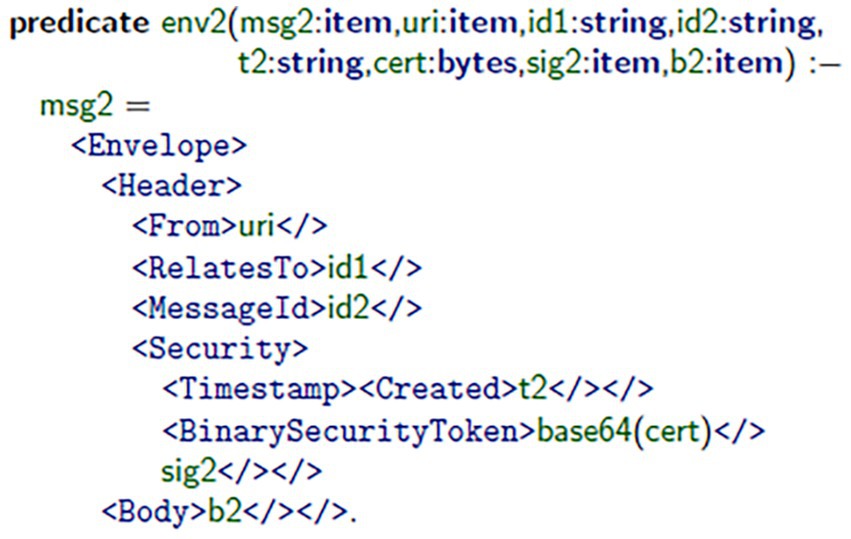
Figure 2. Server-side validation of msg1. Using its certificate, the server parses and verifies the received parameters, extracting session identifiers (S, id1), timestamp (t1), and security bindings (b1) from the message.

Figure 3. Client-side validation of msg2 to ensure session freshness and prevent replay attacks. The figure illustrates how the client verifies the nonce and timestamp to confirm mutual agreement and authentication continuity.
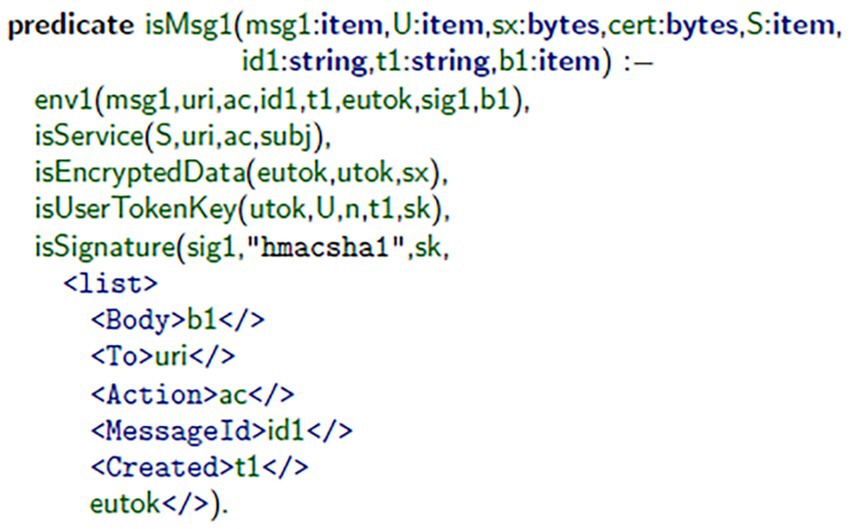
Figure 4. Server-side construction of msg2. The server uses the session ID and client-provided parameters to generate a secure reply that finalizes the authentication exchange.
3.1 Simplified authentication flow
1. Client sends msg1
2. Server verifies and replies with msg2
3. Client checks msg2
4. Authentication completes
The practical implications of flaws detected in the preliminary code of SOAP-based web services can have significant ramifications for security. These flaws may include vulnerabilities in authentication mechanisms, cryptographic protocols, or error handling, which can be exploited by attackers to have unauthorized access, launch denial-of-service attacks, or manipulate data. Such vulnerabilities can result in data breaches, financial losses, reputational damage, compromised user credentials, and legal obligations for organizations. Addressing these flaws is crucial for enhancing the security of SOAP-based web services. By identifying and rectifying these vulnerabilities, organizations can strengthen the authentication process, ensuring that only authorized users can access the services. This helps mitigate the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive information and protects against identity theft or impersonation attacks.
Furthermore, addressing these flaws improves the robustness of cryptographic protocols used in SOAP. This includes ensuring secure encryption, digital signatures, and key management practices, which are fundamental for protecting data confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity. By addressing vulnerabilities in these protocols, organizations can prevent cryptographic attacks, such as tampering, replay attacks, or disclosure of sensitive information. Additionally, addressing flaws in error-handling mechanisms helps in preventing information leakage or unintended exposure of system details that could be exploited by attackers. By implementing proper error handling practices, organizations can minimize the risk of exposing sensitive information, such as system configurations, error messages, or stack traces, which can be utilized by malicious actors to gain insights into the system architecture and exploit weaknesses.
3.2 Processes and assertions
3.2.1 Understanding the verification framework
Formal verification in this paper is based on the applied pi-calculus, which is a mathematical language used to model secure communication protocols. TulaFale extends this framework by offering a readable syntax that parallels the form of the XML used for web services. To reach a larger audience within cybersecurity, the key terms and relationships specific to SOAP authentication have been summarized. For example, predicates are a type of logical statement describing the structure or attributes of a Message, assertions confirm the existence of a security property, and Channels model the communication of messages between two distinct entities, and the entity can be a client or a server. The goal of this section is to clarify and explain the mechanics involved in securely constructing, exchanging, and reassuring mutual authentication of SOAP messages within this formal system.
3.2.2 Translation from TulaFale to applied pi-Calculus
TulaFale scripts are translated into the applied pi-calculus as part of the verification process. The applied pi-calculus is a formal language used to model and analyze concurrent systems, including cryptographic protocols. It provides a mathematical framework for reasoning about the interactions and behavior of various processes within a system.
During the translation process, TulaFale scripts are converted into the syntax and semantics of the applied pi-calculus. This involves mapping TulaFale constructs, such as processes, channels, declarations, and assertions, into their corresponding representations in the pi-calculus. The translated pi-calculus representation captures the behavior and communication patterns specified in the original TulaFale script. Once the TulaFale script is translated into the pi-calculus, a resolution-based protocol verifier is applied to analyze the protocol’s security properties. The resolution-based protocol verifier is a formal verification tool that employs logical inference rules to reason about the correctness and security of cryptographic protocols. The verifier performs an analysis of the translated pi-calculus representation to verify specific security properties embedded by compliant principles. This includes checking for properties like authentication, data integrity, confidentiality, or secure session establishment. The verifier uses a resolution-based approach, which involves applying deduction rules to derive logical conclusions and establish the desired security properties. The resolution-based protocol verifier operates by systematically exploring the potential execution paths and interactions between processes in the pi-calculus representation. The process of verifying security properties within protocols involves checking for vulnerabilities, potential attacks, or breaches of specified security standards. The aim is to either confirm the protocol’s adherence to desired security properties or uncover and address potential weaknesses. Using a resolution-based protocol verifier on the translated pi-calculus representation, the TulaFale tool automates the authentication property verification and other security aspects in SOAP protocols. This systematic approach ensures the identification and rectification of vulnerabilities, thereby ensuring a secure design and implementation of SOAP-based web services.
3.2.3 Formalization of system processes and threats
In TulaFale scripting, a system is defined as a collection of concurrent processes that internally evaluate using predicates and relations and communicate by exchanging terms through predefined channels. Such a script reflects the behavior of entities within the system, such as servers and clients. An attacker is modeled as a separate process interacting with the system via public channels. The cryptographic standards are represented explicitly within the system through a defined process, while the attacker’s behavior is implicitly based on arbitrary processes in the pi-calculus. TulaFale’s syntax involves several non-terminals or metavariables, representing algebraic terms, sorts, and logical formulas. These assertions embedded within the pi-calculus in the process language serve to specify particular security properties adhered to by compliant principles.
An announcement channel ide (sort1,…, sortn) presents ide that has been assigned a name, for switching n-tuples of terms with sorts sort1,…, sortn. In the asynchronous pi-calculus, channels are named, unordered queues of messages. Each channel is public, by default, so that the attacker may input or output messages on the channel. The declarations may be directed by the private keyword to restrain the attacker from retrieving the channel.
An announcement correspondence ide (sort1,…, sortn) presents a label, ide, for events denoted by n-tuples such that sort1,…, sortn. Either an event is a begin-event or an end-event. A begin-event is responsible for recording the initiation of a session, while an end-event records the completion of the session. We use correspondences to formalize the properties. We named this property Robust Safety. Strong safety implies that two acquiescent processes have reached an agreement based on the data, which comprises the contents of a sequence typically of one or more messages. Next, the various kinds of TulaFale processes:
• A process in ide (ide1,…, iden); proc. blocks pending a tuple (tm1,…, tmn) on the ide channel; if one reaches, the process performs as a proc., with its parameters ide1,…, iden bound to tm1,…, tmn, respectively.
• A process out ide (tm1,…, tmn); proc. sends the tuple (tm1,…, tmn) on the ide channel, and then it runs the proc.
• A process proc1 |proc2 is an equivalent configuration of sub-procedures proc1 and proc2; they run in equivalence and may interconnect on common channels.
• Process new ide: bytes; proc. limits the variable ide to a new byte array, to a typical cryptographic key or nonce generation, for instance, then runs proc. Similarly, a process new ide: string; proc. binds the variable ide to a fresh string, to model password generation, for instance, then it runs the proc.
• A process let ide = tm; proc. fixes the term tm to the variable ide, then it runs the proc.—A process filter form → ide1,…, iden; proc. binds terms tm1,…, tmn to the variables ide1,…, iden in such a way that the formula holds, then it runs the proc. (The terms tm1,…, tmn are figured by pattern-matching.
• A process! Proc is an equivalent configuration of a limitless array of imitations of the process Proc. Process 0 is not responsible for anything.
• A process end ide(tm1,…, tmn); proc. logs an end-event labeled with ide and tuple (tm1,…, tmn), then it runs the proc.
• A process ide (tm1,…, tmn), ide resembles a declaration process ide (ide1:sort1,…, iden:sortn) = proc. limits the terms tm1,…, tmn to the variables ide1,…, iden, then it runs the proc.—A process initiates ide (tm1,…, tmn); proc. logs an initial event labeled with ide, and the tuple (tm1,…, tmn), now runs proc.
• Lastly, the process logs a complete event (Checking for the reachability of the final event, which is assured to be done. Consequently, an elementary check of the functionality of the procedure, which can run to completion, is taken).
3.2.4 Proposed verification pipeline and customization
While the proposed framework builds upon established tools like TulaFale and ProVerif, our contribution lies in the customized adaptation of these tools to model dynamic, enterprise-level SOAP authentication flows under WS-Security. In contrast to previous research, which presented standalone protocol checks known to be immediately usable together, the work adopts a structured verification pipeline that includes modularizing protocols via predicates, mapping real-world message schema, and providing stage gates for verification (i.e., separating confidentiality, freshness, and authentication). The proposed model offers a structural layering of TulaFale scripts, with the layers representing modular security enforcement by WS-Security plans, including UsernameToken, Timestamp, and Digital Signature, and can offer independent verification and even reuse by separating security objectives in the verification pipeline. In addition, a lesser weight threat modeling approach derived from attacker interaction channels established in the pi-calculus, permitting a view of developer requirements with visibility of interaction and how threats (like XML Signature Wrapping, Replay Attacks) could be caught by formal predicates.
4 Experimental evaluation and results
To assess the practical viability of the proposed TulaFale-based verification model for SOAP-based authentication, a controlled experimental methodology was established to formally assess the model strengths and weaknesses back to formal verification.
4.1 Implementation environment
Modeling of the typical SOAP authentication scenarios using TulaFale scripts was undertaken, which incorporated the use of UsernameToken, Timestamp, and X.509 digital certificates. These scripts were transcribed into applied pi-calculus to enable formal analysis using the ProVerif tool. The experimental environment was a Windows 10 (64-bit) operating system running on a machine with an Intel Core i7 processor (3.4 GHz) with 16 GB of RAM. The tools that were used were TulaFale version 1.1 and ProVerif version 2.02. The verification of scenarios included both valid authentication flows and adversarial flows such as XML Signature Wrapping, Replay Attacks, and XML Injection of the model.
4.2 Testbed configuration
A simulated communication framework, having a combination of client–server SOAP architecture, was created to simulate secure message exchange. In this environment, a client application was built to create msg1 using the mkMsg1 predicate, as illustrated in Figure 1. The server received msg1, validated msg1, and then also extracted the three primary elements of msg1: timestamps, bindings, and session identifiers, highlighted in Figure 2. After receiving msg2 from the server, the client application verifies that msg2 was fresh and only produced once it first received msg1, omitting any replay attacks (see Figure 3). Lastly, the server generates msg2 to complete the authentication exchange as depicted in Figure 4. Throughout this dialogue, predicates and assurances Throughout this process, predicates and assertions were embedded in the TulaFale scripts to enforce and verify properties related to authentication integrity, message freshness, and secure communication.
4.3 Evaluation metrics
The model was assessed based on several dimensions of interest: verification time; how scalable the model is; how often attacks are detected; and how often the model produces false positives or false negatives. Verification time was measured by examining how long ProVerif took to verify the authentication and secrecy properties. Scalability was tested by increasing the number of concurrent SOAP message exchanges, and noting if ProVerif was still able to verify under higher workloads. The ability to detect attacks was examined by injecting malformed or malicious SOAP messages and determining whether the model would report them as insecure. In addition, the number of false positives and false negatives was noted, counting the number of legitimate messages that were incorrectly flagged, and the number of attacks that went undetected.
4.4 Results and observations
The model indicated the identified security failings in SOAP-based web services by showing the authentication and cryptographic failings and message integrity limits. With the use of TulaFale and ProVerif, the solution indicates no security failings, verifying security automatically, it guarantees WS-Security compliance and prevents unauthorized access (Figure 1). The model improves authentication by means of encryption and the use of X.509 certificates and digital signatures to safeguard the SOAP messages against various attacks like replay attacks, and artefacts of signature verification (Figure 2). Moreover, time-stamp verification adds to the deterrence of replay attacks so that only legitimate users may communicate with other legitimate users. In addition, timestamp verification improves replay attack prevention to ensure only legitimate users can communicate with the web service (Figure 3). The formal verification process validates the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of SOAP-based communications, demonstrating the model’s potential to secure interactions with the web services in advance of a production release (Figure 4).
Though TulaFale and its encoding into the applied pi-calculus facilitate a useful means for validating authentication properties of the SOAP protocol, there are limitations and challenges. One of these limitations is TulaFale’s reliance on existing rules or patterns used in its automated verification processes. Deviating from these patterns in a protocol can be an impediment for the tool to accurately represent and examine the behavior. Further, TulaFale can require a substantial amount of user guidance to properly verify behavior in complex or non-standard initial versions of the protocol. As SOAP protocols become more intricate, with additional processes, channels, and interactions, the computational complexity during verification becomes challenging for scalability. It is important to address these scalability challenges for the tool to be applicable in the real world.
4.5 Scalability considerations
Handling large-scale enterprise environments through SOAP, offering the ability to accommodate thousands of concurrent user sessions, or deeply nested XML structures, can present severe scalability challenges for formal verification tools such as TulaFale and ProVerif. In this research study, we successfully modeled SOAP authentication protocols, enabling us to verify the specifications using TulaFale. However, we acknowledge that the application of our approach in large-scale environments (>100 concurrent user sessions) risks performance bottlenecks in formal verification due mainly to the exponential growth in the state space and message complexity. To ease the burden of scalability in future extensions of our framework, we could pursue some approaches and adapt other existing methods. Using a modular verification approach divides our verification tasks into smaller components that can be verified independently. A modular verification approach promotes the scaling of the verification process while maintaining the modular architecture. Similarly, protocol abstraction, in which patterns of repetitive authentication or messaging are abstractly represented, will greatly reduce the overhead of a verification step. If we could apply an existing, more scalable formal verification tool, like Tamarin Prover or SmartVerif, we could potentially apply more efficient proof strategies or allow guided exploration to help perform verification methods in larger SOAP scenarios. Lastly, caching intermediate verification results, particularly for stable or reused SOAP components, would help to decrease the existing redundancy and overall execution time of the verification efforts during an iterative environment. Utilizing these ideas would help us extend our model to be more widely applicable for real-world, enterprise-scale usage, therefore improving both robustness and practicality.
The effectiveness of the resolution-based protocol verifier hinges on the accuracy of the underlying logical inference rules and the completeness of the analysis. Ongoing research challenges include developing and refining these rules to encompass a wide range of security properties and potential attack scenarios. The present study contributes to the existing literature by comprehensively addressing SOP vulnerabilities, cloud security, attack types, and countermeasures. In particular, it identifies authentication weaknesses in SOAP protocols due to XML attacks and develops a model from Blanchet’s ProVerif. The model supports organizations in integrating automated verification into their existing scripts, speeding up efficient and trustworthy verification of the correctness of TulaFale scripts.
4.6 Empirical validation and benchmarking considerations
The scope of this study is primarily focused on the formal modeling and verification of SOAP-based authentication mechanisms using the TulaFale language and ProVerif tool. We recognize that this absence of empirical benchmarking with a comparative performance study limits our practical evaluation for real-world use. Future work will place an empirical testing angle on our proposed framework within simulated SOAP service environments and production-like SOAP service environments, in order to observe runtime efficiency, detection latency, and resource consumption. Benchmarking will be used to compare our approach to existing SOAP security frameworks and intrusion detection systems (e.g., implementations of XML firewalls and rule-based XML anomaly detectors) with respect to accuracy, scalability, and false positive generation. Thus, empirical investigations will provide valuable insights into our approach, in terms of what operational parameters came into play when the model was subjected to realistic messages, how it interacted with a WS-Security policy in systems where they were deployed, and the accuracy of detections with regard to other existing approaches. Moreover, we will be able to quantitatively measure mitigation success by testing the model’s resilience under simulated attack scenarios, such as XML Injection, XXE, and Signature Wrapping.
For further context as to the applicability and originality of our model, Table 1 compares XML threat mitigation methods in the recent literature for SOAP-based web services by tool, threat coverage, deployment complexity, and formal guarantees. This comparison situates our model in the present context of SOAP security solutions, while demonstrating our model’s formal verification, modularity, and adherence to WS-Security capabilities.
5 Practical implications
To show how a developer might deploy the TulaFale verifications model into a “real” SOAP application, imagine a health information system that exchanges patient data between hospitals and insurance companies, and a developer developing a secure SOAP-based interface to authenticate insurance claim submissions. The developer must ensure that only hospital systems authorized to submit claims can do so, and any messages sent must be tamper-proof and confidential. The developer first creates an authentication workflow that includes UsernameToken and Timestamp, which must have a digital signature, conforming to WS-Security. Then the developer creates TulaFale models of the creation of the SOAP message and validation of receipt of the SOAP message, with predicates such as mkMsg1 and checkMsg2, and real codes of the hospital system’s message schemas (see Figures 1–4). The developer will turn the scripts into the applied pi-calculus format and run verification on their model in ProVerif, validating authentication properties and resistance to replay. Following successful verification, the model will be incorporated into the web services application stack (which is commonly developed either in Java or NET) so that pre-established assumptions on security are enforced with X.509 digital certificates. It is only at that point that we test the solution in. We monitor the system logs to ensure that the model is successfully blocking invalid messages along secure, traceable authentication flows. This situation serves as an example of how formal verification has been applied within real-world SOAP implementations to improve security and confidence during development.
6 Limitations and future directions
Future research projects could include exploring how TulaFale may be integrated into other formal verification tools and methodologies. Integrating TulaFale with model checking, theorem proving, or other formal analysis techniques might provide more effective verification of SOAP protocol security attributes. Extending the verification outside of authentication, including data confidentiality, integrity, and access control, justifies new patterns, assertions, and verification methods to be developed. This comprehensive method can be used to provide end-to-end assurance of SOAP-based web services. In addition, given the dynamic nature of web services, future research can target how to extend TulaFale to check the security properties of new emerging SOAP-related protocols or identify how it can be used in other web service models, e.g., RESTful services. The novelty of the proposed model is in its automated method of checking SOAP protocol authentication properties to assist in unrolling and examining web service security aspects. Future analyses will examine more complex SOAP conventions for WS-Secure Conversation to strengthen client–server encounters.
7 Conclusion
The proposed model was implemented in a simulated SOAP environment and verified using TulaFale and ProVerif. The evaluation confirmed that the framework could detect XML-based attacks, enforce WS-Security properties, and maintain integrity and confidentiality in authentication workflows. These implementation results support the model’s viability for integration into real-world SOAP systems. The rapid growth of cloud computing offers users access to a wide range of on-demand services. However, ensuring privacy and security remains a critical concern. Cloud environments are susceptible to vulnerabilities, which malicious actors exploit to their advantage. To provide better services to cloud clients, it is essential to identify and address security vulnerabilities. One crucial aspect of SOAP security is the adoption of Web Standard Security (WS-Security), which standardizes SOAP messages through authentication and confidentiality processes. XML encryption plays a vital role in preventing unauthorized access to data. This paper has explored flaws at the core of SOAP security, examining the abuse of cloud storage services, data breaches, and attacks on cloud protection. By leveraging TulaFale, a high-level language built on XML with symbolic cryptography correspondence assertions and pi-calculus procedures, this research has presented a valuable approach to modeling WS security. TulaFale’s conversion into the applied pi-calculus enables the analysis of single-message conventions and the development of accuracy proofs. The choice of the pi-calculus for modeling WS-security was driven by its threat model’s generalizability and its suitability for security applications. The economic benefits of cloud computing make it an advantageous solution for non-profit organizations and developing countries. By embracing cloud infrastructure, these regions can enhance their e-governance efforts, establish information centers, and promote rural development. This transformative technology opens doors for increased connectivity, knowledge sharing, and economic efficiency. It is crucial to address security concerns and leverage the potential of cloud computing to create a safer and more inclusive digital landscape for all.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
MM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study is supported by funding from Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University project number (PSAU/2025/R/1446).
Acknowledgments
The author is very thankful to all the associated personnel who contributed/to this research.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ajvazi, G., and Halili, F. (2022). “SOAP messaging to provide quality of protection through Kerberos authentication,” in 2022 29th Int. Conf. Syst. Signals Image Process. IWSSIP. pp. 1–4.
Alquwayzani, A., Aldossri, R., and Frikha, M. (2024). Prominent security vulnerabilities in cloud computing. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 15, 803–813. doi: 10.14569/ijacsa.2024.0150281
Arquint, L., Wolf, F.A., Lallemand, J., Sasse, R., Sprenger, C., Wiesner, S.N., et al. (2023).” Sound verification of security protocols: from design to interoperable implementations,” in 2023 IEEE Symp. Secur. Priv. (SP). pp. 1077–1093.
Bhargavan, K., Fournet, C., Gordon, A.D., and Pucella, R. (2004). TulaFale: A security tool for web services, form. methods components objects 2, 197–222.
Blanchet, B. (2022). The security protocol verifier ProVerif and its horn clause resolution algorithm. arXiv [preprint]. Available online at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.12227 (Accessed March 14, 2025).
Chaudhary, S., Singh, V., Malik, N., Sidhu, K.S., Kirola, M., and Joshi, K. (2024). “Digital signature security enhancement: using X-OR operation on RSA and AES with 4096 bits key length,” in 2024 Int. Conf. Comput. Sci. Commun. (ICCSC). pp. 1–6.
Chen, J., Li, Q., Mao, C., Towey, D., Zhan, Y., and Wang, H. (2014). A web services vulnerability testing approach based on combinatorial mutation and SOAP message mutation. Serv. Orient. Comput. Appl. 8, 1–13. doi: 10.1007/s11761-013-0139-1
Cui, H., Yang, X., Yang, W., Qin, B., and Yi, X. (2023). Token-based biometric enhanced key derivation for authentication over wireless networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 10, 2347–2357. doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2023.3246439
Ding, S., and Xu, X. (2025). Vulnerability mining method of SOAP based on black-box fuzzing. Internet Technol. Lett. 8:e553. doi: 10.1002/itl2.553
Garg, G., and Garg, A. (2024). Advancements in authentication methods: A comprehensive review of techniques, challenges, and future directions.
Gupta, C., Singh, R. K., and Mohapatra, A. K. (2023). Secure XML parsing pattern for prevention of XML attacks, Inf. Commun. Technol. Compet. Strateg. ICTCS 2022. Intell. Strateg. ICT 2023, 759–770.
Hamouda, M.. (2025). An Ontology-Based Approach for Detecting SOAP Message Attacks. Zenodo, 15024575.
Höller, P., Krumeich, A., and Lo Iacono, L.. (2021). Xml signature wrapping still considered harmful: A case study on the personal health record in Germany. In IFIP international conference on ICT systems security and privacy protection. Springer Int. Publ. 625, 3–18.
Horne, R., Mauw, S., and Yurkov, S. (2023). When privacy fails, a formula describes an attack: a complete and compositional verification method for the applied π-calculus. Theor. Comput. Sci. 959:113842. doi: 10.1016/j.tcs.2023.113842
Hulloowan, B., and Bekaroo, G.. (2024).” Defending against XML external entity (XXE) attacks: A review and comparative analysis of prevention mechanisms,” in 2024 Int. Conf. Next Gen. Comput. Appl. NextComp. pp. 1–6.
Jagruti, B., Nidhi, P., and Pandya, D. (2018). “A survey on web service security techniques”, 2018 4th Int. Conf. Comput. Commun. Autom. ICCCA. pp. 1–5.
Kornienko, D. V., Mishina, S. V., Shcherbatykh, S. V., and Melnikov, M. O. (2021). Principles of securing RESTful API web services developed with Python frameworks. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2094:032016.
Krishnamoorthy, N., and Umarani, S. (2021a). An experimental study on cloud computing security issues and a framework for XML DDoS attack prevention. J. Phys. 1:012058.
Krishnamoorthy, E., and Umarani, R. (2021b). AI-assisted SOAP-based secure communication model for preventing XML attacks. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 183.
Lanckriet, E., Busi, M., and Devriese, D.. (2023). “πRA: A π-calculus for verifying protocols that use remote attestation,” in 2023 IEEE 36th Comput. Secur. Found. Symp. (CSF). pp. 537–551.
Le, X. T., and Pham, V. T. (2024). Advancing security protocol verification: a comparative study of Scyther, Tamarin. J. Tech. Educ. Sci. 19, 43–53e. doi: 10.54644/jte.2024.1523
Linker, F., and Basin, D.. (2024). “SOAP: A social authentication protocol,” in 33rd USENIX Secur. Symp. (USENIX Secur. 24). pp. 3223–3240.
May, M. J., Lux, K. D., and Gunter, C. A. (2020). WSEmail: an architecture and system for secure internet messaging based on web services. Serv. Orient. Comput. Appl. 14, 5–17. doi: 10.1007/s11761-019-00283-9
Modak, S., Majumder, K., and De, D. (2021). “Vulnerability of cloud: analysis of XML signature wrapping attack and countermeasures.” in Proc. Int. Conf. Front. Comput. Syst.: COMSYS 2020.755–765
Mohana, R. (2018). A proposed SOAP model in WS-security to avoid rewriting attacks and ensuring secure conversation. Int. J. Inf. Secur. Priv. 12, 74–88. doi: 10.4018/IJISP.2018010107
Padon, O.. (2022). Verification of distributed protocols: decidable modeling and invariant inference, 2022 form. Methods Comput.-Aided Des. (FMCAD). 4–4.
Parast, F. K., Sindhav, C., Nikam, S., Yekta, H. I., Kent, K. B., and Hakak, S. (2022). Cloud computing security: a survey of service-based models. Comput. Secur. 114:102580. doi: 10.1016/j.cose.2021.102580
Raimondo, M., Ciatto, G., and Omicini, A. (2022). Model-driven engineering for formal verification and security testing of authentication protocols. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.11206.
Reaz, K., and Wunder, G. (2024). Formal verification of permission voucher. arXiv [preprint]. Available online at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.16224 (Accessed March 14, 2025).
Sakshi, S. (2023). Assessment of web services based on SOAP and REST principles using different metrics for mobile environment and multimedia conference. IJAREEIE 12, 1701–1709.
Saxena, S., Bansal, S., and Kumar, R. (2021). Xml external entity attacks and mitigation in XML parsers. J. Emerg. Technol. Innov. 8, 563–568.
Shahid, R., Marwat, S.N.K., Al-Fuqaha, A., and Brahim, G.B. (2022). “A study of XXE attacks prevention using XML parser configuration,” in 2022 14th Int. Conf. Comput. Intell. Commun. Netw. CICN. pp. 830–835
Tabasum, H., Samuvel, S.G., Shilpa, A.N., Niranjan, L., Sridhar, N., and Shwetha, N.. (2023). A novel based NSEC system for integrating network capability with wireless sensor network using web services. (ICSSES). pp. 1–6.
Vijayvargiya, S., Shinde, S., Ogale, N., and Dhanasekar, V. K.. (2020). Anticancer compounds. U.S. patent no. 10,855,644. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent And Trademark Office.
Washizaki, H., Xia, T., Kamata, N., Fukazawa, Y., Kanuka, H., Kato, T., et al. (2021). Systematic literature review of security pattern research. Information 12:36. doi: 10.3390/info12010036
Wu, F., Liu, J., Li, Y., and Ni, M. (2023). LpiCT: a logic security analysis framework for protocols. arXiv [preprint]. Available online at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.02171 (Accessed March 14, 2025).
Keywords: authentication, access control, pseudonymity, anonymity, privacy-preserving protocols, digital rights management
Citation: Saeed MM (2025) Cloud security and authentication vulnerabilities in SOAP protocol: addressing XML-based attacks. Front. Comput. Sci. 7:1595624. doi: 10.3389/fcomp.2025.1595624
Edited by:
Xiaoguang Wang, University of Illinois Chicago, United StatesReviewed by:
Rakesh K. Kadu, Shri Ramdeobaba College of Engineering and Management, IndiaTarun Kumar Vashishth, IIMT University, India
Copyright © 2025 Saeed. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mozamel M. Saeed, bS5tdXNhQHBzYXUuZWR1LnNh; bW96YW1lbDg4ODhAZ21haWwuY29t
 Mozamel M. Saeed
Mozamel M. Saeed