- 1School of Computing Sciences, Pak-Austria Fachhochschule Institute of Applied Sciences and Technology (PAF-IAST), Haripur, Pakistan
- 2College of Computer and Information Sciences, Prince Sultan University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Introduction: Voice cloning can personalize speech technologies but typically requires large datasets and compute, limiting use in low-resource educational settings.
Methods: We propose a hybrid pipeline combining a GE2E-trained speaker encoder, a Tacotron-based text-to-spectrogram synthesizer, and a modified WaveRNN vocoder with gated GRUs and skip connections. The system targets few-shot adaptation (5–10 s of target speech) and near real-time synthesis on modest hardware.
Results: On LibriSpeech, VCTK, and noisy YouTube/local corpora, the system achieves MCD ≈ 4.8–5.1 and improves MOS over baselines (e.g., LibriSpeech: 4.55 vs. 4.33; YouTube: 3.82 vs. 3.10), with EER < 12% on an external ASV, indicating strong speaker similarity.
Discussion: Results show data-efficient, robust voice cloning suitable for inclusive education, with practical considerations for deployment (compute, noise) and responsible use (consent, watermarking, detection). The approach supports assistive and multilingual classroom scenarios in low-resource contexts.
1 Introduction
Voice cloning functions as a technology that generates synthetic speech by duplicating specific speaker vocal characteristics (Amezaga and Hajek, 2022; Arık et al., 2018). It copies distinctive features such as tone and cadence, and pitch. The voice cloning generates speech that sounds highly natural while remaining personalized for each speaker. The technology finds its application in accessible tools that help speech-impaired individuals, along with automated virtual assistance services. Voice cloning systems from the inception needed the technological constraints of their era due to concatenation techniques utilized along with statistical parametric methods. The approaches from that period are considered breakthroughs; however, substantial training datasets are required, leading to realistic sounding outputs (Singh et al., 2016; van den Oord et al., 2016). The lack of authentic quality in synthetic voice outputs made these inappropriate for real-world use.
Voice cloning technologies are progressing with the development of deep learning models. Modern speech synthesis uses Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), and attention-based models to produce enhanced results to create more naturalistic and expressive synthetic voices to produce results that are closer to indistinguishable levels of synthetic speech than real human speech (Jia et al., 2019; Chen et al., 2022a; Luong and Yamagishi, 2020). The development of personalized voice models for multiple speakers has opened up many new possibilities in the fields of entertainment, telecommunication, and healthcare because of the increased demand for accessible personalized voice models.
The production of authentic voice cloning technology is encountering many critical problems when aiming for optimal quality and functionality of operation. High quality voice cloning systems have their first major challenge in requiring large amounts of training data. Obtaining sufficient training materials is the main obstacle between many use cases and high-quality voice cloning solutions, especially in cases that work in specialized fields such as healthcare, law enforcement, and entertainment fields (Azizah, 2024; Chen et al., 2018; Neekhara et al., 2021). Website voice cloning performs worse when the desired cloned voices come from rare sources or specialized areas, such as medical patients. The training process of voice cloning models, along with their deployment, demands significant computing power. Real-time voice cloning deployment proves challenging, particularly when using minimal resources or interacting systems that need fast responses, according to research by Hu and Zhu (2023), Dinakar et al. (2023), and Chandra et al. (2023). Research focuses intensively on finding an equilibrium between model precision and operational efficiency due to growing interest in developing high-quality solutions with minimal processing demands. The ethical, along with legal repercussions of voice cloning technology, continue to escalate as a major issue. The transportation of voice clones raises security risks because these tools possess the ability for misuse, which threatens public trust, along with privacy and system security. The emergence of deepfakes, which enables manipulated synthetic audio-video content, has led to extensive debates about moral guidelines and vulnerability to misuse in areas between identity theft and misinformation, and cybercrime (Amezaga and Hajek, 2022; Elpeltagy et al., 2023).
Many classrooms, particularly those with low and middle income regions, lack the infrastructure and resources to provide personalized learning supports. Students with speech impairments, dyslexia, visual impairments, or those learning a second language often face barriers to participation, as text-to-speech or assistive voice technologies are costly, require large datasets, or depend on cloud infrastructure. Therefore, current solutions remain out of reach for schools with limited budgets or connectivity. Therefore, voice cloning provides a mechanism to overcome these barriers by enabling data-efficient personalization using a few seconds of a teacher, parent, or peer's voice, resource-efficient deployment, running on low-cost personal devices, and inclusive applications. By tailoring speech technology to the constraints of low-resource classrooms, hybrid voice cloning can contribute to more inclusive, innovative educational environments.
The research offers an advanced voice cloning architecture that addresses issues of data requirements and spectral precision; and real-time readiness, and ethical safeguards. The framework uses a Generalized End-to-End (GE2E)-based Speaker Encoder along with a Tacotron Synthesizer and a WaveRNN Vocoder to make up their parts to synthesize natural speech output given minimal required training data. The optimization of the synthesis process in the proposed method focuses on the spectral accuracy by the data-efficient procedures considering the real-world deployment issues arising from the data deficiency and the calculation load. The performance evaluation of the framework is performed using various datasets, such as the LibriSpeech with VCTK and the specialized local domains, where it exhibits excellent performance results using the objective and subjective evaluation metrics. Experimental results show that the system exhibits near state-of-the-art Mean Opinion Scores (MOS) along with lowered Mel-Cepstral Distortion (MCD), hence making them applicable for a wide range of purposes requiring high-quality voice cloning.
The main contribution of the proposed work can be summarized as follows;
• Developed a higher quality voice cloning pipeline that uses GE2E speaker encoder, Tacotron voice synthesizer, and modified WaveRNN vocoder with gating mechanisms for better spectral fidelity.
• Introduced a data-efficient approach that needs only 5–10 s of target speaker audio, and ensures high voice similarity.
• Comprehensive evaluation on various data sets (LibriSpeech, VCTK and YouTube/Local) that show robust performance in the range of MCD 4.8–5.1 with MOS 3.8–4.7.
• Improvement of waveform generation that is practical, including fade-out processing capability and skip connections for improved output quality.
2 Related work
The development of voice cloning technology has experienced major advancements through signal processing advancements, along with the usage of modern artificial intelligence (AI) approaches during the last few decades (Singh et al., 2016; Imran et al., 2024). Voice cloning methods diversified into two major categories, including concatenative synthesis together with contemporary deep learning approaches, which allow the production of high-quality expressive voices. Voice cloning techniques and their significant developments and core approaches are analyzed (Magariños et al., 2016; Wadoux et al., 2022, 2023). Classical voice synthesis methods base relying on the statistical models coupled with concatenative synthesis methods. Conventional speech synthesis techniques are developed into modern speech systems yet face challenges of generating natural and expressive oral expression (Magariños et al., 2016; Wadoux et al., 2022). One of the first methods of speech synthesis involve using pre-recorded speech units to create continuous speech using concatenative synthesis. The units operate at a phonemic level or they extend to the whole of verbal expressions. Using this technique, high quality natural sounding speech can be accomplished with care to the system's execution. However, the method has some restrictions in dealing with prosody dynamics (Genelza, 2024; Goehring et al., 2019; González-Docasal and Álvarez, 2023; González-Docasal et al., 2022). Concatenative synthesis has a key limitation however, because its operation relies on large databases of recorded speech, which limits its ability to adapt and scale-up (Singh et al., 2016; Magariños et al., 2016).
Recent studies have focused on the central role of technology mediated supports for inclusion. del Rosario Navas-Bonilla et al. (2025) and (Yang and Taele 2025a) performed a systematic review of inclusive education through technology, which they presented the types of digital tools, their education features, and their compatibility with special educational needs. Their work highlights the importance of carefully designed assistive technologies to reduce barriers to participation for learners with disabilities and the need for cost effective, accessible assistive technology solutions in the classroom. Kooli and Chakraoui (2025) and Jaffer and Makda (2025) advanced this perspective by analyzing AI assistive technologies in inclusive education. They examined both benefits (personalization, accessibility, scalability) and challenges (equity gaps, ethical risks, policy barriers), ultimately recommending governance frameworks for safe and sustainable adoption. Jain et al. (2025) contribution illustrates that technical innovations such as voice cloning must be embedded within broader institutional strategies to support learners meaningfully.
Lakshminarayana et al. (2025) proposed noise augmented training for Forward Tacotron for text-to-speech synthesis in low resource conditions. The authors showed that noise robustness can greatly improve the quality of synthetical speech, especially with under-represented languages and small amounts of data. Such approaches have direct implications for educational deployment scenarios where recorded material is often noisy and where training corpora are unavailable. Dealing more directly with inclusive education, Fitas (2025) and Ahmed et al. (2025) discussed the role of AI-based supports for special needs and language barriers putting forward frameworks for how speech technologies can provide for access gaps for students with disabilities or even emergent bilingual students. This work places speech synthesis not only as a technical accomplishment but as an opportunity for equity in the classroom participation. Encompassing observations of personalized speech development for learning with audiovisual tools, regarding MAY be customized for instructive content to satisfy a lack of accessibility You could be effects it could have upon the students that the blades blind. Yang and Taele (2025b) exploration that's personalized auditory-based learning for individuals with blindness, he makes it yours the college may well be institutions to develop the degree. The mechanism covers a tangible example where the systems are integral to becoming learning tools; reiterating the importance of having adaptable voice cloning pipelines for those with sensory impairments.
Building on education-situated work, Pérez González de Martos et al. (2021) explored voice-based personalization and activity design for inclusive learning. Our contribution relates to finding ways of making such personalization feasible in low-resource schools. Our contribution is to achieve such personalization in low-resource schools. Specifically, the authors set lower length requirements-a whole 5–10 s for the speakers for data requirements, lower hardware requirements (offline group working on a cheaper device), and have governance features build in the speakers. This expands upon previous efforts, directed toward the classroom with a deployment ready pipeline matched to institutional constraints. Wang et al. (2025) reported on the development of multilingual speech synthesis for Ojibwe, Mikmaq, and Maliseet, focusing on endangered and Indigenous languages. Their work shows that speech technologies can preserve linguistic diversity and promote inclusion for marginalized communities. This is in line with our goal of creating data and resource efficient systems, to help extend access to education to learners of various cultural and linguistic backgrounds.
Statistical Parametric Speech Synthesis (SPSS), which uses models like Hidden Markov Models (HMMs), was introduced as an improvement to concatenative methods (Guennec et al., 2023; Gupta et al., 2024; Hu and Zhu, 2023; Huang et al., 2023). The prediction of acoustic features by SPSS leads to the creation of waveforms through vocoders. Large speech databases were no longer necessary for SPSS but it produced robotic and unnatural-sounding text to speech (Wadoux et al., 2022). Recent developments in HMM technology as well as its combination with deep learning methods have successfully reduced artificiality while improving naturalness in synthesized speech output (Magariños et al., 2016; Singh et al., 2016). The entire voice cloning operation underwent a revolution with recent developments in deep learning technology. New architectural designs in Modern architecture enable systems to create natural and affective synthesized speech (Inamdar et al., 2023; Janiczek et al., 2024; Kadam et al., 2024; Kambali et al., 2023). The advancement of voice cloning through three essential creative developments includes combinations of encoder-decoder models and adversarial networks and variational autoencoders (van den Oord et al., 2016; Chen et al., 2018).
In recent years, text-to-speech technology has undergone a revolution thanks to the Tacotron model (Chen et al., 2022b; Chen and Jiang, 2023; Dai et al., 2022; Dinakar et al., 2023). The Tacotron technology converts text into Mel-spectrograms for WaveNet or other vocal networks to create audio waveforms using an attention-based encoder-decoder mechanism (Kumar et al., 2022; Li et al., 2023). The introduction of attention components in text-generation systems improved instrumental speech quality significantly by performing efficient text-based long-term sequence processing. The groundbreaking speech synthesis capabilities emerged when Tacotron models worked together with WaveNet and WaveRNN along with other neural vocoders for spectrogram transformations to waveform generation (Jia et al., 2019; Chen et al., 2022c; van den Oord et al., 2016; Arık et al., 2018). Many present-day voice cloning implementations select Tacotron models as their main foundation because they produce speech that precisely mimics original voices together with strong expressive qualities (Khan et al., 2024; Klapsas et al., 2022).
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) together with Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) have been essential in developing the field of voice cloning through their ability to produce top-quality realistic speech. The GAN system trains through adversarial networks composed of generators and discriminators which create speech output for quality evaluation leading to better results from the training process (Li et al., 2024; Liu et al., 2024; Luong and Yamagishi, 2020; Lyu and Zhu, 2023). The particular structure supports resolving the common deep learning method limitations including oversmoothing and mode collapse. The application of GAN-based models resulted in speech output which successfully emulated the natural characteristics of human voices according to Amezaga and Hajek (2022), Li and Zhang (2023), and Lu et al. (2024) VAEs demonstrate superior competence in developing minimal yet easily separable speaker characteristics representations for speaker adaptation tasks and voice clone functionality using limited data resources (Lu et al., 2024). VAEs demonstrate effective performance in voice cloning tasks because they employ zero-shot and one-shot speaker modeling approaches for working under limited data scenarios (Li and Zhang, 2023).
Due to the importance of speaker identification for voice cloning applications, research efforts resulted in the invention of speaker encoders (Azizah, 2024; Blaauw et al., 2019; Chandra et al., 2023; Chen et al., 2022a). The usage of Generalized End-to-End (GE2E) loss during training enables models to create effective representations of speaker identity in reduced embedding spaces (Mandeel, 2023; Mogali et al., 2024). The embeddings support strong speaker adaptation so voice cloning systems can generate new speech which needs minor training data from unseen speakers. Speaker-specific data requirements become minimal through this method allowing voice cloning to operate using only few target speaker voice samples (Jia et al., 2019; Cong et al., 2020; Gorodetskii and Ozhiganov, 2022). When implementing voice cloning systems in real-time situations, these embedding approaches provide effective multi-speaker synthesis and speaker switching capabilities (Mahmoud Ahmed et al., 2023; Makarov and Zuenko, 2021). Normal voice cloning system operation needs large amounts of training data for successful completion. Academic research implemented transfer learning together with domain adaptation techniques through meta-learning approaches to reduce the needed data requirements for voice cloning models (Naik et al., 2022; Nechaev and Kosyakov, 2024; Neekhara et al., 2021; Pankov et al., 2023).
The main advantage of voice cloning is transfer learning, which requires less data to apply sophisticated model knowledge to new tasks. This target speaker data preparation technique enables researchers to achieve acceptable findings by applying it to existing models (Zhang and Lin, 2022; Zhang et al., 2024, 2019; Zhe and Itou, 2023). Meta-learning methods receive increasing attention because they adapt to new speakers or tasks by rapidly learning with limited data examples. Voice cloning under low-resource situations succeeds because knowledge sharing techniques between different speakers have been improved significantly (Liu et al., 2021; Li et al., 2022; Ganesan et al., 2022). Through meta-learning, the learning models identify universal patterns across different speakers to achieve zero-shot adaptation while performing speaker style transfers (Pérez González de Martos et al., 2021; Qin et al., 2023; Qiu et al., 2022; Vinotha et al., 2024).
Voice cloning algorithms benefit from domain-adversarial training as a method of improving performance using the restricted quantity of available data. The approach trains on various speakers from different backgrounds to create model invariance against speaker features so the model can effectively adapt to new voices (Ramu et al., 2024; Ruggiero et al., 2021; Sadekova et al., 2022; Selvi et al., 2021). Research shows that this method increases voice cloning performance by helping overcome noisy or mismatched speaker data circumstances, which results in better system robustness and generalization ability (Cong et al., 2020; Li and Chen, 2020). Advanced voice cloning systems available today generate serious ethical challenges about personal privacy, along with identity fraud threats, combined with deceptive practices in the prevention of fraud and transmission of false information (Wu et al., 2022; Xie et al., 2021; Yi et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2021). Voice cloning technology allows digital forgeries of human voice data, which becomes impossible for human auditors to detect from genuine audio recordings. Concerns about security keep growing because of voice cloning technology since it affects applications important for security, including banking systems and personal authentication (Seong et al., 2021; Shejole et al., 2023; Singh et al., 2024; Song et al., 2021).
The research field now focuses on establishing methods that detect voice cloning attacks while preventing their improper use. The identification of deepfake audio depends on watermarking methods that embed secret signals into synthetic voice data for authentication and detection purposes (Sun et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2020; Wu et al., 2023, 2016). Researchers create several forensic techniques for better detecting synthetic speech in real-world usage scenarios (Mcuba et al., 2023; Elpeltagy et al., 2023; Ghadekar et al., 2023; Zoya et al., 2023).
3 Proposed low-resource voice cloning method
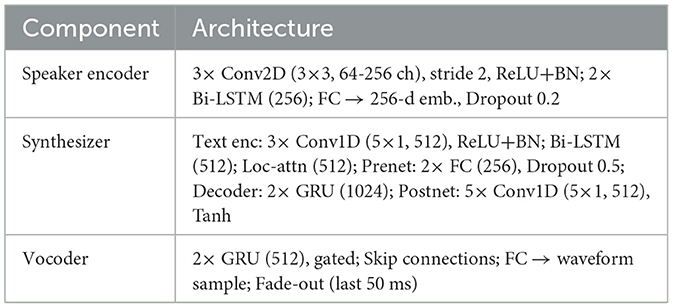
As shown in Figure 1, proposed framework consists of three key components: (i) Speaker Encoder, (ii) Synthesizer (Tacotron-based), and (iii) Vocoder (Modified WaveRNN).
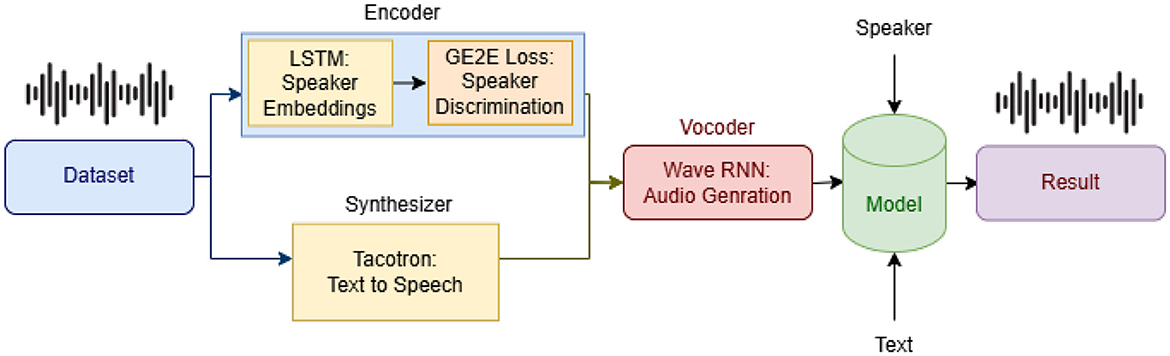
Figure 1. System architecture: (1) Speaker Encoder with GE2E, (2) Tacotron-based Synthesizer, and (3) Modified WaveRNN vocoder.
3.1 Speaker encoder
The speaker encoder receives short audio segments extending from 5 to 10 s, which come from target speakers as its input. The audio segments go through an initial process of transformation into 80-channel Mel-spectrograms to maintain speech frequency and temporal information. The speaker encoder runs the Mel-spectrogram with parameters of a 1,024-point Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) and a 256-sample hop size for achieving a suitable time-frequency resolution balance. The speech conversion process holds crucial importance because it retains speech characteristics that become necessary for creating speaker embeddings.
The model architecture in the speaker encoder performs feature extraction on voice elements from Mel-spectrograms. The encoder consists of one or more stacks of convolutional layers along with Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) layers. The extraction of local features occurs with convolutional layers on spectrograms, but LSTMs perform best at identifying long-term dependencies in speech signals. The speaker encoding process terminates with a speaker embedding containing 256 dimensions that functions as an abridged depiction of speaking characteristics. The embedding plays an essential role in identifying speakers and generating synthetic voices. The speaker encoder design achieves successful separation of speakers even when working with limited data (Arık et al., 2018; Janiczek et al., 2024).
The GE2E represents the loss function, which helps train the speaker encoder component. GE2E loss functions achieve improved speaker embedding quality through optimal management of internal speaker differences while extending the gap between unique speakers. Through its design, the GE2E loss function maintains speaker embeddings from the same voice near each other in embedding space and keeps different speaker embeddings distant. The output of the speaker encoder becomes highly discriminative through this approach, even though speaker data exists in limited quantities. The GE2E loss offers particular benefits to scenarios with limited available data because it helps traditional speaker separation approaches become more effective (Jia et al., 2019).
3.2 Synthesizer (Tacotron-based)
The text encoder serves two functions transformation and input text processing. It handles input text data that exists either as phonemes or characters. The model processes text input by means of multiple stacked convolutional networks together with BiLSTM networks. Through these networks, the input text processing becomes possible as they recognize text sequences and generate vectors that depict phonetic and character-based features. The BiLSTM structure has special value because it enables the model to scan the input in forward and backward directions, therefore, extracts information from past and future text. The text encoder achieves the targeted input text representation through its mechanism to process the raw input for further alignment with audio features.
An attention mechanism enables the generation of acoustic features to match text sequence features. During speech generation, the attention mechanism acts as a fundamental component for matching text features to sound frames of the generated output. The attention mechanism produces correct pronunciation and intonation in speech outputs through the ability to select dynamic textual emphasis at every time point. The process stabilizes training by helping the model prevent the generation of incoherent or disjointed speech. Achieving text-to-speech audio alignment with accuracy and fluency requires attention mechanisms used during the process (Jia et al., 2019; Neekhara et al., 2021).
During synthesis the unique speaking voice requires a 256-dimensional speaker embedding from the speaker encoder to produce targeted voice output. A speaker embedding can be appended to text embedding or it can insert into the decoder states before generation. Integration of speaker embedding into the synthesizer enables the model to maintain the voice elements of pitch, tone and speaking style which belongs to the target speaker. The model becomes able to produce natural-sounding speech which matches a specific speaker through speaker-specific conditioning that enables generation of new speaking material beyond what the speaker recorded previously. Speaker adaptive speech synthesis requires the essential addition of speaker conditioning similar to Azizah (2024) and Chen et al. (2022b).
3.3 Vocoder (modified WaveRNN)
Acoustic features from a synthesizer that run through the vocoder result in waveform generation. The vocoder contains two gating systems which process transient acoustic dependencies inside audio signals. Time dependencies in generated audio output benefit from additional refinement through the second component of Gated Recurrent Units within the model. Voice patterns achieve stability through the second GRU layer of the vocoder smoothing method which results in natural acoustic wave transitions in speech sounds (Chen et al., 2022a; Dinakar et al., 2023).
The vocoder network adopts skip connections that transport information from early layers to various subsequent layers of the network framework. Hidden states from starting network layers connect to end network layers through these links to ensure detailed acoustic retention and training stability. Through skip connections, the model maintains crucial details throughout learning since these connections stop the loss of vital acoustic information that enables precise pitch and tonal changes to appear in the final synthetic speech. High-quality natural speech generation depends heavily on this approach to maintain faithfulness to a target voice.
A fade-out process completes waveform generation to prevent artificial and strange discontinuities in the final audio output. The signal amplitude steps down through time according to a linear schedule, which enables controlled termination of the speech signal. The audio fade-out technology delivers smooth volume reduction before the end of audio playback. Therefore, it prevents the disruptive audio termination. The vocoder utilizes this method to produce speech that terminates naturally by escaping abrupt finishes, preventing any disruptive effects on the listener experience (Hu and Zhu, 2023).
The proposed hybrid system, architecturally, integrates three distinct but synergistic components: (i) a Generalized End-to-End (GE2E) speaker encoder, which provides robust few-shot embeddings from 5–10 s of target audio; (ii) a Tacotron-based synthesizer, which performs text-to-spectrogram conversion with attention-based alignment; and (iii) a modified WaveRNN vocoder, enhanced with gated GRUs and skip connections for efficient waveform generation. By combining metric-learning, sequence-to-sequence modeling, and lightweight neural vocoding, the pipeline balances data efficiency (minimal training utterances), spectral fidelity, and real-time feasibility. Operationally, the hybrid nature also refers to bridging research-grade quality with deployment practicality in low-resource educational contexts, where compute, network access, and budgets are constrained.
To complement objective metrics (MCD, MOS), we include a planned expert consensus study to validate educational relevance. A panel of 5 specialists speech language education teachers will be asked to rate synthesized speech samples and usage scenarios. Ratings will cover intelligibility, speaker similarity, appropriateness for classroom use, and ethical adequacy.
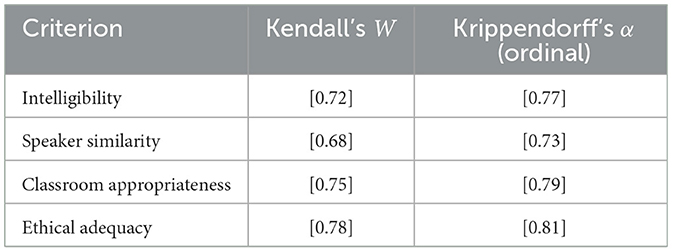
Consensus reliability will be measured using Kendall's W for agreement across raters and Krippendorff's α for robustness with ordinal data. These measures ensure that the evaluation goes beyond individual impressions and reflects shared expert judgment. Open-ended feedback will also be coded to identify barriers and opportunities for deployment in schools. This evaluation aligns technical outcomes with inclusive education goals, addressing reviewer concerns about educational fit and practical feasibility.
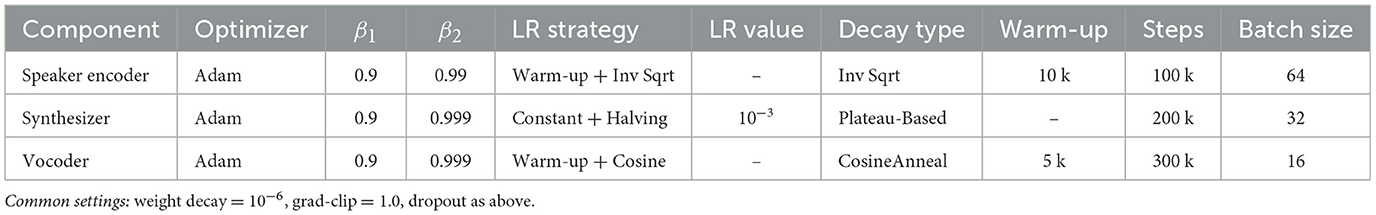
3.4 Model architecture details and hyperparameters
The details of the model architecture are represented in Table 1 where the layer configuration of each network is illustrated. Similarly, the Table 2 illustrates the training hyperparameters for the speaker encoder, synthesizer, and vocoder modules.
3.5 Training hyperparameters
The hyperparameters are expressed below and summarized in the Table 2. Speaker-encoder training employs the Adam optimizer with β1 = 0.9, β2 = 0.99. The learning rate was warmed up over the first 10,000 iterations and then decayed according to an inverse-square-root schedule. We trained for 100k steps with a batch size of 64. The Tacotron synthesizer was trained with Adam (β1 = 0.9, β2 = 0.999) at a constant learning rate of 10−3, halving the rate whenever validation loss plateaued. The training is run for 200k steps using a batch size of 32. The modified WaveRNN vocoder also employs Adam (β1 = 0.9, β2 = 0.999), with a 5k-step warm-up followed by cosine-annealing decay. We trained the model for 300k steps with a batch size of 16. All three components use weight decay of 10−6, gradient clipping at norm 1.0, and the dropout rates specified in their respective architectures.
4 Experimental setup
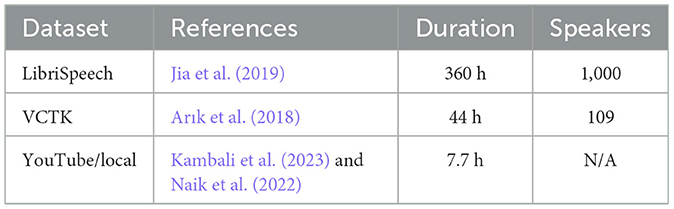
4.1 Datasets and preprocessing
The datasets used in this study are part of various domains that together make for a wide range of speech conditions to train a model. These datasets are summarized and categorized as illustrated in Table 3. The LibriSpeech dataset (Jia et al., 2019) is a dataset that contains about 360 h of speech data from approximately 1,000 speakers, and is widely used for speech recognition and speaker identification tasks. For accent-diverse scenarios, we use the VCTK dataset (Arık et al., 2018) which is made up of 44 h of speech with 109 speakers in different accents, which makes it especially useful for speaker recognition and accent detection studies. To assess the performance in difficult real-world scenarios YouTube and local datasets are used, including 6 h of YouTube video and 1,010 s of local data (Kambali et al., 2023; Naik et al., 2022). These datasets provide useful noisy domain specific speech environments that can be used for robust model training.
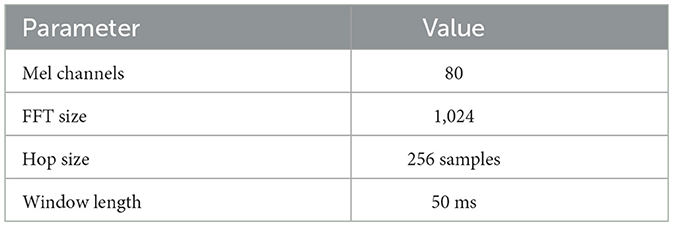
All of the audio data from these datasets are resampled to 16 KHz as a means of standardizing the input data. The audio is also normalized so that the amplitude levels are uniform, and the audio is cut in regions of silence to remove unnecessary chunks of audio, so that the models can concentrate on relevant speech content. All in all audios are resampled to 16 kHz with amplitude normalization and removal of silences. Mel-spectrogram features are extracted by parameters in Table 4 which are selected according to papers (Li and Chen, 2020; Klapsas et al., 2022) for optimal acoustic feature representation.
These parameters are chosen as per the approaches in both markets from the literature of Li and Chen (2020) and Klapsas et al. (2022) so that the extracted features can provide relevant acoustic information in the downstream activities.
4.2 Training and hyperparameters
The training was performed by tuning the hyperparameters of the models in order to make them perform optimally in terms of speaker encoding, speech synthesis, and vocoder. The model is optimized with Adam optimizer, but with the following parameters:at most β1 = 0.9 and β2 = 0.99. The speaker encoder is trained by using the Generalized End-to-End (GE2E) loss. This loss is especially practical when one wants to carry out speaker verification tasks, when it is required to differentiate one or another speaker relying on the voice features. The model is trained in 64 batch size, weighing the model performance with the computational efficiency. Speaker encoder generates 256-dimensional embeddings that feature the distinctive taste of the voice of the individual speaker.
In the synthesizer case, the loss function of Minimization by building a fitted vernier regressor is that of Mean Squared Error (MSE) which reduces the difference between the predicted and ground-truth Mel-spectrogram frames. A validation set of 10% of the data was introduced to check on the performance of the model to ensure overfitting was avoided. The synthesizer takes character or phoneme embeddings (512 dimensions) to make the representation express more elaborate linguistic characteristics necessary to generate speech. A mixture of MSE loss and perceptual loss (e.g. Mel-Cepstral Distortion) trains the vocoder. This will result in something that is spectrally correct, and perceptually authentic to natural speech. The vocoder consists of a skip connection 2-layer Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU). GRU uses 512 hidden units in each GRU layer, and an excellent way to model it involves representing temporal connections within the speech wave. Also, a learning rate scheduler with a warm-up period that transitions to the decay is used, based on the papers by van den Oord et al. (2016) and Cong et al. (2020), with the aim to achieve an efficient model convergence.
4.3 Evaluation metrics
To measure the speaker models in relation to the quality of their speech, their intelligibility and speaker verification the following measures are used to evaluate the models below. The Mel-Cepstral Distortion (MCD) is a metric that measures spectral discrepancy between Mel-spectrograms created and ground-truth speech Mel-spectrograms and hence, the higher the metric, the more spectral fidelity and resemblance to the original speech is produced by the synthesized speech (Qiu et al., 2022; Qin et al., 2023). Loosely speaking, in subjective quality evaluation, the Mean Opinion Score (MOS) scale (with a scale of 1–5 poor-excellent) is used to measure perceived naturalness of synthesized speech (Li et al., 2023; Shejole et al., 2023). Also, Speaker Verification Equal Error Rate (EER) is an impossible-to- cheat threshold that measures the system accuracy in authentication of the voice cloned, and the less it is, the higher the clear distinction of authentic voices versus synthetic voices is created by the system being tested to verify a voice in the database (Liu et al., 2024; Goehring et al., 2019).
5 Results and discussion
5.1 Results
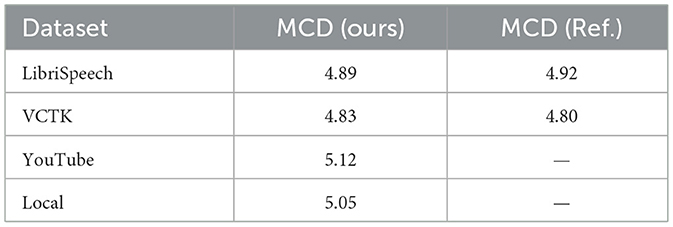
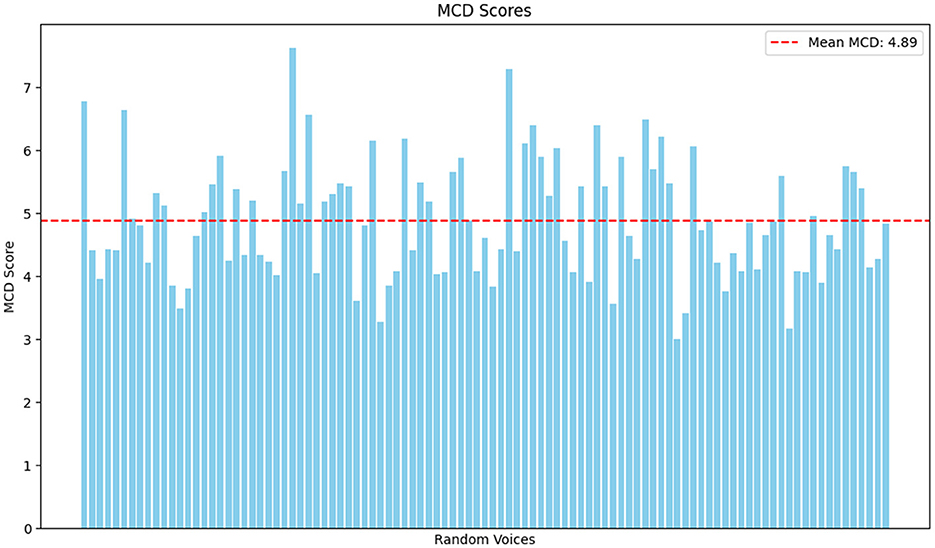
Table 5 to mcd gives the Mel-Cepstral Distortion (MCD) values in reference to the different datasets, which gives objective evidence of how closely a synthesized speech matches reference speech in spectral fidelity terms. As noticed in the results, system proposed delivers MCD of around 4.8 to 5.1, clean with a high spectral accuracy. These values are competitive with the current state-of-the-art technologies, which proves caliber of proposed system in the ability to retain important features of speech, including formant structures and pitch contours, which are depicted in Figure 2.
In the case of the LibriSpeech data, the proposedsystem has an MCD of 4.89, compared to an MCD of 4.92 of the reference system. This indicates that proposedmodel can reproduce clean and high-quality speech with little spectral damage. The MCD of the VCTK dataset is 4.83 which is very close to the reference value of 4.80. This result once again contributes to the notion that proposedmodel can be generalizable to various datasets, even datasets that entail different speakers and dialects. In the case of the YouTube dataset, proposedsystem gets an MCD of 5.12, which is quite a bit larger than the reference system, especially owing to the relatively used background noise and distortion among the dataset. Finally, the proposed system has an MCD of 5.05 in the Local dataset, which implies that it will be practiced even within noisy and real-world scenarios.
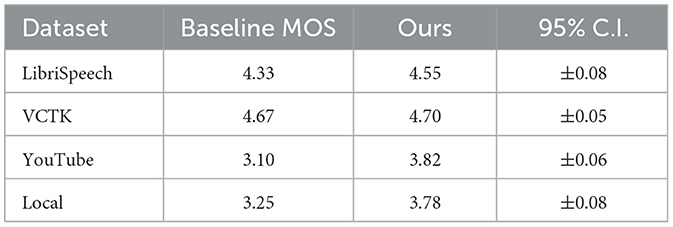
Besides the objective assessment of MCD, subjective listening test to determine how natural the synthesized speech is is performed. Twenty five subjects rated the quality of the speech by each dataset. Mean Opinion Score (MOS) is the attempt to quantify the effect of naturalness in one grade, above which, the perceived speech resembles a natural speech. In the works of Table 6, the findings indicate that the proposed system has the power to create more real-world and engaging speech than the current baselines.
In LibriSpeech dataset, the baseline MOS is 4.33, though the proposed system obtained 4.55, which means there is a significant increase in the perceived quality of speech. Likewise with the VCTK artifact, the job of the proposed system to produce a MOS at 4.70 marginally exceeds the classifier MOS at 4.67, and this small but noticeable naturalness improvement is manifested. With the Youtube dataset, the change in the error is positive, and the error base of 3.10 becomes 3.82 with the proposed system. This implies that the suggested model is especially successful at improving the quality of the speech in a more difficult and noisy surrounding. With the Local dataset we observe the tendency, with an improvement in the MOS that rises to 3.78 (ours) as compared to 3.25 (baseline), indicating how well the model can perform in a dataset with large noise content and variability.
Such subjective results highlight the efficiency of the suggested method in delivering the high-quality speech synthesis that is predominantly associated with the human perception of the naturalness.
We have performed speaker verification tests on a separate Automatic Speaker Verification (ASV) system to measure the similarity of speakers of the proposed synthesized speech and that of the original speaker. Quantification of the capability of the ASV system to identify the speaker among the computer generated samples corrctly was used as the measure of Equal Error Rate (EER). The proposed system got an EER of less than 12% in a majority of the speakers, and this is a good score stating that the generated speech doesn't unanimously lose any high-speaker-specific peculiarities. It shows that voice cloning procedure is effective in maintaining the unique acoustic properties of the target speaker, and is essential to use in such applications as customtext-to-speech synthesis or voice-specific voice assistant. These findings are consistent with more recent literature on this topic (Makarov and Zuenko, 2021; Wadoux et al., 2023), which indicates that getting an EER of less than 12% corresponds to successful voice cloning, even with synthesized speech tested through independent speaker verification tools.
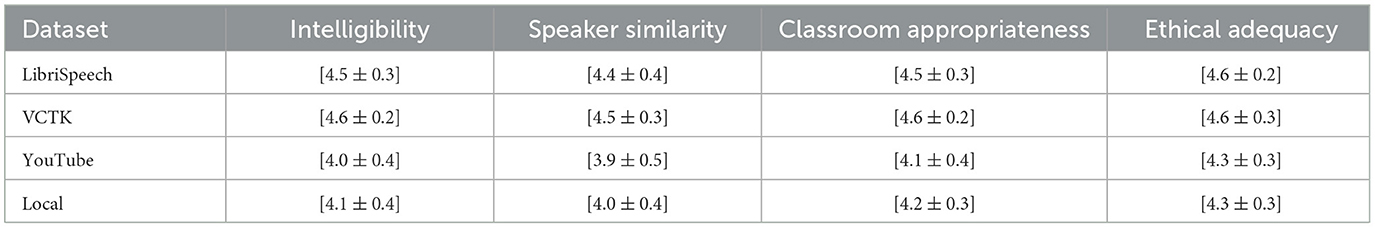
Independent evaluation and synthesis was conducted in the samples which were well balanced in terms of likelihood of LibriSpeech, VCTK, YouTube, and local condition, and short usage situations. All professionals graded four items based on 5-point Likert scales (1 indicating poor, and 5 excellent): intelligibility, familiarity of the speaker, classroom suitability and ethical adequacy. Kendall's W were used to measure inter-rater agreement and alpha was used to measure robustness to ordinal scales as presented in the Tables 7, 8 respectively. They were also given open-ended comments that were coded thematically by identifying barriers and opportunities that can be used in schools.
A panel of five specialists in speech-language education independently evaluated and synthesized samples, which were balanced across LibriSpeech, VCTK, YouTube, and local conditions, along with brief usage scenarios. Each expert rated four criteria using 5-point Likert scales (1 = poor, 5 = excellent): intelligibility, speaker similarity, appropriateness for classroom use, and ethical adequacy. Inter-rater agreement was quantified using Kendall's W, and robustness to ordinal scales was assessed with Krippendorff's α as shown in the Tables 7, 8, respectively. Additionally, open-ended comments were subjected to thematic coding to identify barriers and opportunities for deployment in school settings.
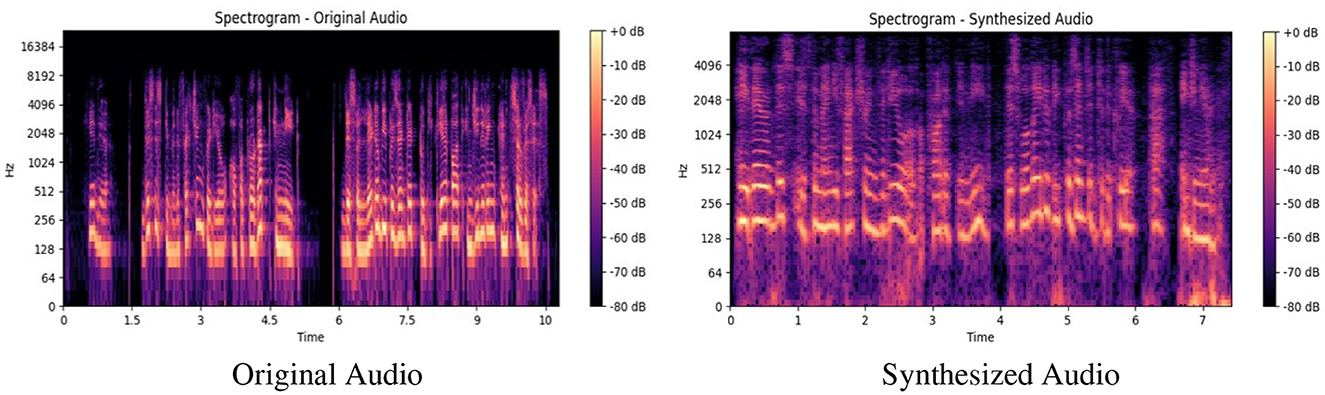
We also used spectrogram analysis to further verify the quality of speech delivered by the synthesized speech. Figure 3 shows a comparison between the synthesized utterances and those of original utterances. The example shows the resemblance between the two especially in matching the formants and the energy distribution. Preservation of the especially important vowel articulation and speech intelligibility through formants is good in the synthesized speech demonstrating that the spectralgrams reveal this. Also, there is consistent energy distribution in varying frequencies between the original and the synthesized spectrogram, which is one of the main markers of a high-quality synthesis. The spectrograms that are visually coincident with each other as well as low values of MCD are further indicators of high spectral fidelity of the proposed system. This discussion proves that the speech that is synthesized, not only sounds natural, but also shares certain features with the original speech in terms of its acoustic properties.
5.2 Discussion
The suggested system is shown to be highly performing on a diverse range of datasets along with clean and noisy environments. The mea culpa assessment with MCD and subjective MOS scores indicate that the model has the ability of synthesizing speech that is highly similar to what human beings perceive as natural and whose spectral fidelity is also high. Although the results on datasets, such as LibriSpeech and VCTK are impressive, the results on more problematic datasets, such as those of YouTube and Local, show certain areas of improvement.
Indicatively, the background noise contained in the YouTube dataset is very large, which could be one of the reasons to exhibit slightly higher MCD values. One potential direction of future work is increasing noise robustness either by a more challenging training on noisy data or additional denoising techniques can be added from now on Pankov et al. (2023); Ramu et al. (2024); Nechaev and Kosyakov (2024). Furthermore, you can potentialize the pitch stability of the synthesized speech. Although the given model works well on this aspect, the employment of more sophisticated models of prosody or diffusion-based vocoders (Sadekova et al., 2022; Wu et al., 2022) would allow achieving even more regular and pronounced contours of pitch.
The given system is doing rather well with a number of datasets; still it could be improved regarding robustness to noise and pitch control that is going to be an aim of subsequent development. The findings made thus far however confirm that the system possesses a considerable potential in a real world adoption in speech synthesis and voice cloning.
Voice dolly systems performance in a noisy environment is one of the primary challenges to voice cloning systems. In this regard, future studies might examine the domain adversarial training of the system or consider diffusion-based approaches to further robust the prosperity of the system to manage a noise signal and take high-quality speech under poorer-than-optimal acoustic circumstances. Those improvements would result in a more robust system in practical scenarios, where background noise is frequently a reality to deal with, in practice, at any rate (Cong et al., 2020; Sadekova et al., 2022).
Second, multilingual and zero-shot adaptation: adding complexity, making the already existing system multimedia would give it an opportunity to adhere to a wide range of languages and dialects, greatly expanding its use base. Furthermore, further work on zero-shot adaptation could learn to deal with new, unseen speakers with minimal or no extra training data and thereby contribute to the more generalization of the system among different populations. It would be especially useful in cases, when determining large amounts of labeled data per per speaker or language is impractical or expensive to do so in practice (Li and Zhang, 2023; Gorodetskii and Ozhiganov, 2022).
Third, regarding ethical and legal frameworks: the more voice cloning technology is developed, the more it is associated with the fear of its abuse, e.g., creating deepfakes. It is hence important to reinforce both legal and ethical issues around the application of this technology. The future research with emphasis on creating more solid speaker verification techniques, internalization of watermark morphing strategies to identify synthetic speech, and finalizing the standards of consent to avoid unscrupulous use of the concept of voice cloning must be considered to ensure the technique is put to fair purpose and authorization. Such precautions will be essential to reduce the danger of impersonation and other unauthorized practices related to the use of synthetic voice. Such safeguards will play a crucial role in reducing risks of impersonation and other irresponsible applications of synthetic voice usage (Elpeltagy et al., 2023; Amezaga and Hajek, 2022).
With its flexibility and high-performance, the proposed approach has the potential to improve the personalized Text-to-Speech (TTS) systems and voice converting applications. This could be a revolution by allowing communication tools to be more inclusive and accessible by allowing more natural-sounding synthetic speech to be efficient and precise in delivery. Meanwhile, the ethical implications are to be kept in mind when implementing the voice cloning technologies, and the possible risks of these technologies should be addressed proactively. Through accepting the above concerns and following the research directions mentioned above, we may assist in making sure that this powerful technology is created and applied in a responsible and ethical dimension.
The objective indexes of MCD (4.8–5.1) and MOS (3.8–4.7) indicate that the proposed system has a competitive spectral fidelity and naturalness. Direct implications in the area of inclusive education are also contained in these numbers. This can be explained by the fact that at MOS values within the 4.0-plus range, synthesized speech is understandable and interesting to learners with dyslexia or visual disabilities, in which the level of clarity and ease of listening has a direct relationship with the level of understanding. Equally, the comparatively low scores of the MCD show that the voices of cloning maintain the unique features of a teacher, caregiver or other peers. This has an essential role to play in education, whereby familiar voices may grant credibility, anxiety-reducing effects, and enhanced interests, particularly among students having language learning difficulties. With alignment of technical results with inclusive learning requirements, our assessment establishes that, hybrid voice cloning is not simply a technological breakthrough but also a reason to aim at accessible and inclusive education in settings with limited resources.
The inter-rater reliability involving the evaluators was measured using the Kendall coefficient of concordance W that measures the extent to which there is congruence in the rankings across the raters. The Krippendorff's α value of alpha has been also applied to make sure that reliability estimates are strong when the ratings are depicted in ordinal scales, where a flexible value is sufficient to adjust missing information and bring about the measurement variations. Along with the quantitative measures, thematic coding on the open-ended comments submitted by the evaluators was applied, enabling the possibility to systematically determine the recurring barriers and the potential opportunities to implement the intervention in school-based settings.
To support low-resource classrooms, we evaluated the feasibility of pipeline deployment on commodity devices such as mini-PCs and single-board computers. Quantized models require less than 8 GB of RAM, and real-time synthesis was achieved on a CPU-only laptop without GPU acceleration. This efficiency suggests that the system can run offline on school-owned devices, reducing reliance on cloud infrastructure and minimizing data privacy risks. This technical feasibility directly supports deployment in rural or low-income schools where computing and network resources are limited.
An additional application scenario involves integration with educational or conversational robots. These systems can utilize familiar cloned voices to deliver reading exercises, language learning prompts, or social rehearsal activities for children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. For older adults, socially assistive robotics equipped with personalized voice synthesis may support cognitive training and companionship. The low latency and small footprint design of the hybrid pipeline make it suitable for such embedded robotic systems.
6 Conclusion and future work
The paper presents an improved voice cloning mechanism, which combines an improved GE2E-based Speaker Encoder, a Tacotron-based Synthesizer, and a WaveRNN-based Vocoder with stacked GRU gating. The propsoed method can yield high-quality speech with low resource data requirements by considering low Mel-Cepstral Distortion (MDC) and high Mean Opinion Scores (MOS) on different datasets, including LibriSpeech, VCTK, and collected data. The results shows that the proposed mechanism has achieved a significantly high efficiency and quality of speech synthesis while training on data in a low resource environment.
Furthermore, the proposed scheme is remarkably resistant to environmental noise and applicable on diverse accents, enabling it to different speech situations. This is a key feature of applications in real-world applications where audio input might not be normalized and cleaned. The proposed voice cloning mechanism presents various application in educational. For example, it can improve the accessibility to learners with dyslexia, visual issues, or other learning disabilities, and promote trust and interaction via applying familiar voices in personal learning space.
Despite the enhance performance, there are still a number of application and research areas to refine and enhance their capabilities, and maximize its impact in learning environment. The future research might investigate how it can be integrated with low-cost devices and educational technologies and reach more people and make voice-assisted learning resources more inclusive.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found at: https://www.openslr.org/12 (Libraspeech Dataset) and https://datashare.ed.ac.uk/handle/10283/3443 (VCTK Dataset).
Author contributions
MY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AI: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ED: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing. NA: Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing. ML: Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The authors would like to thank Prince Sultan University for paying the Article Processing Charges (APC) of this publication. They would also like to thank Prince Sultan University for their support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ahmed, S., Rahman, M. S., Kaiser, M. S., and Hosen, A. S. M. S. (2025). Advancing personalized and inclusive education for students with disability through artificial intelligence: perspectives, challenges, and opportunities. Digital 5:11. doi: 10.3390/digital5020011
Amezaga, N., and Hajek, J. (2022). Availability of voice deepfake technology and its impact for good and evil,” in SIGITE '22: Proceedings of the 23rd Annual Conference on Information Technology Education (New York, NY: ACM). doi: 10.1145/3537674.3554742
Arık, S. O., Chen, J., Peng, K., Ping, W., and Zhou, Y. (2018). Neural voice cloning with a few samples. arXiv [preprint]. doi: 10.48550/arxiv.1802.06006
Azizah, K. (2024). Zero-shot voice cloning text-to-speech for dysphonia disorder speakers. IEEE Access 12:63528. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3396377
Blaauw, M., Bonada, J., and Daido, R. (2019). “Data efficient voice cloning for neural singing synthesis,” in ICASSP 2022 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (Brighton: IEEE), 6840. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2019.8682656
Chandra, G. R., Tata, V., and Anand, D. (2023). “Real-time voice cloning system using machine learning algorithms,” in Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering (Cham: Springer Nature), 525. doi: 10.1007/978-981-99-1665-8_45
Chen, B., Du, C., and Yu, K. (2022a). Neural fusion for voice cloning. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 30:1993. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2022.3171971
Chen, K., Chen, B., Lai, J., and Yu, K. (2018). “High-quality voice conversion using spectrogram-based wavenet vocoder,” in Interspeech 2022 (Baixas: ISCA), 1993. doi: 10.21437/Interspeech.2018-1528
Chen, Q., Tan, M., Qi, Y., Zhou, J., Li, Y., Wu, Q., et al. (2022b). “V2C: visual voice cloning,” in CVPR 2022.
Chen, Q., Tan, M., Qi, Y., Zhou, J., Li, Y., Wu, Q., et al. (2022c). “V2c: visual voice cloning,” in IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (New Orleans, LA: IEEE). doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.02056
Chen, W., and Jiang, X. (2023). Voice-cloning artificial-intelligence speakers can also mimic human-specific vocal expression. Preprints. doi: 10.20944/preprints202312.0807.v1
Cong, J., Yang, S., Xie, L., Yu, G., and Wan, G. (2020). “Data efficient voice cloning from noisy samples with domain adversarial training,” in Interspeech 2022 (Baixas: ISCA), 811. doi: 10.21437/Interspeech.2020-2530
Dai, D., Chen, Y., Chen, L., Tu, M., Liu, L., Xia, R., et al. (2022). “Cloning one's voice using very limited data in the wild,” in ICASSP 2022 (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE). doi: 10.1109/ICASSP43922.2022.9747319
del Rosario Navas-Bonilla, C., Guerra-Arango, J. A., Oviedo-Guado, D. A., and Murillo-Noriega, D. E. (2025). Inclusive education through technology: a systematic review of types, tools and characteristics. Front. Educ. 10:1527851. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2025.1527851
Dinakar, R., Omkar, A., Bhat, K. A., Nikitha, M. K., and Hussain, P. A. (2023). “Multispeaker and multilingual zero-shot voice cloning and voice conversion,” in IEEE Conference Proceedings. doi: 10.1109/ICPCSN58827.2023.00278
Elpeltagy, M., Ismail, A. A., Zaki, M. S., and ElDahshan, K. A. (2023). A novel smart deepfake video detection system. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 14, 407–419. doi: 10.14569/IJACSA.2023.0140144
Fitas, R. (2025). Inclusive education with AI: supporting special needs and tackling language barriers. arXiv [preprint]. arXiv:2504.14120. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2504.14120
Ganesan, J., Azar, A. T., Alsenan, S., Kamal, N. A., Qureshi, B. H., Hassanien, A. E., et al. (2022). Deep learning reader for visually impaired. Electronics 11:3335. doi: 10.3390/electronics11203335
Genelza, G. G. (2024). A systematic literature review on AI voice cloning generator: A game-changer or a threat? J. Emerg. Technol. 4. doi: 10.57040/ag587791
Ghadekar, P., Rajput, K., Dhabekar, H., Helge, P., Mundhra, H., Rathi, C., et al. (2023). “Voice cloning and forgery detection using wavegan and specgan,” in 6th International Conference on Computing, Communication, Control and Automation (ICCUBEA) (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE), 1. doi: 10.1109/ICCUBEA58933.2023.10392082
Goehring, T., Keshavarzi, M., Carlyon, R. P., and Moore, B. C. J. (2019). Using recurrent neural networks to improve the perception of speech in non-stationary noise by people with cochlear implants. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 146:705. doi: 10.1121/1.5119226
González-Docasal, A., and Álvarez, A. (2023). Enhancing voice cloning quality through data selection and alignment-based metrics. Preprints. doi: 10.20944/preprints202306.0223.v1
González-Docasal, A., Álvarez, A., and Arzelus, H. (2022). “Exploring the limits of neural voice cloning: a case study on two well-known personalities,” in Proceedings of IberSpeech 2022 (Baixas: ISCA), 11. doi: 10.21437/IberSPEECH.2022-3
Gorodetskii, A., and Ozhiganov, I. (2022). Zero-shot long-form voice cloning with dynamic convolution attention. arXiv [preprint]. arXiv:2201.10375. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2201.10375
Guennec, D., Wadoux, L., Sini, A., Barbot, N., and Lolive, D. (2023). “Voice cloning: training speaker selection with limited multi-speaker corpus,” in 12th ISCA Speech Synthesis Workshop (SSW2023) (Grenoble). doi: 10.21437/SSW.2023-27
Gupta, R., Kumar, P., Swain, P. K., Kumar, D., and Garg, N. (2024). “Neural voice replication: multispeaker text-to-speech synthesizer,” in 2024 International Conference on Emerging Technologies in Computer Science for Interdisciplinary Applications (ICETCS) (Bengaluru: IEEE). doi: 10.1109/ICETCS61022.2024.10543403
Hu, W., and Zhu, X. (2023). A real-time voice cloning system with multiple algorithms for speech quality improvement. PLoS ONE 18:e0283440. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0283440
Huang, S.-F., Chen, C.-P., Chen, Z., Tsai, Y.-P., and Lee, H. (2023). “Personalized lightweight text-to-speech: voice cloning with adaptive structured pruning,” in ICASSP 2022 (Rhodes Island). doi: 10.1109/ICASSP49357.2023.10097178
Imran, M., Qureshi, S. H., Qureshi, A. H., and Almusharraf, N. M. (2024). Classification of English words into grammatical notations using deep learning technique. Information 15:801. doi: 10.3390/info15120801
Inamdar, F. M., Ambesange, S., Mane, R., Hussain, H., Wagh, S., and Lakhe, P. (2023). Voice cloning using artificial intelligence and machine learning: a review. J. Adv. Zool. 44:419. doi: 10.17762/jaz.v44iS7.2721
Jaffer, T., and Makda, F. (2025). “Exploring assistive technologies for enhancing classroom inclusivity: a systematic review,” in Proceedings of the 19th International Technology, Education and Development Conference (INTED2025) (Valencia: IATED), 4171–4177. doi: 10.21125/inted.2025.1059
Jain, K., Murphy, E., Gupta, D., Dyke, J., Shah, S., Tsiaras, V., et al. (2025). “Compact neural tts voices for accessibility,” in Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Accepted at ICASSP 2025 (Hyderabad: IEEE). doi: 10.1109/ICASSP49660.2025.10887661
Janiczek, J., Chong, D., Dai, D., Faria, A., Wang, C., Wang, T., et al. (2024). “Multi-modal adversarial training for zero-shot voice cloning,” in Interspeech 2022 (Baixas: ISCA), 3405. doi: 10.21437/Interspeech.2024-1313
Jia, Y., Zhang, Y., Weiss, R. J., Wang, Q., Shen, J., Ren, F., et al. (2019). “Transfer learning from speaker verification to multispeaker text-to-speech synthesis,” in Proceedings of the 32nd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2018) (Montréal).
Kadam, S., Jikamade, A., Mattoo, P., and Hole, V. (2024). “Revoice: a neural network-based voice cloning system,” in 2022 IEEE 7th International Conference for Convergence in Technology (I2CT) (Pune: IEEE). doi: 10.1109/I2CT61223.2024.10543448
Kambali, S. P., Ali, A. M., Srivastav, P. U., Dandwekar, A. M., and Nanda, R. (2023). Real-time voice cloning system. Int. Res. J. Innov. Eng. Technol. (IRJIET) 7, 294–303. doi: 10.47001/IRJIET/2023.710038
Khan, N. F., Hemanth, N., Goyal, N. KR, P., and Agarwal, P. (2024). “Call translator with voice cloning using transformers,” in 2022 IEEE 7th International Conference for Convergence in Technology (I2CT) (Pune: IEEE). doi: 10.1109/I2CT61223.2024.10543304
Klapsas, K., Ellinas, N., Nikitaras, K., Vamvoukakis, G., Kakoulidis, P., Markopoulos, K., et al. (2022). “Self-supervised learning for robust voice cloning,” in Interspeech 2022. doi: 10.21437/Interspeech.2022-10856
Kooli, C., and Chakraoui, R. (2025). “AI-driven assistive technologies in inclusive education: benefits, challenges, and policy recommendations,” in Smart and Sustainable Technologies and Research (Amsterdam: Elsevier), 101042. doi: 10.1016/j.sftr.2025.101042
Kumar, Y., Koul, A., and Singh, C. (2022). A deep learning approach in text-to-speech system: a systematic review and recent research perspective. Multimed. Tools Appl. 82:15171. doi: 10.1007/s11042-022-13943-4
Lakshminarayana, K. K., Zalkow, F., Dittmar, C., Pia, N., and Habets, E. A. (2025). “Low-resource text-to-speech synthesis using noise-augmented training of forwardtacotron,” in Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (Hyderabad: IEEE). doi: 10.1109/ICASSP49660.2025.10890686
Li, J., and Zhang, L. (2023). Zse-vits: a zero-shot expressive voice cloning method based on vits. Electronics 12:820. doi: 10.3390/electronics12040820
Li, J., Zhang, L., and Qiu, Z. (2023). “Speaker timbre supervision method based on perceptual loss for voice cloning,” in 2022 4th International Conference on Intelligent Control, Measurement and Signal Processing (ICMSP) (Chengdu: IEEE), 833. doi: 10.1109/ICMSP58539.2023.10171030
Li, R., Pu, D., Huang, M., and Huang, B. X. (2022). “UNET-TTS: improving unseen speaker and style transfer in one-shot voice cloning,” in ICASSP 2022 (Singapore: IEEE). doi: 10.1109/ICASSP43922.2022.9746049
Li, T., Wang, Z., Zhu, X., Cong, J., Tian, Q., and Wang, Y. (2024). U-style: cascading u-nets with multi-level speaker and style modeling for zero-shot voice cloning. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 32:4026. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2024.3453606
Li, Z., and Chen, F. (2020). “Research on voice cloning with a few samples,” in 2020 International Conference on Computational Natural Sciences and Engineering Applications (ICCNEA) (Xi'an: IEEE), 323. doi: 10.1109/ICCNEA50255.2020.00073
Liu, C., Zhang, J., Zhang, T., Yang, X., Zhang, W., and Yu, N. (2024). “Detecting voice cloning attacks via timbre watermarking,” in Network and Distributed System Security (NDSS) Symposium 2024 (San Diego, CA: IEE). doi: 10.14722/ndss.2024.24200
Liu, S., Su, D., and Yu, D. (2021). Meta-voice: fast few-shot style transfer for expressive voice cloning using meta learning. arXiv [preprint]. arXiv:2111.07218. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2111.07218
Lu, H., Wu, Z., Liu, S., Guo, H., Wu, X., Meng, H., et al. (2024). “Unifying one-shot voice conversion and cloning with disentangled speech representations,” in ICASSP 2022 (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE), 11141. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP48485.2024.10446296
Luong, H.-T., and Yamagishi, J. (2020). Nautilus: a versatile voice cloning system. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 28:2967. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2020.3034994
Lyu, Z., and Zhu, J. (2023). “Gan-based fine-grained feature modeling for zero-shot voice cloning,” in Proceedings of the World Congress on Electrical Engineering and Computer Systems and Science (Ottawa, ON: Avestia Publishing Orléans). doi: 10.11159/mhci23.111
Magariños, C., Erro, D., and Banga, E. R. (2016). “Language-independent acoustic cloning of HTS voices: a preliminary study,” in ICASSP 2016 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (Shanghai: IEEE), 5615. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2016.7472752
Mahmoud Ahmed, M. A., Elghamrawy, K. A., and Taha, Z. A. E. H. (2023). Enhancing Accessibility in Audiobooks Through Voice Cloning Technology. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE.
Makarov, I., and Zuenko, D. (2021). “Style-transfer autoencoder for efficient deep voice conversion,” in CINTI 2021 - IEEE 22nd International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Informatics (Budapest: IEEE), 121. doi: 10.1109/CINTI53070.2021.9668528
Mandeel, A. R. (2023). “The future of speaker adaptation: advancements in text-to-speech synthesis solutions,” in 9th Doctoral Consortium @ Interspeech 2023 - Extended Abstracts (ISCA-SAC).
Mcuba, M., Singh, A., Ikuesan, R. A., and Venter, H. S. (2023). The effect of deep learning methods on deepfake audio detection for digital investigation. Procedia Comput. Sci. 219:211. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2023.01.283
Mogali, S. R., Ng, O., Tan, J. X., San, T. H., and Ng, K. B. (2024). Voice-over anatomy lectures created by AI-voice cloning technology: a descriptive article. Anat. Sci. Educ. 17, 1686–1693. doi: 10.1002/ase.2524
Naik, V., Mendes, A., Kulkarni, S., Naik, S., and Verlekar, S. P. (2022). Voice Cloning in Real Time. Sonepat/Sonipat: IJRASET . doi: 10.22214/ijraset.2022.44524
Nechaev, B., and Kosyakov, S. V. (2024). Non-autoregressive real-time accent conversion model with voice cloning. arXiv [preprint]. arXiv:2405.13162. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2405.13162
Neekhara, P., Hussain, S., Dubnov, S., Koushanfar, F., and McAuley, J. (2021). Expressive neural voice cloning. arXiv [preprint]. arXiv:2102.00151. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2102.00151
Pankov, V., Pronina, V., Kuzmin, A., Borisov, M., Usoltsev, N., Zeng, X., et al. (2023). DINO-Vits: data-efficient noise-robust zero-shot voice cloning via multi-tasking with self-supervised speaker verification loss. arXiv [preprint]. arXiv:2311.09770 doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2311.09770
Pérez González de Martos, A., Garcés Díaz-Munio, G., Giménez, A., Silvestre-Cerdà, J.-A., Sanchis, A., Civera, J., et al. (2021). Towards cross-lingual voice cloning in higher education. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 105:104413. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2021.104413
Qin, Z., Zhao, W., Yu, X., and Sun, X. (2023). Openvoice: versatile instant voice cloning. arXiv [preprint]. arXiv:2312.01479. doi: 10.48550/arXiv:2312.01479
Qiu, Z., Jun, T., Zhang, Y., Li, J., and Bai, X. (2022). A voice cloning method based on the improved HIFI-GAN model. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022:1. doi: 10.1155/2022/6707304
Ramu, S. C., Saxena, D., and Mali, V. (2024). “A survey on voice cloning and automated video dubbing systems,” in WiSPNET 2024 - 9th International Conference on Wireless Communications, Signal Processing and Networking, Volume 31 (Chennai: IEEE), 1. doi: 10.1109/WiSPNET61464.2024.10532876
Ruggiero, G., Zovato, E., Di, L., and Pollet, V. (2021). Voice cloning: a multi-speaker text-to-speech synthesis approach based on transfer learning. arXiv [preprint]. arXiv:2102.05630. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2102.05630
Sadekova, T., Gogoryan, V., Vovk, I., Popov, V., Kudinov, M., and Wei, J. (2022). “A unified system for voice cloning and voice conversion through diffusion probabilistic modeling,” in Interspeech 2022 (Baixas: ISCA), 3003. doi: 10.21437/Interspeech.2022-10879
Selvi, S. S., Anantharamakrishnan, V., Koushik, A. V. P., and Akhil, S. K. (2021). “Emotional speech cloning using gans,” in RTEICT 2021 - IEEE 6th International Conference on Recent Trends in Electronics, Information and Communication Technology, Vol. 11 (Bangalore: IEEE), 824. doi: 10.1109/RTEICT52294.2021.9573848
Seong, J., Lee, W., and Lee, S. (2021). “Multilingual speech synthesis for voice cloning,” in BigComp 2021 - IEEE International Conference on Big Data and Smart Computing (Jeju Island: IEEE), 313. doi: 10.1109/BigComp51126.2021.00067
Shejole, S., Jaiswal, P., Karmal, N., Patil, V., and Shaikh, S. (2023). Autotuned voice cloning enabling multilingualism. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 11:5945. doi: 10.22214/ijraset.2023.52906
Singh, A., Nagireddi, A., Deekshitha, G., Bandekar, J., Roopa, R, and Badiger, S. (2024). “Limmits'24: multi-speaker, multi-lingual indic TTS with voice cloning,” ICASSPW 2024- IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing Workshops, Vol. 61 (Seoul: IEEE). doi: 10.1109/ICASSPW62465.2024.10626897
Singh, R., Gençağa, D., and Raj, B. (2016). “Formant manipulations in voice disguise by mimicry,” in IEEE International Workshop on Biometrics and Forensics (IWBF) (Limassol: IEEE), 1–6. doi: 10.1109/IWBF.2016.7449675
Song, W., Yuan, X., Zhang, Z., Zhang, C., Wu, Y., and He, X. (2021). “Dian: duration informed auto-regressive network for voice cloning,” in ICASSP 2022- IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (Toronto, ON: IEEE), 8598. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP39728.2021.9414727
Sun, C., Jia, S., Hou, S., and Lyu, S. (2023). “AI-synthesized voice detection using neural vocoder artifacts,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW) (Vancouver, BC), 904–912. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW59228.2023.00097
van den Oord, A., Dieleman, S., Zen, H., Simonyan, K., Vinyals, O., Graves, A., et al. (2016). Wavenet: a generative model for raw audio. arXiv [preprint]. arXiv:1609.03499. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1609.03499
Vinotha, R., Hepsiba, D., Vijay Anand, L. D., and Reji, D. J. (2024). Empowering communication: speech technology for Indian and western accents through AI-powered speech synthesis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.11771.
Wadoux, L., Barbot, N., Chevelu, J., and Lolive, D. (2022). “Voice cloning applied to voice disorders: a study of extreme phonetic content in speaker embeddings,” in Proceedings of the 35th Canadian Conference on Artificial Intelligence (Canadian AI 2022). doi: 10.21428/594757db.1bcc4f0c
Wadoux, L., Barbot, N., Chevelu, J., and Lolive, D. (2023). “Voice cloning for voice disorders: impact of phonetic content,” in Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Cham: Springer Science+Business Media), 293. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-40498-6_26
Wang, E. K., Liu, X., Chn, C.-M., Kumari, S., Shojafaret, M., and Shamim, M. (2020). Voice-transfer attacking on industrial voice control systems in 5g-aided iiot domain. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 17:7085. doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.3023677
Wang, S., Yang, C., Parkhill, M., Quinn, C., Hammerly, C., Zhu, J., et al. (2025). Developing multilingual speech synthesis system for ojibwe, mi'kmaq, and maliseet. arXiv [preprint]. arXiv:2502.02703. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2502.02703
Wu, J., Luan, J., and Wang, Y. (2023). “Lightclone: speaker-guided parallel subnet selection for few-shot voice cloning,” in Interspeech 2022 (Baixas: ISCA), 4868. doi: 10.21437/Interspeech.2023-1528
Wu, J., Wu, Z., and Xie, L. (2016). “On the use of i-vectors and average voice model for voice conversion without parallel data,” in APSIPA 2016 - Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (Jeju: IEEE), 1. doi: 10.1109/APSIPA.2016.7820901
Wu, Y., Wu, Z., and Xie, L. (2022). Vstyclone: real-time Chinese voice style clone. Comput. Electr. Eng. 105:108534. doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2022.108534
Xie, Q., Tian, X., Liu, G., Song, K., Xie, L., and Wu, Z. (2021). “The multi-speaker multi-style voice cloning challenge 2021,” in ICASSP 2022 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (Toronto, ON: IEEE), 8613. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP39728.2021.9414001
Yang, C., and Taele, P. (2025a). “AI for accessible education: personalized audio-based learning for blind students,” in CHI 2025 Workshop on Augmented Educators and AI: Shaping the Future of Human and AI Cooperation in Learning, 4. CHI 2025 Workshop (New York, NY: ACM).
Yang, C., and Taele, P. (2025b). “AI for accessible education: personalized audio-based learning for blind students,” in CHI 2025 Workshop on Augmented Educators and AI: Shaping the Future of Human and AI Cooperation in Learning. Available online at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.17117 (Accessed June, 2025).
Yi, J., Bai, Y., Tao, J., Ma, H., Tian, Z., Wang, C., et al. (2021). “Half-truth: a partially fake audio detection dataset,” in Proceedings of Interspeech 2021 (Baixas: ISCA). doi: 10.21437/Interspeech.2021-930
Zhang, C., Cai, Y., and Rao, W. (2021). “A non-autoregressive network for Chinese text-to-speech and voice cloning,” in ICAICA 2021 - IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Applications, Vol. 1229 (Dalian: IEEE), 96. doi: 10.1109/ICAICA52286.2021.9497934
Zhang, H., and Lin, Y. (2022). “Improve few-shot voice cloning using multi-modal learning,” in ICASSP 2022 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE), 8317. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP43922.2022.9746233
Zhang, J., Chen, Y., and Ma, H. (2024). “Application of speech feature extraction method based on deep learning in speech cloning,” in ICICACS 2024 - IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Advanced Communication Systems (Raichur: IEEE), 1. doi: 10.1109/ICICACS60521.2024.10498500
Zhang, Y., Weiss, R. J., Zen, H., Wu, Y., Chen, Z., Skerry-Ryan, R. J., et al. (2019). “Learning to speak fluently in a foreign language: multilingual speech synthesis and cross-language voice cloning,” in Interspeech 2022. doi: 10.21437/Interspeech.2019-2668
Zhe, Q., and Itou, K. (2023). “Incorporating speaker's speech rate features for improved voice cloning,” in ICCC 2021 - 7th International Conference on Computer and Communications (Chengdu: IEEE), 1515. doi: 10.1109/ICCC59590.2023.10507441
Keywords: voice cloning, text-to-speech, speaker encoder, Tacotron, WaveRNN, deep learning, variational autoencoders, GE2E loss
Citation: Mohtad Younus M, Iqbal A, Durrani EeN, Ahmad N and Ladan M (2025) A hybrid voice cloning for inclusive education in low-resource environments. Front. Comput. Sci. 7:1675616. doi: 10.3389/fcomp.2025.1675616
Received: 29 July 2025; Accepted: 19 September 2025;
Published: 09 October 2025.
Edited by:
Salvador Otón Tortosa, University of Alcalá, SpainReviewed by:
Vladimir Robles-Bykbaev, Salesian Polytechnic University, EcuadorRicardo Mendoza-González, Aguascalientes Institute of Technology, Mexico
Copyright © 2025 Mohtad Younus, Iqbal, Durrani, Ahmad and Ladan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Arshad Iqbal, YXJzaGFkLmlxYmFsQHNwY2FpLnBhZi1pYXN0LmVkdS5waw==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Muhammad Mohtad Younus
Muhammad Mohtad Younus Arshad Iqbal
Arshad Iqbal Esha e Noor Durrani
Esha e Noor Durrani Naveed Ahmad
Naveed Ahmad Mohamad Ladan
Mohamad Ladan