- 1Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology Surgery, Hubei Cancer Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
- 2Colorectal Cancer Clinical Research Center of Hubei Province, Wuhan, Hubei, China
- 3Colorectal Cancer Clinical Research Center of Wuhan, Wuhan, Hubei, China
- 4Department of Abdominal Oncology, Hubei Cancer Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
Objectives: To develop and validate a user-oriented nomogram of suicide risk in thyroid cancer patients to enable clinicians to identify and intervene in a timely manner with high-risk subgroups.
Methods: This was a retrospective, population-based cohort study in which patients with thyroid cancer diagnosed from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database between 2000 and 2020 were include. Optimized features were screened by the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression model. Subsequently, we selected variables with nonzero coefficients, entered them into a Cox proportional hazards regression model and constructed a visualized nomogram model predicting suicide. We implemented receiver operating characteristic curves (ROC), calibration curves, decision curve analysis (DCA), and internal validation to assess the discrimination, calibration, clinical applicability, and generalizability of the nomogram.
Results: To our knowledge, this is the first nomogram specifically designed for thyroid cancer patients, integrating histopathological, therapeutic, and socioeconomic predictors. Furthermore, the calibration curves for this nomogram fit well with the diagonal, and the C-indexes for the training and testing sets were 0.760 and 0.724, respectively, and the decision curve analysis indicated clinical benefit.
Conclusion: This study successfully identified risk factors for suicide in patients with thyroid cancer and developed a nomogram that provides patients with an individualized, quantifiable assessment of suicide risk and assists clinicians in identifying and intervening in potential suicides.
1 Introduction
With advances in diagnostic imaging and surveillance, the detection rate of thyroid cancer continues to increase. According to the International Agency for Research on Cancer of the World Health Organization, the incidence of thyroid cancer is the ninth highest in the world (1, 2). In addition, thyroid cancer is the most common malignant tumor among women in the United States (3). Thyroid cancer patients have a cumbersome financial burden, and the bankruptcy rate among survivors is higher than for other cancer types in America (4).
Suicide, the tenth leading cause of death in North America, confronts us with a great public health challenge (5). The last decade has seen the development of novel molecular-based individualized systematic management, leading to an improving prognosis for thyroid cancer (6). Despite a favorable prognosis, the risk of suicide in thyroid cancer patients is 5.3 times higher than in the general population (95% CI 3.8-7.1), and this “survival-psychological paradox” constitutes a central research gap (7). A meta-analysis based on the SEER database showed that the standardized suicide mortality rate (SMR=8.6) was significantly higher in thyroid cancer patients than in solid tumors such as breast cancer (SMR=1.9) (8). A multi-layered connection exists between thyroid cancer and elevated suicide risk. Biologically, thyroid hormone dysregulation directly affects mood regulation centers, particularly through hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis modulation of serotonin systems (9). Psychosocially, the misperception of thyroid cancer as a “good cancer” leads to systemic minimization of patient distress, creating a unique “diagnosis-expectation disparity” trauma (10). Once upon a time, prolonging survival time was the main goal of cancer treatment, sometimes even at the expense of the patient’s quality of life and psychological well-being. The long series of cancer diagnosis, treatment, and recovery brings great emotional trauma to the patient, which in turn affects their ability to fight cancer. Some scholars argue that suicides caused by difficult or hopeless situations, such as terminal illness, are socially and legally recognizable and can be considered a rational as well as dignified behavior (11).
There is little literature that focuses on suicide in thyroid cancer patients singularly rather than as part of head and neck cancer. Much of the past research has been invested more in head and neck cancer suicides (8, 12, 13), possibly because its treatment modalities tend to cause disfigurement and impairments in swallowing, breathing, and speech (14). Despite the generally excellent prognosis of thyroid cancer, survivors’ quality of life of is troubling (15). The quality of life in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) is worse than that of the general population and, surprisingly, even worse than that of survivors of other colorectal, breast, and malignant glioma types with lower survival rates and more aggressive treatments (16). A survey of suicide mortality among U.S. pediatric cancer survivors noted the highest rate of 39.8 per 100,000 person-years among thyroid cancer patients (17). Surgery, the cornerstone of thyroid cancer treatment, has two major complications: recurrent laryngeal nerve injury and permanent hypoparathyroidism, which are major risk factors for anxiety in thyroid cancer patients (18). Some patients are overly concerned about the unsightliness associated with horizontal neck incisions, which affects their quality of life (19) and even suicide (20). Secondly, TSH suppression by high-dose thyroxine replacement postoperatively is associated with worse energy status and immense fatigue (21). In addition, among patients treated with radioiodine, those with doses greater than 150 mCi tended to have more severe pain, swallowing, chewing, speech, taste, anxiety, and mixed disorders (22). Furthermore, the characteristics of younger age at thyroid cancer onset and good survival rates increase the risk of subsequent second tumors (23), which is part of the rationale for its high suicide rate. Therefore, more attention should be paid to the risk management of suicide deaths in patients with thyroid cancer.
Therefore, to identify high-risk subgroups of patients with thyroid cancer who die by suicide, we executed a population-based cohort study. This study is expected to provide a scientific basis for the development of specific suicide death management strategies for patients with thyroid cancer, thereby reducing distress, anxiety and suicide risk in survivors.
2 Methods
2.1 Data source
Thyroid cancer cases diagnosed during 2000-2020 were selected from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database. The database is structured by National Cancer Institute (NCI) and contains information from 17 population-based registries (SEER-17; Alaska, Connecticut, Atlanta, Greater Georgia, Rural Georgia, San Francisco-Oakland, San Jose-Monterey, Greater California, Hawaii, Iowa, Kentucky, Los Angeles, Louisiana, New Mexico, New Jersey, Seattle-Puget Sound, and Utah). The SEER-17 database covers approximately 26.5% of the U.S. population and racially representative, which contains patient demographics (gender, age, race, marital status), tumor diagnostic information (stage, grading, histological type, tumor size), treatment and follow-up data. No Institutional Review Board approval was required for the Hubei Cancer Hospital since this study involved neither interaction with human participants nor the use of any personally identifiable information.
2.2 Study population
Cases of thyroid cancer diagnosed during the period 2000-2020 were included, which were categorized according to histological type (International Classification of Diseases in Oncology, Third Edition; topography code C73): papillary thyroid cancer (histological codes 8050, 8260, 8340-8344, 8350, 8450-8460), follicular thyroid cancer (8290, 8330-8335), medullary thyroid carcinoma (8345, 8510-8513), anaplastic thyroid cancer (8000, 8012, 8020-8022, 8030-8032, 8337) and others. Only microscopically confirmed cases and the corresponding first record were selected, while cases identified only from autopsy records or death certificates were excluded. We extracted patient demographic data (age, sex, race, marital status, annual household income, place of residence), tumor-related details (histologic type, surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy), and follow-up information (survival status, cause of death, and time to survival) through the SEER*Stat Version 8.4.2.0.
Reasons for death were assigned on the basis of the death certificate documented and confirmed by the attending physician, with deaths due to “suicide and self-inflicted injury” following a diagnosis of thyroid cancer being the main outcome. Survival time is measured in months, with a minimum non-zero value of 1 month. Marital status was portrayed as married/cohabiting, divorced/separated/windowed and single (never married). We define place of residence as metropolitan (population greater than or equal to 1 million), middle urban (population greater than or equal to 250 thousand), small urban (population less than 250 thousand), and rural area based on the urban-rural continuum code provided by the SEER database.
2.3 Statistical methods
Data were randomly and non-returned drawn into training and testing cohorts in a ratio of 7:3. Predictor screening and model construction were performed in the training cohort, while model evaluation was accomplished in the testing cohort. Student’s t-test was used to analyze continuous variables while chi-square or Fisher’s exact test was used to compare categorical variables. R software 4.2.2 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) was deployed for all statistical analyses. Statistical significance was evaluated at the alpha level of P< 0.05, and all assumptions were two-sided.
To construct the final predictive model, we employed the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) combined with Cox proportional hazards regression to identify significant suicide risk factors. As a regularized regression method, LASSO regression not only performs well in screening variables and creating simple models, but is also more effective in solving overfitting problems (24). LASSO regression is highly suitable for models with high degree of multicollinearity and it helps in variable selection and parameter elimination by shrinking the values towards the center point. In addition, it adds a penalty value equal to the absolute value of the coefficients, and variables with zero coefficients will eventually be dropped from the model (25). Cox proportional hazards model is suitable for analyzing survival data over time (26), and it can be used to adjust for baseline differences between groups and provide hazard ratios (calculation of confidence intervals by 1000 iterations) to quantify the effect of any single factor on the survival curve (27, 28).
The discriminative efficacy and generalization ability of the model for the LASSO-Cox model was evaluated by Harrell’s concordance index (C-index). We next plotted calibration curves using the Bootstrap method of resampling 1000 times to assess the agreement between observed and predicted probabilities. The total score of each patient in the nomogram was extracted, and the ROC curve was used to obtain the best cutoff value. Based on this cutoff value, all patients were categorized into high-risk and low-risk groups, and Kaplan-Meier (K-M) curves were used to describe the survival curves for suicide in the two groups, and the differences between the groups were compared using the log-rank test. In addition, decision curve analysis (DCA) quantified the net benefit at different probability thresholds to assess clinical applicability.
3 Results
3.1 Characteristics of patients
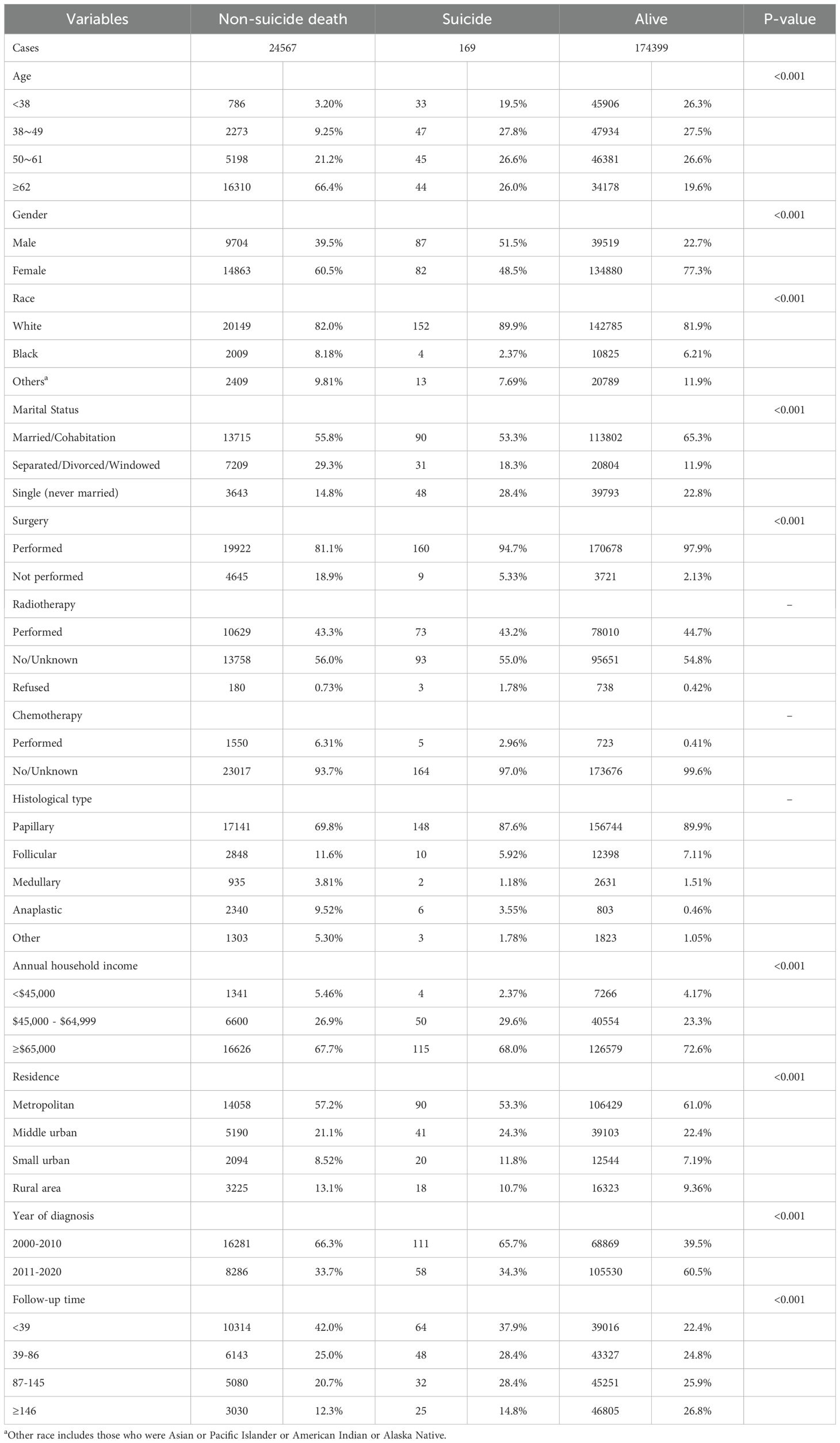
Of the 213,932 thyroid cancer cases diagnosed among residents of SEER-17 region during 2000-2020, 199,135 (93.1%) were finally included in this study (Table 1). Females (149,825 [75.2%]) and white patients (163,086 [81.9%]) comprised the majority of cases. The mean (± standard deviation) age at diagnosis was 50.2 (± 15.9) years. The most common histological types were PTC (87.4%) and FTC (7.7%). The other features selected for inclusion are shown in Table 1. During the period 2000-2020, 169 of the eligible cases died by suicide, of which 51.5% were male and 89.9% were white. The correlation between patients who survived, died by suicide, and those who died by non-suicide and baseline information is shown in Table 2, with significant differences between the three in terms of age, gender, race, marital status, histological type, surgery, annual household income, place of residence, year of diagnosis, and duration of follow-up.
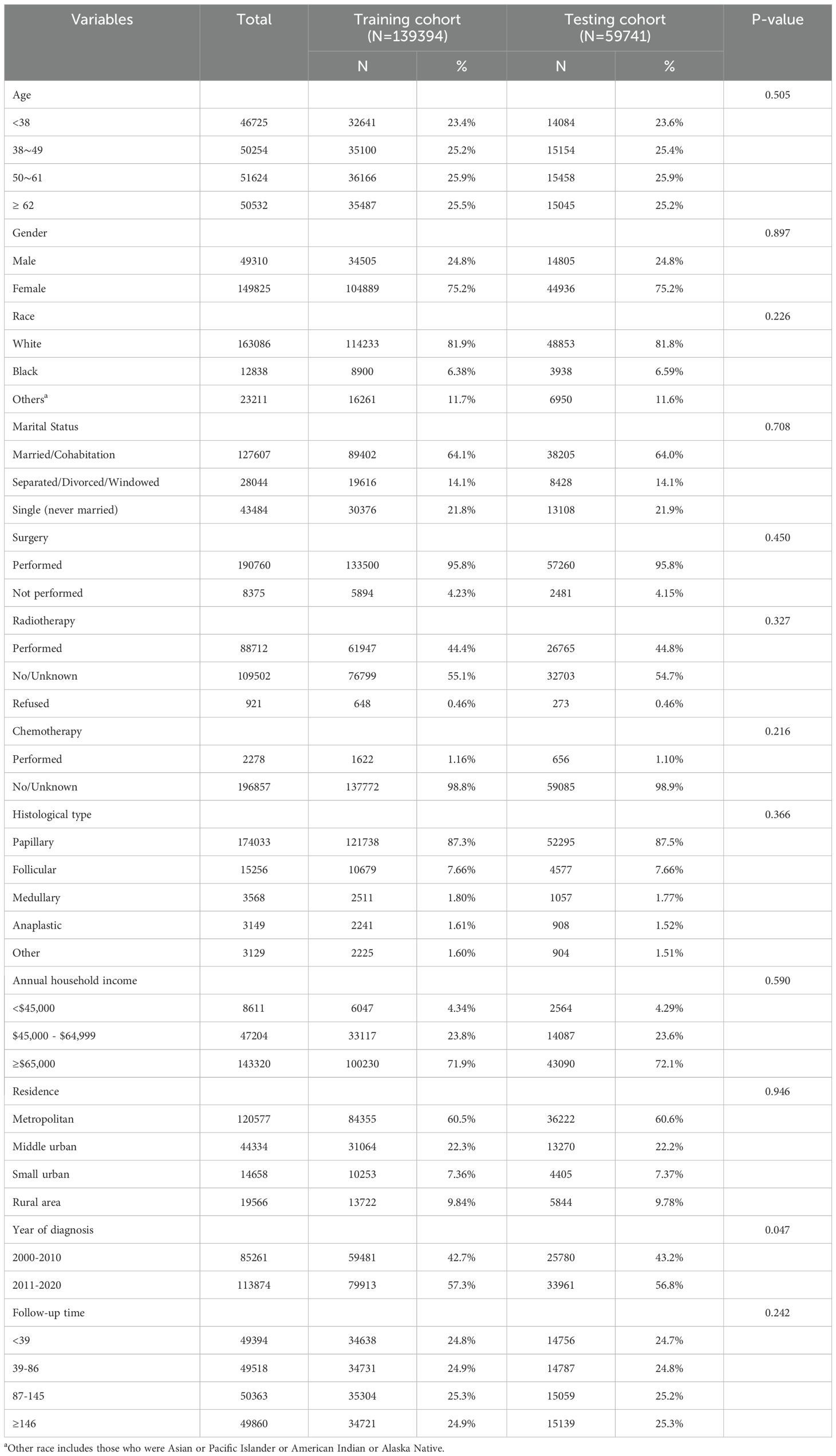
Table 1. Baseline clinicopathological characteristics of patients in training and testing cohorts (N=199,135).
3.2 Prediction model built based on Lasso-Cox regression
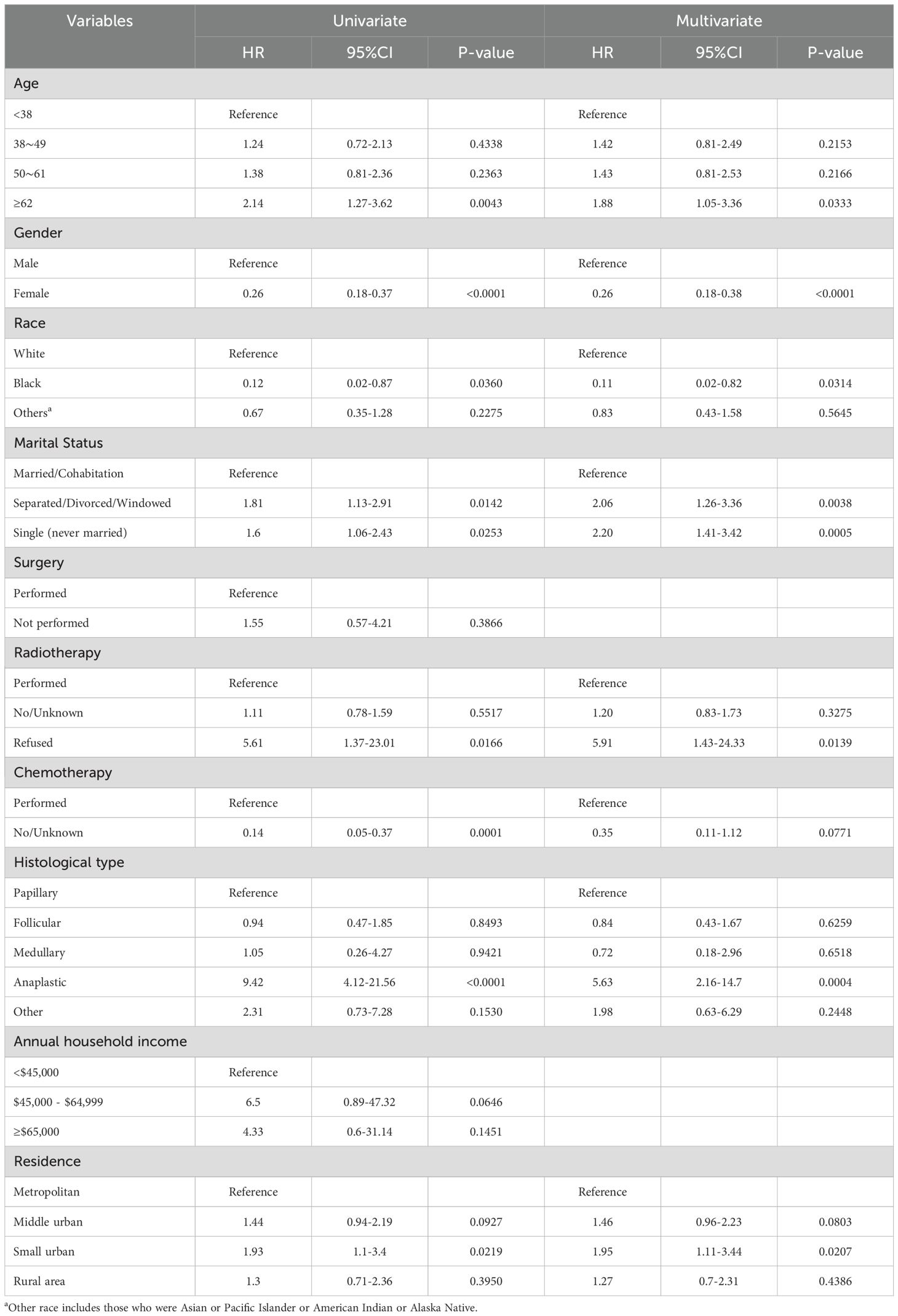
We used LASSO regression model to screen for risk factors, and the variation in the coefficients of these variables is characterized in Figure 1A. Applying the 10-fold cross-validation method to the iterative analysis, we compared the model with less than one standard error and fewer variables with the minimum error to obtain the best lambda, corresponding to the model with superior performance but the smallest number of variables (Figure 1B). The selected 11 features with non-zero coefficients include age, gender, race, marital status, surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, histological type, annual family income, and place of residence.
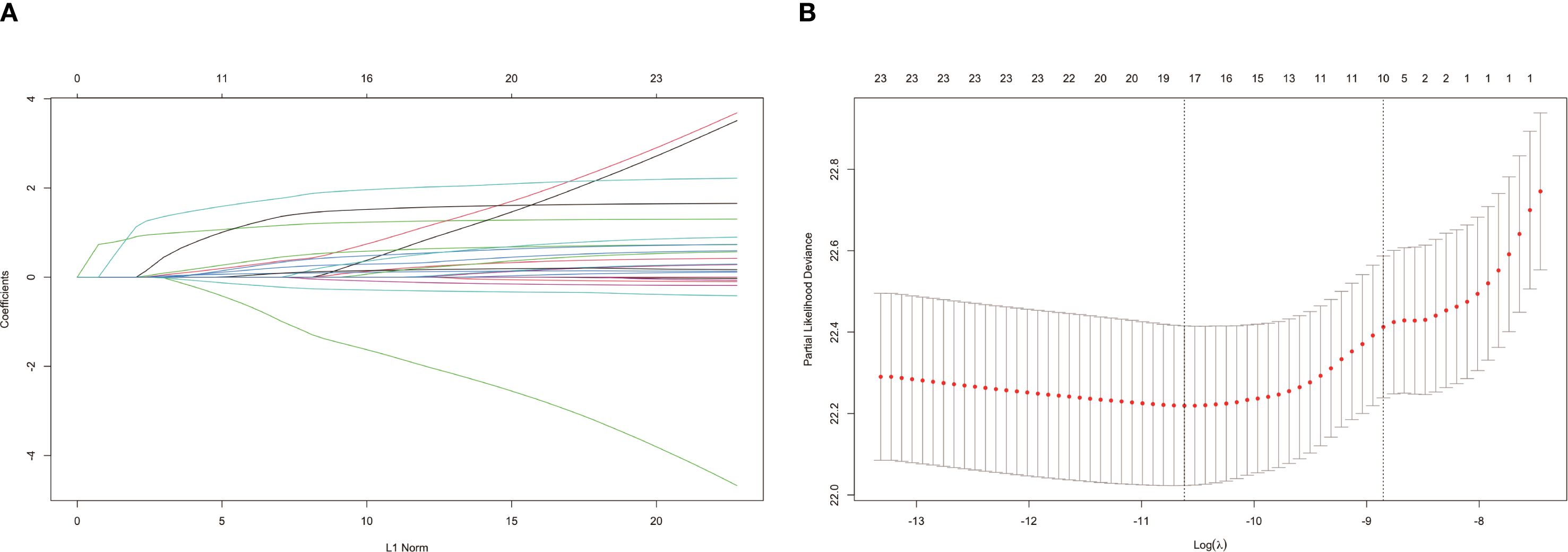
Figure 1. Filtrating prediction factors using the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression. (A) LASSO coefficient path diagram for risk factors; (B) Cross validation curve.
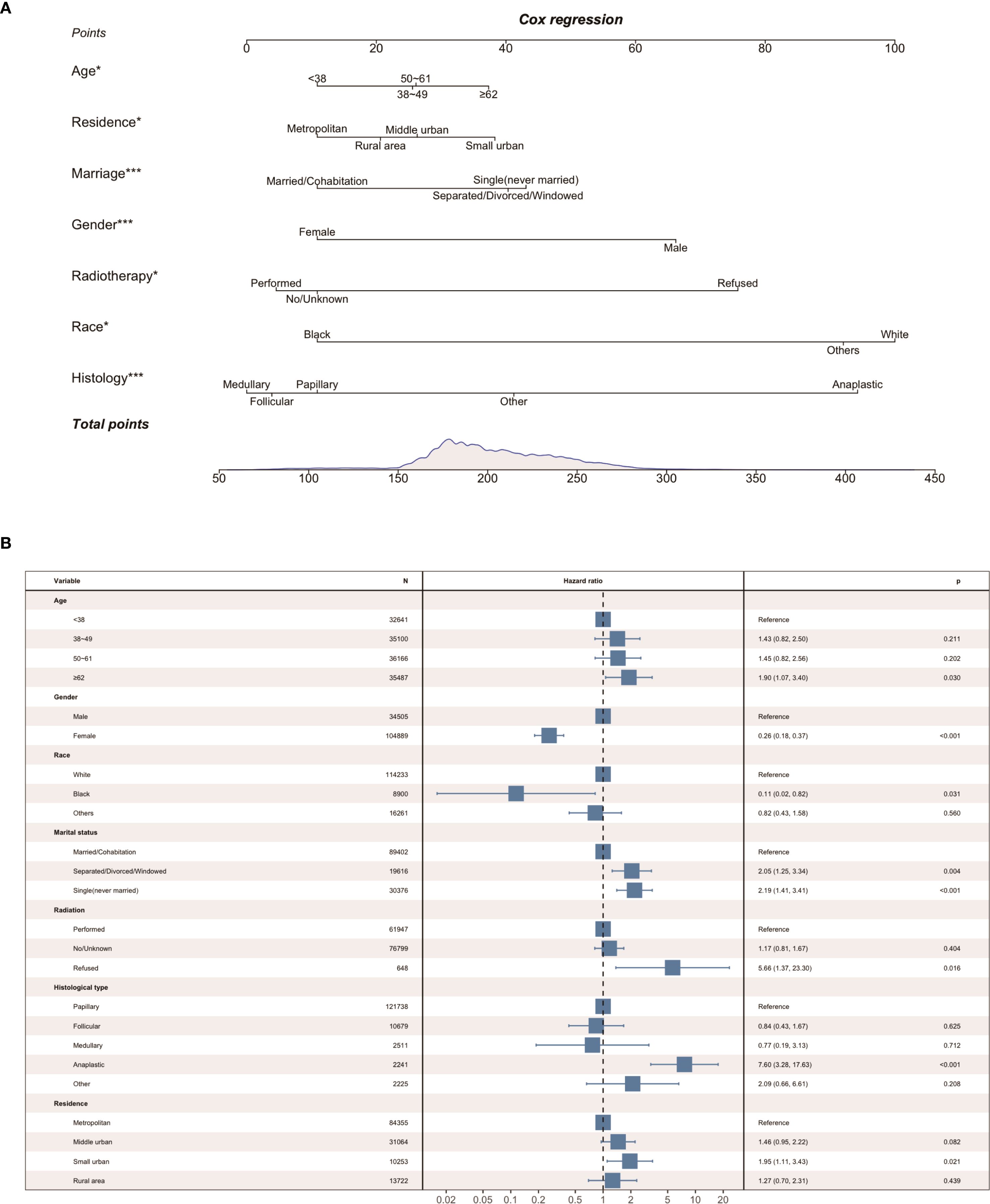
Parameters screened based on LASSO regression were incorporated into the next univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression models. As shown in Table 3, we identified the seven best predictors, including age at diagnosis, place of residence, marital status, gender, radiotherapy, race, and histological type. Subsequently, we constructed a nomogram based on these results (Figure 2A), and the forest plot of the model is shown in Figure 2B.
3.3 Performance and internal validation of the nomogram
The calibration curves used to predict the nomogram for suicide risk in thyroid cancer patients showed good agreement in both the training and testing cohorts (Figure 3). The C-index for the predicted nomogram was 0.760 (95% CI: 0.717-0.802) in the training cohort and 0.724 (95% CI: 0.644-0.803) in the testing cohort, suggesting a superior discriminative capability of the model. The sensitivity and specificity of the training set were 0.677 and 0.642, respectively, with an optimal cut-off of 0.306 (Figure 4).
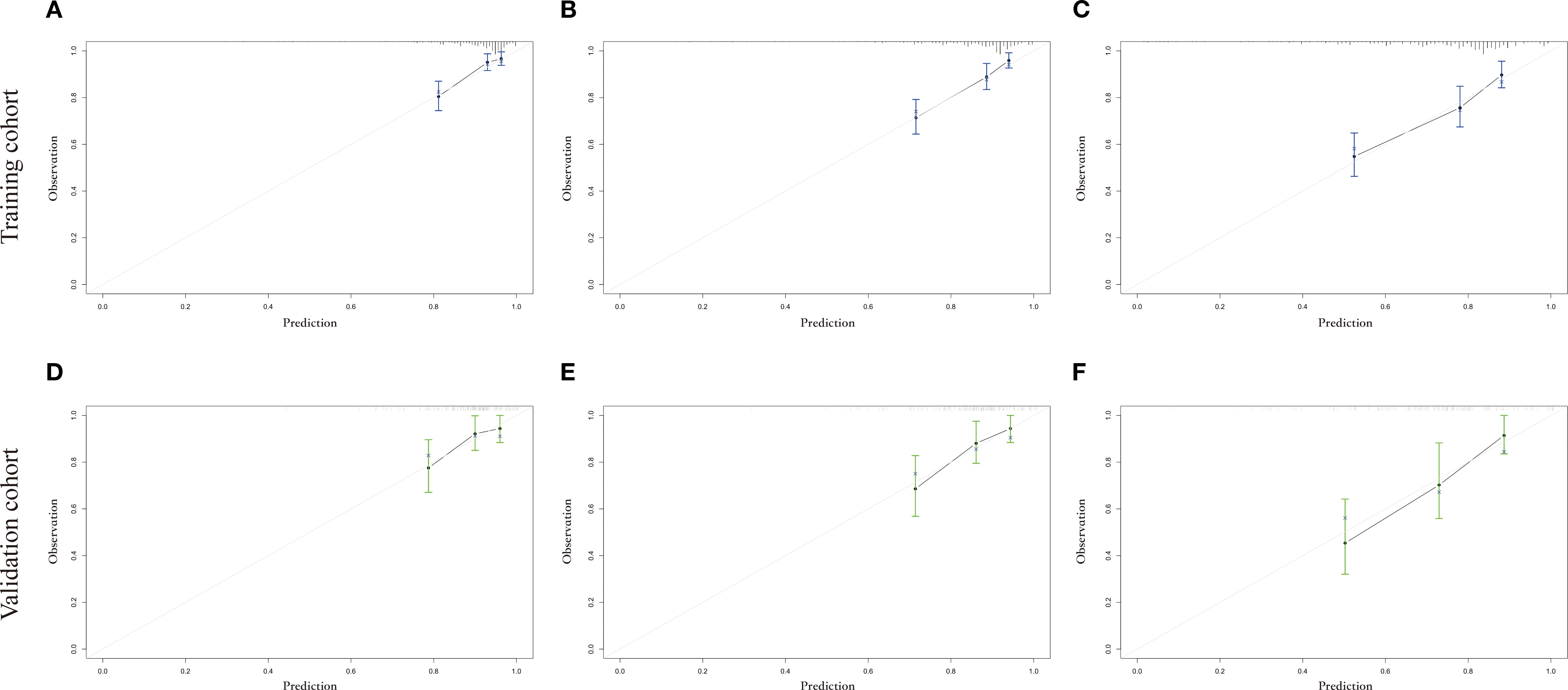
Figure 3. The calibration plot for prediction in the training and testing cohorts. (A-C) shows the 3-year, 5-year and 10-year suicide survival endpoints in the training cohort, and (D-F) shows the 3-year, 5-year and 10-year suicide survival endpoints in the testing cohort.
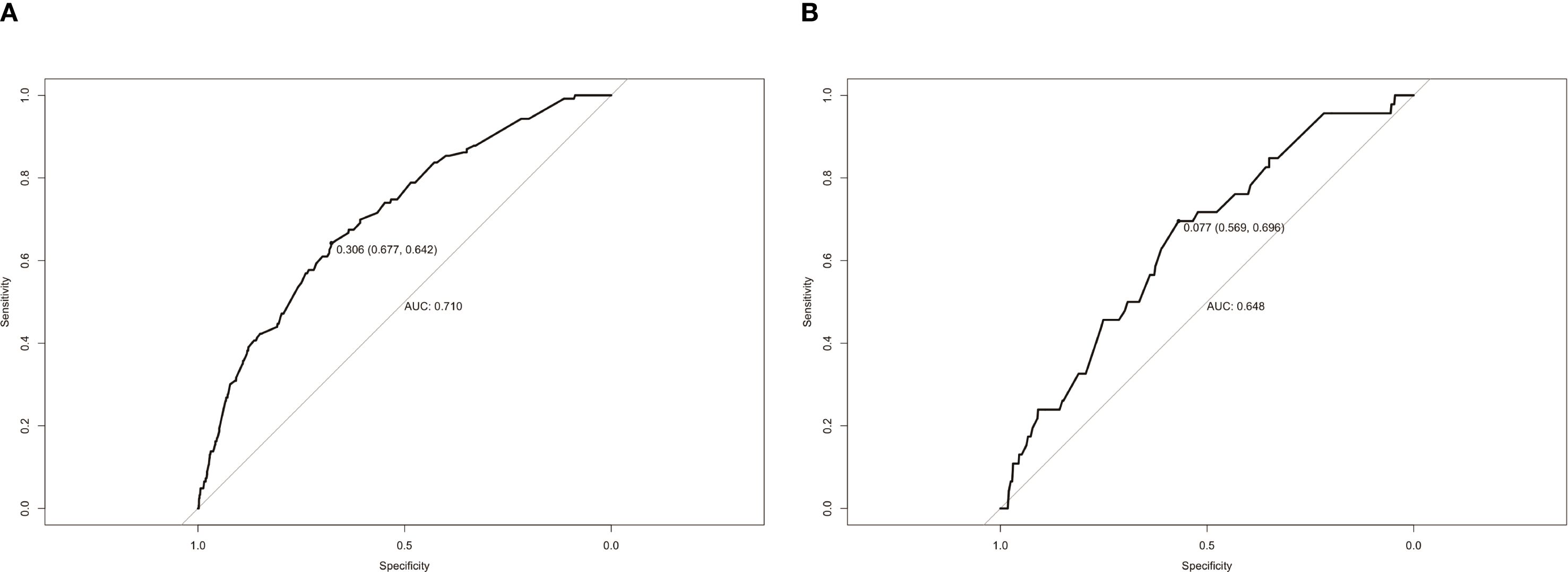
Figure 4. ROC curves of the study’s generated nomogram in the (A) training cohort; (B) testing cohort.
3.4 Clinical application
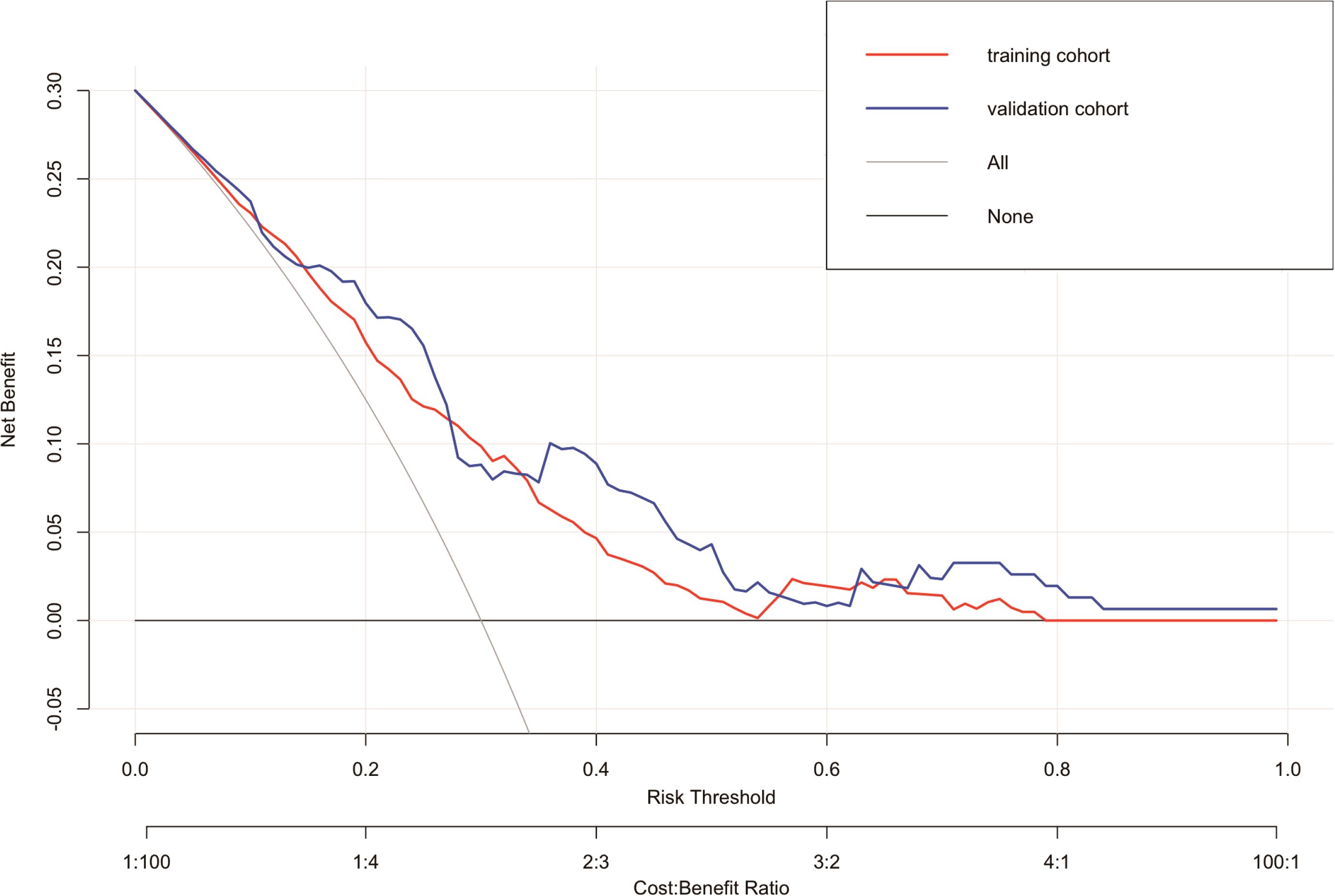
In the suicide nomogram, the decision curve analysis (DCA) is shown in Figure 5. The decision curves for both the training and testing cohorts demonstrate that using the predictive model to predict suicide risk in thyroid cancer patients may add additional clinical benefit if the probability threshold for suicide is not less than 5%. That is, when the threshold for the incidence of suicide is not less than 5%, using the model to predict suicide risk is more beneficial than intervening or not intervening for all patients. Meanwhile, patients were categorized into low-risk (total score < 173.934) and high-risk groups (total score≥ 173.934) based on the best cutoff value of the total risk score in the nomogram. The K-M curves for both the training and testing sets showed that there was a significant difference in suicide survival between the different risk groups (Figures 6A, B).
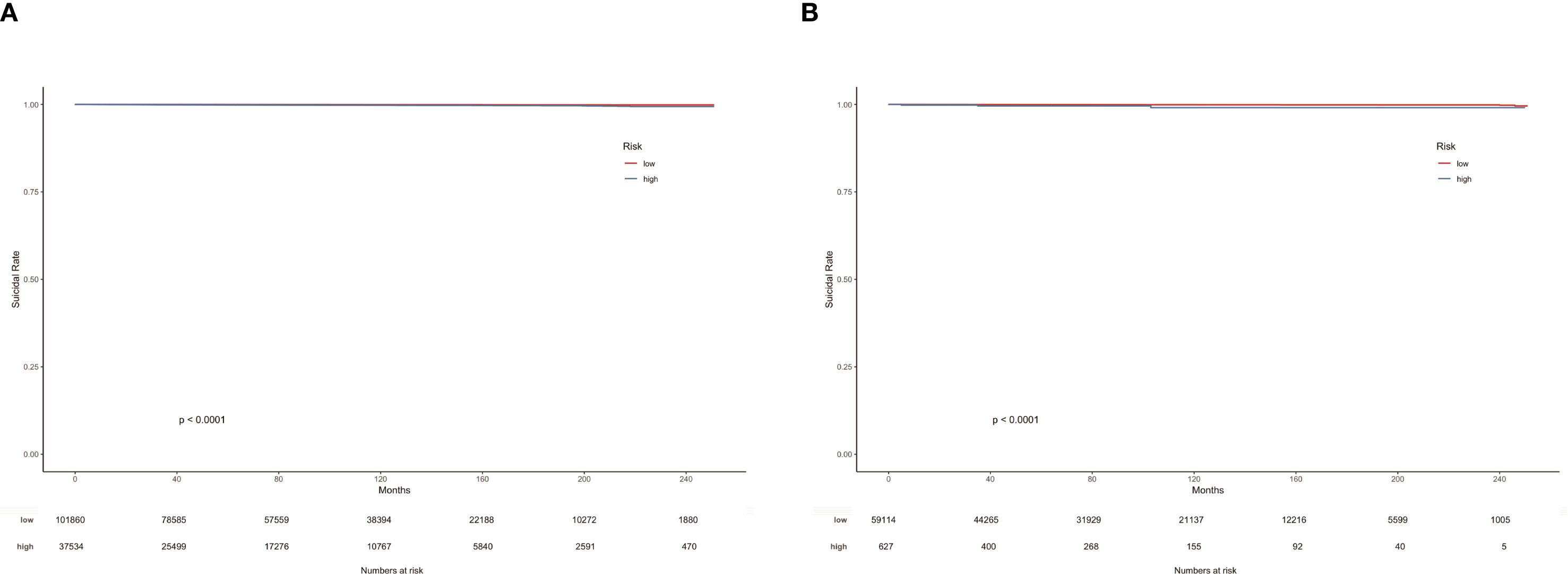
Figure 6. K-M curves of TC patients in the training cohort (A) and testing cohort (B) according to risk grouping.
4 Discussion
Differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) occupies about 80% to 90% of all cases and consists mainly of papillary and follicular carcinomas (29). Total thyroidectomy (TT) and thyroid lobectomy (TL) are the main surgical approaches for DTC, and its most common complications include recurrent laryngeal nerve injury, hypoparathyroidism, hematoma, and wound infection. In this study, as many as 95.79% of patients underwent lesion excision, however postoperatively patients often experience additional psychological burdens, including anxiety and depression. On the one hand, this may be due to the high rate of postoperative complications in patients that undermine their confidence in healing (30), and on the other hand, it is related to fluctuating levels of thyroxine (31) and thyrotropin (32) in the postoperative period. In addition, thyroid autoimmune diseases are inextricably linked to affective disorders (33). In contrast to the overall favorable prognosis, thyroid cancer survivors experience poorer quality of life and a higher risk of suicide. Then, this study is the first to construct a predictive model of suicidal risk factors in thyroid cancer patients and will provide a bridge for oncologists and psychologists to efficiently communicate in order to intervene early in potential suicide attempt and complete suicide.
In the risk factor analysis of this study, age, place of residence, marital status, gender, radiotherapy, race and histologic type were associated with suicide in thyroid cancer patients. We combined just seven easily available and meaningful parameters, and an efficient tool for predicting suicide risk in thyroid cancer patients was built. The nomogram integrates risk factors such as demographic characteristics, socioeconomic status, tumor and treatment characteristics to individualize the prediction of suicide in thyroid cancer patients. We constructed a relatively credible and efficacious suicide prediction model for thyroid cancer using the training cohort. Through internal validation, we confirmed the superior discriminative and calibration capabilities of the model. In addition, the exceptional C-index and decision curve performance contributes to the wide application of the nomogram to a high volume of thyroid cancer samples.
4.1 Gender difference
Men are one of the independent risk factors for suicide in thyroid cancer patients, which is consistent with other previously reported cancers (34, 35). As for the general population, three times as many men as women die by suicide in high-income countries, compared with 1.6 times as many in low- and middle-income countries (36). While women are generally considered to be more susceptible to mood disorders and depression, men usually tend to resort to more violent and irreversible ways of contributing to full suicide (37). Secondly, Men have more difficulty regulating mood changes (38) and are more reluctant to seek formal channels of mental health care than women due to stereotypes of traditional masculinity (39). Thyroid cancer is the only nonreproductive cancer with a female predominance, but it is more malignant and more likely to recur in male patients (40), and the despair associated with treatment failure and limited survival expectations makes them more likely to commit suicide (41). In addition, men are at high risk of suicide because they are more susceptible to social isolation that cuts across all spheres of life, including family and society (42, 43).
4.2 Age stratification
Advanced age is another independent risk factor for suicide in thyroid cancer patients. Patients <45 years of age have a significantly better prognosis than patients> 45 years of age, even when the degree of cancer aggressiveness is the equal (44). Mortality from thyroid cancer climbs gradually from age 40-45, with recurrence rates peaking from age 60 (45). Individuals with serious illnesses are also more likely to report suicide attempts among those 65 years and older (46). The experience of cancer is one that promotes tremendous personal and spiritual growth (47), and poor physical health and dysfunction also increase suicide risk. Second, older adults who have no income or are not gainfully active are more likely to attempt suicide (37), and the breakdown of relationships with family members and other sources of support contributes in part to suicide in later life (48). Biologically, age-related chronic inflammation may represent a biological substrate linking advanced age to suicide risk (49). In addition, the use of psychotropic medications may be partially involved in the high rates of suicide among older persons, with a much higher number of older persons attempting suicide using tranquilizers and hypnotics than would be expected (50).
4.3 The marriage protection effect
With regard to marital status, the risk of suicide was elevated in divorced, separated, windowed, and single (never married) thyroid cancer patients compared to those who were married or cohabiting. Social support, a complex structure containing the important functional and structural parameter of marriage, has traditionally been recognized as having both a direct and buffering effect on the well-being and emotional regulation of cancer patients (51, 52). What’s more, married patients with less lethal cancers, such as thyroid cancer, have higher 5-year survival rates (53). Marriage increases personal fortune as well as pleasurable experiences and, more importantly, prevents suicide by providing social integration and support (54–56). In the 30+ age group, marriage was more protective against suicide in men than in women (57, 58). Similarly, divorce had a significantly greater suicide risk for men than for women (59), which may be due to the fact that women tend to take on the role of caregiver in a marriage and excel in integrating into social networks, while men are more likely to fall into social isolation and loneliness (60). Additionally, suicide in the face of a change in marital status is significantly greater among older people than among younger people, especially in the first year after a marital change (61).
4.4 Collective resilience
Studies show a statistically significant difference in suicide rates between racial groups with thyroid cancer, with lower incidence observed in Black patients versus White patients. This, of course, is inextricably linked to the fact that white people are overwhelmingly represented in the SEER database. Compared to other races, black person appear to have lower suicide rates despite social margaretization, racism and colorism, poor access to mental and physical health care, and disproportionately high rates of poverty (62). States with higher proportions of African Americans have lower suicide rates, with interpersonal relationships (i.e., a stronger sense of collectivity in racially dense areas) playing an essential protective role (63). In other words, social support through “racial density” is effective in reducing suicide risk in predominantly African American areas (63–65). Also, strong family ties are key to lowering the risk of suicide among low-income black women (66), and the existence of hope is a significant contributor to the protective factors against suicide among African American (67). Moreover, having a strong and positive racial identity or personal beliefs about being Black has been shown to be protective for women who have attempted suicide (68), and may even confront the negative influence of racism and colorism on suicide (62).
4.5 Economic area factor
Our study shows that living in a small urban is considered as one of the independent risk factors for suicide in thyroid cancer patients compared to metropolitan. In fact, the incidence of thyroid cancer is higher in cities than in towns or rural areas in Canada (69). A California-based report claims that rural youth are more likely to have suicide ideation, suicide attempt, even full suicide than urban youth (70). Another Hong Kong-based study has pointed that the strong association between life satisfaction and regional socio-economic characteristics affects suicide (71). Ambient temperature (72), daylight hours (73), firearms support availability (74, 75), socioeconomic status (76), cancer care level (77), and access to mental health care (78, 79) differed by region and were associated with changes in suicide mortality across the United States. From a mathematical or statistical point of view, metropolitan areas, while having the advantage of large sample sizes, inevitably introduce measurement or specification bias. Smaller regions are less susceptible to ecological bias due to less heterogeneity than larger agglomerations (80). However, because small sample sizes lead to highly variable rates, little attention has been focused on suicide-related research in rural-level areas, which may also partially explain the fact that the independent risk factor in this study was small urban rather than the rural area. By the way, more research is needed in the future to further refine the relationship between geographic region type and suicide among thyroid cancer patients, which may help policymakers understand where to focus their improvement efforts.
4.6 Treatment denial and the dignity crisis
Refusal of radiotherapy as a risk factor for suicide in patients with thyroid cancer may be related to patients’ desire to maintain autonomy over their lives and loss of confidence in health care. Declining radiotherapy may reflect anticipatory loss of autonomy in end-stage decision-making. Thyroid cancer patients disproportionately value bodily integrity due to visible surgical scars and voice changes, making treatment refusal a potential marker of dignity-related distress (81). A qualitative case study based on the wishes to die of patients with advanced cancer in Switzerland (where assisted suicide is permitted by law) reported that four oncology patients asked to maintain (or regain) control and self-determination over their deaths at the end of their lives (82). They did not want to remain in a state of dependency for a long period of time, fearing that they would not receive appropriate treatment or that they would not be subjected to conventional treatment and non-personalized care in hospitals, nor would they want their doctors to make decisions for them. Other factors such as the fear of being an emotional and financial burden on others, loss of dignity, choice of treatment or meaning in life, and freedom from the confinement of a painful and disfigured body are all possible reasons why oncology patients “long for a self-determined end of life”.
4.7 The psychological dilemma of undifferentiated cancer
Our study also found that the histologic type Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma (ATC) increased the risk of suicide death in patients. The phenomenon that histological type of tumor is associated with suicide has been reported in other cancer types such as ovarian cancer (83). The extreme lethality of ATC (median survival <6 months) creates existential distress distinct from other cancers. Patients face rapid functional decline with limited palliative options, amplifying feelings of hopelessness – a well-established suicide precursor (84). Thyroid cancer patients have many unmet psychosocial support needs (85). A serious life-threatening illness may threaten basic expectations of safety, relationships, justice, controllability, certainty, and a long and rewarding life (84). A subgroup of thyroid cancer patients experiencing distress and worry during diagnosis and treatment demonstrated susceptibility to clinical anxiety and depression (86). Although ATC accounts for only 2% of thyroid cancer patients, clinicians should not ignore the exuberant psychological needs of this rare group.
5 Advantages and limitations
The main strengths of our study are the large sample of thyroid cancer patients in the United States and the translation of evidence-based risk factors into quantifiable risk factors to help identify high-risk groups and provide transparency and consistency in suicide risk decision-making. Second, our nomogram model balances sensitivity and specificity and provides an overall suicide risk score. Additionally, this model can provide patients with a baseline assessment during contact with a clinician and provide interventions for those predicted to be at high risk for suicide.
There are still some shortcomings in our study. First, psychosocial confounders (e.g., psychiatric diagnoses, substance abuse, childhood trauma) were unavailable in the SEER registry. Future studies integrating electronic health records or patient-reported outcomes may enhance predictive accuracy by capturing these dimensions. Similarly, we did not differentiate between the concepts of suicidal ideation, suicide attempts, and complete suicide when assessing risk factors in patients with thyroid cancer. Second, specific causes of death are often difficult to determine, and ICD-10 cause-of-death codes in the SEER database are unique, so there may be a misclassification bias for causes of death. Third, although the stability and validity of our nomogram have been internally validated, external validation with multiple centers should be performed in the future. Furthermore, the rarity of suicide outcomes (n=169) fundamentally constrained our ability to conduct meaningful subgroup analyses. Finally, the results of this study should be contextualized when generalizing to other countries and regions, as the SEER-17 database originates from a specific region.
6 Conclusion
In our study, seven risk factors were screened by combining LASSO and Cox proportional risk regression, and a nomogram was constructed to assess the risk of suicide in thyroid cancer patients. Age at diagnosis, gender, race, marital status, histologic type, radiation therapy, and place of residence were included in the suicide nomogram to quantify the risk of suicide in individual thyroid cancer patients. This nomogram enables early identification of high-risk subgroups who may benefit from targeted psychosocial interventions tailored to thyroid cancer survivorship challenges. Future studies need to be externally validated in multicenter cohorts and should test whether timely individualized interventions can reduce the risk of suicide and further improve mental health and quality of life in patients with thyroid cancer.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: SEER Research Data,17 Registries, Nov 2022 sub (2000-2020)(https://seer.cancer.gov/).
Author contributions
JZ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MT: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. XZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft. LX: Data curation, Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft. JH: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. MX: Conceptualization, Software, Supervision, Writing – original draft. XL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Writing – review & editing. SW: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Cancer Center Climbing Fund (Grant numbers: NCC201917A01), Health Commission of Hubei Province scientific research project (grant numbers: WJ2021Z001), and the 2023 ~ 2024 Annual Scientific Research Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine from Hubei Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Grant Number: ZY2023Z005).
Acknowledgments
The authors are sincerely grateful to the SEER database.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
2. Pizzato M, Li M, Vignat J, Laversanne M, Singh D, La Vecchia C, et al. The epidemiological landscape of thyroid cancer worldwide: GLOBOCAN estimates for incidence and mortality rates in 2020. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2022) 10:264–72. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00035-3
3. Cabanillas ME, McFadden DG, and Durante C. Thyroid cancer. Lancet. (2016) 388:2783–95. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30172-6
4. Uppal N, Cunningham Nee Lubitz C, and James B. The cost and financial burden of thyroid cancer on patients in the US: A review and directions for future research. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. (2022) 148:568–75. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2022.0660
6. Kobaly K, Kim CS, and Mandel SJ. Contemporary management of thyroid nodules. Annu Rev Med. (2022) 73:517–28. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-042220-015032
7. Oh CM, Lee D, Kong HJ, Lee S, Won YJ, Jung KW, et al. Causes of death among cancer patients in the era of cancer survivorship in Korea: Attention to the suicide and cardiovascular mortality. Cancer Med. (2020) 9:1741–52. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2813
8. Osazuwa-Peters N, Simpson MC, Zhao L, Boakye EA, Olomukoro SI, Deshields T, et al. Suicide risk among cancer survivors: Head and neck versus other cancers. Cancer. (2018) 124:4072–9. doi: 10.1002/cncr.31675
9. Feldt-Rasmussen U, Effraimidis G, and Klose M. The hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid (HPT)-axis and its role in physiology and pathophysiology of other hypothalamus-pituitary functions. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2021) 525:111173. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2021.111173
10. Randle RW, Bushman NM, Orne J, Balentine CJ, Wendt E, Saucke M, et al. Papillary thyroid cancer: the good and bad of the “Good cancer. Thyroid. (2017) 27:902–7. doi: 10.1089/thy.2016.0632
11. van Wijngaarden E, Merzel M, van den Berg V, Zomers M, Hartog I, and Leget C. Still ready to give up on life? A longitudinal phenomenological study into wishes to die among older adults. Soc Sci Med. (2021) 284:114180. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2021.114180
12. Kam D, Salib A, Gorgy G, Patel TD, Carniol ET, Eloy JA, et al. Incidence of suicide in patients with head and neck cancer. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. (2015) 141:1075–81. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2015.2480
13. Osazuwa-Peters N, Barnes JM, Okafor SI, Taylor DB, Hussaini AS, Adjei Boakye E, et al. Incidence and risk of suicide among patients with head and neck cancer in rural, urban, and metropolitan areas. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. (2021) 147:1045–52. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2021.1728
14. Howren MB, Christensen AJ, Karnell LH, and Funk GF. Psychological factors associated with head and neck cancer treatment and survivorship: evidence and opportunities for behavioral medicine. J Consult Clin Psychol. (2013) 81:299–317. doi: 10.1037/a0029940
15. Aschebrook-Kilfoy B, James B, Nagar S, Kaplan S, Seng V, Ahsan H, et al. Risk factors for decreased quality of life in thyroid cancer survivors: initial findings from the north American thyroid cancer survivorship study. Thyroid. (2015) 25:1313–21. doi: 10.1089/thy.2015.0098
16. Applewhite MK, James BC, Kaplan SP, Angelos P, Kaplan EL, Grogan RH, et al. Quality of life in thyroid cancer is similar to that of other cancers with worse survival. World J Surg. (2016) 40:551–61. doi: 10.1007/s00268-015-3300-5
17. Fu XL, Wu H, Qian Y, Jin XH, Yu HR, Du L, et al. Incidence of suicide mortality among childhood cancer survivors: A population-based retrospective study. Psychiatry Res. (2021) 304:114119. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2021.114119
18. Noto B, Asmus I, Schäfers M, Görlich D, and Riemann B. Predictors of anxiety and depression in differentiated thyroid cancer survivors: results of a cross-sectional study. Thyroid. (2022) 32:1077–85. doi: 10.1089/thy.2022.0067
19. Kurumety SK, Helenowski IB, Goswami S, Peipert BJ, Yount SE, and Sturgeon C. Post-thyroidectomy neck appearance and impact on quality of life in thyroid cancer survivors. Surgery. (2019) 165:1217–21. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2019.03.006
20. Barker DJ and Barker MJ. The body as art. J Cosmet Dermatol. (2002) 1:88–93. doi: 10.1046/j.1473-2165.2002.00027.x
21. Hughes DT, Reyes-Gastelum D, Kovatch KJ, Hamilton AS, Ward KC, and Haymart MR. Energy level and fatigue after surgery for thyroid cancer: A population-based study of patient-reported outcomes. Surgery. (2020) 167:102–9. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2019.04.068
22. Almeida JP, Vartanian JG, and Kowalski LP. Clinical predictors of quality of life in patients with initial differentiated thyroid cancers. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. (2009) 135:342–6. doi: 10.1001/archoto.2009.16
23. Teng CJ, Hu YW, Chen SC, Yeh CM, Chiang HL, Chen TJ, et al. Use of radioactive iodine for thyroid cancer and risk of second primary Malignancy: A nationwide population-based study. J Natl Cancer Inst. (2016) 108:djv314. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djv314
24. Jacobucci R, Grimm KJ, and McArdle JJ. Regularized structural equation modeling. Struct Equ Modeling. (2016) 23:555–66. doi: 10.1080/10705511.2016.1154793
25. Yang C, Delcher C, Shenkman E, and Ranka S. Machine learning approaches for predicting high cost high need patient expenditures in health care. BioMed Eng Online. (2018) 17:131. doi: 10.1186/s12938-018-0568-3
26. Guller U and DeLong ER. Interpreting statistics in medical literature: a vade mecum for surgeons. J Am Coll Surg. (2004) 198:441–58. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2003.09.017
27. Clark TG, Bradburn MJ, Love SB, and Altman DG. Survival analysis part I: basic concepts and first analyses. Br J Cancer. (2003) 89:232–8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601118
28. Bradburn MJ, Clark TG, Love SB, and Altman DG. Survival analysis part II: multivariate data analysis–an introduction to concepts and methods. Br J Cancer. (2003) 89:431–6. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601119
29. Husson O, Haak HR, Buffart LM, Nieuwlaat WA, Oranje WA, Mols F, et al. Health-related quality of life and disease specific symptoms in long-term thyroid cancer survivors: a study from the population-based PROFILES registry. Acta Oncol. (2013) 52:249–58. doi: 10.3109/0284186X.2012.741326
30. Hauch A, Al-Qurayshi Z, Randolph G, and Kandil E. Total thyroidectomy is associated with increased risk of complications for low- and high-volume surgeons. Ann Surg Oncol. (2014) 21:3844–52. doi: 10.1245/s10434-014-3846-8
31. Djurovic M, Pereira AM, Smit JWA, Vasovic O, Damjanovic S, Jemuovic Z, et al. Cognitive functioning and quality of life in patients with Hashimoto thyroiditis on long-term levothyroxine replacement. Endocrine. (2018) 62:136–43. doi: 10.1007/s12020-018-1649-6
32. Chen W, Li J, Peng S, Hong S, Xu H, Lin B, et al. Association of total thyroidectomy or thyroid lobectomy with the quality of life in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer with low to intermediate risk of recurrence. JAMA Surg. (2022) 157:200–9. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2021.6442
33. Jucevičiūtė N, Žilaitienė B, Aniulienė R, and Vanagienė V. The link between thyroid autoimmunity, depression and bipolar disorder. Open Med (Wars). (2019) 14:52–8. doi: 10.1515/med-2019-0008
34. Henson KE, Brock R, Charnock J, Wickramasinghe B, Will O, and Pitman A. Risk of suicide after cancer diagnosis in England. JAMA Psychiatry. (2019) 76:51–60. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.3181
35. Liu L, Xiao Y, Wei D, Wang Q, Zhang JK, Yuan L, et al. Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting suicide risk and prognostic factors in bladder cancer patients following diagnosis: A population-based retrospective study. J Affect Disord. (2024) 347:124–33. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2023.11.086
36. Motillon-Toudic C, Walter M, Séguin M, Carrier JD, Berrouiguet S, and Lemey C. Social isolation and suicide risk: Literature review and perspectives. Eur Psychiatry. (2022) 65:e65. doi: 10.1192/j.eurpsy.2022.2320
37. Beghi M, Butera E, Cerri CG, Cornaggia CM, Febbo F, Mollica A, et al. Suicidal behaviour in older age: A systematic review of risk factors associated to suicide attempts and completed suicides. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. (2021) 127:193–211. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.04.011
38. Nolen-Hoeksema S. Emotion regulation and psychopathology: the role of gender. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. (2012) 8:161–87. doi: 10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032511-143109
39. Möller-Leimkühler AM. Barriers to help-seeking by men: a review of sociocultural and clinical literature with particular reference to depression. J Affect Disord. (2002) 71:1–9. doi: 10.1016/S0165-0327(01)00379-2
40. Shobab L, Burman KD, and Wartofsky L. Sex differences in differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid. (2022) 32:224–35. doi: 10.1089/thy.2021.0361
41. Spoletini I, Gianni W, Caltagirone C, Madaio R, Repetto L, and Spalletta G. Suicide and cancer: where do we go from here? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. (2011) 78:206–19. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2010.05.005
42. Oliffe JL, Broom A, Popa M, Jenkins EK, Rice SM, Ferlatte O, et al. Unpacking social isolation in men’s suicidality. Qual Health Res. (2019) 29:315–27. doi: 10.1177/1049732318800003
43. Oliffe JL, Creighton G, Robertson S, Broom A, Jenkins EK, Ogrodniczuk JS, et al. Injury, interiority, and isolation in men’s suicidality. Am J Mens Health. (2017) 11:888–99. doi: 10.1177/1557988316679576
44. Dean DS and Hay ID. Prognostic indicators in differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Cancer Control. (2000) 7:229–39. doi: 10.1177/107327480000700302
45. Mazzaferri EL and Kloos RT. Clinical review 128: Current approaches to primary therapy for papillary and follicular thyroid cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2001) 86:1447–63. doi: 10.1210/jcem.86.4.7407
46. Cabello M, Miret M, Ayuso-Mateos JL, Caballero FF, Chatterji S, Tobiasz-Adamczyk B, et al. Cross-national prevalence and factors associated with suicide ideation and attempts in older and young-and-middle age people. Aging Ment Health. (2020) 24:1533–42. doi: 10.1080/13607863.2019.1603284
47. Samson A and Zerter B. The experience of spirituality in the psycho-social adaptation of cancer survivors. J Pastoral Care Counsel. (2003) 57:329–43. doi: 10.1177/154230500305700308
48. Beautrais AL. A case control study of suicide and attempted suicide in older adults. Suicide Life Threat Behav. (2002) 32:1–9. doi: 10.1521/suli.32.1.1.22184
49. Cattaneo A, Ferrari C, Turner L, Mariani N, Enache D, Hastings C, et al. Whole-blood expression of inflammasome- and glucocorticoid-related mRNAs correctly separates treatment-resistant depressed patients from drug-free and responsive patients in the BIODEP study. Transl Psychiatry. (2020) 10:232. doi: 10.1038/s41398-020-00874-7
50. Soriano Barceló J, Portes Cruz J, Cornes Iglesias JM, Portela Traba B, Brenlla González J, and Mateos Álvarez R. Health care contact prior to suicide attempts in older adults. A field study in Galicia, Spain. Actas Esp Psiquiatr. (2020) 48:106–15.
51. Akechi T, Okamura H, Yamawaki S, and Uchitomi Y. Predictors of patients’ mental adjustment to cancer: patient characteristics and social support. Br J Cancer. (1998) 77:2381–5. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1998.396
52. Nausheen B and Kamal A. Familial social support and depression in breast cancer: an exploratory study on a Pakistani sample. Psychooncology. (2007) 16:859–62. doi: 10.1002/pon.1136
53. Merrill RM and Johnson E. Benefits of marriage on relative and conditional relative cancer survival differ between males and females in the USA. J Cancer Surviv. (2017) 11:578–89. doi: 10.1007/s11764-017-0627-y
54. Stephenson M, Prom-Wormley E, Lannoy S, and Edwards AC. The temporal relationship between marriage and risk for suicidal ideation. J Affect Disord. (2023) 343:129–35. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2023.10.007
55. Hann D, Baker F, Denniston M, Gesme D, Reding D, Flynn T, et al. The influence of social support on depressive symptoms in cancer patients: age and gender differences. J Psychosom Res. (2002) 52:279–83. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3999(01)00235-5
56. Aizer AA, Chen MH, McCarthy EP, Mendu ML, Koo S, Wilhite TJ, et al. Marital status and survival in patients with cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2013) 31:3869–76. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.49.6489
57. Kyung-Sook W, SangSoo S, Sangjin S, and Young-Jeon S. Marital status integration and suicide: A meta-analysis and meta-regression. Soc Sci Med. (2018) 197:116–26. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2017.11.053
58. Kim JW, Jung HY, Won DY, Noh JH, Shin YS, and Kang TI. Suicide trends according to age, gender, and marital status in South Korea. Omega (Westport). (2019) 79:90–105. doi: 10.1177/0030222817715756
59. Mann JJ and Kuehn BM. Rate of suicide increases in middle age: primary care key to suicide prevention. Jama. (2014) 312:1727–8. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.12816
60. Bergman Levy T, Barak Y, Sigler M, and Aizenberg D. Suicide attempts and burden of physical illness among depressed elderly inpatients. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. (2011) 52:115–7. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2010.02.012
61. Roškar S, Podlesek A, Kuzmanić M, Demšar LO, Zaletel M, and Marušič A. Suicide risk and its relationship to change in marital status. Crisis. (2011) 32:24–30. doi: 10.1027/0227-5910/a000054
62. Perry BL, Stevens-Watkins D, and Oser CB. The moderating effects of skin color and ethnic identity affirmation on suicide risk among low-SES African American women. Race Soc Probl. (2013) 5:1–14. doi: 10.1007/s12552-012-9080-8
63. Tondo L, Albert MJ, and Baldessarini RJ. Suicide rates in relation to health care access in the United States: an ecological study. J Clin Psychiatry. (2006) 67:517–23. doi: 10.4088/JCP.v67n0402
64. Kuramoto SJ, Wilcox HC, and Latkin CA. Social integration and suicide-related ideation from a social network perspective: a longitudinal study among inner-city African Americans. Suicide Life Threat Behav. (2013) 43:366–78. doi: 10.1111/sltb.12023
65. Wingate LR, Bobadilla L, Burns AB, Cukrowicz KC, Hernandez A, Ketterman RL, et al. Suicidality in African American men: the roles of southern residence, religiosity, and social support. Suicide Life Threat Behav. (2005) 35:615–29. doi: 10.1521/suli.2005.35.6.615
66. Compton MT, Thompson NJ, and Kaslow NJ. Social environment factors associated with suicide attempt among low-income African Americans: the protective role of family relationships and social support. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. (2005) 40:175–85. doi: 10.1007/s00127-005-0865-6
67. Davidson CL, Wingate LR, Slish ML, and Rasmussen KA. The Great Black Hope: Hope and its relation to suicide risk among African Americans. Suicide Life Threat Behav. (2010) 40:170–80. doi: 10.1521/suli.2010.40.2.170
68. Street JC, Taha F, Jones AD, Jones KA, Carr E, Woods A, et al. Racial identity and reasons for living in African American female suicide attempters. Cultur Divers Ethnic Minor Psychol. (2012) 18:416–23. doi: 10.1037/a0029594
69. Guay B, Johnson-Obaseki S, McDonald JT, Connell C, and Corsten M. Incidence of differentiated thyroid cancer by socioeconomic status and urban residence: Canada 1991-2006. Thyroid. (2014) 24:552–5. doi: 10.1089/thy.2013.0308
70. Goldman-Mellor S, Allen K, and Kaplan MS. Rural/Urban disparities in adolescent nonfatal suicidal ideation and suicide attempt: A population-based study. Suicide Life Threat Behav. (2018) 48:709–19. doi: 10.1111/sltb.12390
71. Hsu CY, Chang SS, and Yip PSF. Subjective wellbeing, suicide and socioeconomic factors: an ecological analysis in Hong Kong. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. (2019) 28:112–30. doi: 10.1017/S2045796018000124
72. Akkaya-Kalayci T, Vyssoki B, Winkler D, Willeit M, Kapusta ND, Dorffner G, et al. The effect of seasonal changes and climatic factors on suicide attempts of young people. BMC Psychiatry. (2017) 17:365. doi: 10.1186/s12888-017-1532-7
73. Vyssoki B, Kapusta ND, Praschak-Rieder N, Dorffner G, and Willeit M. Direct effect of sunshine on suicide. JAMA Psychiatry. (2014) 71:1231–7. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2014.1198
74. Anestis MD, Selby EA, and Butterworth SE. Rising longitudinal trajectories in suicide rates: The role of firearm suicide rates and firearm legislation. Prev Med. (2017) 100:159–66. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2017.04.032
75. Branas CC, Nance ML, Elliott MR, Richmond TS, and Schwab CW. Urban-rural shifts in intentional firearm death: different causes, same results. Am J Public Health. (2004) 94:1750–5. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.94.10.1750
76. Denney JT, Rogers RG, Krueger PM, and Wadsworth T. Adult suicide mortality in the United States: marital status, family size, socioeconomic status, and differences by sex. Soc Sci Q. (2009) 90:1167. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-6237.2009.00652.x
77. Walker BB, Schuurman N, Auluck A, Lear SA, and Rosin M. Socioeconomic disparities in head and neck cancer patients’ access to cancer treatment centers. Rural Remote Health. (2017) 17:4210. doi: 10.22605/RRH4210
78. Cyr ME, Etchin AG, Guthrie BJ, and Benneyan JC. Access to specialty healthcare in urban versus rural US populations: a systematic literature review. BMC Health Serv Res. (2019) 19:974. doi: 10.1186/s12913-019-4815-5
79. Morales DA, Barksdale CL, and Beckel-Mitchener AC. A call to action to address rural mental health disparities. J Clin Transl Sci. (2020) 4:463–7. doi: 10.1017/cts.2020.42
80. Wakefield J. Ecologic studies revisited. Annu Rev Public Health. (2008) 29:75–90. doi: 10.1146/annurev.publhealth.29.020907.090821
81. Ohnsorge K, Gudat H, and Rehmann-Sutter C. Intentions in wishes to die: analysis and a typology–a report of 30 qualitative case studies of terminally ill cancer patients in palliative care. Psychooncology. (2014) 23:1021–6. doi: 10.1002/pon.3524
82. Ohnsorge K, Gudat H, and Rehmann-Sutter C. What a wish to die can mean: reasons, meanings and functions of wishes to die, reported from 30 qualitative case studies of terminally ill cancer patients in palliative care. BMC Palliat Care. (2014) 13:38. doi: 10.1186/1472-684X-13-38
83. Chen Y, Yu K, Xiong J, Zhang J, Zhou S, Dai J, et al. Suicide and accidental death among women with primary ovarian cancer: A population-based study. Front Med (Lausanne). (2022) 9:833965. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.833965
84. Vehling S and Kissane DW. Existential distress in cancer: Alleviating suffering from fundamental loss and change. Psychooncology. (2018) 27:2525–30. doi: 10.1002/pon.4872
85. Banach R, Bartès B, Farnell K, Rimmele H, Shey J, Singer S, et al. Results of the Thyroid Cancer Alliance international patient/survivor survey: Psychosocial/informational support needs, treatment side effects and international differences in care. Hormones (Athens). (2013) 12:428–38. doi: 10.1007/BF03401308
Keywords: suicide, thyroid cancer, nomogram, predictors, SEER, population-based study
Citation: Zhou J, Tian M, Zhang X, Xiong L, Huang J, Xu M, Liang X and Wei S (2025) Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting suicide risk factors in thyroid cancer patients following diagnosis: a population-based retrospective study. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1392283. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1392283
Received: 27 February 2024; Accepted: 08 September 2025;
Published: 30 September 2025.
Reviewed by:
Kuanjun He, Inner Mongolia University for Nationalities, ChinaAnam Mehmood, Shenzhen University, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhou, Tian, Zhang, Xiong, Huang, Xu, Liang and Wei. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shaozhong Wei, d2Vpc2hhb3pob25nQDE2My5jb20=; Xinjun Liang, ZG9jdG9ybHhqQDE2My5jb20=
 Jie Zhou
Jie Zhou Mengjie Tian2,3,4
Mengjie Tian2,3,4 Xinjun Liang
Xinjun Liang Shaozhong Wei
Shaozhong Wei