- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Jiangxi Provincial People's Hospital, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang Medical College, Nanchang, China
- 2Department of Reproductive Medicine, Jiangxi Maternal and Child Health Hospital, Nanchang, China
- 3Department of Gynecology, Jiangxi Maternal and Child Health Hospital, Nanchang, China
- 4Department of Clinical Medicine, Nanchang University, Nanchang, China
Introduction: This study aimed to assess the impact of inactivated COVID-19 vaccine on Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels in Chinese women.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on women aged 18-45 who had undergone two AMH tests between March 2020 and September 2021. Participants were grouped based on vaccine doses (two- and three-dose), time intervals since vaccination, and manufacturers. The difference in AMH levels and the percentage changes in AMH were measured.
Results: The results revealed no significant differences in AMH levels between the vaccinated groups (two- and three-dose) and the control group, both in unadjusted and adjusted analyses. Subgroup analysis showed no statistical difference in either absolute or percentage changes of AMH levels among different time-interval groups and manufacturer groups.
Discussion: In conclusion, the number of doses, time interval, and manufacturer of the inactivated COVID-19 vaccine did not affect AMH levels in Chinese women.
1 Introduction
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), or the “new coronavirus pneumonia,” is a respiratory infectious disease that has been spreading rapidly worldwide since December 2019. The COVID-19 epidemic is the most severe global public health outbreak since World War II, and it seriously threatens human health. As the first country to be hit by the COVID-19 epidemic (1), China is the best place for the research on the novel coronavirus and its vaccines. The Chinese government announced the lifting of epidemic control on December 7, 2022, implying that the focus of epidemic prevention and control has shifted from controlling the source of infection and blocking transmission routes to the direction of protecting susceptible populations, representing a need for more people to participate in vaccination in the face of a raging epidemic, resulting in a surge in demand for vaccines. Driven by policy support and media coverage, the vast majority of Chinese residents choose to be vaccinated against the COVID-19 epidemic. However, young people who are planning to become pregnant are hesitant to receive vaccination because of the concern about the safety of the vaccination. A survey in 2023 showed that the COVID-19 vaccination rate of men and women preparing for pregnancy was significantly lower than the average vaccination rate in China (2). On the other hand, some people who have been vaccinated also worry about the harm to their physical health. Among these concerns, apprehensions regarding reproductive health are notably prevalent.
First, some evidence supports that coronaviruses may have an impact on human reproductive health. COVID-19 is caused by SARS-CoV-2 pathogen infection (3–6), a single positive-stranded RNA coronavirus with regularly arranged spines on the envelope. The virus binds to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), mediated by the viral surface spine glycoprotein (S protein), to enter cells (6, 7). ACE2 has been detected in human tissues of different organs, including the heart, kidney, intestine, and blood vessels. ACE2 has also been detected in organs related to reproduction, such as ovaries, uterus, vagina, placenta, and testes (8, 9). Based on the considerable regulatory role of ACE2 on reproduction (10, 11), SARS-CoV-2 may affect female reproductive function by affecting ACE2. Studies have shown that SARS-CoV-2 affects ovarian reserve in women. A study by Ding et al. in March 2021 showed that women infected with COVID-19 had lower Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels, higher FSH levels, and higher levels of testosterone and prolactin than healthy women (12).
Secondly, a vaccine is a biological agent derived from a virus. If a virus exerts a specific effect on the body, it is plausible that the vaccine may elicit similar effects. Since the outbreak of COVID-19, many types of vaccines, such as mRNA vaccines, DNA vaccines, inactivated vaccines, recombinant protein subunit vaccines, virus vector vaccines, and virus-like particle vaccines, have been used. Studies have shown that other new crown vaccines, such as mRNA vaccines, impact women’s ovarian reserve (13–15). Inactivated vaccines, widely administered in China, are known to retain the intact structure of the virus, so inactivated vaccines may be more likely to cause damage to reproductive health than other types of vaccines. However, current research on the impact of inactivated vaccines on female reproductive health in China is rather limited.
Therefore, the purpose of this study was to investigate whether the COVID-19 vaccination of inactivated vaccines in China would affect AMH in Chinese women, and thus indirectly assess whether it would affect ovarian function in Chinese women.
2 Methods
2.1 Subjects
This study was a retrospective study of patients admitted to a provincial tertiary hospital in China from March 2020 to September 2021. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects. Inclusion criteria are as follows: female, aged between 18 and 45; received two or more AMH tests between March 2020 and September 2022; the first AMH was within the normal range (16). The exclusion criteria were as follows: postmenopausal women, those with polycystic ovarian syndrome, those who were pregnant, and those who had ovarian surgery during this period. The cases with incomplete information were excluded in our analysis.The cases with incomplete information were excluded in our analysis. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Jiangxi Provincial Maternal and Child Health Hospital (approval number: EC-KT-202309). We certify that the study was performed in accordance with the 1964 declaration of HELSlNKl and later amendments.
2.2 Vaccination strategy
The vaccination strategy in China is as follows: voluntary principle, available to people ≥ 18 years, with two doses routinely administered by intramuscular injection into the deltoid muscle of the upper arm, and the interval between the two doses should be ≥ 3 weeks but ≤ 8 weeks. The third dose (booster) should not be given until 6 months after the second dose. If the vaccination is not completed in accordance with the procedure, making up the vaccination as soon as possible is recommended. Patients who received Sinopharm vaccine or Sinovac vaccine were included in this study, and some patients who received both vaccines were also included in this study. Vaccination information from official immunization records was collected in a personal mobile application (app).
2.3 Research grouping criteria
In this study, the subjects were divided into three groups in accordance with the number of doses received and whether they received the vaccine: a two-dose group (two doses received), a three-dose group (three doses received), and control group (no vaccination due to voluntary principle). From March 2020 to September 2022, women who received two or 3 doses of the vaccine and were tested for AMH before the first dose and after the last dose were included in the two- or three-dose vaccine group. During the same period, women who underwent two AMH tests at the research hospital and had never been vaccinated were included in the control group. In current studies focusing on the effects of inactivated vaccines on AMH, participants who received two doses of the vaccine were included as subjects (17). In addition to investigating the effects of two doses of vaccination, this study also incorporated individuals who received booster shots (three-dose groups). Due to the novelty of designing two vaccine regimens and the uncertainty surrounding the effect of vaccination on AMH levels, the sample size could not be predetermined.
In the end, 526, 79, and 389 women were included in the two-dose, three-dose, and control groups, respectively (Figure 1).
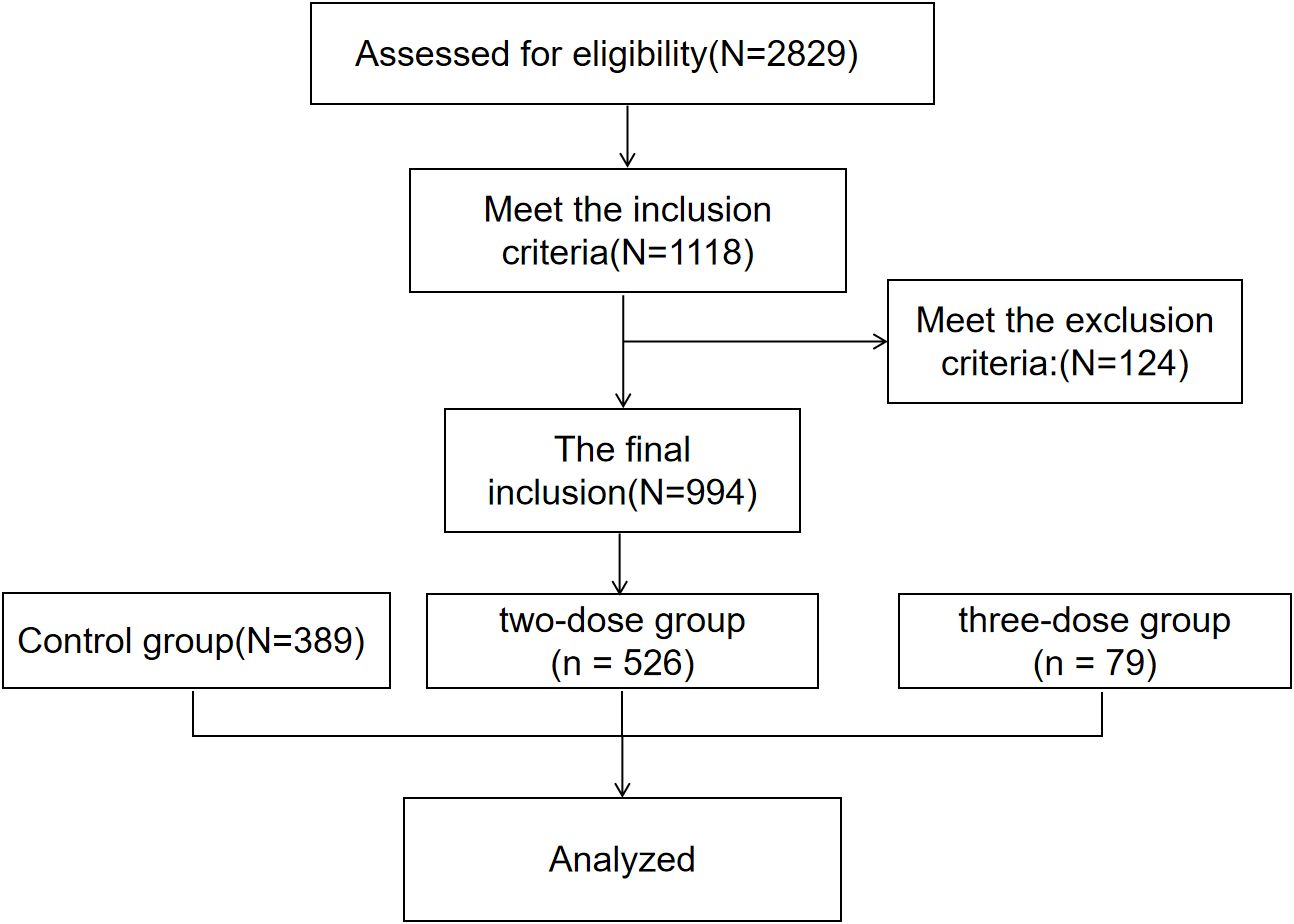
Figure 1. Flow chart showing the design, inclusion and exclusion criteria of patients in the study. The Inclusion criteria: female, aged between 18 and 45; received two or more AMH tests between March 2020 and September 2022; the first AMH was within the normal range. The exclusion criteria: postmenopausal women, those with polycystic ovarian syndrome, those who were pregnant, and those who had ovarian surgery during this period.
2.4 Study indicators
AMH was measured by Elecsys®AMH Plus immunoassay in this provincial tertiary hospital in China. After taking venous blood at the blood sampling window, the serum was obtained by centrifugation by experienced laboratory staff, and the serum was obtained by Cobas e 801 analyzer 127 (Roche Diagnostics, Switzerland) for testing.The study metrics were as follows: the difference in AMH (last AMH – first AMH) and the percentage change in AMH [(last AMH – first AMH)/first AMH)].
2.5 Statistical methods
SAS 9.4 software was applied for statistical analysis. Count data were described by frequencies or percentages, and the chi-square test was applied for comparisons. The measurement data were tested for normality by the Shapiro–Wilk test. The data conforming to a normal distribution were compared by t-test and expressed as mean ± standard deviation (x ± s), whereas those not conforming to a normal distribution were expressed as median P50 (25th percentile, P25; 75th percentile, P75) and compared by Kruskal–Wallis rank sum test. The AMH change values were used in the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. A generalized linear model was applied for multivariate analysis of AMH change values. p < 0.05 was considered a statistically significant difference.
3 Results
3.1 The baseline characteristics of the study participants
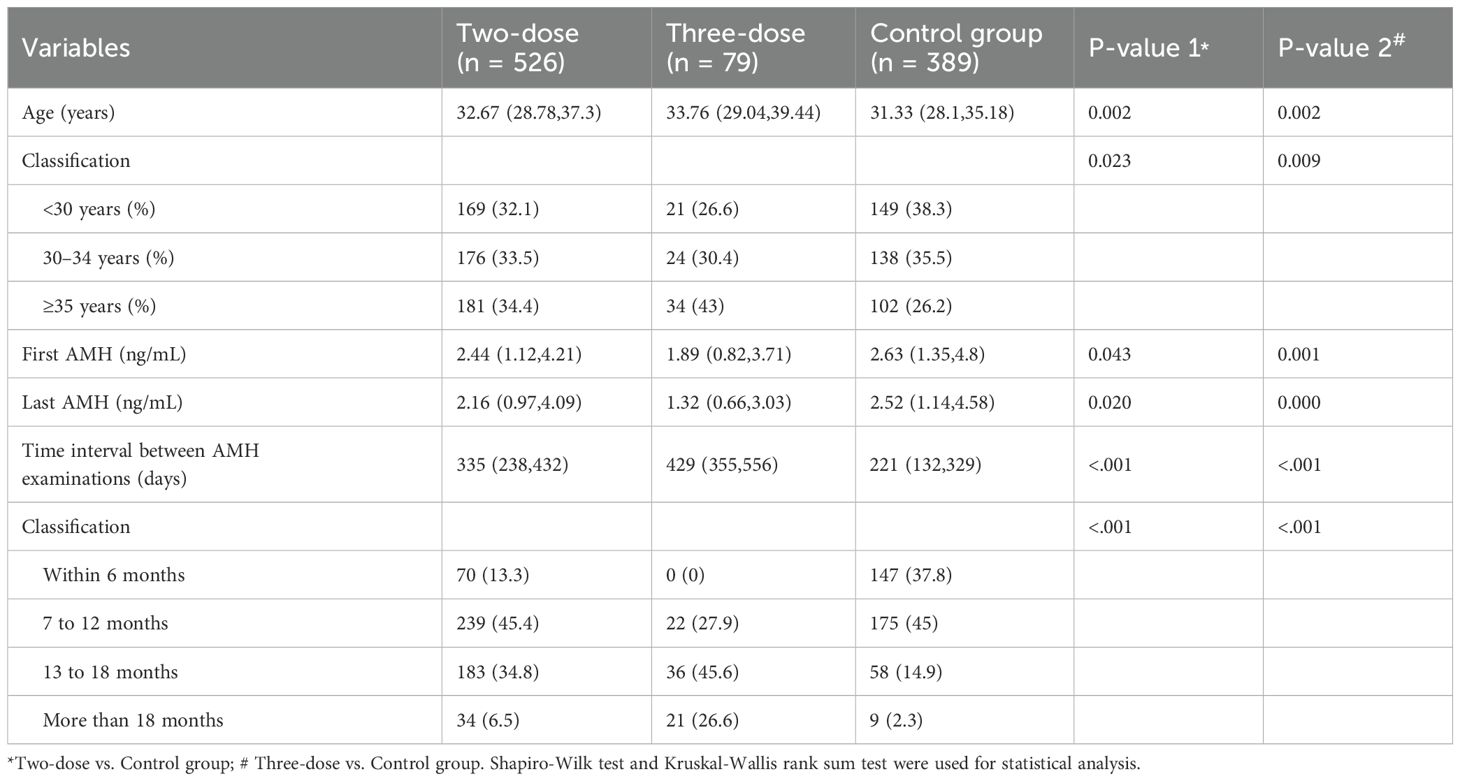
Table 1 shows the baseline characteristics of the study participants. The data were presented in the form of median after normality test. Among the 994 women included in the study, significant differences were observed in terms of median age, first AMH level, and the time interval between AMH (days) in the two-dose (n = 526) and three-dose (n = 79) groups compared with the control group (n = 389). Due to the differences in the underlying information, multifactorial analysis was applied to adjust the data for the following statistical analysis to increase the credibility of the study results.
3.2 Difference and percentage change in AMH among the three groups
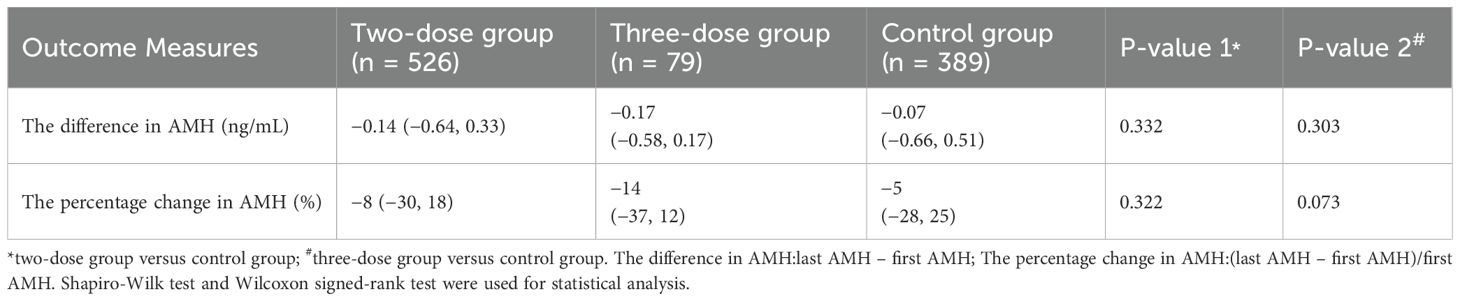
As illustrated in Table 2, compared with the control group, the two-dose (−0.14 vs. −0.07, P = 0.332; −8% vs. −5%, P = 0.322) and three-dose groups (−0.17 vs. −0.07, P = 0.303; −14% vs. -5%, P = 0.073) showed non-statistically significant difference in the difference and percentage change in AMH, respectively.
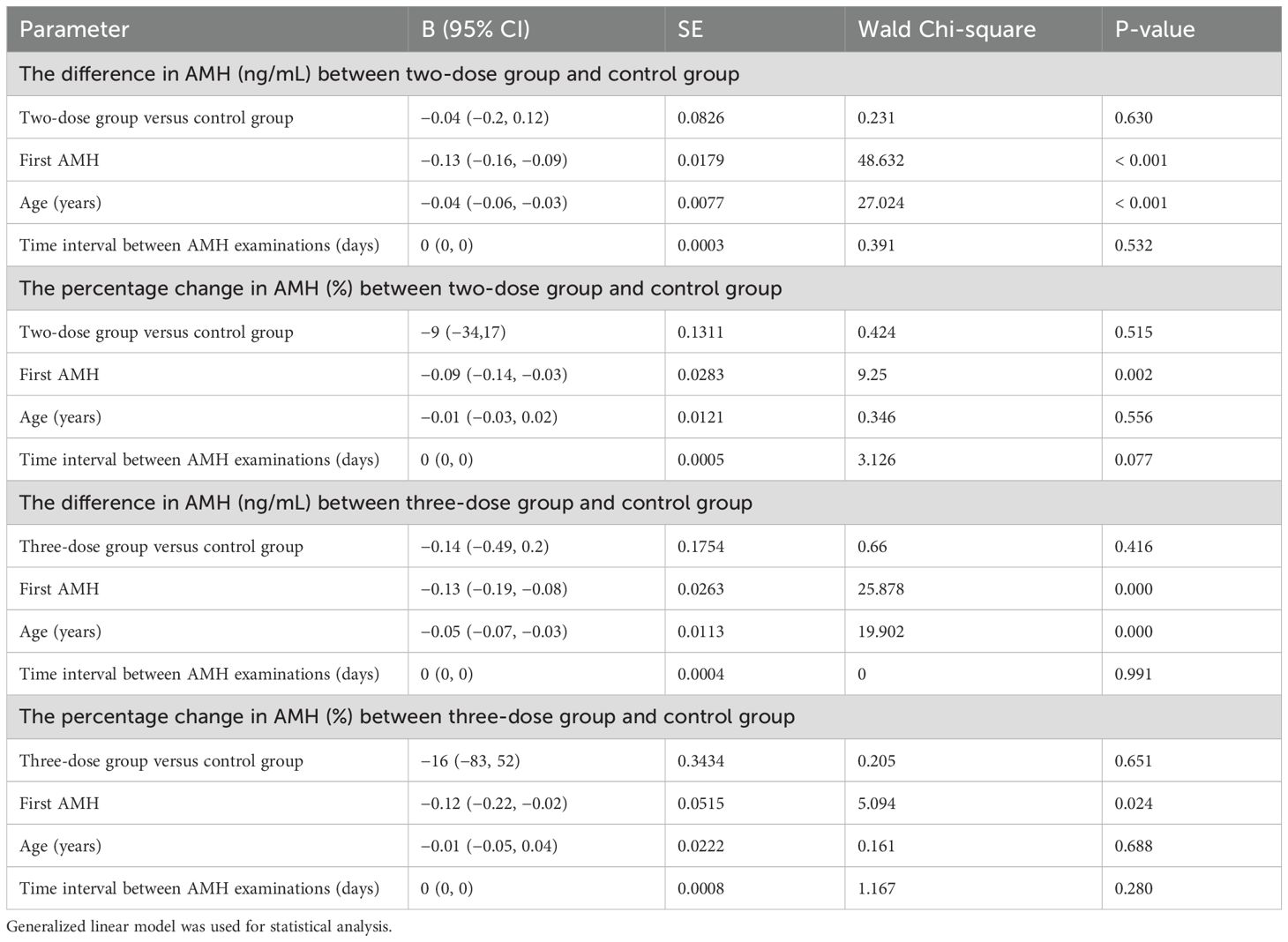
Table 3 also shows no significant difference in the difference in AMH between the two/three-dose groups and the control group after adjusting for the first AMH, age, and time interval between AMH examinations by using a generalized linear model for the analysis (P = 0.630; P = 0.416). In addition, the percentage change in AMH (P = 0.515; P = 0.651) was not statistically significant.
3.3 Effect of time interval on the difference and percentage change in AMH
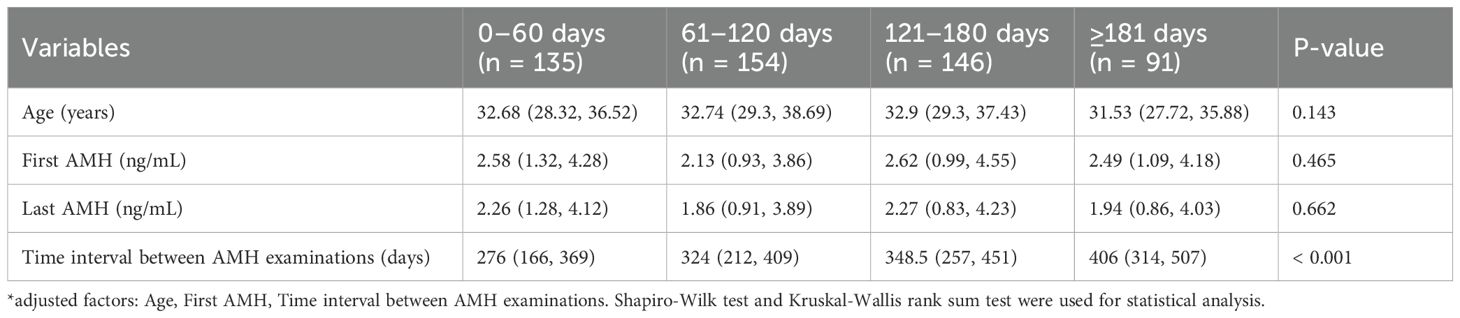
Table 4a and Table 4b shows the influence of the time interval from the last vaccine injection to the last AMH examination over the difference in AMH and the percentage change in AMH. All patients in the two-dose group were grouped by the time interval from the last vaccine injection to the last AMH examination received, and they were divided into four groups of up to 0–60 days (n = 135), 61-120days (n = 154), 121–180 days (n = 146), and more than 180 days (n = 91). The median age of patients and the first-time AMH median values were not significantly different among the four groups. The results of the statistical analysis found no significant change in the difference and percentage change in AMH among the four groups. By using data within 0–60 days as a reference, the difference in AMH adjusted β values (95% CI) of the other groups were −0.01 (−0.26, 0.24), −0.16 (−0.42, 0.09), and −0.25 (−0.55, 0.06), respectively, and the adjusted β values (95% CI) for the percentage change in AMH were 0.1 (−0.13, 0.32), −0.03 (−0.26, 0.2), and −0.02 (−0.29, 0.25), there was no statistical difference.
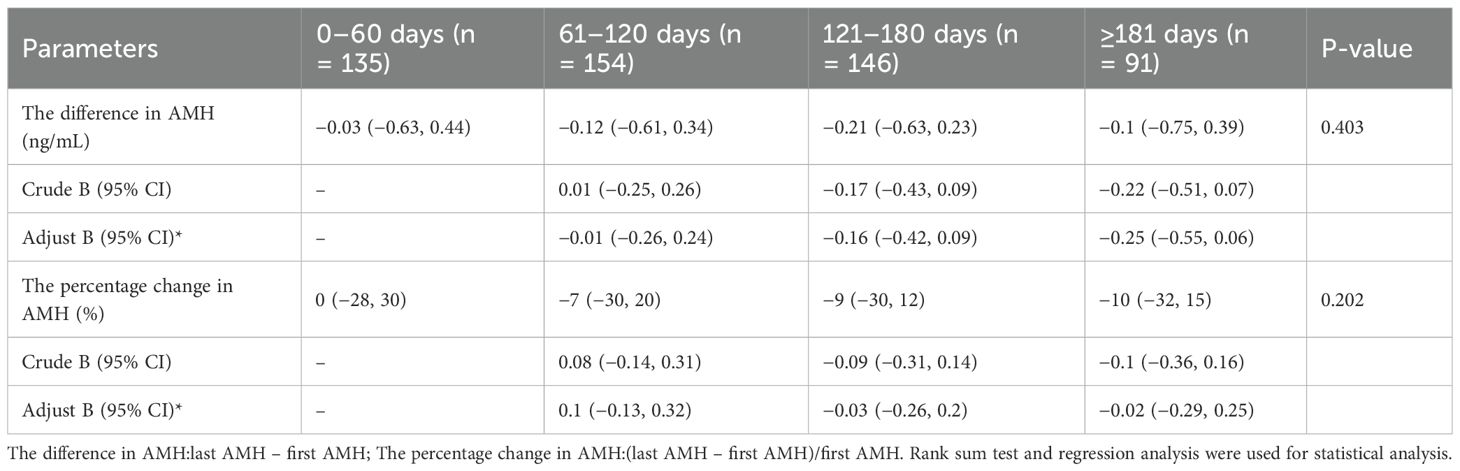
Table 4b. Effect of the time interval on the difference in AMH and the percentage change in AMH in the two-dose group.
3.4 Effect of vaccine manufacturers on the difference in AMH and the percentage change in AMH
Table 5a and Table 5b shows the effect of vaccine manufacturers on AMH. In this study, the vaccine manufacturers in the two-dose group were analyzed, which included China National Pharmaceutical Group Co. Ltd. (Sinopharm vaccine) and Sinovac Life Sciences Co., Ltd. (Sinovac vaccine). The participants were further divided in accordance with the vaccine manufacturer: Sinopharm group (Sinopharm Vaccine only, n = 129), Sinovac group (Sinovac vaccine only, n = 153), and a mixed group (inoculated against Sinopharm and Sinovac vaccines, n = 244). The results found no significant difference in the AMH difference and the percentage change in AMH among these three groups. As shown in Table 5b, with Sinopharm as the reference, the adjusted β values (95% CI) for the difference in AMH were −0.05 (−0.3, 0.2) and 0.01 (−0.21, 0.24), and those for the percentage change in AMH were −0.11 (−0.34, 0.11) and −0.07(−0.27, 0.14), there was no statistical difference.
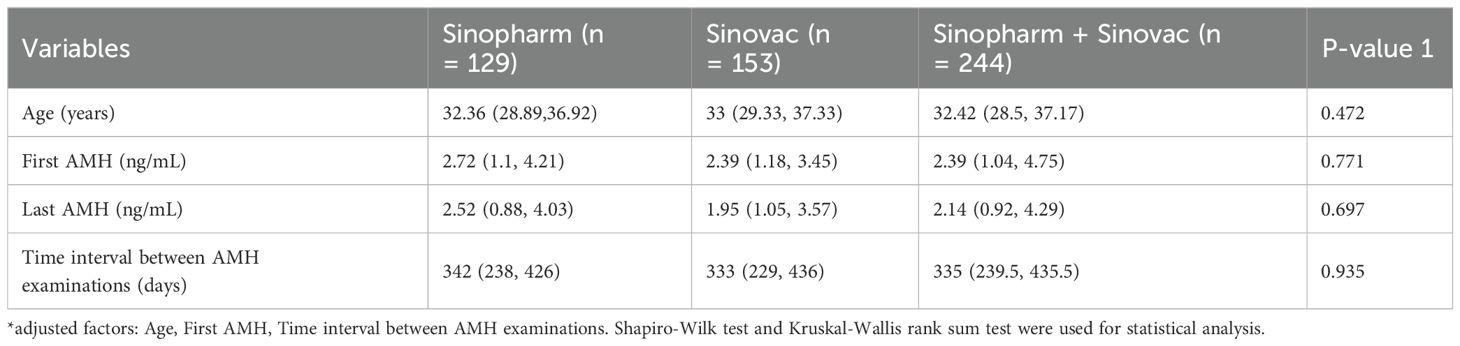
Table 5a. Statistical characteristics of different vaccine manufacturers in the 2-dose group. Effect of vaccine dose manufacturer on the difference in AMH and the percentage change in AMH in the two-dose group.
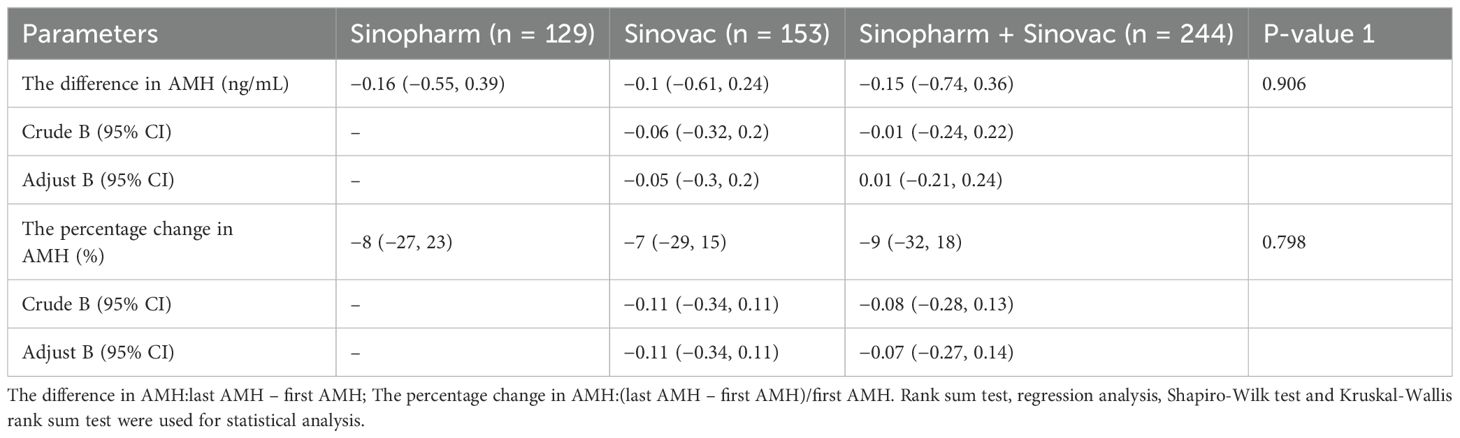
Table 5b. Effect of vaccine dose manufacturer on the difference in AMH and the percentage change in AMH in the two-dose group(before and after adjustment).
DFor requirements for a specific article type please refer to the Article Types on any Frontiers journal page. Please also refer to Author Guidelines for further information on how to organize your manuscript in the required sections or their equivalents for your field1.
4 Discussion
Indicators reflecting ovarian reserve include inhibin B, estradiol (E2), FSH, etc. However, these indicators are affected by the menstrual cycle (18). AMH is produced by stratum granulosum cells of small ovarian follicles and is not affected by the dominant follicle. Therefore, the circulating level of AMH is unaffected by the menstrual cycle and can be used to measure ovarian follicular reserve. So, they are now considered the preferred measure for ovarian reserve assessment (19–22). As AMH testing is not typically included in routine gynecological examinations, it is generally conducted in most hospitals only when female patients present with symptoms indicative of abnormal ovarian function, such as insomnia, hyperhidrosis, or infertility related to ovulation. Consequently, in numerous retrospective studies, establishing a control group with normal AMH levels poses a significant challenge. However, this research relies on a sizeable Grade 3A provincial obstetrics and gynecology hospital, where the reproductive center is the main specialty. In order to screen for the causes of infertility, women visiting the reproductive center at this hospital undergo routine AMH testing, resulting in a substantial collection of samples with normal AMH levels. This includes women with other fertility issues, such as uterine adhesions and blocked fallopian tubes, who also seek treatment at the reproductive center. Consequently, this pool of patients provides the source of the research samples included in this study. Therefore, in this study, AMH was chosen as the indicator of ovarian reserve. Retrospective analysis from different angles was applied to investigate the effect of the inactivated COVID-19 vaccine on AMH levels among women. The results showed that the inactivated vaccine in China did not affect the AMH levels in women.
As a member of the TGF-β superfamily (23–25), AMH follows the classical SMAD signal transduction pathway to transmit its biological information. In the case of COVID-19 virus infection, the lungs and other affected organs trigger an inflammatory response, and in this inflammatory microenvironment, the expression of transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) is significantly increased. In theory, when the TGF-β signaling pathway is overactive, the activity or effective concentration of the Smad protein may encounter some threshold or saturation state, which prevents the Smad protein from receiving more upstream signal input or efficiently transmitting the signal further to the nucleus. If this hypothesis is true, then during COVID-19 infection, AMH may be affected by a receptor shared with the inflammatory mediator TGF-β, and interestingly, studies have shown that AMH does change significantly during COVID-19 infection (26, 27). In addition, it is worth noting that the severity of COVID-19 disease is generally thought to be related to sex (28); After COVID-19 infection, women produce fewer inflammatory factors than men (28). And mortality rates are observed to be higher in males compared to females, which suggests that premenopausal status may confer some protection against COVID-19 infection (29), This protective effect may be attributed to AMH competitively occupying a greater number of Smad receptors, and consequently, AMH may be less able to exert its effects because of this competitive binding.This may be explained from the perspective of alleviating the inflammatory response, which in turn demonstrates the association of AMH with COVID-19 infection. However, there is no conclusive evidence to confirm this saturation property of Smad protein, and more rigorous experimental studies are needed to verify this hypothesis.
Whether vaccines have the same effect on AMH levels as viruses is equally essential. This study used univariate and multivariate analyses to investigate whether the vaccine affected AMH. First, compared with the control group, the two- and three-dose groups showed no statistically significant difference in the difference and percentage change in AMH. Next, after adjusting for the first AMH, age, and time interval between AMH examinations by using a generalized linear model, no statistically significant difference in the difference and percentage change in AMH was observed among the three groups. These results suggested that different inactivated vaccine doses did not affect AMH.
A prospective study has been conducted to determine whether mRNA vaccines affect AMH. Statistical analysis of AMH levels in subjects before and after the first vaccination and three months after that study showed that AMH levels did not change significantly before and after mRNA vaccination (12). In particular, the authors mentioned that AMH changes may occur after three months or longer and require further long-term follow-up. Therefore, this study was also designed to investigate the effect of time interval after vaccination on AMH. In the two-dThe author(s) declare that fose group with the largest sample size, the patients were divided into four groups (0–60 days, 61–120 days, 121–180 days, and more than 180 days) according to the time interval from the last vaccine dose injection to the last AMH examination. The results of multivariate analysis showed no significant difference in AMH difference and percentage change of AMH in each group when the data within 0–60 days were used as a reference. This suggests that AMH levels did not change significantly after vaccination, at least during the time interval of this study. As the novel coronavirus is a recently emerged virus, it is currently unfeasible to collect samples at longer intervals to study the effect of time intervals post-vaccination on AMH levels. Our findings indicate that AMH levels remained relatively stable beyond a six-month period following vaccination. Our future research will track AMH fluctuations over a more extended duration.
The inactivated vaccines commonly administered to the Chinese population are those manufactured by Sinopharm and Kexing. The vaccination authorities do not have strict regulations on whether the manufacturer of the second dose of vaccine should be the same as the first dose, resulting in some of the population receiving vaccines from different manufacturers. Therefore, information on vaccine manufacturers was collected, and subgroup analysis was performed. The results suggested that the vaccine manufacturers did not affect the AMH level.
In conclusion, the inactivated COVID-19 vaccine, including the different vaccine doses, the time interval after vaccination, and the different vaccine manufacturers, did not affect AMH. This is consistent with the results of previous studies on the effects of other types of COVID-19 vaccines on human reproduction and female fertility. In 2022, Mohr-Sasson et al. found that ovarian reserve, as assessed by serum AMH levels, was not altered 3 months after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination (12). In 2023, Another prospective study found that although menstruation in adolescent girls may be affected by the COVID-19 mRNA vaccine, ovarian reserve did not appear to be impaired, as estimated by AMH (13).In a prospective cross-sectional study in Turkey, vaccination with COVID-19 mRNA was found to have no effect on AMH levels (30). The present study was a retrospective study to examine whether inactivated vaccines produce changes in female AMH levels in Chinese inactivated vaccine recipients. In some existing prospective analyses, due to the effect of ethics and policies actively promoting vaccination, a blank control group without vaccination was not set up (12). In the present study, a large number of samples that did not receive vaccine due to social or health factors were collected for blank control analysis, which significantly increased the credibility of the results. In addition, for the first time, this study provides a separate analysis of populations who were offered inactivated vaccines of different doses and different manufacturers. As a result, our study provides richer and more credible data on the effects of vaccines on AMH level in women.
Although AMH is widely used as a representative marker of ovarian function, studies on AMH alone to reflect the impact of COVID-19 vaccines on female reproductive capacity are far from sufficient. In fact, researchers have conducted different studies to understand the impact of various COVID-19 vaccines on female reproduction. First of all, menstruation is an essential physiological phenomenon in women of reproductive age, and the results of a study from the United States on the relationship between menstrual cycle length and COVID-19 vaccination show that the change in menstrual cycle after vaccination is less than 1 day (31). Another study examining the relationship between multiple types of COVID-19 vaccines worldwide and menstrual cycle length further found that multiple types of COVID-19 vaccination (such as mRNA vaccine, inactivated vaccine, etc.) are not associated with menstrual cycle length (32). Second, pregnancy is the most direct manifestation of average female reproductive capacity. An Internet-based pre-pregnancy cohort study in the United States found that COVID-19 vaccination had no significant correlation with the pregnancy rate of either party, and COVID-19 vaccination did not harm the fertility of either party (33). Researchers are also concerned about whether the vaccination of the COVID-19 vaccine will have an impact on assisted reproduction. A study examining women undergoing in vitro fertilization revealed that administration of China’s novel coronavirus inactivated vaccine did not impact key parameters in the in vitro fertilization process, including the number of oocytes retrieved, the implantation rate, and the sustained pregnancy rate (34). These studies, together with this and other studies on the effects of COVID-19 vaccines on AMH, provide evidence that vaccination does not have an impact on women’s reproductive health.
By analyzing a substantial amount of data, this study conclusively demonstrates that there is no basis for concern regarding reproductive health safety following administration of China’s inactivated COVID-19 vaccine. The study’s findings hold significant clinical relevance. Firstly, it dispels prevalent societal apprehensions and misconceptions about the safety of COVID-19 vaccines, thereby alleviating the need for women planning pregnancies to postpone their family planning due to vaccination concerns. Secondly, it offers a valuable perspective for women experiencing long-term infertility, suggesting that their infertility may stem from factors unrelated to vaccination.
However, this study has some limitations. Compared with those prospective studies, the age distribution of the samples in each group, the time interval between vaccinations, and the time interval between AMH examinations could not be strictly controlled. In particular, AMH is greatly affected by time factors, and AMH was measured over a long time span in this study, which may bring some errors to the results of the study. This study might benefit from additional sensitivity analyses to account for potential confounding variables or different age groups. So, a multicenter study with a larger sample size is recommended. In addition, a study by Rasa Khodavirdilou in 2022 found that AMH fluctuates significantly with the change in the menstrual cycle and that AMH at the stage of ovulation is recommended as a research indicator in clinical research on AMH (35), which may bring particular information bias to the results of this study.
5 Conclusion
This study demonstrated that the COVID-19 inactivated vaccine did not affect AMH levels in Chinese women from the number of doses, the manufacturer and the time interval after vaccination. The findings of this study present compelling clinical proof in support of the safety of COVID-19 vaccination, with particular emphasis on the reproductive health safety of Chinese women. These findings effectively address the concerns that vaccines might adversely affect AMH levels. Consequently, healthcare professionals can confidently recommend the COVID-19 vaccine to female patients without hesitation regarding its potential negative impact on fertility. This not only boosts public trust in vaccination and increases vaccination rates but also serves as a crucial measure to safeguard public health and promote women’s health and well-being.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
This retrospective study utilized anonymized medical records without additional patient intervention. The protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Jiangxi Provincial Maternal and Child Health Hospital (Approval No. EC-KT-202309). All procedures complied with the Declaration of Helsinki and relevant Chinese ethical regulations to protect patient privacy and data security.
Author contributions
MB: Investigation, Writing – original draft. LX: Visualization, Writing – original draft. YL: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. QW: Writing – review & editing. XS: Writing – review & editing. TW: Writing – review & editing. SQ: Writing – review & editing. LW: Writing – review & editing. CW: Writing – review & editing. SP: Writing – review & editing. YPZ: Writing – review & editing. SZ: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. HX: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 82360299 and 81660265), the Key project of Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation (grant number 20232ACB206011), the Applied Research and Cultivation Program of Jiangxi Province (grant number 20212BAG70049), the Key Research and Development Program of Jiangxi Province (grant number 20202BBGL73065), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (grant numbers 20224BAB206026 and 20181BAB205015); the Science and Technology Plan of Jiangxi Provincial Health Commission (grant numbers 202130758 and 202210060); the Science and Technology Program of Health Commission of Jiangxi Province(grant number 202310061).
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge EnPapers editorial team for editing this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
- ^ For Original Research articles, please note that the Material and Methods section can be placed in any of the following ways: before Results, before Discussion or after Discussion.
References
1. Ashouri M, Nehzat Norozi Tehrani S, Govindasamy K, and Zouhal H. Effect of covid-19 on the lifestyles of vaccinated and unvaccinated elite athletes: A cross-country analysis. Health Nexus. (2023) 1:1–6. doi: 10.61838/kman.hn.1.2.1
2. Lei A, Xi C, Luo X, Pu Y, and You H. COVID-19 vaccine uptake and hesitation among men and women preparing for pregnancy: a cross-section survey based on the theory of planned behavior. BMC Public Health. (2023) 23:227. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-15171-3
3. Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. (2020) 395:497–506. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
4. Coronaviridae Study Group of the International Committee on Taxonomy of V. The species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat Microbiol. (2020) 5:536–44. doi: 10.1038/s41564-020-0695-z
5. Weiss SR and Navas-Martin S. Coronavirus pathogenesis and the emerging pathogen severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. (2005) 69:635–64. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.69.4.635-664.2005
6. Hu Y, Sun J, Dai Z, Deng H, Li X, Huang Q, et al. Prevalence and severity of corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Virol. (2020) 127:104371. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104371
7. Lukassen S, Chua RL, Trefzer T, Kahn NC, Schneider MA, Muley T, et al. SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 and TMPRSS2 are primarily expressed in bronchial transient secretory cells. EMBO J. (2020) 39:e105114. doi: 10.15252/embj.20105114
8. Reis FM, Bouissou DR, Pereira VM, Camargos AF, dos Reis AM, and Santos RA. Angiotensin-(1-7), its receptor Mas, and the angiotensin-converting enzyme type 2 are expressed in the human ovary. Fertil Steril. (2011) 95:176–81. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2010.06.060
9. la Pena Sol D, Isela SR, Zendy OV, Monica NM, Irene XR, and Omar AH. Changes in trophoblasts gene expression in response to perchlorate exposition. Toxicol In Vitro. (2018) 50:328–35. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2018.04.006
10. Li R, Yin T, Fang F, Li Q, Chen J, Wang Y, et al. Potential risks of SARS-CoV-2 infection on reproductive health. Reprod BioMed Online. (2020) 41:89–95. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2020.04.018
11. Jing Y, Run-Qian L, Hao-Ran W, Hao-Ran C, Ya-Bin L, Yang G, et al. Potential influence of COVID-19/ACE2 on the female reproductive system. Mol Hum Reprod. (2020) 26:367–73. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gaaa030
12. Hu Y, Tao R, Chen L, Xiong Y, Xue H, Hu L, et al. Exosomes derived from pioglitazone-pretreated MSCs accelerate diabetic wound healing through enhancing angiogenesis. J Nanobiotechnol. (2021) 19:150. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-00894-5
13. Bentov Y, Beharier O, Moav-Zafrir A, Kabessa M, Godin M, Greenfield CS, et al. Ovarian follicular function is not altered by SARS-CoV-2 infection or BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccination. Hum Reprod. (2021) 36:2506–13. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deab182
14. Mohr-Sasson A, Haas J, Abuhasira S, Sivan M, Doitch Amdurski H, Dadon T, et al. The effect of Covid-19 mRNA vaccine on serum anti-Mullerian hormone levels. Hum Reprod. (2022) 37:534–41. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deab282
15. Mohr-Sasson A, Haas J, Sivan M, Zehori Y, Hemi R, Orvieto R, et al. The effects of Covid-19 mRNA vaccine on adolescence gynecological well-being. Arch Gynecol Obstet. (2023) 307:1625–31. doi: 10.1007/s00404-023-06981-2
16. Ferraretti AP, La Marca A, Fauser BC, Tarlatzis B, Nargund G, Gianaroli L, et al. ESHRE consensus on the definition of ‘poor response’ to ovarian stimulation for in vitro fertilization: the Bologna criteria. Hum Reprod. (2011) 26:1616–24. doi: 10.1093/humrep/der092
17. Huang J, Guan T, Tian L, Xia L, Xu D, Wu X, et al. Impact of inactivated COVID-19 vaccination on female ovarian reserve: a propensity score-matched retrospective cohort study. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1198051. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1198051
18. Shrikhande L, Shrikhande B, and Shrikhande A. AMH and its clinical implications. J Obstet Gynaecol India. (2020) 70:337–41. doi: 10.1007/s13224-020-01362-0
19. Russell N, Gilmore A, and Roudebush WE. Clinical utilities of anti-mullerian hormone. J Clin Med. (2022) 11(23):7209. doi: 10.3390/jcm11237209
20. Tal R and Seifer DB. Ovarian reserve testing: a user’s guide. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2017) 217:129–40. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2017.02.027
21. Gat I, Kedem A, Dviri M, Umanski A, Levi M, Hourvitz A, et al. Covid-19 vaccination BNT162b2 temporarily impairs semen concentration and total motile count among semen donors. Andrology. (2022) 10:1016–22. doi: 10.1111/andr.13209
22. Carlsen E, Andersson AM, Petersen JH, and Skakkebaek NE. History of febrile illness and variation in semen quality. Hum Reprod. (2003) 18:2089–92. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deg412
23. Josso N. Anti-mullerian hormone: hormone or growth factor? Prog Growth Factor Res. (1990) 2:169–79. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(90)90003-3
24. Arai H, Minami Y, Chi S, Utsu Y, Masuda S, and Aotsuka N. Molecular-targeted therapy for tumor-agnostic mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Biomedicines. (2022) 10(12):3008. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10123008
25. Josso N and Picard JY. Genetics of anti-Mullerian hormone and its signaling pathway. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2022) 36:101634. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2022.101634
26. Ding T, Wang T, Zhang J, Cui P, Chen Z, Zhou S, et al. Analysis of ovarian injury associated with COVID-19 disease in reproductive-aged women in wuhan, China: an observational study. Front Med (Lausanne). (2021) 8:635255. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.635255
27. Gullo G, Lopez A, Loreto C, Cucinella G, La Verde M, Andrisani A, et al. COVID-19 and female fertility: an observational prospective multicenter cohort study: upholding reproductive rights in emergency circumstances. Diagnostics (Basel). (2024) 14(19):2118. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14192118
28. Yalcin AD and Yalcin AN. Future perspective: biologic agents in patients with severe COVID-19. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. (2021) 43:1–7. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2020.1818770
29. Fidecicchi T, Fruzzetti F, Lete Lasa LI, and Calaf J. COVID-19, gender and estroprogestins, what do we know? Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care. (2022) 27:67–74. doi: 10.1080/13625187.2021.2000959
30. Soysal C and Yilmaz E. The effect of COVID-19 vaccine on ovarian reserve. Saudi Med J. (2022) 43:486–90. doi: 10.15537/smj.2022.43.5.20220007
31. Edelman A, Boniface ER, Benhar E, Han L, Matteson KA, Favaro C, et al. Association between menstrual cycle length and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccination: A U.S. Cohort. Obstet Gynecol. (2022) 139:481–9. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000004695
32. Edelman A, Boniface ER, Male V, Cameron ST, Benhar E, Han L, et al. Association between menstrual cycle length and covid-19 vaccination: global, retrospective cohort study of prospectively collected data. BMJ Med. (2022) 1(1):e000297. doi: 10.1136/bmjmed-2022-000297
33. Wesselink AK, Hatch EE, Rothman KJ, Wang TR, Willis MD, Yland J, et al. A prospective cohort study of COVID-19 vaccination, SARS-coV-2 infection, and fertility. Am J Epidemiol. (2022) 191:1383–95. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwac011
34. Wu Y, Cao M, Lin Y, Xu Z, Liang Z, Huang Q, et al. Inactivated COVID-19 vaccination does not affect in vitro fertilization outcomes in women. Hum Reprod. (2022) 37:2054–62. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deac160
Keywords: COVID-19 vaccine, COVID-19 inactivated vaccine, anti-Müllerian hormone, ovarian reserve, reproductive health
Citation: Bao M, Xia L, Ling Y, Wen Q, Shen X, Wang T, Qian S, Wang L, Wang C, Peng S, Zhang Y, Zhong S, Xu H and Zhu Y (2025) Effect of COVID-19 inactivated vaccine on anti-Müllerian hormone in Chinese women: a retrospective cohort study. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1403722. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1403722
Received: 19 March 2024; Accepted: 01 May 2025;
Published: 04 June 2025.
Edited by:
Kamyar Asadipooya, University of Kentucky, United StatesReviewed by:
Khadijeh Irandoust, Imam Khomeini International University, IranWarda Abdullah, Hawler Medical University, Iraq
Copyright © 2025 Bao, Xia, Ling, Wen, Shen, Wang, Qian, Wang, Wang, Peng, Zhang, Zhong, Xu and Zhu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yuan Zhu, emh1eXVhbjA1MjhAYWxpeXVuLmNvbQ==; Hongying Xu, anh4dWhvbmd5aW5nQDE2My5jb20=; Shaoping Zhong, emhvbmdfaHVhODZAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Mingjie Bao
Mingjie Bao Leizhen Xia
Leizhen Xia Yan Ling1†
Yan Ling1† Quan Wen
Quan Wen Ting Wang
Ting Wang Changhua Wang
Changhua Wang Yuan Zhu
Yuan Zhu