- 1Medical Center of Maternity and Child Health, Shengli Clinical Medical College of Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou University Affiliated Provincial Hospital, Fuzhou, China
- 2Department of Urology, Fujian Medical University Union Hospital, Fuzhou, China
Background: Diet, lifestyle, and oxidative stress have been linked to female infertility, with the Oxidative Balance Score (OBS) serving as a comprehensive indicator of an individual’s oxidative and antioxidant status. This study aims to investigate the correlation between OBS and female infertility.
Methods: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) from 2013 to 2020 were utilized. Weighted multivariate regression analyses and restricted cubic splines (RCS) were employed to analysis. Additionally, subgroup analyses and multiple imputat6ions (MI) were carried out as sensitivity analyses to ensure the strength and reliability of the findings.
Results: A total of 3,905 individuals were involved in the study, the prevalence of female infertility was 11.96%. Individuals with infertility exhibited significantly lower OBS compared to those with normal fertility (19.74 ± 0.37 vs. 21.42 ± 0.20). The OBS dietary and lifestyle components also had lower scores, with averages of 15.98 ± 0.33 vs. 17.12 ± 0.18 and 3.76 ± 0.11 vs. 4.29 ± 0.05, respectively. Weighted logistic regression results revealed that a one-point increase in OBS score was associated with a 3% decrease in infertility risk (Odds Ratio (OR) 0.97, 95% Confidence Interval (CI): 0.95, 0.99). Similarly, a one-point increase in OBS lifestyle score was linked to a 15% decrease in infertility risk (OR: 0.85, 95% CI: 0.75, 0.96), and a one-point increase in OBS dietary score was associated with a 2% decrease in infertility risk (OR: 0.98, 95% CI: 0.96, 0.99). Subgroup analyses revealed that individuals with no prior history of pregnancy benefited more from OBS and OBS lifestyle in terms of infertility risk reduction compared to those with a history of pregnancy.
Conclusion: OBS is found to have a negative correlation with infertility, particularly in cases of primary infertility. The results of this study indicate that adopting an antioxidant-rich diet and lifestyle could potentially lower the risk of infertility.
Introduction
Infertility, defined as the inability to conceive after at least 12 months of consistent, unprotected sexual activity (1) affects approximately 15% of couples worldwide during their reproductive years. This rate is on a steadily increasing year by year. Previous studies (2, 3) on the global burden of infertility from 1990 to 2017 showed a 0.37% yearly rise in the age-standardized prevalence of infertility. Beyond its direct impact on reproductive health, female infertility has been identified as a potential risk factor for the development of cancers in the reproductive system and metabolic disorders (4, 5). This escalating prevalence, coupled with its broad-ranging implications, underscores the urgent need to address infertility as a critical global health issue.
The etiology of female infertility encompasses multiple factors, including ovulatory dysfunction, fallopian tube pathology, endometriosis, uterine abnormalities, and unexplained causes (6, 7). While medical conditions contribute significantly to infertility, modifiable lifestyle and environmental factors are increasingly recognized for their role. Many of these factors exert their effects through oxidative stress pathways, which may present opportunities for targeted intervention.
Oxidative stress, characterized by an imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and the body’s antioxidant defense mechanisms, is recognized as a crucial factor in the development of various chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and osteoarthritis (8–12). To assess this complex interplay, the Oxidative Balance Score (OBS) was developed (13, 14). The OBS is a comprehensive measure that integrates dietary and lifestyle factors to evaluate an individual’s oxidative and antioxidant status. Unlike individual biomarkers, the OBS provides a holistic assessment by incorporating both pro-oxidant and antioxidant dietary components, alongside lifestyle factors such as physical activity, body mass index (BMI), alcohol consumption, and smoking status. The OBS is calculated based on a weighted combination of these factors, with specific weights assigned to each component according to its relative contribution to oxidative stress. Over time, the OBS has been refined to enhance its predictive accuracy and applicability across diverse populations, emphasizing its growing importance as an epidemiological tool.
Additionally, the OBS offers valuable insights into the potential benefits of lifestyle modifications in reducing oxidative stress. Our study aims to fill this gap by providing a comprehensive evaluation of the relationship between OBS and female infertility.
Although previous studies (15–17) have examined isolated aspects of oxidative stress in relation to fertility, the association between comprehensive oxidative balance and female infertility remains largely unexplored. We hypothesize that a higher OBS, indicative of better oxidative balance, is associated with a lower risk of infertility, potentially with differential effects based on age and pregnancy history. This hypothesis is supported by the known age-related changes in oxidative stress and the varying etiologies of infertility across different age groups. This population-based study leverages NHANES data to investigate the relationship between OBS and female infertility, with a particular focus on examining variations across different subgroups of women. Our findings may have significant clinical implications, suggesting that targeted lifestyle interventions aimed at improving oxidative balance could be an effective strategy for reducing the risk of infertility.
Methods
Study population
This cross-sectional study leveraged data from the NHANES, conducted between 2013 and 2020. The NHANES, managed by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), is carried out every two years to assess the health and nutritional status of the non-institutionalized civilian population in the United States. Using a complex, multistage stratified sampling approach, NHANES collects data from a diverse group of participants through surveys, physical exams, and lab tests, offering a thorough and scientifically sound evaluation of public health. The initial screening encompassed 15,689 participants. After excluding females outside the age range of 20 to 45 years (n=10,380), those without reproductive health data (n=223), and participants lacking obstetric service information (n=1,181), the final study population comprised 3,905 women.
Measurement of OBS
The OBS is derived from a comprehensive assessment that integrates 16 dietary components and 4 lifestyle elements, encompassing 15 antioxidants and 5 pro-oxidants (13, 14). Supplementary Table 1 illustrates the detailed scoring system for OBS. Dietary antioxidants are scored from 0 to 2, with the highest tertile receiving a score of 0 and the lowest tertile a score of 2 for pro-oxidants. Lifestyle factors were assessed using a standardized scoring system: individuals received 0 points for engaging in less than 400 MET-minutes per week, 1 point for 400 to 1,000 MET-minutes, and 2 points for exceeding 1,000 MET-minutes weekly in terms of physical activity. For alcohol consumption, a score of 0 was assigned for intakes above 30 g/day, 1 point for 0 to 30 g/day, and 2 points for abstainers. Body Mass Index (BMI) was categorized as 0 points for obesity, 1 point for overweight, and 2 points for normal weight individuals. Serum cotinine levels were scored as 0 points for concentrations above 0.038 ng/mL, 1 point for levels between 0.038 to 1.13 ng/mL, and 2 points for values below 1.13 ng/mL. This systematic scoring system facilitated the evaluation of lifestyle-related health risks in the study population (18, 19).
Measurement of infertility
The primary outcome variable of this study was infertility. Infertility status was determined based on self-reported data from women who participated in the NHANES Reproductive Health Questionnaire (RHQ). Specifically, the response to item RHQ074, “Have you ever attempted to become pregnant over a period of at least a year without becoming pregnant?” was used to classify women. Those who answered “yes” to this question were categorized as having infertility (20).
Covariables
The collection of variables in this study includes demographic characteristics such as age, BMI, race, marital status, education level, poverty-income ratio (PIR), history of ever pregnancies. Comorbid conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, metabolic syndrome, as well as laboratory biochemical indicators like estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), HDL cholesterol, HbA1c, and albumin.
Diabetes mellitus was identified based on a combination of factors: a hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) concentration of 6.5% or greater, a fasting plasma glucose (FPG) level exceeding 126 mg/dL, documented use of hypoglycemic agents, or a self-reported medical history of diabetes. Hypertension was diagnosed when systolic and diastolic blood pressure measurements reached or surpassed 140/90 mmHg, patients were on antihypertensive therapy, or there was a self-reported history of hypertension. For the identification of metabolic syndrome in the adult population, the criteria established by the National Cholesterol Education Program’s Adult Treatment Panel III (NCEP-ATP III) (21, 22) were applied. These criteria provide a standardized approach for the clinical assessment and diagnosis of these conditions.
Statistical analysis
Data processing in our study adhered to NHANES analysis guidelines, ensuring that no variable had missing data exceeding 10%. All analyses incorporated appropriate sampling weights. Continuous variables were presented as weighted means accompanied by standard errors, while categorical variables were depicted as weighted percentages with their respective standard errors. Disparities in continuous baseline attributes were assessed using Student’s t-test, and for categorical variables, the chi-square test was applied. A weighted multiple logistic regression model was utilized to investigate the association between OBS and infertility, adjusting for various demographic and health-related variables such as age, race, marital status, educational attainment, PIR, DM, hypertension, MetS, eGFR, HDL cholesterol, HbA1c, and albumin. OBS was categorized into quartiles for trend analysis and subgroup analyses were conducted to explore relationships within different demographic and health characteristic strata. Interaction tests were performed to assess consistency across subgroups. Nonlinear relationships were examined using RCS and multiple imputation techniques were employed for reliability. Statistical analyses were carried out using R software (version 4.3.0) and Free Statistics software (version 1.9.2).
Results
Baseline characteristics
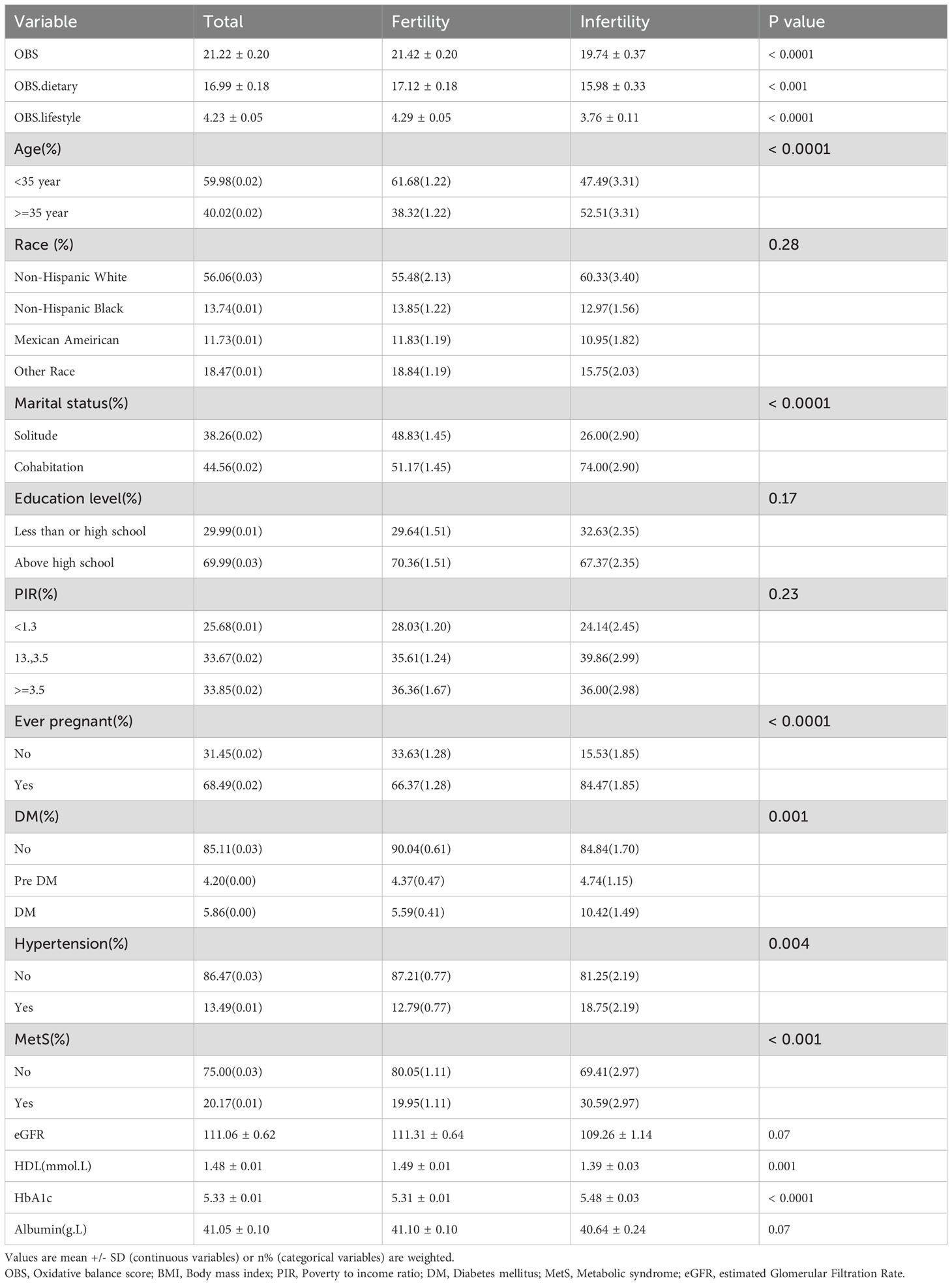
Figure 1 shows a flowchart of the data integration procedure. Table 1 presents the initial demographic and characteristics of the participants in the study, stratified by the presence of infertility. Participants with infertility had significantly lower scores in the OBS, OBS dietary, and OBS lifestyle categories compared to their fertile counterparts. Infertile participants showed distinct characteristics, such as older age and a higher prevalence of prior pregnancies. Furthermore, this group had a higher occurrence of comorbidities like diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and metabolic syndrome. On the other hand, individuals in the infertile group had lower levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol and albumin compared to fertile individuals. These results indicate an intricate relationship between fertility status and different health factors.
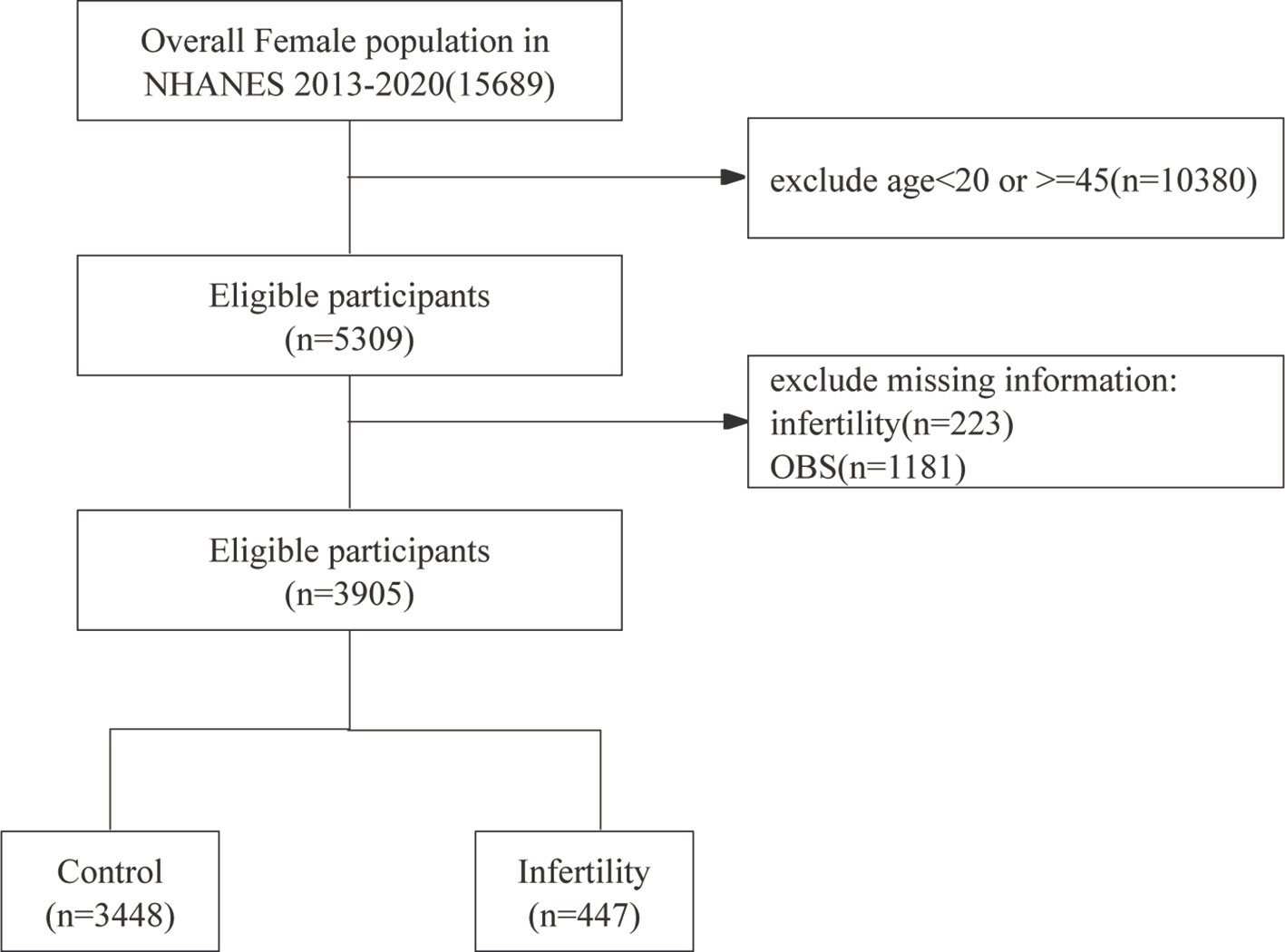
Figure 1. Flow chart of participants selection. NHANES, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
Association between oxidative balance score and infertility
Table 2 presents the results of a weighted regression analysis that examines the relationship between the OBS and the prevalence of infertility. The analysis revealed that for each one-unit increase in the OBS, there was a corresponding decrease in the likelihood of experiencing infertility, with an OR of 0.97 and a 95%CI of 0.95 to 0.98. These findings suggest a small but statistically significant protective impact of higher OBS against infertility. This association was consistent across different models, with the OR remaining stable. In the fully adjusted model, an increment of one point in OBS corresponded to a 3% decrease in the likelihood of infertility (OR: 0.97, 95% CI: 0.95, 0.99).
When OBS was modeled as a quadratic variable, the unadjusted model showed that, compared to the first quartile, the adjusted ORs for the second, third, and fourth quartiles were 0.7 (95% CI: 0.54-0.91), 0.7 (95% CI: 0.51-0.96), and 0.42 (95% CI: 0.30-0.59), respectively. After adjusting for relevant covariates, the analysis found no statistically significant disparities between the second (Q2) and third (Q3) quartiles compared to the first quartile (Q1). However, the fourth quartile (Q4) displayed a significant decrease (Model 3 adjusted OR: 0.47, 95% CI: 0.31-0.72), suggesting a linear trend for OBS in relation to infertility diagnosis (trend p < 0.05).
Additionally, we examined the distinct relationships between OBS dietary and OBS lifestyle components with infertility. The data in Table 2 indicate that both OBS dietary and OBS lifestyle components are significantly correlated with infertility in both unadjusted and adjusted models.
Subgroup analyses
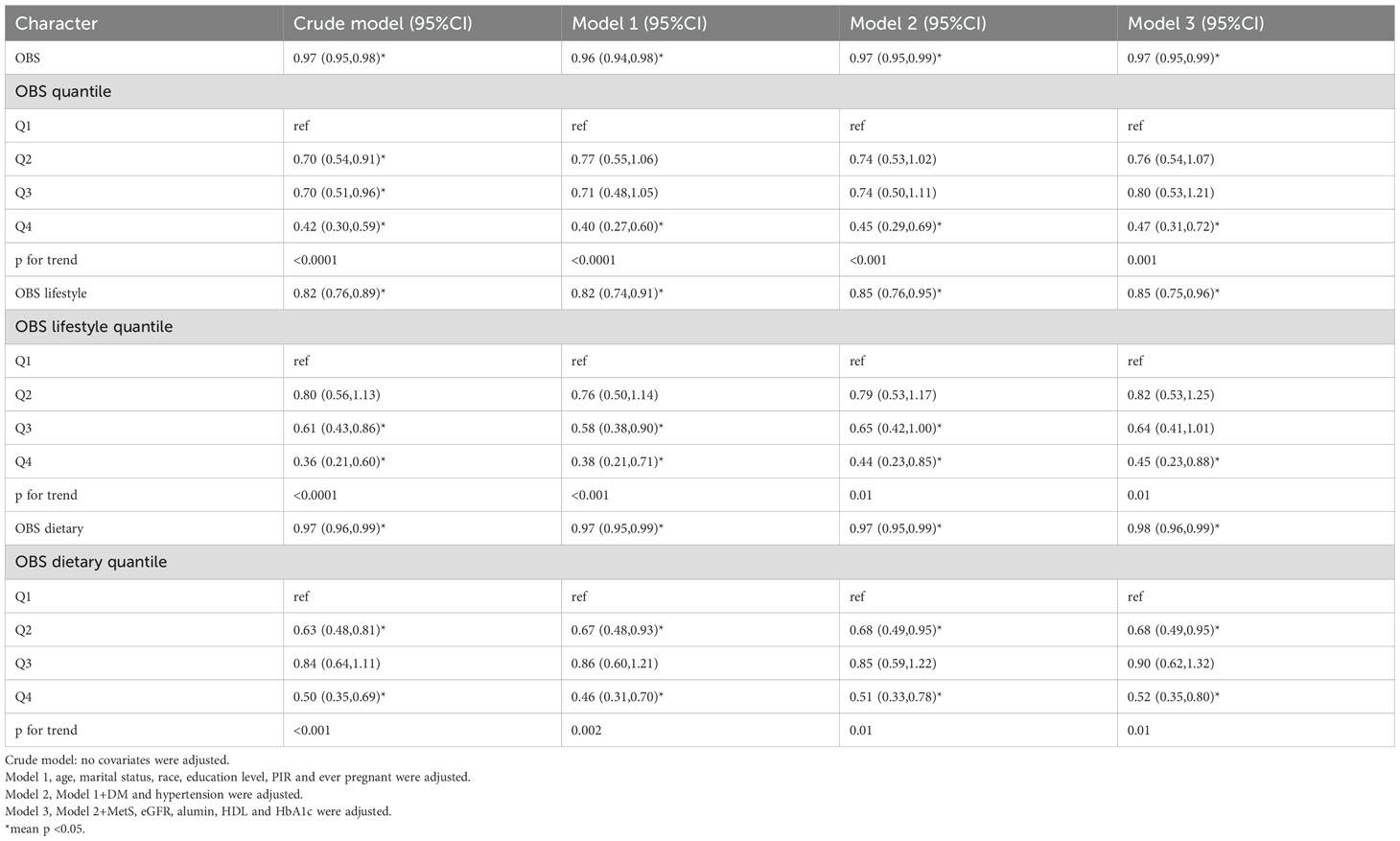
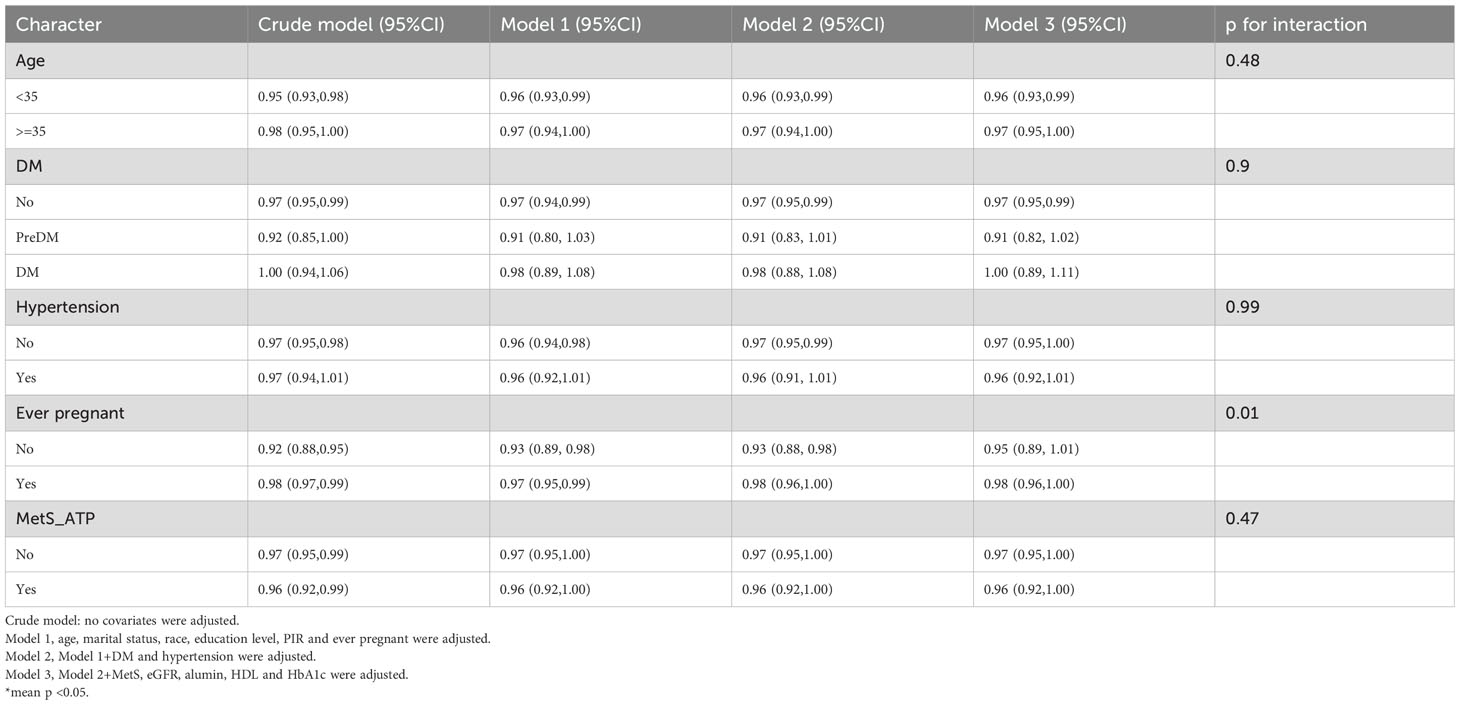
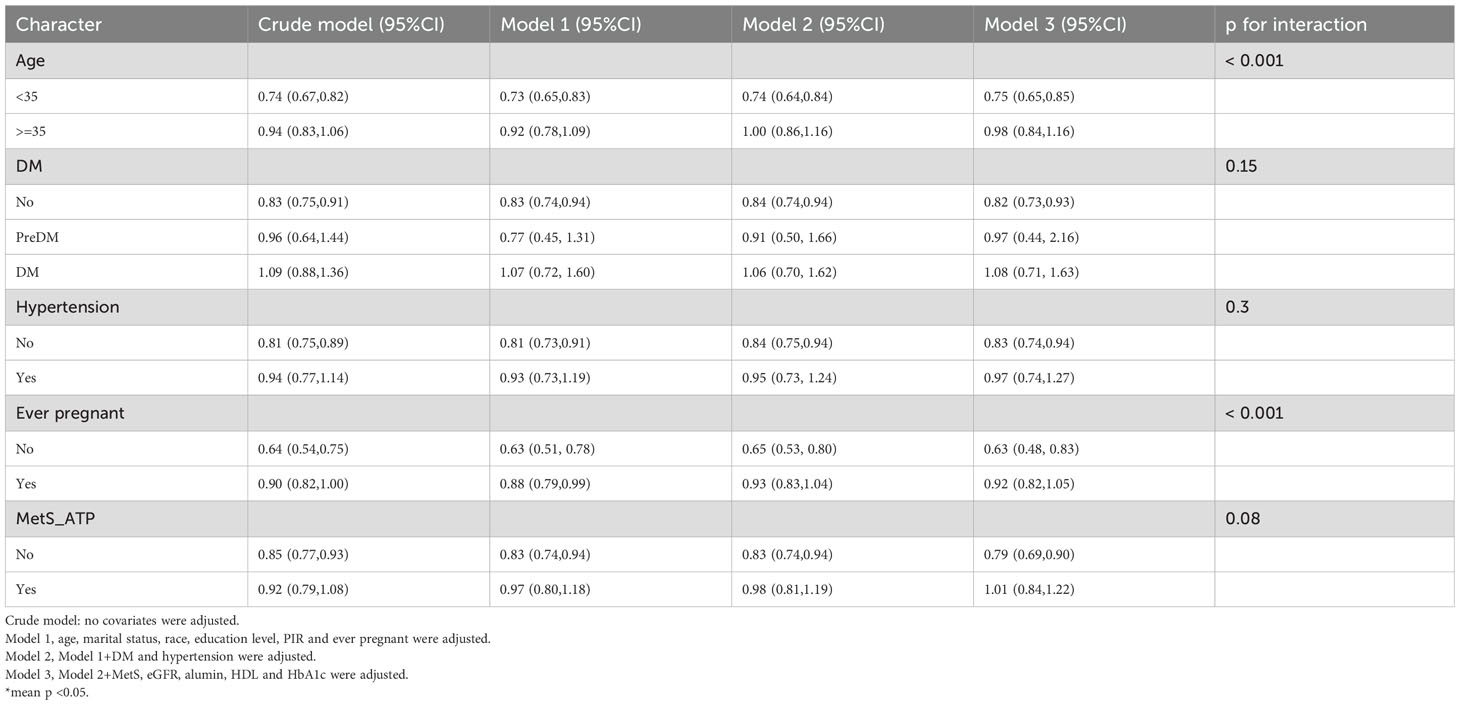
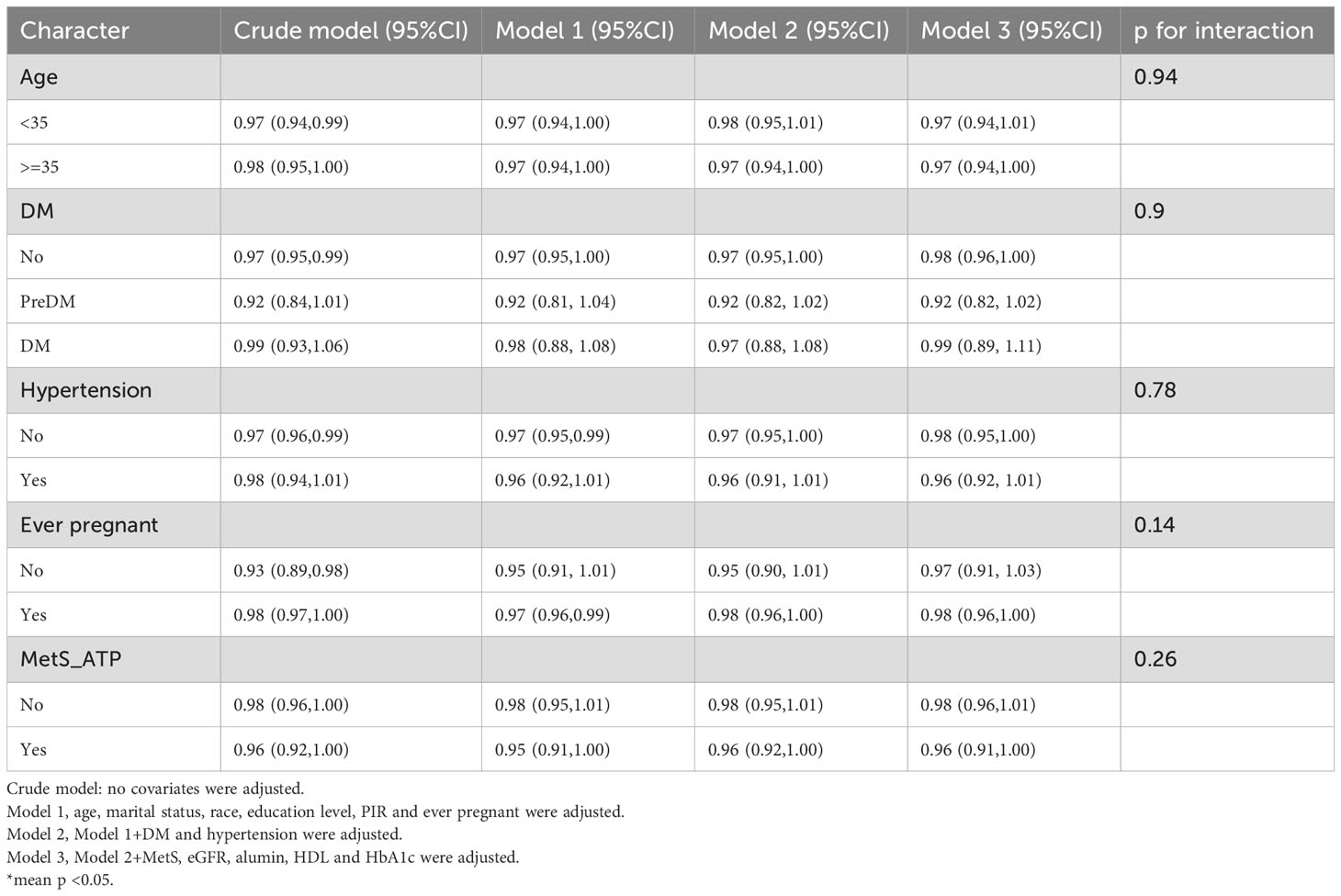
Subgroup and interaction analyses were performed, stratified by age, diabetes, hypertension, history of previous pregnancies, and metabolic syndrome, to evaluate the relationship between the OBS and infertility and to identify potential modifiers of this relationship. Table 3 indicates no statistically significant differences in the associations with age, diabetes, hypertension, or metabolic syndrome. However, a significant interaction was observed for the history of previous pregnancies (interaction p < 0.05).
Among individuals without a history of previous pregnancies, OBS showed a stronger negative correlation with infertility [OR 0.95, 95% CI (0.89, 1.01)] than among those with such a history [OR 0.98, 95% CI (0.96, 1)]. A significant interaction between age and history of previous pregnancies was noted in the OBS lifestyle component (interaction p < 0.05) (Table 4). For individuals under 35 years, OBS demonstrated a significantly stronger negative correlation with infertility [OR 0.75, 95% CI (0.65, 0.85)] compared to those aged 35 and above [OR 0.98, 95% CI (0.84, 1.16)]. Additionally, in individuals without a history of previous pregnancies, OBS lifestyle had a notably stronger negative correlation with infertility [OR 0.63, 95% CI (0.48, 0.83)] than among those with a history [OR 0.92, 95% CI (0.82, 1.05)]. In the case of OBS dietary (Table 5), no interaction was observed, yet individuals without a history of previous pregnancies showed a slightly stronger negative association with infertility [OR 0.97, 95% CI (0.91, 1.03)] compared to those with a history [OR 0.98, 95% CI (0.96, 1)].
Figure 2 illustrates that OBS was significantly higher in individuals without a history of previous pregnancies compared to the infertile population, a difference not observed in those with a history of previous pregnancies. Similar findings were noted for OBS dietary.
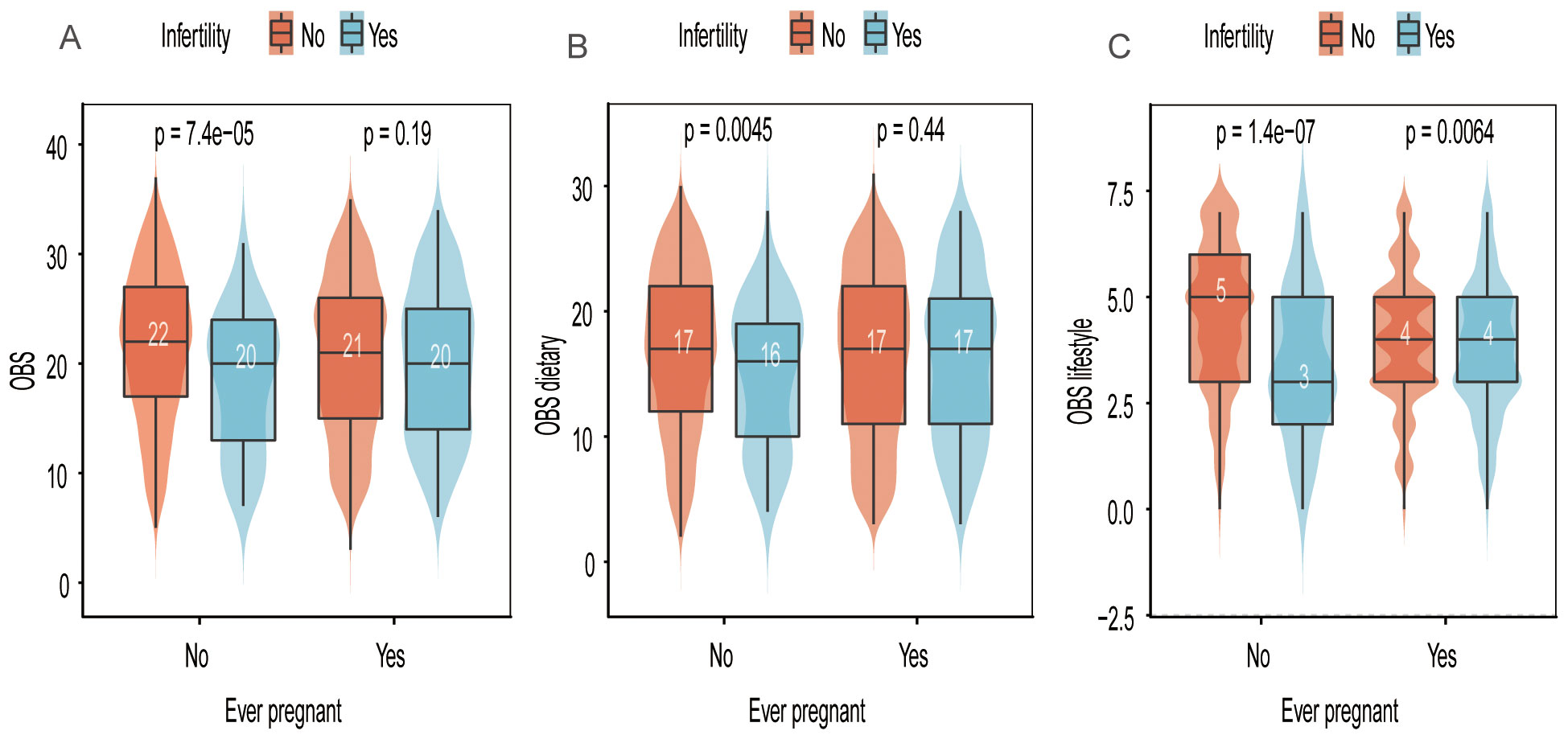
Figure 2. Distribution of OBS, OBS dietary, and OBS lifestyle scores in relation to “ever pregnant” and infertility status. (A) OBS scores stratified by infertility and pregnancy history. (B) OBS dietary scores stratified by infertility and pregnancy history. (C) OBS lifestyle scores stratified by infertility and pregnancy history.
Restricted cubic spline analysis
To investigate the potential non-linear association between the OBS and infertility, we performed RCS analysis. Employing a logistic regression model with smooth curve fitting, after controlling for additional factors, we found that the non-linear connection between OBS and infertility was not statistically significant. (Figure 3). Additionally, the non-linear associations between OBS dietary, OBS lifestyle components, and infertility were also found to be non-significant.
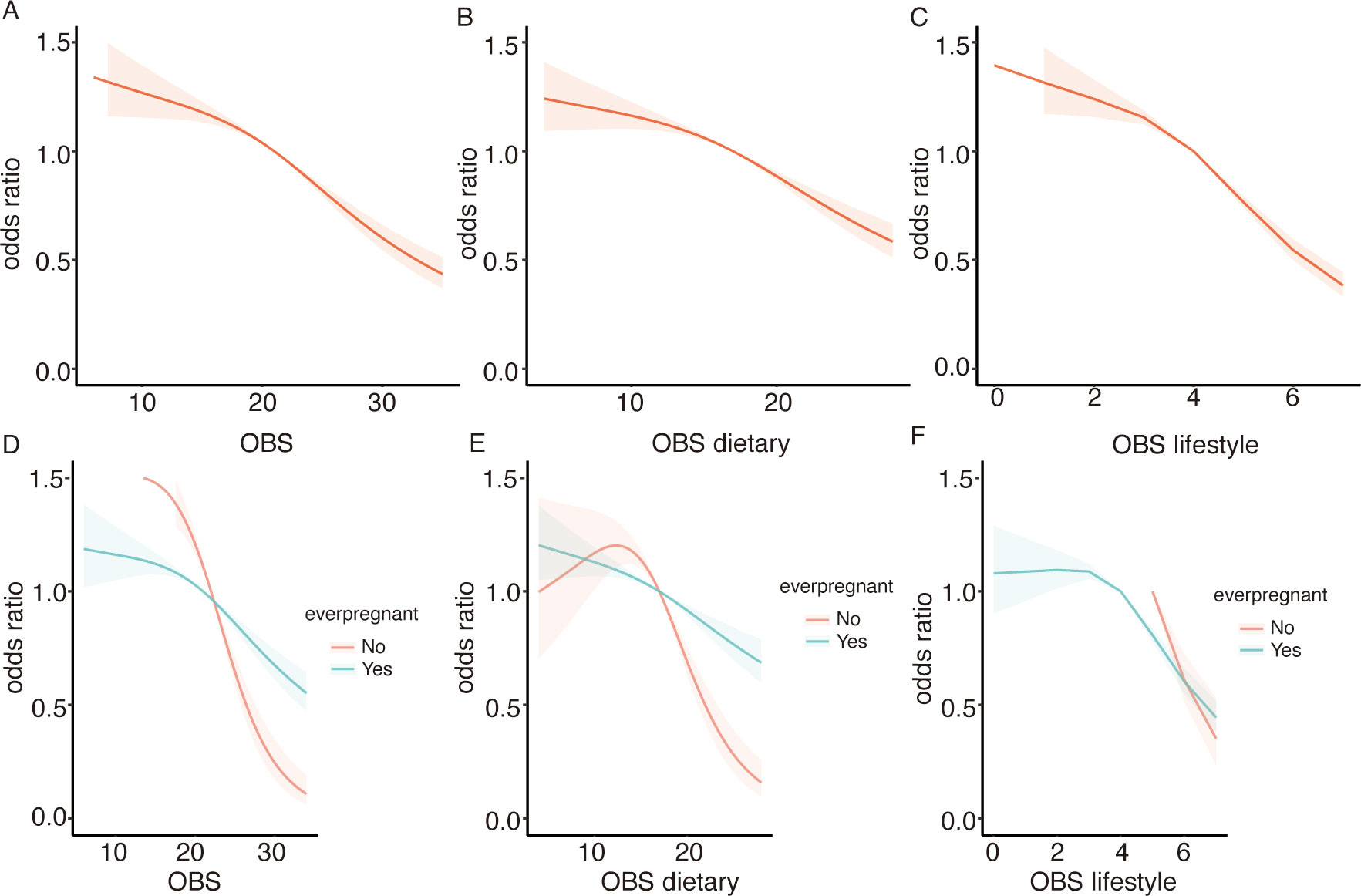
Figure 3. Displays the association between the OBS and infertility risk using RCS. (A) for the overall OBS, (B) for the dietary component, and (C) for the lifestyle component. Stratified analyses by ever pregnant status are presented in (D–F), with adjustments for confounding variables.
Sensitivity analysis
Supplementary Table 2 presents the findings from a re-analysis of the raw data without multiple imputing missing values, which corroborates the main study findings. Regardless of how OBS was considered - as either a continuous or categorical variable - a significant negative correlation with infertility was observed.
Discussion
Our analysis revealed a significant negative correlation between the OBS and female infertility. Specifically, we found that higher OBS levels were associated with a decreased incidence of infertility, with each one-point increase in OBS corresponding to a 3% reduction in infertility risk. This relationship remained consistent across multiple adjusted models, suggesting a robust association independent of demographic and clinical confounders.
The subgroup analyses yielded particularly insightful findings. The protective effect of OBS was significantly more pronounced among women under 35 years compared to their older counterparts. While the total OBS showed similar trends across age groups, the lifestyle component of OBS demonstrated a significant interaction with age, with younger women experiencing a substantially stronger protective effect (25% risk reduction per point) than women aged 35 and older. This age-dependent relationship reflects the differing etiologies of infertility across age groups. In younger women, conditions potentially more responsive to oxidative balance modulation—such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, and unexplained infertility—predominate. Oxidative stress in PCOS affects ovarian follicles, disrupting their development and maturation, which can impair fertility (23–25). Similarly, oxidative stress is implicated in endometriosis and unexplained infertility, leading to poor endometrial receptivity and negatively affecting pregnancy outcomes (26–28). Conversely, in women over 35, age-related decline in ovarian reserve becomes the primary driver of infertility, a process less amenable to improvement through oxidative balance enhancement.
Younger women benefit more from lifestyle interventions that enhance oxidative balance due to their greater biological plasticity and antioxidant capacity. Studies demonstrate that while older women can improve oxidative stress markers through resistance training, the improvements are more substantial in younger women due to their naturally higher baseline antioxidant capacity (29–31). The biological mechanisms underlying this age-dependent response involve multiple pathways. Younger women possess more robust antioxidant defense systems, greater mitochondrial efficiency, and enhanced cellular repair mechanisms (2, 32). Oxidative stress negatively affects reproductive processes by causing DNA damage and mitochondrial dysfunction, which are more pronounced in older women, while younger women are better equipped to manage oxidative stress due to more efficient cellular repair mechanisms (33–35). Antioxidants play a critical role in protecting oocytes from oxidative damage, and younger women benefit more from these protective mechanisms, which help maintain oocyte quality and fertility (36, 37).
Another key finding was the differential impact of OBS based on previous pregnancy history. The protective association between OBS and infertility was significantly stronger in women with primary infertility compared to those with secondary infertility. This suggests that women who have never achieved pregnancy represent a distinct population in which oxidative stress plays a more prominent pathophysiological role. Primary infertility may involve more significant underlying oxidative-mediated pathologies that could potentially be mitigated through antioxidant-rich diets and lifestyle modifications. Conversely, women with secondary infertility may have different etiologies less responsive to oxidative balance modulation.
Women with primary infertility exhibit significantly higher levels of oxidative stress compared to fertile women, with elevated levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), a marker of lipid peroxidation (28). This finding is consistent across various studies (38, 39), highlighting the role of oxidative stress in infertility. While data on secondary infertility are limited, the general impact of oxidative stress on reproductive health suggests it plays a role in both conditions, though potentially through different mechanisms or to varying degrees.
These findings align with our understanding of the mechanistic role of oxidative stress in female reproduction. Physiological levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) are essential for normal follicular development, ovulation, and fertilization (40–42). However, excessive ROS production can damage cellular components, impair mitochondrial function, and trigger apoptotic pathways in reproductive tissues. Low ROS levels in follicular fluid correlate with successful pregnancy outcomes in IVF treatments (43), suggesting a potential prognostic indicator for IVF efficacy. Our study extends these mechanistic insights by demonstrating that a comprehensive measure of oxidative balance correlates with fertility outcomes at the population level, particularly in specific subgroups of women.
The individual components of OBS provide further insights into potential intervention strategies. Dietary antioxidants, including vitamins C and E, protect reproductive cells against oxidative damage.
Amini et al (44) demonstrated that supplementation with vitamins C and E can reduce serum ROS levels compared to a control group, resulting in increased antioxidant concentrations in serum and follicular fluid. This leads to enhanced oocyte and IVF embryo quality, as well as improved pregnancy outcomes (45). Research (46) from the NHANES indicated a negative correlation between dietary fiber intake and female infertility. Li et al (47) found that Erastin, an inducer of ferroptosis, elevated ROS levels in mice under iron accumulation conditions, potentially triggering cell death mechanisms that could alleviate endometriosis and improve fertility. A Nigerian study (48) comparing serum metal levels in women with unexplained infertility to those with normal fertility revealed lower copper, zinc, and selenium levels in the infertile group. These micronutrients serve as essential cofactors for antioxidant enzymes, and their deficiency may compromise oxidative defense mechanisms in reproductive tissues.
Lifestyle factors within the OBS showed particularly strong associations with fertility outcomes. Smoking, for instance, induces oxidative stress in reproductive tissues, with women who smoke exhibiting lower success rates in assisted reproductive technologies (ART). Smoking increases ROS levels and reduces antioxidant defenses, affecting both sperm and oocyte quality (28, 49, 50). Meta-analyses show that smoking decreases live birth rates and clinical pregnancy rates per ART cycle, while increasing miscarriage rates. These effects are significant and highlight the detrimental impact of smoking on ART success (51–53).
Alcohol consumption similarly promotes oxidative stress through its metabolism, with even moderate intake potentially affecting fertility outcomes (28, 54). Obesity, another pro-oxidant factor in the OBS, is associated with both systemic inflammation and oxidative stress, contributing to ovulatory dysfunction and decreased endometrial receptivity (55–57). A cohort study by Jose Bellver et al (58) indicates that obesity may impair endometrial receptivity, contributing to infertility and negative outcomes in ART.
Our study has several methodological strengths. The use of a nationally representative NHANES population enhances generalizability, while the comprehensive adjustment for confounding variables increases confidence in the observed associations. Furthermore, our approach, which examines both total OBS and its components, provides greater insight into the relative contributions of dietary and lifestyle factors to fertility outcomes.
Nevertheless, this research has limitations that warrant consideration. The cross-sectional design precludes establishment of causality, and the reliance on self-reported infertility data may introduce recall bias. Additionally, while we adjusted for numerous potential confounders, residual confounding cannot be entirely ruled out. The NHANES database lacks comprehensive data on environmental exposures, such as air pollution, pesticides, and endocrine-disrupting chemicals, which may influence both oxidative stress and fertility.
In conclusion, our findings demonstrate that higher OBS is associated with lower infertility risk, with particularly strong effects observed in younger women and those with primary infertility. These results suggest that optimizing oxidative balance through dietary and lifestyle modifications may represent an effective strategy for reducing infertility risk in specific populations. Future longitudinal studies and clinical trials are needed to establish causality and determine whether targeted interventions to improve oxidative balance can enhance fertility outcomes in women attempting conception
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/search/default.aspx.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by National Center for Health Statistics Research Ethics Review Board. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
PX: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. XC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. RL: Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing. XS: Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. YY: Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing. LL: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Startup Fund for Scientific Research, Fujian Medical University [Grant numbers: 2020QH1184 and 2020QH1081], and the Joint Funds for the Innovation of Science and Technology, Fujian Province (Grant number: 2024Y9066).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2025.1444832/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Table 1 | Oxidative balance score assignment scheme.
Supplementary Table 2 | Sensitivity Analysis of the Association between OBS and Infertility after Multiple Imputation Crude model: no covariates were adjusted. Model 1, age, marital status, race, education level, PIR and ever pregnant were adjusted. Model 2, Model 1+DM and hypertension were adjusted. Model 3, Model 2+MetS, eGFR, alumin, HDL and HbA1c were adjusted. * mean p <0.05.
References
1. Hyun JY, Jung HS, and Park JY. Herbal therapeutics for female infertility: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Ethnopharmacol. (2024) 319:117258. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117258
2. Carson SA and Kallen AN. Diagnosis and management of infertility: A review. Jama. (2021) 326:65–76. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.4788
3. Zegers-Hochschild F, Adamson GD, Dyer S, Racowsky C, de Mouzon J, Sokol R, et al. The international glossary on infertility and fertility care, 2017. Hum Reprod. (2017) 32:1786–801. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dex234
4. Meirow D and Schenker JG. The link between female infertility and cancer: epidemiology and possible etiologies. Hum Reprod Update. (1996) 2:63–75. doi: 10.1093/humupd/2.1.63
5. Chodick G, Porath A, Alapi H, Sella T, Flash S, Wood F, et al. The direct medical cost of cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, diabetes, cancer, pregnancy and female infertility in a large HMO in Israel. Health Policy. (2010) 95:271–6. doi: 10.1016/j.healthpol.2009.12.007
6. Briceag I, Costache A, Purcarea VL, Cergan R, Dumitru M, Briceag I, et al. Fallopian tubes–literature review of anatomy and etiology in female infertility. J Med Life. (2015) 8:129–31.
7. Gu R, Wu T, Fu J, Sun YJ, and Sun XX. Advances in the genetic etiology of female infertility. J Assist Reprod Genet. (2024) 41:3261–86. doi: 10.1007/s10815-024-03248-w
8. Yang J, Luo J, Tian X, Zhao Y, Li Y, and Wu X. Progress in understanding oxidative stress, aging, and aging-related diseases. Antioxidants (Basel). (2024) 13(4):394. doi: 10.3390/antiox13040394
9. Moradnia M, Mohammadkhani N, Azizi B, Mohammadi M, Ebrahimpour S, Tabatabaei-Malazy O, et al. The power of Punica granatum: A natural remedy for oxidative stress and inflammation; a narrative review. J Ethnopharmacol. (2024) 330:118243. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118243
10. Cinato M, Andersson L, Miljanovic A, Laudette M, Kunduzova O, Borén J, et al. Role of perilipins in oxidative stress-implications for cardiovascular disease. Antioxidants (Basel). (2024) 13:209. doi: 10.3390/antiox13020209
11. Das AK, Kalra S, Punyani H, Deshmukh S, and Taur S. ‘Oxidative stress’-A new target in the management of diabetes mellitus. J Family Med Prim Care. (2023) 12:2552–7. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_2249_21
12. Kishi S, Nagasu H, Kidokoro K, and Kashihara N. Oxidative stress and the role of redox signaling in chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2024) 20:101–19. doi: 10.1038/s41581-023-00775-0
13. Hernández-Ruiz Á, García-Villanova B, Guerra-Hernández E, Amiano P, Ruiz-Canela M, and Molina-Montes E. A review of A priori defined oxidative balance scores relative to their components and impact on health outcomes. Nutrients. (2019) 11(4):774. doi: 10.3390/nu11040774
14. Ashoori M and Saedisomeolia A. Riboflavin (vitamin B2) and oxidative stress: a review. Br J Nutr. (2014) 111:1985–91. doi: 10.1017/S0007114514000178
15. Su Z, Ding P, Su W, Li X, Li Y, Li X, et al. Association between oxidative balance score and female infertility from the national health and nutrition examination survey 2013-2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2024) 15:1386021. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1386021
16. Lei X, Liu X, Yu C, Xia L, Zhou L, Yao C, et al. Higher oxidative balance score is associated with lower female infertility: a cross-sectional study. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1484756. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1484756
17. Ma M, Xu H, Wang K, Chen Y, Pan T, and Zhu Q. Higher oxidative balance score is associated with a decreased risk of infertility: an analysis of NHANES 2013-2020. Front Nutr. (2025) 12:1493253. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1493253
18. Cho AR, Kwon YJ, Lim HJ, Lee HS, Kim S, Shim JY, et al. Oxidative balance score and serum γ-glutamyl transferase level among Korean adults: a nationwide population-based study. Eur J Nutr. (2018) 57:1237–44. doi: 10.1007/s00394-017-1407-1
19. Zhang W, Peng SF, Chen L, Chen HM, Cheng XE, and Tang YH. Association between the oxidative balance score and telomere length from the national health and nutrition examination survey 1999-2002. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:1345071. doi: 10.1155/2022/1345071
20. Wu Y, Weng X, Liu S, Tan Y, Liang H, Li Y, et al. Associations of single and multiple organophosphate pesticide exposure with female infertility in the USA: data from the 2015–2018 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Environ Sci pollut Res Int. (2023) 30:23411–21. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-23624-2
21. Cleeman JI. Executive summary of the third report of the national cholesterol education program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (Adult treatment panel III). Jama. (2001) 285:2486–97. doi: 10.1001/jama.285.19.2486
22. Grundy SM, Brewer HB Jr., Cleeman JI, Smith SC Jr., and Lenfant C. Definition of metabolic syndrome: Report of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute/American Heart Association conference on scientific issues related to definition. Circulation. (2004) 109:433–8. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000111245.75752.C6
23. Zeber-Lubecka N, Ciebiera M, and Hennig EE. Polycystic ovary syndrome and oxidative stress-from bench to bedside. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24(18):14126. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814126
24. Gao Y, Zou Y, Wu G, and Zheng L. Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction of granulosa cells in polycystic ovarian syndrome. Front Med (Lausanne). (2023) 10:1193749. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1193749
25. Rudnicka E, Duszewska AM, Kucharski M, Tyczyński P, and Smolarczyk R. OXIDATIVE STRESS AND REPRODUCTIVE FUNCTION: Oxidative stress in polycystic ovary syndrome. Reproduction. (2022) 164:F145–f154. doi: 10.1530/REP-22-0152
26. Shan H, Luo R, Guo X, Li R, Ye Z, Peng T, et al. Abnormal endometrial receptivity and oxidative stress in polycystic ovary syndrome. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:904942. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.904942
27. Lu J, Wang Z, Cao J, Chen Y, and Dong Y. A novel and compact review on the role of oxidative stress in female reproduction. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. (2018) 16:80. doi: 10.1186/s12958-018-0391-5
28. Agarwal A, Aponte-Mellado A, Premkumar BJ, Shaman A, and Gupta S. The effects of oxidative stress on female reproduction: a review. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. (2012) 10:49. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-10-49
29. Ribeiro AS, Deminice R, Schoenfeld BJ, Tomeleri CM, Padilha CS, Venturini D, et al. Effect of resistance training systems on oxidative stress in older women. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. (2017) 27:439–47. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.2016-0322
30. Alikhani S and Sheikholeslami-Vatani D. Oxidative stress and anti-oxidant responses to regular resistance training in young and older adult women. Geriatr Gerontol Int. (2019) 19:419–22. doi: 10.1111/ggi.2019.19.issue-5
31. Tomeleri CM, Ribeiro AS, Cavaglieri CR, Deminice R, Schoenfeld BJ, Schiavoni D, et al. Correlations between resistance training-induced changes on phase angle and biochemical markers in older women. Scand J Med Sci Sports. (2018) 28:2173–82. doi: 10.1111/sms.2018.28.issue-10
32. Poljšak B and Milisav I. Decreasing intracellular entropy by increasing mitochondrial efficiency and reducing ROS formation-the effect on the ageing process and age-related damage. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25(12):6321.
33. Menezo YJ, Silvestris E, Dale B, and Elder K. Oxidative stress and alterations in DNA methylation: two sides of the same coin in reproduction. Reprod BioMed Online. (2016) 33:668–83. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2016.09.006
34. Aitken RJ. Impact of oxidative stress on male and female germ cells: implications for fertility. Reproduction. (2020) 159:R189–r201. doi: 10.1530/REP-19-0452
35. Kaltsas A, Zikopoulos A, Moustakli E, Zachariou A, Tsirka G, Tsiampali C, et al. The silent threat to women’s fertility: uncovering the devastating effects of oxidative stress. Antioxidants (Basel). (2023) 12(8):1490. doi: 10.3390/antiox12081490
36. Aitken RJ, Bromfield EG, and Gibb Z. OXIDATIVE STRESS AND REPRODUCTIVE FUNCTION: The impact of oxidative stress on reproduction: a focus on gametogenesis and fertilization. Reproduction. (2022) 164:F79–f94. doi: 10.1530/REP-22-0126
37. Wang L, Tang J, Wang L, Tan F, Song H, Zhou J, et al. Oxidative stress in oocyte aging and female reproduction. J Cell Physiol. (2021) 236:7966–83. doi: 10.1002/jcp.v236.12
38. Wojsiat J, Korczyński J, Borowiecka M, and Żbikowska HM. The role of oxidative stress in female infertility and in vitro fertilization. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). (2017) 71:359–66. doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0010.3820
39. Zaha I, Muresan M, Tulcan C, Huniadi A, Naghi P, Sandor M, et al. The role of oxidative stress in infertility. J Pers Med. (2023) 13(8):1264. doi: 10.3390/jpm13081264
40. Shkolnik K, Tadmor A, Ben-Dor S, Nevo N, Galiani D, and Dekel N. Reactive oxygen species are indispensable in ovulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2011) 108:1462–7.
41. Li W, Young JF, and Sun J. NADPH oxidase-generated reactive oxygen species in mature follicles are essential for Drosophila ovulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2018) 115:7765–70.
42. Sugino N. Reactive oxygen species in ovarian physiology. Reprod Med Biol. (2005) 4:31–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1447-0578.2005.00086.x
43. Attaran M, Pasqualotto E, Falcone T, Goldberg JM, Miller KF, Agarwal A, et al. The effect of follicular fluid reactive oxygen species on the outcome of in vitro fertilization. Int J Fertil Womens Med. (2000) 45:314–20.
44. Amini L, Chekini R, Nateghi MR, Haghani H, Jamialahmadi T, Sathyapalan T, et al. The effect of combined vitamin C and vitamin E supplementation on oxidative stress markers in women with endometriosis: A randomized, triple-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Pain Res Manag. (2021) 2021:5529741. doi: 10.1155/2021/5529741
45. Lu X, Wu Z, Wang M, and Cheng W. Effects of vitamin C on the outcome of in vitro fertilization-embryo transfer in endometriosis: A randomized controlled study. J Int Med Res. (2018) 46:4624–33. doi: 10.1177/0300060518786918
46. Cai Q and Chen T. Association between dietary fiber and female fertility: a NHANES-based study. Reprod Sci. (2023) 30:1555–64. doi: 10.1007/s43032-022-01103-w
47. Li Y, Zeng X, Lu D, Yin M, Shan M, and Gao Y. Erastin induces ferroptosis via ferroportin-mediated iron accumulation in endometriosis. Hum Reprod. (2021) 36:951–64. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deaa363
48. Adeniyi AA, Ogunbode OO, Adeyanju AS, and Oladokun A. Serum copper, zinc and selenium levels in women with unexplained infertility in Ibadan Nigeria: A cross-sectional analytical study. Niger Postgrad Med J. (2023) 30:269–74. doi: 10.4103/npmj.npmj_144_23
49. Arshad MA, Zil EAA, Iqbal MT, and Majzoub A. The two-tales of smoking: aberrations in sperm parameters and failure in assisted reproduction. Arab J Urol. (2022) 20:195–6. doi: 10.1080/2090598X.2022.2090135
50. Konstantinidou F, Budani MC, Sarra A, Stuppia L, Tiboni GM, and Gatta V. Impact of cigarette smoking on the expression of oxidative stress-related genes in cumulus cells retrieved from healthy women undergoing IVF. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22(23):13147. doi: 10.3390/ijms222313147
51. Budani MC, Fensore S, Di Marzio M, and Tiboni GM. Cigarette smoking impairs clinical outcomes of assisted reproductive technologies: A meta-analysis of the literature. Reprod Toxicol. (2018) 80:49–59. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2018.06.001
52. Zhang RP, Zhao WZ, Chai BB, Wang QY, Yu CH, Wang HY, et al. The effects of maternal cigarette smoking on pregnancy outcomes using assisted reproduction technologies: An updated meta-analysis. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. (2018) 47:461–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jogoh.2018.08.004
53. Waylen AL, Metwally M, Jones GL, Wilkinson AJ, and Ledger WL. Effects of cigarette smoking upon clinical outcomes of assisted reproduction: a meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update. (2009) 15:31–44. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmn046
54. Ruder EH, Hartman TJ, and Goldman MB. Impact of oxidative stress on female fertility. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. (2009) 21:219–22. doi: 10.1097/GCO.0b013e32832924ba
55. Snider AP and Wood JR. Obesity induces ovarian inflammation and reduces oocyte quality. Reproduction. (2019) 158:R79–r90. doi: 10.1530/REP-18-0583
56. Robker RL, Wu LL, and Yang X. Inflammatory pathways linking obesity and ovarian dysfunction. J Reprod Immunol. (2011) 88:142–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2011.01.008
57. Sciorio R, Bellaminutti S, Tramontano L, and Esteves SC. Impact of obesity on medically assisted reproductive treatments. Zygote. (2022) 30:431–9. doi: 10.1017/S0967199421001003
Keywords: oxidative balance score, infertility, antioxidant, lifestyle, NHANES
Citation: Xia P, Chen X, Lin R, Shi X, Yang Y and Lin L (2025) The role of oxidative balance lifestyle factors in reducing female infertility risk: insights from a population-based study. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1444832. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1444832
Received: 06 June 2024; Accepted: 29 May 2025;
Published: 19 June 2025.
Edited by:
Richard Ivell, University of Nottingham, United KingdomReviewed by:
Taylan Onat, İnönü University, TürkiyeUfaque Batool K. Samo, Jinnah Post Graduate Medical Center, Pakistan
Copyright © 2025 Xia, Chen, Lin, Shi, Yang and Lin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Liang Lin, a2l0dHkzNDJAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Ping Xia
Ping Xia Xiaobao Chen
Xiaobao Chen Rong Lin1
Rong Lin1 Liang Lin
Liang Lin