Abstract
Background:
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a major cause of mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Statins are essential for the primary prevention of CVD in this high-risk group. Despite guideline recommendations, statin use remains suboptimal in clinical practice. Assessing statin utilization and identifying factors influencing their prescription are vital for enhancing evidence-based care, especially in resource-limited settings. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate statin use and its predictors for primary CVD prevention among diabetic patients at Arsi Teaching and Referral Hospital in 2023.
Methods:
A hospital-based cross-sectional study was carried out among 351 diabetic patients at Arsi Teaching and Referral Hospital (ARTH) between February and September 2022. Participants were selected using a systematic random sampling method. Data were collected through a pretested, interviewer-administered structured questionnaire and a checklist. Trained nurses from the diabetic clinic conducted data collection. The collected data were initially entered into Epi Data version 7.2, then exported to SPSS version 26 (IBM, USA) for analysis. The association between statin use and potential predictors was examined using odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Variables with a p-value below 0.05 in the multivariable logistic regression were considered statistically significant.
Results:
The prevalence of statin utilization for the primary prevention of CVD among type 2 diabetic patients on follow-up at Asella Teaching Hospital was 189 [(53.8%, 95% CI: 48.6%, 59.0%)]. The most commonly prescribed statin was atorvastatin, followed by simvastatin. The probability of statin use was greater in participants with hypertension [AOR=4.8, 95% CI (2.0-11.5)], dyslipidemia [AOR=10.5, 95% CI (2.0-11.5)], and uncontrolled glycemic control [AOR=8.0,95% CI (3.8-17.7)].
Conclusions:
Suboptimal statin utilization (53.8%) for primary CVD prevention in type 2 diabetes was observed, with utilization heavily influenced by comorbidities. Urgent quality improvement initiatives are needed to ensure statin access aligns with guideline recommendations for patients with hypertension, dyslipidemia, and poor glycemic control in the study area.
Introduction
Background
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a chronic and progressive metabolic disorder resulting from inadequate insulin secretion or the body’s ineffective use of insulin (1, 2). According to a report published by the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) in 2021, the global prevalence of diabetes among individuals aged 20 to 79 years is estimated to be approximately 537 million. However, this number is expected to rise significantly, reaching approximately 643 million by 2030 and a staggering 783 million by 2045 (3). Diabetes mellitus significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular disease (2, 4).
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the leading cause of morbidity and mortality among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) (5). This increased risk is largely due to higher concentrations of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles in diabetic patients. These LDL particles tend to be smaller, denser, and more susceptible to oxidation, which enhances the risk of cardiovascular events (6, 7). Therefore, managing cardiovascular risk factors like dyslipidemia is vital to lowering the risk of heart-related complications in people with diabetes. As a result, several clinical practice guidelines have outlined strategies to prevent these complications. One of the key recommendations is the use of lipid-lowering therapies (LLTs), particularly statins, which play a significant role in reducing cardiovascular disease (CVD) among diabetic patients (5, 8, 9).
Statins are lipid-lowering agents that competitively inhibit HMG-CoA reductase, the rate-limiting enzyme in hepatic cholesterol biosynthesis. This inhibition directly reduces cholesterol synthesis (9). Statins are divided into three intensity levels based on their LDL cholesterol-lowering capacity: high-intensity statins reduce LDL levels by over 50%, moderate-intensity statins lower them by 30% to 50%, and low-intensity statins decrease LDL by less than 30% (10, 11).
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends moderate-intensity statin therapy for all individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D) aged 40 to 75 years as a measure for primary prevention (12). Similarly, the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) advise that patients within this age range who have T2D and an LDL-C level of ≥70 mg/dL should start moderate-intensity statins, without the need to assess their 10-year ASCVD risk (13). These recommendations highlight the crucial role of statins in preventing cardiovascular events in people with T2D. Numerous studies have also supported the effectiveness of statins in lowering cardiovascular events and mortality in diabetes. A population-based study in Korea found that statin use in diabetic patients reduced the risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, and mortality by 28% (14). Despite this, statin use remains low: only 37.7% of diabetic patients in the USA (15) and 33.8% in Hong Kong (16) received prescriptions. In sub-Saharan Africa, data are limited, but studies in Ethiopia show low prescription rates of 36.7% in Jimma (17), and 40% in Bonga (18). Statin utilization for primary CVD prevention is influenced by multifaceted determinants: patient demographics (age, sex, education, diabetes duration), clinical comorbidities (hypertension, dyslipidemia, uncontrolled glycemia), and systemic factors (medication access, provider prescribing patterns, and guideline adherence) (17–20).
As the global prevalence of diabetes continues to rise (21), Different international guidelines strongly recommend the use of statins for the primary prevention of cardiovascular events in individuals with type 2 diabetes. However, their actual implementation in clinical practice remains suboptimal in many healthcare systems. This gap is particularly concerning in low- and middle-income countries, where the diabetes burden is rapidly increasing. In Ethiopia—specifically in our study area—there is limited and inconsistent data regarding statin utilization and its predictors. Therefore, this study aims to assess the extent of statin utilization and identify its key predictors among diabetic patients attending Arsi Teaching and Referral Hospital, a major facility serving a large diabetic population. Assessing statin utilization patterns and their determinants at Arsi Hospital provides critical insights for developing targeted strategies to improve cardiovascular risk prevention among individuals with diabetes. This localized evidence will support healthcare professionals and policymakers in making evidence-based decisions that optimize patient care, strengthen adherence to clinical guidelines, and reduce the cardiovascular burden associated with diabetes. Furthermore, improving statin use can help reduce long-term healthcare costs by preventing expensive hospitalizations and complications. The findings will also serve as a valuable benchmark for future researchers interested in this area of study.
Materials and methods
Study design and setting
A hospital-based cross-sectional study was conducted at Arsi Referral and Teaching Hospital, Arsi University, from January 1, 2022, to August 30, 2022. The hospital is located in the Arsi Zone of Oromia, approximately 175 km from the Ethiopian capital, Addis Ababa. At the outpatient level, the diabetic clinic provides treatment and checks by trained nurses, medical interns, residents, and specialists (22).
Population
The study population included all adult type two diabetes mellitus patients who underwent diabetic follow-up at Arsi Teaching and Referral Hospital, while adult type two diabetes mellitus patients who underwent diabetic follow-up at Arsi Teaching and Referral Hospital during the study period were considered the study population.
Sample size and sampling technique
The sample size was calculated based on the single population proportion formula using a 36.67% incidence of statin utilization among diabetic patients from a study conducted in Jimma (17), a 5% margin of error, a 95% confidence level, and a 10% non-response rate.
With adjustment for 5% nonresponse (n=358 + 18), the final sample size was 376
where n is the sample size
z = value of the standard normal distribution corresponding to 95% CI
p = expected proportion in the population
q = 1 - p = 1 - 0.37 = 0.63
d = desired degree of precision 0.05
Finally, a systematic random sampling technique was employed to recruit the required sample size. The value of K was calculated by dividing the estimated total number of diabetic patients who visited the hospital’s diabetic follow-up clinic during the study period (approximately 4800 patients for eight months) by the total number of required samples (376). Then, samples were selected every thirteen (13) intervals based on their order of clinic visits, while the first study subject was chosen by the lottery method (which was the second case).
Eligibility criteria
All adult type two diabetes mellitus patients who underwent diabetic follow-up at Arsi Teaching and Referral Hospital were included, while diabetic patients who were less than 40 years old, patients taking statins for secondary/tertiary prevention of CVD, and pregnant patients were excluded from the study.
Study variables: The dependent variable was statin utilization, while sociodemographic factors, lifestyle parameters, comorbidities, clinical profiles, anthropometric measurements, and diabetes-related complications were the independent variables.
Operational definition
Statin utilization was assessed by reviewing documented prescriptions issued throughout the patients’ clinical follow-up period. High-intensity statin therapy was classified as atorvastatin at doses of 40–80 mg or rosuvastatin at 20–40 mg, while moderate-intensity therapy included atorvastatin 10–20 mg or rosuvastatin 5–10 mg (23).
Uncontrolled blood glucose level: Fasting blood sugar level greater than 130 mg/dL (17).
Dyslipidemia: It was defined by any of the following lipid abnormalities: total cholesterol levels of ≥200 mg/dL, LDL-C ≥ 100 mg/dL, triglycerides ≥150 mg/dL, HDL-C ≤ 40 mg/dL in males, or HDL-C ≤ 50 mg/dL in females (24, 25).
Data collection procedures
A structured interviewer-administered questionnaire was developed by reviewing different literature in English, translated into Afan Oromo (the local language), and then retranslated back into English to check its consistency. Finally, the data were collected using the Afan Oromo version of the questionnaire by three trained nurse professionals who work at the diabetic clinic of the hospital. A review of medical records was performed to collect clinical data using a prepared checklist.
Anthropometric measurements
Physical measurements: Height and weight were measured using an inelastic measuring tape and weight scale, respectively. Repeated blood pressure measurements were performed at the hospital by trained nurse professionals using standardized operating procedures after the participants rested for approximately five minutes. The height (to the nearest 0.1 cm), weight (to the nearest 0.1 kg), hip and waist circumferences (to the nearest 0.1 cm), and BP (to the nearest 0.5 mmHg) of the patients were measured.
Data quality assurance
To ensure the quality of the collected data, the questionnaire was translated from English to Afan Oromo (a local language) and then retranslated back to English to maintain consistency. The questionnaire was also pretested with 5% of the diabetic patients at Adama Teaching Hospital. Furthermore, one day training was given to the data collectors and supervisors. Furthermore, the primary investigator visited the data collectors once a day to ensure that the data were collected correctly.
Data management and statistical analysis
The collected data were checked for completeness, coded, entered into Epi Data 7.2 software, cleaned, and exported to SPSS version 26 (IBM, USA) for statistical analysis. The Kolmogorov–Smirnov test and box plots were used to examine the data distribution and detect outliers. The results of the descriptive analyses are presented as frequencies or means ± SDs, depending on the nature of the data. Finally, the results are presented in the form of tables, figures, and narratives. The Hosmer–Lemeshow test and the multicollinearity test were used to measure model fitness. A chi-square test was used to analyze the associations between categorical variables. The strength of the association between different independent factors and statin utilization was assessed using odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) from logistic regression. Variables with p-values< 0.25 were considered candidate variables for multivariable logistic regression. Finally, variables with a P value less than 0.05 in multivariate logistic regression were considered to be significantly different.
Ethical considerations
This study was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Arsi University on behalf of the College of Health Science Research Ethical Committee. A signed permission letter was obtained from the hospital medical director. Finally, participants were informed about the study’s aims, objectives, and potential outcomes. Written informed consent was obtained before the data collection started. All the information obtained in the study was kept confidential, and no records identifying patients were recorded. There was no payment for participating in the study.
Results
Sociodemographic, clinical, and lifestyle characteristics
This study included 351 randomly selected study participants, for a response rate of 93.4%, of whom more than half (213, 60.7%) were men. The majority of the study participants (207, 59%) were aged 40–60 years, while 323 (92%) of the participants were married. In terms of respondents’ residency, 212 (60.4%) of the participants lived in urban areas. The occupations of the study participants were also reported. Approximately one-quarter (104, 29.6%) of the participants were farmers, while 78 (22.2%) were housewives. Furthermore, 327 (93.2%) of the study participants had government insurance (Table 1).
Table 1
| Variables | Category | Frequency (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 40-60 | 207 (59.0) |
| 61-75 | 144 (41.0 | |
| Sex | Females | 138 (39.3) |
| Males | 213 (60.7) | |
| Residence | Rural | 139 (39.6) |
| Urban | 212 (60.4) | |
| Marital Status | Married | 323(92.0) |
| Single | 3 (0.9) | |
| Divorced | 16 (4.6) | |
| Widowed | 9 (2.6) | |
| Education level | Never attended school | 121 (34.5) |
| Primary School | 107 (30.5) | |
| Secondary School | 49 (14.0) | |
| College/University | 74 (21.1) | |
| Occupation | Farmers | 104 (29.6) |
| Housewives | 78 (22.2) | |
| Private jobs | 97(27.6) | |
| Retired | 33 (9.4) | |
| Government employee | 39 (11.1) | |
| Government insurance | Yes | 327 (93.2) |
| No | 24 (6.8) |
Socio-demographic characteristics of type 2 DM patients on follow-up at ARTH in Asella, Oromia, Ethiopia, 2022 (n=351).
Clinical characteristics of the study participants
The clinical characteristics of the study participants were also reported. More than half of the 204 (58.1%) participants had more than five years of diabetes history. The most prevalently reported comorbidity was dyslipidemia, which was present in 193 (63.5%) participants, followed by hypertension in 190 (54.1%) participants and chronic kidney disease (CKD) in 38 (11.8%) participants. Similarly, more than half of the study participants, 219 (62.4%) and 205 (58.4%), had blood pressure below 140/90 mmHg and a normal BMI (18.5–25 kg/m²), respectively. Moreover, nearly two-thirds of the 250 participants (71.2%) had a normal waist-to-hip ratio (WHR). Screening for diabetic complications was also reported. Nearly two-thirds of the patients (233, 66.4%) were screened for diabetic retinopathy, and 52 (22.3%) had complications. However, diabetic nephropathy was detected in only 2 (0.6%) patients. Peripheral neuropathy was also found in 66 (18.8%) of the study participants (Table 2).
Table 2
| Variables | Category | Frequency | Percent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetes duration | <5 years | 147 | 41.9 |
| ≥5 years | 204 | 58.1 | |
| Blood Pressure (mmHg) | <140/<90 | 219 | 62.4 |
| ≥140/90 | 132 | 37.6 | |
| WHR | >0.9 (M) or >0.85(F) | 101 | 28.8 |
| ≤0.9 (M) or ≤0.85 (F) | 250 | 71.2 | |
| BMI (kg/m²) | <18.5 | 9 | 2.6 |
| 18.5-25 | 205 | 58.4 | |
| 25-30 | 87 | 24.8 | |
| >30 | 50 | 14.2 | |
| Hypertension | Yes | 190 | 54.1 |
| No | 161 | 45.9 | |
| Dyslipidemia | Yes | 193 | 63.5 |
| No | 111 | 36.5 | |
| CKD | Yes | 38 | 11 |
| No | 307 | 89.0 | |
| Diabetic retinopathy | Yes | 52 | 22.3 |
| No | 181 | 77.7 | |
| Peripheral neuropathy | Yes | 66 | 18.8 |
| No | 285 | 81.2 | |
| Diabetic nephropathy | Yes | 2 | 0.6 |
| Never screened | 349 | 99.4 |
Clinical characteristics of selected type 2 DM patients on follow-up at ARTH Asella, Ethiopia, 2022 (n=351).
WHR, Weight-to-hip ratio; BMI, Body mass index; CKD, Chronic kidney disease.
Behavioral characteristics of the study participants
The behavioral characteristics of the study participants were also reported; 19 (5.4%) and 42 (31.7%) had past histories of smoking and alcohol consumption, respectively. The majority of participants (212, 60.4%) had never performed physical exercise (Table 3).
Table 3
| Variables | Category | Frequency | Percent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drinking alcohol | Never | 307 | 87.5 |
| Sometimes | 42 | 12.0 | |
| Regularly | 2 | 0.6 | |
| Cigarette smoking | Never | 330 | 94.0 |
| Current smoker | 2 | 0.6 | |
| Former smoker | 19 | 5.4 | |
| Physical exercise | Regularly | 26 | 7.4 |
| Sometimes | 113 | 32.2 | |
| Never | 212 | 60.4 |
Behavioral characteristics of selected type 2 DM patients at follow-up at ARTH Asella, Ethiopia, 2022 (n=351).
Clinical parameters of the study participants
Regarding the clinical parameters, the lipid profile was determined in 304 (86.6%) of the participants, where the most common lipid abnormality was a low level of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) in 134 (44.1%), followed by high triglycerides in 121 (39%) and high LDL in 104 (34.2%). In addition, high total cholesterol was reported in one-third of the 111 (36.5%) patients. Based on fasting blood glucose levels, the majority, 199 (56.7%), of the patients had an uncontrolled glucose level (≥130 mg/dl), while one-third, 114 (32.5%), of the patients had a HgA1C concentration >8%, 70 (19.9%) of whom had an uncontrolled glucose level (Table 4).
Table 4
| Variables | Category | Frequency | Percent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lipid profile | Yes | 304 | 86.6 |
| No | 47 | 13.4 | |
| LDL | ≥130 | 104 | 34.2 |
| <130 | 200 | 65.8 | |
| HDL | ≤40(M) ≤ 50(F) | 134 | 44.1 |
| >41 (M) >51(F) | 170 | 55.9 | |
| TC | ≥200 | 111 | 36.5 |
| <200 | 193 | 63.5 | |
| TG | ≥150 | 121 | 39.8 |
| <150 | 183 | 60.2 | |
| Average FBS over three consecutive visits | <130 | 152 | 43.3 |
| ≥130 | 199 | 56.7 | |
| HgA1C (%) | <8% | 44 | 12.5 |
| ≥8% | 70 | 19.9 | |
| Total | 114 | 32.5 | |
| RFT (eGFR) | >60 ml/min/1.73m2 | 307 | 89.0 |
| 45–60 ml/min/1.73 m² | 26 | 7.5 | |
| 30–45 ml/min/1.73 m² | 11 | 3.2 | |
| 15–30 ml/min/1.73 m² | 1 | 0.3 |
Clinical parameters of type 2 DM patients at follow-up at ARTH, Asella, Ethiopia, 2022 (N=351).
All lipid profile parameters and fasting blood glucose level were measured in a unit of mg/dl, and eGFR was measured by mL/min/1.73 m². LDL, Low-Density Lipoprotein; HDL, High-Density Lipoprotein; FBS (in mg/dL), TC, Total Cholesterol; TG, Triglycerides; Fasting Blood Sugar; HbA1C, Hemoglobin A1C; RFT, Renal Function Test; and eGFR, Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate.
Regarding the types of hypoglycemic agents, almost half of the diabetic patients, 174 (49.6%), were treated with oral hypoglycemic agents, while 94 (26.7%) and 82 (23.4%) were treated with insulin and both insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents, respectively (Figure 1).
Figure 1

Medication for diabetes in selected type 2 DM patients on follow-up at ARTH Asella, Ethiopia, 2022 (n=351). OHA stands for oral hypoglycemic agents (metformin, glibenclamide, and others), and lifestyle modification includes regular exercise and diet modification.
Statin utilization for primary prevention of cardiovascular diseases
In this study, statins were prescribed to more than half 189 (53.8%) of the study participants; the most commonly prescribed statin was atorvastatin 40 mg per day in 164 (86.3%) participants, followed by atorvastatin 20 mg in 12% of participants (Table 5).
Table 5
| Variables | Category | Frequency | Percent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Statin prescription | No | 162 | 46.2 |
| Yes | 189 | 53.8 | |
| Type and dose of statin | Atorvastatin 20 mg | 24 | 12.6 |
| Atorvastatin 40 mg | 163 | 86.3 | |
| Simvastatin 20 mg | 2 | 1.1 |
Statin prescriptions for the primary prevention of cardiovascular diseases for type 2 DM patients on follow-up at ARTH, Asella, Ethiopia, 2022 (N=351).
Among hypertensive study participants, more than two-thirds 149 (78.4%) were prescribed a statin. However, non-hypertensive patients made up only 31 (19.3%) of the patients (Figure 2). Based on glycemic control status, 152 (76.3%) patients with uncontrolled glycemic control were prescribed statins, whereas 46 (30.3%) of the participants had controlled FBS (Figure 3).
Figure 2
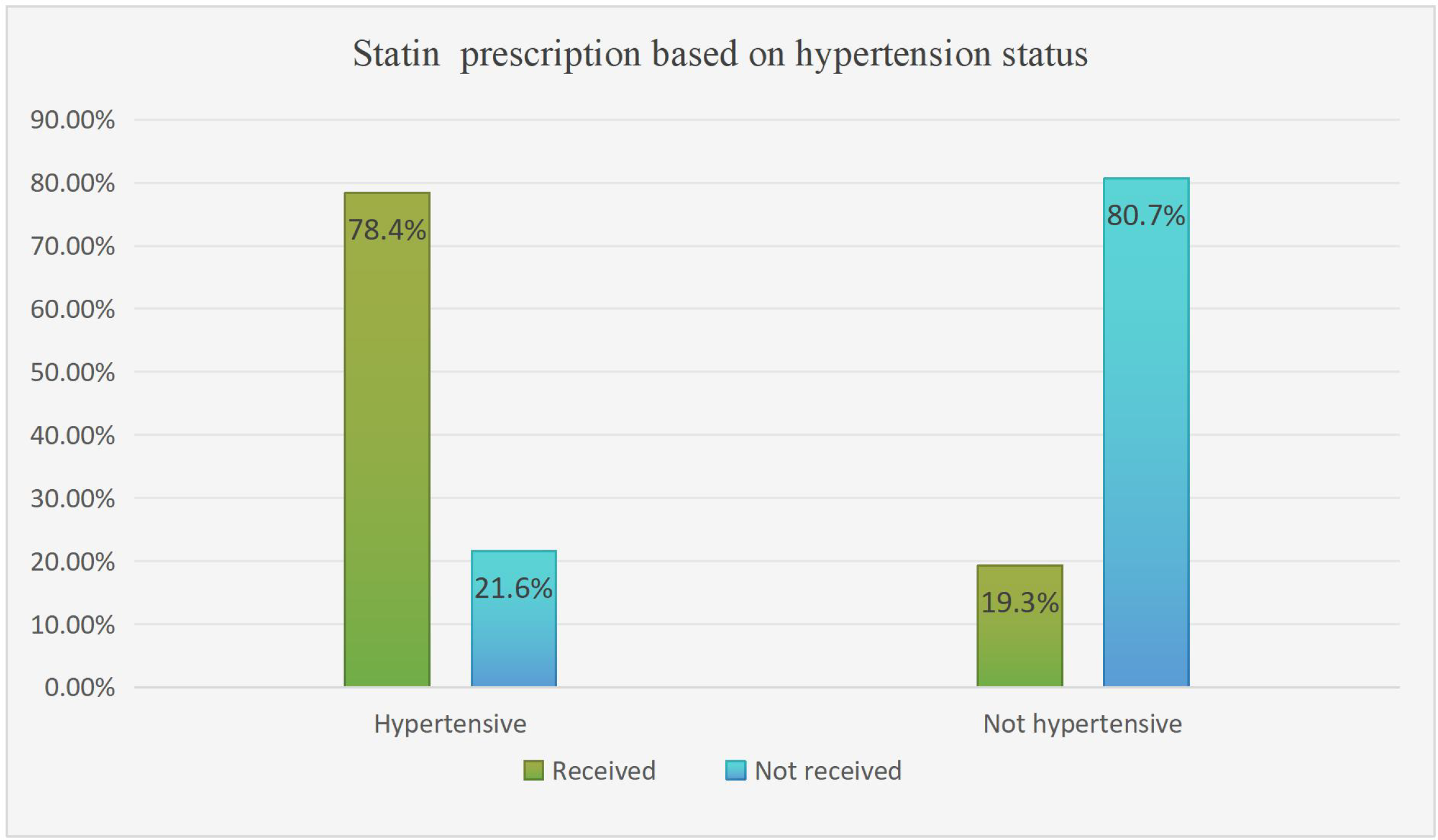
Statin utilization pattern based on hypertension status among type 2 DM patients on follow-up at ARTH, Asella, Ethiopia, 2022 (N=351).
Figure 3
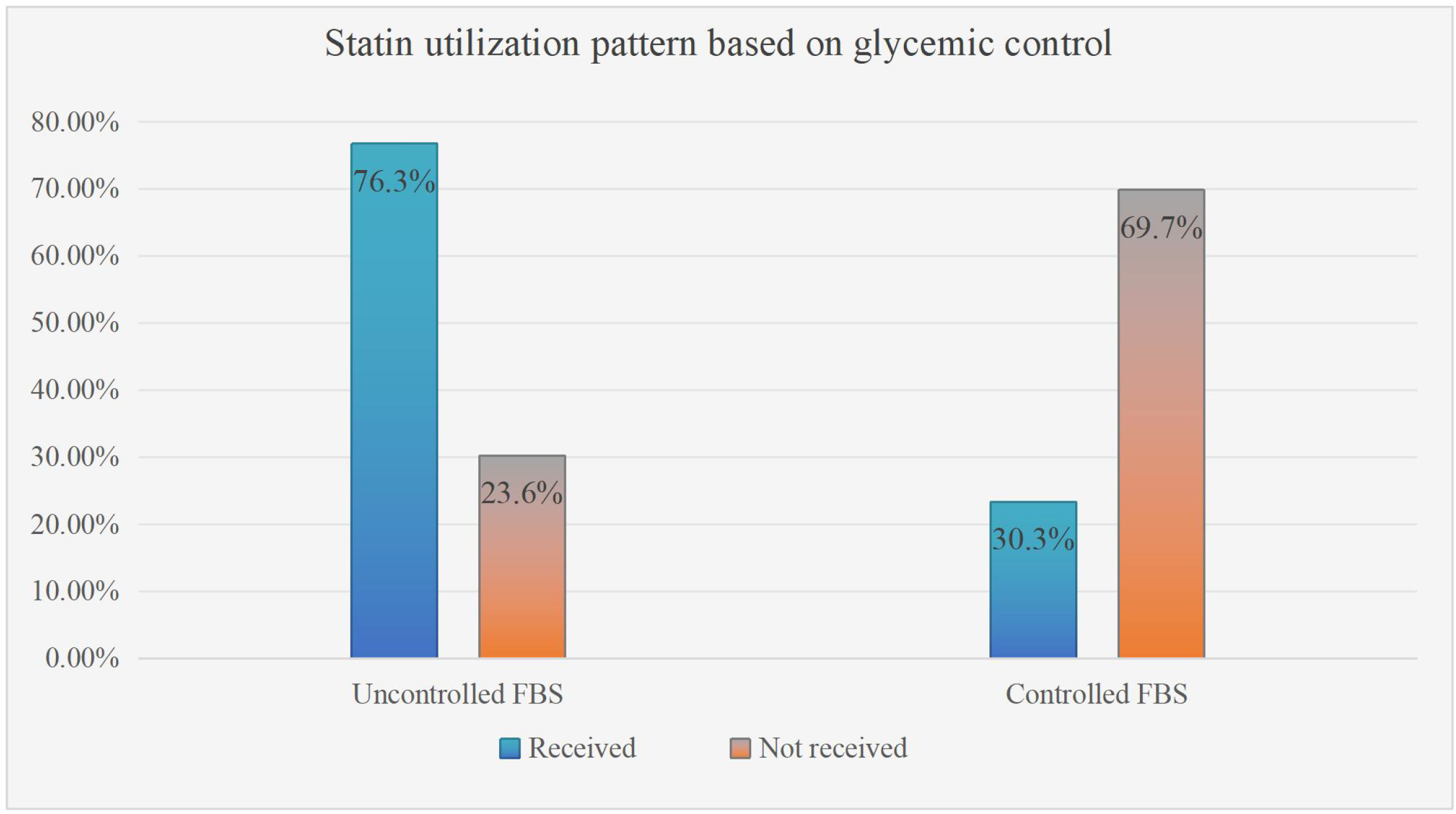
Statin utilization pattern based on glycemic control of type 2 DM patients on follow-up at ARTH, Asella, Ethiopia. September 2022 (N=351). Note: Uncontrolled FBS stands for fasting blood glucose (FBS) level >126 mg/dl.
Predictors of statin utilization for the primary prevention of cardiovascular events among diabetic patients
According to bivariate logistic regression, age, duration of diabetes (years), waist-to-hip ratio, body mass index (BMI), government insurance status, hypertension status, dyslipidemia status, high FBS, high LDL, low HDL, high total cholesterol, hypertriglyceridemia status, and type of treatment for diabetes were fitted into a multivariable binary logistic regression model for further analysis. The multivariable analysis results showed that hypertension, dyslipidemia, and uncontrolled hyperglycemia remained significantly associated with statin utilization.
According to this study, hypertensive participants were found to have an approximately five-fold greater likelihood of being on statins [AOR=4.837, 95% CI (1.936-11.587)] than those who were not hypertensive. Similarly, the odds of using statins were almost ten times greater among participants with abnormal lipid profiles (dyslipidemia) [AOR=10.5, 95% CI (2.185–11.116)] as compared to those with a normal lipid profile. In addition, patients with uncontrolled blood sugar levels were also eight times more likely to use statins [AOR=8.049, 95% CI (3.87-17.7)] than patients with controlled glycemic levels (Table 6).
Table 6
| Variables | Category | Statins utilization | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | COR (95% CI) | AOR (95% CI) | P value | ||
| Age (years) | 40-60 | 104 | 103 | 1 | 1 | |
| 60-75 | 85 | 59 | 1.4 (1.1-2.3) | 1.1 (0.6-2.4) | 0.767 | |
| Duration of diabetes (years) | <5 years | 60 | 87 | 1 | ||
| ≥5 years | 129 | 75 | 2.5 (1.6-3.9) | 1.8 (0.86-4.0) | 0.128 | |
| WHR | >0.9 (M) or >0.85 (F) | 86 | 15 | 8.2 (4.5-15) | 2.1 (0.5-8.1) | 0.280 |
| <0.9 (M) or<0.85 (F) | 103 | 147 | 1 | 1 | ||
| BMI (kg/m²) | <18.5 | 4 | 5 | 0.1 (0.02-0.4 | 0.6 (0.4-8.6) | 0.687 |
| 18.5-25 | 68 | 137 | 0.05 (0.0-0.1) | 0.2 (0.03-1.2) | 0.057 | |
| 25-30 | 72 | 15 | 0.5 (0.2-1.6) | 0.97 (0.2-4.77) | 0.971 | |
| >30 | 45 | 5 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Insurance | Yes | 182 | 145 | 3.0 (1.2-7.5) | 1.6 (0.28-9.2) | 0.602 |
| No | 7 | 7 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Dyslipidemia | Yes | 142 | 51 | 6.3 (3.8-10.6) | 10.5 (2-11.5) | 0.001* |
| No | 34 | 77 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Hypertension | Yes | 149 | 41 | 11 (6.7-18.1) | 4.8 (2.0-11.5) | 0.000* |
| No | 40 | 121 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Average FBS | ≥130 | 145 | 49 | 7.6 (4.7-12.2) | 8 (3.8-17.7) | 0.000* |
| <130 | 44 | 113 | 1 | 1 | ||
| LDL | ≥130 | 72 | 32 | 2.1 (1.3-3.4) | 0.62 (0.24-1.6) | 0.316 |
| <130 | 104 | 96 | 1 | 1 | ||
| HDL | ≤40 (M), ≤ 50 (F) | 95 | 39 | 2.6 (1.6-4.3) | 0.6 (0.2-1.7) | 0.390 |
| >41 (M), >51 (F) | 81 | 89 | 1 | 1 | ||
| TC | ≥200 | 74 | 37 | 1.8 (1.1-2.9) | 0.4 (0.2-1.2) | 0.100 |
| <200 | 102 | 91 | 1 | 1 | ||
| TG | ≥150 | 87 | 34 | 2.7 (1.6-4.4) | 1.2 (0.5-3.1) | 0.652 |
| <150 | 89 | 94 | 1 | 1 | ||
Determinants of statin utilization in selected type 2 DM patients on follow-up at ARTH, Asella, Ethiopia, 2022 (N=351).
*significantly associated at p<0.05, 1.0=reference
All lipid profile parameters and fasting blood glucose level were measured in a unit of mg/dl. LDL, Low-Density Lipoprotein; HDL, High-Density Lipoprotein; TC, Total Cholesterol; TG, Triglycerides; FBS, Fasting Blood Sugar; WHR, weight for hip ratio; BMI, Body mass index.
The bold value indicates the p- value for the significant variables.
Discussion
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a prevalent noncommunicable disease characterized by significant chronic complications that contribute substantially to the healthcare burden. Contemporary clinical guidelines recommend the use of statins as a preventive measure to mitigate the risk of further diabetes-related complications (8). This study found that only 189 [(53.8%, 95% CI:48.6%, 59.0%)] of eligible individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus attending the ARTH diabetic clinic, were prescribed statins for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. This result is comparable to findings from previous studies conducted in Ethiopia (26), India (27), and Thailand (28) which reported statin prescription rates of 55.7%, 55.2%and 58%, respectively. However, the observed statin utilization rate was higher than those reported in previous studies conducted in Jimma Ethiopia (29.10%) (17). This discrepancy could be due to differences in several risk factors (lipid profile status) and sample size differences. The reference study has smaller sample size as compared to the current study. In addition This finding is also higher to the finding from the study conducted in China (16) 33.8%. the plausible justification could be that this study is conducted in a teaching and referral hospital, where healthcare providers are more likely to follow international guidelines and apply evidence-based practices, particularly in high-risk patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. In contrast, the Chinese study may have been conducted in in the public hospitals, where guideline adherence can be more variable due to resource constraints or differences in clinical training. To the contrary, this finding is lower than the result of a study conducted in Malaysia (29), which reported that 65% of the participants had statin utilization. This discrepancy could be attributed to differences in healthcare systems, prescribing practices, and population characteristics. In Malaysia, the implementation of national treatment protocols and active engagement by primary care providers may contribute to the higher rate of statin use among appropriate patients (30). Moreover, discrepancies in patient adherence to treatment, societal beliefs regarding cardiovascular disease and pharmacological interventions and the accessibility of lipid-lowering therapies may contribute to the observed variation (31, 32).
According to the study, atorvastatin constituted approximately 99% of all statin therapy prescriptions for primary prevention of CVD in T2DM patients who attended the diabetes clinic, which is in consistent with the findings of a study conducted in India (27). However, this finding contradicts the findings of a study conducted in Ethiopia, where simvastatin was the most frequently prescribed drug (37.2%), followed by atorvastatin (32.8%) and rosuvastatin (15.6%) (26). This variation could be attributed to differences in physician prescribing preference, insurance coverage, or local drug availability (33, 34).
This study aimed to identify the significant predictors influencing statin use for the primary prevention of cardiovascular diseases (CVD). Participants with a history of hypertension were significantly more likely to receive statin prescriptions, This finding is the same as those of a previous study conducted in Eastern Ethiopia (35), Germany (36),Tanzania (34), and the USA (37). This positive association could be justified by the fact that hypertension significantly increases cardiovascular risk, making patients more likely to meet guideline-based criteria for statin therapy (38). Moreover, hypertensive patients typically have more frequent healthcare visits, providing more opportunities for preventive interventions. This frequent contact may also encourage physicians to take timely action to manage their condition effectively and reduce the risk of fatal cardiovascular events.
The findings of the present study also revealed that participants with dyslipidemia had greater odds of statin prescription than did those without dyslipidemia. This pattern of association has also been reported in previous studies conducted in Germany (36), India (27), and Botswana (16). This positive association could be justified by both clinical evidence and guideline-driven practice. Dyslipidemia, particularly elevated LDL-C levels, is a key modifiable risk factor for atherosclerosis, the underlying cause of most cardiovascular events (39, 40). Statins are the first-line treatment to lower LDL-C, making their prescription routine in patients with abnormal lipid profiles. Moreover, dyslipidemia plays a central role in cardiovascular risk assessment tools like the ASCVD risk score (41), which help determine the need for preventive treatment. The presence of elevated lipid levels contributes to a higher calculated risk, often making patients eligible for statin therapy based on clinical guidelines. Routine lipid monitoring and frequent risk evaluations in patients with dyslipidemia further contribute to their higher rates of statin use.
Moreover, statin use was significantly associated with uncontrolled blood sugar level. Statin use is greater in patients with poor glycemic control than in those with controlled glycemic levels. This finding is in line with the finding from the study conducted at Jimma (Ethiopia) (42) and Texas USA (43). This relationship can be explained by the fact that uncontrolled blood glucose level contributes to endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and chronic inflammation that collectively hasten the progression of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) (44, 45). Consequently, individuals with poorly managed glycemic levels are considered to be at significantly higher cardiovascular risk, which often leads to the early initiation of statin therapy, even in the absence of classical dyslipidemia. Furthermore, inadequate glycemic control is frequently linked to diabetic dyslipidemia, typically marked by elevated triglycerides, reduced HDL-C, and a higher proportion of small, dense LDL particles (46). These lipid abnormalities further exacerbate cardiovascular risk, thereby increasing the likelihood of statin prescription (47).
On the other hand, several studies have reported that patients taking statins may be at increased risk of developing dyslipidemia and insulin resistance (48–50). This observed association could potentially be linked to the effects of statin therapy; however, due to the cross-sectional nature of our study, it is not possible to establish a definitive cause-and-effect relationship. Hence, the observed association between uncontrolled blood glucose and statin use aligns with evidence-based, risk-oriented clinical guidelines designed to minimize long-term cardiovascular complications in patients with diabetes.
Conclusion
This study underscores a suboptimal yet comparable rate of statin prescription (53.8%) for primary cardiovascular disease prevention among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus at the ARTH diabetic clinic, aligning with findings from others lower and middle income countries. Statin use was significantly influenced by clinical factors such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, and poor glycemic control, reflecting adherence to risk-based clinical guidelines. Atorvastatin was the predominant statin prescribed, consistent with international prescribing trends but diverging from local variations. Therefore, it is imperative to implement strategies aimed at optimizing the prescription of statins for the primary prevention of CVD, especially among individuals with comorbidities such as hypertension and dyslipidemia, as well as those with poorly controlled glycemic levels.
Limitations of the study
While this study has several strengths, it is important to acknowledge its limitations. First, the study design was cross-sectional and limited to a single clinic, which restricts the generalizability of the findings to other healthcare institutions in the country. Moreover, this study design does not allow for the determination of a bidirectional relationship between statin use and the risk of developing dyslipidemia. Additionally, due to the unavailability of certain laboratory investigations, some patients were not fully diagnosed. For instance, the absence of a 24-hour urine protein test at the hospital resulted in many potential cases of diabetic nephropathy being undiagnosed.
Recommendations
Based on the study findings, it is recommended that institutional guidelines and provider awareness initiatives be strengthened to improve adherence to evidence-based lipid management protocols. Targeted strategies should prioritize high-risk subgroups, including patients with hypertension, dyslipidemia, and poor glycemic control, who are significantly more likely to benefit from statin therapy. Clinical training and continuous medical education focusing on cardiovascular risk stratification and statin prescribing patterns should be emphasized to enhance preventive care practices. Additionally, integrating electronic clinical decision support tools may help identify high-risk individuals and ensure the timely initiation of statins, particularly among those with hypertension, dyslipidemia, or uncontrolled blood glucose levels. Moreover, routine audit and feedback systems should be implemented to monitor and improve prescribing behaviors over time. Future researchers should also focus on investigating the association between dyslipidemia and statin utilization patterns using prospective study designs.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
This study was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Arsi University on behalf of the College of Health Science Research Ethical Committee. A signed permission letter was obtained from the hospital medical director. Finally, participants were informed about the study's aims, objectives, and potential outcomes. Written informed consent was obtained before the data collection started. All the information obtained in the study was kept confidential, and no records identifying patients were recorded.
Author contributions
FD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. WA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. FK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. KT: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. KA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
ARTH, Asella Referral and Teaching Hospital; CDC, Centre for Disease Control; CCS, Chronic coronary syndrome; CVD, Cardiovascular disease; DM, Diabetes mellitus; FBS, Fasting Blood Sugar; HDL, High-density lipoprotein; HgA1c, Glycated hemoglobin; PPBS, Post-prandial blood sugar; PAD, Peripheral arterial disease; RBS, Random blood sugar; WHR, waist-to-hip ratio.
References
1
Association AD . Standards of medical care in diabetes—2022 abridged for primary care providers. Clin Diabetes. (2022) 40:10–38.
2
Zakir M Ahuja N Surksha MA Sachdev R Kalariya Y Nasir M et al . Cardiovascular complications of diabetes: from microvascular to macrovascular pathways. Cureus. (2023) 15:e45835. doi: 10.7759/cureus.45835
3
Sun H Saeedi P Karuranga S Pinkepank M Ogurtsova K Duncan BB et al . IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin practice. (2022) 183:109119. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119
4
Mosenzon O Cheng AY Rabinstein AA Sacco S . Diabetes and stroke: what are the connections? J stroke. (2023) 25:26–38.
5
Members ATF Rydén L Grant PJ Anker SD Berne C Cosentino F et al . ESC Guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD: the Task Force on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and developed in collaboration with the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Eur Heart J. (2013) 34:3035–87. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht108
6
Rizvi AA Stoian AP . Lipoproteins and cardiovascular disease: an update on the clinical significance of atherogenic small, dense LDL and new therapeutical options. Biomedicines. (2021) 9:1579. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9111579
7
Li Y Liu Y Liu S Gao M Wang W Chen K et al . Diabetic vascular diseases: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8:152. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01400-z
8
Arnett DK Blumenthal RS Albert MA Buroker AB Goldberger ZD Hahn EJ et al . ACC/AHA guideline on the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. (2019) 140:e596–646.
9
Mach F Baigent C Catapano AL Koskinas KC Casula M Badimon L et al . ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk: the Task Force for the management of dyslipidaemias of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS). Eur Heart J. (2019) 41:111–88.
10
Sagris M Katsaros I . Statins and statin intensity in peripheral artery disease. Vasa (2022) 51:198–211. doi: 10.1024/0301-1526/a001012
11
Karlson BW Palmer MK Nicholls SJ Lundman P Barter PJ . To what extent do high-intensity statins reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in each of the four statin benefit groups identified by the 2013 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guidelines? A VOYAGER meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis. (2015) 241:450–4. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.05.029
12
Committee ADAPP . 10. Cardiovascular disease and risk management: standards of medical care in diabetes—2022. Diabetes Care. (2021) 45:S144–S74.
13
Joseph JJ Deedwania P Acharya T Aguilar D Bhatt DL Chyun DA et al . Comprehensive management of cardiovascular risk factors for adults with type 2 diabetes: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2022) 145:e722–e59. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001040
14
Jun JE Jeong I-K Ahn KJ Chung HY Hwang Y-C . Statin use for primary prevention in patients with type 2 diabetes: Can it benefit all ages?–A nationwide propensity-matched cohort study. Diabetes Res Clin Practice. (2021) 180:109044. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109044
15
Pauff BR Jiroutek MR Holland MA Sutton BS . Statin prescribing patterns: an analysis of data from patients with diabetes in the national hospital ambulatory medical care survey outpatient department and national ambulatory medical care survey databases, 2005–2010. Clin Ther. (2015) 37:1329–39. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.03.020
16
Lee VW Ho IC Chan WS Tam KY Lee KK . Statin utilization patterns for the primary prevention of cardiovascular events: a retrospective study in patients with diabetes mellitus in Hong Kong. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. (2008) 8:199–205. doi: 10.2165/00129784-200808030-00006
17
Melaku T Solomon Y Chelkeba L . Statin utilization patterns among Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with high cardiovascular disease risks in Ethiopia. J Pharm Care. (2018) 6:44–51.
18
Kebede zelalem B Feyisa D . Determinants of statin initiation among adult diabetic patients in bonga, Ethiopia. Diabetes Metab Syndrome Obes. (2020) 13:4839–47. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S283993
19
Mwita JC Godman B Esterhuizen TM . Statin prescription among patients with type 2 diabetes in Botswana: findings and implications. BMC endocrine Disord. (2020) 20:1–9. doi: 10.1186/s12902-020-0516-7
20
Ismail HM Shora HA Al-Nozha O Yamany HA Al-Nozha F Zaitone SA et al . Pattern of Statin use in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2 for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease in Saudi Arabia. Afr J Diabetes Med. (2020) 28:1-9.
21
Ogurtsova K da Rocha Fernandes J Huang Y Linnenkamp U Guariguata L Cho NH et al . IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res Clin practice. (2017) 128:40–50. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2017.03.024
22
Sorsa A . Epidemiology of neonatal sepsis and associated factors implicated: observational study at neonatal intensive care unit of Arsi University Teaching and Referral Hospital, South East Ethiopia. Ethiopian J Health Sci. (2019) 29:333-42.
23
Matthias AT Kaushalya J Somathilake G Garusinghe C . Utilization of statins in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: the practice in a lower middle income South Asian country. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries.. (2023) 43:405–11. doi: 10.1007/s13410-022-01107-x
24
Li J Nie Z Ge Z Shi L Gao B Yang Y . Prevalence of dyslipidemia, treatment rate and its control among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Northwest China: a cross-sectional study. Lipids Health Disease. (2022) 21:77. doi: 10.1186/s12944-022-01691-1
25
Narindrarangkura P Bosl W Rangsin R Hatthachote P . Prevalence of dyslipidemia associated with complications in diabetic patients: a nationwide study in Thailand. Lipids Health disease. (2019) 18:1–8. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-1034-3
26
Demoz GT Wahdey S Kasahun GG Hagazy K Kinfe DG Tasew H et al . Prescribing pattern of statins for primary prevention of cardiovascular diseases in patients with type 2 diabetes: insights from Ethiopia. BMC Res Notes. (2019) 12:1–7. doi: 10.1186/s13104-019-4423-9
27
Gupta R Lodha S Sharma KK Sharma SK Gupta S Asirvatham AJ et al . Evaluation of statin prescriptions in type 2 diabetes: India Heart Watch-2. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. (2016) 4:e000275. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2016-000275
28
Chaiyakunapruk N Asuphol O Dhippayom T Poowaruttanawiwit P Jeanpeerapong N . Statins utilisation pattern: a retrospective evaluation in a tertiary care hospital in Thailand. Int J Pharm Practice. (2011) 19:129–35. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7174.2010.00089.x
29
Elnaem M Nik Mohamed M Huri H Azarisman S . Patterns of statin therapy prescribing among hospitalized patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus in two Malaysian tertiary hospitals. Trop J Pharm Res. (2017) 16::3005-3011.
30
Fadzilah A Azima R Khalsom S Rosliza A . Governance framework in non-communicable disease (NCD) control and prevention programme at primary care level in Malaysia. Int J Public Health Clin Sci. (2020) 7:167–85.
31
Nanna MG Navar AM Zakroysky P Xiang Q Goldberg AC Robinson J et al . Association of patient perceptions of cardiovascular risk and beliefs on statin drugs with racial differences in statin use: insights from the patient and provider assessment of lipid management registry. JAMA Cardiol. (2018) 3:739–48. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2018.1511
32
Schroff P Gamboa CM Durant RW Oikeh A Richman JS Safford MM . Vulnerabilities to health disparities and statin use in the REGARDS (Reasons for geographic and racial differences in stroke) study. J Am Heart Assoc. (2017) 6:e005449. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.005449
33
Pedan A Varasteh LT Schneeweiss S . Analysis of factors associated with statin adherence in a hierarchical model considering physician, pharmacy, patient, and prescription characteristics. J managed Care pharmacy. (2007) 13:487–96. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2007.13.6.487
34
Bideberi AT Mutagaywa R . Statin Prescription Patterns and Associated Factors Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Attending Diabetic Clinic at Muhimbili National Hospital, Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. Diabetes Metab Syndrome Obes. (2022) 15:633–46. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S347765
35
Nigussie S Demeke F . Prescribing patterns of statins and associated factors among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients attended at Jugol General Hospital in eastern Ethiopia: A cross-sectional study. Front Clin Diabetes healthcare. (2023) 4:1061628. doi: 10.3389/fcdhc.2023.1061628
36
Berthold HK Gouni-Berthold I Böhm M Krone W Bestehorn KP . Patterns and predictors of statin prescription in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc diabetology. (2009) 8:1–12. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-8-25
37
Fu AZ Zhang Q Davies MJ Pentakota S-R Radican L Seck T . Underutilization of statins in patients with type 2 diabetes in US clinical practice: a retrospective cohort study. Curr Med Res opinion. (2011) 27:1035–40. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2011.567257
38
Force UPST . Statin use for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in adults: US preventive services task force recommendation statement. Jama. (2016) 316:1997–2007. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.15450
39
Brunham LR Lonn E Mehta SR . Dyslipidemia and the current state of cardiovascular disease: epidemiology, risk factors, and effect of lipid lowering. Can J Cardiol. (2024) 40:S4–s12. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2024.04.017
40
Vasan RS Pan S Larson MG Mitchell GF . Arteriosclerosis, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular health: joint relations to the incidence of cardiovascular disease. Hypertension. (2021) 78:1232–40. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.18075
41
Moradi Ardekani F Zibaeenezhad MJ Sayadi M Jafari F Javidi Al-e-Saadi S Karami H et al . Ten-year Atherosclerosis Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD) risk score and its components among nomadic population in southern Iran: A population-based study. Clin Epidemiol Global Health. (2025) 31:101913. doi: 10.1016/j.cegh.2025.101913
42
Melaku T Solomon Y Chelkeba L . Statin utilization patterns among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with high cardiovascular disease risks in Ethiopia. J Pharm Care. (2019) 2019:44–51.
43
Mansi IA Chansard M Lingvay I Zhang S Halm EA Alvarez CA . Association of statin therapy initiation with diabetes progression: A retrospective matched-cohort study. JAMA Internal Med. (2021) 181:1562–74. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.5714
44
Mastrogiacomo L Ballagh R Venegas-Pino DE Kaur H Shi P Werstuck GH . The effects of hyperglycemia on early endothelial activation and the initiation of atherosclerosis. Am J Pathology. (2023) 193:121–33. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2022.09.004
45
Eckel RH Bornfeldt KE Goldberg IJ . Cardiovascular disease in diabetes, beyond glucose. Cell Metab. (2021) 33:1519–45. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.07.001
46
Brady RP Shah AS Jensen ET Stafford JM D’Agostino RB Jr. Dolan LM et al . Glycemic control is associated with dyslipidemia over time in youth with type 2 diabetes: The SEARCH for diabetes in youth study. Pediatric diabetes. (2021) 22:951–9. doi: 10.1111/pedi.13253
47
Khanal MK Bhandari P Dhungana RR Gurung Y Rawal LB Pandey G et al . Poor glycemic control, cardiovascular disease risk factors and their clustering among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional study from Nepal. PloS One. (2022) 17:e0271888. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271888
48
Alvarez-Jimenez L Morales-Palomo F Moreno-Cabañas A Ortega JF Mora-Rodríguez R . Effects of statin therapy on glycemic control and insulin resistance: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Pharmacol. (2023) 947:175672. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175672
49
She J Tuerhongjiang G Guo M Liu J Hao X Guo L et al . Statins aggravate insulin resistance through reduced blood glucagon-like peptide-1 levels in a microbiota-dependent manner. Cell Metab. (2024) 36:408–21. e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.12.027
50
Abbasi F Lamendola C Harris CS Harris V Tsai M-S Tripathi P et al . Statins are associated with increased insulin resistance and secretion. Arteriosclerosis thrombosis Vasc Biol. (2021) 41:2786–97. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.121.316159
Summary
Keywords
diabetes mellitus, statin, primary prevention, cardiovascular disease, Ethiopia
Citation
Dhaba FA, Alemu WA, Kitila FL, Tolla KS, Alene A, Wendimagegn ZS, Getahun KA, Yesuf HA and Woldeyes SM (2025) Statin utilization and its predictors for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease among type 2 diabetic patients in a resource-limited setting. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1472300. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1472300
Received
29 January 2025
Accepted
17 June 2025
Published
04 July 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Robert Kiss, McGill University, Canada
Reviewed by
Omer Faruk Hatipoglu, Kindai University Hospital, Japan
Cyndiana Widia Dewi Sinardja, Udayana University, Indonesia
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Dhaba, Alemu, Kitila, Tolla, Alene, Wendimagegn, Getahun, Yesuf and Woldeyes.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hassen Ahmed Yesuf, hassenibnahmed@gmail.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.