- 1Department of Medicine, Lishui University, Lishui, China
- 2The First Affiliated Hospital of Lishui University, Lishui, China
Background: Suboptimal insulin injection is widely used to treat Chinese patients with diabetes, with most patients being treated in primary care institutions. However, research on community nurses’ knowledge, attitude, and practice concerning insulin injection in less developed areas of China is extremely scarce.
Objective: To investigate the knowledge, attitude, and practice of community nurses concerning insulin injection in a mountainous area of southwest, Zhejiang, China.
Methods: We employed a cross-sectional study in 30 community healthcare service centers and 1911 randomly selected community nurses between 20th June to 20th July 2023. The Chinese insulin injection knowledge, attitude, and practice questionnaire was used to collect data. Descriptive, correlational, and multivariate linear regression analyses were performed by Stata version 15.0.
Results: In total, 47.7% of nurses had poor insulin injection knowledge, while only 3.7% and 2.5% had poor levels of attitude and practice concerning insulin injection. Sex, location of the institution, working period, marital status, institutional manager, knowledge of the latest guidelines, and undertaking insulin injection training over the last year (all p<0.05) were all identified as independent predictors of insulin injection knowledge. Sex, working period, experience of delivering insulin education to patients, knowledge of the latest guidelines, and undertaking insulin injection training over the previous year (all p<0.05) were identified as independent predictors of insulin injection attitude. Location of the institution, sex, knowledge of the latest guidelines, and undertaking insulin injection training over the last year (all p<0.05) were all independent predictors of insulin injection practice.
Conclusion: Community nurses in this study (Southwest Zhejiang) had relatively good attitudes and practices towards insulin injection, although their specific knowledge was poor. Sex, location of the institution, working period, marital status, knowledge of the guidelines, experience in delivering education, and training experience exhibited significant relationships with the knowledge, attitude, and practice of insulin injection. Therefore, effective tailored, standardized guideline-based training should be recommended to improve the knowledge, attitude, and practice of community nurses regarding insulin injection, especially for married and younger male nurses.
1 Introduction
The prevalence, disability and mortality rates of diabetes continue to rise, meaning that this disease has become a major global public health concern (1, 2). China has the largest number of individuals living with diabetes worldwide (approximately 25% of global cases), with a prevalence surging from 7.53% in 2005 to 13.67% in 2023 (3). Diabetes, and its related complications and treatments, have caused severe physiological, psychological, social and economic burdens to patients, families, the medical system, and society. In 2009, China began to implement the National Basic Public Health Service Project and grass-roots medical institutions have assumed the main function of preventing and treating chronic disease; these institutions have become the main driving force for the clinical management of diabetic patients. In 2021, approximately 87% of diabetic patients in China were treated in healthcare institutions at or below the county level (4). Community healthcare providers are now heavily responsible for the prevention and treatment of chronic disease and represent the predominant bodies responsible for the health management of patients with type 2 diabetes. However, the 2018 Report on Chinese Chronic Disease Risk Factor Surveillance showed that the rates of awareness, treatment and control of diabetes in China were only 38.0%, 34.1% and 33.1%, respectively (5). In addition, previous studies have shown that diabetes in China is affecting younger individuals and that the prevalence of diabetes in the rural population is increasing rapidly (2). Therefore, the prevention and control of diabetes in China remains challenging, especially in primary healthcare institutions.
Insulin therapy stands as a critical strategy for achieving glycemic control targets and is widely utilized among diabetic patients (6, 7). For individuals with type 1 diabetes, insulin remains the first-line treatment. In cases of type 2 diabetes, insulin therapy is recommended if glycemic targets are not met following a three-month regimen combining lifestyle interventions and oral hypoglycemic agents (6, 8). For instance, an outpatient survey of type 2 diabetes patients in Sanming City, China, revealed that approximately 44.5% were undergoing insulin therapy (9). Furthermore, a large multicenter cross-sectional survey in China focusing on insulin injection techniques demonstrated that 97.81% of insulin-treated patients had type 2 diabetes, whereas only 2.19% had type 1 diabetes (10). Although China has not implemented a universal free insulin policy, significant cost reductions (exceeding 70% for certain drugs) have been achieved through medical insurance reimbursements and volume-based procurement initiatives (11, 12). Specific regions and vulnerable populations (e.g., low-income residents, elderly island residents) may qualify for free insulin access (13). Nevertheless, substantial economic burdens persist for broader low-income demographics. Beyond financial constraints, other critical issues demand attention with regards to the widespread adoption of insulin therapy. Notable problems include pervasive needle reuse (93.87%) and improper injection site rotation (only 33% performed correctly), contributing to high complication rates such as lipohypertrophy (affecting 48.25% of patients) (10). These practices directly undermine therapeutic efficacy. Consequently, promoting and disseminating standardized insulin injection techniques is imperative (6, 7, 14). Incorrect injection techniques can precipitate complications including subcutaneous lipohypertrophy or lipoatrophy, edema and allergic reactions. These may subsequently lead to suboptimal glycemic control or hypoglycemic events, significantly compromising the therapeutic effectiveness of insulin (15). The 2014–2015 Global Survey of Insulin Injection Techniques indicated limited awareness among healthcare professionals regarding how injection techniques impact glycemic control (6), a finding corroborated by subsequent studies (16–19).
In China, Wu et al. conducted a national cross-sectional study to investigate the knowledge, attitudes, and practices of nurses in China with regard to insulin injection (20). These researchers found that Chinese nurses had a good attitude and practice towards insulin injection, although their knowledge of insulin injection was insufficient. In addition, they demonstrated that knowledge of insulin injection can directly or indirectly influence insulin injection practice through attitude. Because Chinese primary care settings have the majority of chronic patients and are associated with an unmet need for high-quality insulin injection techniques, it is necessary to investigate the knowledge, attitudes, and practices of primary healthcare providers with regard to insulin injection. However, an obvious limitation of this previous study (21) was that the sample cohort predominantly consisted of secondary and tertiary hospitals (99.29%); only 0.71% were primary institutions. The specific situation of primary healthcare providers, especially community nurses, remains unknown. Although other researchers also investigated the knowledge, attitude and practice of nurses towards insulin injection, and the factors that can influence these parameters, in different areas of China, including Liao et al. (22), Zheng et al. (23), Liu et al. (24), these researchers did not focus specifically on community nurses, who remain as the main management force for primary diabetes care in China. Nurses in community healthcare institutions primarily educate DM patients on insulin use, self-management, and lifestyle adjustments, and administer insulin during home visits for vulnerable patients according to prescriptions from the physician (25), especially for patients using insulin for the first time. For these patients, nurses need to thoroughly explain the mechanism of insulin action, the necessity of injection, and common misconceptions (26).
Moreover, while previous studies have considered the levels of knowledge, attitude, and practice of community nurses in relation to insulin injection (20, 22, 27), findings were inconsistent (20, 22). In addition, the sample size of the study reported by Wang et al. (27) was small (a total sample size of 340 nurses with only 63 nurses from community healthcare institutions), and convenient sampling also challenged the reliability of their conclusion and the generalizability of their findings. Finally, most of these previous studies focused on developed areas of China, including Beijing (24), Shanghai (27), and Guangdong (22); few studies have focused on less developed areas or rural areas. Thus, there is still a significant gap in our understanding of the knowledge, attitude, and practice of community nurses in China, especially those from less-developed areas. Therefore, in this study, we investigated the specific knowledge, attitudes, and practices of community nurses with regard to insulin injection, and the factors that can influence these parameters, in less developed areas of China: Lishui City, Zhejiang Province.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study design and setting
This cross-sectional study was conducted at multiple community healthcare service centers across Lishui City in Zhejiang Province of China, between 20th June and 20th July 2023. Lishui City is a less-developed mountainous area of Zhejiang Province and has the lowest Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of the province (21). Approximately 90% of its land is mountains and 47 minorities live in this city. Most inhabitants live in the less developed remote mountainous area, especially the She minority. There are nine counties and 227 healthcare service centers, 181 of these service centers are in rural areas, while 46 are in the urban area of Lishui City (22).
2.2 Samples and sampling
This study was conducted in 30 healthcare service centers from three counties and employed cluster random sampling. Economic level (GDP) was used to select the three counties (28). First, a simple random method selected one low, medium, economic level county. Then, ten healthcare service centers were randomly selected from each county, including eight in rural and two in urban areas. All registered community nurses in the selected 30 centers were invited to participate in the investigation. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (a) ≥ 18 years of age; (b) had been hired in a community healthcare institution as a registered nurse; and (c) had performed at least one insulin injection in the previous year. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (a) nurses in training, interns, and nursing students; and (b) nurses who were temporarily in the institution, such as those who were studying or on vacation.
The sample size was calculated as follows: n = z2 p (1-p)/d2, where α represents the level of significance. When α= 0.05, Z= 1.96; n represents the sample, d represents the allowable error, and P represents the estimated poor knowledge value of the population rate (π). The poor knowledge rate determined by the pre-test survey was approximately 27% (P = 0.27; α = 0.05; d = 0.027). We increased the sample size to 15% to account for non-responders, meaning that 1223 healthcare providers were needed. Finally, the survey included 1911 healthcare providers from 30 healthcare service centers in three counties. This study was approved by the ethical review committee of Lishui University (Reference: xx). All participants provided written and informed consent prior to enrollment. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
2.3 Outcome definition and measurement
A 15–20 min self-administrated questionnaire was developed which consisted of two parts: (1) sociodemographic and baseline characteristics, including age, sex, working period, location of institution, educational level, having delivered insulin educations to patients, knowing the latest guidelines of insulin delivery, numbers of insulin injection training in last year. These variables were extracted from related research and guidelines (8, 16, 17, 19, 23), and (2) the Chinese Insulin Injection Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice Questionnaire. Based on the Knowledge, Attitude, and Practices (KAP) model (24) and related guidelines, Wu et al. (16) developed the Chinese Insulin Injection Knowledge, Attitude and Practice questionnaire, consisting of 45 items and three dimensions: knowledge (21 items), attitude (6 items), and practice (18 items). Specifically, the knowledge dimension covers relevant topics such as insulin drugs, injection techniques, and prevention of hypoglycemia; the attitude dimension includes aspects like the importance, standardization, and confidence in insulin injection techniques; and the practice dimension addresses behaviors such as the use of insulin devices and injection techniques. When developing the original questionnaire, Cronbach’s α for insulin injection knowledge, attitude, and practice was 0.686, 0.785, and 0.886, respectively, thus indicating good internal consistency. We also confirmed a satisfactory internal consistency; Cronbach’s α for insulin injection knowledge, attitude, and practice was 0.717, 0.816, and 0.944, respectively. For the insulin injection knowledge dimension, there was 1 point for each item, with a total of 21 points. A total score of <13 points indicated a poor knowledge of insulin injection, 13–17 points were satisfactory, and >17 points were good. In the dimension of insulin injection attitude, 1–5 points were given for items 1–4, and no point was assigned to items 5 and 6. The total score was 20 points; a total score of <12, 12–16, and >16 points indicated poor, satisfactory, and good insulin injection attitude, respectively. In the dimension of insulin injection practice, items 1–14 and 16–18 were given 1 –5 points according to the choice order, and item 15 was given 5–1 points according to the choice order, with a total score of 90 points. A total score of <54 points indicated poor insulin injection practice, 54–72 points was satisfactory and >72 points was good.
2.4 Data collection
A total of three data collectors participated in institutional outreach efforts. Data collectors received face-to-face training on ethical liaison protocols with the principal investigator (PI) before the survey. Following ethical approval, the PI and data collectors contacted the directors of participating healthcare centers. During structured meetings, a comprehensive briefing covered: (1) research objectives, (2) questionnaire self-administration procedures, (3) participant eligibility criteria, and (4) data confidentiality protocols. Subsequently, with institutional authorization, QR codes and web links to the online consent form and survey platform (http://www.wjx.cn) were disseminated via designated WeChat groups during June 20–July 20, 2023. All eligible participants in the 30 selected healthcare service centers were invited to participate in the survey autonomously without interviewer involvement. If the participants had any questions about the survey, they were able to contact the researchers by telephone or WeChat. To avoid duplicate entries, we restricted IP access; only one IP address was allowed to complete the survey.
2.5 Data analysis
The STATA 15.0 software (Stata Corp. LP, College Station, TX, USA) was used for data analysis. Descriptive statistics, including frequency, percentage, mean, and standard deviation, were used to analyze the sociodemographic and baseline characteristics of the participants. Pearson’s and Spearman’s correlation analyses were used to analyze correlations between knowledge, attitude, and behavior relating to insulin injection. Considering the numbers of sociodemographic and clinical variables, the findings of previous research, and correlation analysis, demonstrated that all independent and dependent variables did not exhibit multicollinearity and were therefore considered as independent variables. The scores for insulin injection knowledge, attitude, and behavior were considered dependent variables. These variables were used to conduct multiple linear regression analysis to investigate the factors that could potentially influence the dimension of insulin injection. p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Sociodemographic and baseline characteristics
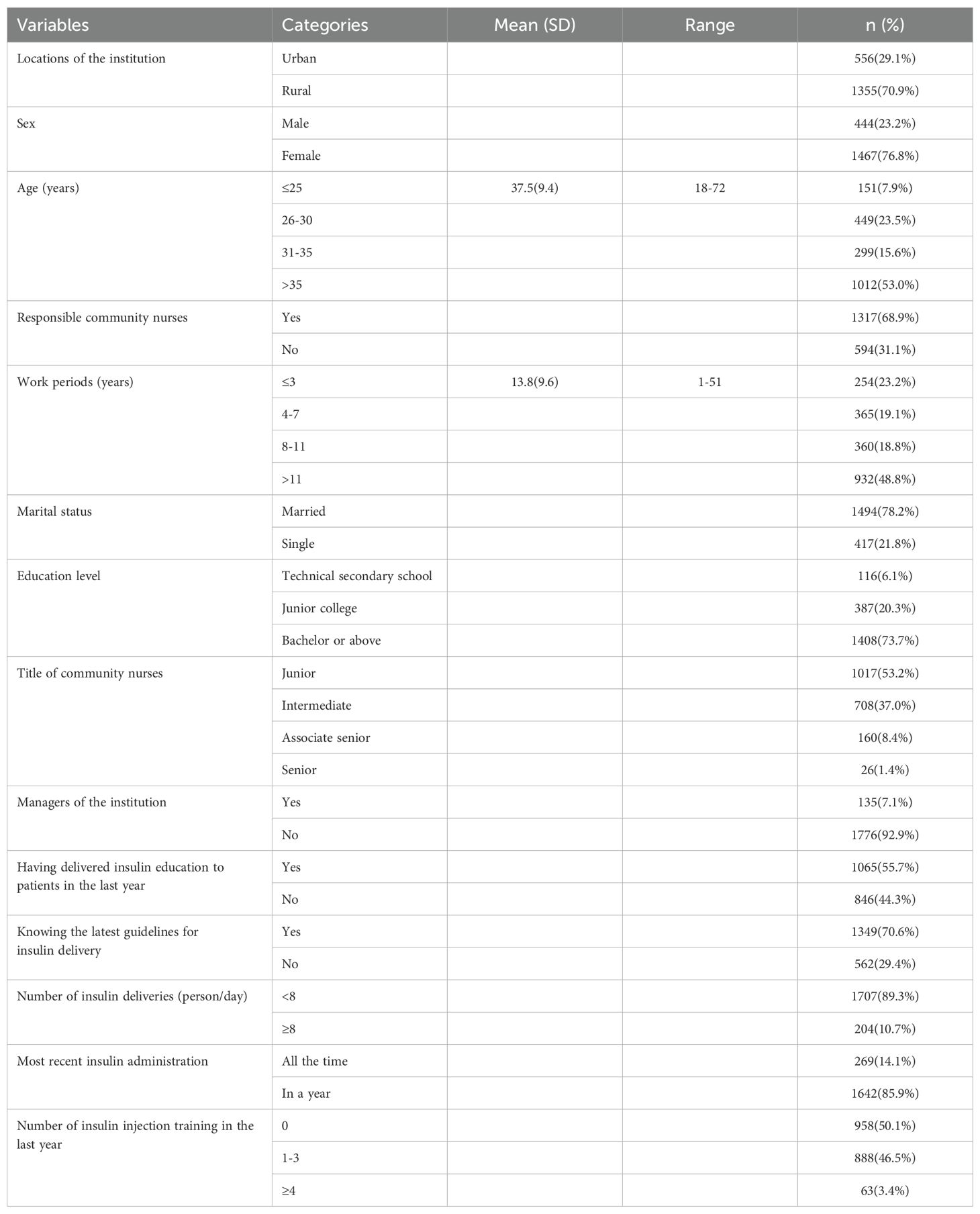
In total, 1911 community nurses accepted and completed this online survey (Table 1). Approximately 71% of nurses were from rural areas. Of these, 76.8% were female, and most were married (78.2%) and had a bachelor’s degree (73.3%). Half of the nurses were above 35 years of age, with a median age of 37 (30–45) years (range: 18 to 72 years). In total, 48.8% of nurses had worked more than 11 years with a median of 11 (6–20) years. However, only a few of the nurses had a senior title (9.8%) or had a managerial role in their institution (7.1%). When considering all subjects, 68.9% were responsible community nurses, 55.7% had delivered insulin education to patients, and 70.6% knew the latest guidelines associated with the delivery of insulin. In total, 1276 (66.8%) of the respondents had administered insulin over 12 months, 366 (19.2%) had administered insulin over 6 months, and 204 (10.7%) had administered insulin all the time. In terms of training related to the injection of insulin, almost 50% of participants did not receive any form of training over the previous 12 months, 46.5% had received one to three sessions of training, and 3.4% had received more than four sessions of training.
3.2 Insulin injection knowledge score
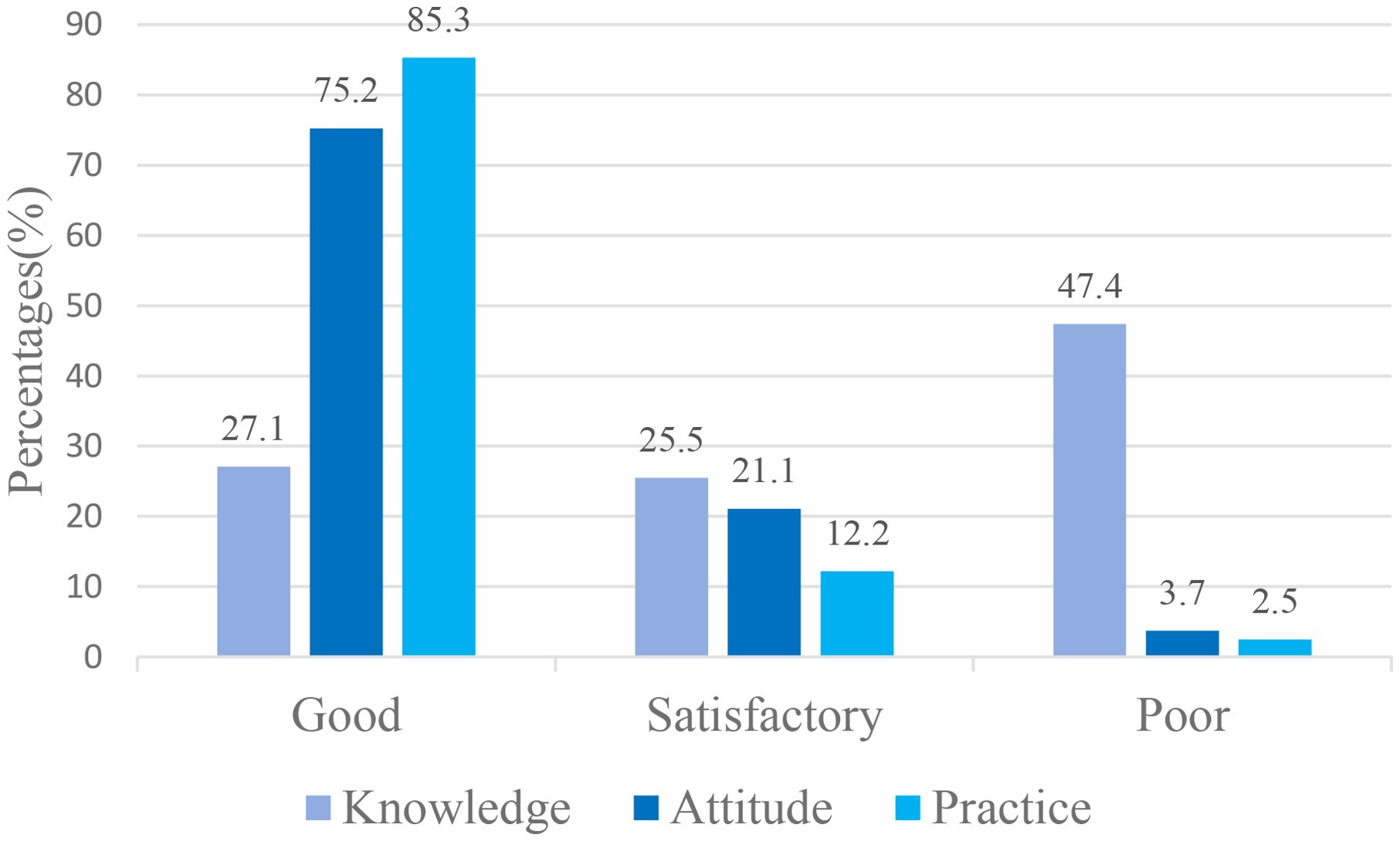
The mean insulin injection knowledge score for community nurses was 13.2 ± 4.87; Figure 1 showed that 27.1% of nurses had a good knowledge score, 25.5% had a satisfactory knowledge score, and 47.4% had a poor knowledge score. Considering the three dimensions of the knowledge score, the mean master basic knowledge score (items 1, 2, 6, 16, 19–21) was 3.85 ± 1.877, the mean master insulin storage knowledge score (items 3–5) was 2.4 ± 0.828, and the mean master insulin injection knowledge score (items 7–15, 17–18) was 6.98 ± 2.765. The mean accuracy rates for the three dimensions were 55%, 80% and 63%, respectively. Figure 2 shows the overall status of insulin injection knowledge. Items for which less than half of the participants knew included (from low to high): item 11 (the interval between two injections at the same site; 23%), item 21 (hypoglycemia management; 26%), item 1 (types of aspartic insulin; 36%), item 17 (needle disposal method; 36%), item 19 (mixing method for insulin; 39%), and item 18 (injection site administration after withdrawal of needle; 40%).
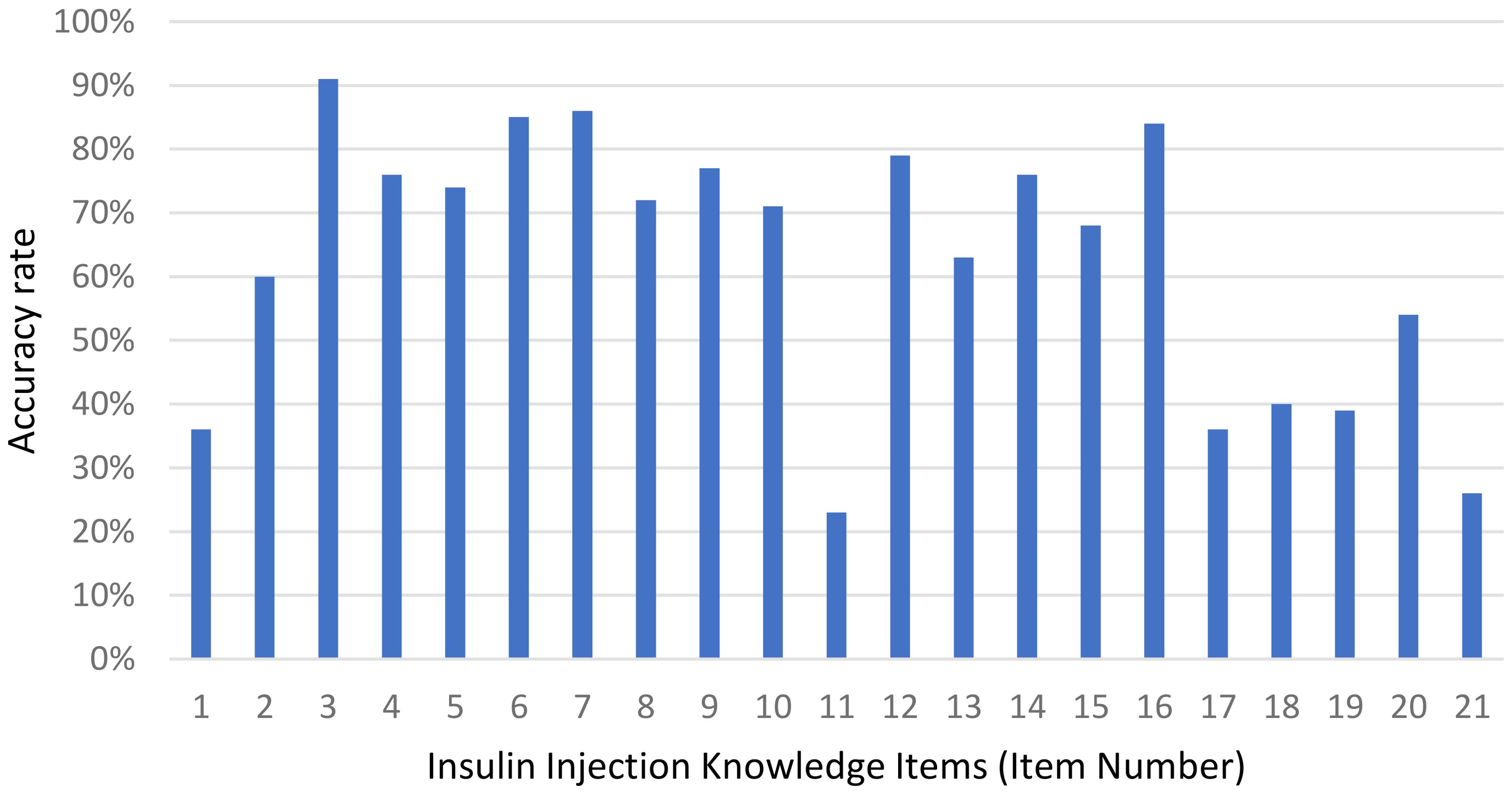
Figure 2. Accuracy rate of the responses to each insulin injection knowledge item among community nurses. Most bars exceed sixty percent, peaking at over eighty percent for items three, six, seven and sixteen, while item eleven falls below twenty-five percent.
3.3 Insulin injection attitude score
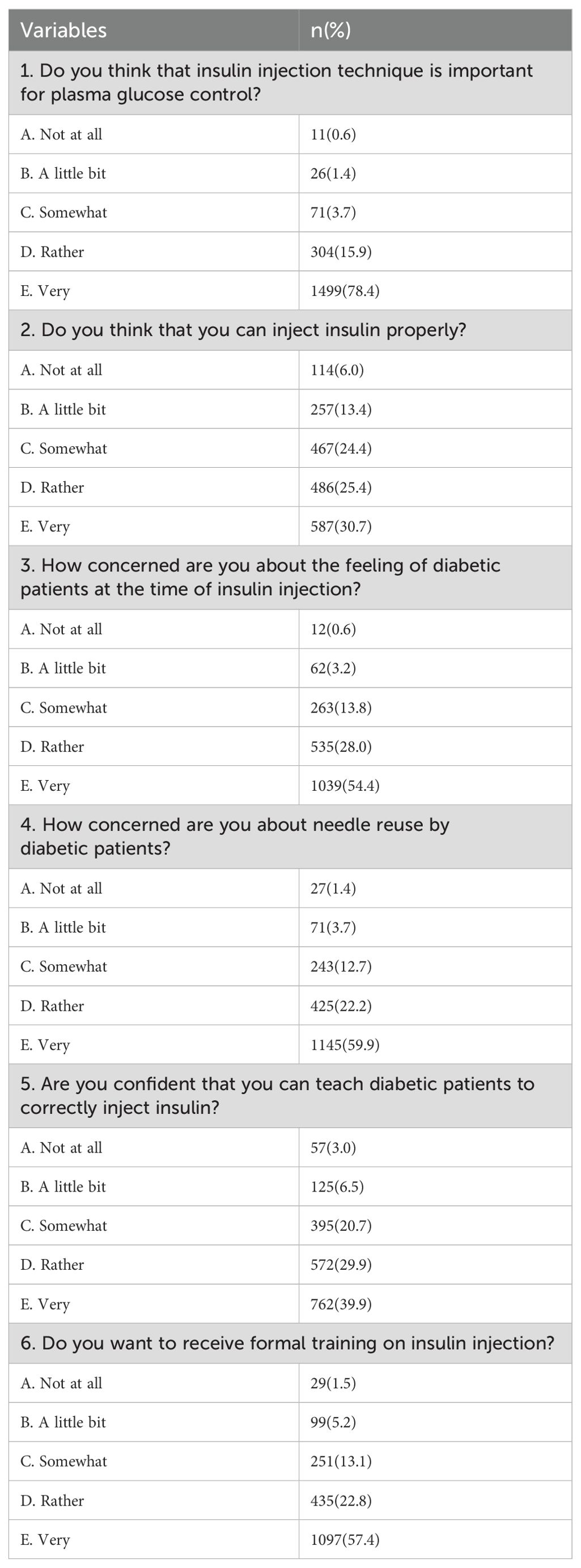
The attitude score for community nurses ranged from 4 to 20, with a mean of 17.0 ± 2.7. Figure 1 showed that most of the nurses (75.2%) had a good attitude score. Only a few nurses (3.7%) had a poor attitude score, and 21.1% had a satisfactory score. In addition, Table 2 showed 78.4% of participants considered that the insulin injection technique is important for blood glucose control, 30.7% and 39.9% of participants believed that they could inject insulin in an appropriate manner and were very confident in guiding patients with diabetes to inject insulin correctly, respectively. Moreover, more than 80% of participants were rather or very concerned about the feelings of diabetic patients with regards to insulin injections and the re-use of needles. Approximately 57% of nurses wanted to receive standardized insulin injection training.
3.4 Insulin injection practice score
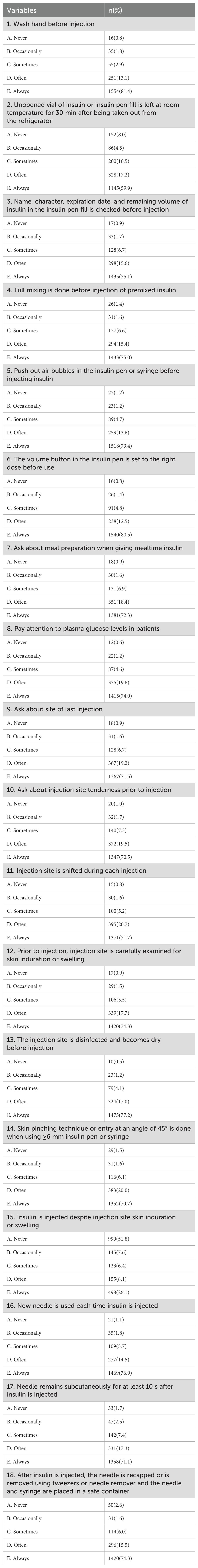
The mean insulin injection practice score for the community nurses was 80.7 ± 10.7, with a range of 18 to 90. Figure 1 showed that more than half of the nurses (85.3%) had a high practice score, and 12.2% had a satisfactory practice score. Very few nurses (2.5%) had a poor insulin injection practice score. The five most commonly performed practices (Table 3), including those performed on a regular basis, were washing hands before injection (94.5%), disinfecting the injection site and allowing to dry before injection (94.2%), caring about plasma glucose levels (93.6%), removing air bubbles prior to injection (93%), and setting the appropriate dose of insulin volume before use (93%). However, some practices were performed less commonly, including not injecting insulin when skin induration or swelling was evident (59.4%), leaving an unopened vial of insulin or leaving a full insulin pen at room temperature for 30 min after being removed from a refrigerator (77.1%), leaving the needle subcutaneously for at least 10s following insulin injection (88.4%) and checking tenderness prior to injection (90%).
3.5 Correlations between insulin injection knowledge, attitude and practice scores
Table 4 shows the results of our correlation analysis for insulin injection knowledge, attitude and practice scores in community nurses. Pearson’s correlation analysis showed that there were linear correlations between insulin injection knowledge and attitude (r=0.27, p<0.001), between insulin injection attitude and practice (r=0.54, p<0.001), and between insulin injection knowledge and practice (r=0.22, p<0.001). Spearman’s correlation analysis further confirmed these correlations between insulin injection knowledge, attitude and practice. The strongest correlations were between insulin injection attitude and practice (r=0.40), between insulin injection knowledge and attitude, and between knowledge and practice (r=0.17, p<0.001).
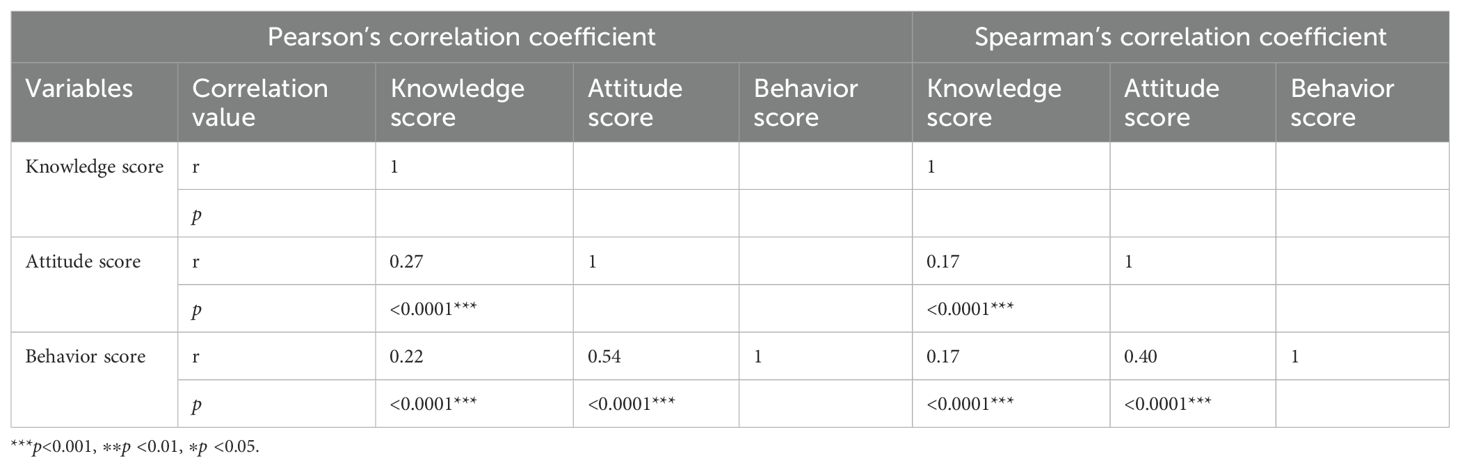
Table 4. Correlation of the insulin injection knowledge, attitude, and practice scores of community nurses (n=1911).
3.6 Factors affecting the insulin injection knowledge, attitude and practice scores
Multivariable linear regression identified distinct predictors for KAP domains (see Table 5). For knowledge, we identified area of institution (β=0.082, 95%CI: 0.371 to 1.381, p<0.01), sex (β=-0.049, 95%CI:-2.237 to -1.197, p<0.001), working experience (β=0.125, 95%CI:0.230 to 0.872, p<0.01), marital status (β=-0.074, 95%CI:-1.462 to -0.285, p<0.01), managers of the institution (β=0.052, 95%CI:0.095 to 1.862, p<0.05), knowing the latest guideline of insulin delivery (β=0.107, 95%CI:0.615 to 1.670, p<0.001) and the number of insulin injection training sessions in the last year (β=0.078, 95%CI:0.246 to 1.105, p<0.01). For attitude, we identified sex (β=-0.059, 95%CI:-0.673 to -0.073, p<0.05), working experience (β=0.146, 95%CI:0.170 to 0.544, p<0.001), having delivered insulin educations to patients (β=0.117, 95%CI: 0.353 to 0.917, p<0.001), knowing the latest guideline of insulin delivery (β=0.134, 95%CI:0.491 to 1.091, p<0.001) and numbers of insulin injection training in last year (β=0.118, 95%CI:0.337 to 0.789, p<0.001). For practice, we identified the area of institution (β=-0.047, 95%CI:-2.166 to -0.048, p<0.05), sex (β=-0.112, 95%CI:-4.107 to -1.558, p<0.001), knowing the latest guideline of insulin delivery (β=0.160, 95%CI: 2.486 to 5.303, p<0.001) and the number of insulin injection training sessions in the last year (β=0.096, 95%CI: 0.916 to 2.718, p<0.001).
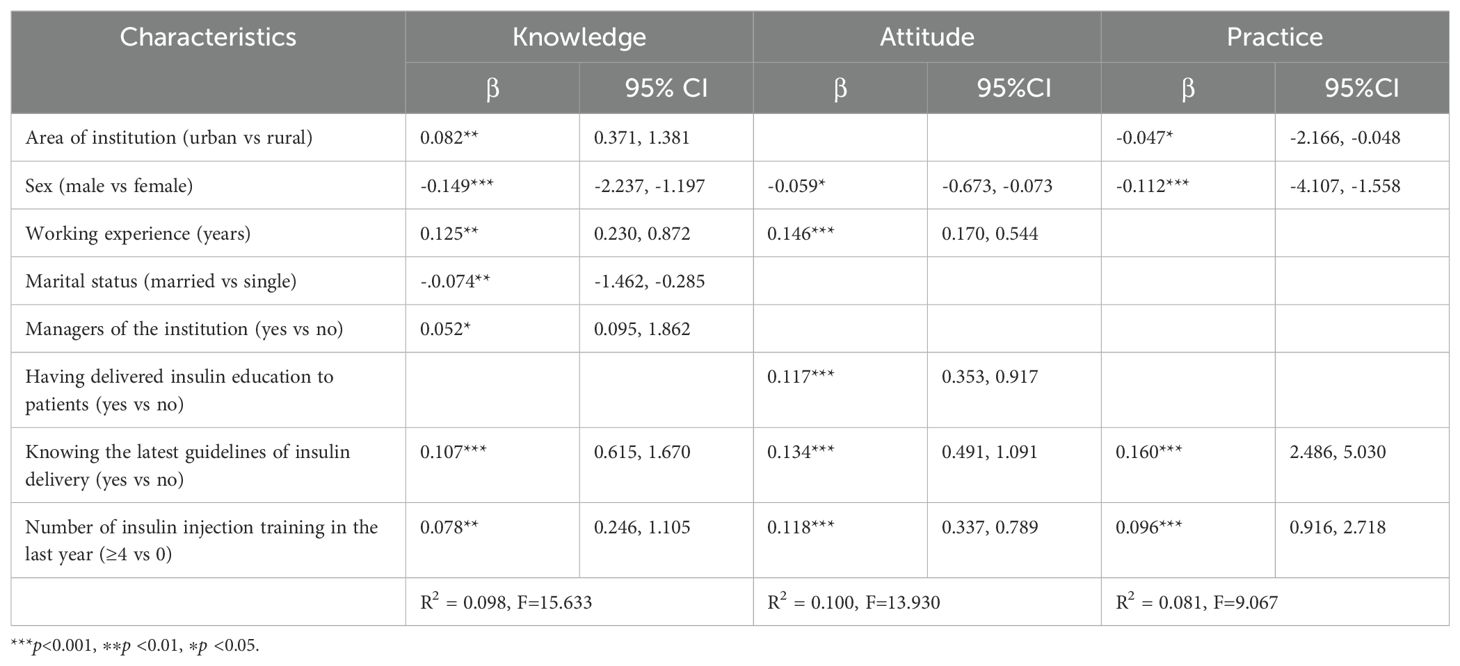
Table 5. Factors associated with insulin injection knowledge, attitude, and practice among community nurses (n=1911).
4 Discussion
Our study reveals a critical gap in delivery in that despite positive attitudes (poor attitude only 3.7%), almost half of community nurses (47.7%) had deficient knowledge; this finding is consistent with previous studies (20, 21, 27, 29, 30) but was found to be more pronounced in rural settings. More specifically, the mean level of insulin injection knowledge for community nurses in Lishui was lower than the national level (20), Guangdong province (22), and Anhui province (23), and the proportion of nurses with poor knowledge was also higher than in the areas described previously. Moreover, the mean level of insulin injection practice for community nurses in Lishui was lower than the national level (20), Guangdong province (22), and Beijing City (24), although the mean level of insulin injection practice for community nurses in Lishui was similar to that reported by Zheng et al. (23) and Liao et al. (22). These findings confirmed that the levels of knowledge, attitude, and practice related to insulin injection differ across regions of China. Nurses from primary healthcare institutions had lower levels of knowledge, attitude, and with regard to insulin injection than those in secondary or tertiary institutions (27). These findings highlight that primary healthcare institutions and nursing managers need to pay more attention to community nurses and the improvement of knowledge, attitude and practice related to insulin injections. These community nurses are primarily responsible for the prevention and treatment of diabetes at the grass-roots level; a lack of specialized knowledge, skills, and ability will not only lead to the failure of basic diabetes screening, treatment, nursing and management tasks, but also reduce the trust of residents with regards to the quality of primary care, thus affecting implementation of the National Basic Public Health Service Project; consequently, primary diagnosis and patient triage will be heavily compromised (31). Furthermore, more than half of the community nurses surveyed in Lishui City did not have adequate knowledge of the interval between two injections at the same site, the management of hypoglycemia, types of aspartic insulin, needle disposal methods, mixing methods for insulin, and the treatment of an injection site following needle withdrawal. These findings were similar to those of a previous study (22) and provide direction for future insulin injection training and education for community nurses.
In terms of the attitude of community nurses towards insulin injection training, only 57% of community nurses were willing to receive standardized training for insulin injection; this proportion was lower than the national level (67%) (20). This discrepancy may be due to limited primary care training resources, including teaching, time, and finance, and because the work of community nurses is more focused on chronic disease screening, health education, and vaccination. While the overall practice score was generally adequate, specific deficits were identified in community settings: (1) Injection into indurated/swollen skin sites, (2) Prolonged room-temperature storage (>30 minutes) of opened vials/insulin pens, (3) Premature needle withdrawal (<10 seconds post-injection). These unsafe practices—attributable to knowledge and technique gaps—demand urgent interventions to mitigate risks to patient safety, therapeutic efficacy, and primary care quality. This pattern suggests nurses may execute basic procedures correctly (potentially due to initial training or routine), but lack updated knowledge for full guideline compliance, as evidenced by a Shanghai cross-sectional study: A significant discrepancy persists between clinical practice and current guidelines regarding nurse knowledge, attitude, and practice on insulin injection (32). Thus, implementing practical, hands-on training targeting these suboptimal practices is recommended to address this knowledge-practice gap.
In addition, we identified statistically significant correlations between the knowledge, attitude and behavior scores of community nurses, thus indicating that enhancing insulin injection knowledge and attitude could improve insulin injection practice, highlighting the importance of standard insulin injection interventions or training for community nurses.
To provide tailored and effective interventions or training to improve insulin injection knowledge, attitude and practice, we should also consider the factors that influence these parameters. Male nurses had consistently lower KAP scores, potentially reflecting gendered roles in rural China where females dominate in primary care roles, leading to reduced male exposure to insulin management. These findings concurred with a previous study (33). Training emerged as a pivotal modifiable predictor across all KAP domains, underscoring an urgent need for standardized programs—particularly as 50.1% of participants received no training in the preceding year. Consequently, implementation of evidence-based training guidelines is recommended to enhance insulin injection practices (34). Furthermore, we found that sex can affect insulin injection knowledge, attitude and practice; female community nurses exhibited better performance. A previous study also reported this finding and stated that this may be due to the basic characteristics of females in that they tend to be more careful than males and pay more attention to detail (23). Furthermore, married nurses had better insulin injection knowledge than those who were single; this was consistent with the findings reported previously by Li et al. (35). It may be related to better social support from their partners and families.
Our study revealed significant geographic disparities in insulin injection knowledge and practice among community nurses. Quantitative analysis demonstrated that nurses affiliated with urban healthcare institutions exhibited superior theoretical knowledge, yet paradoxically possessed inferior practical skills compared to their rural counterparts. This dichotomy may be attributed to differential access to continuing education programs. Conversely, the enhanced procedural proficiency observed in rural nurses likely stems from higher patient volume in community care settings, providing greater opportunities for skill reinforcement. This finding aligns with the competency-development paradox described by Zhou et al. in their analysis of skill acquisition patterns among Chinese healthcare professionals (36). With the deepening implementation of the Chinese hierarchical medical system, urban-rural nursing capacity building should shift toward a Context-Adapted Development Paradigm, ultimately achieving systematic evolution from “disparity differentiation” to “functional complementarity”.
The working period was another factor that could influence insulin injection knowledge and attitude. Community nurses who had worked for a longer period had better knowledge and attitude. This finding was consistent with those reported by Zheng et al. (23) and Liao et al. (22). Managers of institutions also had a more positive attitude towards insulin injections. Working for a longer period, or being promoted to managerial level, led to an increase in clinical experience and working ability, while also creating more opportunities to participate in relevant training, thus increasing insulin injection knowledge and attitude.
Another important factor that influences insulin injection attitude is the experience of delivering education to patients. Those who had experience delivering education to patients had a more positive attitude towards insulin injections. This may be related to the fact that health education forces community nurses to systematically integrate knowledge relating to insulin injection, expose their own cognitive contradictions during the process of answering questions from patients, and through self-convincing, reconstruct their technical beliefs (such as deepening the recognition of standardized operation when explaining the impact of injection angle on absorption rate), thereby forming an internal driving force for positive attitudes. In addition, their successful health education experience continuously enhances professional confidence through the ‘ability manifestation-positive feedback’ path of social cognitive theory (37), and then positively transfers to the attitude towards injection practice.
Our findings highlight the development and delivery of standardized training sessions aligned with the latest insulin injection guidelines, focusing on high-risk groups such as unmarried and younger male community nurses. These programs should emphasize practical and hands-on components such as injection site rotation, hypoglycemia management, insulin storage/mixing and needle reuse prevention to address specific knowledge deficits identified in the study (e.g., 47.7% poor knowledge rate). In addition, healthcare institutions and policy makers should establish quarterly or bi-annual refresher workshops incorporating case-based simulations and peer evaluations. This ensures sustained knowledge retention and practice improvement, leveraging the positive attitudes of nurses while mitigating factors, such as limited training experience or rural location disparities, highlighted in the regression analyses.
This study employed a rigorously calculated sample size of 1,911 community nurses across 30 healthcare centers in Southwest Zhejiang, covering diverse economic regions (low, medium and high GDP counties) and both urban/rural settings. The cluster random sampling method ensured proportional representation of the target population (less-developed mountainous areas), addressing a critical gap in existing research that typically focuses on developed regions. This enhances the external validity and generalizability of findings to similar underserved areas in China.
Some limitations of this study should be considered. Firstly, this study was conducted exclusively in Lishui, a mountainous region characterized by economic constraints (the lowest GDP in Zhejiang), ethnic diversity (a minority group settlement area), and geographic isolation (90% mountainous terrain). These factors may limit the direct extrapolation of our findings to other Chinese regions. Therefore, our findings cannot be generalized to other community nurses. Despite regional specificity, our results may reflect challenges faced by nurses in comparable underdeveloped or rural areas of China, such as limited training resources, high patient loads in primary care, and geographic barriers to continuing education. We recommend replicating this study in other underdeveloped provinces (e.g., Guizhou and Yunnan) to assess the transferability of our conclusions. Secondly, the instruments used in this study were self-rated and therefore lacked objectivity. Future studies should aim to combine subjective and objective instruments, including an on-site operation checklist, to acquire stronger evidence relating to insulin injection among community nurses. Thirdly, the relatively low explanatory power of our regression models (R²=0.08-0.10) highlights constraints in capturing the full complexity of insulin injection KAP. This likely stems from unmeasured contextual variables (e.g., institutional training resources, nurse-patient interaction time) and the binary operationalization of some predictors. Crucially, our sampling design (nurses were nested within centers) suggests that multi-level modeling could better disentangle individual- and organizational-level effects. Future investigations should adopt Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) or multi-level analysis to incorporate center-specific variables (e.g., rural/urban resource disparities) and explore cross-level interactions.
5 Conclusion
Community nurses in Southwest Zhejiang demonstrated suboptimal knowledge regarding insulin injection techniques and management despite generally positive attitudes and practices. To address this identified deficiency, we propose the implementation of mandatory, evidence-based training programs aligned with current clinical guidelines, with prioritization given to identified high-risk subgroups (e.g., male, newly employed nurses). Furthermore, healthcare institutional administrators and policy makers should leverage telehealth platforms and mobile supervision systems to mitigate urban-rural disparities in knowledge accessibility during this digital transformation era.
Original Research article.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the ethical review committee of Lishui University (2023YR0029). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
XL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SZ: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. XJ: Data curation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. LC: Data curation, Investigation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. LZ: Data curation, Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. BY: Data curation, Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. QZ: Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. XZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. SL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Health Science and Technology Program of Zhejiang Province, China (No. 2025KY2003).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all community nurses for participating in this study. Additionally, the authors express gratitude to EditSprings (https://www.editsprings.cn) for their expert linguistic services.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. Author Contributions XL, XZ and SL were responsible for conceptualization, design, and data acquisition. MC, SZ, LC, LZ, XJ, and BY conducted data acquisition and analysis. XL, XZ, and SL was responsible for drafting the manuscript. MC, SL and XL were responsible for the literature review. XL, XZ, and SL made critical revisions to the paper. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript. XL and XZ are the guarantors of this work.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2025.1501992/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Basu S, Yoffe P, Hills N, and Lustig RH. The relationship of sugar to population-level diabetes prevalence: an econometric analysis of repeated cross-sectional data. PloS One. (2013) 8:e57873. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057873
2. International diabetes federation[IDF]. International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas 2021, 10th Edition. Belgium, Brussels: International Diabetes Federation (2022).
3. Zhou Y, Liu JM, Zhao Z, Zhou M, and Ng M. The national and provincial prevalence and non-fatal burdens of diabetes in China from 2005 to 2023 with projections of prevalence to 2050. Mil Med Res. (2025) 12:28. doi: 10.1186/s40779-025-00615-1
4. Chinese Association of Diabetes and Microcirculation Department of Primary Diabetes Care, Primary Health Branch of China International Exchange and Promotion Association for Medical and Healthcare, and Jiangsu Incubation Federation for Specialized Endocrinology Department of Communite Hospital. Expert consensus on screening and prevention of diabetic microangiopaopathy (2021 edition). Chin J Front Med Science(Electronic Version). (2021) 13:16–38.
5. Chinese Center for the Prevention and Control of Chronic Non-communicable Diseases. Chronic Diseases and Risk Factors Surveillance Report in China. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House (2021).
6. Ji L, Guo X, Huang J, and Ji Q. China diabetes medication injection technical guidelines (2016 edition). Chin J Diabetes Mellitus. (2017) 9:79–106. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-5809.2017.02.005
7. Gorska-Ciebiada M, Masierek M, and Ciebiada M. Improved insulin injection technique, treatment satisfaction and glycemic control: results from a large cohort education study. J Clin Transl Endocrinol. (2020) 19:100217. doi: 10.1016/j.jcte.2020.100217
8. Chinese Diabetes Society and National Office for Primary Diabetes Care. National guidelines for the prevention and control of diabetes in primary care (2022). Chin J Intern Med. (2022) 61:249–62. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112138-20220120-000063
9. Lin J, Xiao X, and Chen J. Analysis on the use of hypoglycemic drugs in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes New World. (2022) 25:107–10. doi: 10.16658/j.cnki.1672-4062.2022.19.107
10. Zhou T, Zheng Y, Li J, and Zou X. Insulin injection technique and related complications in patients with diabetes in a Northwest City of China. J Eval Clin Pract. (2024) 1–13. doi: 10.1111/jep.14226
12. He J. Analysis on the Procurement of Diabetes Drugs and Influencing Factors in Gansu Province from 2018 to 2022. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University (2024).
13. Li J. The Free Medication Policy for Patients with Hypertension and Diabetes on the Small Island of Xuanshui Has Benefited 12,446 People, Reducing the Medication Expenses for the Masses by over 260,000 Yuan. Zhoushan, Zhejiang: Putuo News Network (2024). Available online at: https://ptnews.zjol.com.cn/putuo/system/2024/08/15/034707928.shtml (Accessed July 25, 2025).
14. Kalra S, Pathan F, Kshanti IAM, Bay NQ, Nagase T, Oliveria T, et al. Optimising insulin injection techniques to improve diabetes outcomes. Diabetes Ther. (2023) 14:1785–99. doi: 10.1007/s13300-023-01460-y
15. Spollett G, Edelman SV, Mehner P, Walter C, and Penfornis A. Improvement of insulin injection technique: examination of current issues and recommendations. Diabetes Educ. (2016) 42:379–94. doi: 10.1177/0145721716648017
16. Sow A, Boiro D, Sow PS, Niang B, Mbaye A, Barrage AL, et al. Insulin therapy in childhood type 1 diabetes: knowledge and practice in Senegal. Arch Pediatr. (2021) 28:307–10. doi: 10.1016/j.arcped.2021.02.006
17. Dagdelen S, Deyneli O, Olgun N, Siva ZO, Sargin M, Hatun S, et al. Turkish insulin injection techniques study: complications of injecting insulin among turkish patients with diabetes, education they received, and the role of health care professional as assessed by survey questionnaire. Diabetes Ther. (2018) 9:1615–28. doi: 10.1007/s13300-018-0463-8
18. Kalra S, Mithal A, Sahay R, John M, Unnikrishnan AG, Saboo B, et al. Indian injection technique study: injecting complications, education, and the health care professional. Diabetes Ther. (2017) 8:659–72. doi: 10.1007/s13300-017-0244-9
19. Khan AR, Al Abdul Lateef ZN, Khamseen MB, Al Aithan MA, Khan SA, and Al Ibrahim I. Knowledge, attitude and practice of ministry of health primary health care physicians in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional study in the al hasa district of Saudi Arabia, 2010. Niger J Clin Pract. (2011) 14:52–9. doi: 10.4103/1119-3077.79241
20. Wu X, Zhao F, Zhang M, Yuan L, Zheng Y, Huang J, et al. Insulin injection knowledge, attitudes, and practices of nurses in China: A cross-sectional nationwide study. Diabetes Ther. (2021) 12:2451–69. doi: 10.1007/s13300-021-01122-x
21. Adhikari S, Poudel RS, Rajbanshi L, and Shrestha S. Assessment of insulin injection practice of nurses working in a tertiary healthcare center of Nepal. Nurs Res Pract. (2018) 2018:9375067. doi: 10.1155/2018/9375067
22. Liao Y, Liu X, Huang J, Chen Q, Li N, and Zhou P. Insulin injection knowledge, attitude and behaviour of nurses: A cross-sectional study in guangdong province. Nurs Open. (2023) 10:3754–65. doi: 10.1002/nop2.1633
23. Zheng J, Guan X, Zheng H, Wu C, Xu J, and Zhang Y. Analysis of the present situation and influencing factors of nurses’ Knowledge, belief and practice of insulin injection in Anhui Province. J Shenyang Med Coll. (2023) 25:278–83. doi: 10.16753/j.cnki.1008-2344.2023.03.012
24. Liu F, Zhao S, Peng T, Shao Y, Wang Q, Zhang M, et al. A cross-sectional study on the status of insulin injection knowledge, belief and practice among non-endocrinology internal medicine nurses in Beijing. J China-Jap Fri Hosp. (2022) 36(5):287–90,294. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0025.2022.05.007
25. Commission. NH. Notice from the Office of the National Health Commission on Issuing the Evaluation Guidelines for Service Capabilities of Township Health Centers (2023 Edition) and the Evaluation Guidelines for Service Capabilities of Community Health Centers (2023 Edition) (2023). Available online at: https://www.nhc.gov.cn/wjw/c100175/202312/c3c0678f2f0a489ea668783ce43d6b97.shtml (Accessed July 25, 2025).
26. Liu H and Li Y. Exploring the importance of community nurses in the initiation of insulin therapy for type 2 diabetes patients. Chin Remedies Clin. (2017) 17:1675–96. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn114798-20200401-00401
27. Wang Y, Wang Y, Lu J, Pan X, and Hu Y. The knowledge, attitude, practice and training demands of insulin injection among nurses in a medical alliance in Shanghai. Nurs J Chin PLA. (2019) 36:75–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9993.2019.06.021
28. Er. SYM. The Gdp Rankings for Various Districts and Counties of Lishui in 2024 Have Been Released: Liantuo Remains at the Top, While Longquan Has Surpassed 20 Billion Yuan (2025). Available online at: https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1823949913503054471&wfr=spider&for=pc (Accessed July 25, 2025).
29. Yacoub MI, Demeh WM, Darawad MW, Barr JL, Saleh AM, and Saleh MY. An assessment of diabetes-related knowledge among registered nurses working in hospitals in Jordan. Int Nurs Rev. (2014) 61:255–62. doi: 10.1111/inr.12090
30. Theofanidis D. In-hospital administration of insulin by nurses in northern Greece: an observational study. Diabetes Spectr. (2017) 30:175–81. doi: 10.2337/ds16-0001
31. Yuan B, He P, Xu J, Zhang W, Xu H, Wei Q, et al. Integration of medical care and preventionin primary health care system: construction of conceptual framework and measurement index system. Chin J Health Policy. (2022) 15:11–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2982.2022.09.003
32. Cui P, Zhou Y, Zhang M, Zhao F, Yuan L, Xiao L, et al. Investigation and research of the gap between clinical practice and guidelines of nurse knowledge, attitude and practice on insulin injection. Chin J Nurs. (2023) 58:1179–85. doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2023.10.004
33. Dai M, Liang H, and Huang J. Investigation of insulin injection knowledge, belief and practice among clinical nurses from grade three general hospitals. J Nurs Sci. (2019) 34:60–3. doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.2019.24.060
34. Yang W. Effects of Guidence Training on Intravenous Injection of Insulin in Non-Endocrine Nurses. Suzhou: Suzhou University (2017).
35. Li S, Fu R, Zhang H, Zhang N, and Gu T. Status quo of knowledge, attitude and behavior of insulin injection among nurses of non-endocrinology department and analysis of structural equation model. China Med Herald. (2020) 17:161–5. doi: 10.20047/j.issn1673-7210.2020.26.038
36. Zhou C, Wu L, Wu X, Xiao H, Wang J, and Bai G. Investigation and analysis of training needs for community nurses in urban and rural areas. Chin Nurs Manage. (2013) 13:84–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1756.2013.010.030
Keywords: diabetes mellitus, insulin injection, community nurses, knowledge, attitude, practice, determinants
Citation: Lan X, Zheng S, Ji X, Chen L, Zhou L, Ye B, Zhu Q, Zheng X and Lu S (2025) Insulin injection knowledge, attitude, and practice of community nurses in a mountainous area of southwest Zhejiang in China: a multi-center cross-sectional study. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1501992. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1501992
Received: 05 November 2024; Accepted: 29 July 2025;
Published: 18 August 2025.
Edited by:
Muhammad Shahzad Aslam, Xiamen University, Malaysia, MalaysiaReviewed by:
Samar Ahmed Amer, Zagazig University, EgyptSusan Míriam Oblitas Guerrero, Lord of Sipan University, Peru
Mulugeta Russom, Eritrean Pharmacovigilance Centre, Eritrea
Copyright © 2025 Lan, Zheng, Ji, Chen, Zhou, Ye, Zhu, Zheng and Lu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaojia Zheng, enhqcXF6akAxMjYuY29t; Shunfei Lu, bHVzaHVuZmVpQGxzdS5lZHUuY24=
 Xuefen Lan
Xuefen Lan Simin Zheng1
Simin Zheng1