- 1Department of Endocrinology, Nanjing First Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China
- 2Department of Endocrinology, the Affiliated Wuxi People’s Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Wuxi People’s Hospital, Wuxi Medical Center, Nanjing Medical University, Wuxi, China
Aim: Patients on premixed insulin therapy usually have poor glycemic control. This study aimed to investigate the effect of vildagliptin in these patients.
Methods: This real-world study included patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), who were poorly glycemic controlled on premixed insulin therapy and were subsequently added vildagliptin. The control group consisted of patients who only had their insulin doses adjusted without adding vildagliptin, matched for age, diabetic duration, HbA1c, and BMI. All patients underwent FGM, glycated hemoglobin(HbA1c), and glycated albumin(GA) measurements at baseline and three months after the treatment adjustment.
Results: Patients receiving vildagliptin treatment demonstrated significant reductions in HbA1c and GA levels (P<0.001 and P=0.009, respectively). The vildagliptin group exhibited a remarkable decrease in the mean amplitude of glycemic excursion (MAGE) (8.58 ± 0.36 vs. 6.62 ± 0.47, P<0.001), along with notable reductions in mean blood glucose (MBG) (10.7 ± 0.34 vs. 8.82 ± 0.39, P<0.001) and time above the target range (TAR) (52.60 ± 3.44 vs. 31.59 ± 4.31, P<0.001) compared to the control group. Moreover, there were notable improvements in the duration spent within the target range (TIR) (45.64 ± 3.33 vs. 64.22 ± 4.00, P<0.001), along with increases in the areas under the curve (AUC) for blood glucose levels above 4.4 (426.82 ± 83.19 vs. 892.16 ± 185.27, P=0.018) and 3.9 (213.81 ± 47.20 vs. 454.77 ± 103.21, P=0.029). Hourly mean blood glucose levels over a 2-week period monitored by FGM indicated lower blood glucose levels in the vildagliptin group, particularly after dinner (P=0.022).
Conclusion: Vildagliptin added to premixed insulin effectively lowers blood glucose levels and reduces glycemic variability in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Clinical Trial Registration: https://clinicaltrials.gov, identifier NCT04847219.
1 Introduction
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) has become increasingly prevalent worldwide, emerging as a major public health concern (1). The disease is characterized by sustained hyperglycemia, often accompanied by pancreatic β-cell dysfunction, insulin resistance, and immune inflammation, which collectively contribute to its progression (2). Disruptions in multiple metabolic pathways play a crucial role in the development of T2DM complications, which are major drivers of morbidity and mortality (3). The increasing prevalence of T2DM, along with its long-term complications, imposes a substantial economic burden on healthcare systems worldwide (4).
As the disease progresses, in many cases patients with T2DM need to be treated with insulin to help them better achieve their intended therapeutic goals (5). This indicates the necessity of insulin regimens that focus on strict postprandial glucose control. As a result, premixed insulin has become a widely used option for initiating insulin therapy in China due to its greater convenience in managing both basal and prandial glucose (6). Premixed insulin combines both basal and prandial insulin, and while this simplifies the dosing regimen, it leads to less flexibility in managing glucose levels. This reduced flexibility can result in a mismatch between insulin action and meal timing, increasing the likelihood of both mild and severe hypoglycemia (7). Studies indicate that patients using premixed insulin tend to experience more frequent hypoglycemic events compared to those on basal-bolus regimens (8). Premixed insulin may also cause larger fluctuations in blood glucose levels. Its fixed ratio of rapid-acting and long-acting components makes it difficult to adjust insulin doses precisely to cover varying postprandial and fasting glucose needs (9).
As a result, patients on premixed insulin therapy often experience significant swings in blood glucose levels, which can increase the risk of complications. Large blood glucose variability may be a risk factor for stroke and heart disease in individuals with T2DM, regardless of their glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels (10). Studies also indicate that glucose variability is associated with microvascular complications such as retinopathy, neuropathy, and nephropathy. These fluctuations lead to cellular damage by inducing excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), exacerbating oxidative stress, and inflammation and activating harmful signaling pathways (11).Aggressive modification of the treatment regimen is needed to reduce the patient’s level of glycemic fluctuation and to reduce complications.
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4(DPP-4)inhibitors can effectively improve blood glucose control in individuals with T2DM and notably decrease glucose variability when compared to alternative oral medications for diabetes (12, 13). Vildagliptin is one of the drugs in the class of DPP-4 inhibitors (14). This DPP-4 inhibitor enhances islet cell function by promoting insulin secretion and suppressing glucagon release. Patients with T2DM have been observed to have altered levels of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), which may contribute to glucose regulation (15, 16). As an adjunct therapy for patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes, vildagliptin produces dose-dependent reductions in HbA1c and FPG (17). A systematic review also concluded that vildagliptin has a good safety profile and a relatively low risk of causing hypoglycemia compared with other diabetes medications (18). Vildagliptin improves blood glucose variability by reducing metrics such as the Mean Amplitude of Glycemic Excursions (MAGE). Therefore, the efficacy and safety of the combination of vildagliptin with premixed insulin remains unclear.
Therefore, we conducted this real-world study to assess the effect of vildagliptin on glycemic variability using FGM before and after a 90-day treatment in patients on premixed insulin therapy.
2 Methods
2.1 Subjects
This research project is a secondary analysis of a premixed insulin study, which was conducted in the outpatients from the department of Endocrinology of five hospitals in Jiangsu Province from October 2019 to April 2021(ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04847219). The study was approved by the ethics committee of Nanjing First Hospital before it was conducted. All operations were in accordance with the ethical standards of the hospital and the 1964 Helsinki Declaration revised in 2013. Every patient submitted signed consent forms to participate in this study.
The inclusion criteria were as follows: 1)type 2 diabetes patients who met WHO1999 diagnostic criteria injected premix insulin subcutaneously, used a single drug or a combination of oral hypoglycemic medications for more than two months were on a stable treatment regimen; 2)no acute complications associated with diabetes, such as ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar disease; 3)FGM examinations, diets, and exercises are readily accepted by the subjects.
Exclusion criteria included the following: 1)within the last 3 months, patients who have taken GLP-1 agonists; 2)patients with insulin allergies; 3)the ALT was 2.5 times higher than the upper limit of normal value, and the serum creatinine level was 1.3 times higher than the upper limit of normal; both liver and renal function were impaired; 4)an alcohol or drug abuse history within the last five years; 5)last 3 months have been treated with systemic hormones; 6)poorly compliant and irregularly exercising patients; 7)infected and stressed patients within four weeks; 8)patients who cannot tolerate flash glucose monitoring; 9)pregnant, nursing, or pregnant patients; 10)additional conditions or complications that the investigator determines to be present, including severe heart disease, endocrine disease, lung disease, tumor disease, neurological disease, past mental illness, etc.
Both the control and experimental groups were selected using identical inclusion and exclusion criteria.
2.2 Study design
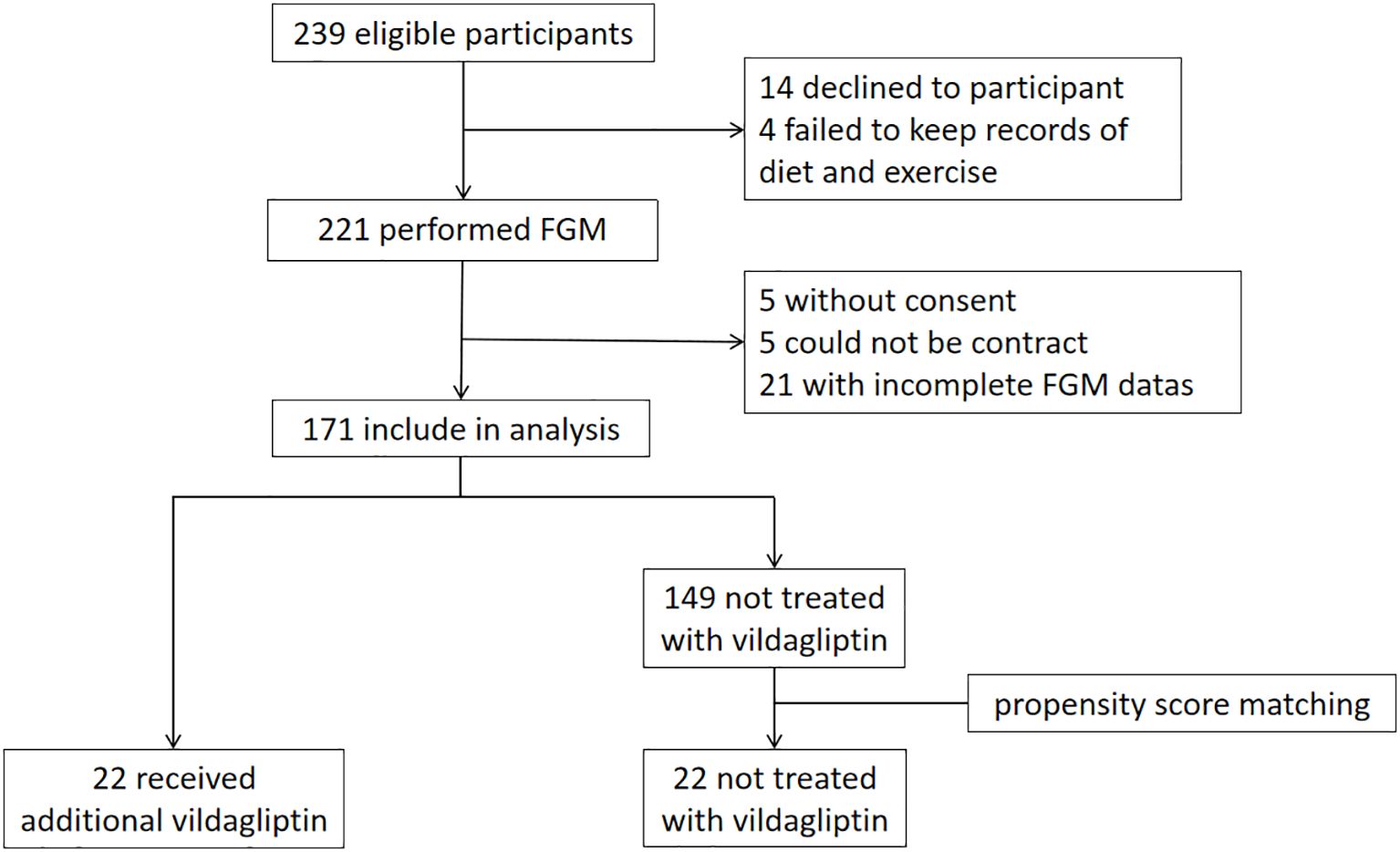
Figure 1 shows the outline of the study. Patients received FGM testing for 14 days at the beginning of the study. C-peptide, HbA1c, GA, glucagon and insulin levels were tested. Height, weight, and insulin dosage were recorded. Patients made adjustments to their insulin or oral medication regimen based on the results of FGM and the blood tests. Insulin doses were further adjusted during follow-up visits according to blood glucose levels, with FGM testing repeated after 3 months and subsequent reassessment of C-peptide levels, HbA1c, etc.
Based on this study, patients who received additional vildagliptin treatment during the premixed insulin study were chosen as the vildagliptin group (n=22). The control group was selected from the remaining patients who were not treated with vildagliptin through propensity score matching adjusted for age, duration of diabetes, HbA1c, BMI, and metformin dosage (n=22).
The blood glucose changes before and after treatment were compared between the two groups of patients. Glucagon and insulin concentrations in plasma were measured by radioimmunoassay, and C-peptide concentrations were measured by electrochemiluminescence. We measured HbA1c with high-performance liquid chromatography (BioRad, Diastat HbA1c analyzer) and glycated albumin (GA) with a peroxidase kit (Jiuqiang).
2.3 Statistical analysis
The statistical analysis was carried out utilizing SPSS23.0 software (SPSS, IL, USA). Data from normal distribution were expressed as mean ± standard error (SE), and data from nonnormal distribution were expressed as median in quartile ranges. The percentage of hypoglycemic drugs and the number of subjects with diabetes complications were analyzed using the chi-square test, and the data collected before and after treatment were evaluated using the Student paired t-test or Wilcoxon test. Hourly mean blood glucose concentrations assessed by two FGMs at baseline and endpoint were analyzed by Repeated Measures ANOVA with time as the within-subject factor and groups as the between-subject factor. The significance level was 5%.
3 Results
3.1 Baseline characteristics
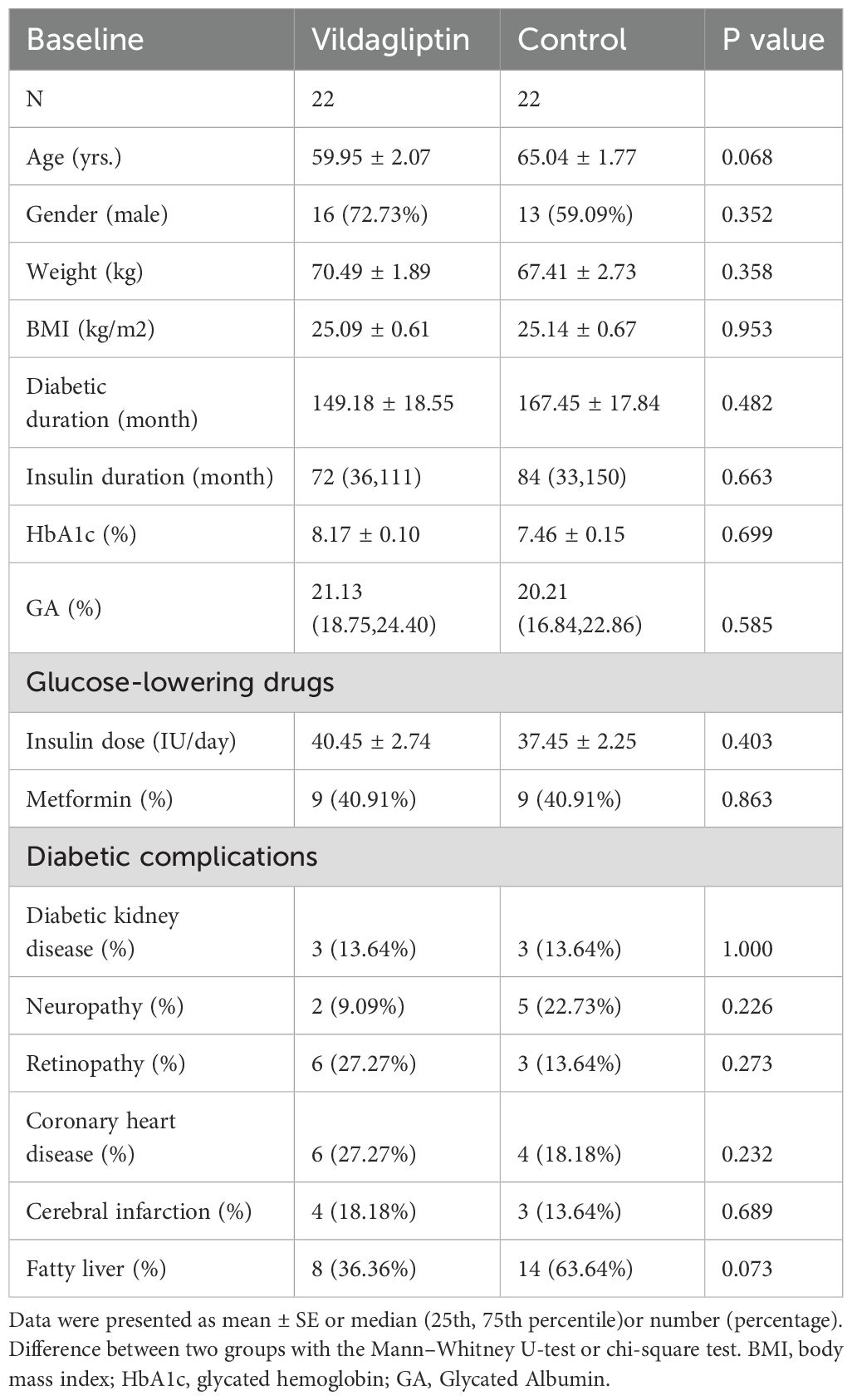
In this study, 44 patients with T2DM were enrolled. 22 patients were enrolled in the vildagliptin group, and another 22 patients who did not take vildagliptin were matched as controls. Baseline characteristics included age, gender, weight, BMI, diabetic duration, insulin duration, HbA1c, GA, glucose-lowering drugs, and diabetic complications. At baseline, no significant differences were found between the two groups in terms of any of the characteristics (P all > 0.05, Table 1).
3.2 Blood parameters
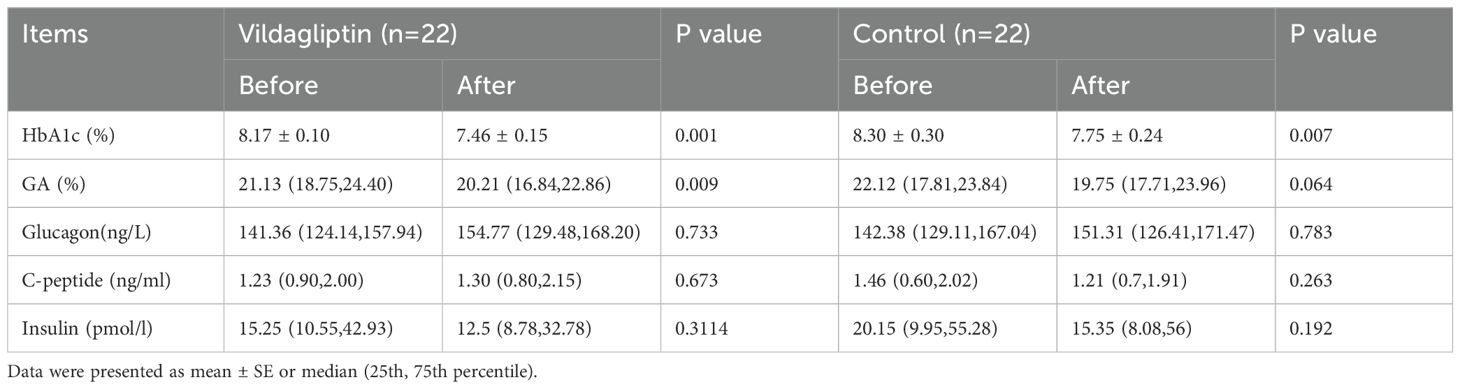
HbA1C levels significantly decreased after 3 months in both groups, while GA levels only showed a superior decrease in the vildagliptin group (P<0.05). No significant difference was found in the change of glucose, C-peptide, and insulin between the two groups (Table 2).
3.3 Glycemic control
After vildagliptin treatment, significant reductions were observed in mean blood glucose (MBG), MAGE, time above the target range (TAR)(P all <0.05), and significant increases in time in the target range (TIR), time below the target range (TBR), AUC(Area Under the Curve)>4.4, and AUC>3.9 after treatment as compared with those before treatment (P all <0.05) (Table 3).
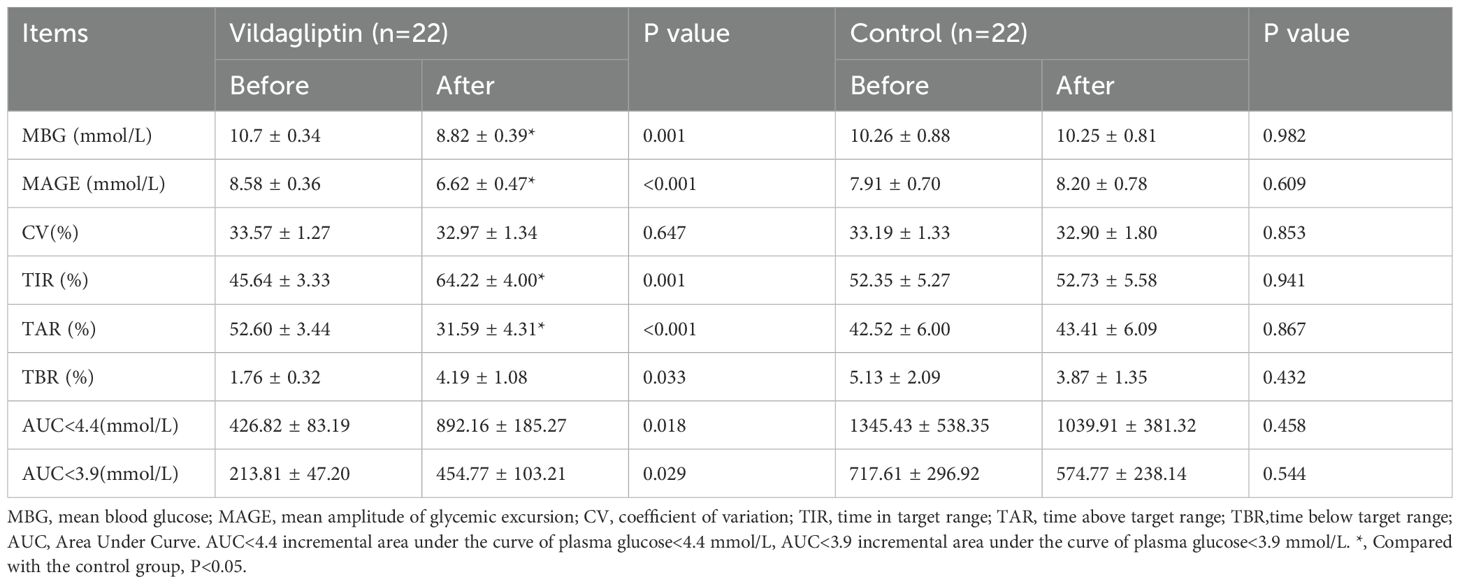
Table 3. Changes in blood glycemic excursion parameters in the the vildagliptin and control groups before and after therapy.
In addition, we compared the vildagliptin group with the control group after treatment using covariance analysis. In the vildagliptin group, MBG, MAGE, and TAR were significantly lower than in the control group at the end of treatment, while TIR showed a significant increase (P<0.05) (Table 3).
The change of blood glucose levels = blood glucose levels after treatment - blood glucose levels before treatment. Compared to the control group, patients taking vildagliptin showed superior reductions in MBG, MAGE and TAR (estimated treatment difference: -1.871 ± 0.734, -2.264 ± 0.75, -21.9 ± 7.223, P=0.015, 0.003 and 0.004, respectively, Figure 2A-C) and superior increase in TIR (estimated treatment difference:18.21 ± 6.971, P=0.012, Figures 2D). In either group, there were no significant differences in the change of TBR (Figure 2E).
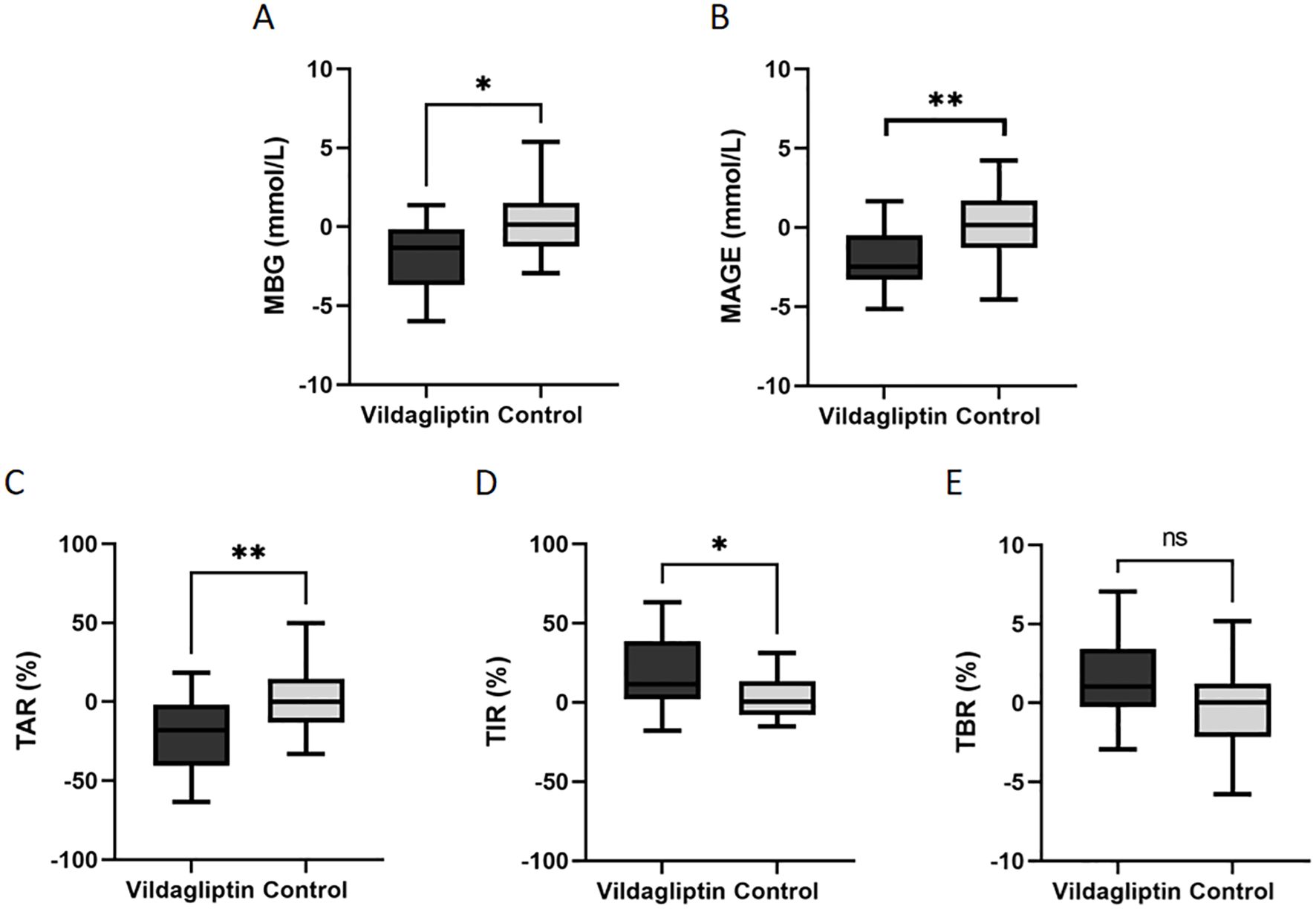
Figure 2. Changes in the levels of mean blood glucose(MBG), mean amplitude of glycemic excursion(MAGE), time above the target range(TAR), time in the target range (TIR) and time below the target range(TBR) between the vildagliptin and control groups. Data are mean ± SE. *, p < 0.05 between the two groups; **, p < 0.001 between the two groups. ns, not significant (P ≥ 0.05).
3.4 The insulin dosage
Compared to the control group (30.45 ± 10.55vs.37.09 ± 11.30, P=0.603), patients in the vildagliptin group experienced a more significant reduction in daily insulin dosage before and after treatment (40.45 ± 1.86vs.36.68 ± 15.13, P=0.050). However, there was no significant difference in daily insulin dosage between the two groups after treatment(37.09 ± 11.30vs.36.68, P=0.705).
3.5 The change in hourly mean blood glucose concentrations
The vildagliptin group had significantly lower hourly mean blood glucose concentrations following 3 months of treatment than the control group (P=0.016, Figure 3). Participants who took vildagliptin after two 14-day FGM periods had lower blood glucose levels as measured by hourly mean blood glucose, especially after dinner (18:00) (8.53 ± 0.41vs.10.01 ± 0.59, P=0.022, Figure 3) which were similar between the two groups at baseline (P all >0.05). Nocturnal blood glucose changed similar (P all >0.05, Figure 3). Compared to the FGM at baseline, vildagliptin significantly decreased the hourly mean blood glucose during the second FGM (P=0.001).
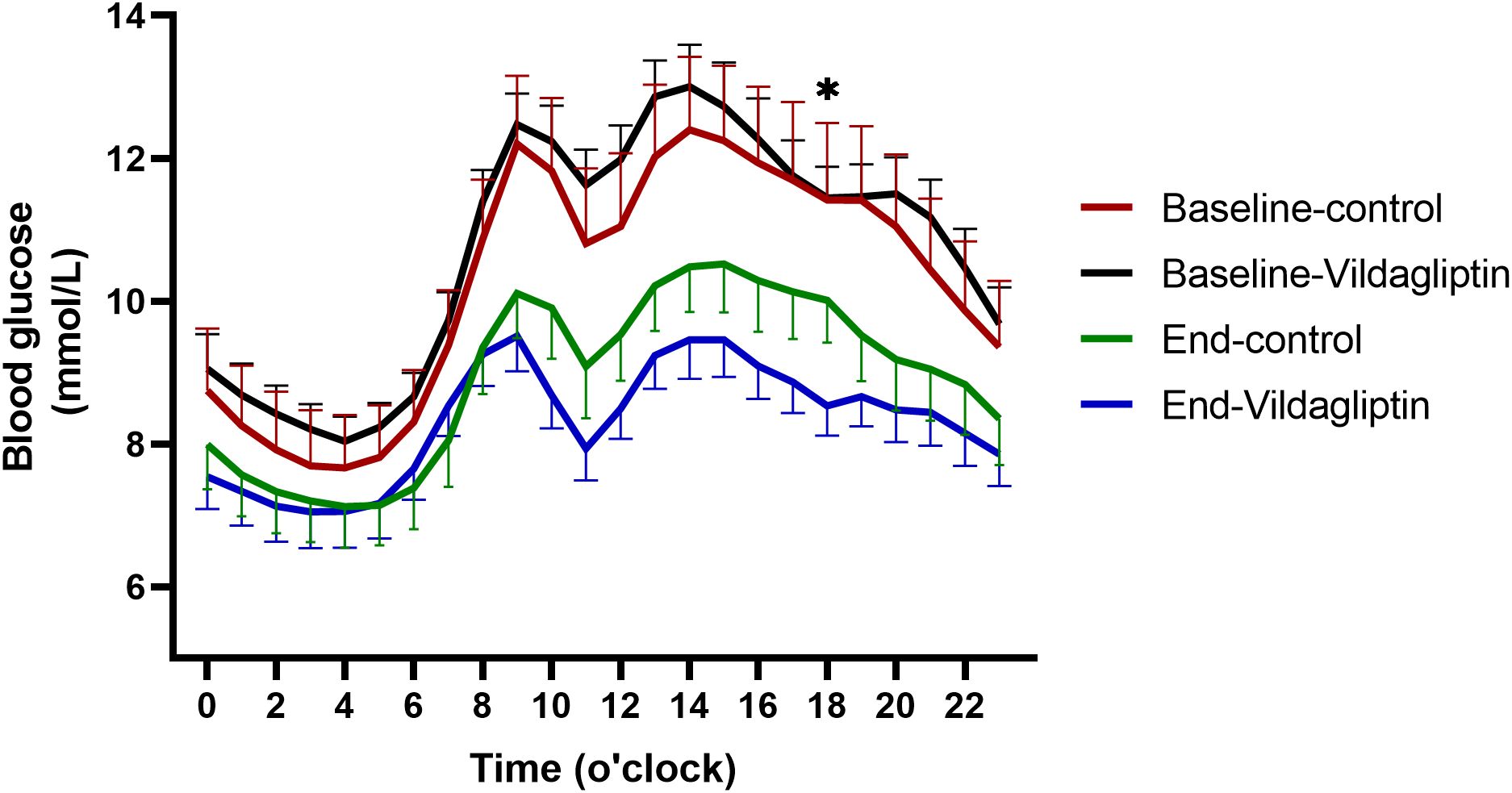
Figure 3. Hourly mean blood glucose during the first and second FGMs. Red solid line, first FGM in the control group(n=22); green solid line, second FGM in the control group; black solid line, first FGM in the vildagliptin group(n=22); blue solid line, second FGM in the vildagliptin group. *p < 0.05 between the end of two groups.
4 Discussion
In this real-world study, it can be inferred that vildagliptin, acting as a DPP-4 inhibitor, demonstrates efficacy in lowering average blood glucose levels and diminishing the average magnitude of glycemic fluctuations in individuals.
Vildagliptin can prolong the half-life of incretin hormones such as glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), by inhibiting the activity of DPP-4 (19). GLP-1 and GIP stimulate insulin secretion and suppress glucagon release in the gastrointestinal tract, aiding in the maintenance of blood sugar levels (20). Consequently, the use of vildagliptin is associated with reducing blood glucose variability, contributing to improved glycemic control in patients.
We found that vildagliptin significantly reduced HbA1c and GA levels in patients treated with premixed insulin. At the endpoint of the study, HbA1c levels in the vildagliptin group showed a notable reduction of 1.1%, compared to a 0.6% decrease in the control group. Previous studies in western populations have demonstrated similar outcomes (21), but the more pronounced reduction observed in our study suggests that Asian patients may exhibit heightened responsiveness to vildagliptin (22). Asians tend to have a higher proportion of visceral fat, and even those with normal or low body weight often exhibit higher insulin sensitivity (23, 24), which may contribute to better glycemic control. A study conducted in Japanese patients showed similar findings, with an HbA1c reduction of 1.0% following vildagliptin treatment (25).
Through FGM we observed that after 3 months of treatment with vildagliptin add-on premixed insulin, the hourly mean blood glucose concentration was significantly lower than treatment with premixed insulin alone. Vildagliptin particularly reduced postprandial glucose levels following dinner. Previous studies have similarly found that compared to gliclazide or other diabetes-lowering medications, vildagliptin provides a more pronounced improvement in postprandial glucose control (26, 27). This may be attributed to its beneficial effects on β-cell function, which helps in achieving better overall glycemic control throughout the day (28, 29). In our study, the addition of vildagliptin was associated with reduced 24-hour glucose variability. Similar results have been observed in comparisons between vildagliptin and sitagliptin, where vildagliptin demonstrated a lower MAGE and reduced postprandial glucose levels (30), contributing to improved overall glucose management.
After treatment with vildagliptin, a significant reduction in the daily insulin dosage was observed. This aligns with previous studies that have reported decreased daily insulin requirements in patients receiving combined vildagliptin and insulin therapy (31). The reduction was particularly pronounced in patients who had been on high insulin doses for many years (32). A lower insulin dosage reduces the risk of hypoglycemia and mitigates weight gain associated with high insulin intake (33). Additionally, decreasing insulin requirements alleviates the treatment burden on patients, enhances their quality of life, improves adherence to therapy, and contributes to better overall treatment outcomes (34).
Previous studies have demonstrated that vildagliptin exhibits both strong efficacy and safety, particularly by reducing the incidence of hypoglycemic events when used as monotherapy (35, 36). However, due to the insulin-sensitizing effects of DPP-4 inhibitors and the inherent risk of hypoglycemia associated with premixed insulin (6, 37), we hypothesize that the combination of vildagliptin and premixed insulin may lead to an increased likelihood of hypoglycemic episodes. In this study, we observed a significant increase in TBR in the vildagliptin group compared to the control group, which has seldom been reported in prior research on the combination of vildagliptin with insulin. In the study by Ippei Kanazawa et al., the number of patients experiencing three or more hypoglycemic episodes per year was significantly lower in the vildagliptin group than in the control group (38). However, their study did not use FGM for continuous 24-hour glucose monitoring, potentially overlooking asymptomatic hypoglycemia. FGM provides a more comprehensive depiction of daily glucose fluctuations (39), suggesting that when treating with the combination of vildagliptin and premixed insulin, clinicians should be particularly vigilant for potential hypoglycemic events. Furthermore, additional research is required to determine whether the hypoglycemic risk associated with vildagliptin is a widespread phenomenon in combination therapies.
Our study has certain design limitations that should be acknowledged. First, the modest sample size may limit the generalizability of our findings, particularly given the predominance of patients using premixed insulin in our cohort. Secondly, the relatively short study duration of three months prevents us from assessing the long-term impact of vildagliptin on diabetes-related complications. Since improved glycemic variability has been associated with a reduced risk of complications, future studies with extended follow-up periods are warranted to determine whether the observed improvements in glucose stability translate into lasting clinical benefits.
In conclusion, vildagliptin effectively reduces mean blood glucose levels and decreases glycemic variability in patients with T2DM. However, caution is warranted regarding the potential hypoglycemia associated with vildagliptin.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Nanjing First Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin.
Author contributions
DK: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZS: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Resources, Validation, Writing – original draft. LJ: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Funding acquisition. XX: Validation, Writing – review & editing, Project administration. RY: Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Investigation. TJ: Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Supervision. YH: Writing – review & editing. JM: Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82270838), Nanjing Medical Science and Technology Development Fund (No. ZKX22038) and Top Talent Support Program for young and middle-aged people of Wuxi Health Committee (No. BJ2023010).
Acknowledgments
We thank the members of Endocrinology department of Nanjing First Hospital for their support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Magliano DJ, and Bennett PH. Diabetes mellitus statistics on prevalence and mortality: facts and fallacies. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2016) 12:616–22. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2016.105
2. Singh A, Shadangi S, Gupta PK, and Rana S. Type 2 diabetes mellitus: A comprehensive review of pathophysiology, comorbidities, and emerging therapies. Compr Physiol. (2025) 15:e70003. doi: 10.1002/cph4.70003
3. Yu MG, Gordin D, Fu J, Park K, Li Q, and King GL. Protective factors and the pathogenesis of complications in diabetes. Endocrine Rev. (2024) 45:227–52. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnad030
4. Pousinho S, Morgado M, Plácido AI, Roque F, Falcão A, and Alves G. Clinical pharmacists´ Interventions in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review. Pharm Pract. (2020) 18:2000. doi: 10.18549/PharmPract.2020.3.2000
5. Wallia A and Molitch ME. Insulin therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Jama. (2014) 311:2315–25. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.5951
6. Bellido V, Suarez L, Rodriguez MG, Sanchez C, Dieguez M, Riestra M, et al. Comparison of basal-bolus and premixed insulin regimens in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. (2015) 38:2211–6. doi: 10.2337/dc15-0160
7. Giugliano D, Tracz M, Shah S, Calle-Pascual A, Mistodie C, Duarte R, et al. Initiation and gradual intensification of premixed insulin lispro therapy versus basal {+/-} Mealtime insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes eating light breakfasts. Diabetes Care. (2014) 37:372–80. doi: 10.2337/dc12-2704
8. Polinski JM, Kim SC, Jiang D, Hassoun A, Shrank WH, Cos X, et al. Geographic patterns in patient demographics and insulin use in 18 countries, a global perspective from the multinational observational study assessing insulin use: understanding the challenges associated with progression of therapy (Mosaic). BMC endocrine Disord. (2015) 15:46. doi: 10.1186/s12902-015-0044-z
9. Tambascia MA, Nery M, Gross JL, Ermetice MN, and de Oliveira CP. Evidence-based clinical use of insulin premixtures. Diabetol Metab syndrome. (2013) 5:50. doi: 10.1186/1758-5996-5-50
10. Nalysnyk L, Hernandez-Medina M, and Krishnarajah G. Glycaemic variability and complications in patients with diabetes mellitus: evidence from a systematic review of the literature. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2010) 12:288–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2009.01160.x
11. Zhang ZY, Miao LF, Qian LL, Wang N, Qi MM, Zhang YM, et al. Molecular mechanisms of glucose fluctuations on diabetic complications. Front Endocrinol. (2019) 10:640. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00640
12. Kurozumi A, Okada Y, Mori H, Arao T, and Tanaka Y. Efficacy of α-glucosidase inhibitors combined with dipeptidyl-peptidase-4 inhibitor (Alogliptin) for glucose fluctuation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus by continuous glucose monitoring. J Diabetes Invest. (2013) 4:393–8. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12059
13. Chai S, Zhang R, Zhang Y, Carr RD, Zheng Y, Rajpathak S, et al. Influence of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors on glycemic variability in patients with type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Endocrinol. (2022) 13:935039. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.935039
14. Wiciński M, Górski K, Wódkiewicz E, Walczak M, Nowaczewska M, and Malinowski B. Vasculoprotective effects of vildagliptin. Focus on atherogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:2275. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072275
15. Altunkaynak Y, Yavuz Ö, and Levent A. Firstly electrochemical examination of vildagliptin at disposable graphite sensor: sensitive determination in drugs and human urine by square-wave voltammetry. Microchemical J. (2021) 170:106653. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2021.106653
16. Altunkaynak Y, Önal G, and Levent A. Application of boron-doped diamond electrode for rapid and sensitive voltammetric detection of vildagliptin in anionic surfactant medium. Monatshefte für Chemie - Chem Monthly. (2023) 154:181–90. doi: 10.1007/s00706-022-03020-9
17. Bosi E, Camisasca RP, Collober C, Rochotte E, and Garber AJ. Effects of vildagliptin on glucose control over 24 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin. Diabetes Care. (2007) 30:890–5. doi: 10.2337/dc06-1732
18. Bekiari E, Rizava C, Athanasiadou E, Papatheodorou K, Liakos A, Karagiannis T, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of vildagliptin for treatment of type 2 diabetes. Endocrine. (2016) 52:458–80. doi: 10.1007/s12020-015-0841-1
19. Foley JE. Insights into glp-1 and gip actions emerging from vildagliptin mechanism studies in man. Front Endocrinol. (2019) 10:780. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00780
20. Holst JJ. The incretin system in healthy humans: the role of gip and glp-1. Metabolism: Clin Exp. (2019) 96:46–55. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2019.04.014
21. Pan C, Xing X, Han P, Zheng S, Ma J, Liu J, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of vildagliptin as add-on therapy to metformin in chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2012) 14:737–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2012.01593.x
22. Zang L, Han Y, Chen L, Hu D, Jin H, Yang N, et al. Comparison of the effectiveness and safety of vildagliptin add-on to metformin versus other oral dual antidiabetes agents in patients with type 2 diabetes: the China prospective diabetes study. Diabetes therapy: research Treat Educ Diabetes related Disord. (2019) 10:1391–405. doi: 10.1007/s13300-019-0645-z
23. Kodama K, Tojjar D, Yamada S, Toda K, Patel CJ, and Butte AJ. Ethnic differences in the relationship between insulin sensitivity and insulin response: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care. (2013) 36:1789–96. doi: 10.2337/dc12-1235
24. Wu ZE, Fraser K, Kruger MC, Sequeira IR, Yip W, Lu LW, et al. Metabolomic signatures for visceral adiposity and dysglycaemia in asian chinese and caucasian European adults: the cross-sectional tofi_Asia study. Nutr Metab. (2020) 17:95. doi: 10.1186/s12986-020-00518-z
25. Saito D, Kanazawa A, Shigihara N, Sato F, Uchida T, Sato J, et al. Efficacy and safety of vildagliptin as an add-on therapy in inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes patients treated with basal insulin. J Clin Med Res. (2017) 9:193–9. doi: 10.14740/jocmr2874w
26. Hissa MR, Cavalcante LL, Guimarães SB, and Hissa MN. A 16-week study to compare the effect of vildagliptin versus gliclazide on postprandial lipoprotein concentrations and oxidative stress in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin monotherapy. Diabetol Metab syndrome. (2015) 7:62. doi: 10.1186/s13098-015-0058-8
27. Kim NH, Kim DL, Kim KJ, Kim NH, Choi KM, Baik SH, et al. Effects of vildagliptin or pioglitazone on glycemic variability and oxidative stress in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin monotherapy: A 16-week, randomised, open label, pilot study. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul Korea). (2017) 32:241–7. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2017.32.2.241
28. Shirakawa J, Okuyama T, Kyohara M, Yoshida E, Togashi Y, Tajima K, et al. Dpp-4 inhibition improves early mortality, β Cell function, and adipose tissue inflammation in db/db mice fed a diet containing sucrose and linoleic acid. Diabetol Metab syndrome. (2016) 8:16. doi: 10.1186/s13098-016-0138-4
29. Omar BA, Vikman J, Winzell MS, Voss U, Ekblad E, Foley JE, et al. Enhanced beta cell function and anti-inflammatory effect after chronic treatment with the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor vildagliptin in an advanced-aged diet-induced obesity mouse model. Diabetologia. (2013) 56:1752–60. doi: 10.1007/s00125-013-2927-8
30. Sakamoto M, Nishimura R, Irako T, Tsujino D, Ando K, and Utsunomiya K. Comparison of vildagliptin twice daily vs. Sitagliptin once daily using continuous glucose monitoring (Cgm): crossover pilot study (J-victoria study). Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2012) 11:92. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-11-92
31. Fonseca V, Schweizer A, Albrecht D, Baron MA, Chang I, and Dejager S. Addition of vildagliptin to insulin improves glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. (2007) 50:1148–55. doi: 10.1007/s00125-007-0633-0
32. Okura T, Fujioka Y, Nakamura R, Ito Y, Kitao S, Anno M, et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor improves insulin resistance in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: A single-arm study, a brief report. Diabetol Metab syndrome. (2022) 14:78. doi: 10.1186/s13098-022-00850-9
33. Jakubowicz D, Landau Z, Tsameret S, Wainstein J, Raz I, Ahren B, et al. Reduction in glycated hemoglobin and daily insulin dose alongside circadian clock upregulation in patients with type 2 diabetes consuming a three-meal diet: A randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Care. (2019) 42:2171–80. doi: 10.2337/dc19-1142
34. Sarbacker GB and Urteaga EM. Adherence to insulin therapy. Diabetes spectrum: Publ Am Diabetes Assoc. (2016) 29:166–70. doi: 10.2337/diaspect.29.3.166
35. Ji LN, Pan CY, Lu JM, Li H, Li Q, Li QF, et al. Efficacy and safety of combination therapy with vildagliptin and metformin versus metformin up-titration in chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: study design and rationale of the vision study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2013) 12:118. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-12-118
36. Dejager S and Schweizer A. Minimizing the risk of hypoglycemia with vildagliptin: clinical experience, mechanistic basis, and importance in type 2 diabetes management. Diabetes therapy: research Treat Educ Diabetes related Disord. (2011) 2:51–66. doi: 10.1007/s13300-010-0018-0
37. Omar B and Ahrén B. Pleiotropic mechanisms for the glucose-lowering action of dpp-4 inhibitors. Diabetes. (2014) 63:2196–202. doi: 10.2337/db14-0052
38. Kanazawa I, Tanaka KI, Notsu M, Tanaka S, Kiyohara N, Koike S, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of vildagliptin add-on therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus with insulin treatment. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2017) 123:9–17. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2016.11.010
39. Yan RN, Cai TT, Jiang LL, Jing T, Cai L, Xie XJ, et al. Real-time flash glucose monitoring had better effects on daily glycemic control compared with retrospective flash glucose monitoring in patients with type 2 diabetes on premix insulin therapy. Front Endocrinol. (2022) 13:832102. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.832102
Keywords: vildagliptin, type 2 diabetes mellitus, glycemic excursion, flash glucose monitoring, premixed insulin
Citation: Kong D, Shen Z, Jiang L, Xie X, Yan R, Jing T, Hu Y and Ma J (2025) The effects of vildagliptin on glycemic variability in patients with type 2 diabetes on premixed insulin therapy. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1508918. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1508918
Received: 10 October 2024; Accepted: 04 June 2025;
Published: 20 June 2025.
Edited by:
Abdulkadir Levent, Batman University, TürkiyeReviewed by:
Mansoor Ahmed Mahar, Dow University of Health Sciences, PakistanMehmet Sanli, Batman University, Türkiye
Copyright © 2025 Kong, Shen, Jiang, Xie, Yan, Jing, Hu and Ma. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianhua Ma, bWFqaWFuaHVhMTk2NTAzQDEyNi5jb20=; Yun Hu, aHV5dW53dXhpQDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Deyue Kong
Deyue Kong Ziyang Shen
Ziyang Shen Lanlan Jiang1
Lanlan Jiang1 Yun Hu
Yun Hu Jianhua Ma
Jianhua Ma