- College of Acupuncture and Tuina, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, China
Background: Diabetic gastroparesis (DGP) is a common complication in the later stage of diabetes mellitus (DM). The aim of this study was to investigate the protective effect of long-term tuina on gastrointestinal (GI) function and the occurrence of DGP in diabetic rats.
Methods: Twenty healthy male SD rats were randomly divided into four groups: NC, DM, DM + GT, and DM + TT. DM was induced with streptozotocin and a high-fat, high-sugar diet for 6 weeks. The DM + TT group received tuina therapy (20 min/session, 5 times/week) for 6 weeks. Weekly random blood glucose, gastric emptying rate, and small intestinal propulsion rate were measured. Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining assessed gastric antrum and ileum pathology. Ca2+-Mg2+-ATPase and CS activities, and neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), calmodulin (CaM), and myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) mRNA and protein expressions were evaluated by PCR and Western blot. 5-HT content was measured by ELISA. Piezo2 and 5-HT4R expressions were analyzed by immunofluorescence staining to observe tuina’s protective effect on GI function in DM rats.
Results: Random blood glucose measurements showed normal levels in the NC group, while other groups remained above 16.7 mmol/L. The DM group exhibited reduced gastric emptying and small intestinal propulsion rates, along with gastric antrum and ileum damage. The DM + TT group showed significant improvements in gastric emptying and intestinal propulsion rates, and reduced tissue damage compared to the DM group. In the DM + TT group, mRNA and protein expressions of CaM and MLCK in antrum tissue, and nNOS, CaM, and MLCK in ileum tissue, were significantly increased. Activities of Ca2+-Mg2+-ATPase and CS enzymes in ileum tissue were also elevated, indicating enhanced GI function. Further analysis showed increased mRNA expressions of Piezo2 and 5-HT4R, and protein expressions of Piezo2, 5-HT, and 5-HT4R in the ileum tissues of the DM + TT group. Immunofluorescence intensity of Piezo2 and 5-HT in the ileum was also heightened. These results suggest that tuina’s protective effect on GI function is related to the expression of Piezo2 ion channels.
Conclusions: Long-term tuina protects the GI function of DM rats and inhibits the occurrence of DGP, which might be related to the Piezo2/5-HT pathway.
Introduction
Diabetic gastroparesis (DGP) is a common complication in the later stage of diabetes mellitus (DM). It refers to a disorder characterized by delayed gastric emptying and upper abdominal discomfort, which is caused by gastrointestinal (GI) motility dysfunction without mechanical obstruction of the GI tract. The main manifestations are early satiety, nausea, vomiting, abdominal distension, and other symptoms, which seriously affect the quality of life of patients (1–3). Also, these GI symptoms may originate not only from the stomach but also from the small intestine (1, 4).
The digestive functions of the GI tract, such as gastric emptying and small intestinal peristalsis, depend on the coordinated secretion and movement of fluid in response to mechanical stimulation within the lumen (5). Studies have shown that force can cause neuroendocrine cells to release 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) (6–8). Mechanical stimulation of the GI mucosa results in 5-HT release (9–11), which stimulates fluid secretion (11, 12) and GI motility (13). Enterochromaffin (EC) cells are the largest group of intestinal epithelial enteroendocrine (EE) cells. EC cells are thought to be specialized mechanosensory cells that release 5-HT in response to epithelial forces, thereby regulating intestinal fluid secretion (5, 14). The mechanical sensitivity of the ion channel Piezo2 acts as touch and proprioception receptors, expressed in the EC cells of mice and humans (8, 15–18). Piezo2 is required for sensing intestinal contents and slowing the rate of food transport in the stomach, small intestine, and colon, and humans lacking Piezo2 exhibit impaired GI sensation and motility (19). Piezo2 mechanosensors are essential for the coupling force of 5-HT release and intestinal secretion (14).
Tuina therapy is a mechanical therapy with regular, rhythmic movement and more power than touch, which is applied to the surface skin or muscles and has been widely used in alternative and complementary medicine (20, 21). Tuina therapy can reduce gastric retention, reduce the gastric residual volume (22, 23), improve gastric antrum and feeding intolerance, and reduce the incidence of abdominal distension, vomiting, and diarrhea (24–27). It can also improve the overall symptoms and constipation symptoms of patients with functional dyspepsia (28–31).
However, we lack sufficient understanding of the molecular mechanisms of tuina therapy in alleviating GI dysfunction, especially the mechanism of long-term tuina therapy in protecting gastric emptying, and small intestinal propulsion function is still unclear. Piezo2 ion channel is considered to play a role in Gl diseases and its potential impact on tuina. We hypothesize that long-term tuina improves GI function in diabetic rats by modulating the Piezo2/5-HT signaling pathway. By using real-time quantitative PCR, Western blot (WB), and immunofluorescence technology, we demonstrate the important role of Piezo2 in helping the gut to sense the mechanical force stimulus of tuina and thus modulate GI function.
Methods
Experimental animals and grouping
A total of 20 healthy SPF male Sprague-Dawley rats, aged 8 weeks, weighing 180–220 g, were provided by Sichuan Research Institute of Biomedical Industry and Technology [production license number: SYXK (Sichuan) 2020-199]. The animals were raised in the Sichuan Institute of Biomedical Industry Technology. The ambient temperature was 20–25°C, lights on at 8:00–20:00, the relative humidity was 45%–60%, and the animals were free to drink and eat. All animal feeding and experimental procedures comply with the Guidelines for the Management and Use of Laboratory Animals. The trial protocol of this study was implemented with reference to ARRIVE guidelines (32). This project passed the ethical review of the Animal Ethics Committee of Sichuan Research Institute of Biomedical Industry Technology (No. 2021-07-15).
DM and DGP rat models
After 1 week of adaptive feeding, the rats were randomly assigned to four groups using a random number table method: the normal control group (NC group), the diabetes mellitus group (DM group), the diabetes mellitus + gentle touch group (DM + GT group), and the diabetes mellitus + tuina treatment group (DM + TT group), with 5 rats in each group.
The modeling method of Srinivasan was used (33). The DM group, DM + GT group, and DM + TT group were fed a high-fat and high-sugar diet (60% fat, 20% protein, and 20% carbohydrate) and 5% sucrose water for 2 weeks. Two weeks later, streptozotocin (STZ) (35 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally after 12 h of fasting. The rats in the NC group were fed a normal diet and intraperitoneally injected with sodium citrate buffer (1 mL/kg). Blood samples were collected from the tail vein of the rats 72 hours after the injection to measure random blood glucose levels. The DM model was successfully established when the random blood glucose levels reached ≥16.7 mmol/L. The DM, DM + GT, and DM + TT groups were fed a high-fat and high-sugar diet and 5% sucrose water for 6 weeks. Random blood glucose was measured once a week during this period, and rats with random blood glucose < 16.7 mmol/L or dead rats were excluded (Figure 1).
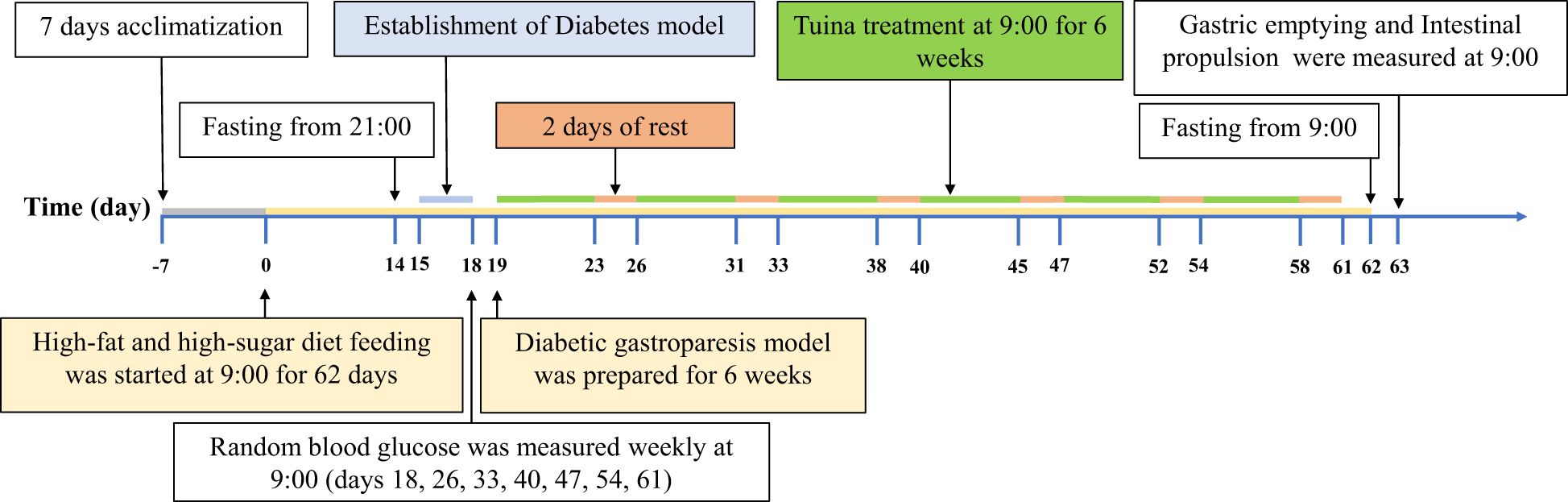
Figure 1. Experimental protocol. After 7 days of adaptive feeding, the rats in the DM group, DM + GT group, and DM + TT group were fed a high-fat and high-sugar diet for 62 days, and the rats in the NC group were fed a conventional diet. Fifteenth day STZ injection solution. Random blood glucose was measured every 7 days starting from day 18. After the DM model was successfully established, tuina treatment was started on the 19th day, 5 times a week for 6 weeks, for a total of 30 times. The 63rd day based measurement.
Successful DGP modeling criteria (34): Random blood sugar is not less than 16.7 mmol/L. There were significant differences in hair color, behavior, mental state, and stool characteristics between the two groups. The semisolid gastric emptying rate and small intestinal propulsion rate in the DM group were lower than those in the NC group.
Tuina treatment
After successful establishment of the DM model, rats in the DM + TT group received tuina therapy. The rats were immobilized using a custom-made rat tuina restraining device. Abdominal kneading: the operator’s right index finger and middle finger are naturally close together, and the rest of the palms are naturally flexed. The finger thread surface was attached to both sides of Shenque point (CV8), and clockwise rhythmic ring kneading was performed, with a frequency of 80 times/min, and the operation time was 10 min. Kneading Pishu (BL20): the operator’s right index finger and middle finger are naturally close together, and the rest of the palms are naturally flexed. The center of the finger thread surface was attached to the Pishu point (between the two ribs under the 12th thoracic vertebra, 6 mm away from the dorsal midline), the frequency of clockwise rhythmic ring kneading was 80 times/min, and the operation time was 10 min. The tuina therapy will be administered 5 times a week for a total of 30 sessions (Figure 1).
The DM + GT group, which serves as the sham tuina control, used a fine brush to perform gentle combing of localized hair areas. The fixing method and the position, frequency, and time of carding operation are consistent with the DM + TT group. The NC group and the DM group were fixed.
Measurement of random blood glucose
All data collectors, testers, and analysts in this study were blinded to the grouping. The experiment was carried out at 9:00 a.m. on days 18, 26, 33, 40, 47, 54, and 61. Blood was collected from the tail of the rat while it was in a conscious state. Random blood glucose values were measured and recorded using a blood glucose meter and blood glucose test strips (ACCU-CHEK Performa, Roche Diagnostic Products Shanghai Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China).
Measurement of gastric emptying rate and small bowel propulsive rate
After 6 weeks of tuina intervention, the rats were fasted for 24 h and fed 3 mL of semi-solid nutritional paste containing carbon powder (carboxymethylcellulose sodium 10 g, milk powder 16 g, starch 8 g, white sugar 8 g, activated carbon 2 g, dissolved in distilled water 250 mL mixed to make 300 mL, approximately 300 g of black semi-solid paste). Thirty minutes later, the whole stomach was weighed with intraperitoneal injection of 3% sodium pentobarbital at 5 mL·kg−1 under anesthesia. The stomach was cut along the greater curvature and rinsed thoroughly with 0.9% NaCl solution, the net weight of the stomach was weighed, and the gastric emptying rate was calculated. Gastric emptying rate = [1 − (total weight of stomach − net weight of stomach) ÷ weight of char powder semi-solid nutritional paste] ×100%. The total length of the small intestine (pylorus to ileocecal junction) and the propulsion length of the semi-solid nutritional paste containing charcoal powder were measured, and the propulsion rate of the small intestine was calculated. Intestinal propulsion rate = advancement distance of black paste measured from pylorus as starting point/total intestinal distance of small intestine ×100%.
Observation by hematoxylin and eosin staining
Fresh gastric antral and ileal tissues were obtained and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde solution (G1101, servicebio, Wuhan, China) for 24 h. The embedding machine (JB - P5, Wuhan Junjie Electronics Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China) was used for paraffin embedding. Sections (4 μm) were made on a microtome (HM325, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (HE). The specimens were examined under a light microscope (400×), and the images were collected and analyzed.
Enzyme activity was detected via the biochemical method
The ileal segment tissue was harvested and homogenized by adding ninefold homogenization medium, and the supernatant was used for quantification by BCA (BL521A, biosharp, Beijing, China). In accordance with the ATP enzyme kit (A016-1-1, Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Research Institute Co., LTD., Nanjing, China) and citrate synthase (CS) kit (E-BC-K178-M, Elabscience Biotechnology Co., Ltd, Wuhan, China) operating instructions, biochemical detection analysis of Ca2+-Mg2+-atpase and CS enzyme activities is performed.
Real-time quantitative PCR
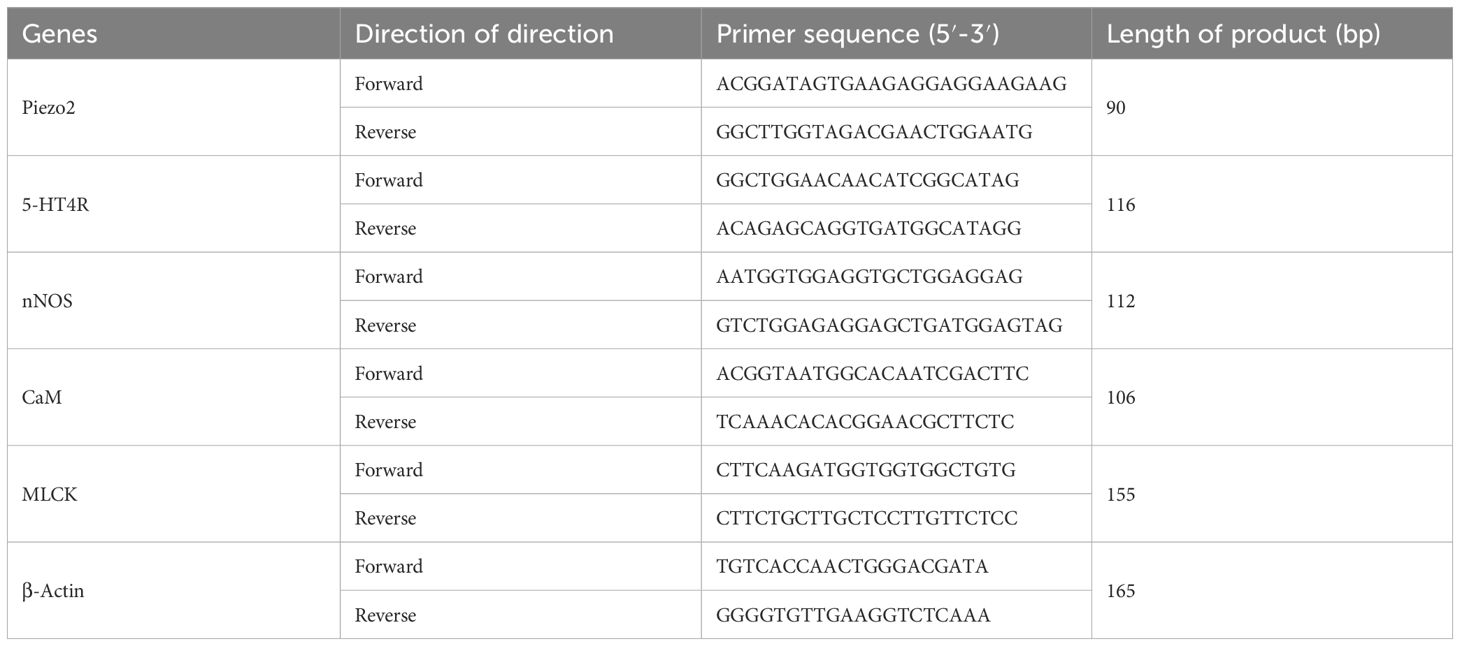
Gastric antrum and ileal segment tissues were harvested for total RNA extraction using Trizol reagent. Synthetic cDNA was obtained using the AccuRT Genomic DNA Removal kit (G492, Applied Biological Materials Inc, Richmond, Canada) standard. Real-time quantitative PCR assays were performed using EvaGreen Express 2X qPCR MasterMix-No Dye (G891, Applied Biological Materials Inc., Richmond, Canada) on a fully automated medical PCR analysis system (Shanghai Hongshi Medical Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). Primer design methods and primer sequences are shown in Table 1.
Western blotting
Apply an adequate amount to the gastric antrum and ileum segment organization, using RIPA (BL504A biosharp, Beijing, China) pyrolysis liquid. Centrifuge for 10 minutes for the total protein solution. Protein concentrations were determined using the enhanced BCA protein kit (BL507A, biosharp, Beijing, China). Equal amounts of proteins were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and transferred to PVDF membranes. The membranes were blocked with 5% skim milk for 1 h at room temperature. Primary antibodies Piezo2 (1:500, PA5-72976, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), 5-HT4R (1:1,000, DF3503, Affinity Biosciences Pty Ltd, Melbourne, Australia), neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) (1:1,000, AF6249, Affinity Biosciences Pty Ltd, Melbourne, Australia), calmodulin (CaM) (1:1,000, ab45689, abcam, Cambridge, UK), myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) (1:500, AF5314, Affinity Biosciences Pty Ltd, Melbourne, Australia), and β-Actin (1:5,000, AF7018, Affinity Biosciences Pty Ltd, Melbourne, Australia) were incubated overnight at 4°C. The specimens were incubated with the secondary Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H + L) HRP (1:10,000, GAR0072, Multisciences, Hangzhou, China) for 1 h at room temperature. In the chemidoc™ XRS imaging system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Hercules, CA, USA) on the image.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
Add a ninefold homogenate culture medium preparation to the ileal tissue. After centrifugation, the supernatant was extracted for quantification by BCA (BL521A, biosharp, Beijing, China). The content of 5-HT in ileum tissue was determined according to the instruction from the 5-HT ELISA kit (E-EL-0033c, Elabscience Biotechnology Co., Ltd, Wuhan, China). The OD values of each well were measured at a wavelength of 450 nm using a microplate reader.
Immunofluorescence staining
The ileal segment tissue was fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (G1101, servicebio, Wuhan, China) for 24 h. Embedding paraffin was acquired after ileal cross-sectional slices of the organization. Antigen repair was performed using citrate antigen repair solution (G1219, servicebio, Wuhan, China). The cells were incubated with 5% goat serum for 30 min. Primary antibodies Piezo2 (1:50, PA5-72976, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and 5-HT (1:200, sc-58031, Santacruz Biotech, Texas, USA) were added and incubated overnight at 4°C. They were washed three times in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (G4202, biosharp, Beijing, China). The cells were incubated with secondary antibodies Cy3-conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG H&L (1:200, GB21303, servicebio, Wuhan, China) and FITC-conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG H&L (1:200, GB22303, servicebio, Wuhan, China) for 1 h at room temperature. Nuclei were counterstained with 4′,6-diamino-2-phenylindole (G1012, servicebio, Wuhan, China). Images were observed and collected under an ICX41 fluorescence microscope (Ningbo Sunny Instrument Co., Ltd., Ningbo, China) (400×).
Statistical analysis
IBM SPSS 26.0 software (IBM Statistics, Armonk, NY, USA) was used for statistical analysis. GraphPad Prism 10 Software (GraphPad Software, Boston, MA, USA) was used for plotting. Measurement data were expressed as mean ± SEM. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to test the differences between groups. If the data were normally distributed, followed by the Bonferroni post-hoc test was used for pairwise comparisons. Otherwise, Kruskal–Wallis test was performed, followed by the Tukey or Dunn test for pairwise comparisons. Repeated measurement data were analyzed by repeated-measures ANOVA. A p-value of less than 0.05 is considered statistically significant.
Results
Effect of long-term tuina on random blood glucose in DM rats
During the long-term tuina treatment, random blood glucose detection was carried out once a week. The results showed that the rats in the DM group, DM + GT group, and DM + TT group were fed a high-fat and high-sugar diet for 6 weeks after the establishment of the DM model. The random blood glucose value of rats was maintained above 16.7 mmol/L, which met the basic conditions for the preparation of DGP GI dysfunction. There was no significant decrease in the DM + TT group compared with the DM group, which may be related to the continuous feeding of a high-fat and high-sugar diet (Figure 2).
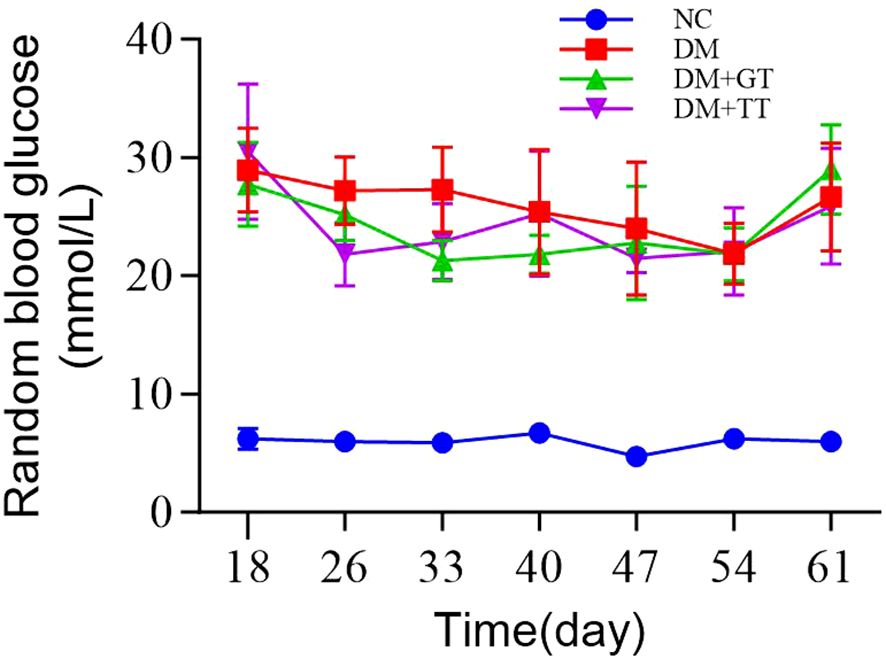
Figure 2. Groups of rats at different time points of random blood glucose. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation, n = 5. NC, normal control group; DM, diabetes mellitus group; DM + GT, diabetes mellitus + gentle touch group; DM + TT, diabetes mellitus + tuina treatment group.
Long-term tuina protects the gastric emptying rate and small intestinal propulsion rate in DM rats
In order to observe the protective effects of long-term tuina on GI function in DM rats. After completing 30 tuina treatments, we measured the gastric emptying rate and the small bowel propulsion rate. Compared with the NC group, the gastric emptying rate (Figure 3A) and the small intestinal propulsion rate (Figure 3B) in the DM group were significantly decreased (p < 0.01). Compared with the DM group, the levels in the DM + TT group were significantly increased (p < 0.01). The DM + TT group was superior to the DM + GT group (p < 0.01). The results showed that long-term tuina could significantly protect gastric emptying and small intestinal propulsion in DM rats.
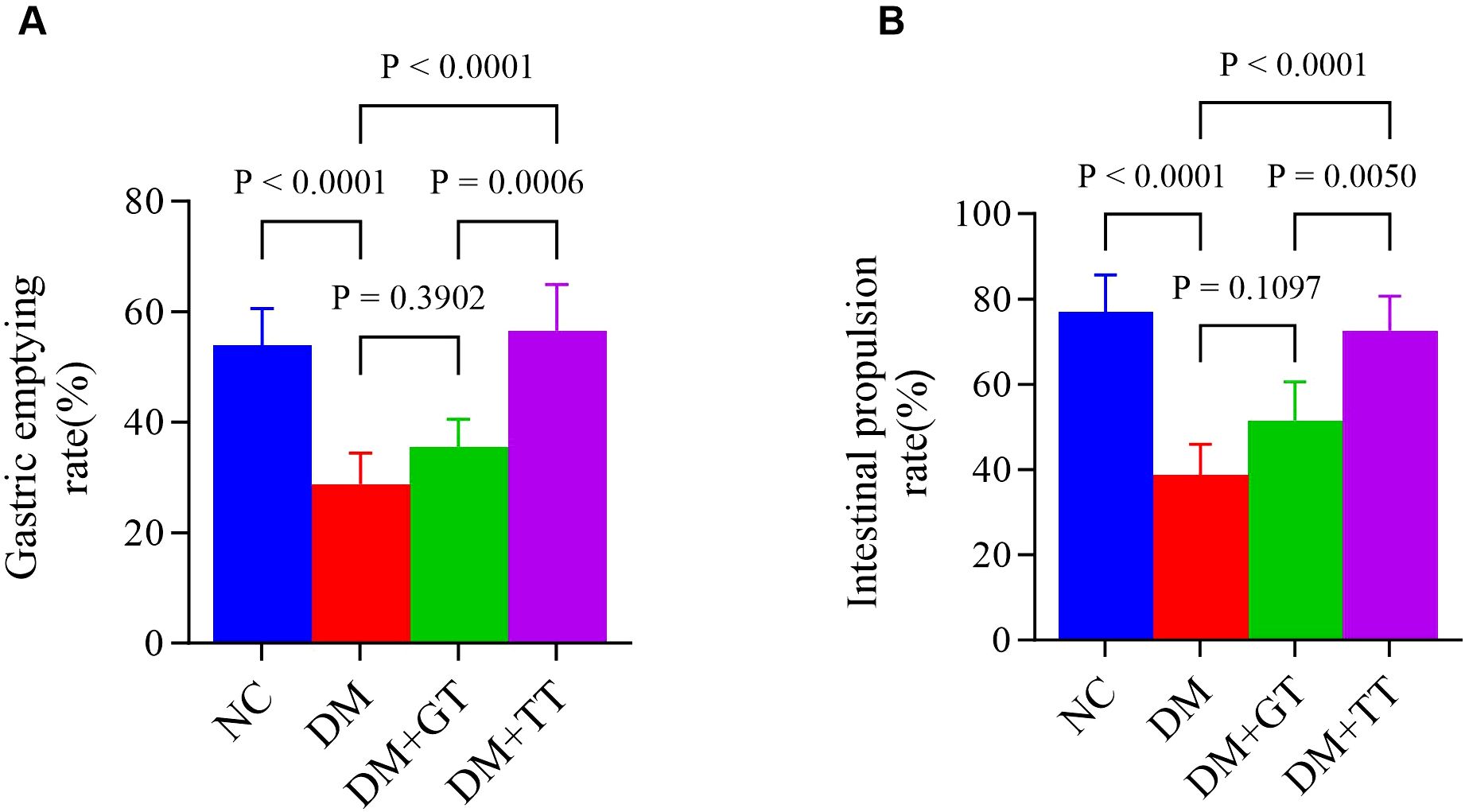
Figure 3. Comparison of gastric emptying rate and small intestinal propulsive rate in each group. (A) Gastric emptying rate. (B) Small intestinal propulsive rate. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation, n = 5. NC, normal control group; DM, Diabetes mellitus group; DM + GT, Diabetes mellitus + gentle touch group; DM + TT, Diabetes mellitus + tuina treatment group.
Long-term tuina protects the morphology of GI tissue in DM rats
To observe the effect of long-term tuina on the morphology of GI tissue in DM rats, we performed HE staining of tissue from the antrum and ileum (Figure 4). There were no obvious pathological changes in the gastric antrum and ileum in the NC group and the DM + TT group. In the DM group, gastric mucosal hemorrhage, necrosis and exfoliation of mucosal epithelial cells, cell vacuolization, and inflammatory cell infiltration were observed. The structure of intestinal mucosa was destroyed, the apical structure of villi was dissolved, and the epithelial cells were necrotic and exfoliated. Vacuolization of gastric epithelial cells and edema of submucosa were observed in the DM + GT group. Local exfoliation of villous epithelial cells and histolysis were observed in the intestinal mucosa.
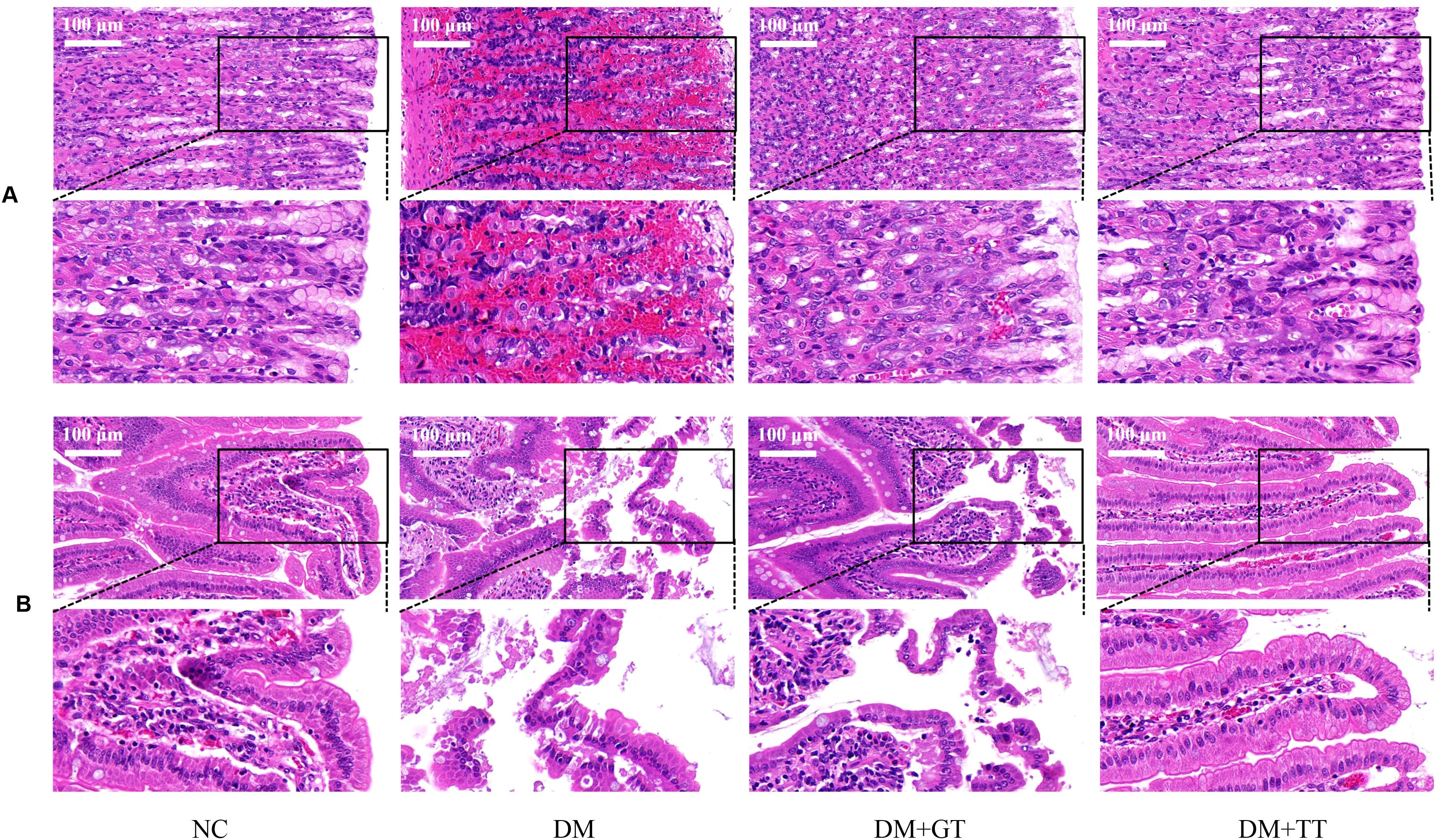
Figure 4. HE staining results of gastric antrum and ileum of rats in each group (400×). (A) Gastric antrum tissue. (B) Ileum tissue. NC, Normal control group; DM, Diabetes mellitus group; DM + GT, Diabetes mellitus + gentle touch group; DM + TT, Diabetes mellitus + tuina treatment group.
Long-term tuina upregulates the expression of CaM and MLCK in the gastric antrum tissue of DM rats
CaM and MLCK molecules play an important role in regulating the contraction behavior of GI smooth muscle through the CaM/MLCK pathway (35). In order to further verify the regulatory effect of long-term tuina on gastric motility, antral tissue was assayed for CaM and MLCK mRNA and protein by RT-qPCR (Figures 5A, B) and WB (Figures 5C–E). Compared with the NC group, the mRNA and protein expressions of CaM and MLCK in the gastric antrum tissue of the DM group were significantly decreased (p < 0.01). Compared with the DM group, the expression of CaM protein in the DM + GT group was significantly increased (p < 0.05), and the expression of CaM and MLCK mRNA and protein in the DM + TT group was significantly increased (p < 0.01). Compared with the DM + GT group, the mRNA and protein expressions of CaM and MLCK in the DM + TT group were increased (p < 0.01).
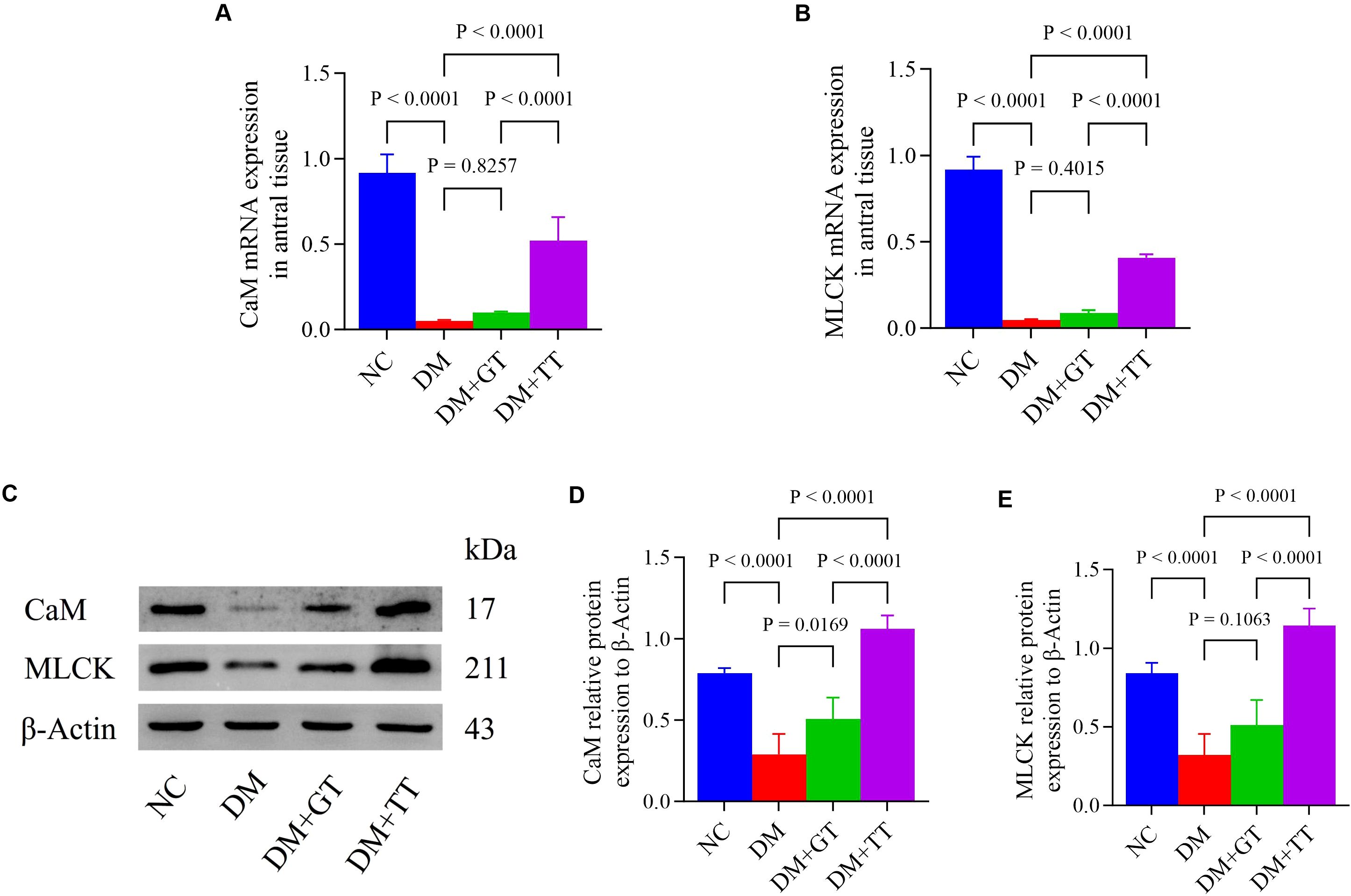
Figure 5. mRNA and protein expression of CaM and MLCK in gastric antrum tissues of rats in each group. (A, B) Gastric antrum tissue CaM and MLCK mRNA expression. (C–E) Expression of CaM and MLCK protein in gastric antrum tissue. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation, n = 5. NC, Normal control group; DM, Diabetes mellitus group; DM + GT, Diabetes mellitus + gentle touch group; DM + TT, Diabetes mellitus + tuina treatment group. CaM, Calmodulin; MLCK, Myosin light chain kinase.
Long-term tuina upregulates the expression of nNOS, CaM, and MLCK in ileum of DM rats
nNOS is involved in the maintenance of normal intestinal peristalsis. To verify the regulatory effect of long-term tuina on small intestinal motility, we examined the expression of nNOS, CaM, and MLCK molecules (mRNA: Figures 6A–C) (protein: Figures 6D–G) in ileal tissues. Compared with the NC group, the mRNA and protein expressions of nNOS, CaM, and MLCK in the DM group were significantly decreased (p < 0.01). Compared with the DM group, the protein expression of nNOS and MLCK in the DM + GT group was significantly increased (p < 0.01, p < 0.05). The mRNA and protein expressions of nNOS, CaM, and MLCK in the DM + TT group were significantly increased (p < 0.01). Compared with the DM + GT group, the mRNA and protein expressions of nNOS, CaM, and MLCK in the DM + TT group were significantly increased (p < 0.01).
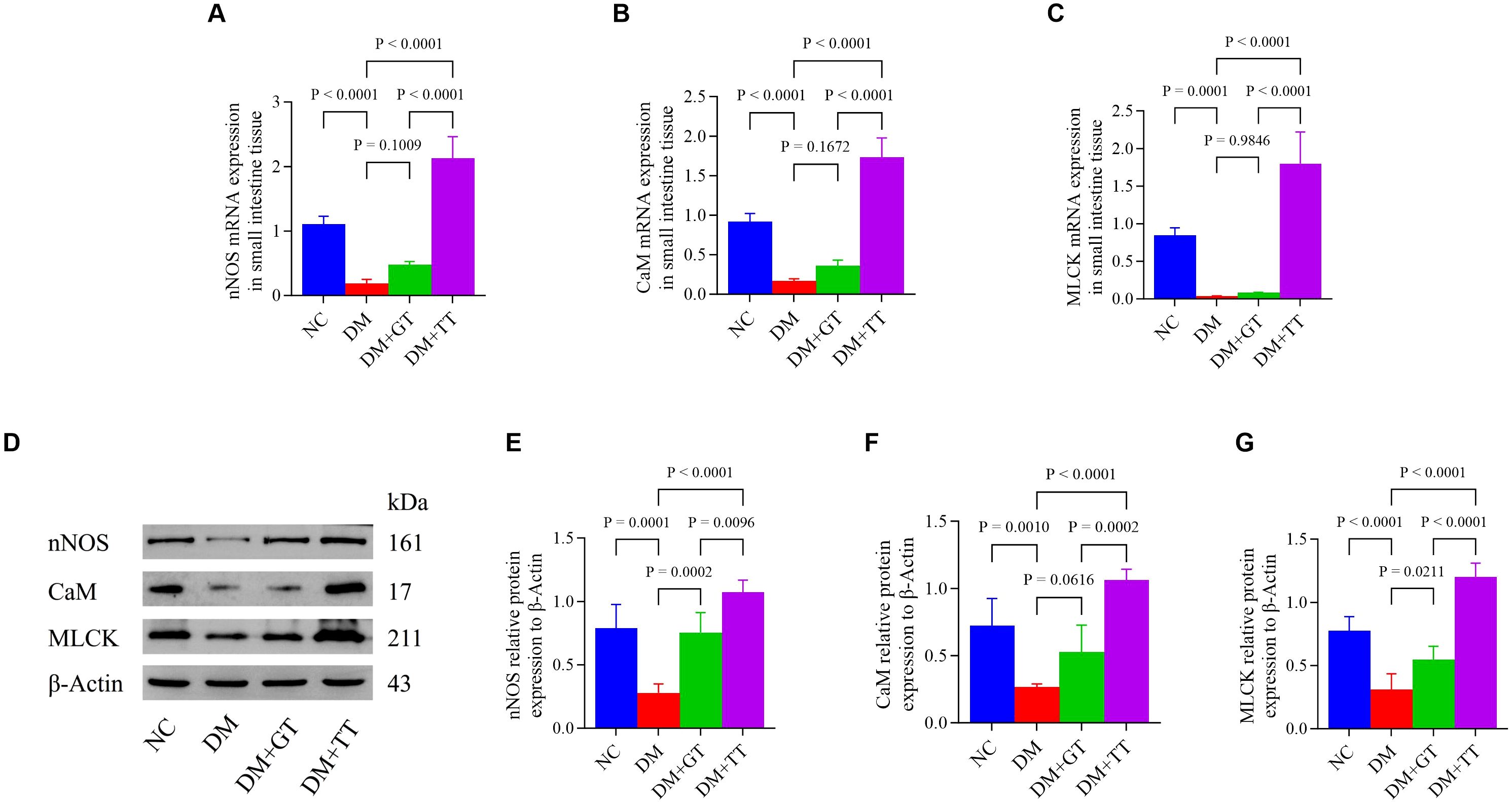
Figure 6. Expression of nNOS, CaM, and MLCK mRNA and protein in the ileum tissue of rats in each group. (A–C) Expression of nNOS, CaM, and MLCK mRNA in ileum tissue. (D–G) Protein expression of nNOS, CaM, and MLCK in ileum tissue. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation, n = 5. NC, Normal control group; DM, Diabetes mellitus group; DM + GT, Diabetes mellitus + gentle touch group; DM + TT, Diabetes mellitus + tuina treatment group. nNOS, Neuronal nitric oxide synthase; CaM, Calmodulin; MLCK, Myosin light chain kinase.
Long-term tuina upregulates the activities of Ca2+-Mg2+-ATPase and CS enzyme in the ileum of DM rats
Ca2+-Mg2+-ATPase and CS enzyme activities are involved in energy metabolism in the regulation of GI motility. In order to further verify the regulatory effect of long-term tuina on small intestinal motility, we examined the Ca2+-Mg2+-ATPase (Figure 7A) and CS enzyme (Figure 7B) activities in ileal tissues. Compared with the NC group, the activities of Ca2+-Mg2+-ATPase and CS enzyme in the ileum tissue of the DM group were significantly decreased (p < 0.01). Compared with the DM group, the activities of Ca2+-Mg2+-ATPase and CS enzyme in the DM + GT group and DM + TT group were significantly increased (p < 0.01). Compared with the DM + GT group, the activities of Ca2+-Mg2+-ATPase and CS enzyme in the DM + TT group were higher (p < 0.01).
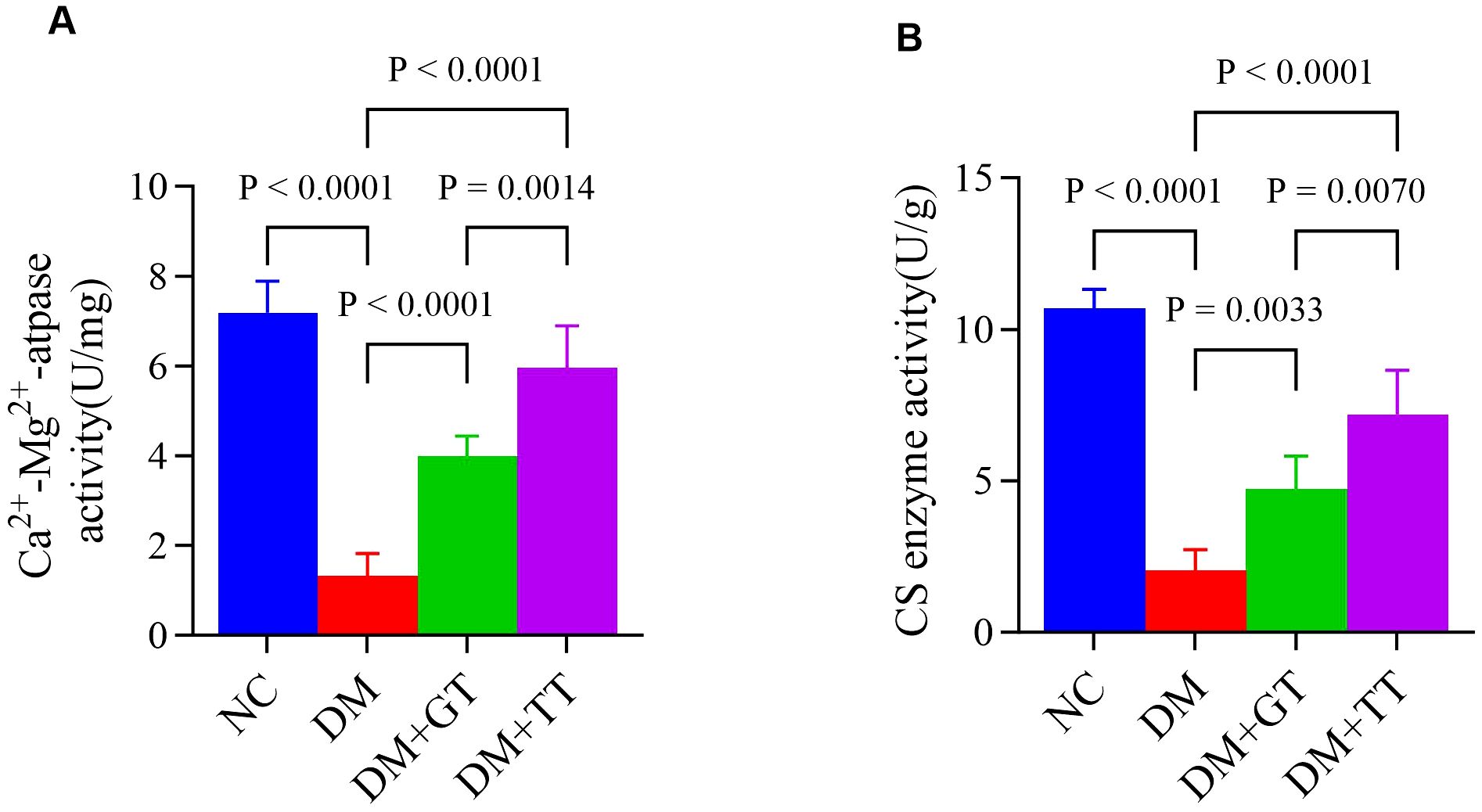
Figure 7. Comparison of ileum tissue enzyme activity between rat groups. (A) Activities of Ca2+-Mg2+-ATPase. (B) Activities of CS enzyme. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation, n = 5. NC, Normal control group; DM, Diabetes mellitus group; DM + GT, Diabetes mellitus + gentle touch group; DM + TT, Diabetes mellitus + tuina treatment group.
Long-term tuina upregulates the expression of Piezo2 and 5-HT4R mRNA in the ileum tissue of DM rats
To verify whether the protection of GI function by long-term tuina is related to the expression of Piezo2 and 5-hydroxytryptamine 4 receptor (5-HT4R) molecules, we examined Piezo2 and 5-HT4R mRNA expression in ileum tissue (Figures 8A,B). Compared with the NC group, the expression of Piezo2 and 5-HT4R mRNA in the DM group was significantly decreased (p < 0.01, p < 0.05). Compared with the DM group, the DM + TT group’s Piezo2, 5-HT4R mRNA expression was significantly increased (p < 0.01). Compared with the DM + GT group, the mRNA expression of Piezo2 and 5-HT4R in the DM + TT group was higher (p < 0.01, p < 0.05).
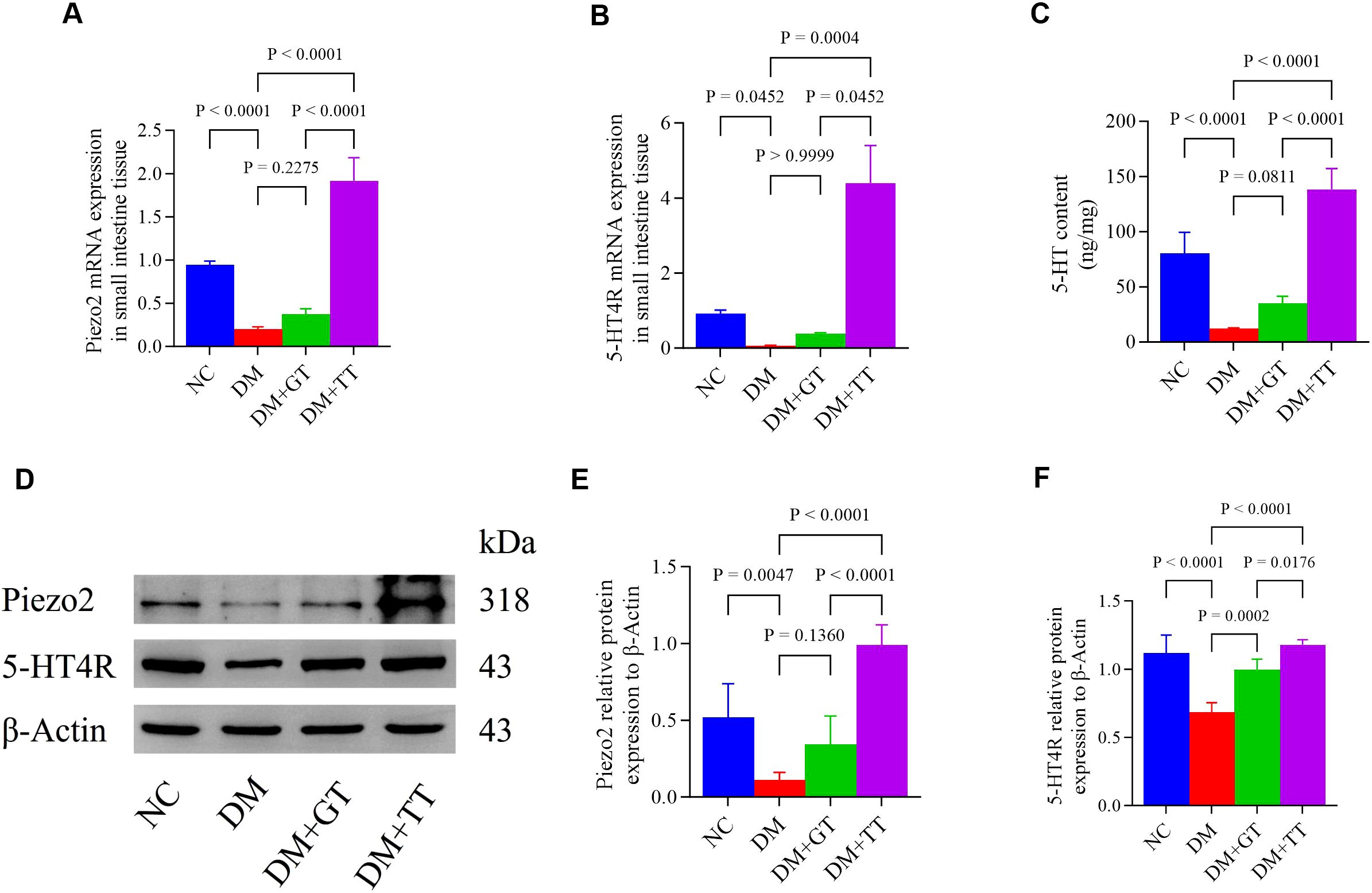
Figure 8. Ileum tissue Piezo2, 5-HT, and 5-HT4R protein expression in rat groups. (A, B) Expression of Piezo2 and 5-HT4R mRNA in ileum tissue. (C) Expression of 5-HT protein was detected by ELISA. (D–F) Western blotting was used to detect the expression of Piezo2 and 5-HT4R protein. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation, n = 5. NC, Normal control group; DM, Diabetes mellitus group; DM + GT, Diabetes mellitus + gentle touch group; DM + TT, Diabetes mellitus + tuina treatment group. Piezo2, The mechanically sensitive ion channel Piezo2; 5-HT, 5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT4R, 5-hydroxytryptamine 4 receptor.
Long-term tuina regulates the expression of Piezo2, 5-HT, and 5-HT4R protein in the ileum tissue of DM rats
To further verify whether long-term tuina protection of GI function is related to the expression of Piezo2, 5-HT, and 5-HT4R, which are important molecules regulating Piezo2/5-HT signaling pathway, we used WB, ELISA, and immunofluorescence staining techniques for detection. The results showed that compared with the NC group, the protein expression of Piezo2, 5-HT, and 5-HT4R in the ileum tissue of the DM group was significantly decreased (p < 0.01) (Figures 8C–F). Compared with the DM group, the expression of 5-HT4R protein in the DM + GT group was significantly increased (p < 0.01), and the expression of Piezo2, 5-HT, and 5-HT4R protein in the DM + TT group was significantly increased (p < 0.01). Compared with the DM + GT group, the protein expressions of Piezo2, 5-HT, and 5-HT4R in the DM + TT group were higher than those in the DM + GT group (p < 0.01, p < 0.05).
Immunofluorescence staining results showed that compared with the NC group, the DM group’s ileum tissue, Piezo2, and 5-HT positive fluorescent expression reduced significantly (p < 0.01) (Figures 9A, B). Merge images showed that Piezo2 and 5-HT co-expression fluorescence was significantly reduced (Figure 9). Compared with the DM group, the positive fluorescence expression of Piezo2 and 5-HT in the DM + TT group was significantly increased (p < 0.01). Merge images showed that the co-expression fluorescence of Piezo2 and 5-HT was significantly increased. Compared with the DM + GT group, the positive fluorescence expression of Piezo2 in the DM + TT group was higher than that in the DM + GT group (p < 0.01).
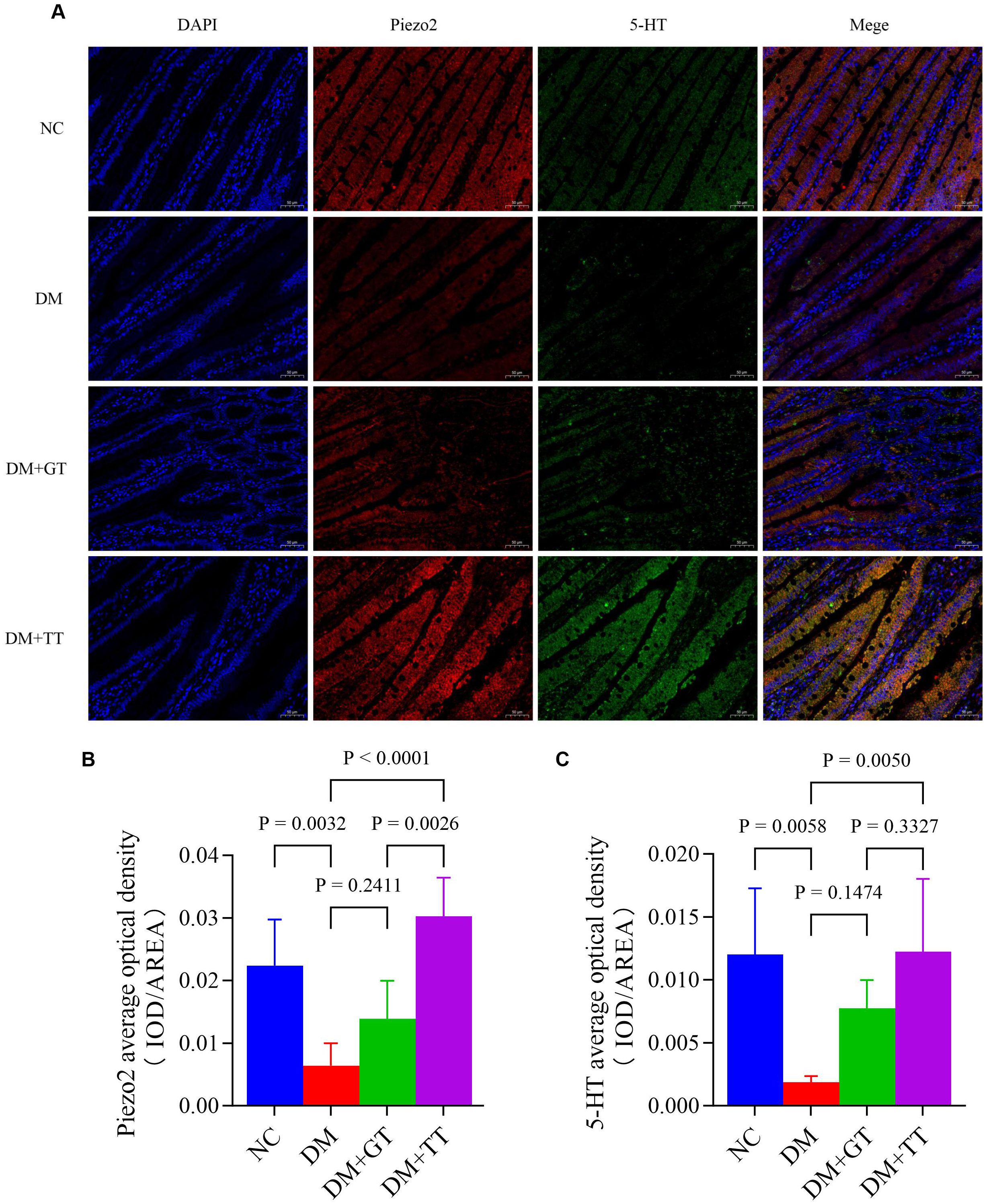
Figure 9. Immunofluorescence staining of Piezo2 and 5-HT in ileum tissue of rats in each group (400×). (A) Immunofluorescence staining. (B) Average optical density of Piezo2. (C) Average optical density of 5-HT. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation, n = 5. NC, Normal control group; DM, Diabetes mellitus group; DM + GT, Diabetes mellitus + gentle touch group; DM + TT, Diabetes mellitus + tuina treatment group. Piezo2, The mechanically sensitive ion channel Piezo2; 5-HT, 5-hydroxytryptamine.
Discussion
In this study, it was confirmed that long-term abdominal and back tuina could significantly protect the gastric emptying function of DM rats, inhibit the deterioration of gastric antrum morphology, regulate the expression of CaM and MLCK in gastric antrum tissue, and slow down the progression of DGP. Meanwhile, we examined the small intestine propulsion rate; histological characteristics; the activities of Ca2+-Mg2+-ATPase and CS enzyme in the ileum; the mRNA and protein expression of nNOS, CaM, MLCK, Piezo2, and 5-HT4R; the protein expression of 5-HT in the ileum; and the co-expression of Piezo2 and 5-HT by immunofluorescence. The results showed that long-term tuina could not only significantly protect the gastric emptying function, but also protect the intestinal propulsion function, increase the activities of Ca2+-Mg2+-ATPase and CS in the ileum, and regulate the expression of nNOS, CaM, MLCK, Piezo2, 5-HT, and 5-HT4R.
The gentle touch intervention used as a sham tuina control is designed to mimic the effects of a light fingertip touch on the skin. It can regulate the expression of CaM protein in gastric antrum tissue, as well as the expression of MLCK and 5-HT4R proteins and the activity of Ca²+-Mg²+-ATPase and CS enzymes in ileal tissue. However, the gentle touch intervention does not significantly protect gastric emptying and small intestinal propulsion function.
The clinical manifestations of DGP and delayed gastric emptying may be caused by physiological changes, including dyskinesia, small bowel motility disorders, diminished pyloric relaxation, hypomotility of the antrum, and impaired regulation of the fundus/corpus (36, 37). A large number of studies confirm that the CaM/MLCK pathway on the GI smooth muscle contraction behavior plays an important regulatory role (35). When GI smooth muscle cells are stimulated by external electrical signals, extracellular Ca2+ enters the cell and binds to CaM to form a complex that activates CaM. The complex, in turn, activates MLCK, a key protein in calcium-dependent channels. This results in an increase in Mg2+-ATPase activity of the myosin head, hydrolyzes ATP, and provides energy for the relative sliding of myosin to actin, causing GI smooth muscle contraction (38–40). Our findings suggest that tuina therapy modulates CaM and MLCK expression in the gastric antrum tissue, which may contribute to improved GI smooth muscle contraction. However, whether these molecular changes directly mediate the observed functional improvements requires further investigation through measurements of intracellular Ca2+ dynamics and contractile force. nNOS plays a crucial role in intestinal peristalsis, and Akt phosphorylation of nNOS regulates ileogastric peristalsis in mice and induces cGMP-dependent GI smooth muscle relaxation, thereby promoting digestion (41–44). Hyperglycemia can reduce the number of intestinal neurons and the expression of nNOS mRNA and protein in the GI tract, which is the main factor causing abnormal intestinal motility. Restoring the expression of nNOS mRNA and protein in the GI tract can help reverse the delayed gastric emptying (45, 46).
Ca2+-Mg2+-ATPase and CS enzyme play a crucial role in maintaining the normal metabolic function of the body. Ca2+-ATPase is responsible for transporting Ca2+ from the cytoplasm to the mitochondria to ensure the maintenance of Ca2+ homeostasis, and the decrease of ATPase activity will destroy the intracellular energy metabolism (47–51). We observed a significant increase in the activity of these enzymes in the ileal tissue, which reflects an enhancement in the motility function of the small intestine.
DGP is more closely related to the 5-HT receptor. 5-HT distributed throughout the GI tract of the 5-HT receptor regulates GI function (52). 5-HT4 agonists were found to successfully treat various functional GI motility problems, such as constipation, constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome, functional dyspepsia, and DGP (53). A large number of studies have confirmed that the Piezo2/5-HT pathway is involved in the regulation of GI motility. EC cells are rare excitable, serotonergic neuroendocrine cells of intestinal epithelial cells that detect and transmit stimulus signals to nearby mucosal nerve terminals (5, 54–56). Meanwhile, in mouse small and large intestinal epithelial cells, Piezo2 is expressed in a subset of EC cells and localized on the membrane adjacent to 5-HT vesicles, where Piezo2 is essential for the coupling force of EC cell 5-HT release and enteroendocrine function (14).
Tuina therapy is a mechanical therapy of force stimulation, which can significantly improve gastric retention, reduce gastric residual volume, and improve gastric emptying function, so as to alleviate GI motility disorders (23–25). According to the results of this study, we hypothesize that the protective effects of long-term tuina on GI function in DM and inhibition of DGP might be associated with upregulating Piezo2 expression in intestinal epithelial EE cells and promoting 5-HT release from EC cells. However, further mechanistic studies with Piezo2/5-HT pathway inhibitors are required to confirm this causal relationship. Unfortunately, we did not adequately address alternative mechanisms or establish causation. Our findings only demonstrate that long-term tuina preserves GI function in DM and inhibits DGP development, which is associated with the upregulation of Piezo2/5-HT pathway-related proteins in the ileum.
In addition, during tuina therapy, mechanical stimulation may regulate nerve conduction and autonomic nervous system balance by activating Piezo1 ion channels or Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid (TRPV) ion channel family members. A study indicates that the Piezo1 mechanosensor is specifically expressed in cholinergic enteric neurons and is directly involved in the regulation of GI motility (57). Optogenetic stimulation of Piezo1+ cholinergic enteric neurons drives colonic motility, while Piezo1 deficiency reduces cholinergic neuronal activity and slows peristalsis. Additionally, Piezo1 deficiency in cholinergic enteric neurons abolishes exercise-induced acceleration of GI motility (57). Another study showed that TRPV4 is expressed and functional in intestinal epithelial cells; its activation in the GI tract causes increases in intracellular calcium concentrations, chemokine release, and colitis (58).
The molecular mechanisms, signaling pathways, and downstream effects by which tuina activates channels such as Piezo and TRPV remain unclear, and further in-depth investigation will require the development of additional animal models and cell-based experiments. Currently, clinical trials of tuina for DGP have relatively small sample sizes. Future multi-center, large-scale randomized controlled trials are needed to validate the long-term efficacy and safety of tuina. Therefore, future research should focus on the molecular mechanisms and signaling cascades of tuina activating mechanically sensitive ion channels, as well as multi-center, large-sample randomized controlled clinical trials. Simultaneously, it should explore the synergistic effects of tuina with other therapeutic interventions and the development of individualized treatment plans, providing theoretical support and practical evidence for the precision treatment of DGP.
This study has some limitations. First of all, we used authentic hands-on tuina techniques. The operators were trained uniformly, and the procedures, manipulation frequency, and duration of tuina manipulations were restricted. We conduct tuina therapy with a level of force that ensures the comfort of the rats. This is similar to the actual effort in clinical settings. The downside is that it is impossible to accurately quantify the force of the tuina. Secondly, this study has a sample size of five rats per group, which may pose a risk of result bias due to the relatively small sample size. Thirdly, owing to certain reasons, this study did not set up control groups with Piezo2 inhibitors, 5-HT antagonists, or Piezo2 knockout mice. The mechanism by which long-term tuina upregulates the mechanoreceptor Piezo2 and promotes the release of 5-HT from EC cells has not been elucidated. In future research, we will further refine the experimental design and conduct in-depth mechanism studies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, our study suggests that the protective effects of long-term tuina on GI motility are associated with the modulation of CaM, MLCK, nNOS, Piezo2, 5-HT, and 5-HT4R. A potential mechanism may involve Piezo2-mediated mechanical sensitivity and 5-HT signaling, but causal validation is required. This study provides not only evidence for tuina therapy as a potential alternative therapy for the prevention and treatment of DGP but also a basis for further research on the potential mechanism of tuina therapy in the prevention and treatment of DGP. Future studies should explore how tuina therapy can play a protective role in the GI tract and inhibit the occurrence and development of DGP through the mechano-chemical signal coupling of the Piezo2/5-HT pathway.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by Animal Ethics Committee of Sichuan Research Institute of Biomedical Industry Technology (No. 2021-07-15). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
J-zJ: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. W-qL: Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. K-lK: Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. Y-qJ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. Z-xH: Writing – review & editing. L-jZ: Writing – review & editing. J-yC: Writing – review & editing. DW: Writing – review & editing. X-yZ: Writing – review & editing. Z-lT: Writing – review & editing. JZ: Writing – review & editing. D-zP: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Sichuan Science and Technology Program. To explore the mechanism of tuina intervention on DGP GI motility disorder based on Piezo2 mechanistically sensitive ion channel and acupoint sensitization (No. 2021JDRC0157). The bidirectional regulation of puncturing at front Mu-back Shu combination on the autophagy balance to improving the intestinal motility via 5-HT/5-HTR-AMPK-mTOR pathway (No. 2023NSFSC1820).
Acknowledgments
Thanks to the Sichuan Province Science and Technology Program (nos. 2021JDRC0157 and 2023NSFSC1820). We thank the School of Acupuncture and Tuina, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine for the support of this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2025.1536567/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Bharucha AE, Kudva YC, and Prichard DO. Diabetic gastroparesis. Endocrine Rev. (2019) 40:1318–52. doi: 10.1210/er.2018-00161
2. Drewes AM, Søfteland E, Dimcevski G, Farmer AD, Brock C, Frøkjær JB, et al. Brain changes in diabetes mellitus patients with gastrointestinal symptoms. World J diabetes. (2016) 7:14–26. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i2.14
3. Lacy BE, Crowell MD, Mathis C, Bauer D, and Heinberg LJ. Gastroparesis: quality of life and health care utilization. J Clin gastroenterol. (2018) 52:20–4. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000000728
4. Yarandi SS and Srinivasan S. Diabetic gastrointestinal motility disorders and the role of enteric nervous system: current status and future directions. Neurogastroenterol motility. (2014) 26:611–24. doi: 10.1111/nmo.2014.26.issue-5
5. Bayrer JR, Castro J, Venkataraman A, Touhara KK, Rossen ND, Morrie RD, et al. Gut enterochromaffin cells drive visceral pain and anxiety. Nature. (2023) 616:137–42. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-05829-8
6. Chin A, Svejda B, Gustafsson BI, Granlund AB, Sandvik AK, Timberlake A, et al. The role of mechanical forces and adenosine in the regulation of intestinal enterochromaffin cell serotonin secretion. Am J Physiol Gastrointestinal liver Physiol. (2012) 302:G397–405. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00087.2011
7. Kim M, Javed NH, Yu JG, Christofi F, and Cooke HJ. Mechanical stimulation activates Galphaq signaling pathways and 5-hydroxytryptamine release from human carcinoid BON cells. J Clin Invest. (2001) 108:1051–9. doi: 10.1172/JCI12467
8. Wang F, Knutson K, Alcaino C, Linden DR, Gibbons SJ, Kashyap P, et al. Mechanosensitive ion channel Piezo2 is important for enterochromaffin cell response to mechanical forces. J Physiol. (2017) 595:79–91. doi: 10.1113/tjp.2017.595.issue-1
9. Bulbring E and Crema A. The release of 5-hydroxytryptamine in relation to pressure exerted on the intestinal mucosa. J Physiol. (1959) 146:18–28. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006175
10. Bertrand PP. Real-time detection of serotonin release from enterochromaffin cells of the Guinea-pig ileum. Neurogastroenterol motility. (2004) 16:511–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2004.00572.x
11. Sidhu M and Cooke HJ. Role for 5-HT and ACh in submucosal reflexes mediating colonic secretion. Am J Physiol. (1995) 269:G346–51. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1995.269.3.G346
12. Cooke HJ, Sidhu M, and Wang YZ. 5-HT activates neural reflexes regulating secretion in the Guinea-pig colon. Neurogastroenterol motility. (1997) 9:181–6. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2982.1997.d01-41.x
13. Heredia DJ, Dickson EJ, Bayguinov PO, Hennig GW, and Smith TK. Localized release of serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) by a fecal pellet regulates migrating motor complexes in murine colon. Gastroenterology. (2009) 136:1328–38. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.12.010
14. Alcaino C, Knutson KR, Treichel AJ, Yildiz G, Strege PR, Linden DR, et al. A population of gut epithelial enterochromaffin cells is mechanosensitive and requires Piezo2 to convert force into serotonin release. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2018) 115:E7632–e41. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1804938115
15. Drokhlyansky E, Smillie CS, Van Wittenberghe N, Ericsson M, Griffin GK, Eraslan G, et al. The human and mouse enteric nervous system at single-cell resolution. Cell. (2020) 182:1606–22.e23. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.003
16. Morarach K, Mikhailova A, Knoflach V, Memic F, Kumar R, Li W, et al. Diversification of molecularly defined myenteric neuron classes revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing. Nat Neurosci. (2021) 24:34–46. doi: 10.1038/s41593-020-00736-x
17. Woo SH, Lukacs V, de Nooij JC, Zaytseva D, Criddle CR, Francisco A, et al. Piezo2 is the principal mechanotransduction channel for proprioception. Nat Neurosci. (2015) 18:1756–62. doi: 10.1038/nn.4162
18. Chesler AT, Szczot M, Bharucha-Goebel D, Čeko M, Donkervoort S, Laubacher C, et al. The role of PIEZO2 in human mechanosensation. New Engl J Med. (2016) 375:1355–64. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1602812
19. Servin-Vences MR, Lam RM, Koolen A, Wang Y, Saade DN, Loud M, et al. PIEZO2 in somatosensory neurons controls gastrointestinal transit. Cell. (2023) 186:3386–99.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.07.006
20. Seo BR, Payne CJ, McNamara SL, Freedman BR, Kwee BJ, Nam S, et al. Skeletal muscle regeneration with robotic actuation-mediated clearance of neutrophils. Sci Trans Med. (2021) 13:eabe8868. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abe8868
21. Liu B, Qiao L, Liu K, Liu J, Piccinni-Ash TJ, and Chen ZF. Molecular and neural basis of pleasant touch sensation. Sci (New York NY). (2022) 376:483–91. doi: 10.1126/science.abn2479
22. Zhang W, Zhou W, Kong Y, Li Q, Huang X, Zhao B, et al. The effect of abdominal massage on enteral nutrition tolerance in patients on mechanical ventilation: A Randomized Controlled Study. Intensive Crit Care nursing. (2023) 75:103371. doi: 10.1016/j.iccn.2022.103371
23. Momenfar F, Abdi A, Salari N, Soroush A, and Hemmatpour B. Studying the effect of abdominal massage on the gastric residual volume in patients hospitalized in intensive care units. J Intensive Care. (2018) 6:47. doi: 10.1186/s40560-018-0317-5
24. Deng LX, Lan C, Zhang LN, Dun T, Yang S, Qing Y, et al. The effects of abdominal-based early progressive mobilisation on gastric motility in endotracheally intubated intensive care patients: A randomised controlled trial. Intensive Crit Care nursing. (2022) 71:103232. doi: 10.1016/j.iccn.2022.103232
25. Ridley EJ and Chapple LS. Time to combine: Integrating physical therapy and nutrition. Intensive Crit Care nursing. (2022) 71:103263. doi: 10.1016/j.iccn.2022.103263
26. Wang X, Sun J, Li Z, Luo H, Zhao M, Li Z, et al. Impact of abdominal massage on enteral nutrition complications in adult critically ill patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Complementary therapies Med. (2022) 64:102796. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2021.102796
27. Kahraman BB and Ozdemir L. The impact of abdominal massage administered to intubated and enterally fed patients on the development of ventilator-associated pneumonia: a randomized controlled study. Int J Nurs Stud. (2015) 52:519–24. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2014.11.001
28. Dai N, He Q, Liu X, Fang M, Xiong M, Li X, et al. Therapeutic massage/Tuina for treatment of functional dyspepsia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Qual Life research: an Int J Qual Life aspects treatment Care rehabilitation. (2023) 32:653–67. doi: 10.1007/s11136-022-03228-6
29. McClurg D, Hagen S, Hawkins S, and Lowe-Strong A. Abdominal massage for the alleviation of constipation symptoms in people with multiple sclerosis: a randomized controlled feasibility study. Multiple sclerosis (Houndmills Basingstoke England). (2011) 17:223–33. doi: 10.1177/1352458510384899
30. Gu X, Zhang L, Yuan H, and Zhang M. Analysis of the efficacy of abdominal massage on functional constipation: A meta-analysis. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e18098. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18098
31. Lämås K, Lindholm L, Stenlund H, Engström B, and Jacobsson C. Effects of abdominal massage in management of constipation–a randomized controlled trial. Int J Nurs Stud. (2009) 46:759–67. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2009.01.007
32. Percie du Sert N, Ahluwalia A, Alam S, Avey MT, Baker M, Browne WJ, et al. Reporting animal research: Explanation and elaboration for the ARRIVE guidelines 2.0. PloS Biol. (2020) 18:e3000411. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000411
33. Srinivasan K, Viswanad B, Asrat L, Kaul CL, and Ramarao P. Combination of high-fat diet-fed and low-dose streptozotocin-treated rat: a model for type 2 diabetes and pharmacological screening. Pharmacol Res. (2005) 52:313–20. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2005.05.004
34. Han X, Chen X, Wang X, Gong M, Lu M, Yu Z, et al. Electroacupuncture at ST36 improve the gastric motility by affecting neurotransmitters in the enteric nervous system in type 2 diabetic rats. Evidence-Based complementary Altern medicine: eCAM. (2021) 2021:6666323. doi: 10.1155/2021/6666323
35. Fang X, Bogdanov V, Davis JP, and Kekenes-Huskey PM. Molecular insights into the MLCK activation by caM. J Chem Inf modeling. (2023) 63:7487–98. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.3c00954
36. Grover M, Farrugia G, and Stanghellini V. Gastroparesis: a turning point in understanding and treatment. Gut. (2019) 68:2238–50. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318712
37. Wegeberg AM, Bertoli D, Ejskjaer N, Brock B, Drewes AM, and Brock C. Gastrointestinal function in diabetes is affected regardless of asymptomatic appearance. J Internal Med. (2022) 291:505–12. doi: 10.1111/joim.v291.4
38. Tang Z, Chen H, Yang J, Dai S, and Lin Y. The comparison of Ca2+/CaM-independent and Ca2+/CaM-dependent phosphorylation of myosin light chains by MLCK. Physiol Res. (2005) 54:671–8. doi: 10.33549/physiolres
39. He WQ, Peng YJ, Zhang WC, Lv N, Tang J, Chen C, et al. Myosin light chain kinase is central to smooth muscle contraction and required for gastrointestinal motility in mice. Gastroenterology. (2008) 135:610–20. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.05.032
40. Somlyo AP and Somlyo AV. Ca2+ sensitivity of smooth muscle and nonmuscle myosin II: modulated by G proteins, kinases, and myosin phosphatase. Physiol Rev. (2003) 83:1325–58. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00023.2003
41. Guerra DD, Bok R, Vyas V, Orlicky DJ, Lorca RA, and Hurt KJ. Akt phosphorylation of neuronal nitric oxide synthase regulates gastrointestinal motility in mouse ileum. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2019) 116:17541–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1905902116
42. Lefebvre RA, Smits GJ, and Timmermans JP. Study of NO and VIP as non-adrenergic non-cholinergic neurotransmitters in the pig gastric fundus. Br J Pharmacol. (1995) 116:2017–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb16406.x
43. Rameau GA, Tukey DS, Garcin-Hosfield ED, Titcombe RF, Misra C, Khatri L, et al. Biphasic coupling of neuronal nitric oxide synthase phosphorylation to the NMDA receptor regulates AMPA receptor trafficking and neuronal cell death. J Neurosci. (2007) 27:3445–55. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4799-06.2007
44. Huang PL, Dawson TM, Bredt DS, Snyder SH, and Fishman MC. Targeted disruption of the neuronal nitric oxide synthase gene. Cell. (1993) 75:1273–86. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90615-W
45. Bulc M, Palus K, Dąbrowski M, and Całka J. Hyperglycaemia-induced downregulation in expression of nNOS intramural neurons of the small intestine in the pig. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20(7):1681. doi: 10.3390/ijms20071681
46. Watkins CC, Sawa A, Jaffrey S, Blackshaw S, Barrow RK, Snyder SH, et al. Insulin restores neuronal nitric oxide synthase expression and function that is lost in diabetic gastropathy. J Clin Invest. (2000) 106:803. doi: 10.1172/JCI8273C1
47. Carminita E, Crescence L, Brouilly N, Altié A, Panicot-Dubois L, and Dubois C. DNAse-dependent, NET-independent pathway of thrombus formation in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2021) 118(28):e2100561118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2100561118
48. Shattock MJ, Ottolia M, Bers DM, Blaustein MP, Boguslavskyi A, Bossuyt J, et al. Na+/Ca2+ exchange and Na+/K+-ATPase in the heart. J Physiol. (2015) 593:1361–82. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2015.593.issue-6
49. Leijding C, Viken I, Bruton JD, Andersson DC, Cheng AJ, and Westerblad H. Increased tetanic calcium in early fatigue of mammalian muscle fibers is accompanied by accelerated force development despite a decreased force. FASEB J. (2023) 37:e22978. doi: 10.1096/fj.202300401R
50. O’Malley J, Kumar R, Inigo J, Yadava N, and Chandra D. Mitochondrial stress response and cancer. Trends cancer. (2020) 6:688–701. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2020.04.009
51. Hu R, Shah AM, Han Q, Ma J, Dai P, Meng Y, et al. Proteomics reveals the obstruction of cellular ATP synthesis in the ruminal epithelium of growth-retarded yaks. Animals: an Open Access J MDPI. (2024) 14(8):1243. doi: 10.3390/ani14081243
52. Qian QH, Wang ZC, Zhao Y, Liu DW, and Qian WB. Effects of Tangweian granule on 5-HT(2A)R in rat model with diabetic gastroparesis. Zhongguo Zhong yao za zhi = Zhongguo zhongyao zazhi = China J Chin materia medica. (2008) 33:541–4.
53. Chedid V, Brandler J, Arndt K, Vijayvargiya P, Wang XJ, Burton D, et al. Randomised study: effects of the 5-HT(4) receptor agonist felcisetrag vs placebo on gut transit in patients with gastroparesis. Alimentary Pharmacol Ther. (2021) 53:1010–20. doi: 10.1111/apt.16304
54. Bellono NW, Bayrer JR, Leitch DB, Castro J, Zhang C, O’Donnell TA, et al. Enterochromaffin cells are gut chemosensors that couple to sensory neural pathways. Cell. (2017) 170:185–98.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.034
55. Racké K and Schwörer H. Characterization of the role of calcium and sodium channels in the stimulus secretion coupling of 5-hydroxytryptamine release from porcine enterochromaffin cells. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol. (1993) 347:1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00168764
56. Strege PR, Knutson K, Eggers SJ, Li JH, Wang F, Linden D, et al. Sodium channel Na(V)1.3 is important for enterochromaffin cell excitability and serotonin release. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:15650. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-15834-3
57. Xie Z, Rose L, Feng J, Zhao Y, Lu Y, Kane H, et al. Enteric neuronal Piezo1 maintains mechanical and immunological homeostasis by sensing force. Cell. (2025) 188:2417–32.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2025.02.031
Keywords: long-term tuina, diabetes mellitus, diabetic gastroparesis, gastrointestinal function, Piezo2/5-HT pathway
Citation: Jiang J-z, Li W-q, Kuang K-l, Jiang Y-q, He Z-x, Zhang L-j, Cao J-y, Wang D, Zhang X-y, Tian Z-l, Zhu J and Peng D-z (2025) Long-term tuina can inhibit the occurrence of gastroparesis by protecting gastrointestinal function in diabetic rats. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1536567. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1536567
Received: 29 November 2024; Accepted: 29 May 2025;
Published: 25 June 2025.
Edited by:
Vijaya Juturu, Independent researcher, Flemington, NJ, United StatesReviewed by:
Matthew Vincent, Washington University in St. Louis, United StatesEclésio Batista De Oliveira Neto, Centro Universitário de Maceió (Unima) - Maceió University Center, Brazil
Copyright © 2025 Jiang, Li, Kuang, Jiang, He, Zhang, Cao, Wang, Zhang, Tian, Zhu and Peng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: De-zhong Peng, MTU4MjgwNTU2OThAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Jun Zhu, emh1anVudGNtQDE2My5jb20=; Jian-zhen Jiang, MTUxODgzNTE1OThAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jian-zhen Jiang
Jian-zhen Jiang Wan-qiu Li
Wan-qiu Li Kun-lin Kuang†
Kun-lin Kuang† Jing-ya Cao
Jing-ya Cao Dan Wang
Dan Wang Xin-yue Zhang
Xin-yue Zhang Zi-lei Tian
Zi-lei Tian Jun Zhu
Jun Zhu De-zhong Peng
De-zhong Peng