- Department of Orthopedics, Jiading District Central Hospital Affiliated Shanghai University of Medicine & Health Sciences, Shanghai, China
Purpose: The atherogenic index of plasma (AIP), recognized as a marker of atherosclerosis, which also has a profound impact on bone metabolism. However, research exploring the association between the AIP and the probability of vertebral fractures in populations is still relatively scarce. The study aims to evaluate the association between the AIP and vertebral fractures probability in individuals in a longitudinal study.
Patients and methods: A total of 1395 subjects who were older than 55 years and underwent CT scans for lung cancer screening between July 2019 and July 2021 were enrolled and followed up for a duration ranging from 8 months to 6 years. Among them, 91 individuals experienced new vertebral fractures. Participants were stratified into four groups based on AIP quartiles. The association between the AIP and vertebral fractures probability was then assessed by cox proportional hazards model.
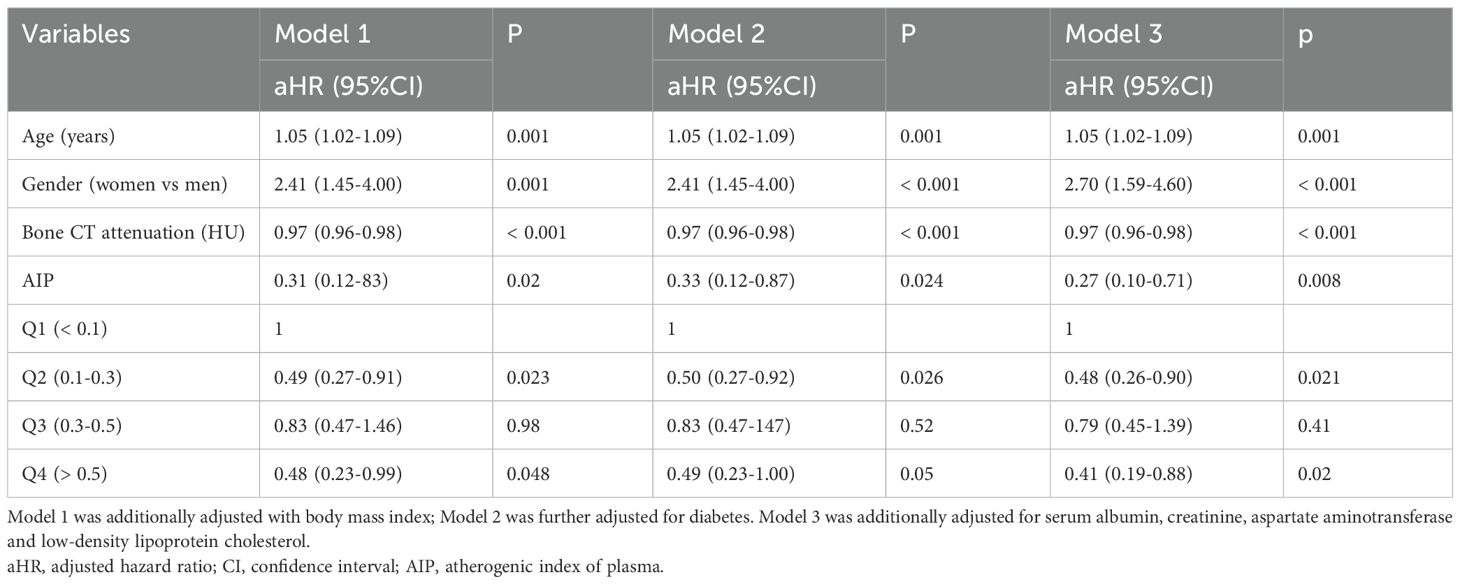
Results: The incidence of vertebral fracture decreased with increasing AIP (p for trend = 0.001). Kaplan-Meier survival analysis indicated that vertebral fractures were more likely to occur in patients with low levels of AIP (log-rank, all P < 0.05). Multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that AIP was negatively associated with the probability of vertebral fractures even after accounting for confounding factors (adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) = 0.27, 95%CI = 0.10-0.71 for continuous AIP; aHR = 0.48, 95%CI = 0.26-0.90 for Q2; aHR = 0.41, 95%CI = 0.19-0.88 for Q4, respectively). Subgroup analysis showed that such associations were mainly observed in male subjects. Restricted cubic splines further showed that the probability of vertebral fracture decreased with the increasing of AIP after adjusting with confounders in overall population and men, but not in women.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated a strong association between the AIP and the probability of vertebral fracture. Low AIP may be an associated factor of vertebral fracture.
Introduction
Blood lipids, including triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c), have been implicated in bone metabolism. Studies suggest that dysregulation in lipid metabolism can lead to bone metabolic disorders, potentially causing conditions such as osteoporosis, bone loss, and bone fractures (1–4). However, the association between lipids levels and bone metabolism is complicated. Some studies indicate that higher levels of HDL-c are associated with a lower risk of osteoporotic fractures (5). However, opposite result was also reported. Hussain et al. showed that higher levels of HDL-c are associated with an increased fracture risk (6). Conversely, elevated levels of LDL-c and TG have been linked to an increased risk of fractures, indicating a potential negative impact on bone health (7, 8).
The atherogenic index of plasma (AIP) was defined as the base 10 logarithm of the ratio of the molar concentration of triglycerides (TG) to HDL-c. Considering both TG and HDL-c levels may be more accurately reflecting dyslipidemia’s (9). AIP is a valuable tool in cardiovascular disease risk and prognosis assessment (10, 11). It provides a measure of the balance between the potentially atherogenic lipoproteins and the cardioprotective HDL-c. A higher AIP value indicates a greater risk of developing atherosclerosis and related cardiovascular events. Monitoring AIP can help in the management of cardiovascular health. Some studies also showed that AIP is related to metabolism diseases, such as diabetes (12, 13) and metabolic syndrome (14, 15).
Interestingly, several studies have shown that AIP was related to bone metabolism. Xu reported that femur BMD and lumbar spine BMD were both increased with increasing AIP (16). However, He and colleagues reported completely opposite results. They observed a negative correlation between the AIP and total BMD (17). A study also showed that AIP is related to a degraded trabecular bone score (TBS) which is an important biomarker of bone fracture (18). However, to our knowledge, the association between AIP and fracture in general population has not been clarified. In the present longitudinal study, we investigated such association in a population who underwent CT lung cancer screening.
Methods
Subjects
CT lung cancer screening was recommended to subjects aged 50–80 years (19). We confirmed 1874 individuals who were older than 55 years and underwent clinical CT scans of the chest or lumbar spine for lung cancer screening between 2019 July and July 2021. A total of 1395 participants were identified and followed up for 8 months to 6 years. The exclusion criteria are as follows: (1) received only one time scan or lost to follow-up; (2) missing demographic, clinical and laboratory information; (3) poor imaging quality for fracture evaluation; (4) spine fracture at baseline; (5) history of metabolic bone diseases, cancer, rheumatic diseases, and severe kidney and liver dysfunction. Two radiologists determine whether a new fracture has occurred by observing the baseline and follow-up radiographic images. Consequently, 91 patients in the study developed new osteoporotic fractures during the follow-up period. The Ethics Committee of the Jiading District Central Hospital approved this trial’s conduct. Informed consent was waived because of the retrospective design.
Data collection
The data, which included demographic information, such as age and sex, body mass index (BMI), and laboratory biochemical indicators were collected. The following biochemical indicators were obtained from the medical system records: aspartate aminotransferase (AST), serum creatinine, fasting blood glucose level, serum TG, TC, HDL-c, LDL-c, serum albumin, fasting blood glucose level. AIP was calculated using the following equation: log10 [TG(mg/dL)/HDL-c (mg/dL)].
Bone CT assessment
Trabecular bone CT attenuation was used as indicator of bone mass. All CT scans were performed in one CT (GE Optima CT680, USA). The scan protocol was as follows: voltage of 120 kV, 100–120 mAs, thickness of 0.625 mm. The CT images were reconstructed in the workstation using 0.625-mm section thickness and 0.5-mm increments. A 2–3 cm2 region of interest (ROI) was placed in the cancellous bone region of the medium level of T12 and L1 vertebral body. For each measurement, we avoided cortical bone, the posterior venous plexus, bone islands, and other heterogeneous areas. The mean CT attenuation of T12 and L1 was calculated and used for analyses. Incident vertebral fractures was defined as any vertebra that was graded as normal (grade 0) at baseline and exhibited at least mild deformation (grades 1-3, or a reduction in height of approximately 20-25%) at follow-up based on Gennant’s classification. All individuals underwent CT scans for lung cancer screening at baseline.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS version 26.0 or R version 4.1.2. Continuous variables with normal distributions are expressed as mean (± SD), while those with non-normal distributions are presented as median (interquartile ranges). Categorical variables are represented by frequencies. The chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test was employed to assess differences between groups for categorical variables, whereas independent samples t-tests or the Mann-Whitney U test were utilized for continuous variables. According to the quartiles of the AIP, participants were divided into four groups: Q1 (< 0.10), Q2 (0.1-0.30), Q3 (0.30-0.50) and Q4 (> 0.50). Cox proportional hazards model was applied to evaluate the association between the AIP and the risk of vertebral fractures, yielding adjusted hazard ratios (aHRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for each indicator. Then, three multivariate Cox models were built and used to gradually adjust for potential confounding factors for a fragility fracture endpoint event. Additionally, cumulative hazard curves are presented. Participants were stratified by sex to examine sex-specific associations. The restricted cubic splines analysis was used to illustrate the multivariable-adjusted hazard ratios for the risk of vertebral fracture across varying levels of the AIP. A P value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Baseline characteristics
The baseline characteristics are given in Table 1. The study group included 1395 individuals. Significant differences were observed in age, sex, bone CT attenuation (HU), AST, albumin, blood glucose and serum lipids levels (TC, TG, HDL-c and LDL-c) among different AIP groups (all p < 0.01). The incidence rates of vertebral fracture were related to the levels of the AIP (fracture: 10.5%, 4.8%, 8.3% and 3.8% for Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4 of the AIP, respectively; p for trend = 0.001).
Cox proportional hazard models for the risk of vertebral fracture
The association of the AIP and vertebral fracture risk were firstly showed by cumulative hazard curve (Figure 1). During the follow-up period, out of 1395 subjects, 91 experienced vertebral fracture events (6.57%). In total population and female, the Kaplan-Meier survival curve analysis showed that compared with the participants with low level of AIP (Q1), those with Q2 and Q4 of AIP had a significantly decreased probability of vertebral fracture during follow-up (log-rank, all P < 0.05).
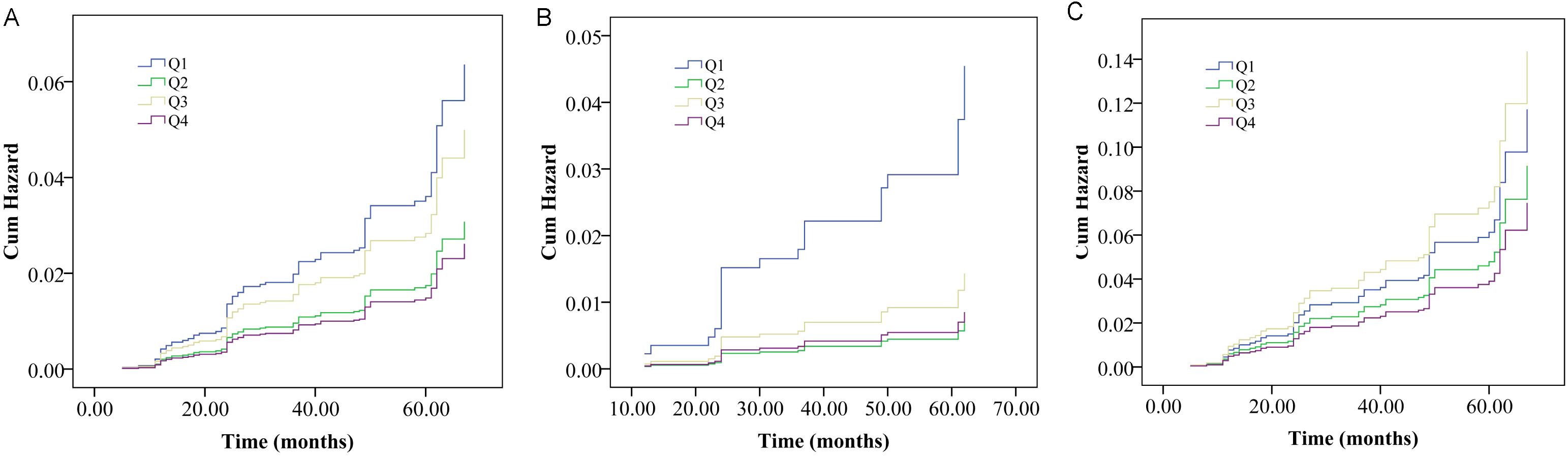
Figure 1. Cumulative probability curves of vertebral fracture probability divided by interquartile range of the atherogenic index of plasma (AIP) in overall population (A), male (B) and female (C) populations.
The association of the AIP and vertebral fracture probability was further evaluated by multivariate Cox regression analysis (Table 2). In model I which was adjusted with age, gender, bone CT attenuation and BMI, the higher AIP was associated with the lower probability of vertebral fracture (aHR = 0.49, 95%CI = 0.27-0.91 for Q2 and aHR = 0.48, 95%CI:0.23-0.99 for Q4) compared with low AIP (Q1). In fully adjusted model which was adjusted with age, gender, bone CT attenuation, BMI, diabetes, creatinine, albumin, AST and LDL-c, the negative association between the AIP and the probability of the vertebral fracture remained statistically significant respectively (aHR = 0.48, 95%CI = 0.26-0.90 for Q2; aHR = 0.41, 95%CI = 0.19-0.88 for Q4).
Restricted cubic splines further showed that the probability of vertebral fracture decreased with the increasing of AIP after adjusting with confounders (Figure 2A).
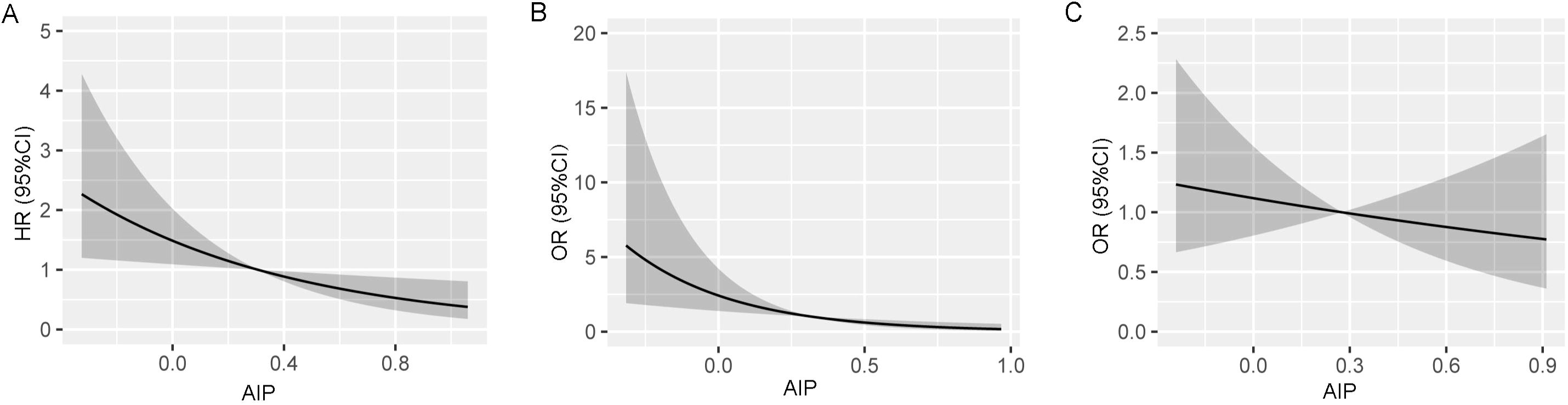
Figure 2. Restricted cubic splines show the multivariable adjusted hazard ratio for the probability of vertebral fracture according to the level of atherogenic index of plasma (AIP) in the overall population (A), male (B) and female (C) populations. Age, sex (overall population), body mass index, serum albumin, creatinine, aspartate aminotransferase, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and bone attenuation or diabetes were adjusted.
Subgroup analysis
Subsequently, we showed the association between AIP and the probability of vertebral fracture in men and women, respectively (Table 3). No significant associations were found between AIP and probability of vertebral fracture in all the three models in women (aHR = 0.79, 95%CI: 0.38-1.63 for Q2, aHR = 1.23, 95%CI: 0.62-2.43 for Q3 and aHR = 0.65, 95%CI: 0.26-1.66 for Q4). For male population, the association between AIP and probability of vertebral fracture was similar with the overall population. In model I which was adjusted with age, gender, bone CT attenuation and BMI, the higher AIP was associated with the lower probability of vertebral fracture (adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) = 0.16,95%CI = 0.04-0.56 for Q2, aHR = 0.33, 95%CI:0.11-0.99 for Q3 and aHR = 0.19, 95%CI:0.05-0.71) compared with low AIP (Q1). In fully adjusted Model, the probability of the vertebral fracture remained statistically significant (aHR = 0.15, 95%CI=0.04-0.56 for Q2; aHR = 0.19, 95%CI = 0.05-0.70 for Q4).
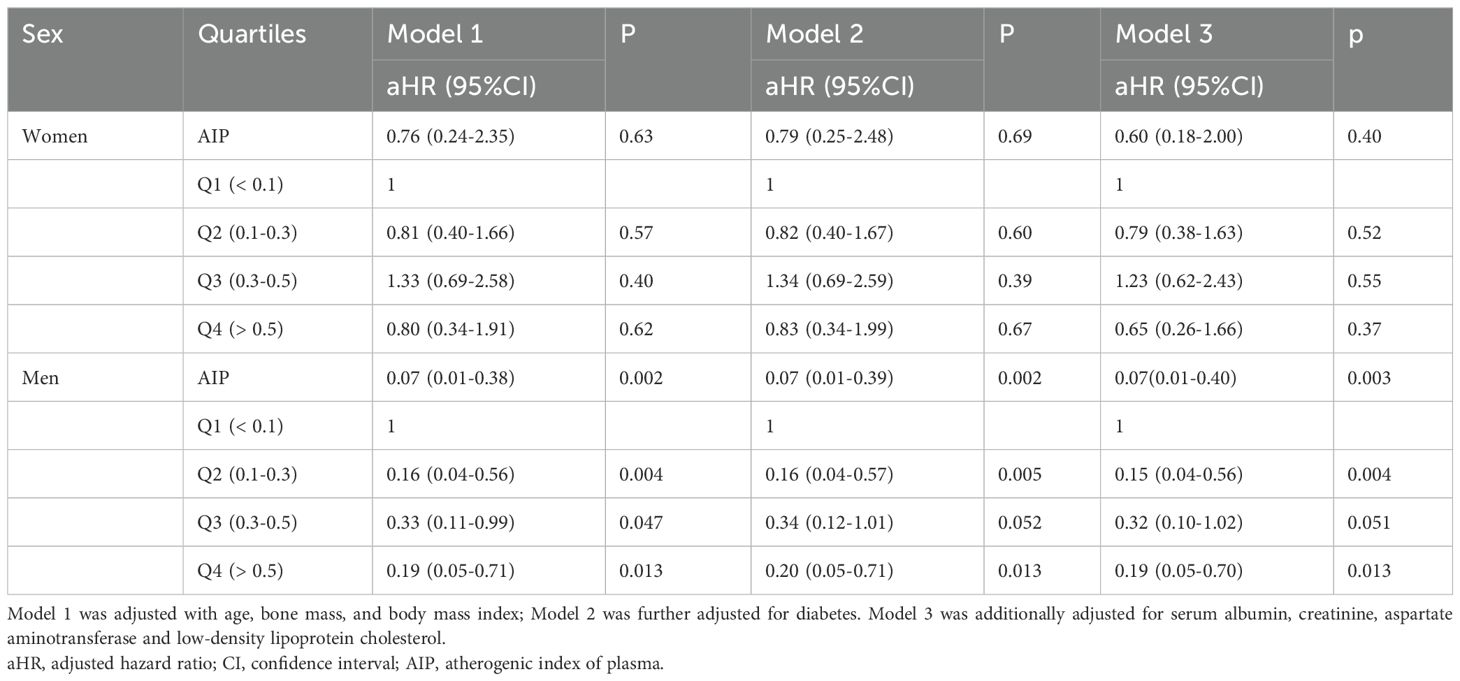
Table 3. Association between the atherogenic index of plasma and the risk of vertebral fracture divided by sex.
Restricted cubic splines further showed that the probability of vertebral fracture decreased with the increasing of AIP after adjusting with confounders in men (Figure 2B), but not in women (Figure 2C).
Discussion
Associations of serum lipid levels and fracture risk have been reported. However, the results are conflicting. Moreover, the association between AIP and fracture probability has not been well studied. This longitudinal study in a Chinese population is the first report which showed that AIP was associated with the probability of vertebral fracture. However, such associations were mainly observed in overall population and male subjects, but not female subjects. The probability of vertebral fracture was 52% lower in subjects with high AIP (≥ 0.50) than in those with low AIP (< 0.10). This study reported a novel associated factor for vertebral fracture, which may be useful for detecting high fracture probability early and fracture management.
Fractures are the most serious clinical outcome of osteoporosis. Interestingly, some studies also suggest a link between blood lipid levels and the risk of fractures. A meta-analysis indicated that serum TC concentration is positively correlated with the risk of fractures (20). A U-shaped relationship between high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c) and hip fractures has been reported (21). In contrast, a recent study showed an association between HDL-c levels and the risk of fractures in the age group of 60 years and above, but not in the age group below 60 (22). Similar results have been reported in healthy elderly individuals over the age of 65 (6). The association between TG and fracture risk was also reported in women (23). However, those studies mainly focused on single lipids marker. Considering the different role of TG and HDL-c, it would be better to combine them together to obtain a new comprehensive index and show its role in fracture. Interestingly, AIP had been reported in literature and many studies have shown the association of AIP and cardiovascular diseases (10, 11, 24). The association between AIP and metabolic diseases was also reported (12, 13). Two recent studies also found that AIP was associated with bone mineral density (16, 17). However, no study has shown the link between AIP and fracture probability. Our study showed that high AIP was a protective factor for spine fracture, especially for men. Our data demonstrated that AIP should be considered during the fracture management in older adults.
For overall population, AIP at Q3 did not show statistical significance compared to that in Q1. But the OR was still lower than 1.0, which also indicated that a low risk of fracture in Q3 group. We speculated that the association may be sex-dependent. Therefore, we performed subgroup analysis. The data of subgroup analysis confirmed that the association was sex-dependent. Why Q3 did not show statistical significance compared to Q1 in overall population may be affected by sex. Although AIP at Q3 also did not show statistical significance in fully adjusted model compared to Q1 in male population, the OR was 0.32, which also indicated that a low risk of fracture in Q3 group. Moreover, the sample size of our study was relatively small which may affect the statistical power. The restricted cubic splines showed that fracture probability decreased by increasing of AIP. The relationship could be seen as a monotonic relationship between AIP and the number of fractures observed in male population. Why there was a sex-difference was unclear. One possible reason may be the high prevalence of osteoporosis in older women. Osteoporosis may play a more critical role for fracture in women. Interestingly, a recent study also showed that association of HDL-c and fracture risk were more common in men compared to women (25).
How AIP affects the risk of spine fracture is not understood. One of possible reason is that the positive relationship between HDL-c and fracture. A subjects with a high HDL-c may have a lower AIP because AIP was calculated by the 10 logarithm of the ratio of the TG to HDL-c. Another reason is that great level of TG may be associated with high bone mineral density (26). High bone mineral density will cause low probability of fracture. Moreover, AIP can be used as an indicator of atherosclerosis. A high AIP means a high risk of atherosclerosis. Blood vessels play a role in osteogenesis and osteoporosis (27). The atherosclerosis in bone arteries will result in bone loss. Consequently, the probability of fracture increased. High atherosclerosis burden is also associated with high inflammatory status (28, 29) which may be related excessive bone resorption. It has been shown that subclinical atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is associated with high risk of hip fracture (30).
Our study has several advantages. This was a longitudinal study with relatively large sample size. In addition, to our knowledge, the present study may be the first to show the association of AIP and fracture probability in general population. Several limitations should be acknowledged. First, our study reported only the association between AIP and vertebral fracture probability. whether such associations exist between AIP and nonspine fractures has not been studied. Second, our study only simply discussed the probable mechanisms. The underlying cellular or molecular mechanisms were not studied. Third, although several variables were adjusted, other factors, such as drinking or smoking habits, physical exercise, were not controlled. Fourth, our study had the unequal sample size of male and female population. One possible reason for the small number of female subjects was the high prevalence of osteoporosis and vertebral fracture. More women was excluded at baseline because of the osteoporotic vertebral fracture. Our study only included subjects without vertebral fracture at baseline. Finally, our population is Chinese population. The generalizability of our results should be validated in other populations.
In summary, this study revealed that the AIP were independently associated with the probability of vertebral fracture. Our study reported a novel associated factor of bone fracture. Monitoring AIP may be useful for identifying subjects with high-risk fractures earlier. However, further studies are needed to reveal the mechanisms by which AIP affects bone metabolism and fracture.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of Shanghai Jiading District Central Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because our study was a retrospective study.
Author contributions
XZ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. PX: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YY: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. XL: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The present study was supported by grants from the Foundation of the Key scientific research project of Shanghai Jiading District Health Commission (2024-KY-ZD-02).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Kim J, Ha J, Jeong C, Lee J, Lim Y, Jo K, et al. Bone mineral density and lipid profiles in older adults: a nationwide cross-sectional study. Osteoporos Int. (2023) 34:119–28. doi: 10.1007/s00198-022-06571-z
2. Zhang Q, Zhou J, Wang Q, Lu C, Xu Y, Cao H, et al. Association between Bone Mineral Density and lipid Profile in Chinese women. Clin Interv Aging. (2020) 15:1649–64. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S266722
3. Li S, Guo H, Liu Y, Wu F, Zhang H, Zhang Z, et al. Relationships of serum lipid profiles and bone mineral density in postmenopausal Chinese women. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). (2015) 82:53–8. doi: 10.1111/cen.12616
4. Tohidi M, Barzegar N, Hasheminia M, Azizi F, and Hadaegh F. Association of different lipid measures with incident bone fractures: Tehran lipid and glucose study. Postgrad Med. (2022) 134:326–32. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2022.2050980
5. Ghorabi S, Shab-Bidar S, Sadeghi O, Nasiri M, Khatibi SR, and Djafarian K. Lipid profile and risk of bone fracture: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Endocr Res. (2019) 44:168–84. doi: 10.1080/07435800.2019.1625057
6. Hussain SM, Ebeling PR, Barker AL, Beilin LJ, Tonkin AM, and McNeil JJ. Association of plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol Level With Risk of Fractures in healthy older adults. JAMA Cardiol. (2023) 8:268–72. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2022.5124
7. Wang Y, Dai J, Zhong W, Hu C, Lu S, and Chai Y. Association between serum cholesterol level and osteoporotic Fractures. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2018) 9:30. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00030
8. Yamauchi M, Yamaguchi T, Nawata K, Tanaka K, Takaoka S, and Sugimoto T. Increased low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level is associated with non-vertebral fractures in postmenopausal women. Endocrine. (2015) 48:279–86. doi: 10.1007/s12020-014-0292-0
9. Fernández-Macías JC, Ochoa-Martínez AC, Varela-Silva JA, and Pérez-Maldonado IN. Atherogenic index of plasma: Novel Predictive Biomarker for Cardiovascular illnesses. Arch Med Res. (2019) 50:285–94. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2019.08.009
10. Ulloque-Badaracco JR, Hernandez-Bustamante EA, Alarcon-Braga EA, Mosquera-Rojas MD, Campos-Aspajo A, Salazar-Valdivia FE, et al. Atherogenic index of plasma and coronary artery disease: A systematic review. Open Med (Wars). (2022) 17:1915–26. doi: 10.1515/med-2022-0590
11. Rabiee Rad M, Ghasempour Dabaghi G, Darouei B, and Amani-Beni R. The association of atherogenic index of plasma with cardiovascular outcomes in patients with coronary artery disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2024) 23:119. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02198-y
12. Shi Y and Wen M. Sex-specific differences in the effect of the atherogenic index of plasma on prediabetes and diabetes in the NHANES 2011–2018 population. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2023) 22:19. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01740-8
13. Yin B, Wu Z, Xia Y, Xiao S, Chen L, and Li Y. Non-linear association of atherogenic index of plasma with insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2023) 22:157. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01886-5
14. Li YW, Kao TW, Chang PK, Chen WL, and Wu LW. Atherogenic index of plasma as predictors for metabolic syndrome, hypertension and diabetes mellitus in Taiwan citizens: a 9-year longitudinal study. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:9900. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89307-z
15. Zhang X, Zhang X, Li X, Feng J, and Chen X. Association of metabolic syndrome with atherogenic index of plasma in an urban Chinese population: A 15-year prospective study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2019) 29:1214–9. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2019.07.006
16. Xu B, Ma G, Yang L, Chen X, Bian B, Yang B, et al. Non-linear association of atherogenic index of plasma with bone mineral density a cross-sectional study. Lipids Health Dis. (2024) 23:181. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02180-3
17. He Q, Chen B, Liang F, and Zhang Z. Association between the atherogenic index of plasma and bone mineral density among adult women: NHANES (2011-2018). Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2024) 15:1363889. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1363889
18. Hernández JL, Olmos JM, Pariente E, Ramos C, Martínez J, and Nan D. The atherogenic index of plasma is related to a degraded bone microarchitecture assessed by the trabecular bone score in postmenopausal women: The Camargo Cohort Study. Maturitas. (2021) 148:1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2021.03.008
19. Chinese expert group on early diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer and China lung oncology group. China national lung cancer screening guideline with low-dose computed tomography (2023 version). Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. (2023) 26:1–9. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2023.102.10
20. Ghorabi S, Shab-Bidar S, Sadeghi O, Nasiri M, Khatibi SR, and Djafarian K. Lipid Profile and risk of Bone Fracture: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Endocr Res. (2019) 44:168–84. doi: 10.1080/07435800.2019.1625057
21. Barzilay JI, Buzkova P, Kuller LH, Cauley JA, Fink HA, Sheets K, et al. The association of lipids and lipoproteins with hip Fracture Risk: the cardiovascular health study. Am J Med. (2022) 135:1101–8.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2022.05.024
22. Kunutsor SK and Laukkanen JA. The interplay between circulating high-density lipoprotein, age and fracturerisk: a new cohort study and systematic meta-analysis. Geroscience. (2023) 45:2727–41. doi: 10.1007/s11357-023-00801-w
23. Chang PY, Gold EB, Cauley JA, Johnson WO, Karvonen-Gutierrez C, Jackson EA, et al. Triglyceride levels and fracture risk in midlife women: study of women’s health across the nation (SWAN). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2016) 101:3297–305. doi: 10.1210/jc.2016-1366
24. Huang Q, Liu Z, Wei M, Huang Q, Feng J, Liu Z, et al. The atherogenic index of plasma and carotid atherosclerosis in a community population: a population-based cohort study in China. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2023) 22:125. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01839-y
25. Xiong X, Lui DTW, Ju C, Zhou Z, Xu C, Welsh P, et al. Associations of serum lipid traits with fracture and osteoporosis: A prospective cohort study from the UK biobank. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2024) 15:2669–83. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13611
26. Tang YJ, Sheu WH, Liu PH, Lee WJ, and Chen YT. Positive associations of bone mineral density with body mass index, physical activity, and blood triglyceride level in men over 70 years old: a TCVGHAGE study. J Bone Miner Metab. (2007) 25:54–9. doi: 10.1007/s00774-006-0727-7
27. Wu J, Hu M, Jiang H, Ma J, Xie C, Zhang Z, et al. Endothelial cell-derived lactate triggers bone mesenchymal stem cell histone lactylation to attenuate osteoporosis. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2023) 10:e2301300. doi: 10.1002/advs.202301300
28. Wolf D and Ley K. Immunity and inflammation in atherosclerosis. Circ Res. (2019) 124:315–27. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.313591
29. Weber C, Habenicht AJR, and von Hundelshausen P. Novel mechanisms and therapeutic targets in atherosclerosis: inflammation and beyond. Eur Heart J. (2023) 44:2672–81. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad304
Keywords: atherogenic index of plasma, fracture, spine, longitudinal study, general population
Citation: Zhang X, Xie P, Yin Y and Li X (2025) Atherogenic index of plasma is associated with vertebral fracture: a longitudinal study. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1540558. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1540558
Received: 06 December 2024; Accepted: 12 May 2025;
Published: 28 May 2025.
Edited by:
Antonino Catalano, University of Messina, ItalyReviewed by:
Michael Edwin Edmonds, King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, United KingdomGrzegorz Tatoń, Jagiellonian University, Poland
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Xie, Yin and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yong Yin, eWlueW9uZzkxMDQyOEAxMjYuY29t; Xinfeng Li, eGluZmVuZ2xpQDEyNi5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xin Zhang†
Xin Zhang† Yong Yin
Yong Yin Xinfeng Li
Xinfeng Li