- 1Changzhou Medical Centre, Nanjing Medical University, Changzhou, Jiangsu, China
- 2Department of Cardiology, Affiliated Changzhou No.2 People’s Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Changzhou, Jiangsu, China
- 3School of International Education, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
Objective: Despite positive impacts of lipid-lowering therapies (LLTs), the low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) target attainment remains suboptimal. This study aimed to investigate LDL-C goal achievement per the 2023 China guideline for lipid management among rehospitalized hypertriglyceridemia patients, who had higher chances to access the knowledge associated with lipid management and treatment, and evaluate the risk factors for LDL-C.
Methods: This retrospective study was performed among rehospitalized hypertriglyceridemia patients between July 2020 and May 2023. The department-specific latent class trajectory modeling was implemented to assess the longitudinal lipid profiles. The risk factors of goal attainment were evaluated using multivariate Cox regression analysis.
Results: Among 8905 readmitted patients, 5045 (56.7%) had two admissions. Only 27.1% consistently achieved LDL-C targets, while 25% never did. Nearly half were eligible for LLTs, but only 25% received them. Continuous LLT use was associated with higher goal attainment (HR: 1.23 [95% CI: 1.12–1.36]). Most readmissions (92.15%) had increasing LDL-C trajectories and less odds of achieving the LDL goals at the last hospitalization. At the latest hospitalization, patients with higher atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk had higher chances of achieving their LDL-C targets (hazard ratio 2.00 [95% CI, 1.70-2.36]).
Conclusions: LDL-C control remains poor in this population. Continuous LLT use and ASCVD risk stratification are important factors for goal attainment, highlighting the need for better long-term management and closer monitoring of low-risk patients.
1 Introduction
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in China, affecting over 330 million individuals (1). In 2019, CVD caused 46.7% and 44.3% of deaths in rural and urban areas in China, respectively (1). Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) is the major subset of CVD caused by deposition of plaques in the arteries, involving conditions including coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, and peripheral artery disease (2). Notably, the formation of these plaques is directly related to excess lipids in the circulation, such as low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and triglycerides; hence, hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia are risk factors for ASCVD, while reaching the LDL-C target is the primary goal in ASCVD risk intervention. The American Heart Association incorporated blood lipids as one of the elements in ‘Life’s Essential 8’, an important guideline for maintaining cardiovascular health, to form a novel composite cardiovascular health score (3). The latest China guideline for lipid management has also redefined the new ASCVD risk stratification and updated more stringent LDL-C control goals accordingly (4).
Unfortunately, achieving the appropriate levels of LDL-C remains a challenge in clinical practice. The DA VINCI study showed that 60.4% of enrolments did not achieve guideline-recommended risk-based LDL-C goals (5). Moreover, in patients with Type 1 diabetes mellitus (DM), only 6.16% reached the recommended LDL-C goal, while 11.81% reached the goal in Type 2 DM (6), and the LDL-C goal attainment rate of DM increased to 30.2% in six months (7). A multicenter observational study indicated that patients who suffered from their first major acute cardiovascular event (MACE) while on statin therapy were undertreated, and only 10% of the patients at very high cardiovascular risk reached their lipid targets (8). Another recent report also showed that among patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting, only 14.9% could achieve the guideline-recommended goals after one year (9).
The gap between guidelines and clinical practice calls for concern. In this retrospective study, we aim to investigate the LDL-C goal attainment among rehospitalized hypertriglyceridemia patients and to reveal the risk factors associated with successful or unsuccessful lipid management. We choose these patients because 1) we aim to investigate the trajectory of lipid profiles of these patients, which required at least two valid LDL-C measurements, and 2) these patients may have higher chances to access the knowledge associated with lipid management, as well as treatment; therefore, this cohort may better highlight the gap between guideline and practice. This study will describe the clinical characteristics of these patients, elaborate on the prescription rate of lipid-lowering therapies (LLTs), and assess the LDL-C goal attainment according to the 2023 China guidelines for lipid management. In addition, we contoured the trajectories of LDL-C and evaluated the risk factors of LDL-C goal attainment before the last admission.
2 Methods
2.1 Study design and population
This single-centered, retrospective study collected in-hospital information through the electronic health record system from July 2020 to May 2023. The inclusion criteria are 1) patients with complete medical records, including lipid profile (at least one valid LDL-C measurement during each admission), age, comorbidities (e.g., diabetes and hypertension), and previous history of ASCVD; 2) triglycerides (TG) were more than 1.7 mmol/L (150 mg/dl); 3) admitted twice or more than twice. The exclusion criteria are: 1) patients admitted to pediatrics, obstetrics, and neonatology departments; 2) TG below 1.7 mmol/L; and 3) admitted only once.
2.2 Data collection and definition
According to the latest guideline (4), the patients were classified into hierarchical ASCVD risk groups: low-risk, medium and high-risk, very high risk, and ultra-high risk. The target values for LDL-C vary based on these ASCVD risk classes (low risk: less than 130 mg/dl, medium and high risk: less than 100 mg/dl, very high risk: less than 70 mg/dl and more than 50% reduction from baseline, ultra-high risk: less than 55 mg/dl and more than 50% reduction from baseline) (4). For each patient, risk evaluation was performed independently using the data collected at every admission. The risk group at the first admission, and the lowest and highest risk stratifications for each patient were recorded for analysis.
Considering that physicians in some departments are more likely to treat patients with ASCVD, more accessible to lipid-lowering guidelines, and may have a better acquirement and implementation of the latest lipid management guidelines, we categorized all departments into either ASCVD-related departments, which had a higher incidence of ASCVD (including departments of cardiology, cardiac surgery, neurology, endocrinology, nephrology, vascular surgery, geriatrics, rheumatology, and general practice), or non-ASCVD related departments (departments other than the above).
2.3 Statistical analysis
All analyses were performed using the R software (version 4.1.1; R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria). Diagrams were plotted using R package ggplot2(3.4.1), RcppCGAL, WeightedTreemaps, Waffle, corrplot, and Forestplot (V3.1.3). Continuous variables were expressed as mean ± SD or median (interquartile ranges), and Student’s t-tests or chi-square tests were used to compare two groups. Categorical variables were expressed as frequency and proportion and were compared using the chi-square test. The Holm-Sidak post hoc test was used for repeated comparisons between multiple groups.
To illustrate the prevalence of LLTs prescription against different lipid profile backgrounds, a correlation plot was used to calculate the proportion among readmissions. Considering the non-independence of the lipid profile from repeated hospitalizations, we implemented mixed-effects models to explore the trajectories in continuous variables at different times. Finally, department-specific latent class trajectory modeling (LCTM) for LDL-C was used. The chosen number of models was based on the lowest Bayesian information criterion while maintaining the posterior probabilities by class (>0.7) and class size (more than 2% of the population). We calculated the posterior probabilities of patients for each trajectory and assigned participants to the trajectory with the highest probability. The Cox proportional hazards model was used to predict LDL-C goal-attainment factors. A forest plot of the likelihood of reaching the LDL-C target among patients during their last hospitalization was generated based on adjusted hazard ratios derived from the constructed multivariate model. A two-sided P value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Baseline characteristics
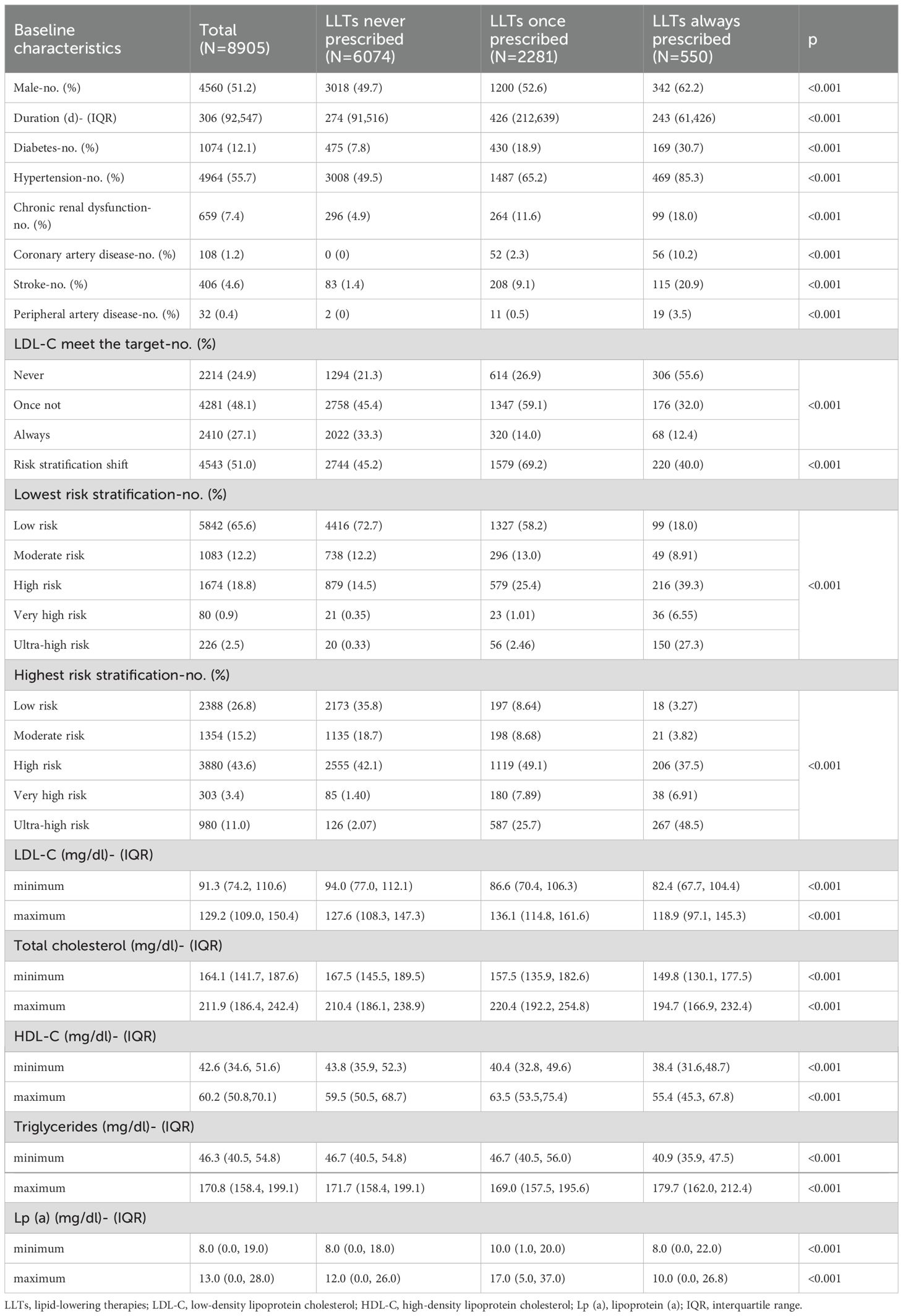
The overall screening procedure is shown in Figure 1. In total, the analysis included 59,452 hypertriglyceridemia patients. The mean age of all patients was 57.53 ± 14.37 years and males accounted for 52.17%. The baseline characteristics of all patients are shown in Table 1.
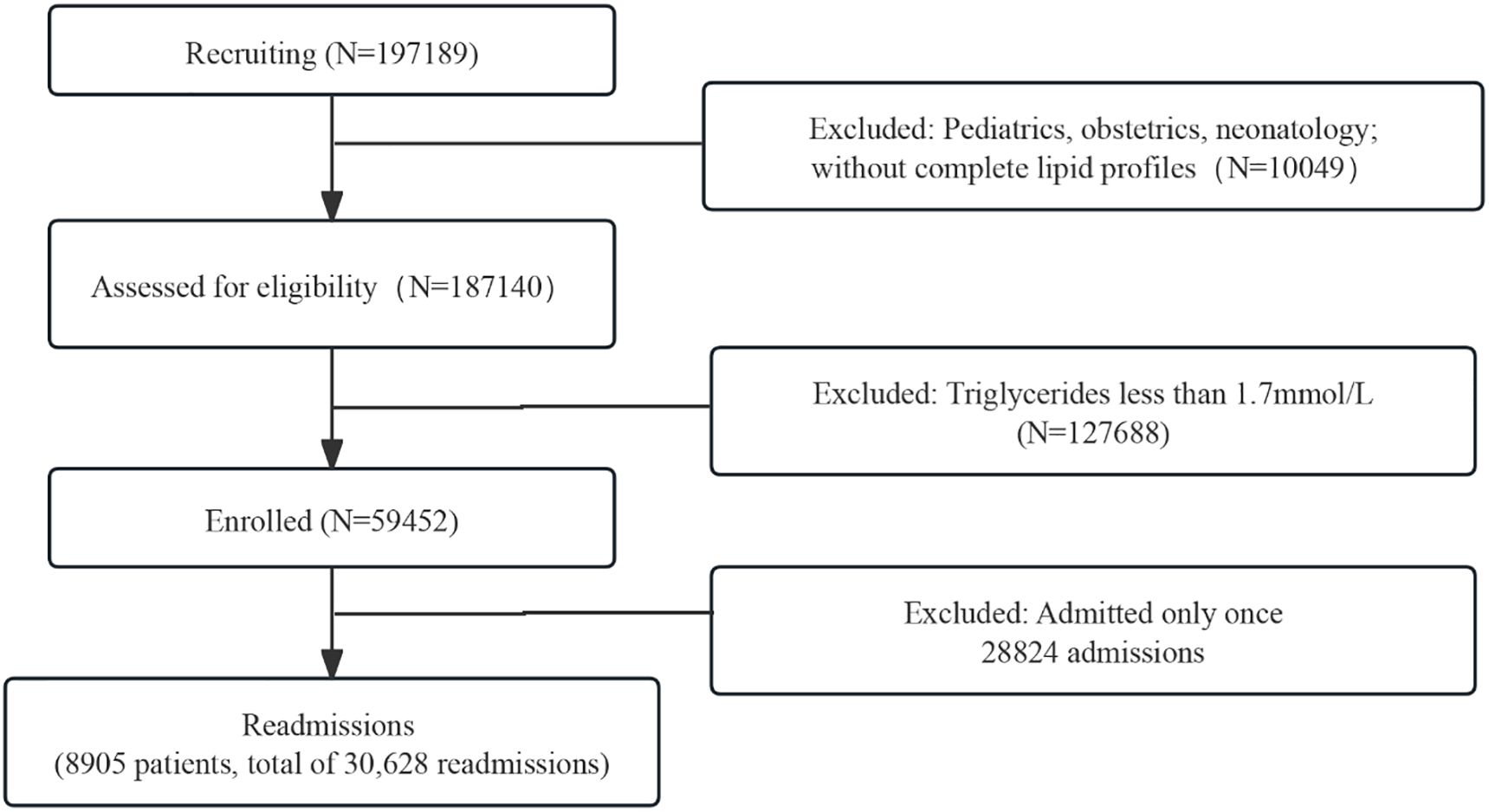
Figure 1. The study flowchart. A total of 59,452 hypertriglyceridemia patients were enrolled, and 8,905 readmitted patients were finally included based on complete lipid profile data and readmission criteria.
3.2 Clinical characteristics of hypertriglyceridemia among readmissions
Among 8905 readmitted patients diagnosed with hypertriglyceridemia, 5045 (56.7%) of them were discharged twice, 1563 (17.6%) were discharged three times, and 1577 (17.7%) were discharged more than five times (Figure 2). Among these patients, 1074 (12.1%) and 4964 (55.7%) were diagnosed with DM and hypertension, respectively. A total of 5492 (61.7%) patients were discharged from the same department, whereas 960 (17.5%) were from ASCVD-related departments (i.e., had at least one hospitalization at any of the ASCVD-related departments). The top reason for readmission was carcinoma-related, accounting for 38%, and recurrent ASCVD events requiring emergency procedures accounted for 2.4%.
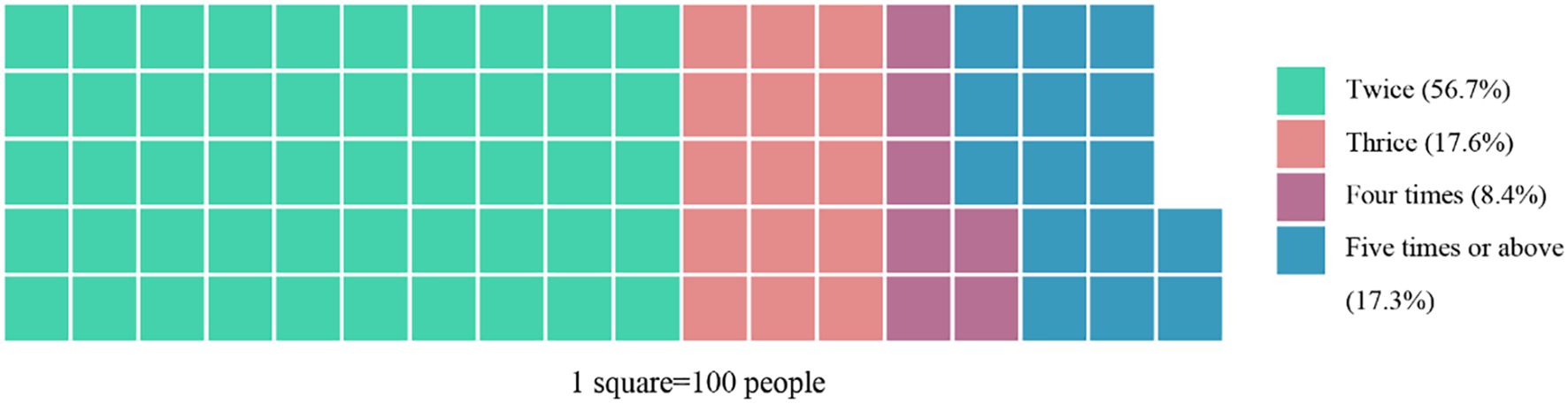
Figure 2. Distribution of readmission frequency. More than half of the patients (56.7%) were admitted twice, with a notable portion (25.7%) admitted more than three times.
3.3 Risk stratification re-evaluation, lipid profile, LLTs, and LDL-C goal attainment among readmissions
During the readmissions, 51% of the patients were upgraded to a higher category compared with the first admission. The shift in ASCVD risk stratification, the prescription of LLTs, and the LDL-C goal attainment during readmissions are shown in a Voronoi treemap (Figure 3). The specific percentages are presented in Table 1. Notably, the number of patients in the ultra-high-risk group was more than tripled, from 226(2.5%) to 980(11.0%) after re-evaluation. Despite their ASCVD risk, 68.2% of the readmitted patients were never prescribed LLTs; 24.9% of the readmitted patients never met their LDL-C target, while only 27.1% consistently achieved the target according to the Chinese guidelines. Even for the patients who were prescribed LLTs continuously, only 12.4% of them kept reaching the optimal LDL-C target level (Table 1). It is also important to note that, compared with other groups, the group prescribed LLTs had significantly lower minimum and maximum LDL-C and TC values, as well as lower minimum TG values (Table 1).
Figure 3. Voronoi treemap showing dynamic changes in ASCVD risk stratification at the first and last time of admission, LLT prescription, and LDL-C goal attainment across readmissions. Each cell represents a patient subgroup defined by their stratification change and treatment pattern. Area size corresponds to the number of patients in each subgroup. LLTs, lipid-lowering therapies; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
We then performed a cross-tabulation analysis between the LLTs and lipid profiles of the patients (Figure 4, Supplementary Data 1). A total of 48% of the readmitted patients met the indications for receiving LLTs; however, only 25% of them were finally prescribed. Even for those with severely elevated LDL-C levels (LDL-C more than 4.9 mmol/L or 189 mg/dl), only 35% were prescribed. This proportion increased to 65% among readmissions when LDL-C was more than two times the guideline-recommended level. Most LLTs relied on monotherapy (99%), particularly moderate-intensity statins (94%). Only 9% of the patients with very high LDL-C levels (more than two times over the guideline-recommended level) were prescribed high-intensity statins. Meanwhile, 15% of the readmissions with severely elevated LDL-C levels had concomitant severely elevated TG levels (TG more than 5.6 mmol/L or 496 mg/dl); however, even among these mixed dyslipidemia patients, only one-fifth were prescribed combination therapy consisting of both LDL-C and TG-lowering medications.
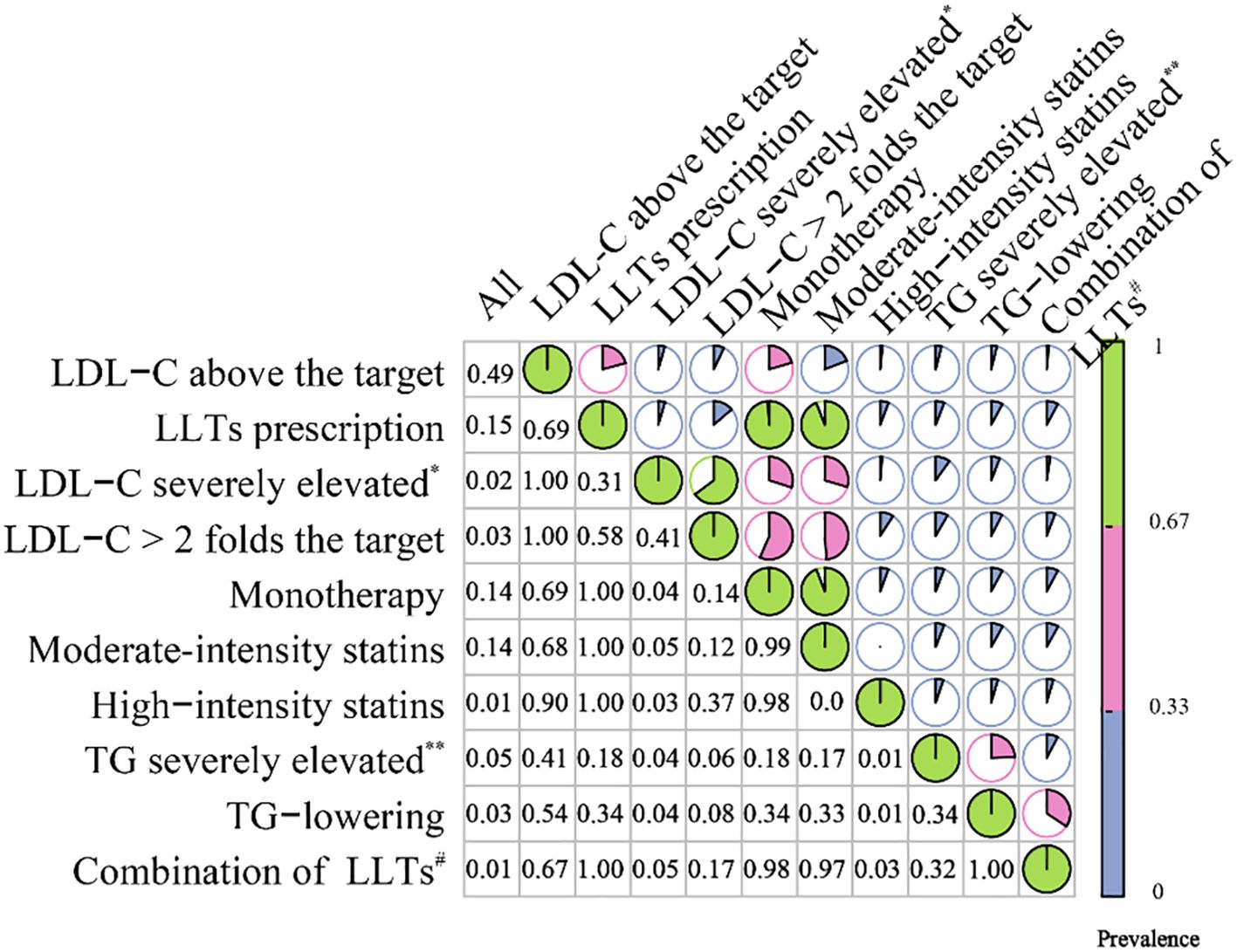
Figure 4. Correlation matrix plot for the cross-tabulation among LLTs and lipid profile. Rows represent conditions such as elevated LDL-C or TG; columns show their co-occurrence rates. The size and intensity of the colored circles indicate the strength of co-occurrence. LLTs, lipid-lowering therapies; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol *LDL-C>4.9 mmol/L (189 mg/dl); **TG more than 5.6 mmol/L (496 mg/dl); #combination of TG and LDL-C lowering therapies. Correlation matrix plot for the cross-tabulation among LLTs and lipid profile. The figure reports the prevalence of each condition (rows) among the overall readmissions and among each other condition (columns).
3.4 Trajectories among readmissions
We implemented the LCTM analysis to contour the lipid trajectories and determine the LDL-C changes among readmissions. The trajectories were divided into two classes, considering the departments, LLT frequencies, and risk stratification (Figure 5). Patients were stratified into ASCVD-related departments (solid lines) and non-ASCVD-related departments (dotted lines). Most patients (n=8311, 93.33%) were classified as Class 2 (the blue line) with an increasing LDL-C trajectory, while the others were classified as Class 1 (the red line) with a decreasing trajectory.
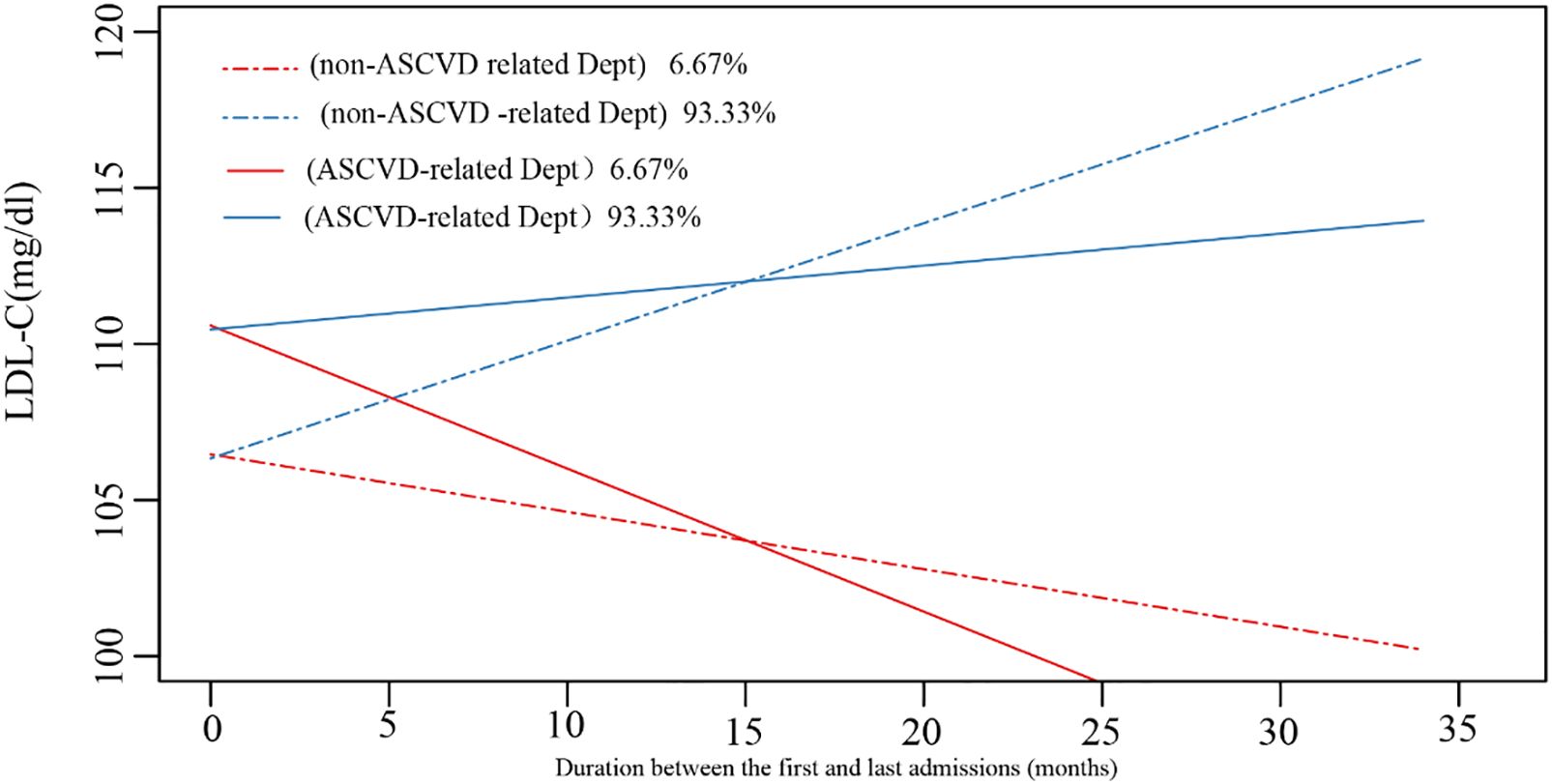
Figure 5. The trajectories of LDL-C profile among readmissions. ASCVD, atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; Dept, department.
Only 51.8% of all patients achieved the target level during their last admission, and the percentage of patients reaching the target level was 82.5% and 49.6% in Class 1 and Class 2, respectively, during their latest admission. Class 2 trajectory was mainly seen in low, moderate, and high-risk groups, while class 1 was only seen in very high and ultra-high-risk groups. Compared to Class 2, patients in Class 1 showed lower levels of minimum and maximum LDL-C, HDL-C, and TC. Neither the minimum nor the maximum level of TG demonstrated the difference between the two groups. The minimum Lp(a) in the Class 1 group was higher than in the Class 2 group, while the maximum level showed no difference (Table 2).
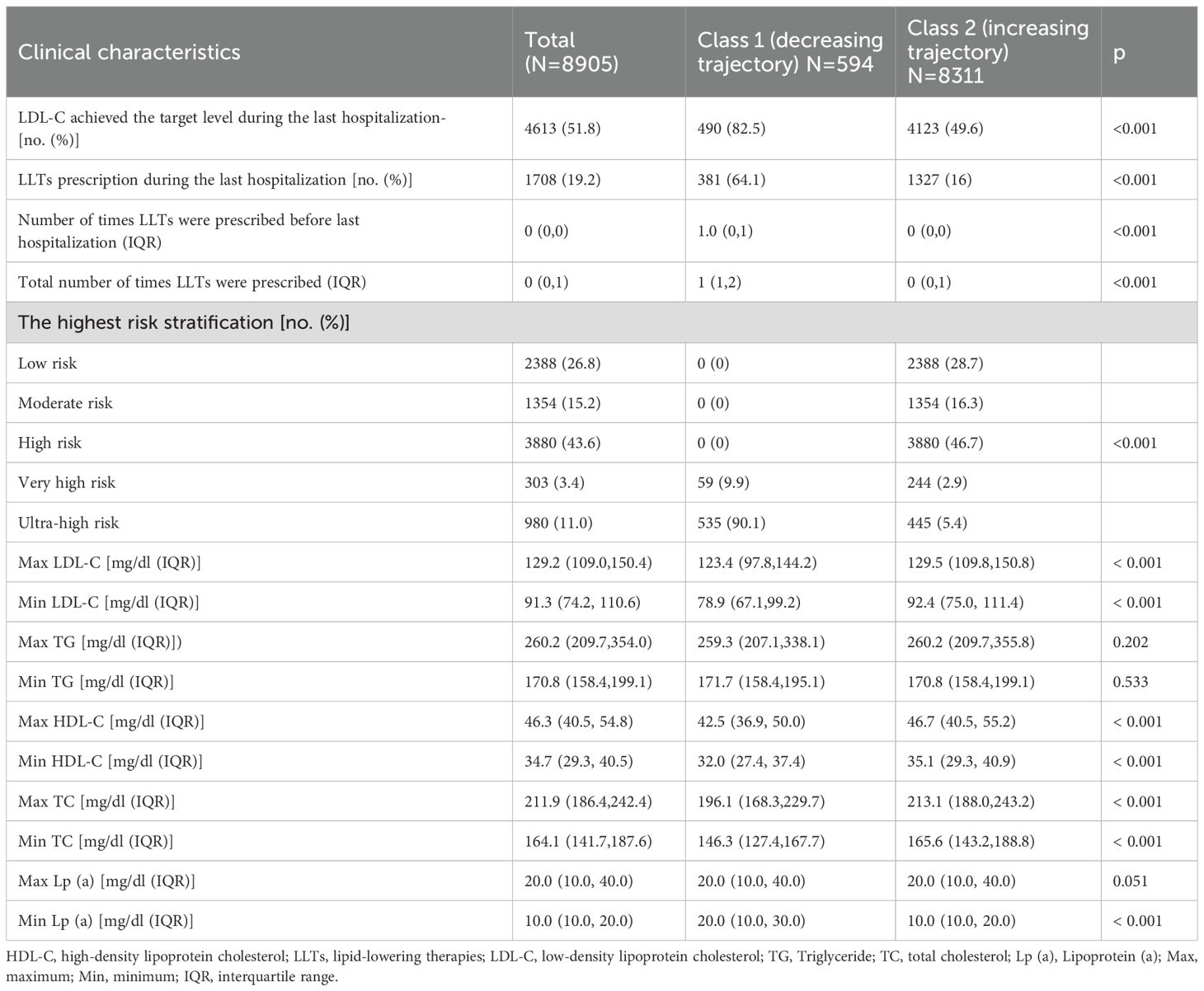
Table 2. Clinical characteristics between different trajectories among readmissions in all departments.
3.5 Risk factors for LDL-C goal attainment
Factors influencing LDL-C treatment control were analyzed using the multivariate COX regression. Due to the unfulfilled COX proportional hazard assumptions, age and the ASCVD-related departments’ hospitalization rate were treated as stratification factors. The model included LLTs proportions (before the last admission), gender, LDL-C trajectories, and the highest risk stratification. Figure 6 shows that the patients who were always prescribed LLTs had 23% [HR: 1.23 (95%, 1.12-1.36)] higher chances of attaining the LDL-C goals in the last readmission compared to the never prescribed ones, and those with increasing trajectories had 19% [HR: 0.81 (95%, 0.69-0.95)] lower chance of LDL-C goal-attainment, compared to the group with decreasing trajectories. Compared with the low-risk group, other groups achieved better goal attainment. Notably, the ultra-high-risk group had a goal-attainment rate twice that in the low-risk group [HR: 2.00 (1.70,2.36), p<0.001].
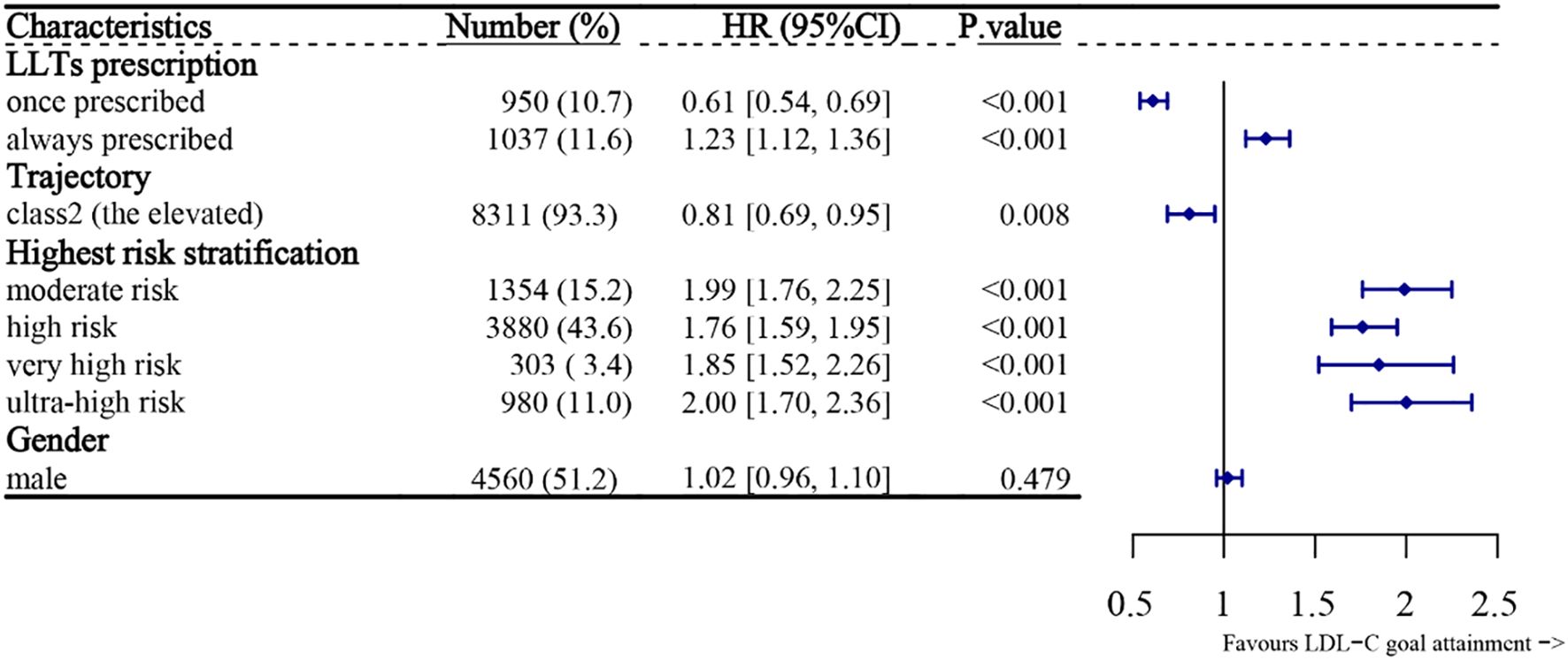
Figure 6. Forest plot for the predictors and LDL-C goal attainment during the last hospitalization. Factors include LLT prescription continuity, LDL-C trajectory, and highest ASCVD risk level. HRs and 95% confidence intervals are shown. Values >1 indicate higher likelihood of goal attainment. LLTs, lipid-lowering therapies; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval.
4 Discussion
4.1 Main interpretation
This study has revealed poor LDL-C target attainment among the readmitted hypertriglyceridemia patients. Nearly half of the readmissions with hypertriglyceridemia were indicated for LLTs (excluding those with obvious contraindications, such as liver or renal dysfunction), but only 25% of them were finally prescribed, whereas about one-fourth of the total readmissions never met their LDL-C target. Even for the patients prescribed LLTs continuously, only 12.4% kept reaching the optimal target. Still, patients with continuous LLT before the last visit had significantly better target attainment than those without prescribed LLT. Further analysis revealed that over 90% of the patients showed an increasing LDL-C trajectory since the first admission. To better understand this phenomenon, we further analyzed possible causes including insufficient LLT prescription rates, underuse of high-intensity or combination therapies, and lack of treatment adjustment based on risk reassessment.
This study suggests a significant awareness gap between clinical practice and guidelines, as LLT prescription is far less than expected, and LDL-C goal attainment is suboptimal. Previous studies have shown that among acute coronary syndrome patients, LDL-C goal attainment at discharge was less than 20% and increased to 38%-64% in 12 months (10), which was consistent with our results: after a median follow-up of 306 days, 51.8% of patients achieved the LDL-C target. Other previous studies also affirmed this (11–13), which is even worse in middle-income regions (14, 15). These results suggest that lack of intensification of LLTs and inadequate combined LLT medication may be important factors contributing to the low rates of LDL-C goal attainment.
In order to reduce the overall risk of ASCVD, guidelines have lowered the LDL-C management goal thresholds, aiming to cover more patients using LLTs prescription. The 2022 American College of Cardiology (ACC) expert consensus set the LDL-C standard at less than 55 mg/dl (1.4mmol/L) with at least 50% reduction from baseline for adults in very high-risk groups (16). It was also recommended that this goal be achieved by a combination with non-statin therapy, such as ezetimibe or a proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitor (PCSK9i). The 2019 European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) guidelines called for similar recommendations for LDL-C goals but lowered the threshold to 40 mg/dl (1.0 mmol/L) for ASCVD patients with a second event within two years while on maximally tolerated LLTs (17). However, “the lower (level of LDL-C), the better (outcome)” translates to “the lower (target according to the updated guideline recommendation), the tougher (goal attainment).” More stringent standards lead to lower LDL-C goal attainment (18), highlighting the importance of more interventions and management.
Besides LLTs prescription rate, LLTs strategy is also critical to LDL-C goal attainment. Chinese guidelines recommend moderate-intensity statin therapy as an initial prescription (4). As verified in our research, moderate-intensity statins were the most frequently prescribed LLTs covering all the ASCVD risk stratification groups. Meanwhile, in our study, high-intensity statins were only administered for about 12-13% of very high and ultra-high-risk patients, agreeing with a previous report that only 11% of patients were prescribed high-intensity statins for primary prevention (19). Another study reported that only 15% of the high or very high-risk groups received high-intensity statins at the time of their first MACE (8). However, it should be emphasized that most patients in the high ASCVD risk group require combined high-intensity LLTs, which may result in greater reduction in LDL-C (5); also, high-intensity statins are assumed to lower the LDL-C by more than 50%. We also found that statin monotherapy was the most prescribed, consistent with other literature (7, 13). These results suggest that lack of intensification of LLTs and inadequate combined LLT medication may be important factors contributing to the low rates of LDL-C goal attainment. In addition, the under-prescription of LLTs may be attributed to the lack of guideline awareness in non-ASCVD departments and limited access to non-statin therapies. It is also worth noting that non-statin therapies may serve as an effective alternative for statin intolerant patients, who may discontinue statin-based LLT due to its side effects (20). Similar opportunities for improvement have also been highlighted in coronary artery disease populations, emphasizing the need for intensification of lipid-lowering strategies and improved multidisciplinary management (21).
Another prominent factor contributing to the undermanagement of LDL-C levels may be therapeutic delay and nonadherence to medication. The present research concluded that continuous prescription of LLTs might contribute to higher goal achievement, while no significant protective effect was observed for those with LLTs prescribed only once. Nonadherence to medication may result from a general lack of public awareness, i.e., of both physicians and patients, of the management and therapy suggested by the guidelines. Improving physicians’ compliance with guidelines (22) and patients’ adherence may improve low LDL-C goal attainment, suggesting an urgent need for a comprehensive, cross-disciplinary guide for physicians and a detailed instruction oriented toward patients. Also, the fact that patients at low risk for ASCVD had lower LDL-C goal-attainment rates than other groups suggested that this broader population may be overlooked. Physicians may need to improve their awareness and embrace cross-disciplinary cooperation for better LDL-C management.
The present study also emphasizes the importance of dynamic evaluation and adjustment among readmissions, including ASCVD risk stratification and assessment of treatment efficacy. More than half of readmissions shifted to higher risk stratification, whereas less than 15% kept reaching the LDL-C goal even under continuous LLTs. Failure to adjust the treatment regimens (including combination with non-statin medications or upgraded statin intensity) promptly based on reassessed risk stratification may be a nonnegligible factor for the undermanagement of dyslipidemia. Previous studies showed gender disparities in LDL-C goal attainment: women were less likely to attain LDL-C goals than men (13, 23). However, our present study showed that the prescription continuity of LLTs and the decreased trajectory were the main factors promoting goal attainment, while gender showed no significance. The effect of gender on LDL-C goal attainment may be associated with differences in the societal roles and dietary habits of male and female patients in different areas of China, which is worth further investigation.
In the present study, readmissions exemplified two trends: the “stably increasing” and “moderately decreasing” trajectories in non-ASCVD-related departments and the “moderately increasing” and “stably decreasing” trajectories in ASCVD-related departments. The increasing trajectory predominated among the longitudinal cohort with a median follow-up of 306 days and is associated with poorer LDL-C goal attainment compared with the group with the decreasing trajectory. The group with decreasing trajectory is mainly composed of patients with high ASCVD risks at their first admissions; therefore, these patients were more likely to be treated early and continuously, resulting in higher chances to reach their LDL-C goals. In addition, the clinicians in ASCVD-related departments are more likely to focus on the patients’ lipid management, emphasizing LLT prescription, close lipid monitoring, and patient education, since lipid management is critical to the management of their primary diseases (e.g., stroke and coronary heart disease). These clinicians may also be more experienced in treating patients with high risks of hypertriglyceridemia and/or tend to strictly follow the guidelines, which is consistent with a previous study (24). In contrast, the clinicians in non-ASCVD-related departments may focus more on other primary diseases that led to hospitalization, leading to reduced focus on lipid management. To eliminate this disparity, multidisciplinary team-based care and shared decision-making may be effective in promoting the awareness of both patients and clinicians across different departments (25). Previous studies also applied trajectory analysis on lipid profiles: Finnish type 2 DM cohort showed that the majority of patients (85.9%) had relatively stable LDL-C levels, around 2.3 mmol/L (89 mg/dl) (26). A community-based US cohort study showed a decreasing LDL-C trajectory in approximately 80% of the enrollments (27). The disparities between our study and previous studies may result from different enrollment strategies, trajectory approaches, and the follow-up duration.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first retrospective research on the LDL-C goal attainment among readmitted hypertriglyceridemia patients according to the updated China guidelines for lipid management. This study utilized different target levels of lipid criteria corresponding to the ASCVD risk stratification. Considering the variations in guideline recommendations across other regions, country-specific recommendations regarding hyperlipidemia screening and LDL-C goal thresholds may be appropriate when analyzing the regional conditions (28). Few previous studies have focused on LDL-C goal achievement for readmissions. The findings in this study provide a more concise estimation of the dyslipidemia problem by analyzing longitudinal data on readmissions. Also, we utilized trajectory analysis to illustrate dynamic patterns over time and provide more comprehensive information with repeated measurements than a baseline parameter or average level. Furthermore, we employed the LCTM method to identify heterogeneity in the LDL-C profile, which the conventional approach cannot fulfill. In addition, while elevated TG levels may be correlated to ASCVD risks, previous clinical trials controlling TG levels with fibrates did not significantly reduce ASCVD outcomes (12–14). Moving forward, future studies should include multicenter, prospective cohorts and incorporate direct LDL-C measurement for improved accuracy. Furthermore, systematic educational interventions, discharge LDL-C checklists, and cross-departmental collaboration may help improve LLT implementation and LDL-C goal attainment.
4.2 Limitations
However, this study is not without limitations. Firstly, this study is constrained by its retrospective nature, though we analyzed over 8000 patients. Therefore, there is a potential selection bias (e.g., from including only readmitted patients with available LDL-C data) and information bias (e.g., misclassification or missing treatment records). The specific follow-up information, such as LLT adherence and persistence, which played an essential role in hyperlipidemia control (19, 29), was not available. Since we focused on LDL-C goal attainment, we did not analyze the management of other concomitant risk factors, such as blood pressure and glucose, which may also have cardiovascular impacts. We failed to collect data related to death as no recorded available data could be retrieved in this population. Furthermore, as this was a single-center study conducted in a general hospital, where neurology and internal medicine clinics are the primary departments managing hypertriglyceridemia, there may have been an overrepresentation of ischemic stroke patients compared to those with coronary artery disease, which could limit the generalizability of these findings to the broader ASCVD population. Secondly, LDL-C was estimated using the Friedewald equation since direct measurement was not available. Therefore, its accuracy may be affected in patients with triglyceride levels above 4.52 mmol/L (400 mg/dL). In our dataset, 19.3% of patients had a maximum TG value exceeding this threshold during at least one admission, which could introduce potential bias in LDL-C estimation. In future studies, we will consider incorporating direct LDL-C measurements to improve accuracy. Thirdly, many non-statin LLTs were unavailable to most patients due to the longer approval time in China at the time of investigation. It is worth mentioning that LDL-C goal attainment may be higher with PCSK9i, small/short interfering (siRNA), and other novel medications that show more effective LDL-C reduction. Future clinical data, including new LLTs, may lead to better LDL-C goal attainment.
4.3 Conclusion
In conclusion, this study suggested poor LDL-C target attainment among the readmitted hypertriglyceridemia patients, which may be attributed to low LLT prescription rate and limited dose and treatment strategies. Most patients showed an increasing LDL-C trajectory during readmission, which was associated with poor LDL-C goal attainment compared with those showing a decreasing LDL-C trajectory. Efforts should be made to bridge the gap between the guidelines and clinical practice for better LDL-C goal attainment and ASCVD risk control.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
This study was approved by the institutional research Ethics Committee of Changzhou No.2 People’s Hospital ((2023) KY104-01). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The informed consent waiver was granted as it was a retrospective study.
Author contributions
YJ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AK: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SH: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Changzhou Medical Centre, Nanjing Medical University (CMCC202207,CMC2024PY28).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2025.1553173/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
LLTs, lipid-lowering therapies; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; ASCVD, atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; CVD, Cardiovascular disease; MACE, major acute cardiovascular event; LCTM, latent class trajectory modeling; siRNA, small/short interfering; TG, triglycerides; PCSK9i, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitor; DM, diabetes mellitus.
References
1. The Writing Committee of the Report on Cardiovascular Health and Diseases in China and Hu SS. Report on cardiovascular health and diseases in China 2021: an updated summary. J Geriatr Cardiol. (2023) 20:399–430. doi: 10.26599/1671-5411.2023.06.001
2. Li Y, Du Y, Zhou Y, Chen Q, Luo Z, Ren Y, et al. Iron and copper: critical executioners of ferroptosis, cuproptosis and other forms of cell death. Cell Commun Signal. (2023) 21:327. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01267-1
3. Lloyd-Jones DM, Allen NB, Anderson CAM, Black T, Brewer LC, Foraker RE, et al. Life’s essential 8: updating and enhancing the american heart association’s construct of cardiovascular health: A presidential advisory from the American heart association. Circulation. (2022) 146:e18–43. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001078
4. Li JJ, Zhao SP, Zhao D, Lu GP, Peng DQ, Liu J, et al. 20223 China guidelines for lipid management. J Geriatr Cardiol. (2023) 20:621–63. doi: 10.26599/1671-5411.2023.09.008
5. Brandts J, Bray S, Villa G, Catapano AL, Poulter NR, Vallejo-Vaz AJ, et al. Optimal implementation of the 2019 ESC/EAS dyslipidaemia guidelines in patients with and without atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease across Europe: a simulation based on the DA VINCI study. Lancet Reg Health Eur. (2023) 31:100665. doi: 10.1016/j.lanepe.2023.100665
6. Brandts J, Tittel SR, Bramlage P, Danne T, Brix JM, Zimny S, et al. Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes: Lipid goal attainment in a large German-Austrian diabetes registry. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2023) 25:3700–8. doi: 10.1111/dom.15264
7. Guo T, Chu C, Wang Y, He M, Jia H, Sun Y, et al. Lipid goal attainment in diabetes mellitus patients after acute coronary syndrome: a subanalysis of Dyslipidemia International Study II-China. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2023) 23:337. doi: 10.1186/s12872-023-03312-w
8. Masana L, Diaz Moya G, Perez de Isla L, and HEARTBEAT study investigators. Patients who suffer a first atherosclerotic cardiovascular event while taking statins are often far off of lipid targets. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2024) 34:90–7. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2023.09.022
9. Tang L, Chen H, Hu XQ, Fang ZF, Liao XB, Zhou XM, et al. Intensive lipid-lowering therapy as per the latest dyslipidemia management guideline in predicting favorable long-term clinical outcomes in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting: A retrospective cohort study. J Am Heart Assoc. (2023) 12:e029397. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.029397
10. Chen YS, Lin HH, Tsai HY, Lee CL, Yeh YT, and Wu YW. Association of health information technology-driven multidisciplinary approaches with low-density lipoprotein cholesterol target achievement in patients with an acute coronary syndrome. Am J Prev Cardiol. (2024) 17:100613. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpc.2023.100613
11. Mazhar F, Hjemdahl P, Clase CM, Johnell K, Jernberg T, and Carrero JJ. Lipid-lowering treatment intensity, persistence, adherence and goal attainment in patients with coronary heart disease. Am Heart J. (2022) 251:78–90. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2022.05.021
12. Marquina C, Talic S, Zomer E, Vargas-Torres S, Petrova M, Wolfe R, et al. Attainment of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol goals in patients treated with combination therapy: A retrospective cohort study in primary care. J Clin Lipidol. (2022) 16:498–507. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2022.05.002
13. Gong Y, Li X, Ma X, Yu H, Li Y, Chen J, et al. Lipid goal attainment in post-acute coronary syndrome patients in China: Results from the 6-month real-world dyslipidemia international study II. Clin Cardiol. (2021) 44:1575–85. doi: 10.1002/clc.23725
14. Barreto J, Luchiari B, Wolf VLW, Bonilha I, Bovi TG, Assato BS, et al. Compliance with cardiovascular prevention guidelines in type 2 diabetes individuals in a middle-income region: A cross-sectional analysis. Diagnostics (Basel). (2022) 12:814–25. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12040814
15. Vrablik M, Seifert B, Parkhomenko A, Banach M, Jozwiak JJ, Kiss RG, et al. Lipid-lowering therapy use in primary and secondary care in Central and Eastern Europe: DA VINCI observational study. Atherosclerosis. (2021) 334:66–75. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2021.08.035
16. Writing C, Lloyd-Jones DM, Morris PB, Ballantyne CM, Birtcher KK, Covington AM, et al. 2022 ACC expert consensus decision pathway on the role of nonstatin therapies for LDL-cholesterol lowering in the management of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk: A report of the American college of cardiology solution set oversight committee. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2022) 80:1366–418. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2022.07.006
17. Mach F, Baigent C, Catapano AL, Koskinas KC, Casula M, Badimon L, et al. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur Heart J. (2020) 41:111–88. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz455
18. Ray KK, Molemans B, Schoonen WM, Giovas P, Bray S, Kiru G, et al. EU-wide cross-sectional observational study of lipid-modifying therapy use in secondary and primary care: the DA VINCI study. Eur J Prev Cardiol. (2021) 28:1279–89. doi: 10.1093/eurjpc/zwaa047
19. Mazhar F, Hjemdahl P, Sjolander A, Kahan T, Jernberg T, and Carrero JJ. Intensity of and adherence to lipid-lowering therapy as predictors of goal attainment and major adverse cardiovascular events in primary prevention. Am Heart J. (2024) 269:118–30. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2023.12.010
20. Bosco G, Di Giacomo Barbagallo F, Spampinato S, Lanzafame L, Di Pino A, Piro S, et al. Management of statin intolerant patients in the era of novel lipid lowering therapies: A critical approach in clinical practice. J Clin Med 12. (2023) 12(6):2444–58. doi: 10.3390/jcm12062444
21. Martin GJ, Teklu M, Mandieka E, and Feinglass J. Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in coronary artery disease patients: opportunities for improvement. Cardiol Res Pract. (2022) 2022:7537510. doi: 10.1155/2022/7537510
22. Vrablik M, Sarkanova I, Brecikova K, Sedova P, Satny M, and Tichopad A. Low LDL-C goal attainment in patients at very high cardiovascular risk due to lacking observance of the guidelines on dyslipidaemias. PLoS One. (2023) 18:e0272883. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0272883
23. Gavina C, Araujo F, Teixeira C, Ruivo JA, Corte-Real AL, Luz-Duarte L, et al. Sex differences in LDL-C control in a primary care population: The PORTRAIT-DYS study. Atherosclerosis. (2023) 384:117148. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2023.05.017
24. Mosca L, Linfante AH, Benjamin EJ, Berra K, Hayes SN, Walsh BW, et al. National study of physician awareness and adherence to cardiovascular disease prevention guidelines. Circulation. (2005) 111:499–510. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000154568.43333.82
25. Lan NSR, Chen RT, Dwivedi G, Watts GF, Nicholls SJ, and Nelson AJ. Learnings from implementation strategies to improve lipid management. Curr Cardiol Rep. (2025) 27:9. doi: 10.1007/s11886-024-02174-8
26. Inglin L, Lavikainen P, Jalkanen K, and Laatikainen T. LDL-cholesterol trajectories and statin treatment in Finnish type 2 diabetes patients: a growth mixture model. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:22603. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-02077-6
27. Koohi F, Khalili D, Mansournia MA, Hadaegh F, and Soori H. Multi-trajectories of lipid indices with incident cardiovascular disease, heart failure, and all-cause mortality: 23 years follow-up of two US cohort studies. J Transl Med. (2021) 19:286. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-02966-4
28. Mancini GBJ, Ryomoto A, Yeoh E, Brunham LR, and Hegele RA. Recommendations for statin management in primary prevention: disparities among international risk scores. Eur Heart J. (2024) 45:117–28. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad539
Keywords: low-density lipoprotein cholesterol goal, trajectory, lipid-lowering therapy, dyslipidemia, retrospective study
Citation: Ji Y, Chadha A, Krity A and Huang S (2025) A retrospective study on LDL-C goal attainment in readmitted hypertriglyceridemia patients: risk factor analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1553173. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1553173
Received: 30 December 2024; Accepted: 28 July 2025;
Published: 13 August 2025.
Edited by:
Jerzy Beltowski, Medical University of Lublin, PolandReviewed by:
Zhenjun Ji, Southeast University, ChinaBelma Pojskic, Medical Faculty University Zenica, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Copyright © 2025 Ji, Chadha, Krity and Huang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shenglan Huang, Y3pfZHJodWFuZ0AxNjMuY29t
 Yuan Ji
Yuan Ji Arsheen Chadha
Arsheen Chadha Abhash Krity
Abhash Krity Shenglan Huang
Shenglan Huang