- 1Department of Diabetes, Endocrinology and Nutrition, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan
- 2Radioisotope Research Center, Agency for Health, Safety and Environment, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan
- 3Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan
- 4Department of Diagnostic Pathology, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan
- 5Department of Surgery, Graduate School of Medicine Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan
- 6Department of Diabetes, Shizuoka General Hospital, Shizuoka, Japan
- 7Medical Research Institute Kitano Hospital, PIIF Tazuke-kofukai, Osaka, Japan
Background: Insulinomas, the most common functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, cause hypoglycemia due to excessive insulin production, leading to severe clinical symptoms like coma or death. Resection surgery is the major curative treatment, but preoperative localization is challenging due to their small size. Traditional imaging methods like computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) often fail to detect tumors, while more invasive procedures like endoscopic ultrasound tissue acquisition (EUS-TA) and the selective arterial calcium stimulation test (SACST), though informative, depend heavily on operator skill and may not always provide conclusive results. There is an urgent need for non-invasive, sensitive localization methods for insulinomas. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP-1R) targeted PET imaging has emerged as a promising tool. We present a clinical case where [18F] FB (ePEG12)12-exendin-4 positron emission tomography/CT (18F-exendin-4 PET/CT) successfully detected insulinoma, unachievable by conventional imaging, underscoring its potential in guiding minimally invasive surgery.
Case description: A 67-year-old female developed hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia but could not undergo surgery as conventional imaging methods failed to localize the insulinoma. She was managed with diazoxide for six years, but her symptoms worsened. At 73, she was referred to our hospital. CT, MRI, endoscopic ultrasound, and SACST failed to detect the tumor in any artery. However, 18F-exendin-4 PET/CT revealed a nodule with uptake in the dorsal pancreas, suspected to be the culprit lesion. The patient underwent surgery, and although the tumor appeared discontinuous with the pancreas macroscopically, histopathology confirmed it was microscopically continuous, identifying it as a primary pancreatic insulinoma. Post-surgery, she achieved complete remission of symptoms and fully recovered.
Discussion: This case demonstrates the utility of 18F-exendin-4 PET/CT, a novel GLP-1 receptor-targeted imaging technique, in accurately localizing an occult insulinoma even with negative findings of SACST, enabling minimally invasive curative surgery.
Conclusion: The 18F-exendin-4 PET/CT successfully localized an insulinoma undetectable by other methods, enabling minimally invasive curative resection. This technique offers a valuable diagnostic option for enabling minimally invasive surgery in occult insulinoma cases.
1 Background
Insulinomas, the most common functional pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms, are observed in 1–4 individuals per million globally (1–4). These tumors cause hypoglycemia provoked by excessive insulin production, which manifests clinically as affected behavior, memory loss, palpitations, tremors, and diaphoresis, potentially resulting in seizures, loss of consciousness, coma, or death (2, 4, 5).
The primary curative treatment option for insulinoma is surgical resection, and precise preoperative localization is crucial for enabling less invasive surgery and minimizing the loss of unaffected pancreatic tissue. Although endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation (EUS-RFA) has recently been proposed as a potential alternative to surgery in some cases (6), accurate tumor localization remains essential for either approach. Because most insulinomas measure <2 cm in diameter, commonly used imaging modalities such as computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are sometimes not sufficient to localize them (7–10). Somatostatin receptor (SSTR)-targeted imaging is also an option; however, it is less sensitive in diagnosing insulinomas compared with other pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms (11, 12) and does not provide information on its endocrine function, such as insulin secretion. In these situations, endoscopic ultrasound tissue acquisition (EUS-TA) and the selective arterial calcium stimulation test (SACST) are utilized as they can give insight into the tumor’s endocrine nature. Nonetheless, these procedures are invasive and mostly rely on operator skills (7–10). Additionally, EUS-TA sometimes cannot be performed safely or tissue samples are insufficient to establish a definitive diagnosis (13). Besides, the sensitivity of SACST is not 100%, and SACST sometimes yields negative results despite the tumor’s presence (14, 15).
Therefore, there has been an urgent demand for non-invasive, highly sensitive diagnostic methods for insulinoma, also reflecting the tumor’s insulin secretion function and serving as an alternative option to currently employed diagnostic interventions with significant patient burden (8). Thus, positron emission tomography (PET) targeting the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP-1R) has evolved as a noninvasive specific tool for the diagnosis of insulinoma (10, 11, 16).
The importance of accurately localizing insulinoma for the success of minimally invasive surgery has been highlighted, and GLP-1R-targeting imaging is considered a promising approach, especially when other diagnostic tests prove ineffective (10).
Exendin-4 is a 39-amino acid peptide originally isolated from the venom of Heloderma suspectum, which shares approximately 53% sequence identity with human glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and functions as a GLP-1 receptor agonist (17, 18). Based on its pharmacological profile, exenatide (a synthetic version of exendin-4) was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in 2005 (18).
We recently experienced a case in which [18F] FB (ePEG12)12-exendin-4 PET/CT (18F-exendin-4 PET/CT) allowed the successful detection of insulinoma, which was not achievable by other multiple conventional imaging tests.
2 Case description
A 67-year-old female patient manifested visual disturbances and deteriorated concentration during waking. Her fasting blood glucose level was found to be 32 mg/dL, prompting a visit to the physician. Blood tests after three hours of fasting revealed plasma glucose levels of 32 mg/dL, serum insulin level of 2.5 μU/mL, and serum C-peptide level of 1.26 ng/mL. Following a glucagon stimulation test, the blood glucose levels rose to 80 mg/dL (10 minutes) and 106 mg/dL (30 minutes), thus confirming a diagnosis of hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. The test for anti-insulin antibodies was negative, and the other potential causes of hypoglycemia, such as adrenal insufficiency, were ruled out, strongly suggesting insulinoma.
However, no tumor was apparent as contrast-enhanced CT, MRI, or endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) failed to detect any, classifying the case as one with an unknown tumor location. The patient was administered diazoxide at a dose of 125 mg/day. Without any surgical intervention, over the following 6 years, the manifestation of symptoms worsened despite diazoxide therapy, and at the age of 73 years, the patient was directed to our hospital for further examinations.
The patient underwent a hysterectomy for uterine fibroids 30 years ago and was diagnosed with Hashimoto’s disease at the age of 71 years; however, her thyroid functioning parameters were within normal limits. The medication regimen included only diazoxide at a dose of 125 mg four times a day. No alcohol consumption and anti-diabetic medications were recorded in the medical anamnesis.
Upon admission, the patient’s blood pressure was 101/63 mmHg, and the heart rate was 56 bpm. She was 153.5 cm tall and weighed 43.7 kg. There was no change in weight during the last 6 years of illness.
Fasting blood glucose testing performed in the early morning was indicative of hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia (plasma glucose level of 49 mg/dL, serum insulin of 6.8 μU/mL, and C‐peptide of 1.91 ng/mL). She tested negative for anti-insulin antibodies. Her hemoglobin A1C (HbA1c) level was 5.7%. The levels of adrenocorticotropic hormone, cortisol, thyroid‐stimulating hormone, free thyroxine, and insulin-like growth factor 1 were normal (17.8 pg/mL, 10.1 μg/dL, 3.916 μIU/mL, 1.17 ng/dL, and 71 ng/mL, respectively).
Contrast-enhanced CT and MRI failed to visualize suspected insulinoma. By EUS, a polycystic lesion was found in the body of the pancreas; however, its morphology was more representative of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm, while it was not thought to be the lesion responsible for hypoglycemia. For SSTR-targeted imaging, [111In-DTPA-D-Phe]-octreotide single-photon emission CT (SPECT) was performed, and no significant uptake was detected (Figure 1A).
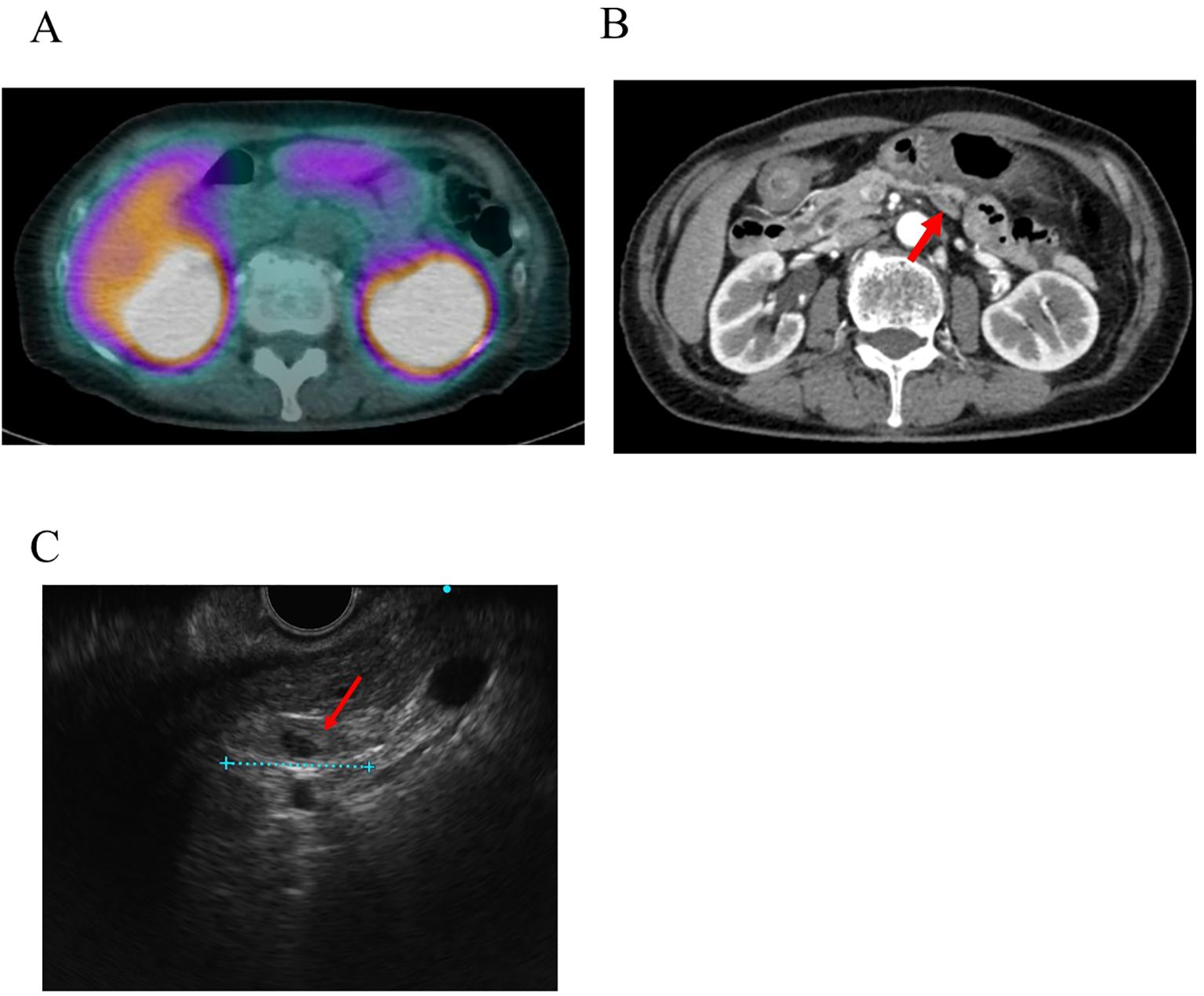
Figure 1. Images produced by conventional techniques. (A) [111In-DTPA-D-Phe]-octreotide single-photon emission CT (SPECT). No abnormal uptake was observed at the site where the tumor was later identified. (B) The nodule identified by [18F] FB (ePEG12)12-exendin-4 PET/CT results in contrast-enhanced CT. The red arrow indicates the nodule. (C) Nodule detected by endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) conducted after [18F] FB (ePEG12)12-exendin-4 PET/CT. The red arrow indicates the nodule.
Selective arterial calcium stimulation tests (SACST) performed in the superior mesenteric, gastroduodenal, right hepatic, and splenic arteries all failed to demonstrate insulin level increments, which left the tumor’s location undetermined.
18F-exendin-4 was synthesized as depicted in previous studies (19, 20), and 18F-exendin-4 PET/CT scans were performed 1 and 2 hours after intravenous administration of the probe. 18F-exendin-4 PET/CT showed nodular hyperaccumulation in the dorsal part of the pancreatic body at both 1 and 2 h after the intravenous probe administration (Figures 2A–D). The uptake was remarkably higher than it was in the unaffected pancreatic tissue or those of nearby organs, except for the kidney and gallbladder (Figures 2A–D). The nodule signals were easily differentiated from the mentioned structures. No other focal uptakes were observed in the whole body (Figures 2A, B). No adverse events were observed during the scans.
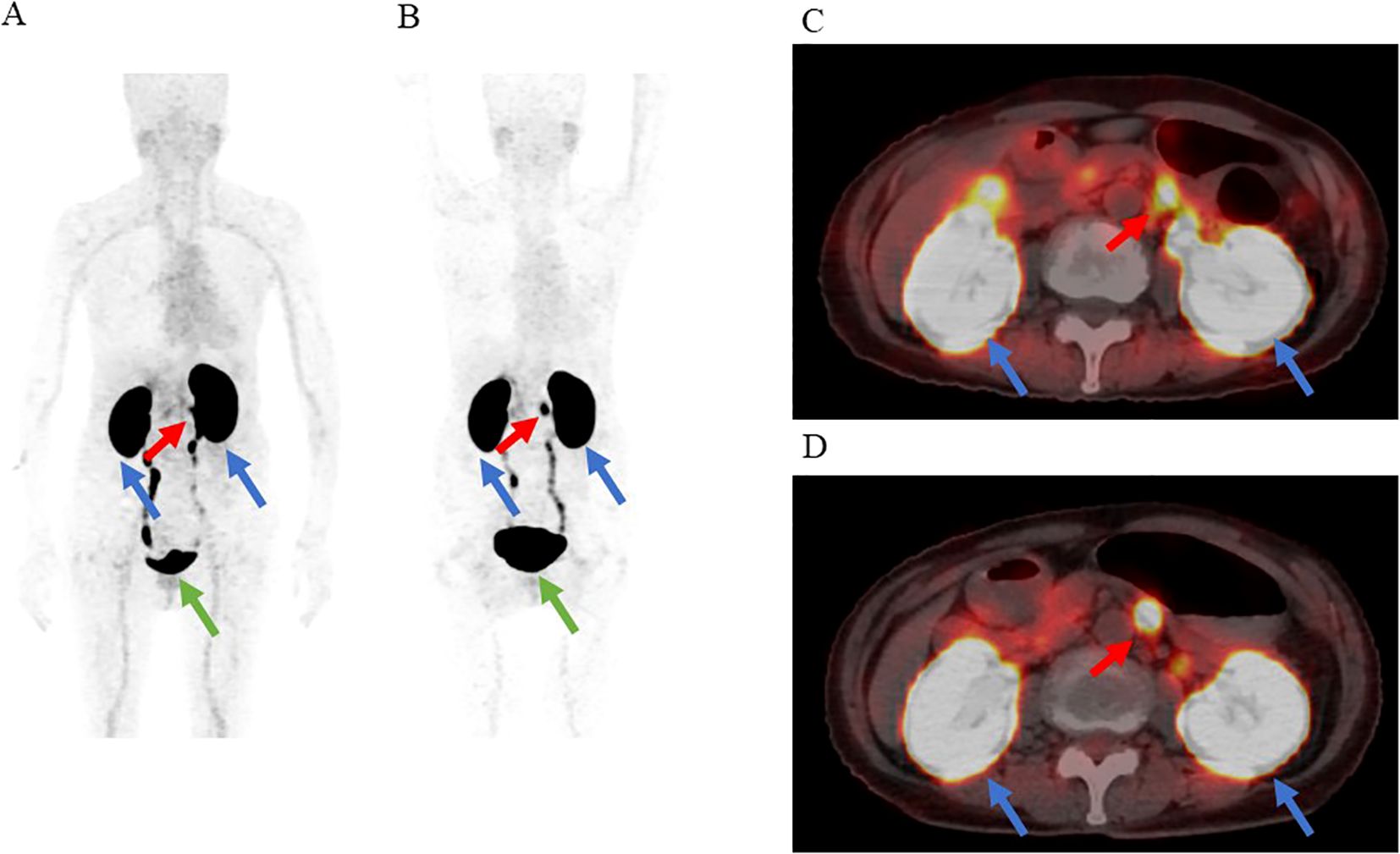
Figure 2. The results of [18F] FB (ePEG12)12-exendin-4 positron emission tomography (18F-exendin-4 PET)/CT. The red arrow indicates the nodular hyperaccumulation in the dorsal part of the pancreatic body. the blue arrows indicate the kidneys, and the green arrow indicates the bladder. (A) Maximum intensity projection of PET 1 h after administration. (B) Maximum intensity projection of PET 2 h after administration. (C) Fusion imaging of PET/CT 1 h after administration. (D) Fusion imaging of PET/CT 2 h after administration.
In the retrospective evaluation of CT images based on 18F-exendin-4 PET/CT findings, we identified an extremely flat nodule on the dorsal side of the pancreas measuring approximately 18 mm in diameter. Initially, based solely on the findings of conventional modalities, the lesion was mistaken for either a normal lymph node, part of the unaffected pancreatic structure, or part of the surrounding connective tissue because of its extremely flat shape and its position appearing to extend outside the pancreatic parenchyma. Consequently, it was not recognized as the culprit lesion. (Figure 1B). Subsequent re-evaluations with EUS after the received findings of 18F-exendin-4 PET/CT identified an 18 mm hypoechoic, flat structure in the dorsal pancreas (Figure 1C). Sonazoid contrast-enhanced ultrasonography captured the lesion before detecting the pancreatic parenchyma. Since the tumor was located on the dorsal side of the pancreas and possibly outside this anatomic structure, it was determined that EUS-TA posed a significant risk of complications and was therefore not conducted. Despite the possible presence of an extrapancreatic lesion or a metastatic lymph node, no other potential culprit lesions were identified by 18F-exendin-4 PET/CT, allowing the laparoscopic enucleation of the tumor. The nodule measured 23 × 12 × 2 mm and was extremely flat. Intraoperative macroscopic findings suggested that the tumor’s structure may not have been continuous with that of the pancreas.
Histopathological analyses performed using hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining characterized the tumor as a well-differentiated pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor exhibiting trabecular cell proliferation with oval nuclei and eosinophilic cytoplasm (Figure 3A). The cells of the nodule tested positive for synaptophysin (Figure 3B), insulin (Figure 3C), and insulinoma-associated protein 1 (INSM1) (Figure 3D). The Ki-67 labeling index was 0.8% (Figure 3E). The tumor cells also tested positive for GLP-1 receptors (Figure 3F). Although the tumor’s structure seemed to be discontinuous with that of the pancreatic parenchyma during the intraoperative macroscopic evaluation, microscopically, the tumor was continuous with the pancreatic parenchyma, and the insulinoma was identified as a primary pancreatic tumor (Figures 3G, H). GLP-1 receptor staining revealed that its expression was more pronounced in the tumor area than in the unaffected pancreatic parenchyma (Figure 3H). The tumor was classified as insulinoma, falling under the category of NET G1 according to the WHO (2022) (21).
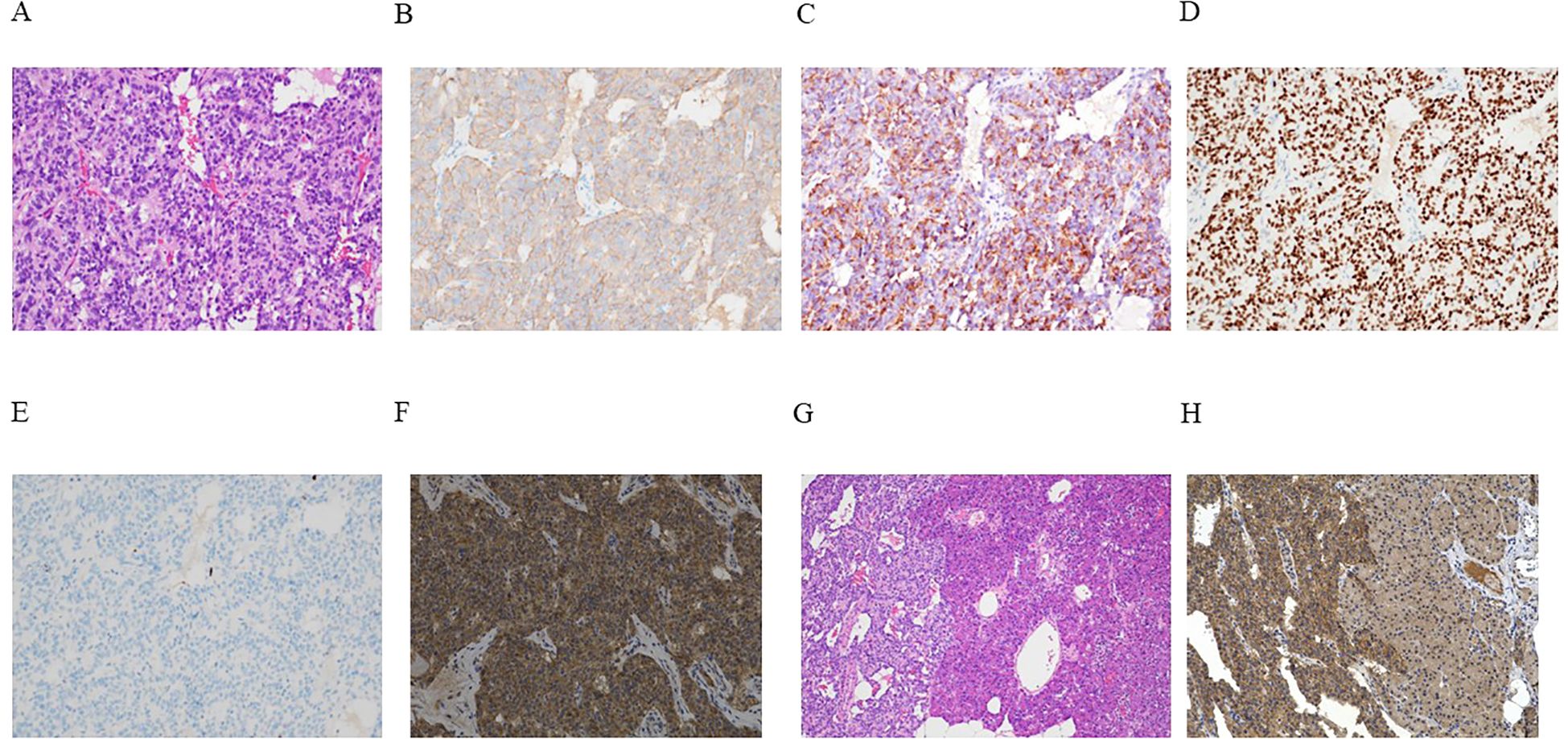
Figure 3. (A–H) Outcomes of microscopic analyses of the representative resected tumor. (A) Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining demonstrated a characteristic pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor manifesting histologically with the trabecular proliferation of cells having oval nuclei and eosinophilic cytoplasm. (B–G) Immunohistochemical staining revealed tumor cells that tested positive for synaptophysin (B), insulin (C), and insulinoma-associated protein 1 (INSM1) (D). The Ki-67 labeling index was 0.8% (E). Neoplastic cells also tested positive for the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor (F). (G) Continuous HE-stained sections of the tumor (left) and unaffected pancreatic parenchyma (right). (H) GLP-1 receptor staining showed that GLP-1 receptor expression was more pronounced in the tumor area (left) than in the unaffected pancreatic parenchyma (right). Magnification: ×200 (A–F, H), ×40 (G).
Following the intervention, the patient’s hypoglycemia and its associated symptoms disappeared. Fasting plasma glucose levels normalized (88 mg/dL), insulin levels changed to 2.8 μU/mL, and C-peptide levels changed to 0.9 ng/mL. Six months after the surgery, hypoglycemia did not recur, and HbA1c levels reached 6.0%. Considering the complication-free postoperative clinical course and the pathological findings, the patient’s complete postoperative recovery was noted.
3 Discussion
Patients with insulinoma can develop hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia; however, there are often diagnostic and treatment delays when conventional techniques fail to localize a tumor, as seen in the reported case (8). In our case, although the tumor appeared slowly progressive, with no apparent enlargement observed over several years following diagnosis, the patient experienced severe hypoglycemia despite diazoxide therapy, resulting in impaired quality of life. This illustrates how such delays in localization and treatment can negatively impact patient well-being.
Some patients cannot undergo surgery and need to be assigned to continuous medical therapy, while others may require extensive surgery that can lead to postoperative diabetes mellitus (8). Hypoglycemia induced by insulinoma can result in coma or even death (2, 4, 5). To prevent such outcomes, it is essential to enable minimally invasive curative surgery (including resection), which would require tumor localization via an accurate, prompt, and non-invasive method that surpasses the diagnostic capacity of conventional examinations (10).
GLP-1 receptor-targeted imaging has been identified as a promising diagnostic technique (10). In the pancreas, GLP-1 receptors are exclusively expressed in β-cells (22), and this is significantly more pronounced in cells of insulinoma compared with normal pancreatic β-cells (16, 23); thus, GLP-1 receptors are considered an ideal target for insulinoma imaging (8, 16). Clinical studies have demonstrated the utility of several exendin-4-based probes for SPECT and PET/CT imaging (11, 16, 24–30). A recent meta-analysis reported that GLP-1 receptor-targeted PET/CT using 68Ga-labeled exendin-4 (including 68Ga-NODAGA-exendin-4, 68Ga-NOTA-exendin-4, and 68Ga-DOTA-exendin-4) achieved a sensitivity of 94% and a specificity of 83%, whereas SPECT/CT using 111In-DOTA-exendin-4 or 99mTc-EDDA NH2-exendin-4 showed lower diagnostic performance, with a sensitivity of 63% and specificity of 45% (31). However, 68Ga-based PET/CT may have limitations such as difficulty in localizing tumors near the kidneys due to physiological renal uptake (32), whereas 18F-labeled probes are theoretically expected to provide higher spatial resolution than 68Ga-based agents (33). Further accumulation of cases is necessary to assess the diagnostic performance of 18F-exendin-4 PET/CT.
We elaborated a novel GLP-1 receptor-targeted imaging method involving a polyethylene glycol (PEG) conjugated (PEGylated) exendin-4-based probe known as 18F-exendin-4 (19, 20). 18F-exendin-4 PET/CT proved to be highly sensitive and specific in the detection of insulinomas in mice injected with rat insulinoma cells (INS-1 cells), as well as in disease models of mice with multiple insulinomas (19). The probe has been found to be clinically safe in healthy individuals (20). Additionally, clinical cases of insulinoma in which 18F-exendin-4 PET/CT enabled the successful detection of this pathologic condition have been detected (24, 25).
In the present case, the tumor was undetectable by CT, MRI, or EUS. It was also not visualized by SSTR-targeted imaging. Although SSTR PET/CT provides higher sensitivity for diagnosis of insulinoma than SSTR SPECT (10, 11), the evaluation was limited to SPECT in this case, as SSTR PET/CT was not available under the national health insurance system in Japan.
SACST also failed to localize the insulinoma, as insulin secretion was not induced by stimulation from any arteries. The non-response of the insulinoma to SACST in this case may be attributed to its unique vascular supply due to its protruding location or an incidental low expression of calcium sensing receptor. After the result of 18F-exendin-4 PET/CT was confirmed, the patient was reexamined and the nodule could be detected by EUS, but due to the location of the tumor, EUS-TA could not be performed. However, the information obtained from PET/CT provided accurate localization and led to curative surgery by enucleation.
SACST and GLP-1 receptor-targeted PET/CT are based on fundamentally different physiological mechanisms. SACST assesses insulin secretion in response to calcium stimulation via vascular routes, while GLP-1 receptor imaging reflects receptor expression in tumor tissue. Given these differences, the two modalities may be complementary rather than mutually exclusive. Notably, the present case represents a rare instance in which SACST failed to localize the tumor, whereas GLP-1 receptor-targeted imaging successfully did so, supporting the potential utility of this modality even in SACST-negative cases.
In previous reports of the other GLP-1 receptor-targeted imaging, several cases have been documented in which tumors undetectable by CT or MRI were successfully localized (27–30). However, in most of these cases, the patients were either positive on SACST or did not undergo SACST evaluation (27–30). Therefore, the clinical information regarding the usefulness of GLP-1 receptor-targeted imaging in comparison with SACST is still lacking and the finding of GLP-1 receptor-targeted imaging in cases with SACST-negative is rare. As for 111In-DOTA-exendin-4 SPECT/CT, among six insulinoma cases diagnosed, three did not undergo SACST and the other three (including a case of ectopic insulinoma) were all positive in SACST (27). In a multicenter study using 111In-DTPA-exendin-4 SPECT/CT, only seven out of 25 cases underwent SACST; although two of these were false-positive, none were false-negative (28). In the report that verified the diagnostic ability of 68Ga-NOTA-Exendin-4, there was no mention of comparison with the results of SACST (29). Notably, in a report comparing 68Ga-DOTA-exendin-4 PET/CT and 111In-DOTA-exendin-4 SPECT/CT, 10 out of 52 participants underwent SACST. Among these, only three cases were identified where tumors were detected by 68Ga-DOTA-exendin-4 PET/CT and confirmed as insulinoma in the final pathological diagnosis, despite being false-negative in SACST (30). The summary of the SACST-false-negative cases is shown in Table 1.
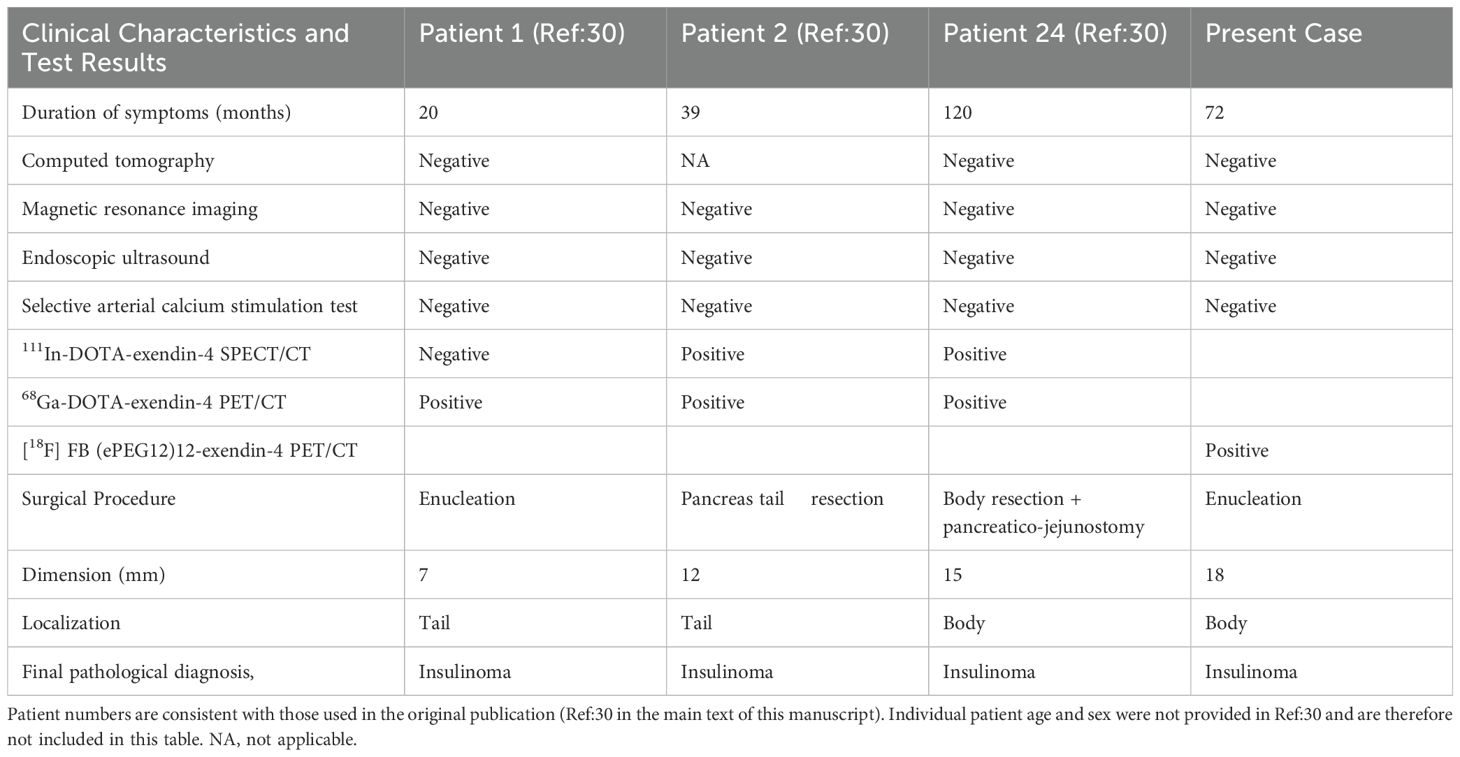
Table 1. Comparison of clinical characteristics and results of conventional tests of previously reported occult insulinoma cases and the present case.
In addition, endoscopic ultrasound can provide high-resolution anatomical information, including the spatial relationship between the tumor and the main pancreatic duct, which is useful for determining the appropriate surgical approach (34). These facts underscore the importance of individualized strategies for diagnosis and preoperative evaluation with appropriate understanding of complementary roles of each modality. To date, however, no studies have systematically evaluated the diagnostic accuracy or clinical impact of combining GLP-1 receptor-targeted imaging and EUS. Further investigations are warranted to establish optimized multimodal approaches for the localization and management of insulinoma.
The present case is the first case in which 18F-exendin-4 PET/CT successfully localized an occult insulinoma that remained elusive by CT, MRI, EUS, and even SACST. Even with all GLP-1 receptor-targeted imaging, only a few cases demonstrated that GLP-1 receptor-targeted imaging can localize occult insulinoma that was false-negative in SACST. This case highlights both the critical importance of precise tumor localization in optimizing the treatment of insulinoma and the utility of 18F-exendin-4 PET/CT, even in the most challenging clinical scenarios including negative findings of SACST.
4 Conclusion
The 18F-exendin-4 PET/CT method provided comprehensive localization information for the insulinoma that could not be detected by other techniques and finally enabled the minimally invasive curative resection of the neoplasm. Thus, 18F-exendin-4 PET/CT could be a promising diagnostic option that facilitates a minimally invasive approach in the surgical treatment of insulinomas.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the institutional review boards of Kyoto University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article. Written informed consent was obtained from the participant/patient(s) for the publication of this case report.
Author contributions
KS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TM: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. HF: Writing – review & editing. YS: Writing – review & editing. KM: Writing – review & editing. DO: Writing – review & editing. SO: Writing – review & editing. HS: Writing – review & editing. KN: Writing – review & editing. TN: Writing – review & editing. DY: Writing – review & editing. YN: Writing – review & editing. NI: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by grants from Manpei Suzuki Diabetes Foundation, Japan Foundation for Applied Enzymology, The Japan Health Foundation, Kyoto Health Management Research Foundation, Japan Health Promotion Foundation, and Advanced Science, Technology & Management Research Institute of KYOTO (ASTEM RI/KYOTO), MEXT/JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 24K02359, TERUMO LIFE SCIENCE FOUNDATION, and Moriya Scholarship Foundation.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the patient and all the clinical staff who participated in the treatment of the patient.
Conflict of interest
NI received joint research grants from Asken, Terumo, and Drawbridge Health, received speaker honoraria from Novo Nordisk Pharma, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim, Kyowa Kirin, Sanofi, Eli Lilly Japan, Sumitomo Pharma, and Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, and received scholarship grants from Daiichi-Sankyo, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Takeda, Kyowa Kirin, Sumitomo Pharma, MSD, Eli Lilly Japan, Ono, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim, Kowa, and Life Scan Japan.
DY received consulting or speaker fees from Sumitomo Pharma Co., Ltd, Eli Lilly Japan K.K., MSD K.K., Novo Nordisk Pharma Ltd., Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co. Ltd, and Tanabe Mitsubishi Pharma, Co. Ltd, and clinically commissioned/joint research grants from Taisho, Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd, Novo Nordisk Pharma Ltd, Arklay Co. Ltd and Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co. Ltd.
TM received joint research grants from Sumitomo pharma.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Grant CS. Insulinoma. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. (2005) 19:783–98. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2005.05.008
2. Okabayashi T, Shima Y, Sumiyoshi T, Kozuki A, Ito S, Ogawa Y, et al. Diagnosis and management of insulinoma. World J Gastroenterol. (2013) 19:829–37. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i6.829
3. Masui T, Ito T, Komoto I, Kojima S, Kasai Y, Tanabe M, et al. Nationwide registry for patients with neuroendocrine neoplasm of pancreas, gastrointestinal tract, lungs, bronchi, or thymus in Japan. Int J Clin Oncol. (2022) 27:840–9. doi: 10.1007/s10147-022-02130-y
4. Kinova MK. Diagnostics and treatment of insulinoma. Neoplasma. (2015) 62:692–704. doi: 10.4149/neo_2015_083
5. Murakami T, Yamashita T, Yabe D, Masui T, Teramoto Y, Minamiguchi S, et al. Insulinoma with a history of epilepsy: still a possible misleading factor in the early diagnosis of insulinoma. Intern Med. (2017) 56:3199–204. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8932-17
6. Armellini E, Facciorusso A, Crinò SF. Efficacy and safety of endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: A systematic review and metanalysis. Medicina (Kaunas). (2023) 59:359. doi: 10.3390/medicina59020359
7. Mehrabi A, Fischer L, Hafezi M, Dirlewanger A, Grenacher L, Diener MK, et al. A systematic review of localization, surgical treatment options, and outcome of insulinoma. Pancreas. (2014) 43:675–86. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000110
8. Murakami T, Yabe D, Inagaki N. Unmet needs in current clinical practice for insulinoma: lessons from nationwide studies in Japan. J Diabetes Invest. (2022) 13:429–31. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13730
9. Hatoko T, Murakami T, Sone M, Yabe D, Masui T, Nakamoto Y, et al. Low-dose selective arterial calcium stimulation test for localizing insulinoma: a single-center experience of five consecutive cases. Intern Med. (2020) 59:2397–403. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.4396-20
10. Murakami T, Yabe D, Inagaki N. Case 23-2018: a man with episodes of confusion and hypoglycemia. N Engl J Med. (2018) 379:1881–2. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1811310
11. Wild D, Antwi K, Fani M, Christ ER. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor as emerging target: will it make it to the clinic? J Nucl Med. (2021) 62:44S–50S. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.120.246009
12. Kwekkeboom DJ, Krenning EP, Scheidhauer K, Lewington V, Lebtahi R, Grossman A, et al. ENETS Consensus Guidelines for the Standards of Care in Neuroendocrine Tumors: somatostatin receptor imaging with (111)In-pentetreotide. Neuroendocrinology. (2009) 90:184–9. doi: 10.1159/000225946
13. Toshiyama R, Noda T, Eguchi H, Iwagami Y, Yamada D, Asaoka T, et al. Two cases of resectable pancreatic cancer diagnosed by open surgical biopsy after endoscopic ultrasound fine-needle aspiration failed to yield diagnosis: case reports. Surg Case Rep. (2017) 3:39. doi: 10.1186/s40792-017-0314-2
14. Morera J, Guillaume A, Courtheoux P, Palazzo L, Rod A, Joubert M, et al. Preoperative localization of an insulinoma: selective arterial calcium stimulation test performance. J Endocrinol Invest. (2016) 39:455–63. doi: 10.1007/s40618-015-0406-4
15. Nakamura Y, Doi R, Kohno Y, Shimono D, Kuwamura N, Inoue K, et al. High-dose calcium stimulation test in a case of insulinoma masquerading as hysteria. Endocrine. (2002) 19:127–30. doi: 10.1385/ENDO:19:2:127
16. Murakami T, Fujimoto H, Inagaki N. Non-invasive beta-cell imaging: visualization, quantification, and beyond. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2021) 12:714348. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.714348
17. Eng J, Kleinman WA, Singh L, Singh G, Raufman JP. Isolation and characterization of exendin-4, an exendin-3 analogue, from Heloderma suspectum venom. Further evidence for an exendin receptor on dispersed acini from Guinea pig pancreas. J Biol Chem. (1992) 267:7402–5. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)42531-8
18. Furman BL. The development of Byetta (exenatide) from the venom of the Gila monster as an anti-diabetic agent. Toxicon. (2012) 59:464–71. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2010.12.016
19. Murakami T, Fujimoto H, Hamamatsu K, Yamauchi Y, Kodama Y, Fujita N, et al. Distinctive detection of insulinoma using [18F] FB (ePEG12)12-exendin-4 PET/CT. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:15014. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-94595-6
20. Fujimoto H, Fujita N, Hamamatsu K, Murakami T, Nakamoto Y, Saga T, et al. First-in-human evaluation of positron emission tomography/computed tomography with [18F] FB (ePEG12)12-Exendin-4: a Phase 1 clinical study targeting GLP-1 receptor expression cells in pancreas. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2021) 12:717101. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.717101
21. WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Endocrine and neuroendocrine tumours. 5th ed. Lyon (France: International Agency for Research on Cancer. (2022). Available at: https://tumourclassification.iarc.who.int/chapters/53 (Accessed August 25, 2024).
22. Tornehave D, Kristensen P, Rømer J, Knudsen LB, Heller RS. Expression of the GLP-1 receptor in mouse, rat, and human pancreas. J Histochem Cytochem. (2008) 56:841–51. doi: 10.1369/jhc.2008.951319
23. Waser B, Blank A, Karamitopoulou E, Perren A, Reubi JC. Glucagon-like-peptide-1 receptor expression in normal and diseased human thyroid and pancreas. Mod Pathol. (2015) 28:391–402. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2014.113
24. Sakaki K, Murakami T, Fujimoto H, Shimizu Y, Miyake KK, Otani D, et al. 18F-labeled pegylated exendin-4 imaging noninvasively differentiates insulinoma from an accessory spleen: the first case report of [18F]FB(ePEG12)12-exendin-4 positron emission tomography/computed tomography for insulinoma. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2023) 14:1245573. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1245573
25. Otani D, Murakami T, Murakami S, Hanaoka I, Fujimoto H, Shimizu Y, et al. 18F]FB(ePEG12)12-exendin-4 noninvasive imaging of insulinoma negative for insulin immunostaining on specimen from endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine needle aspiration: a case report with review of literature. Endocr J. (2024) 71:925–33. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ24-0187
26. Murakami T, Nakamura T, Fujimoto H, Fujikura J, Shimizu Y, Miyake KK, et al. Noninvasive evaluation of donor and native pancreases following simultaneous pancreas–kidney transplantation using positron emission tomography/computed tomography. J Diabetes Invest. (2023) 14:1187–91. doi: 10.1111/jdi.14045
27. Christ E, Wild D, Forrer F, Brändle M, Sahli R, Clerici T, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor imaging for localization of insulinomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2009) 94:4398–405. doi: 10.1210/jc.2009-1082
28. Christ E, Wild D, Ederer S, Béhé M, Nicolas G, Caplin ME, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor imaging for the localisation of insulinomas: a prospective multicentre imaging study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2013) 1:115–22. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(13)70049-4
29. Luo Y, Pan Q, Yao S, Yu M, Wu W, Xue H, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor PET/CT with 68Ga-NOTA-Exendin-4 for detecting localized insulinoma: a prospective cohort study. J Nucl Med. (2016) 57:715–20. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.115.167445
30. Antwi K, Fani M, Heye T, Nicolas G, Rottenburger C, Kaul F, et al. Comparison of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) PET/CT, SPECT/CT and 3T MRI for the localization of occult insulinomas: evaluation of diagnostic accuracy in a prospective crossover imaging study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2018) 45:2318–27. doi: 10.1007/s00259-018-4101-5
31. Shah R, Garg R, Majmundar M, Purandare N, Malhotra G, Patil V, et al. Exendin-4-based imaging in insulinoma localization: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). (2021) 95:354–64. doi: 10.1111/cen.14406
32. Antwi K, Hepprich M, Müller NA, Reubi JC, Fani M, Rottenburger C, et al. Pitfalls in the detection of insulinomas with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor imaging. Clin Nucl Med. (2020) 45:e386–92. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000003124
33. Braune A, Oehme L, Freudenberg R, Hofheinz F, van den Hoff J, Kotzerke J, et al. Comparison of image quality and spatial resolution between 18F, 68Ga, and 64Cu phantom measurements using a digital Biograph Vision PET/CT. EJNMMI Phys. (2022) 9:58. doi: 10.1186/s40658-022-00487-7
34. Giuliani T, Marchegiani G, Girgis MD, Crinò SF, Muthusamy VR, Bernardoni L, et al. Endoscopic placement of pancreatic stent for “Deep” pancreatic enucleations operative technique and preliminary experience at two high-volume centers. Surg Endosc. (2020) 34:2796–802. doi: 10.1007/s00464-020-07501-y
Keywords: exendin-4, PET, insulinoma, GLP-1 receptor, β-cell imaging
Citation: Sakaki K, Murakami T, Fujimoto H, Shimizu Y, Miyake KK, Otani D, Otsuki S, Shimizu H, Nagai K, Nomura T, Yabe D, Nakamoto Y and Inagaki N (2025) Case Report: A case of occult insulinoma localized by [18F] FB (ePEG12)12-exendin-4 positron emission tomography with negative findings of selective arterial calcium stimulation test. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1556813. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1556813
Received: 07 January 2025; Accepted: 16 April 2025;
Published: 08 May 2025.
Edited by:
Nils Lambrecht, United States Department of Veterans Affairs, United StatesReviewed by:
Stefano Francesco Crinò, University of Verona, ItalyEmre Gezer, Kocaeli University, Türkiye
Yuta Nakamura, St. Marianna University School of Medicine, Japan
Copyright © 2025 Sakaki, Murakami, Fujimoto, Shimizu, Miyake, Otani, Otsuki, Shimizu, Nagai, Nomura, Yabe, Nakamoto and Inagaki. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Takaaki Murakami, dG11cmFrYW1Aa3VocC5reW90by11LmFjLmpw
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Kentaro Sakaki
Kentaro Sakaki Takaaki Murakami
Takaaki Murakami Hiroyuki Fujimoto
Hiroyuki Fujimoto Yoichi Shimizu
Yoichi Shimizu Kanae Kawai Miyake
Kanae Kawai Miyake Daisuke Otani
Daisuke Otani Shinya Otsuki
Shinya Otsuki Hironori Shimizu3
Hironori Shimizu3 Daisuke Yabe
Daisuke Yabe Yuji Nakamoto
Yuji Nakamoto