- 1Department of Pharmacy, Affiliated Hospital of Shaoxing University, Shao Xing, Zhejiang, China
- 2Endoscopic center, Affiliated Hospital of Shaoxing University, Shao Xing, Zhejiang, China
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of endogenous, non-coding RNAs, that have been implicated in cardiovascular diseases. Recent studies have suggested that dysregulated miRNAs accumulate in the heart and may be associated with impaired cardiac glucose metabolism. However an inconsistent direction of expression was observed in the current available literature. The aim of this study was to characterize miRNA expression profiles associated with glucose metabolism, and to explore their potential as biomarkers for glucose metabolism disorders in diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM).
Methods: A systematic search of electronic databases, including Embase, PubMed, and the Cochrane Library, was conducted until October 1, 2024. Studies reporting on miRNAs expression profiles that regulate glucose metabolism in the heart were selected for inclusion. Pooled results were presented as log10 odds ratios (logORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs), using random-effect models. Subgroup analyses were conducted based on species, region, and sample source. Analyses by species focused specifically on humans and mice. The quality of included articles was assessed using the modified Diagnostic Accuracy Study 2 (QUADAS-2) tool. All workflows, including abstract screening, full-text review, data extraction, and quality assessment, were independently performed by two reviewers.
Results: A total of 47 eligible articles were included in this study, identifying 70 dysregulated miRNAs. Further analysis revealed that compared with the non-DCM group, the DCM group exhibited differential miRNA expression, with 12 miRNAs consistently upregulated and 8 consistently downregulated. Among these miRNAs, miR-199a (logOR 4.59; 95% CI: 3.02-6.15) was the most upregulated and frequently reported (n=7 studies), while let-7 (logOR 4.48; 95% CI: 2.41-6.55) was the most downregulated (4 studies). Subgroup analysis indicated that miRNA-21 was the most upregulated in cardiac tissue, and miRNA-133 was the most downregulated in cardiomyocytes. Additionally, miRNA-21 was found to be the most upregulated across different species. In the region subgroups, miRNA-199a and miRNA-503 were the most upregulated and downregulated in Asian countries, whereas miRNA-378 was the most dysregulated in non-Asian countries.
Conclusion: In summary, this study identified 20 consistently dysregulated miRNAs assocaited with myocardial glucose metabolism. Six dysregulated miRNAs, including miRNA-199a, let-7, miRNA-21, miRNA-133, miRNA-503 and miRNA-378, have potential as candidate miRNA biomarkers of glycometabolism in the heart. These findings require further validation in future larger-scale studies.
Introduction
The rising prevalence of diabetes mellitus (DM), including type 1, type 2, and other subtypes, poses a significant socioeconomic burden worldwide. Notably, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a metabolic disorder characterized by systemic and myocardial insulin resistance, thereby increasing the risk of cardiovascular complications (1). Diabetic cardiomyopathy, a common complication of diabetes, is marked by myocardial hypertrophy, myocardial fibrosis, and cardiac dysfunction (2–4). While the molecular mechanisms underlying insulin resistance have been extensively studied, the pathophysiology of myocardial insulin resistance remains poorly understood, necessitating further investigation. Abnormal glucose metabolism, observed in patients with diabetic cardiomyopathy, has been identified to be associated with cardiac dysfunction (5). Several key regulators, including GLUT-4, Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDH), Glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK-3β), and Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R), are critical for cardiac glucose metabolism (6–8).
MicroRNAs (miRNAs), a class of small non-coding RNAs, have been recognized for their role in regulating gene expression through binding to the 3’ untranslated region (3’-UTR) of target mRNAs (9). Previous studies have reported that miRNAs play a crucial role in glucose metabolism across various organs. MiR-146a has been shown to enhance hepatic glucose tolerance by targeting the oxidative metabolism of fatty acids (10). MiR-140-5p mitigates high glucose-induced apoptosis and inflammation in the kidney (11). Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that miRNAs are involved in the development of glucose metabolism in metabolic diseases (12, 13). For instance, miR-29 is dysregulated in muscle, fat, and liver tissues, where it regulates insulin-stimulated glucose uptake (14). Importantly, growing evidence demonstrates that miRNAs play a significant role in the development of various cardiac diseases, particularly in cardiac hypertrophy and glucose metabolism (15, 16). MiR-150 regulates glucose utilization through GLUT-4 in insulin-resistant heart muscle (17). GLUT-4, a key target gene, plays a critical role in myocardial insulin resistance (18).
Taken together, these findings in the current literature highlight the importance of miRNAs in glucose metabolism in the heart. However, the expression profiles of miRNAs across individual studies have yielded inconsistent results. This variability may stem from differences in miRNA sources. For example, miRNA-499 was found to be down-regulated in cardiomyocytes (19), yet up-regulated in myocardium (20). Moreover, even in the same tissue type, the direction of miRNA expression may vary across different studies. Wang et al. indicated a significant downregulation of miR-221 in myocardium (21), whereas another study observed upregulation of miR-221 (20). These conflicting findings underscore the critical impact of heterogeneity among individual studies in miRNA expression profiles. Therefore, this study aims to summarize dysregulated miRNAs in cardiac glucose metabolism, explores their pathological contributions to metabolic dysregulation, and identifies potential biomarkers for myocardial glucose metabolism monitoring.
Methods
Search strategy
A comprehensible search was performed across the PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases to identify relevant miRNA expression profiling articles from inception until October 1, 2024. The following items were used in the title/abstract: (microRNA or miR- or miRNA), (glucose metabolism or glycometabolism), (expression or profiling or profile). Detailed search queries are provided in Supplementary Table 1. Furthermore, a manual search was supplemented by screening the reference lists of retrieved studies. Two reviewers independently performed the literature search, and any discrepancies were resolved through discussion with a third reviewer to reach a consensus.
Literature selection
The retrieved articles were screened to identify eligible studies. After removing duplicates, an initial screening was performed to identify potentially eligible studies according to their titles and abstracts. Afterwards, two investigators independently reviewed the full-text studies based on pre-defined criteria, and any discrepancies were resolved through consensus by a third researcher.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The eligibility criteria were as follows: (1) observational studies (including cohort,
cross-sectional, and case-control studies) that investigated miRNA expression patterns or the diagnostic value of miRNAs in myocardial glucose metabolism; (2) studies must report sample sizes for differentially expressed miRNAs between the normal and abnormal glycometabolism groups; (3) miRNA expression profiles were assessed using techniques such as qPCR, real-time PCR, and microarray; (4) only papers written in English were included. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) studies that examined glucose metabolism in organs other than heart (e.g., liver, kidney, adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, etc.); (2) various types of literature, including conference abstracts, case reports, meta-analyses, letters, comments, editorials, and reviews; (3) articles lacking essential data. In cases of duplicate studies from the same research, the study most closely aligned with the inclusion criteria was selected.
Data extraction and collection
Two reviewers independently extracted essential information from the included articles, with any discrepancies resolved through consensus after in-depth discussion involving a third researcher. The extracted data included the following details: first author, year of publication, country, ethnicity, species, detection methods, sample types, sample size, expressed direction, number of dysregulated miRNAs, and the regulatory mechanism of miRNAs.
Quality assessment
The Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies-2 (QUADAS-2) was utilized to assess quality of the included studies. This tool consists of eight questions, each of which is rated as “yes”, “no” and “unclear”. Two independent authors appraised the quality of all eligible articles, and any discrepancies were resolved through discussion with a third reviewer to reach a final consensus.
Data synthesis and statistical analysis
The extracted data were subjected to statistical analysis using Stata software version 13 (Statacorp, College Station, Texas, United States). Results were presented as log odds ratios (logORs) with corresponding 95% confidence interval (CI), refecting number and direction of dysregulation between the normal and abnormal glucose metabolism groups. Compared to the normal group, logOR values greater than 1 in the abnormal group indicate upregulation. Conversely, a logOR value greater than 1 in the normal group relative to the abnormal group indicates downregulation. A P-value<0.05 was considered statistically significant. Heterogeneity was assessed using the Q test and I2 statistics by random-effects model, I2< 50% suggests minimal heterogeneity among studies. The significance of dysregulated miRNAs in the abnormal group was ranked based on: (1) number of consistent sub-studies; (2) total sample size; (3) the magnitude of logOR values. Subgroup analysis were performed according to species, ethnicity and tissue type.
Results
Literature retrieval and search results
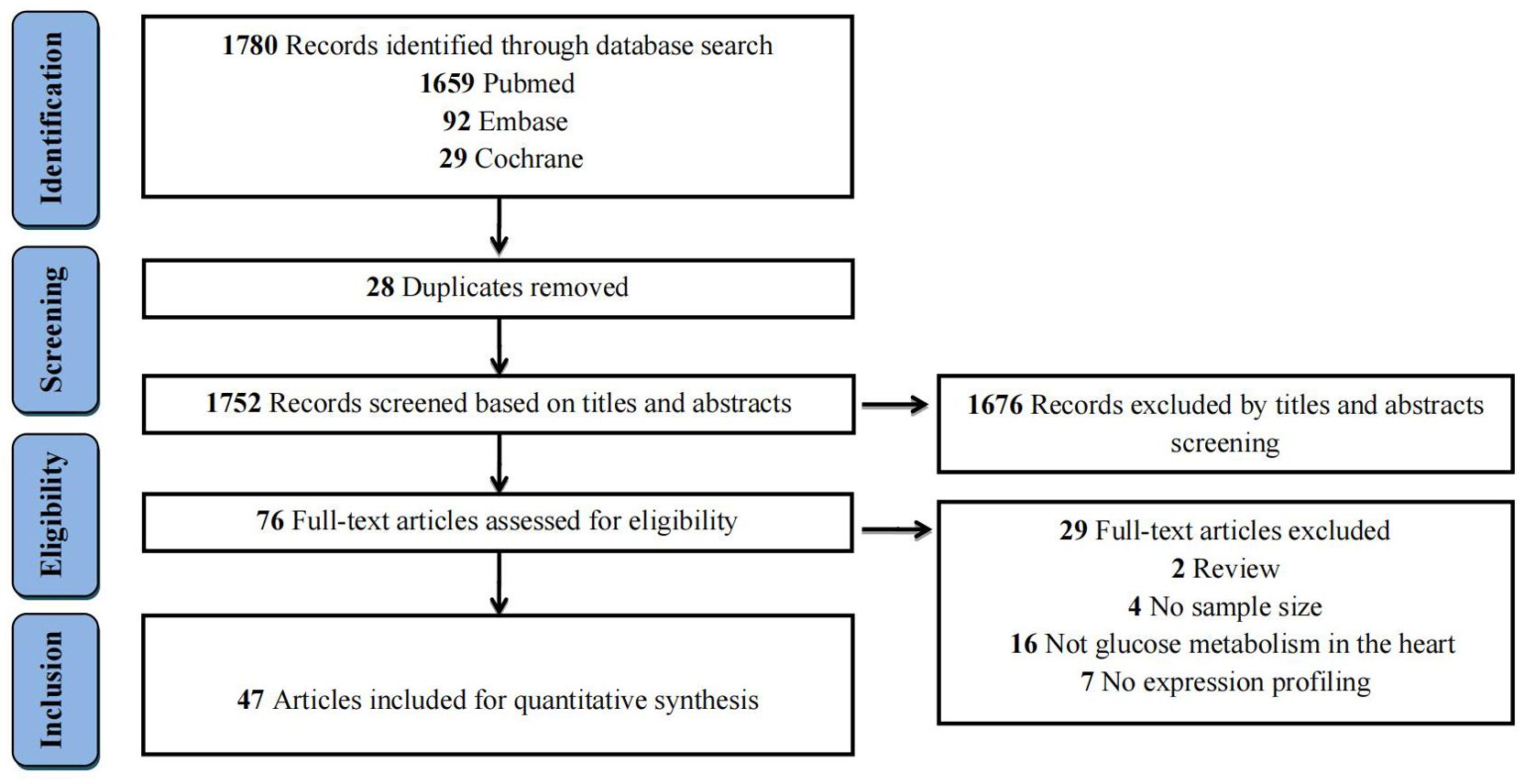
The literature search process and study selection were illustrated in Figure 1. The initial literature search yielded a total of 1,780 records (PubMed = 1,659, Embase = 92, and Cochrane = 29) according to the eligibility criteria (Supplementary Table 1). After removing 28 duplicates, the remaining 1,752 records were further screened based on their titles and abstracts. Subsequently, 76 full-text articles were assessed for eligibility. Ultimately, 47 studies were selected for the quantitative analysis. The specific reasons for excluding studies were displayed in Supplementary Table 2.
Study characteristics
All the included studies were published between 2009 and 2023, and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was used as the technique for evaluating miRNA expression in all studies. The number of differentially expressed miRNAs in individual studies ranged from 1 to 16, with the majority of miRNAs showing upregulation in studies of abnormal glucose metabolism. Sample sizes varied from 6 to 120 across the studies. Different specimen types were utilized, primarily including cardiomyocyte and myocardium. Detailed characteristics of the 47 eligible studies are provided in Table 1.
Quality assessment results
The quality of all included literature was assessed by The QUADAS-2 tool. Detailed information and results of quality assessment was presented in Supplementary Table 3. The validated and enhanced methodological standards were applicable to the eligible studies. The evaluation results indicated that the overall risk of bias was low, and the included studies met the majority of quality appraisal criteria.
Results of the dysregulated miRNAs in overall analysis
We conducted a comprehensive analysis of 47 articles encompassing 70 dysregulated miRNAs comparing the normal glycometabolism group with the abnormal glycometabolism group. Among these miRNAs, 20 (12 upregulated and 8 downregulated) were reported in two or more studies (Figures 2, 3). Detailed information for each miRNA is provided in Supplementary Figures 1-20. Additionally, 50 dysregulated miRNAs (34 upregulated and 16 downregulated) were reported only once (Supplementary Table 4). Based on the results from 7 sub-studies involving 82 samples, miRNA-199a (logOR 4.59; 95% CI: 3.02-6.15) was identified as the most significantly upregulated miRNA, followed by miRNA-21 (logOR 4.69; 95% CI: 2.63-6.75) due to myocardial glucose metabolism disorder. The most frequently reported downregulated miRNAs were let-7 (logOR 4.48; 95% CI: 2.41-6.55), followed by miRNA-378 (logOR 4.62; 95% CI: 2.24-7.00).
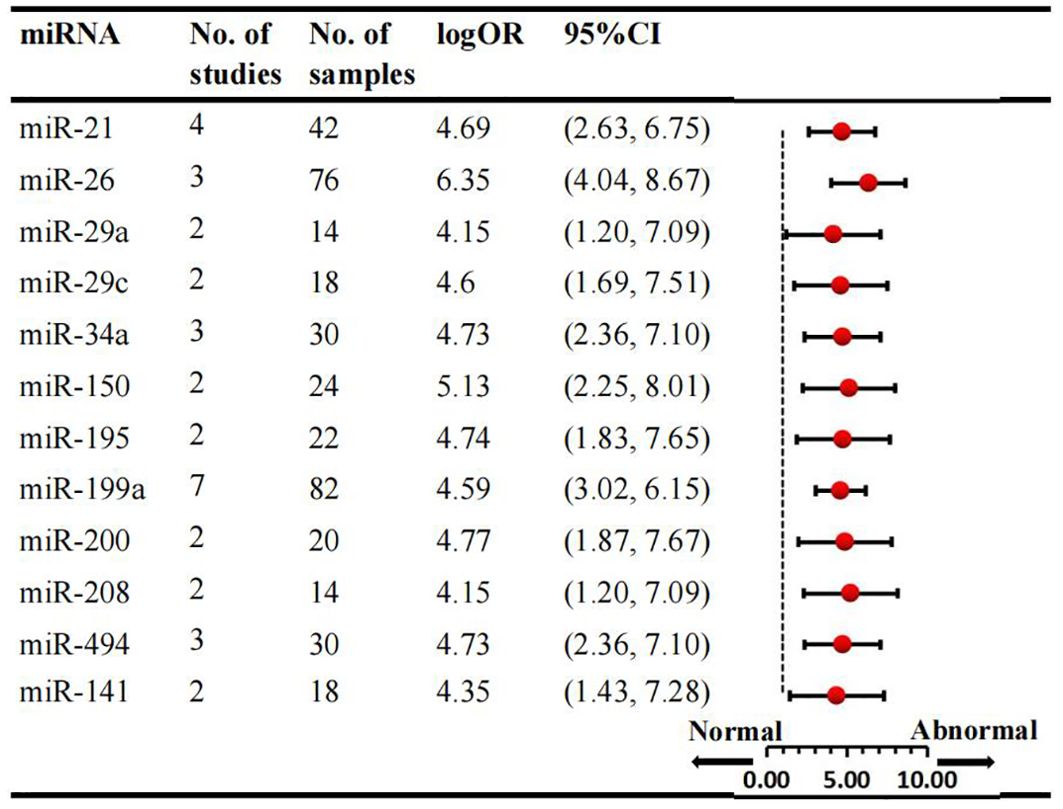
Figure 2. Consistently upregulated miRNAs in overall analysis. miR: microRNA; No.: number of included studies.
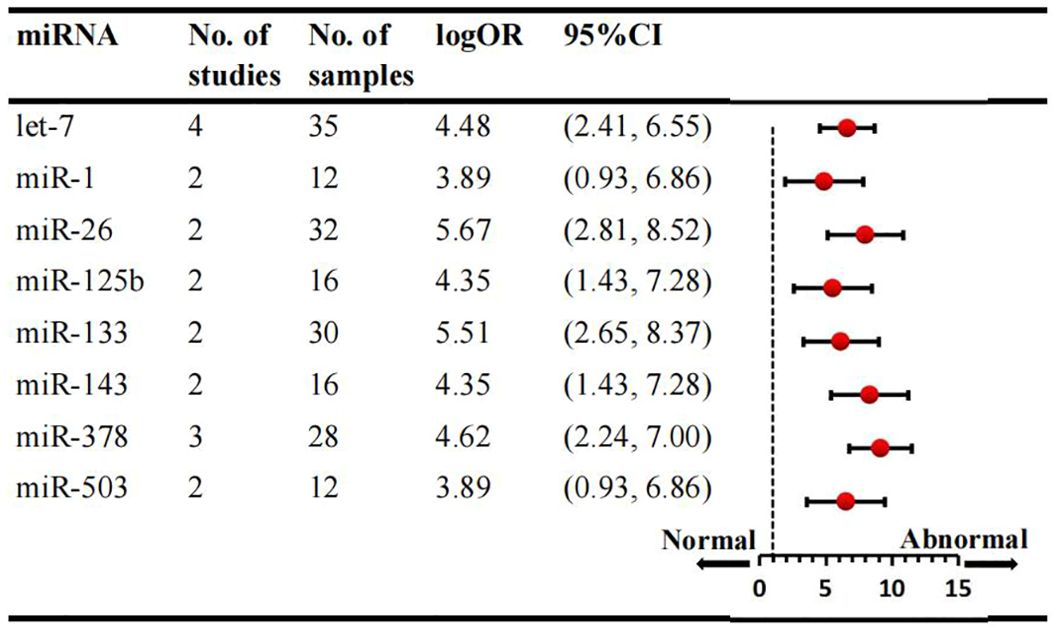
Figure 3. Consistently downregulated miRNAs in overall analysis. miR: microRNA; No.: number of included studies.
Results of subgroup analysis
Subgroup analysis was conducted according to sample source, which included tissue and cell samples. Six studies examined miRNAs in myocardial tissue, while four studies focused on miRNAs in myocardial cells. Overall, three consistently upregulated miRNAs (miRNA-21, miRNA-195, miRNA-208) were identified as aberrantly expressed in myocardial tissue samples, with miRNA-21 being the most upregulated (logOR 4.69; 95% CI: 2.63-6.75). The summary results of the tissue source subgroup were presented in Supplementary Table 5. Sub-analyses based on species revealed that the number of studies in mice was the largest. Consequently, three consistantly upregulated miRNAs were identified, and the detailed results are provided in Supplementary Table 6. Among the animal studies, several miRNAs were consistently upregulated in two studies, including miRNA-21, miRNA-29a, miRNA-208, with the miRNA-21 being the most upregulated (logOR 4.69; 95% CI: 2.63-6.75). Subgroup analyses by ethnicity were conducted for Asian and non-Asian countries. When examining various species types, 8 dysregulated miRNAs were identified in Asian countries and 3 miRNAs in non-Asian studies. The expression signature of miRNAs is region-specific. In the Asian subgroup, 4 miRNAs were upregulated and 4 were downregulated, while in the non-Asian subgroup, 3 miRNAs were upregulated (Supplementary Table 7). Notably, miRNA-199a (logOR 4.59; 95% CI: 3.02-6.15) was consistently increased, and miRNA-26 (logOR 5.67; 95% CI: 2.81-8.52) was downregulated in Asian studies. In non-Asian countries, miRNA-29c was upregulated, and miRNA-378 was significantly downregulated.
Regulatory mechanisms of miRNAs in cardiac glucose metabolism
Dysregulated miRNAs have been identified to play critical roles by regulating glucose metabolism in the heart. The specific roles of miRNAs in cardiac glucose metabolism were summarized in Table 2. For instance, miRNA-200, miRNA-223, miRNA-150, and miRNA-141 regulate glucose transport via modulating myocardial GLUT4 expression. Additionally, multiple miRNAs, including miRNA-26, miRNA-99b-3p, miRNA-335, and miRNA-26a regulate glycogenesis by targeting Glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK-3β) in the heart. Furthermore, miRNA-34a has been reported to be involved in glycolysis process in the heart. Notably, miRNA-195 enhances the aerobic oxidation of glucose in the myocardium by increasing the acetylation of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH), which promotes the conversion of pyruvate and NAD+ into acetyl-CoA.
Discussion
miRNAs are a class of small non-coding RNAs that modulate gene expression by pairing with the 3’-untranslated region (3’UTR) of target mRNAs. Accumulating evidence suggests that miRNAs play pivotal roles in multiple facets of cardiac diseases, including myocardial injury, cardiac fibrosis, and heart failure (63, 64). Notably, prior studies have demonstrated that dysregulated miRNAs in the heart significantly influence cardiac glucose homeostasis (15, 65). However, a significant challenge remains the inconsistency in miRNA expression profiles across different studies. To date, there is a paucity of research providing a comprehensive overview of dysregulated miRNAs involved in myocardial glucose metabolism regulation. Consequently, we undertook an integrative analysis to summarize the differentially expressed miRNAs implicated in myocardial glucose metabolism regulation, based on the available evidence.
In this study, we identified 20 consistently dysregulated miRNAs involved in cardiac glucose metabolism. Among theses, the expression levels of twelve miRNAs were elevated, whereas those of eight miRNAs was reduced. Further analysis revealed that six miRNAs, miRNA-199a, let-7, miRNA-21, miRNA-133, miRNA-503, and miRNA-378, were recognized as potential biomarkers and deemed crucial in the pathogenesis of myocardial glucose metabolism disorder. MiRNAs exhibit differential expression in the cardiovascular system, and play a regulatory role in the pathophysiology of cardiovascular diseases (66). Under normal physiological conditions, heart requires a continuous energy supply to support electrical and mechanical functions, primarily generated through mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (67). The involvement of miRNAs in cardiovascular diseases via the regulation of glucose metabolism has been extensively investigated. Previous studies have elucidated the mechanisms by which miRNAs influence various pathological processes, including glucose transport, glycolysis, aerobic oxidation of glucose, and glycogenesis in the heart (22–25).
It is well established that the enhanced glucose uptake primarily results from the translocation of glucose transporter 4 (GLUT-4) and GLUT-1 from intracellular compartments to the surface of cardiomyocytes (68, 69). Upon insulin stimulation, GLUT-4 translocates from the intracellular vesicles to the sarcolemma, thereby increasing glucose uptake and transport (70). Studies have shown that the expression and translocation of GLUT-4 in cardiac myocytes are regulated by miRNAs. Specifically, miRNA-133 and miRNA-223 modulate glucose uptake in cardiomyocytes by targeting GLUT-4 (42, 51). MiRNAs could affect glucose transport in cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. For instance, miRNA-133 has been found to reduce KLF15 expression, a direct upstream regulator of GLUT-4 (51), and decreased level of miR-133a lead to reduced GLUT-4 glucose transporters on the cell membranes in hypertrophic cells (37). Furthermore, cardiac glucose uptake is diminished due to decreased GLUT-4, contributing to impaired myocardial glucose utilization in diabetic cardiomyopathy (37). Additionally, the upregulation of let-7 family enhances glucose utilization via GLUT-4 pathways (48). In summary, dysredulated miRNAs play a crucial role in the regulation of glucose transport in cardiomyocytes.
Cardiomyocytes primarily produce ATP through the glycolysis of glucose, and myocardial glycolysis has been found to convert glucose to macromolecular precursors (71). Several studies have reported on the role of differentially expressed miRNAs in myocardial glycolysis. Mallet et al. discovered that miRNA-378 regulates cardiac energy metabolism by balancing oxidative phosphorylation and glycolysis (41). MiRNAs also influence glycolysis to regulate cardiac function under conditions of myocardial ischemia (59). Upregulated miRNA-21 facilitates increased glycolysis via Per2-dependent mechanisms in myocardial ischemia (61). It is noteworthy that upregulation of miRNA-195 modulates cardiac energy metabolism by directly targeting the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDH) (7). Oxidative phosphorylation of glucose sustains energy necessary for cardiomyocyte function, and multiple miRNAs have been identified as regulators of mitochondrial function in the heart. For instance, miRNA-30 influences apoptosis by targeting the mitochondrial fission machinery (72), while overexpression of miRNA-761 suppresses mitochondrial fission and reduces cardiomyocyte apoptosis (44).
In addition to glucose consumption, excess glucose can be converted into glycogen to provide the high energy demands of the heart (73, 74). A study by Wei et al. demonstrated that the downregulation of miRNA-1 altered glycolysis and glycogenesis by upregulating the expression of related genes (35). Furthermore, miRNAs can target key enzymes in glycogenesis, such as glycogen synthase kinase-3α (GSK3α) and glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK3β) in various cardiac pathological processes involving glycogen synthesis. Several miRNAs, miRNA-21, miRNA-199a, miRNA-26, miRNA-378, and miRNA-29c have been shown to regulate the development of pathological cardiac hypertrophy by targeting GSK3β (19, 25, 30, 40, 47). Additionally, other miRNAs, including miRNA-34a, miRNA-199a, and miRNA-26a, affect myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via the GSK3β pathway (33, 43, 45, 75). However, the explicit mechnism by which these miRNAs are involved in glucose metabolism in the heart remain to be elucidated.
According to the current inconsistency in miRNA expression profiles, it is crucial to summarize the role of miRNAs in cardiac glucose metabolism. This study evaluated miRNA expression signatures during the pathological process of myocardial glucose metabolism and identified six miRNAs that may serve as potential biomarkers in glycometabolism. Systematic evaluation serves as a robust framework for addressing complex clinical challenges, generating evidence-based solutions through rigorous synthesis of available data (36, 76–79). While a comprehensive analysis of miRNA levels based on available evidence is a significant strength, several limitations must be acknowledged. First, the limited number of individual studies included in the pooled analysis weakens the robustness of conclusions. To ensure statistical power and reliability, we integrated data from 47 articles. Second, due to the insufficient sample size, studies with small sample sizes were not excluded. Finally, the results presented in this article are preliminary, and there is a scarcity of research explicitly investigating the pathological roles of differentially expressed miRNAs in cardiac glucose metabolism. Further experimental validation is essential to ascertain the role of these miRNAs in glycometabolism. Overall, our findings suggest that these miRNAs have the potential to serve as reliable biomarkers for myocardial glycometabolism. Nevertheless, caution is advised in interpreting these results, and rigorous experimental verification remains essential in future investigations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this study identified 20 significantly dysregulated miRNAs. Specifically, miRNA-199a, let-7, miRNA-21, miRNA-133, miRNA-503, and miRNA-378 may serve as potential biomarkers for myocardial glucose metabolism. However, their clinical feasibility and applicability remain to be validated, and further investigations is necessary to elucidate the underlying mechanism of these dysregulated miRNAs in cardiac glucose metabolism.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
HQ: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. Y-FZ: Data curation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. N-NS: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Zhongnanshan Medical Foundation of Guangdong Province (ZNSXS-20240069), Shaoxing health science and technology plan project (2023SKY079), Clinical Medical Research Special Fund Project of Zhejiang Medical Association (2023ZYC-A55), Clinical Medical Research Special Fund Project of Zhejiang Medical Association (2022ZYC-Z37), and Program of General Scientific Project of Zhejiang Education Department (Y202249053), Research Project of Grassroots health science of Zhejiang Province (2022ZD09), Zhejiang Pharmaceutical Society Hospital pharmacy special research project (2016ZYY29).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2025.1565385/full#supplementary-material.
References
1. Dutka DP, Pitt M, Pagano D, Mongillo M, Gathercole D, Bonser RS, et al. Myocardial glucose transport and utilization in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, left ventricular dysfunction, and coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2006) 48:2225–31. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.06.078
2. Boudina S and Abel ED. Diabetic cardiomyopathy revisited. Circulation. (2007) 115:3213–23. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.679597
3. Li J, Zhu H, Shen E, Wan L, Arnold JM, and Peng T. Deficiency of rac1 blocks nadph oxidase activation, inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress, and reduces myocardial remodeling in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. (2010) 59:2033–42. doi: 10.2337/db09-1800
4. Zhu L, Li D, Zhang X, Wan S, Liu Y, Zhang H, et al. Comparative efficacy on outcomes of c-cabg, opcab, and onbeat in coronary heart disease: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J surgery. (2023) 109:4263–72. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000000715
5. Scheuermann-Freestone M, Madsen PL, Manners D, Blamire AM, Buckingham RE, Styles P, et al. Abnormal cardiac and skeletal muscle energy metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes. Circulation. (2003) 107:3040–6. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000072789.89096.10
6. Wang XH, Qian RZ, Zhang W, Chen SF, Jin HM, and Hu RM. Microrna-320 expression in myocardial microvascular endothelial cells and its relationship with insulin-like growth factor-1 in type 2 diabetic rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. (2009) 36:181–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2008.05057.x
7. Zhang X, Ji R, Liao X, Castillero E, Kennel PJ, Brunjes DL, et al. Microrna-195 regulates metabolism in failing myocardium via alterations in sirtuin 3 expression and mitochondrial protein acetylation. Circulation. (2018) 137:2052–67. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.030486
8. Armoni M, Harel C, Bar-Yoseph F, Milo S, and Karnieli E. Free fatty acids repress the glut4 gene expression in cardiac muscle via novel response elements. J Biol Chem. (2005) 280:34786–95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M502740200
9. Bartel DP. Micrornas: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. (2004) 116:281–97. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00045-5
10. Li K, Zhao B, Wei D, Wang W, Cui Y, Qian L, et al. Mir−146a improves hepatic lipid and glucose metabolism by targeting med1. Int J Mol Med. (2020) 45:543–55. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4443
11. Su J, Ren J, Chen H, and Liu B. Microrna-140-5p ameliorates the high glucose-induced apoptosis and inflammation through suppressing tlr4/nf-kappab signaling pathway in human renal tubular epithelial cells. Bioscience Rep. (2020) 40:1–12. doi: 10.1042/BSR20192384
12. Poy MN, Eliasson L, Krutzfeldt J, Kuwajima S, Ma X, Macdonald PE, et al. A pancreatic islet-specific microrna regulates insulin secretion. Nature. (2004) 432:226–30. doi: 10.1038/nature03076
13. Coort SL, Bonen A, van der Vusse GJ, Glatz JF, and Luiken JJ. Cardiac substrate uptake and metabolism in obesity and type-2 diabetes: Role of sarcolemmal substrate transporters. Mol Cell Biochem. (2007) 299:5–18. doi: 10.1007/s11010-005-9030-5
14. He A, Zhu L, Gupta N, Chang Y, and Fang F. Overexpression of micro ribonucleic acid 29, highly up-regulated in diabetic rats, leads to insulin resistance in 3t3-l1 adipocytes. Mol endocrinology. (2007) 21:2785–94. doi: 10.1210/me.2007-0167
15. Shen E, Diao X, Wei C, Wu Z, Zhang L, and Hu B. Micrornas target gene and signaling pathway by bioinformatics analysis in the cardiac hypertrophy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2010) 397:380–5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.05.116
16. Kolfschoten IG, Roggli E, Nesca V, and Regazzi R. Role and therapeutic potential of micrornas in diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2009) 11 Suppl 4:118–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2009.01118.x
17. Ju J, Xiao D, Shen N, Zhou T, Che H, Li X, et al. Mir-150 regulates glucose utilization through targeting glut4 in insulin-resistant cardiomyocytes. Acta Biochim Biophys Sinica. (2020) 52:1111–9. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmaa094
18. Cook SA, Varela-Carver A, Mongillo M, Kleinert C, Khan MT, Leccisotti L, et al. Abnormal myocardial insulin signalling in type 2 diabetes and left-ventricular dysfunction. Eur Heart J. (2010) 31:100–11. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehp396
19. Guedes EC, Franca GS, Lino CA, Koyama FC, Moreira Ldo N, Alexandre JG, et al. Microrna expression signature is altered in the cardiac remodeling induced by high fat diets. J Cell Physiol. (2016) 231:1771–83. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25280
20. Diao X, Shen E, Wang X, and Hu B. Differentially expressed micrornas and their target genes in the hearts of streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Mol Med Rep. (2011) 4:633–40. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2011.489
21. Wang T, Yuan L, Chen Y, Wang J, Li N, and Zhou H. Expression profiles and bioinformatic analysis of micrornas in myocardium of diabetic cardiomyopathy mice. J Diabetes Metab Disord. (2023) 45:1003–11. doi: 10.1007/s13258-023-01403-8
22. Zuo Y, Wang Y, Hu H, and Cui W. Atorvastatin protects myocardium against ischemia-reperfusion injury through inhibiting mir-199a-5p. Cell Physiol biochemistry: Int J Exp Cell physiology biochemistry Pharmacol. (2016) 39:1021–30. doi: 10.1159/000447809
23. Zhu H, Xue H, Jin QH, Guo J, and Chen YD. Mir-138 protects cardiac cells against hypoxia through modulation of glucose metabolism by targetting pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1. Bioscience Rep. (2017) 37:1–9. doi: 10.1042/BSR20170296
24. Zhang Y, Liu G, and Gao X. Attenuation of mir-34a protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxic stress through maintenance of glycolysis. Bioscience Rep. (2017) 37:1–10. doi: 10.1042/BSR20170925
25. Zhang ZH, Li J, Liu BR, Luo CF, Dong Q, Zhao LN, et al. Microrna-26 was decreased in rat cardiac hypertrophy model and may be a promising therapeutic target. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. (2013) 62:312–9. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e31829b82e6
26. Zhang LF, Lou JT, Lu MH, Gao C, Zhao S, Li B, et al. Suppression of Mir-199a maturation by Hur is crucial for hypoxia-induced glycolytic switch in hepatocellular carcinoma. EMBO J. (2015) 34:2671–85. doi: 10.15252/embj.201591803
27. Yu YH, Zhang YH, Ding YQ, Bi XY, Yuan J, Zhou H, et al. Microrna-99b-3p promotes angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibrosis in mice by targeting Gsk-3beta. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica.. (2021) 42:715–25. doi: 10.1038/s41401-020-0498-z
28. Yang T, Liu T, Cao C, and Xu S. Mir-200a-5p augments cardiomyocyte hypertrophy induced by glucose metabolism disorder via the regulation of selenoproteins. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234:4095–103. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27206
29. Yang Y, Ishak Gabra MB, Hanse EA, Lowman XH, Tran TQ, Li H, et al. Mir-135 suppresses glycolysis and promotes pancreatic cancer cell adaptation to metabolic stress by targeting phosphofructokinase-1. Nat Commun. (2019) 10:809. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08759-0
30. Yan M, Chen C, Gong W, Yin Z, Zhou L, Chaugai S, et al. Mir-21-3p regulates cardiac hypertrophic response by targeting histone deacetylase-8. Cardiovasc Res. (2015) 105:340–52. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvu254
31. Xu CR and Fang QJ. Inhibiting Glucose Metabolism By miR-34a and miR-125b Protects Against Hyperglycemia-Induced Cardiomyocyte Cell Death. Biomedicines. (2021) 116(3):415–422. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9040401
32. Wu J, Qin XH, Hou ZX, Fu ZH, Li GH, Yang HY, et al. MiR-494-3p reduces insulin sensitivity in diabetic cardiomyocytes by down-regulation of insulin receptor substrate 1. Sheng Li Xue Bao. (2019) 71(2): 271–278. doi: 10.2486/ShengLiXueBao2458139
33. Wu N, Zhang X, Bao Y, Yu H, Jia D, and Ma C. Down-regulation of gas5 ameliorates myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury via the mir-335/rock1/akt/gsk-3beta axis. J Cell Mol Med. (2019) 23:8420–31. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14724
34. Wu Y, Li L, Zhang L, Liu G, Wang R, You P, et al. MiR-200a-3p overexpression alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy injury in mice by regulating autophagy through the FOXO3/Mst1/Sirt3/AMPK axis. J Diabetes. (2023) 11(2):e15840. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.1347123.10.7717/peerj.15840
35. Wei Y, Peng S, Wu M, Sachidanandam R, Tu Z, Zhang S, et al. Multifaceted roles of mir-1s in repressing the fetal gene program in the heart. Cell Res. (2014) 24:278–92. doi: 10.1038/cr.2014.12
36. Wang J, Liu Q, Jiang S, Zhang J, He J, Li Y, et al. Preoperative alpha-blockade versus no blockade for pheochromocytoma-paraganglioma patients undergoing surgery: A systematic review and updated meta-analysis. Int J surgery. (2023) 109:1470–80. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000000390
37. Trotta MC, Maisto R, Alessio N, Hermenean A, D’Amico M, and Di Filippo C. The melanocortin mc5r as a new target for treatment of high glucose-induced hypertrophy of the cardiac h9c2 cells. Front Physiol. (2018) 9:1475. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01475
38. Ruiz-Velasco A, Zi M, Hille SS, Azam T, Kaur N, Jiang J, et al. Targeting miR128-3p alleviates myocardial insulin resistance and prevents ischemia-induced heart failure. Mol Cell Endocrinology.. (2020) 9:110793. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2020.110793
39. Park H, Park H, Mun D, Kang J, Kim H, Kim M, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from hypoxic human mesenchymal stem cells attenuate GSK3β expression via miRNA-26a in an ischemia-reperfusion injury model. Yonsei Med J. (2018) 59:736–45. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.6.736
40. Nagalingam RS, Sundaresan NR, Gupta MP, Geenen DL, Solaro RJ, and Gupta M. A cardiac-enriched microrna, mir-378, blocks cardiac hypertrophy by targeting ras signaling. J Biol Chem. (2013) 288:11216–32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.442384
41. Mallat Y, Tritsch E, Ladouce R, Winter DL, Friguet B, Li Z, et al. Proteome modulation in h9c2 cardiac cells by micrornas mir-378 and mir-378. Mol Cell proteomics: MCP. (2014) 13:18–29. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M113.030569
42. Lu H, Buchan RJ, and Cook SA. Microrna-223 regulates glut4 expression and cardiomyocyte glucose metabolism. Cardiovasc Res. (2010) 86:410–20. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvq010
43. Lu S and Lu Y. Mir-26a inhibits myocardial cell apoptosis in rats with acute myocardial infarction through gsk-3beta pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2020) 24:2659–66. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202003_20535
44. Long B, Wang K, Li N, Murtaza I, Xiao JY, Fan YY, et al. Mir-761 regulates the mitochondrial network by targeting mitochondrial fission factor. Free Radical Biol Med. (2013) 65:371–9. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.07.009
45. Liu DW, Zhang YN, Hu HJ, Zhang PQ, and Cui W. Downregulation of microrna−199a−5p attenuates hypoxia/reoxygenation−induced cytotoxicity in cardiomyocytes by targeting the hif−1alpha−gsk3beta−mptp axis. Mol Med Rep. (2019) 19:5335–44. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.11329
46. Liu L, Chen Y, Shu J, Tang CE, Jiang Y, and Luo F. Identification of microRNAs enriched in exosomes in human pericardial fluid of patients with atrial fibrillation based on bioinformatic analysis. J Thorac Disease.. (2020) 12:5617–27. doi: 10.21037/jtd-20-2066
47. Li Z, Song Y, Liu L, Hou N, An X, Zhan D, et al. Mir-199a impairs autophagy and induces cardiac hypertrophy through mtor activation. Cell Death differentiation. (2017) 24:1205–13. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.95
48. Li J, Ren Y, Shi E, Tan Z, Xiong J, Yan L, et al. Inhibition of the let-7 family micrornas induces cardioprotection against ischemia-reperfusion injury in diabetic rats. Ann Thorac surgery. (2016) 102:829–35. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2016.02.016
49. Lei D, Wang Y, Zhang L, and Wang Z. Circ_0010729 regulates hypoxia-induced cardiomyocyte injuries by activating TRAF5 via sponging miR-27a-3p. Life Sci. (2020) 262:118511. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118511
50. Kim SW, Kim HW, Huang W, Okada M, Welge JA, Wang Y, et al. Cardiac stem cells with electrical stimulation improve ischaemic heart function through regulation of connective tissue growth factor and miR-378. Cardiovasc Res. (2013) 100:241–51. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvt192
51. Horie T, Ono K, Nishi H, Iwanaga Y, Nagao K, Kinoshita M, et al. Microrna-133 regulates the expression of glut4 by targeting klf15 and is involved in metabolic control in cardiac myocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2009) 389:315–20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.08.136
52. He M, Lu Y, Xu S, Mao L, Zhang L, Duan W, et al. miRNA-210 modulates a nickel-induced cellular energy metabolism shift by repressing the iron-sulfur cluster assembly proteins ISCU1/2 in Neuro-2a cells. Cell Death Disease.. (2014) 5:e1090. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.60
53. Gong DD, Yu J, Yu JC, and Jiang XD. Effect of miR-26a targeting GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway on myocardial apoptosis in rats with myocardial ischemia-reperfusion. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2019) 23:7073–82. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201908_18751
54. Fan JL, Zhu TT, Xue ZY, Ren WQ, Guo JQ, Zhao HY, et al. lncRNA-XIST protects the hypoxia-induced cardiomyocyte injury through regulating the miR-125b-hexokinase 2 axis. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol - Animal.. (2020) 56:349–57. doi: 10.1007/s11626-020-00459-0
55. Du H, Fu Z, He G, Wang Y, Xia G, Fang M, et al. MicroRNA-218 targets adiponectin receptor 2 to regulate adiponectin signaling. Mol Med Rep. (2015) 11:4701–5. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3282
56. Dong W, Xie F, Chen XY, Huang WL, Zhang YZ, Luo WB, et al. Inhibition of Smurf2 translation by miR-322/503 protects from ischemia-reperfusion injury by modulating EZH2/Akt/GSK3β signaling. Am J Physiol - Cell Physiol. (2019) 317:C253–61. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00375.2018
57. Dong P, Liu WJ, and Wang ZH. MiR-154 promotes myocardial fibrosis through β-catenin signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2018) 22:2052–60. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201804_14735
58. Das S, Ferlito M, Kent OA, Fox-Talbot K, Wang R, Liu D, et al. Nuclear miRNA regulates the mitochondrial genome in the heart. Circ Res. (2012) 110:1596–603. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.267732
59. Borden A, Kurian J, Nickoloff E, Yang Y, Troupes CD, Ibetti J, et al. Transient introduction of mir-294 in the heart promotes cardiomyocyte cell cycle reentry after injury. Circ Res. (2019) 125:14–25. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.314223
60. Baseler WA, Thapa D, Jagannathan R, Dabkowski ER, Croston TL, and Hollander JM. MiR-141 as a regulator of the mitochondrial phosphate carrier (SLC25A3) in the type 1 diabetic heart. Am J Physiol - Cell Physiol. (2012) 303:C1244–51. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00137.2012
61. Bartman CM, Oyama Y, Brodsky K, Khailova L, Walker L, Koeppen M, et al. Intense light-elicited upregulation of mir-21 facilitates glycolysis and cardioprotection through per2-dependent mechanisms. PloS One. (2017) 12:e0176243. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176243
62. Arnold N, Koppula PR, Gul R, Luck C, and Pulakat L. Regulation of cardiac expression of the diabetic marker microRNA miR-29. PloS One. (2014) 9:e103284. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103284
63. Callis TE and Wang DZ. Taking micrornas to heart. Trends Mol Med. (2008) 14:254–60. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2008.03.006
64. Wang Z, Luo X, Lu Y, and Yang B. Mirnas at the heart of the matter. J Mol Med (Berlin Germany). (2008) 86:771–83. doi: 10.1007/s00109-008-0341-3
65. Sayed D, Hong C, Chen IY, Lypowy J, and Abdellatif M. Micrornas play an essential role in the development of cardiac hypertrophy. Circ Res. (2007) 100:416–24. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000257913.42552.23
66. Wojciechowska A, Braniewska A, and Kozar-Kaminska K. Microrna in cardiovascular biology and disease. Adv Clin Exp medicine: Off Organ Wroclaw Med University. (2017) 26:865–74. doi: 10.17219/acem/62915
67. Hata A. Functions of micrornas in cardiovascular biology and disease. Annu Rev Physiol. (2013) 75:69–93. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-030212-183737
68. Shao D and Tian R. Glucose transporters in cardiac metabolism and hypertrophy. Compr Physiol. (2015) 6:331–51. doi: 10.1002/j.2040-4603.2016.tb00680.x
69. Kolwicz SC Jr. and Tian R. Glucose metabolism and cardiac hypertrophy. Cardiovasc Res. (2011) 90:194–201. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvr071
70. Young LH, Coven DL, and Russell RR 3rd. Cellular and molecular regulation of cardiac glucose transport. J Nucl cardiology: Off Publ Am Soc Nucl Cardiol. (2000) 7:267–76. doi: 10.1016/S1071-3581(00)70016-X
71. Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC, and Thompson CB. Understanding the warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Sci (New York N.Y.). (2009) 324:1029–33. doi: 10.1126/science.1160809
72. Li J, Donath S, Li Y, Qin D, Prabhakar BS, and Li P. Mir-30 regulates mitochondrial fission through targeting p53 and the dynamin-related protein-1 pathway. PloS Genet. (2010) 6:e1000795. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000795
73. Henning SL, Wambolt RB, Schonekess BO, Lopaschuk GD, and Allard MF. Contribution of glycogen to aerobic myocardial glucose utilization. Circulation. (1996) 93:1549–55. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.93.8.1549
74. Allard MF, Henning SL, Wambolt RB, Granleese SR, English DR, and Lopaschuk GD. Glycogen metabolism in the aerobic hypertrophied rat heart. Circulation. (1997) 96:676–82. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.96.2.676
75. Akbari G. Role of zinc supplementation on ischemia/reperfusion injury in various organs. Biol Trace element Res. (2020) 196:1–9. doi: 10.1007/s12011-019-01892-3
76. Chen X, Li H, Li S, Wang Y, Ma R, Qian W, et al. Comparison of risk of complication between neuraxial anaesthesia and general anaesthesia for hip fracture surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J surgery. (2023) 109:458–68. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000000291
77. Fu G, Zhu J, Song W, Bagaber G, Wang C, Chen J, et al. Transcatheter tricuspid valve intervention versus medical therapy for symptomatic tricuspid regurgitation: A meta-analysis of reconstructed time-to-event data. Int J surgery. (2024) 110:6800–9. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001773
78. Luo Y, Leng J, Shi R, Jiang Y, Chen D, Wu Q, et al. Concomitant tricuspid valve surgery in patients undergoing left ventricular assist device: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J surgery. (2024) 110:3039–49. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001189
Keywords: miRNAs, heart, glucose metabolism, systematic review, biomarker
Citation: Shen N-N, Qian H and Zhu Y-F (2025) The expression profiles and roles of microRNAs in cardiac glucose metabolism. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1565385. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1565385
Received: 23 January 2025; Accepted: 30 June 2025;
Published: 23 July 2025.
Edited by:
Jaideep Menon, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham University, IndiaReviewed by:
Jaycob Dalton Warfel, University of Tennessee at Martin, United StatesQihang Yuan, Dalian Medical University, China
Meihang Li, McGill University Health Centre, Canada
Copyright © 2025 Shen, Qian and Zhu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hua Qian, MTA0NDE2MDU4MkBxcS5jb20=; Ya-Fang Zhu, MTc3NzQyMDExODVAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Nan-Nan Shen
Nan-Nan Shen Hua Qian1*
Hua Qian1*