- 1Affiliated Cixi Hospital, Wenzhou Medical University, Ningbo, China
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, The Affiliated Lihuili Hospital of Ningbo University, Ningbo, China
- 3School of Basic Medical Sciences, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, China
- 4Ningbo Municipal Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Affiliated Hospital to Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Ningbo, China
Purpose: Jinkui Shenqi Pill (JKSQP), a traditional Chinese herbal formula, is clinically utilized in China for managing bone disorders secondary to kidney deficiency, including osteoporotic fractures (OPFs). The present study aims to elucidate the pharmacological mechanism underlying JKSQP’s therapeutic effects on OPF healing.
Methods: LC-MS/MS was employed to characterize the chemical constituents of JKSQP. Two-month-old female C57BL/6J mice underwent bilateral ovariectomy (OVX) followed by transverse tibial osteotomy to establish the OPF model. These OPF mice were randomly divided into the JKSQP group and OPF group, in which mice were gavaged with 1 g/kg/day JKSQP and equivalent volume of normal saline, respectively. At 4, 14, and 24 days post-fracture, biological specimens including serum, tibiae, dorsal root ganglion (DRG) and hypothalamus were collected for ELISA assay, μCT analysis and histopathology staining. Primary bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) were treated with the serum obtained from Sprague-Dawley rats administered with 1.5 g/kg/day JKSQP via oral gavage for three consecutive days. The conditioned medium derived from these JKSQP serum-treated BMSCs and the serum collected from the JKSQP-treated mice were applied to the DRG neurons. The levels of COX-2, PGE2, EP4 and CGRP in vitro were detected using qRT-PCR, western blot, ELISA and immunofluorescence (IF).
Results: LC-MS/MS analysis identified 1872 chemical components in JKSQP. μCT evaluation demonstrated accelerated healing of OPF in JKSQP-treated mice. Histomorphometric analysis combined with Calcein double-labeling revealed enhanced bone formation within the fracture callus. Compared with OPF controls, mice in the JKSQP group exhibited elevated serum PGE2 levels, upregulated Osterix, COX-2 and EP4 expression in fracture callus, increased EP4 and CGRP in DRG, and enhanced p-CREB in hypothalamus. In vitro, JKSQP-containing serum increased both PGE2 secretion and COX-2 expression in BMSCs. Furthermore, qRT-PCR and IF analyses confirmed that both conditioned medium from JKSQP-treated BMSCs and serum from JKSQP-administered mice upregulated EP4 and CGRP expressions in DRG neurons.
Conclusion: Jinkui Shenqi Pill accelerates OPF healing by promoting bone formation possibly through activation of neurosensory PGE2/EP4/p-CREB axis.
1 Introduction
Osteoporosis is a common skeletal disease characterized by decreased bone mass and deterioration of bone structure, resulting in an increased risk of fragility fracture (1). Osteoporotic fractures (OPFs) frequently occurring in the spine, hip and distal radius, affect more than 9 million individuals worldwide, particularly among post-menopausal women. OPFs are associated with a high risk of disability and mortality because osteoporotic bones heal poorly and tend to break into complex fracture patterns (2). The management of OPFs costs billions of dollars annually, placing a substantial burden on both national economies and healthcare systems (3). Current drugs for OPFs have limited clinical utility due to dose-dependent adverse effects such as osteonecrosis and gastrointestinal complications (4). In contrast, natural productions with relative efficacy and safety are emerging as promising candidates for developing novel OPF therapeutics (5).
OPF healing is a complex process involving a tight coordination of diverse cell types (6). Following an initial inflammatory immune response at the fracture site, bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs), a heterogeneous population comprising mesenchymal stem cells, macrophages, endothelial cells and other, are recruited (7). Within the fracture gap, BMSC-derived stem cells differentiate into chondrocytes to form a temporary cartilaginous template. This template undergoes chondrocyte apoptosis, chondrocyte-to-osteoblast transdifferentiation, matrix calcification and bone-forming osteoblasts invasion, and is finally replaced by bone (8). Concurrently, at the rims of the fracture callus, BMSCs directly differentiate into osteoblasts to form woven bone (9). Bone formation is a crucial step for successful fracture healing, as bony bridging not only restores the mechanical properties of broken bone but also enable subsequent osteoclast-mediated remodeling (10).
Bone is richly innervated by sensory nerves which is essential for bone regeneration (11). Massive evidence showed that sensory denervation leads to a mechanically insufficient fracture callus because of poor osteogenesis (12). Following OPF, various inflammatory mediators are largely produced, among which prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) exerts bone anabolic effects by sensory nerves (13). The synthesis of PGE2 is controlled by the limiting enzyme cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2). After PGE2 binds to EP4 receptor on sensory nerves, the signal transmits through dorsal root ganglion (DRG) to phosphorylate cAMP response element binding (CREB) in hypothalamus for osteogenesis (13, 14). Thus, this neurosensory PGE2/EP4/p-CREB axis is regarded as a potential therapeutic target to accelerate OPF healing.
Jinkui Shenqi Pill (JKSQP) first recorded in Synopsis of Golden Chamber (金匮要略), is a classical prescription composed of 8 herbs (Listed in Table 1). JKSQP has effects of tonifying kidney, and thus has been widely used to treat various kidney deficiency-induced diseases for thousands of years (15). OPFs are also called fragility fracture as they are caused even under a slight trauma. According to the Chinese medicine theory of “kidney governing bones” (16), the pathologic changes including bone loss and deterioration in OPFs are thought to be rooted in kidney deficiency (5, 17). Clinical application of JKSQP has obtained satisfactory outcomes on acceleration of OPF healing (18), while its pharmacological mechanism remains largely unclear. Here, we hypothesized that JKSQP accelerates OPF healing by promoting bone formation via neurosensory PGE2/EP4/p-CREB axis, and animal and cellular experiments were performed to test this hypothesis.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 LC-MS/MS analysis and administration of JKSQP
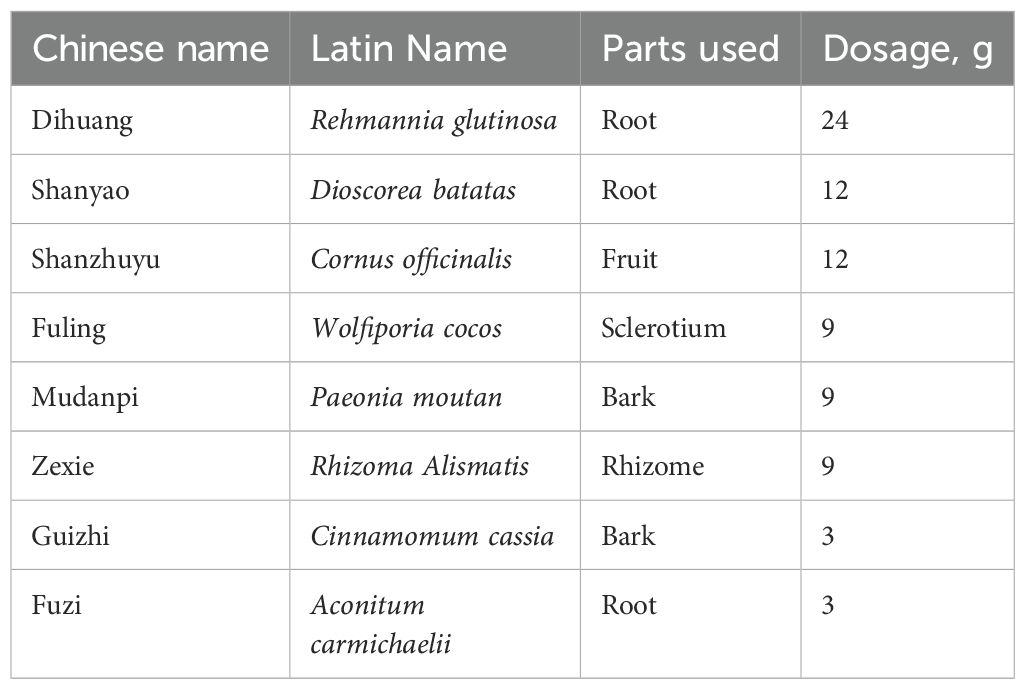
JKSQP is composed of 24g Rehmannia glutinosa (Dihuang), 12g Rehmannia glutinosa (Shanyao), 12g Cornus officinalis (Shanzhuyu), 9g Wolfiporia cocos (Fuling), 9g Paeonia moutan (Mudanpi), 9g Rhizoma alismatis (Zexie), 3g Cinnamomum cassia (Guizhi) and 3g Aconitum carmichaelii (Fuzi). JKSQP in the form of Chinese patent medicine was purchased from Beijing Tongrentang Co., Ltd, and made into the solution by mixed with pure water. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) was performed to analyze the chemical ingredients in the solution of JKSQP. According to the dose conversion factor between human beings and mice, JKSQP was orally gavaged at the dosage of 1 g/kg/day.
2.2 Mice and grouping
A total of 78 female C57BL/6J mice (2-month-old, weighing 22 ± 2g) were purchased from the Experimental Animal Center of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University. The mice were housed in a barrier facility under controlled conditions: a 12-hour light/dark cycle, constant temperature of 25°C and 40-60% humidity, and had free access to water and food. After 1 week of adaptive feeding, the mice were divided into 4 groups including the sham group (n=12), the OVX group (n=8), the OPF group (n=29), and the JKSQP group (n=29). Mice in the OVX group underwent bilateral ovariectomy (OVX), whereas the sham group received surgical removal of an equivalent volume of periovarian adipose tissue. Femoral samples were collected from sham-operated and OVX mice at 8 weeks post-surgery for micro-computed tomography (μCT) analysis. The remaining two groups of mice underwent bilateral OVX followed by tibial osteotomy 8 weeks post-initial surgery to establish OPF model. Mice in the JKSQP group received daily oral gavages of JKSQP (1 g/kg/day, converted from human adult doses via body surface area), while the OPF group received equal-volume saline. The mice in both the JKSQP and OPF groups were sacrificed at 4, 14 and 24 days post-fracture (n=8 per group per time point), and their biological specimens including serum, tibiae, DRG, and hypothalamic tissues were collected for subsequent analyses. The 5 mice remaining in per OPF and JKSQP groups were sacrificed at 14 days post-fracture for Calcein double-labeling. No mice died accidentally or for other factors in the process of experiment.
2.3 OPF model
Mouse OPF model was established as previous described (19, 20). C57BL/6J mice were anesthetized by continuous inhalation with isoflurane, and bilateral ovariectomy (OVX) was performed via two small incisions on either side of the lower back. After 8 weeks of OVX surgery, the femurs were scanned by micro-computed tomography (μCT) to detect bone loss in mice. Then, these OVX mice underwent a unilateral transverse tibial fracture. Briefly, an incision of 1 cm was made along the surface of tibial crest. Through the tibial platform, a 26-gauge needle was longitudinally inserted into tibial cavity. After removal of the needle, tibia was transversely cut by a NO.11 surgical blade at the midpoint. Then, the transverse fracture was fixed again by the needle.
2.4 μCT analysis
Femur and fractured tibia tissues were scanned with μCT (Skyscan1176, Belgium) at a resolution of 9 μm. Image reconstruction was performed using NRecon software with parameters set to 6 for ring artifact correction and 30% for beam hardening correction, followed by three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction in CTVol software. For femoral morphometric analysis, a region of interest (ROI) was defined in the distal femur metaphysis with cortical bone excluded. Quantitative parameters including bone mineral density (BMD, g/cm³), bone volume fraction (BV/TV, %), and trabecular separation (Tb.Sp, mm) were analyzed to assess osteoporotic changes. For fracture healing evaluation, the medial side fracture callus excluded cortical bone was selected as a ROI. Total bone volume (mm³) and BV/TV were calculated as previously described (8).
2.5 Histology and histomorphometry
After fixation with 4% paraformaldehyde (Beijing Solebio Technology Co., LTD., China), dehydration with gradient alcohol and decalcification with 14% EDTA solution, tibia samples were processed for paraffin sections of 3-μm-thick as previously described (21). The sections were stained with Alcian Blue Hematoxylin (ABH)/Orange G for morphological analysis. By using OsteoMetrics software (Decatur, GA, USA), the percentage of cartilage callus area over the total fracture callus area (Cg.Ar/Ps.CI.Ar, %) and the percentage of woven bone area over the total fracture callus area (Md.Ar/Ps.CI.Ar, %) were calculated to evaluate enchondral bone formation during OPF healing.
2.6 Calcein double-labeling
Mice in each of the OPF and JKSQP groups were intraperitoneally injected with 10 mg/kg calcein (Sigma, St. Louis, USA) 7 days and 12 days post-fracture, and sacrificed at 14 days post-fracture. After fixation and dehydration, tibia samples were embedded with polymethyl methacrylate, and cut into 20 μm sections for fluorescence examination. Mineral apposition rate (MAR) and bone formation rate/bone surface (BF/BS) were measured using Image J software.
2.7 Preparation of JKSQP-containing serum and BMSCs intervention
Six 2-month-old Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were obtained from the Experimental Animal Center of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University and administered 1.5 g/kg/day JKSQP or normal saline via oral gavage for three consecutive days. Whole blood was collected through abdominal aorta puncture under anesthesia and centrifuged at 200 ×g for 10 minutes at 4°C to separate serum. The JKSQP-containing serum and JKSQP-free serum from saline-treated rats were stored at -80°C for subsequent cellular experiments.
BMSCs were isolated from the proximal femur of 2-month-old C57BL/6J mice. After centrifugation at 200 ×g for 10 minutes, cells were resuspended with α-MEM (Gibco, Grand Island, NY) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Gibco). Through changing the medium 48 hours later, non-adherent cells were removed and the primary BMSCs were harvested. Next, BMSCs were treated with JKSQP-containing serum (250 μL and 750 μL doses), using JKSQP-free serum as the control. Following a 24-hour intervention, both BMSCs and culture medium were collected for western blot analysis and ELISA, respectively.
2.8 Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay analysis
Mouse blood samples from the OPF group and JKSQP group were obtained by eyeball extirpating, and centrifuged at 200 × g for 30 min to extract serum. The conditional culture medium were collected after the intervention of BMSCs. The concentration of PGE2 in both mouse serum and conditioned medium were subsequently measured according to the instructions of the serum Elisa kit (Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China).
2.9 Western blot analysis on BMSCs
BMSCs from each group were lysed by protein extraction reagent. Total protein were obtained and quantified by a BCA Protein Assay Kit (Beyotime, CN). Next, protein samples were separated by electrophoresis and transferred to PVDF membranes (BIO-RAD, USA). After blocking for 20 min, the membranes were incubated overnight at 4°C with primary antibody of COX-2 (diluted 1:1000, Abcam, ab15191, UK). Following washing with TBST, the membranes were incubated with secondary antibodies for 2 hour. The immune complexes were detected with a chemiluminescent HRP substrate and visualized via the Chemiluminescence Image Analysis System (Tanon 5200, CN).
2.10 Mouse DRG neuron isolation, identification and intervention
The vertebral column was isolated from 8-week-old C57BL/6 mice anesthetized by an overdose of isoflurane. Bilateral DRGs in lumbar 1–3 were localized and collected from intervertebral foramina under a stereomicroscope. The DRGs were digested with the enzymatic solution containing 5 mg/mL collagenase type I (GIBCO, 17100-017, USA) and 5 mg/mL dispase type II (Yuanye Biotechnology, S25046, CN) for 1 hour in a water bath at 37°C. The resulting cell suspension was filtered by a 200 µm cell strainer to remove undigested tissue debris. After centrifugation at 200 ×g for 10 minutes, the enzymatic solution was aspirated, and the cell suspension was resuspended in α-MEM medium (Gibco, Grand Island, NY) containing 10% FBS (Gibco) and 1 μM 5-fluoro-2’-deoxyuridinem, and then plated on fibronectin-coated petri dishes for cell adherence.
After 5–7 days of cultivation, glial proliferation could be inhibited by 5-fluoro-2’-deoxyuridine, yielding purified DRG neurons for subsequent identification and intervention. Two biomarkers, β3-tubulin stained neuronal cytoskeleton and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) used to exclude astrocytes, were employed to identify DRG neurons via IF staining. The DRG neurons were treated for 24 hours with serum obtained from JKSQP-treated mice or OPF controls, and conditioned medium from BMSCs exposed to either JKSQP-containing serum or control serum.
2.11 Quantitative gene expression analysis on DRG neurons
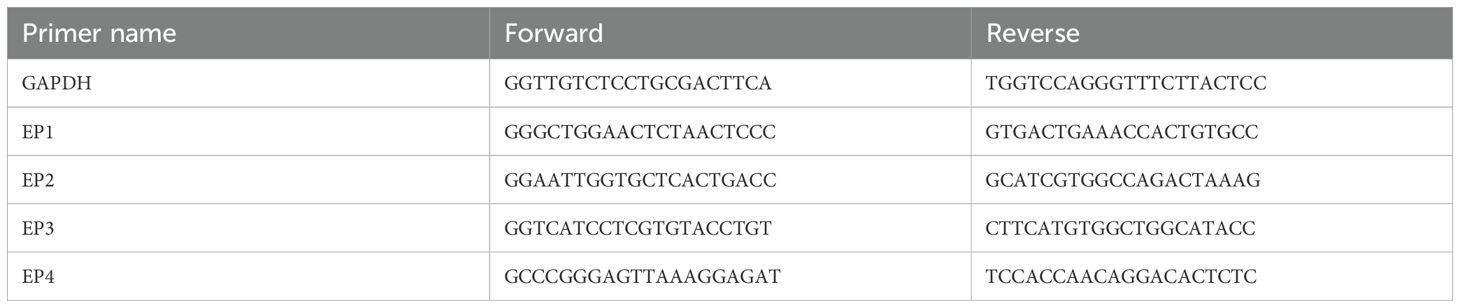
Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR) were performed on DRG neurons as previous described (22). Total RNA was isolated from DRG neurons using RNA-Quick Purification Kit (TransGen Biotech, Beijing, CN) according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. After quantification with the photometric method, 500 ng of total RNA was reverse-transcribed into cDNA using PrimeScript™ RT reagent Kit (Takara, Japan). Real-time PCR was performed using Green® Premix Ex Taq™ II FAST (Takara, Japan) and the gene primer sequences (List in Table 2) on a QuantStudio™ 5 real-time PCR system (Applied Biosystems, USA). Gene expression analysis was conducted using the 2−ΔΔCt method, and GAPDH was used as the internal control.
2.12 Immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence assay
The tibia sections were treated with 0.01 mol/L citrate buffer at 60°C for 4 hours as antigen retrieval. Then, the sections were incubated in the primary antibodies of osterix (diluted 1:300, Abcam, ab22552, UK), COX-2 (diluted 1:200, Abcam, ab15191, UK), EP4 (diluted 1:200, Abcam, ab92763, UK), Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP, diluted 1:200, Abcam, ab81887, UK), p-CREB (diluted 1:200, Abcam, ab32096, UK) overnight at 4°C. After reaction with secondary antibodies including Goat anti-mouse/rabbit IgG-HRP (diluted 1:1000, Beijing Zhongshan Jinqiao Biotechnology, Beijing, China), Goat anti-mouse/rabbit IgG H&L (Alexa Fluor® 488) (diluted 1:500, Abcam, UK) for 20 minutes, the sections were stained with diaminobenzidine solution followed by hematoxylin for IHC assay, or stained with 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) for IF assay. The quantification of positive area was calculated using Image-Pro Plus software (Media Cybernetics, Silver Spring, USA).
Primary DRG neurons were cultured on poly-L-lysine-coated coverslips. After fixation with 4% paraformaldehyde and blocking with 3% bovine serum albumin for each 30 minutes, the coverslips were incubated with primary antibodies including β3-tubulin (diluted 1:300, wanleibio, wl03860, CN), GFAP (diluted 1:100, wanleibio, wl0836, CN), EP4 (diluted 1:200, abcam, ab92763, UK) and CGRP (diluted 1:200, Abcam, ab81887, UK) overnight at 4°C. Then, a secondary antibody (Alexa Fluor® 488, abcam, UK) and DAPI were applied on the coverslips for IF staining. Quantitative analysis of positive staining in mouse tissues and DRG cells were evaluated using Image-Pro Plus software (Media Cybernetics, Silver Spring, USA).
2.13 Statistical analysis
All data were presented as mean ± standard deviation. One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test was performed using SPSS 20.0 software. The value of p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001; “ns” indicated non-significance.
3 Results
3.1 Chemical component analysis of JKSQP by LC-MS/MS
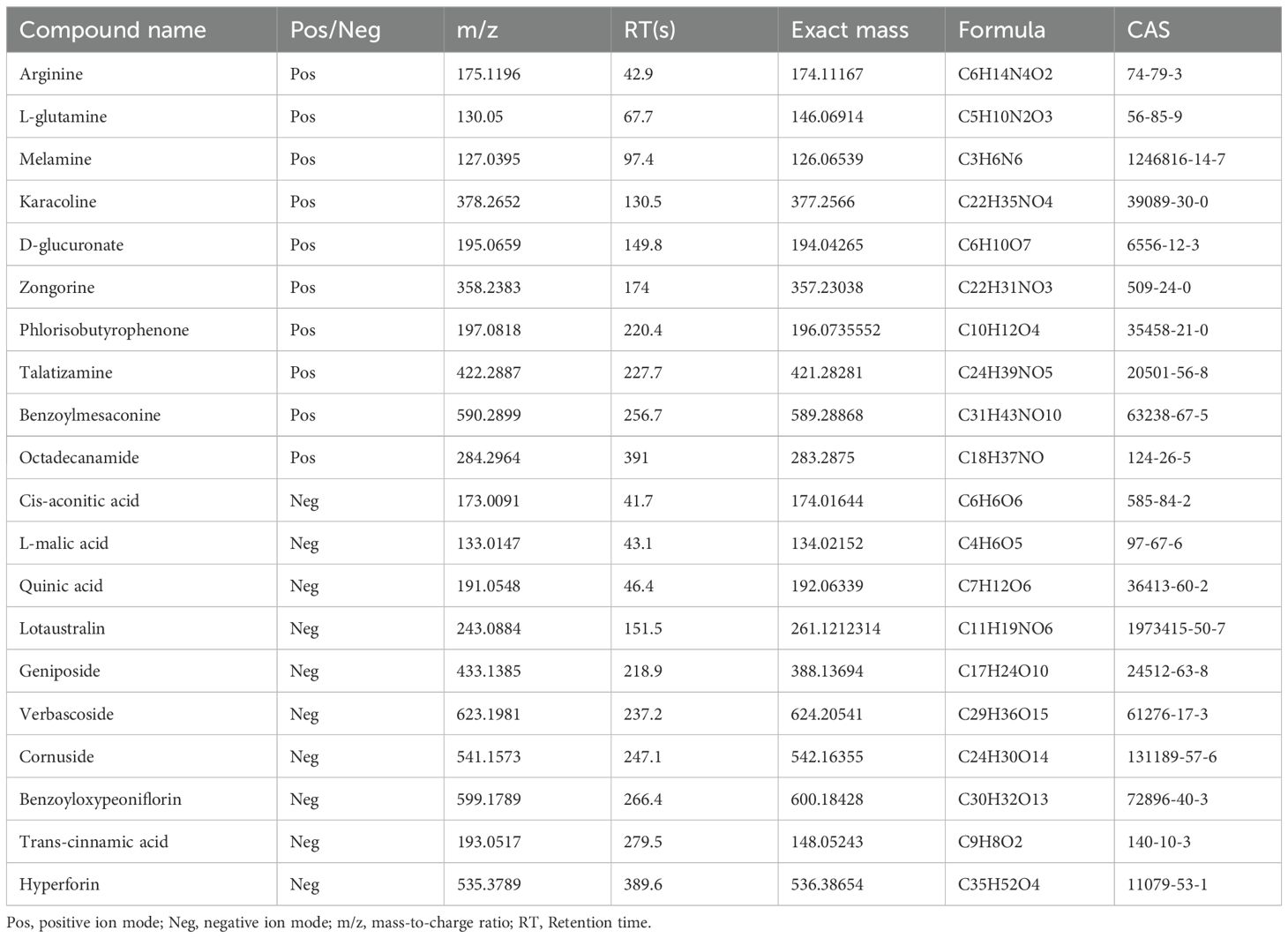
The chemical components in the aqueous solution of JKSQP were qualitatively analyzed using LC-MS/MS. A total of 1872 chemical components were identified, with 1185 components detected in positive ionization mode (Figure 1A) and 687 components in negative ionization mode (Figure 1B). Twenty representative compounds from both ionization modes are listed in Table 3.
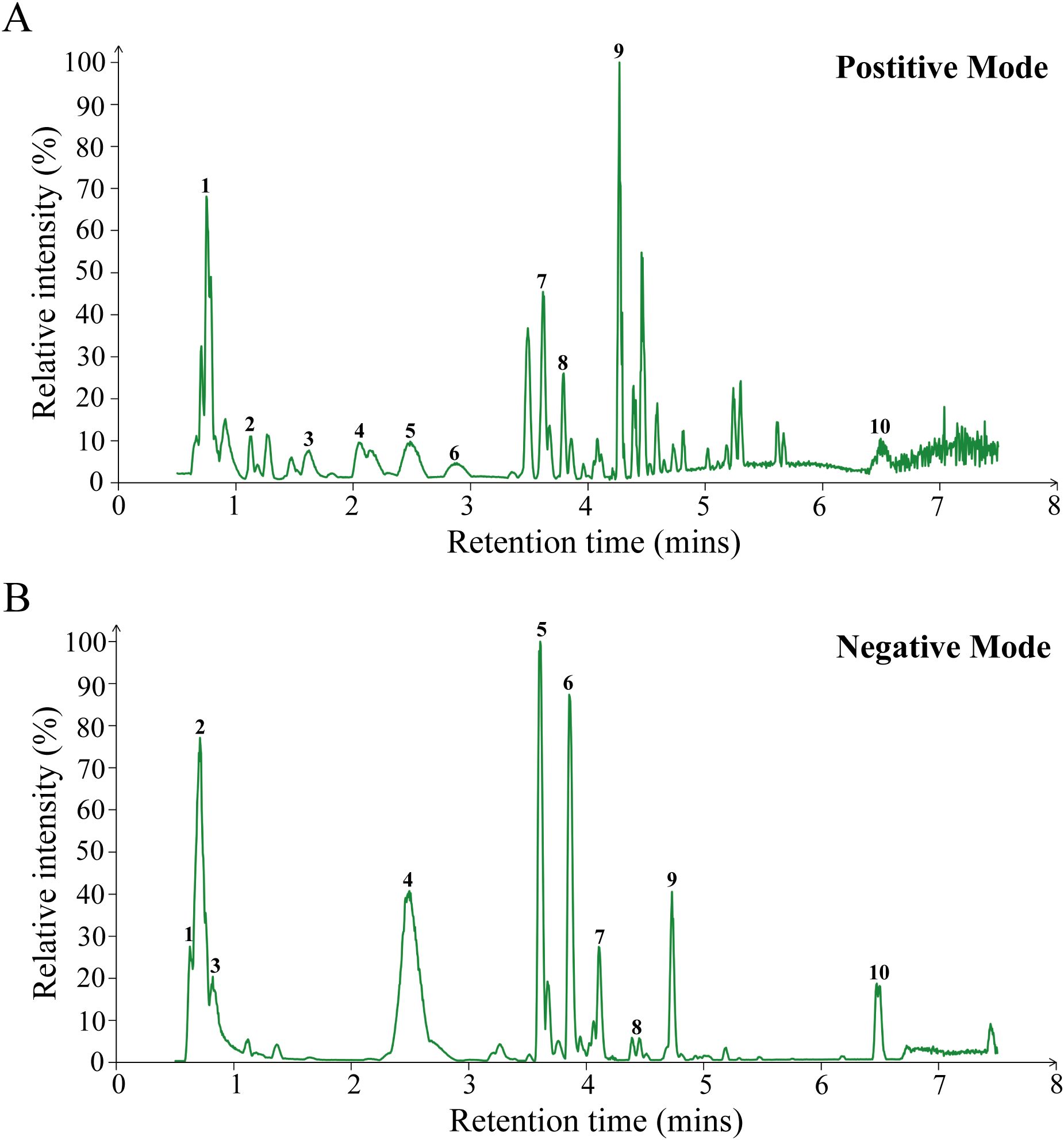
Figure 1. LC-MS/MS analysis of JKSQP compounds. (A) Base peak chromatogram in positive ion mode. Peak assignments: 1. Arginine; 2. L-glutamine; 3. Melamine; 4. Karacoline; 5. D-glucuronate; 6. Zongorine; 7. Phlorisobutyrophenone; 8. Talatizamine; 9. Benzoylmesaconine; 10. Octadecanamide;. (B) Base peak chromatogram in negative ion mode. Peak assignments: 1. Cis-aconitic acid; 2. L-malic acid; 3. Quinic acid; 4. Lotaustralin; 5. Geniposide; 6. Verbascoside; 7. Cornuside; 8. Benzoyloxypeoniflorin; 9. Trans-cinnamic acid; 10. Hyperforin;.
3.2 JKSQP accelerates OPF healing in mice
To investigate the pharmacological mechanism of JKSQP on OPF healing, in vivo animal experiments were conducted following the experimental timeline outlined in Figure 2. Two-month-old female C57BL/6J mice underwent bilateral OVX followed by tibial osteotomy to establish an OPF model. Biological samples including serum, fractured tibiae, DRGs, and hypothalamic tissues, were collected at postoperative days 4, 14, and 24 for subsequent biochemical and histological analyses.
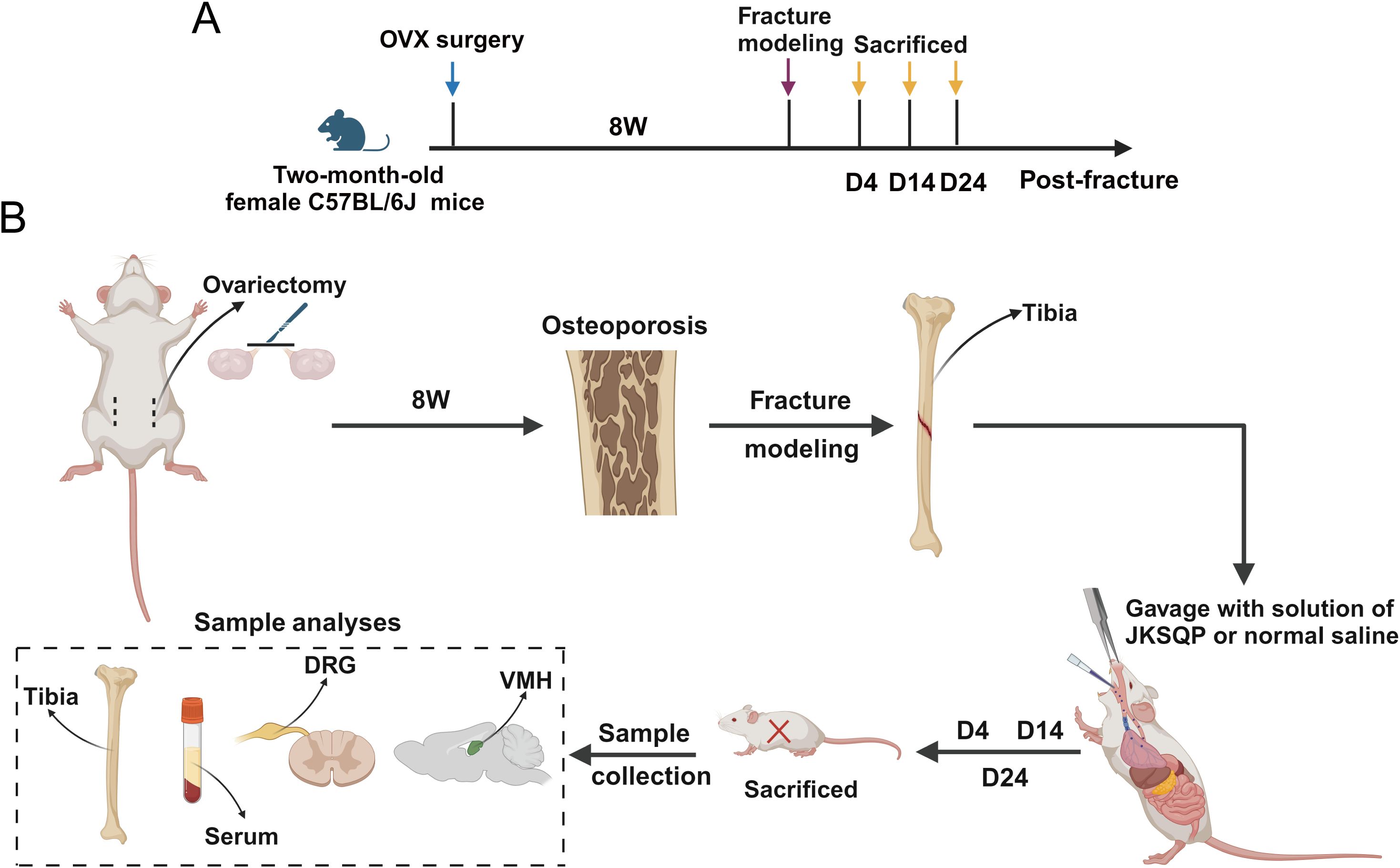
Figure 2. Experimental timeline of the OPF model. (A) Two-month-old female C57BL/6J mice received underwent bilateral ovariectomy (OVX) followed by tibial osteotomy 8 weeks post-initial surgery to establish OPF model. (B) Samples including serum, fractured tibiae, dorsal root ganglion (DRG) and hypothalamic tissue were obtained at 4, 14 and 24 days post-fracture for subsequent analyses.
Initial validation of osteoporosis induction was performed by harvesting femurs 8 weeks post-ovariectomy (OVX). μCT analysis revealed significant bone loss in OVX mice (Figure 3A), with quantitative metrics of reduced BMD, BV/TV and Tb.Th (Figure 3B). Subsequently, tibial osteotomy was performed on the osteoporotic mice to establish the OPF model. μCT images showed a blurry fracture gap at 14 days post-fracture in the JKSQP-treated mice compared to saline-treated OPF controls (Figure 3C, Supplementary Figure 1). Complete fracture union was achieved by day 24 in the JKSQP group, whereas persistent gaps remained in untreated OPF mice (Figure 3C, Supplementary Figure 1). Quantitative morphometry showed increased callus bone volume and BV/TV in JKSQP-treated mice during healing (Figure 3D). These data demonstrate JKSQP’s therapeutic efficacy in accelerating OPF healing.
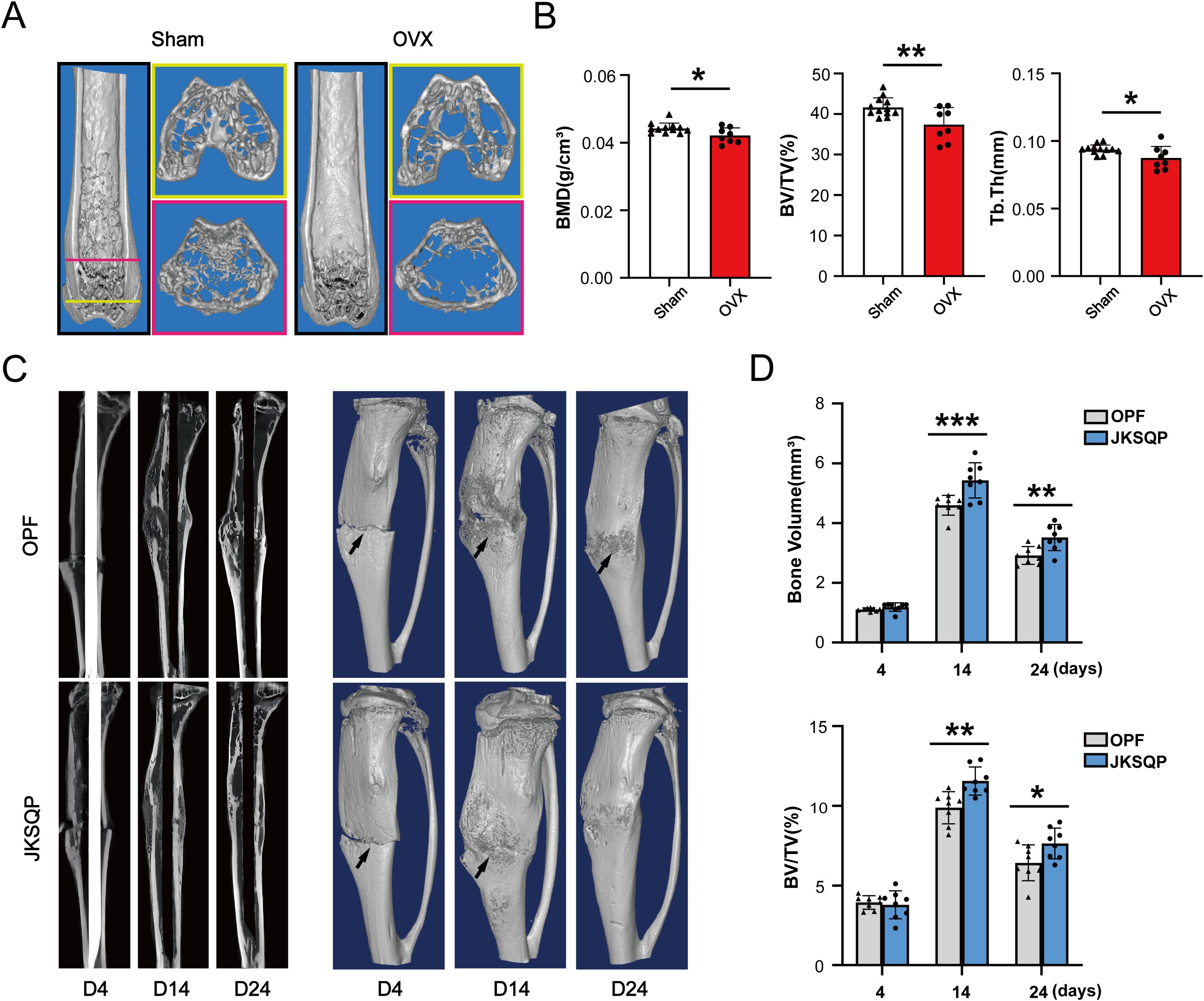
Figure 3. JKSQP accelerates OPF healing in mice. (A) Three-dimensional reconstruction images of μCT showed severe bone loss in the OVX mice compared to sham-operated controls at 8 weeks post-surgery. (B) Quantitative analyses of BMD, BV/TV and Tb.Th in the distal femur metaphysis. (C) μCT images showed fracture callus formation in the JKSQP treated mice at 4, 14 and 24 days post-fracture. The black arrowhead indicates the fracture gap. (D) Quantification of callus bone volume and BV/TV in JKSQP-treated versus vehicle control groups. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
3.3 JKSQP promotes bone formation in the fracture callus of OPF mice
Successful fracture healing requires coordinated bone formation (23). To evaluate JKSQP’s osteogenic effects, tibial tissues from OPF mice were subjected to histopathological analysis. ABH/Orange G staining and quantitative analyses demonstrated enlarged cartilage callus at 4 and 14 days post-fracture, followed by increased mineralized callus at 14 days in JKSQP-treated mice (Figures 4A–C). At 24 days post-fracture, complete fracture union was observed in the JKSQP group, whereas residual callus persisted in untreated OPF controls (Figures 4A–C). Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of kidney and liver tissues revealed no significant structural alterations in JKSQP-treated mice compared to OPF controls, suggesting an absence of toxicity or adverse effects associated with JKSQP administration in mice (Figure 4D). Calcein double-labeling and quantitative analysis of MAR and BF/BS revealed accelerated bone-formation rates in JKSQP-treated callus at 14 days (Figures 4E, F). Osterix is an osteoblast-specific transcription factor, essential for osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. IF staining showed upregulation of Osterix in the JKSQP-treated mice (Figure 4G). These findings demonstrate that JKSQP promotes OPF healing by enhancing bone formation.
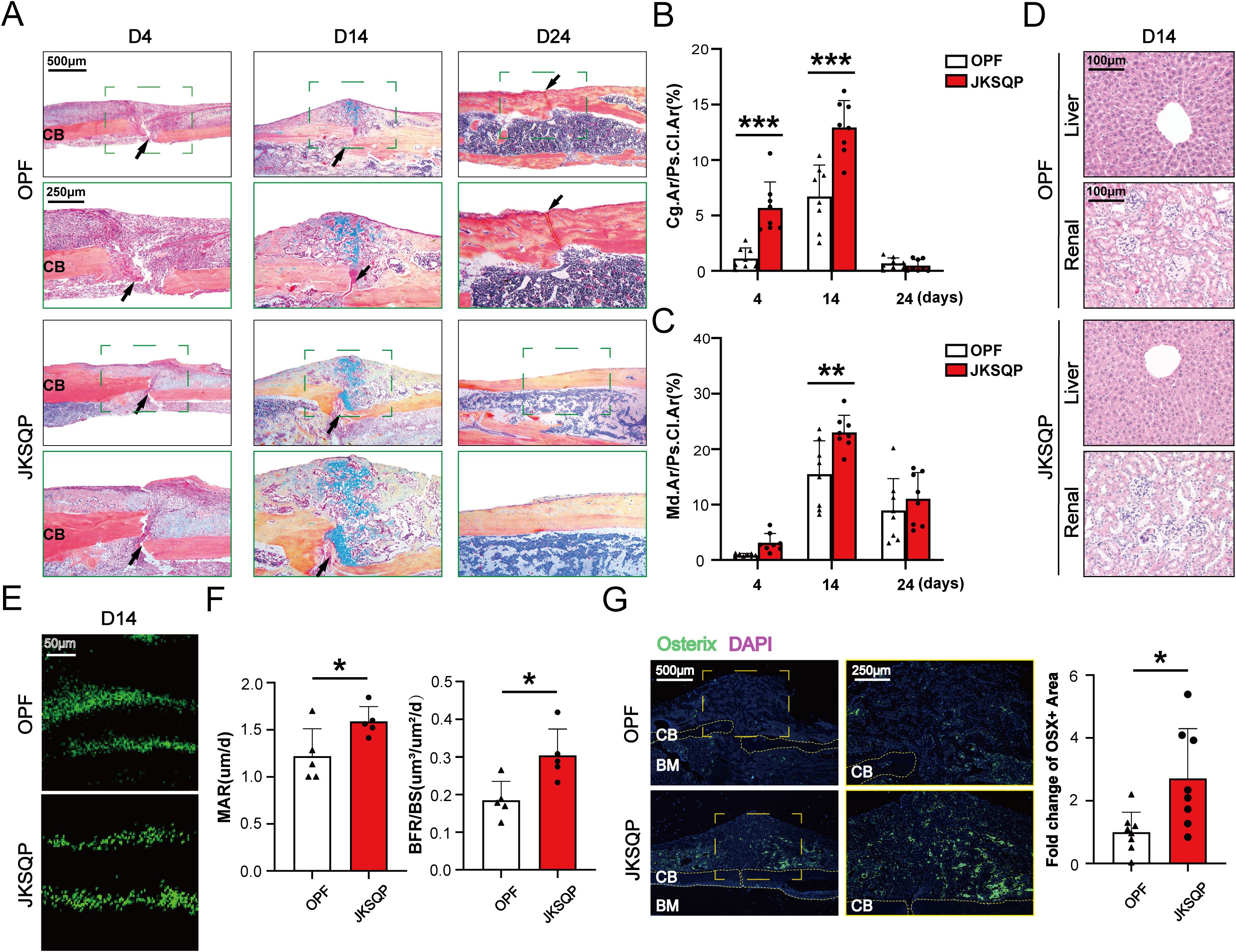
Figure 4. JKSQP promotes bone formation in OPF mice. (A) Alcian blue/hematoxylin (ABH) staining showed a large fracture callus at 14 days post-fracture and complete bridging of the fracture gap at 24 days post-fracture in the JKSQP-treated mice. The black arrowhead indicates the fracture gap. (B) Quantification of cartilage-to-callus area ratio (Cg.Ar/Ps.Cl.Ar, %). (C) Quantification of woven bone-to-callus area ratio (Md.Ar/Ps.CI.Ar, %). (D) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of kidney and liver tissues from JKSQP-treated mice and OPF controls. (E) Calcein double-labeling showed enhanced mineralized tissue formation in the JKSQP-treated callus at 14 days post-fracture. (F) Quantitative analysis of mineral apposition rate (MAR, μm/day) and bone formation rate/bone surface (BF/BS, μm³/μm²/day). (G) Immunofluorescence (IF) staining of Osterix in fracture callus with corresponding quantitative analysis. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
3.4 JKSQP activates COX-2/PGE2 axis in the fracture callus during OPF healing
Multiple lines of evidence have demonstrated the importance of neurosensory PGE2/EP4/p-CREB axis in regulating bone formation (13, 14). To determine the pharmacological mechanism underlying JKSQP’s effect on OPF, we firstly detected the expressions of COX-2 and PGE2 in the OPF mice. COX-2 is the rate-limiting enzyme controlling PGE2 synthesis. The results of ELISA assay and IHC staining showed that serum PGE2 and COX-2 positive area in the fracture callus were significantly increased in the JKSQP treated mice (Figures 5A, B). It is well known that BMSCs are composed of heterogeneous cell populations including mesenchymal stem cells, osteoblasts, macrophages, endothelial cells, and others, and serve as a critical source of PGE2 synthesis within bone (24). To determine whether JKSQP promotes PGE2 synthesis in BMSCs, primary BMSCs were cultured and then treated for 24 hours with JKSQP-free rat serum, low or high concentration of JKSQP-containing rat serum (Figure 5C). No significant morphological differences were observed between the JKSQP-free group and low- or high-concentration JKSQP group (Figure 5D), indicating absence of JKSQP cytotoxicity in BMSCs. Western blot analysis demonstrated significantly upregulated COX-2 expression in BMSCs treated with JKSQP-containing serum (Figure 5E). ELISA quantification revealed elevated PGE2 levels in the culture medium following treatment with JKSQP-containing serum (Figure 5F). Collectively, these findings indicate that JKSQP activates the COX-2/PGE2 axis pathway within the fracture callus during OPF healing.
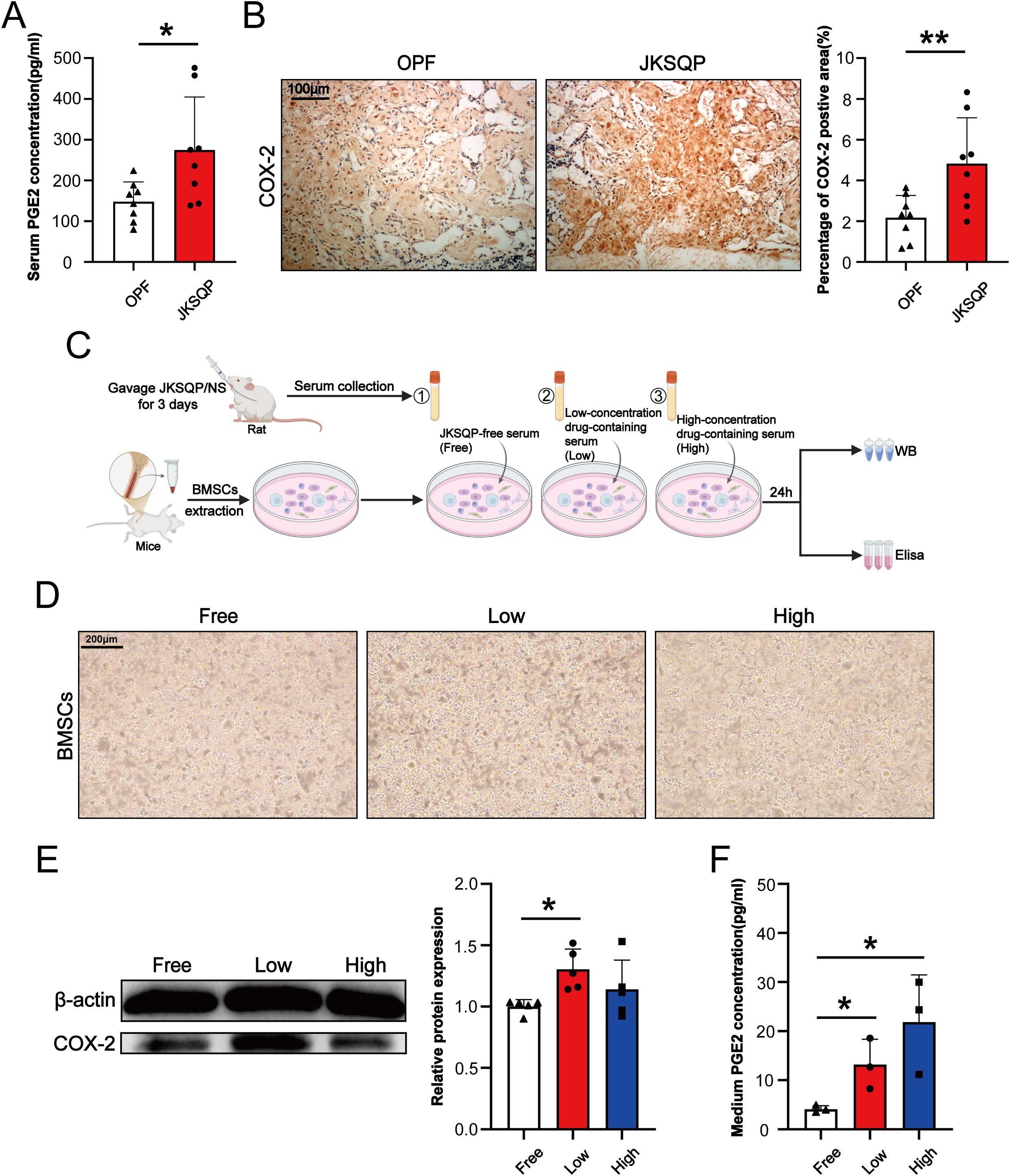
Figure 5. JKSQP upregulates COX-2/PGE2 signaling during OPF healing. (A) Serum PGE2 levels in JKSQP-treated versus control mice at 14 days post-fracture. (B) Immunohistochemical staining of COX-2 in fracture callus and quantification of COX-2-positive area. (C) The flowchart of primary bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) extraction and intervention with JKSQP-free serum, low and high concentration of JKSQP-containing serum. (D) Phase-contrast microscopy of primary BMSCs in each group. (E) Western blot analysis of COX-2 expression in BMSCs post-intervention. (F) PGE2 concentration in conditioned medium from BMSCs post-intervention. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
3.5 JKSQP enhances EP4 expression in DRG and p-CREB levels in hypothalamus in OPF mice
After PGE2 binds to EP4 receptor on the sensory nerve, the signal is transduced to hypothalamus via DRG, resulting in CREB phosphorylation in the hypothalamus (13). The phosphorylated CREB (p-CREB) in hypothalamus can enhance peripheral bone formation by suppressing sympathetic nervous system activity. Here, in vivo and in vitro experiments were performed to determine the involvement of neurosensory PGE2/EP4/p-CREB axis in the JKSQP-induced OPF healing. IF analysis revealed significant upregulation of EP4 expression in both fracture callus and DRG, marked enhancement of CGRP level in the DRG and increased p-CREB in the hypothalamus after JKSQP treatment (Figures 6A–F). Furthermore, DRG neurons were isolated from 8-week-old female C57BL/6J mice, and subsequently treated with JKSQP-free or high JKSQP-containing serum treated BMSCs-conditioned medium, or the serum from OPF mice or JKSQP-treated mice (Figure 6G). DRG neurons were identified through morphological observation and IF staining. Under the microscope, DRG neurons exhibited characteristic oval cell bodies with radiating neurites (Figure 6H). β3-tubulin, a neuron-specific cytoskeletal marker, was largely expressed in DRG neurons, while few GFAP expression served to exclude potential astrocyte contamination (Figure 6I). The results of qRT-PCR and IF staining showed that the expressions of EP4 and CGRP were significantly increased in the DRG neurons after administration of high JKSQP-containing serum treated BMSCs-conditioned medium and the serum from JKSQP-treated mice (Figures 6J, K). All these findings indicate that JKSQP accelerates OPF healing in mice possibly through activation of neurosensory PGE2/EP4/p-CREB axis.
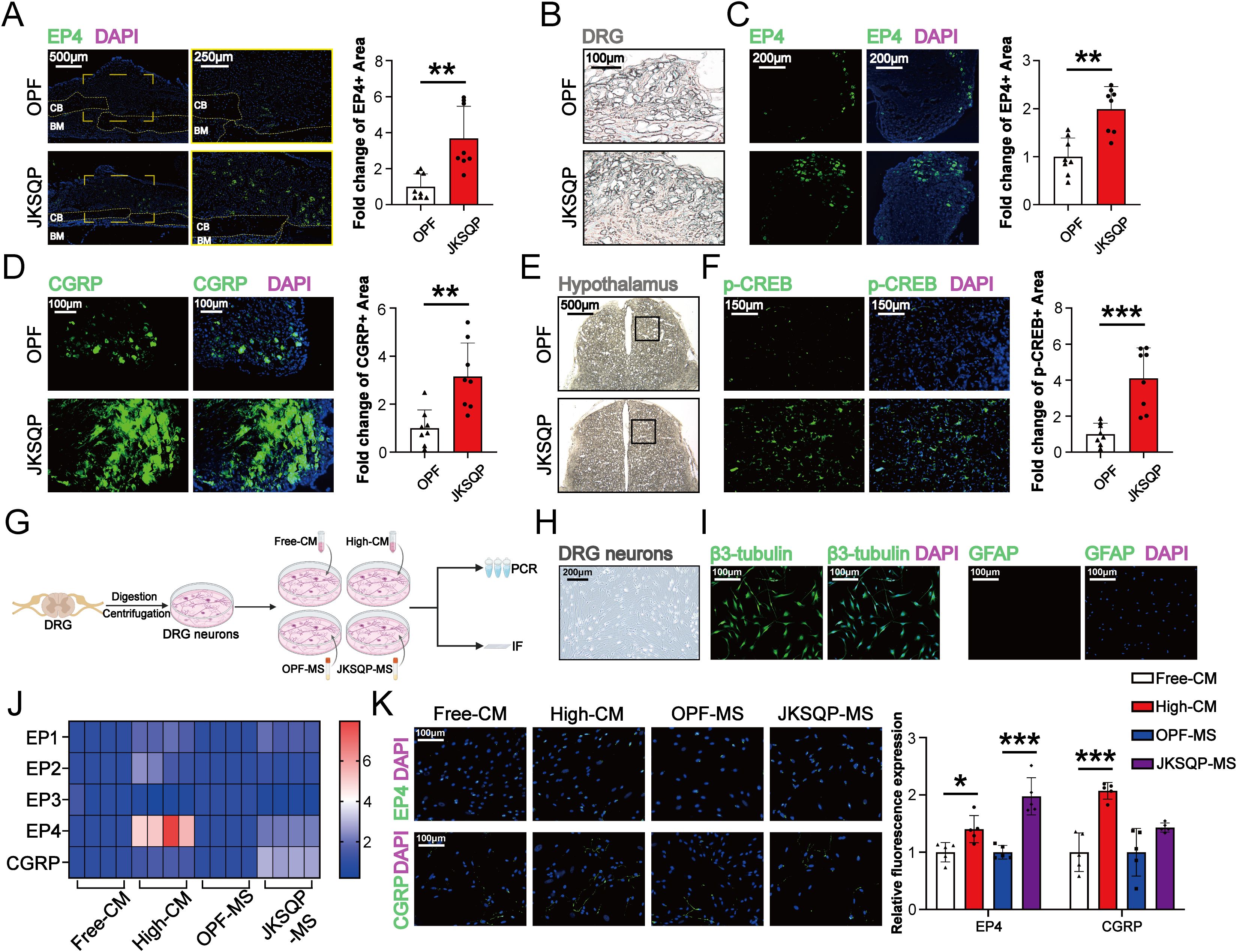
Figure 6. JKSQP promotes EP4 in DRG and p-CREB in hypothalamus during OPF healing. (A) Immunofluorescence (IF) staining of EP4 in the fractured callus of OPF mice at the 14 days post-fracture. (B) Histomorphology of mouse dorsal root ganglion (DRG) at 14 days post-fracture. (C, D) IF staining and quantitative analysis of EP4 and CGRP in DRG at 14 days post-fracture. (E) Histomorphology of mouse brain at 14 days post-fracture. Black boxes: hypothalamus region. (F) IF staining and quantitative analysis of p-CREB in hypothalamus. (G) The flowchart of primary dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons cultivation and intervention. Free-CM: JKSQP-free serum treated BMSCs-conditioned medium; High-CM: high JKSQP-containing serum treated BMSCs-conditioned medium; OPF-MS: the serum from OPF mice; JKSQP-MS: the serum from JKSQP-treated mice. (H) Phase-contrast microscopy of DRG neurons. (I) IF staining of β3-tubulin and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in DRG neurons. (J) Heat map of EP1-EP4 mRNA levels in DRG neurons post-intervention. (K) IF staining of EP4 and CGRP in DRG neurons post-intervention. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
4 Discussion
With the growth of the aging population, OPFs have become a major public health challenge due to its high disability rate and the lack of effective therapeutic agents (25). Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), primarily composed of natural products, is recognized as a valuable resource for developing novel drugs with improved efficacy and safety profiles (26). Guided by the “kidney governing bones” theory in TCM (16), JKSQP, a kidney-tonifying herbal formula, has demonstrated significant clinical efficacy in OPFs management. In this study, we systematically investigated the pharmacological mechanisms of JKSQP using integrated an OPF mouse model and in vitro cellular experiments. μCT analysis and ABH staining on fracture callus at three postoperative time points (days 7/14/21) demonstrated accelerated fracture healing in JKSQP-treated mice. Calcein double-labeling and upregulated Osterix expression confirmed enhanced bone formation in the fracture callus, which mechanistically accelerated mouse OPF healing. Elevated PGE2 levels both in the serum of JKSQP-treated mice and conditioned medium from BMSCs intervened with JKSQP-containing serum, enhanced EP4 expression in the DRG JKSQP-treated mice and primary DRG neurons, and high expression of p-CREB in hypothalamus, revealed that JKSQP promotes bone formation during OPF healing possibly through activating neurosensory PGE2/EP4/p-CREB axis.
OPFs must be established on a pathological foundation of osteoporosis. Bilateral OVX, the gold standard for inducing postmenopausal osteoporosis, reliably produces significant bone loss beginning at 4 weeks postoperatively (27). In our study, we validated substantial bone mass reduction in OVX mice 8 weeks post-surgery using µCT analysis. Subsequently, a standardized tibial osteotomy procedure was performed to successfully establish the OPF model. This mouse OPF model aligns with established methodologies (28–30), in which transverse mid-diaphyseal femoral/tibial fractures are induced following 4–12 weeks of osteoporotic induction.
OPF healing progresses through three overlapping phases including hematoma, callus formation and bone remodeling, mediated by two distinct processes including endochondral ossification and intramembranous ossification (31–33). To analyze the therapeutic mechanism of JKSQP, longitudinal analyses were conducted at 4, 14, and 24 days post-fracture that was corresponded to these defined healing phases as established in previous studies. At 4 days post-fracture, early cartilaginous callus formation was observed in JKSQP-treated mice compared to the OPF controls, indicating that callus initiation was advanced by JKSQP. At 14 days post-fracture, a larger cartilaginous callus was formed at the fracture gap, accompanied by a bigger woven bone deposition at the periphery of the callus after JKSQP treatment. These observations were consistent with the spatial heterogeneity in fracture healing: The relatively unstable fracture gap heals via endochondral ossification, where a cartilage template is initially formed and subsequently replaced by bone (8); The mechanically stable regions at the callus periphery heal through intramembranous ossification, directly forming woven bone (9). Enhanced bone mineralization (as demonstrated by Calcein double-labeling) combined with markedly upregulated Osterix expression, indicated accelerated osteogenesis in the fractured callus after JKSQP treatment. This enhancement of bone formation explains the complete fracture union observed in JKSQP-treated mice by 24 days post-fracture, whereas untreated controls exhibited persistent remodeling without full consolidation. Collectively, these findings demonstrate that JKSQP can promote bone formation to accelerate OPF healing. To our knowledge, no previous studies have investigated the effects of JKSQP on any bone disorders. Notably, JKSQP shares therapeutic characteristics with other documented kidney-tonifying herbs and formulas (e.g., Bushen Huoxue formula (34), Eucommia ulmoides (35), Epimedium (36)) that have demonstrated osteogenic activity in preclinical models. This observed bone-forming capacity of JKSQP aligns with the foundational TCM theory of “kidney governing bones”.
Sensory nerves play a dual regulatory role in skeletal physiology, extending beyond nociception to critically modulate fracture repair processes (11, 37). Emerging evidence demonstrates that sensory denervation disrupts osteogenesis, leading to structurally deficient callus formation with compromised biomechanical integrity (12). The neurosensory PGE2/EP4/p-CREB axis has been identified as critical for mediating sensory nerve-regulated bone formation. Specifically, PGE2 binds to EP4 receptor on sensory nerves, triggering signal transduction to the hypothalamus via DRG. This cascade activates CREB phosphorylation in the hypothalamus, which subsequently suppresses sympathetic nervous activity, thereby creating an osteogenic microenvironment within bone (13, 14). In vivo experiments demonstrated significant up-regulation of COX-2 within fracture callus tissue and elevated serum PGE2 levels in JKSQP-treated mice compared to OPF controls. BMSCs, critical contributors to fracture healing, were identified as the primary cellular source of PGE2 synthesis. In vitro experiments using primary BMSCs demonstrated that JKSQP enhances PGE2 synthesis through activation of COX-2 in BMSCs. Furthermore, JKSQP administration significantly increased EP4 receptor expression in primary DRG neurons and DRG tissues isolated from OPF mice, concomitant with enhanced p-CREB in the hypothalamus. Integratively, JKSQP accelerates OPF healing through a coordinated cascade (Figure 7): Upregulating COX-2 in BMSCs augments PGE2 synthesis; The elevated PGE2 binds to EP4 receptor on DRG neurons to activate hypothalamic p-CREB; This signaling cascade suppresses central nervous system-mediated sympathetic nervous activity, thereby promoting osteogenesis and accelerating OPF repair.
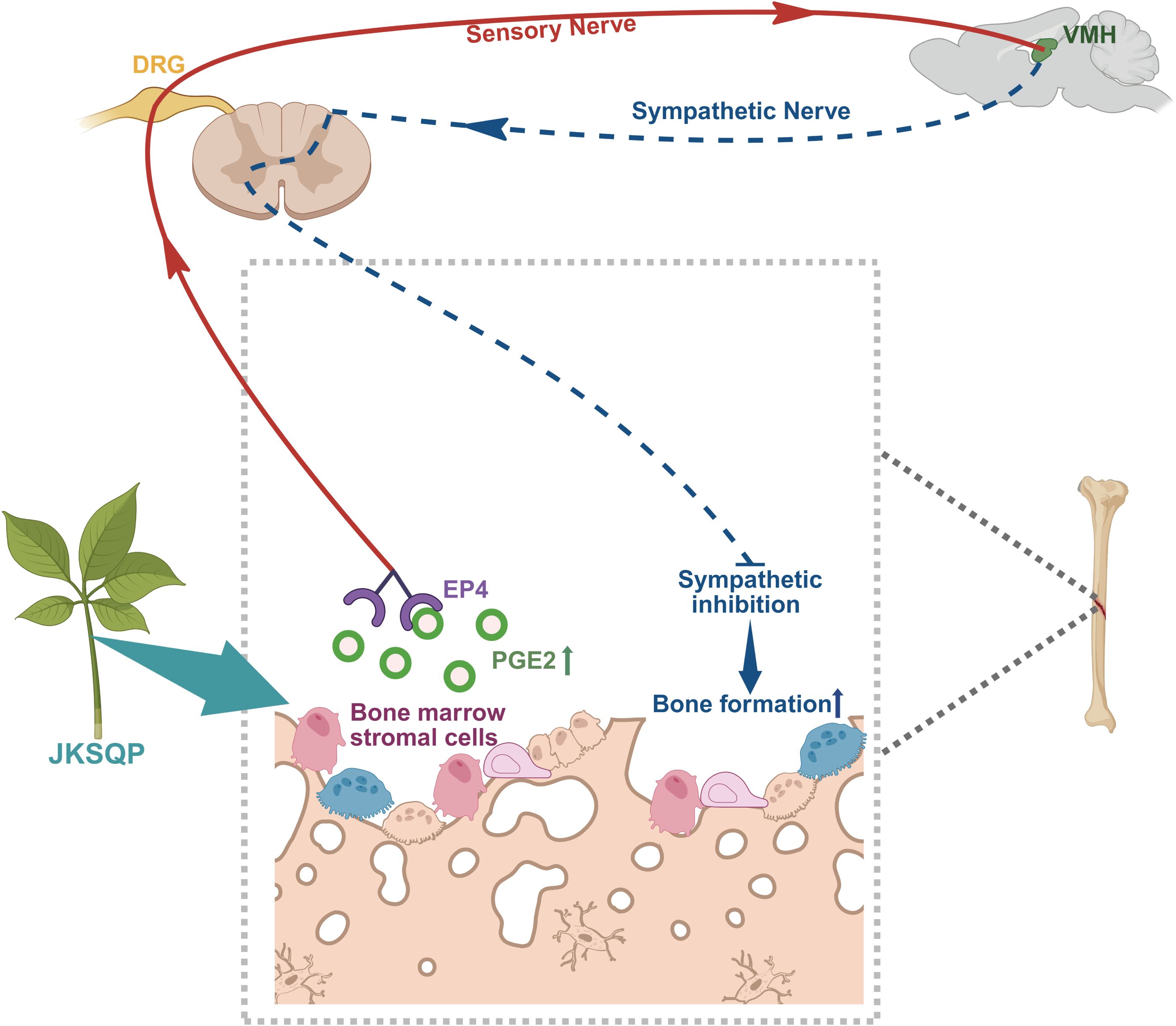
Figure 7. Mechanistic framework of JKSQP in osteoporotic fracture (OPF) healing. JKSQP enhances PGE2 synthesis by upregulating COX-2 expression in bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs). The elevated PGE2 binds to prostaglandin E receptor 4 (EP4) on dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons, activating hypothalamic phosphorylated cAMP response element-binding protein (p-CREB). This signaling cascade suppresses central nervous system-mediated sympathetic nervous activity, thereby promoting osteogenic regeneration and accelerating OPF repair.
Nevertheless, there were some limitations in this study. Firstly, the pharmacological evaluation employed a single dosage based on established human-mouse dose conversion guidelines, potentially overlooking dose-dependent effects. Secondly, although LC-MS/MS analysis identified 1872 chemical components in JKSQP aqueous extract, we did not characterize pharmacologically active metabolites in serum/urine post-administration. Thirdly, this study focused primarily on morphological assessment of OPF healing via micro-CT and histology, missing the functional or pain-related evaluations, such as three-point bending mechanical testing, gait analysis and open field test. Lastly, the therapeutic specificity of the PGE2/EP4/p-CREB axis would be strengthened by incorporating in vivo rescue studies using pathway-specific inhibitors to confirm mechanism-dependent efficacy.
In summary, this study demonstrates that JKSQP accelerates OPF healing by enhancing bone formation through activation of the neurosensory PGE2/EP4/p-CREB signaling axis.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by the Animal Experiments Ethics Committee of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University (IACUC-20240923-01). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
JX: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. DF: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. DX: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. RS: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. HD: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. CX: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. PZ: Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Resources.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82104885); Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (Q22H271191, ZCLQN25H2701); Natural Science Foundation of Ningbo City (2021J308, 2023J215); Ningbo Medical Key Discipline (grant no. 2022-B01), and Ningbo Top Medical and Health Program (grant no. 2022020102).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2025.1570685/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure 1 | μCT images of fracture callus formation in the JKSQP treated mice at 4, 14 and 24 days post-fracture.
References
1. Lo JC, Yang W, Park-Sigal JJ, and Ott SM. Osteoporosis and fracture risk among older US Asian adults. Curr Osteoporos Rep. (2023) 21:592–608. doi: 10.1007/s11914-023-00805-7
2. Ünver G, Özlü A, Erdoğan A, Özdemir MF, and Üstündağ S. Osteoporotic quality of life, self-efficacy, and fracture protection behaviors in postmenopausal women. Arch Osteoporos. (2024) 19:22. doi: 10.1007/s11657-024-01377-4
3. Tran O, Silverman S, Xu X, Bonafede M, Fox K, McDermott M, et al. Long-term direct and indirect economic burden associated with osteoporotic fracture in US postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int. (2021) 32:1195–205. doi: 10.1007/s00198-020-05769-3
4. Kammerlander C, Erhart S, Doshi H, Gosch M, and Blauth M. Principles of osteoporotic fracture treatment. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. (2013) 27:757–69. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2014.02.005
5. Tian S, Zou Y, Wang J, Li Y, An BZ, and Liu YQ. Protective effect of Du-Zhong-Wan against osteoporotic fracture by targeting the osteoblastogenesis and angiogenesis couple factor SLIT3. J Ethnopharmacol. (2022) 295:115399. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115399
6. Saul D and Khosla S. Fracture healing in the setting of endocrine diseases, aging, and cellular senescence. Endocr Rev. (2022) 43:984–1002. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnac008
7. Xu W, Yang Y, Li N, and Hua J. Interaction between mesenchymal stem cells and immune cells during bone injury repair. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:14484. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914484
8. Xia C, Ge Q, Fang L, Yu H, Zou Z, Zhang P, et al. TGF-β/Smad2 signalling regulates enchondral bone formation of Gli1(+) periosteal cells during fracture healing. Cell Prolif. (2020) 53:e12904. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12904
9. Buettmann EG, Yoneda S, Hu P, McKenzie JA, and Silva MJ. Postnatal Osterix but not DMP1 lineage cells significantly contribute to intramembranous ossification in three preclinical models of bone injury. Front Physiol. (2022) 13:1083301. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1083301
10. Miedel EL, Brisson BK, Hamilton T, Gleason H, Swain GP, Lopas L, et al. Type III collagen modulates fracture callus bone formation and early remodeling. J Orthop Res. (2015) 33:675–84. doi: 10.1002/jor.22838
11. Li Z, Meyers CA, Chang L, Lee X, Li Z, Tomlinson R, et al. Fracture repair requires TrkA signaling by skeletal sensory nerves. J Clin Invest. (2019) 129:5137–50. doi: 10.1172/JCI128428
12. Apel PJ, Crane D, Northam CN, Callahan M, Smith TL, and Teasdall RD. Effect of selective sensory denervation on fracture-healing: an experimental study of rats. J Bone Joint Surg Am. (2009) 91:2886–95. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.H.01878
13. Chen H, Hu B, Lv X, Zhu S, Zhen G, Wan M, et al. Prostaglandin E2 mediates sensory nerve regulation of bone homeostasis. Nat Commun. (2019) 10:181. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-08097-7
14. Hu B, Lv X, Chen H, Xue P, Gao B, Wang X, et al. Sensory nerves regulate mesenchymal stromal cell lineage commitment by tuning sympathetic tones. J Clin Invest. (2020) 130:3483–98. doi: 10.1172/JCI131554
15. Gao J, Xu E, Wang H, Wang L, Chen S, Wang C, et al. Integrated serum pharmacochemistry, network pharmacology, and pharmacokinetics to clarify the effective components and pharmacological mechanisms of the proprietary Chinese medicine Jinkui Shenqi Pill in treating kidney yang deficiency syndrome. J Pharm BioMed Anal. (2024) 247:116251. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2024.116251
16. Zhu H, Liu Q, Li W, Huang S, Zhang B, and Wang Y. Biological deciphering of the “Kidney governing bones” Theory in traditional Chinese medicine. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2022) 2022:1685052. doi: 10.1155/2022/1685052
17. Hua Z, Dai S, Li S, Wang J, Peng H, Rong Y, et al. Deciphering the protective effect of Buzhong Yiqi Decoction on osteoporotic fracture through network pharmacology and experimental validation. J Orthop Surg Res. (2023) 18:86. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-03545-7
18. China Association of Chinese Medicine. Guidelines for TCM diagnosis and treatment of osteoporotic fractures. J Traditional Chin Orthopedics Traumatology. (2023) 35:1–9.
19. Shu Y, Tan Z, Pan Z, Chen Y, Wang J, He J, et al. Inhibition of inflammatory osteoclasts accelerates callus remodeling in osteoporotic fractures by enhancing CGRP(+)TrkA(+) signaling. Cell Death Differ. (2024) 31:1695–706. doi: 10.1038/s41418-024-01368-5
20. Cheng S, Hu X, Sun K, Huang Z, Zhao Y, Sun Y, et al. Local Application of Tanshinone IIA protects mesenchymal stem cells from apoptosis and promotes fracture healing in ovariectomized mice. J Orthop Surg Res. (2024) 19:309. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04793-x
21. Xia C, Xu H, Fang L, Chen J, Yuan W, Fu D, et al. β-catenin inhibition disrupts the homeostasis of osteogenic/adipogenic differentiation leading to the development of glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Elife. (2024) 12:RP92469. doi: 10.7554/eLife.92469
22. Xia C, Zou Z, Fang L, Ge Q, Zhang P, Xu H, et al. Bushenhuoxue formula promotes osteogenic differentiation of growth plate chondrocytes through β-catenin-dependent manner during osteoporosis. BioMed Pharmacother. (2020) 127:110170. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110170
23. Haffner-Luntzer M, Ragipoglu D, Ahmad M, Schoppa A, Steppe L, Fischer V, et al. Wnt1 boosts fracture healing by enhancing bone formation in the fracture callus. J Bone Miner Res. (2023) 38:749–64. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.4797
24. Yi L, Qu Y, Zhang Q, Shi S, Li F, Qu C, et al. Enforced hematopoietic cell E-selectin/L-selectin ligand expression enhances bone marrow stromal cells homing and amelioration of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via induction of prostaglandin E2. Stem Cells. (2024) 42:1070–84. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxae062
25. Suen PK and Qin L. Sclerostin, an emerging therapeutic target for treating osteoporosis and osteoporotic fracture: A general review. J Orthop Translat. (2016) 4:1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2015.08.004
26. Abd Jalil MA, Shuid AN, and Muhammad N. Role of medicinal plants and natural products on osteoporotic fracture healing. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2012) 2012:714512. doi: 10.1155/2012/714512
27. Inoue S, Li C, Hatakeyama J, Jiang H, Kuroki H, and Moriyama H. Higher-intensity ultrasound accelerates fracture healing via mechanosensitive ion channel Piezo1. Bone. (2023) 177:116916. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2023.116916
28. Guo J, Tian S, Wang Z, Wang Y, Zhang X, Zhang Y, et al. Hydrogen saline water accelerates fracture healing by suppressing autophagy in ovariectomized rats. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:962303. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.962303
29. Zheng S, Hu G, Zheng J, Li Y, and Li J. Osthole accelerates osteoporotic fracture healing by inducing the osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling of BMSCs via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Phytother Res. (2024) 38:4022–35. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8267
30. Mi J, Xu JK, Yao Z, Yao H, Li Y, He X, et al. Implantable Electrical Stimulation at Dorsal Root Ganglions Accelerates Osteoporotic Fracture Healing via Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2022) 9:e2103005. doi: 10.1002/advs.202103005
31. Coates BA, McKenzie JA, Buettmann EG, Liu X, Gontarz PM, Zhang B, et al. Transcriptional profiling of intramembranous and endochondral ossification after fracture in mice. Bone. (2019) 127:577–91. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2019.07.022
32. Liu R, Jiao YR, Huang M, Zou NY, He C, Huang M, et al. Mechanosensitive protein polycystin-1 promotes periosteal stem/progenitor cells osteochondral differentiation in fracture healing. Theranostics. (2024) 14:2544–59. doi: 10.7150/thno.93269
33. Claes L, Recknagel S, and Ignatius A. Fracture healing under healthy and inflammatory conditions. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2012) 8:133–43. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2012.1
34. Hu S, Ge Q, Xia C, Ying J, Ruan H, Shi Z, et al. Bushenhuoxue formula accelerates fracture healing via upregulation of TGF-β/Smad2 signaling in mesenchymal progenitor cells. Phytomedicine. (2020) 76:153256. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153256
35. Song J, Zhang Y, Jin X, Zhu Y, Li Y, and Hu M. Eucommia ulmoides Oliver polysaccharide alleviates glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis by stimulating bone formation via ERK/BMP-2/SMAD signaling. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:29647. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80859-4
36. Shi W, Gao Y, Wang Y, Zhou J, Wei Z, Ma X, et al. The flavonol glycoside icariin promotes bone formation in growing rats by activating the cAMP signaling pathway in primary cilia of osteoblasts. J Biol Chem. (2017) 292:20883–96. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.809517
Keywords: Jinkui Shenqi Pills, osteoporotic fracture, bone formation, sensory nerve, PGE2/EP4/p-CREB axis
Citation: Xi J, Fu D, Xu D, Shen R, Zhao Y, Dai H, Xia C and Zhou P (2025) Jinkui Shenqi Pill accelerates osteoporotic fracture healing by promoting bone formation through neurosensory PGE2/EP4/p-CREB axis. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1570685. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1570685
Received: 06 February 2025; Accepted: 18 June 2025;
Published: 04 July 2025.
Edited by:
Shuman Yang, Jilin University, ChinaReviewed by:
Bo Kan, Second Affiliated Hospital of Jilin University, ChinaXue Shen, Jilin Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention (JPCDC), China
Copyright © 2025 Xi, Fu, Xu, Shen, Zhao, Dai, Xia and Zhou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Peihong Zhou, MTUwNTg4ODk4OTBAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Chenjie Xia, eGlhY2hlbmppZUB6Y211LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jihao Xi1,2†
Jihao Xi1,2† Danqing Fu
Danqing Fu Chenjie Xia
Chenjie Xia Peihong Zhou
Peihong Zhou