- 1The First Clinical Medical College, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, China
- 2Department of Gynecology, Guang'anmen Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing, China
- 3Department of Reproduction and Genetics, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, China
Premature ovarian insufficiency (POI) is the most common cause of female infertility. With the increase in people’s bad life habits, the causative factors of POI have increased, and its incidence has shown a rising trend year by year. At present, the commonly used clinical treatment for POI is hormonal replacement therapy (HRT), but it is not universally applicable and is prone to cause subsequent complications, posing certain health risks to patients with POI. Therefore, exploring greener, safer, and more efficacious non-hormonal treatments can help to address the clinical challenges of POI-induced infertility better. Studies have shown that autophagy plays a key role in the development and degeneration of oocytes from their origin to the follicle and that any alteration in autophagy affects the ovarian reserve in the follicle. Moreover, certain natural products and human stem cells from different sources can treat POI by modulating the autophagic pathway and have shown good efficacy. Therefore, our study aimed to review and analyze the previous research-based literature on natural product and stem cell therapy based on the autophagy mechanism of POI, and provide new insights and references for related scholars to continue to explore the autophagy mechanism of POI and non-hormone-targeted therapeutic strategies in depth.
1 Introduction
Premature ovarian insufficiency (POI) is a pathological ovarian aging induced by multiple factors (1), characterized by primary or secondary amenorrhea of more than 4 months before the age of 40 in females, and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) levels greater than 25 IU/L in 2 consecutive samples (2), its incidence rate before the age of 40 in women is 1% (3). POI has become one of the leading causes of infertility in women of childbearing age. Not only that, but it is also associated with a variety of health risks including psychological disorders, osteoporosis, cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune diseases, and even leads to an increased risk of death in patients. Presently, about 25% of POIs can be categorized as medical, with chemotherapy or radiotherapy, etc., being the main cause of POIs (4). In addition, with the increase in non-pharmacologic intervention triggers brought about by social development, such as smoking, drinking, staying up late and other unhealthy lifestyles, overexposure to plastic toxins, etc. (5), the incidence of POI has been increasing year by year. HRT and IVF are currently the most common and effective clinical treatments for POI. HRT refers to the use of hormones (primarily estrogen) to simulate estrogen levels in women of childbearing age with normal ovarian function (6), and this therapy has been shown to lead to an increased risk of diseases such as coronary heart disease, endometrial cancer, and breast cancer in women with POI (7) and not all patients with POI are suitable for HRT regimens, e.g., women with POI who have poor uterine conditions (endometrial thickness and poor angiogenesis) show resistance to HRT regimens (8). In addition, despite significant advances in IVF technology, its success rates depend on a variety of factors, including age, ovarian reserve, and oocyte quality, with a success rate of only about 37% per IVF cycle, which continues to decline with age due to the poor prognosis for women with reduced ovarian responsiveness (9). So the search for greener, safer, and more effective therapies is expected to provide new ideas for breakthroughs in the clinical management of POI. Natural products have received increasing attention in the biomedical field due to their multi-component, multi-target, and multi-pathway advantages, showing better efficacy in alleviating aging and resisting oxidative stress damage (10) without obvious toxic side effects (11). Moreover, stem cells have continuous self-renewal and differentiation functions, which can promote tissue repair and regeneration, and produce long-lasting therapeutic effects on damaged senescent cells and tissues, in particular, mesenchymal stem cells have unique advantages over other types of stem cells (12), which have been widely and intensively researched in the treatment of POI. In contrast to the frequently employed hormone replacement therapy, both of these treatment modalities exhibit low rejection rates and broad applicability. It is anticipated that they can decrease the incidence of various complications and enhance the clinical outcomes for patients suffering from POI.
The etiologies contributing to POI are complex and diverse (13), and approximately 90% of spontaneous Premature ovarian insufficiency has no clear underlying etiology (14, 15), and there is still an ongoing quest to understand the exact mechanisms underlying the development of POI. Autophagy, a process of self-degradation of intracellular components that maintain cellular and energetic homeostasis, was discovered as early as 1962 and is highly conserved among species (16). Research evidence suggests that autophagy plays an important role in sustaining and regulating ovarian primordial follicle reserve, anti-ovarian aging, and granulosa cell differentiation (17, 18). The disruption of autophagic mechanisms or excessive autophagic fluxes may lead to cell death, altering the quality and quantity of oocytes, and ultimately affecting female reproductive health which leads to POI (19, 20). The exploration of POI autophagy mechanisms and the discovery of targeting strategies are of great significance for protecting female fertility in reproductive age, improving the fertility level of fertile couples, and maintaining family and social harmony.
In this article, we retrospectively summarized the studies on the potential mechanisms of the autophagy pathway in regulating POI, as well as the current status of natural products and stem cells targeting autophagy in POI, to inform the research on the progress of therapeutic strategies for POI.
2 Autophagy overview
Autophagy is a major intracellular degradation pathway that exists in three main forms, namely: macroautophagy, chaperone-mediated autophagy, and microautophagy, and all three autophagic degradation pathways are centered on the lysosome (21), of which macroautophagy is the only most prevalent autophagic process that contains a double membrane autophagosome structure (22). In this article, we focused on macroautophagy, hereinafter referred to as “autophagy”. Autophagy is an intracellular degradation-recycling pathway with a dual effect (23) that encapsulates intracellularly damaged lipids, proteins, and organelles in double-membrane vesicles and transports them to lysosomes for fusion to form an autophagy-lysosome complex, which is then degraded into amino acids and small molecules and recycled to rejoin the intracellular biogenesis and plays a role in quality control and thus maintaining cellular homeostasis (24).
Autophagy mainly consists of several key steps: autophagy induction, autophagosome assembly and formation (including nucleation of autophagy-associated protein ATG at PAS, elongation of the separating membrane and maturation of autophagosomes, and transport of mature autophagosomes), fusion of autophagosomes and lysosomes, and degradation and reuse of autophagic lysosomal complexes, and the numerous autophagy-associated proteins ATGs and their core complexes endow the autophagy pathway with multiple activities that regulate and control the various stages of the autophagic process described above (25). These proteins and their core complexes can be divided into the following functional units: (1) ULK kinase core complex, including ULK1/2, ATG13, RB1CC1/FIP200, and ATG101; (2) Autophagy-specific class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) complex, including VPS34, VPS15, Beclin1, and ATG14L; (3) ATG9A transporter system, including ATG9A, WIPI1/2, and ATG2; (4) ATG12 ubiquitin-like ligand system, including ATG12, ATG7, ATG10, ATG5, and ATG16L1; (5) LC3/Atg8 ubiquitin-like ligand system, including LC3A/B/C, ATG7, ATG3, the above functional units are involved in the hierarchical regulation of autophagy, and form a tight cascade of reactions during autophagy.
As an evolutionarily highly conserved catabolic process, the protective mechanism of autophagy is unique to biogenesis (26). Under specific circumstances such as ischemia and hypoxia, nutrient deficiency, aging, or injury in cells, autophagy acts as a self-protective mechanism to achieve self-degradation and removal of damaged substances from the cells (27), which plays an important role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and survival, and this is what makes autophagy unique from other modes of programmed cell death. The different biogenesis and morphological alterations of several programmed cell deaths are shown below (Table 1, Figure 1).

Table 1. Biosignature and induction parameter of autophagy, ferroptosis, apoptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis.
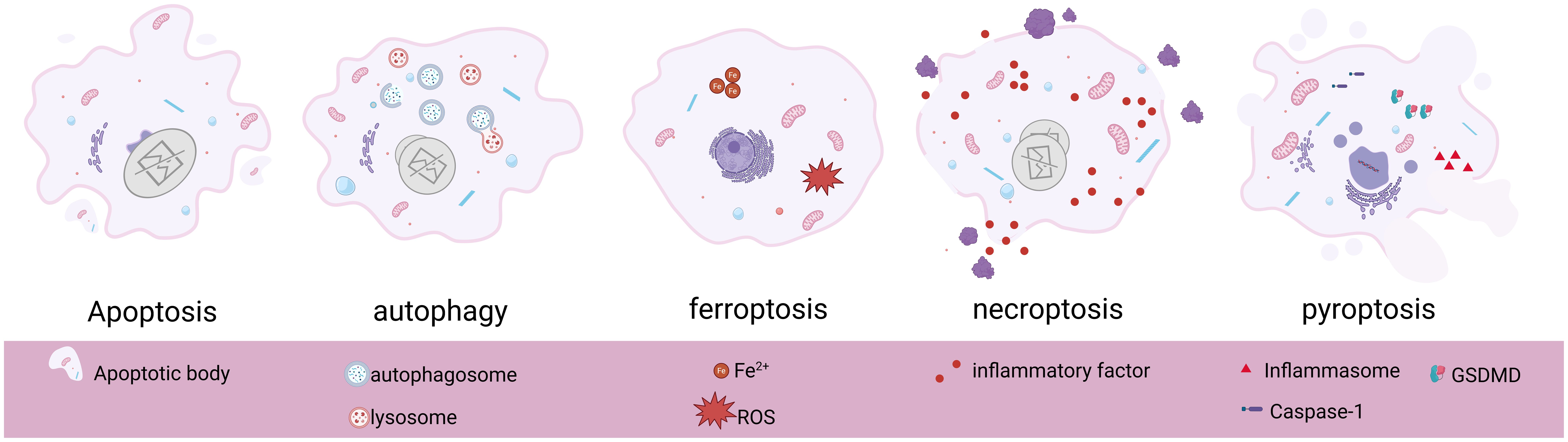
Figure 1. Basic morphological features and pathological changes of apoptosis, autophagy, ferroptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis. Created in BioRender. Yang, X. (2025) https://BioRender.com/s86x403.
3 Autophagy mechanisms
ULK1, the mammalian homolog of the yeast Atg1 kinase, is a key kinase in the initiation of autophagy and nucleation process (53), and interacts with ATG13, FIP200/Atg17, Atg29, and Atg31 to form the ULK1/Atg1 complex, which regulates autophagy in an mTOR-dependent manner (54). Under sufficient nutrition, mTOR C1 is activated to inhibit autophagy by phosphorylating ULK1 and ATG13. Under nutrient limitation, AMPK first responds to hunger signals (55) and inhibits mTOR C1 on the surface of lysosomes, leading to rapid dephosphorylation of ULK1 and ATG13 and activation of ULK1 kinase (56), inducing the formation of autophagy precursor structures (also known as phagophore assembly site complexes, PAS) (57).
The main function of PAS is to recruit autophagic proteins, which play a crucial role in the initiation of autophagy (58), and the ULK1/Atg1 kinase complex is essential for recruiting Atg proteins to PAS (59). Beclin-1, the mammalian cellular homolog of the yeast autophagy-related gene Atg6, is an important component of the autophagy initiation complex and a key regulator of nucleation and can be inhibited by Bcl-2 (60). It can recruit autophagy proteins by interacting with PI3K (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase)-like signaling pathways and forms a PI3K complex with VPS34, VPS15, and Atg14/ATG14L that is recruited to the PAS (61). Recent studies have shown that the PI3K complex targeting the PAS is mediated by the Atg1/ULK1 complex, ATG9, Vac8 (62), subsequently, the PI3K complex that is recruited to the PAS interacts with and binds to ATG13 in the ULK1 complex to participate in phagocytosis vesicle (as known as “detached membrane”) formation (63).
Activation of the PI3K complex leads to localized enrichment of PI3P (64), and the WIPI3/4 proteins sense the presence of PI3P and subsequently recruit the lipid transfer enzyme ATG2 into growing phagocytic vesicles, which subsequently mediates the transfer of lipids to the outer membranes of autophagic vesicles to achieve segregated membrane amplification and gradual segregation of cargoes, promoting autophagosome closure and maturation (65, 66). In addition to ATG2, WIPI1–4 also recruits the ATG5-ATG12-ATG16 complex, which mediates the coupling of LC3 to PE (67) and contributes to the correct assembly of autophagosomes (68). ATG9 is the only transmembrane protein identified in the core macroautophagy machinery (69) and is required for the formation of isolated compartments called autophagosomes (70). Most ATG9 is localized to small vesicles of Golgi origin (71), after autophagy induction, ATG9 is recruited to the PAS in response to Atg17, which is phosphorylated as a direct target of ULK1/Atg1 kinase, and phosphorylated Atg9 also recruits Atg8 and Atg18 to the PAS, which is required for the subsequent elongation of the separation membrane (72). Later studies showed that PAS localization of ATG9 vesicles is also achieved by binding to the HORMA structural domain of Atg13 (73). Notably, ATG9 circulates between the PAS and peripheral reservoirs (74, 75), is involved in the delivery of membranes required for the elongation and closure of separating membranes (58), and is important for autophagic processes. In addition, this cycling process is regulated by Atg18 and Atg2, independent of the Atg1 complex (76). Moreover, the cyclic transport of ATG9 vesicles balances ATG2-mediated lipid transfer, and the two autophagy-associated proteins coordinate to promote autophagosome growth and maturation (77).
In addition, the formation of autophagosomes possessing a bilayer membrane structure cannot be separated from the mediation of two ubiquitin-like coupling systems, ATG12 and LC3/Atg8. As mentioned previously, the ATG12-ATG5- ATG16 complex can mediate the coupling of LC3 to PE and promote the correct assembly of autophagosomes, moreover, it can stabilize PAS by interacting with the Atg1 complex (78). LC3 is widely used as a marker for the detection of autophagy and also serves as a docking site for a growing number of autophagy cargo receptors, LC3 can covalently couple to the membrane lipid phosphatidylinositol PE through a series of protein-lipid cascade reactions, a modification known as LC3 lipoylation, which allows LC3 to attach to autophagic vesicles, not only helping to recognize the vesicles as autophagic vesicles but also contributing to vesicle amplification and recruitment of cargo proteins or other autophagy proteins (79, 80). ATG7 and ATG3 play important roles in LC3 lipidation modification, LC3 I is activated by ATG7 and transferred to Atg3 to bind to PE and be modified to LC3 II, which is subsequently recruited to autophagic vesicle membranes. Notably, the lipidation of LC3 is blocked when ATG7 is deleted, which leads to limited expansion of the phagophore membrane, cells show “autophagy deficiency”, however, the molecular mechanism by which ATG7 activation occurs remains unclear (81). Subsequently, autophagic vesicle membranes continue to elongate and close to form autophagosomes, after which LC3 interacts with a variety of kinesins and kinetics proteins to facilitate autophagosome translocation to the lysosome for fusion (82), which leads to the formation of autophagolysosomal complexes, ultimately, LC3II within the autophagosome is hydrolyzed by lysosomal protein hydrolases, whereas LC3II on the cytoplasmic surface of the autophagosome continues to be lipidated by Atg4 (83), amino acids and other small molecules that are produced by autophagic degradation are transported back to the cytoplasm for recycling or energy generation (84).
In addition, the autophagy process is also regulated by various kinases such as DAPK1 and DAPK2. The death-associated protein kinase DAPK1 phosphorylates Beclin-1, which can promote autophagy both by weakening the interaction of Beclin-1 with Bcl-2 (85) and activating the p53 protein system, which affects the tendency of cellular autophagy (86). DAPK2 acts as a negative regulator of mTOR to modulate autophagy levels (87). P62, as the most important substrate protein for selective autophagy, promotes the recruitment of the ULK1 complex to initiate autophagosome formation by interacting with FIP200 (88) and can be doped for degradation in autophagosomes by interacting directly with LC3 on the separator membrane (89). The interaction of P62 with LC3 facilitates the maintenance of LC3 lipidation-modified separator membrane formation and provides a platform for autophagosome biogenesis, and impaired autophagy is accompanied by the accumulation of p62 (90)(Figure 2).
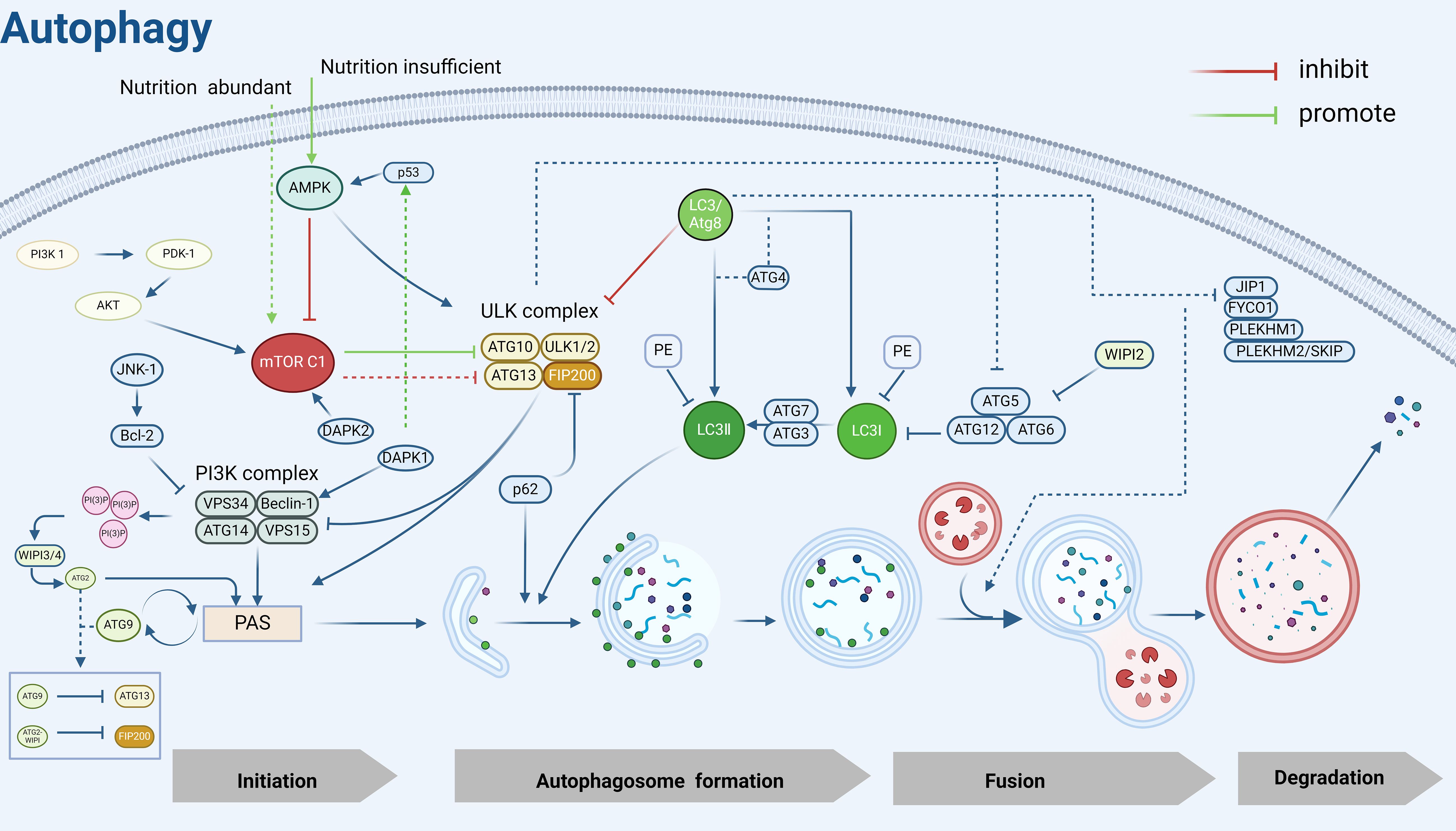
Figure 2. Autophagy mechanism diagram. PI3K, Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PDK-1, 3-Phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1; AKT, Protein kinase B; mTOR C1, Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin Complex 1; AMPK, Adenosine 5’-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase; JNK-1, c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma-2; ULK, UNC51-like kinase; FIP200, FAK family kinase-interacting protein of 200 kDa; VPS34, Vacuolar protein sorting 34; VPS15, Vacuolar protein sorting 15; WIPI2/3/4, WD Repeat Domain, Phosphoinositide Interacting 2/3/4; PAS, Pre-autophagosomal structure; LC3, Microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3; PE, Phosphatidylethanolamine; p53, Tumor protein 53; p62, sequestosome 1(SQSTM1); DAPK2, Death-associated protein kinase 2; DAPK1, Death-associated protein kinase 1; ATG, Autophagy related gene; JIP1, JNK interacting protein 1; FYCO1, FYVE And Coiled-Coil Domain Autophagy Adaptor 1; PLEKHM1, Pleckstrin Homology And RUN Domain Containing M1; PLEKHM2/SKIP, Pleckstrin Homology And RUN Domain Containing M2(also known as SKIP). Created in BioRender. Yang, X. (2025) https://BioRender.com/v58z146.
Because there are excellent articles in specialized fields dedicated to the mechanism of autophagy development, we made the above brief review of the complete autophagy process to elucidate the basic process and mechanism of autophagy development, to facilitate the scholars’ understanding of the autophagy-related mechanisms in the subsequent POI, and focused on the autophagy mechanism of POI and the study of non-hormone replacement targeted therapeutic strategies.
4 Autophagy mechanism in POI and molecular level-based intervention regulation
4.1 Epg5
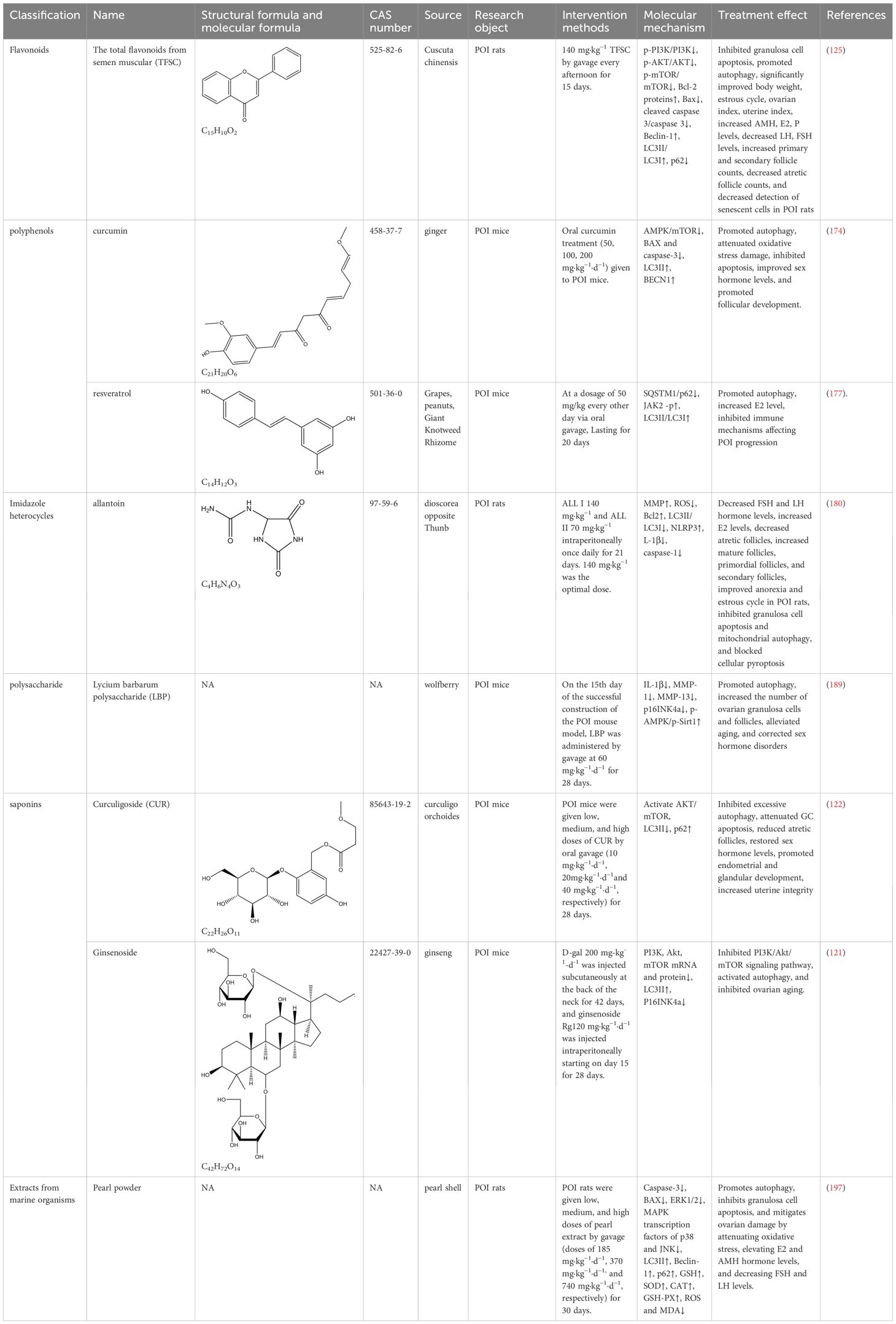
The Ras gene from rat brain (RAB) GTPase is a class of regulatory proteins essential for eukaryotic endosomal membrane trafficking (91). Its member, Rab7, is located on late autophagosomes and lysosomes and is important for autophagosome maturation, autophagosome-lysosome fusion, and subsequent degradation of autophagosome contents (92). Ectopic P-granules autophagy protein 5 homolog (Epg5) is an effector of Rab7 that is recruited to autophagosomes/lysosomes during late autophagy by interacting with Rab7 and binds to LC3 to promote the fusion of autophagosomes and lysosomes (93). Epg5 deficiency leads to impaired autophagic flux and disrupts cellular homeostasis (94). In ovarian granulosa cells (GCs), sufficient autophagy ensures that appropriate levels of Wilms tumor 1 (WT1) protein are maintained to promote GC differentiation, whereas in the presence of insufficient autophagy, overaccumulation of WT1 inhibits the transcription and activation of the estrogen synthase CYP19A1 gene and the follicle-stimulating hormone receptor FSHR, resulting in defective GC differentiation and impaired E2 synthesis, which inhibit GC proliferation and induce cell death (95). However, the selective autophagic degradation of WT1 in GCs is mediated by Epg5, and knockout of Epg5 blocks autophagic flux and exhibits a POI-like phenotype in female mice (96). Therefore, the excessive accumulation of WT1 caused by defective autophagy of EPG5 in GCs is an intrinsic mechanism that causes POI.
4.2 NRF2 and FTO
Autophagy and the NRF2-Keap1 pathway crosstalk through the binding of the autophagy junction protein, p62, to the specific structural domains of both Keap1 (97), which is manifested as a defect in autophagy causes competitive inhibition of the NRF2-Keap1 interaction, resulting in NRF2 stabilization followed by transcriptional activation of NRF2 target genes (98). However, POI-related basic experiments have suggested that changes in NRF2 similarly affect cellular autophagy. In cisplatin-induced POI mice, NRF2 expression was upregulated, but this change was compensatory, and the initiation of “protective autophagy” was inadequate to resist the cumulative stress of cisplatin induction. Overexpression of NRF2 significantly increased the expression of autophagy-related proteins LC3, Beclin-1, and Bcl-2, as well as decreased the levels of autophagy substrate p62 and pro-apoptotic protein Bax, which increased the autophagy level of damaged granulosa cells and significantly enhanced the cellular resistance to apoptosis (99).
Fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) is an antifibrotic factor that inhibits pro-fibrotic gene expression and suppresses fibroblast differentiation (100). It involved in reproductive processes such as follicle development (101–103), sex hormone regulation (104), granulosa cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis (102, 105), which plays a role in regulating ovarian function. Studies have shown that FGF2 plays a vital role in POI repair (105) and that FGF2 is also a key pathway for the induction of autophagy, its expression is upregulated to promote autophagy (106). Studies have shown that treatment of damaged granulosa cells with exogenous FGF2 increases the expression levels of NRF2 and LC3 in ovarian granulosa cells of POI mice, promotes NRF2 nuclear translocation, and enhances the anti-apoptotic capacity of damaged granulosa cells through activation of the autophagy pathway to play a reparative role (99)POI. In addition, FGF2 can activate autophagy and inhibit apoptosis in damaged granulosa cells by promoting the expression of Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO). FTO contributes to the development and maturation of oocytes (107), and its expression is significantly reduced in ovarian tissues of POI patients and mice (108). Exogenous addition of FGF2 up-regulated the expression level of FTO in POI granulosa cells, promoted the accumulation of autophagic follicles, inhibited the apoptosis of granulosa cells, and enhanced the viability of cell proliferation (109). The above findings indicate that NRF2 and FTO are aberrantly expressed in POI and are associated with autophagy mechanisms, moreover, the expression levels of both NRF2 and FTO are regulated through the intervention of FGF2.
4.3 HSP70
Protein quality control is fundamental to the maintenance of cellular homeostasis, which depends on sustained protein degradation and resynthesis, the former is achieved through autophagy, the ubiquitin-proteasome system, and other lysosome-dependent degradation pathways, and the latter concerning the regulation of protein folding and repair by heat shock proteins (110). Autophagy and the heat shock response represent 2 functionally distinct but complementary systems of cellular protein quality control, and the heat shock response inhibits autophagy under conditions where both systems are activated (111). Heat shock protein HSP70 is the central hub of the protein homeostasis network, which protects cells from protein homeostasis disruption induced by oxidative stress, various pathological factors, and organismal aging (112, 113). During female reproduction, hsp70 leads to decreased autophagy and reduced oocyte viability, triggering a Premature ovarian insufficiency-like phenotype that affects fertility and pregnancy outcomes (114), high serum levels of HSP70 have been accepted to reflect ovarian damage and disease severity (115).
4.4 PI3K/AKT, MAPK and mTOR
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a core regulator of autophagy, regulated by different upstream signaling pathways (116), including the most important PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK signaling pathways (117). A review study showed that mTOR signaling plays an important role in female reproduction, such as follicular development, granulosa cell proliferation and ovarian aging, and that activation of the mTOR pathway protects the ovarian reserve and extends the life span of the ovary (118). PI3K/AKT/mTOR has negative feedback regulation of autophagy. Studies have shown that exposure to the organophosphate insecticide diazinon (DZN) leads to excessive ROS accumulation and DNA damage in porcine ovarian granulosa cells, which in turn induces apoptosis and autophagy through inhibition of the PI3K-AKT pathway and increases the risk of Premature ovarian insufficiency and follicular atresia (119). The results of many experimental articles suggest that targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway by certain therapies can promote autophagy or inhibit excessive autophagy, thereby increasing the number of follicles at all levels, reducing follicular atresia, and alleviating ovarian aging (120–125).
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) is a key driver of early autophagy initiation and autophagic vesicle assembly (126). There are multiple mammalian MAPK pathways, including extracellular regulated protein kinase 1/2(ERK1/2); c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) also known as stress protein-activated kinase (SAPK); and p38 MAPK (127).
The above MAPK pathways are linked to autophagy to different degrees, and their functions exhibit differences. JNK not only regulates ATF-2 and p53 transcription factors, but also phosphorylates cytoskeletal proteins, and mitochondria-associated proteins such as Bcl-2 (128, 129), which regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis, and DNA damage repair (130), and activates autophagy by disrupting the Bcl-2/Beclin-1 complex (131). Meanwhile, activation of p38 MAPK induces ULK1 phosphorylation and disrupts the ULK1-Atg13 complex, thereby inhibiting autophagy (132).
ERK regulates the expression of multiple nuclear transcription factors and proteins to participate in various biological responses such as oxidative stress, apoptosis, and autophagy and affects altered mitochondrial dynamics; moreover, inhibition of ERK impairs mitochondrial activity and disrupts intracellular metabolic processes, which enhances dependence on autophagy and increases autophagic flux (133). Distinct from MAPK, adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a key energy sensor that regulates cellular metabolism to maintain energetic homeostasis, and promotes autophagy by activating the mammalian autophagy initiation kinase ULK1 under cellular energy and nutrient deficiency. However, this effect is disrupted by highly active mTOR under nutrient-rich conditions to inhibit the ULK1 activation and the start of autophagy (134). It has been shown that AMPK/mTOR is an important autophagic antioxidant pathway capable of attenuating oxidative stress damage in female reproduction and plays an important role in alleviating oocyte senescence (135).
In the studies of pharmacological interventions in POI cited later in this article, all of the above pathways have been shown to play an important role in regulating autophagy in POI and ameliorating ovarian senescence.
4.5 Mcl-1
Myeloid cell leukemia-1 (Mcl-1) is a unique antiapoptotic Bcl-2 member that is critical for mitochondrial homeostasis (136) and plays a key role in the control of survival and death of a wide range of cells (137). Previous studies have shown that Mcl-1 is not only involved in apoptotic mechanisms but is also involved in mitochondrial quality control via autophagy (138), and is an important molecular bridge between autophagy and apoptosis. Since the current studies are contradictory, Mcl-1 deletion in diverse tissues and organs exerts distinct impacts on autophagy. Therefore, its function in regulating autophagy is unclear as current studies are conflicting (136).
OMARI et al. evaluated the expression of Mcl-1 in mouse oocytes at different developmental stages, and the results showed that the expression of the Mcl-1 transcription factor decreased significantly with age, suggesting that Mcl-1 may be an important regulator of oocyte survival. To further investigate the role of Mcl-1 in oocytes, the researchers specifically excised Mcl-1 from mouse oocytes. The results showed that Mcl-1 defects led to the development of reduced oocyte numbers at all levels, increased follicular atresia, and oocyte depletion, which ultimately led to the ovarian premature aging-like phenotype of mice with impaired ovulation and reduced fertility, and the results at the molecular level showed that the pro-apoptotic factor Bax elevation, increased Beclin-1, LC3, and lysosome-associated membrane protein 2 (LAMP-2), suggesting that Mcl-1 deficiency promotes apoptosis to accelerate oocyte death at all levels to induce Premature ovarian insufficiency, while at the same time being able to activate cellular autophagy in response to mitochondrial dysfunction (139).
4.6 Tet
Tet enzyme is a DNA demethylase that plays an important role in DNA demethylation during meiosis in primordial germ cells and oocytes, as well as in the pluripotent differentiation of embryonic stem cells (140, 141). Tet1 deficiency increases organelle fission in oocytes, which is associated with defective ubiquitination and reduced autophagy, and is detrimental to the removal of damaged or senescent organelles from the cell, leading to a decline in oocyte quality, as well as in oocyte number and follicular reserve, contributing to POI. Moreover, Tet1 accelerates reproductive failure with age (142). However, the exact regulatory mechanism of Tet1 on POI autophagy is yet to be elucidated. Studies have shown that Tet1 mediates the methylation of autophagy promoter regions (143). Thus it is hypothesized that Tet1 affects autophagy in POI oocytes by altering the methylation levels of autophagy-related genes, and the specific molecular mechanisms remain to be further investigated.
4.7 TRIM28
The tripartite motif-containing protein superfamily 28 (TRIM28) is an autophagy regulator, which can inhibit autophagy by promoting the proteasomal degradation of AMPK (144). The level of TRIM28 protein in the ovarian GCs of POI mice was reduced by OS, leading to an increase of autophagy marker proteins ATG5 and LC3B-II, as well as the down-regulation of P62, which triggered the abnormal excessive autophagy. Overexpression of TRIM28 significantly improved the changes of the above indexes, inhibited autophagy in GCs, and increased the levels of P16, HO-1 and SOD2, which alleviated OS and aging, improved hormone levels and restored the ovarian reserve in POI mice (145).
4.8 LncRNA
LncRNAs are key regulators in the development of various human diseases, including reproductive disorders, and regulate the normal development of GC, follicle, and ovary by mediating multiple mechanisms (146), and their aberrant transcription is closely associated with the occurrence and development of POI.
In studies of Premature ovarian insufficiency, lncRNA nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1) and STC2 are downregulated in POI mice (147, 148), whereas miR-654 is upregulated in the plasma of POI patients (149). Bioinformatics software found a direct relationship between miR-654 and NEAT1, and the literature reported that STC2 is one of the targets of miR-654. By overexpressing NEAT1 can reduce the expression of miR-654, and regulate the STC2/MAPK pathway, inhibited cyclophosphamide-induced apoptosis and excessive autophagy in POI granulosa cells (150), and repaired POI ovarian damage. In addition, among cisplatin-induced POI granulosa cells, lncRNA HOTAIR was downregulated, leading to upregulation of miR-148b-3p, downregulation of ATG14, and inhibition of autophagy. Overexpression of HOTAIR not only improved the expression levels of miR-148b-3p and ATG14, but also upregulated the levels of ATG5, Beclin1, and SIRT1, and downregulated P62/SQSTM1, promoting autophagy and alleviating ovarian aging (151).
4.9 miRNA
MicroRNAs are major upstream regulators of the autophagy pathway, regulating autophagy by targeting autophagy-related genes or autophagy complexes at different stages of autophagy induction, autophagic vesicle nucleation, and vesicle elongation and closure (152), for example, MicroRNAs can directly target autophagy key proteins mTOR, ULK1/2, BECN1/Beclin-1, etc. to regulate their activities negatively (153, 154). Notably, microRNAs are the most abundant class of microRNAs in the ovary and play an important role in regulating ovarian function (155). Existing studies have demonstrated the potential of miR-644-5p, miR-21, miR-144-5p, and miR-146b-5p in the treatment of POI and restoration of ovarian function (156–159). In addition, miR-379, miR-15b, miR-691, miR-872, and miR-1897-5p have been reported as potentially useful markers of ovarian dysfunction (160). Extracellular vesicles of embryonic stem cell origin rejuvenate senescent cells both in vivo and in vitro, and the highly enriched miRNA-15b-5p within them are potent activators that mediate the rejuvenation of senescent cells (161). The anti-aging gene Klotho is closely related to the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis and plays a key role in the development of reproductive diseases, participating in the regulation of fibroblast growth factor-Klotho endocrine system dysfunction, the accumulation of oxidative stress, and the inhibition of autophagy, which ultimately affects follicular ontogeny, development, ovulation, or atresia (162). In cyclophosphamide-induced POI mouse granulosa cells, the expression level of miRNA-15b was elevated, and the expression of the anti-aging gene α-Klotho was significantly reduced. MiRNA-15b reduces the oxidative stress-related expression factors Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) and ATP levels by inhibiting the expression of α-Klotho in ovarian granulosa cells, causing ROS accumulation, the expression level of autophagy-related proteins was reduced, and autophagy activity and ROS scavenging ability were weakened (163).
In addition, in the cyclophosphamide-induced POI cell model, miR-497-3p was up-regulated, which inhibited Klotho transcription by targeting KLF4, and ultimately led to the inactivation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, which promoted DNA damage, activated autophagy and apoptosis, and accelerated follicle depletion to trigger ovarian senescence in POI cells, whereas knocking down miR-497-3p reversed the damage and delayed ovarian aging (164). And in 4-Vinylcyclohexene Diepoxide (VCD)-induced POI rats and granulosa cell models, miR-144 was down-regulated, and overexpression of miR-144 increased AKT/mTOR phosphorylation levels, inhibited excessive autophagy, and alleviated ovarian damage (165)(Table 2).
5 Autophagy-based natural product therapeutic strategies for POI
5.1 Natural products of plant origin
5.1.1 Flavonoids
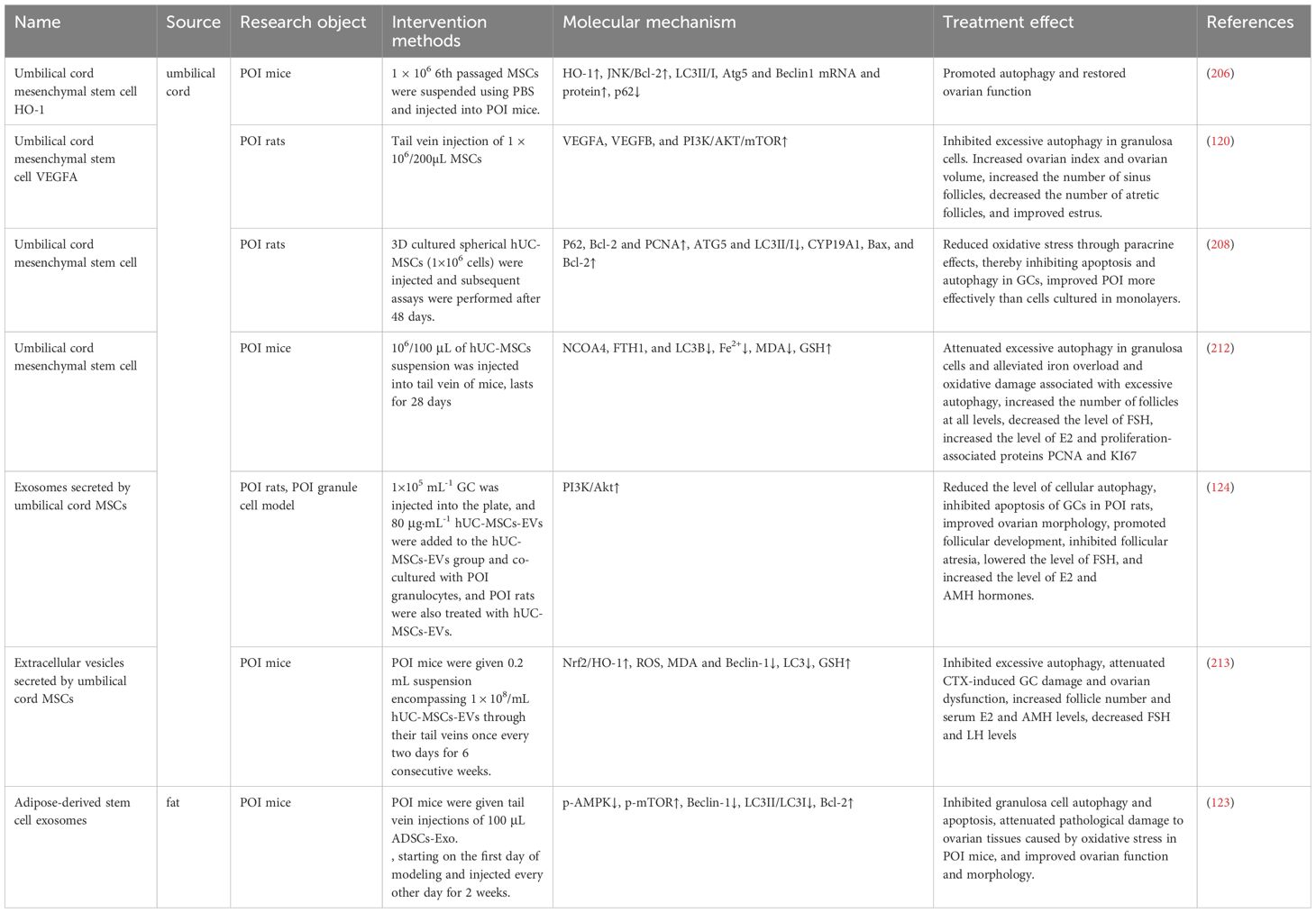
As a kidney tonic Chinese medicine, cuscuta chinensis is commonly used in the treatment of gynecological endocrine diseases, which can reduce free radical production, promote the production of superoxide dismutase, regulate immunity, and delay aging (167). Flavonoids contained in Cuscuta chinensis, which have the effect of delaying aging and improving microcirculation, exert multifaceted effects on the endocrine functions of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, such as regulating the level of ovarian sex hormones (168), protecting the frozen viability of male germ cells and the sexual function of aged male rats (169, 170), improving glycolipid metabolism (135), etc. Total flavonoids from Semen Cuscuta (TFSC) combined with low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) have important roles in improving reproductive endocrine function, anti-menopausal osteoporosis, and antioxidant activity (171, 172). In POI rats, TFSC was able to decrease p-PI3K/PI3K, p-AKT/AKT, and p-mTOR/mTOR, elevate the level of Bcl-2 protein, reduce the expression of Bax, cleaved-caspase 3, as well as the apoptosis rate of granulosa cells. It also promoted the expression of Beclin-1 and LC3II/LC3I in GC cells, decreased the expression level of p62, increased the number of autophagic vesicles in GC, and promoted cellular autophagy. Thus, it significantly improved the estrous cycle, ovarian index and hormone levels of POI rats increased the number of follicles at all levels, inhibited follicular atresia, decreased the detection rate of senescent cells, and alleviated oocyte developmental disorders and hormonal endocrine disorders associated with Premature ovarian insufficiency (125).
5.1.2 Polyphenols
Curcumin is a hydrophobic polyphenol extracted from the rhizome of the ginger family with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic effects (173). Capable of protecting ovarian granulosa cells from oxidative stress damage and inhibiting apoptosis through AMPK/mTOR pathway-mediated autophagy, as well as improving sex hormone levels and promoting follicular development (174). Another study showed that curcumin inhibits oxidative stress through the Nrf2/HO-1 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways, exerts anti-apoptotic effects, increases follicle number, and attenuates the senescence phenotype, rescues ovarian damage induced by D-galactose in POI mice (175). As mentioned earlier, Nrf2/HO-1 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways are related to autophagy regulation, but this study did not detect autophagy-related indexes or illustrate whether curcumin affects the changes of cellular autophagy levels through these two signaling pathways, which is doubtful and needs to be further verified. In addition, resveratrol is a polyphenolic natural compound that can act as an autophagy activator to regulate cell metabolism and differentiation (176). It can reduce selective autophagy cargo receptor-SQSTM1/p62, activate JAK2-p, increase LC3II/LC3I, promote granulocyte autophagy, and impede the immune mechanism of POI progression in mice, thus inhibiting POI and improving hormone levels (177).
5.1.3 Imidazole heterocycles
Allantoin, a nitrogen-rich purine catabolic metabolite from yam, can ameliorate aging by scavenging ROS to alleviate oxidative stress in plants (178). As a natural phytoestrogen, allantoin has a positive effect on ovarian follicle development (179). Studies have shown that the overprotective effects of allantoin are related to apoptosis, autophagy, and pyroptosis. In cyclophosphamide-induced POI rats, allantoin down-regulated the expression of LC3 II/LC3 I, caspase-1, as well as the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin L-1β, up-regulated the level of NLRP3 inflammatory vesicles, inhibited mitochondrial autophagy and cellular pyroptosis and up-regulated the expression of Bcl-2. Reduced the apoptosis rate and ROS level of ovarian granulosa cells in POI rats, lowered the levels of FSH and LH, increased the level of E2, inhibited follicular atresia, increased the number of mature follicles, primordial follicles, and secondary follicles, and ameliorated ovarian injury in rats (180).
It has been previously reported that autophagy removes intracellular inflammatory vesicle components and cytokines such as NLRP3, reducing inflammatory vesicle activation and inflammatory responses and that autophagy dysfunction leads to NLRP3 inflammatory vesicle hyperactivation and hyperinflammation (181). In turn, inflammatory vesicles can modulate the autophagic process, initiating protective autophagy to inhibit excessive intracellular stress (182). Autophagy crosstalk with inflammatory responses regulated by NLRP3 inflammatory vesicles precedes. Therefore, it is hypothesized that the inhibitory effect of allantoin on cellular pyroptosis in this study may be achieved through autophagy regulation of NLRP3 inflammatory vesicle activity. However, the specific regulation mechanism of autophagy by allantoin is not clear, and the deeper regulation mechanism of POI autophagy by allantoin needs to be further investigated.
5.1.4 Polysaccharides
Lycium barbarum polysaccharides (LBP) are the highest percentage of functional components in Chinese wolfberry (183), with anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, and anti-aging effects (184). It has been revealed to play a role in the prevention and treatment of a variety of diseases (185–187). Notably, LBP improves oocyte quality and follicular status, repairs ovarian damage, and enhances ovarian reserve capacity in women (188). In POI, LBP can inhibit the accumulation of POI senescent cells and senescence-related secretory phenotypes (such as the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1β and the matrix-degrading enzymes MMP-1 and MMP-13, etc.), down-regulate the expression of the senescence marker factor p16 INK4a, and promote the activation of the AMPK/Sirt1 pathway, improve autophagy activity, increase the number of ovarian granulosa cells and follicles, alleviate aging and correct sex hormone disorders, and improve D-galactose-induced POI symptoms (189).
5.1.5 Saponins
Curculigoside (CUR) with molecular formula C22H26O11 and molecular weight 466,448 is the main active ingredient in Curculigo orchoides, and exhibits pharmacological effects such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and enhancing immune activity (190). CUR protects ovarian reserve function from CTX-induced injury by activating the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, inhibiting excessive autophagy, and attenuating GC apoptosis. It is capable of elevating antioxidant enzymes and decreasing markers of redox reactions, reducing levels of autophagy markers LC3II, and increasing autophagy substrate p62. The therapeutic effect is mainly characterized by the reduction of atretic follicles, the rebalancing of sex hormone levels, and the development of endometrium and glands (122), unlike the previous promotion of autophagy to improve ovarian function. It is hypothesized that excessive autophagy exists in the ovarian cells of cyclophosphamide-induced POI mice, while CUR negative feedback regulates autophagic flux to protect ovarian function at this time.
Ginsenoside Rg1 belongs to the triterpenoid glycosides and is an abundant active ingredient in ginseng that exerts pharmacological effects in antioxidant and anti-aging and has been regarded as a potent phytoestrogen (191, 192) that exerts its estrogenic effects through the rapid activation of estrogen receptor signaling pathway without relying on ligand estrogenic effects (Q. G. 193). In reproductive disorders, Rg1 was able to improve fertility and reduce ovarian pathological damage in D-galactose (D-gal)-induced POI mice by enhancing anti-inflammatory and antioxidant capacities and reducing the expression of senescence signaling pathway proteins (194).
In POI rats, Rg1 was able to negatively regulate the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, decrease the mRNA and protein expression of ovarian PI3K, Akt, and mTOR, and up-regulate the expression of LC3-II, leading to increased autophagy levels, as well as reduce the staining rate of positive ovarian β-galactosidase and the expression of the senescence marker p16 INK4a, thereby inhibiting the onset of ovarian senescence (121).
5.2 Natural products of marine biological origin
Pearl powder, derived from the marine organism pearl oyster, is widely used in biomedicine as a traditional Chinese medicine with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-aging, immunomodulatory, and wound-healing pharmacological effects (195). Studies have shown that pearl extracts have excellent antioxidant and anti-aging effects both in vivo and in vitro, and can be used to treat various aging diseases (196). Previous literature has indicated that pearl powder has good therapeutic effects on gynecological diseases such as early-onset ovarian insufficiency, menopausal syndrome, abnormal uterine bleeding, etc. It has also been revealed to have a good ovarian protective effect in POI disease, and this protective effect is mediated through the autophagy pathway. It was shown that 740 mg/kg of high-dose pearl powder could regulate hormone levels, improve the estrous cycle, and promote follicular development in rats. Further investigation of its regulatory mechanisms revealed that pearl powder significantly reduced the expression of cleaved caspase-3, Bax, and the MAPK transcription factors of ERK1/2, p38, and JNK, and increased the expression of autophagy proteins LC3II, Beclin-1 and p62, as well as the activities of antioxidant enzymes GSH, SOD, CAT, and GSH-PX, and lowered oxidative stress products ROS and MDA, which ultimately promoted autophagy, inhibited apoptosis, and attenuated oxidative stress in ovarian granulosa cells of POI rats to improve ovarian function (197)(Table 3).
5.3 MSCs and their derivatives from different sources
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are pluripotent mesenchymal stromal cells derived from stromal tissues with plastic adhesion, self-renewal, and multispectral differentiation capabilities (198), which have shown great potential for research and clinical applications in the field of regenerative medicine (199). In addition, MSCs from a wide range of sources and can be extracted from various animal bone marrow, placenta, umbilical cord, amniotic fluid, menstrual blood, and adipose tissue, etc. MSCs from the above sources have been proven to be of great value in the treatment of POI (200), among which human umbilical cord MSCs (hUC-MSCs), with their advantages of being non-invasive, easy to obtain, and free from ethical controversy, have been more widely and intensively investigated in the treatment of POI, and have shown great potential for clinical application through further technological development and safety assessment in research (201). MSC therapy has become a promising therapeutic strategy for POI.
Autophagy can interact with signaling pathways that mediate the functional activity of various types of MSCs to improve the proliferation, differentiation activity, and paracrine effects of MSCs on other cells (202). The self-repairing function of MSCs and its influence on other cellular signaling pathways are closely related to the autophagy process. In addition, MSCs can promote tissue repair and regeneration and improve the microenvironment of damaged tissues by regulating autophagy (203). MSCs and autophagy interact and influence each other.
5.3.1 Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells and their secreted vesicles
HO-1 is an important antioxidant enzyme associated with autophagy, and both HO-1 and autophagy are recognized as part of the overall stress response, with both co-regulating to exert cytoprotective effects (204). Existing studies have shown that HO-1 was able to significantly restore impaired autophagic flux and lysosomal function and delay cellular senescence (99). In senescent mouse ovaries and oocytes, increased iron content and aberrant expression of iron metabolism proteins including HO-1 exhibit elevated lipid peroxidation and mitochondrial dysfunction, leading to localized redox state imbalance and decreased oocyte quality, and persistent iron death and mitochondrial autophagy (205). Yin, N et al. confirmed that the recovery of ovarian function was associated with the HO-1-mediated autophagy mechanism by comparing the results of HO-1/shHO-1 transfected hUC-MSC transplants. Elevated LC3 I/II, Atg5, and Beclin-1 mRNA and protein levels, and decreased p62 were observed in the HO-1 group, and in the shHO-1-MSC transplants of mice, the GCs’ autophagy was inhibited, as evidenced by reduced mRNA and protein levels of LC3 I/II and Beclin-1 and elevated p62. Further studies showed that HO-1 expressed in hUC-MSCs could help restore ovarian function in POI mice by activating autophagy mediated by the JNK/Bcl-2 signaling pathway (206).
Wenjie Dai et al. identified GCs as a regulatory target of MSCs in the improvement of ovarian function and found that hUC-MSCs could also activate the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway through the secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA), which could attenuate oxidative stress and inhibit excessive autophagy in ovarian GCs, leading to an increase in sinus follicles and a decrease in atretic follicles, with a significant improvement in ovarian function and enhancement of fertility in POI rats (120).
In addition, 3D spheroidal hUC-MSCs can more accurately mimic the real microenvironment of cell differentiation, solve the cell adhesion problem (207), reduce tissue damage, promote angiogenesis, maintain their high survival rate and excellent paracrine ability in damaged tissues, and exhibit stronger antioxidant and anti-apoptotic abilities than 2D culture systems (208, 209). Moreover, this spherical MSC concentrated using certain methods can be preserved without refrigeration for easy transportation around the world for research and therapeutic applications (210). It has been shown that 3D spheroidal hUC-MSCs transplantation can improve POI more effectively than monolayer cultured hUC-MSCs and can reduce oxidative stress through paracrine function and prevent GC apoptosis and autophagy (208).
In human ovarian granulosa cells, excessive autophagy activates apoptosis, leading to cell death and accelerating follicle classification lar atresia, which reduces the number of follicles entering the growth pool, thus triggering POI (211), so inhibiting excessive autophagy in granulosa cells is also key to improving POI. Studies have shown that hUC-MSCs can attenuate excessive autophagy in GCs of POI mice, alleviate iron death and oxidative damage associated with excessive autophagy in granulosa cells, increase the number of follicles at all levels, improve the level of sex hormones, elevate the levels of proliferation-associated proteins PCNA and KI67, and slow down the aging of ovarian GCs (212). Moreover, extracellular vesicles secreted by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUC-MSCs-EVs) exhibit typical exosomal characteristics and have therapeutic effects on various degenerative diseases. Studies have shown that activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is the main mechanism by which hUC-MSCs-EVs protect the ovarian function in POI, which can reduce the level of cellular autophagy, significantly inhibit apoptosis in GCs of POI rats, improve ovarian morphology, promote follicular development and inhibit follicular atresia, as well as reduce the level of FSH, increase the level of E2 and AMH, and improve the reserve capacity of the ovary (124). Besides, hUC-MSCs-EVs were able to restore ovarian function in POI mice by up-regulating IGF-1, and hUC-MSCs-EVs carrying IGF-1 inhibited CTX-induced excessive autophagy and attenuated GC injury and ovarian dysfunction by activating the Hrf2/HO-1 pathway (213).
5.3.2 Adipose-derived stem cells and their exosomes
Recent studies have shown that exosomes are closely related to intracellular autophagy in biogenesis and molecular signaling mechanisms (214). Adipose-derived stem cells exosome (ADSCs-Exo), an important intercellular messenger (215), has been identified as an important component of MSC paracrine secretion, and a growing number of studies have shown that ADSCs-Exo can be used as MSC alternative therapies for paracrine effects, including for the treatment of POI (200).
In POI mice, ADSCs-Exo reduced Beclin-1 and LC3II/LC3I protein levels and increased Bcl-2 expression by downregulating p-AMPK and upregulating p-mTOR, thereby inhibiting granulosa cell apoptosis and autophagy, attenuating pathological damage to ovarian tissues caused by oxidative stress, and improving ovarian function and morphology to counteract Premature ovarian insufficiency (123). Furthermore, a recent study demonstrated that hypo-Exos transferred miR-205-5p to enhance endothelial function and angiogenesis and alleviate POI by targeting the PTEN/PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway (216). This recent paper indicates that the treatment of POI by hypo-Exos is achieved through PI3K/AKT/mTOR-mediated angiogenesis. Although autophagy-related content is not mentioned, PI3K/AKT/mTOR is one of the most classical autophagy pathways known, and we believe that based on the results of this article there may be further studies to clarify the effect of hypo-Exos on the POI autophagy-related mechanism potential (Table 4, Figure 3).
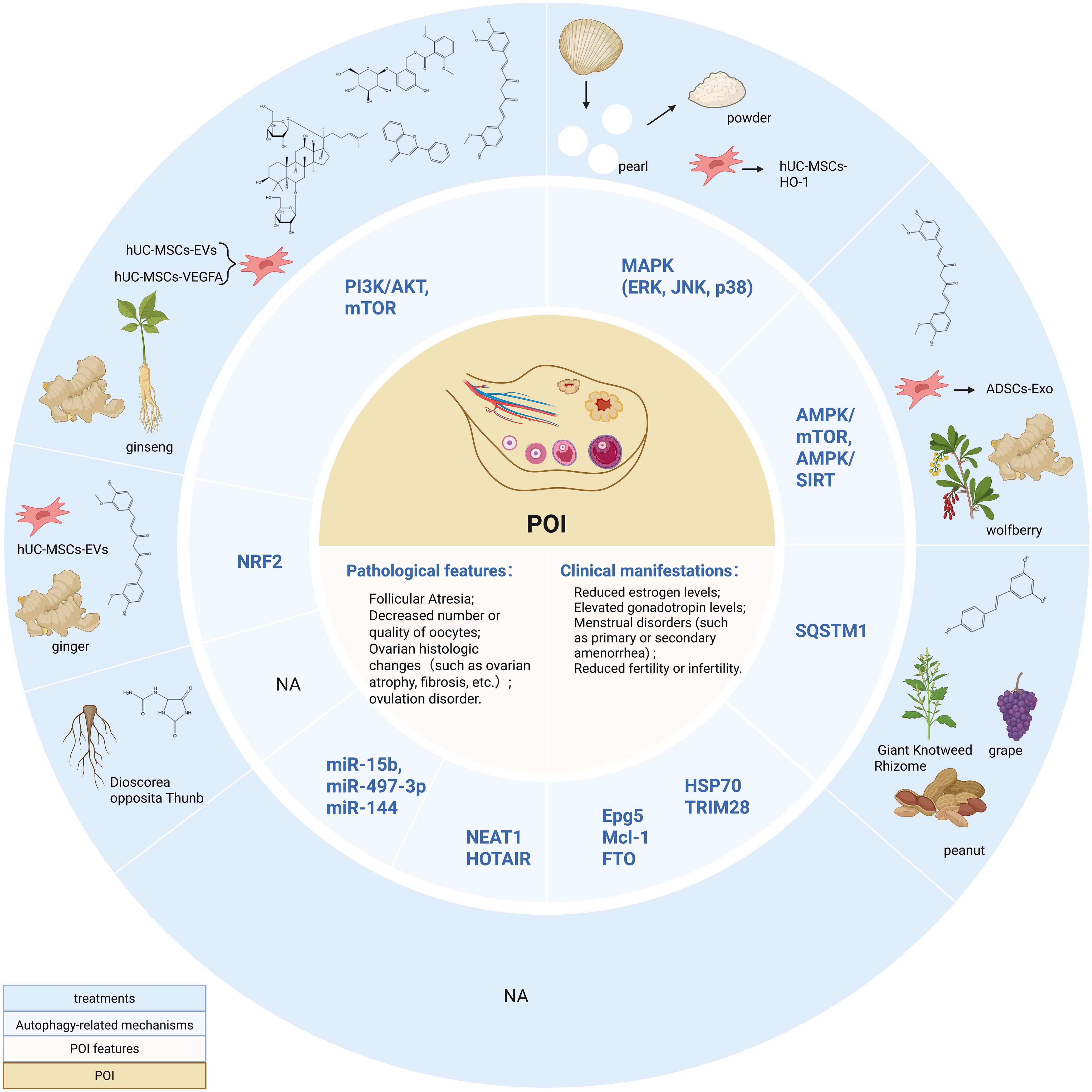
Figure 3. Autophagy-related Mechanisms and non-hormone Replacement Therapy Treatment in POI. PI3K/AKT, Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Protein kinase B; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; MAPK, Mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERK, extracellular regulated protein kinase; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; AMPK, adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; SIRT, silent information regulator 1; Epg5, Ectopic P-granules autophagy protein 5 homologs; Mcl-1, Myeloid cell leukemia-1; HSP70, Heat shock protein 70; FTO, Fat mass and obesity-associated protein; NEAT1, nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1; NRF2, Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2. Created in BioRender. Yang, X. (2025) https://BioRender.com/z84l329.
6 Discussion
Long-term hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is currently the treatment of choice in the clinic, but recent studies have shown that populations receiving HRT are at higher risk for breast cancer (217), endometrial cancer (218), coronary heart disease (219), autoimmune disorders (220), as well as for undergoing a cholecystectomy (G. J. 221), suggesting that HRT produces a range of complications that are detrimental to women’s health, fails to fundamentally restore ovarian function, and has limited effect on improving patient fertility. Natural products and their compound components can inhibit aging by activating autophagy (222) and play a role in a variety of diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease (223), chronic kidney disease (224), and postmenopausal osteoporosis (225). MSCs and their secretions have also been extensively studied in a variety of diseases or pathologies such as acute kidney injury (226), peripheral nerve injury (227), testicular injury and fertility disorders (228), and promotion of skin wound healing (229). Autophagy is an important catabolic process of cellular self-cleansing responsible for the degradation of harmful and damaged intracellular substances, and autophagy has been shown to play a beneficial role in age-related processes and lifespan extension (224).
In recent years, stem cells and natural products have been found to play an important role in alleviating the clinical symptoms of POI and rescuing women’s fertility. In this paper, we explored how the different sources of natural products and stem cells can be used in the treatment of Premature ovarian insufficiency by regulating autophagy. We found that the current research on the molecular mechanism of POI autophagy involves the regulatory factors Epg5, NRF2, and Mcl-1, the transcriptional proteins FTO, HSP70, and Tet, the signaling pathways PI3K/AKT, MAPK, and mTOR, as well as the LncRNAs NEAT1 and miR-15b, miR479-3p. Notably, the aberrant expression of the above regulatory factors in POI other than NRF2 and Mcl-1 inhibits autophagy to varying degrees, leading to ovarian damage and inducing disease. Moreover, the up-regulation of NRF2 expression in POI mice was able to activate protective autophagy in ovarian tissues, but this was compensatory, and only by artificially intervening overexpression of NRF2 could autophagic flux be maximally increased, which could play a real protective role for the damaged ovaries in POI. Although knockdown of Mcl-1 was shown to activate autophagy, the main effect of knockdown was to promote apoptosis and accelerate oocyte depletion. It was hypothesized that the reduction of Mcl-1 in POI might be a slight protective autophagy initiated by cell injury, and this degree of autophagy also counteracts cell injury. In addition, PI3K/AKT/mTOR is a classical autophagy pathway, and the available findings suggest that it regulates autophagy comprehensively and deeply, both inhibiting autophagy and activating autophagic clearance mechanisms in vivo.
However, in general, the current development of non-hormonal replacement therapies targeting the autophagy mechanism of POI mentioned above is not deep and comprehensive enough. Total flavonoids of Cuscuta chinensis, imidazole heterocyclic compounds, polysaccharides, polyphenols, saponins, and pearl shell extracts from marine organisms are among the few active ingredients of natural products that have been investigated to the level of autophagy mechanism. In addition, different sources of MSCs and their exosome therapies are at the forefront of the literature to explore new therapeutic strategies for POI, among which hUC-MSCs are the most richly researched, and their secretion of HO-1, VEGFA, exosomes, and the innovative 3D sphere culture and transplantation technology have achieved remarkable results in the study of targeted autophagy for the treatment of POI.
An important problem in the research of POI natural product therapy is that there is less literature on natural product-targeted autophagy therapy for POI, and the research on the autophagy regulatory mechanism is limited and not extensive enough, in addition, the side effects and safety of natural products are relative, there are potential toxicological mechanisms of many active ingredients of natural products. In the study of POI autophagy, the evaluation of complications or adverse reactions caused by these natural products after treatment is insufficient, the research objects are limited to animals and cells, and the corresponding clinical studies have not been carried out yet. Therefore, multicenter, large-sample, double-blind, high-quality randomized controlled trials as well as scientific and cautious clinical trials are needed to accumulate more scientific evidence to support the safety and efficacy of natural product-targeted autophagy for POI. In addition, it is worth noting that the occurrence of the autophagy process in POI is often accompanied by crosstalk with other programmed cell death modalities or biogenesis processes, such as apoptosis, pyroptosis, mitochondrial autophagy, oxidative stress, and so on. In addition, other sources of natural products, such as terpenoids, glycosides, and other natural active ingredients isolated from algae, sponges, and mosses in the marine environment have antibacterial, antiviral, and antitumor effects (230), which have been demonstrated to be applied in clinical trial studies of neurodegenerative disorders (231) and breast cancer (232). Furthermore, with advances in microbiology, the effects of natural products from fungi on diseases of the female reproductive system have been extensively studied. Zearalenone, an estrogenic mycotoxin produced by Fusarium oxysporum, alters oocyte morphology, disrupts the estrous cycle, reduces hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis activity, and disrupts female fertility (233), and the hyperthermophilic fungus, Aspergillus terraeus TM8, exerts its anticancer activity through apoptosis and has been implicated in the treatment of prostate cancer and breast cancer (234). Trace elements such as vitamins and minerals also play important roles in the female reproductive system. Cadmium and excess molybdenum can exacerbate ovarian damage by mediating necrotic apoptosis triggered by endoplasmic reticulum stress regulated by Th1/Th2 imbalance (235), while zinc and selenium improve follicular quality by improving mitochondrial dynamics and attenuating oxidative stress (236, 237). The above studies have demonstrated that various types of natural products have great potential to be explored in both scientific research and clinical practice of POI. Therefore, in the future, researchers should consider exploring more autophagy targets based on the crosstalk between autophagy and other processes, identifying and developing more diversified natural products with autophagy-regulating functions, and clarifying and evaluating their therapeutic ability for the treatment of POI, so as to promote their application in the treatment of POI.
Important issues identified in studies of MSC therapy for POI are that the use of MSCs for POI is still in the preclinical experimental stage based on concerns about the efficacy and safety of the current clinical application of MSCs in humans (201), and there are no definitive reports of clinical adverse effects, in addition, the significant variability in the different characteristics of different sources of MSCs in POI therapy has not yet been revealed. However, the efficacy of stem cell therapy has been demonstrated in many animal and cellular experiments, and the next step is to increase the research efforts, expand the sample size, and carry out cautious experiments in order to try to reveal the adverse effects and the advantages and disadvantages of stem cell therapy in POI treatment and to promote the clinical application of stem cell therapy. In addition, there is much evidence that MSCs from many different sources can treat POI by improving different pathological features, such as autologous menstrual blood-derived MSC transplantation improves ovarian function and restores the menstrual cycle in patients with POI, endometrial stem cells attenuate cisplatin-induced iron death of granulosa cells in POI by regulating the expression of Nrf2 (238), human embryonic-derived MSCs secreted VEGF, IGF-2, and HGF in vitro, which inhibited granulosa cell apoptosis, promoted angiogenesis and follicular growth, restored injured ovarian tissue structure and function, and salvaged the fertility of POI mice (239), and bone marrow-derived MSCs restored the fertility of POI mice through the up-regulation of FOXO1, GDF-9, and Fst genes and down-regulate TGF-β expression to promote granulosa cell proliferation and follicular development to treat cancer radiotherapy-induced POI (240). However, whether and how the above stem cell therapies treat POI by affecting autophagy has not been revealed, and more experiments are needed to enhance the exploration of the pathways linking MSCs from different sources and autophagy in POI in the future, to provide a molecular basis for stem cell transplantation and drug-targeted treatment of POI. Moreover, different MSCs from young and old, obese and non-obese populations showed differences in their ability to promote vascular endothelial cell formation, inhibit apoptosis, and enhance their proliferation, with senescent and obese-derived MSCs showing decreased protective and proliferative abilities, and obese population-derived MSCs exhibiting a senescence-associated secretory phenotype (241). Therefore, there are significant differences in the function, phenotype, and ethics of MSCs derived from different populations, and their therapeutic effects on POI are quite different, which provides new ideas for studying the therapeutic characteristics of MSCs derived from different populations.
7 Conclusion
In conclusion, future research on natural products and stem cell therapies in POI autophagy mechanism still faces great challenges, and more scientific trials need to be conducted to deeply investigate the mechanism of action, adverse effects, and clinical applications of these non-estrogenic replacement therapies in POI, to enhance the development and utilization of novel natural products in POI, and to accumulate more research evidence for retrospective analysis as well as for the further development of POI therapeutic strategies.
Author contributions
XY: Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZJ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. MS: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YL: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. GZ: Writing – review & editing. PW: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. XS: Validation, Writing – review & editing. WQ: Validation, Writing – review & editing. YG: Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82374505), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2023MH219), and the Taishan Scholar Foundation of Shandong Province (NO. tsqn202211353).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Wang HH, Hu JY, and Yao GD. Research progress on mechanism of premature ovarian failure and its prevention and treatment strategies. J Reprod Med. (2023) 32:1909–14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3845.2023.12.025
2. Bai X and Wang S. Signaling pathway intervention in premature ovarian failure. Front Med (Lausanne). (2022) 9:999440. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.999440
3. Zhang C. The roles of different stem cells in premature ovarian failure. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. (2020) 15:473–81. doi: 10.2174/1574888x14666190314123006
4. Jankowska K. Premature ovarian failure. Menopause Review/Przegląd Menopauzalny. (2017) 16:51–6. doi: 10.5114/pm.2017.68592
5. Sopiarz N and Sparzak PB. Primary Ovarian Insufficiency. [Updated 2023 Mar 6]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing (2025).
6. Verrilli L. Primary ovarian insufficiency and ovarian aging. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. (2023) 50:653–61. doi: 10.1016/j.ogc.2023.08.004
7. Deady J. Clinical monograph: hormone replacement therapy. J Manag Care Pharm. (2004) 10:33–47. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2004.10.1.33
8. Letur-Konirsch H and Delanian S. Successful pregnancies after combined pentoxifylline-tocopherol treatment in women with premature ovarian failure who are resistant to hormone replacement therapy. Fertil Steril. (2003) 79:439–41. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(02)04579-x
9. Martirosyan YO, Silachev DN, Nazarenko TA, Birukova AM, Vishnyakova PA, and Sukhikh GT. Stem-cell-derived extracellular vesicles: unlocking new possibilities for treating diminished ovarian reserve and premature ovarian insufficiency. Life (Basel). (2023) 13(12):2247. doi: 10.3390/life13122247
10. Yang C, Zhang W, Dong X, Fu C, Yuan J, Xu M, et al. A natural product solution to aging and aging-associated diseases. Pharmacol Ther. (2020) 216:107673. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107673
11. Cao M, Tang Y, Luo Y, Gu F, Zhu Y, Liu X, et al. Natural compounds modulating mitophagy: implications for cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. (2024) 582:216590. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216590
12. Gopalarethinam J, Nair AP, Iyer M, Vellingiri B, and Subramaniam MD. Advantages of mesenchymal stem cell over the other stem cells. Acta Histochem. (2023) 125:152041. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2023.152041
13. Sullivan SD, Sarrel PM, and Nelson LM. Hormone replacement therapy in young women with primary ovarian insufficiency and early menopause. Fertil Steril. (2016) 106:1588–99. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2016.09.046
14. De Vos M, Devroey P, and Fauser BC. Primary ovarian insufficiency. Lancet. (2010) 376:911–21. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(10)60355-8
15. Nelson LM. Clinical practice. Primary ovarian insufficiency. N Engl J Med. (2009) 360:606–14. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp0808697
16. Wang H, Li X, Zhang Q, Fu C, Jiang W, Xue J, et al. Autophagy in disease onset and progression. Aging Dis. (2024) 15:1646–71. doi: 10.14336/ad.2023.0815
17. Kumariya S, Ubba V, Jha RK, and Gayen JR. Autophagy in ovary and polycystic ovary syndrome: role, dispute and future perspective. Autophagy. (2021) 17:2706–33. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1938914
18. Dong MZ, Ouyang YC, Gao SC, Gu LJ, Guo JN, Sun SM, et al. Protein phosphatase 4 maintains the survival of primordial follicles by regulating autophagy in oocytes. Cell Death Dis. (2024) 15:658. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07051-4
19. Bhardwaj JK, Paliwal A, Saraf P, and Sachdeva SN. Role of autophagy in follicular development and maintenance of primordial follicular pool in the ovary. J Cell Physiol. (2022) 237:1157–70. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30613
20. Liu S, Yao S, Yang H, Liu S, and Wang Y. Autophagy: regulator of cell death. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:648. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06154-8
21. Yim WW and Mizushima N. Lysosome biology in autophagy. Cell Discov. (2020) 6:6. doi: 10.1038/s41421-020-0141-7
22. Feng Y, He D, Yao Z, and Klionsky DJ. The machinery of macroautophagy. Cell Res. (2014) 24:24–41. doi: 10.1038/cr.2013.168
23. Meyer N, Henkel L, Linder B, Zielke S, Tascher G, Trautmann S, et al. Autophagy activation, lipotoxicity and lysosomal membrane permeabilization synergize to promote pimozide- and loperamide-induced glioma cell death. Autophagy. (2021) 17:3424–43. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1874208
24. Trojani MC, Santucci-Darmanin S, Breuil V, Carle GF, and Pierrefite-Carle V. Autophagy and bone diseases. Joint Bone Spine. (2022) 89:105301. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2021.105301
25. Li X, He S, and Ma B. Autophagy and autophagy-related proteins in cancer. Mol Cancer. (2020) 19:12. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-1138-4
26. Chen T, Tu S, Ding L, Jin M, Chen H, and Zhou H. The role of autophagy in viral infections. J BioMed Sci. (2023) 30:5. doi: 10.1186/s12929-023-00899-2
27. Zhou Y, Chen E, Tang Y, Mao J, Shen J, Zheng X, et al. Mir-223 overexpression inhibits doxorubicin-induced autophagy by targeting foxo3a and reverses chemoresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Death Dis. (2019) 10:843. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2053-8
28. Hosokawa N, Hara Y, and Mizushima N. Generation of cell lines with tetracycline-regulated autophagy and a role for autophagy in controlling cell size. FEBS Lett. (2006) 580:2623–9. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.04.008
29. Nassour J, Radford R, Correia A, Fusté JM, Schoell B, Jauch A, et al. Autophagic cell death restricts chromosomal instability during replicative crisis. Nature. (2019) 565:659–63. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-0885-0
30. Conrad M, Angeli JP, Vandenabeele P, and Stockwell BR. Regulated necrosis: disease relevance and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2016) 15:348–66. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2015.6
31. Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. (2012) 149:1060–72. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
32. Kerr JF, Wyllie AH, and Currie AR. Apoptosis: A basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. (1972) 26:239–57. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1972.33
33. Chen X, He WT, Hu L, Li J, Fang Y, Wang X, et al. Pyroptosis is driven by non-selective gasdermin-D pore and its morphology is different from mlkl channel-mediated necroptosis. Cell Res. (2016) 26:1007–20. doi: 10.1038/cr.2016.100
34. Zhang Y, Chen X, Gueydan C, and Han J. Plasma membrane changes during programmed cell deaths. Cell Res. (2018) 28:9–21. doi: 10.1038/cr.2017.133
35. Yagoda N, von Rechenberg M, Zaganjor E, Bauer AJ, Yang WS, Fridman DJ, et al. Ras-raf-mek-dependent oxidative cell death involving voltage-dependent anion channels. Nature. (2007) 447:864–8. doi: 10.1038/nature05859
36. Yu P, Zhang X, Liu N, Tang L, Peng C, and Chen X. Pyroptosis: mechanisms and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2021) 6:128. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00507-5
37. Rao Z, Zhu Y, Yang P, Chen Z, Xia Y, Qiao C, et al. Pyroptosis in inflammatory diseases and cancer. Theranostics. (2022) 12:4310–29. doi: 10.7150/thno.71086
38. Zhao H, Yang Y, Si X, Liu H, and Wang H. The role of pyroptosis and autophagy in ischemia reperfusion injury. Biomolecules. (2022) 12(7):1010. doi: 10.3390/biom12071010
39. Zhang G, Lv S, Zhong X, Li X, Yi Y, Lu Y, et al. Ferroptosis: A new antidepressant pharmacological mechanism. Front Pharmacol. (2023) 14:1339057. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1339057
40. Perera RM, Stoykova S, Nicolay BN, Ross KN, Fitamant J, Boukhali M, et al. Transcriptional control of autophagy-lysosome function drives pancreatic cancer metabolism. Nature. (2015) 524:361–5. doi: 10.1038/nature14587
41. Chen X, Comish PB, Tang D, and Kang R. Characteristics and biomarkers of ferroptosis. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:637162. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.637162
42. Kurokawa M and Kornbluth S. Caspases and kinases in a death grip. Cell. (2009) 138:838–54. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.08.021
43. Yuan J and Ofengeim D. A guide to cell death pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2024) 25:379–95. doi: 10.1038/s41580-023-00689-6
44. Loveless R, Bloomquist R, and Teng Y. Pyroptosis at the forefront of anticancer immunity. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 40:264. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02065-8
45. Vasudevan SO, Behl B, and Rathinam VA. Pyroptosis-induced inflammation and tissue damage. Semin Immunol. (2023) 69:101781. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2023.101781
46. You R, He X, Zeng Z, Zhan Y, Xiao Y, and Xiao R. Pyroptosis and its role in autoimmune disease: A potential therapeutic target. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:841732. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.841732
47. Kroemer G, Mariño G, and Levine B. Autophagy and the integrated stress response. Mol Cell. (2010) 40:280–93. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.09.023
48. Mazure NM and Pouysségur J. Hypoxia-induced autophagy: cell death or cell survival? Curr Opin Cell Biol. (2010) 22:177–80. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.11.015
49. Zhao H, Fu X, Zhang Y, Chen C, and Wang H. The role of pyroptosis and autophagy in the nervous system. Mol Neurobiol. (2024) 61:1271–81. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03614-2
50. Yang F, Liu W, Huang Y, Yang S, Shao Z, Cai X, et al. Regulated cell death: implications for intervertebral disc degeneration and therapy. J Orthop Translat. (2022) 37:163–72. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2022.10.009
51. Choi ME, Price DR, Ryter SW, and Choi AMK. Necroptosis: A crucial pathogenic mediator of human disease. JCI Insight. (2019) 4(15):e128834. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.128834
52. Wei X, Xie F, Zhou X, Wu Y, Yan H, Liu T, et al. Role of pyroptosis in inflammation and cancer. Cell Mol Immunol. (2022) 19:971–92. doi: 10.1038/s41423-022-00905-x
53. Xiang H, Zhang J, Lin C, Zhang L, Liu B, and Ouyang L. Targeting autophagy-related protein kinases for potential therapeutic purpose. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2020) 10:569–81. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2019.10.003
54. Cheong H, Lindsten T, and Thompson CB. Autophagy and ammonia. Autophagy. (2012) 8:122–3. doi: 10.4161/auto.8.1.18078
55. Audet-Walsh É, Vernier M, and Viollet B. Editorial: ampk and mtor beyond signaling: emerging roles in transcriptional regulation. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2020) 8:641552. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.641552
56. Nazio F and Cecconi F. Autophagy up and down by outsmarting the incredible ulk. Autophagy. (2017) 13:967–8. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2017.1285473
57. Noda T. Regulation of autophagy through torc1 and mtorc1. Biomolecules. (2017) 7(3):52. doi: 10.3390/biom7030052
58. Mari M, Griffith J, Rieter E, Krishnappa L, Klionsky DJ, and Reggiori F. An atg9-containing compartment that functions in the early steps of autophagosome biogenesis. J Cell Biol. (2010) 190:1005–22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200912089
59. Kawamata T, Kamada Y, Kabeya Y, Sekito T, and Ohsumi Y. Organization of the pre-autophagosomal structure responsible for autophagosome formation. Mol Biol Cell. (2008) 19:2039–50. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-10-1048
60. Ye J, Zhang J, Zhu Y, Wang L, Jiang X, Liu B, et al. Targeting autophagy and beyond: deconvoluting the complexity of beclin-1 from biological function to cancer therapy. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2023) 13:4688–714. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.08.008
61. McKnight NC and Zhenyu Y. Beclin 1, an essential component and master regulator of pi3k-iii in health and disease. Curr Pathobiol Rep. (2013) 1:231–8. doi: 10.1007/s40139-013-0028-5
62. Hitomi K, Kotani T, Noda NN, Kimura Y, and Nakatogawa H. The atg1 complex, atg9, and vac8 recruit pi3k complex I to the pre-autophagosomal structure. J Cell Biol. (2023) 222(8):e202210017. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202210017
63. Zachari M and Ganley IG. The mammalian ulk1 complex and autophagy initiation. Essays Biochem. (2017) 61:585–96. doi: 10.1042/ebc20170021
64. Mizushima N. The role of the atg1/ulk1 complex in autophagy regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. (2010) 22:132–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.12.004
65. Luo M, Law KC, He Y, Chung KK, Po MK, Feng L, et al. Arabidopsis autophagy-related2 is essential for atg18a and atg9 trafficking during autophagosome closure. Plant Physiol. (2023) 193:304–21. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiad287
66. Barnaba C, Broadbent DG, Kaminsky EG, Perez GI, and Schmidt JC. Ampk regulates phagophore-to-autophagosome maturation. J Cell Biol. (2024) 223(8):e202309145. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202309145
67. Dooley HC, Razi M, Polson HE, Girardin SE, Wilson MI, and Tooze SA. Wipi2 links lc3 conjugation with pi3p, autophagosome formation, and pathogen clearance by recruiting atg12-5-16l1. Mol Cell. (2014) 55:238–52. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.05.021
68. Feng X, Sun D, Li Y, Zhang J, Liu S, Zhang D, et al. Local membrane source gathering by P62 body drives autophagosome formation. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:7338. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42829-8
69. Guardia CM, Christenson ET, Zhou W, Tan XF, Lian T, Faraldo-Gómez JD, et al. The structure of human atg9a and its interplay with the lipid bilayer. Autophagy. (2020) 16:2292–3. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1830522
70. Feng Y, Backues SK, Baba M, Heo JM, Harper JW, and Klionsky DJ. Phosphorylation of atg9 regulates movement to the phagophore assembly site and the rate of autophagosome formation. Autophagy. (2016) 12:648–58. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2016.1157237
71. Yamamoto H, Kakuta S, Watanabe TM, Kitamura A, Sekito T, Kondo-Kakuta C, et al. Atg9 vesicles are an important membrane source during early steps of autophagosome formation. J Cell Biol. (2012) 198:219–33. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201202061
72. Papinski D, Schuschnig M, Reiter W, Wilhelm L, Barnes CA, Maiolica A, et al. Early steps in autophagy depend on direct phosphorylation of atg9 by the atg1 kinase. Mol Cell. (2014) 53:471–83. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.12.011
73. Suzuki SW, Yamamoto H, Oikawa Y, Kondo-Kakuta C, Kimura Y, Hirano H, et al. Atg13 horma domain recruits atg9 vesicles during autophagosome formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2015) 112:3350–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1421092112
74. Holzer E, Martens S, and Tulli S. The role of atg9 vesicles in autophagosome biogenesis. J Mol Biol. (2024) 436:168489. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2024.168489
75. Shirahama-Noda K, Kira S, Yoshimori T, and Noda T. Trappiii is responsible for vesicular transport from early endosomes to golgi, facilitating atg9 cycling in autophagy. J Cell Sci. (2013) 126:4963–73. doi: 10.1242/jcs.131318
76. Reggiori F, Tucker KA, Stromhaug PE, and Klionsky DJ. The atg1-atg13 complex regulates atg9 and atg23 retrieval transport from the pre-autophagosomal structure. Dev Cell. (2004) 6:79–90. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(03)00402-7
77. Noda NN. Atg2 and atg9: intermembrane and interleaflet lipid transporters driving autophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. (2021) 1866:158956. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2021.158956
78. Shatz O and Elazar Z. Autophagy in a nutshell. FEBS Lett. (2024) 598:7–8. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14679
79. Amaravadi RK, Kimmelman AC, and Debnath J. Targeting autophagy in cancer: recent advances and future directions. Cancer Discov. (2019) 9:1167–81. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-19-0292
80. Jensen LE, Rao S, Schuschnig M, Cada AK, Martens S, Hummer G, et al. Membrane curvature sensing and stabilization by the autophagic lc3 lipidation machinery. Sci Adv. (2022) 8:eadd1436. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.add1436
81. Liu J, Lu S, Zheng L, Guo Q, Cao L, Xiao Y, et al. Atm-chk2-trim32 axis regulates atg7 ubiquitination to initiate autophagy under oxidative stress. Cell Rep. (2023) 42:113402. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113402
82. Ye J and Zheng M. Autophagosome trafficking. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2021) 1208:67–77. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-2830-6_5
83. Tanida I, Ueno T, and Kominami E. Lc3 conjugation system in mammalian autophagy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2004) 36:2503–18. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2004.05.009
84. Mizushima N, Yoshimori T, and Levine B. Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell. (2010) 140:313–26. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.01.028
85. Zalckvar E, Berissi H, Eisenstein M, and Kimchi A. Phosphorylation of beclin 1 by dap-kinase promotes autophagy by weakening its interactions with bcl-2 and bcl-xl. Autophagy. (2009) 5:720–2. doi: 10.4161/auto.5.5.8625
86. Maiuri MC, Tasdemir E, Criollo A, Morselli E, Vicencio JM, Carnuccio R, et al. Control of autophagy by oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. Cell Death Differ. (2009) 16:87–93. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2008.131
87. Ber Y, Shiloh R, Gilad Y, Degani N, Bialik S, and Kimchi A. Dapk2 is a novel regulator of mtorc1 activity and autophagy. Cell Death Differ. (2015) 22:465–75. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2014.177
88. Turco E, Witt M, Abert C, Bock-Bierbaum T, Su MY, Trapannone R, et al. Fip200 claw domain binding to P62 promotes autophagosome formation at ubiquitin condensates. Mol Cell. (2019) 74:330–46.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.01.035
89. Mizushima N and Komatsu M. Autophagy: renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. (2011) 147:728–41. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.10.026
90. Kageyama S, Gudmundsson SR, Sou YS, Ichimura Y, Tamura N, Kazuno S, et al. P62/sqstm1-droplet serves as a platform for autophagosome formation and anti-oxidative stress response. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:16. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20185-1
91. Rodriguez-Furlan C, Borna R, and Betz O. Rab7 gtpases as coordinators of plant endomembrane traffic. Front Plant Sci. (2023) 14:1240973. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1240973
92. Jin X, Wang K, Wang L, Liu W, Zhang C, Qiu Y, et al. Rab7 activity is required for the regulation of mitophagy in oocyte meiosis and oocyte quality control during ovarian aging. Autophagy. (2022) 18:643–60. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1946739
93. Nakamura S and Yoshimori T. New insights into autophagosome-lysosome fusion. J Cell Sci. (2017) 130:1209–16. doi: 10.1242/jcs.196352
94. Nam SE, Cheung YWS, Nguyen TN, Gong M, Chan S, Lazarou M, et al. Insights on autophagosome-lysosome tethering from structural and biochemical characterization of human autophagy factor epg5. Commun Biol. (2021) 4:291. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-01830-x
95. Shao T, Ke H, Liu R, Xu L, Han S, Zhang X, et al. Autophagy regulates differentiation of ovarian granulosa cells through degradation of wt1. Autophagy. (2022) 18:1864–78. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.2005415
96. Liu W, Chen M, Liu C, Wang L, Wei H, Zhang R, et al. Epg5 deficiency leads to primary ovarian insufficiency due to wt1 accumulation in mouse granulosa cells. Autophagy. (2023) 19:644–59. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2022.2094671
97. Jiang T, Harder B, Rojo de la Vega M, Wong PK, Chapman E, and Zhang DD. P62 links autophagy and Nrf2 signaling. Free Radic Biol Med. (2015) 88(Pt B):199–204. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.06.014
98. Inami Y, Waguri S, Sakamoto A, Kouno T, Nakada K, Hino O, et al. Persistent activation of Nrf2 through P62 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Cell Biol. (2011) 193(2):275–84. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201102031
99. Wang L, Lou W, Zhang Y, Chen Z, Huang Y, and Jin H. Ho-1-mediated autophagic restoration protects lens epithelial cells against oxidative stress and cellular senescence. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. (2023) 64:6. doi: 10.1167/iovs.64.15.6
100. Leali D, Bianchi R, Bugatti A, Nicoli S, Mitola S, Ragona L, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 2-antagonist activity of a long-pentraxin 3-derived anti-angiogenic pentapeptide. J Cell Mol Med. (2010) 14:2109–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00855.x
101. Almeida AP, Saraiva MV, Alves Filho JG, Silva GM, Gonçalves RF, Brito IR, et al. Gene expression and immunolocalization of fibroblast growth factor 2 in the ovary and its effect on the in vitro culture of caprine preantral ovarian follicles. Reprod Domest Anim. (2012) 47:20–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0531.2011.01793.x
102. Price CA. Mechanisms of fibroblast growth factor signaling in the ovarian follicle. J Endocrinol. (2016) 228:R31–43. doi: 10.1530/joe-15-0414
103. Santos JM, Menezes VG, Barberino RS, Macedo TJ, Lins TL, Gouveia BB, et al. Immunohistochemical localization of fibroblast growth factor-2 in the sheep ovary and its effects on pre-antral follicle apoptosis and development in vitro. Reprod Domest Anim. (2014) 49:522–8. doi: 10.1111/rda.12322
104. Moayeri A, Rostamzadeh A, Raoofi A, Rezaie MJ, Abasian Z, and Ahmadi R. Retinoic acid and fibroblast growth factor-2 play a key role on modulation of sex hormones and apoptosis in a mouse model of polycystic ovary syndrome induced by estradiol valerate. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. (2020) 59:882–90. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2020.08.004
105. Cheng F, Wang J, Wang R, Pan R, Cui Z, Wang L, et al. Fgf2 promotes the proliferation of injured granulosa cells in premature ovarian failure via hippo-yap signaling pathway. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2024) 589:112248. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2024.112248
106. Zhu W, Zhang H, Gao J, and Xu Y. Silencing of mir-497-5p inhibits cell apoptosis and promotes autophagy in parkinson’s disease by upregulation of fgf2. Environ Toxicol. (2021) 36:2302–12. doi: 10.1002/tox.23344
107. Huang T, Guo J, Lv Y, Zheng Y, Feng T, Gao Q, et al. Meclofenamic acid represses spermatogonial proliferation through modulating M(6)a rna modification. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. (2019) 10:63. doi: 10.1186/s40104-019-0361-6
108. Ding C, Zou Q, Ding J, Ling M, Wang W, Li H, et al. Increased N6-methyladenosine causes infertility is associated with fto expression. J Cell Physiol. (2018) 233:7055–66. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26507
109. Wang R, Wang L, Wang L, Cui Z, Cheng F, Wang W, et al. Fgf2 is protective towards cisplatin-induced kgn cell toxicity by promoting fto expression and autophagy. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:890623. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.890623
110. Dokladny K, Myers OB, and Moseley PL. Heat shock response and autophagy–cooperation and control. Autophagy. (2015) 11:200–13. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1009776
111. Dokladny K, Zuhl MN, Mandell M, Bhattacharya D, Schneider S, Deretic V, et al. Regulatory coordination between two major intracellular homeostatic systems: heat shock response and autophagy. J Biol Chem. (2013) 288:14959–72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.462408
112. Murphy ME. The HSP70 family and cancer. Carcinogenesis. (2013) 34:1181–8. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt111
113. Rosenzweig R, Nillegoda NB, Mayer MP, and Bukau B. The HSP70 chaperone network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2019) 20:665–80. doi: 10.1038/s41580-019-0133-3
114. Sisti G, Kanninen TT, Ramer I, and Witkin SS. Interaction between the inducible 70-kda heat shock protein and autophagy: effects on fertility and pregnancy. Cell Stress Chaperones. (2015) 20:753–8. doi: 10.1007/s12192-015-0609-9
115. Narayansingh RM, Senchyna M, Vijayan MM, and Carlson JC. Expression of prostaglandin G/H synthase (Pghs) and heat shock protein-70 (Hsp-70) in the corpus luteum (Cl) of prostaglandin F2 alpha-treated immature superovulated rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. (2004) 82:363–71. doi: 10.1139/y04-032
116. Wang H, Liu Y, Wang D, Xu Y, Dong R, Yang Y, et al. The upstream pathway of mtor-mediated autophagy in liver diseases. Cells. (2019) 8(12):1597. doi: 10.3390/cells8121597
117. Ba L, Gao J, Chen Y, Qi H, Dong C, Pan H, et al. Allicin attenuates pathological cardiac hypertrophy by inhibiting autophagy via activation of pi3k/akt/mtor and mapk/erk/mtor signaling pathways. Phytomedicine. (2019) 58:152765. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.11.025
118. Guo Z and Yu Q. Role of mtor signaling in female reproduction. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2019) 10:692. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00692
119. Wang W, Luo SM, Ma JY, Shen W, and Yin S. Cytotoxicity and DNA damage caused from diazinon exposure by inhibiting the pi3k-akt pathway in porcine ovarian granulosa cells. J Agric Food Chem. (2019) 67:19–31. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b05194
120. Dai W, Yang H, Xu B, He T, Liu L, Ma X, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (Huc-mscs) alleviate excessive autophagy of ovarian granular cells through vegfa/pi3k/akt/mtor pathway in premature ovarian failure rat model. J Ovarian Res. (2023) 16:198. doi: 10.1186/s13048-023-01278-z
121. Liu XH, Zhao ZH, Zhou Y, Wang CL, Han YJ, and Zhou W. Effect of ginsenoside rg_1 in delaying premature ovarian failure induced by D-gal in mice through pi3k/akt/mtor autophagy pathway. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. (2020) 45:6036–42. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200901.405
122. Meng Y, Lyu Y, Gong J, Zou Y, Jiang X, Xiao M, et al. Therapeutic effects of curculigoside on cyclophosphamide-induced premature ovarian failure in mice. Climacteric. (2024) 27:421–32. doi: 10.1080/13697137.2024.2354742
123. Ren Y, He J, Wang X, Liang H, and Ma Y. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells alleviate premature ovarian failure via blockage of autophagy and ampk/mtor pathway. PeerJ. (2023) 11:e16517. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16517
124. Xu B, Guo W, He X, Fu Z, Chen H, Li J, et al. Repair effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles on ovarian injury induced by cisplatin. Environ Toxicol. (2024) 39(8):4184–95. doi: 10.1002/tox.24303
125. Zhou W, Chen A, Ye Y, Ren Y, Lu J, Xuan F, et al. Lipus combined with tfsc alleviates premature ovarian failure by promoting autophagy and inhibiting apoptosis. Gynecol Endocrinol. (2023) 39:2258422. doi: 10.1080/09513590.2023.2258422
126. White E. Exploiting the bad eating habits of ras-driven cancers. Genes Dev. (2013) 27:2065–71. doi: 10.1101/gad.228122.113
127. Hepworth EMW and Hinton SD. Pseudophosphatases as regulators of mapk signaling. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22(22):12595. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212595
128. Cui J, Zhang M, Zhang YQ, and Xu ZH. Jnk pathway: diseases and therapeutic potential. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2007) 28:601–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2007.00579.x
129. Johnson GL and Nakamura K. The C-jun kinase/stress-activated pathway: regulation, function and role in human disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2007) 1773:1341–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.12.009
130. Sabapathy K. Role of the jnk pathway in human diseases. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. (2012) 106:145–69. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-396456-4.00013-4
131. Wang G, Zhang S, Wang F, Li G, Zhang L, and Luan X. Expression and biological function of programmed death ligands in human placenta mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Biol Int. (2013) 37:137–48. doi: 10.1002/cbin.10024
132. Sui X, Kong N, Ye L, Han W, Zhou J, Zhang Q, et al. P38 and jnk mapk pathways control the balance of apoptosis and autophagy in response to chemotherapeutic agents. Cancer Lett. (2014) 344:174–9. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.11.019
133. Bryant KL, Stalnecker CA, Zeitouni D, Klomp JE, Peng S, Tikunov AP, et al. Combination of erk and autophagy inhibition as a treatment approach for pancreatic cancer. Nat Med. (2019) 25:628–40. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0368-8
134. Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B, and Guan KL. Ampk and mtor regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol (2011) 13(2):132–41. doi: 10.1038/ncb2152
135. Wang Z, Zeng M, Wang Z, Qin F, Chen J, and He Z. Dietary luteolin: A narrative review focusing on its pharmacokinetic properties and effects on glycolipid metabolism. J Agric Food Chem. (2021) 69:1441–54. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c08085
136. Moyzis AG, Lally NS, Liang W, Najor RH, and Gustafsson ÅB. Mcl-1 differentially regulates autophagy in response to changes in energy status and mitochondrial damage. Cells. (2022) 11(9):1469. doi: 10.3390/cells11091469
137. Fu NY, Rios AC, Pal B, Soetanto R, Lun AT, Liu K, et al. Egf-mediated induction of mcl-1 at the switch to lactation is essential for alveolar cell survival. Nat Cell Biol. (2015) 17:365–75. doi: 10.1038/ncb3117
138. Zou Y, Liu W, Zhang J, and Xiang D. Mir-153 regulates apoptosis and autophagy of cardiomyocytes by targeting mcl-1. Mol Med Rep. (2016) 14:1033–9. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5309
139. Omari S, Waters M, Naranian T, Kim K, Perumalsamy AL, Chi M, et al. Mcl-1 is a key regulator of the ovarian reserve. Cell Death Dis. (2015) 6:e1755. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.95
140. Koh KP, Yabuuchi A, Rao S, Huang Y, Cunniff K, Nardone J, et al. Tet1 and tet2 regulate 5-hydroxymethylcytosine production and cell lineage specification in mouse embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. (2011) 8:200–13. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2011.01.008
141. Yamaguchi S, Hong K, Liu R, Shen L, Inoue A, Diep D, et al. Tet1 controls meiosis by regulating meiotic gene expression. Nature. (2012) 492:443–7. doi: 10.1038/nature11709
142. Liu L, Wang H, Xu GL, and Liu L. Tet1 deficiency leads to premature ovarian failure. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:644135. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.644135
143. Ren J, Chen X, Li J, Zan Y, Wang S, Tan Y, et al. Tet1 inhibits the migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells by regulating autophagy. Epigenetics. (2024) 19:2323751. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2024.2323751
144. Pineda CT, Ramanathan S, Fon Tacer K, Weon JL, Potts MB, Ou YH, et al. Degradation of ampk by a cancer-specific ubiquitin ligase. Cell. (2015) 160:715–28. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.034
145. Zhou C, Li D, He J, Luo T, Liu Y, Xue Y, et al. Trim28-mediated excessive oxidative stress induces cellular senescence in granulosa cells and contributes to premature ovarian insufficiency in vitro and in vivo. Antioxid (Basel). (2024) 13(3):308. doi: 10.3390/antiox13030308
146. Tu J, Chen Y, Li Z, Yang H, Chen H, and Yu Z. Long non-coding rnas in ovarian granulosa cells. J Ovarian Res. (2020) 13:63. doi: 10.1186/s13048-020-00663-2
147. Ge P, Xing N, Ren Y, Zhu L, Han D, Kuang H, et al. Preventive effect of american ginseng against premature ovarian failure in a rat model. Drug Dev Res. (2014) 75:521–8. doi: 10.1002/ddr.21234
148. Li M, Peng J, and Zeng Z. Overexpression of long non-coding rna nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1 inhibits the expression of P53 and improves premature ovarian failure. Exp Ther Med. (2020) 20:69. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9197
149. Yang X, Zhou Y, Peng S, Wu L, Lin HY, Wang S, et al. Differentially expressed plasma micrornas in premature ovarian failure patients and the potential regulatory function of mir-23a in granulosa cell apoptosis. Reproduction. (2012) 144:235–44. doi: 10.1530/rep-11-0371
150. Liu YX, Ke Y, Qiu P, Gao J, and Deng GP. Lncrna neat1 inhibits apoptosis and autophagy of ovarian granulosa cells through mir-654/stc2-mediated mapk signaling pathway. Exp Cell Res. (2023) 424:113473. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2023.113473
151. Luo C, Wei L, Qian F, Bo L, Gao S, Yang G, et al. Lncrna hotair regulates autophagy and proliferation mechanisms in premature ovarian insufficiency through the mir-148b-3p/atg14 axis. Cell Death Discov. (2024) 10:44. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-01811-z
152. Qi J, Luo X, Ma Z, Zhang B, Li S, and Zhang J. Downregulation of mir-26b-5p, mir-204-5p, and mir-497-3p expression facilitates exercise-induced physiological cardiac hypertrophy by augmenting autophagy in rats. Front Genet. (2020) 11:78. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00078
153. Chen L, Zhou Y, Sun Q, Zhou J, Pan H, and Sui X. Regulation of autophagy by mirnas and their emerging roles in tumorigenesis and cancer treatment. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. (2017) 334:1–26. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2017.03.003
154. Gozuacik D, Akkoc Y, Ozturk DG, and Kocak M. Autophagy-regulating micrornas and cancer. Front Oncol. (2017) 7:65. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00065
155. Maalouf SW, Liu WS, and Pate JL. Microrna in ovarian function. Cell Tissue Res. (2016) 363:7–18. doi: 10.1007/s00441-015-2307-4
156. Aldakheel FM, Abuderman AA, Alduraywish SA, Xiao Y, and Guo WW. Microrna-21 inhibits ovarian granulosa cell proliferation by targeting snhg7 in premature ovarian failure with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Reprod Immunol. (2021) 146:103328. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2021.103328
157. Liu T, Lin J, Chen C, Nie X, Dou F, Chen J, et al. Microrna-146b-5p overexpression attenuates premature ovarian failure in mice by inhibiting the dab2ip/ask1/P38-mapk pathway and Γh2a. X Phosphorylation Cell Prolif. (2021) 54:e12954. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12954
158. Sun B, Ma Y, Wang F, Hu L, and Sun Y. Mir-644-5p carried by bone mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes targets regulation of P53 to inhibit ovarian granulosa cell apoptosis. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2019) 10:360. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1442-3
159. Yang M, Lin L, Sha C, Li T, Zhao D, Wei H, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal mir-144-5p improves rat ovarian function after chemotherapy-induced ovarian failure by targeting pten. Lab Invest. (2020) 100:342–52. doi: 10.1038/s41374-019-0321-y
160. Furlong HC, Stämpfli MR, Gannon AM, and Foster WG. Identification of micrornas as potential markers of ovarian toxicity. J Appl Toxicol. (2018) 38:744–52. doi: 10.1002/jat.3583
161. Yu L, Wen H, Liu C, Wang C, Yu H, Zhang K, et al. Embryonic stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles rejuvenate senescent cells and antagonize aging in mice. Bioact Mater. (2023) 29:85–97. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.06.011
162. Xie T, Ye W, Liu J, Zhou L, and Song Y. The emerging key role of klotho in the hypothalamus-pituitary-ovarian axis. Reprod Sci. (2021) 28:322–31. doi: 10.1007/s43032-020-00277-5
163. Liu T, Liu Y, Huang Y, Chen J, Yu Z, Chen C, et al. Mir-15b induces premature ovarian failure in mice via inhibition of α-klotho expression in ovarian granulosa cells. Free Radic Biol Med. (2019) 141:383–92. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.07.010
164. Zhou Y, Yuan F, Jia C, Chen F, Li F, and Wang L. Mir-497-3p induces premature ovarian failure by targeting klf4 to inactivate klotho/pi3k/akt/mtor signaling pathway. Cytokine. (2023) 170:156294. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2023.156294
165. Zhou Q, Jin X, Wang J, Li H, Yang L, Wu W, et al. 4-vinylcyclohexene diepoxide induces premature ovarian insufficiency in rats by triggering the autophagy of granule cells through regulating mir-144. J Reprod Immunol. (2023) 157:103928. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2023.103928
166. Witkin SS, Kanninen TT, and Sisti G. The role of Hsp70 in the regulation of autophagy in gametogenesis, pregnancy, and parturition. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. (2017) 222:117–27. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-51409-3_6
167. Lin S, Ye S, Huang J, Tian Y, Xu Y, Wu M, et al. How do chinese medicines that tonify the kidney inhibit dopaminergic neuron apoptosis? Neural Regener Res. (2013) 8:2820–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2013.30.004
168. Zhou Y, Lv L, Liu Q, and Song J. Total flavonoids extracted from nervilia fordii function in polycystic ovary syndrome through il-6 mediated jak2/stat3 signaling pathway. Biosci Rep. (2019) 39(1):BSR20181380. doi: 10.1042/bsr20181380
169. Dhawan K, Kumar S, and Sharma A. Beneficial effects of chrysin and benzoflavone on virility in 2-year-old male rats. J Med Food. (2002) 5:43–8. doi: 10.1089/109662002753723214
170. Partyka A, Kostrzewa Susłow E, Dymarska M, Ligocka Z, Smalec B, Kalinin J, et al. Flavone and 3-hydroxyflavone supplementation in cryopreservation medium protects canine sperm against apoptosis and lipid peroxidation. Theriogenology. (2024) 226:319–27. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2024.06.025
171. Wang Y, Li J, Gu J, He W, Ma B, and Fan H. Hyperoside, a natural flavonoid compound, attenuates triptolide-induced testicular damage by activating the keap1-nrf2 and sirt1-pgc1α Signalling pathway. J Pharm Pharmacol. (2022) 74:985–95. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgac011
172. Zhang B, Su H, Ren XQ, Li WX, Ding Y, Zhang X, et al. Study on mechanism of cuscutae semen flavonoids in improving reproductive damage of tripterygium glycosides tablets in rats based on high-throughput transcriptome sequencing. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. (2019) 44:3478–85. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20190527.402
173. Soleimani V, Sahebkar A, and Hosseinzadeh H. Turmeric (Curcuma longa) and its major constituent (Curcumin) as nontoxic and safe substances: review. Phytother Res. (2018) 32:985–95. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6054
174. Duan H, Yang S, Yang S, Zeng J, Yan Z, Zhang L, et al. The mechanism of curcumin to protect mouse ovaries from oxidative damage by regulating ampk/mtor mediated autophagy. Phytomedicine. (2024) 128:155468. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155468
175. Yan Z, Dai Y, Fu H, Zheng Y, Bao D, Yin Y, et al. Curcumin exerts a protective effect against premature ovarian failure in mice. J Mol Endocrinol. (2018) 60:261–71. doi: 10.1530/jme-17-0214
176. Josifovska N, Albert R, Nagymihály R, Lytvynchuk L, Moe MC, Kaarniranta K, et al. Resveratrol as inducer of autophagy, pro-survival, and anti-inflammatory stimuli in cultured human rpe cells. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21(3):813. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030813
177. Hu B, Zheng X, and Zhang W. Resveratrol-βcd inhibited premature ovarian insufficiency progression by regulating granulosa cell autophagy. J Ovarian Res. (2024) 17:18. doi: 10.1186/s13048-024-01344-0
178. Soltabayeva A, Srivastava S, Kurmanbayeva A, Bekturova A, Fluhr R, and Sagi M. Early senescence in older leaves of low nitrate-grown atxdh1 uncovers a role for purine catabolism in N supply. Plant Physiol. (2018) 178:1027–44. doi: 10.1104/pp.18.00795
179. Zheng XK, Zhang BB, Zeng MN, Li M, Ke YY, Wu GC, et al. Estrogen-like effect of allantoin. Acta Pharm Sin. (2018) 53:68–73. doi: 10.16438/j.0513-4870.2017-0892
180. Wang X, Yuan P, Zeng M, Sun M, Wang X, Zheng X, et al. Allantoin derived from dioscorea opposita thunb ameliorates cyclophosphamide-induced premature ovarian failure in female rats by attenuating apoptosis, autophagy and pyroptosis. Cureus. (2023) 15:e50351. doi: 10.7759/cureus.50351
181. Biasizzo M and Kopitar-Jerala N. Interplay between nlrp3 inflammasome and autophagy. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:591803. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.591803
182. Levine B, Mizushima N, and Virgin HW. Autophagy in immunity and inflammation. Nature. (2011) 469:323–35. doi: 10.1038/nature09782
183. Peng J, Wang L, Wang M, Du R, Qin S, Jin CY, et al. Yeast synthetic biology for the production of lycium barbarum polysaccharides. Molecules. (2021) 26(6):1641. doi: 10.3390/molecules26061641
184. Zhu S, Li X, Dang B, Wu F, Wang C, and Lin C. Lycium barbarum polysaccharide protects hacat cells from pm2.5-induced apoptosis via inhibiting oxidative stress, er stress and autophagy. Redox Rep. (2022) 27:32–44. doi: 10.1080/13510002.2022.2036507
185. Gao YY, Li J, Huang J, Li WJ, and Yu Y. Effects of lycium barbarum polysaccharide on the photoinduced autophagy of retinal pigment epithelium cells. Int J Ophthalmol. (2022) 15:23–30. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2022.01.04
186. Xie W, Chen HG, Chen RH, Zhao C, Gong XJ, and Zhou X. Intervention effect of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on lead-induced kidney injury mice and its mechanism: A study based on the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. (2021) 319(Pt 2):117197. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117197
187. Xie W, Chen HG, Chen RH, Zhao C, Gong XJ, and Zhou X. Intervention effect of lycium barbarum polysaccharide on lead-induced kidney injury mice and its mechanism: A study based on the pi3k/akt/mtor signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. (2024) 319:117197. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117197
188. Liu B, Wang JL, Wang XM, Zhang C, Dai JG, Huang XM, et al. Reparative effects of lycium barbarum polysaccharide on mouse ovarian injuries induced by repeated superovulation. Theriogenology. (2020) 145:115–25. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2020.01.048
189. Jiang Y, Wang H, Yu X, and Ding Y. Lycium barbarum polysaccharides regulate ampk/sirt autophagy pathway to delay D-gal-induced premature ovarian failure. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. (2022) 47:6175–82. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20220614.701
190. Wang S, Liu W, Wang J, and Bai X. Curculigoside inhibits ferroptosis in ulcerative colitis through the induction of gpx4. Life Sci. (2020) 259:118356. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118356
191. Chan RY, Chen WF, Dong A, Guo D, and Wong MS. Estrogen-like activity of ginsenoside rg1 derived from panax notoginseng. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2002) 87:3691–5. doi: 10.1210/jcem.87.8.8717
192. Xu X, Qu Z, Qian H, Li Z, Sun X, Zhao X, et al. Ginsenoside rg1 ameliorates reproductive function injury in C57bl/6j mice induced by di-N-butyl-phthalate. Environ Toxicol. (2021) 36:789–99. doi: 10.1002/tox.23081
193. Gao QG, Zhou LP, Lee VH, Chan HY, Man CW, and Wong MS. Ginsenoside rg1 activates ligand-independent estrogenic effects via rapid estrogen receptor signaling pathway. J Ginseng Res. (2019) 43:527–38. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2018.03.004
194. He L, Ling L, Wei T, Wang Y, and Xiong Z. Ginsenoside rg1 improves fertility and reduces ovarian pathological damages in premature ovarian failure model of mice. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). (2017) 242:683–91. doi: 10.1177/1535370217693323
195. Loh XJ, Young DJ, Guo H, Tang L, Wu Y, Zhang G, et al. Pearl powder-an emerging material for biomedical applications: A review. Mater (Basel). (2021) 14(11):2797. doi: 10.3390/ma14112797
196. Yang HL, Korivi M, Lin MK, Chang HC, Wu CR, Lee MS, et al. Antihemolytic and antioxidant properties of pearl powder against 2,2’-azobis(2-amidinopropane) dihydrochloride-induced hemolysis and oxidative damage to erythrocyte membrane lipids and proteins. J Food Drug Anal. (2017) 25:898–907. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2016.10.007
197. Han S, Li H, Lu R, Feng J, Tang K, Li S, et al. Effect and mechanism of pearl on ovarian function of rats with premature ovarian failure induced by tripterygium glycosides. J Tradit Complement Med. (2023) 13:368–78. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2023.02.004
198. Weiss ML and Troyer DL. Stem cells in the umbilical cord. Stem Cell Rev. (2006) 2:155–62. doi: 10.1007/s12015-006-0022-y
199. Lin Z, Wu Y, Xu Y, Li G, Li Z, and Liu T. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in cancer therapy resistance: recent advances and therapeutic potential. Mol Cancer. (2022) 21:179. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01650-5
200. Fu YX, Ji J, Shan F, Li J, and Hu R. Human mesenchymal stem cell treatment of premature ovarian failure: new challenges and opportunities. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2021) 12:161. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02212-0
201. Umer A, Khan N, Greene DL, Habiba UE, Shamim S, and Khayam AU. The therapeutic potential of human umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of premature ovarian failure. Stem Cell Rev Rep. (2023) 19:651–66. doi: 10.1007/s12015-022-10493-y
202. Menshikov M, Zubkova E, Stafeev I, and Parfyonova Y. Autophagy, mesenchymal stem cell differentiation, and secretion. Biomedicines. (2021) 9(9):1178. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9091178
203. Chai M, Zhang CY, Chen S, and Xu DH. Application of autophagy in mesenchymal stem cells. World J Stem Cells. (2024) 16:990–1001. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i12.990
204. Ryter SW. Heme oxgenase-1, a cardinal modulator of regulated cell death and inflammation. Cells. (2021) 10(3):515. doi: 10.3390/cells10030515
205. Chen Y, Zhang J, Tian Y, Xu X, Wang B, Huang Z, et al. Iron accumulation in ovarian microenvironment damages the local redox balance and oocyte quality in aging mice. Redox Biol. (2024) 73:103195. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103195
206. Yin N, Wu C, Qiu J, Zhang Y, Bo L, Xu Y, et al. Protective properties of heme oxygenase-1 expressed in umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells help restore the ovarian function of premature ovarian failure mice through activating the jnk/bcl-2 signal pathway-regulated autophagy and upregulating the circulating of cd8(+)Cd28(-) T cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2020) 11:49. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1537-x
207. Yuan Y, Zhang X, Zhan Y, Tang S, Deng P, Wang Z, et al. Adipose-derived stromal/stem cells are verified to be potential seed candidates for bio-root regeneration in three-dimensional culture. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2022) 13:234. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02907-y
208. Dai W, Yang H, Xu B, He T, Liu L, Zhang Z, et al. 3d huc-msc spheroids exhibit superior resistance to autophagy and apoptosis of granulosa cells in pof rat model. Reproduction. (2024) 168(2):e230496. doi: 10.1530/rep-23-0496
209. Jiang B, Fu X, Yan L, Li S, Zhao D, Wang X, et al. Transplantation of human esc-derived mesenchymal stem cell spheroids ameliorates spontaneous osteoarthritis in rhesus macaques. Theranostics. (2019) 9:6587–600. doi: 10.7150/thno.35391
210. Yan L, Jiang B, Li E, Wang X, Ling Q, Zheng D, et al. Scalable generation of mesenchymal stem cells from human embryonic stem cells in 3d. Int J Biol Sci. (2018) 14:1196–210. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.25023
211. Jing H, He X, and Zheng J. Exosomes and regenerative medicine: state of the art and perspectives. Transl Res. (2018) 196:1–16. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2018.01.005
212. Dai W, Xu B, Ding L, Zhang Z, Yang H, He T, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate chemotherapy-induced premature ovarian insufficiency mouse model by suppressing ferritinophagy-mediated ferroptosis in granulosa cells. Free Radic Biol Med. (2024) 220:1–14. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.04.229
213. Miao H, Miao C, Li N, and Han J. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles harboring igf-1 improve ovarian function of mice with premature ovarian insufficiency through the nrf2/ho-1 pathway. J Ovarian Res. (2024) 17:224. doi: 10.1186/s13048-024-01536-8
214. Ren H, Su P, Zhao F, Zhang Q, Huang X, He C, et al. Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote skin wound healing in diabetic mice by regulating epidermal autophagy. Burns Trauma. (2024) 12:tkae001. doi: 10.1093/burnst/tkae001
215. Zhang B, Wang M, Gong A, Zhang X, Wu X, Zhu Y, et al. Hucmsc-exosome mediated-wnt4 signaling is required for cutaneous wound healing. Stem Cells. (2015) 33:2158–68. doi: 10.1002/stem.1771
216. Qu Q, Liu L, Wang L, Cui Y, Liu C, Jing X, et al. Exosomes derived from hypoxic mesenchymal stem cells restore ovarian function by enhancing angiogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2024) 15:496. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-04111-6
217. Kim J and Munster PN. Estrogens and breast cancer. Ann Oncol. (2024) 36(2):134–48. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2024.10.824
218. Elsaadany S, Josan A, Crowley R, and Gouldie M. A case report on endometriosis-associated intestinal tumour following hysterectomy: diagnostic challenges and implications for hormone replacement therapy (Hrt) guidelines. Cureus. (2024) 16:e74306. doi: 10.7759/cureus.74306
219. Lobo RA. hormone-replacement therapy: current thinking. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2017) 13:220–31. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2016.164
220. Tskhakaia I, Gonzalez Moret Y, Palmer AK, Lema D, Musri MC, Tsibadze N, et al. Contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy and associations with autoimmune conditions: exploring effects of estrogen analog supplementation. ACR Open Rheumatol. (2025) 7(1):e11774. doi: 10.1002/acr2.11774
221. Ding GJ, Jiang W, Lyu JQ, Ma J, Chen GC, Li FR, et al. Menopausal characteristics and hormone replacement therapy in relation to long-term risk of cholecystectomy in women. Front Med (Lausanne). (2024) 11:1446271. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1446271
222. Park SH, Choi PG, Kim HS, Lee E, Lee DH, Kim MJ, et al. A natural autophagy activator castanea crenata flower alleviates skeletal muscle ageing. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2025) 16:e13710. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13710
223. Zhang J, Jiang P, Wang S, Li M, Hao Z, Guan W, et al. Recent advances in the natural product analogues for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Bioorg Chem. (2024) 153:107819. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107819
224. Teh YM, Mualif SA, Mohd Noh NI, and Lim SK. The potential of naturally derived compounds for treating chronic kidney disease: A review of autophagy and cellular senescence. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 26(1):3. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010003
225. Luo P, Zhong Y, Yang X, Lai Q, Huang S, Zhang X, et al. Self-assembled water soluble and bone-targeting phosphorylated quercetin ameliorates postmenopausal osteoporosis in ovariectomy mice. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. (2025) 249:114495. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2025.114495
226. Zou YX, Kantapan J, Wang HL, Li JC, Su HW, Dai J, et al. Iron-quercetin complex enhances mesenchymal stem cell-mediated hgf secretion and C-met activation to ameliorate acute kidney injury through the prevention of tubular cell apoptosis. Regener Ther. (2025) 28:169–82. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2024.12.003
227. Aldali F, Deng C, Nie M, and Chen H. Advances in therapies using mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes for treatment of peripheral nerve injury: state of the art and future perspectives. Neural Regener Res. (2025) 20:3151–71. doi: 10.4103/nrr.Nrr-d-24-00235
228. Taher M, Jalali H, and Kouchesfehani HM. Small extracellular vesicles derived from nrf2-stimulated bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells ameliorated the testis damage and fertility disorder in doxorubicin-treated mice. Reprod Toxicol. (2025) 132:108847. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2025.108847
229. Li R, Wang H, Wang X, Yang Y, Zhong K, Zhang X, et al. Msc-evs and ucb-evs promote skin wound healing and spatial transcriptome analysis. Sci Rep. (2025) 15:4006. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-87592-6
230. Dias DA, Urban S, and Roessner U. A historical overview of natural products in drug discovery. Metabolites. (2012) 2(2):303–36. doi: 10.3390/metabo2020303
231. Mayer AM, Glaser KB, Cuevas C, Jacobs RS, Kem W, Little RD, et al. The odyssey of marine pharmaceuticals: A current pipeline perspective. Trends Pharmacol Sci. (2010) 31:255–65. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2010.02.005
232. Chin YW, Balunas MJ, Chai HB, and Kinghorn AD. Drug discovery from natural sources. AAPS J. (2006) 8:E239–53. doi: 10.1007/bf02854894
233. Kinkade CW, Rivera-Núñez Z, Gorcyzca L, Aleksunes LM, and Barrett ES. Impact of fusarium-derived mycoestrogens on female reproduction: A systematic review. Toxins (Basel). (2021) 13(6):373. doi: 10.3390/toxins13060373
234. Ghfar AA, El-Metwally MM, Shaaban M, Gabr SA, Gabr NS, Diab MSM, et al. Production of terretonin N and butyrolactone I by thermophilic aspergillus terreus tm8 promoted apoptosis and cell death in human prostate and ovarian cancer cells. Molecules. (2021) 26(9):2816. doi: 10.3390/molecules26092816
235. Cui T, Dai X, Guo H, Wang D, Huang B, Pu W, et al. Molybdenum and cadmium co-induce necroptosis through th1/th2 imbalance-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress in duck ovaries. J Environ Sci (China). (2024) 142:92–102. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2023.07.012
236. Liu WJ, Li LS, Lan MF, Shang JZ, Zhang JX, Xiong WJ, et al. Zinc deficiency deteriorates ovarian follicle development and function by inhibiting mitochondrial function. J Ovarian Res. (2024) 17:115. doi: 10.1186/s13048-024-01442-z
237. Zhao J, Dong L, Lin Z, Sui X, Wang Y, Li L, et al. Effects of Selenium Supplementation on Polycystic ovarian syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on Randomized Clinical Trials. BMC Endocr Disord. (2023) 23:33. doi: 10.1186/s12902-023-01286-6
238. Pan R, Wang R, Cheng F, Wang L, Cui Z, She J, et al. Endometrial stem cells alleviate cisplatin-induced ferroptosis of granulosa cells by regulating nrf2 expression. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. (2024) 22:41. doi: 10.1186/s12958-024-01208-8
239. Bahrehbar K, Rezazadeh Valojerdi M, Esfandiari F, Fathi R, Hassani SN, and Baharvand H. Human embryonic stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells improved premature ovarian failure. World J Stem Cells. (2020) 12:857–78. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i8.857
240. El-Derany MO, Said RS, and El-Demerdash E. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells reverse radiotherapy-induced premature ovarian failure: emphasis on signal integration of tgf-β, wnt/β-catenin and hippo pathways. Stem Cell Rev Rep. (2021) 17:1429–45. doi: 10.1007/s12015-021-10135-9
Keywords: premature ovarian insufficiency, autophagy, molecular mechanisms, nonhormonal therapy, natural products, stem cells
Citation: Yang X, Jia Z, Shi M, Li Y, Zhang G, Wang P, Sun X, Qi W and Guo Y (2025) Non-hormone replacement therapy to overcome premature ovarian insufficiency: advances in natural products and stem cells targeting autophagy. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1571021. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1571021
Received: 04 February 2025; Accepted: 07 May 2025;
Published: 30 May 2025.
Edited by:
Michio Kitajima, Takagi Hospital, JapanReviewed by:
Mosammat Rashida Begum, Infertility Care and Research Center, Dhaka, BangladeshQingchao Qiu, United States Department of Veterans Affairs, United States
Copyright © 2025 Yang, Jia, Shi, Li, Zhang, Wang, Sun, Qi and Guo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ying Guo, NzEwMDA5MTZAc2R1dGNtLmVkdS5jbg==
 Xinxin Yang
Xinxin Yang Zhicheng Jia
Zhicheng Jia Mengyu Shi
Mengyu Shi Yongqian Li
Yongqian Li Guangheng Zhang
Guangheng Zhang Peixuan Wang
Peixuan Wang Xinwei Sun
Xinwei Sun Wenlong Qi
Wenlong Qi Ying Guo
Ying Guo