- 1Department of Pharmacy, Central Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan Central Hospital, Jinan, Shandong, China
- 2Department of Endocrinology, Central Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan Central Hospital, Jinan, Shandong, China
Objective: To develop a predictive model to quantify the possibility of special-grade antimicrobial agents (SGAs) usage in patients with diabetes foot infections (DFIs), providing reference and guidance for clinical practice.
Methods: This is a cross-sectional study of 328 type 2 diabetes patients with DFIs. General clinical characteristics and biochemical indicators were extracted from the Hospital Information System (HIS) of Jinan Central Hospital in Shandong Province, China. Logistic regression analysis was performed to select predictors, and the nomogram was established based on selected viables visually. Then, the receive operating characteristic (ROC) curve, the calibration curve and the decision curve analysis (DCA) were used to evaluate the performance of this prediction model.
Results: 5 predictors were selected by univariate analysis from 21 variables, including duration of hospitalization, Neutrophil, DBIL, ALB and Wagner grade. The multivariate logical regression analysis illustrated that these 5 factors were independent risk factors for SGAs usage in patients with DFIs. The nomogram model developed by these 5 risk predictors exhibited good prediction ability, as shown by the area under curve (AUC) of ROC curve was 0.884 in the training set and 0.825 in the validation set. Calibration curve showed a good calibration degree of the predictive nomogram model. Moreover, DCA curve showed that the nomogram exhibited greater clinical application values when the risk threshold was between 3% and 63%.
Conclusion: Our novel nomogram model showed that duration of hospitalization, Neutrophil, DBIL, ALB and Wagner grade were the independent risk factors of SGAs usage in patients with DFIs. This prediction model behaved a great accurate value and provide reference of SGAs usage in clinic. Further validations are still needed to evaluate and improve the performance of this model.
1 Introduction
As a common epidemic metabolic disease in the 21st century, the prevalence of diabetes is exploding all over the world. According to statistics, more than 550 million people have diabetes worldwide (1). It is estimated that 783.2 million people will have diabetes in 2045 (2). Diabetic foot (DF) is one of the most serious and devastating complications in diabetic patients. Currently, approximately 20 million patients with diabetes suffer from foot ulcer annually (3), which has become one of the leading cause of disability. Moreover, about 50% of diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) become infected (4), and it can lead to amputation and even death without appropriate care. Thus, the management of DFIs is extremely important for improving the outcomes of diabetes patients.
Multiple interventions are typically used to heal DFIs, such as management of infection. Antimicrobial agents treatment is one of main strategy to deal with all kinds of infections, including DFIs. However, the overuse and misuse of antimicrobial agents in the past decades contributes to the emergence of resistant microbials (5–7). To ensure the rational use and avoid the misuse of antimicrobial agents, China formally implemented a decree for the clinical use of antimicrobial agent in 2012. According to this decree, antimicrobial agents were classified as non-restricted, restricted and special-grade (8). It’s noteworthy that the SGAs, with strongest antimicrobial activity, has the strictest rules for prescription and use. However, it’s unclear what state of the patients should be administrated with the SGAs in clinic. And there is no predictive model to estimate the use of SGAs.
Considering these challenges, our study tended to develop a predictive model to quantify the possibility of SGAs usage in patients with DFIs. From this point of view, we hope to provide reference and guidance for the prescription and use of SGAs in DFIs patients clinically.
2 Methods
2.1 Study participants
This study was a cross-sectional study. 328 type 2 diabetes patients with DFIs (hospitalized in Jinan Central Hospital from January 2017 to December 2022) were included in this study. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) all participating patients were confirmed diagnosis of DFIs declared by WHO in 1990. (2) all patients were at least 18 years old. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) patients with other infections except diabetes foot, (2) patients with severe organic disease, such as malignant tumor, etc. (3) patients with serious lack of clinical data.
2.2 Data collection
We collected the clinical data of all patients from the HIS of Jinan Central Hospital, including general information, disease information and the blood biochemical indicator examination results. General information included sex, age, duration of hospitalization, course of diabetes, smoking history, drinking history, cardiovascular history (hypertension, cardiopathy, coronary heart disease, etc.). Blood biochemical indicators examination included γ-glutamyl transferase (GGT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), creatinine (Crea), hemoglobin A1C (HbA1C), total bile acids (TBA), total bilirubin (TBIL), indirect bilirubin (IBIL), direct bilirubin (DBIL), albumin (ALB), urea (Urea). In addition, neutrophil counts (Neutrophil) and platelet (PLT) derived from peripheral blood samples were collected. The severity of DFUs was evaluated according to Wagner classification (9) (grade 0-5). The Wagner system was assessed based on the following grades: 0, pre- or post-ulcerative lesion; 1, partial or full-thickness ulcer; 2, probing to tendon or capsule; 3, deep with osteitis; 4, partial foot gangrene; 5, whole foot gangrene (9, 10).
2.3 Statistical analysis
To explore the influence factors of usage of SGAs, we divided the 328 patients into regular-grade antimicrobials agents (including non-restricted and restricted antimicrobial agents) (RGAs) group and SGAs group. The grade of all kinds of antimicrobial agents is referred to the Shandong Province Classification Management Catalogue for Clinical Application of Antibiotics (2021) in China (11). Then 328 patients were randomly divided into a training cohort and a validation cohort conformed to a ratio of 7:3 for random split validation. Data normality was analyzed by Kolmogorov-Sminov test. Continuous variables were expressed as median ± standard deviation (SD) and tested by t-test. The categorical variables were described as number (percentage) and analyzed by chi-squared test.
Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis were used to identify the influence factors for usage of SGAs in patients with DFIs. Odds ratios (ORs) were calculated with the 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs). P < 0.05 (two-sided) was considered as significant. According to the independent influence factors for usage of SGAs in patients with diabetic mellitus foot, we developed a nomogram prediction model. In addition, several validation methods were performed to evaluate the accuracy of the nomogram prediction model based on the data sets of training cohort and the validation cohort, respectively. AUC of ROC curve was employed to estimate the performance of the model. The calibration curve and the DCA was used to assess the calibration performance and clinical practicability of the prediction model, respectively. All statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics 26.0 and R software (version 3.6.1).
2.4 The list of SGAs and RGAs
The SGAs mainly include lenampicillin, sulbactam, cefepime, ceftazidime and avibactam, meropenem, imipenem and cilastatin, biapenem, ertapenem, aztreonam, flomoxef, tigecycline, sitafloxacin, vancomycin, norvancomycin, teicoplanin, ploymyxin B, polymyxin E, fusidic acid, linezolid, daptomycin, amphotericin B, voriconazole (for injection), itraconazole (for injection), caspofungin and micafungin.
The RGAs mainly include penicillin, amoxicillin, ampicillin, piperacillin, mezlocillin, azlocillin, oxacillin, cloxacillin, flucloxacillin, amoxicillin and clavulanate, ampicillin and sulbactam, mezlocillin and sulbactam, piperacillin and tazobactam, ticarcillin and potassium, cephalosporins (generation 1-4) except cefepime, cefoperazone and sulbactam, cephamicins, latamoxef, faropenem (oral agent), sulphonamides, trimethoprim, macrolides, lincosamides, aminoglycosides, tetracyclines except tigecycline, chloramphenicol, quinolones except sitafloxacin, colistin, nitroimidazole derivatives, nitrofuran derivatives, fosfomycin, rifampicin, rifaximin, rifamycin, fluconazole, nystatin, voriconazole (oral agent), itraconazole (oral agent), flucytosine, posaconazole (oral agent), terbinafine.
3 Results
3.1 Participant characteristics of the study cohort
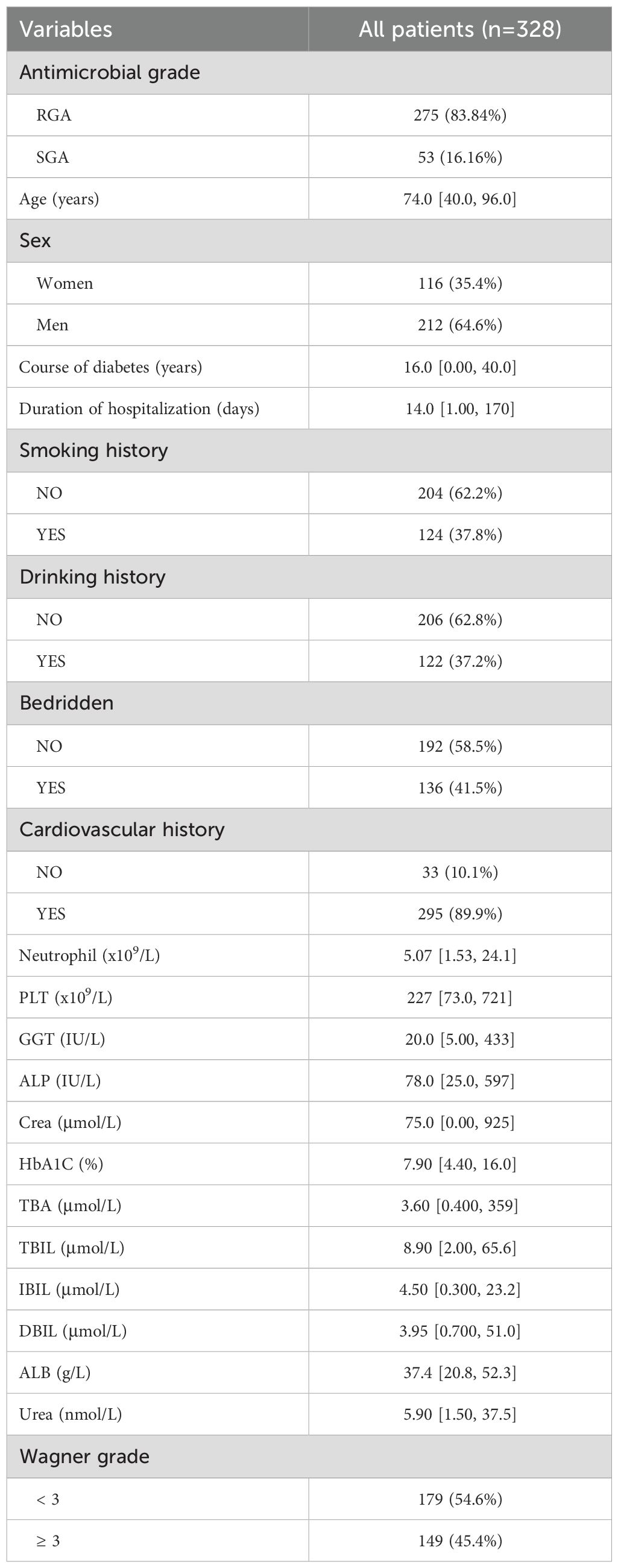
Of the 328 participants enrolled in this study, with a median age of 74.0 years (40.0-96.0), of whom 116 (35.4%) were women and 212 (64.6%) were men. Of these 328 patients, 53 (16.16%) were administrated with the SGA, and 275 (83.84%) were administrated with the RGA. The median course of diabetes was 16.0 years.
The basic characteristics of all patients were shown in Table 1. Among these patients, 124 had a history of smoking, 122 had a history of drinking and 295 had cardiovascular history. The median Neutrophil was 5.07 x 109/L, and the median ALB was 37.4 g/L. There was 179 patients whose Wagner grade less than 3, and 149 not. The clinicopathologic characteristics were shown in Table 1.
3.2 Logistic regression variable screening results
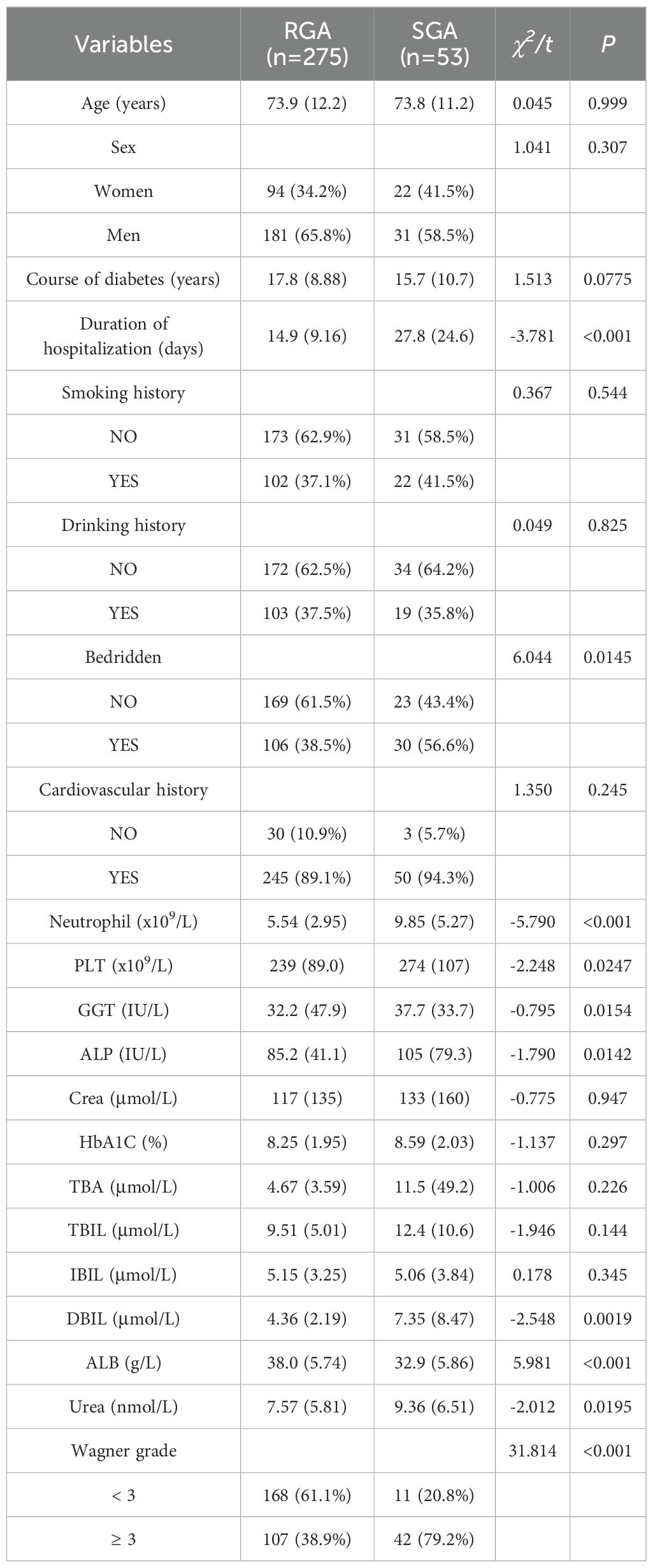
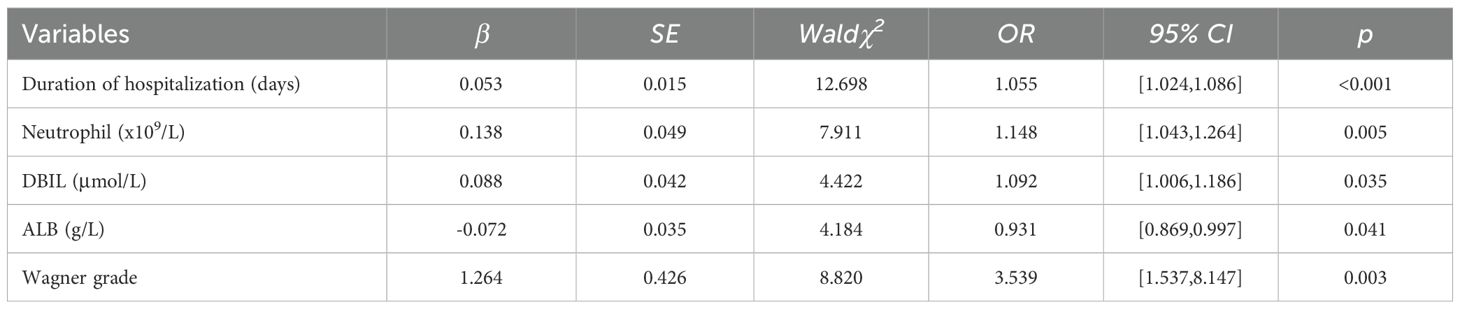
All patients were divided into RGA group and SGA group based on the usage of antimicrobials. The results of univariate analysis presented significant differences in duration of hospitalization, bedridden, Neutrophil, PLT, GGT, ALP, DBIL, ALB, Urea, and Wagner grade (Table 2). Given the bedridden, PLT, GGT, ALP and Urea weren’t highly significant between RGA group and SGA group (P > 0.01), we exclude them and put the other highly significant parameters into multivariate logistic regression analysis (Table 3). The results represented that among our patients with T2DM, duration of hospitalization, Neutrophil, DBIL, ALB and Wagner grade were independent risk factors for SGAs usage.
3.3 Nomogram prediction model construction and validation
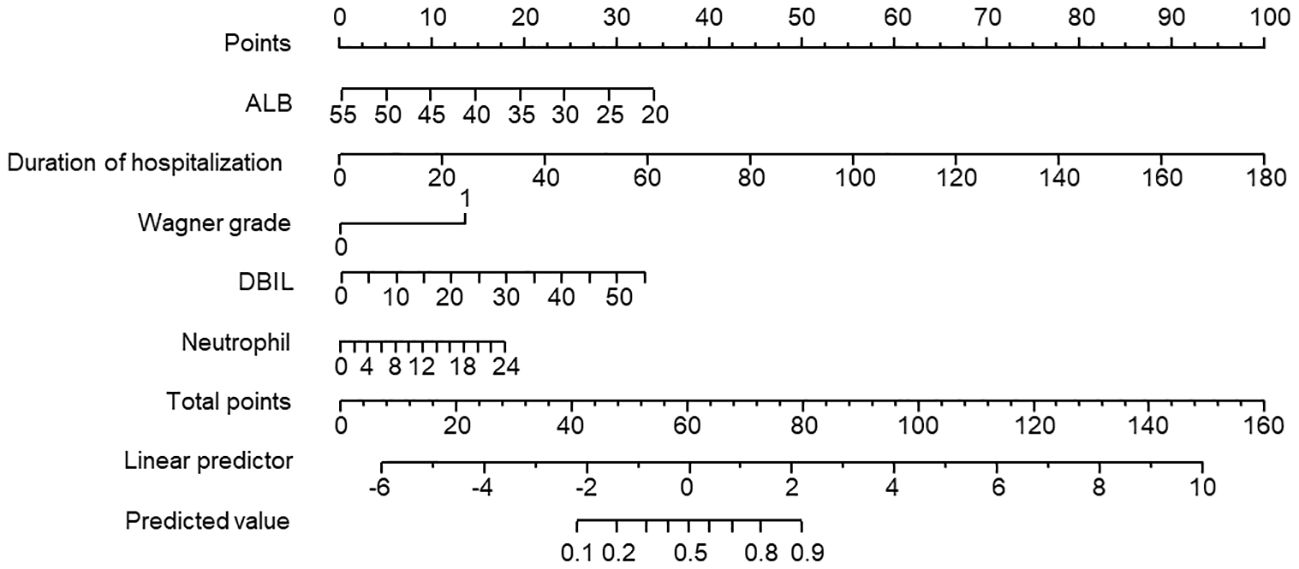
The 5 prediction variables obtained from the logistic regression analysis were incorporated to generate the nomogram prediction model, as shown in Figure 1. The individual variable was projected to obtain the corresponding score and the total score added by all individual scores of each factor was calculated. Then the risk probability could be predicted based on the total score by a vertical line across the total score point line.
The ROC curve was conducted to assess the discriminatory capacity of the nomogram model. The AUC of the prediction model was 0.884 in the training set and 0.825 in the validation set, indicating the good accuracy (Figure 2).
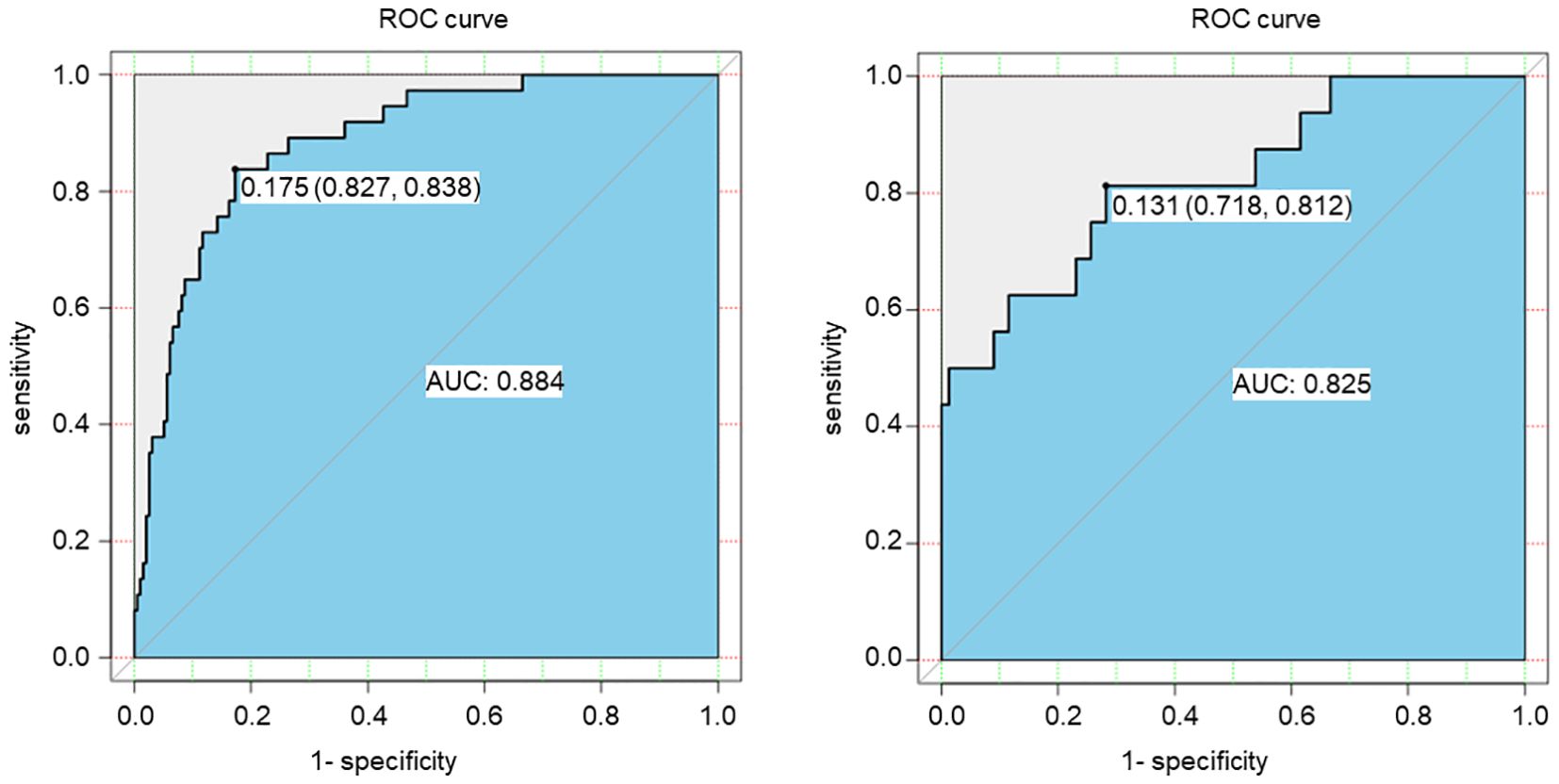
Figure 2. ROC curve of the risk prediction model for SGAs usage in patients with DF based on the training set (left) and the validation set (right).
The calibration curve was conducted to calibration the SGAs usage nomogram model. The calibration curve of the nomogram showed good mostly agreement (Figure 3), indicating good calibration degree of the predictive model.
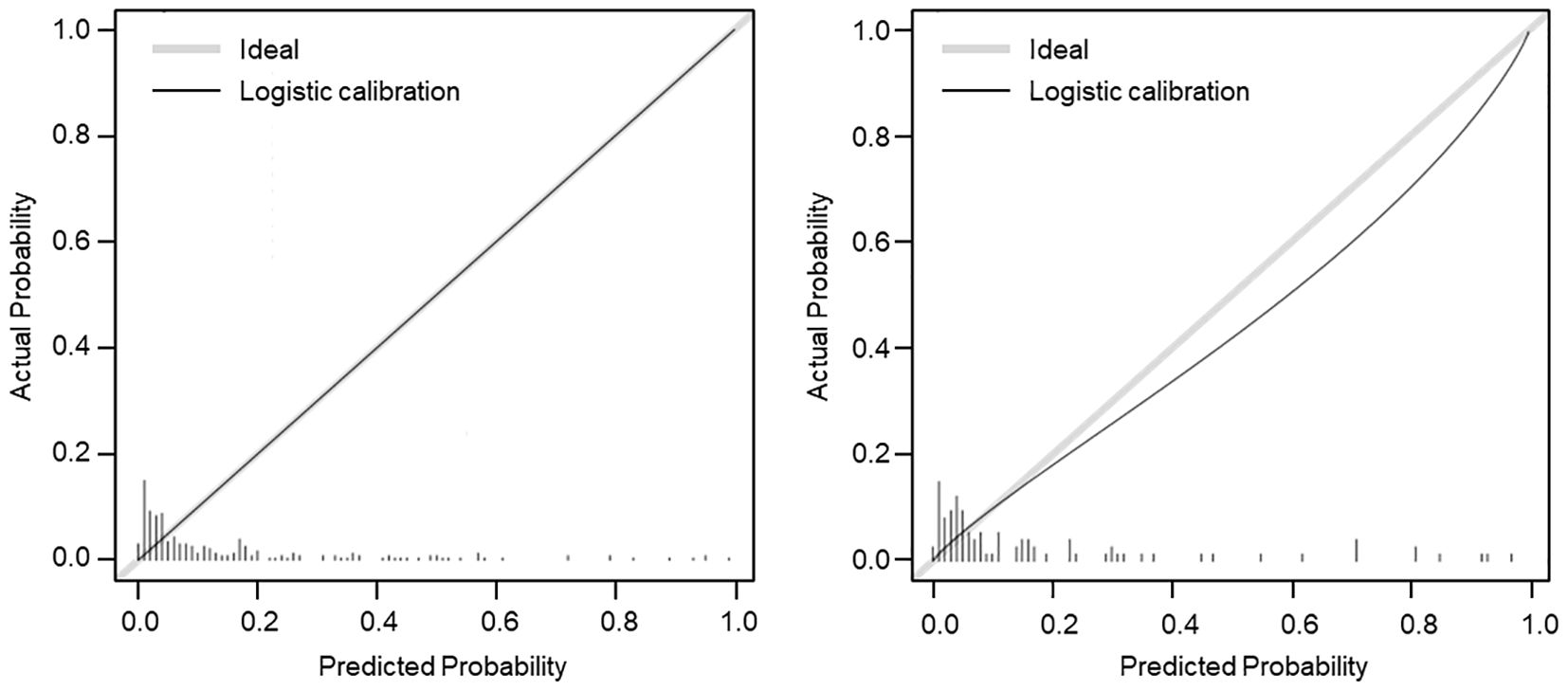
Figure 3. Calibration curve (β = 1000 repetitions, boot) of the SGAs usage risk nomogram. The x-axis represents the predicted probability of SGAs usage, and the y-axis represents the actual probability of SGAs usage. The gray dashed line represented the ideal curve, and the black line of the training set (left) and validation set (right) represented the predictive performance of SGAs usage nomogram. The closer the black line is to the gray dashed line, the better predictive accuracy of the nomogram model.
Moreover, decision curve analysis (DCA) was further applied to validate the clinical benefits of the prediction model. The nomogram showed greater clinical application values when the risk threshold was between 3% and 63% (Figure 4), further demonstrating the good predictive and accuracy values of the model.
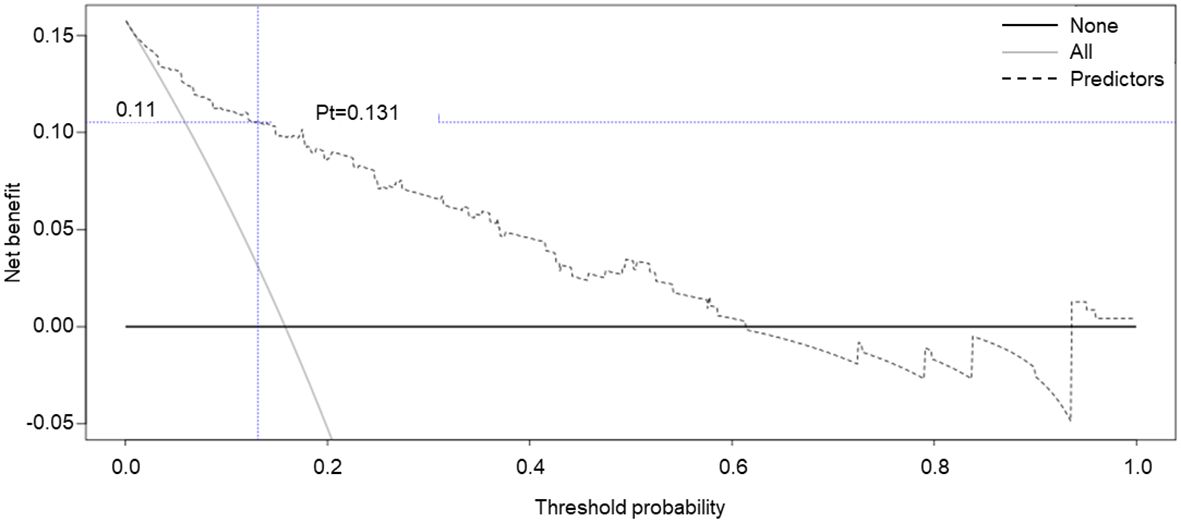
Figure 4. Decision curve analysis for the SGAs usage risk nomogram. The y-axis represents the net benefit.
4 Discussion
As one of the most common complications of diabetes, DFUs is associated with impaired physical function and reduced quality of life (12, 13). If untreated, DFUs can progress to DFIs (14), which is significantly more likely to increased morbidity and cause death of patients with diabetes. DFIs are usually polymicrobial, and many microbials show resistance profiles to conventional antimicrobials resulted from the overuse and misuse of antimicrobial agents in the past decades. Given the abovementioned reasons, SGAs, such as Meropenem, are increasingly used for treatment of DFIs. But in clinic, physicians and pharmacists are unclear the condition to use the SGAs. Also, relevant research that can predict the possibility of SGAs usage in patients with DFI have rarely been conducted.
To do this, in this study, we analyzed the differences between patients with DFIs administrated with RGAs and SGAs. Through the risk factor analysis, duration of hospitalization, Neutrophil, DBIL, ALB and Wagner grade were the independent factors for SGAs usage in patients with DFIs. Based on that, we developed a predictive model for the usage of SGAs in patients with DFIs using these five available variables. This predictive model suggested that longer duration of hospitalization, higher neutrophil, higher DBIL, lower ALB and higher Wagner grade were the key individual factors determining the risk of SGAs usage in patients with DFIs.
Infection is a most common cause of antimicrobial agents usage. Once infected, numerous immune cells are rapidly recruited to the infected sites to recognize and eliminate microbial pathogens. Among these immune cells, neutrophil plays a decisive role. At the onset of infection, neutrophil quickly migrates to the site of infection and destroy microorganisms by phagocytosis, release anti-microbial contents and promotion the recruitment of other immune cell. Therefore, neutrophil is associated with many kinds of infections. As reported in the previous study, neutrophil was a independent risk factor for sepsis in patients with urinary tract infection (15). It is also reported that absolute neutrophil count was a predictor of multidrug-resistant bacteria infection in the patients with biliary tract infection (16). Moreover, Yan et al. also observed that percentage of neutrophils was the risk factor of multidrug-resistant organisms in patients with diabetic foot infection. Here, we found that neutrophil was a risk factor of SGAs usage in patients with DFIs. Antimicrobials agents were usually used for the treatment of infections and multidrug-resistance is a common cause for the usage of SGAs. Thus, our finding also confirmed a close relationship between neutrophils and infection in diabetes patient population.
Albumin is abundant in blood and serum albumin level is a prognostic marker for complications in bacteria and fungal infections (17). Albumin could offer protection microcirculation and tissues from inflammation processes induced by infections (17). It has reported that reduced albumin is a risk factor for bacteria infection of patients carrying non-healing wounds (18). Consistently, Our study showed albumin was a risk factor for SGAs usage in patients with DFIs, which usually accompanied by bacteria or fungal infections.
Total bilirubin (TBIL) is composed of IBIL and DBIL. Serum IBIL is converted to DBIL by hepatic enzyme UDP-glucurony transferase 1A1 in liver. All the TBIL, IBIL and DBIL are traditional liver function index. However, many research has suggested that they have different clinical implications. Several trials have suggested that DBIL is more important than TBIL and IBIL for metabolic syndrome and stroke (19, 20). Notably, a study by Wang et al. found that elevated serum DBIL, not TBIL or IBIL, was associated with the increased risk of T2D (21). Moreover, it has reported that DBIL is associated with insulin resistance risk (22). Here, our study showed that DBIL was a risk factor of SGAs usage in patients with DFIs. Based on the above research, we speculate that higher DBIL may lead to the SGAs usage for DFIs by affecting blood glucose and insulin resistance. Certainly, research including more samples is needed to confirm this association.
Wagner’s classification, used for assess for ulcer depth, osteomyelitis and gangrene, is the most widely accepted grading system for evaluating lesions of diabetes foot (9, 10). A retrospective study reported that Wagner system is a good predictor of lower extremity amputation and in patients with DF (9). A meta-analysis also showed that Wagner grade (≥3) is a risk factor for recurrence of DFU in patients with DF (23). Here, we found that Wagner grade is a risk factor for the SGAs usage in patients with DFIs, further confirming a close relationship between Wagner grade and severity of foot lesions of diabetes patients.
Our study also has several limitations. Firstly, the model was constructed through data collection from HIS, which may result in selection bias due to potential confounders and exclusion of patients with serious lack of clinical data. Secondly, further multi-center research and external validation should be performed to improve the generalizability and clinical applicability.
5 Conclusion
In conclusion, after evaluating multiple variables, we demonstrated that duration of hospitalization, Neutrophil, DBIL, ALB and Wagner grade were the independent risk factors of SGAs usage in patients with DFIs. Based on that, we established a novel nomogram predictive model of the SGAs in patients with DFIs. This predictive model has good performance, exhibiting great accurate value and discrimination. Furthermore, we will actively explore the cooperation with the endocrinologists, infectious disease specialists and other relevant experts, focusing on integrating our nomogram model into existing clinical judgment, so as to provide reference and guidance for the usage of SGAs in DFIs patients clinically.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Jinan Central Hospital Affiliated by Shandong First Medical University (20241010005). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because This study was a retrospective cross-sectional study.
Author contributions
QW: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. HM: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software. QJ: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. LG: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Health Commission of Shandong Province (2017WS774) and Health Commission of Jinan (2022-BD-01).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Armstrong DG, Tan TW, Boulton AJM, and Bus SA. Diabetic foot ulcers: A review. JAMA. (2023) 330:62–75. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.10578
2. Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M, Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2022) 183:109119. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119
3. Bus SA, Armstrong DG, Crews RT, Gooday C, Jarl G, Kirketerp-Moller K, et al. Guidelines on offloading foot ulcers in persons with diabetes (IWGDF 2023 update). Diabetes Metab Res Rev. (2024) 40:e3647. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3647
4. Senneville É, Albalawi Z, Van Asten SA, Abbas ZG, Allison G, Aragón-Sánchez J, et al. IWGDF/IDSA guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes-related foot infections (IWGDF/IDSA 2023). Diabetes Metab Res Rev. (2024) 40:e3687. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3687
5. Bassetti S, Tschudin-Sutter S, Egli A, and Osthoff M. Optimizing antibiotic therapies to reduce the risk of bacterial resistance. Eur J Intern Med. (2022) 99:7–12. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2022.01.029
6. Santacroce L, Di Domenico M, Montagnani M, and Jirillo E. Antibiotic resistance and microbiota response. Curr Pharm Des. (2023) 29:356–64. doi: 10.2174/1381612829666221219093450
7. Nanayakkara AK, Boucher HW, Fowler VG Jr., Jezek A, Outterson K, and Greenberg DE. Antibiotic resistance in the patient with cancer: Escalating challenges and paths forward. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:488–504. doi: 10.3322/caac.21697
8. Xiao Y and Li L. Legislation of clinical antibiotic use in China. Lancet Infect Dis. (2013) 13:189–91. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70011-2
9. Jeon BJ, Choi HJ, Kang JS, Tak MS, and Park ES. Comparison of five systems of classification of diabetic foot ulcers and predictive factors for amputation. Int Wound J. (2017) 14:537–45. doi: 10.1111/iwj.12642
10. Wagner FW Jr. The dysvascular foot: a system for diagnosis and treatment. Foot Ankle. (1981) 2:64–122. doi: 10.1177/107110078100200202
11. Health Commission of Shandong Province in China. Notice on issuing the shandong province classification management catalogue for clinical application of antibiotics. Shandong Government (2021). Available online at: http://www.shandong.gov.cn/art/2021/4/30/art_100619_38303.html (Accessed November 1, 2024).
12. Armstrong DG, Boulton AJM, and Bus SA. Diabetic foot ulcers and their recurrence. N Engl J Med. (2017) 376:2367–75. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1615439
13. Petersen BJ, Linde-Zwirble WT, Tan TW, Rothenberg GM, Salgado SJ, Bloom JD, et al. Higher rates of all-cause mortality and resource utilization during episodes-of-care for diabetic foot ulceration. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2022) 184:109182. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109182
14. Ndosi M, Wright-Hughes A, Brown S, Backhouse M, Lipsky BA, Bhogal M, et al. Prognosis of the infected diabetic foot ulcer: a 12-month prospective observational study. Diabetes Med. (2018) 35:78–88. doi: 10.1111/dme.13537
15. Zhang L, Zhang F, Xu F, Wang Z, Ren Y, Han D, et al. Construction and evaluation of a sepsis risk prediction model for urinary tract infection. Front Med (Lausanne). (2021) 8:671184. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.671184
16. Hu Y, Lin K, Lin K, Lin H, Chen R, Li S, et al. Developing a risk prediction model for multidrug-resistant bacterial infection in patients with biliary tract infection. Saudi J Gastroenterol. (2020) 26:326–36. doi: 10.4103/sjg.SJG_128_20
17. Wiedermann CJ. Hypoalbuminemia as surrogate and culprit of infections. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:4496. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094496
18. Liu J, He Q, Guo G, and Zhai C. Analysis of risk factors related to chronic non-healing wound infection and the construction of a clinical prediction model. Exp Dermatol. (2024) 33:e15102. doi: 10.1111/exd.15102
19. Pineda S, Bang OY, Saver JL, Starkman S, Yun SW, Liebeskind DS, et al. Association of serum bilirubin with ischemic stroke outcomes. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. (2008) 17:147–52. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2008.01.009
20. Jo J, Yun JE, Lee H, Kimm H, and Jee SH. Total, direct, and indirect serum bilirubin concentrations and metabolic syndrome among the Korean population. Endocrine. (2011) 39:182–9. doi: 10.1007/s12020-010-9417-2
21. Wang J, Li Y, Han X, Hu H, Wang F, Li X, et al. Serum bilirubin levels and risk of type 2 diabetes: results from two independent cohorts in middle-aged and elderly Chinese. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:41338. doi: 10.1038/srep41338
22. Sharma K, Zajc I, and Ziberna L. Dietary vitamin D equilibrium in serum ameliorates direct bilirubin associated diabetes mellitus. Chem Biol Interact. (2021) 337:109399. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2021.109399
Keywords: diabetes foot infections, special-grade antimicrobial agents, Wagner grade, multivariate logical regression analysis, nomogram model
Citation: Wang Q, Ma H, Jiang Q and Guo L (2025) Development of predictive nomogram for clinical use of special-grade antimicrobial agents in patients with diabetes foot infections. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1578767. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1578767
Received: 18 February 2025; Accepted: 23 July 2025;
Published: 12 August 2025.
Edited by:
Wael Abdel Halim Hegazy, Zagazig University, EgyptReviewed by:
Michael Edwin Edmonds, King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, United KingdomEnny Suswati, University of Jember, Indonesia
Elly Sakinah, University of Jember, Indonesia
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Ma, Jiang and Guo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lubo Guo, MTMzNzA1ODI3OTlAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Qian Wang1
Qian Wang1 Hui Ma
Hui Ma Lubo Guo
Lubo Guo