- Department of Emergency, Jinhua Municipal Central Hospital, Jinhua, China
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a common inflammatory condition of the pancreas that is often associated with metabolic disturbances resulting from pancreatic injury. This review examines the intricate relationship between metabolic abnormalities, such as changes in lipid and glucose metabolism, and the pathophysiology of AP. While these metabolic disturbances do not directly cause AP, they can significantly worsen the progression and severity of the disease. For instance, hypertriglyceridemia can increase pancreatic necrosis through mechanisms like lipotoxicity and oxidative stress. Similarly, disorders in glucose metabolism can further damage pancreatic cells by heightening inflammatory responses and oxidative stress. Additionally, we investigate novel metabolic interventions, including lipase inhibitors, insulin therapy, and antioxidants, designed to address these metabolic disturbances and reduce the severity of the disease. Understanding how metabolic disturbances contribute to the progression of AP is crucial for developing effective therapeutic strategies and improving patient outcomes.
1 Introduction
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a common acute abdominal disorder characterized by inflammation within the pancreas. Various factors, including gallstones, excessive alcohol consumption, certain medications, and infections, can trigger this condition. Epidemiological data show a gradual increase in the incidence of AP over recent years (1). Globally, the annual incidence of AP is estimated to range from 34 to 80 cases per 100,000 individuals (2). The epidemiological landscape of AP is changing significantly, largely due to socioeconomic development and the increasing prevalence of Westernized dietary patterns. The widespread adoption of high-fat diets and rising obesity rates are key drivers of the growing incidence of AP (3). Notably, in regions characterized by a high prevalence of obesity and diabetes, the incidence of AP is even higher, emphasizing the complex relationship between lifestyle factors and disease occurrence (4). The pathogenesis of AP involves the activation of proteolytic enzymes within pancreatic cells, leading to autodigestion of pancreatic tissue and localized injury (5). As inflammation progresses, immune cells are recruited and activated, and inflammatory cytokines are released, which further increase pancreatic injury and contribute to the development of necrosis. In recent years, the role of metabolic disturbances in AP has gained attention. As both an endocrine and exocrine organ, the pancreas plays a crucial role in metabolic processes that affect its function and modulate the inflammatory response during AP.
Metabolic dysregulation, such as disorders in lipid metabolism, glucose metabolism abnormalities, and issues with amino acid metabolism, exacerbates pancreatic injury and inflammatory responses. For instance, the presence of hyperglycemia and insulin resistance (IR) negatively impacts pancreatic cell function and worsens the clinical outcomes of AP by modulating immune responses, promoting the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and inducing apoptosis (6). Moreover, reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated by oxidative stress play a crucial role in mediating the inflammatory cascade (7), while an abnormal accumulation of fatty acids is linked to cellular injury and tissue necrosis (8).
This review aims to explore the mechanisms behind metabolic alterations in AP, focusing on how metabolic dysregulation contributes to the disease’s pathogenesis and evaluating existing metabolic intervention strategies. Metabolic disturbances significantly impair pancreatic function and alter the cellular microenvironment, leading to enhanced inflammatory responses and disease progression in AP. Understanding how metabolic dysregulation impacts AP is crucial, as it provides insight into the disease’s pathogenesis and opens up potential new avenues for clinical management.
2 The underlying pathological mechanisms of AP
2.1 The early-phase response in AP
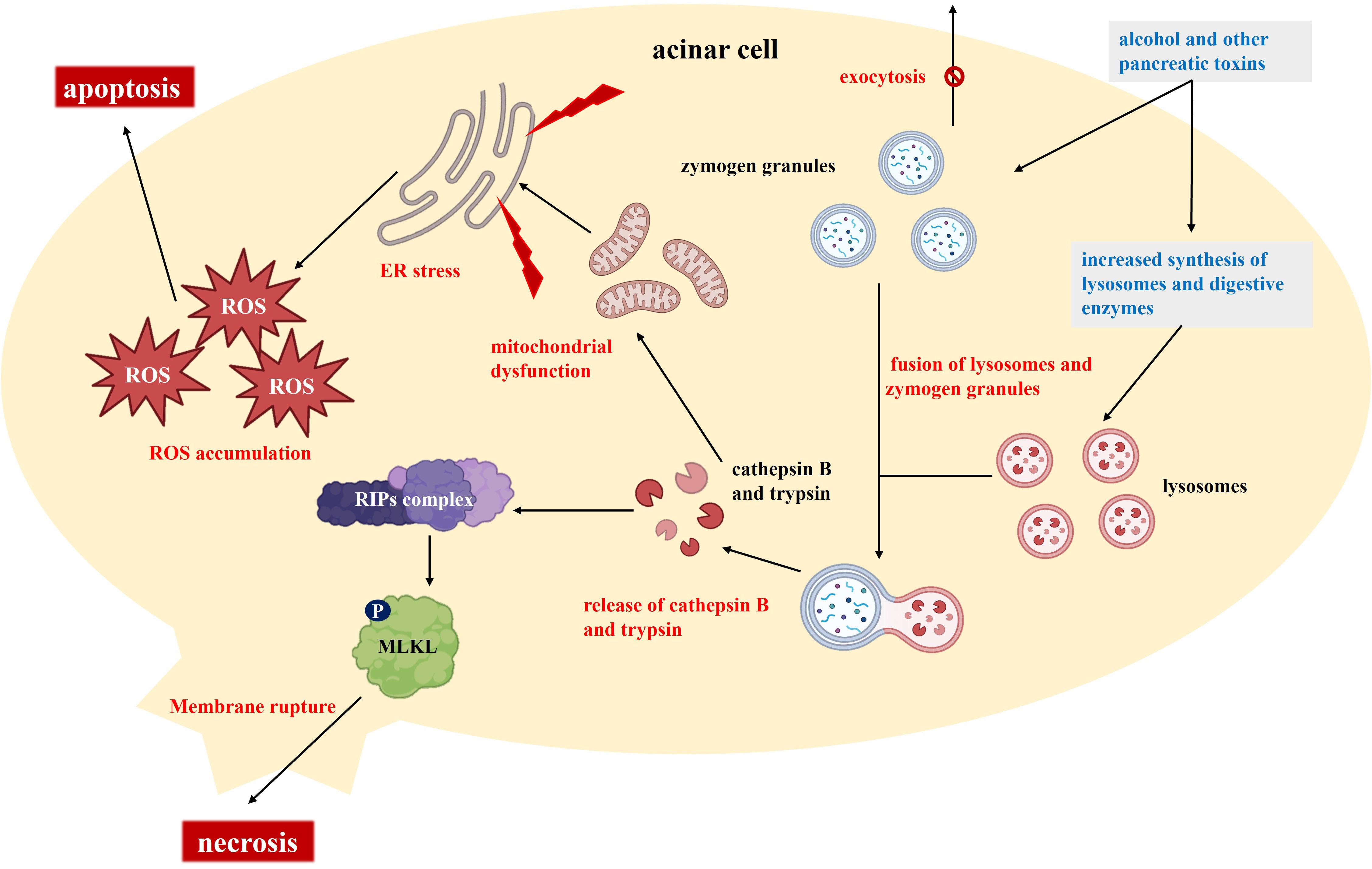
The initial response in AP typically begins with acinar cell injury (Figure 1). In acinar cells, substances like alcohol induce microtubule dysfunction, promote the synthesis of lysosomes and digestive enzymes, and disrupt the exocytosis of trypsinogen granules (9). This process results in the accumulation of enzyme granules within the cells and the fusion of lysosomes with these granules. Cathepsin B, located in lysosomes, co-localizes with trypsinogen, and both cathepsin B and activated trypsin are released into the cytoplasm (10). The release of these proteases has dual effects: it activates receptor-interacting protein kinases (RIPs) and mixed lineage kinase domain-like (MLKL), leading to cell membrane rupture and necrosis, while also causing mitochondrial dysfunction, activating endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, and promoting ROS accumulation (11, 12). Following acinar cell injury, extensive release of proteolytic enzymes occurs, resulting in local tissue autodigestion and necrosis while also initiating inflammatory responses. The activation of additional digestive enzymes and subsequent local cell damage further promote the release of inflammatory mediators, such as cytokines and chemokines, which increase macrophage infiltration and intensify the inflammatory response (13). In this process, oxidative stress and ER stress also contribute to cell death and the expansion of the inflammatory response.
2.2 Clinical presentations of AP
The clinical manifestations of AP can be classified into two categories based on the disease severity: mild and severe. Mild acute pancreatitis (MAP): Patients with MAP typically present with relatively mild symptoms, including persistent upper abdominal pain and associated gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea and vomiting. The majority of patients with MAP can achieve rapid clinical improvement following early supportive care, which commonly includes fluid resuscitation, analgesia, and fasting (14). Severe acute pancreatitis (SAP): In contrast, SAP is frequently complicated by life-threatening conditions such as pancreatic necrosis, multi-organ dysfunction syndrome, and infection. Clinically, it is characterized by severe upper abdominal pain, fever, tachypnea, tachycardia, and even shock (15). The clinical course of SAP is often rapidly progressive, with a significantly higher mortality rate, particularly when complications arise. Owing to the heterogeneous and nonspecific nature of the early symptoms of AP, prompt diagnosis and intervention are essential for optimizing outcomes.
3 Metabolic disturbances in AP
AP is a complex disease characterized by a multifaceted interplay of pancreatic cell injury, enzyme activation, localized inflammatory responses, and systemic metabolic disturbances. The initial inflammatory cascade, triggered by pancreatic injury, is sustained through the activation of digestive enzymes and the subsequent release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. This process can potentially lead to pancreatic necrosis and multi-organ dysfunction syndrome. Furthermore, metabolic disturbances, particularly the dysregulation of glucose and lipid metabolism, play critical roles in the pathogenesis and progression of AP. In this section, we explored the intricate relationships between metabolic disturbances, pancreatic injury, and inflammatory responses, as well as their implications for early diagnosis and therapeutic interventions in AP.
3.1 Dysregulation of lipid metabolism
One pivotal factor in the pathogenesis of AP is the abnormal activation of lipase. Recent studies have highlighted the correlation between hypertriglyceridemia and necrotizing pancreatitis, a severe form of AP that is associated with high morbidity and mortality (16). Under normal physiological conditions, lipase is a digestive enzyme secreted by the pancreas that is primarily responsible for the digestion of dietary fats. However, in cases of AP, obstruction of the pancreatic duct or cellular injury can lead to the premature activation and intracellular release of lipase and other digestive enzymes, which initiates a cascade of pathological events, particularly in the presence of hypertriglyceridemia (17).
Hypertriglyceridemia can exacerbate the inflammatory response and tissue damage in AP, often leading to the development of necrotizing pancreatitis. When triglyceride (TG) levels are excessively high, pancreatic lipase breaks down TGs into free fatty acids (FFA), which can induce lipotoxicity (18). This lipotoxicity disrupts cell membrane integrity, increases intracellular calcium (Ca²+) levels, and NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain associated protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome. These events promote the production and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines (19). The accumulation of FFA also leads to oxidative stress, further damaging pancreatic cells and exacerbating tissue necrosis. The severity of hypertriglyceridemia has a positive correlation with the risk of developing necrotizing pancreatitis (20), with patients showing TG levels exceeding 1000 mg/dL being at significantly higher risk for this progression.
The aberrant activation of lipase exacerbates pancreatic injury through several key mechanisms: 1. Direct cellular damage: Lipase directly targets pancreatic cells, disrupting cell membranes and increasing cellular permeability. This process facilitates the formation of a necrosome through the binding of RIP1 and RIP3, ultimately leading to necrotic cell death (21); 2. Metabolic byproducts and inflammation: The byproducts of lipase activation, such as oleic acid (22), can trigger the release of intracellular Ca²+, inhibit mitochondrial complex I and V functions, and upregulate inflammatory cytokines. These changes lead to acinar cell necrosis and further intensify the inflammatory response within the pancreas. 3. Lipase can also affect local pancreatic blood flow and induce edema, contributing to further tissue necrosis and exacerbating the pathology (23).
Furthermore, it is crucial to explore the relationship between lipase activation and inflammatory pathways beyond necrosome formation, specifically the interaction with the NLRP3 inflammasome (24). The products of lipase activation, such as FFAs, can directly activate the NLRP3 inflammasome. This activation occurs when FFAs are absorbed by immune cells, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction and the production of ROS (25). Elevated levels of ROS then activate the NLRP3 inflammasome, promoting the processing and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-1β and IL-18. This creates a positive feedback loop, where the released cytokines further enhance lipase expression and activity, worsening both lipolysis and inflammation (26).
Additionally, the buildup of fatty acids is a significant pathological phenomenon in AP. During the progression of the disease, fatty acids are released in large quantities due to abnormal lipase activation. The intracellular accumulation of fatty acids can lead to multiple detrimental effects. First, FFAs create a high-oxidative state that triggers the release of calcium ions (Ca²+) from the ER, which increases intracellular Ca²+ concentrations and retroactively activates various digestive enzymes, including trypsin (27). This activation exacerbates the autodigestion of the pancreas, resulting in inflammatory responses and cell death. Fatty acid accumulation also induces ER stress, activates protein kinase Cα, and promotes the activation of activator protein-1 along with the secretion of tumor necrosis factor-α through stress-activated protein kinase signaling pathways. These changes ultimately worsen pancreatic cell injury (28). Moreover, fatty acids can impair mitochondrial function, as high concentrations of FFAs cause mitochondrial membrane depolarization and activate the mitochondrial permeability transition pore related to mitochondrial calcium overload. These alterations exacerbate pancreatic metabolic dysfunction and may lead to pancreatic failure (29).
Clinical studies have indicated that patients with hypertriglyceridemia-induced AP often experience more severe abdominal pain, higher fever, and markedly increased levels of inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) (30). These patients typically require longer hospital stays and may need intensive care. Early intervention to lower triglyceride (TG) levels, including insulin therapy, heparin infusion, or plasma exchange, has been shown to reduce the severity of the disease and decrease the risk of complications (31). For instance, insulin therapy lowers TG levels by stimulating lipoprotein lipase (LPL) activity, while heparin accelerates the breakdown of TG-rich lipoproteins (32). These interventions help alleviate the metabolic burden on the pancreas and prevent the progression of necrotizing pancreatitis.
Another important aspect of the link between hypertriglyceridemia and necrotizing pancreatitis is the role of genetic factors. Certain genetic polymorphisms, such as those in the LPL gene, can predispose individuals to hypertriglyceridemia and increase their susceptibility to SAP (33). Identifying these genetic risk factors may aid in the early detection of high-risk patients and guide personalized treatment strategies.
In summary, dysregulation of lipid metabolism, driven by the abnormal activation of lipase and the accumulation of fatty acids, plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of AP. Lipase activation leads to the release of fatty acids, which exacerbate pancreatic cell injury and accelerate inflammatory responses and cell death through multiple pathways (34). The correlation between hypertriglyceridemia and necrotizing pancreatitis emphasizes the importance of addressing metabolic disturbances in the clinical management of AP (35). Furthermore, lipid metabolic disturbances not only affect enzyme activity within the pancreas but also worsen systemic metabolic disorders, thus driving the progression of AP. Future research should further elucidate the complex interplay between lipid metabolism and AP, focusing on the molecular mechanisms underlying the relationship between hypertriglyceridemia and necrotizing pancreatitis and exploring novel therapeutic strategies to mitigate the damage caused by lipid metabolic disturbances, ultimately improving clinical outcomes in AP.
3.2 Dysregulation of glucose metabolism
Dysregulation of glucose metabolism is another critical component of the metabolic disturbances observed in AP. The development of AP not only impairs the exocrine digestive function of the pancreas but also disrupts its endocrine function, leading to dysregulated insulin secretion (36). Pancreatic injury results in either inhibited or aberrant insulin secretion, while inflammatory responses and metabolic disturbances reduce pancreatic sensitivity to insulin, thereby inducing IR. Research indicates that in the early stages of AP, the function of pancreatic β-cells may be suppressed by acute stress responses, resulting in reduced insulin secretion. Gao et al. (37) demonstrated that in the initial phase of AP, M1 macrophages deliver inflammatory mitochondria to pancreatic β-cells via extracellular vesicles, which subsequently fuse with normal mitochondria. This fusion process leads to iron accumulation in normal mitochondria, increased levels of lipid peroxides, and enhanced mitochondrial membrane permeability. Concurrently, damaged mitochondrial DNA fragments are released into the cytoplasm, activating the stimulator of interferon genes signaling pathway, which further induces apoptosis of pancreatic β-cells.
Systemic inflammatory responses in AP interfere with insulin action through multiple mechanisms, leading to exacerbation of IR For instance, elevated levels of IL-6 in the plasma of patients with AP are positively correlated with IR (38). IL-6 not only inhibits non-oxidative glucose metabolism but also suppresses LPL activity, leading to a continuous increase in plasma TG levels (39). Moreover, IL-6 activates suppressor of cytokine signaling proteins, which block the activation of insulin receptor transcription, reducing the responsiveness of target tissues such as muscle, fat, and liver to insulin. This results in disordered glucose metabolism and exacerbates hyperglycemia (40).
Moreover, adipokines play a significant role in linking obesity to pancreatitis severity. Adipokines such as leptin and adiponectin are involved in IR (41). Leptin, which is elevated in obesity, has pro-inflammatory effects and can exacerbate pancreatic injury. It can activate the NLRP3 inflammasome and promote the release of inflammatory cytokines, thereby contributing to IR and pancreatic inflammation (42). On the other hand, adiponectin has anti-inflammatory and insulin-sensitizing effects. Its levels are typically reduced in obesity, leading to decreased protection against inflammation and IR (43). The imbalance between leptin and adiponectin in obesity can worsen the severity of AP.
Disordered glucose metabolism is closely linked to the severity of AP. During the course of the disease, glucose metabolic disturbances are typically accompanied by pancreatic dysfunction. The presence of hyperglycemia and IR, particularly under the influence of inflammatory responses, exacerbates pancreatic cell injury. Studies have shown that in patients with AP, the degree of glucose metabolic disturbances is positively correlated with the intensity of the inflammatory response (44). Elevated blood glucose levels and IR are often important indicators of disease exacerbation in AP. In severe cases, damage to pancreatic β-cells and worsening IR lead to more glucose metabolic disturbances, resulting in persistent hyperglycemia. This hyperglycemia not only further exacerbates pancreatic inflammation but also affects the function of other organs, increasing the risk of complications in AP (45).
In conclusion, hyperglycemia, IR, abnormal insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells, and glucose metabolic disturbances are closely interrelated and interact synergistically to exacerbate disease severity in AP. Controlling blood glucose levels, improving insulin sensitivity, and restoring pancreatic islet function are essential therapeutic strategies for managing AP. Future research should further elucidate the relationship between glucose metabolism and pancreatic injury, including the role of adipokines in obesity-related pancreatitis, and develop targeted therapeutic strategies to alleviate metabolic disturbances in patients with AP, thereby improving clinical outcomes.
3.3 Amino acid metabolism and protein synthesis
In AP, the inhibition of protein synthesis and the promotion of protein degradation are crucial processes. When AP occurs, pancreatic cells experience severe metabolic stress, especially after inflammatory responses are activated (46). At this stage, pancreatic protein synthesis is often inhibited, primarily due to endoplasmic ER stress, which suppresses protein synthesis in acinar cells through three main signaling pathways.
3.1.1 The protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase signaling pathway
PERK, a serine/threonine protein kinase, catalyzes the phosphorylation of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2α (eIF2α) family of proteins. This action blocks downstream mRNA translation on a large scale, reducing the protein load on the ER (47). In studies involving rats with AP, ER stress can promote caspase-1-dependent pyroptosis in acinar cells via the PERK pathway, intensifying the inflammatory response (48).
3.1.2 The inositol-requiring enzyme 1α signaling pathway
When large quantities of misfolded proteins accumulate in the ER, IRE1α is oligomerized and activated (49). As a bifunctional transmembrane kinase/RNase, IRE1α can cause extensive mRNA degradation to alleviate or terminate ER stress and restore cellular homeostasis (50). During AP, the release of large amounts of FFA activates the IRE1α enzyme, which mediates the splicing of X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1) mRNA. The resulting transcriptional activator, Xbp1s, helps relieve ER stress and protect acinar cells from necrosis (51).
3.1.3 The activating transcription factor 6 signaling pathway
ATF6, a single-pass type II transmembrane protein, has a cytoplasmic domain composed of 370–380 amino acids, followed by a 21-amino-acid transmembrane domain and a cytoplasmic domain of 270 amino acids projecting into the ER lumen (52). When unfolded proteins accumulate in the ER, ATF6 is released and enters the nucleus, activating the transcription of multiple chaperone molecules. This process destabilizes and promotes the degradation of misfolded proteins (53). Tan et al. (54) demonstrated that increased expression of ATF6 was associated with elevated apoptosis, ER, and mitochondrial disorder in pancreatic tissues from SAP patients and humanized serine protease 1 (PRSS1) transgenic mice. Knockout of ATF6 in SAP mice has been shown to attenuate acinar injury, apoptosis, and ER disorder.
ER stress is essentially a protective mechanism that reduces new protein production to alleviate the ER burden and prevent the accumulation of unfolded proteins (55). However, this inhibitory response may also negatively impact pancreatic cell repair and functional recovery, particularly in the later stages of AP (56). Prolonged inhibition of protein synthesis can diminish the repair capacity of pancreatic cells, obstructing the effective recovery of damaged pancreatic tissue and worsening the condition (57).
Protein catabolism is also crucial in AP. Due to pancreatic cell damage and inhibited protein synthesis, the pancreas activates the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway (UPS) and autophagy to process damaged or accumulated proteins (58). For instance, vacuole membrane protein 1 (VMP1), a multi-transmembrane protein in the ER, regulates autophagy by promoting autophagosome closure (58). Studies have shown that in trypsinogen-induced pancreatitis models, VMP1 interacts with the selective autophagy receptor sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1), which removes damaged zymogen granules and prevents premature intracellular trypsinogen activation (59). Protein degradation maintains intracellular homeostasis by breaking down unnecessary or damaged components. In AP, this process eliminates abnormally folded proteins, preventing further cellular damage (60). However, excessive protein degradation, especially the over-release of cytokines and proteases, can intensify inflammation and cell death, leading to further tissue destruction. Thus, the balance between protein synthesis inhibition and degradation is critical in determining the severity of pancreatic inflammation and the pancreas’ repair capacity (61).
Abnormal amino acid metabolism is another key factor affecting pancreatic repair and injury in AP. Amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, are also key metabolic regulators (62). During AP, amino acid metabolism is often disrupted due to pancreatic cell damage and increased metabolic stress (46). For example, studies have confirmed a close association between plasma tryptophan levels and the occurrence of AP (63). Insufficient supply of essential amino acids can reduce cellular protein synthesis capacity, which in turn negatively affects the repair and regeneration of the pancreas. Meanwhile, the metabolism of non-essential amino acids may become disordered, impacting energy metabolism and antioxidant capacity in acinar cells. A meta-analysis by Xue et al. (64) indicated that glutamine (Gln)-enriched nutritional support is more effective than traditional treatments for SAP. Parenteral Gln supplementation has shown greater effectiveness than enteral supplementation, resulting in increased plasma albumin levels, reduced plasma CRP levels, and lower rates of infection (65).
In summary, the inhibition of protein synthesis, degradation of proteins, and abnormalities in amino acid metabolism are closely linked in the pathogenesis of AP (66). While the regulation of protein synthesis and degradation can help alleviate the ER burden, an imbalance in these processes can exacerbate inflammation and lead to cell death (67). Additionally, abnormal amino acid metabolism exacerbates pancreatic injury through multiple pathways, including impaired cell repair, increased oxidative stress, and immune dysfunction (68). Understanding the interplay between these metabolic processes is crucial for uncovering the pathogenesis of AP and identifying potential therapeutic targets.
4 Metabolic interventions and therapeutic approaches
4.1 Interventions in lipid metabolism
In recent years, the development of lipase inhibitors and the potential therapeutic effects of lipid metabolism-modulating drugs have garnered significant attention in the context of AP and other metabolic disorders. These interventions, particularly those targeting fatty acid accumulation, oxidative stress, and pancreatic cell protection, have demonstrated considerable promise for clinical application.
4.1.1 Lipase inhibitors
Lipase inhibitors, which modulate lipid metabolism to treat metabolic disorders, have shown potential in the management of various metabolic diseases. In AP, the abnormal activation of lipase and the excessive accumulation of fatty acids are significant factors that exacerbate disease severity. Lipase, a key enzyme catalyzing the hydrolysis of TGs, can intensify lipid peroxidation of pancreatic cell membranes and trigger local inflammatory responses when overactivated. Thus, inhibiting lipase activity has emerged as a potential therapeutic strategy.
Multiple lipase inhibitors have garnered considerable attention in both clinical and experimental studies. Orlistat, a commonly used lipase inhibitor, reduces dietary fat absorption by inhibiting gastrointestinal lipase activity, thus lowering body fat content (69). Studies have shown that Orlistat can alleviate pancreatic injury and inflammatory responses caused by abnormal lipid metabolism to some extent. By reducing excessive fatty acid accumulation, Orlistat can mitigate pancreatic cell damage, decrease fatty acid-induced oxidative stress, and help relieve the condition of AP (70). In a study by Malecki et al. (71), orlistat was administered to obese mice with AP induced by IL-12 and IL-18. The results showed that orlistat significantly decreased intraabdominal fat necrosis compared to the vehicle group (p<0.05). However, it did not affect pancreatic edema, acinar necrosis, or intrapancreatic fat necrosis significantly. This suggests that orlistat may have a certain protective effect on intraabdominal fat necrosis in obese mice with AP, but its effect on pancreatic tissue damage is limited. Clinical data on Orlistat’s efficacy in AP is still limited and requires further validation.
In addition to gastrointestinal lipase inhibitors, those targeting pancreatic lipase have also been considered as potential therapeutic strategies. Pancreatic lipase plays a crucial role in lipid metabolism within the pancreas, and inhibiting its activity can effectively reduce fatty acid production and lipid accumulation in pancreatic cells, thereby decreasing inflammation caused by fatty acids (72). Novel pancreatic lipase inhibitors, such as RABI-767 (73), have demonstrated efficacy in reducing pancreatic injury and inflammatory responses in animal experiments, offering new hope for the treatment of AP. However, their translation to clinical practice remains to be explored.
4.1.2 Fatty acid oxidation modulators
Drugs that improve lipid metabolism, especially those that enhance fatty acid oxidation, have become a focal point in research. Fatty acids are key contributors to pancreatic injury and inflammatory responses. Medications that regulate fatty acid oxidation can effectively minimize their accumulation in pancreatic tissue, thereby alleviating the oxidative stress and inflammation associated with fatty acids. Conjugated linoleic acid, a common regulator of fatty acid oxidation, promotes fatty acid oxidation and reduces fat accumulation. In animal models of AP, conjugated linoleic acid has been shown to reduce excessive fatty acid accumulation, lessen pancreatic inflammation, and improve pancreatic cell function (74).
Moreover, studies have shown that modulating the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway can effectively promote fatty acid oxidation, decrease fatty acid accumulation, reduce pancreatic inflammation, and improve the condition of AP (75). AMPK agonists, such as AICAR (76), have been proven to alleviate fatty acid metabolic disorders caused by AP in animal models and hold potential for clinical application. Another approach is to regulate fatty acid metabolism by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs). PPAR-α, an important regulator of fatty acid metabolism in the pancreas, has been found to promote fatty acid oxidation and reduce fatty acid accumulation when its receptor is activated (77). PPAR-α agonists, such as Fenofibrate, have shown in animal experiments to reduce fatty acid deposition in pancreatic tissue and significantly alleviate inflammatory responses (78). Additionally, PPAR-γ receptor agonists have demonstrated in some studies the ability to improve fat metabolism and mitigate AP (79). However, clinical trials evaluating these agents in AP are still in early stages, and their efficacy and safety in humans need to be further established.
These findings have shown that interventions targeting lipid metabolism, including lipase inhibitors and fatty acid oxidation modulators, have shown promise in mitigating the severity of AP. Future research should continue to explore the mechanisms of these interventions and their potential clinical applications to develop more effective therapeutic strategies for AP.
4.2 Interventions in glucose metabolism
In the management of AP, insulin therapy and glycemic control are essential therapeutic strategies, as hyperglycemia and IR are critical factors that exacerbate pancreatic injury and promote inflammatory responses. AP is frequently associated with IR and hyperglycemia, particularly in severe cases, where pancreatic function is compromised, leading to reduced insulin secretion capacity. Additionally, the systemic inflammatory response can induce stress hyperglycemia, further worsening pancreatic damage. Therefore, rational control of hyperglycemia and improvement of IR hold significant clinical importance in the treatment of AP.
4.2.1 Insulin therapy and glycemic control
The occurrence of hyperglycemia in AP is not only directly related to pancreatic dysfunction but also closely associated with systemic stress responses. Due to impaired insulin secretion by the pancreas, patients with pancreatitis often experience a degree of insulin deficiency, which exacerbates hyperglycemia. Insulin therapy plays a crucial role in managing hyperglycemia in AP. Studies have shown that insulin can effectively regulate blood glucose levels, reduce inflammatory responses, and improve pancreatic function. In the early stages of AP, maintaining blood glucose within normal or near-normal ranges through rational insulin therapy helps prevent further damage to the pancreas and other organs caused by glucose fluctuations (80). Insulin’s effects extend beyond glycemic control; it can also inhibit hepatic gluconeogenesis, promote glucose utilization by peripheral tissues, and enhance cellular insulin sensitivity, thereby further reducing IR and improving the patient’s metabolic state (81). In clinical practice, insulin therapy typically includes intravenous insulin infusion and subcutaneous insulin injections. Intravenous insulin therapy is commonly used in severe cases of AP, as these patients often have significant hyperglycemia and require rapid and precise glycemic control (82). Intravenous insulin can quickly take effect, stabilize blood glucose levels, and avoid excessive or insufficient glucose fluctuations. For mild or stable cases of AP, subcutaneous insulin injections are usually effective in controlling blood glucose and are more convenient to administer. The dose and regimen of insulin should be individually adjusted based on the patient’s blood glucose levels and the severity of pancreatitis. Glycemic control not only improves IR but also reduces adverse effects caused by hyperglycemia, such as metabolic disorders, immune suppression, and tissue oxidative damage. Studies have shown that controlling blood glucose can reduce pancreatic injury, shorten hospital stays, lower the incidence of complications, and significantly improve the prognosis of patients with AP (83). Therefore, early detection and timely correction of hyperglycemia are crucial in the treatment of AP.
Insulin lowers serum TG levels by stimulating LPL activity. LPL, produced by capillary endothelial cells in muscles and adipose tissues, hydrolyzes TG into glycerol and fatty acids (84). Insulin triggers LPL activity, metabolizing TG-rich lipoproteins such as chylomicrons and very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), thus reducing serum TG levels. In a retrospective study on 12 hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis (HTG-AP) patients, serum TG levels dropped to below 500 mg/dL within 2–3 days of insulin therapy, with no complications and good clinical outcomes (85). A comparative review of 34 HTG-AP cases showed that insulin therapy effectively reduced TG levels, with most patients recovering after 3–5 days of treatment (86).
In addition to lowering TG levels, insulin can inhibit inflammatory responses in HTG-AP. When TG levels are high, pancreatic enzymes break down TG into toxic FFA, inducing inflammation. Insulin reduces TG levels, decreases FFA production, and suppresses inflammatory mediator release, thereby alleviating inflammation (87). A study found that insulin therapy lowers serum CRP, an inflammation marker, indicating its anti-inflammatory effects. Insulin therapy may also improve pancreatic function (88). In HTG-AP, pancreatic inflammation and injury can lead to functional impairment. By reducing inflammation and lowering TG levels, insulin protects pancreatic tissue and promotes functional recovery (88). For example, after insulin therapy, serum amylase and lipase levels gradually normalize, indicating improved pancreatic secretory function (89). Insulin may also promote pancreatic cell repair and regeneration.
Insulin therapy is suitable for all HTG-AP patients, with diabetic patients benefiting from simultaneous glucose and TG control. Insulin is administered intravenously at 0.1-0.3 units/kg/h, with blood glucose monitoring to avoid hypoglycemia. When blood glucose falls below 200 mg/dL, 5% dextrose solution is co-infused. TG levels are regularly monitored to assess therapeutic effects (90). Numerous studies support insulin therapy for HTG-AP. Future research could explore optimal insulin doses, timing, and treatment durations. More randomized controlled trials (RCT) are needed to clarify the role and mechanism of insulin therapy in HTG-AP, providing stronger evidence for clinical practice.
4.2.2 Interventions for IR
IR is a common metabolic abnormality in AP, particularly in severe cases. It plays a key role in leading to hyperglycemia and metabolic disorders. The development of IR occurs due to impaired insulin signaling pathways, which hinder insulin’s ability to effectively promote glucose uptake and metabolism, resulting in elevated blood glucose levels.
Currently, intervention strategies for IR can be categorized into pharmacological and non-pharmacological approaches. In terms of pharmacological interventions, several medications have been widely used and have demonstrated significant efficacy. Metformin, a well-established treatment for Type 2 diabetes, has increasingly been applied to address IR in recent years (91). In clinical practice, metformin has been used to treat many patients with mild to moderate AP complicated by obesity and IR. Clinical research indicates that metformin effectively improves IR by inhibiting hepatic gluconeogenesis, enhancing peripheral tissue insulin sensitivity, and reducing fatty acid release from adipocytes (92). One clinical trial involving a large cohort of patients with mild to moderate AP, obesity, and IR found that metformin treatment led to significant decreases in fasting blood glucose levels, 2-hour postprandial glucose levels, and HOMA-IR scores, alongside improvements in lipid profiles (6). The rate of adverse reactions was acceptable, primarily consisting of mild gastrointestinal issues that most patients could tolerate.
Thiazolidinediones, such as rosiglitazone and pioglitazone, have also been used to treat AP patients with metabolic syndrome and IR. These drugs work by activating PPAR-γ, which regulates fat tissue metabolism and improves adipocyte function to enhance insulin action (93). Clinical studies have shown that after several weeks of treatment with thiazolidinediones, patients exhibited significant improvements in insulin sensitivity markers, as well as correction of lipid metabolic abnormalities, such as reduced TG levels and increased high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol (44). Furthermore, observations related to AP disease indicators revealed that patients receiving these medications experienced a quicker reduction in pancreatic inflammatory markers like amylase and lipase and exhibited less severe pancreatic tissue pathology, demonstrating potential protective effects on the pancreas (94).
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, including liraglutide and saxagliptin, are emerging antidiabetic drugs that show promise in improving IR in AP patients. Clinical trials targeting AP patients with cardiovascular risk factors have indicated that GLP-1 receptor agonists lead to more precise blood glucose control, reduced fluctuations in blood glucose levels, and a steady decrease in glycated hemoglobin levels (95). Ongoing research has suggested that these drugs not only enhance insulin sensitivity but also exhibit anti-inflammatory properties and promote pancreatic cell repair (96). Researchers have observed significant reductions in inflammatory markers such as CRP and IL-6 in patients receiving GLP-1 receptor agonists, indicating their ability to mitigate inflammatory responses in AP (97). Additionally, these drugs have demonstrated potential in activating pancreatic cell repair mechanisms.
In conclusion, these drugs have shown promise for treating AP patients with IR. Ongoing research is expected to further refine treatment strategies and improve patient outcomes in the future.
4.2.3 Combined insulin and heparin therapy in hyperlipidemic pancreatitis
For patients with hyperlipidemic pancreatitis, combined insulin and heparin therapy is a clinically used approach for rapid TG reduction (98). This therapy is particularly effective in patients with severe hypertriglyceridemia (serum TG levels >1,000 mg/dl), where the goal is to lower TG levels and reduce pancreatic injury (99). Insulin activates LPL, an enzyme that accelerates the degradation of chylomicrons into glycerol and FFA, thereby lowering serum TG levels (100). Heparin stimulates the release of endothelial LPL into circulation, further enhancing the breakdown of TG-rich lipoproteins. Together, insulin and heparin work synergistically to promote TG metabolism and alleviate the metabolic burden on the pancreas (101).
Studies demonstrated that combined insulin and heparin therapy can significantly reduce serum TG levels within a short period. For example, Berger et al (102). used continuous infusions of insulin and heparin in patients with hyperlipidemic pancreatitis and observed rapid declines in TG levels. Some case reports have documented the use of intravenous heparin (5000U twice daily) combined with intravenous insulin and achieved similar results (103). The dosage and route of administration may vary, but the goal is to maintain TG levels below 500 mg/dl to expedite clinical improvement (104).
While combined therapy is effective, there are some controversies regarding heparin use. Heparin can initially increase circulating LPL levels, but prolonged use may lead to depletion of LPL stores in the liver, potentially causing a rebound effect (105). Animal models have confirmed that heparin accelerates the transport of LPL to the liver, long-term use can result in LPL deficiency and may need to be carefully considered (106). Despite these concerns, the short-term use of heparin in combination with insulin remains a valuable option for rapidly reducing TG levels in acute settings.
In summary, the regulation of glucose metabolism is of vital importance in the treatment of AP. Insulin therapy and glycemic control are key strategies to prevent further pancreatic and organ damage, improve IR, and enhance patient outcomes. Intervention strategies for IR, including pharmacological and non-pharmacological approaches, have shown potential in improving IR and reducing metabolic disorders. Combined insulin and heparin therapy has demonstrated efficacy in rapidly lowering TG levels in hyperlipidemic pancreatitis. However, research into these therapeutic interventions is still ongoing, and optimizing dosing regimens and understanding long-term effects remain crucial areas for future exploration.
4.3 Antioxidant therapy
In the management of AP, the control of oxidative stress is an essential component, as it not only exacerbates pancreatic injury but also promotes the development and progression of metabolic disturbances, thereby further intensifying the inflammatory response. Antioxidants, such as vitamin C and vitamin E, have garnered increasing attention in the treatment of AP due to their ability to mitigate oxidative damage. By reducing the generation of free radicals and enhancing antioxidant defense mechanisms, these agents play a significant role in alleviating oxidative stress, improving metabolic disturbances, and inhibiting inflammatory responses.
4.3.1 Oxidative stress responses in AP
In the pathogenesis of AP, the generation of ROS, and the disruption of redox homeostasis are pivotal factors. AP is often triggered by acute inflammatory responses within pancreatic tissue, where ROS serve as critical modulators of cellular stress, contributing to various aspects of pancreatic injury (107). Under normal physiological conditions, ROS are natural byproducts of cellular metabolism, primarily generated through the mitochondrial electron transport chain. However, during AP, ROS production is significantly increased due to cellular injury or stress (108). Elevated ROS levels can induce lipid peroxidation, protein denaturation, and direct DNA damage, ultimately triggering apoptosis or necrosis (109). In AP, both inflammatory cells (such as neutrophils and macrophages) and damaged pancreatic cells themselves produce substantial amounts of ROS (110). These ROS activate a cascade of signaling pathways, further exacerbating the inflammatory response and leading to pancreatic tissue damage (7). The role of oxidative stress in AP is twofold. First, oxidative stress promotes the initiation and amplification of inflammatory responses by activating various signaling pathways (111).
ROS can activate transcription factors such as nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and activator protein-1 (AP-1) (112), thereby inducing the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factors and interleukins. These cytokines attract additional immune cells to the site of inflammation, intensifying pancreatic injury. Second, oxidative stress induces necrosis or apoptosis by damaging lipids, proteins, and DNA within pancreatic cells (113). Excessive ROS targets the cell membranes of pancreatic cells, initiating lipid peroxidation reactions that compromise membrane integrity and lead to cell death. ROS can oxidize proteins and DNA, disrupt their normal biological functions, and induce genetic mutations or damage, further exacerbating pancreatic injury (114). Moreover, redox imbalance impacts the autophagy process in the pancreas (115). Autophagy is a critical metabolic pathway that degrades damaged organelles and proteins to maintain cellular homeostasis. In AP, excessive ROS not only inhibits the normal function of autophagy but may also alter autophagy regulation by activating autophagy-related genes, such as glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase, leading to the accumulation of damaged materials within cells and exacerbating pancreatic injury (116). In summary, there is a close relationship between redox imbalance and the progression of AP. Excessive ROS generation and oxidative stress exacerbate pancreatic cell injury, promote inflammatory responses, and ultimately lead to extensive pancreatic tissue damage and functional failure (117). Therefore, modulating ROS generation and restoring redox balance may represent a promising therapeutic strategy for AP. The use of antioxidants or modulation of antioxidant enzyme activity may help mitigate oxidative stress-induced pancreatic damage and improve clinical outcomes.
Controlling oxidative stress is an essential component in managing AP, as it not only exacerbates pancreatic injury but also promotes the development and progression of metabolic disturbances, thereby intensifying the inflammatory response (118). Antioxidants, such as vitamin C and vitamin E, have garnered increasing attention in the treatment of AP due to their ability to mitigate oxidative damage (119). By reducing the generation of free radicals and enhancing antioxidant defense mechanisms, these agents play a significant role in alleviating oxidative stress, improving metabolic disturbances, and inhibiting inflammatory responses.
4.3.2 Vitamin C
Vitamin C and vitamin E are two widely recognized antioxidants used in clinical practice. Vitamin C, being a water-soluble antioxidant, can directly scavenge free radicals, which helps reduce intracellular oxidative damage, particularly lipid peroxidation (120). In AP, pancreatic tissue often undergoes severe oxidative stress due to excessive free radicals, such as superoxide anions, hydrogen peroxides, and hydroxyl radicals. This oxidative stress leads to lipid peroxidation of cell membranes, DNA damage, and protein denaturation, all of which worsen pancreatic injury and inflammatory responses. Vitamin C protects pancreatic cells from oxidative damage by inhibiting the generation of harmful free radicals, thereby reducing inflammation and improving the conditions. Clinical and animal studies have shown that vitamin C supplementation can significantly improve the prognosis of patients with AP, especially in severe cases, by reducing oxidative stress and organ damage (121). Vitamin C also regulates immune responses, reduces cellular inflammation and immune activation, thereby lowering the risk of multi-organ failure (122). Additionally, vitamin C enhances the antioxidant capacity of endothelial cells, improving microcirculatory blood flow and effectively alleviating pancreatic ischemic injury caused by AP (123).
In recent years, numerous clinical studies have explored the efficacy of vitamin C in the treatment of AP. For instance, a prospective cohort study involving 43 patients with mild to moderate AP found that those who received vitamin C supplementation (1–2 g/day) experienced a significant reduction in serum amylase and lipase levels within three days of treatment. The average hospital stay for these patients was shortened by approximately two days compared to the control group (123). Another RCT with 84 SAP patients revealed that high-dose vitamin C infusion (3–6 g/day) administered over 7–14 days was linked to a 30% lower incidence of pancreatic necrosis and a 20% reduction in the risk of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) (124). Furthermore, in a multicenter study involving 418 patients with AP, vitamin C supplementation not only improved pancreatic outcomes but also enhanced overall recovery (121). Patients receiving vitamin C had a 25% lower rate of infectious complications and a 15% decrease in the need for intensive care unit (ICU) admission. Collectively, these studies highlight the therapeutic potential of vitamin C in managing AP and its complications. However, it is worth noting that the optimal dose and duration of vitamin C administration may vary depending on the severity of the disease and individual patient factors. Further large-scale, well-designed clinical trials are needed to establish standardized treatment protocols for vitamin C in AP.
4.3.3 Vitamin E
Vitamin E, a lipid-soluble antioxidant, primarily protects cell membranes from oxidative damage by inhibiting lipid peroxidation. Patients with AP often exhibit increased lipid peroxidation, and vitamin E can help reduce cell membrane damage by decreasing the formation of peroxidized lipids, thereby minimizing pancreatic cell injury. Clinically, vitamin E has been shown to lower the release of inflammatory mediators and the infiltration of inflammatory cells, thereby alleviating pancreatic tissue inflammation (125). Moreover, vitamin E enhances antioxidant capacity by regulating the intracellular antioxidant enzyme system (such as glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase), further reducing oxidative stress-induced pancreatic injury (126).
Multiple clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of vitamin E in treating AP. For example, a multicenter prospective cohort study involving 39 patients with AP found that those receiving vitamin E supplementation (400–800 IU/day) showed a significant reduction in serum levels of inflammatory markers such as CRP and IL-6 within five days of treatment. The average severity score of pancreatitis in these patients dropped by approximately 1.2 points compared to the control group (127). An RCT with 100 SAP patients revealed that combination therapy with vitamin E (400 IU/day) and vitamin C (2 g/day) over 10–14 days was associated with a 35% lower incidence of pancreatic necrosis and a 25% reduction in the risk of SIRS (128). Additionally, histopathological examination of pancreatic tissue from animal models of AP confirmed that vitamin E could reduce pancreatic tissue edema, inflammatory cell infiltration, and acinar cell necrosis (126). Collectively, these studies highlight the therapeutic potential of vitamin E in managing AP and its complications. However, it is worth noting that the optimal dose and duration of vitamin E administration may vary depending on the severity of the disease and individual patient factors. Further large-scale, well-designed clinical trials are needed to establish standardized treatment protocols for vitamin E in AP.
In summary, the use of antioxidants such as vitamin C and vitamin E in AP is of significant clinical importance. These agents reduce oxidative stress, improve metabolic disturbances, mitigate lipid and glucose metabolic disorders, help alleviate pancreatic injury, inhibit inflammatory responses, and potentially prevent complications and disease progression in AP. Antioxidant supplementation in the treatment of AP has therapeutic value, but further clinical research is needed to verify its long-term effects and optimal usage protocols. Future studies should focus on elucidating the mechanisms of action of these antioxidants and exploring their potential synergistic effects with other therapeutic interventions to optimize clinical outcomes in patients with AP.
4.4 Emerging therapies
Recent advances have provided insights into novel therapeutic approaches for acute AP, particularly in the areas of metabolic regulation and gut microbiome modulation. Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) analogs have emerged as promising candidates for treating AP. FGF21 is a metabolic hormone that affects glucose and lipid metabolism, as well as insulin sensitivity. Preclinical studies have shown that FGF21 alleviates cerulein-induced AP by activating the Sirt1-autophagy signaling pathway (129). This activation aids in repairing damaged mitochondria and lysosomes, reducing autophagic damage, and mitigating systemic inflammation (130). Furthermore, FGF21 demonstrates protective effects against pancreatic fibrosis and inflammation. Moreover, mRNA-based therapies that deliver FGF21 and apolipoprotein A1 (APOA1) have been explored as innovative treatments for AP. These therapies utilize liver-targeted lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) to facilitate the production of endogenous proteins, resulting in sustained therapeutic effects (131). Experimental studies indicate that these therapies can reduce pancreatic injury and improve histological outcomes in models of AP.
In parallel, gut microbiome modulation has gained significant attention due to its critical role in the pathogenesis of AP. The condition is often associated with intestinal dysbiosis, characterized by a decrease in beneficial bacteria such as Bifidobacteria, and an increase in potentially harmful bacteria like Enterococcus (132). Strategies such as probiotics or fecal microbiota transplantation have shown promise in restoring intestinal barrier function and reducing systemic inflammation in patients with AP (133). Probiotics can enhance the epithelial barrier and modulate the composition of commensal microbiota, while fecal microbiota transplantation can help reconstruct normal intestinal flora, aiding in the treatment of both intestinal and extraintestinal diseases (134).
In summary, these emerging therapies reflect the multifaceted nature of AP treatment and offer new possibilities for improving patient outcomes. FGF21 analogs and gut microbiome modulation are pivotal in advancing the management of this complex disease.
4.5 Challenges of metabolic disturbances in the treatment of AP
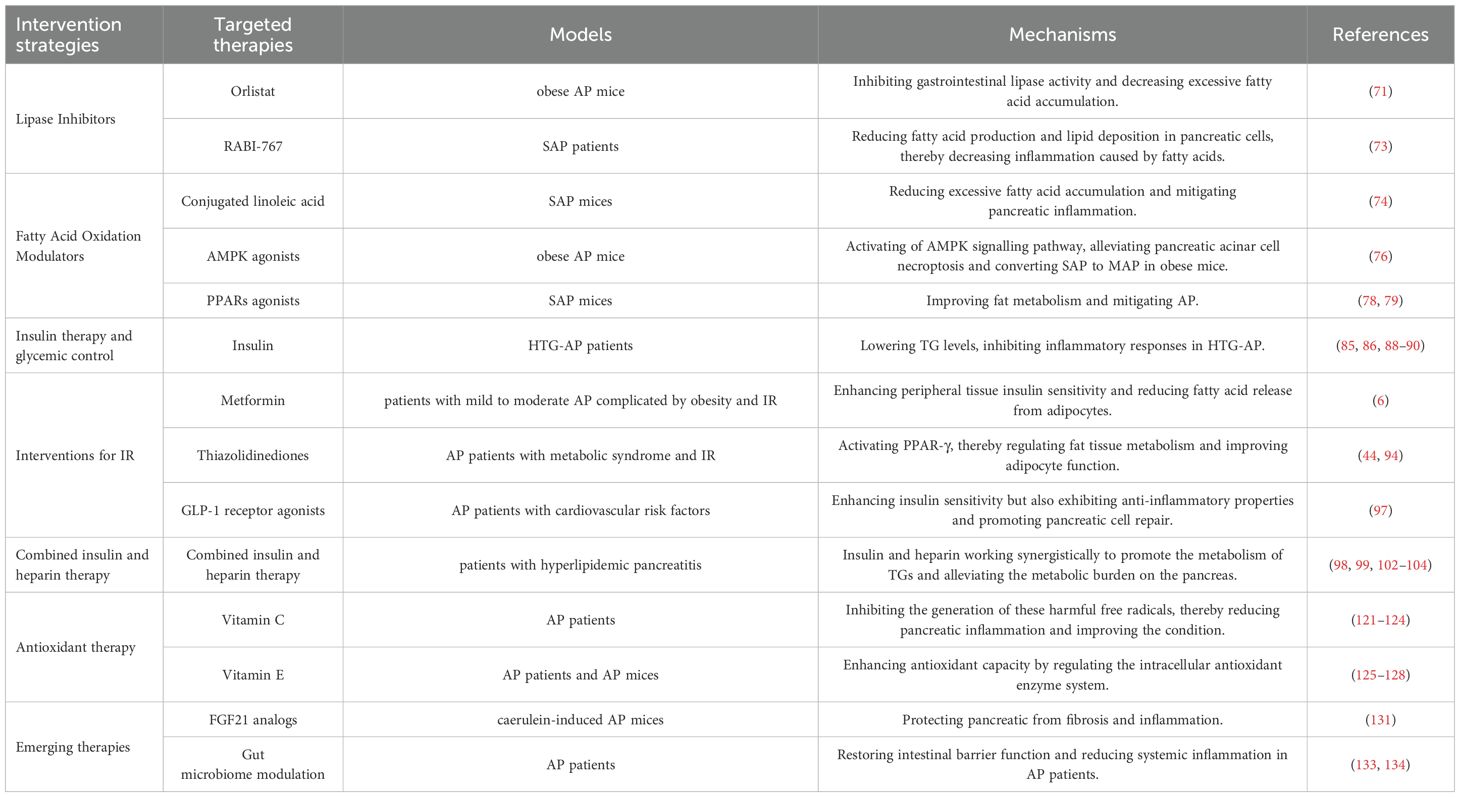
The metabolic profiles of patients with AP are highly heterogeneous, demonstrating significant individual variability. This heterogeneity poses a substantial challenge for developing standardized therapeutic protocols for metabolic interventions (Table 1). Given this complexity, a precision medicine approach is essential. This approach tailors treatment strategies to the specific metabolic status of each patient. For instance, patients experiencing severe lipid metabolic disturbances may benefit from fatty acid metabolism modulators (135), while those with abnormal glucose metabolism might require insulin therapy or insulin sensitizers (136).
In the realm of precision medicine for AP, biomarkers play a pivotal role. Fatty acid profiles can serve as key biomarkers. By analyzing the composition and ratios of different fatty acids in patients, clinicians can gain insights into the lipid metabolic state (137). For example, elevated levels of certain saturated fatty acids could indicate a heightened risk of lipotoxicity, which would guide the appropriate use of fatty acid metabolism modulators (138). Oxidative stress markers are another crucial category of biomarkers, reflecting the balance between oxidative and anti-oxidative mechanisms in the body. Increased levels of oxidative stress markers may suggest ongoing tissue damage and inflammation, assisting in determining the timing and intensity of antioxidant therapy as part of metabolic interventions (139). Future research should focus on designing personalized treatment plans based on these biomarkers to enhance therapeutic efficacy, minimize adverse effects, and maximize the success rate of AP treatments.
Despite the promising potential of metabolic regulation in treating AP, many questions remain unanswered. Future studies should further explore the intricate relationship between metabolic disturbances and AP, emphasizing the underlying mechanisms of various metabolic pathways, including lipid, glucose, and amino acid metabolism. Additionally, researchers should investigate the correlation between metabolic regulation and clinical manifestations of AP, examining how different metabolic disturbances relate to disease progression, complications, and prognosis.
Finally, addressing the challenges of translating findings from animal models to human trials is important. Species-specific metabolic differences can significantly impact the outcomes of metabolic interventions. For example, rodents, which are commonly used in animal studies, possess distinct lipid metabolism patterns compared to humans, potentially leading to discrepancies in the efficacy and safety profiles of metabolic modulators as research transitions from animal models to human applications (140). Understanding and accounting for these species-specific metabolic differences is crucial for the successful translation of pre-clinical findings into effective clinical therapies for patients with AP.
Through systematic and comprehensive research into metabolic mechanisms, a more precise theoretical basis can be established to guide clinical practice and improve patient outcomes in the treatment of AP.
5 Conclusion
The accumulation of fatty acids, dysfunction in amino acid metabolism, and disorders in glucose metabolism are the common metabolic disturbances associated with AP. These factors can exacerbate pancreatic injury and promote inflammation. Specifically, the accumulation of fatty acids not only directly activates inflammatory responses but also disrupts cell membranes and increases oxidative stress, which further worsens pancreatic injury. Furthermore, hyperglycemia and IR intensify pancreatic damage and inflammation by enhancing oxidative stress and fatty acid metabolic disturbances.
The interventions for metabolic regulation in the treatment of AP have been extensively explored. Interventions aimed at lipid metabolic disturbances, such as lipase inhibitors and fatty acid oxidation modulators, have shown promise in mitigating pancreatic injury. Insulin therapy has proven effective in managing hyperglycemia, potentially slowing the inflammatory process by reducing the burden on the pancreas. The use of antioxidants, such as vitamin C and vitamin E, may also help alleviate oxidative stress and protect pancreatic cells. However, despite the significant potential of metabolic regulation in treating AP, the underlying mechanisms need further clarification.
Future research should focus on the complex relationship between metabolic disturbances and AP, particularly the correlation between metabolic profiles, disease progression, and clinical outcomes. Personalized treatments and the development of drugs targeting specific metabolic pathways should also be prioritized as key directions for future therapies. Through these studies, more precise and effective intervention strategies may be developed for the clinical management of AP.
In conclusion, metabolic disturbances play a crucial role in the pathogenesis, progression, and clinical manifestations of AP. Metabolic regulation not only represents a promising therapeutic approach but also offers a broad framework for future research initiatives.
Author contributions
CF: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YD: Writing – original draft. XW: Writing – review & editing. XT: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
AP, acute pancreatitis; IR, insulin resistance; RIP, receptor-interacting protein kinase; MLKL, mixed lineage kinase domain-like; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; MAP, mild acute pancreatitis; SAP, severe acute pancreatitis; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TG, triglyceride; FFA, free fatty acid; NLRP3, NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain associated protein 3; Ca²+, calcium; CRP1, C-reactive protein 1; IL-6, interleukin-6; LPL, lipoprotein lipase; PERK, protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; eIF2α, eukaryotic initiation factor 2α; IRE1α, inositol-requiring enzyme 1α; XBP1, X-box binding protein 1; ATF6, activating transcription factor 6; PRSS1, humanized serine protease 1; UPS, ubiquitin-proteasome pathway; VMP1, vacuole membrane protein 1; SQSTM1, selective autophagy receptor sequestosome 1; Gln, glutamine; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; VLDL, very low-density lipoprotein; HTG-AP, hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide-1; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; AP-1, activator protein-1; ICU, intensive care unit; FGF21, fibroblast growth factor 21; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; RCT, randomized controlled trial.
References
2. Tenner S, Vege SS, Sheth SG, Sauer B, Yang A, Conwell DL, et al. American college of gastroenterology guidelines: management of acute pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. (2024) 119:419–37. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000002645
3. Sohail Z, Shaikh H, Iqbal N, and Parkash O. Acute pancreatitis: A narrative review. J Pak Med Assoc. (2024) 74:953–8.
4. Iannuzzi JP, King JA, Leong JH, Quan J, Windsor JW, Tanyingoh D, et al. Global incidence of acute pancreatitis is increasing over time: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. (2022) 162:122–34. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.043
5. Strum WB and Boland CR. Advances in acute and chronic pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. (2023) 29:1194–201. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i7.1194
6. Cho SK, Huh JH, Yoo JS, Kim JW, and Lee KJ. HOMA-estimated insulin resistance as an independent prognostic factor in patients with acute pancreatitis. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:14894. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51466-5
7. Escobar J, Pereda J, López-Rodas G, and Sastre J. Redox signaling and histone acetylation in acute pancreatitis. Free Radic Biol Med. (2012) 52:819–37. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.11.009
8. Hernandez P, Passi N, Modarressi T, Kulkarni V, Soni M, Burke F, et al. Clinical management of hypertriglyceridemia in the prevention of cardiovascular disease and pancreatitis. Curr Atheroscler Rep. (2021) 23:72. doi: 10.1007/s11883-021-00962-z
9. Storz P. Acinar cell plasticity and development of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2017) 14:296–304. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.12
10. Fortunato F, Bürgers H, Bergmann F, Rieger P, Büchler MW, Kroemer G, et al. Impaired autolysosome formation correlates with Lamp-2 depletion: role of apoptosis, autophagy, and necrosis in pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. (2009) 137:350–60. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.04.003
11. Wu J, Mulatibieke T, Ni J, Han X, Li B, Zeng Y, et al. Dichotomy between receptor-interacting protein 1- and receptor-interacting protein 3-mediated necroptosis in experimental pancreatitis. Am J Pathol. (2017) 187:1035–48. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.12.021
12. Mensah EA, Sarfo B, Bonney EY, Parbie PK, and Ocloo A. Symptoms of toxicity and plasma cytochrome c levels in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients receiving anti-retroviral therapy in Ghana: A cross-sectional study. Infect Disord Drug Targets. (2020) 20:88–97. doi: 10.2174/1871526518666181102112010
13. Habtezion A. Inflammation in acute and chronic pancreatitis. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. (2015) 31:395–9. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000195
14. Leppäniemi A, Tolonen M, Tarasconi A, Segovia-Lohse H, Gamberini E, Kirkpatrick AW, et al. 2019 WSES guidelines for the management of severe acute pancreatitis. World J Emerg Surg. (2019) 14:27. doi: 10.1186/s13017-019-0247-0
15. Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, Gooszen HG, Johnson CD, Sarr MG, et al. Classification of acute pancreatitis–2012: revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut. (2013) 62:102–11.
16. Van Wieren A, Guild M, Raucci N, and Meyer S. Managing severe acute and necrotizing pancreatitis. Jaapa. (2022) 35:15–20.
17. Ben-Ami Shor D, Ritter E, Borkovsky T, and Santo E. The multidisciplinary approach to acute necrotizing pancreatitis. J Clin Med. (2025) 14. doi: 10.3390/jcm14092904
18. Yang AL and McNabb-Baltar J. Hypertriglyceridemia and acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology. (2020) 20:795–800.
19. Stefanutti C, Labbadia G, and Morozzi C. Severe hypertriglyceridemia-related acute pancreatitis. Ther Apher Dial. (2013) 17:130–7. doi: 10.1111/1744-9987.12008
20. Lindberg DA. Acute pancreatitis and hypertriglyceridemia. Gastroenterol Nurs. (2009) 32:75–82. doi: 10.1097/SGA.0b013e31819de3e0
21. Liang QQ, Shi ZJ, Yuan T, Chen SY, Li YP, Zhang HR, et al. Celastrol inhibits necroptosis by attenuating the RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL pathway and confers protection against acute pancreatitis in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 117:109974. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.109974
22. Navina S, Acharya C, DeLany JP, Orlichenko LS, Baty CJ, Shiva SS, et al. Lipotoxicity causes multisystem organ failure and exacerbates acute pancreatitis in obesity. Sci Transl Med. (2011) 3:107ra10. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002573
23. Obermaier R, Benz S, Kortmann B, Benthues A, Ansorge N, and Hopt UT. Ischemia/reperfusion-induced pancreatitis in rats: a new model of complete normothermic in situ ischemia of a pancreatic tail-segment. Clin Exp Med. (2001) 1:51–9. doi: 10.1007/PL00012237
24. Gao L, Lu GT, Lu YY, Xiao WM, Mao WJ, Tong ZH, et al. Diabetes aggravates acute pancreatitis possibly via activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in db/db mice. Am J Transl Res. (2018) 10:2015–25.
25. Blanc M, Habbouche L, Xiao P, Lebeaupin C, Janona M, Vaillant N, et al. Bax Inhibitor-1 preserves pancreatic β-cell proteostasis by limiting proinsulin misfolding and programmed cell death. Cell Death Dis. (2024) 15:334. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06701-x
26. Ye Z, Cheng L, Xuan Y, Yu K, Li J, and Gu H. Chlorogenic acid alleviates the development of severe acute pancreatitis by inhibiting NLPR3 Inflammasome activation via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. Int Immunopharmacol. (2025) 151:114335. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114335
27. Gao Z, Zhang C, Yu S, Yang X, and Wang K. Vanadyl bisacetylacetonate protects β cells from palmitate-induced cell death through the unfolded protein response pathway. J Biol Inorg Chem. (2011) 16:789–98. doi: 10.1007/s00775-011-0780-0
28. Han X, Li B, Bao J, Wu Z, Chen C, Ni J, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress promoted acinar cell necroptosis in acute pancreatitis through cathepsinB-mediated AP-1 activation. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:968639. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.968639
29. Ding WX, Ma X, Kim S, Wang S, and Ni HM. Recent insights about autophagy in pancreatitis. eGastroenterology. (2024) 2. doi: 10.1136/egastro-2023-100057
30. Molnár G, Gyarmathy VA, Zádori N, Hegyi P, and Kanizsai P. Severe hypertriglyceridemia-induced acute pancreatitis. Case Rep Gastroenterol. (2021) 15:218–24. doi: 10.1159/000511017
31. Kayataş SE, Eser M, Cam C, Cogendez E, and Guzin K. Acute pancreatitis associated with hypertriglyceridemia: a life-threatening complication. Arch Gynecol Obstet. (2010) 281:427–9. doi: 10.1007/s00404-009-1183-0
32. Altinkaya E and Aktas A. Insulin and heparin therapies in acute pancreatitis due to hypertriglyceridemia. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. (2021) 31:1337–40. doi: 10.29271/jcpsp.2021.11.1337
33. Bruin T, Tuzgöl S, van Diermen DE, Hoogerbrugge-van der Linden N, Brunzell JD, Hayden MR, et al. Recurrent pancreatitis and chylomicronemia in an extended Dutch kindred is caused by a Gly154–>Ser substitution in lipoprotein lipase. J Lipid Res. (1993) 34:2109–19. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2275(20)35352-9
34. Guo YY, Li HX, Zhang Y, and He WH. Hypertriglyceridemia-induced acute pancreatitis: progress on disease mechanisms and treatment modalities. Discov Med. (2019) 27:101–9.
35. Cao L, Chen Y, Liu S, Huang W, Wu D, Hong D, et al. Early plasmapheresis among patients with hypertriglyceridemia-associated acute pancreatitis. JAMA Netw Open. (2023) 6:e2320802. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.20802
36. He W, Cai W, Yang X, Camilleri G, Zheng X, Wang Q, et al. Insulin or blood purification treatment for hypertriglyceridaemia-associated acute pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pancreatology. (2022) 22:846–57. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2022.07.013
37. Gao Y, Mi N, Wu W, Zhao Y, Fan F, Liao W, et al. Transfer of inflammatory mitochondria via extracellular vesicles from M1 macrophages induces ferroptosis of pancreatic beta cells in acute pancreatitis. J Extracell Vesicles. (2024) 13:e12410. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12410
38. Mititelu A, Grama A, Colceriu MC, Benţa G, Popoviciu MS, and Pop TL. Role of interleukin 6 in acute pancreatitis: A possible marker for disease prognosis. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158283
39. Guo L, Rong L, and Xu X. The changes of triacylglycerol and inflammatory factors during dialysis treatment of hypertriglyceridemia during pregnancy and analysis of nursing countermeasure. Am J Transl Res. (2021) 13:6745–51.
40. Rehman K, Akash MSH, Liaqat A, Kamal S, Qadir MI, and Rasul A. Role of interleukin-6 in development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. (2017) 27:229–36. doi: 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2017019712
41. Koenen M, Hill MA, Cohen P, and Sowers JR. Obesity, adipose tissue and vascular dysfunction. Circ Res. (2021) 128:951–68. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318093
42. Kim Y, Wang W, Okla M, Kang I, Moreau R, and Chung S. Suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome by γ-tocotrienol ameliorates type 2 diabetes. J Lipid Res. (2016) 57:66–76. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M062828
43. Caselli C. Role of adiponectin system in insulin resistance. Mol Genet Metab. (2014) 113:155–60. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2014.09.003
44. Hart PA, Bradley D, Conwell DL, Dungan K, Krishna SG, Wyne K, et al. Diabetes following acute pancreatitis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2021) 6:668–75. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00019-4
45. Richardson A and Park WG. Acute pancreatitis and diabetes mellitus: a review. Korean J Intern Med. (2021) 36:15–24. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2020.505
46. Rooman I, Lutz C, Pinho AV, Huggel K, Reding T, Lahoutte T, et al. Amino acid transporters expression in acinar cells is changed during acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology. (2013) 13:475–85.
47. Wiseman RL, Mesgarzadeh JS, and Hendershot LM. Reshaping endoplasmic reticulum quality control through the unfolded protein response. Mol Cell. (2022) 82:1477–91. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.03.025
48. Yan C, Ma Y, Li H, Cui J, Guo X, Wang G, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress promotes caspase-1-dependent acinar cell pyroptosis through the PERK pathway to aggravate acute pancreatitis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 120:110293. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110293
49. Hwang J and Qi L. Quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum: crosstalk between ERAD and UPR pathways. Trends Biochem Sci. (2018) 43:593–605. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2018.06.005
50. Hetz C. The unfolded protein response: controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2012) 13:89–102. doi: 10.1038/nrm3270
51. Yang G and Zhang X. TMAO promotes apoptosis and oxidative stress of pancreatic acinar cells by mediating IRE1α-XBP-1 pathway. Saudi J Gastroenterol. (2021) 27:361–9. doi: 10.4103/sjg.sjg_12_21
52. Hetz C and Papa FR. The unfolded protein response and cell fate control. Mol Cell. (2018) 69:169–81. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.06.017
53. Huang W, Gong Y, and Yan L. ER stress, the unfolded protein response and osteoclastogenesis: A review. Biomolecules. (2023) 13. doi: 10.3390/biom13071050
54. Tan JH, Cao RC, Zhou L, Zhou ZT, Chen HJ, Xu J, et al. ATF6 aggravates acinar cell apoptosis and injury by regulating p53/AIFM2 transcription in Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Theranostics. (2020) 10:8298–314.
55. Chen X, Shi C, He M, Xiong S, and Xia X. Endoplasmic reticulum stress: molecular mechanism and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8:352. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01570-w
56. Habtezion A, Gukovskaya AS, and Pandol SJ. Acute pancreatitis: A multifaceted set of organelle and cellular interactions. Gastroenterology. (2019) 156:1941–50. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.11.082
57. Lee PJ and Papachristou GI. New insights into acute pancreatitis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2019) 16:479–96. doi: 10.1038/s41575-019-0158-2
58. Wang D, Han S, Lv G, Hu Y, Zhuo W, Zeng Z, et al. Pancreatic acinar cells-derived sphingosine-1-phosphate contributes to fibrosis of chronic pancreatitis via inducing autophagy and activation of pancreatic stellate cells. Gastroenterology. (2023) 165:1488–504.e20. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.08.029
59. Wang S, Chao X, Jiang X, Wang T, Rodriguez Y, Yang L, et al. Loss of acinar cell VMP1 triggers spontaneous pancreatitis in mice. Autophagy. (2022) 18:1572–82.
60. Mareninova OA, Gretler SR, Lee GE, Pimienta M, Qin Y, Elperin JM, et al. Ethanol inhibits pancreatic acinar cell autophagy through upregulation of ATG4B, mediating pathological responses of alcoholic pancreatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. (2023) 325:G265–g78. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00053.2023
61. Choi J, Oh TG, Jung HW, Park KY, Shin H, Jo T, et al. Estrogen-related receptor γ Maintains pancreatic acinar cell function and identity by regulating cellular metabolism. Gastroenterology. (2022) 163:239–56.
62. Qiu H, Shao N, Liu J, Zhao J, Chen C, Li Q, et al. Amino acid metabolism in tumor: New shine in the fog? Clin Nutr. (2023) 42:1521–30.
63. Zhou Q, Tao X, Guo F, Wu Y, Deng D, Lv L, et al. Tryptophan metabolite norharman secreted by cultivated Lactobacillus attenuates acute pancreatitis as an antagonist of histone deacetylases. BMC Med. (2023) 21:329. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-02997-2
64. Jiang X, Pei LY, Guo WX, Qi X, and Lu XG. Glutamine supported early enteral therapy for severe acute pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. (2020) 29:253–61.
65. Jabłońska B and Mrowiec S. Nutritional support in patients with severe acute pancreatitis-current standards. Nutrients. (2021) 13. doi: 10.3390/nu13051498
66. Borrello MT, Martin MB, and Pin CL. The unfolded protein response: An emerging therapeutic target for pancreatitis and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreatology. (2022) 22:148–59. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2021.10.007
67. van Dijk DPJ, Horstman AMH, Smeets JSJ, den Dulk M, Grabsch HI, Dejong CHC, et al. Tumour-specific and organ-specific protein synthesis rates in patients with pancreatic cancer. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2019) 10:549–56. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12419
68. Zhang GF, Jensen MV, Gray SM, El K, Wang Y, Lu D, et al. Reductive TCA cycle metabolism fuels glutamine- and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Cell Metab. (2021) 33:804–17.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.11.020
69. Khera R, Murad MH, Chandar AK, Dulai PS, Wang Z, Prokop LJ, et al. Association of pharmacological treatments for obesity with weight loss and adverse events: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Jama. (2016) 315:2424–34. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.7602
70. Xu T, Sheng L, Guo X, and Ding Z. Free fatty acid increases the expression of NLRP3-caspase1 in adipose tissue macrophages in obese severe acute pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. (2022) 67:2220–31. doi: 10.1007/s10620-021-07027-w
71. Malecki EA, Castellanos KJ, Cabay RJ, and Fantuzzi G. Therapeutic administration of orlistat, rosiglitazone, or the chemokine receptor antagonist RS102895 fails to improve the severity of acute pancreatitis in obese mice. Pancreas. (2014) 43:903–8. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000115
72. Xie X, Liu Y, Yang Q, Ma X, Lu Y, Hu Y, et al. Adipose triglyceride lipase-mediated adipocyte lipolysis exacerbates acute pancreatitis severity in mouse models and patients. Am J Pathol. (2024) 194:1494–510. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2024.03.014
73. Borah AK, Sharma P, Singh A, Kalita KJ, Saha S, and Chandra Borah J. Adipose and non-adipose perspectives of plant derived natural compounds for mitigation of obesity. J Ethnopharmacol. (2021) 280:114410. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114410
74. Noto A, Zahradka P, Ryz NR, Yurkova N, Xie X, and Taylor CG. Dietary conjugated linoleic acid preserves pancreatic function and reduces inflammatory markers in obese, insulin-resistant rats. Metabolism. (2007) 56:142–51.
75. Wang K, Zhao A, Tayier D, Tan K, Song W, Cheng Q, et al. Activation of AMPK ameliorates acute severe pancreatitis by suppressing pancreatic acinar cell necroptosis in obese mice models. Cell Death Discov. (2023) 9:363. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01655-z
76. Srinivasan MP, Bhopale KK, Caracheo AA, Amer SM, Khan S, Kaphalia L, et al. Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase attenuates ethanol-induced ER/oxidative stress and lipid phenotype in human pancreatic acinar cells. Biochem Pharmacol. (2020) 180:114174. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114174
77. Zhang L, Li Y, Wang Y, Qiu Y, Mou H, Deng Y, et al. mTORC2 facilitates liver regeneration through sphingolipid-induced PPAR-α-fatty acid oxidation. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2022) 14:1311–31. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2022.07.011
78. Tong L, Xu S, Chen Z, Gao J, Huang Q, Lin X, et al. Clinical analysis of atorvastatin calcium, fenofibrate, and acipimox in the treatment of hypertriglyceridemia-induced acute pancreatitis. Altern Ther Health Med. (2024) 30:200–7.
79. Xu P, Lou XL, and Chen C. Apoptotic mechanisms of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ Activation in acinar cells during acute pancreatitis. Pancreas. (2016) 45:179–86.
80. Kikuta K, Masamune A, and Shimosegawa T. Impaired glucose tolerance in acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. (2015) 21:7367–74. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7367
81. Śliwińska-Mossoń M, Bil-Lula I, and Marek G. The cause and effect relationship of diabetes after acute pancreatitis. Biomedicines. (2023) 11. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030667
82. Perez V, Faust AC, Taburyanskaya M, Patil RA, and Ortegon A. Effectiveness of an intravenous insulin-based treatment protocol for the management of hypertriglyceridemia-associated acute pancreatitis. J Pharm Technol. (2023) 39:55–61. doi: 10.1177/87551225231151570
83. Mentula P, Kylänpää M-L, Kemppainen E, Jansson S-E, Sarna S, Puolakkainen P, et al. Early prediction of organ failure by combined markers in patients with acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. (2005) 92(1):68–75. doi: 10.1002/bjs.4786
84. Orabueze I, Masucci A, and Cluzet V. Plasmapheresis vs conventional insulin therapy in hypertriglyceridemia-induced acute pancreatitis. Cureus. (2023) 15:e40568. doi: 10.7759/cureus.40568
85. Coskun A, Erkan N, Yakan S, Yildirim M, Carti E, Ucar D, et al. Treatment of hypertriglyceridemia-induced acute pancreatitis with insulin. Prz Gastroenterol. (2015) 10:18–22. doi: 10.5114/pg.2014.45412
86. Inayat F, Zafar F, Baig AS, Chaudhry NA, Aslam A, Khan ZH, et al. Hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis treated with insulin therapy: A comparative review of 34 cases. Cureus. (2018) 10:e3501. doi: 10.7759/cureus.3501
87. Li J, Chen TR, Gong HL, Wan MH, Chen GY, and Tang WF. Intensive insulin therapy in severe acute pancreatitis: a meta-analysis and systematic review. West Indian Med J. (2012) 61:574–9.
88. Araz F, Bakiner OS, Bagir GS, Soydas B, Ozer B, and Kozanoglu I. Continuous insulin therapy versus apheresis in patients with hypertriglyceridemia-associated pancreatitis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2022) 34:146–52. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000002025
89. de Pretis N, Amodio A, and Frulloni L. Hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis: Epidemiology, pathophysiology and clinical management. United Eur Gastroenterol J. (2018) 6:649–55. doi: 10.1177/2050640618755002
90. Meng Y, Han P, Ma X, He Y, Chen H, and Ren H. Research progress on the mechanism of acute hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis. Pancreas. (2024) 53:e700–e9. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000002364
91. Garg R and Rustagi T. Management of hypertriglyceridemia induced acute pancreatitis. BioMed Res Int. (2018) 2018:4721357. doi: 10.1155/2018/4721357
92. Grigore M, Balaban DV, Jinga M, Ioniță-Radu F, Costache RS, Dumitru AL, et al. Hypertriglyceridemia-induced and alcohol-induced acute pancreatitis-A severity comparative study. Diagnostics (Basel). (2025) 15.
93. Wang S, Dougherty EJ, and Danner RL. PPARγ signaling and emerging opportunities for improved therapeutics. Pharmacol Res. (2016) 111:76–85. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.02.028
94. Wilhite K, Reid JM, and Lane M. Risk of pancreatitis with incretin therapies versus thiazolidinediones in the veterans health administration. Ann Pharmacother. (2024) 58:685–9. doi: 10.1177/10600280231205490
95. Nakamura T, Ito T, Uchida M, Hijioka M, Igarashi H, Oono T, et al. PSCs and GLP-1R: occurrence in normal pancreas, acute/chronic pancreatitis and effect of their activation by a GLP-1R agonist. Lab Invest. (2014) 94:63–78. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2013.133
96. Nakamura Y, Kanai T, Saeki K, Takabe M, Irie J, Miyoshi J, et al. CCR2 knockout exacerbates cerulein-induced chronic pancreatitis with hyperglycemia via decreased GLP-1 receptor expression and insulin secretion. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. (2013) 304:G700–7. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00318.2012
97. Ryder RE. The potential risks of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer with GLP-1-based therapies are far outweighed by the proven and potential (cardiovascular) benefits. Diabetes Med. (2013) 30:1148–55. doi: 10.1111/dme.12301
98. Syed-Abdul MM, Tian L, Hegele RA, and Lewis GF. Futility of plasmapheresis, insulin in normoglycaemic individuals, or heparin in the treatment of hypertriglyceridaemia-induced acute pancreatitis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2025) 13:528–36. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(25)00028-2
99. Kuchay MS, Farooqui KJ, Bano T, Khandelwal M, Gill H, and Mithal A. Heparin and insulin in the management of hypertriglyceridemia-associated pancreatitis: case series and literature review. Arch Endocrinol Metab. (2017) 61:198–201. doi: 10.1590/2359-3997000000244
100. He W and Lu N. Emergent triglyceride-lowering therapy for hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis. Hepatogastroenterology. (2015) 62:429–34.
101. Tsuang W, Navaneethan U, Ruiz L, Palascak JB, and Gelrud A. Hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis: presentation and management. Am J Gastroenterol. (2009) 104:984–91. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2009.27
102. Berger Z, Quera R, Poniachik J, Oksenberg D, and Guerrero J. heparin and insulin treatment of acute pancreatitis caused by hypertriglyceridemia. Exp 5 cases] Rev Med Chil. (2001) 129:1373–8.
103. Alagözlü H, Cindoruk M, Karakan T, and Unal S. Heparin and insulin in the treatment of hypertriglyceridemia-induced severe acute pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. (2006) 51:931–3. doi: 10.1007/s10620-005-9006-z
104. Jain P, Rai RR, Udawat H, Nijhawan S, and Mathur A. Insulin and heparin in treatment of hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. (2007) 13:2642–3. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i18.2642
105. Näsström B, Olivecrona G, Olivecrona T, and Stegmayr BG. Lipoprotein lipase during continuous heparin infusion: tissue stores become partially depleted. J Lab Clin Med. (2001) 138:206–13. doi: 10.1067/mlc.2001.117666
106. Neuger L, Vilaró S, Lopez-Iglesias C, Gupta J, Olivecrona T, and Olivecrona G. Effects of heparin on the uptake of lipoprotein lipase in rat liver. BMC Physiol. (2004) 4:13. doi: 10.1186/1472-6793-4-13
107. Zorov DB, Juhaszova M, and Sollott SJ. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ROS-induced ROS release. Physiol Rev. (2014) 94:909–50. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00026.2013
108. Li Y, Yin B, Song Y, Chen K, Chen X, Zhang Y, et al. A novel ROS-Related chemiluminescent semiconducting polymer nanoplatform for acute pancreatitis early diagnosis and severity assessment. J Nanobiotechnology. (2023) 21:173. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-01937-9
109. Sastre J, Pérez S, Sabater L, and Rius-Pérez S. Redox signaling in the pancreas in health and disease. Physiol Rev. (2025) 105:593–650. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00044.2023
110. Hackert T and Werner J. Antioxidant therapy in acute pancreatitis: experimental and clinical evidence. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2011) 15:2767–77. doi: 10.1089/ars.2011.4076
111. Booth DM, Mukherjee R, Sutton R, and Criddle DN. Calcium and reactive oxygen species in acute pancreatitis: friend or foe? Antioxid Redox Signal. (2011) 15:2683–98.
112. Zhang F and Xu D. Zerumbone ameliorates the inflammatory response and organ damage in severe acute pancreatitis via the ROS/NF-κB pathway. BMC Gastroenterol. (2023) 23:333. doi: 10.1186/s12876-023-02962-6
113. He J, Hou X, Wu J, Wang K, Qi X, Wei Z, et al. Hspb1 protects against severe acute pancreatitis by attenuating apoptosis and ferroptosis via interacting with Anxa2 to restore the antioxidative activity of Prdx1. Int J Biol Sci. (2024) 20:1707–28. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.84494
114. Li X, Wang T, Zhou Q, Li F, Liu T, Zhang K, et al. Isorhamnetin alleviates mitochondrial injury in severe acute pancreatitis via modulation of KDM5B/htrA2 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073784
115. Xue Q, Yan D, Chen X, Li X, Kang R, Klionsky DJ, et al. Copper-dependent autophagic degradation of GPX4 drives ferroptosis. Autophagy. (2023) 19:1982–96.
116. Kong L, Deng J, Zhou X, Cai B, Zhang B, Chen X, et al. Sitagliptin activates the p62-Keap1-Nrf2 signalling pathway to alleviate oxidative stress and excessive autophagy in severe acute pancreatitis-related acute lung injury. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12:928. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04227-0
117. Zhang D, Wang X, Li W, Wan D, Zhou Y, Ma C, et al. A single-cell atlas-inspired hitchhiking therapeutic strategy for acute pancreatitis by restricting ROS in neutrophils. Adv Mater. (2025):e2502200. doi: 10.1002/adma.202502200
118. Xia CC, Chen HT, Deng H, Huang YT, and Xu GQ. Reactive oxygen species and oxidative stress in acute pancreatitis: Pathogenesis and new therapeutic interventions. World J Gastroenterol. (2024) 30:4771–80. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i45.4771
119. Cai Y, Yang F, and Huang X. Oxidative stress and acute pancreatitis (Review). BioMed Rep. (2024) 21:124. doi: 10.3892/br.2024.1812
120. Doseděl M, Jirkovský E, Macáková K, Krčmová LK, Javorská L, Pourová J, et al. Vitamin C-sources, physiological role, kinetics, deficiency, use, toxicity, and determination. Nutrients. (2021) 13.
121. Sun W, Zhao B, Li J, Wang Y, Qi X, Ning N, et al. Effect of high-dose intravenous vitamin C therapy on the prognosis in patients with moderately severe and severe acute pancreatitis: protocol of a prospective, randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study. Front Med (Lausanne). (2023) 10:1278167. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1278167
122. Gui M, Huang J, Sheng H, Chen Y, Yang Z, Ma L, et al. High-dose vitamin C alleviates pancreatic necrosis by inhibiting platelet activation through the CXCL12/CXCR4 pathway in severe acute pancreatitis. J Inflammation Res. (2023) 16:2865–77. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S415974
123. Siriwardena AK, Mason JM, Balachandra S, Bagul A, Galloway S, Formela L, et al. Randomised, double blind, placebo controlled trial of intravenous antioxidant (n-acetylcysteine, selenium, vitamin C) therapy in severe acute pancreatitis. Gut. (2007) 56:1439–44.
124. Du WD, Yuan ZR, Sun J, Tang JX, Cheng AQ, Shen DM, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of high-dose vitamin C on acute pancreatitis and its potential mechanisms. World J Gastroenterol. (2003) 9:2565–9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i11.2565
125. Monteiro TH, Silva CS, Cordeiro Simões Ambrosio LM, Zucoloto S, and Vannucchi H. Vitamin E alters inflammatory gene expression in alcoholic chronic pancreatitis. J Nutrigenet Nutrigenomics. (2012) 5:94–105. doi: 10.1159/000336076
126. Al-Hashem F, Abd Ellatif M, ShamsEldeen AM, Kamar SS, Al-Ani B, and Haidara MA. Vitamin E protects against the modulation of TNF-α-AMPK axis and inhibits pancreas injury in a rat model of L-arginine-induced acute necrotising pancreatitis. Arch Physiol Biochem. (2023) 129:148–56. doi: 10.1080/13813455.2020.1806330
127. Curran FJ, Sattar N, Talwar D, Baxter JN, and Imrie CW. Relationship of carotenoid and vitamins A and E with the acute inflammatory response in acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. (2000) 87:301–5. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2168.2000.01375.x
128. Bansal D, Bhalla A, Bhasin DK, Pandhi P, Sharma N, Rana S, et al. Safety and efficacy of vitamin-based antioxidant therapy in patients with severe acute pancreatitis: a randomized controlled trial. Saudi J Gastroenterol. (2011) 17:174–9. doi: 10.4103/1319-3767.80379
129. Yang X, Jin Z, Lin D, Shen T, Zhang J, Li D, et al. FGF21 alleviates acute liver injury by inducing the SIRT1-autophagy signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. (2022) 26:868–79. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17144
130. Shenoy VK, Beaver KM, Fisher FM, Singhal G, Dushay JR, Maratos-Flier E, et al. Elevated serum fibroblast growth factor 21 in humans with acute pancreatitis. PloS One. (2016) 11:e0164351. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164351
131. Lopez-Pascual A, Santamaria E, Ardaiz N, Uriarte I, Palmer T, Graham AR, et al. FGF21 and APOA1 mRNA-based therapies for the treatment of experimental acute pancreatitis. J Transl Med. (2025) 23:122. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06129-7
132. Zhao MQ, Fan MY, Cui MY, Chen SM, Wang JJ, Lu YY, et al. Profile of intestinal fungal microbiota in acute pancreatitis patients and healthy individuals. Gut Pathog. (2025) 17:1. doi: 10.1186/s13099-024-00675-z
133. Jin M, Zhang H, Wu M, Wang Z, Chen X, Guo M, et al. Colonic interleukin-22 protects intestinal mucosal barrier and microbiota abundance in severe acute pancreatitis. FASEB J. (2022) 36:e22174. doi: 10.1096/fj.202101371R
134. Li XY, He C, Zhu Y, and Lu NH. Role of gut microbiota on intestinal barrier function in acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. (2020) 26:2187–93. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i18.2187
135. Rodoman GV, Shalaeva TI, and Dobretsov GE. Blood fatty acid transporters in acute pancreatitis. Vopr Med Khim. (2001) 47:633–41.
136. Bi Z, Liang Y, Liu S, and Li Y. Acute uveitis caused by abnormal glucose and lipid metabolism: a case report. BMC Ophthalmol. (2023) 23:264. doi: 10.1186/s12886-023-02997-z
137. Kupčinskas J, Gedgaudas R, Hartman H, Sippola T, Lindström O, Johnson CD, et al. Intestinal fatty acid binding protein as a marker of necrosis and severity in acute pancreatitis. Pancreas. (2018) 47:715–20.
138. Goswami P, Sonika U, Moka P, Sreenivas V, and Saraya A. Intestinal fatty acid binding protein and citrulline as markers of gut injury and prognosis in patients with acute pancreatitis. Pancreas. (2017) 46:1275–80.
139. Schoenberg MH, Birk D, and Beger HG. Oxidative stress in acute and chronic pancreatitis. Am J Clin Nutr. (1995) 62:1306s–14s. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/62.6.1306S
Keywords: metabolic disturbances, acute pancreatitis, lipid metabolism, glucose metabolism, oxidative stress
Citation: Fang C, Ding Y, Wang X and Teng X (2025) Metabolic disturbances in acute pancreatitis: mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1579457. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1579457
Received: 19 February 2025; Accepted: 24 July 2025;
Published: 27 August 2025.
Edited by:
Shizhan Ma, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Huang Xiaofei, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, ChinaYaodong Wang, Yangzhou University, China
Copyright © 2025 Fang, Ding, Wang and Teng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xusheng Teng, amh6eHl5MDU3OUAxNjMuY29t
 Chao Fang
Chao Fang Yingwei Ding
Yingwei Ding Xiaojun Wang
Xiaojun Wang