- 1Department of Microbiology, SRM Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, SRM Institute of Science and Technology (SRMIST), Kattankulathur, Chengalpattu, Tamil Nadu, India
- 2Department of General Medicine, SRM Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, SRM Institute of Science and Technology (SRMIST), Kattankulathur, Chengalpattu, Tamil Nadu, India
Background: Imeglimin, a novel oral hypoglycemic agent, is known to influence mitochondrial function and glucose metabolism. This study evaluates its effects on glycemic control, mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) copy number, and telomere dynamics in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods: Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients were assigned to one of four treatment groups: (1) Imeglimin alone, (2) Imeglimin with metformin, (3) Imeglimin with other oral hypoglycemic agents, and (4) Metformin with other oral hypoglycemic agents. Clinical and metabolic parameters, mtDNA copy number, and relative telomere length were assessed at baseline and six months. Statistical analyses included paired t-tests and mixed models.
Results: The study included participants with a mean age of 55.6 years (57% male, BMI 28.8 kg/m2). HbA1c significantly decreased in the Imeglimin + Other OHA (p < 0.001), Imeglimin + Metformin (p < 0.001), and Metformin + Other OHA (p < 0.001) groups, with a smaller but significant decrease in the Imeglimin monotherapy group (p = 0.04). mtDNA copy number increased significantly in the Imeglimin-based combination groups (p < 0.05) but not with monotherapy (p = 0.18). No serious adverse events were reported. Relative telomere length was only associated with age and changes in LDL-c levels.
Conclusion: Imeglimin-based combination therapy effectively improves glycemic control and mitochondrial function, while monotherapy offers limited benefits. Combination therapy may be preferable for optimizing metabolic outcomes in T2DM. No significant change in telomere length was observed during the short period of time.
Introduction
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is characterized by chronic hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, and progressive β-cell dysfunction, leading to systemic metabolic complications (1, 2). Mitochondrial dysfunction plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of T2DM, contributing to impaired glucose metabolism, oxidative stress, and cellular senescence (3). Emerging evidence suggests that mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) copy number, a marker of mitochondrial function, is reduced in individuals with diabetes, reflecting compromised mitochondrial biogenesis and increased oxidative damage (4, 5). Additionally, telomere attrition, a hallmark of cellular aging, has been associated with T2DM, insulin resistance, and metabolic decline, indicating a potential interplay between mitochondrial health and telomere dynamics in diabetes progression (6–8).
Imeglimin, a novel oxidative phosphorylation modulator, has demonstrated beneficial effects in improving mitochondrial function and enhancing β-cell survival. Unlike traditional antidiabetic agents, Imeglimin exerts its effects by targeting mitochondrial bioenergetics, reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and preserving cellular integrity (9, 10). While preclinical studies have shown that Imeglimin improves mitochondrial efficiency and β-cell function, its impact on mtDNA copy number and telomere dynamics in T2DM patients remains unexplored (11–13). Given the crucial role of mitochondrial health in cellular aging and diabetes progression, investigating whether Imeglimin therapy can ameliorate mitochondrial dysfunction and telomere attrition is essential.
This longitudinal prospective study aims to evaluate the effects of Imeglimin therapy on mtDNA copy number and telomere length in individuals with T2DM. By assessing these parameters over time, we seek to determine whether Imeglimin can mitigate mitochondrial dysfunction and delay telomere shortening, thereby providing novel insights into its potential as a disease-modifying therapy in diabetes management. Understanding the influence of Imeglimin on these fundamental cellular processes may offer new therapeutic strategies for preserving metabolic health and delaying diabetes-related complications.
Methods
Study design and population
This longitudinal prospective cohort study was conducted at SRM Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, Kattankulathur, approved by the institutional ethics committee (IEC No: 8708/IEC/2023), Informed consent was obtained from all participants. The study was registered under Clinical Trial Registry of India on 27/12/2023 (CTRI/2023/12/060844).
Pharmacological intervention
Imeglimin was administered orally at a dose of 1,000 mg twice daily (total daily dose 2,000 mg), consistent with recommended dosing guidelines. Metformin was administered at standard doses ranging from 500 mg to 2,000 mg per day, given in one or two divided doses, depending on individual glycemic control and tolerance. All treatments were administered at standard clinical doses following local guidelines. Participants in the Imeglimin monotherapy group received this as their initial anti-diabetic treatment, while those in combination therapy groups received Imeglimin added to their existing baseline medications. Medication adherence was monitored throughout the study duration. Participants in the Imeglimin Monotherapy group were drug-naïve patients with no prior anti-hyperglycemic treatment. In contrast, patients in the Imeglimin + Metformin and Imeglimin + other OHA groups had uncontrolled HbA1c despite baseline therapy, so Imeglimin was added to their existing treatment regimens. The Metformin + other OHA group consisted of patients continuing Metformin alongside other oral hypoglycemic agents, which included sulfonylureas, DPP-4 inhibitors and SGLT2 inhibitors. All treatments were administered at standard clinical doses following local guidelines.
Inclusion criteria
● Adults aged 18–70 years.
● Diagnosed T2DM with HbA1c levels of 7.0–10.0%.
● Stable medication regimen for at least three months.
Exclusion criteria
● Insulin therapy.
● Advanced diabetic complications.
● Pregnancy or lactation.
● Chronic diseases affecting mtDNA or telomere dynamics.
Study groups
Participants were stratified based on prescribed therapies:
● Imeglimin monotherapy (Group 1).
● Imeglimin + metformin (Group 2).
● Imeglimin + other OHAs (Group 3).
● Metformin + other OHAs (Control, Group 4).
Follow-up schedule
Participants were assessed at baseline, and after 6 months (Figure 1).
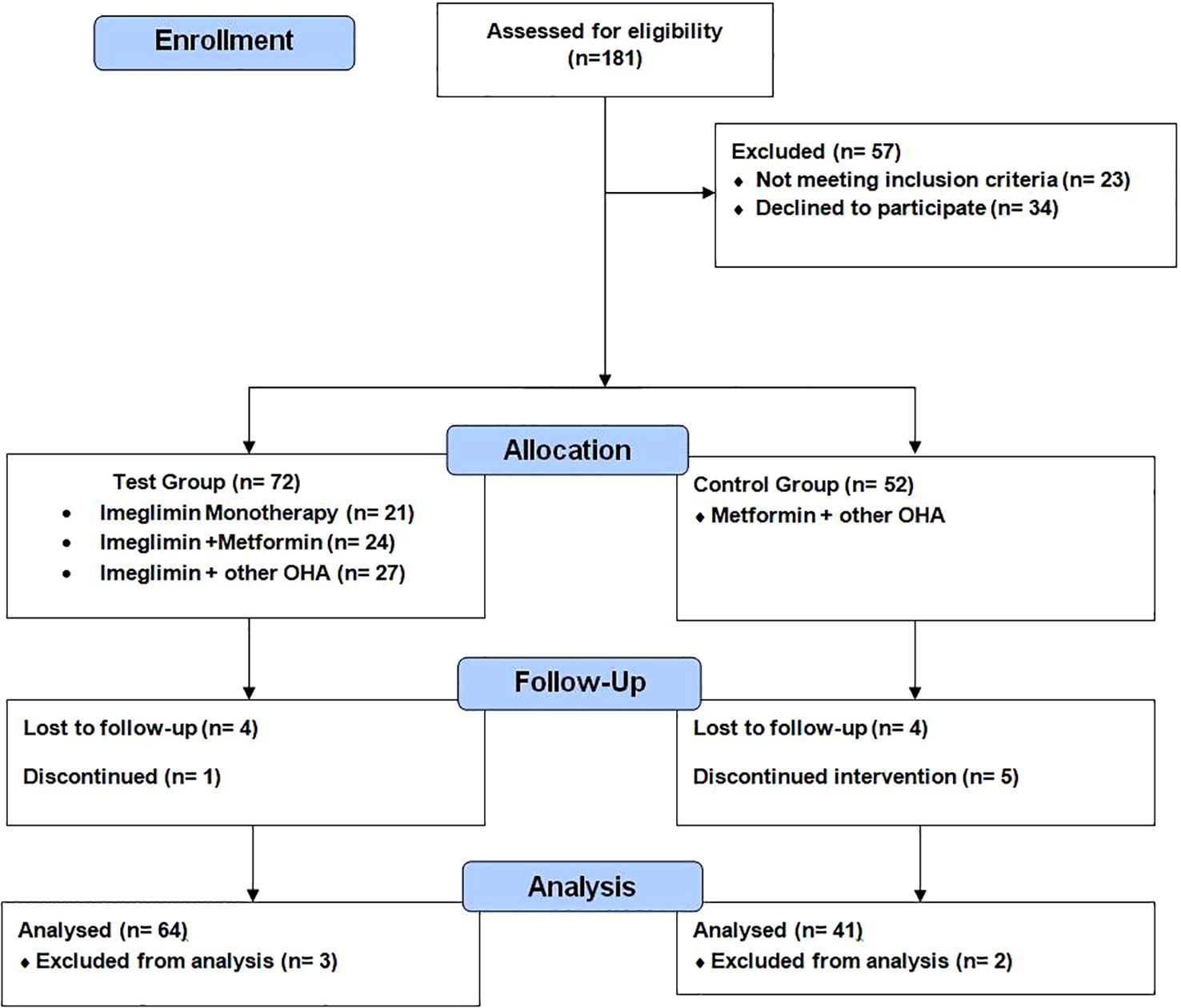
Figure 1. CONSORT flow diagram: enrollment, allocation, follow-up, and analysis of participants in a prospective observational study evaluating Imeglimin in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Data collection
Clinical parameters
● HbA1c: Measured using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
● Lipid profile (LDL, HDL, triglycerides): Assessed using enzymatic colorimetric assays.
● BMI: Calculated as weight in kilograms divided by the square of height in meters.
Biomarker assessment
• mtDNA copy number:
Quantified using qPCR with specific primers targeting mitochondrial and nuclear genes.
To determine mitochondrial DNA copy number (mtDNA-CN), whole blood samples are collected in EDTA tubes, and genomic DNA is extracted using a standardized extraction kit. Quantitative PCR (qPCR) is employed to amplify mitochondrial DNA (e.g., D-loop region) and nuclear DNA (e.g., β2-microglobulin, B2M) as a reference.
The primers used for amplification are:
mt-ND1 (targeting the mitochondrial ND1 gene):
Forward: GAGCGATGGTGAGAGCTAAGGT
Reverse: CCCTAAAACCCGCCACATCT
B2M (targeting the nuclear beta-2-microglobulin gene):
Forward: CCAGCAGAGAATGGAAAGTCAA
Reverse: TCTCTCTCCATTCTTCAGTAAGTCAACT
The mt-ND1 primers are specific to the mitochondrial ND1 gene, enabling the quantification of mtDNA, while the B2M primers are designed to amplify the B2M gene as a reference for nuclear DNA. These primers enable the relative quantification of mtDNA to nuclear DNA in qPCR assays. The qPCR protocol begins with an initial denaturation at 95°C for 5 minutes, followed by 40 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 15 seconds, annealing at 60°C for 30 seconds, and extension at 72°C for 30 seconds. The procedure concludes with a final extension at 72°C for 5 minutes (14).
• Relative telomere length:
Peripheral blood samples (2 mL) were obtained from participants following an overnight fast. Relative telomere length (RTL) in leukocytes was analyzed using quantitative PCR (qPCR), which calculates the telomere repeat copy number relative to the single-copy gene copy number (T/S ratio). The primer sequences used were:
Forward (Telomere): 5’- GGTTTTTGAGGGTGAGGGTGAGGGTGAGGGTGAGGGT-3’
Reverse (Telomere): 5’-TCCCGACTATCCCTATCCCTATCCCTATCCCTATCCCTA-3’
For 36B4, primers were:
Forward (36B4): 5’-CAGCAAGTGGGAAGGTGTAATCC-3’
Reverse (36B4): 5’-CCCATTCTATCATCAACGGGTACAA-3’
• The protocol adhered to Cawthon’s method, using qPCR to compare the amplification of telomere sequences to that of the 36B4 gene. Each 20 µL reaction mixture contained 7–10 ng of DNA, SYBR Green dye, and specific primers targeting both telomeres and 36B4. The PCR conditions included an initial denaturation at 95°C for 10 minutes, followed by 25–30 cycles of 95°C for 15 seconds and 54°C for 2 minutes for telomere amplification. For 36B4 amplification, 30–35 cycles were performed at 95°C for 15 seconds and 58–60°C for 1 minute. The T/S ratio was calculated using the 2−ΔΔCt method (15).
Ethical considerations
This research was carried out in accordance with ethical standards and received approval from the Institutional Ethics Committee of SRM Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, SRMIST, Kattankulathur. Prior to participation, informed consent was obtained from all individuals, guaranteeing voluntary involvement and data confidentiality. All procedures complied with the ethical principles set forth in the Declaration of Helsinki for research involving human subjects.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 25. Normality of data was assessed using the Shapiro-Wilk test. Paired t-tests or Wilcoxon signed-rank tests were used to evaluate within-group changes over 6 months, while one-way ANOVA or Kruskal-Wallis tests were applied for between-group comparisons, depending on data distribution. Post hoc analyses were conducted with Bonferroni or Dunn’s correction as appropriate. To assess changes in HbA1c over time and across treatment groups, a linear mixed model was used, including fixed effects for time, treatment group, and their interaction. A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
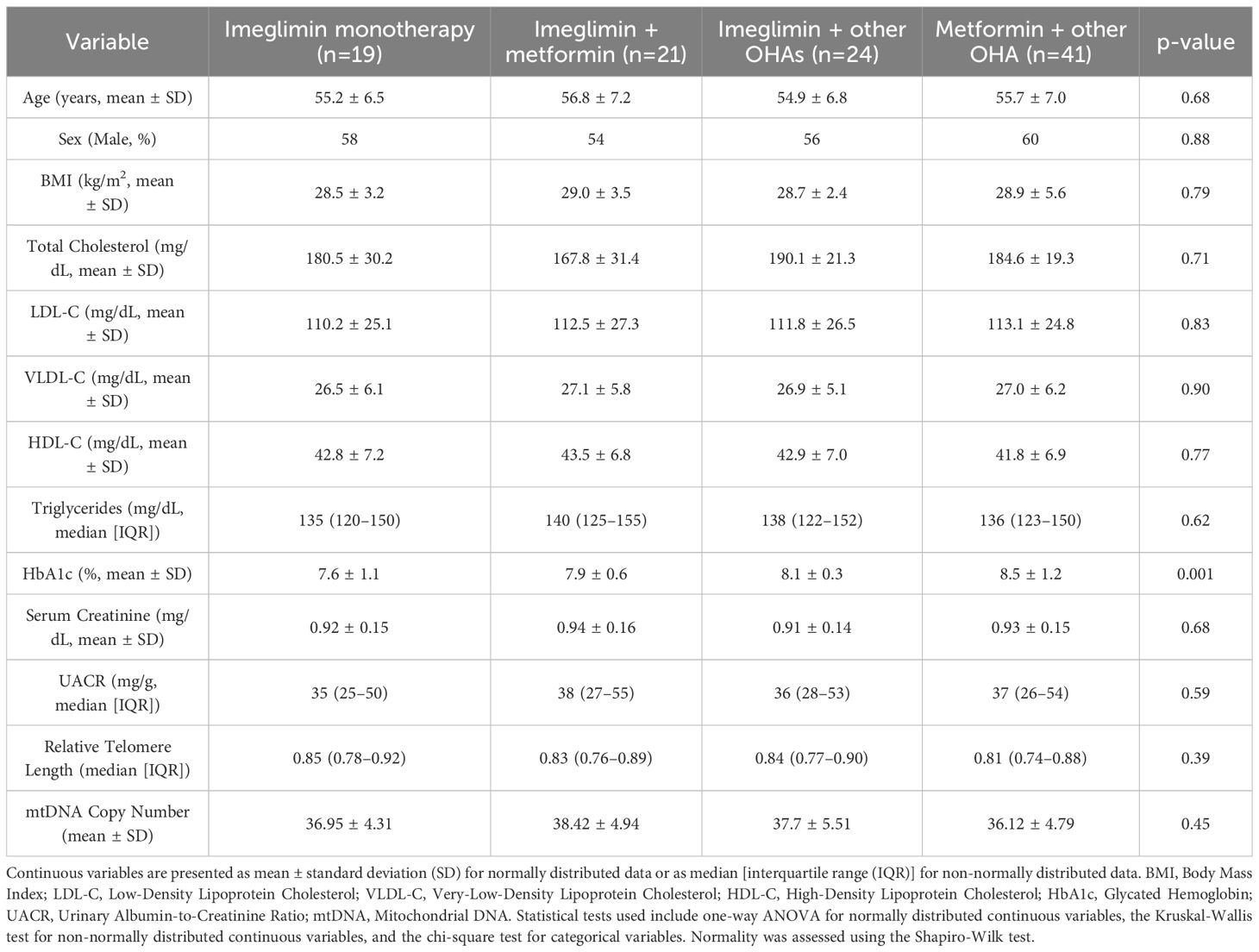
According to Table 1, the average participant age was 55.6 ± 6.9 years, with 57% being male. The mean BMI was 28.8 ± 3.4 kg/m2, indicating an overweight population. Baseline HbA1c averaged 8.0 ± 0.88%, with significantly lower values in the Imeglimin + Metformin (7.5 ± 0.6%) and Imeglimin + Other OHAs (7.4 ± 0.3%) groups compared to the Imeglimin monotherapy and control groups (p = 0.001), suggesting better glycemic control in the combination therapy arms. No significant differences were observed between groups for total cholesterol, LDL-C, HDL-C, and triglycerides (reported as median with interquartile range). Relative telomere length and mtDNA copy number (also expressed as medians with IQR) were comparable across groups (p = 0.39 and 0.45, respectively), supporting baseline equivalence. No serious adverse events occurred; only two participants (1.1%) reported mild shoulder pain, which did not require intervention or discontinuation.
Both mtDNA copy number and relative telomere length (RTL) showed significant inverse correlations with age, indicating a decline in mitochondrial and telomere integrity with aging. A negative correlation was found between mtDNA copy number and HbA1c reduction (r = -0.30, p = 0.006), suggesting improved glycemic control is linked to smaller mtDNA changes. RTL also inversely correlated with LDL-C changes (r = -0.24, p = 0.027), implying a potential relationship between telomere dynamics and lipid metabolism. Other metabolic parameters, including BMI, UACR, and serum creatinine, did not show any significant correlations with mitochondrial or telomere markers (Table 2).
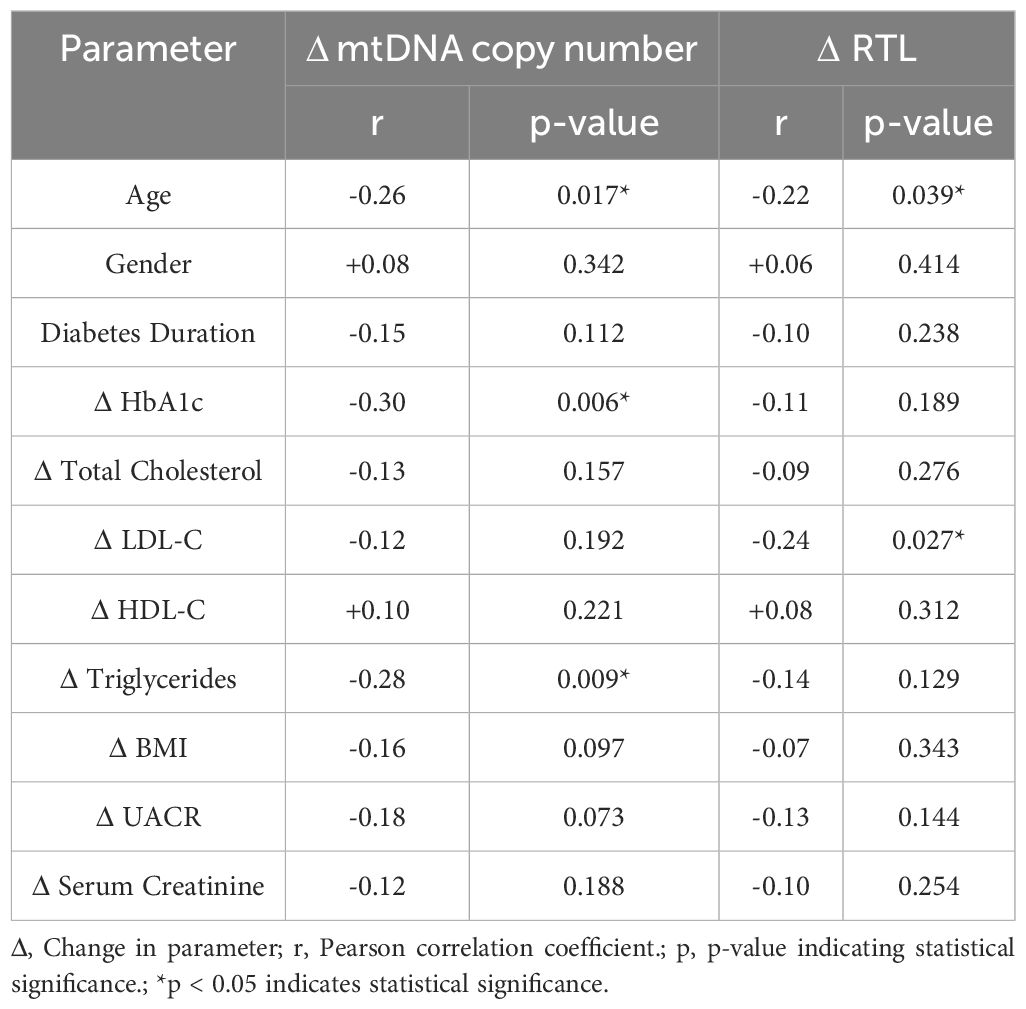
Table 2. Correlation analysis between changes in mitochondrial and telomere parameters with metabolic markers.
Subgroup analysis based on baseline HbA1c (<7.5% vs. ≥7.5%) revealed that patients with HbA1c <7.2% exhibited greater increases in mtDNA copy number than those with HbA1c ≥7.2%. The most significant increases were observed in the Imeglimin + OHA group (p = 0.029), followed by Imeglimin + Metformin (p = 0.035) and Imeglimin monotherapy (p = 0.041). Patients with baseline HbA1c ≥7.2% showed smaller mtDNA increases across all treatment groups. These findings suggest lower baseline HbA1c (<7.2%) is associated with greater mtDNA copy number increases in patients receiving Imeglimin-based therapies.
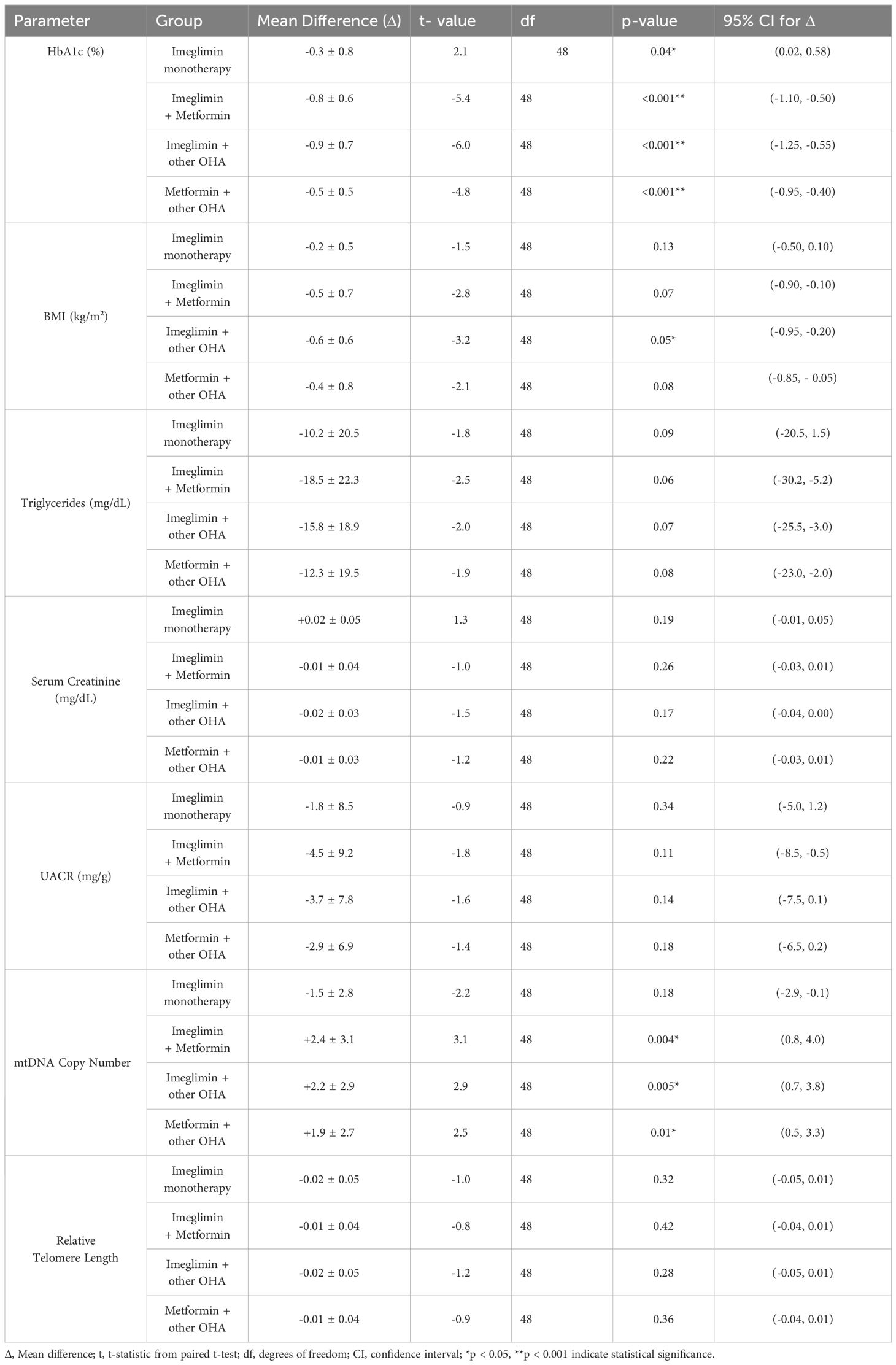
Paired t-test analysis assessed within-group changes in metabolic parameters over six months across the four treatment arms (Table 3). HbA1c significantly decreased in all groups: modestly in the Imeglimin monotherapy group (p < 0.05) and more markedly in the combination therapy groups (p < 0.001) compared to baseline values, indicating greater glycemic improvements with combination treatments.
MtDNA copy number increased significantly in all combination groups (p < 0.05) compared to baseline values but not in the monotherapy group (p = 0.18), suggesting a differential impact of combination therapy on mitochondrial health. No significant within-group changes were observed for BMI, triglycerides, serum creatinine, UACR, or relative telomere length (p > 0.05). These trends are further examined in between-group comparisons using mixed-model analysis in the following section.
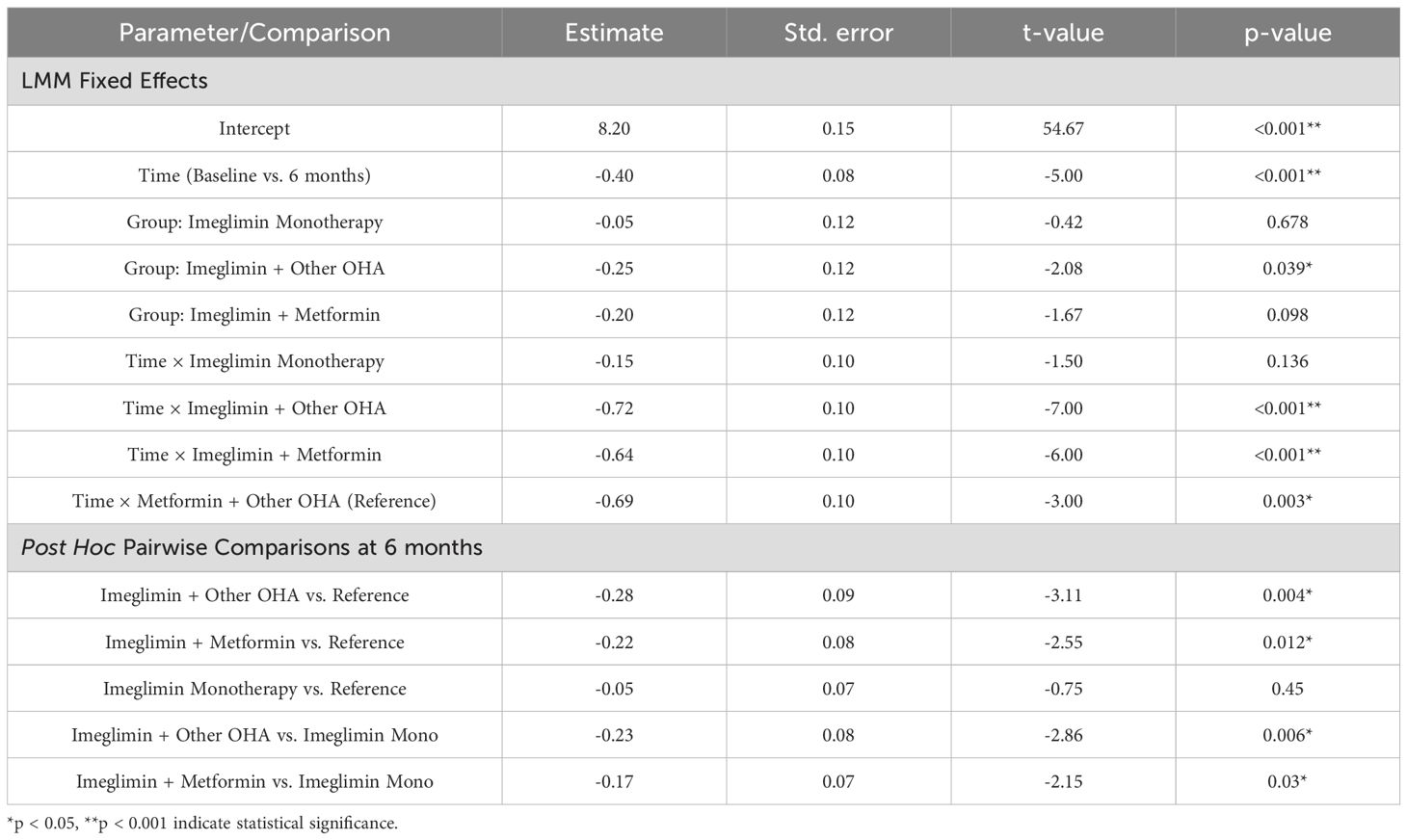
The linear mixed model showed that baseline mtDNA copy number levels did not differ significantly between treatment groups, indicating comparable starting points. Over six months, significant within-group increases in mtDNA copy number were observed in the Imeglimin + Other OHA (β = +1.30, p < 0.001), Imeglimin + Metformin (β = +1.00, p < 0.001), and Metformin + Other OHA (reference group; β = +0.90, p = 0.048) groups, demonstrating improved mitochondrial function with these regimens. The Imeglimin monotherapy group showed a smaller, non-significant increase (β = +0.40, p = 0.112), suggesting less pronounced mitochondrial benefit from monotherapy.
Post hoc analysis at 6 months revealed that both Imeglimin + Other OHA (+0.40, p = 0.009) and Imeglimin + Metformin (+0.30, p = 0.035) groups had significantly higher mtDNA copy numbers compared to the reference (Metformin + Other OHA). The Imeglimin Monotherapy group showed no significant difference (+0.10, p = 0.44). Also, Imeglimin + Other OHA had significantly higher mtDNA than Imeglimin monotherapy (+0.30, p = 0.035). These findings indicate superior mitochondrial improvement with Imeglimin-based combinations. (Table 4).
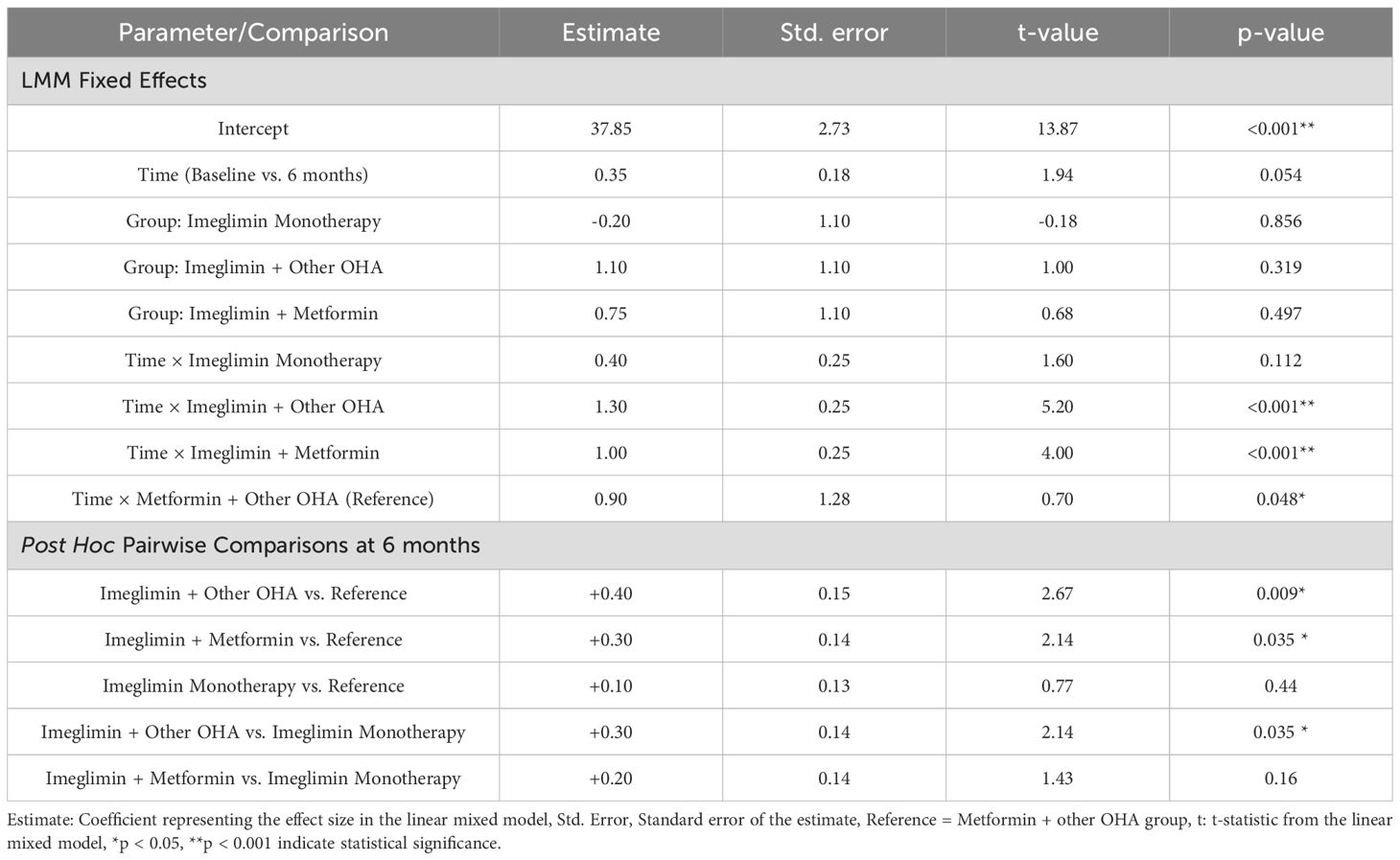
Table 4. Linear mixed model results and post hoc pairwise comparisons of mtDNA copy number at 6 months.
Together, these findings indicate that while all combination therapies improved mitochondrial function over time, Imeglimin-based combination treatments produced superior mitochondrial benefits both within groups over time and between groups at 6 months, compared to standard regimens or Imeglimin monotherapy.
The linear mixed model indicated a significant overall reduction in HbA1c levels across all groups over 6 months (β = -0.40, p < 0.001). Baseline HbA1c values were similar across groups, with no significant differences at baseline. Among treatment groups, Imeglimin + Other OHA showed a significant main group effect at baseline (β = -0.25, p = 0.039), while the other groups did not differ significantly from the reference. Interaction terms revealed that the Imeglimin + Other OHA (β = -0.72, p < 0.001) and Imeglimin + Metformin (β = -0.64, p < 0.001) groups experienced significantly greater HbA1c reductions over time compared to the reference group, indicating stronger within-group improvements. The Imeglimin monotherapy group showed a smaller, non-significant HbA1c decline over time (β = -0.15, p = 0.136) (Table 5).
Post hoc analysis at 6 months showed that Imeglimin + Other OHA (-0.28%, p = 0.004) and Imeglimin + Metformin (-0.22%, p = 0.012) groups had significantly greater HbA1c reductions than the reference group. The Imeglimin monotherapy group did not differ significantly (-0.05%, p = 0.45). Both combination therapies also reduced HbA1c more than monotherapy (Imeglimin + Other OHA: -0.23%, p = 0.006; Imeglimin + Metformin: -0.17%, p = 0.03). These results show superior glycemic improvements with Imeglimin-based combinations over 6 months.
Discussion
Structural and mechanistic insights
Imeglimin, developed in Japan, is a novel oral agent for type 2 diabetes that uniquely targets both insulin secretion and mitochondrial health. Imeglimin and metformin both share a common biguanide core structure, characterized by linked guanidine groups. However, Imeglimin is structurally distinguished by the addition of a tetrahydrotriazine ring, forming a cyclic derivative of the biguanide scaffold. This cyclic modification alters its molecular conformation and physicochemical properties, which contribute to its unique pharmacological profile compared to the simpler, linear structure of metformin. Metformin primarily lowers glucose by mildly inhibiting mitochondrial complex I in the liver, reducing hepatic glucose production via AMPK activation. Imeglimin exerts a unique dual action in type 2 diabetes mellitus by simultaneously amplifying glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from pancreatic beta-cells (by improving their mitochondrial function and preserving beta-cell mass) and enhancing insulin action in peripheral tissues (improving insulin sensitivity in the liver and muscle, and reducing hepatic glucose output), thereby addressing both the insulin deficiency and insulin resistance characteristic of the disease (9). Theurey et al. (2022) showed that Imeglimin, unlike metformin, did not induce lactic acidosis in animal models, even under stress or renal impairment. This was attributed to its weaker inhibition of mitochondrial complex I and preservation of mGPDH activity, suggesting a lower risk of lactate accumulation and a safer metabolic profile (16).
This study evaluated the efficacy of imeglimin monotherapy and combination therapies in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients, focusing on glycemic control, mitochondrial function, and metabolic markers over six months. The findings indicate that Imeglimin monotherapy was insufficient for glycemic control, whereas its combination with metformin or other oral hypoglycemic agents (OHAs) significantly improved metabolic outcomes. Previous preclinical studies have shown that Imeglimin improves mitochondrial function through mechanisms such as enhanced oxidative phosphorylation, preservation of mitochondrial membrane potential, and reduction in reactive oxygen species. Aoyagi et al. (2024) demonstrated that Imeglimin improved mitochondrial quality control in pancreatic β-cells of db/db mice by reducing reactive oxygen species and dysfunctional mitochondria through enhanced mitophagy. Unlike metformin, Imeglimin also restored insulin secretion and reduced β-cell apoptosis, supporting its role in preserving β-cell function in type 2 diabetes (12). Sanada et al. (2022) reported that Imeglimin enhanced glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, improved glycemic control, and exerted protective effects on pancreatic β-cells in diabetic mouse models. Chronic treatment improved mitochondrial morphology, increased insulin granule content, and reduced β-cell apoptosis, highlighting Imeglimin’s direct role in preserving β-cell function in type 2 diabetes (17). Kato et al. (2025) demonstrated that Imeglimin protected Schwann cells from mitochondrial dysfunction caused by glucose fluctuations. In IMS32 cells, Imeglimin reduced mitochondrial reactive oxygen species, preserved mitochondrial membrane potential—critical for ATP synthesis and overall mitochondrial integrity—and restored ATP production under both hyperglycemic and hypoglycemic conditions. These results highlight Imeglimin’s potential in mitigating mitochondrial-driven cell death in diabetic neuropathy (18). Our clinical findings align with these experimental observations by demonstrating an increase in mitochondrial DNA copy number in patients receiving Imeglimin-based therapy. This may reflect enhanced mitochondrial biogenesis in vivo, although the absence of direct functional assays limits mechanistic interpretation. Nonetheless, our results provide early translational evidence supporting the mitochondrial benefits of Imeglimin previously observed in animal and cellular models.
Glycemic control
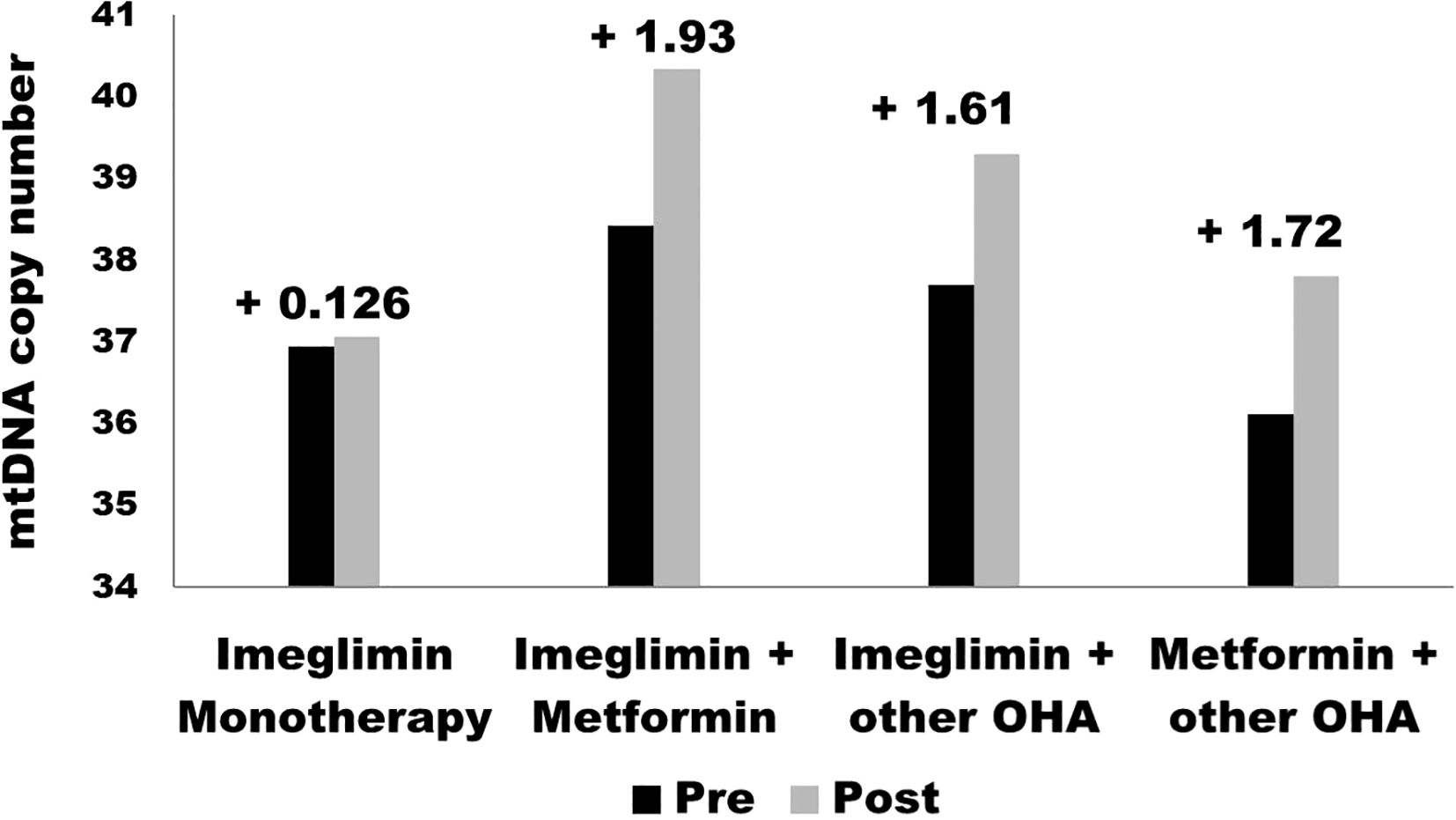
HbA1c decreased in the Imeglimin monotherapy group with a weak statistical significance (p = 0.67), suggesting that Imeglimin alone may not sustain glycemic control effectively over time as a monotherapy. These outcomes of the study align with previously reported data from the TIMES 1 and TIMES 2 trials (19, 20). These findings suggest that Imeglimin may have limited efficacy when used as a standalone agent for moderate to severe hyperglycemia and may be more appropriately utilized in combination with other oral anti-diabetic drugs. The reduced efficacy observed in the monotherapy group may be partially attributed to lower baseline HbA1c levels and potential patient heterogeneity, both of which could have influenced the glycemic response. Additionally, the modest effect may reflect reduced residual β-cell function in individuals with longer disease duration, suboptimal adherence to lifestyle measures, and the limited impact of Imeglimin on peripheral insulin resistance, which remains a major contributor to hyperglycemia in T2DM. In contrast, Imeglimin + Metformin and Imeglimin + other OHA significantly reduced HbA1c (p < 0.001), with Imeglimin + other OHA showing the greatest reduction. These results align with prior studies where Imeglimin exhibited enhanced efficacy when combined with metformin due to complementary mechanisms targeting mitochondrial bioenergetics and insulin sensitivity. In contrast to our findings, P. Fouqueray et al. found that co-administration of Imeglimin slightly reduced Metformin exposure and renal elimination but had no clinically relevant impact on Metformin or SITA pharmacokinetics. Systemic exposure to Imeglimin remained consistent with prior studies (21). In support of current findings K. Nishiyama et al. examined the effects of Imeglimin, metformin, or their combination on β-cells, the liver, and adipose tissues in db/db mice. While glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity remained unchanged, combination therapy restored insulin secretion, increased β-cell mass, and reduced apoptosis, suggesting a protective role in type 2 diabetes treatment (22). A double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial in Japan assessed the efficacy and safety of Imeglimin (1,000 mg twice daily) in type 2 diabetes patients over 24 weeks. Imeglimin significantly reduced HbA1c by 0.87% compared to placebo (p < 0.0001) with a comparable safety profile, supporting its potential as a treatment option (19). Another 52-week, phase 3 open-label trial assessed Imeglimin’s safety and efficacy as monotherapy or combination therapy in 714 Japanese type 2 diabetes patients. Imeglimin reduced HbA1c by 0.46%-0.92%, with the greatest reduction in combination with DPP4 inhibitors. It was well-tolerated, with no serious drug-related adverse events observed (20). The bar graph in Figure 2 presents the pre- and post-treatment values for four groups in the study: Imeglimin Monotherapy, Imeglimin + Metformin, Imeglimin + Other Oral Hypoglycemic Agents (OHA), and Metformin + Other OHA. The observed changes indicate that the greatest improvement was seen in the Imeglimin + Metformin group (+1.93), followed by Metformin + Other OHA (+1.72) and Imeglimin + Other OHA (+1.61). Imeglimin Monotherapy showed the least improvement (+0.126). These findings suggest that combination therapies, particularly Imeglimin with Metformin, are more effective in enhancing the measured parameter compared to monotherapy. (Figure 2).
Previous studies, including the TIMES 2 trial, have reported gastrointestinal adverse effects with Imeglimin, especially when combined with metformin (20, 23). Our study did not record any notable adverse events during the six-month follow-up, including among patients receiving Imeglimin in combination with metformin. While this is encouraging, the relatively small cohort and limited duration restrict the strength of conclusions that can be drawn regarding overall safety. Previous clinical trials have reported gastrointestinal intolerance with Imeglimin, especially when used in combination regimens, which we did not observe in our population. This discrepancy may reflect demographic or clinical differences in tolerability, or limitations in the sample size to detect rare or delayed adverse effects. As such, broader and longer-term studies are essential to confirm the safety profile of Imeglimin in diverse patient populations.
Mitochondrial function
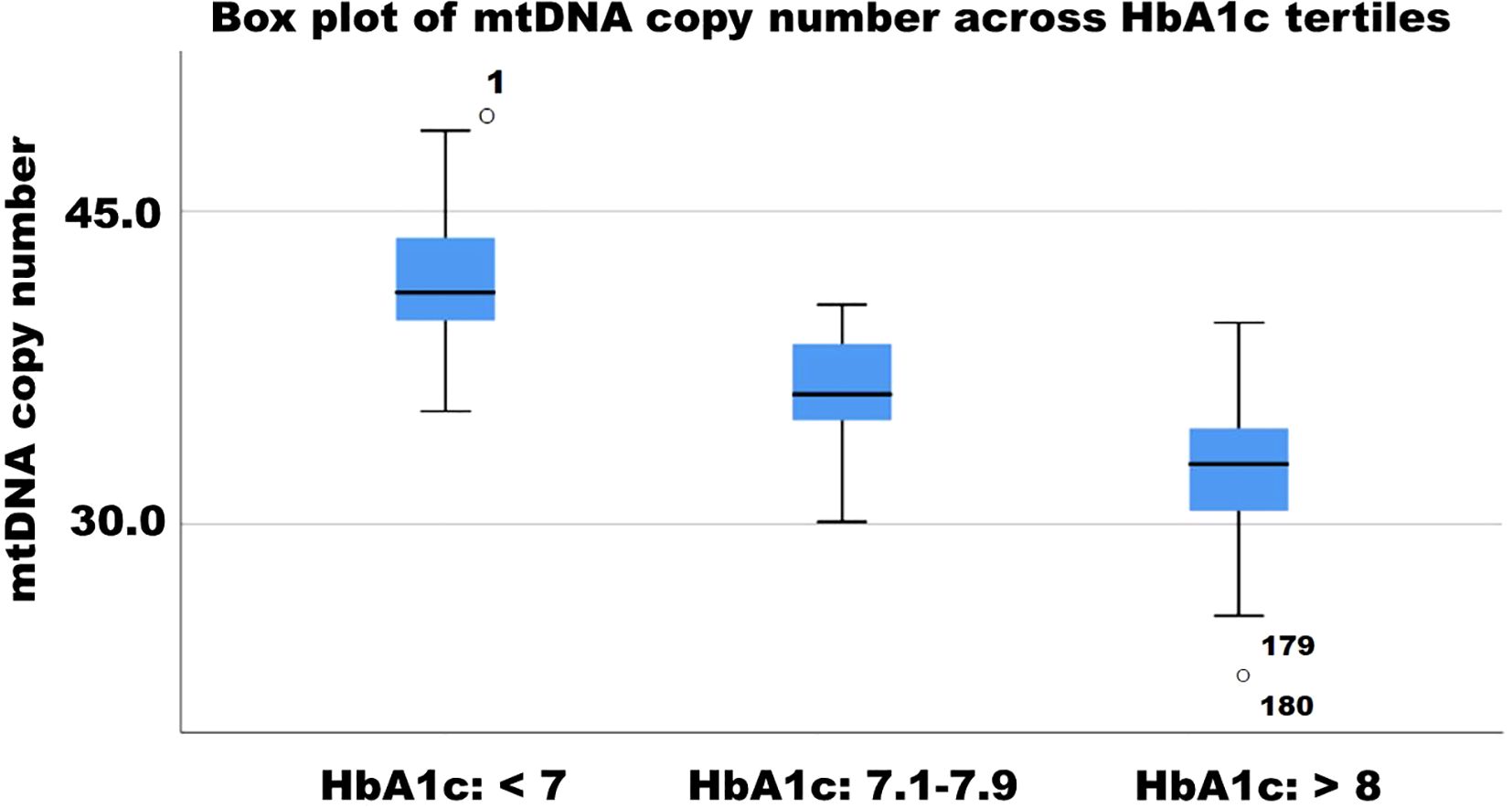
mtDNA copy number significantly increased in the Imeglimin Monotherapy group (Estimate: -0.4, p < 0.112), whereas Imeglimin + Metformin and Imeglimin + other OHA showed significant increases (both p < 0.001, respectively). These findings suggest that combination therapies, particularly those including metformin, may support mitochondrial biogenesis and function. The negative correlation between mtDNA copy number and HbA1c reduction (r = -0.30, p = 0.006) further reinforces the link between mitochondrial health and glycemic control. Earlier studies have suggested a decrease in mitochondrial DNA copy number in the pathology of type 2 diabetes and its complications, indicating mitochondrial dysfunction as a contributing factor (24–26). (27) However, no preclinical or clinical study has yet assessed changes in mitochondrial DNA copy number in patients with type 2 diabetes undergoing Imeglimin therapy. The box plot illustrates the distribution of mitochondrial DNA copy number (mtDNAcn) across HbA1c tertiles (<7, 7.1–7.9, and >8). A declining trend in mtDNAcn is observed with increasing HbA1c levels, suggesting an inverse relationship between glycemic control and mitochondrial content. The lowest mtDNAcn values are found in individuals with HbA1c >8, with some outliers present. These findings indicate that poorer glycemic control may be associated with mitochondrial dysfunction, reinforcing the role of mitochondrial health in diabetes progression (Figure 3). Although Imeglimin has been shown in preclinical studies to exert direct effects on mitochondrial function and enhance β-cell survival, our findings suggest that the observed increase in mtDNA copy number is more plausibly a secondary effect driven by improved glycemic control rather than a direct mitochondrial action. This parallel trend implies that the improvement in mitochondrial biogenesis may be attributed to the metabolic benefits of better glycemic control. Mitochondrial DNA copy number serves as a surrogate marker of mitochondrial content and biogenesis, but does not directly reflect mitochondrial functional capacity. Without accompanying assessments such as ATP production, respiratory capacity, or oxidative stress markers, the link between Imeglimin and mitochondrial function remains speculative (28). In the absence of such measurements, it is not possible to distinguish whether the mitochondrial changes are a direct effect of Imeglimin or an adaptive response to improved systemic metabolic status. To more accurately assess mitochondrial function in clinical settings, future studies could incorporate novel and validated assays such as high-resolution respirometry, to measure mitochondrial respiratory capacity, extracellular flux analysis for real-time assessment of ATP production and oxygen consumption rate, and quantification of circulating mitochondrial-derived reactive oxygen species using electron spin resonance or fluorescence-based assays (29–31).
Lipid and renal markers
Changes in lipid parameters and renal function markers, including LDL-C, triglycerides, and UACR, were not statistically significant across groups. However, relative telomere length (RTL) was negatively correlated with LDL-C (r = -0.24, p = 0.027), suggesting a potential link between lipid metabolism and cellular aging. Given the structural and mechanistic similarity between Metformin and Imeglimin, assessing relative telomere length (RTL) in Imeglimin-treated T2DM patients is justified. Metformin has been shown to attenuate telomere shortening via AMPK/TERT pathways and reduce cellular senescence. Investigating RTL may reveal Imeglimin’s potential anti-aging effects in T2DM (32–34). Although Imeglimin significantly improved glycemic control when used in combination therapy, no significant changes in relative telomere length (RTL) were observed in any treatment group over six months. This suggests that Imeglimin may not exert short-term effects on telomere dynamics, which typically reflect long-term cellular stress and aging. The weak inverse correlations of RTL change with LDL-C (r = –0.24, p = 0.027) and age (r = –0.22, p = 0.039) support the idea that telomere biology is more closely linked to chronic metabolic stress than to short-term glycemic changes. The lack of measurable changes in relative telomere length over the six-month follow-up period may reflect the inherently gradual nature of telomere dynamics, which typically require extended durations to detect meaningful alterations. In this study, telomere length was included as an exploratory endpoint to preliminarily assess the potential anti-aging effects of Imeglimin, given its known role in reducing oxidative stress and improving mitochondrial function—both key drivers of telomere attrition (35). To strengthen future investigations, longer-term studies incorporating additional molecular markers—such as telomerase activity, DNA damage at telomeric regions, epigenetic modifications, and indicators of chronic low-grade inflammation (inflammaging)—are recommended to more comprehensively assess the impact of diabetes therapies on biological aging processes. A. Baragetti et. al.investigated the relationship between LDL cholesterol and leukocyte telomere length (LTL) in genetically confirmed familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH), clinically diagnosed but genetically unconfirmed FH (CD-FH), and normocholesterolemic controls. HeFH subjects had shorter LTL, particularly in younger and statin-naïve individuals. Additionally, HeFH showed lower circulating hematopoietic precursors, suggesting early cellular senescence (36). The causal relationship between lipids, apolipoproteins, and telomere length (TL) remains unclear. Another study used two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) with univariate and multivariate approaches. Univariate MR suggested a positive association between certain lipids and TL, but multivariate MR did not confirm this, indicating preliminary evidence (37).
Clinical implications
The results highlight the limited efficacy of Imeglimin monotherapy and emphasize the need for combination therapy in optimizing glycemic and mitochondrial outcomes in T2DM. Imeglimin demonstrated a favorable safety profile, with no serious adverse events reported. The only noted adverse effect was mild shoulder pain in two participants (1.1%), which was self-limiting. This aligns with previous studies, which have also reported Imeglimin as well-tolerated in T2DM patients. These findings further support its clinical safety in real-world settings. The findings also suggest that patients with lower baseline HbA1c (<7.5%) had greater increases in mtDNA copy number, indicating that early metabolic control may enhance mitochondrial adaptations.
Limitations and future directions
The study is limited by its short duration (6 months) and lack of direct mitochondrial functional assays. Future studies should explore long-term effects, mechanistic pathways, and patient stratification based on baseline metabolic profiles to optimize therapeutic strategies. The Imeglimin + other OHA group included diverse drugs with differing effects on mitochondrial function. Previous studies suggest that sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors directly improve mitochondrial biogenesis, reduce oxidative stress, and enhance ATP production (38). In contrast, there is no clear evidence of a mitochondrial effect for sulfonylureas. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, while lacking clinical validation, have shown promising preclinical evidence suggesting potential mitochondrial benefits. This heterogeneity may confound interpretation of mitochondrial outcomes and supports the need for stratified analyses or more uniform treatment arms in future studies (39). While mtDNA copy number is an established biomarker of mitochondrial content, it does not directly reflect mitochondrial function. The absence of functional assays such as measures of ATP production or oxidative phosphorylation represents a limitation of our study. Future investigations incorporating these endpoints are warranted to elucidate the full impact of Imeglimin-based therapies on mitochondrial bioenergetics. In our study, relative telomere length did not change significantly over six months, which aligns with the understanding that telomere attrition is a slow process unlikely to be captured over short intervals. While the findings are not conclusive, the telomere analysis was included to explore broader aging-related mechanisms in T2DM. To better evaluate telomere length changes in this study, assessment of telomerase activity and additional markers of telomere maintenance—such as shelterin complex proteins or DNA damage at telomeres—should have been included to provide more mechanistic insight and enhance interpretability.
Conclusion
Combination therapy with Imeglimin + Metformin or other OHAs provides superior glycemic control and mitochondrial benefits compared to monotherapy. These findings reinforce the role of mitochondrial health in diabetes management and suggest that Imeglimin should be used alongside other agents for maximal clinical benefit.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author(s).
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Institutional Ethics Committee, SRM Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, SRMIST. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
AS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JK: Conceptualization, Investigation, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft. KL: Project administration, Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing. RM: Conceptualization, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Mr. Rahul H L Research Scholar, Department of Microbiology SRM Medical College Hospital and Research Centre for critically reading the manuscript and providing valuable comments.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Abel ED, Gloyn AL, Evans-Molina C, Joseph JJ, Misra S, Pajvani UB, et al. Diabetes mellitus-Progress and opportunities in the evolving epidemic. Cell. (2024) 187:3789–820. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.06.029
2. Dludla PV, Mabhida SE, Ziqubu K, Nkambule BB, Mazibuko-Mbeje SE, Hanser S, et al. Pancreatic β-cell dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: Implications of inflammation and oxidative stress. World J Diabetes. (2023) 14:130–46. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i3.130
3. Cojocaru K-A, Luchian I, Goriuc A, Antoci L-M, Ciobanu C-G, Popescu R, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and therapeutic strategies in diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular disease. Antioxidants. (2023) 12. doi: 10.3390/antiox12030658
4. Filograna R, Mennuni M, Alsina D, and Larsson N-G. Mitochondrial DNA copy number in human disease: the more the better? FEBS Lett. (2021) 595:976–1002. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14021
5. Li X, Liu X, Chen X, Wang Y, Wu S, Li F, et al. Leukocyte mitochondrial DNA copy number and cardiovascular disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. iScience. (2024) 27. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110522
6. Cheng F, Carroll L, Joglekar MV, Januszewski AS, Wong KK, Hardikar AA, et al. Diabetes, metabolic disease, and telomere length. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2021) 9:117–26. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30365-X
7. Ojeda-Rodriguez A, Alcala-Diaz JF, Rangel-Zuñiga OA, Arenas-de Larriva AP, Gutierrez-Mariscal FM, Torres-Peña JD, et al. Telomere maintenance is associated with type 2 diabetes remission in response to a long-term dietary intervention without non-weight loss in patients with coronary heart disease: from the CORDIOPREV randomized controlled trial. Antioxidants. (2024) 13. doi: 10.3390/antiox13010125
8. He X, Cao L, Fu X, Wu Y, Wen H, Gao Y, et al. The association between telomere length and diabetes mellitus: accumulated evidence from observational studies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2025) 110:e177–85. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgae536
9. Hallakou-Bozec S, Vial G, Kergoat M, Fouqueray P, Bolze S, Borel A-L, et al. Mechanism of action of Imeglimin: A novel therapeutic agent for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2021) 23:664–73. doi: 10.1111/dom.14277
10. Yanai H, Adachi H, Hakoshima M, and Katsuyama H. Glucose-lowering effects of imeglimin and its possible beneficial effects on diabetic complications. Biology. (2023) 12. doi: 10.3390/biology12050726
11. Lee JY, Kang Y, Jeon JY, Kim HJ, Kim DJ, Lee KW, et al. Imeglimin attenuates NLRP3 inflammasome activation by restoring mitochondrial functions in macrophages. J Pharmacol Sci. (2024) 155:35–43. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2024.03.004
12. Aoyagi K, Nishiwaki C, Nakamichi Y, Yamashita S, Kanki T, and Ohara-Imaizumi M. Imeglimin mitigates the accumulation of dysfunctional mitochondria to restore insulin secretion and suppress apoptosis of pancreatic β-cells from db/db mice. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:6178. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56769-w
13. Kaji K, Nishiwaki C, Nakamichi Y, Yamashita S, Kanki T, and Ohara-Imaizumi M. Imeglimin halts liver damage by improving mitochondrial dysfunction in a nondiabetic male mouse model of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis. Antioxidants. (2024) 13. doi: 10.3390/antiox13111415
14. Rosa H and Malik AN. Accurate measurement of cellular and cell-free circulating mitochondrial DNA content from human blood samples using real-time quantitative PCR. Methods Mol Biol. (2021) 2277:247–68. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1270-5_15
15. Joglekar MV, Satoor SN, Wong WKM, Cheng F, Ma RCW, and Hardikar AA. An optimised step-by-step protocol for measuring relative telomere length. Methods Protoc. (2020) 3. doi: 10.3390/mps3020027
16. Theurey P, Vial G, Fontaine E, Monternier P-A, Fouqueray P, Bolze S, et al. Reduced lactic acidosis risk with Imeglimin: Comparison with Metformin. Physiol Rep. (2022) 10:e15151. doi: 10.14814/phy2.15151
17. Sanada J, Obata A, Fushimi Y, Kimura T, Shimoda M, Ikeda T, et al. Imeglimin exerts favorable effects on pancreatic β-cells by improving morphology in mitochondria and increasing the number of insulin granules. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:13220. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17657-3
18. Kato A, Nihei W, Yako H, Tatsumi Y, Himeno T, Kondo M, et al. Imeglimin improves hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia-induced cell death and mitochondrial dysfunction in immortalized adult mouse Schwann IMS32 cells. J Diabetes Investig. (2025). doi: 10.1111/jdi.70092
19. Dubourg J, Fouqueray P, Thang C, Grouin J-M, and Ueki K. Efficacy and safety of imeglimin monotherapy versus placebo in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes (TIMES 1): A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter phase 3 trial. Diabetes Care. (2021) 44:952–9. doi: 10.2337/dc20-0763
20. Dubourg J, Fouqueray P, Quinslot D, Grouin J-M, and Kaku K. Long-term safety and efficacy of imeglimin as monotherapy or in combination with existing antidiabetic agents in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes (TIMES 2): A 52-week, open-label, multicentre phase 3 trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2022) 24:609–19. doi: 10.1111/dom.14613
21. Fouqueray P, Perrimond-Dauchy S, and Bolze S. Imeglimin does not induce clinically relevant pharmacokinetic interactions when combined with either metformin or sitagliptin in healthy subjects. Clin Pharmacokinet. (2020) 59:1261–71. doi: 10.1007/s40262-020-00886-y
22. Nishiyama K, Ono M, Tsuno T, Inoue R, Fukunaka A, Okuyama T, et al. Protective effects of imeglimin and metformin combination therapy on β-cells in db/db male mice. Endocrinology. (2023) 164:bqad095. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqad095
23. Oda T, Satoh M, Nagasawa K, Sasaki A, Hasegawa Y, Takebe N, et al. The effects of imeglimin on the daily glycemic profile evaluated by intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitoring: retrospective, single-center, observational study. Diabetes Ther. (2022) 13:1635–43. doi: 10.1007/s13300-022-01298-w
24. Al−Kafaji G, Aljadaan A, Kamal A, and Bakhiet M. Peripheral blood mitochondrial DNA copy number as a novel potential biomarker for diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes patients. Exp Ther Med. (2018) 16:1483–92. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6319
25. Fazzini F, Lamina C, Raftopoulou A, Koller A, Fuchsberger C, Pattaro C, et al. Association of mitochondrial DNA copy number with metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes in 14 176 individuals. J Intern Med. (2021) 290:190–202. doi: 10.1111/joim.13242
26. DeBarmore B, Longchamps RJ, Zhang Y, Kalyani RR, Guallar E, Arking DE, et al. Mitochondrial DNA copy number and diabetes: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. (2020) 8:e001204. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2020-001204
27. Memon AA, Sundquist J, Hedelius A, Palmér K, Wang X, and Sundquist K. Association of mitochondrial DNA copy number with prevalent and incident type 2 diabetes in women: A population-based follow-up study. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:4608. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84132-w
28. Picard M. Blood mitochondrial DNA copy number: What are we counting? Mitochondrion. (2021) 60:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2021.06.010
29. Mihaela-Roxana G, Theia S-L, Oana-Maria A, Anca-Mihaela B, Vlad-Florian A, Lavinia B, et al. Impairment of platelet mitochondrial respiration in patients with chronic kidney disease with and without diabetes. Mol Cell Biochem. (2025). doi: 10.1007/s11010-025-05280-5
30. Kalantar GH, Saraswat S, SantaCruz-Calvo S, Gholamrezaeinejad F, Javidan A, Agrawal M, et al. Fasting and glucose metabolism differentially impact peripheral inflammation in human type 2 diabetes. Nutrients. (2024) 16. doi: 10.3390/nu16101404
31. Eftekharpour E and Fernyhough P. Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction associated with peripheral neuropathy in type 1 diabetes. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2021) 37:578–96. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0152
32. Huang J, Peng X, Dong K, Tao J, and Yang Y. The association between antidiabetic agents and leukocyte telomere length in the novel classification of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Gerontology. (2020) 67:60–8. doi: 10.1159/000511362
33. Sung JY, Kim SG, Park S-Y, Kim J-R, and Choi HC. Telomere stabilization by metformin mitigates the progression of atherosclerosis via the AMPK-dependent p-PGC-1α pathway. Exp Mol Med. (2024) 56:1967–79. doi: 10.1038/s12276-024-01297-w
34. Garcia-Martin I, Penketh RJA, Janssen AB, Jones RE, Grimstead J, Baird DM, et al. Metformin and insulin treatment prevent placental telomere attrition in boys exposed to maternal diabetes. PLoS One. (2018) 13:e0208533. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0208533
35. Cancello R, Rey F, Carelli S, Cattaldo S, Fontana JM, Goitre I, et al. Telomere length and mitochondrial DNA copy number variations in patients with obesity: effect of diet-induced weight loss—A pilot study. Nutrients. (2022) 14. doi: 10.3390/nu14204293
36. Baragetti A, Bonacina F, Da Dalt L, Moregola A, Zampoleri V, Pellegatta F, et al. Genetically determined hypercholesterolaemia results into premature leucocyte telomere length shortening and reduced haematopoietic precursors. Eur J Prev Cardiol. (2022) 29:721–9. doi: 10.1093/eurjpc/zwaa115
37. Zhu G, Xu J, Guo G, and Zhu F. Association between lipids, apolipoproteins and telomere length: A mendelian randomization study. Nutrients. (2023) 15. doi: 10.3390/nu15214497
38. Mone P, Varzideh F, Jankauskas SS, Pansini A, Lombardi A, Frullone S, et al. SGLT2 inhibition via empagliflozin improves endothelial function and reduces mitochondrial oxidative stress: insights from frail hypertensive and diabetic patients. Hypertension. (2022) 79:1633–43. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.122.19586
39. Pipatpiboon N, Pintana H, Pratchayasakul W, Chattipakorn N, and Chattipakorn SC. DPP4-inhibitor improves neuronal insulin receptor function, brain mitochondrial function and cognitive function in rats with insulin resistance induced by high-fat diet consumption. Eur J Neurosci. (2013) 37:839–49. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12088
Keywords: Imeglimin, mitochondrial DNA, telomere length, type 2 diabetes, glycemic control
Citation: Satheesan A, Kumar J, Leela KV and Murugesan R (2025) Effect of Imeglimin on mitochondrial function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a prospective cohort study. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1585834. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1585834
Received: 01 March 2025; Accepted: 15 July 2025;
Published: 01 August 2025.
Edited by:
Dorota Katarzyna Dymkowska, Polish Academy of Sciences, PolandReviewed by:
Angelika Buczyńska, Medical University of Bialystok, PolandRanjodh Singh Sandhu, National Institutes of Health (NIH), United States
Copyright © 2025 Satheesan, Kumar, Leela and Murugesan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Abhishek Satheesan, YWJoaXNoZWtzYXQ5OEBnbWFpbC5jb20=; Janardanan Kumar, a3VtYXJqMUBzcm1pc3QuZWR1Lmlu
†ORCID: Janardanan Kumar, orcid.org/0000-0003-1355-5833
 Abhishek Satheesan
Abhishek Satheesan Janardanan Kumar
Janardanan Kumar Kakithakara Vajravelu Leela
Kakithakara Vajravelu Leela Ria Murugesan
Ria Murugesan