- 1Medical Imaging Department, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, China
- 2Department of Interventional Therapy, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, China
- 3Department of Interventional Therapy, The First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, China
- 4Department of Interventional Therapy, Shanxi Province Cancer Hospital/ Shanxi Hospital Affiliated to Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences/ Cancer Hospital Affiliated to Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, China
- 5Obstetrics and Gynecology Department, Lishi District People’s Hospital of Lvliang City, Lvliang, Shanxi, China
- 6Obstetrics and Gynecology Department, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, China
Background: Ghrelin, a peptide composed of 28 amino acids, is recognized for its role in regulating appetite and energy balance. Recently, it has also been identified as an immunomodulator that could significantly influence immune responses in chronic inflammatory conditions. The role of ghrelin on cell viability and cytokine expression is presented here for human endometrial stromal (hEM15A) cells, with attention to the way this peptide could modulate inflammation.
Methods: In this study, the hEM15A cells were cultured and treated with Ghrelin at concentrations ranging from 1 μM to 1000 μM. Cell viability was assessed using the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. Levels of the cytokines TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 were measured by ELISA, and the expression of the Ghrelin receptor was confirmed through Western blot (WB) analysis.
Results: The results demonstrated successful expression of the Ghrelin receptor (GHSR) in hEM15A cells. Analysis of cell viability indicated that Ghrelin positively affected cell proliferation, particularly at higher concentrations. ELISA results showed a significant decrease in pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6, coupled with a notable increase in the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10, in a dose-dependent manner.
Conclusion: Ghrelin can exert its effects through its receptor GHSR. Meanwhile, Ghrelin stimulates cell growth without causing decrease in viability; it has cell protective effect by regulating inflammation at the molecular level by balancing the release of some key pro-inflammatory cytokines. This study discovered and validated the anti-inflammatory effect of Ghrelin in patients with endometriosis. Thus, the data presented open a potential use of Ghrelin as therapy for chronic inflammation-related disorders as endometriosis.
1 Introduction
Ghrelin, primarily secreted by the stomach (1) and, to a lesser extent, by other tissues, acts as an endogenous agonist for the growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR), a G-protein-coupled receptor widely expressed in various tissues, including the brain (2), pancreas (3), and reproductive organs. Beyond its well-established roles in regulating appetite and energy balance, ghrelin has been identified as a key modulator of growth hormone secretion (4), gastrointestinal motility (5), glucose and lipid metabolism, and numerous other physiological processes (6). Emerging evidence suggests that ghrelin exerts significant anti-inflammatory effects, positioning it as a promising pharmacological candidate for managing inflammatory diseases (7).
Ghrelin has been shown to influence immune responses in chronic inflammatory conditions, including endometriosis (8), rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (9), and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) (10). The immune response during inflammation involves the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, activation of immune cells, and tissue destruction (11). Chronic inflammation is a major contributor to the pathogenesis of various diseases, particularly those affecting the reproductive system (12). For example, in the endometrium, key cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interleukin-10 (IL-10) play pivotal roles in inflammation. TNF-α and IL-6 are recognized as pro-inflammatory cytokines (13), whereas IL-10 functions as an anti-inflammatory cytokine that mitigates tissue damage and promotes healing (14). Maintaining a delicate balance among these cytokines is essential for preserving physiological homeostasis and preventing pathological progression.
Recent studies have highlighted ghrelin’s anti-inflammatory properties in various models of inflammation, demonstrating its ability to reduce pro-inflammatory cytokine levels (15, 16). Thus, ghrelin is not only a metabolic regulator but also an immunomodulator, making it an attractive target for therapeutic interventions in inflammatory diseases (17, 18).
The human endometrium is particularly susceptible to inflammatory reactions. Dysregulated immune responses in the endometrium can lead to disorders such as endometriosis, which is characterized by chronic inflammation and aberrant tissue proliferation (19). The hEM15A cell line serves as a valuable model for studying the effects of ghrelin on endometrial inflammation. Investigating ghrelin’s role in modulating immune responses in endometrial cells, including its effects on cytokine production and interactions with immune cells, may provide novel insights into its therapeutic potential for reproductive disorders (20).
This study aims to evaluate the effects of ghrelin on hEM15A cell viability and cytokine production, specifically focusing on its role in modulating inflammatory responses. By examining ghrelin’s interactions with GHSR and associated downstream signaling pathways, this research seeks to elucidate its protective effects against endometrial inflammation. Additionally, the study will explore ghrelin’s dose-dependent effects on the secretion of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 to identify potential pharmacological strategies for managing endometrial-related inflammatory disorders.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Reagents
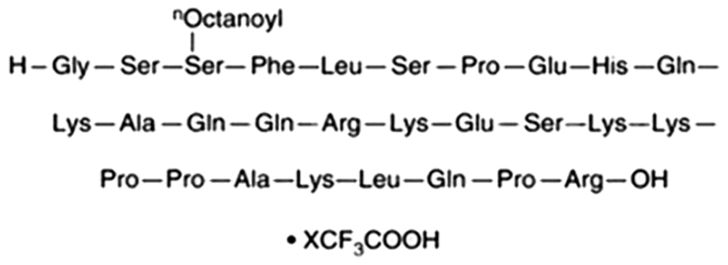
Ghrelin (purity > 98%; Figure 1) was obtained from ChemeGen Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The CCK-8 reagent was obtained from YOBIBlO Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). ELISA kits for TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 were sourced from Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). WB detection kits, beta-actin polyclonal antibody, and horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibodies were acquired from Elabscience Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Wuhan, China). GHSR Rabbit pAb were sourced from Zen-Bioscience Co., Ltd. (Chengdu, China).
2.2 Cell culture
The hEM15A cells obtained from the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC, Wuhan, China), and provided with authentication testing reports. The hEM15A cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium/F-12 (DMEM/F-12, Zhongqiao Xinzhou, Shanghai, China) enriched with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Cellmax, SA211, Beijing, China). The cells were maintained at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2 for 24 hours. Cells were stained with Hoechst 33258 and visualized under fluorescence microscopy to confirm the absence of Mycoplasma. Following this, cells were trypsinized for 2 minutes, resuspended in fresh DMEM/F-12 with 10% FBS, and incubated for an additional 24 hours. Ghrelin was then administered in varying concentrations (1000 μM, 100 μM, 10 μM, 1 μM) for 12 hours. A PBS-treated group acted as the negative control. Both culture supernatants and cells were collected for subsequent analyses.
2.3 CCK-8 assay
Cell viability was evaluated using the CCK-8 assay. hEM15A cells were plated at 1×105 cells per well in 96-well plates and incubated for 24 hours. The cells were exposed to different concentrations of Ghrelin (1000 μM, 100 μM, 10 μM, 1 μM) for 24 hours, followed by the addition of 10 μL of CCK-8 reagent to each well. Make 5 repeated wells for each concentration. After a further 2-hour incubation, optical density (OD) was measured at 450 nm using a Multiskan FC microplate reader (MA, USA). Cell viability percentage was determined using the formula: (OD treatment–OD blank)/(OD control–OD blank) × 100%.
2.4 Cytokine assay by ELISA
Cytokine levels for IL-10, TNF-α, and IL-6 were quantified using ELISA kits, under the same experimental conditions as previously described. Supernatants from hEM15A cells were used for cytokine measurements following the protocols provided with ELISA kits from Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). A PBS-treated group served as the negative control. Repeat the experiment three times.
2.5 Western blot
Proteins were extracted from tissues/cells using RIPA buffer supplemented with protease/phosphatase inhibitors, and concentrations were determined via BCA assay. Equal amounts of protein (50 μg) were separated by SDS-PAGE (10% gels) and transferred to PVDF membranes. After blocking with 5% non-fat milk in TBST, membranes were incubated overnight at 4 °C with primary antibodies (1:1000), followed by HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies (1:5000, 1 h at RT). Signals were detected using ECL substrate and quantified with ImageJ, normalized to β-actin as loading controls.
2.6 Statistical analysis
Data analysis was performed using SPSS 23.0 and GraphPad Prism 8.0, with results presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Group differences were evaluated using a t-test or one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by Bonferroni post hoc tests as needed. Pearson correlation analysis was applied to explore the association between cytokine levels and GHSR expression. A p-value of <0.05 was deemed statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 GHSR expression in hEM15A cells
To investigate the potential protective effect of Ghrelin on endometrial stromal cell inflammation and its associated signaling mechanisms, the expression of the GHSR was first confirmed in hEM15A cells. WB analysis revealed a significant expression of GHSR in these cells, validating its suitability for subsequent studies involving Ghrelin (Figure 2).
3.2 Effect of Ghrelin on cell viability
The CCK-8 assay was employed to assess the impact of Ghrelin on the viability of hEM15A cells. Cells were exposed to varying Ghrelin concentrations for 24 hours. As depicted in Figure 3, cell viability remained over 80% across all concentrations, including the highest at 1000 μM, suggesting that Ghrelin does not adversely affect cell survival. It is of interest that cell viability exceeded 100% at higher Ghrelin concentrations, which may point toward a proliferative effect of Ghrelin. This makes it probable that Ghrelin promotes proliferation, though this is an interesting phenomenon that needs further investigation.
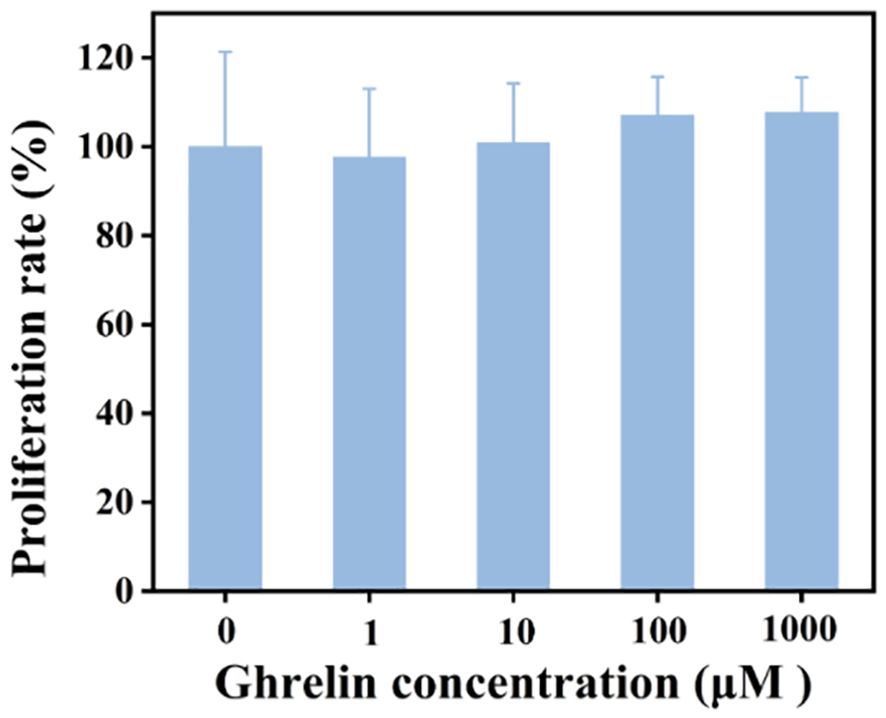
Figure 3. Comparison of cell survival rates for hEM15A cells incubated with various concentrations of Ghrelin over 24 hours (n = 5).
3.3 Effect of Ghrelin on cytokine expression
The effect of Ghrelin on inflammatory cytokine production was quantified using ELISA in hEM15A cell supernatants. Post-Ghrelin treatment, there was a significant reduction in the levels TNF-α and IL-6, while IL-10 showed. Compared with the control group, the Ghrelin group with a concentration of 1000 μ M showed a 86% reduction in TNF - α, a 64% reduction in IL-6, and a261% increase in IL-10 (Figure 4). Notably, increases in Ghrelin concentration led to a dose-dependent decrease in TNF-α and IL-6 levels, alongside an increase in IL-10 levels, illustrating Ghrelin’s anti-inflammatory action through the suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and enhancement of anti-inflammatory cytokine secretion.
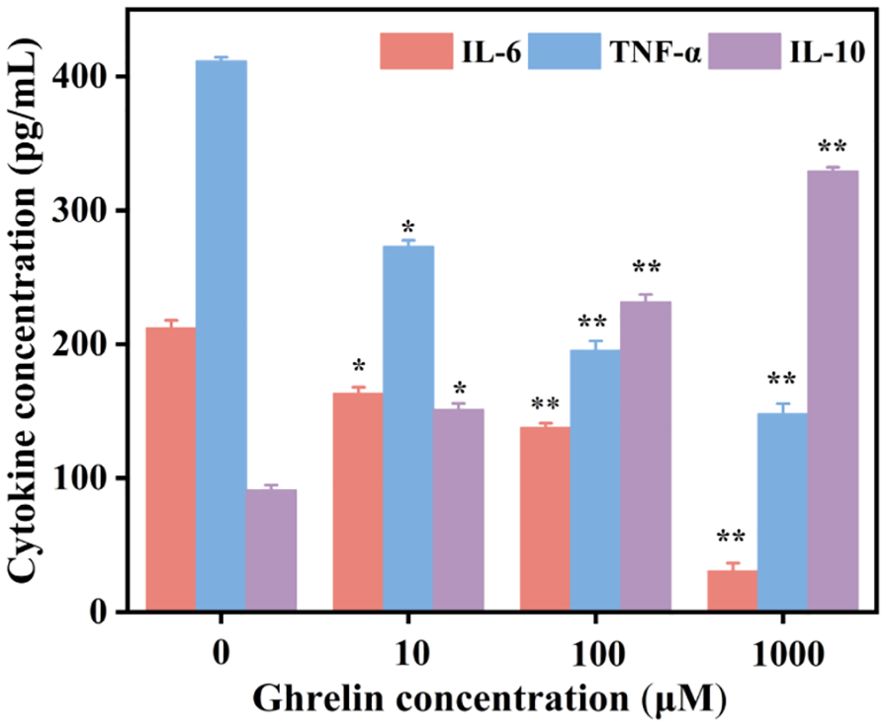
Figure 4. The concentrations of IL-10, TNF-α, and IL-6 in supernatants following treatment with different concentrations of Ghrelin were quantified by ELISA (n = 3). Data in panels are presented as mean ± standard deviation. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
In summary, Ghrelin demonstrated no negative effect on cell viability at lower concentrations, while promoting cell proliferation at higher doses. Furthermore, Ghrelin regulated immune responses in hEM15A cells by diminishing TNF-α and IL-6, and augmenting IL-10 production in a concentration-dependent manner. These findings indicate Ghrelin’s potential as a therapeutic agent in conditions requiring immune response modulation.
4 Discussion
Ghrelin is a peptide initially recognized for its role in appetite regulation and energy homeostasis. Recently, it has garnered attention as a key mediator of immune functions, particularly in chronic inflammatory disorders (1). This study evaluated the effects of Ghrelin on cell viability and cytokine production using hEM15A cells as a model for endometrial inflammation. The results demonstrate that Ghrelin enhances cell proliferation and exhibits anti-inflammatory properties in hEM15A cells, suggesting its potential utility in treating inflammatory diseases such as endometriosis.
The expression of the Ghrelin receptor (GHSR) in hEM15A cells was confirmed through WB analysis. Previous studies have established the involvement of Ghrelin and GHSR in activating intracellular pathways, including MAPK and NF-κB, which are critical regulators of immune responses. The high expression of GHSR observed in hEM15A cells supports their suitability as a model for investigating Ghrelin’s role in endometrial inflammation. This finding aligns with earlier research reporting GHSR expression in various peripheral tissues, immune cell lineages, and other cell types, highlighting Ghrelin’s broad regulatory influence on immune responses beyond its metabolic functions.
Cell viability was assessed using the CCK-8 assay. The results indicate that Ghrelin does not reduce cell viability at concentrations of 1000 μM, 100 μM, 10 μM, or 1 μM. Notably, at 1000 μM, cell viability exceeded 100%, indicating a proliferative effect. This suggests that Ghrelin promotes the proliferation of endometrial stromal cells, consistent with its known proliferative effects on other cell types, such as adipocytes (21) and pancreatic cells (22). Further research is warranted to elucidate the mechanisms underlying this proliferative response and to determine whether it operates in a universal or cell-specific manner.
The study also investigated Ghrelin’s role in modulating inflammatory cytokine release in hEM15A cells. The findings reveal that Ghrelin significantly reduced the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6 while increasing the production of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 in a dose-dependent manner. The marked reduction in TNF-α and IL-6 is particularly noteworthy, as these cytokines are central to the pathology of chronic inflammatory diseases such as endometriosis (23), rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (24), and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) (25). The upregulation of IL-10 further underscores Ghrelin’s immunomodulatory capabilities, as it not only suppresses pro-inflammatory mediators but also promotes anti-inflammatory pathways (26). These results are consistent with prior studies highlighting Ghrelin’s role in immune modulation across various inflammatory models.
The anti-inflammatory effects of Ghrelin may involve GHSR-mediated inhibition of inflammatory cascades, including the downregulation and degradation of NF-κB-related factors and the activation of their antagonistic modulators, particularly MAP kinases (27, 28). These pathways are known to influence both innate and adaptive immune responses, affecting macrophages and T cells, which regulate cytokine production and cellular proliferation (29, 30). Ghrelin’s ability to modulate cytokine profiles in inflammatory contexts positions it as a promising candidate for developing novel therapeutic strategies for inflammatory diseases of the endometrium, such as endometriosis, which is characterized by cytokine imbalances.
These findings suggest that Ghrelin could serve as a therapeutic agent in diseases characterized by chronic inflammation, particularly in reproductive organs. By restoring immune homeostasis and modulating cytokine-induced inflammation, Ghrelin may help reduce disease severity in conditions like endometriosis. Additionally, its proliferative effects at higher concentrations indicate potential applications in tissue regeneration, such as post-surgical recovery or repair of damage caused by chronic inflammation (31). This dual role of Ghrelin in immune modulation and tissue healing underscores its significance as a therapeutic target, extending its potential applications in medical treatment.
Although this study explores the potential immunomodulatory role of ghrelin in endometrial cells, certain limitations warrant consideration. First, the present research relies on in vitro experiments using a cell line, which cannot fully replicate the complexity of in vivo conditions. Therefore, further studies employing animal models are recommended to investigate the effects of ghrelin under more physiologically relevant conditions. Additionally, further research is necessary to elucidate the precise molecular mechanisms by which ghrelin modulates the NF-κB and MAPK pathways, as well as to identify the optimal therapeutic concentration.
Moreover, the long-term effects of ghrelin on tissue remodeling and immune function require further investigation. Clinical trials are critical to assess whether therapeutic strategies involving ghrelin are effective in managing inflammatory disorders, particularly those associated with reproductive health.
5 Conclusion
In conclusion, this study provides the first mechanistic insights into Ghrelin’s pivotal role in modulating inflammatory responses in endometrial cells, promoting anti-inflammatory cytokine secretion while repressing pro-inflammatory mediators. These results bolster the potential of Ghrelin as an effective therapeutic agent against chronic inflammatory diseases impacting the endometrium and other tissues. Future studies should investigate Ghrelin’s effects in animal models of endometriosis and explore optimal dosing strategies that balance its anti-inflammatory and proliferative effects.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available. The findings of this study are derived from in vitro experiments using the immortalized human endometrial stromal cell line hEM15A. While this model provides a controlled system for mechanistic investigations, the results may not fully replicate the complexity of in vivo endometrial tissue microenvironments or patient-specific variations. Additionally, the cytokine analysis was limited to TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10; other inflammatory mediators or signaling pathways potentially influenced by Ghrelin were not explored. Dose-dependent effects were tested within a predefined concentration range, and extrapolation to physiological or therapeutic doses requires further validation. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to MTM4MzUxODQ3NzRAMTYzLmNvbQ==.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by The Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University (Shanxi, China) Animal Welfare and Research Ethics Committee (Ethics No. DW2022047). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
WD: Writing – original draft. HM: Writing – original draft. FJ: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YW: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. JL: Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. SZ: Investigation, Software, Writing – review & editing. SY: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. TL: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82172048, U21A20378); Shanxi Center of Technology Innovation for Controlled and Sustained Release of Nano-drugs (202104010911026), Foundational Research Project of Shanxi Province (202103021224424, 202103021223439, 202203021211159); Shanxi-Zheda Institute of Advanced Materials and Chemical Engineering (2021SX-FR010); Shanxi Scholarship Council of China (2024-058, 2022-039); Four “Batches” Innovation Project of Invigorating Medical through Science and Technology of Shanxi Province (2023XM012); The Science and Education Cultivation Fund of the National Cancer and Regional Medical Center of Shanxi Provincial Cancer Hospital (TD2023003, BD2023004); Research Project of Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University (202302-3); and Research Project of Health Commission of Shanxi Province (2023120).
Acknowledgments
The aseptic surgery was performed at the Animal Experimental Center of Shanxi Province Cancer Hospital.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Kulkarni SS, Singh O, and Zigman JM. The intersection between ghrelin, metabolism and circadian rhythms. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2024) 20:228–38. doi: 10.1038/s41574-023-00927-z
2. Sassi M, Morgan AH, and Davies JS. Ghrelin acylation-A post-translational tuning mechanism regulating adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Cells. (2022) 11:765. doi: 10.3390/cells11050765
3. Ma Y, Zhang H, Guo W, and Yu L. Potential role of ghrelin in the regulation of inflammation. FASEB J. (2022) 36:e22508. doi: 10.1096/fj.202200634R
4. Lewiński A, Karbownik-Lewińska M, Wieczorek-Szukała K, Stasiak M, and Stawerska R. Contribution of ghrelin to the pathogenesis of growth hormone deficiency. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:9066. doi: 10.3390/ijms22169066
5. Deloose E, Janssen P, Depoortere I, and Tack J. The migrating motor complex: control mechanisms and its role in health and disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2012) 9:271–85. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2012.57
6. Yanagi S, Sato T, Kangawa K, and Nakazato M. The homeostatic force of ghrelin. Cell Metab. (2018) 27:786–804. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.02.008
7. Kasprzak A and Adamek A. Role of the ghrelin system in colitis and hepatitis as risk factors for inflammatory-related cancers. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:11188. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911188
8. Krasnyi AM, Sadekova AA, Smolnova TY, Chursin VV, Buralkina NA, Chuprynin VD, et al. The levels of ghrelin, glucagon, visfatin and glp-1 are decreased in the peritoneal fluid of women with endometriosis along with the increased expression of the CD10 protease by the macrophages. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:10361. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810361
9. Francisco V, Tovar S, Conde J, Pino J, Mera A, Lago F, et al. Levels of the novel endogenous antagonist of ghrelin receptor, liver-enriched antimicrobial peptide-2, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Nutrients. (2020) 12:1006. doi: 10.3390/nu12041006
10. Jabłońska B and Mrowiec S. Nutritional status and its detection in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. Nutrients. (2023) 15:1991. doi: 10.3390/nu15081991
11. Yu H, Gao R, Liu Y, Fu L, Zhou J, and Li L. Stimulus-responsive hydrogels as drug delivery systems for inflammation targeted therapy. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2024) 11:e2306152. doi: 10.1002/advs.202306152
12. Leuti A, Fazio D, Fava M, Piccoli A, Oddi S, and Maccarrone M. Bioactive lipids, inflammation and chronic diseases. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. (2020) 159:133–69. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2020.06.028
13. Górecka M, Krzemiński K, Mikulski T, and Ziemba AW. ANGPTL4, IL-6 and TNF-α as regulators of lipid metabolism during a marathon run. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:19940. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17439-x
14. York AG, Skadow MH, Oh J, Qu R, Zhou QD, Hsieh W-Y, et al. IL-10 constrains sphingolipid metabolism to limit inflammation. Nature. (2024) 627:628–35. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07098-5
15. García-Hermoso A, Ramírez-Vélez R, Díez J, González A, and Izquierdo M. Exercise training-induced changes in exerkine concentrations may be relevant to the metabolic control of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Sport Health Sci. (2023) 12:147–57. doi: 10.1016/j.jshs.2022.11.003
16. Saeidi A, Saei MA, Mohammadi B, Zarei HRA, Vafaei M, Mohammadi AS, et al. Supplementation with spinach-derived thylakoid augments the benefits of high intensity training on adipokines, insulin resistance and lipid profiles in males with obesity. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2023) 14:1141796. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1141796
17. Mathur N, Mehdi SF, Anipindi M, Aziz M, Khan SA, Kondakindi H, et al. Ghrelin as an anti-sepsis peptide: review. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:610363. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.610363
18. Raghay K, Akki R, Bensaid D, and Errami M. Ghrelin as an anti-inflammatory and protective agent in ischemia/reperfusion injury. Peptides. (2020) 124:170226. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2019.170226
19. Comninos AN, Jayasena CN, and Dhillo WS. The relationship between gut and adipose hormones, and reproduction. Hum Reprod Update. (2014) 20:153–74. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmt033
20. van Loenen MR, Geenen B, Arnoldussen IAC, and Kiliaan AJ. Ghrelin as a prominent endocrine factor in stress-induced obesity. Nutr Neurosci. (2022) 25:1413–24. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2020.1863740
21. Kratofil RM, Shim HB, Shim R, Lee WY, Labit E, Sinha S, et al. A monocyte-leptin-angiogenesis pathway critical for repair post-infection. Nature. (2022) 609:166–73. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05044-x
22. Gupta D, Burstein AW, Schwalbe DC, Shankar K, Varshney S, Singh O, et al. Ghrelin deletion and conditional ghrelin cell ablation increase pancreatic islet size in mice. J Clin Invest. (2023) 133:e169349. doi: 10.1172/JCI169349
23. Taylor HS, Kotlyar AM, and Flores VA. Endometriosis is a chronic systemic disease: clinical challenges and novel innovations. Lancet. (2021) 397:839–52. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00389-5
24. Smolen JS, Aletaha D, and McInnes IB. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. (2016) 388:2023–38. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30173-8
26. Meeks KAC, Bentley AR, Assimes TL, Franceschini N, Adeyemo AA, Rotimi CN, et al. Mendelian randomization analyses suggest a causal role for circulating GIP and IL-1RA levels in homeostatic model assessment-derived measures of β-cell function and insulin sensitivity in Africans without type 2 diabetes. Genome Med. (2023) 15:108. doi: 10.1186/s13073-023-01263-7
27. Liu Y, Wang J, and Zhang X. An update on the multifaceted role of NF-kappaB in endometriosis. Int J Biol Sci. (2022) 18:4400–13. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.72707
28. Choi J, Jo M, Lee E, Lee D-Y, and Choi D. Nuclear factor-kappa B signaling in endometriotic stromal cells is not inhibited by progesterone owing to an aberrant endoplasmic reticulum stress response: a possible role for an altered inflammatory process in endometriosis. Mol Hum Reprod. (2021) 27:gaab002. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gaab002
29. Mehdi SF, Pusapati S, Anwar MS, Lohana D, Kumar P, Nandula SA, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1: a multi-faceted anti-inflammatory agent. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1148209. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1148209
30. Sonali S, Ray B, Ahmed Tousif H, Rathipriya AG, Sunanda T, Mahalakshmi AM, et al. Mechanistic insights into the link between gut dysbiosis and major depression: an extensive review. Cells. (2022) 11:1362. doi: 10.3390/cells11081362
Keywords: Ghrelin, inflammation, cytokines, endometrial stromal cells, anti-inflammatory, chronic inflammatory diseases
Citation: Dong W, Mu H, Jia F, Wei Y, Lv J, Zhou S, Yu S and Liang T (2025) Ghrelin’s potential as a therapeutic target for chronic inflammatory diseases: evidence from human endometrial stromal cells. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1587490. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1587490
Received: 04 March 2025; Accepted: 18 August 2025;
Published: 01 September 2025.
Edited by:
Zahid Pranjol, University of Sussex, United KingdomReviewed by:
Anitha Myla, Mississippi State Department of Health, United StatesEugenia Mercedes Luque, National University of Cordoba, Argentina
Copyright © 2025 Dong, Mu, Jia, Wei, Lv, Zhou, Yu and Liang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shiping Yu, eXVzaGlwaW5nNkAxMjYuY29t; Tingting Liang, MTM4MzUxODQ3NzRAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Wenhui Dong
Wenhui Dong Hongkai Mu2†
Hongkai Mu2† Fan Jia
Fan Jia Shiping Yu
Shiping Yu Tingting Liang
Tingting Liang