- 1Pancreatic Center, Department of Gastroenterology, Yangzhou Key Laboratory of Pancreatic Disease, The Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China
- 2School of Nursing, School of Public Health, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China
- 3Clinical Medical College, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China
- 4Department of Health Management Center, The Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China
Objective: Many researches have demonstrated an association between intra-pancreatic fat deposition (IPFD) and several pancreatic pathological conditions, including pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The aim of this study is to investigate the influence of pancreatic diseases on the accumulation of pancreatic fat, to further explore which kind of pancreatic disease is significant, and to find out the possible mediating factors.
Methods: A cross-sectional study based on the UK Biobank (UKB) data categorized participants by pancreatic disease status and collated relevant information. IPFD was measured using MRI in combination with a deep learning-based organ segmentation model, nnUNet. Linear regression models and mediation analysis were employed to explore the association between pancreatic diseases and IPFD.
Results: Among 61,088 participants, those with pancreatic diseases exhibited higher IPFD than those without (pancreatic endocrine diseases: 11.72% vs 7.94%, P<0.001; pancreatic exocrine diseases: 9.44% vs 8.03%, P<0.001). After adjusting for multiple variables, a positive association between pancreatic endocrine diseases (particularly T2DM) and IPFD persisted, but not for pancreatic exocrine diseases. Obesity and dyslipidemia partially explained the relationship between T2DM and IPFD.
Conclusion: Pancreatic exocrine disorders are not associated with an increased risk of IPFD, whereas pancreatic endocrine disorders, particularly T2DM, may exhibit a positive relationship. However, the possibility of reverse causation cannot be discounted.
Introduction
The accumulation of adipose tissue in the pancreas is referred to as “intra-pancreatic fat deposition (IPFD)” (1). Fatty pancreas (FP), also termed pancreatic steatosis, pancreatic fat infiltration, or non-alcoholic fatty pancreas disease, is the excessive deposition of fat in pancreatic tissue (2). A threshold of 6.2% for quantification of normal pancreatic fat content has been established in one study (3).
IPFD lacks specific clinical manifestations, but the development of advanced methods for detecting pancreatic fat has provided avenues for understanding the disease, such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). An efficacious methodology for the evaluation of adipose tissue is the utilization of magnetic resonance imaging proton density fat fraction (MRI-PDFF). MRI-PDFF is frequently employed as a biomarker for the quantification of liver fat. This is achieved by quantifying the relative amounts of water and fat signals in tissue through MRI scans of the liver, thereby enabling the accurate and rapid quantification of liver fat content. It is also applicable to pancreatic tissue.
There is a notable relationship between excessive IPFD, or FP, and the development of pancreatic diseases. A large number of studies have shown that IPFD was a significant contributing factor to a series of pancreatic diseases, including but not limited to acute pancreatitis, chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, and T2DM (4). In a cohort study, FP was proven to be independently associated with the subsequent development of diabetes (5). Makoto Fujii found in his 6-year cohort study that IPFD may be a risk factor for subclinical chronic pancreatitis (6). In addition, the causal role of IPFD in pancreatitis was confirmed by a Mendelian randomization (MR) study, which suggested that reducing fat deposition in the pancreas meant a reduced risk of pancreatitis (7). However, the reverse MR analysis did not support the reverse causal relationship between pancreatitis and IPFD.
High IPFD and FP were demonstrated to be important risk factors for pancreatic endocrine and exocrine diseases. However, whether pancreatic diseases have an impact on pancreatic fat content, there are very few studies on this issue. The objective of this study is to explore the relationship between previous pancreatic diseases and IPFD through a cross-sectional study, utilizing MRI to quantify pancreatic fat content.
Methods
Participants
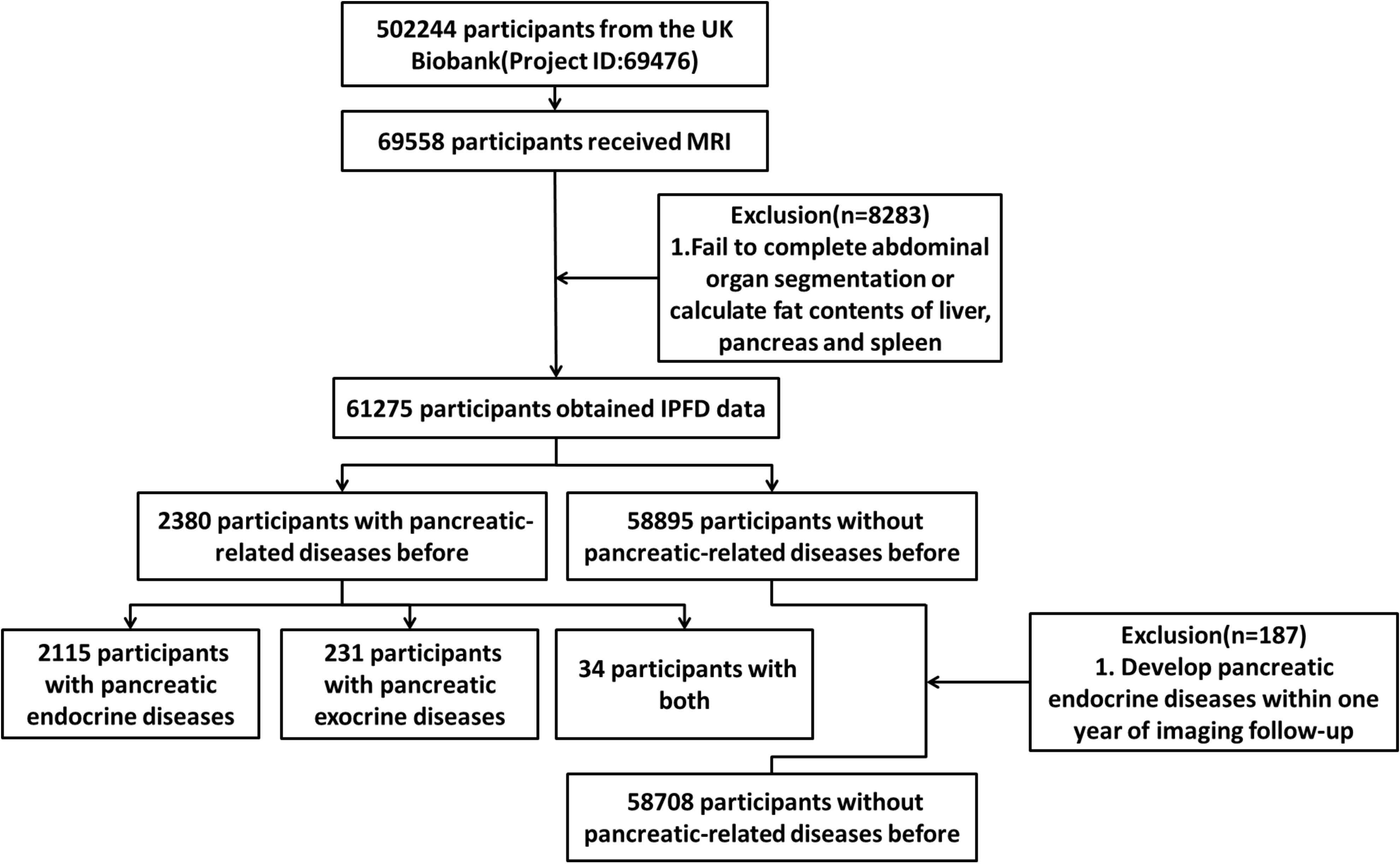
The UK Biobank recruited 502,244 participants from the general population. Since the recruitment, researchers have conducted multiple follow-ups, among which 69,558 participants underwent an abdominal Dixon MRI examination during the second follow-up. We followed the methodology of a previous study by our research group and calculated the level of IPFD (8). A total of 61,275 participants from the UK Biobank were therefore included in the analysis, including 2,380 participants with previous pancreatic diseases and 58,895 participants without previous pancreatic diseases. To minimize the risk of reverse causality, a 12-month period free of pancreatic endocrine disease was defined. This excluded participants (n=187) who developed pancreatic endocrine diseases within one year after the imaging follow-up, resulting in a final sample of 58,708 participants without previous pancreatic diseases. (Figure 1).
At the outset of the study, a total of 51 pancreatic diseases, according to the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) (Supplementary Tables S1, S2), were identified through a search of the UK Biobank diagnosis database which were further classified. There were 2,115 participants with pancreatic endocrine diseases (n=2,115), 231 participants with pancreatic exocrine diseases (n=231), and 34 participants with both pancreatic endocrine and exocrine diseases (n=34) before imaging follow-up (Figure 1). During the further screening for pancreatic endocrine disorders, four conditions (C254, E144, E164, and E168) were identified due to their diagnosis post-radiological follow-up. It should be particularly pointed out that in the ICD-10 coding system, E10 denotes type 1 diabetes mellitus, while E11 denotes type 2 diabetes mellitus (9).
The study was approved by the North West Multi-Center Research Ethics Committee, and all participants provided written informed consent. Furthermore, this study was reviewed and approved by the UK Biobank (project ID: 69476).
Study design
The study was conducted using a cross-sectional design. The clinical characteristics, lifestyle habits, and lipid metabolism situation were compared in the pancreatic endocrine disease group and the pancreatic exocrine disease group separately. Lipid metabolism status (categorical) was defined based on the E78 series of codes in ICD-10. Linear regression models were used to analyze the association between pancreatic diseases and IPFD. The initial model, designated as Model 0, was a single-variable model. Model 1 was adjusted for age, sex (biological), ethnicity, and body mass index (BMI). Model 2 was further adjusted for smoking and drinking status, television watching duration, sleep duration, and weekly exercise duration. In the final model (Model 3), the lipid metabolism situation was additionally adjusted. Multiple linear regression was employed once again for an in-depth analysis of pancreatic endocrine diseases and IPFD.
R Software was used to estimate whether the association between T2DM and IPFD was mediated by obesity (a BMI of 28 or higher) or lipid metabolism situation, using the ‘mediate’ function from the mediation package in R, with the ‘sims’ parameter set to 1,000 to ensure the reproducibility of the results. The mediation effect with its 95%CI was estimated using the bootstrap method and the routes were as follows:
Route 1: T2DM (exposure) → IPFD (outcome).
Route 2: T2DM (exposure) → Obesity or dyslipidemia (mediator) → IPFD (outcome).
It should be mentioned that, like most clinical studies, this study had missing data, and the missing observations might affect the accuracy and reliability of the analysis results. To address this issue, we used the random forest imputation method to estimate missing values. This method predicts and imputes missing values by constructing multiple decision trees and leveraging the information of other variables in the dataset. In comparison to traditional interpolation techniques, it is capable of capturing complex relationships among variables more effectively, thereby enhancing the accuracy of interpolation. We implemented this approach using the R package `mice` with the following code: `micedata <- mice(data_Y, m=5, maxit=50, method=“rf”, seed=500)`, which generated five imputed datasets. Subsequently, we selected the dataset with the lowest AIC and BIC values from the generated datasets for further analysis (10). This selection criterion ensures optimal model fit and prediction accuracy. Before imputing data, we conducted statistical tests to ensure that there were no significant differences in the distribution of data before and after imputation.
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables were expressed as median (interquartile range). Categorical variables were expressed as n (percentage). Non-parametric tests for continuous variables were used to compare basic characteristics and differences between groups. Chi-square tests were used to analyze categorical variables. We extracted the data through SAS and performed data cleaning and statistical analysis in R version 4.3.2. A p-value of less than 0.05 (two-sided) was considered statistically significant.
Sensitivity analysis
In the Supplementary Materials, we conducted a sensitivity analysis. The method of deleting missing data was used to handle missing observations for we wanted to avoid the potential bias introduced by imputation. After deleting data, the sample size was reduced from 61,088 to 47,292, but we observed that the overall characteristics of the data, such as median and interquartile range, remained relatively stable. We then conducted baseline analysis, model adjustment, and mediation analysis as well.
Results
Characteristics of the participants
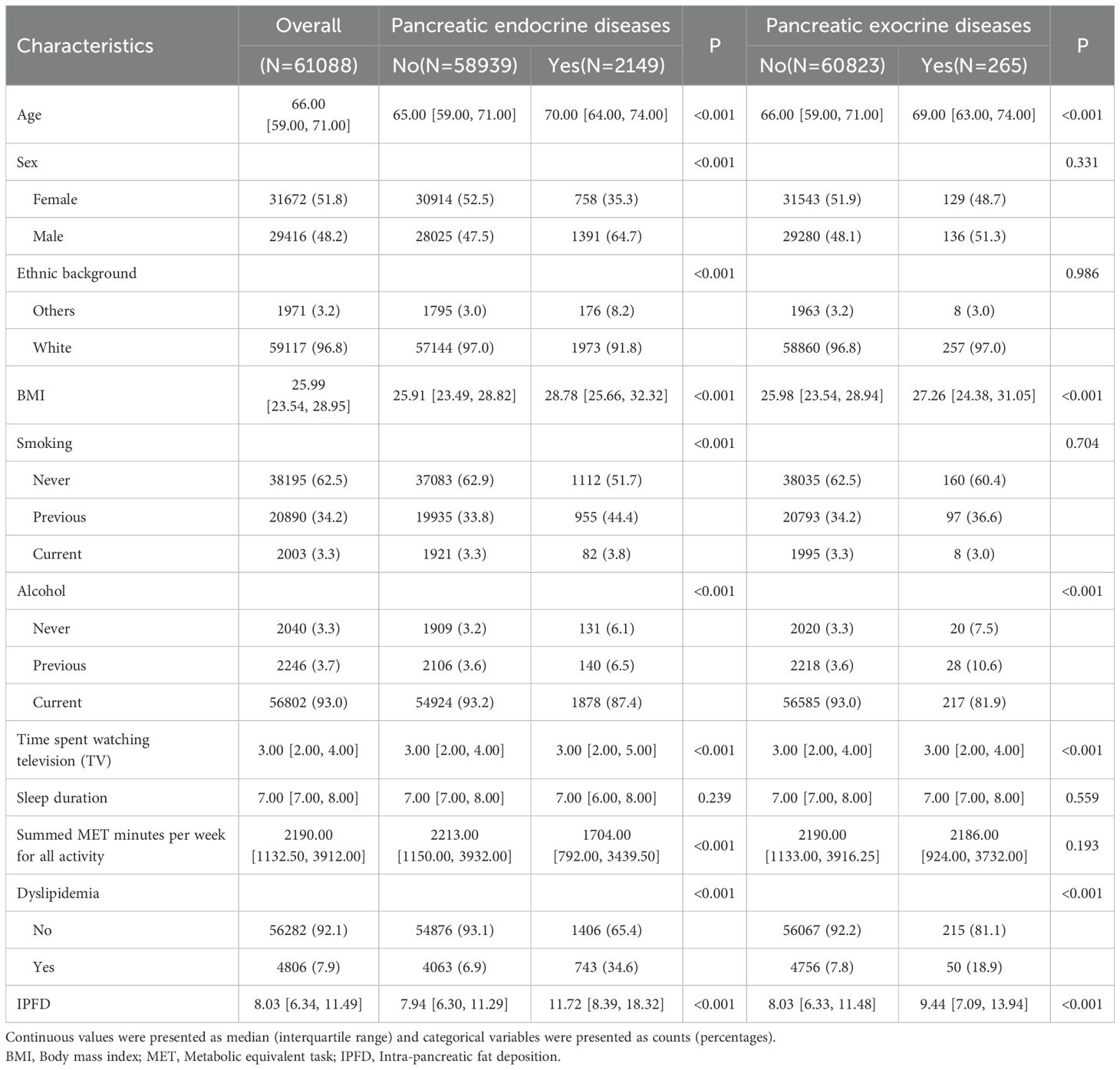
Table 1 summarized the baseline characteristics of individuals with and without pancreatic diseases (Table 1). Individuals with pancreatic endocrine diseases were observed to be older, more frequently male white, and exhibited higher BMI values compared to those without such diseases. There were also significant differences in smoking or drinking status and lipid metabolism situation (P<0.001). Furthermore, individuals with the diseases exhibited increased sedentary time and reduced weekly physical activity.
When analyzing the characteristics of individuals with and without pancreatic exocrine diseases, the results revealed that those with the disease also showed relatively older age and higher BMI values. There were significant differences in drinking status and lipid metabolism situation as well (P<0.001).
Associations of IPFD with pancreatic diseases
Through the table and vioplot (Table 1, Supplementary Figure S1), we found that the pancreatic fat content of individuals with pancreatic diseases was significantly higher than those without, whether it was pancreatic endocrine diseases or pancreatic exocrine diseases (pancreatic endocrine diseases: 11.72% vs 7.94%, P<0.001; pancreatic exocrine diseases: 9.44% vs 8.03%, P<0.001).
Linear regression analysis
In the UKB, the linear regression model 0 demonstrated a positive association between pancreatic endocrine diseases and IPFD (regression coefficient (β) = 4.76; 95% confidence interval (CI): 4.47-5.06; P<0.001). After adjusting for covariates, the association between pancreatic endocrine diseases and IPFD still existed. Upon the inclusion of additional blood lipid factors in the linear regression model, the regression coefficient associated with pancreatic endocrine diseases also underwent a change (regression coefficient (β) =1.86; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.60-2.13; P<0.001) (Table 2).

Table 2. The extent to which pancreatic diseases alone and in combination with traditional independent variables, lifestyle habits and dyslipidemia affect IPFD.
In contrast, pancreatic exocrine diseases in the linear regression model were only related to IPFD when they existed as a standalone condition (regression coefficient (β) =1.89; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.05-2.72; P<0.001). Following adjustment for other variables, the results were no longer statistically significant (Table 2).
In order to further explore the relationship between pancreatic endocrine diseases and IPFD, we also employed multiple linear regression for analysis. After adjusting for potential confounding factors, the results indicated a significant association between T2DM and IPFD (regression coefficient (β) =2.15; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.87-2.43; P<0.001), as opposed to type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) (regression coefficient (β) =-0.62; 95% confidence interval (CI): -1.48-0.25; P=0.165) (Supplementary Table S3).
Mediation analysis
In light of the strong association between T2DM and IPFD, mediation analysis (Figure 2) was performed to examine whether the association could be explained by obesity or dyslipidemia while adjusting for confounders. The results showed that the association was mediated by obesity (indirect coefficient (95%CI): 0.913(0.814-1.010), P<0.001) and dyslipidemia (indirect coefficient (95%CI): 0.158(0.101-0.220), P<0.001) in the UKB dataset. And the proportion of mediation was different: 26.10% of the association could be explained by obesity and only 6.83% by dyslipidemia.
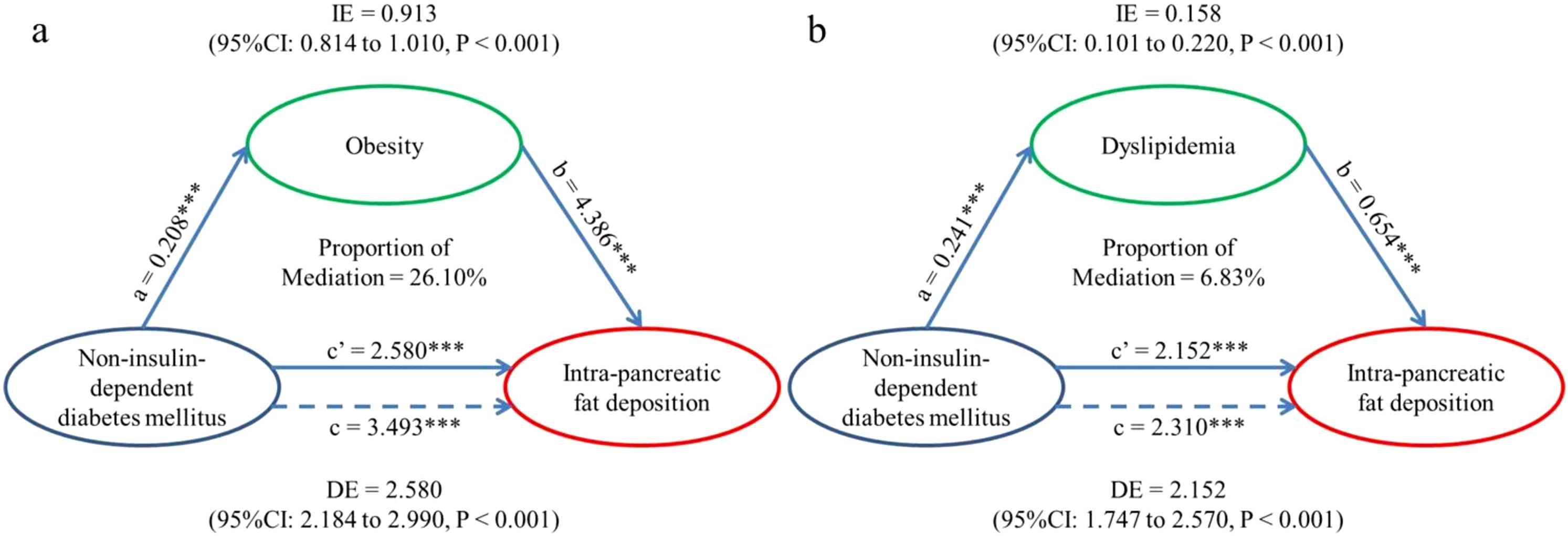
Figure 2. Mediation models. (a) Indirect effect (0.913; P < 0.001) of T2DM (exposure) towards IPFD (outcome) which was transmitted through obesity (mediator). Direct effect (2.580; P < 0.001) of T2DM (exposure) towards IPFD (outcome) which was the residual influence after accounting for obesity (mediator). Total effect (3.493; P < 0.001) of T2DM (exposure) towards IPFD (outcome) without considering the effect of obesity. (b) Indirect effect (0.158; P < 0.001) of T2DM (exposure) towards IPFD (outcome) which was transmitted through dyslipidemia (mediator). Direct effect (2.152; P < 0.001) of T2DM (exposure) towards IPFD (outcome) which was the residual influence after accounting for dyslipidemia (mediator). Total effect (2.310; P < 0.001) of T2DM (exposure) towards IPFD (outcome) without considering the effect of dyslipidemia. IPFD, Intra-pancreatic fat deposition; IE, Indirect effect, equivalent to a*b; DE, Direct effect, equivalent to c’; TE, Total effect, equivalent to c. ∗∗∗P, < 0.001.
Sensitivity analysis
Through sensitivity analysis (Supplementary Tables S4-S6, Supplementary Figures S2, S3), we observed that the impact of parameter changes on the results was negligible, indicating a high degree of consistency in our research outcomes.
Discussion
The study revealed a significant relationship between pancreatic diseases and pancreatic fat content. In particular, individuals with a history of pancreatic endocrine diseases (T2DM) might exhibit elevated pancreatic fat content in comparison to others.
In the academic community, two main perspectives existed regarding the relationship between pancreatic diseases and IPFD. One perspective posited that IPFD was a direct consequence of pancreatic disease development. The opposing view was based on PANDORA’s theory (11), which proposed an inverse causal chain, highlighting fatty pancreas as a mechanistic driver of most non-genetic pancreatic diseases. Our team previously validated the scientific merit of PANDORA’s theory through experimentation (8). We now aim to delve deeply into the hypothesis that IPFD is a consequence of pancreatic diseases, exploring the first perspective in greater detail.
After adjusting for variables, only pancreatic endocrine diseases were related to an increased risk of IPFD. We similarly utilized multiple linear regression analysis to dig into the finding which indicated a significant association between T2DM and IPFD. The pancreatic fat content of men with T2DM and non-diabetic men was assessed by Tushuizen, and the results showed that the average pancreatic fat content of diabetic patients was 20.4% compared to 9.7% in the control group (12). T2DM was regarded as a significant contributing factor in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) (13). Meanwhile, Juyeon noted that IPFD and liver fat were interrelated, and used mediation analysis to demonstrate that the effect of liver fat on IPFD was both direct and indirect (14). So there was reason to believe that T2DM would increase the risk of IPFD. From another point of view, Patel et al. advanced the proposition that a fatty pancreas could result from a condition of insulin resistance, a hallmark feature of T2DM (15). Furthermore, it was demonstrated that hyperglycemia gave rise to a sequence of enzymatic reactions, which in turn resulted in the inhibition of mitochondrial β-oxidation in pancreatic β-cells, ultimately leading to the accumulation of intracellular triglycerides (16). Taken together, these findings favored the view of IPFD as a consequence of pancreatic endocrine diseases, not just a contributing factor.
In T2DM with insulin resistance, the body secretes more insulin (17), which hinders the body’s ability to break down fat (18), to regulate blood glucose levels. Researches have also shown that pharmacologic reduction of insulin would alleviate hyperphagia and weight gain in a variety of species (17). On the other hand, a high BMI would increase the tendency to accumulate ectopic fat in the pancreas and subsequent pancreatic dysfunction (19). Obesity was also positively correlated with FP, consistent with the observations of Wu and Wang (20). Dyslipidemia is typically defined as an elevation in the concentration of lipids (such as cholesterol and triglycerides) in the bloodstream above the normal range, which is often considered to be a key factor contributing to fat deposition in tissues (21). Specifically speaking, Singh noted a positive correlation of IPFD with hypertriglyceridemia and noticed reduced concentrations of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) as well when reviewing markers of pancreatic fat in blood (22). In short, obesity and dyslipidemia (as components of MetS) were both significant factors in the development of IPFD (23). Considering all the above, it was reasonable to suppose that the relationship between T2DM and IPFD could be explained by obesity and dyslipidemia and our findings in the mediation analysis supported the assumption: obesity and dyslipidemia mediated the association, although the effects were different (26.10% of the association explained by obesity and only 6.83% explained by dyslipidemia). Given that the proportions were relatively modest, it was necessary to further explore the mechanisms involved to better explain the association. However, some observational studies conducted on non-diabetic obese individuals using ultrasonography have indicated that pancreatic fat accumulation may not always be significantly associated with systemic insulin resistance (24).
Some researchers hypothesized that the pathophysiology related to pancreatic fat deposition was pancreatic acinar cell death and replacement by fat cells which were caused by pancreatic-related diseases, such as pancreatic duct obstruction (chronic obstructive pancreatitis) (25). However, in PANDORA’s theory (11), Petrov MS concluded that pancreatic cancer was a result of fatty pancreas, not a promoter, and in our study’s multi-factor analysis, no relationship was found between pancreatic exocrine diseases and IPFD as well. The preliminary finding was intriguing and merited further exploration in subsequent studies.
Additionally, it was estimated that 16% to 35% of the general population would have pancreatic steatosis, depending on race and age (26). Age was identified as an independent risk factor for FP (27). Saisho (28) reported that pancreatic fat content increased with age throughout childhood until it reached a plateau at the age of 50. In a study (29) on sex and IPFD, it was found that men had significantly greater visceral fat deposits than women. Additionally, men exhibited significantly elevated triglyceride levels in their blood. This may be due to hormonal differences between men and women, but the specific mechanism was not clear. What’s more, the study (29) also pointed out the association between IPFD and the pancreatic site. This part of the research was exactly what our study lacked. For smoking and alcohol consumption, they both contributed to IPFD (30). Prolonged television viewing represented a sedentary lifestyle and might be associated with an increased risk of visceral fat accumulation. The finding of our study corroborated that of Sugiura’s study (31).
Prior researches have indicated that an elevation in pancreatic fat content contributed to an increased likelihood of developing pancreatic diseases. A prospective cohort study conducted by our team (8) investigated the association between IPFD and pancreatic endocrine and exocrine diseases and found that excessive IPFD, or FP, was an important risk factor for some pancreatic diseases (AP, PC, and DM). And the results of our study suggested a potential association between previous pancreatic endocrine diseases (T2DM) and an increased risk of IPFD. It can be seen, therefore, that IPFD and pancreatic diseases may interact with each other in a manner that results in the continuous promotion of disease progression. In the clinical management of T2DM, it is crucial to monitor the changes in pancreatic fat content. Clinicians should be vigilant regarding the potential for increased pancreatic fat content to exacerbate insulin resistance and impair islet β-cell function, thereby contributing to the progression of diabetes.
Our study enabled us to gain insight into the characteristics of individuals with pancreatic diseases and to examine the potential association between pancreatic diseases and pancreatic fat content. It should be noted, however, that the present study was not without limitations. Firstly, it was not possible to determine the causal relationship between pancreatic diseases and pancreatic fat content using cross-sectional studies. Secondly, the majority of the data were derived from the white population. Given the considerable genetic heterogeneity among human populations, the findings of this study should be interpreted with caution when extrapolated to other groups. Thirdly, it was not possible to discount the potential influence of unidentified or unquantified confounding factors on the relationship between pancreatic diseases and IPFD. Fourth, this study aimed to explore the association between previously diagnosed pancreatic diseases and pancreatic fat content, but during this data collection process, it was not possible to rule out the possibility that participants had IPFD before the diagnosis of pancreatic diseases (meaning that it may be the case that a participant had IPFD before being diagnosed with pancreatic-related diseases, but the UKB imaging data collection time was later than both the pancreatic disease diagnosis time and IPFD onset time. In this way, in data analysis, it was impossible to determine the causality).
In summary, there is an association between pancreatic diseases and increased pancreatic fat content, with a stronger association observed between T2DM and IPFD. It would be beneficial for future studies to employ longitudinal designs to ascertain the causal relationship.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the studies involving humans because this data is secondary data and does not contain any data which can identify individuals. Therefore, ethical approval is exempted. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The human samples used in this study were acquired from the UK Biobank. Data are available from the UK Biobank on request (www.ukbiobank.ac.uk/) and our access to data was approved (Project ID: 69476). Written informed consent to participate in this study was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Author contributions
JG: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. XD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XS: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YY: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. WC: Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. WX: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. GL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing. XY: Conceptualization, Resources, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 82200720, 82200996, 82474309); and Yangzhou Key Discipline Critical Care Medicine Laboratory (grant number YZYXZDXK-11).
Acknowledgments
We extended our gratitude to the participants of the UK Biobank.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2025.1591652/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
IPFD, intra-pancreatic fat deposition; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; T1DM, type 1 diabetes mellitus; UKB, UK Biobank; FP, fatty pancreas; CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; MRI-PDFF, magnetic resonance imaging proton density fat fraction; MR, Mendelian randomization; ICD-10, International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision; BMI, body mass index; CI, confidence interval; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; MetS, metabolic syndrome; AP, acute pancreatitis; PC, pancreatic cancer; DM, diabetes mellitus; MET, metabolic equivalent task; IE, indirect effect; DE, direct effect; TE, total effect.
References
1. Mak AL, Wassenaar N, van Dijk AM, Troelstra M, Houttu V, van Son K, et al. Intrapancreatic fat deposition is unrelated to liver steatosis in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. JHEP Rep. (2024) 6:100998. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2023.100998
2. Catanzaro R, Cuffari B, Italia A, and Marotta F. Exploring the metabolic syndrome: Nonalcoholic fatty pancreas disease. World J Gastroenterol. (2016) 22:7660–75. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i34.7660
3. Singh RG, Yoon HD, Wu LM, Lu J, Plank LD, and Petrov MS. Ectopic fat accumulation in the pancreas and its clinical relevance: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Metabolism. (2017) 69:1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2016.12.012
4. Petrov MS and Taylor R. Intra-pancreatic fat deposition: bringing hidden fat to the fore. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2022) 19:153–68. doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00551-0
5. Chan TT, Tse YK, Lui RN, Wong GL, Chim AM, Kong AP, et al. Fatty pancreas is independently associated with subsequent diabetes mellitus development: A 10-year prospective cohort study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2022) 20:2014–22.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.09.027
6. Fujii M, Ohno Y, Yamada M, Kamada Y, and Miyoshi E. Impact of fatty pancreas and lifestyle on the development of subclinical chronic pancreatitis in healthy people undergoing a medical checkup. Environ Health Prev Med. (2019) 24:10. doi: 10.1186/s12199-019-0763-2
7. Yamazaki H, Heni M, Wagner R, Fukuhara S, Grossman SR, Han S, et al. The causal effect of intrapancreatic fat deposition on acute and chronic pancreatitis: A Mendelian randomization study. Am J Gastroenterol. (2024) 119:2540–4. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000003048
8. Dong X, Zhu Q, Yuan C, Wang Y, Ma X, Shi X, et al. Associations of intrapancreatic fat deposition with incident diseases of the exocrine and endocrine pancreas: A UK biobank prospective cohort study. Am J Gastroenterol. (2024) 119:1158–66. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000002792
9. Eastwood SV, Mathur R, Atkinson M, Brophy S, Sudlow C, Flaig R, et al. Algorithms for the capture and adjudication of prevalent and incident diabetes in UK biobank. PLoS One. (2016) 11:e0162388. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162388
10. Wu Z, Cheng C, Sun X, Wang J, Guo D, Chen S, et al. The synergistic effect of the triglyceride-glucose index and serum uric acid on the prediction of major adverse cardiovascular events after coronary artery bypass grafting: a multicenter retrospective cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2023) 22:103. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01838-z
11. Petrov MS. Fatty change of the pancreas: the Pandora’s box of pancreatology. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 8:671–82. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(23)00064-X
12. Tushuizen ME, Bunck MC, Pouwels PJ, Bontemps S, van Waesberghe JH, Schindhelm RK, et al. Pancreatic fat content and beta-cell function in men with and without type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. (2007) 30:2916–21. doi: 10.2337/dc07-0326
13. Vieira Barbosa J and Lai M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease screening in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in the primary care setting. Hepatol Commun. (2020) 5:158–67. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1618
14. Ko J, Sequeira IR, Skudder-Hill L, Cho J, Poppitt SD, and Petrov MS. Metabolic traits affecting the relationship between liver fat and intrapancreatic fat: a mediation analysis. Diabetologia. (2023) 66:190–200. doi: 10.1007/s00125-022-05793-4
15. Patel NS, Peterson MR, Lin GY, Feldstein A, Schnabl B, Bettencourt R, et al. Insulin resistance increases MRI-estimated pancreatic fat in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and normal controls. Gastroenterol Res Pract. (2013) 2013:498296. doi: 10.1155/2013/498296
16. Yu TY and Wang CY. Impact of non-alcoholic fatty pancreas disease on glucose metabolism. J Diabetes Investig. (2017) 8:735–47. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12665
17. Erion KA and Corkey BE. Hyperinsulinemia: a cause of obesity? Curr Obes Rep. (2017) 6:178–86. doi: 10.1007/s13679-017-0261-z
18. Norton L, Shannon C, Gastaldelli A, and DeFronzo RA. Insulin: The master regulator of glucose metabolism. Metabolism. (2022) 129:155142. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155142
19. Lim S and Meigs JB. Links between ectopic fat and vascular disease in humans. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2014) 34:1820–6. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.303035
20. Wu WC and Wang CY. Association between non-alcoholic fatty pancreatic disease (NAFPD) and the metabolic syndrome: case-control retrospective study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2013) 12:77. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-12-77
21. Kopin L and Lowenstein C. Dyslipidemia. Ann Intern Med. (2017) 167:ITC81–96. doi: 10.7326/AITC201712050
22. Singh RG, Yoon HD, Poppitt SD, Plank LD, and Petrov MS. Ectopic fat accumulation in the pancreas and its biomarkers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. (2017) 33:e2918. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2918
23. Chen Y, Zhang P, Lv S, Su X, Du Y, Xu C, et al. Ectopic fat deposition and its related abnormalities of lipid metabolism followed by nonalcoholic fatty pancreas. Endosc Ultrasound. (2022) 11:407–13. doi: 10.4103/EUS-D-21-00167
24. Emir SN and Emir S. Association of insulin resistance and ectopic fat accumulation with HOMA indices: A single-centre observational study. Turk J Diabetes Obes. (2024) 2:97–106. doi: 10.25048/tudod.1461623
25. Silva LLSE, Fernandes MSS, Lima EA, Stefano JT, Oliveira CP, and Jukemura J. Fatty pancreas: disease or finding? Clinics (Sao Paulo). (2021) 76:e2439. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2021/e2439
26. Wagner R, Eckstein SS, Yamazaki H, Gerst F, Machann J, Jaghutriz BA, et al. Metabolic implications of pancreatic fat accumulation. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2022) 18:43–54. doi: 10.1038/s41574-021-00573-3
27. Han F, Yin L, Yu X, Xu R, Tian M, Liu X, et al. High circulating fibroblast growth factor-21 levels as a screening marker in fatty pancreas patients. PeerJ. (2023) 11:e15176. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15176
28. Saisho Y, Butler AE, Meier JJ, Monchamp T, Allen-Auerbach M, Rizza RA, et al. Pancreas volumes in humans from birth to age one hundred taking into account sex, obesity, and presence of type-2 diabetes. Clin Anat. (2007) 20:933–42. doi: 10.1002/ca.20543
29. Ookura R, Usuki N, and Miki Y. Correlation between pancreatic fat deposition and metabolic syndrome: relationships with location in the pancreas and sex. Intern Med. (2024) 63:2113–23. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.2450-23
30. Stuart CE, Ko J, Modesto AE, Alarcon Ramos GC, Bharmal SH, Cho J, et al. Implications of tobacco smoking and alcohol consumption on ectopic fat deposition in individuals after pancreatitis. Pancreas. (2020) 49:924–34. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001600
Keywords: intra-pancreatic fat deposition, pancreatic diseases, type 2 diabetes mellitus, UK Biobank, mediation analysis
Citation: Gao J, Dong X, Shi X, Yang Y, Chen W, Xiao W, Lu G and Yu X (2025) The association between pancreatic diseases and pancreatic fat content: a cross-sectional study from the UK Biobank. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1591652. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1591652
Received: 11 March 2025; Accepted: 19 May 2025;
Published: 06 June 2025.
Edited by:
Nazarii Kobyliak, Bogomolets National Medical University, UkraineReviewed by:
Brittany Bruggeman, University of Florida, United StatesSevde Nur Emir, University of Health Sciences, Türkiye
Copyright © 2025 Gao, Dong, Shi, Yang, Chen, Xiao, Lu and Yu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaoping Yu, eHB5dUB5enUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jing Gao1†
Jing Gao1† Xiaolei Shi
Xiaolei Shi Weiwei Chen
Weiwei Chen Weiming Xiao
Weiming Xiao Guotao Lu
Guotao Lu Xiaoping Yu
Xiaoping Yu