- Department of Radiology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
Background: The effect of MS on coronary artery plaques detected by coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients is not fully understood. This study aimed to investigate the effect of MS and its components on coronary artery plaques by comparing CCTA characteristics, including plaque types, the severity of coronary plaques and high-risk plaques between T2DM patients with and without MS.
Methods: This study retrospectively enrolled 2,431 patients with T2DM who underwent Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CCTA) at West China Hospital between January 2015 to February 2022. These patients were divided into two groups based on the presence or absence of metabolic syndrome (MS). The plaque type, coronary artery stenosis, extent of coronary artery plaques, high-risk coronary plaque features, the segment involvement score (SIS), the segment stenosis score (SSS) and multivessel disease (MVD) based on CCTA data were evaluated and compared between two groups.
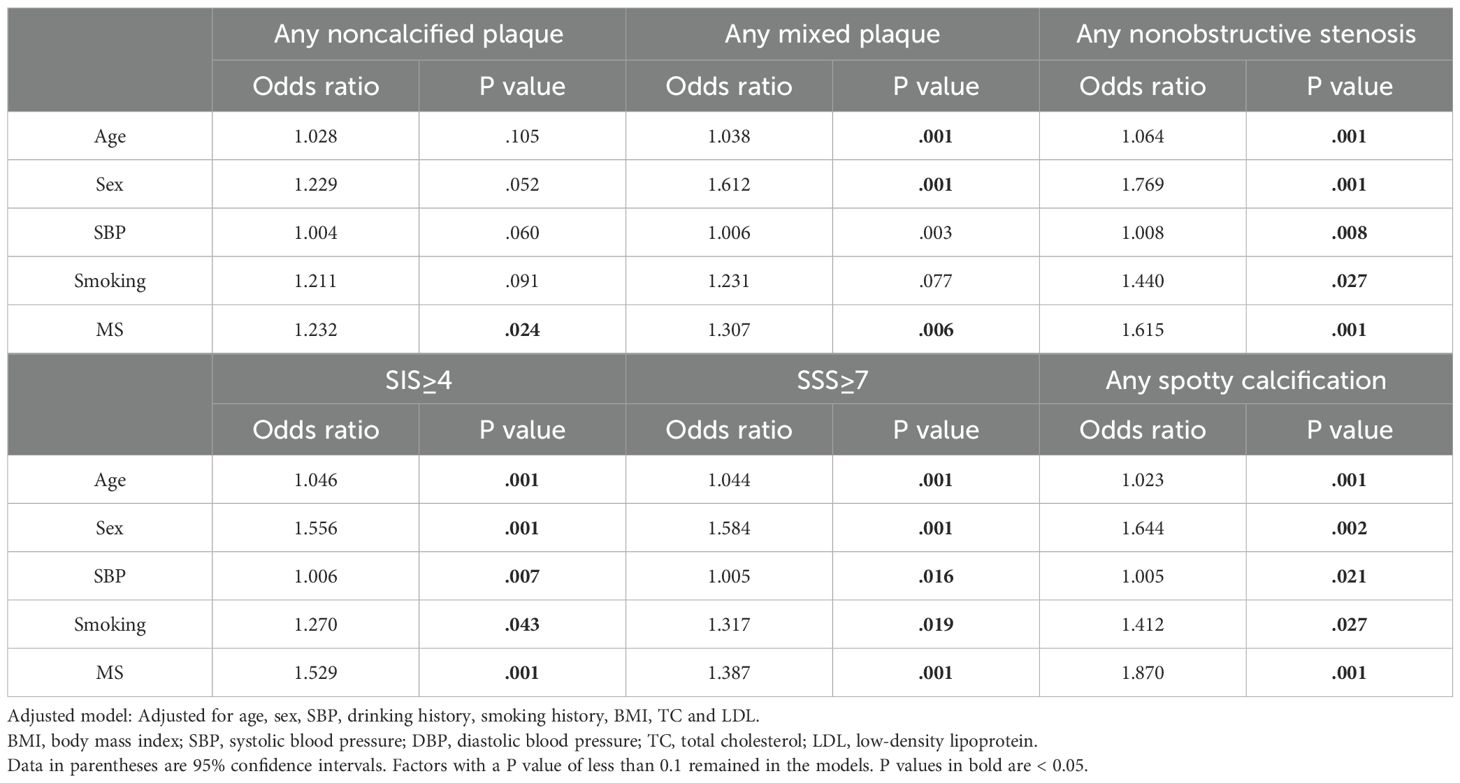
Results: For T2DM patients, those with MS (61.5%, n=1496) had more noncalcified/mixed plaques, more nonobstructive stenosis and higher SIS and SSS values than those without (P < 0.05 for all). The proportion of patients with any noncalcified plaque, any mixed plaque, SIS≥4 and SSS≥7were in parallel with the numbers of MS components (P for trend<0.01 for all). Multivariate logistic regression revealed that MS were independently associated with any noncalcified plaque (OR=1.232, P =0.024), any mixed plaque (OR=1.307, P=0.006), any nonobstructive stenosis(OR=1.615, P = 0.001), SIS≥4 (OR=1.529; P<0.001), SSS≥7 (OR=1.387; P=0.001), and any spotty calcification (OR=1.870, P =0.001) in T2DM patients after adjusting for the confounding factors.
Conclusion: MS is independently associated with adverse coronary artery plaque characteristics in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) patients, including increased mixed, noncalcified, nonobstructive, spotty calcification plaques, as well as extensive coronary artery disease (CAD). These findings highlight the need for early detection and management of MS to reduce cardiovascular risks in T2DM patients.
Introduction
As a global health emergency of the 21st century, type 2 diabetes(T2DM) is growing at an alarming rate across all regions, imposing severe socioeconomic burden (1). Cardiovascular involvement significantly increases the risk of adverse events in diabetic patients (2). Previous trials of intensive glucose control have failed to reduce CVD in T2DM, suggesting a more complex pathophysiological than hyperglycemia alone (3). Therefore, exploration for other abnormal metabolic factors contributing to the progression of coronary atherosclerosis in T2DM patients is crucial.
Metabolic syndrome (MS) is characterized by a cluster of cardiovascular risk factors, including insulin resistance (IR) (42), impaired glucose tolerance, obesity, hypertension, and dyslipidemia, which collectively increase the risk of cardiovascular disease (4). MS significantly increases the risk of developing T2DM and major cardiovascular events by a factor of 5 and 3 respectively, and thus leading to an approximately 1.6-fold increase in mortality (5). Insulin resistance is known to play a central role in the pathogenesis of MS, and is also a primary cause of T2DM (6, 7), indicating a frequent coexistence between diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Previous studies using coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) to evaluate the adverse effects of MS on coronary artery plaques were limited to asymptomatic individuals or populations undergoing routine health examinations, and failed to evaluate high-risk plaque characteristics (8, 9). This study conducted a more comprehensive analysis of CCTA images in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), exploring the impact of MS on plaque types, the severity of coronary plaques and high-risk plaques in T2DM patients, which could facilitate better risk stratification for diabetic patients with coexisting cardiovascular diseases.
Methods
Study population
This study is a single-center, retrospective, observational cohort study. A total of 3,372 hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM) at West China Hospital from January 2015 to February 2022 were included, all of whom underwent coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) within one week prior to admission or during hospitalization. Exclusion criteria (1): CCTA images with significant artifacts or poor quality (2); history of stent implantation, artificial valve replacement, or coronary artery fistula (3); missing critical clinical data, such as the data used for the diagnosis of MS; incomplete or missing clinical medical records. This retrospective study was approved by the ethics committee of our institution, which waived the requirement for informed consent. After applying these criteria, 2,431 patients were enrolled and categorized into MS group and non-MS group based on their adherence to the diagnostic criteria of MS.
T2DM was defined according to American Diabetes Association guidelines or treated with oral glucose-lowering agents or insulin (10). In accordance with modified National Cholesterol Education Program–Adult Treatment Panel III criteria (11), MS was diagnosed when at least three of the following conditions were present (1): waist circumference ≥ 90 cm in men and ≥ 80 cm in women, using the International Obesity Task Force criteria for the Asian-Pacific population to determine waist circumference criteria (2); triglyceride levels≥150 mg/dL (1.7 mmol/L) (3); HDL-cholesterol level < 40 mg/dL (1.0 mmol/L) in men and < 50 mg/dL (1.3 mmol/L) in women (4); blood pressure ≥130/85 mmHg or the use of antihypertensive medication; and (5) fasting glucose level ≥ 100 mg/dL (6.1 mmol/L) or the self-reported use of antidiabetic medication (insulin or oral agents) (11). For patients without waist circumference measurement, body mass index (BMI) was used instead of waist circumference and BMI > 25 kg/m2 was considered as exceeding the waist circumference threshold MS (12).
Hypertension was defined as having two consecutive systolic/diastolic blood pressure readings exceeding 140/90 mm Hg or the current use of antihypertensive medication. Dyslipidemia was diagnosed based on the presence of one or more of the following conditions: (1) hypercholesterolemia (TC ≥ 6.2 mmol/L), (2) hyper-LDL-C (LDL-C≥ 4.1 mmol/L), (3) hypertriglyceridemia (TG ≥ 2.3 mmol/L), and (4) hypo-HDL-C (HDL-C < 1.0 mmol/L in men and < 1.3 mmol/L in women) (13, 14). A history of smoking was recorded regardless of smoking cessation status, as was a history of alcohol consumption.
CCTA scanning protocols
CCTAs indications, data acquisition and image post-processing were performed in accordance with the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography guidelines (15). CCTA was performed using multiple-detector computed tomography (GE Healthcare, Waukesha, WI, USA) or multidetector CT systems (SOMATOM Definition, Siemens Medical Solutions, Forchheim, Germany; and SOMATOM Definition FLASH, Siemens Medical Solutions, Forchheim, Germany). Beta-blockers were not administered to lower the heart rate. The scan range extended from the tracheal bifurcation to 20 mm below the cardiac apex. All patients were positioned in the supine position and received an intravenous infusion of 70 to 90 ml (adjusted for body weight) of iodine contrast agent, followed by an injection of 30 ml of normal saline at the same flow rate. The Revolution CT system utilizes kV Assist and Smart-mA to automatically adjust tube voltage and tube current based on the patient’s scout image, with a collimation of 256 × 0.625 mm and rotation time of 0.28 s. The SOMATOM Definition system operates at a tube voltage of 100 ~ 120 kV, tube current of 220 mAs, collimation of 64/128 × 0.6mm, and rotation time of 0.33s. After the scan is completed, the initial dataset is immediately reconstructed, and the highest-quality images are transferred to a post-processing workstation (Syngo-Imaging, Siemens Medical Solution Systems, Forchheim, Germany) for image analysis. When plaques are highly calcified, Sinogram Affirmed Iterative Reconstruction (SAFIRE) is utilized to reduce image noise and optimize image quality. Coronary artery plaques are evaluated using maximum intensity projection, multiplanar reconstruction, curved planar reconstruction, and volumetric reconstruction.
Image analysis
The plaque type, coronary artery stenosis, extent of coronary artery plaques and high-risk coronary plaque features based on CCTA data was qualitatively analyzed by two professional cardiologists who were masked to the clinical results and group identities. For segment-wise analysis, coronary artery trees were divided into 16 separate segments according to the revised standards of the American Heart Association (Figure 1) (16, 17). Each plaque was categorized based on its composition as (a) calcified plaque (plaques with higher density than contrast-enhanced lumen); (b) non-calcified plaque (plaques with lower CT attenuation than contrast-enhanced lumen, no calcification);(c) Mixed plaques (calcified with non-calcified components in a single plaque) (18). The severity of lumen stenosis caused by detected plaques was quantified and graded as a 5-point scale based on the Coronary Artery Disease(CAD)-Reporting and Data System: Grade 0, no visible luminal stenosis; Grade 1, lumen stenosis < 25%; Grade 2, lumen stenosis 25-49%; Grade 3, lumen stenosis 50-69%; Grade 4, lumen stenosis 70-99%; Grade 5, completely occluded (19). Obstructive stenosis was defined as lumen stenosis ≥50%. SIS represented the sum of coronary artery segments involved by plaque, with each segment’s plaque and lumen stenosis recorded as 1 point (0–16 points), which indicates the extent of coronary plaque involvement. SSS was defined as the sum of the stenosis scores of the relevant stenosis grades of all segments for each patient (0–80 points), which indicates the degree of stenosis of the coronary arter of coronary artery (16, 20). According to the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guidelines, multivessel obstructive disease (MVD) was defined as the presence of more than one vessel with stenosis ≥ 70% or LM stenosis ≥ 50% (21). The high-risk plaque features comprised of low-attenuation noncalcified plaque, positive remodeling, spotty calcification and “napkin ring” signs. The low-attenuation noncalcified plaques was defined as areas within plaques >1 mm2 with CT values <30 Hounsfield Units (HU). The remodeling index (RI) was defined as the ratio of the maximum vascular diameter at the lesion site (including plaque and lumen) to the diameter of the normal proximal lumen (arterial remodeling index = lesion plaque area/reference area). A RI of ≥ 1.1 indicates positive remodeling (outward expansion of the vessel wall). Spotty calcification was characterized as small focal calcifications of <3mm in any direction with a length diameter of < 3 mm in any plane within a non-calcified plaque, with a length diameter less than 1.5 times the vessel diameter and a short diameter of less than 2/3 the vessel diameter. The napkin-ring sign was described as a plaque core with low CT attenuation surrounded by an annular area with slightly higher CT attenuation (22–24).
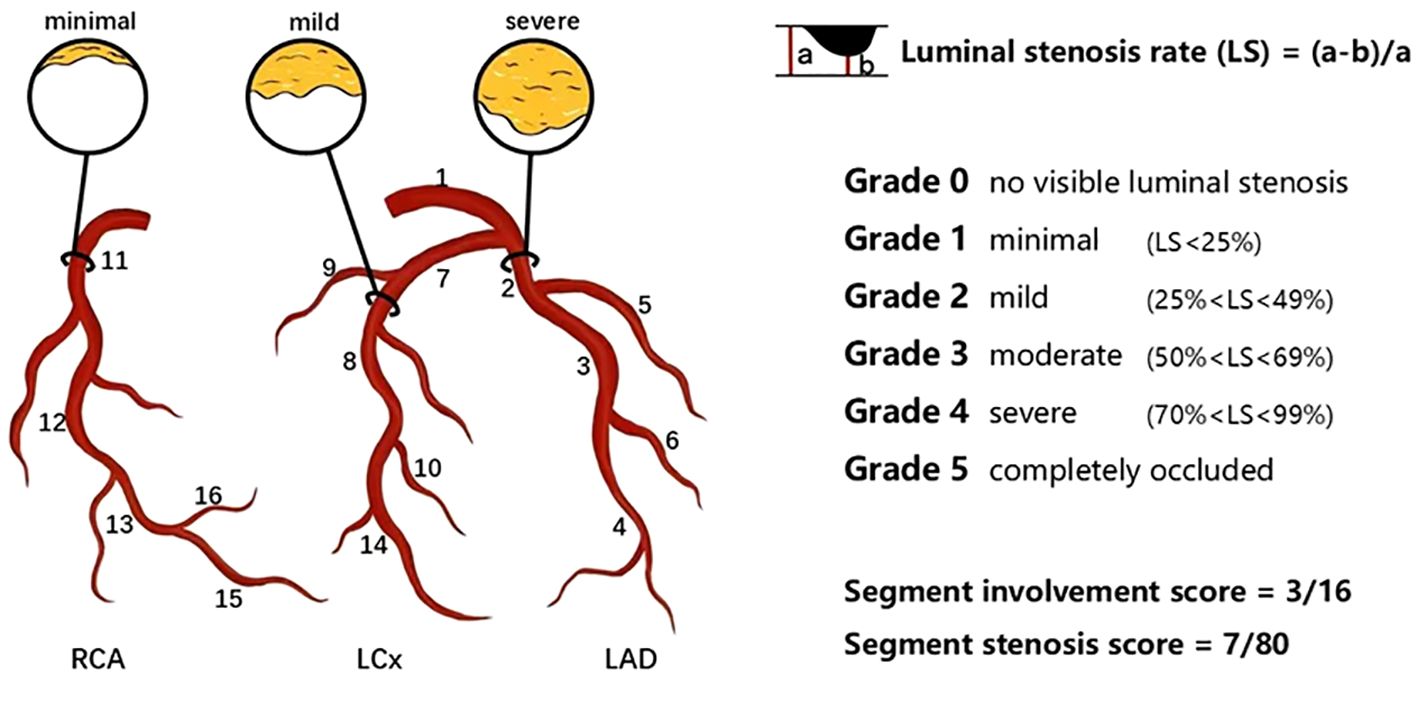
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the degree of coronary artery stenosis and coronary artery segmentation. In this example, plaques distribute on proximal RCA, mid-LAD and proximal LCx. SIS was calculated by the number of coronary artery segments observed with plaques, which was 3 out of a possible 16 in this example. SSS was calculated by the minimal plaque in the proximal RCA (scored 1), mild plaque in the mid-LAD (scored 2) and severe plaque in the proximal LCx (scored 4). Thus, the SSS was 7 out of a possible 80. LAD left anterior descending artery; LCx left circumflex; RCA right coronary artery; SIS segment involvement score; SSS segement stenosis score. 1 left main coronary artery; 2 proximal LAD; 3 mid-LAD; 4 distal LAD; 5 first diagonal branch; 6 second diagonal branch; 7 proximal LCx; 8 distal LCx; 9 first obtuse marginal branch; 10 second obtuse marginal branch; 11 proximal RCA; 12 mid-RCA; 13 distal RCA; 14 left posterolateral artery; 15 right posterolateral artery; 16 posterior descending artery.
Statistical analysis
The baseline clinical and imaging data of the patients were stratified based on the presence of MS, and comparisons were made between the MS group and non-MS group in terms of differences in clinical baseline features and multi-row CT findings. Categorical variables were presented as number (%) and compared using a Chi-Square test. Continuous variables with normal distribution, such as age, height, weight, etc., were expressed as mean ± standard deviation and analyzed using student’s t-test. Non-normally distributed continuous variables, such as number of patches, were presented as median (interquartile range) and analyzed using Wilcoxon rank sum tests. χ2 tests with linear-by-linear associations were applied to examine the significance of any linear trend of presence of any coronary artery plaque and extensive coronary plaques according to the number of MS components. Multivariate logistic regression was employed to analyze the relationship between coronary artery disease and MS along with other common cardiovascular risk factors. A two-tailed P value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Study population
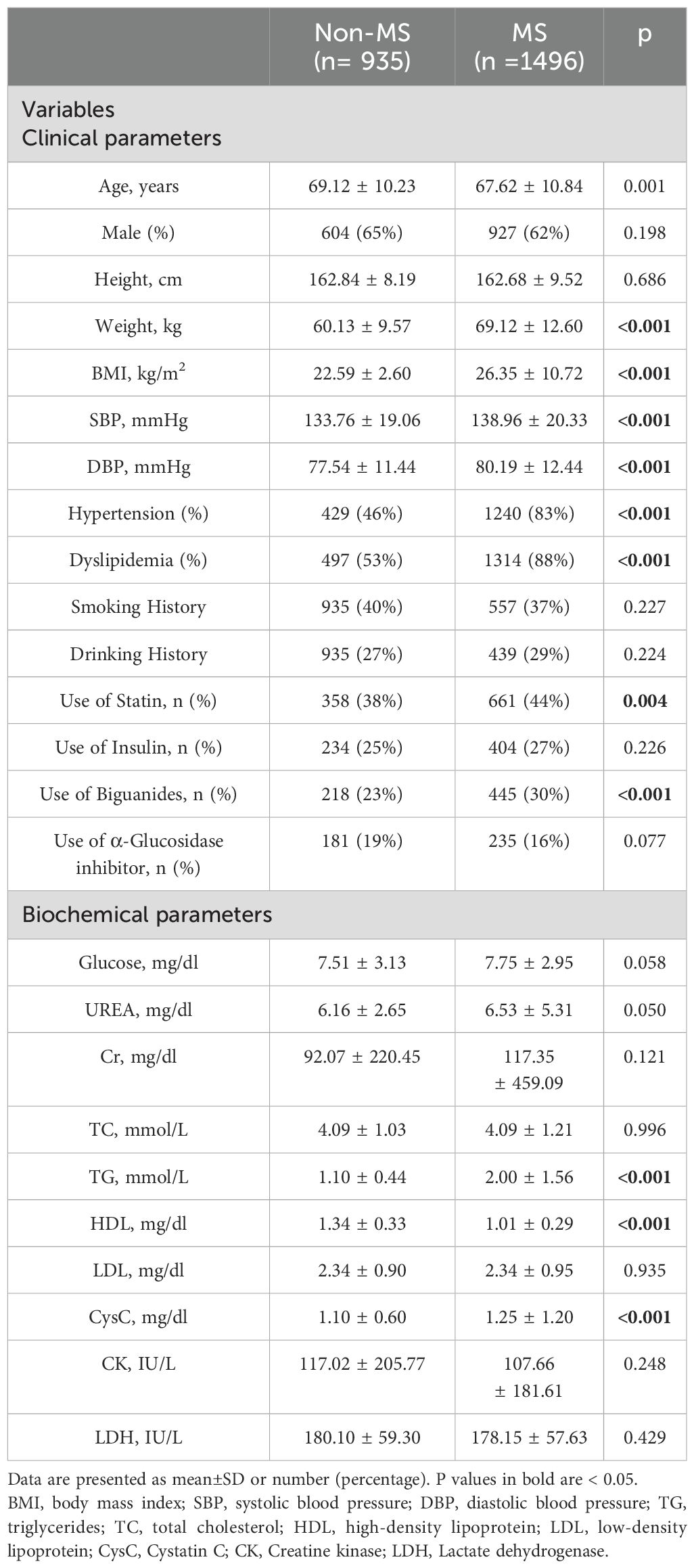
A total of 3349 T2DM patients were included in this study in the beginning, and after using exclusion criteria 2431 participants (935 patients without MS, 1496 patients with MS) were studied. The main clinical characteristics of the subjects were compared according to the presence or absence of MS (Table 1). The mean age of the participants was 69.2 ± 10.6 years, and 63% were male. The patients in the MS group had higher weight (non-MS vs. MS: 60.1 ± 9.6 vs. 69.1 ± 12.6, P<0.001) and body mass index (BMI, non-MS vs. MS: 22.6 ± 2.60 vs. 26.4 ± 10.7, P< 0.001) values. The MS group showed a higher prevalence of hypertension (46% vs. 83%, P<0.001), dyslipidaemia (53% vs. 88%, P< 0.001) and more frequent use of statin (38% vs. 44%, P= 0.004) and Biguanides (23% vs. 30%, P< 0.001). The level of cystatin C (CysC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and plasma triglyceride (TG) was higher in patients with MS than those without MS (p<0.05 for all). There were no significant differences observed in sex, height, smoking history, drinking history, the use of insulin, the use of α-Glucosidase inhibitor and other laboratory measures between the two groups (p>0.05).
CCTA findings in non-MS and MS group
A total of 10549 coronary plaques were analyzed [non-MS vs. MS 3752 vs. 6797]. The plaque types, coronary artery stenosis, extent of coronary artery plaques, and high-risk coronary plaque features between MS and non-MS groups were compared in Table 2. Regarding plaque types, the MS group exhibited a higher number of mixed plaques and noncalcified plaques compared to the non-MS group [non-MS vs. MS mixed plaques: 1.7 ± 2.3 vs. 2.0 ± 2.6, P =0.001; noncalcified plaques: 0.8± 1.2 vs. 0.9 ± 1.3, P values=0.004] (Figure 2, Table 2). No significant difference observed in the number of calcified plaques between two groups(p>0.05). The MS group had a higher proportion of patients with any noncalcified plaques than the non-MS group [non-MS vs. MS: 43.2% vs. 49.3%, P < 0.001] (Table 2). There were no significant differences in the proportion of patients with any calcified plaque or mixed plaque in between the MS and non-MS groups, nor in the proportion of patients with obstructive CAD (P > 0.05). The distribution of plaque types and high-risk plaque features within the coronary tree for the different groups is illustrated in Figure 3.
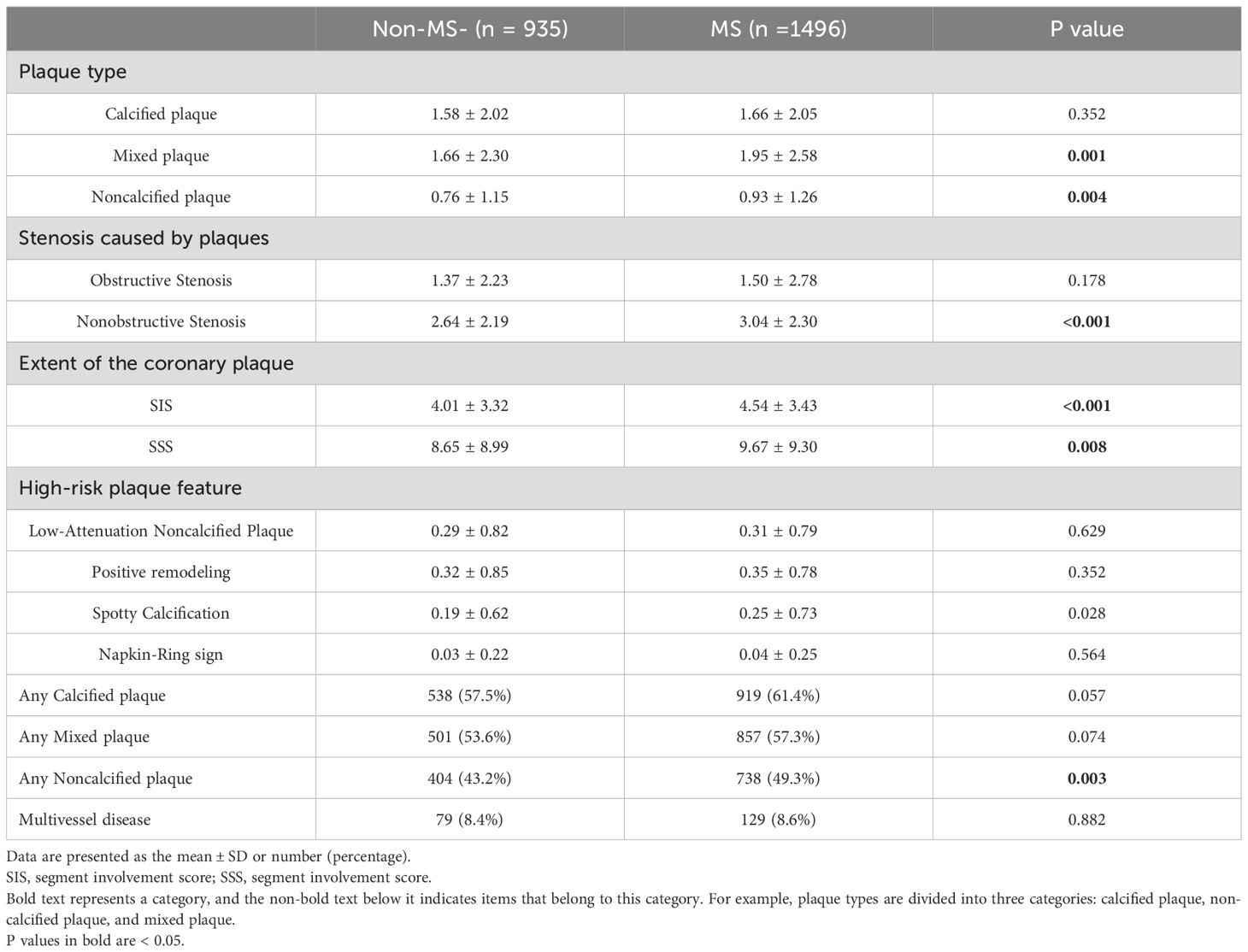
Table 2. Characteristics of coronary artery plaques detected by CCTA in DM patients with and without MS.
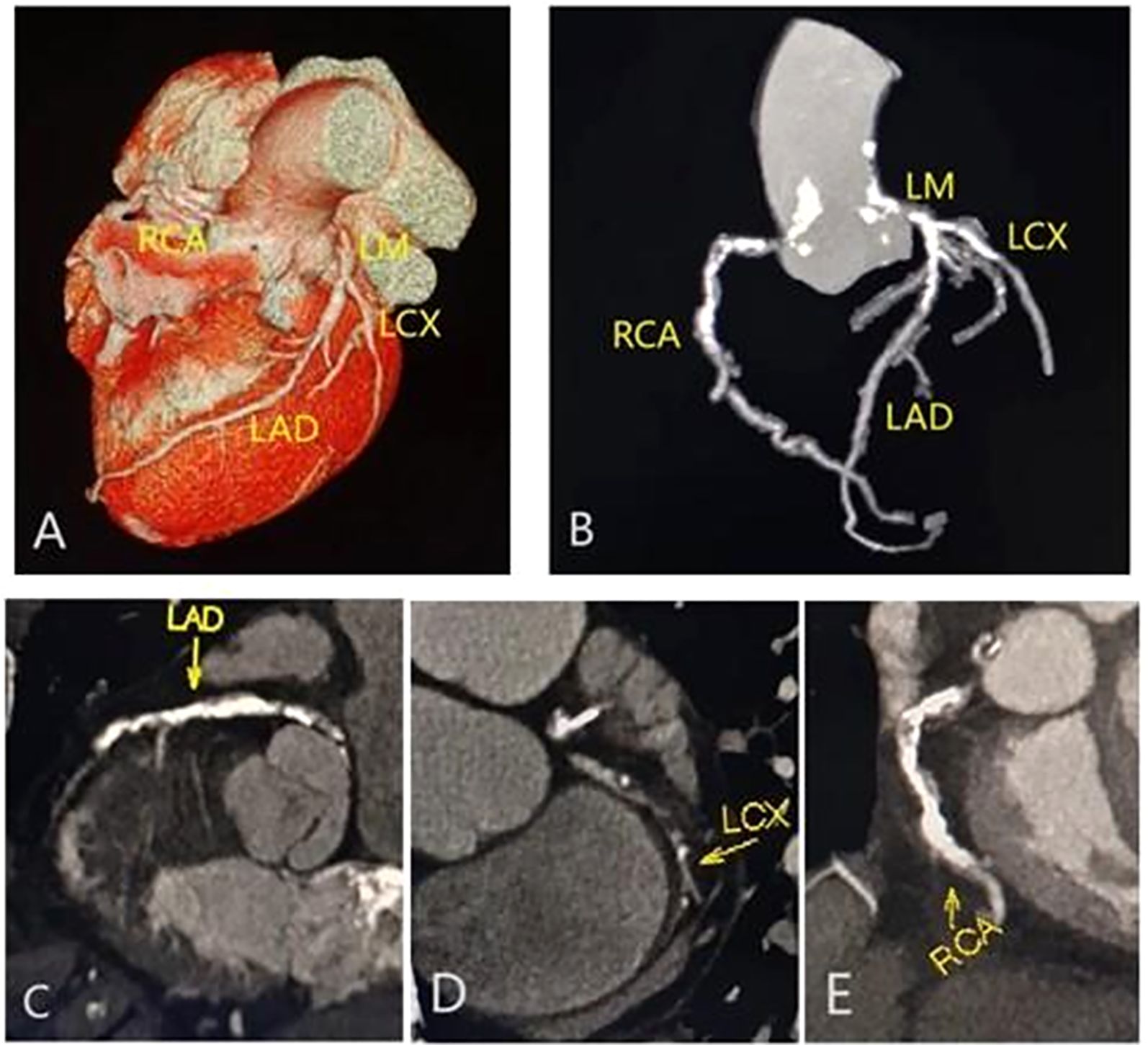
Figure 2. |Representative CCTA images of multivessel disease in a male with type 2 diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome. Volume rendering image (A); maximum intensity projection (MIP) CT image (B); and curvature plane reconstruction images (C-E) show the non-smooth edges, diffuse calcified, and mixed plaques of the LM, LAD, RCA and LCX.
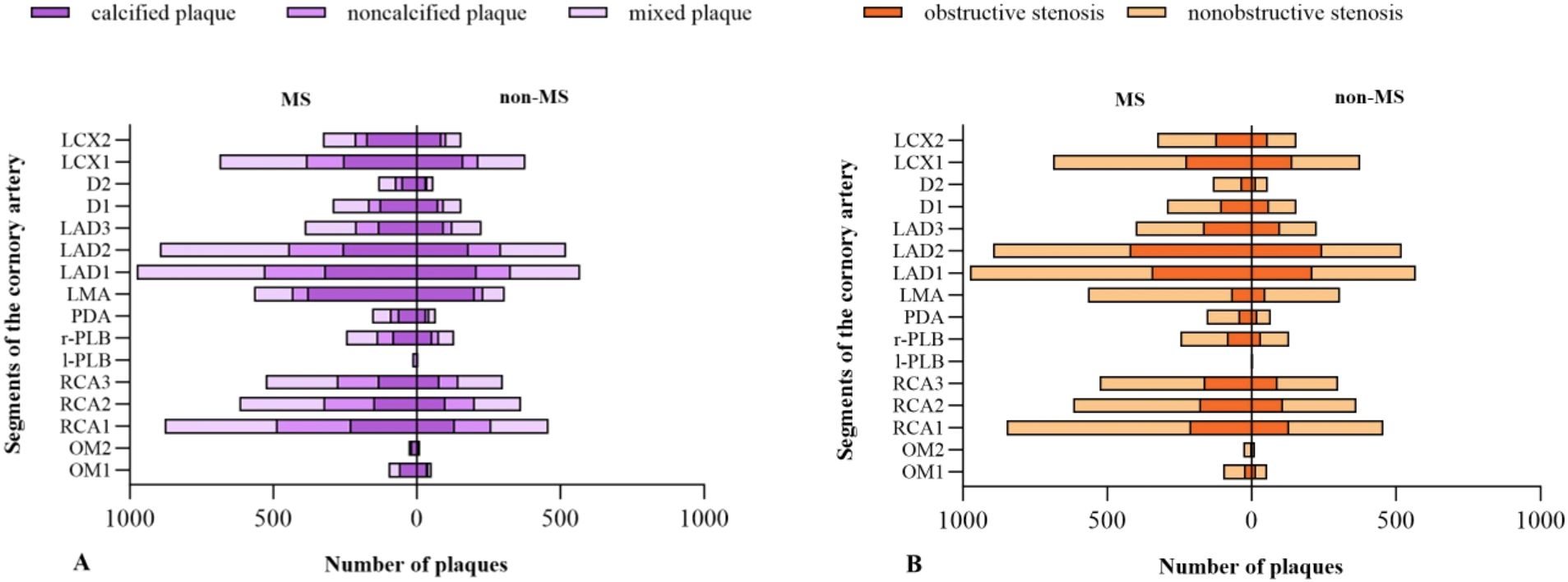
Figure 3. Anatomical distribution of plaques in different groups. Distribution of different types of plaque (A); Obstructive and nonobstructive stenosis (B).
Regarding the coronary artery stenosis, nonobstructive stenosis was more frequently observed in patients with MS than those without [non-MS vs. MS: 2.6 ± 2.1 vs. 3.0 ± 2.3 P < 0.001]. No significant difference showed in the number of obstructive stenosis between the MS and non-MS group (p>0.05). Regarding the high-risk plaque features, the subjects in the MS group had a higher prevalence of spotty calcification compared to the non-MS group [non-MS vs. MS: 0.2 ± 0.6 vs. 0.3 ± 0.7, P=0.028] (Table 2).
The subjects in MS group had higher SIS and SSS scores compared to those in the non-MS group [non-MS vs. MS SIS: 4.0 ± 3.3 vs. 4.5 ± 3.4 P values< 0.001; SSS: 8.7 ± 9.0 vs. 9.7 ± 9.3, P =0.008]. The difference in the proportion of subjects with multivessel disease between the MS and non-MS group was not statistically significant (p>0.05).
The association between the number of MS components and coronary artery atherosclerosis
The correlation between the number of MS components and coronary artery atherosclerosis was showed in Figure 4. As the number of MS components increased, so did the proportion of patients with noncalcified/mixed plaques, SIS≥4 and SSS≥7. The percent of patients with noncalcified plaques increased gradually from 42% in subjects without any MS component to 54% in those with three components, and then maintained relatively stable (P for trend <0.001; Figure 4). A similar trend was observed in the association between MS components and the proportion of patients with mixed plaques, SIS≥4 and SSS≥7 (mixed plaques: P for trend <0.001; SIS≥4: P for trend <0.01; SSS≥7: P for trend <0.01. Figure 4).
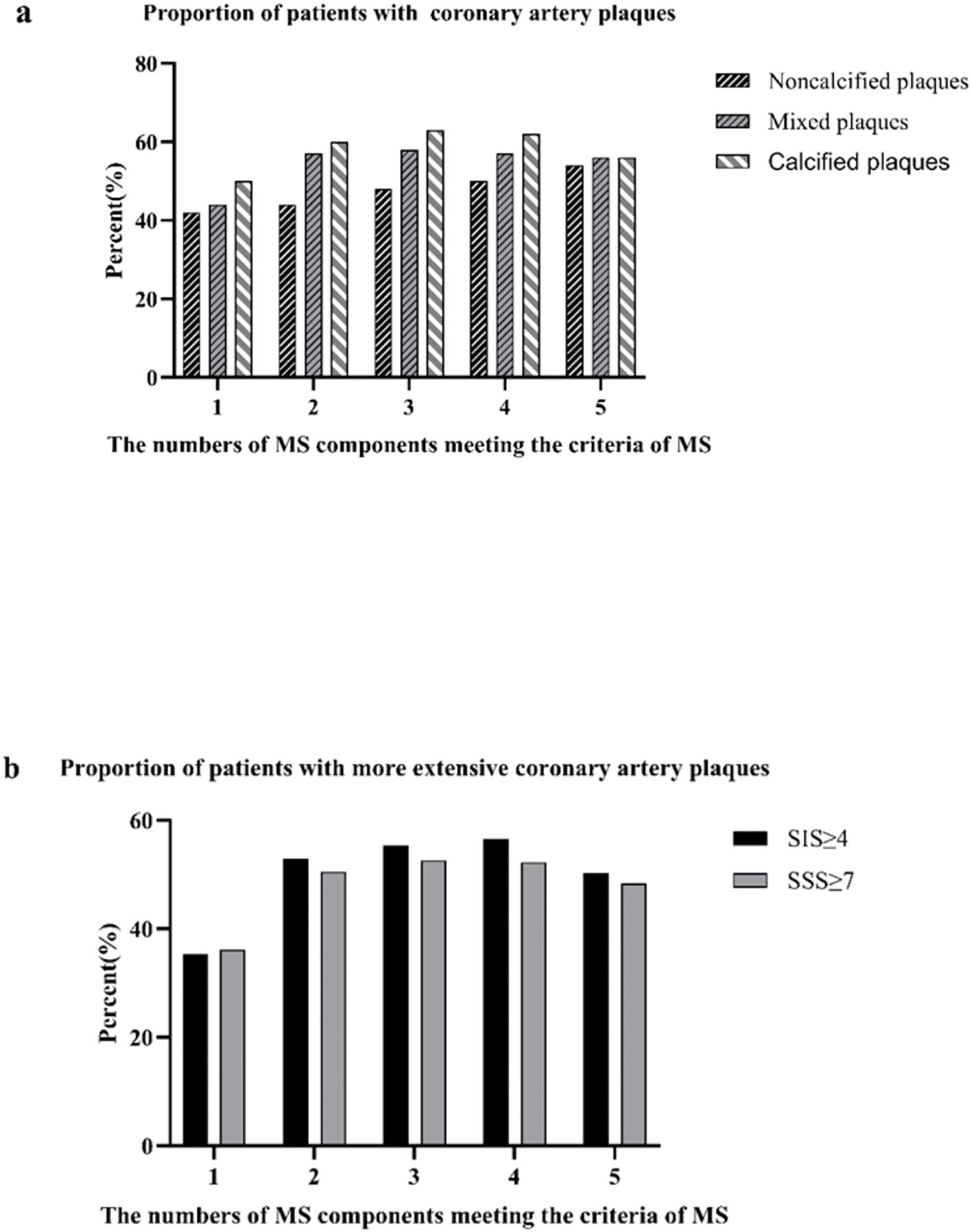
Figure 4. |Proportions of patients with coronary artery atherosclerosis according to the number of the metabolic syndrome (MS) components present (a); proportion of patients with coronary artery plaques proportions of patients with extensive coronary artery plaques (b).
Multivariate logistic regression analysis for variables associated with CCTA findings
Multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to determine if MS was an independent risk factor for the presence of coronary artery plaques, extensive coronary artery plaques and high-risk plaque features. After adjustment for confounding factors including age, sex, SBP, etc., MS was found to be an independent risk factor for the presence of any mixed plaque, any noncalcified plaque and any nonobstructive stenosis [non-MS vs. MS, any mixed plaque: odds ratio=1.232, P=0.024; any noncalcified plaques: odds ratio=1.307, P=0.006; and any nonobstructive stenosis: odds ratio=1.615, P=0.001] (Table 3). MS was also significantly associated with more extensive and severe CAD (SIS≥4 and SSS≥7) and spotty calcification plaques after adjusting for the same confounding factors [non-MS vs. MS, SIS≥4: odds ratio=1.529, P=0.024; SSS≥7: odds ratio=1.387, P=0.006; and spotty calcification: odds ratio=1.870, P =0.001] (Table 3).
We performed the same analysis to compare the effects of different components of MS on coronary atherosclerosis, the results of which are shown in Table 4. After adjusting for confounding factors, abnormal level of HDL and TG did not have statistically significant effects on most CCTA results(p>0.05); only HDL had significant effects on the presence of spotty calcification plaques [non-MS vs. MS, odds ratio=1.411, P=0.010]. Obesity is an independent factor for the presence of obstructive stenosis, low-attenuation plaques, SSS≥7, and multiple vessel disease. Hypertension is an independent factor for calcified/noncalcified plaques, obstructive/nonobstructive stenosis, SIS≥4, SSS≥7, most high-risk plaques, and multivessel disease, and it also exhibited a higher odds ratio than obesity.
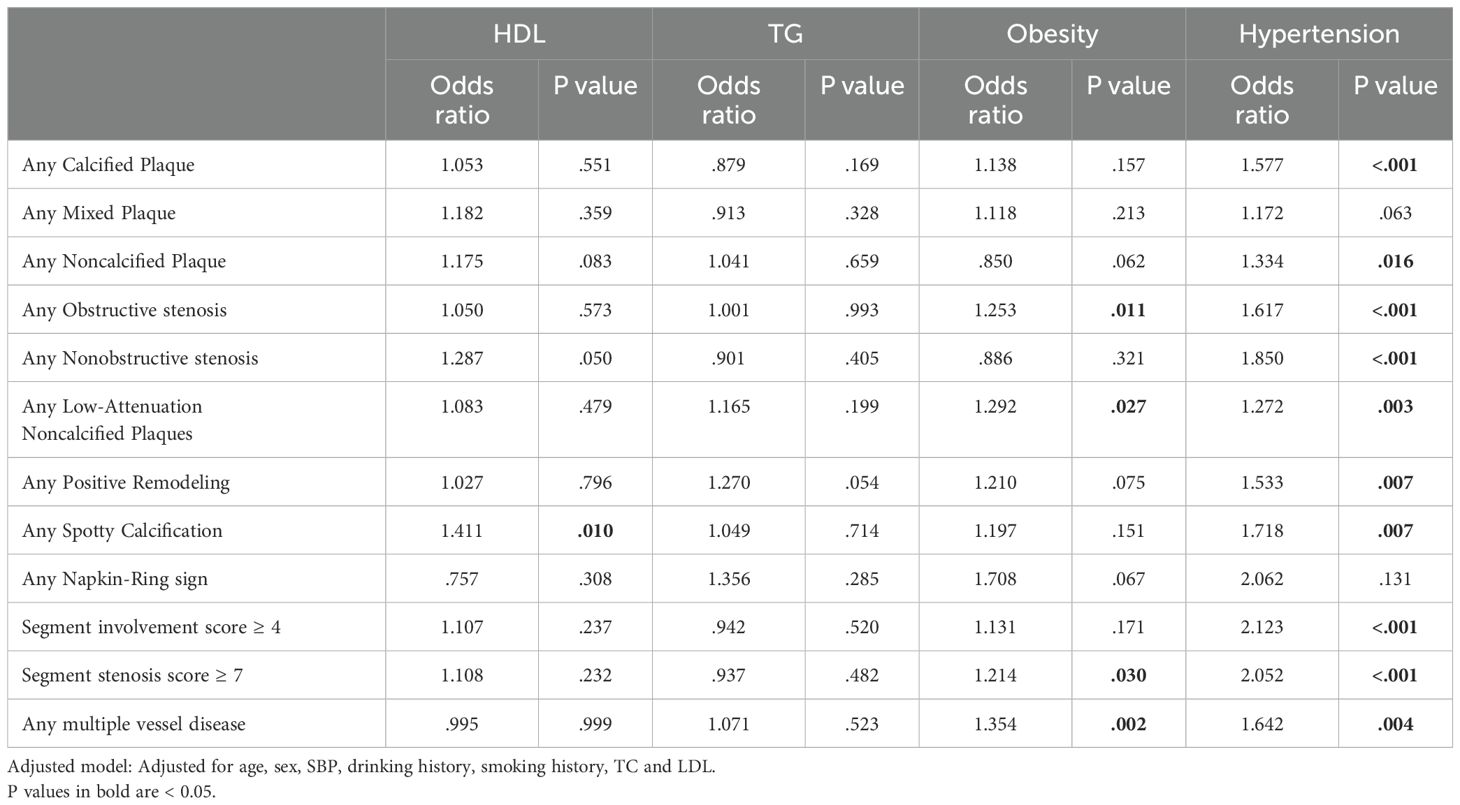
Table 4. Multivariate logistic regression analysis for different components of MS associated with CCTA findings.
Discussion
This retrospective study demonstrated that compared to patients without MS (non-MS group), those with T2DM and concurrent MS displayed a significantly higher burden of coronary plaques. Specifically, these patients exhibited a higher prevalence of noncalcified/mixed plaques, a greater number of high-risk plaques, more extensive and severe CAD. Furthermore, the proportion of patients with noncalcified/mixed plaques and extensive coronary plaques showed a positive association with the numbers of MS components. Multivariate analysis showed that MS was independently associated with more extensive and severe CAD. This association extended to the occurrence of mixed, noncalcified, nonobstructive plaques, as well as spotty calcification plaques.
The additive effect of MS on plaque type in T2DM
This study highlighted a significant increase in the presence of noncalcified and mixed plaques among MS patients compared to those without MS. It is well documented that mixed or noncalcified plaques correlates strongly with an increased risk of adverse cardiovascular events (25, 26). The elevated occurrence of noncalcified plaques in the MS group may be attributed to heightened inflammatory activity characteristic of MS, which can lead to increased plaque instability. The probable explanation for this greater number of noncalcified/mixed plaques and higher proportion of patients with noncalcified plaques in the MS group may be that MS can increase inflammatory activity and lead to atherosclerotic plaque instability. Furthermore, this study revealed no significant difference in the number of calcified plaques between MS and non-MS groups, which may indicate that in addition to MS, the formation of calcified plaques is also influenced by factors such as age, sex, smoking history, and alcohol consumption history.
Lee et al. revealed that rapid development or progression of CACS, coronary artery stenosis, and vulnerable plaque had a positive correlation with the number of MS components in their long-term follow-up observation (8). Our study had similar results; as the number of MS components increased, so did the proportion of T2DM patients with any noncalcified or mixed plaque and extensive CAD. These findings highlight the need to manage the number of abnormal metabolic markers in patients with diabetes to effectively inhibit the development of coronary atherosclerosis.
MS increase the presence of high-risk plaque features in T2DM
According to our data, MS was associated with a higher prevalence of spotty calcification in T2DM patients, identifying MS as an independent predictor for this kind of high-risk plaques even after adjusting for confounding factors. It is noteworthy that MS demonstrated a higher OR value in comparison to other established cardiovascular risk factors. Spotty calcification has been more closely linked with acute coronary events than common mixed or non-calcified plaques. According to Ehara S et al, the spotty calcification in plaques is often observed in the culprit lesions of acute myocardial infarction(AMI) patients, suggesting a significant role in clinical outcomes (27). The increased prevalence of these plaques in AMI patients is thought to be due to early he spotty calcification (< 1mm) or microcalcification (< 50mm), which may trigger local tissue stress and lead to plaque instability and subsequent rupture (28, 29).
MS aggravate extent and severity of CAD in T2DM
Our study demonstrated that T2DM patients with MS are more prone to have extensive and severe CAD. Patients with diabetes typically exhibit a significant burden of coronary plaques. The likey explanation is that diabetes promotes microvascular dysfunction through increased oxidative stress and the production of more proinflammatory substrate, which may faciliatate the formation and progression of plaques (30, 31). This condition is further exacerbated in the presence of MS, which enhances both the occurrence and progression of coronary atherosclerosis (32, 33). MS may facilitate the development of coronary atherosclerosis through multiple mechanisms, one of which is oxidative stress. In patients with MS, insulin resistance and abnormal deposition of adipose tissue elevate oxidative stress and inflammatory responses, which collectively impair endothelial function. And endothelial dysfunction is a key initiating event in the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in the coronary arteries (34, 35).
Furthermore, MS is associated with altered levels of adipose-derived hormones and cytokines, commonly referred to as adipokines. With the progression of obesity, there is an expansion in the volume of cardiac adipose tissue, which tends to accumulate preferentially around the coronary arteries. This phenomenon results in a higher incidence of atherosclerotic plaques in arteries surrounded by perivascular adipose tissue (PVAT). The adipokines secreted by PVAT are known to play a pivotal role in vascular dysfunction, influencing the integrity and function of adjacent blood vessels and promoting the development of atherosclerosis (6). These adipokines not only contribute to vascular inflammation but also to the modulation of arterial remodeling and plaque instability, thereby increasing the risk of cardiovascular events.
Impact of various components of MS on coronary plaques
Through our multivariate analysis assessing the impact of various components of MS and findings from CCTA, it was evident that hypertension exerted the most significant influence on coronary plaque, followed by obesity. TG and HDL levels showed comparatively less effect. Obesity, historically a core criterion in the diagnosis of MS, plays a crucial role in both the occurrence and development of MS (36). The relationship between obesity, prolonged sedentary behavior, and insulin resistance is well-established. The resultant hyperinsulinemia from these conditions can lead to a cascade of metabolic disturbances, including disrupted glucose metabolism and elevated levels of fatty acids, as well as activation of the sympathetic nervous system, all of which significantly contribute to the onset of cardiovascular diseases (6). Hypertension impacts coronary health by impairing vascular endothelial function, altering wall shear stress, and heightening oxidative stress. These changes initiate a host of pathophysiological responses, including the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells, vascular remodeling, and apoptosis, as well as increased cell permeability and expression of adhesion molecules, thereby accelerating the development of atherosclerotic plaques (37, 38). Research by Jiang Yu et al. corroborates the pronounced impact of hypertension on coronary plaque formation in patients with T2DM (39).Given these findings, a stronger emphasis on meticulous blood pressure management in diabetic patients is imperative to mitigate the risk of cardiovascular complications.
The prevention of coronary artery damage
The current management paradigm for atherosclerotic coronary artery disease (CAD) focuses on comprehensive prevention by addressing major modifiable risk factors (smoking, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and hypercholesterolemia) while promoting lifestyle modifications through healthy dietary habits, maintenance of normal body weight, and regular physical activity (40). Substantial evidence demonstrates that smoking prevention/cessation, blood pressure normalization, plasma cholesterol reduction, and targeted diabetes management in specific clinical contexts can collectively reduce the incidence of coronary events (41).
Limitations
Our study has several limitations. First, its cross-sectional design prevents us from interpreting the results as definitive causal relationships, and the mechanism underlying the association between MS and coronary atherosclerotic plaques remains to be clarified. Second, potential confounding factors that may influence lipid levels were not obtained and analyzed in this study, which to some extent limits the scientific rigor of the findings. Third, all participants in this study were recruited from a single hospital center, which may restrict the generalizability of our results.
Conclusion
MS is independently associated with adverse coronary artery plaque characteristics among patients with T2DM. This association includes a higher prevalence of mixed, noncalcified, nonobstructive, and spotty calcification plaques, along with more extensive overall coronary plaque burden. And among the components of MS, hypertension has the greatest influence on coronary atherosclerosis in DM patients. These findings underscore the critical importance of early detection and effective management of MS in T2DM patients to mitigate cardiovascular risk. Targeted interventions aimed at controlling MS components could potentially reduce the progression of coronary atherosclerosis, thereby improving cardiovascular outcomes in this high-risk population.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The requirement of ethical approval was waived by West-China Hospital of Sichuan University Biomedical Research Ethics Committee for the studies involving humans because This is a retrospective study. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board also waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because This is a retrospective study. All the data we used were from the patients’ medical records in our hospital, and we kept these data strictly confidential. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
Y-SZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. Y-NJ: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YG: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. JW: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YL: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. Z-GY: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (821201080), the Science and Technology Support Program of Sichuan Province (2022NSFSC0828), the 1-3–5 project for disciplines of excellence of West China Hospital, Sichuan University (ZYGD23019), and the Postdoctoral Fellowship Program of CPSF under Grant Number GZC20241142.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
MS, Metabolic Syndrome; T2DM, Type 2 diabetes mellitus; MVD, multivessel disease; CVD, cardiovascular disease; CAD, coronary artery disease; CCTA, coronary computed tomography angiography; SIS, segment involvement scores; SSS, segment stenosis scores; LM, left main; RCA, right coronary artery; LAD, left anterior descending; LCX, left circumflex; CVD, cardiovascular disease; ACS, acute coronary syndrome; LDL-C, Low-density protein cholesterol; TC Total cholesterol; TG Triglyceride; HDL-C High density lipoprotein cholesterol; CysC, cystatin C.
References
1. Ruze R, Liu T, Zou X, Song J, Chen Y, Xu R, et al. Obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus: connections in epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatments. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2023) 14:1161521. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1161521
2. Mohammedi K, Woodward M, Marre M, Colagiuri S, Cooper M, Harrap S, et al. Comparative effects of microvascular and macrovascular disease on the risk of major outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2017) 16:95. doi: 10.1186/s12933-017-0574-y
3. Mitchell JD. Personalizing risk assessment in diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. (2021) 14:230–2. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2020.11.002
4. Alberti KG, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Forceon Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World HeartFederation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Obes Metabol. (2010) 7:63–5. doi: 10.14341/2071-8713-5281
5. O’Neill S and O’Driscoll L. Metabolic syndrome: a closer look at the growing epidemic and its associated pathologies. Obes Rev. (2015) 16:1–12. doi: 10.1111/obr.12229
6. Tune JD, Goodwill AG, Sassoon DJ, and Mather KJ. Cardiovascular consequences of metabolic syndrome. (2018). doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2017.01.001
8. Kim LK, Yoon JW, Lee D-H, Kim KM, Choi SH, Park KS, et al. Impact of metabolic syndrome on the progression of coronary calcium and of coronary artery disease assessed by repeated cardiac computed tomography scans. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2016) 15:92. doi: 10.1186/s12933-016-0404-7
9. Lim S, Shin H, Lee Y, Won Yoon J, Kang SM, Choi SH, et al. Effect of metabolic syndrome on coronary artery stenosis and plaque characteristics as assessed with 64–detector row cardiac CT. Radiology. (2011) 261:437–45. doi: 10.1148/radiol.11101725
10. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 6. Glycemic targets: standards of medical care in diabetes—2022. Diabetes Care. (2022) 45:S83–96. doi: 10.2337/dc22-S006
11. Alberti KGMM, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation. (2009) 120:1640–5. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.192644
12. Campbell DJ, Somaratne JB, Jenkins AJ, Prior DL, Yii M, Kenny JF, et al. Impact of type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome on myocardial structure and microvasculature of men with coronary artery disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2011) 10:80. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-10-80
13. Koh N, Ference BA, Nicholls SJ, Navar AM, Chew DP, Kostner K, et al. Asian pacific society of cardiology consensus recommendations on dyslipidaemia. Eur Cardiol. (2021) 16:e54. doi: 10.15420/ecr.2021.36
14. Jin E-S, Shim J-S, Kim SE, Bae JH, Kang S, Won JC, et al. Dyslipidemia fact sheet in South Korea, 2022. J Lipid Atheroscler. (2023) 12:237. doi: 10.12997/jla.2023.12.3.237
15. Abbara S, Blanke P, Maroules CD, Cheezum M, Choi AD, Han BK, et al. SCCT guidelines for the performance and acquisition of coronary computed tomographic angiography: A report of the society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography Guidelines Committee: Endorsed by the North American Society for Cardiovascular Imaging (NASCI). J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. (2016) 10:435–49. doi: 10.1016/j.jcct.2016.10.002
16. Shi R, Shi K, Yang Z, Guo Y, Diao K, Gao Y, et al. Serial coronary computed tomography angiography-verified coronary plaque progression: comparison of stented patients with or without diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2019) 18:123. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0924-z
17. Austen W, Edwards J, Frye R, Gensini G, Gott V, Griffith L, et al. A reporting system on patients evaluated for coronary artery disease. Report of the Ad Hoc Committee for Grading of Coronary Artery Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Surgery, American Heart Association. Circulation. (1975) 51:5–40. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.51.4.5
18. Jiang Y, Pang T, Shi R, Qian W, Yan W, Li Y, et al. Effect of smoking on coronary artery plaques in type 2 diabetes mellitus: evaluation with coronary computed tomography angiography. Front Endocrinol. (2021) 12:750773. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.750773
19. Cury RC, Abbara S, Achenbach S, Agatston A, Berman DS, Budoff MJ, et al. CAD-RADSTM Coronary Artery Disease – Reporting and Data System. An expert consensus document of the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography (SCCT), the American College of Radiology (ACR) and the North American Society for Cardiovascular Imaging (NASCI). Endorsed by the American College of Cardiology. J Cardiovasc Computed Tomography. (2016) 10:269–81. doi: 10.1016/j.jcct.2016.04.005
20. Jiang Y, Yang Z-G, Wang J, Shi R, Han P-L, Qian W-L, et al. Unsupervised machine learning based on clinical factors for the detection of coronary artery atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2022) 21:259. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01700-8
21. Patel MR, Calhoon JH, Dehmer GJ, Grantham JA, Maddox TM, Maron DJ, et al. ACC/AATS/AHA/ASE/ASNC/SCAI/SCCT/STS 2017 appropriate use criteria for coronary revascularization in patients with stable ischemic heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2017) 69:2212–41. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.02.001
22. Andreini D, Magnoni M, Conte E, Masson S, Mushtaq S, Berti S, et al. Coronary plaque features on CTA can identify patients at increased risk of cardiovascular events. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. (2020) 13:1704–17. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2019.06.019
23. Motoyama S, Sarai M, Harigaya H, Anno H, Inoue K, Hara T, et al. Computed tomographic angiography characteristics of atherosclerotic plaques subsequently resulting in acute coronary syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2009) 54:49–57. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.02.068
24. Maurovich-Horvat P, Hoffmann U, Vorpahl M, Nakano M, Virmani R, and Alkadhi H. The napkin-ring sign: CT signature of high-risk coronary plaques? JACC: Cardiovasc Imaging. (2010) 3:440–4. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2010.02.003
25. Han D, Berman DS, Miller RJH, Andreini D, Budoff MJ, Cademartiri F, et al. Association of cardiovascular disease risk factor burden with progression of coronary atherosclerosis assessed by serial coronary computed tomographic angiography. JAMA Netw Open. (2020) 3:e2011444. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.11444
26. Yoon SH, Kim E, Jeon Y, Yi SY, Bae H-J, Jang I-K, et al. Prognostic value of coronary CT angiography for predicting poor cardiac outcome in stroke patients without known cardiac disease or chest pain: the assessment of coronary artery disease in stroke patients study. Korean J Radiol. (2020) 21:1055. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2020.0103
27. Ehara S, Kobayashi Y, Yoshiyama M, Shimada K, Shimada Y, Fukuda D, et al. Spotty calcification typifies the culprit plaque in patients with acute myocardial infarction: an intravascular ultrasound study. Circulation. (2004) 110:3424–9. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000148131.41425.E9
28. Nakahara T, Dweck MR, Narula N, Pisapia D, Narula J, and Strauss HW. Coronary artery calcification. JACC: Cardiovasc Imaging. (2017) 10:582–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2017.03.005
29. Maldonado N, Kelly-Arnold A, Vengrenyuk Y, Laudier D, Fallon JT, Virmani R, et al. A mechanistic analysis of the role of microcalcifications in atherosclerotic plaque stability: potential implications for plaque rupture. Am J Physiology-Heart Circulatory Physiol. (2012) 303:H619–28. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00036.2012
30. Yahagi K, Kolodgie FD, Lutter C, Mori H, Romero ME, Finn AV, et al. Pathology of human coronary and carotid artery atherosclerosis and vascular calcification in diabetes mellitus. ATVB. (2017) 37:191–204. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.306256
31. Del Buono MG, Montone RA, Camilli M, Carbone S, Narula J, Lavie CJ, et al. Coronary microvascular dysfunction across the spectrum of cardiovascular diseases. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2021) 78:1352–71. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.07.042
32. Grundy SM. Obesity, metabolic syndrome, and coronary atherosclerosis. Circulation. (2002) 105:2696–8. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000020650.86137.84
33. Olijhoek J. The Metabolic Syndrome is associated with advanced vascular damage in patients with coronary heart disease, stroke, peripheral arterial disease or abdominal aortic aneurysm. Eur Heart J. (2004) 25:342–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ehj.2003.12.007
34. Shi M, Han S, Klier K, Fobo G, Montrone C, Yu S, et al. Identification of candidate metabolite biomarkers for metabolic syndrome and its five components in population-based human cohorts. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2023) 22:141. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01862-z
35. Luna-Luna M, Medina-Urrutia A, Vargas-Alarcón G, Coss-Rovirosa F, Vargas-Barrón J, and Pérez-Méndez Ó. Adipose tissue in metabolic syndrome: onset and progression of atherosclerosis. Arch Med Res. (2015) 46:392–407. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2015.05.007
36. Howard WJ. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American heart association/national heart, lung, and blood institute scientific statement. Yearbook Endocrinol. (2006) 2006:113–4. doi: 10.1016/S0084-3741(08)70316-0
37. Lehoux S and Jones EA. Shear stress, arterial identity and atherosclerosis. Thromb Haemost. (2016) 115:467–73. doi: 10.1160/th15-10-0791
38. Hurtubise J, McLellan K, Durr K, Onasanya O, Nwabuko D, and Ndisang JF. The different facets of dyslipidemia and hypertension in atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep. (2016) 18:82. doi: 10.1007/s11883-016-0632-z
39. Jiang Y, Li Y, Shi K, Wang J, Qian W-L, Yan W-F, et al. The additive effect of essential hypertension on coronary artery plaques in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a coronary computed tomography angiography study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2022) 21:1. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01438-9
40. Authors/Task Force Members, Perk J, De Backer G, Gohlke H, Graham I, Reiner Z, et al. European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice (version 2012): The Fifth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and Other Societies on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice (constituted by representatives of nine societies and by invited experts) * Developed with the special contribution of the European Association for Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation (EACPR). Eur Heart J. (2012) 33:1635–701. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs092
41. Steg PG and Ducrocq G. Future of the prevention and treatment of coronary artery disease. Circ J. (2016) 80:1067–72. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-16-0266
42. Expert Panel On Detection, Evaluation, And Treatment Of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults. Executive summary of the third report of the national cholesterol education program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (Adult treatment panel III). JAMA. (2001) 285:2486–97. doi: 10.1001/jama.285.19.2486
Keywords: metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes mellitus, coronary computed tomography angiography, atherosclerotic, coronary artery plaque
Citation: Zhang Y-s, Shi R, Jiang Y-N, Gao Y, Wang J, Li Y and Yang Z-G (2025) Effect of metabolic syndrome on coronary artery atherosclerotic plaque in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1595475. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1595475
Received: 18 March 2025; Accepted: 15 July 2025;
Published: 03 September 2025.
Edited by:
Mohamed Rahouma, NewYork-Presbyterian, United StatesReviewed by:
Michael Edwin Edmonds, King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, United KingdomSoukaina Wakrim, Université Ibn Zohr, Morocco
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Shi, Jiang, Gao, Wang, Li and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yuan Li, ZHIubGl5dWFuQDE2My5jb20=
 Yu-shan Zhang
Yu-shan Zhang Yuan Li
Yuan Li