- 1Department of Cardiology, Changzhi People’s Hospital, Changzhi, China
- 2Department of Endocrinology, Changzhi Medical College, Changzhi, China
- 3School of Public Health, Jilin University, Changchun, China
Aim: This study aimed to investigate the association between the serum uric acid to creatinine ratio (SUA/Cr) and long-term target vessel events (TVEs) in diabetes mellitus (DM) patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with drug-eluting stents (DES).
Methods: From July 2009 to August 2011, a total of 2533 patients with coronary heart disease (CHD) who underwent PCI with DES implantation were enrolled to evaluate the relationship between the SUA/Cr and TVEs during a median follow-up of 29.8 months. Multivariable logistic regression and restricted cubic spline analyses were performed, and subgroup analyses were conducted to explore potential effect modifiers.
Results: The TVEs were significantly associated with previous male gender (OR=1.58, 95%CI: 1.07~2.32, p=0.021), PCI (OR=3.58, 95% CI: 2.27~5.67, p<0.001),previous stroke(OR=2.19,95%CI:1.24~3.89,p=0.007),triglyceride(OR=1.15, 95%CI:1.06~1.26, p=0.002), length of stent (OR=1.01, 95%CI:1~1.01, p<0.001), and diameter of stent (OR=0.62,95%CI:0.41~0.92,p=0.019). In DM patients, Multivariable logistic regression analyses revealed that higher SUA/Cr was independently associated with a reduced risk of TVEs (adjusted OR=0.72, 95% CI: 0.53–0.97, p=0.031). Restricted cubic spline analysis confirmed a linear inverse relationship between SUA/Cr and TVEs (p for non-linearity=0.782). Subgroup analyses revealed stronger protective effects in non-smokers and non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome (NSTE-ACS) patients within the DM cohort.
Conclusion: A higher SUA/Cr is independently associated with a reduced risk of TVEs in DM patients undergoing PCI with DES. SUA/Cr holds promise as a potential prognostic biomarker for risk stratification in DM patients undergoing PCI.
1 Introduction
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is an escalating global health challenge and a well-established risk factor for coronary heart disease (1). Its rising prevalence has led to a growing burden of cardiovascular complications. Compared to non-DM individuals, DM patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) face a significantly higher incidence of postoperative target vessel events (TVEs), including target vessel revascularization (TVR) and in-stent restenosis (ISR), resulting in poorer long-term outcomes (2). Given these risks, the identification of reliable biomarkers for more precise risk stratification and improved post-PCI management in DM patients is of critical clinical importance.
Serum uric acid (SUA), the end product of purine metabolism, has long been implicated in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular events (3, 4) However, its role as an independent predictor of cardiovascular risk remains controversial (5–7). Some studies suggest that elevated SUA levels contribute to an increased risk of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular events by inducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction (8). Conversely, other research indicates that uric acid may exert antioxidant properties under certain conditions, offering potential protective effects on the cardiovascular system (9–11). Given these conflicting findings, relying solely on SUA as a cardiovascular risk marker may be inherently limited. Since SUA levels are largely influenced by renal excretion, recent studies have increasingly focused on renal function-normalized SUA, expressed as the serum uric acid to creatinine ratio (SUA/Cr), as a more robust biomarker. Emerging evidence suggests that SUA/Cr is closely associated with metabolic disorders and plays a crucial role in predicting the progression and prognosis of acute myocardial infarction (AMI), heart failure, hypertension, diabetes, hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, ischemic stroke, and fatty liver disease (5, 12–20). On the other hand, there is a lack of data on the clinical value of SUA/Cr in patients with diabetes undergoing PCI, and few published large-scale validation studies have included this population. In addition, the vast majority of available research have concentrated either upon the independent effects of SUA or Cr on long-term outcomes in DM patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) while the possible prognostic value of SUA/Cr as an independent risk predictor was less extensively explored.
Although recent studies, such as the URRAH project by D’Elia et al. (12), have suggested a potential association between SUA/Cr and cardiovascular mortality in diabetic individuals, these studies primarily focused on all-cause or cardiovascular mortality without evaluating PCI-specific outcomes. Similarly, Casiglia et al. (21) reported prognostic cut-off values for SUA/Cr in general cardiovascular events but did not explore post-PCI restenosis or revascularization events. Importantly, to our knowledge, no prior large-scale study has comprehensively evaluated the prognostic significance of SUA/Cr on long-term TVEs, specifically in the high-risk diabetic population undergoing PCI with drug-eluting stents (DES). Thus, our study fills this critical gap by providing focused insights into the association between SUA/Cr and post-PCI vascular outcomes.
Therefore, the aim of this study was to examine the potential association between SUA/Cr and the risk of long-term TVEs in patients with DM undergoing PCI with DES implantation. Our prespecified hypothesis was that a higher SUA/Cr ratio would be independently associated with an increased risk of long-term TVEs, offering novel insights into cardiovascular risk stratification for DM patients.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study design and population
This retrospective cohort study utilized a publicly available dataset from patients who underwent PCI with drug-eluting stents (DES) at the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, between July 2009 and August 2011. The original cohort comprised 2,533 patients diagnosed with coronary artery disease (CAD).
After applying exclusion criteria—patients with implausible values (n = 2), incomplete data (n = 422), and outliers in the serum uric acid to creatinine ratio (SUA/Cr, below the 0.5th or above the 99.5th percentile, n = 22)—a final cohort of 2,087 patients was included in the analysis.
All patients underwent PCI following standard protocols, with a median follow-up duration of 29.8 months (interquartile range: 25.6–34.0 months). The dataset was accessed from the Dryad repository (https://doi.org/10.5061/dryad.13d31) and was originally published by Yao et al. (22).
This study adheres to the Declaration of Helsinki and received a waiver for informed consent due to the secondary use of publicly available data. A detailed flowchart of participant selection is provided in Figure 1.
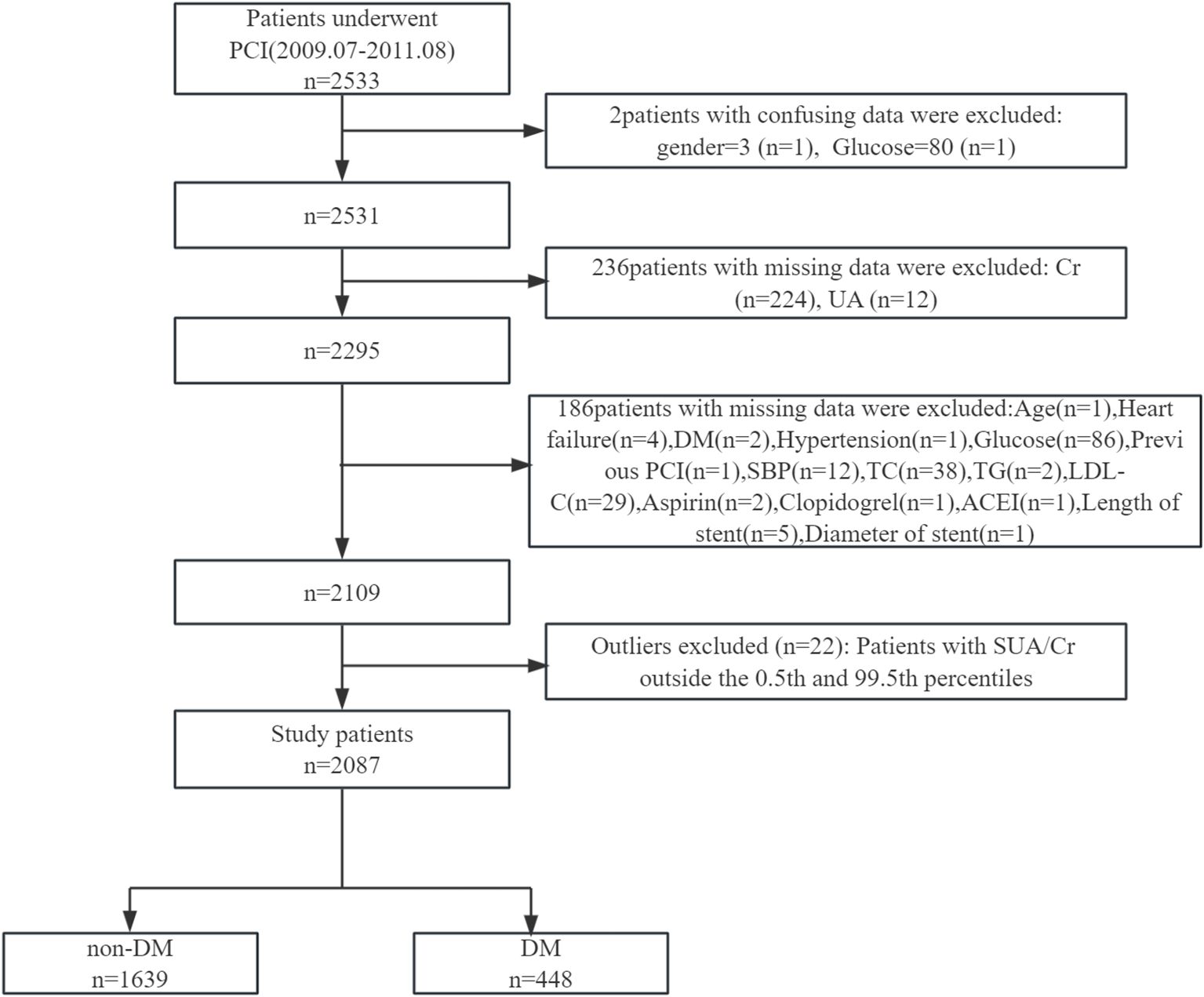
Figure 1. Flowchart of participant selection. PCI, percutaneous coronary intervention; Cr, creatinine; UA, uric acid; DM, diabetes mellitus; SBP, systolic blood pressure; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; ACEI, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor.
2.2 Data collection
Data collection encompassed baseline demographics, clinical characteristics, comorbidities, laboratory test results, procedural details, and follow-up information. These data were recorded electronically and obtained from various sources, including hospital electronic medical records, medical insurance data, telephone interviews, and in-person follow-ups at the research site.
2.3 Definitions
The SUA/Cr was calculated as the ratio of SUA (µmol/L) to serum creatinine (µmol/L). Smoking history was defined as any smoking within the past 10 years. DM was defined as a fasting plasma glucose level >6.1 mmol/L, hemoglobin A1c >6.5%, or current treatment with insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents. Hypertension was defined as systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥140 mmHg, diastolic blood pressure (DBP) ≥90 mmHg, or the use of antihypertensive medications. The estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was calculated using the modified MDRD equation: eGFR=175×SCr−1.234×Age−0.179×0.79 (if female), where SCr is serum creatinine in mg/dL, Age is in years (23). TVR was defined as any repeat revascularization, either PCI or coronary artery bypass graft (CABG), within the target vessel. ISR was defined as ≥50% diameter stenosis within the stented segment, as identified by follow-up coronary angiography.
2.4 Study outcomes
For cardiovascular disease events, an independent clinical endpoint committee adjudicated all outcomes strictly according to established guidelines and contemporary diagnostic criteria. The primary endpoint of TVE was defined as a composite of TVR and ISR, ensuring precise and standardized outcome assessment.
2.5 Statistical analysis
Continuous variables were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) for normally distributed data or median with interquartile range (IQR) for skewed data. Categorical variables were presented as frequencies and percentages. Differences between groups were assessed using the chi-square test for categorical variables, one-way ANOVA for normally distributed continuous variables, and the Kruskal-Wallis test for skewed continuous variables.
Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were conducted to evaluate the association between SUA/Cr and TVEs. Covariates for the multivariate models were selected based on a univariate p-value <0.1 or clinical relevance. Clinically important variables, even if not statistically significant, were included based on prior research and clinical judgment. The restricted cubic splines were used to assess whether there was a linear or nonlinear correlation between SUA/Cr and TVEs in patients with DM (with a threshold of P < 0.10).
To minimize the influence of extreme outliers, we focused on the central 99% of the data by excluding values of the SUA/Cr below the 0.5th percentile and above the 99.5th percentile. This method, implemented using the quantile function in R, is a common practice in clinical research to reduce the impact of extreme values and enhance the reliability of findings. This approach is supported by previous studies that emphasize the importance of outlier removal to improve statistical robustness in clinical data analysis (24, 25).
All the analyses were performed with the statistical software packages R 3.3.2 (http://www.R-project.org, The R Foundation) and Free Statistics software versions 1.9.2.A two-tailed test was performed, and p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Characteristics of the study population by diabetes mellitus
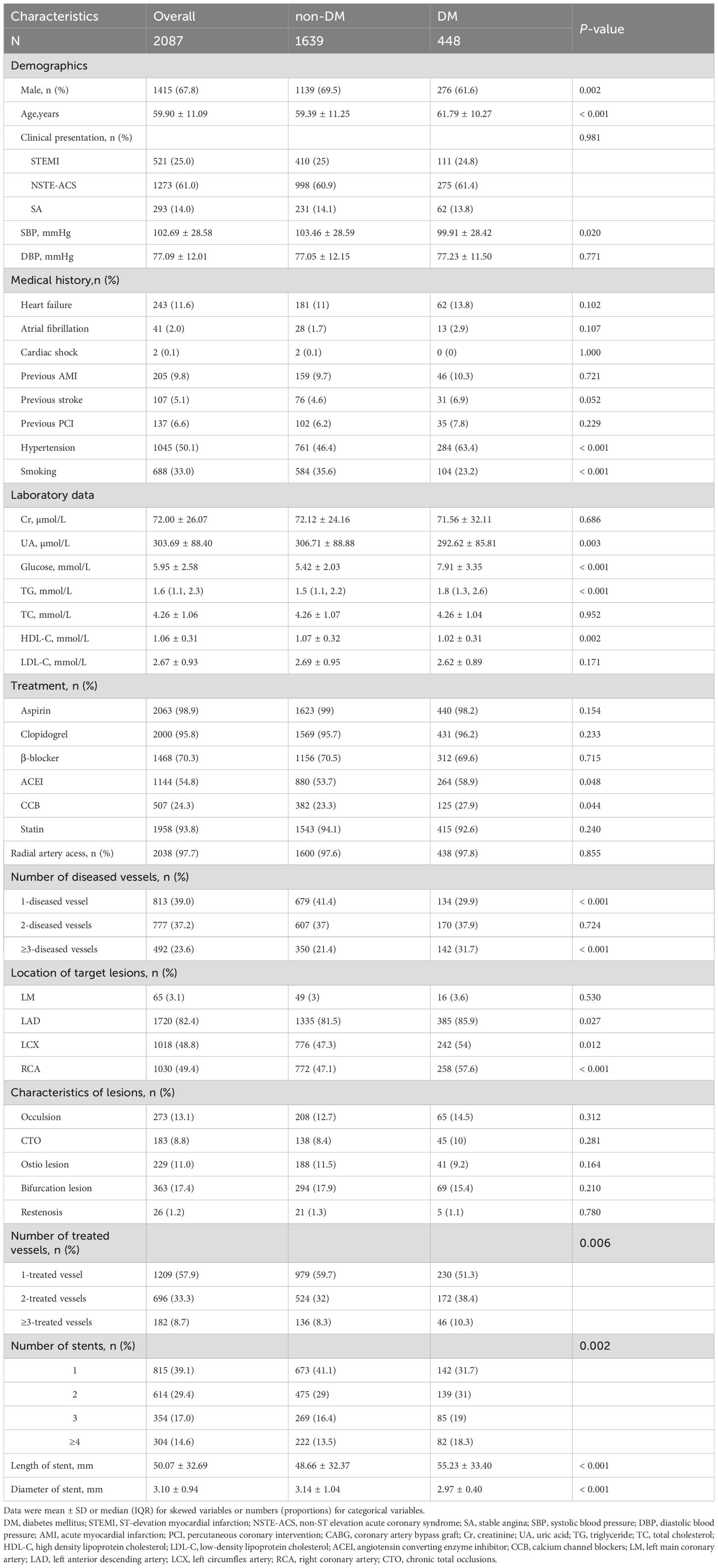
Among the 2,087 participants, 448 (21.5%) had DM). Compared to non-DM patients, DM patients were older (61.79 ± 10.27 vs. 59.39 ± 11.25 years, p < 0.001) and had a higher prevalence of hypertension (63.4% vs. 46.4%, p < 0.001). DM patients were also less likely to smoke (23.2% vs. 35.6%, p < 0.001). The general baseline data of the study subjects are shown in Table 1.
Laboratory results revealed that DM patients had higher fasting glucose (7.91 ± 3.35 vs. 5.42 ± 2.03 mmol/L, p < 0.001) and TG levels (1.8 [1.3–2.6] vs. 1.5 [1.1–2.2] mmol/L, p < 0.001). However, their SUA (292.62 ± 85.81 vs. 306.71 ± 88.88 μmol/L, p = 0.003) and HDL-C levels (1.02 ± 0.31 vs. 1.07 ± 0.32 mmol/L, p = 0.002) were lower.
Procedurally, DM patients had a higher proportion of multivessel disease (31.7% vs. 21.4%, p < 0.001) and received longer stents (55.23 ± 33.40 vs. 48.66 ± 32.37 mm, p < 0.001), but stent diameters were smaller (2.97 ± 0.40 vs. 3.14 ± 1.04 mm, p < 0.001).
3.2 Risk factors for TVEs in the overall population
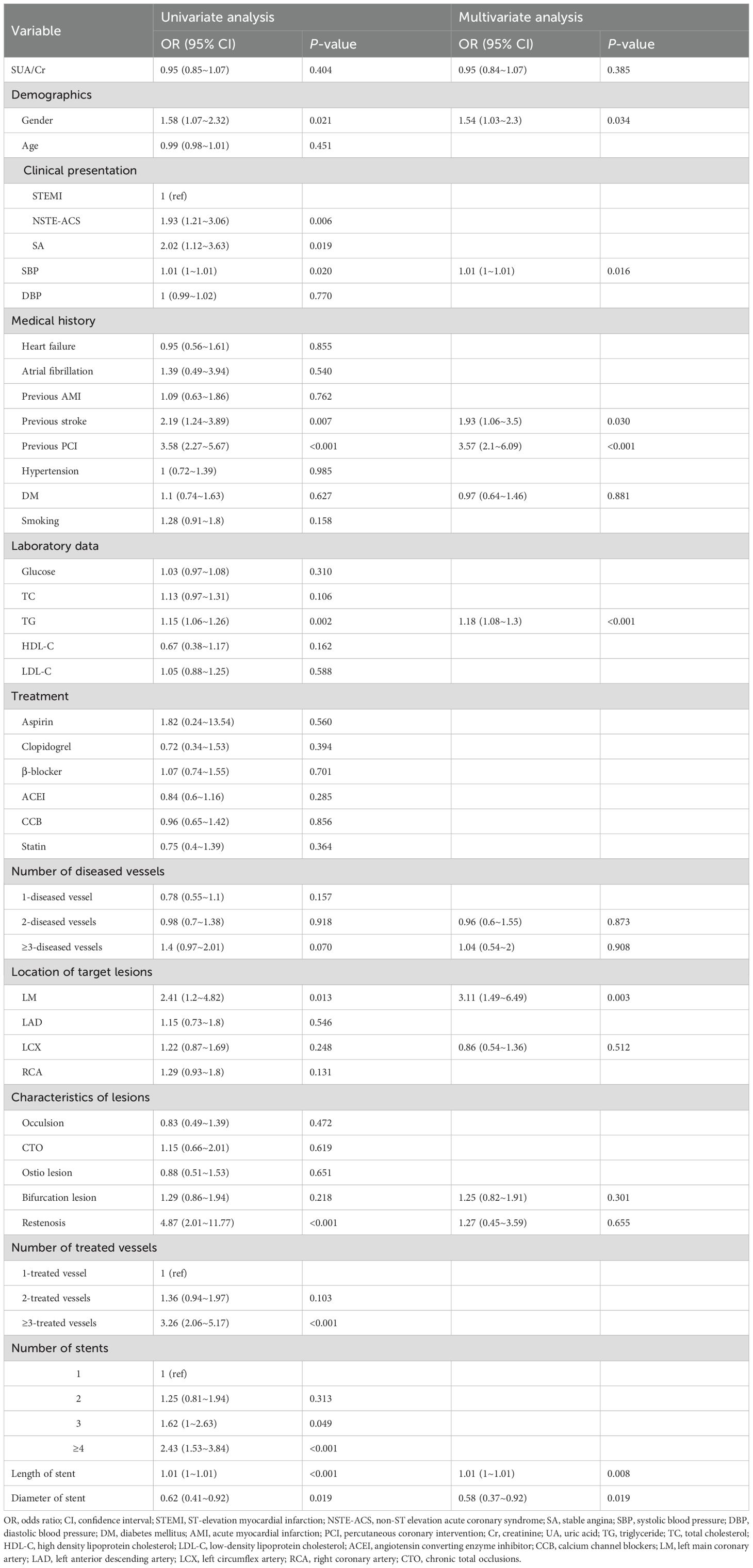
As shown in Table 2, both univariate and multivariate analyses identified male gender, previous PCI, previous stroke, elevated triglyceride levels, longer stent length, and smaller stent diameter as significant risk factors for TVEs (all p < 0.05).In contrast, the SUA/Cr ratio was not significantly associated with TVEs in univariate analysis (OR = 0.95, 95% CI: 0.85–1.07, p = 0.404). Even after adjusting for potential confounders in multivariate analysis, SUA/Cr remained non-significant (OR = 0.95, 95% CI: 0.84–1.07, p = 0.385).
3.3 Subgroup analyses
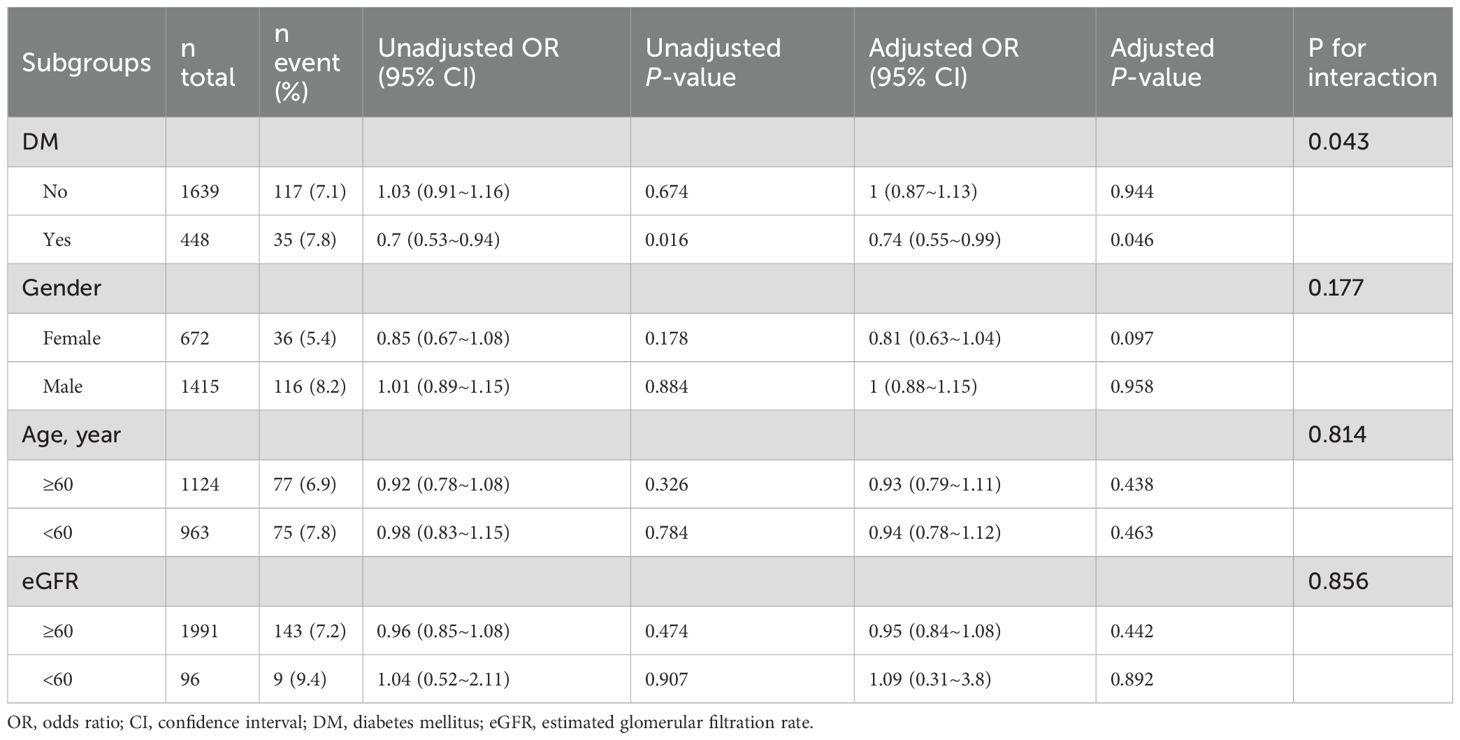
Subgroup analyses were performed to explore the association between SUA/Cr and TVEs across different strata, including DM), sex, age, and eGFR (Table 3).
In the DM subgroup, SUA/Cr was significantly associated with a lower risk of TVEs (adjusted OR = 0.74, 95% CI: 0.55–0.99, p = 0.046). However, no significant association was observed in the non-DM subgroup (adjusted OR = 1.00, 95% CI: 0.87–1.13, p = 0.944), with a significant interaction effect (p for interaction = 0.043).
Stratified by sex, age, and eGFR categories, SUA/Cr showed no significant association with TVEs in females (adjusted OR = 0.81, 95% CI: 0.63–1.04, p = 0.097), males (adjusted OR = 1.00, 95% CI: 0.88–1.15, p = 0.958), or any subgroup (all p for interaction > 0.05).
3.4 Association of SUA/Cr with TVEs in DM patients
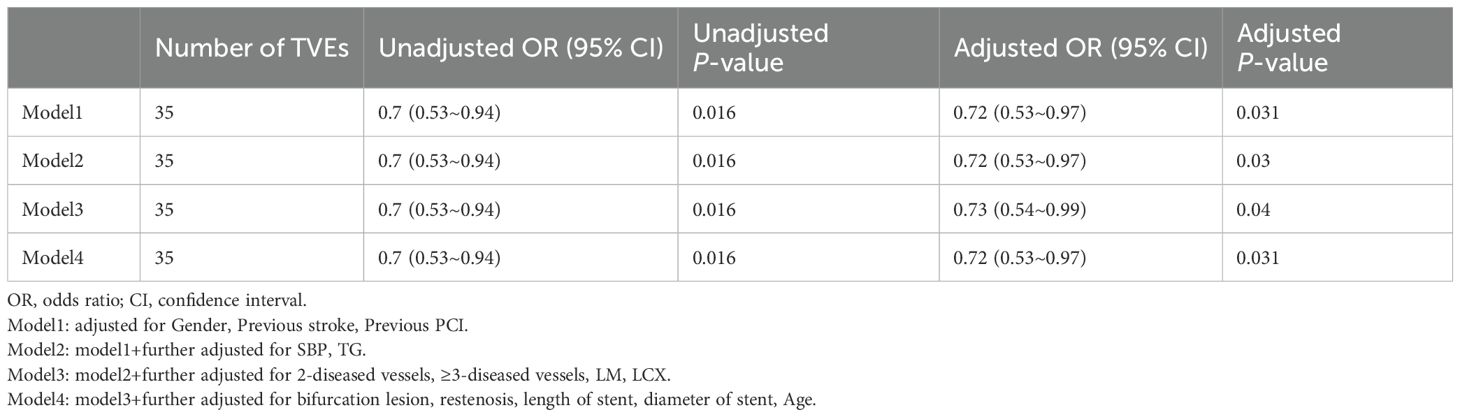
Multivariable logistic regression analyses demonstrated that higher SUA/Cr was significantly associated with a reduced risk of TVEs in DM patients (Table 4). The association remained consistent across all four models: Model 1 (OR = 0.72, 95% CI: 0.53–0.97, p = 0.031), Model 2 (OR = 0.72, 95% CI: 0.53–0.97, p = 0.030), Model 3 (OR = 0.73, 95% CI: 0.54–0.99, p = 0.040), and Model 4 (OR = 0.72, 95% CI: 0.53–0.97, p = 0.031).
The dose-response analysis, adjusted for variables in Model 4, revealed a linear inverse relationship between SUA/Cr and the risk of TVEs in DM patients (Figure 2). Restricted cubic spline analysis confirmed this linear and negative association, with a threshold (knot) at 4.158 (p for non-linearity = 0.782).
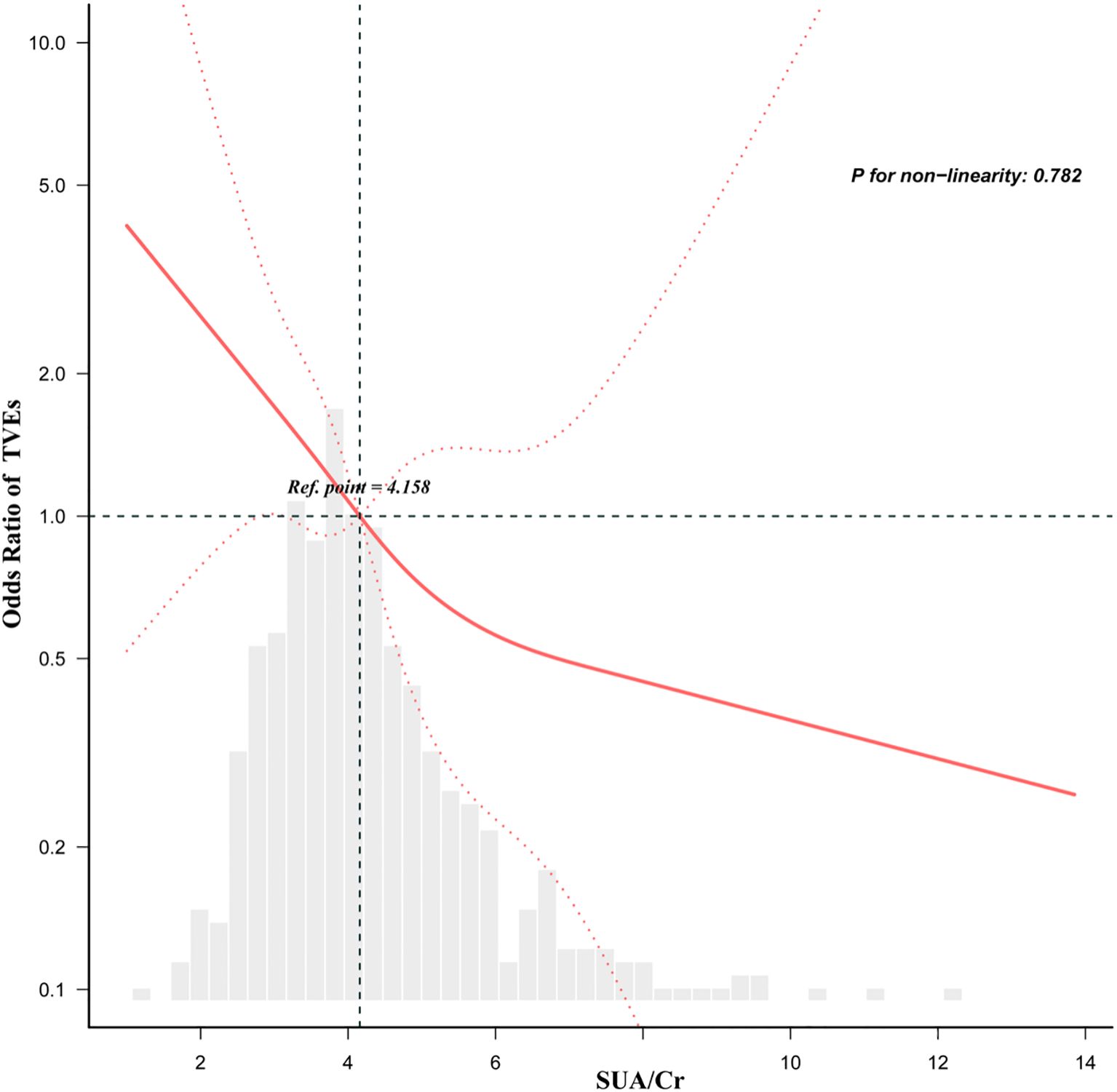
Figure 2. Dose-response relationship between the SUA/Cr and TVEs in DM patients adjusted for model 4. Gender, Previous stroke, Previous PCI, SBP, TG, 2-diseased vessels, ≥3-diseased vessels, LM, LCX, bifurcation lesion, restenosis, length of stent, diameter of stent, Age. All of the datas are displayed. Odds ratios are indicated by solid lines and 95% CIs by dashed areas.
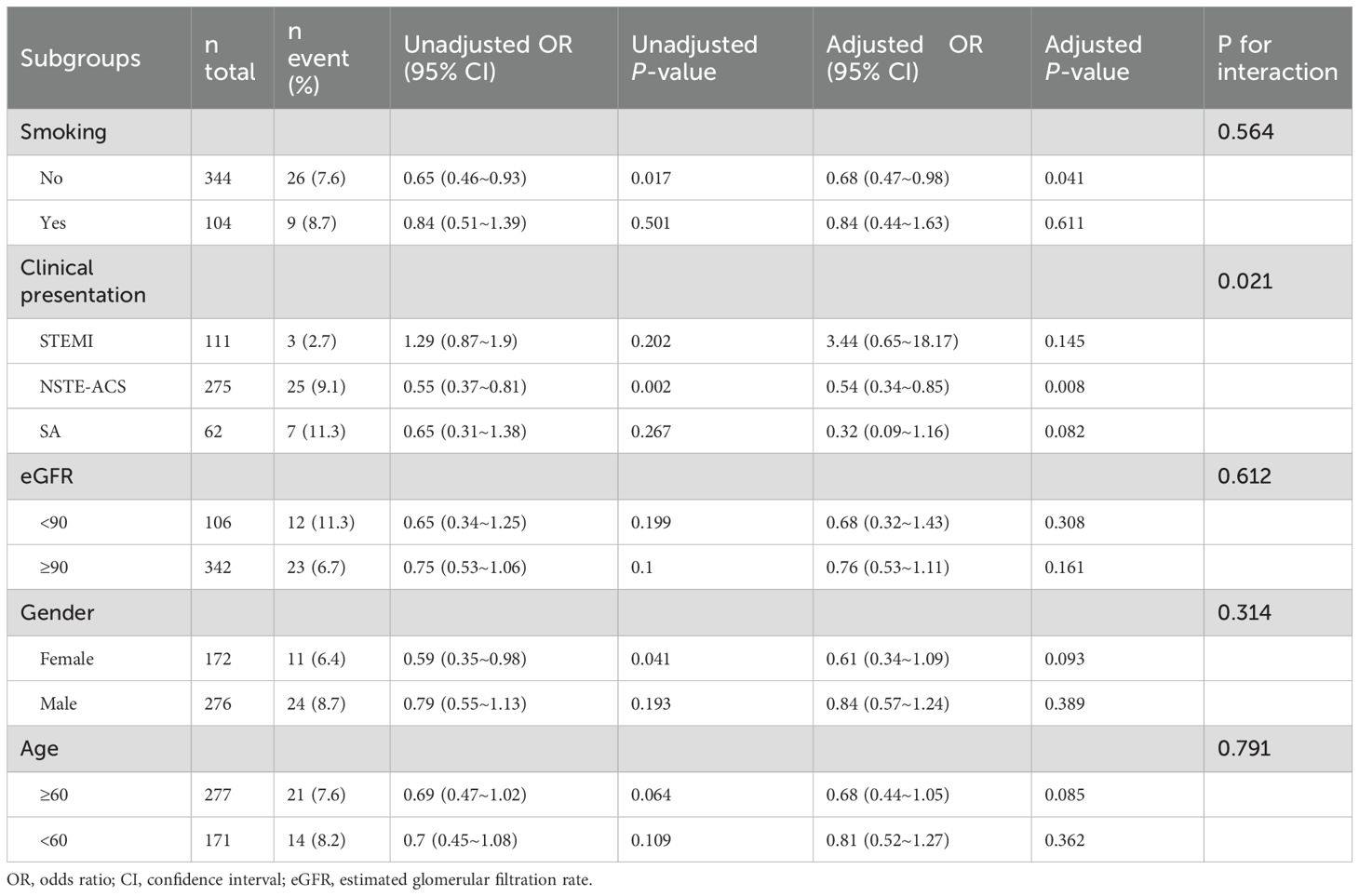
In DM patients, subgroup analysis revealed that SUA/Cr was significantly associated with a lower risk of TVEs among non-smokers (adjusted OR = 0.68, 95% CI: 0.47–0.98, p = 0.041) and those presenting with NSTE-ACS (adjusted OR = 0.54, 95% CI: 0.34–0.85, p = 0.008) (Table 5). However, no significant associations were observed in other subgroups, including smokers, STEMI patients, or those with SA (all p for interaction > 0.05).
4 Discussion
In this study, we found that a higher SUA/Cr ratio was independently associated with a significantly lower risk of TVEs in DM patients. Notably, SUA/Cr exhibited a linear inverse relationship with TVEs risk, with a threshold identified at 4.158, suggesting that the risk continuously declines as SUA/Cr levels increase. Subgroup analysis further demonstrated that this protective effect was particularly evident in non-smokers and DM patients with NSTE-ACS. These findings underscore the potential of SUA/Cr as a prognostic biomarker for DM patients undergoing PCI, providing valuable insights for risk stratification and long-term management strategies. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to systematically examine the association between SUA/Cr and long-term adverse target vessel outcomes in DM patients post-PCI. Unlike previous research, which has largely overlooked procedural cardiovascular outcomes such as TVEs or stent-related complications, our study addresses this gap. Moreover, earlier studies often lacked comprehensive subgroup stratification or dose–response analyses, limiting their clinical relevance. By employing advanced modeling approaches in a well-defined post-PCI diabetic cohort, our study overcomes these limitations and enhances the applicability of the findings.
Hyperuricemia has long been recognized as a condition closely linked to cardiovascular disease (CVD) and is considered a potential cardiovascular risk factor (26). Elevated SUA levels have been associated with an increased risk of CAD, hypertension, heart failure, and chronic kidney disease (27), with potential underlying mechanisms involving oxidative stress, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction (8). However, recent studies suggest that SUA may have a dual role in cardiovascular health, where moderately elevated levels could confer protective effects, while both excessively high and low SUA levels may contribute to a greater CVD risk (28). Notably, SUA exhibits antioxidant properties under certain conditions, particularly in maintaining vascular homeostasis. As a free radical scavenger, it can mitigate oxidative stress-induced vascular injury and provide endothelial protection (9–11).
Lazzeri et al. reported that elevated SUA levels were associated with higher in-hospital mortality in patients with STEMI, independent of Killip classification (5). Similarly, Li et al. identified hyperuricemia as an independent risk factor for short-term adverse cardiovascular events in STEMI patients (6). However, Liu et al. found no significant association between SUA levels and mortality risk in STEMI patients with Killip class II-IV (7). Additionally, some studies have suggested that SUA is not an independent predictor of cardiovascular events or all-cause mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes (29).These discrepancies may stem from the influence of renal clearance on SUA levels, as evaluating SUA in isolation may be confounded by renal function status, thereby limiting its accuracy as a prognostic indicator (12). To address this issue, the SUA/Cr has been introduced as a composite biomarker that accounts for both SUA and renal function. Emerging evidence suggests that SUA/Cr provides a more accurate reflection of metabolic abnormalities and serves as a more reliable predictor of metabolic syndrome compared to SUA or creatinine alone (30).
In recent years, accumulating evidence has underscored a strong association between the SUA/Cr and adverse cardiovascular events. However, its precise role remains controversial, as some studies identify SUA/Cr as an independent risk factor for cardiovascular complications, while others report conflicting findings. A nationwide multicenter study from Italy demonstrated that SUA/Cr independently predicted cardiovascular events in DM patients (21). Further investigations revealed a nonlinear association between SUA/Cr levels and cardiovascular mortality risk in this population. Specifically, among DM patients with preserved renal function, the risk of cardiovascular mortality increased significantly when SUA/Cr exceeded 5.35, whereas in those with impaired renal function, the threshold for heightened risk was SUA/Cr >7.5 (12).Additionally, Zeng et al. reported a U-shaped nonlinear relationship between SUA/Cr and all-cause mortality in hypertensive patients, with a critical turning point at 4.3 (31). Similarly, Zhang YD et al. found that elevated preoperative SUA/Cr levels were significantly associated with a higher risk of atrial fibrillation (AF) recurrence following catheter ablation, suggesting that SUA/Cr may serve as a novel prognostic biomarker for AF recurrence (32).
Notably, the relationship between SUA/Cr and cardiovascular outcomes may vary across different populations. Tang Z et al. reported a linear inverse association between SUA/Cr and cardiovascular mortality in hypertensive patients, with a continuous decline in mortality risk as SUA/Cr increased (P for nonlinearity = 0.32) and a threshold identified at 6.54 (13). Similarly, Jiang L et al. found that lower SUA/Cr levels were associated with an increased risk of in-hospital adverse cardiovascular events in elderly patients with AMI, with this association being more pronounced in males (14).However, studies investigating the prognostic value of SUA/Cr in post-PCI outcomes remain limited. In the present study, we found that higher SUA/Cr levels were significantly associated with a lower risk of TVEs in DM patients following PCI, and this association remained robust after adjusting for multiple confounders (Gender, Previous stroke, Previous PCI, SBP, TG, 2-diseased vessels, ≥3-diseased vessels, LM, LCX, bifurcation lesion, restenosis, length of stent, diameter of stent, Age).The observed protective effect may be attributed to the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of SUA. DM patients are typically in a state of chronic low-grade inflammation and oxidative stress, both of which contribute to coronary artery remodeling and an increased risk of in-stent restenosis following PCI (33). Emerging evidence suggests that in DM patients, dysregulated uric acid metabolism may serve as a compensatory mechanism to counteract oxidative stress-induced vascular damage (34). Moderately elevated SUA levels may function as an endogenous antioxidant, scavenging free radicals, mitigating endothelial dysfunction, and inhibiting low-density lipoprotein oxidation, thereby slowing the progression of atherosclerosis and potentially reducing the risk of TVEs (35–37).
These findings, supported by biological plausibility, suggest that SUA/Cr may serve as a compensatory antioxidant factor in specific clinical contexts, particularly in diabetic patients post-PCI. However, the relationship between SUA/Cr and cardiovascular outcomes remains inconsistent across studies. For instance, while the URRAH project (12), reported a U-shaped association between SUA/Cr and cardiovascular mortality, our study demonstrated a linear inverse relationship with target vessel events in PCI-treated diabetic patients. These discrepancies likely arise from key methodological and clinical differences. First, outcome definitions varied significantly: previous studies primarily examined all-cause or cardiovascular mortality, whereas we focused on procedural outcomes (target vessel revascularization and in-stent restenosis). Second, our study population was strictly limited to PCI-treated CAD patients with diabetes, unlike broader community-based cohorts in prior research. Third, earlier studies frequently omitted adjustments for critical angiographic and procedural variables (e.g., stent diameter, lesion complexity, or prior PCI history) that may influence the SUA/Cr-TVE relationship. Finally, while some studies categorized SUA/Cr into quantiles assuming nonlinearity, we employed restricted cubic spline models to objectively confirm a consistent linear inverse association. These collective differences underscore how clinical context and study design fundamentally shape the interpretation of SUA/Cr’s prognostic value.
Furthermore, our study demonstrated that the association between SUA/Cr and TVEs risk was particularly pronounced in non-smokers and DM patients with NSTE-ACS. Specifically, higher SUA/Cr levels were significantly correlated with a lower risk of TVEs in non-smokers, while this protective effect was even more pronounced in NSTE-ACS patients. This differential effect may be attributed to variations in oxidative stress burden and systemic inflammation. In non-smokers, relatively lower oxidative stress and inflammatory activity may allow the antioxidant and endothelial-protective properties of uric acid to exert greater benefits (38). Additionally, unlike STEMI, where ischemic events are predominantly driven by acute thrombotic occlusion, NSTE-ACS is characterized by chronic inflammation and atherosclerotic plaque instability, which play a central role in disease progression (39). In this context, uric acid, functioning as an endogenous antioxidant, may contribute to plaque stabilization and attenuation of inflammation-mediated endothelial dysfunction, thereby mitigating the risk of TVEs.
While some studies, such as those from the URRAH project (12), reported a U-shaped or nonlinear association between SUA/Cr and cardiovascular mortality, our study identified a linear inverse relationship between SUA/Cr and target vessel events in diabetic patients undergoing PCI. These differences may stem from multiple factors. First, the outcome definitions differ: prior studies focused on all-cause or cardiovascular mortality, whereas we specifically assessed target vessel revascularization and in-stent restenosis—which are procedural and lesion-level outcomes. Second, our study population consisted entirely of PCI-treated CAD patients, with a defined post-intervention context, while others included broader community or hospital cohorts. Third, previous studies often did not adjust for detailed angiographic and procedural characteristics such as stent diameter, lesion complexity, or prior PCI, which may confound the SUA/Cr–TVE relationship. Finally, some earlier studies categorized SUA/Cr into quantiles and assumed nonlinear relationships, whereas our study confirmed a linear trend using restricted cubic spline analysis. These methodological and population-level distinctions may explain the observed differences and suggest that the prognostic significance of SUA/Cr may be context-dependent—particularly relevant for stent-related vascular outcomes in diabetic populations.
There are several limitations to this study. First, as a retrospective single-center study, it is subject to selection bias and information bias, which may limit the external validity of our findings. Although the sample size was relatively large (n = 2087), further validation through large-scale, multicenter studies is required to enhance the robustness of our results. Second, this study only established an association between SUA/Cr and post-PCI TVEs, precluding any inference of causality. Future prospective, multicenter, and long-term follow-up studies are warranted to further elucidate the prognostic value of SUA/Cr and its potential role in post-PCI risk stratification and clinical management.
5 Conclusion
This study found that higher SUA/Cr levels were associated with a lower risk of TVEs in DM patients following PCI, suggesting that SUA/Cr may serve as a biomarker for cardiovascular risk assessment. Given its ease of measurement and cost-effectiveness, SUA/Cr has the potential to facilitate early risk identification and personalized management in high-risk post-PCI patients, thereby improving clinical outcomes. However, its clinical utility requires further validation. Future large-scale prospective studies are needed to establish the definitive role of SUA/Cr in this patient population and to explore its potential applications in routine cardiovascular risk stratification.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by The First Affiliated Hospital, Zhengzhou University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
PC: Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Methodology, Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. SW: Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Investigation. ZZ: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Formal analysis. RW: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2025.1599158/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Xie Q, Huang J, Zhu K, and Chen Q. Percutaneous coronary intervention versus coronary artery bypass grafting in patients with coronary heart disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus: Cumulative meta-analysis. Clin Cardiol. (2021) 44:899–906. doi: 10.1002/clc.23613
2. Farkouh ME, Dangas G, Leon MB, Smith C, Nesto R, Buse JB, et al. Design of the Future REvascularization Evaluation in patients with Diabetes mellitus: Optimal management of Multivessel disease (FREEDOM) Trial. Am Heart J. (2008) 155:215–23. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2007.10.012
3. Rahimi-Sakak F, Maroofi M, Rahmani J, Bellissimo N, and Hekmatdoost A. Serum uric acid and risk of cardiovascular mortality: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of cohort studies of over a million participants. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2019) 19:218. doi: 10.1186/s12872-019-1215-z
4. Ndrepepa G. Uric acid and cardiovascular disease. Clin Chim Acta; Int J Clin Chem. (2018) 484:150–63. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2018.05.046
5. Lazzeri C, Valente S, Chiostri M, Sori A, Bernardo P, and Gensini GF. Uric acid in the acute phase of ST elevation myocardial infarction submitted to primary PCI: its prognostic role and relation with inflammatory markers: a single center experience. Int J Cardiol. (2010) 138:206–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2008.06.024
6. Li L, Ma Y, Shang X-M, Hong Y, Wang J-H, Tan Z, et al. Hyperuricemia is associated with short-term outcomes in elderly patients with acute myocardial infarction. Aging Clin Exp Res. (2018) 30:1211–5. doi: 10.1007/s40520-018-0903-3
7. Liu C-W, Liao P-C, Chen K-C, Chiu Y-W, Liu Y-H, Ke S-R, et al. Relationship of serum uric acid and Killip class on mortality after acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction and primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Int J Cardiol. (2017) 226:26–33. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.10.025
8. Huang J. Uric acid in metabolic syndrome: An innocent bystander or a central player? Int J Cardiol. (2025) 421:132884. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2024.132884
9. Yu M-A, Sánchez-Lozada LG, Johnson RJ, and Kang D-H. Oxidative stress with an activation of the renin-angiotensin system in human vascular endothelial cells as a novel mechanism of uric acid-induced endothelial dysfunction. J Hypertens. (2010) 28:1234–42. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e328337da1d
10. Kang D-H, Park S-K, Lee I-K, and Johnson RJ. Uric acid-induced C-reactive protein expression: implication on cell proliferation and nitric oxide production of human vascular cells. J Am Soc Nephrol: JASN. (2005) 16:3553–62. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2005050572
11. Johnson RJ, Lanaspa MA, and Gaucher EA. Uric acid: a danger signal from the RNA world that may have a role in the epidemic of obesity, metabolic syndrome, and cardiorenal disease: evolutionary considerations. Semin Nephrol. (2011) 31:394–9. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2011.08.002
12. D’Elia L, Masulli M, Cirillo P, Virdis A, Casiglia E, Tikhonoff V, et al. Serum uric acid/serum creatinine ratio and cardiovascular mortality in diabetic individuals-the uric acid right for heart health (URRAH) project. Metabolites. (2024) 14:164. doi: 10.3390/metabo14030164
13. Tang Z, Liu H, Ding Y, Yuan C, and Shao Y. Association between serum uric acid to serum creatinine ratio with cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in adults with hypertension. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:18008. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69057-4
14. Jiang L, Jin J, He X, Hu X, Guo L, Chen G, et al. The association between serum uric acid/serum creatinine ratio and in-hospital outcomes in elderly patients with acute myocardial infarction. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2024) 24:52. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-03720-6
15. Xi X, Cai J, Zhang C, and Wang X. Does serum uric acid to creatinine ratio predict mortality risk in patients with heart failure? Tex Heart Inst J. (2024) 51:e238210. doi: 10.14503/THIJ-23-8210
16. Al-Daghri NM, Al-Attas OS, Wani K, Sabico S, and Alokail MS. Serum uric acid to creatinine ratio and risk of metabolic syndrome in Saudi type 2 diabetic patients. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:12104. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12085-0
17. Zhao L and Qiu X. Higher ratio of serum uric acid to serum creatinine (SUA/SCr) increases the risk of metabolic unhealthy phenotype. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis: NMCD. (2023) 33:1981–8. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2023.07.013
18. Sun X, Lv J, Wu Z, Shi J, and Huang H. Serum uric acid to serum creatinine ratio and risk of stroke recurrence in young adults with ischemic stroke. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. (2022) 18:2031–9. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S378576
19. Choi J, Joe H, Oh J-E, Cho Y-J, Shin H-S, and Heo NH. The correlation between NAFLD and serum uric acid to serum creatinine ratio. PloS One. (2023) 18:e0288666. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288666
20. Weerasekera DS and Peiris H. The significance of serum uric acid, creatinine and urinary microprotein levels in predicting pre-eclampsia. J Obstet Gynaecol: J Inst Obstet Gynaecol. (2003) 23:17–9. doi: 10.1080/0144361021000043155
21. Casiglia E, Tikhonoff V, Virdis A, Grassi G, Angeli F, Barbagallo CM, et al. Serum uric acid/serum creatinine ratio as a predictor of cardiovascular events. Detection of prognostic cardiovascular cut-off values. J Hypertens. (2023) 41:180–6. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000003319
22. Yao H-M, Wan Y-D, Zhang X-J, Shen D-L, Zhang J-Y, Li L, et al. Long-term follow-up results in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with drug-eluting stents: results from a single high-volume PCI centre. BMJ Open. (2014) 4:e004892. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-004892
23. Levey AS, Coresh J, Greene T, Stevens LA, Zhang YL, Hendriksen S, et al. Using standardized serum creatinine values in the modification of diet in renal disease study equation for estimating glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med. (2006) 145:247–54. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-145-4-200608150-00004
24. Horn PS, Feng L, Li Y, and Pesce AJ. Effect of outliers and nonhealthy individuals on reference interval estimation. Clin Chem. (2001) 47:2137–45. doi: 10.1093/clinchem/47.12.2137
25. Leys C, Ley C, Klein O, Bernard P, and Licata L. Detecting outliers: Do not use standard deviation around the mean, use absolute deviation around the median. J Exp Soc Psychol. (2013) 49:764–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jesp.2013.03.013
26. Feig DI, Kang D-H, and Johnson RJ. Uric acid and cardiovascular risk. N Engl J Med. (2008) 359:1811–21. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra0800885
27. Kuwabara M. Hyperuricemia, cardiovascular disease, and hypertension. Pulse (Basel Switz). (2016) 3:242–52. doi: 10.1159/000443769
28. Johnson RJ, Kang D-H, Feig D, Kivlighn S, Kanellis J, Watanabe S, et al. Is there a pathogenetic role for uric acid in hypertension and cardiovascular and renal disease? Hypertens (Dallas Tex,: 1979). (2003) 41:1183–90. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000069700.62727.C5
29. Ong G, Davis WA, and Davis TME. Serum uric acid does not predict cardiovascular or all-cause mortality in type 2 diabetes: the Fremantle Diabetes Study. Diabetologia. (2010) 53:1288–94. doi: 10.1007/s00125-010-1735-7
30. She D, Xu W, Liu J, Zhang Z, Fang P, Li R, et al. Serum uric acid to creatinine ratio and risk of metabolic syndrome in patients with overweight/obesity. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes: Targets Ther. (2023) 16:3007–17. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S427070
31. Zeng Y, Chen Y, Li J, and Chen L. Nonlinear association between the serum uric acid-to-creatinine ratio and all cause mortality in patients with hypertension: a ten-year cohort study using the NHANES database. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:31423. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-83034-x
32. Zhang Y, Wang Y, Yang X, Li Z, Shang L, and Hou Y. Serum uric acid: creatinine ratio (UCR) is associated with recurrence of atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation. Front Endocrinol. (2023) 14:1110102. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1110102
33. Weinberg Sibony R, Segev O, Dor S, and Raz I. Overview of oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetes. J Diabetes. (2024) 16:e70014. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.70014
34. Li C, Hsieh M-C, and Chang S-J. Metabolic syndrome, diabetes, and hyperuricemia. Curr Opin Rheumatol. (2013) 25:210–6. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e32835d951e
35. Lin Y, Xie Y, Hao Z, Bi H, Liu Y, Yang X, et al. Protective Effect of Uric Acid on ox-LDL-Induced HUVECs Injury via Keap1-Nrf2-ARE Pathway. J Immunol Res. (2021) 2021:5151168. doi: 10.1155/2021/5151168
36. Kanbay M, Siriopol D, Nistor I, Elcioglu OC, Telci O, Takir M, et al. Effects of allopurinol on endothelial dysfunction: a meta-analysis. Am J Nephrol. (2014) 39:348–56. doi: 10.1159/000360609
37. Glantzounis GK, Tsimoyiannis EC, Kappas AM, and Galaris DA. Uric acid and oxidative stress. Curr Pharm Des. (2005) 11:4145–51. doi: 10.2174/138161205774913255
38. Af Geijerstam P, Janryd F, and Nyström FH. Smoking and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: a prospective observational study. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerst Md). (2023) 24:802–7. doi: 10.2459/JCM.0000000000001540
Keywords: diabetes mellitus, coronary heart disease, target vessel events, serum uric acid to creatinine ratio, percutaneous coronary intervention
Citation: Cui P, Wang S, Zhang Z and Wang R (2025) Serum uric acid to creatinine ratio and long-term target vessel events in diabetes patients undergoing PCI with drug-eluting stents implantation: a retrospective study. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1599158. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1599158
Received: 24 March 2025; Accepted: 02 June 2025;
Published: 27 June 2025.
Edited by:
Jerzy Beltowski, Medical University of Lublin, PolandReviewed by:
Brendon Pearce, Stellenbosch University, South AfricaTakuma Inagawa, National Center of Neurology and Psychiatry, Japan
Copyright © 2025 Cui, Wang, Zhang and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ruihua Wang, d3JoOTc5OEAxNjMuY29t
 Penghui Cui
Penghui Cui Shuting Wang2
Shuting Wang2