- School of Life Sciences and Medicine, Shandong University of Technology, Zibo, China
Follicular atresia is a critical physiological process that ensures the selection of high-quality oocytes by eliminating non-viable follicles. In women, 99.9% of follicles undergo atresia naturally, the premature or dysregulated atresia follicle can lead to pathological conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and premature ovarian failure (POF). Recent studies highlight the roles of apoptosis, autophagy, and ferroptosis in regulating follicular atresia. This review integrates molecular mechanisms of programmed cell death with follicular dynamics, emphasizing how aberrant atresia disrupts reproductive health. We discuss therapeutic strategies targeting these pathways to mitigate pathological atresia, offering insights into preserving ovarian reserve and improving fertility outcomes.
1 Introduction
In mammals, 99.9% of follicles die by atresia, an irreversible physiological feature that is important for maintaining ovarian homeostasis and selecting viable oocytes (1). A massive reduction in the number of oocytes occurs during the germline cyst breakdown and formation of primordial follicles, with only 20% of the follicles surviving by the time of birth, and many molecules are involved (2). Follicular atresia persists in the ovaries after birth, and in humans, only about 400 follicles develop, mature, and ovulate normally during the reproductive years (3). Follicular atresia is a process of degenerative death of oocytes and somatic cells and can occur at all stages of follicular development. Among them, primordial follicular atresia is rare, and primary follicular atresia is the most common (4). The morphological features are: nuclear condensation of the oocyte, chromosomal and cytoplasmic lysis, reduction of the granulosa cell layer, hypertrophy of the follicular membrane cells, and the appearance of lipids in the cytoplasm, luteinization, and scattering in connective tissues, which constitute the so-called “interstitial glands (5, 6).”Subsequently, the oocytes degenerate and the granulosa cells and follicular membrane cells evolve into fibrous bodies that can be absorbed by the follicular mesenchyme (7). At the same time, granulosa cells in atretic follicles produce less estrogen, increased progesterone production, decreased number of gonadotropin receptors, and enhanced expression of IGF-binding proteins (8–10). In addition, decreased expression of the gap junction protein connexin43 and enhanced expression of the sulfated glycoprotein sP-2 are observed in atretic follicles (11, 12). Therefore, exploring the molecular mechanisms regulating follicular atresia not only helps to elucidate the cause of massive follicle loss under physiological conditions, but also is of great significance in revealing the onset mechanism of premature ovarian aging and slowing down ovarian aging.
Programmed cell death is generally defined as a spontaneous form of cell death regulated by a variety of biomolecules (11, 13). Apoptosis was widely recognized by the general public as the main mode of programmed cell death, and more modes of programmed cell death have gradually emerged with the intensive study of cell biology, such as autophagy and ferroptosis (8, 14, 15). Programmed cell death plays an important role in maintaining homeostasis in the body, sustaining normal physiological functions, host defense against pathogens, cancer, and a wide range of other pathological processes (16). During follicular formation and development, follicular atresia is closely associated with programmed cell death within the follicle. There is a close interaction between the oocyte and other somatic cells within the follicle that collectively leads to the development of follicular atresia (17).
Physiological follicular atresia eliminates defective follicles, ensuring optimal reproductive capacity. Follicular atresia occurs at all developmental stages, from primordial to antral follicles, driven by complex interactions between oocytes and somatic cells (3). Morphologically, atresia involves oocyte degeneration, granulosa cell apoptosis, and follicular remodeling (4). Dysregulation of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/AKT serine/threonine kinase (PI3K/AKT) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathways and oxidative stress exacerbate pathological atresia, linking it to PCOS and chemotherapy-induced ovarian damage (5, 6). We can use this as an entry point to inhibit follicular atresia by regulating the programmed death of follicular cells using drugs or other means. The goal is to prevent premature ovarian failure, maintain the number and quality of oocytes in the follicles, and prolong reproductive age as well as improve fertility.
2 Follicular atresia across primordial and developmental follicles stages
Follicular atresia is a phenomenon in which a follicle stops growing and begins to degenerate during follicular development for a variety of reasons. This process is a natural part of the ovarian cycle, but when follicular atresia occurs in excess or at inappropriate times, it can lead to fertility problems (14). Follicular atresia can be achieved by inhibiting the development of most follicles, ensuring the quality of oocytes as well as the production of superior offspring. After the formation of primordial follicles, follicular atresia is accompanied by various stages of follicular development, including apoptosis, autophagy, and ferroptosis, all of which are involved in regulating follicular atresia (Figure 1).
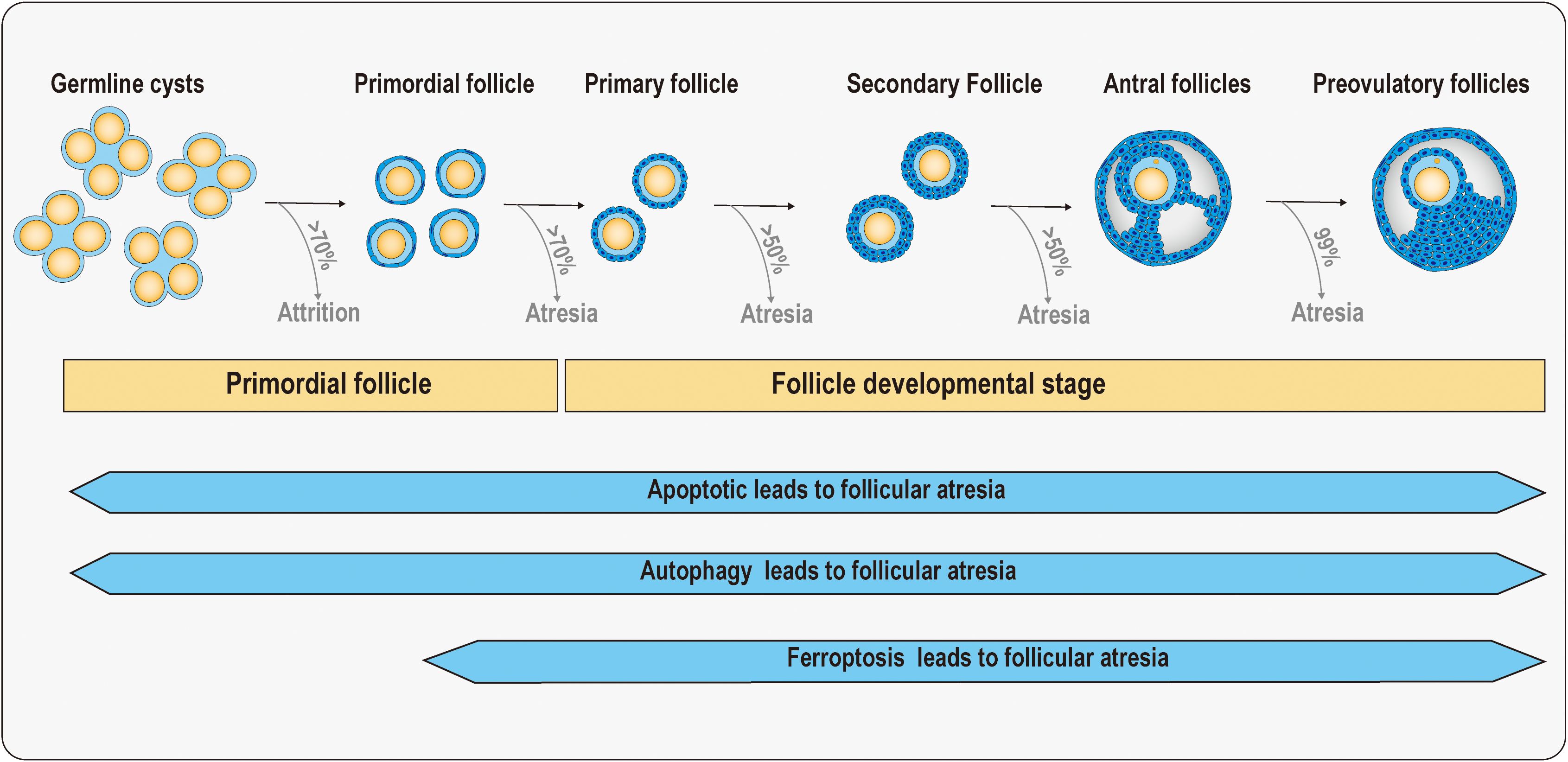
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of follicular atresia at primordial follicle and follicle developmental stage. In the ovaries of a human fetus at 20 weeks of age, there are approximately 7 million germ cells. There are approximately 1–2 million primordial follicles in the ovaries of newborns in the early stages, but by the age of 7, only about three hundred thousand primordial follicles remain. More than 50% of follicles will experience atresia in both primary and secondary follicular stages. Before ovulation, 99% of antral follicles will undergo atresia, with only one or a few follicles ovulating. When the follicle reserve is depleted, the ovaries rapidly age as women enter menopause. Meanwhile, apoptosis, autophagy, and ferroptosis have been found to be associated with follicular atresia.
2.1 Primordial follicle
At this stage, the atresia of the primordial follicle is mainly related to the signal imbalance between oocytes and granulosa cells. Some studies have confirmed this. For example, glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK3β) plays a crucial role in the survival of oocytes during prophase I of meiosis. By regulating the transcriptional activity of β-catenin, GSK3β influences the spatiotemporal expression pattern of P63, ensuring the normal progression of meiotic prophase. Furthermore, in mice with germ cell-specific knockout of Gsk-3β, a significant increase in oocyte apoptosis was observed, accompanied by a marked reduction in the number of primordial follicles (18). Specificity protein 1 (SP1) regulates the formation and activation of primordial follicles. Deletion of Sp1 resulted in impaired breakdown of germ cell cysts and reduced primordial follicle pool (19). The mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1/KIT ligand (mTOR1/KITL) pathway is also involved in this process. mTORC1 activates KITL in granulosa cells, promoting survival of the primordial follicle and inhibiting its premature activation (20). Studies have also revealed that iroquois homeobox 3 (IRX3) and iroquois homeobox 5 (IRX5) are key factors for the crosstalk between oocytes and granulosa cells (21). A recent study also found that protein phosphatase 4 regulates the autophagy of oocytes to maintain the survival of primordial follicles (22). In conclusion, the interactions between oocytes and granulosa cells are crucial for follicle survival and atresia.
Recent investigations have further identified neurotrophins (NTs) as potential regulators of primordial follicle activation (23). Inhibition of nerve growth factor (NGF) or its receptor neurotrophic receptor tyrosine kinase 1 (NTRK1) significantly reduces oocyte numbers and impairs primordial follicle numbers in mouse ovaries. Conversely, supplementation with connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) markedly increases primordial follicle numbers in vitro (24). These findings collectively highlight the importance of coordinated and efficient communication between oocytes and granulosa cells during folliculogenesis. Such cellular interactions are essential for optimizing follicular development, maintaining the balance between primordial follicle survival and atresia, and ensuring the provision of high-quality oocytes for reproductive success.
Furthermore, in vitro culture of embryonic mouse ovaries with transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1) suppresses primordial follicle activation and reduces the primordial follicle pool, whereas supplementation with SD208, a TGF-β1 inhibitor, significantly promotes primordial follicle development (25). These findings collectively highlight the critical roles of signaling molecules and their regulatory networks in primordial follicle assembly and maintenance.
As the most critical component of primordial follicles, oocytes secrete some specific molecules that are necessary for the activation or atresia of primordial follicles, including factor in the germline alpha (FIGα), newborn ovary homeobox gene (NOBOX), spermatogenesis and oogenesis specific basic helix-loop-helix 1 and 2 (SOHLH1 and 2), and lim homeobox 8 (LHX8) (26–29). Research has demonstrated that Figα knockout mice fail to form primordial follicles, leading to a rapid loss of oocytes postnatally, while male development remains unaffected (30). Consequently, the ovarian failure phenotype in these mice positions FIGα as a candidate gene for human premature ovarian failure. Additionally, homozygous deletion of Nobox results in follicle atresia after birth (31).
2.2 Follicle developmental stage
The development and ovulation of oocytes within follicles in mammals are tightly regulated by gonadotropins. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) plays an indispensable role in the selection of follicles and the development of dominant follicles. Insufficient FSH secretion or reduced sensitivity of follicles to FSH can lead to follicular atresia. The differentiation of follicular sensitivity is likely the result of a combination of endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine factors; however, the precise molecular mechanisms underlying this process remain largely unclear. A recent study revealed that lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1) can regulate granulosa cell autophagy levels, thereby participating in FSH-mediated antral follicle formation and fate determination (32). Nevertheless, the critical scientific question of how LSD1 regulates follicle stimulating hormone receptor (FSHR) to enhance follicular sensitivity to antrum formation remains unanswered. Although lots of follicles ultimately undergo atresia, under physiological conditions, the arrival of FSH can promote follicular development and survival. Research has demonstrated that, in the presence of energy stimulation, the FSHR-mTOR-HIF1 signaling pathway can rescue follicles from atresia (33). However, the origin of the energy differences driving follicular atresia and how a cohort of follicles can transmit FSH signals into their microenvironment remain unresolved. These important questions warrant further investigation.
During follicular development, the abnormal development of granulosa cells is often the main cause of follicular atresia. The study found that forkhead box L2 (FOXL2) can negatively regulate splicing factor 1 (SF1) to activate cytochrome P450 family 17 subfamily A member 1 (CYP17A1) transcription, leading to granulosa cell development defects, and consequently inducing follicular confinement (34). The imbalance of BCL2 apoptosis regulator/BCL2 associated X (BCL-2/BAX) in granulosa cells and the overexpression of BAX lead to the release of cytochrome C by mitochondria, activation of Caspase-3 and apoptosis (17). The PI3K/AKT pathway is also involved in regulation. FSH and IGF-1 activate PI3K/AKT, phosphorylate forkhead box O3, (FOXO3) and inhibit its nuclear translocation, reducing the expression of pro-apoptotic genes such as fas ligand (FASLG) (35). In addition, growth differentiation factor 9 (GDF9) inhibits granulosa cell apoptosis through SMAD family member 3 (SMAD3) and collaborates with PI3K/AKT to enhance survival signals (36). At secondary and antral follicles stage, besides apoptosis, autophagy and ferroptosis pathways are gradually involved in follicular atresia. Autophagy plays a dual role. Protective autophagy can remove damaged organelles and maintain granulosa cell homeostasis (37). Excessive autophagy, such as nutrient deficiency or BPA (Bisphenol-A) exposure, activates adenosine 5’-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin/Unc-51 like autophagy activating kinase 1 (AMPK/mTOR/ULK1) pathways, upregulates microtubule associated protein 1 light chain 3 beta (LC3B), beclin 1 (BECN1), and accelerates follicular atresia (38). Ferroptosis generally occurs under specific circumstances, such as when chemotherapy drugs (such as cyclophosphamide) induce lipid peroxidation through heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1) and mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS), inhibit glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), lead to ferroptosis, and induce follicular atresia (39). Oocyte basonuclin zinc finger protein 1 (BNC1) defects promote acyl-CoA synthetase long chain family member 4, (ACSL4) expression through the NF2, Moesin-ezrin-radixin like (MERLIN) tumor suppressor-yes-associated protein (NF2-YAP) pathway, increase lipid ROS, and induce ferroptosis (40). Sirtuin 3 (SIRT3) loss in trophoblast cells activates AMPK/mTOR and inhibits GPX4, leading to autophagy dependent ferroptosis (41).
3 The apoptosis and follicular atresia
Apoptosis is a genetically regulated, energy-dependent form of programmed cell death characterized by cell shrinkage, chromatin condensation, membrane blebbing, and the formation of apoptotic bodies. It plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis during mammalian embryonic development, particularly in follicular atresia. Many studies have explored the mechanisms underlying granulosa cell apoptosis during follicular development and atresia (Figure 2). The following sections provide an overview of these processes.
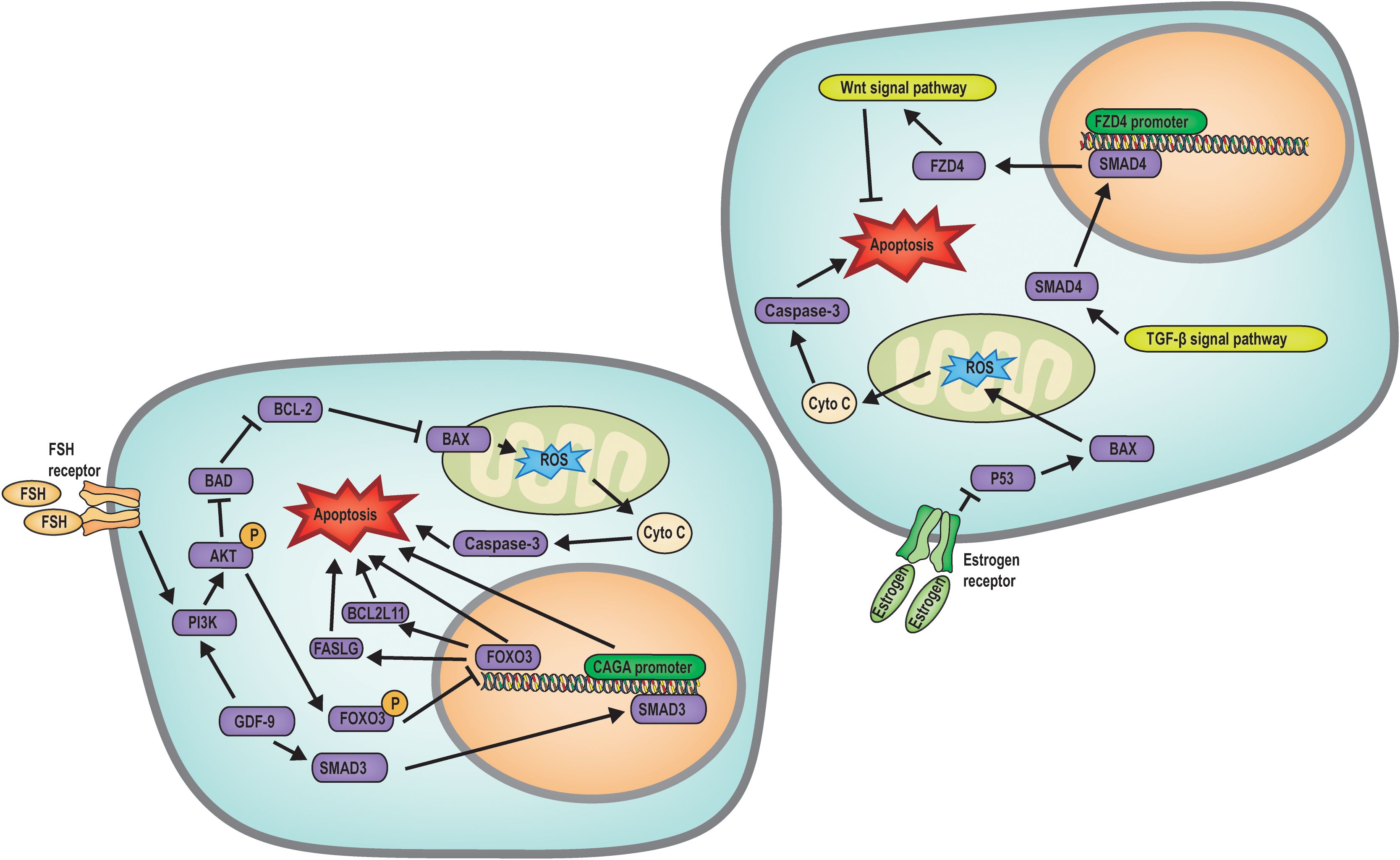
Figure 2. Mechanism diagram of apoptosis regulated follicular atresia. FSH regulates the PI3K/AKT/FOXO3 signaling pathway to inhibit apoptosis, while GDF9 upregulates SMAD3 transcription to promote apoptosis; Estrogen, Wnt and TGF-β signaling pathways inhibits apoptosis.
Biochemical analysis of ovarian tissue has identified nuclear chromatin fragmentation within atretic follicles, a definitive indicator of apoptotic cell death (42). Research has established the expression of BCL-2 gene family members within oocytes, underscoring the pivotal role of oxidative stress in mediating apoptosis (17, 43). Recent investigations have elucidated that a physiological balance of ROS is crucial for modulating follicular development, angiogenesis, and steroidogenesis within the ovary. ROS can directly inflict DNA damage by oxidizing nucleic acid bases and deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs), thereby impairing polymerase activity and diminishing the rate of in vitro DNA replication. An imbalance between ROS and antioxidant defenses precipitates oxidative stress (19). In oocytes, phosphorylation of FOXO3 can be promoted through the PI3K/AKT pathway. FOXO3 can regulate the apoptosis of oocytes and granulosa cells through transcription, and phosphorylated FOXO3 is inhibited from entering the nucleus. In this way, the PI3K/AKT pathway regulates follicle atresia and activation. In addition, AKT can regulate the expression of BAX and BCL-2 proteins, inducing mitochondrial oxidative stress and increased ROS levels, leading to the release of cytochrome c by mitochondria, which in turn activates Caspase3 and ultimately leads to oocyte apoptosis (35). This regulatory mechanism can diminish the ovarian reserve function and precipitate follicular atresia.
In addition, GDF9 has been found to inhibit granulosa cell apoptosis by stimulating SMAD3-induced CAGA promoter activity, thereby preventing follicular atresia (44). Furthermore, GDF9 exerts its anti-apoptotic effects in granulosa cells through the PI3K/Akt pathway (36). The transcription factor SMAD family member 4 (SMAD4), a downstream effector of the TGF-β signaling pathway, can directly control frizzled class receptor 4 (FZD4) transcription and promote FZD4-dependent Wnt signaling pathway, thereby triggering granulosa cell apoptosis (45). Hormonal and hormonemimetics factors also play a role in the regulation of this process. FSH activates the PI3K/AKT pathway in granulosa cells and phosphorylates the FOXO3 transcription factor, sequestering FOXO3 in the cytoplasm and preventing it from entering the nucleus. This action inhibits the activation of pro-apoptotic factors such as FASLG and BCL2 like 11 (BCL2L11), thus inhibiting follicular atresia (35). Moreover, estradiol directly suppresses the transcription of pro-apoptotic genes P53 and Bax in granulosa cells, thereby inhibiting apoptosis-induced follicular atresia (46).
Small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) derived from embryonic stem cells have been demonstrated to attenuate the expression of proteins associated with apoptosis. Post-transplantation of sEVs, serum hormone levels normalize, the count of follicles notably increases, and the incidence of apoptotic cells declines. sEVs significantly enhance the proliferation of granulosa cells, upregulate the expression of phosphorylated PI3K and AKT, and stimulate the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, thereby curtailing granulosa cell apoptosis and follicle atresia. sEVs play a role in follicle formation to maturation (47).
Research has indicated that adipose-derived stem cell (ADSC) transplantation can curtail apoptosis in ovarian granulosa cells from follicle formation to follicle maturation and augment the quantity of total, primordial, primary, and mature follicles. ADSCs have been shown to markedly reduce senescence and apoptosis in granulosa cells triggered by the chemotherapeutic agent cyclophosphamide (CTX). At the molecular level, ADSCs curb apoptosis in granulosa cells by modulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling cascade (48). This may be a method for the treatment of abnormal follicular atresia and the maintenance of follicular activity.
Certain pharmacological agents have demonstrated efficacy in curbing apoptosis-induced follicular atresia and promoting the activation of primordial follicles. Antioxidants, including vitamin C, vitamin E, glutathione, sulforaphane, American cockroach peptide, and resveratrol, have been shown to mitigate cellular oxidative stress, thereby inhibiting follicular atresia. Moreover, anti-inflammatory medications, such as select corticosteroids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, attenuate inflammatory responses and redue oxidative stress levels, consequently inhibiting follicular atresia (49, 50).
The issue of chemotherapy-induced follicular atresia has garnered significant interest in the field of female reproductive health. In addition to the ADSCs, which can mitigate chemotherapy-induced granulosa cell damage via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, metformin has been demonstrated to prevent cell apoptosis through activate the AMPK pathway, thereby protecting granulosa cells in chemotherapy-induced follicular atresia (51). Furthermore, traditional Chinese herbal medicines such as Angelica sinensis (dong quai), Codonopsis pilosula (dang shen), Astragalus membranaceus, and Cuscuta seed have been reported to modulate BCL-2 family proteins, inhibiting cell apoptosis, promoting follicular development, and reducing follicular atresia (52, 53).
4 The autophagy and follicular atresia
Autophagy is a cellular self-degradation process in all eukaryotes, functioning under virous physiological and pathological conditions. This mechanism requires the degradation and recycling of excess or damaged cellular components, including proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and specific organelles such as mitochondria and peroxisomes. Autophagy is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and metabolic balance (54).
Research has illuminated that apoptosis is not the exclusive determinant of follicular atresia; rather, autophagy also exerts a distinct influence on follicular atresia (Figure 3). Autophagy has a dual function, with basal autophagy supporting the survival of granulosa cells by clearing damaged organelles. However, nutrient deprivation or PCOS caused by hormone imbalance can over-activate the AMPK/mTOR pathway, upregulate LC3B and Beclin1, and induce autophagy-mediated follicular atresia (55, 56). Examination of gene expression profiles coupled with bioinformatics analyses has uncovered the upregulation of autophagy-related genes, including autophagy related 4B cysteine peptidase (ATG4B), autophagy related 3 (ATG3), autophagy related 13 (ATG13), and ULK1, during granulosa cell demise, underscoring the potential pivotal role of autophagy in the etiology and molecular underpinnings of follicular atresia. This discovery lays a molecular foundation for the diagnosis and therapeutic intervention of follicular atresia (57).
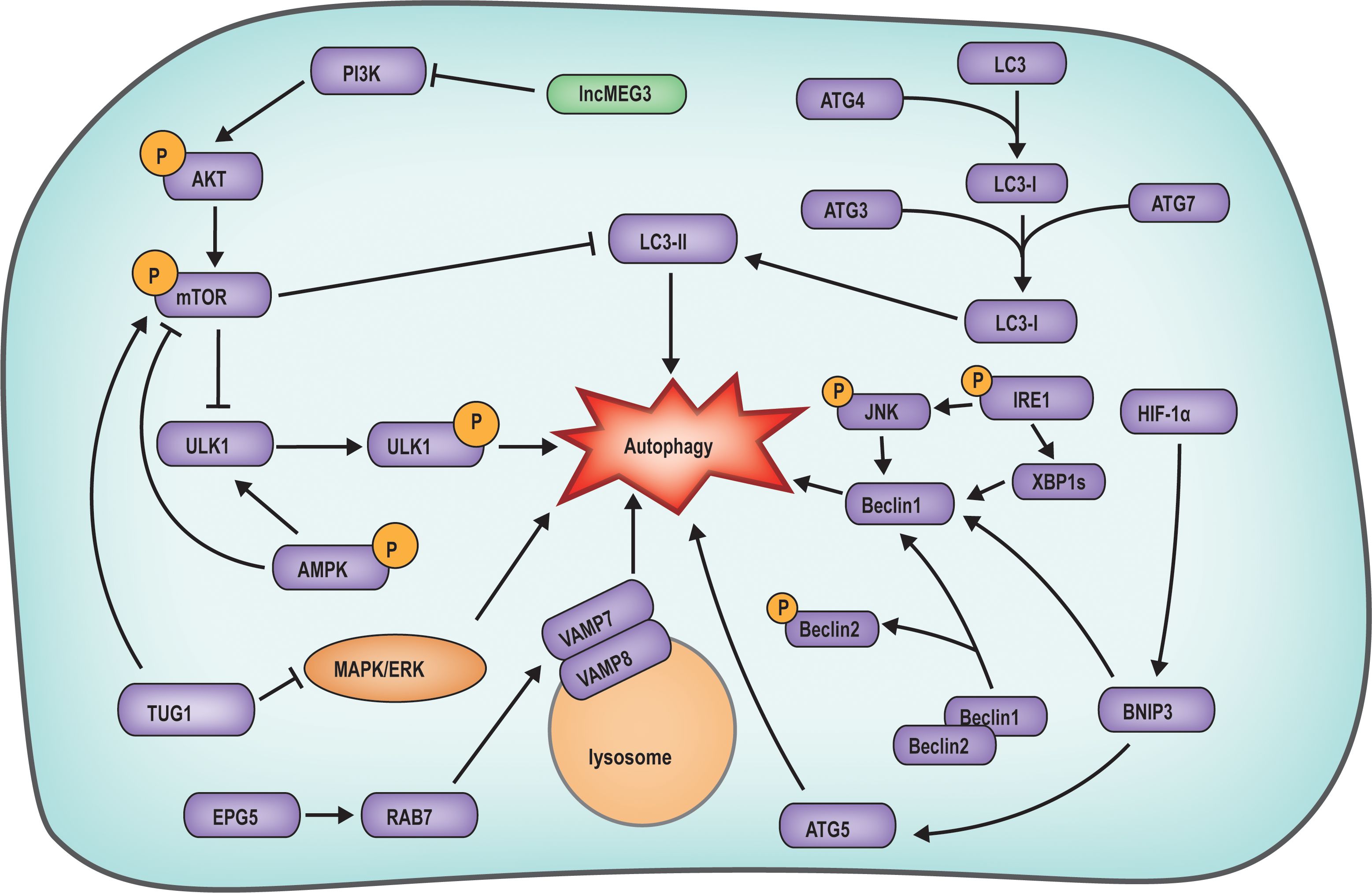
Figure 3. Mechanism diagram of autophagy regulated follicular atresia. The AKT/mTOR signaling suppresses autophagy by downregulating the expression of LC3-II and ULK1. TUG1 in follicular cells suppresses autophagy by inhibiting MAPK/ERK pathway. IRE1 can enhance Beclin1 expression by activating XBP1S expression and HIF-1α phosphorylation, with the latter directly activating autophagy. The expression of EPG5 activates RAB7, which interacts with the VAMP7/VAMP8 complex on the lysosomal membrane, facilitating the initiation of autophagy.
Investigations have demonstrated that during the primary to antral follicle phase, the autophagy-related protein ATG family is involved in the regulation of follicle atresia, and the classic autophagy pathways of autophagy related 5 (ATG5), Beclin1 and LC3 are all activated, and autophagy occurs in granulosa cells, which directly leads to follicular atresia (58). In endometriosis studies, Beclin1, a crucial autophagy protein, typically interacts with dephosphorylated Beclin2. However, phosphorylation of Beclin2 leads to the dissociation of Beclin1, enabling it to directly trigger granulosa cell autophagy. This, in turn, stimulates low-density lipoprotein-induced progesterone synthesis, culminating in follicle atresia (59). Current research indicates that during the primary to antral follicle phase well-characterized signaling pathways, such as PI3K/AKT/mTOR, mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MAPK/ERK), AMPK, and inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1), by inducing granulosa cell autophagy, the primordial follicle formation is altered, resulting in a decrease in oocyte count and the occurrence of follicular atresia (60). The expression of maternally expressed gene 3 (lncMEG3) within granulosa cells can also curtail autophagy by regulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, thereby restoring granulosa cell proliferation (56). In a study on polycystic ovary syndrome, taurine up-regulated 1 (TUG1) expression was found to inhibit autophagy by obstructing the MAPK/ERK pathway, while concurrently activating the mTOR pathway to suppress autophagy, leading to aberrant follicle growth (61). In a study on autophagy in mouse ovarian cells, it was observed that IRE1 could induce the phosphorylation of its downstream molecule c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and the expression of X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1) through phosphorylation, subsequently leading to increased expression of Beclin1 and triggering ovarian cell autophagy (62). Additionally, Ectopic p-granules 5 autophagy tethering factor (EPG5) deficiency is correlated with primary ovarian insufficiency due to ovarian failure. EPG5 in granulosa cells induces autophagy by directly interacting with ras-related protein rab-7a (RBA7) and binding to the vesicle associated membrane protein 7-vesicle associated membrane protein 8 (VAMP7-VAMP8) complex on lysosomes, facilitating its transfer to autophagosomes, culminating in follicle atresia (63).
Numerous hormones, biomolecules, and chemicals can induce autophagy in follicular cells by modulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. The AKT protein, previously mentioned, not only engages in the regulation of cell apoptosis but is also recognized as a key regulator of autophagy. In the presence of FSH, AKT suppresses granulosa cell autophagy by modulating the phosphorylation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, consequently diminishing the expression of LC3B (64). Moreover, melatonin has been demonstrated to modulate autophagy in ovarian granulosa cells via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway (65). Studies on the endocrine-disrupting chemical Bisphenol A (BPA) have revealed that BPA, exhibiting estrogen-like effects, activates the AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 pathway. Phosphorylated AMPK can directly activate ULK1 or indirectly activate it by inhibiting mTOR, promoting granulosa cell autophagy and subsequently precipitating follicle atresia (66).
Some pharmacological interventions have demonstrated efficacy in mitigating autophagy-induced follicular atresia and promoting the activation of primordial follicles. Clomiphene, an orally administered medication, modulates ovarian cell autophagy by targeting the mTOR pathway and LC3, and is utilized in the clinical management of PCOS (67). Metformin, a widely recognized antidiabetic drug, has also been employed in the treatment of patients exhibiting follicular atresia. Studies indicate that metformin ameliorates PCOS by attenuating oxidative stress-induced autophagy via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling cascade (68, 69). Furthermore, research suggests that cyclosporine A activates autophagy associated with hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1-Alpha/BCL2 interacting protein 3 (HIF1α/BNIP3) pathway. Hyperoside protects against ovarian damage and reduced fertility induced by cyclosporine A by inhibiting HIF-1α/BNIP3-mediated autophagy, thereby preserving the follicular reserve (70).
Overall, these observations imply that the modulation of autophagy could present novel therapeutic avenues for the management of follicular atresia. The manipulation of the autophagy pathway using pharmacological agents or bioactive molecules may constitute a promising treatment strategy. Additional investigative efforts are warranted to dissect the intricate interplay between autophagy and follicular atresia, and to assess the feasibility of harnessing the autophagy pathway as a therapeutic target for follicular atresia.
5 The ferroptosis and follicular atresia
Ferroptosis is an iron-dependent, novel form of programmed cell death that differs from apoptosis, necrosis, and autophagy (39). The main mechanism of ferroptosis involves a decrease in cellular antioxidant capacity and accumulation of ROS due to the direct or indirect impact on glutathione peroxidase by ferrous iron or lipoxygenases. The interaction between ROS and Fe2+ causes a Fenton reaction, ultimately resulting in cell death (39, 41). During the developmental progression of female follicles, follicular atresia has been associated with the cellular mechanism of ferroptosis. Current investigative efforts are primarily focused on the diverse molecular triggers of the ferroptosis pathway, which result in excessive ROS production, oxidative stress, and the subsequent destruction of cellular and organelle membranes, culminating in follicular atresia (Figure 4).
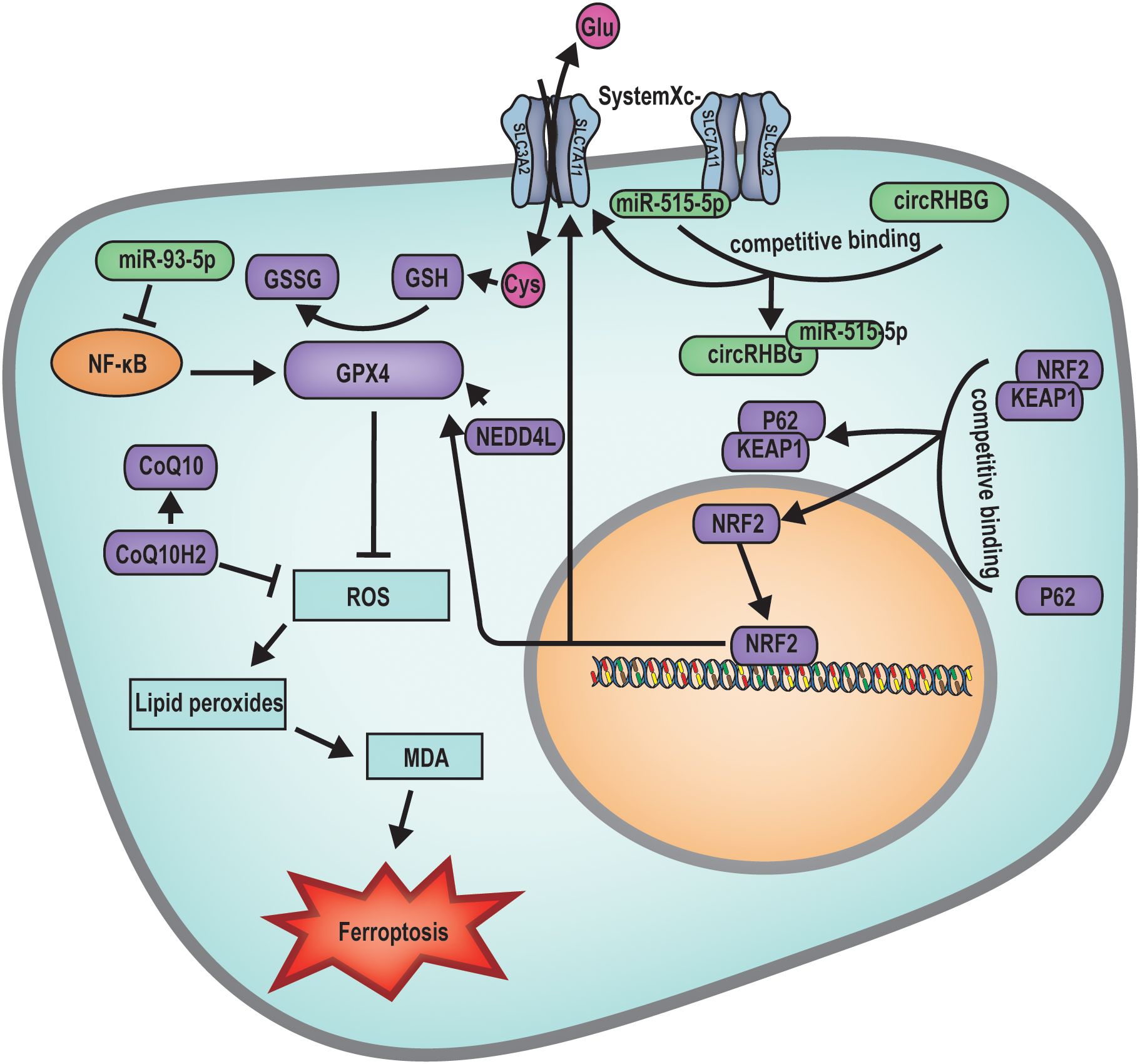
Figure 4. Mechanism diagram of ferroptosis regulated follicular atresia. miR-93-5p inhibits the NF-κB pathway, subsequently suppressing the expression of GPX4, leading to increased ROS production inducing ferroptosis. circRHBG promotes the expression of SLC7A11, enhancing the GSH/GSSG ratio, inhibiting ferroptosis. BNC1 directly participates in the regulation of the NF2-YAP signaling pathway, regulates the transcription of ACSL4. The expression of SIRT3 inhibits the expression of GPX4, facilitating the occurrence of ferroptosis. On the other hand, it can activate the AMPK-mTOR signaling pathway, inducing autophagy-dependent ferroptosis. NEDD4L acts on GPX4 to suppress ROS production, thereby inhibiting cellular ferroptosis. P62 binds to the KEAP1/NRF2 complex, releasing the transcription factor NRF2. Once NRF2 enters the nucleus, it can regulate the expression of SLC7A11 and GPX4, thus inhibiting ferroptosis.
At the primordial follicle stage, mutations in genes such as Bnc1 can precipitate ferroptosis, leading to follicular atresia. BNC1 directly modulates the NF2-YAP signaling pathway, and its deficiency downregulates NF2 expression, reduces YAP phosphorylation, promotes YAP nuclear accumulation, triggers increased iron uptake, and enhances lipid ROS production. These changes result in oocyte ferroptosis and ultimately follicular atresia (40). Research has further demonstrated that elevated ovarian SIRT3 expression can induce autophagy-dependent ferroptosis by activating the AMPK-mTOR pathway and inhibiting GPX4 expression, thereby promoting oocyte ferroptosis (40).
During the follicle development stage, research has indicated that a multitude of miRNAs and lncRNAs are implicated in the modulation of ferroptosis-induced follicular atresia. For example, aberrant expression of miR-93-5p within granulosa cells can affect follicle development through multiple mechanisms, including the induction of apoptosis via the nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) pathway and the suppression of Gpx4 gene expression, leading to the accumulation of lipid ROS and subsequent ferroptosis of granulosa cells (71). Furthermore, elevated levels of the circular RNA Homo sapiens RBM39 binding protein 1 (circRHBG) in granulosa cells have been shown to upregulate solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11) expression, increase the glutathione (GSH)/oxidized glutathione (GSSG) ratio, enhance GPX4 activity, and inhibit ferroptosis in granulosa cells, thereby preventing follicular atresia (72).
Beyond RNA molecules, various biological factors also contribute to the pathogenesis of follicular atresia. Studies have revealed that dehydro-epiandrosterone (DHEA), ubiquinol CoQ10, and Cleo-20 T3 significantly diminish the expression of genes associated with the intracellular ferroptosis pathway, including transferrin receptor (TFRC), nuclear receptor coactivator 4 (NCOA4), and solute carrier family 3 member 2 (SLC3A2) and elevates GPX4 levels, indicative of ferroptosis suppression and thus the inhibition of follicular atresia (73). Moreover, it has been discovered that NEDD4 like E3 ubiquitin protein ligase (NEDD4L) in granulosa cells can induce ferroptosis by promoting the ubiquitination and degradation of GPX4, culminating in follicular atresia (74).
In the context of ovarian cancer treatment, chemotherapy drugs often inadvertently damage normal cells alongside their intended impact on cancer cells. For example, following exposure to chemotherapy drugs, granulosa cells undergo mitochondrial damage, leading to decreased GPX4 expression, ROS accumulation, and subsequent ferroptosis, which results in follicular atresia (75). Endometrial stem cells (EnSCs) can upregulate NF-E2-related factor 2 (NRF2) expression in granulosa cells, which in turn suppresses ferroptosis in granulosa cells by promoting the SLC7A11-GPX4 axis expression and thereby inhibiting follicular atresia (76).
Certain pharmacological agents and molecular entities have demonstrated the capacity to effectively suppress the ferroptosis pathway, thereby inhibiting the onset of follicular atresia. Iron chelators, such as deferoxamine and hydroxylamine-methanesulfonic acid, can sequester excess free iron ions, thus averting follicular damage (77, 78). The ferroptosis inhibitor, ferrostatin-1 (Fer-1), and endometrial stem cells (EnSCs) have been shown to restore cellular viability by inhibiting ferroptosis, which mitigates the detrimental effects of chemotherapeutic agents on granulosa cells (76). Cyclophosphamide has been reported to induce ferroptosis in ovarian granulosa cells through pathways involving HO-1 and ROS-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction (39).
All, ferroptosis is posited to play a pivotal role in the activation of primordial follicles, the preservation of the primordial follicle pool, and the modulation of follicular atresia (79, 80). Further investigation is imperative to clarify the precise mechanisms through which ferroptosis precipitates follicular atresia and to explore the therapeutic potential of targeting ferroptosis in female reproductive health.
6 Outlook and discussion
Ovarian follicle atresia is a common phenomenon in the female reproductive system characterized by impaired or halted follicle development. Physiological follicle atresia is indispensable, its dysregulation underlies major reproductive pathologies (81). This condition has been associated with disorders such as PCOS and POF (82, 83). The current clinical approaches to managing follicular atresia primarily encompass surgical intervention and hormonal therapy. For example, FSH interacts with its receptors to promote the growth and maturation of follicles, thereby potentially ameliorating abnormal follicular atresia (84, 85). Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) functions in a manner analogous to luteinizing hormone (LH) by binding to LH receptors, stimulating the ovaries and facilitating the ovulation of mature follicles (86, 87). Estrogens, including estradiol, modulate follicular development and enhance the follicular environment through their action on estrogen receptors (88).
Additionally, adjunctive therapeutics, such as spironolactone, an anti-androgen agent that targets androgen receptors, which can bolster follicular development in patients afflicted with PCOS (89). Insulin sensitizers, exemplified by metformin, indirectly promote follicle maturation by mitigating insulin resistance, thus providing supplementary therapeutic benefits for PCOS management (90, 91). Nonetheless, these treatment modalities have inherent limitations and carry the potential for adverse effects.
Recent investigations have increasingly revealed that cellular mechanisms such as apoptosis, autophagy, and ferroptosis contribute to ovarian follicle atresia (91–95). These processes often coexist; for example, SIRT3 activates both autophagy and ferroptosis in aging ovaries. Consequently, a more profound exploration of the interplay between these cell death pathways and ovarian follicle atresia could elucidate the underlying mechanismsand pave the way for innovative treatment strategies (96, 97). Future research endeavors could focus on the development of targeted therapies or specific pharmaceutical interventions that modulate the molecular underpinnings of these cell death pathways, potentially enhancing fertility rates and improving the quality of life for individuals with ovarian follicle atresia.
In summary, a detailed study of the effects of apoptosis, autophagy, and ferroptosis on follicular atresia can provide a solid foundation for a more comprehensive understanding of the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying this condition and facilitate the discovery of new treatment approaches. This research also offers new perspectives and opportunities for addressing challenges associated with follicular atresia.
Author contributions
JZ: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. TZ: Writing – original draft. ML: Writing – original draft. CW: Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (32400707); Shandong University of Technology Science and Technology Doctor Start-up Fund (423041).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Telfer EE, Grosbois J, Odey YL, Rosario R, and Anderson RA. Making a good egg: human oocyte health, aging, and in vitro development. Physiol Rev. (2023) 103:2623–77. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00032.2022
2. Zhou J, Wang W, Xia G, and Wang C. The programmed death of fetal oocytes and the correlated surveillance mechanisms. Reprod Dev Med. (2022) 6:181–93. doi: 10.1097/RD9.0000000000000016
3. Hillier SG. Current concepts of the roles of follicle stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone in folliculogenesis. Hum Reprod. (1994) 9:188–91. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a138480
4. Campos-Junior PH, Marinho Assuncao C, Carvalho BC, Batista RI, Garcia RM, and Viana JH. Follicular populations, recruitment and atresia in the ovaries of different strains of mice. Reprod Biol. (2012) 12:41–55. doi: 10.1016/S1642-431X(12)60076-X
5. Yu C, Zhang YL, and Fan HY. Selective Smad4 knockout in ovarian preovulatory follicles results in multiple defects in ovulation. Mol Endocrinol. (2013) 27:966–78. doi: 10.1210/me.2012-1364
6. Mokhtar DM and Hussein MM. Microanalysis of fish ovarian follicular atresia: A possible synergic action of somatic and immune cells. Microsc Microanal. (2020) 26:599–608. doi: 10.1017/S1431927620001567
7. Lange-Consiglio A, Capra E, Herrera V, Lang-Olip I, Ponsaerts P, and Cremonesi F. Application of perinatal derivatives in ovarian diseases. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. (2022) 10:811875. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.811875
8. Dhanasekaran N, Sheela Rani CS, and Moudgal NR. Studies on follicular atresia: lysosomal enzyme activity and gonadotropin receptors of granulosa cells following administration or withdrawal of gonadotropins in the rat. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (1983) 33:97–112. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(83)90059-X
9. Henderson KM, McNatty KP, Smith P, Gibb M, O'Keeffe LE, Lun S, et al. Influence of follicular health on the steroidogenic and morphological characteristics of bovine granulosa cells. vitro. J Reprod Fertil. (1987) 79:185–93. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0790185
10. Wandji SA, Wood TL, Crawford J, Levison SW, and Hammond JM. Expression of mouse ovarian insulin growth factor system components during follicular development and atresia. Endocrinology. (1998) 139:5205–14. doi: 10.1210/endo.139.12.6367
11. Hurwitz A, Ruutiainen-Altman K, Marzella L, Botero L, Dushnik M, and Adashi EY. Follicular atresia as an apoptotic process: atresia-associated increase in the ovarian expression of the putative apoptotic marker sulfated glycoprotein-2. J Soc Gynecol Investig. (1996) 3:199–208. doi: 10.1177/107155769600300407
12. Wiesen JF and Midgley AR Jr. Expression of connexin 43 gap junction messenger ribonucleic acid and protein during follicular atresia. Biol Reprod. (1994) 50:336–48. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod50.2.336
13. Festjens N, Vanden Berghe T, and Vandenabeele P. Necrosis, a well-orchestrated form of cell demise: signalling cascades, important mediators and concomitant immune response. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2006) 1757:1371–87. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2006.06.014
14. Kaipia A and Hsueh AJ. Regulation of ovarian follicle atresia. Annu Rev Physiol. (1997) 59:349–63. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.59.1.349
15. Son WY, Das M, Shalom-Paz E, and Holzer H. Mechanisms of follicle selection and development. Minerva Ginecol. (2011) 63:89–102.
16. Rodrigues P, Limback D, McGinnis L, Marques M, Aibar J, and Plancha CE. Germ-somatic cell interactions are involved in establishing the follicle reserve in mammals. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:674137. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.674137
17. Ratts VS, Flaws JA, Kolp R, Sorenson CM, and Tilly JL. Ablation of bcl-2 gene expression decreases the numbers of oocytes and primordial follicles established in the post-natal female mouse gonad. Endocrinology. (1995) 136:3665–8. doi: 10.1210/endo.136.8.7628407
18. Wen J, Yan H, He M, Zhang T, Mu X, Wang H, et al. GSK-3β protects fetal oocytes from premature death via modulating TAp63 expression in mice. BMC Biol. (2019) 17:23. doi: 10.1186/s12915-019-0641-9
19. Cai H, Liu B, Wang H, Sun G, Feng L, Chen Z, et al. SP1 governs primordial folliculogenesis by regulating pregranulosa cell development in mice. J Mol Cell Biol. (2020) 12:230–44. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjz059
20. Zhao Y, Zhang Y, Li J, Zheng N, Xu X, Yang J, et al. MAPK3/1 participates in the activation of primordial follicles through mTORC1-KITL signaling. J Cell Physiol. (2018) 233:226–37. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25868
21. Fu A, Oberholtzer SM, Bagheri-Fam S, Rastetter RH, Holdreith C, Caceres VL, et al. Dynamic expression patterns of Irx3 and Irx5 during germline nest breakdown and primordial follicle formation promote follicle survival in mouse ovaries. PloS Genet. (2018) 14:e1007488. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007488
22. Dong MZ, Ouyang YC, Gao SC, Gu LJ, Guo JN, Sun SM, et al. Protein phosphatase 4 maintains the survival of primordial follicles by regulating autophagy in oocytes. Cell Death Dis. (2024) 15:658. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07051-4
23. Nilsson E, Dole G, and Skinner MK. Neurotrophin NT3 promotes ovarian primordial to primary follicle transition. Reproduction. (2009) 138:697–707. doi: 10.1530/REP-09-0179
24. Kerr B, Garcia-Rudaz C, Dorfman M, Paredes A, and Ojeda SR. NTRK1 and NTRK2 receptors facilitate follicle assembly and early follicular development in the mouse ovary. Reproduction. (2009) 138:131–40. doi: 10.1530/REP-08-0474
25. Rosairo D, Kuyznierewicz I, Findlay J, and Drummond A. Transforming growth factor-beta: its role in ovarian follicle development. Reproduction. (2008) 136:799–809. doi: 10.1530/REP-08-0310
26. Qin Y, Choi Y, Zhao H, Simpson JL, Chen ZJ, and Rajkovic A. NOBOX homeobox mutation causes premature ovarian failure. Am J Hum Genet. (2007) 81:576–81. doi: 10.1086/519496
27. Ren Y, Suzuki H, Jagarlamudi K, Golnoski K, McGuire M, Lopes R, et al. Lhx8 regulates primordial follicle activation and postnatal folliculogenesis. BMC Biol. (2015) 13:39. doi: 10.1186/s12915-015-0151-3
28. Shin YH, Ren Y, Suzuki H, Golnoski KJ, Ahn HW, Mico V, et al. Transcription factors SOHLH1 and SOHLH2 coordinate oocyte differentiation without affecting meiosis I. J Clin Invest. (2017) 127:2106–17. doi: 10.1172/JCI90281
29. Wang Z, Liu CY, Zhao Y, and Dean J. FIGLA. LHX8 and SOHLH1 transcription factor networks regulate mouse oocyte growth and differentiation. Nucleic Acids Res. (2020) 48:3525–41. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa101
30. Soyal SM, Amleh A, and Dean J. FIGalpha, a germ cell-specific transcription factor required for ovarian follicle formation. Development. (2000) 127:4645–54. doi: 10.1242/dev.127.21.4645
31. Rajareddy S, Reddy P, Du C, Liu L, Jagarlamudi K, Tang W, et al. p27kip1 (cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B) controls ovarian development by suppressing follicle endowment and activation and promoting follicle atresia in mice. Mol Endocrinol. (2007) 21:2189–202. doi: 10.1210/me.2007-0172
32. Zhu Z, He M, Zhang T, Zhao T, Qin S, Gao M, et al. LSD1 promotes the FSH responsive follicle formation by regulating autophagy and repressing Wt1 in the granulosa cells. Sci Bull (Beijing). (2024) 69:1122–36. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2024.01.015
33. Liu L, Hao M, Zhang J, Chen Z, Zhou J, Wang C, et al. FSHR-mTOR-HIF1 signaling alleviates mouse follicles from AMPK-induced atresia. Cell Rep. (2023) 42:113158. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113158
34. Takasawa K, Kashimada K, Pelosi E, Takagi M, Morio T, Asahara H, et al. FOXL2 transcriptionally represses Sf1 expression by antagonizing WT1 during ovarian development in mice. FASEB J. (2014) 28:2020–8. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-246108
35. Matsuda F, Inoue N, Maeda A, Cheng Y, Sai T, Gonda H, et al. Expression and function of apoptosis initiator FOXO3 in granulosa cells during follicular atresia in pig ovaries. J Reprod Dev. (2011) 57:151–8. doi: 10.1262/jrd.10-124H
36. Orisaka M, Orisaka S, Jiang JY, Craig J, Wang Y, Kotsuji F, et al. Growth differentiation factor 9 is antiapoptotic during follicular development from preantral to early antral stage. Mol Endocrinol. (2006) 20:2456–68. doi: 10.1210/me.2005-0357
37. Zhou J, Peng X, and Mei S. Autophagy in ovarian follicular development and atresia. Int J Biol Sci. (2019) 15:726–37. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.30369
38. Anand SK, Sharma A, Singh N, and Kakkar P. Activation of autophagic flux via LKB1/AMPK/mTOR axis against xenoestrogen Bisphenol-A exposure in primary rat hepatocytes. Food Chem Toxicol. (2020) 141:111314. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2020.111314
39. Chen H, Nie P, Li J, Wu Y, Yao B, Yang Y, et al. Cyclophosphamide induces ovarian granulosa cell ferroptosis via a mechanism associated with HO-1 and ROS-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction. J Ovarian Res. (2024) 17:107. doi: 10.1186/s13048-024-01434-z
40. Wang F, Liu Y, Ni F, Jin J, Wu Y, Huang Y, et al. BNC1 deficiency-triggered ferroptosis through the NF2-YAP pathway induces primary ovarian insufficiency. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:5871. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33323-8
41. Han D, Jiang L, Gu X, Huang S, Pang J, Wu Y, et al. SIRT3 deficiency is resistant to autophagy-dependent ferroptosis by inhibiting the AMPK/mTOR pathway and promoting GPX4 levels. J Cell Physiol. (2020) 235:8839–51. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29727
42. Chun SY and Hsueh AJ. Paracrine mechanisms of ovarian follicle apoptosis. J Reprod Immunol. (1998) 39:63–75. doi: 10.1016/S0165-0378(98)00013-8
43. Michurina SV, Kolesnikov SI, Bochkareva AL, Ishchenko IY, and Arkhipov SA. Expression of Apoptosis Regulator Proteins Bcl-2 and Bad in Rat Ovarian Follicular Apparatus during Recovery after Extreme Hypothermia. Bull Exp Biol Med. (2019) 168:205–9. doi: 10.1007/s10517-019-04675-x
44. Spicer LJ, Aad PY, Allen D, Mazerbourg S, and Hsueh AJ. Growth differentiation factor-9 has divergent effects on proliferation and steroidogenesis of bovine granulosa cells. J Endocrinol. (2006) 189:329–39. doi: 10.1677/joe.1.06503
45. Du X, Li Q, Yang L, Liu L, Cao Q, and Li Q. SMAD4 activates Wnt signaling pathway to inhibit granulosa cell apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11:373. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2578-x
46. Matsuda F, Inoue N, Manabe N, and Ohkura S. Follicular growth and atresia in mammalian ovaries: regulation by survival and death of granulosa cells. J Reprod Dev. (2012) 58:44–50. doi: 10.1262/jrd.2011-012
47. Liu M, Qiu Y, Xue Z, Wu R, Li J, Niu X, et al. Small extracellular vesicles derived from embryonic stem cells restore ovarian function of premature ovarian failure through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [published correction appears in. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2023) 14:276. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03512-3
48. Ai G, Meng M, Guo J, Li C, Zhu J, Liu L, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells promote the repair of chemotherapy-induced premature ovarian failure by inhibiting granulosa cells apoptosis and senescence. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2023) 14:75. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03297-5
49. Yang W, Liu R, Sun Q, Huang X, Zhang J, Huang L, et al. Quercetin alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in buffalo ovarian granulosa cells. Anim (Basel). (2022) 12:787. doi: 10.3390/ani12060787
50. Yang W, Liu R, Sun Q, Huang X, Zhang J, Huang L, et al. Effect of nutrition on plasma lipid profile and mRNA levels of ovarian genes involved in steroid hormone synthesis in Hu sheep during luteal phase. J Anim Sci. (2013) 91:5229–39. doi: 10.2527/jas.2013-6450
51. Yang Y, Tang X, Yao T, Zhang Y, Zhong Y, Wu S, et al. Metformin protects ovarian granulosa cells in chemotherapy-induced premature ovarian failure mice through AMPK/PPAR-γ/SIRT1 pathway. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:1447. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-51990-z
52. Wang L, Liu J, Nie G, Li Y, and Yang H. Danggui buxue tang rescues folliculogenesis and ovarian cell apoptosis in rats with premature ovarian insufficiency. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2021) 2021:6614302. doi: 10.1155/2021/6614302
53. Wang Y, Teng X, and Liu J. Research progress on the effect of traditional chinese medicine on signal pathway related to premature ovarian insufficiency. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2022) 2022:7012978. doi: 10.1155/2022/7012978
54. Mizushima N and Komatsu M. Autophagy: renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. (2011) 147:728–41. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.10.026
55. D'Herde K, De Prest B, and Roels F. Subtypes of active cell death in the granulosa of ovarian atretic follicles in the quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica). Reprod Nutr Dev. (1996) 36:175–89. doi: 10.1051/rnd:19960203
56. Lin M, Hua R, Ma J, Zhou Y, Li P, Xu X, et al. Bisphenol A promotes autophagy in ovarian granulosa cells by inducing AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 signalling pathway. Environ Int. (2021) 147:106298. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.106298
57. Lv S, Sun J, and Sun J. Identification and validation of autophagy-related genes in primary ovarian insufficiency by gene expression profile and bioinformatic analysis. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). (2022) 2022:9042380. doi: 10.1155/2022/9042380
58. Yefimova MG, Lefevre C, Bashamboo A, Eozenou C, Burel A, Lavault MT, et al. Granulosa cells provide elimination of apoptotic oocytes through unconventional autophagy-assisted phagocytosis. Hum Reprod. (2020) 35:1346–62. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deaa097
59. Ding Y, Zhu Q, He Y, Lu Y, Wang Y, Qi J, et al. Induction of autophagy by Beclin-1 in granulosa cells contributes to follicular progesterone elevation in ovarian endometriosis. Transl Res. (2021) 227:15–29. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2020.06.013
60. Bhardwaj JK, Paliwal A, Saraf P, and Sachdeva SN. Role of autophagy in follicular development and maintenance of primordial follicular pool in the ovary. J Cell Physiol. (2022) 237:1157–70. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30613
61. Kumariya S, Ubba V, Jha RK, and Gayen JR. Autophagy in ovary and polycystic ovary syndrome: role, dispute and future perspective. Autophagy. (2021) 17:2706–33. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1938914
62. Ma Y, Liu H, Du X, Petlulu P, Chen X, Wang R, et al. IRE1 and CaMKKβ pathways to reveal the mechanism involved in microcystin-LR-induced autophagy in mouse ovarian cells. Food Chem Toxicol. (2021) 147:111911. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2020.111911
63. Liu W, Chen M, Liu C, Wang L, Wei H, Zhang R, et al. Epg5 deficiency leads to primary ovarian insufficiency due to WT1 accumulation in mouse granulosa cells. Autophagy. (2023) 19:644–59. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2022.2094671
64. Zheng Y, Ma L, Liu N, Tang X, Guo S, Zhang B, et al. Autophagy and apoptosis of porcine ovarian granulosa cells during follicular development. Anim (Basel). (2019) 9:1111. doi: 10.3390/ani9121111
65. Xie F, Zhang J, Zhai M, Liu Y, Hu H, Yu Z, et al. Melatonin ameliorates ovarian dysfunction by regulating autophagy in PCOS via the PI3K-Akt pathway. Reproduction. (2021) 162:73–82. doi: 10.1530/REP-20-0643
66. Chen X, Tang H, Liang Y, Wu P, Xie L, Ding Y, et al. Acupuncture regulates the autophagy of ovarian granulosa cells in polycystic ovarian syndrome ovulation disorder by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway through LncMEG3. BioMed Pharmacother. (2021) 144:112288. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112288
67. Kuşçu GC, Gürel Ç, Buhur A, Oltulu F, Akman L, Köse T, et al. The regulatory effects of clomiphene and tamoxifen on mTOR and LC3-II expressions in relation to autophagy in experimental polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Mol Biol Rep. (2022) 49:1721–9. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06981-y
68. Xu B, Dai W, Liu L, Han H, Zhang J, Du X, et al. Metformin ameliorates polycystic ovary syndrome in a rat model by decreasing excessive autophagy in ovarian granulosa cells via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Endocr J. (2022) 69:863–75. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ21-0480
69. Hu B, Zheng X, and Zhang W. Resveratrol-βcd inhibited premature ovarian insufficiency progression by regulating granulosa cell autophagy. J Ovarian Res. (2024) 17:18. doi: 10.1186/s13048-024-01344-0
70. Zhu F, Gao J, Zeng F, Lai Y, Ruan X, and Deng G. Hyperoside protects against cyclophosphamide induced ovarian damage and reduced fertility by suppressing HIF-1α/BNIP3-mediated autophagy. BioMed Pharmacother. (2022) 156:113743. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113743
71. Tan W, Dai F, Yang D, Deng Z, Gu R, Zhao X, et al. MiR-93-5p promotes granulosa cell apoptosis and ferroptosis by the NF-kB signaling pathway in polycystic ovary syndrome. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:967151. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.967151
72. Zhang D, Yi S, Cai B, Wang Z, Chen M, Zheng Z, et al. Involvement of ferroptosis in the granulosa cells proliferation of PCOS through the circRHBG/miR-515/SLC7A11 axis. Ann Transl Med. (2023) 11:380. doi: 10.21037/atm-2023-13
73. Lin PH, Su WP, Li CJ, Lin LT, Sheu JJ, Wen ZH, et al. Investigating the role of ferroptosis-related genes in ovarian aging and the potential for nutritional intervention. Nutrients. (2023) 15:2461. doi: 10.3390/nu15112461
74. Tang H, Jiang X, Hua Y, Li H, Zhu C, Hao X, et al. NEDD4L facilitates granulosa cell ferroptosis by promoting GPX4 ubiquitination and degradation. Endocr Connect. (2023) 12:e220459. doi: 10.1530/EC-22-0459
75. Zhang S, Liu Q, Chang M, Pan Y, Yahaya BH, Liu Y, et al. Chemotherapy impairs ovarian function through excessive ROS-induced ferroptosis. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:340. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05859-0
76. Pan R, Wang R, Cheng F, Wang L, Cui Z, She J, et al. Endometrial stem cells alleviate cisplatin-induced ferroptosis of granulosa cells by regulating Nrf2 expression. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. (2024) 22:41. doi: 10.1186/s12958-024-01208-8
77. Ni Z, Li Y, Song D, Ding J, Mei S, Sun S, et al. Iron-overloaded follicular fluid increases the risk of endometriosis-related infertility by triggering granulosa cell ferroptosis and oocyte dysmaturity. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13:579. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05037-8
78. Zhang Y, Liu X, Deng M, Xu C, Zhang Y, Wu D, et al. Ferroptosis induced by iron overload promotes fibrosis in ovarian endometriosis and is related to subpopulations of endometrial stromal cells. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:930614. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.930614
79. Tang X, Dong H, Fang Z, Li J, Yang Q, Yao T., et alUbiquitin-like modifier 1 ligating enzyme 1 relieves cisplatin-induced premature ovarian failure by reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress in granulosa cells. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. (2022) 20(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s12958-022-00956-9
80. Chesnokov MS, Mamedova AR, Zhivotovsky B, and Kopeina GS. A.A matter of new life and cell death: programmed cell death in the mammalian ovary. J Biomed Sci. (2024) 31(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s12929-024-01017-6
81. Pan B and Li J. The art of oocyte meiotic arrest regulation. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. (2019) 17:8. doi: 10.1186/s12958-018-0445-8
82. Szeliga A, Calik-Ksepka A, Maciejewska-Jeske M, Grymowicz M, Smolarczyk K, Kostrzak A, et al. Autoimmune diseases in patients with premature ovarian insufficiency-our current state of knowledge. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:2594. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052594
83. Liao B, Qi X, Yun C, Qiao J, and Pang Y. Effects of androgen excess-related metabolic disturbances on granulosa cell function and follicular development. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:815968. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.815968
84. Qiang J, Cao ZM, Zhu HJ, Tao YF, He J, and Xu P. Knock-down of amh transcription by antisense RNA reduces FSH and increases follicular atresia in female Oreochromis niloticus. Gene. (2022) 842:146792. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2022.146792
85. Chu YL, Xu YR, Yang WX, and Sun Y. The role of FSH and TGF-β superfamily in follicle atresia. Aging (Albany NY). (2018) 10:305–21. doi: 10.18632/aging.101391
86. Biswas S and Maitra S. Altered redox homeostasis in steroid-depleted follicles attenuates hCG regulation of follicular events: Cross-talk between endocrine and IGF axis in maturing oocytes. Free Radic Biol Med. (2021) 172:675–87. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.07.023
87. Chakravarthi VP, Hung WT, Yellapu NK, Gunewardena S, and Christenson LK. LH/hCG regulation of circular RNA in mural granulosa cells during the periovulatory period in mice. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:13078. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713078
88. Ding L, Yan G, Wang B, Xu L, Gu Y, Ru T, et al. Transplantation of UC-MSCs on collagen scaffold activates follicles in dormant ovaries of POF patients with long history of infertility. Sci China Life Sci. (2018) 61:1554–65. doi: 10.1007/s11427-017-9272-2
89. Zeng X, Xie YJ, Liu YT, Long SL, and Mo ZC. Polycystic ovarian syndrome: Correlation between hyperandrogenism, insulin resistance and obesity. Clin Chim Acta. (2020) 502:214–21. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.11.003
90. Siddiqui S, Mateen S, Ahmad R, and Moin S. A brief insight into the etiology, genetics, and immunology of polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS). J Assist Reprod Genet. (2022) 39:2439–73. doi: 10.1007/s10815-022-02625-7
91. Hu W, Xie N, Pan M, Zhang Q, Zhang H, Wang F, et al. Chinese herbal medicine alleviates autophagy and apoptosis in ovarian granulosa cells induced by testosterone through PI3K/AKT1/FOXO1 pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. (2024) 318:117025. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117025
92. Huang J, Fan H, Li C, Yang K, Xiong C, Xiong S, et al. Dysregulation of ferroptosis-related genes in granulosa cells associates with impaired oocyte quality in polycystic ovary syndrome. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2024) 15:1346842. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1346842
93. Ren P, Tong X, Li J, Jiang H, Liu S, Li X, et al. CRL4DCAF13 E3 ubiquitin ligase targets MeCP2 for degradation to prevent DNA hypermethylation and ensure normal transcription in growing oocytes. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2024) 81:165. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05185-4
94. Dai W, Xu B, Ding L, Zhang Z, Yang H, He T, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate chemotherapy-induced premature ovarian insufficiency mouse model by suppressing ferritinophagy-mediated ferroptosis in granulosa cells. Free Radic Biol Med. (2024) 220:1–14. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.04.229
95. Zhou S, Zhao A, Wu Y, Bao T, Mi Y, and Zhang C. Protective effect of follicle-stimulating hormone on DNA damage of chicken follicular granulosa cells by inhibiting CHK2/p53. Cells. (2022) 11:1291. doi: 10.3390/cells11081291
96. Li J, Cao F, Yin HL, Huang ZJ, Lin ZT, Mao N, et al. Ferroptosis: past, present and future. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11:88. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2298-2
Keywords: follicle atresia, apoptosis, autophagy, ferroptosis, premature ovarian failure
Citation: Zhang T, Lin M, Wang C and Zhou J (2025) Mechanisms of follicular atresia: focus on apoptosis, autophagy, and ferroptosis. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1603467. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1603467
Received: 31 March 2025; Accepted: 05 September 2025;
Published: 23 September 2025.
Edited by:
Richard Ivell, University of Nottingham, United KingdomReviewed by:
Takuo Hojo, National Agriculture and Food Research Organization (NARO), JapanMuhammad Khan, University of the Punjab, Pakistan
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Lin, Wang and Zhou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiaqi Zhou, amlhcWl6aG91YmlvbG9neUAxMjYuY29t
 Tongqing Zhang
Tongqing Zhang Jiaqi Zhou
Jiaqi Zhou