- 1The First Clinical Medical College, Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China
- 2Department of Endocrinology II, The First Affiliated Hospital of Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China
Objective: This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Qingre Lishi decoction (QRLSD) for type 2 diabetes (T2D), thereby providing new evidence-based insights into the role of traditional Chinese medicine in treating T2D.
Methods: WanFang, Embase, Web of Science, PubMed, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, and the Cochrane Library were searched up to January 2025. Studies assessing the efficacy and safety of QRLSD in treating T2D were included. Data were pooled using standardized mean difference (SMD) and risk ratio (RR). Sensitivity and subgroup analyses were performed to assess the stability of the results and investigate potential sources of heterogeneity. Statistical analyses were conducted using RevMan 5.4 and Stata 18.0.
Results: A total of 18 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were included. Our results showed that QRLSD reduced the levels of fasting blood glucose (SMD: -15.09; 95% CI: [-18.27, -11.90], I² = 99%, P < 0.00001), 2-hour postprandial blood glucose (SMD: -17.71; 95% CI: [-21.70, -13.71], I² = 98%, P < 0.00001), glycated hemoglobin (SMD: -18.93; 95% CI: [-22.77, -15.09], I² = 98%, P < 0.00001), as well as other metabolic parameters, indicators of insulin resistance, and body mass index. No significant difference in the incidence of adverse events between the intervention and control groups was found (RR: 1.8; 95% CI: [0.57, 5.68], I² = 9%, P=0.32).
Conclusion: For T2D, QRLSD can significantly improve clinical outcomes and may serve as a more effective therapy than single Western medicine therapy. Moreover, it was not related to significant adverse events. Given the inherent limitations of this study, large-scale, multicenter international RCTs are needed to further validate these findings in the future.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, identifier CRD420251000585.
1 Introduction
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disease with a rising prevalence worldwide. In China, the prevalence of diabetes increased from only 0.67% in 1980 to 12.4% by 2010 (1). This trend is mirrored globally: by 2021, approximately 537 million people were affected by diabetes, corresponding to a global prevalence of 6.1% (1). The number is expected to continue rising, with global prevalence projected to reach 10% by 2050, and no country is expected to experience a decline (2). The majority of new cases are from low- and middle-income countries, posing substantial challenges to their healthcare systems and public finances. Diabetes ranks as the eighth leading cause of death and disability worldwide (3). In China, type 2 diabetes (T2D) remains the predominant form of the disease, with its high prevalence driven by urbanization, lifestyle changes, overweight and obesity, as well as genetic susceptibility (4). Given the serious health and societal burdens posed by diabetes both globally and domestically, it remains a critical public health concern requiring continued attention and the development of novel solutions.
According to the Prevention or Delay of Diabetes and Associated Comorbidities: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2025 (5), current treatment strategies for T2D include lifestyle interventions, weight management, insulin injection, and metformin, along with newer pharmacological agents such as GLP-1 receptor agonists, SGLT-2 inhibitors, and DPP-4 inhibitors.
However, conventional treatments are associated with various adverse effects. For instance, SGLT-2 inhibitors are related to genitourinary infections, fournier gangrene, lower-limb amputations, euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis, fractures, and orthostatic hypotension; GLP-1 receptor agonists may elevate the risk of pancreatitis, acute cholecystitis, and diabetic retinopathy; and DPP-4 inhibitors might elevate the risk of chronic heart failure (6). When the levels of blood glucose are extremely high, insulin injection is typically recommended for treatment. The latest medications, such as once-weekly insulin icodec and basal insulin BIF, are in clinical development. Nevertheless, challenges including poor patient adherence, increased insulin resistance, and high costs remain unresolved (7). Thus, it is important to explore new therapies for T2D. Diabetes has long been studied in Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), and it is defined as an emaciation-thirst disease. Modern TCM practitioners often correlate its pathogenesis with damp-heat syndrome (8). Some researchers suggest that T2D is frequently accompanied by insulin resistance, which is closely linked to inflammation. Qingre Lishi decoction (QRLSD) can improve the prognosis of T2D by modulating inflammatory levels, thus serving as a prospective treatment option (9). In this study, the Qingre Lishi decoction (QRLSD) included only those formulas explicitly indicated in treatment principles to have heat-clearing and dampness-draining effects. The constituent herbs in these formulas were broadly categorized as either heat-clearing or dampness-draining. Due to the complex naming conventions of TCM formulas, some classical decoctions are named after their main herb or the original targeted effect. For example, in Qingxin Lianzi Yin decoction, “Qingxin” indicates its function of clearing heart heat, while “Lianzi” refers to its main active ingredient, Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn. A similar example is Qinlian decoction combined with Pingwei San. Other formulas, such as Yinchen Wuling San, Gegen Qinlian decoction (GQD), and Yinchenhao decoction (YCHD), are named directly after their primary ingredients. Given the long history of TCM, classical formulas are sometimes repurposed for modern indications, and certain traditional formulas exhibit clear efficacy for such diseases as T2D. Additionally, some ancient formulas and modern formulations created by contemporary practitioners are directly named according to their therapeutic effects, such as the Qingre Lishi formula, with occasional repetition of names (10). Regardless of naming, all included formulas were explicitly reported by the investigators to exert heat-clearing and dampness-draining effects. The aforementioned GQD and YCHD are examples of formulas that fall within this category. Studies have found that GQD can significantly lower the levels of fasting blood glucose (FBG), as well as alleviate ectopic fat deposition, oxidative stress, and inflammation in the liver tissue of obese rats (11). Other studies have demonstrated that YCHD can suppress cellular inflammatory responses by modulating inflammatory signaling pathways. Thus, it is effective in treating diabetes and its complications (12).
Although a large number of relevant studies have been published, most are limited to small-sample clinical or non-clinical trials conducted at single centers. TCM decoctions are highly diverse, and even among formulas with heat-clearing and dampness-eliminating effects, their names vary. For example, GQD and YCHD have not been systematically categorized. Moreover, outcome measures differ widely, focusing either on changes in serum levels or on improvements in physical indicators. Furthermore, the overall level of evidence is low, primarily based on clinical observations, lacking data linking results to the broader category of heat-clearing and dampness-eliminating treatments (13). In addition, evidence supporting the efficacy of QRLSD in treating diabetes is scarce, and no systematic evaluation of its effectiveness has been conducted. Therefore, a systematic analysis and assessment of the efficacy and safety of QRLSD for the treatment of T2D is warranted.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Protocol and registration
This study was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis) 2020 statement released by Cochrane (14) and was registered in the PROSPERO database (CRD420251000585).
2.2 Search methods
WanFang, PubMed, the Cochrane Library, Embase, Web of Science, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure were searched up to February 2025 to select randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and cohort studies assessing the efficacy and safety of QRLSD in treating T2D. The Chinese search terms included Qingre Lishia decoction and diabetes, while the English search terms were Type 2 Diabetes & T2DM and Qingrelishi & Qingre Lishia. There were no language or geographical restrictions. Additionally, references to the selected studies were reviewed for additional eligible studies. The search strategy is presented in Supplementary File 1.
2.3 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Eligible RCTs and cohort studies were selected after reviewing titles, abstracts, and full texts according to the following criteria.
The inclusion criteria were as follows: (i) population: adults (aged ≧̸18 years) clinically diagnosed with T2D, with no restrictions on sex or race; (ii) intervention and comparison: the control group received Western medicine therapy and/or lifestyle interventions or other treatments. The intervention group received either QRLSD alone or QRLSD in combination with the treatment administered to the control group; (iii) outcomes: studies included at least one of the following outcomes: primary outcomes included clinical efficacy and the incidence of adverse events; secondary outcomes included the levels of FBG, 2-hour postprandial blood glucose (2hPG), and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c).
The exclusion criteria were as follows: (i) case-control studies, single-arm trials, review articles, animal studies, and cross-sectional studies; (ii) participants with elevated levels of blood glucose caused by other conditions; (iii) intervention groups received other types of TCM therapy (Chinese medicine pills, massage, acupuncture, injections, Chinese patent medicine, or auricular acupuncture); (iv) studies with inaccurate data or incomplete outcome measurements, or with inaccessible data from the original authors; (v) duplicate publications.
2.4 Data extraction
Two reviewers (Zimei Lin and Yi Sun) independently extracted data based on the search strategy and inclusion criteria. The extracted data included: (i) publication information: publication year, first author, and title; (ii) study characteristics: study design and duration of the intervention; (iii) participant characteristics: age, sex distribution, number of participants, average FBG, average age, and average BMI; (iv) intervention: medication, frequency, dosage, and route of administration for the control group; dosage, the composition of the TCM formula, and frequency for the intervention group; (v) outcomes (primary and secondary outcomes): continuous data were expressed as means or standard deviations, and categorical data were expressed as event counts or total numbers. Disagreements were resolved by a third reviewer (Juan Li).
2.5 Quality assessment
The Cochrane Risk of Bias (RoB) tool was utilized to evaluate the quality of included RCTs by two reviewers (Zimei Lin and Yi Sun) (15). Moreover, they cross-examined the evaluation results. The assessment encompassed seven domains: allocation concealment, blinding of participants and personnel, reporting bias, incomplete outcome data, random sequence generation, blinding of outcome assessment, and other bias. The methodological quality of the eligible studies was categorized as low, high, or unclear. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) was applied to evaluate the quality of the included cohort, with 7–9 points indicating high quality (16). Any disagreements were resolved by a third reviewer (Juan Li).
2.6 Statistical analysis
Literature management was carried out using EndNote X9, and data were organized in Excel. Statistical analyses were conducted through RevMan 5.4 and Stata 18.0. For categorical variables, effect sizes were presented as risk ratios (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI). For continuous variables, effect sizes were expressed as mean differences (MD) or standardized mean differences (SMD) with 95% CIs. Heterogeneity was assessed using the Cochrane Q test and the I² statistic. If P < 0.05 and I² ≥ 50%, which suggested significant heterogeneity, a random-effects model was applied for all analyses. Sensitivity and subgroup analyses were carried out to investigate the stability of the results and sources of heterogeneity. The funnel plots and Egger’s test were used to assess publication bias, with a significance level of P < 0.05. Additionally, according to GRADE, the quality of evidence for each outcome was assessed and graded as “high”, “moderate”, “low”, or “very low” to draw conclusions (17).
3 Results
3.1 Research and selection
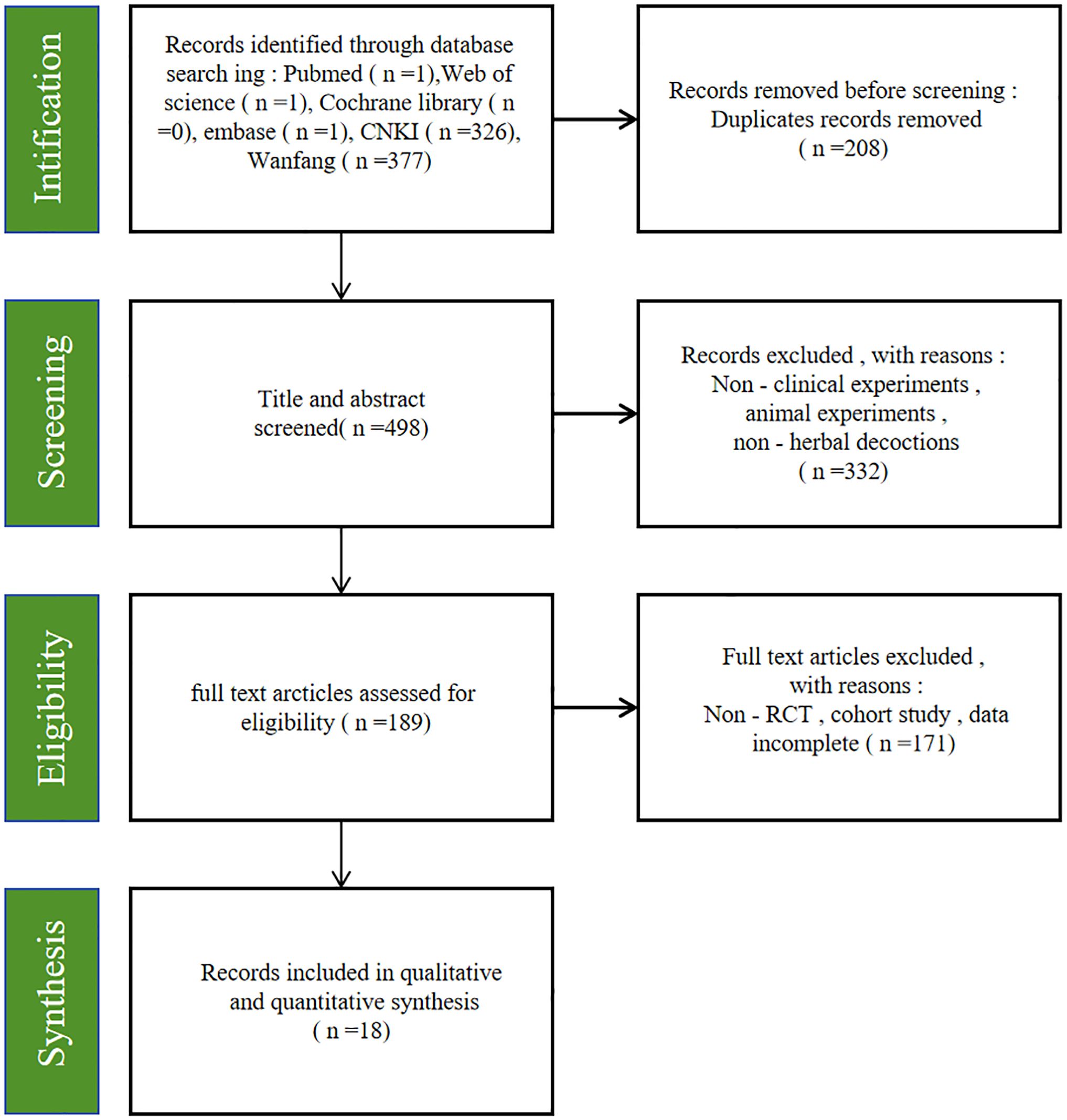
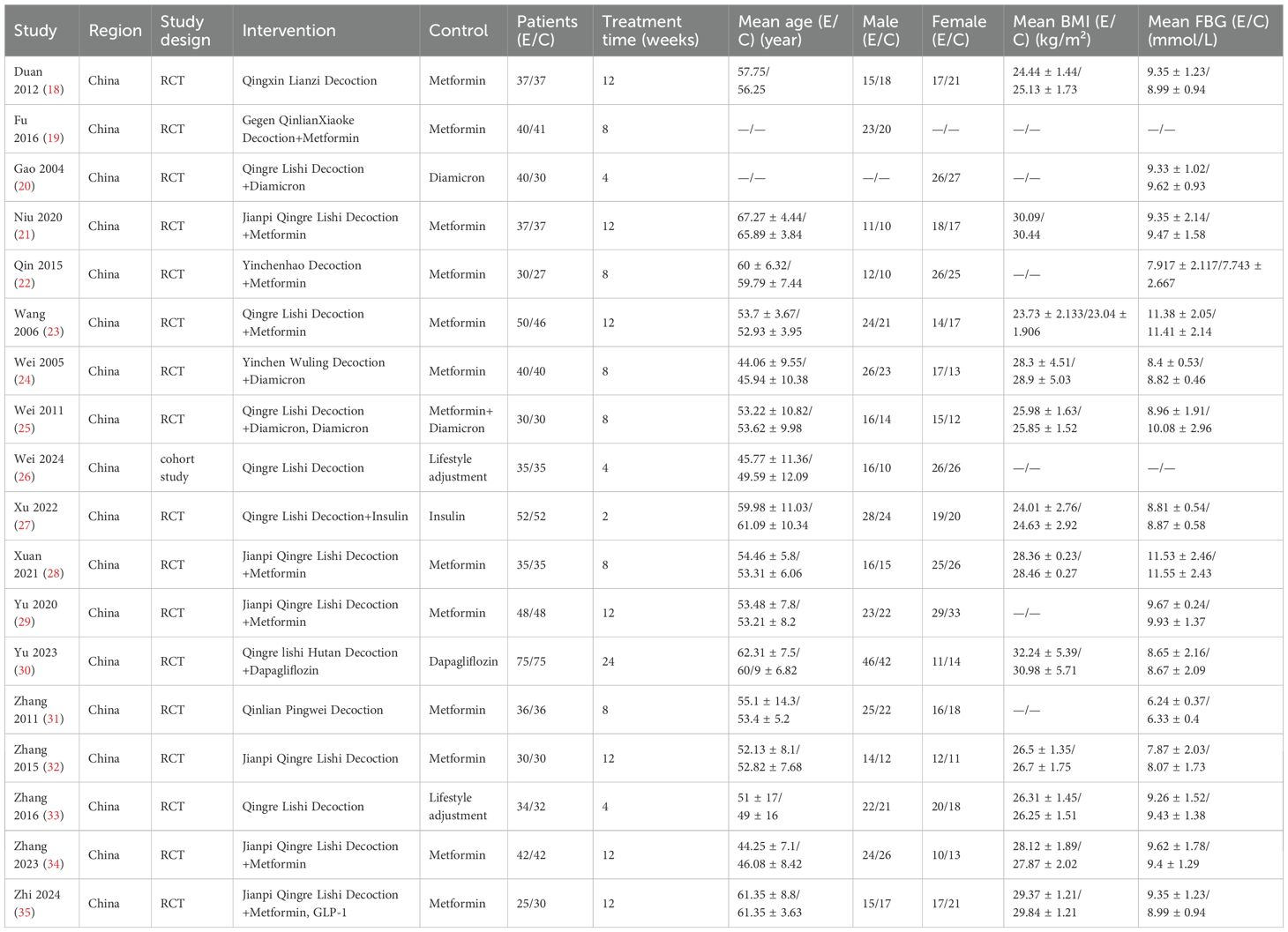
A total of 706 relevant studies were identified from the databases. After removing 208 duplicate records, 498 studies remained. Subsequently, 332 studies were further removed after reviewing titles and abstracts. A total of 189 studies remained for full-text review. Finally, 18 studies were included in this study (18–35). Figure 1 illustrates the selection process, and Table 1 provides the basic characteristics of the eligible studies.
3.2 Study characteristics
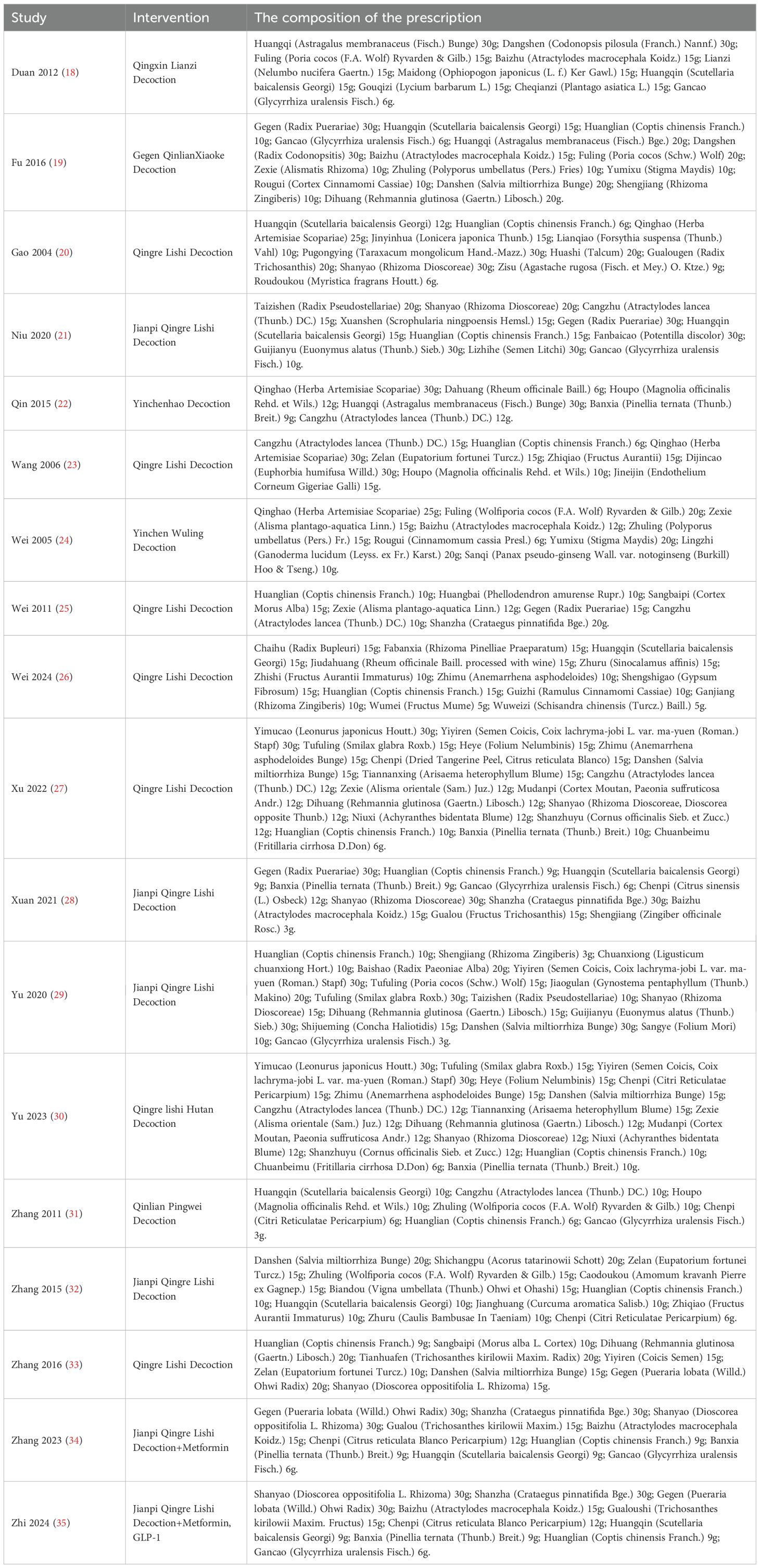
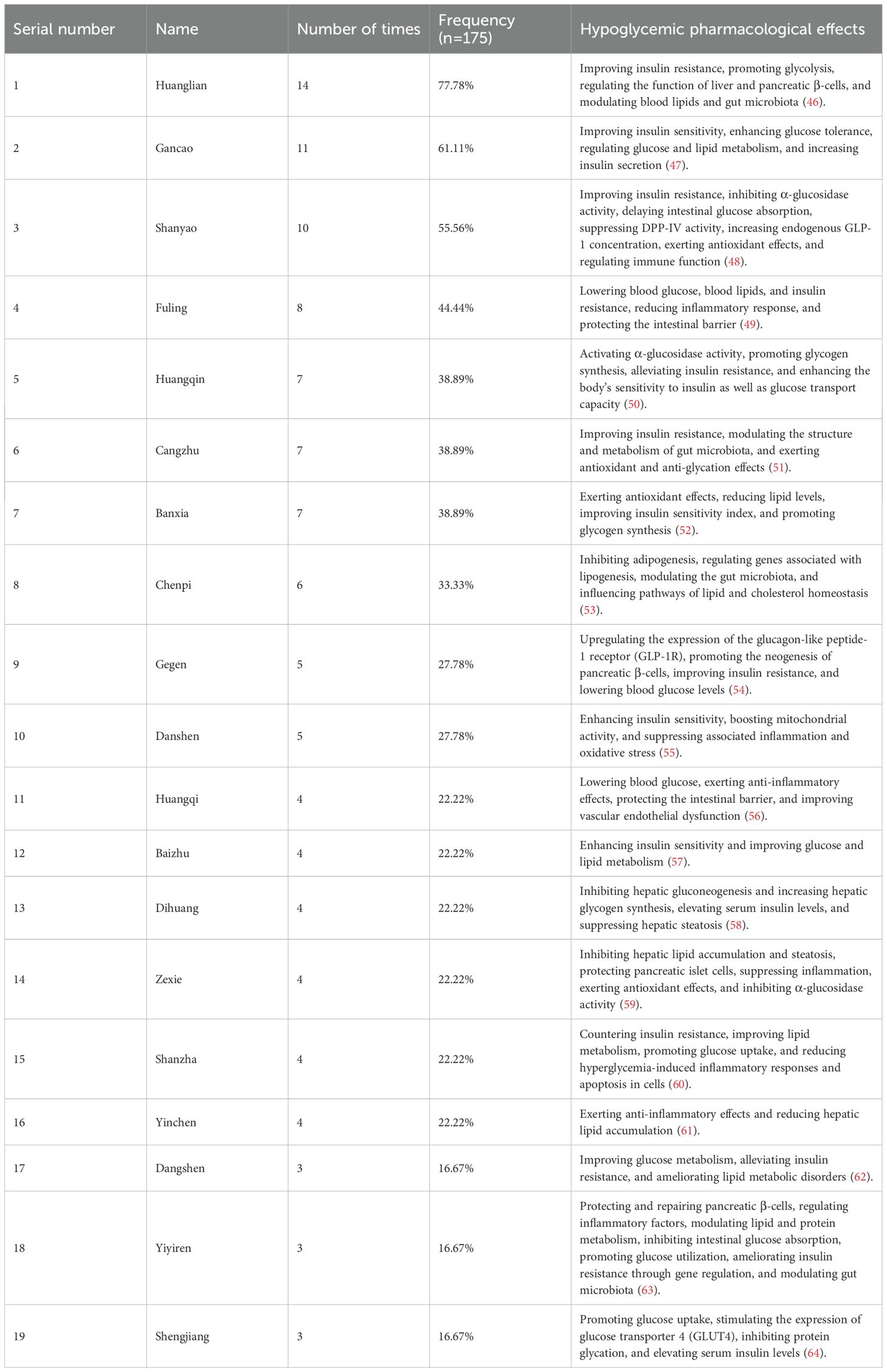
The 18 eligible studies involved 1419 individuals, with 716 in the intervention group and 703 in the control group. The sample sizes in both groups exceeded 25 cases. All included patients were from China. The mean age varied from 44.06 to 67.27 years in the intervention cohort and 45.94 to 65.89 years in the control cohort. The duration of the intervention in all studies was more than two weeks. The control group received conventional treatment, including insulin, metformin, sulfonylureas, and GLP-1 agonists. The intervention group received either QRLSD alone or in combination with the treatments administered to the control group. The QRLSD included YCHD, GQD, and customized formulas with commonly used herbs such as Qinghao (herba artemisiae scopariae), Fuling [wolfiporia cocos (F.A. Wolf) ryvarden and gilb], Gegen (radix puerariae), and Huanglian (coptis chinensis Franch.) (as illustrated in Table 2).
3.3 Bias risk assessment results
Among the 18 included studies, 17 were RCTs, and one was a cohort study. The quality of the RCTs was evaluated by the Cochrane RoB tool. In terms of random sequence generation, the eligible studies were identified as low risk, except for two studies (20, 24) that did not report the randomization process. Regarding allocation concealment, one study (20) was assessed as unclear risk as it did not specify the method. All studies employed blinding and reported treatment efficacy. Regarding the integrity of outcome data, one study (22) was rated as having an unclear risk as it did not provide sufficient details. In terms of selection bias, one study (20) was assessed as high risk as it specifically targeted an older population. Regarding other biases, all studies were assessed as low risk. The NOS was utilized to assess the quality of the cohort study. Except for the unclear risk of the comparability for additional factors, the cohort study was assessed as low risk for the other items, with an overall score of eight.
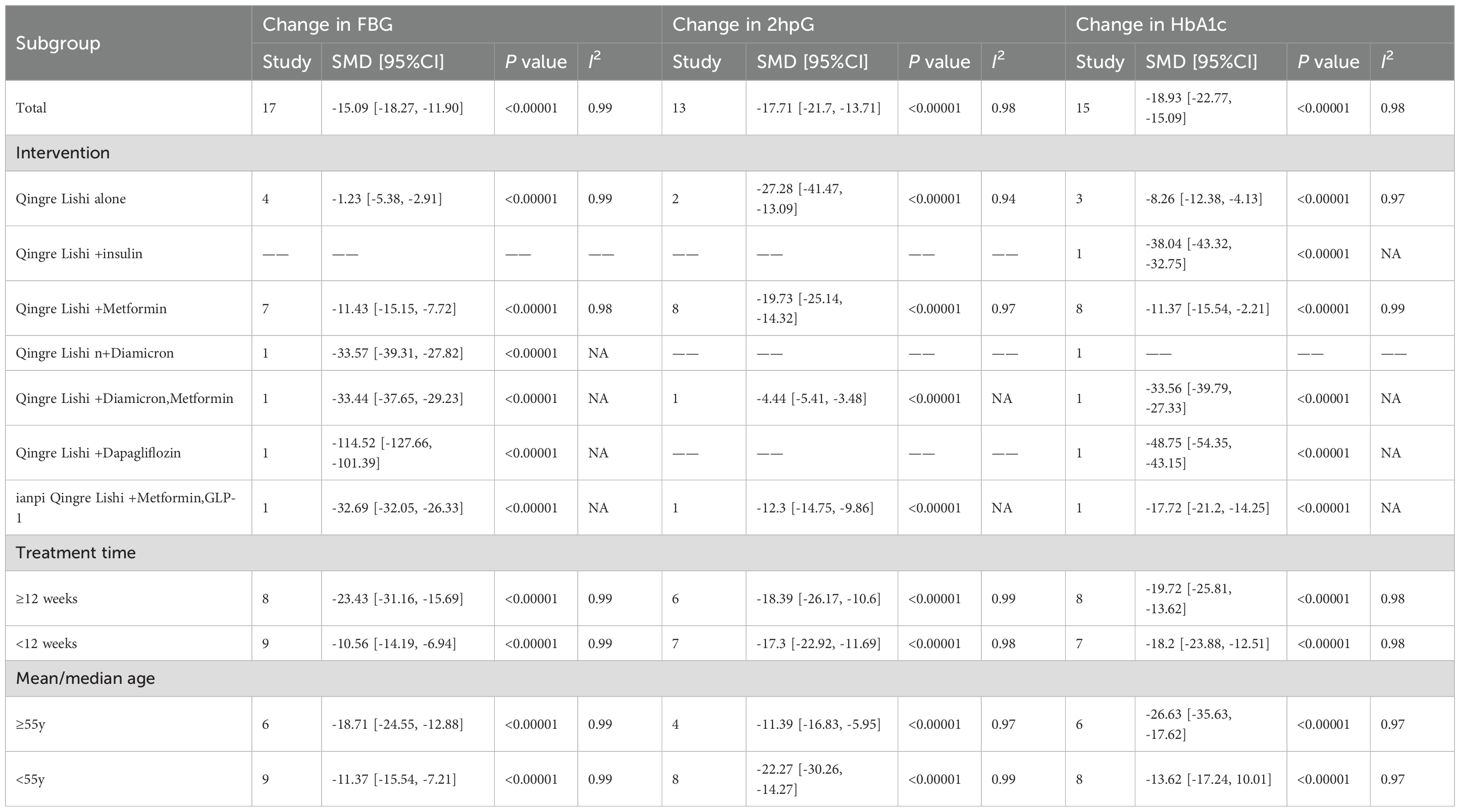
3.4 Change in FBG
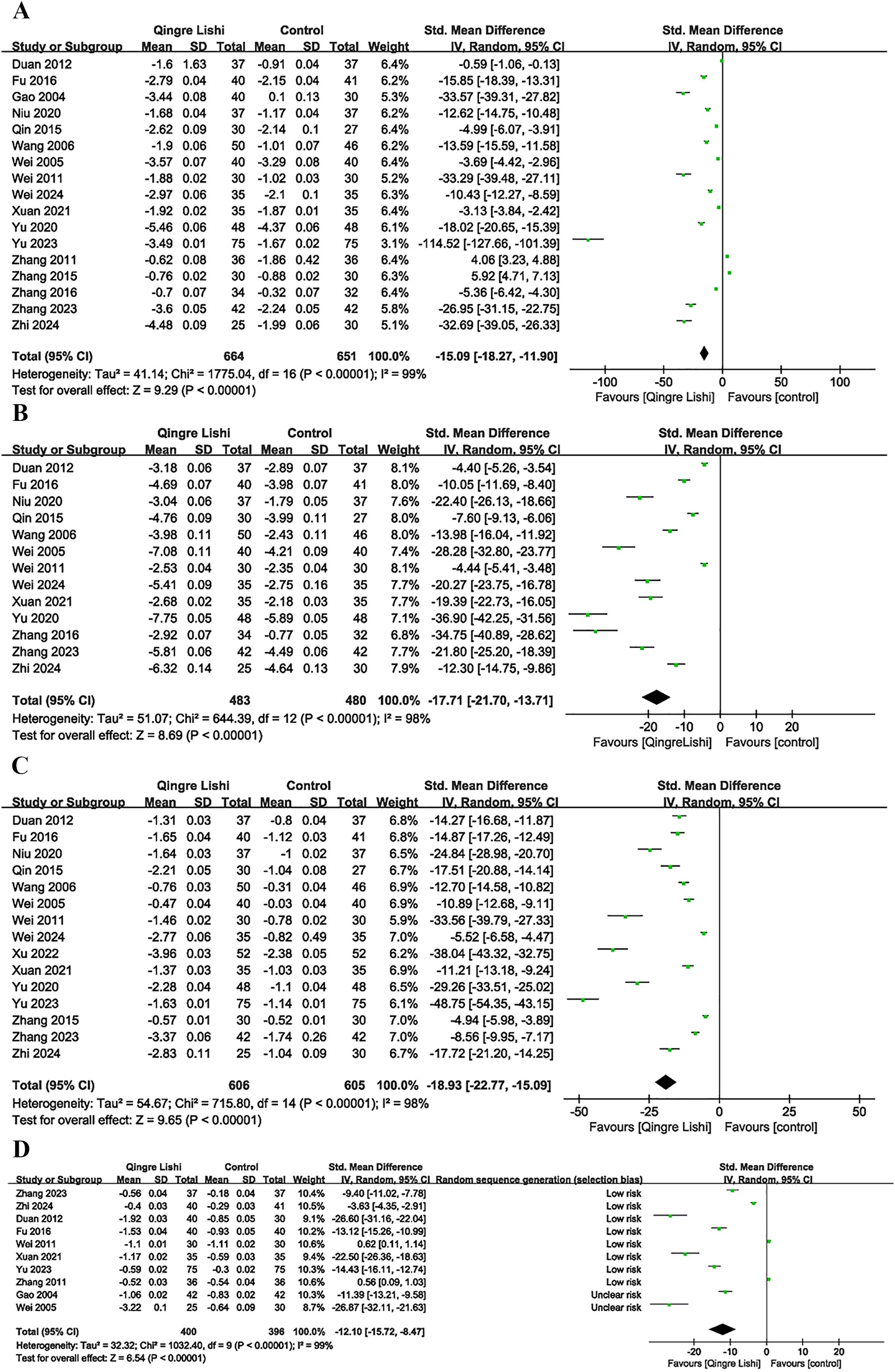
Among the 18 studies, 17 measured the levels of FBG as an outcome indicator. The results demonstrated that QRLSD, as an adjunct therapy, was significantly more effective in lowering FBG levels than treatments used in the control group (Figure 2A; SMD: -15.09; 95% CI: [-18.27, -11.90], I² = 99%, P < 0.00001). Subgroup analyses based on the changes in FBG were carried out. Seven subgroups were stratified by different interventions combined with QRLSD. The results showed that the efficacy of QRLSD and interventions combined with QRLSD was superior to that of the treatments employed in the control group. Out of the eligible studies, four employed QRLSD as a standalone intervention, seven combined it with metformin, one combined it with diamicron MR, one combined it with both diamicron MR and metformin, one combined it with dapagliflozin, and one combined it with metformin and GLP-1 agonists. The results all demonstrated statistical significance. Two subgroups were stratified by intervention duration (12 weeks and above vs. less than 12 weeks), and the results indicated that QRLSD was effective in lowering FBG levels in both subgroups. Two subgroups were stratified by patient age (55 years and above vs. below 55 years), and the results demonstrated that QRLSD effectively reduced FBG levels in both subgroups, with P values indicating statistical significance. The subgroup analyses are illustrated in Table 3.
3.5 Change in 2hpG
A total of 13 studies included 2hPG as an outcome indicator (Figure 2B; SMD: -17.71; 95% CI: [-21.7, -13.71], I² = 98%, P < 0.00001). The results indicated that QRLSD, as an adjunct therapy, effectively reduced 2hPG levels and outperformed the treatments used in the control group. Subgroup analyses based on the changes in 2hPG were carried out. Seven subgroups were stratified by different interventions combined with QRLSD. The results demonstrated that the QRLSD and interventions combined with QRLSD both effectively lowered the 2hPG levels. Among the included studies, two employed the QRLSD alone, eight combined it with metformin, one combined it with metformin and diamicron MR, and one combined it with metformin and GLP-1 agonists, with all results suggesting p < 0.00001. Two subgroups were stratified by intervention duration (12 weeks and above vs. less than 12 weeks), and the results demonstrated that QRLSD was more effective in lowering 2hPG levels than treatments used in the control group. Two subgroups were stratified by patient age (55 years and above vs. below 55 years), and the results showed that QRLSD effectively reduced 2hPG levels in both subgroups.
3.6 Change in HbA1c
A total of 15 studies included HbA1c as an outcome indicator (Figure 2C; SMD: -18.93; 95% CI: [-22.77, -15.09], I² = 98%, P < 0.00001). The results demonstrated that QRLSD reduced the levels of HbA1c, an indicator of blood glucose changes over time, as an adjunct therapy for treating T2D and was more effective than the treatments used in the control group. Subgroup analyses based on the changes in HbA1c were carried out. Seven subgroups were stratified by different interventions combined with QRLSD. The results showed that the QRLSD and interventions combined with QRLSD both effectively lowered the HbA1c levels. Among the included studies, three used QRLSD alone, eight combined it with metformin, one combined it with insulin, one combined it with metformin and diamicron MR, one combined it with dapagliflozin, and one combined it with metformin and GLP-1 agonists. The results all demonstrated the efficacy of these interventions in reducing HbA1c levels, with P values all suggesting statistical significance. Two subgroups were stratified by intervention duration (12 weeks and above vs. less than 12 weeks), and the results were statistically significant in both subgroups. Two subgroups were stratified by patient age (55 years and above vs. below 55 years), and the results indicated that QRLSD was effective in lowering HbA1c levels in both subgroups.
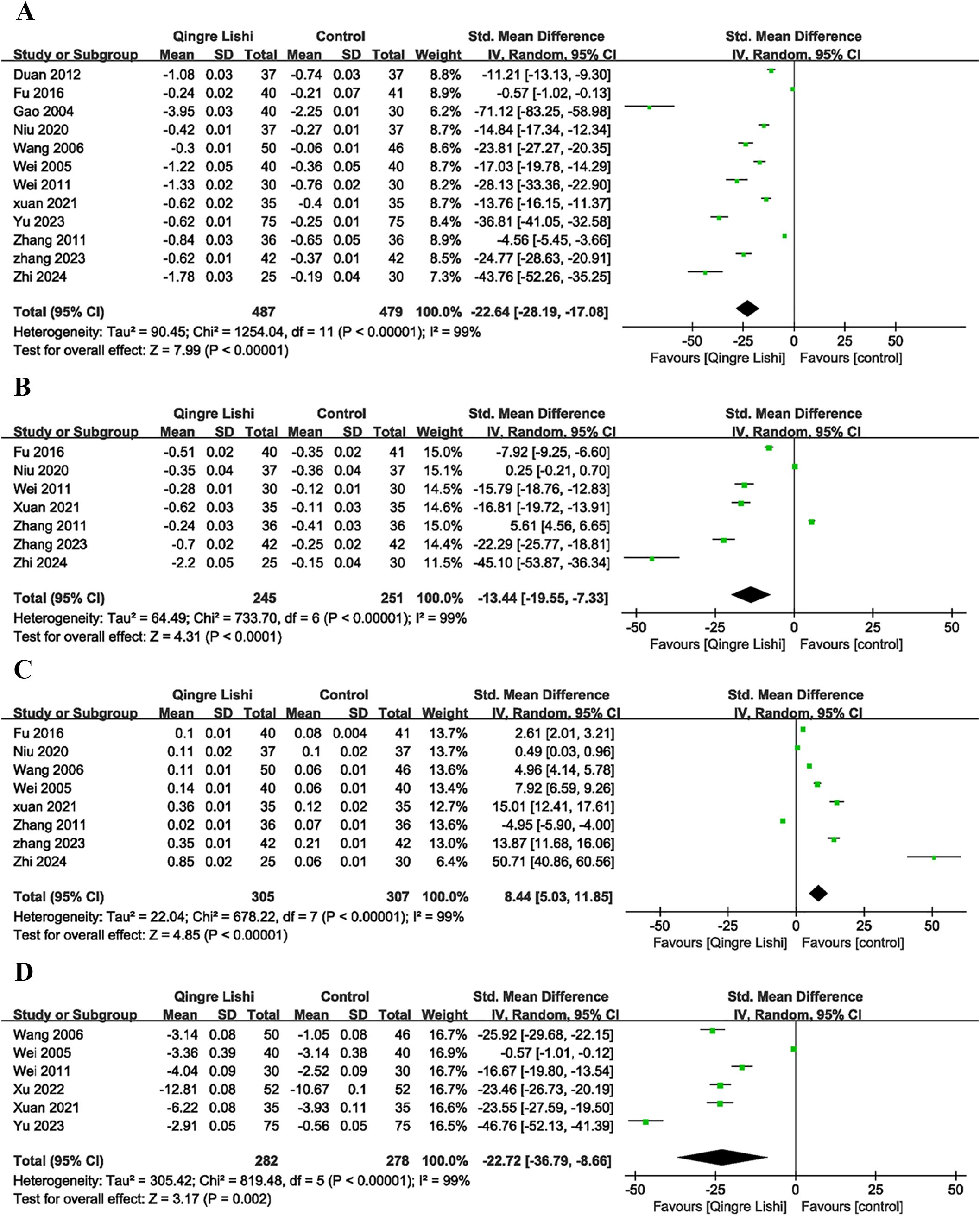
3.7 Change in blood lipids
Some studies included the efficacy of QRLSD in modulating lipid metabolism as the outcome indicator, and reported its positive impact on blood lipid. The results demonstrated that QRLSD, as an adjunct therapy, effectively improved lipid metabolism. The evaluation indicators included improvements in total cholesterol (TC) (Figure 2D; SMD: -12.1; 95% CI: [-15.72, -8.47], I² = 99%, P < 0.00001), triglycerides (TG) (Figure 3A; SMD: -22.64; 95% CI: [-28.19, -17.08], I² = 99%, P < 0.00001), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) (Figure 3B; SMD: -13.44; 95% CI: [-19.55, -7.33], I² = 99%, P < 0.00001), and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) (Figure 3C; SMD: 8.44; 95% CI: [5.03, 11.85], I² = 99%, P <0.00001).
3.8 Change in insulin assessment parameters
Considering the impact of T2D on insulin sensitivity, several studies also measured insulin-related indicators. Six studies measured the levels of fasting insulin (FINs) (Figure 3D; SMD: -22.72; 95% CI: [-36.79, -8.66], I² = 99%, P=0.002), and five measured the homeostasis model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) index (Figure 4A; SMD: -26.36; 95% CI: [-33.64, -19.08], I² = 93%, P=0.01). The results showed that QRLSD improved insulin-related indicators as an adjuvant therapy.
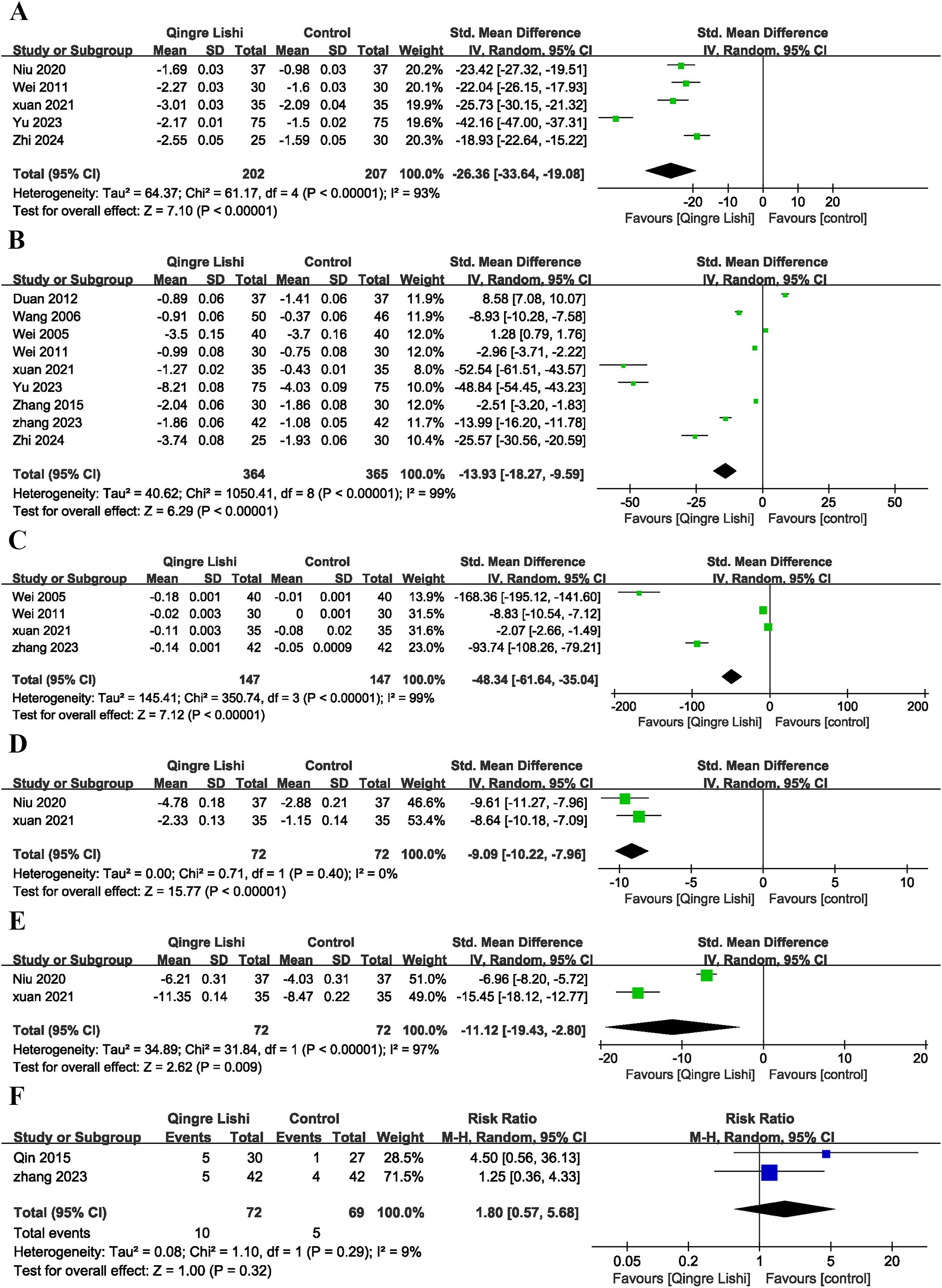
Figure 4. Forest plot. (A) HOME-IR; (B) BMI; (C) WHR; (D) Weight; (E) Waistline; (F) Plot of adverse effects.
3.9 Change in anthropometric indicators
Several studies reported changes in BMI (Figure 4B; SMD: -13.93; 95% CI: [-18.27, -9.59], I² = 99%, P < 0.00001), waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) (Figure 4C; SMD: -48.34; 95% CI: [-61.64, -35.04], I² = 99%, P <0.00001), weight (Figure 4D; SMD: -9.09; 95% CI: [10.22, -7.96], I² = 0%, P <0.00001), and waist circumference (Figure 4E; SMD: -11.12; 95% CI: [-19.43, -4.15], I² = 97%, P=0.009). The results demonstrated that QRLSD, as an adjuvant therapy, was effective in treating T2D, suggesting its role in improving anthropometric indicators.
3.10 Adverse effects
Adverse effects analysis suggested that T2D patients receiving QRLSD as the adjuvant treatment had no significant adverse effects, and the results demonstrated no statistical significance (Figure 4F; RR: 1.8; 95% CI: [0.57, 5.68], I² = 9%, P=0.32).
3.11 Publication bias and sensitivity analysis
Sensitivity analyses for FBG (Figure 5A), 2hpG (Figure 5B), HbA1c (Figure 5C), TC (Figure 5D), TG (Figure 5E), LDL-C (Figure 5F), HDL-C (Figure 5G), FINs (Figure 5H), HOMA-IR (Figure 5I), and BMI (Figure 5J) demonstrated that the results across all indicators were stable. Funnel plots and Egger’s tests demonstrated significant publication bias in FBG (P=0.0001; Figure 6A), 2hPG (P=0.0001; Figure 6B), HbA1c (P=0.0001; Figure 6C), TC (P=0.0001; Figure 6D), TG (P=0.0001; Figure 6E), LDL-C (P=0.039; Figure 6F), HDL-C (P=0.0001; Figure 6G), FINs (P=0.0001; Figure 6H), OME-IR(P=0.004; Figure 6I), and BMI (P=0.027; Figure 6J).
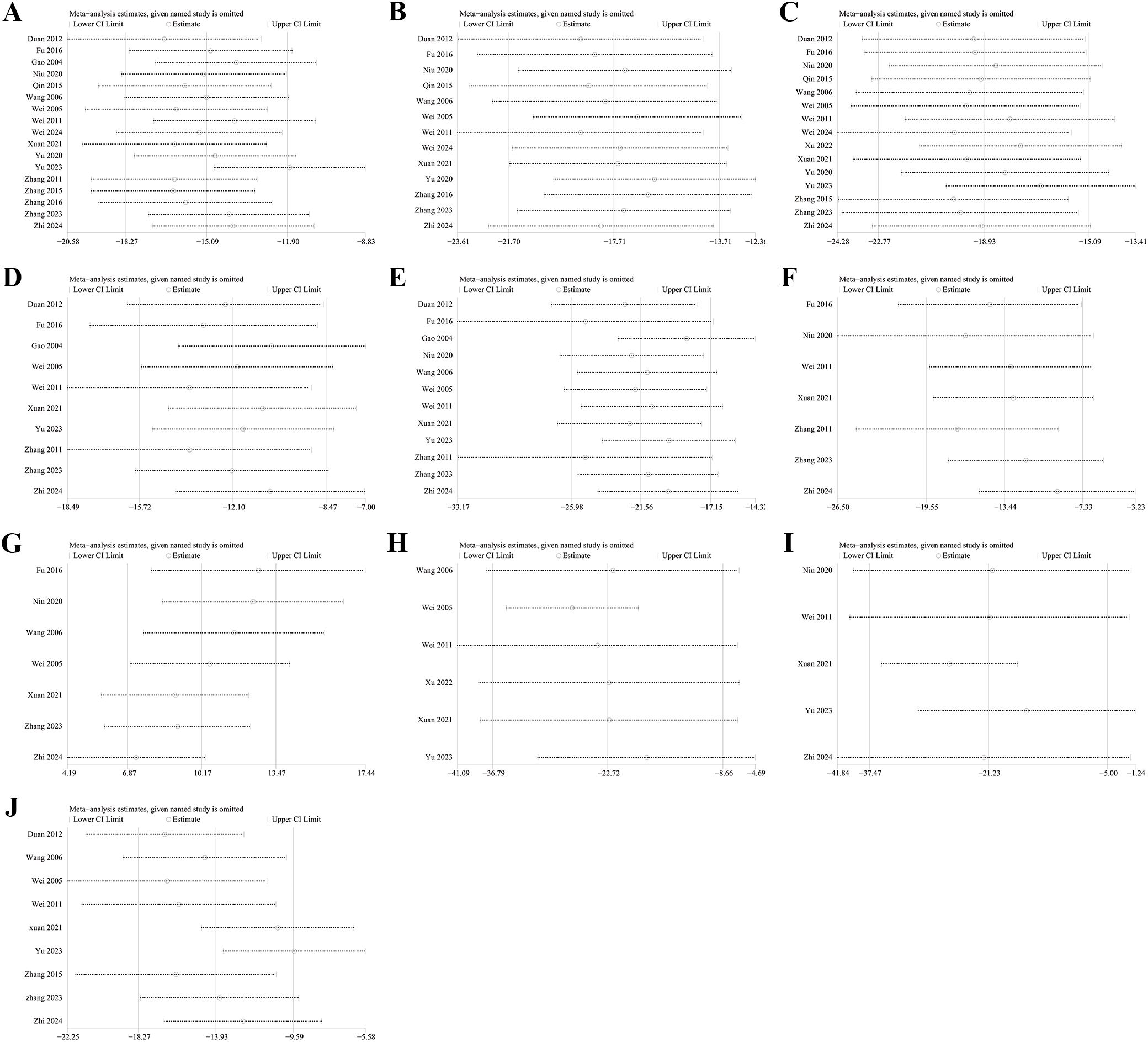
Figure 5. Sensitivity analysis. (A) FBG; (B) 2hPG; (C) HbA1c; (D) TC; (E) TG; (F) LDL-C; (G) HDL-C; (H) FINs; (I) HOME-IR; (J) BMI.
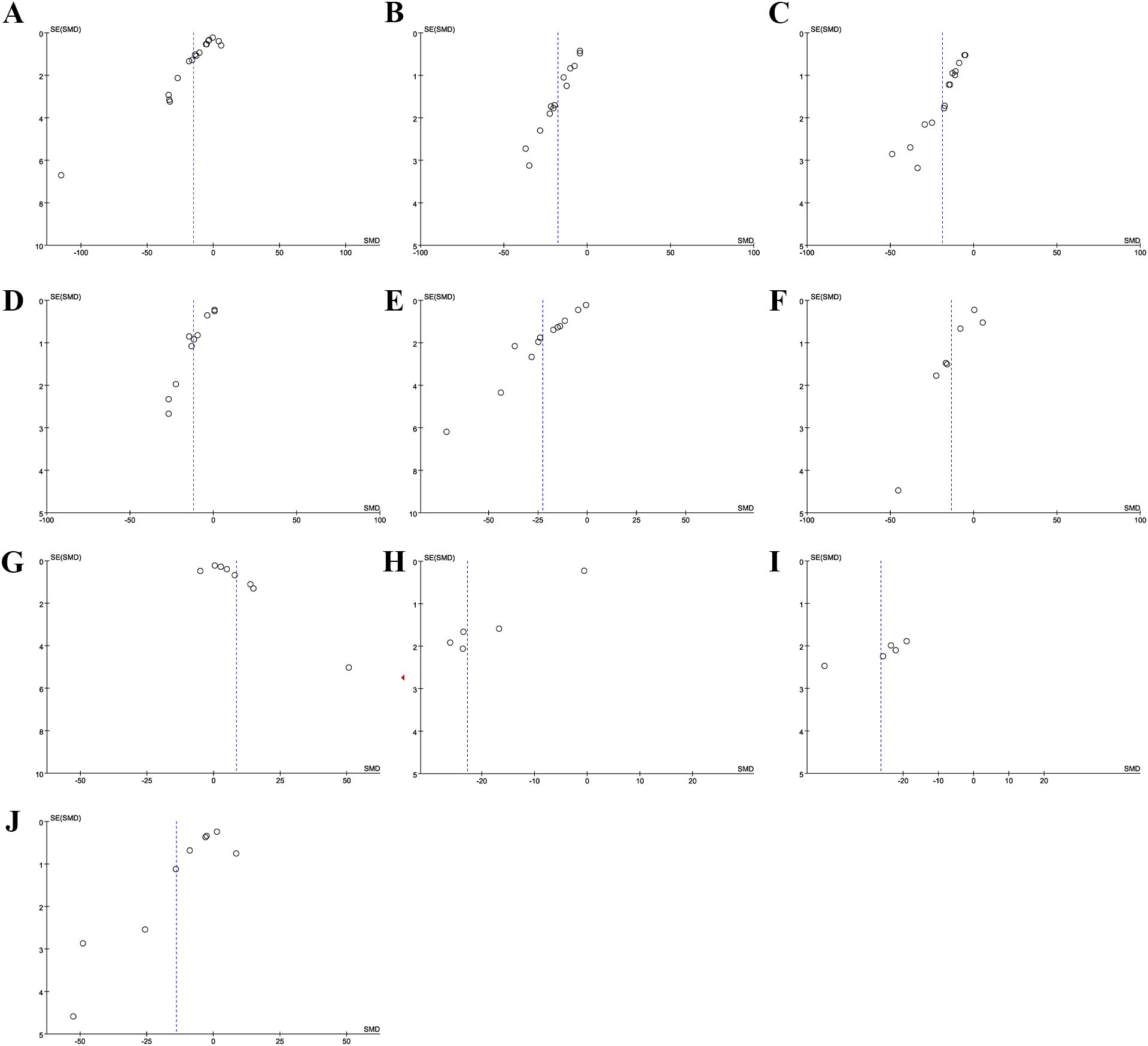
Figure 6. Funnel plot. (A) FBG; (B) 2hPG; (C) HbA1c; (D) TC; (E) TG; (F) LDL-C; (G) HDL-C; (H) FINs; (I) HOME-IR; (J) BMI.
3.12 GRADE assessment
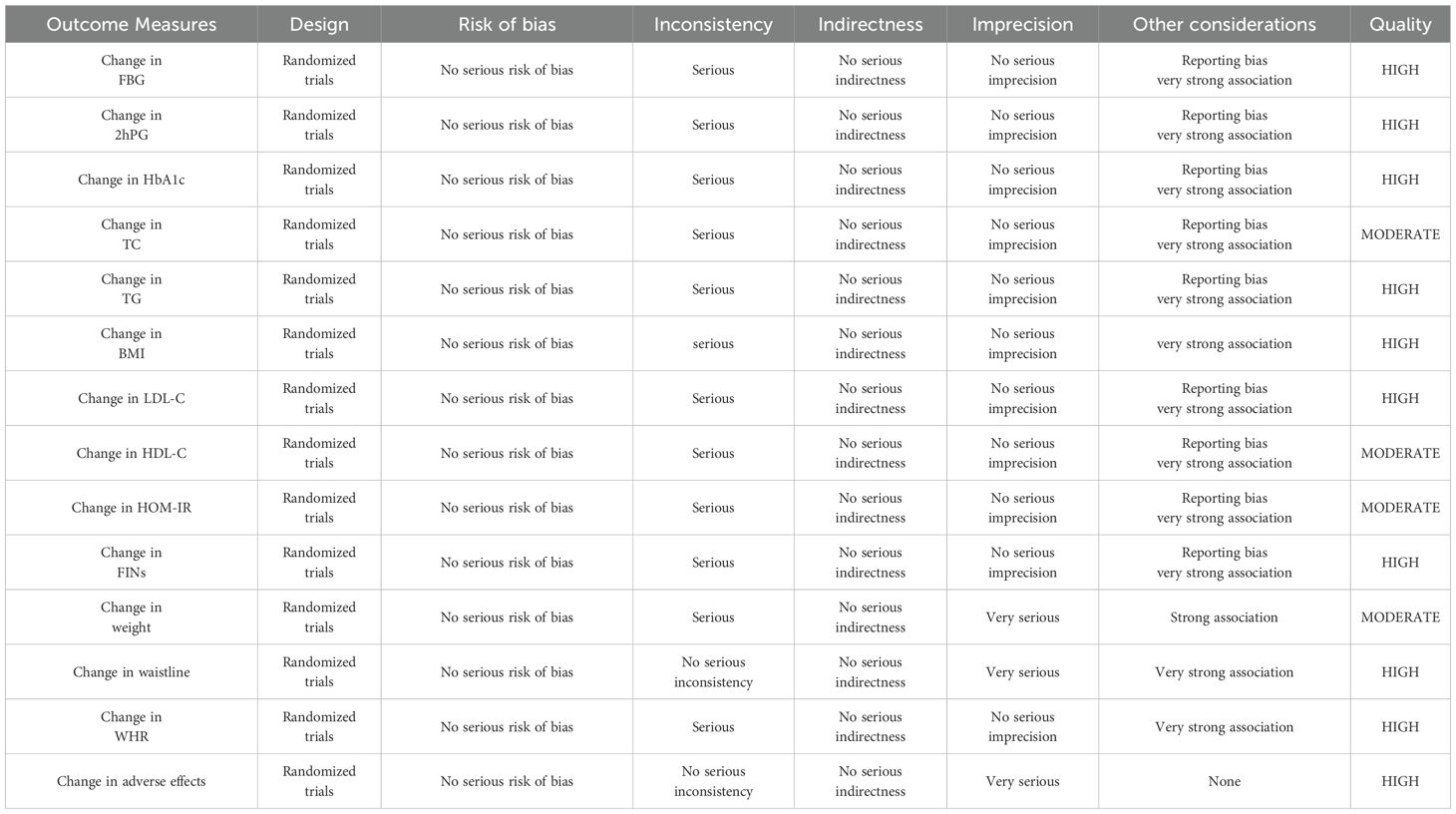
The GRADE approach was used to assess the quality of evidence for all outcomes (Table 4). A total of 14 outcomes were evaluated. For glycemic outcomes, including changes in FBG, 2hPG, and HbA1c, the evidence was rated as high. However, inconsistency was considered serious, primarily due to heterogeneity among patient populations, such as differences in age and BMI. Regarding other considerations, publication bias was detected based on funnel plots and Egger’s test, which was accounted for as a reporting bias.
For lipid-related outcomes, the quality of evidence for improvements in TG and LDL-C was rated as high, and risk factors were similarly stemmed from population differences and potential risk of bias. The quality of evidence for changes in TC and HDL-C was rated as moderate. Although the evidence was directly applicable to the outcomes and sensitivity analyses indicated stability, heterogeneity among populations and risk of bias persisted. For insulin-related outcomes, the quality of evidence for change in FINs was rated as high, and the six included studies differed in population characteristics and were subject to publication bias. The quality of evidence for HOMA-IR improvement was rated as moderate, and the five included studies varied in population characteristics and intervention methods, and were also subject to publication bias. For anthropometric outcomes, the quality of evidence for BMI improvement was rated as high. Although there were differences in baseline body weight and intervention methods, no publication bias was detected. The quality of evidence for waist circumference and WHR was also rated as high, with no publication bias. Waist circumference showed no serious inconsistency. However, due to the small sample size, the precision was rated as very serious. The quality of evidence for weight was rated as moderate, with risks of inconsistency and imprecision. The quality of evidence for adverse events was rated as high. Although the number of included participants was small, the results exhibited a clearly defined null effect range.
4 Discussion
China currently has the largest number of people with diabetes globally, accounting for approximately one-quarter of the world’s total cases. Since the 1970s, lifestyle changes, stress, obesity, and aging have contributed to a persistently high prevalence of T2D in China (36). By 2050, the global death toll from diabetes is projected to reach 1.59 million. While the death rate of type 1 diabetes in China has declined, T2D mortality remains uncontrolled (37). Early diagnosis and treatment of T2D are crucial for improving patients’ quality of life, reducing death rates, and alleviating financial burdens. The treatment of T2D has long been researched in TCM, and it is defined as an emaciation-thirst disease. The classic symptoms of this disease are “three excesses and one deficiency” (polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia, and weight loss). TCM attributes the pathogenesis of T2D to “stagnation, heat, deficiency, and damage,” corresponding to the four stages of diabetes. The treatment of T2D primarily focuses on “heat and deficiency” (38). Some researchers have proposed the “damp-heat-induced thirst” theory, suggesting that damp-heat is the dominant syndrome in T2D patients. Moreover, they have conducted clinical studies based on QRLSD (39).
Our results showed that QRLSD significantly reduced the levels of FBG, 2hPG, and HbA1c. Additionally, QRLSD lowered the values of TC, LDL-C, and TG, as well as elevated the values of HDL-C, suggesting its role in improving metabolism. Furthermore, QRLSD decreased the values of HOMA-IR and FINs, and lowered BMI, WHR, and the values of WC and body weight. Sensitivity analyses indicated stable outcomes across the included studies. Egger’s test suggested potential publication bias, which is a crucial factor affecting the quality of the study.
In recent years, studies focused on TCM decoctions have increased due to their efficacy and minimal side effects. Studies on TCM formulations for treating diabetes have continued, including both classical prescriptions and new therapeutic approaches developed by modern TCM practitioners. A review by X Meng (40) demonstrated that TCM decoctions can reduce insulin resistance, increase the expression of insulin receptors, and stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic β cells, thus effectively controlling blood glucose and mitigating target organ damage. Numerous systematic reviews have also examined the efficacy of TCM decoctions in treating T2D. B Zhou (41) conducted a systematic review on the efficacy of Xiaoke decoction in treating T2D. The results showed that conventional Western medicine treatment combined with Xiaoke decoction was more effective than single Western medicine therapy in improving overall efficacy and lowering the levels of FBG, 2hPG, and HbA1c. Z Zhang (42) evaluated the efficacy of Da Chaihu decoction (DCHD) in treating T2D through a systematic review. It is suggested that when used alone, DCHD can reduce the levels of blood glucose and is relatively safe. Moreover, Western medicine therapy combined with DCHD can provide superior efficacy in regulating glucose-lipid metabolism and improving pancreatic function. A systematic review by Y Tian (43) demonstrated that Huanglian Wendan decoction significantly lowered the levels of blood glucose and lipids when used as an adjunct therapy. These findings validate the reliability of integrating TCM decoctions into T2D treatment.
T2D is closely linked to inflammatory cytokines, with elevated serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 observed in T2D patients. These inflammatory cytokines can impair signal transduction by interfering with insulin-binding sites in insulin signaling pathways, thus causing insulin resistance (44). Additionally, recent studies suggested a strong correlation between gut microbiota and T2D. It indicated that microbiota dysbiosis can trigger inflammation, thereby causing impaired intestinal permeability and glucose-lipid metabolism (45). In TCM, inflammatory diseases are often defined as damp-heat syndrome, and QRLSD can modulate inflammation levels (10).
TCM decoctions are known for their multi-target, holistic regulatory effects. The glucose-lowering pharmacological effects of the most frequently used herbs are summarized in Table 5 (46–64). For compound formulations, these advantages are even more pronounced. GQD, a QRLSD formula, was commonly used in treating T2D. A study indicated that GQD can modulate gut microbiota and maintain intestinal homeostasis (65). Berberine, one of its key components, plays a critical role in modulating gut microbiota for treating T2D and reducing systemic and localized inflammation. Moreover, GQD can prevent high-fat diet-induced obesity and reduce the body weight of the mice models. Compared to metformin, berberine exhibits superior efficacy in regulating gut microbiota (66). Other commonly used QRLSD formulations include YinChen WuLing Powder and YCHD. Qinghao (artemisia annua), a primary component, can regulate metabolism by downregulating the expression of fatty acid synthase via the miR-122 pathway, thereby reducing the levels of blood glucose and lipid (67). A study demonstrated that YCHD can modulate inflammation, remodel vessels, and inhibit the formation and metabolism of adipose tissue. Moreover, it showed that compared to single herbs, decoction formula can significantly enhance the bioactivity of some active components (68). A study indicated that, in comparison to the control group receiving insulin, the levels of interleukin-1 beta, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, and HMGB1 significantly decreased in T2D patients receiving interventions combined with QRLSD. It suggested that active components such as coptis chinensis and anemarrhena asphodeloides contributed to anti-inflammatory effects (27).
A total of 18 studies assessing the efficacy of QRLSD for T2D were included. The efficacy and safety of QRLSD in treating T2D were validated through a comprehensive analysis. Moreover, heterogeneity among major outcomes was investigated through subgroup analyses. Therefore, our findings may provide evidence-based support for further clinical studies.
Due to substantial heterogeneity in some key outcomes, sensitivity analyses were conducted and suggested stable results. To explore potential sources of this heterogeneity, data from the included studies were examined. Notably, the composition of QRLSD varied. The formulations were designed to achieve the effect of clearing heat and removing dampness, and drew on both historical knowledge and clinical experience. The selected herbs belonged to the same functional category but differed in type, which may contribute to heterogeneity. Additionally, intervention methods varied, with some studies applying QRLSD alone and others combining it with other therapies, further contributing to heterogeneity. Subgroup analyses indicated that, for key indicators including FBG, HbA1c, and 2hPG, both QRLSD alone and in combination with Western medicine were effective. The included RCTs and cohort studies involved populations of different ages and baseline indicators. In the intervention groups, mean ages ranged from 44.06 ± 9.55 to 67.27 ± 4.44 years, and in the control groups, from 45.94 ± 10.38 to 65.89 ± 3.84 years. Subgroup analysis using 55 years as a cutoff showed that QRLSD improved key glycemic indicators regardless of age. Follow-up durations also varied across studies, ranging from 4 to 24 weeks, which could contribute to heterogeneity. Subgroup analysis using 12 weeks as a cutoff revealed that the treatment was effective regardless of whether the follow-up duration was longer or shorter than 12 weeks. The included literature comprised 17 RCTs and one cohort study, and differences in study design may also account for some heterogeneity.
Some RCTs did not report allocation concealment or blinding, which may introduce a non-negligible risk of bias. The sample size meeting the inclusion criteria was relatively small, and most studies originated from China. Therefore, significant regional variations within China, along with differences in individual constitutions and local backgrounds, may contribute to publication bias and region-specific selection bias. In addition, studies with positive outcomes are more likely to be published, which could be a source of publication bias. Therefore, further high-quality trials are needed to strengthen the level of evidence.
5 Conclusion
QRLSD can improve the management of T2D by lowering the levels of FBG, 2hPG, HbA1c, LDL-C, BMI, TC, TG, HDL-C, HOMA-IR, body weight, WC, and WHR. Moreover, when combined with conventional Western medications, QRLSD demonstrated superior efficacy compared with Western medications alone, without causing significant adverse effects. These findings suggest that QRLSD may serve as a safe and effective comprehensive treatment option for T2D. However, as most of the included studies were conducted in China and potential heterogeneity and publication bias may exist, further international, multicenter, large-scale RCTs are required to validate the efficacy and safety of QRLSD in T2D management.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
ZL: Formal Analysis, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YS: Writing – review & editing. JL: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. LD: Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2025.1604633/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary File 1 | Search strategy. PRISMA Checklist.
References
1. Wang L, Peng W, Zhao Z, Zhang M, Shi Z, Song Z, et al. Prevalence and treatment of diabetes in China, 2013-2018. JAMA. (2021) 326:2498–506. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.22208
2. GBD 2021 Diabetes Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of diabetes from 1990 to 2021, with projections of prevalence to 2050: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet. (2023) 402:203–34. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(23)01301-6
3. GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. (2020) 396:1204–22. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30925-9
4. Yin JX, Yu L, Pu DL, Xu XL, and Liao Y. Interpretation of the China Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Diabetes. 2024 Edition. Chongqing, China: Journal of Chongqing Medical University (2025) p. 1–8. doi: 10.13406/j.cnki.cyxb.003749
5. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 3. Prevention or delay of diabetes and associated comorbidities: standards of care in diabetes-2025. Diabetes Care. (2025) 48:S50–s8. doi: 10.2337/dc25-S003
6. Qaseem A, Obley AJ, Shamliyan T, Hicks LA, Harrod CS, Crandall CJ, et al. Newer pharmacologic treatments in adults with type 2 diabetes: A clinical guideline from the American college of physicians. Ann Intern Med. (2024) 177:658–66. doi: 10.7326/m23-2788
7. Galdón Sanz-Pastor A, Justel Enríquez A, Sánchez Bao A, and Ampudia-Blasco FJ. Current barriers to initiating insulin therapy in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2024) 15:1366368. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1366368
8. Gao XD and Deng DQ. Research progress on traditional Chinese medicine syndrome type distri-bution in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes New World. (2024) 27:196–8. doi: 10.16658/j.cnki.1672-4062.2024.18.196
9. Zhu L, Li SD, Ye ZG, Cai QJ, Li Z, and Dang HX. Analysis of naming rules of ancient prescriptions based on the names of classical famous TCM prescriptions. J Traditional Chin Med. (2018) 59:1291–4. doi: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2018.15.009
10. Lou YQ and Jiang XH. Research progress on the role of inflammatory factors in the pathogenesis of damp-heat type-2 diabetes and traditional Chinese medicine treatment. J Zhejiang Chin Med University. (2024) 48:881–5, 94. doi: 10.16466/j.issn1005-5509.2024.07.020
11. Zhang QY, Gao JQ, Jiang L, Li BT, Li J, and Xu G. Gegen Qinlian decoction intervention on lipid metabolism of liver fat heterotopic deposition in obese type 2 diabetes. Jiangxi J Traditional Chin Med. (2025) 56:59–62, 6. doi: 10.20141/j.0411-9584.2025.02.16
12. Song Y, Sun YG, Zhang YY, Zhou SQ, Zhang L, Li W, et al. Study on the mechanism of yinchenhao decoction in treating diabetes mellitus based on network pharmacology and experimental verification. China Anim Husbandry Veterinary Med. (2024) 51:4106–19. doi: 10.16431/j.cnki.1671-7236.2024.09.038
13. Wang XC. Study on the Correlation of Metabolic Syndrome Based on the Dampness-Heat Theory of Warm Diseases. Shandong, China: Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2021).
14. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
15. Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. (2011) 343:d5928. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d5928
16. Kim SR, Kim K, Lee SA, Kwon SO, Lee JK, Keum N, et al. Effect of red, processed, and white meat consumption on the risk of gastric cancer: an overall and dose-Response meta-analysis. Nutrients. (2019) 11. doi: 10.3390/nu11040826
17. Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. J Clin Epidemiol. (2011) 64:383–94. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.04.026
18. Duan JN. Clinical study on the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (deficiency of qi and yin and dampness) by adding flavored clear heart and lotus seed drink. Chengdu, China: Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2012).
19. Fu YH. Therapeutic efficacy of Pueraria Mirifica Scutellaria Lian Quenching Thirst Elimination Formula in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus with dampness-heat impregnating the spleen. Gaungzhou, China: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (2016).
20. Gao XF. Clinical observation on the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus by method of clearing heat and inducing dampness. J Zhejiang Chin Med University. (2004) 28:41–2. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5509.2004.05.029
21. Niu S. Clinical observation on the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus with abdominal obesity in the elderly by Strengthening the Spleen, Clearing Heat and Promoting Dampness Soup. Yunnan, China: Yunnan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2020).
22. Qin CY and Liu XX. Clinical efficacy observation on 30 cases of type 2 diabetes mellitus with dampness-heat trapped spleen type treated with addition and subtraction of Artemisia capillaris soup. Diabetes New World. (2015) 5):56–. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4062.2015.05.049
23. Wang ZG. Clinical observation on improvement of insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus by clearing heat and inducing dampness with compound traditional Chinese medicine. Gaungzhou, China: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (2006).
24. Wei D. Clinical study on the treatment of damp-heat pattern of thirst-quenching disease by adding flavored Yin Chen Wu Ling San. Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (2005).
25. Wei LL. Study on the effect of Qingre-Lishi Recipe on insulin resistance in patients with obese type 2 diabetes. Int J Traditional Chin Med. (2011) 33:777–9. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4246.2011.09.003
26. Wei B, Gao T, Li M, Tian X, and Wang J. A real-world observational study on the effect of Qingre Lishi decoction on glycemic profile using continuous glucose monitoring in obese type 2 diabetes adults. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2024) 15:1372593. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1372593
27. Xu J, Tang M, Chen YL, Mi Y, Wu F, and Hu LL. Effects of Qingre Lishi Huatan recipe on TCM syndrome scores,Blood glucose metabolism and serum levels of MCP-1,IL-1βand HMGB1 in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with phlegm-damp-stasis-heat type. Prog Modern Biomed. (2022) 22:3922–6. doi: 10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2022.20.024
28. Xuan CH. Therapeutic efficacy of Clearing Heat, Relieving Dampness and Strengthening the Spleen Formula in treating obese type 2 diabetes mellitus with dampness-heat trapped spleen type. Tangsahn, China: North China University of Science and Technology (2021).
29. Yu B and Lu ZL. Clinical efficacy of spleen-strengthening, heat-removing and dampness-inducing method in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus. Health Guide. (2020) 3):27–8.
30. Yu YM, Ni WH, Qu YH, and Li F. Clinical observation of Qing’re Lishi Huatan Decction and dapagliflozin on type 2 diabetes. J Hubei Univ Chin Med. (2023) 25:29–32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-987x.2023.05.07
31. Zhang GQ, Zhang JF, and Zhao JW. Qinlian Pingwei powder in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and the influence on the blood glucose and lipids. Shaanxi J Traditional Chin Med. (2011) 32:425–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7369.2011.04.022
32. Zhang M and Yue YH. A clinical observation of Jianpi Lishi Fang in treatment of diabetes of early stage. Clin J Traditional Chin Med. (2015) 27:1712–4. doi: 10.16448/j.cjtcm.2015.0634
33. Zhang LY. Clinical efficacy observation of clearing heat and inducing dampness in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus with damp-heat syndrome. Beijing, China: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine (2016).
34. Zhang J, Yang LP, and Pan J. Clinical observation of Qingre Lishi Jianpi Jiangtang recipe combined with acu-point catgut embedding in the treatment of obese type 2 diabetes with dampness-heat disturbing spleen. World J Integrated Traditional Western Med. (2023) 18:98–103. doi: 10.13935/j.cnki.sjzx.230115
35. Zhi BQ, Zhao QJ, Su YJ, Wang HL, Lyu Y, and Hou JJ. Effect of Qingre Lishi Jianpi Jiangtang recipe combined with smeglutide in the treatment of overweight/obesity type 2 diabetes and its effect on glucose and lipid metabolism and insulin secretion. Prog Modern Biomed. (2024) 24:2934–8. doi: 10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2024.15.025
36. Xu Y, Lu J, Li M, Wang T, Wang K, Cao Q, et al. Diabetes in China part 1: epidemiology and risk factors. Lancet Public Health. (2024) 9:e1089–e97. doi: 10.1016/s2468-2667(24)00250-0
37. Dong C, Wu G, Li H, Qiao Y, and Gao S. Type 1 and type 2 diabetes mortality burden: Predictions for 2030 based on Bayesian age-period-cohort analysis of China and global mortality burden from 1990 to 2019. J Diabetes Investig. (2024) 15:623–33. doi: 10.1111/jdi.14146
38. Tong XL, Jia WP, Wang XG, Yang SY, Ni Q, and Li M. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus with integrated Chinese and western medicine. Jilin J Traditional Chin Med. (2024) 44:1117–27. doi: 10.13463/j.cnki.jlzyy.2024.10.001
39. Xu CQ, Zheng CX, Xu T, Cheng RD, and Fang CH. Exploration of the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus based on the theory of “dampness-heat-induced thirst. J Shaanxi Coll Traditional Chin Med. (2023) 46:36–9. doi: 10.13424/j.cnki.jsctcm.2023.01.007
40. Meng X, Liu X, Tan J, Sheng Q, Zhang D, Li B, et al. From Xiaoke to diabetes mellitus: a review of the research progress in traditional Chinese medicine for diabetes mellitus treatment. Chin Med. (2023) 18:75. doi: 10.1186/s13020-023-00783-z
41. Zhou B, Zhang G, Guo W, Ren C, and Li M. Xiaoke Decoction in treatment of type II diabetes: A Meta-analysis. Chin Herb Med. (2022) 14:130–41. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2021.08.004
42. Zhang Z, Leng Y, Fu X, Yang C, Xie H, Yuan H, et al. The efficacy and safety of dachaihu decoction in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:918681. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.918681
43. Tian Y, Pang G, and Pan L. Clinical efficacy of Huanglian Wendan decoction in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Med (Baltimore). (2023) 102:e35299. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000035299
44. Wei YQ. Research progress in the relationship between chronic inflammation and insulin resistance. J Clin Pathological Res. (2019) 39:640–5. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2095-6959.2019.03.030
45. Gurung M, Li Z, You H, Rodrigues R, Jump DB, Morgun A, et al. Role of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology. EBioMedicine. (2020) 51:102590. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.11.051
46. Chen ZX and Zhai CM. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Coptis chinensis. Harbin Med J. (2025) 45:131–5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8131.2025.01.043
47. Tan D, Tseng HHL, Zhong Z, Wang S, Vong CT, and Wang Y. Glycyrrhizic acid and its derivatives: promising candidates for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23. doi: 10.3390/ijms231910988
48. Sun L, Di YM, Lu C, Guo X, Tang X, Zhang AL, et al. Additional benefit of chinese medicine formulae including dioscoreae rhizome (Shanyao) for diabetes mellitus: current state of evidence. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2020) 11:553288. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.553288
49. Zhang DD, Wan WB, Yao Q, Li F, Yao ZY, and Ye XC. Exploring the mechanism of Poria cocos aqueous extract in lowering blood glucose by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS combined with network pharmacology and experimental verification. China J Chin Materia Medica. (2025) 50:3980–9. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20250304.403
50. Yingrui W, Zheng L, Guoyan L, and Hongjie W. Research progress of active ingredients of Scutellaria baicalensis in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and its complications. BioMed Pharmacother. (2022) 148:112690. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112690
51. Jia YH, Song K, and Tian Y. Research progress on main chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Atractylodes macrocephala. Shanghai J Traditional Chin Med. (2025) 59:96–100. doi: 10.16305/j.1007-1334.2025.z20250228006
52. Zuo J, Mu JG, and Hu XY. Research progress on chemical constituents and modern pharmacological effects of Pinellia ternata. J Liaoning Univ Traditional Chin Med. (2019) 21:26–9. doi: 10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2019.09.007
53. Guan XT, Yang HN, Zhang JC, and Xu JY. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium. Chin Arch Traditional Chin Med. (2024) 42:41–9 + 8. doi: 10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2024.06.008
54. Kou B, Meng L, Zhao M, Wang H, Lu C, Yan M, et al. Unveiling the power of Pueraria lobata: a comprehensive exploration of its medicinal and edible potentials. Front Pharmacol. (2025) 16:1578472. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1578472
55. Li J, Liu J, Shi W, and Guo J. Role and molecular mechanism of Salvia miltiorrhiza associated with chemical compounds in the treatment of diabetes mellitus and its complications: A review. Med (Baltimore). (2024) 103:e37844. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000037844
56. Zhang Y, Chen Z, Chen L, Dong Q, Yang DH, Zhang Q, et al. Astragali radix (Huangqi): a time-honored nourishing herbal medicine. Chin Med. (2024) 19:119. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-00977-z
57. Zhang N, Ren L, Li CY, Luo BB, Tao Y, and Guo C. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of volatile oil from Atractylodes macrocephala. Chin Arch Traditional Chin Med. (2025) 43:179–85 + 262. doi: 10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2025.09.033
58. Zhao JH, Li X, Wu WX, Hu JH, Duan Y, Wu XH, et al. Research progress on pharmacological effects of Rehmanniae Radix extract and its active components. Drug Eval Res. (2024) 47:2443–8. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-6376.2024.10.026
59. Hu ZQ, Cheng BB, Jia JJ, Bian XR, He XLS, Chen SH, et al. Research progress on the mechanism of Alisma orientale and its active components in treating metabolic diseases. Chin J Modern Appl Pharmacy. (2024) 41:2156–66. doi: 10.13748/j.cnki.issn1007-7693.20231126
60. Zhao Y, Zuo J, Hu XY, and Yu ZN. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Crataegi Folium and Crataegi Fructus. Guiding J Traditional Chin Med Pharmacy. (2025) 31:145–51. doi: 10.13862/j.cn43-1446/r.2025.08.023
61. Huang LP, Xu YH, Deng MZ, and Zhou ZL. Research progress on chemical constituents, pharmacological mechanism and clinical application of Artemisiae Scopariae Herba. Natural Product Res Dev. (2021) 33:676–90. doi: 10.16333/j.1001-6880.2021.4.018
62. Zhao X, Jia W, Liu L, Bi Q, Zhang G, and Xu J. Study on the therapeutic effect of active components of Codonopsis pilosula on type II diabetic mice. Qinghai Sci Technol. (2023) 30:73–80. doi: CNKI:SUN:QKKJ.0.2023-01-010
63. Pan YL, Zhao CK, Li H, Zheng ZZ, and Zheng XY. Research progress on the effect of Coicis Semen on type 2 diabetes. J Shanxi Univ Chin Med. (2024) 25:224–8. doi: 10.19763/j.cnki.2096-7403.2024.02.20
64. Gong DH, Leng JC, and Yang YJ. Application technology of Zingiber officinale and its active functions in regulating and lowering blood glucose. China Condiment. (2020) 45:190–3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2020.09.038
65. Wang X, Quan J, Xiu C, Wang J, and Zhang J. Gegen Qinlian decoction (GQD) inhibits ulcerative colitis by modulating ferroptosis-dependent pathway in mice and organoids. Chin Med. (2023) 18:110. doi: 10.1186/s13020-023-00819-4
66. Xu X, Gao Z, Yang F, Yang Y, Chen L, Han L, et al. Antidiabetic effects of Gegen Qinlian decoction via the gut microbiota are attributable to its key ingredient berberine. Genomics Proteomics Bioinf. (2020) 18:721–36. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2019.09.007
67. Tavares WR, Seca AML, and Barreto MC. Exploring the therapeutic potential of artemisia and salvia genera in cancer, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases: A short review of clinical evidence. J Clin Med. (2025) 14. doi: 10.3390/jcm14031028
Keywords: efficacy, Qingre Lishi decoction, type 2 diabetes, systematic review, meta-analysis
Citation: Lin Z, Sun Y, Li J and Du L (2025) Efficacy and safety of Qingre Lishi decoction for type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1604633. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1604633
Received: 02 April 2025; Accepted: 02 October 2025;
Published: 20 October 2025.
Edited by:
Sunil Christudas, The University of Texas Health Science Center at Tyler, United StatesReviewed by:
Xiaofei Yang, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, ChinaVishal Dubey, Sundyota Numandis Probioceuticals Pvt. Ltd., India
Copyright © 2025 Lin, Sun, Li and Du. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Likun Du, ZHVsaWt1bkBobGp1Y20uZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Zimei Lin
Zimei Lin Yi Sun2†
Yi Sun2†