- 1Department of Pathology, Deyang People’s Hospital, Deyang, China
- 2Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, The Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China
- 3Department of Ophthalmology, First People’s Hospital of Zigong, Zigong, Sichuan, China
- 4Department of Oncology, the Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China
- 5Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, The Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China
Background: Diabetes is a prevalent chronic metabolic disorder, and the rising rates of this condition, along with its complications, significantly threaten public health. Traditional treatments for diabetes have certain limitations in practical applications, and it is particularly important to find new, effective treatments with fewer side effects. With a long history and rich experience, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) effectively treats diabetes.
Methods: Data from randomized controlled trials concerning TCM and its effects on diabetes were gathered and analyzed from various databases. A meta-analysis was conducted on the 58 selected articles, and the potential mechanisms of action of the active ingredients in TCM were examined using network pharmacology techniques.
Results: Meta-analysis of 58 randomized trials (n=7,318) demonstrated significant improvements in fasting glucose (MD=-0.53 mmol/L [-0.67,-0.39], P<0.00001), HbA1c (MD=-0.40% [-0.61,-0.20], P = 0.0001), and insulin resistance (HOMA-IR: MD=-0.90 [-1.51,-0.29], P = 0.004), alongside favorable lipid modulation (LDL: MD=-0.14 mmol/L, P = 0.0002). Network pharmacology revealed six core herbs (Astragalus membranaceus, Coptis chinensis, etc.) targeting 32 hub genes (AKT1, IL1B, PPARG, etc.) through three key pathways: insulin signaling (PI3K-AKT), inflammatory regulation (TNF/IL-17), and oxidative stress response (HIF-1/NRF2 axis). The polypharmacological effects were mediated by multi-component interactions involving quercetin, kaempferol, and stigmasterol.
Conclusion: TCM has demonstrated considerable effectiveness in managing diabetes. Through meta-analysis and network pharmacology research, this translational study establishes Level 1a evidence for TCM’s antidiabetic efficacy while decoding its systems-level mechanisms. The integrated methodology provides a paradigm for evaluating complex herbal interventions in metabolic disorders.
Systematic Review Registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO, identifier CRD42024572433.
1 Introduction
Diabetes, a chronic metabolic disease prevalent worldwide, is marked by persistently elevated blood glucose levels. This condition results from either inadequate insulin secretion or diminished insulin sensitivity. As per the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), the global adult population affected by diabetes exceeded 536.6 million in 2021, and this figure is expected to rise in the future (1). Diabetes has profound effects on patients’ quality of life and can lead to several complications, such as cardiovascular disease, nephropathy, retinopathy, and neuropathy. These complications present significant challenges to public health (2).
Currently, traditional diabetes treatment strategies primarily include lifestyle interventions (dietary control, exercise therapy) (3) and pharmacological interventions (oral hypoglycemic agents such as metformin, sulfonylureas, thiazolidinediones, SGLT2 inhibitors, GLP-1 RAs, DPP-4 inhibitors, as well as insulin injections, etc.) (4). Although these methods have achieved certain efficacy in glycemic control, they still face numerous challenges and limitations in clinical application. Long-term medication may induce a series of side effects, such as hypoglycemia risk (especially with sulfonylureas and insulin therapy), weight gain, gastrointestinal discomfort (metformin, GLP-1 receptor agonists), genitourinary tract infections (SGLT2 inhibitors), and potential hepatorenal toxicity (5–9). Furthermore, poor long-term treatment adherence is also a widespread issue; complex medication regimens, frequency of drug administration, frequent blood glucose monitoring, and the discomfort associated with injection therapy all impact treatment effectiveness (10–13). More critically, diabetes and its complications impose a substantial economic burden on patients and society, including high drug costs, frequent medical visits, hospitalization expenses, and disability and reduced work capacity due to complications (14). These challenges and limitations in clinical practice underscore the urgent need for effective, safe, economical, and patient-friendly alternative or complementary therapies.
Against this backdrop, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), with its millennia-long history and unique theoretical framework, offers valuable insights and perspectives for diabetes management. Accumulating clinical and preclinical evidence, particularly in recent years, continues to highlight the potential advantages of TCM interventions in diabetes care. Firstly, unlike single-target Western drugs, TCM formulas—typically comprising multiple herbs—exert synergistic effects on multiple pathways involved in glucose metabolism, insulin resistance, beta-cell function, inflammation, and oxidative stress. This multi-target action aligns with TCM’s holistic philosophy and may address diabetes’ complex pathophysiology more comprehensively (15, 16). Critically, modern phytochemical research has identified a plethora of bioactive metabolites isolated from TCM herbs that underpin these therapeutic effects. Key compounds such as berberine (from Coptis chinensis), astragaloside IV (from Astragalus membranaceus), ginsenosides (from Panax ginseng), and polyphenols (e.g., from Quinoa) have demonstrated significant anti-diabetic properties in mechanistic studies. These include enhancing insulin sensitivity, promoting β-cell regeneration, and suppressing inflammatory cascades (17–19). This scientific validation of active constituents provides a molecular basis for TCM’s efficacy and bridges traditional knowledge with modern pharmacology. Secondly, TCM employs individualized treatment through Syndrome Differentiation and Treatment (A core principle of TCM that involves identifying syndromes based on clinical manifestations and formulating corresponding therapies). Diagnosis classifies diabetic patients into distinct patterns (e.g., Yin Deficiency with Dryness-Heat, Qi and Yin Deficiency, Spleen Deficiency with Dampness), enabling customized herbal prescriptions, potentially yielding better personalized outcomes (20–22). Thirdly, TCM demonstrates potential for reducing complications. Specific herbs and formulas show protective effects against diabetic nephropathy, retinopathy, and neuropathy in preclinical and clinical studies, primarily through anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and microcirculation-improving mechanisms (23–25).Finally, systematic reviews and meta-analyses indicate TCM interventions, when properly administered, exhibit a relatively favorable safety profile. They are associated with lower incidence of adverse events—particularly severe hypoglycemia and gastrointestinal issues—compared to conventional hypoglycemic agents. This suggests suitability for long-term management or adjunctive therapy (26, 27).
However, despite its promising prospects, the application of TCM in diabetes remains challenging. Clinical evidence remains heterogeneous due to differences in study design (e.g., sample size, duration of treatment, and control settings), TCM formulations (standardization, batch variability), and populations (ethnicity, region, and syndrome type). Furthermore, the complex multi-component and multi-target nature of TCM poses significant challenges to elucidating its precise mechanisms of action using traditional single-target approaches, which, to a certain extent, limits its wider understanding and acceptance. In order to more systematically evaluate clinical efficacy, overcome the limitations of individual studies, and deeply explore its complex mechanism of action, this study employs an integrated strategy combining meta-analysis and network pharmacology. This methodological choice is critical: Meta-analysis provides a rigorous quantitative synthesis of existing randomized controlled trial (RCT) data to derive more precise and generalizable estimates of TCM’s overall clinical efficacy and safety profile in DM management (27, 28), overcoming the limitations of individual studies and establishing robust clinical evidence. Meanwhile, network pharmacology offers a powerful systems biology framework to systematically predict and analyze the interactions between bioactive TCM components, their potential targets, and the associated biological pathways and networks involved in DM pathogenesis (29, 30), uniquely suited to decipher the complex, multi-target mechanisms underlying TCM’s therapeutic effects.
Therefore, the objective of this study is to comprehensively assess the effectiveness and safety of TCM for treating diabetes mellitus, and to investigate its mechanism of action through the integration of meta-analysis and network pharmacology. We will analyze the advantages and shortcomings of TCM in diabetes management by reviewing relevant literature and experimental studies, providing scientific basis and new ideas for comprehensive treatment of diabetes, and promoting the application and development of TCM in modern medicine.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Meta-analysis
2.1.1 Literature search strategy
In line with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines, the meta-analysis ensured methodological rigor and high-quality reporting, enhancing the study’s reliability and transparency. Electronic and manual literature searches were conducted independently by two authors in PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases for reports published up to December 15, 2024, with no language restrictions. The comprehensive search strategy is outlined in the Supplementary Material. The protocol for this review was registered with PROSPERO (CRD42024572433).
2.1.2 Criteria of eligibility
The criteria for inclusion and exclusion are detailed in Table 1.
2.1.3 Study selection and data extraction
In alignment with PRISMA guidelines, the literature search and screening processes were conducted independently by two researchers using the predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria. For doubtful pilot studies, which could not be determined after full discussion, the corresponding author ruled on inclusion. Extracted information for inclusion in the study included: first author, year of publication, sample content, mean age or age range, commonly used treatments (protocols), TCM interventions, control interventions, duration, and outcome indicators.
2.1.4 Risk of methodological bias assessment
To assess the methodological rigor of the selected literature, two investigators independently appraised it using the Cochrane Handbook for Evaluating Randomized Controlled Trials (version 5.1.0). Results were cross-verified to ensure consistency. The manual covers randomization of sequence generation (selection bias), allocation concealment (selection bias), blinding of participants and personal (performance bias), blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias), incomplete outcome data (attrition bias), selective reporting (reporting bias), and other biases. To complete this section, we utilized the risk assessment tool in Review Manager 5.3 software. Disagreements in risk evaluations were resolved through discussion or, if necessary, consultation with an impartial third party.
2.1.5 Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis of the data was performed using RevMan 5.3 software for meta-analysis and STATA SE18.0 for comprehensive statistical evaluation. This included data summarization and the creation of forest plots. Continuous variables were represented as mean difference (MD), and the effect size indicator was presented with a 95% confidence interval (CI). If significant heterogeneity was detected between the groups (p < 0.1 or I² > 50%), either a subgroup analysis or sensitivity analysis was performed to identify and address potential sources of heterogeneity. In cases where heterogeneity persisted despite clinical homogeneity, a random effects model was employed; otherwise, a fixed effects model was utilized. Sensitivity analysis, conducted using STATA SE18.0, assessed the robustness of the included studies against various methodological biases. Additionally, publication bias was evaluated through Begg’s test (31) and Egger’s test (32), using STATA SE18.0 software.
2.2 Network pharmacology
2.2.1 Network pharmacology study of effective TCM components for diabetes
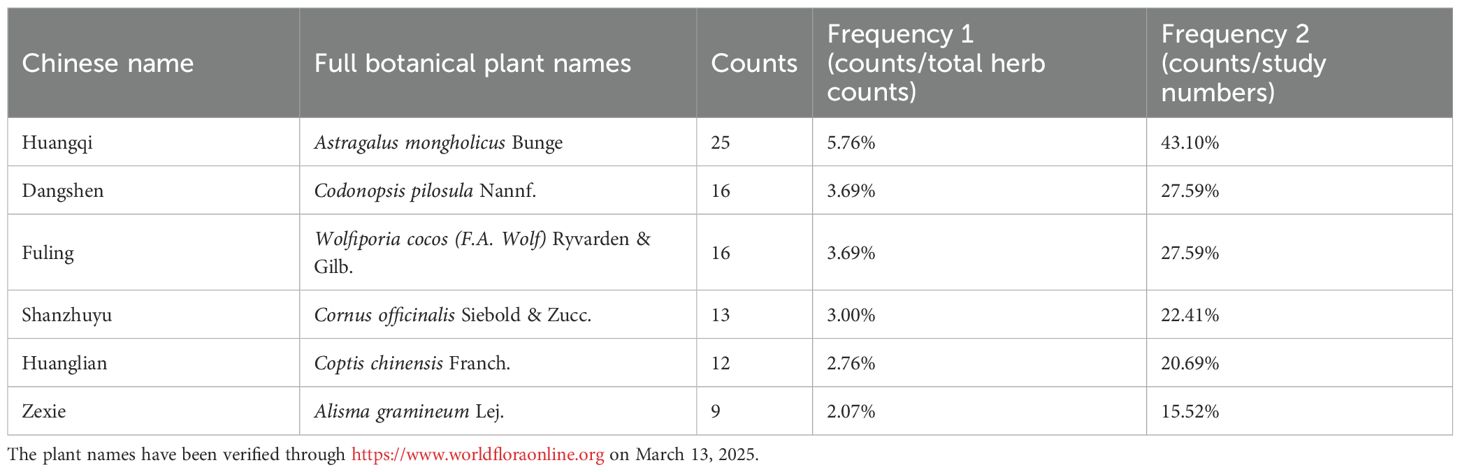
TCM prescriptions identified from the meta-analyses were organized according to their frequency of use. Herbs that appeared more than seven times were selected as primary research targets, including Huangqi (Astragalus mongholicus Bunge), Fuling (Wolfiporia cocos (F.A. Wolf) Ryvarden & Gilb.), Shanzhuyu (Cornus officinalis Siebold & Zucc.), Huanglian (Coptis chinensis Franch.), Zexie (Alisma gramineum Lej.), and Dangshen (Codonopsis pilosula Nannf.). The bioactive compounds of the herbal medicines identified from the meta-analysis were retrieved from the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform (TCMSP, http://www.tcmsp-e.com/) (33). For each herb, all compounds listed in TCMSP were collected. Compounds were then screened according to the commonly applied pharmacokinetic parameters: oral bioavailability (OB) ≥ 30% and drug-likeness (DL) ≥ 0.18. These criteria are recommended in TCMSP to select compounds with favorable absorption and drug-like properties. The herb–compound relationships were directly obtained from the TCMSP records, ensuring that each bioactive compound was accurately linked to its source herb. After screening, compounds present in multiple herbs and/or with high degree values in the subsequent network analysis, such as quercetin, kaempferol and stigmasterol, were identified as representative constituents for further network pharmacology analysis. Human gene information was then obtained from The Universal Protein Database (UniProt, https://www.uniprot.org/) (34) to annotate the target sites of these bioactive components.
2.2.2 Identifying disease targets for diabetes
Our team employed the keyword “diabetes” to identify disease targets related to diabetes across several databases, including DisGeNet (https://www.disgenet.org/), GeneCards (https://www.genecards.org/), OMIM (http://omim.org/), TTD (http://db.idrblab.net/ttd/), and CTD (https://ctdbase.org/).
2.2.3 Acquisition of TCM-diabetes intersection genes and construction of protein interaction network
The Venn package was utilized to identify intersecting genes between TCM components and diabetes. These intersecting genes were subsequently imported into the STRING database (https://stringdb.org/), with the selection criteria set to humans as the genus group and a confidence score > 0.4, while excluding independent protein molecules. The resulting data were then imported into Cytoscape 3.8.2 (35) to construct a molecular network diagram illustrating the interactions between TCM components and the identified intersecting genes.
2.2.4 TCM-Determination of core genes in diabetes
Hub genes were identified using the cytoHubba plug-in within Cytoscape software. To evaluate and select the core genes, six commonly used algorithms were applied: MNC (Maximum Neighborhood Component), Degree, Closeness, Radiality, Stress, and EPC (Edge Percolated Component).
2.2.5 GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis
To elucidate the enriched pathways associated with drug targets and diabetes-related genes, we performed functional enrichment analysis on significant gene clusters. This included Gene Ontology (GO) analysis, which covered Biological Processes (BP), Cellular Components (CC), and Molecular Functions (MF). Additionally, KEGG pathway analysis and Disease Ontology (DO) analysis was conducted. The analyses were carried out using several R packages, including clusterProfiler, org.Hs.eg.db, enrichplot, circlize, RColorBrewer, and ComplexHeatmap. Filtering criteria were applied with p-value < 0.05 and q-value < 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Meta-analysis
3.1.1 Identification and selection
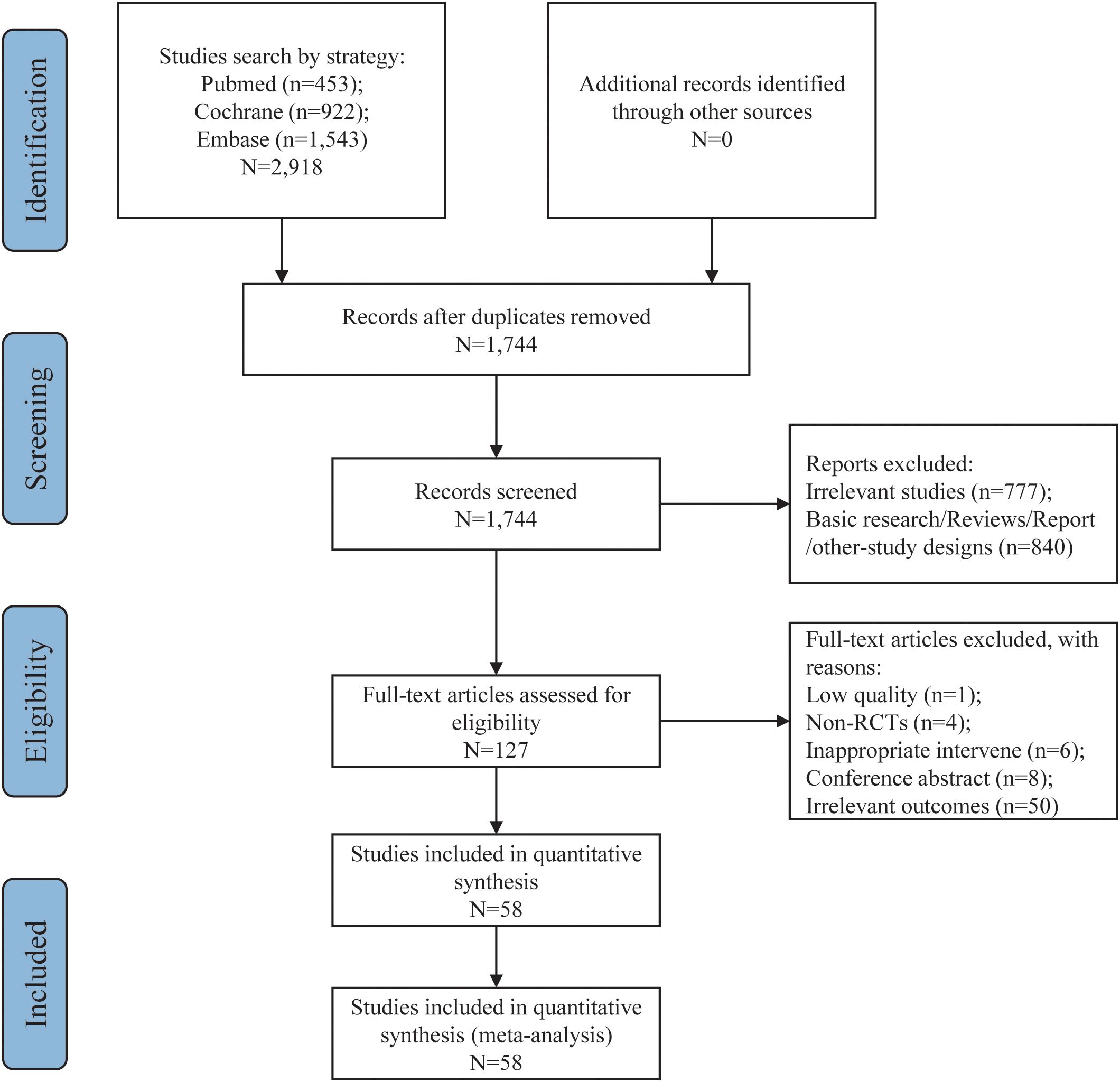
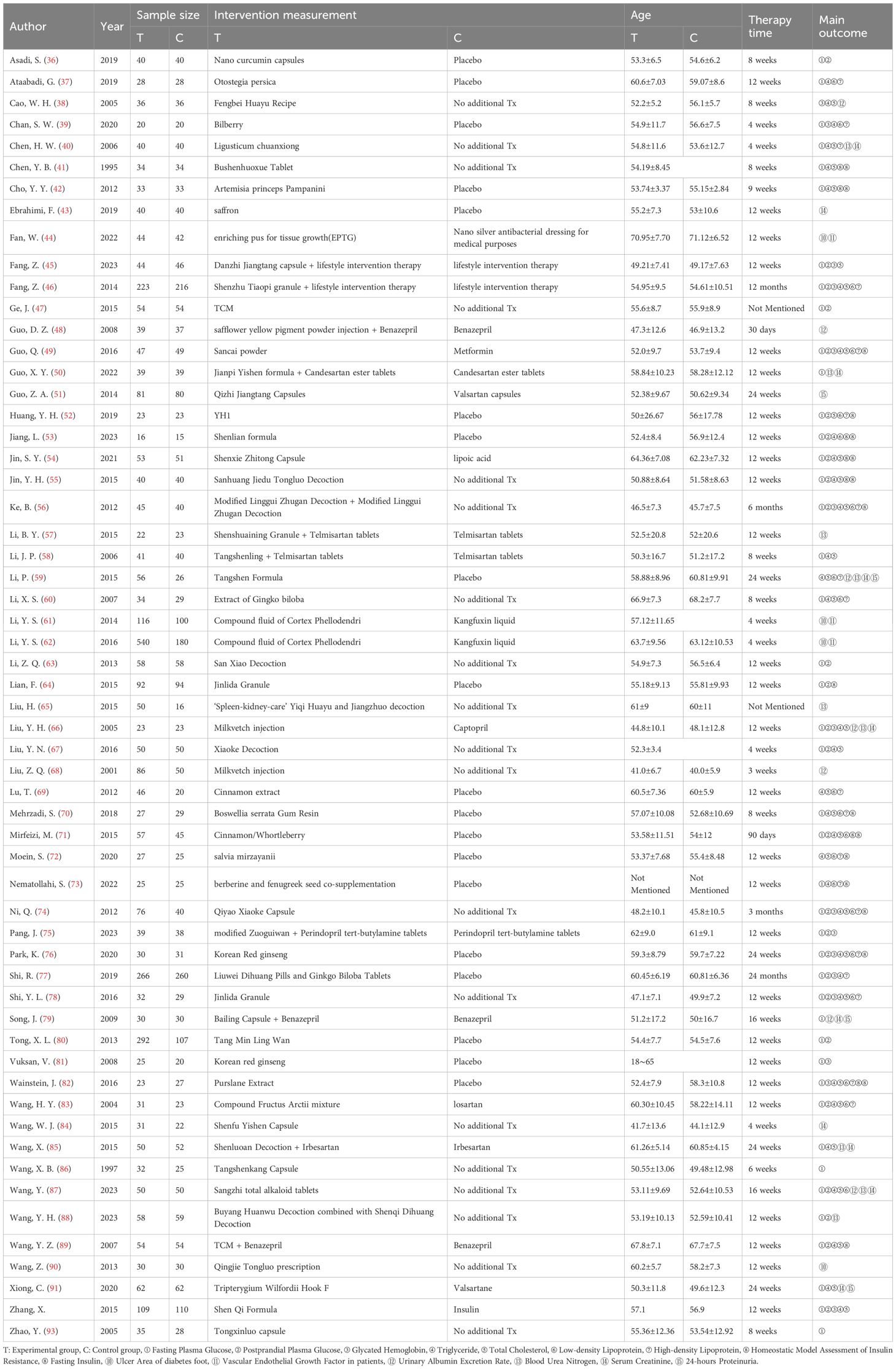
From an initial pool of 2,918 documents, 1,744 candidate articles were identified following the removal of 1,174 duplicates. After reviewing titles and abstracts, 1,617 irrelevant papers were excluded. The remaining 127 articles were further evaluated in full text according to the predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria. This process led to the selection of 58 articles for inclusion in the meta-analysis (36–93). The study selection flowchart is illustrated in Figure 1, and Table 2 provides a summary of the key characteristics of these 58 articles.
3.1.2 Assessment of risk of bias
The results of the risk of bias assessment are detailed in Figure 2. All studies included in the analysis employed randomization techniques. Specifically, 18 studies used the random number table method, while the remaining 4 used various techniques: permuted block randomization (36), paired randomization (41), random allocation software (78), and stratified randomization (88). These studies were classified as having a low risk of bias. Studies that did not specify their randomization methods were categorized as having an unclear risk of bias. Three studies (48, 75, 82) implemented allocation concealment through group randomization, whereas other studies did not report this approach. Additionally, 20 studies specified the use of double-blinding, while 3 studies (44, 53, 71) indicated blinding of outcome assessors. The remaining studies did not provide details on blinding procedures for investigators, patients, or outcome assessors. All studies with available data were generally assessed as having a low risk of bias. Furthermore, there was no evidence of other biases or selective reporting across the trials.
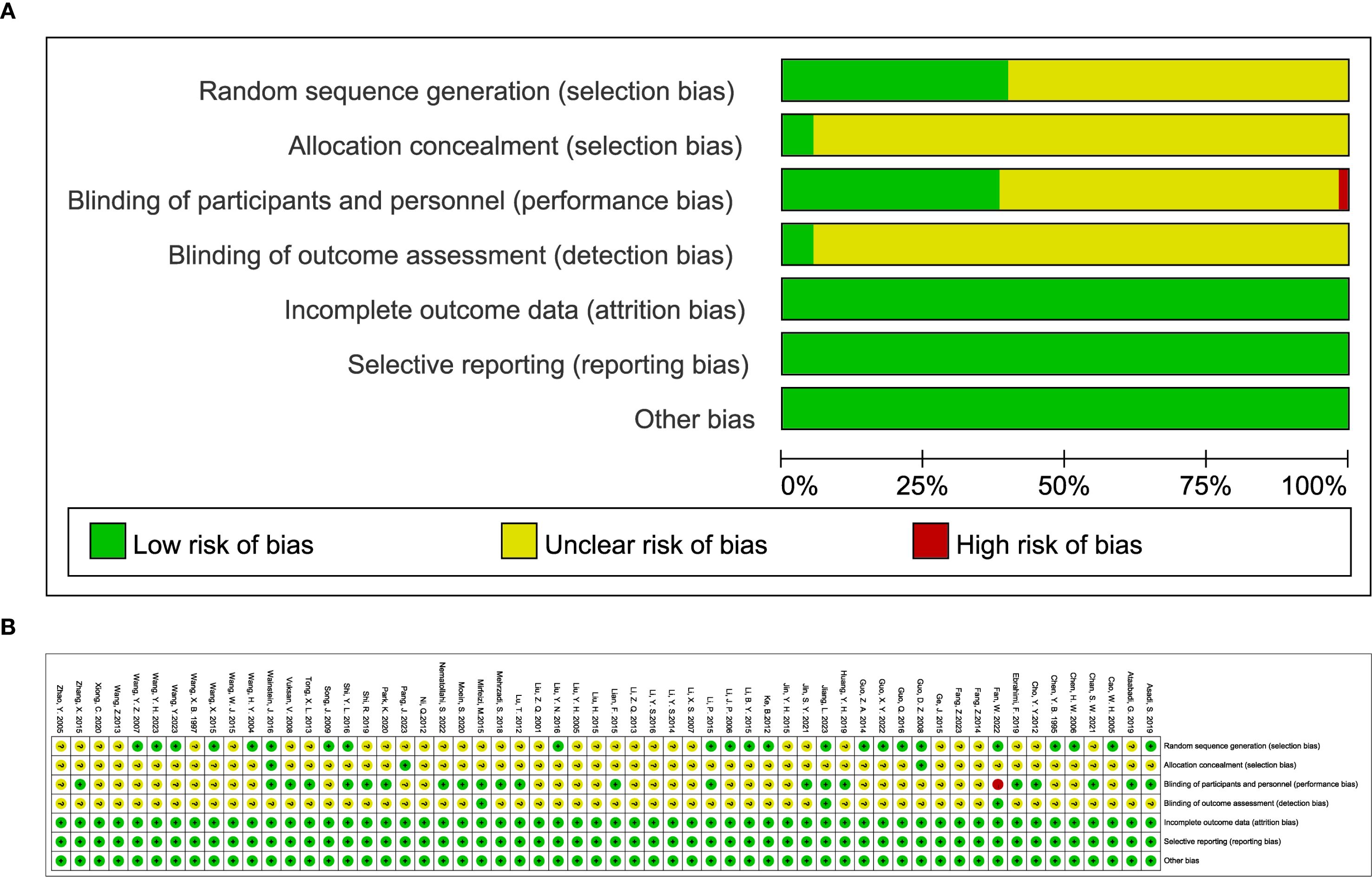
Figure 2. (A) classification of bias risk of included articles and (B) bias characteristics of each included article.
3.1.3 Glycemic indicators
The impact of TCM on blood glucose levels was assessed across several key metrics. Fasting blood glucose levels were analyzed across 43 studies, encompassing 2,480 participants in the experimental group and 2,206 in the control group. The analysis demonstrated that TCM treatment significantly reduced fasting blood glucose levels in diabetic patients compared to the control group (MD = -0.53, 95% CI = [-0.67, -0.39], P < 0.00001), as shown in Figure 3A. For 2-hour postprandial blood glucose levels, data from 26 studies were evaluated, involving 1,902 participants in the experimental group and 1,645 in the control group. The results indicated that TCM treatment significantly decreased 2-hour postprandial blood glucose levels in diabetic patients compared to the control group (MD = -1.15, 95% CI = [-1.48, -0.82], P < 0.00001), as illustrated in Figure 3B. Twenty-two studies assessed HbA1c levels, including 1,123 participants in the experimental group and 977 in the control group. The analysis revealed that TCM treatment significantly lowered HbA1c levels in diabetic patients compared to the control group (MD = -0.40, 95% CI = [-0.61, -0.20], P = 0.0001), as depicted in Figure 3C.
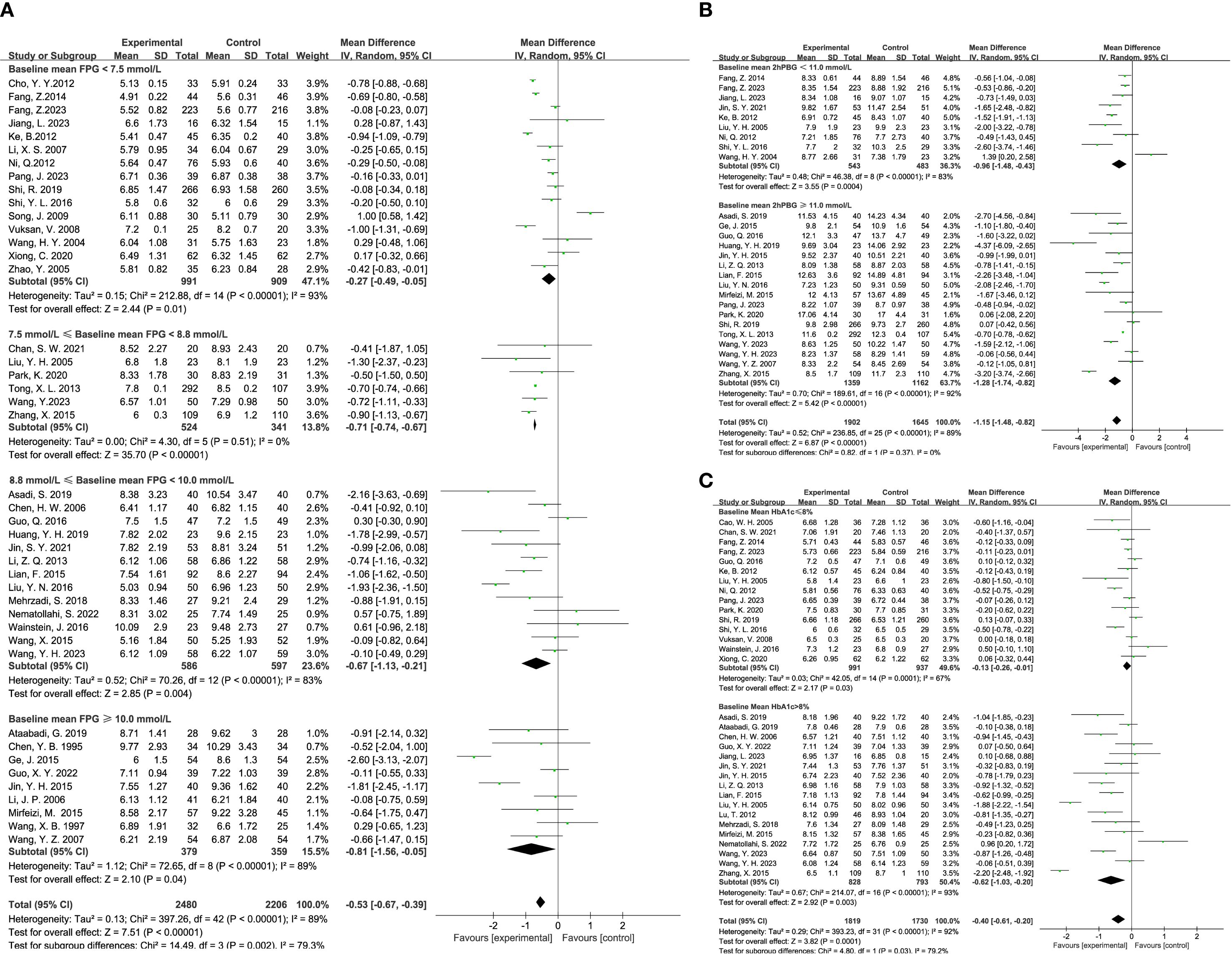
Figure 3. Results of a meta-analysis: (A) Forest plot and subgroup analysis of Fasting Plasma Glucose comparison between TCM and control group, (B) Forest plot and subgroup analysis of Postprandial Plasma Glucose comparison between TCM and control group, (C) Forest plot and subgroup analysis of Glycated Hemoglobin comparison between TCM and control group.
3.1.4 Insulin levels
The effect of TCM on insulin-related metrics was evaluated through several studies. Eight studies reported on fasting insulin levels, including 324 participants in the experimental group and 279 in the control group. The analysis revealed that TCM significantly reduced fasting insulin levels in diabetic patients compared to the control group (MD = -2.63, 95% CI = [-3.71, -1.55], P < 0.00001), as illustrated in Figure 4A. Additionally, 11 studies assessed HOMA-IR (Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance), with 1,123 participants in the experimental group and 977 in the control group. The results indicated that TCM treatment significantly decreased HOMA-IR levels in diabetic patients compared to the control group (MD = -0.90, 95% CI = [-1.51, -0.29], P = 0.004), as depicted in Figure 4B.
![Two forest plots (A and B) display the mean differences between experimental and control groups across multiple studies. Plot A shows a total mean difference of -2.63 with a 95% confidence interval of [-3.71, -1.55], favoring the experimental group. Plot B shows a total mean difference of -0.90 with a 95% confidence interval of [-1.51, -0.29], also favoring the experimental group. Heterogeneity and overall effect statistics are provided for each plot.](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1605091/fendo-16-1605091-HTML/image_m/fendo-16-1605091-g004.jpg)
Figure 4. Results of a meta-analysis: (A) Forest plot of Fasting Insulin comparison between TCM and control group, (B) Forest plot of Homeostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance comparison between TCM and control group.
3.1.5 Kidney function level
The impact of TCM on kidney function was assessed through several key indicators across various studies. Four studies reported on 24-hour proteinuria, with 229 participants in the experimental group and 198 in the control group. The analysis demonstrated that TCM significantly reduced 24-hour proteinuria levels compared to the control group (MD = -0.78, 95% CI = [-1.48, -0.08], P = 0.03), as shown in Figure 5A. UAER (Urinary Albumin Excretion Rate) was evaluated in 7 studies, including 338 participants in the experimental group and 267 in the control group. The results indicated that TCM significantly lowered UAER levels compared to the control group (MD = -17.89, 95% CI = [-21.49, -14.29], P < 0.00001), as depicted in Figure 5B. BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen) levels were assessed in 9 studies, involving 458 participants in the experimental group and 364 in the control group. The findings revealed that TCM significantly reduced BUN levels compared to the control group (MD = -1.25, 95% CI = [-2.08, -0.42], P = 0.003), as illustrated in Figure 5C. Scr (Serum Creatinine) levels were reported in 11 studies, including 529 participants in the experimental group and 454 in the control group. The analysis showed that TCM significantly lowered Scr levels compared to the control group (MD = -9.21, 95% CI = [-11.47, -6.96], P < 0.00001), as shown in Figure 5D.
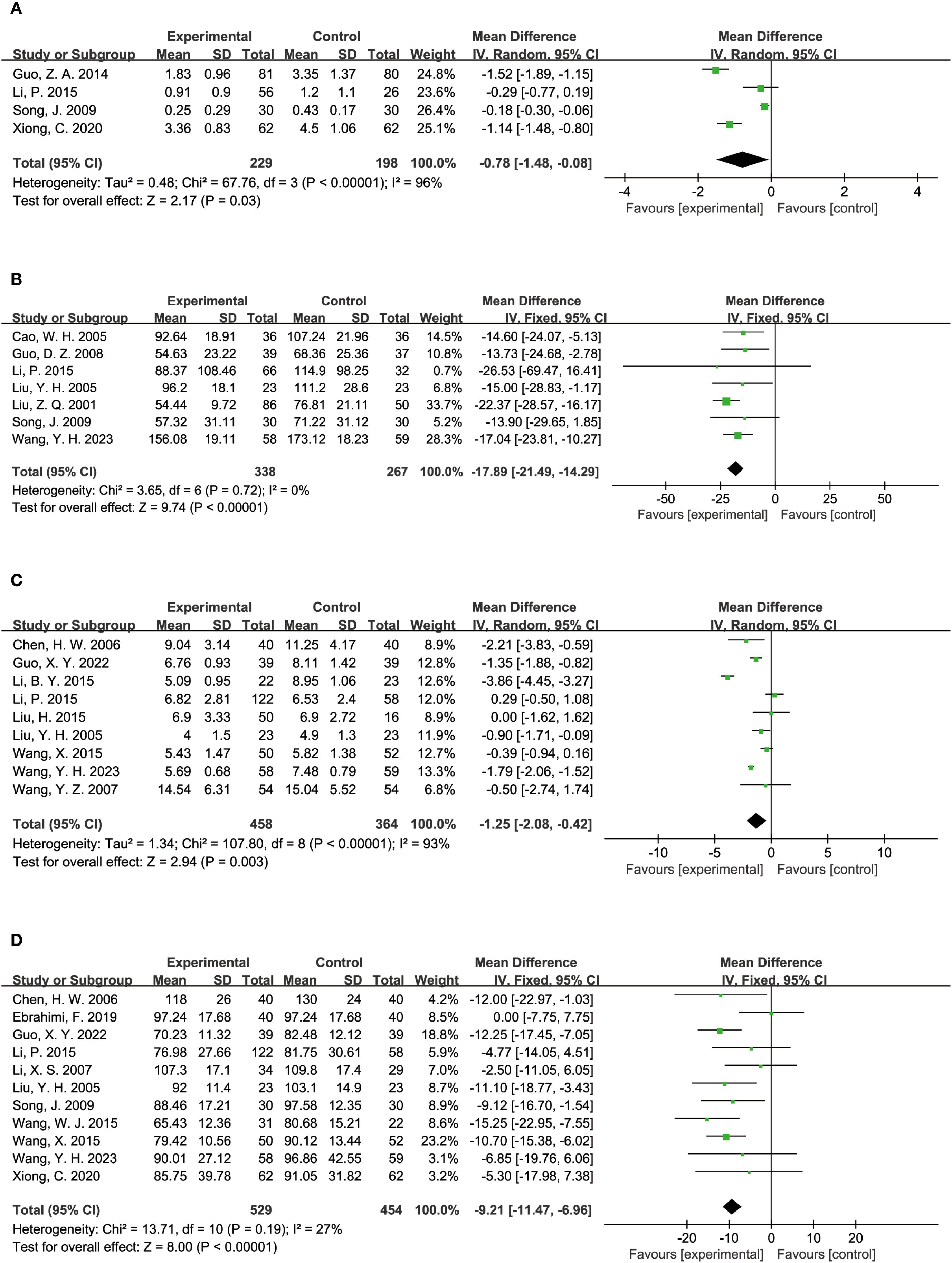
Figure 5. Results of a meta-analysis: (A) Forest plot of 24-hours Proteinuria comparison between TCM and control group, (B) Forest plot of Urinary Albumin Excretion Rate comparison between TCM and control group, (C) Forest plot of Blood Urea Nitrogen between TCM and control group, (D) Forest plot of Serum Creatinine comparison between TCM and control group.
3.1.6 Blood lipid indicators
The influence of TCM on blood lipid levels was examined across several studies. Triglyceride levels were reported in 33 studies, involving 1,675 participants in the experimental group and 1,519 in the control group. The analysis indicated that TCM significantly reduced triglyceride levels compared to the control group (MD = -0.16, 95% CI = [-0.28, -0.04], P = 0.008), as shown in Figure 6A. Total cholesterol levels were assessed in 29 studies, with 1,513 participants in the experimental group and 1,359 in the control group. The results demonstrated that TCM significantly lowered total cholesterol levels compared to the control group (MD = -0.37, 95% CI = [-0.52, -0.21], P < 0.00001), as depicted in Figure 6B. LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein) levels were reported in 22 studies, including 914 participants in the experimental group and 762 in the control group. The findings revealed that TCM significantly reduced LDL levels compared to the control group (MD = -0.14, 95% CI = [-0.21, -0.07], P = 0.0002), as illustrated in Figure 6C. HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) levels were analyzed in 22 studies, with 1,123 participants in the experimental group and 762 in the control group. The results indicated that TCM significantly improved HDL levels compared to the control group (MD = 0.03, 95% CI = [0.01, 0.06], P = 0.02), as shown in Figure 6D.
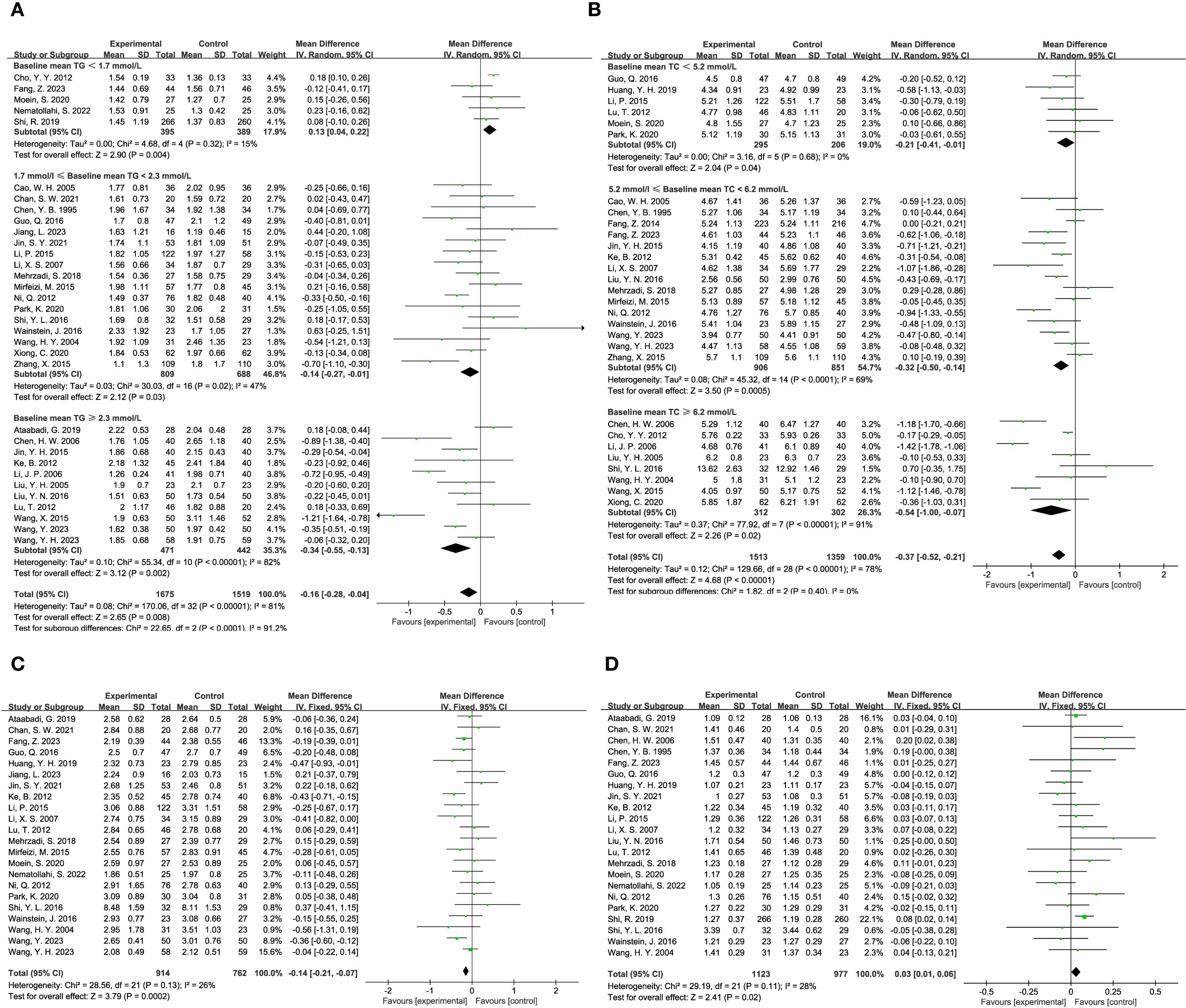
Figure 6. Results of a meta-analysis: (A) Forest plot and subgroup analysis of Triglyceride comparison between TCM and control group, (B) Forest plot and subgroup analysis of Total Cholesterol comparison between TCM and control group, (C) Forest plot of Low-density Lipoprotein between TCM and control group, (D) Forest plot of High-density Lipoprotein between TCM and control group.
3.1.7 Others
The efficacy of TCM in managing diabetic foot was evaluated through various indicators. Five studies examined the ulcer area in diabetic foot patients, with a total of 780 participants in the experimental group and 402 in the control group. The analysis showed a significant reduction in ulcer area for those receiving TCM compared to the control group (MD = -1.80, 95% CI = [-2.96, -0.64], P = 0.002), as illustrated in Figure 7A. In addition to ulcer area, three studies investigated the levels of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF), which plays a crucial role in wound healing and vascularization. This analysis included 700 participants in the experimental group and 322 in the control group. The findings indicated that TCM treatment substantially lowered VEGF levels in diabetic foot patients compared to the control group (MD = -19.25, 95% CI = [-29.48, -9.03], P = 0.0002), as shown in Figure 7B.
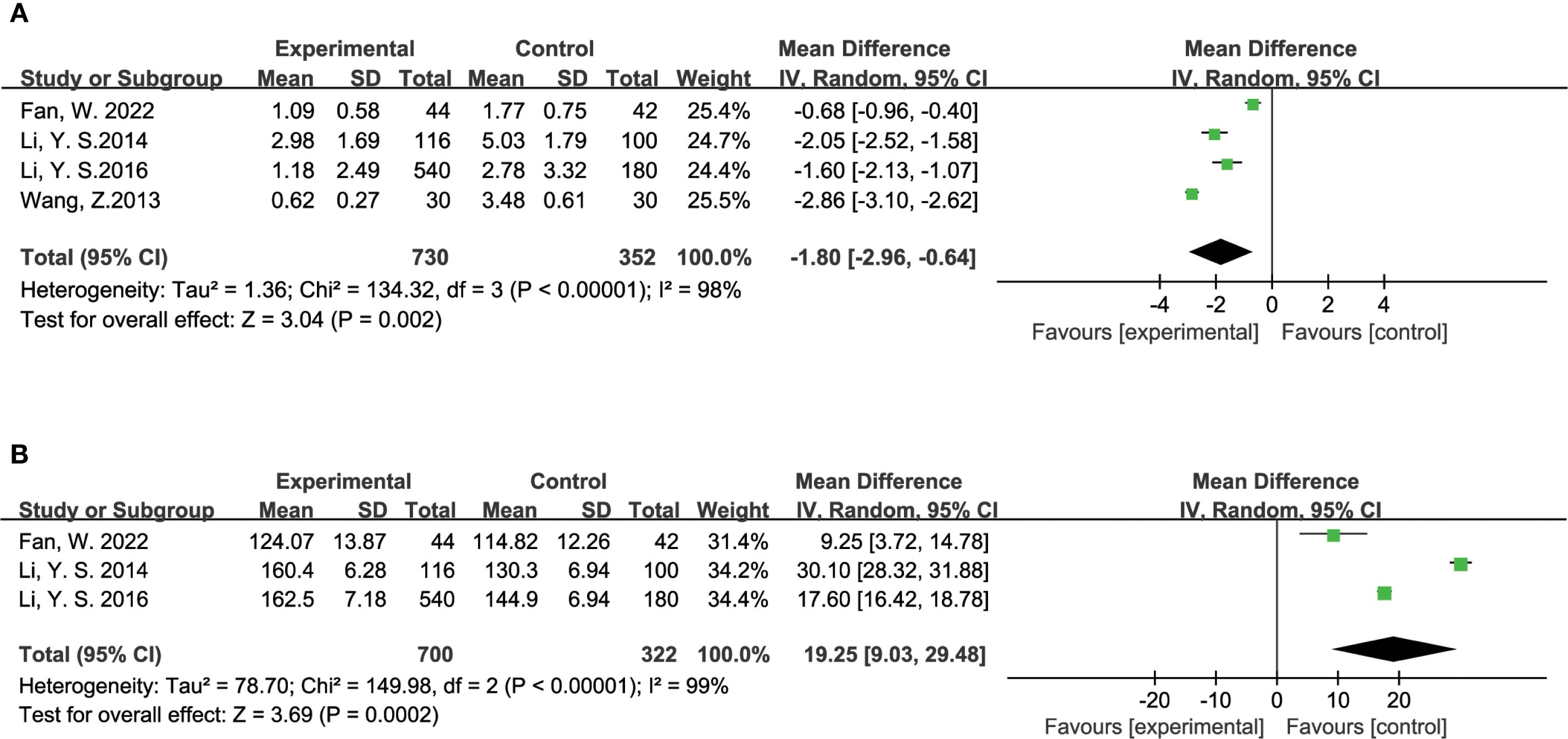
Figure 7. Results of a meta-analysis: (A) Forest plot of Ulcer Area of diabetes foot comparison between TCM and control group, (B) Forest plot of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in patients with diabetes foot comparison between TCM and control group.
3.1.8 Sensitivity analysis and publication bias
To evaluate the robustness of our meta-analysis results, sensitivity analysis was conducted by systematically excluding each study one at a time and re-assessing the remaining studies. This approach ensured that no single study had a disproportionate impact on the overall outcomes of the meta-analysis, confirming the stability and reliability of our findings. In addition, publication bias was assessed using both Begg’s and Egger’s tests. The results of these tests indicated no evidence of publication bias, as shown by the relevant P values in Supplementary Table S1. The outcomes of the sensitivity analysis, along with the corresponding funnel plots, are presented in Supplementary Figure S1 through S5.
3.2 Network pharmacology
3.2.1 Effective herbs extraction
We examined the frequency of herbs in the TCM formulas cited in the included studies. Based on their occurrence, the most commonly used and effective herbs were Astragalus mongholicus Bunge (Fabaceae, Astragali radix), Codonopsis pilosula Nannf. (Campanulaceae, Codonopsis pilosulae radix), Wolfiporia cocos (F.A. Wolf) Ryvarden & Gilb. (Polyporacea, Wolfiporia cocos sclerotium), Cornus officinalis Siebold & Zucc. (Cornaceae, Cornus officinalis fruit), Coptis chinensis Franch. (Ranunculaceae, Coptis chinensis radix), Alisma gramineum Lej. (Alismataceae, Alisma gramineum tuber) (Table 3). A new formula, incorporating these six herbs, was created for network pharmacology analysis.
3.2.2 Screening of drug-diabetes genes and construction of drug-ingredient-target
Initially, we pinpointed the target genes associated with the active ingredients of TCM. Our search of the prescription database identified six effective TCMs, encompassing 67 compounds and 210 target genes. A Venn diagram illustrating the overlap of drug target genes across these six TCMs was constructed (Figure 8A). This analysis revealed that several TCMs share common target genes, suggesting a potential for multiple TCMs to influence the same genetic targets. Subsequently, we identified disease-related genes associated with diabetes, retrieving a total of 34,497 diabetes-related targets from five public disease databases (Figure 8B). The Venn diagram analysis indicated an intersection of 210 drug-disease targets (Figure 8C). Finally, we utilized Cytoscape to develop a network diagram that integrates TCM components with their corresponding disease targets, as shown in Figure 8D. The results suggest that a specific component of traditional Chinese medicine often corresponds to multiple molecular targets of diabetes. We ranked them according to the frequency of the corresponding targets. The top three are quercetin, kaempferol, and Stigmasterol. For the rest of the results, please refer to the Supplementary Table S2.
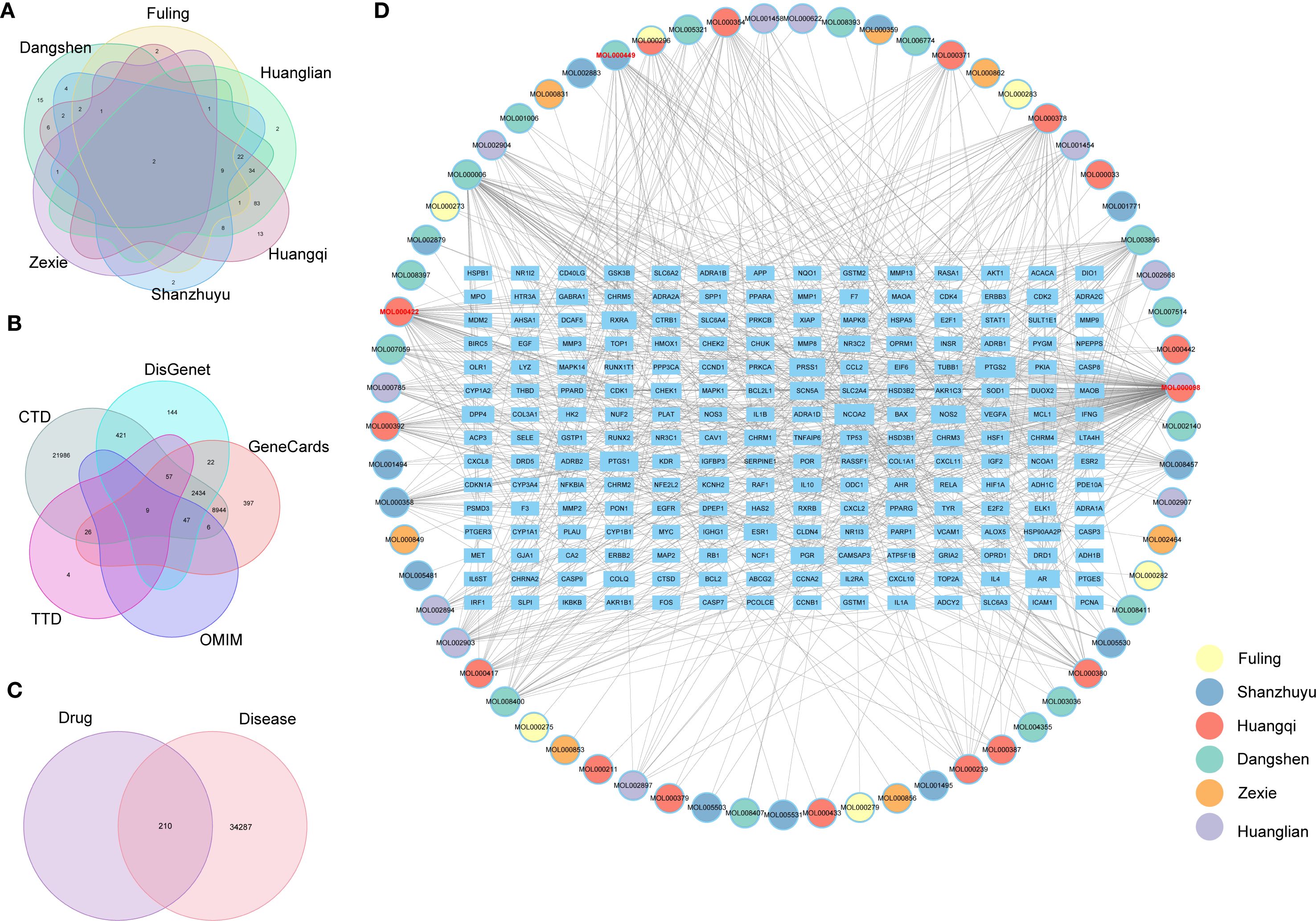
Figure 8. (A) Venetian diagram of drug targets of important traditional Chinese medicines, (B) Venetian diagram of diabetes disease targets, (C) Venetian diagram of traditional Chinese medicine-disease intersection genes, (D) Network diagram of drug ingredients and drug-disease targets.
3.2.3 Screening of core genes and functional enrichment analysis
The TCM-targets were subsequently uploaded to the STRING database, which produced a network consisting of 208 nodes and 3,740 edges, and a PPI enrichment p-value of ≤ 1.0e-16 (Figure 9A). By applying seven algorithms from the cytoHubba plugin, we identified the top 50 genes, detailed in Supplementary Table S3. Through intersection analysis, we isolated 32 core genes that fulfilled all criteria. These include AKT1, IL1B, TP53, PTGS2, ESR1, CASP3, MMP9, EGFR, BCL2, HIF1A, FOS, MYC, PPARG, GSK3B, CCND1, EGF, ERBB2, IL10, CCL2, IFNG, CXCL8, IL1A, ICAM1, RELA, MMP2, HMOX1, NFE2L2, APP, CASP9, MAPK1, SERPINE1, and CAV1 (Figure 9B). Gene Ontology (GO) analysis demonstrated that these core genes are predominantly involved in the cellular responses to oxidative stress and oxygen levels (Figure 9C, Supplementary Table S4). Additionally, KEGG pathway analysis revealed that these genes are mainly associated with the TNF signaling pathway, the IL-17 signaling pathway, and the HIF-1 signaling pathway (Figure 9D, Supplementary Table S5). These pathways are intricately connected to diabetes.
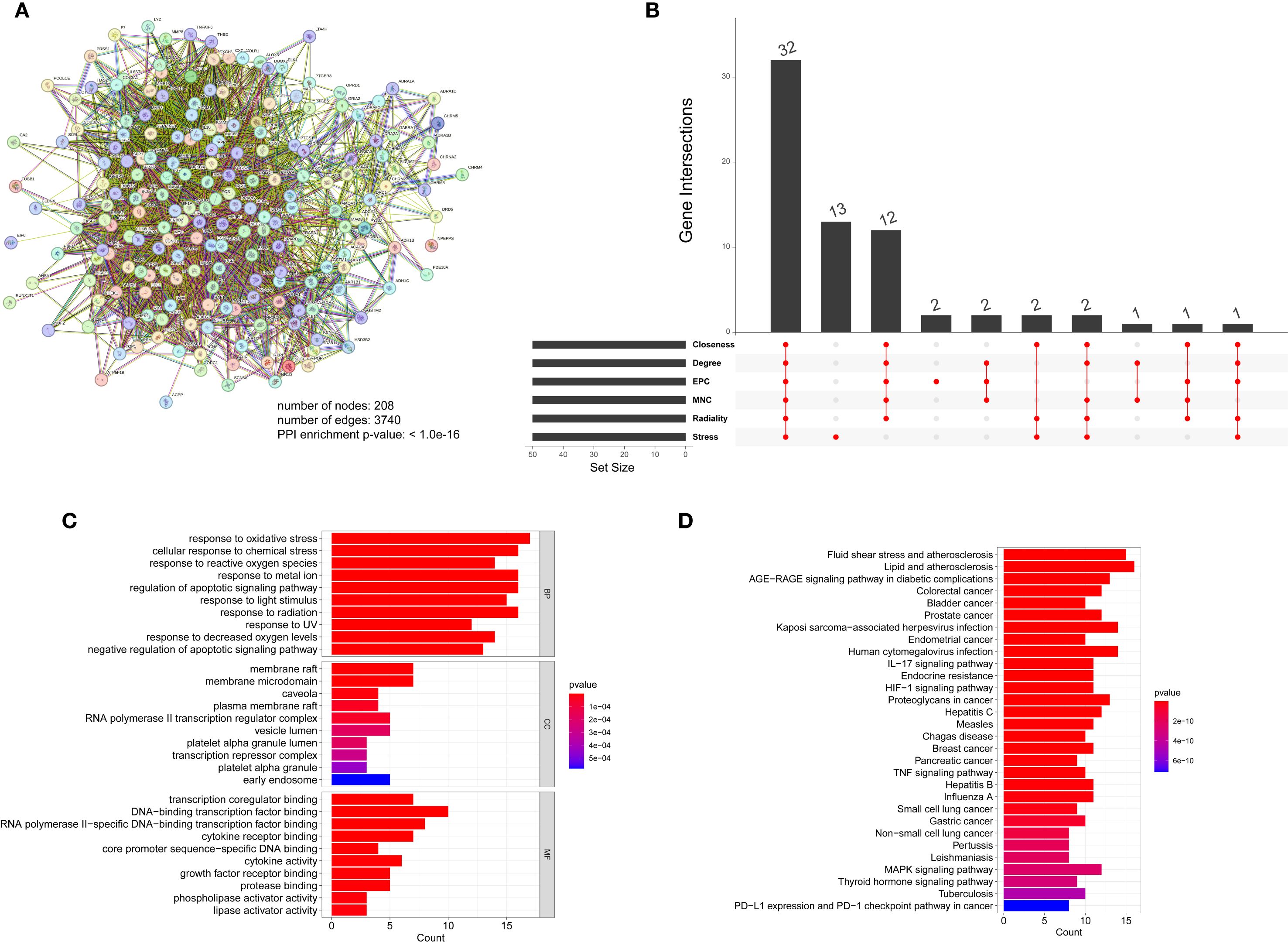
Figure 9. (A) Protein molecular network diagram of TCM-disease intersection genes, (B) Venetian display, 6 algorithms screened out 32 core genes in total, (C) GO analysis of core genes, (D) KEGG analysis of core genes.
4 Discussion
Diabetes is a global chronic metabolic condition with a rising incidence, presenting significant health risks and economic challenges for patients. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) adheres to a holistic view of health, regarding the human body as an organic whole influenced by both internal and external factors. Its various components are interconnected and mutually influential, forming a complex dynamic system. TCM, with its multi-target, multi-component, and multi-pathway approach, offers considerable promise as a comprehensive treatment for diabetes (94). Research indicates that the potential mechanisms by which TCM regulates blood glucose include: improving insulin resistance (95–97), enhancing insulin sensitivity (98–100), promoting insulin secretion (101–103), and stimulating glucose uptake (104–106). Notably, recent studies have found that TCM can also improve glucose metabolism disorders by remodeling the balance of the gut microbiota (101, 107, 108), working through the perspective of the “Gut-Pancreas” axis. However, although existing retrospective studies have confirmed the clinical value of TCM (26, 28), there remain significant gaps in screening the optimal medication regimens and elucidating the molecular mechanisms of action. Therefore, this study aims to provide new scientific evidence for TCM in treating diabetes, in order to promote more precise individualized treatment strategies.
This meta-analysis provides robust evidence that TCM can significantly improve glycemic control (e.g., HbA1c, fasting blood glucose), lipid profile (e.g., total cholesterol, triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol), and renal function indicators (e.g., serum creatinine, urinary albumin excretion rate) in diabetic patients. These improvements are directly linked to the pathophysiological mechanisms of core diabetic complications: optimizing glycemic fluctuations reduces microvascular damage (109); regulating dyslipidemia delays atherosclerosis (110); and protecting nephron function lowers the risk of nephropathy (111). This suggests that TCM intervention holds significant clinical value in the comprehensive management of diabetes and its common complications. This conclusion is supported by the consistently observed effects in the included studies and the results obtained after our rigorous assessment of potential biases and heterogeneity.
The synergistic improvements in blood glucose, lipids, and renal function observed in this study possess dual clinical significance. On one hand, they pertain to the restoration of metabolic homeostasis: the simultaneous optimization of blood glucose and lipids may directly delay vascular endothelial damage by reducing glucolipotoxicity (112, 113). On the other hand, they indicate a forward shift in the window for complication prevention: improvements in Scr and BUN suggest TCM may potentially block the “hyperglycemia-glomerular hypertension-renal fibrosis” pathway, offering a novel strategy for the primary prevention of diabetic nephropathy (114). This provides evidence-based support for an integrated approach combining Chinese and Western medicine, aligning with the “individualized metabolic goal management” proposed in the ADA/EASD guidelines.
The meta-analysis results further indicate that Astragali Radix (Huangqi), Codonopsis Radix (Dangshen), Poria (Fuling), Corni Fructus (Shanzhuyu), Coptidis Rhizoma (Huanglian), and Alismatis Rhizoma (Zexie) are the high-frequency herbs used in TCM for diabetes treatment. Relevant studies support their efficacy. For instance, Chao et al. found that a traditional Chinese herbal compound (containing Coptidis Rhizoma, Astragali Radix, and Lonicerae Japonicae Flos) ameliorated insulin resistance in T2D patients and also improved glucose metabolism (including FPG, PPG, and HbA1c) and blood pressure to some extent (115). A multicenter study by Chan et al. demonstrated that adding Astragali Radix to standard treatment significantly slowed the decline in renal function in patients with diabetic nephropathy (116). The mechanisms by which these herbs treat diabetes align with those described previously: by optimizing glycemic fluctuations, regulating dyslipidemia, and protecting renal function to reduce the risk of nephropathy. Specifically, Corni Fructus ameliorates diabetic nephropathy through its effects of lowering blood glucose, regulating lipids, and reducing oxidative stress; its renal protective mechanism is closely associated with activating the PPARγ signaling pathway (117). The aqueous extract of Codonopsis Radix ameliorates insulin resistance (IR) by increasing Akt and GSK-3β phosphorylation, reduces hepatic triglyceride content via AMPK phosphorylation, and protects β-cell function by reducing β-cell apoptosis (118). Furthermore, extracts of Codonopsis Radix and Polygonati Rhizoma (Huangjing) can also ameliorate IR, lower blood glucose, and reduce lipid levels by activating the IRS1/PI3K/AKT pathway (119). For Astragali Radix, its polysaccharide component (APS) promotes GLUT4 translocation and upregulates PPAR-γ expression by activating the AMPK/PI3K/AKT pathway, thereby ameliorating IR. It also possesses anti-inflammatory effects, inhibits pancreatic β-cell apoptosis, and promotes insulin secretion (120). Meanwhile, both the saponin (ASS) and flavonoid (ASF) components of Astragali Radix combat hyperglycemia by activating the adiponectin-AMPK pathway and its downstream factors, although their effect intensities vary across different tissues (121).
Notably, the network pharmacology analysis in this study identified quercetin, kaempferol, and stigmasterol as the core active components of the aforementioned high-frequency TCM herbs (e.g., Astragali Radix, Codonopsis Radix, Corni Fructus). A total of 32 potential targets for TCM in treating diabetes were identified. These active components exert their therapeutic effects through synergistic regulation of core pathological pathways in diabetes. Specifically, quercetin activates the AMPK/PI3K/Akt pathway to enhance GLUT4 translocation efficiency in skeletal muscle, promoting glucose uptake and increase insulin sensitivity (122, 123). It also inhibits the activation of the TNF-α/NF-κB pathway by enhancing Akt phosphorylation, thereby alleviating inflammatory insulin resistance (124, 125). Furthermore, quercetin inhibits ferroptosis by activating the Nrf2 pathway (e.g., upregulating GPX4/xCT) and chelating iron ions. In the kidneys, this manifests as protection of renal tubular mitochondria and reduction of proteinuria. In the pancreas, it improves insulin secretion by reducing iron deposition in β-cells, thereby providing protection against diabetic kidney disease (DKD) and for pancreatic β-cells (126, 127). By activating PPARγ, kaempferol enhances downstream PI3K/AKT signaling activity to promote glucose uptake in peripheral tissues and inhibit hepatic gluconeogenesis, thereby effectively lowering blood glucose and improving glucose tolerance, while ameliorating lipid metabolism disorders and reducing lipotoxicity through activation of the PPARγ/LXRα/ABCA1 pathway (128, 129). Kaempferol also inhibits IKKβ/IKKα phosphorylation and activation, blocking the TNF-α/NF-κB pathway, reducing serum pro-inflammatory cytokines, and increasing IRS-1 protein expression, thereby improving insulin resistance (130). It has also been found to modulate the gut microbiota (e.g., reversing the relative abundance of Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes), which may be related to its amelioration of high-fat diet-induced lipid metabolism abnormalities (131). In terms of renal protection, kaempferol inhibits RhoA/ROCK signaling, downregulates pro-fibrotic factors such as TGF-β1 and CTGF, reduces extracellular matrix (ECM) accumulation, protects podocyte structure, and delays renal fibrosis while improving renal function (132). Stigmasterol acts by increasing the expression of SREBP2 and its target gene LDLR while decreasing the expression of the cholesterol efflux transporter ABCA1. This reduces free cholesterol levels induced by glucolipotoxicity. Combined with its antioxidant effects to lower ROS, stigmasterol restores glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) capacity, increases total insulin content, and alleviates pancreatic β-cell dysfunction (133). Additionally, stigmasterol increases GLUT4 translocation and expression, enhancing insulin sensitivity to improve insulin resistance (134).
This association pattern of “TCM - active component clusters - multi-target pathways - synergistic effects” profoundly elucidates the material basis and mechanisms of action underlying TCM in treating diabetes. The core components (quercetin, kaempferol, stigmasterol) identified by network pharmacology and their 32 regulated targets not only validate the efficacy mechanisms of the high-frequency TCM herbs but also reveal, at the molecular level, how different herbs collectively target core pathological aspects of diabetes. This collective action occurs through shared or complementary active components and action pathways, addressing key pathological processes including insulin resistance, glucose and lipid metabolism disorders, inflammatory responses, oxidative stress, β-cell dysfunction, and renal injury. Ultimately, this leads to the synergistic improvement of blood glucose, lipid profile, and renal function. This provides a critical scientific foundation for understanding the holistic effects of TCM formulas and for developing novel therapeutic strategies based on active component clusters.
Beyond the small-molecule active components mentioned above, macromolecular components in TCM (such as polysaccharides and polypeptides) have been widely confirmed to possess significant anti-diabetic activity. Particularly in the core herbs screened in this study, the effects of APS on improving insulin resistance and modulating gut microbiota (120, 135), the hypoglycemic and renal protective effects of Coptidis Rhizoma polysaccharides (CCPW) (136, 137), and the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of Codonopsis Radix polysaccharides (CPPS) and Corni Fructus polysaccharides (COPs) (138, 139) are all significant contributors to their overall therapeutic efficacy. However, it should be noted that the network pharmacology methodology applied subsequently in this study has an inherent design primarily reliant on small-molecule-oriented databases (e.g., TCMSP, PubChem) and prediction tools (e.g., molecular docking). Consequently, it is challenging to systematically analyze the complex mechanisms of action of these macromolecular components. The primary value of this study lies in its focus on the clusters of small-molecule compounds within these same core herbs (e.g., quercetin/kaempferol in Astragali Radix, berberine/palmatine in Coptidis Rhizoma, alisol derivatives in Alismatis Rhizoma). It reveals the potential molecular mechanisms by which they exert anti-diabetic effects through the regulation of key targets (e.g., AKT1, PPARG) and signaling pathways (e.g., TNF signaling pathway). This provides an important perspective for understanding the small-molecule pharmacodynamic material basis of the core herbs. We emphasize that the overall efficacy of high-frequency herbs like Astragali Radix and Codonopsis Radix stems from the synergistic action of their multiple components. This includes both the small-molecule mechanisms predicted in this study (e.g., targeted regulation of inflammatory factors like TNF or the PI3K-Akt pathway) and the well-documented macromolecular components (e.g., the immune/gut microbiota modulatory functions of polysaccharides). Together, they constitute a modern scientific interpretation of TCM’s characteristic “multi-component, multi-target” integrative regulation. Future studies should integrate multi-omics approaches and macromolecule-specific methodologies to more comprehensively parse the synergistic networks of both large and small molecular components within the core herbs.
This multi-target and multi-component characteristic is the core of the unique advantages of TCM in treating diabetes. Unlike Western medicine with a single target, TCM for the treatment of diabetes usually does not rely on a single ingredient or a single medicine, but adopts a compound form. TCM can intervene in the complex pathological mechanism of diabetes in an all-round way through the synergistic effect of multiple active ingredients. The multiple drugs in the combination can synergize or inhibit each other, enhancing the efficacy and reducing the side effects. This not only helps to lower blood sugar, but also may have a protective effect on diabetes-related complications such as neuropathy, nephropathy and cardiovascular disease. While this study highlights the considerable potential of TCM in treating diabetes, its clinical application continues to encounter several challenges. First of all, the efficacy and safety of TCM are affected by many factors, including the origin of the medicinal materials, processing methods and individual differences. Secondly, most current clinical trials have problems such as small sample sizes and loose designs, which limit the wide application of the results. Therefore, future research should include more large-scale, high-quality randomized controlled trials to further validate the effectiveness and safety of traditional Chinese medicine for treating diabetes. In addition, diabetes is a highly heterogeneous disease with significant differences in pathophysiology between patients. The personalized treatment approach of TCM, which involves modifying drug formulas based on the patient’s unique condition, constitution, and other factors, may lead to more effective outcomes. Additionally, since diabetes is a chronic condition necessitating ongoing management, it is important to assess the long-term efficacy and safety of TCM treatments.
It is important to specifically note that the meta-analysis in this study only included adult patients aged 18 and above. While this aligns with the population scope of most current randomized controlled trials, it may limit the applicability of the study conclusions to adolescent patients with youth-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Notably, the disease burden of this special population has been rapidly increasing worldwide in recent years, with overweight/obesity further elevating the risk (140, 141). Existing evidence indicates that, compared to youth-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM), youth-onset T2DM not only has a worse clinical prognosis but also exhibits more pronounced metabolic abnormalities and potentially distinct pathogenesis compared to adult-onset T2DM. These characteristics collectively lead to an elevated risk of vascular complications in young patients (142). More concerningly, the current treatment options approved by the U.S. FDA, the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and Health Canada for youth-onset T2DM are very limited. This scarcity of treatment choices may lead to more adverse clinical outcomes for this population. Based on this, our future research will expand the cohort of young patients to systematically evaluate the synergistic effects of TCM-modern drug combination therapy, analyze differential treatment responses among different age groups, and elucidate the mechanisms of action of TCM interventions for youth-onset T2DM. These studies will provide crucial evidence for developing targeted intervention strategies, holding significant clinical value for preventing disease progression and reducing the risk of complications in adolescent patients.
Of course, this study also has some limitations. First, our meta-analysis and network pharmacology analysis are based on existing literature and databases, which may have problems with publication bias and incomplete data. Second, the prediction results of network pharmacology analysis need further experimental verification. Moreover, the complexity of TCM involves various components that may undergo intricate metabolic processes and interactions within the body. These processes not only affect the efficacy of the drug, but may also cause adverse reactions. Our understanding of its multi-component and multi-target mechanisms is still limited, and further research is needed in combination with more systems biology approaches. Future research should focus on the following aspects: First, conducting large-scale, high-quality clinical trials to provide more reliable evidence support; Second, conducting an in-depth analysis of the multi-component and multi-target mechanisms of TCM using multi-omics technologies and systems biology approaches.; Third, exploring the combined application of TCM and modern drugs to give play to their synergistic and enhancing effects; Fourth, strengthening the standardization and quality control of TCM to ensure the safety and effectiveness of clinical application.
5 Conclusions
This study systematically evaluated the efficacy and potential mechanisms of TCM in the treatment of diabetes through meta-analysis and network pharmacology. The results indicated that TCM can significantly improve blood glucose control in diabetic patients, reduce glycated hemoglobin levels, and alleviate insulin resistance. Additionally, network pharmacology analysis revealed that TCM exerts its effects through multiple targets and pathways, including the regulation of insulin signaling pathways, inflammatory responses, and oxidative stress. These findings provide scientific evidence for the use of TCM in diabetes treatment, supporting its clinical application.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
ST: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JL: Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing. GL: Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing. HG: Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CL: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. FW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank all the study participants and the staff involved in facilitating and conducting the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2025.1605091/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M, Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, et al. Idf diabetes atlas: global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2022) 183:109119. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119
2. American Diabetes AssociationDiagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. (2011) 34 Suppl 1:S62–9. doi: 10.2337/dc11-S062
3. Committee ADAPP. 2. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes: standards of care in diabetes—2025. Diabetes Care. (2024) 48:S27–49. doi: 10.2337/dc25-S002
4. Committee ADAPP. 9. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of care in diabetes—2025. Diabetes Care. (2024) 48:S181–206. doi: 10.2337/dc25-S009
5. Thomas CC, Chopra K, and Davis AM. Management of outpatients with diabetes at high risk of hypoglycemia. Jama. (2024) 331:1145–6. doi: 10.1001/jama.2024.1137
6. Li M, Yang Y, Jiang D, Ying M, Wang Y, and Zhao R. Efficacy and safety of liraglutide versus sitagliptin both in combination with metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine. (2017) 96:e8161. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000008161
7. Shetty R, Basheer FT, Poojari PG, Thunga G, Chandran VP, and Acharya LD. Adverse drug reactions of glp-1 agonists: A systematic review of case reports. Diabetes Metab syndrome. (2022) 16:102427. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2022.102427
8. Kittipibul V, Cox ZL, Chesdachai S, Fiuzat M, Lindenfeld J, and Mentz RJ. Genitourinary tract infections in patients taking sglt2 inhibitors: jacc review topic of the week. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2024) 83:1568–78. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2024.01.040
9. Lv W, Wang X, Xu Q, and Lu W. Mechanisms and characteristics of sulfonylureas and glinides. Curr Top Med Chem. (2020) 20:37–56. doi: 10.2174/1568026620666191224141617
10. Elangwe A, Katte JC, Tchapmi D, Figueras A, and Mbanya JC. Adverse drug reactions to anti-diabetic drugs are commonest in patients whose treatment do not adhere to diabetes management clinical guidelines: cross-sectional study in a tertiary care service in Sub-Saharan Africa. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. (2020) 76:1601–5. doi: 10.1007/s00228-020-02949-2
11. Böhm AK, Schneider U, Aberle J, and Stargardt T. Regimen simplification and medication adherence: fixed-dose versus loose-dose combination therapy for type 2 diabetes. PloS One. (2021) 16:e0250993. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250993
12. Sagalla N, Yancy WS Jr., Edelman D, Jeffreys AS, Coffman CJ, Voils CI, et al. Factors associated with non-adherence to insulin and non-insulin medications in patients with poorly controlled diabetes. Chronic illness. (2022) 18:398–409. doi: 10.1177/1742395320968627
13. Aronson R. The role of comfort and discomfort in insulin therapy. Diabetes Technol Ther. (2012) 14:741–7. doi: 10.1089/dia.2012.0038
14. Parker ED, Lin J, Mahoney T, Ume N, Yang G, Gabbay RA, et al. Economic costs of diabetes in the U.S. In 2022. Diabetes Care. (2023) 47:26–43. doi: 10.2337/dci23-0085
15. Zhang Q, Hu S, Jin Z, Wang S, Zhang B, and Zhao L. Mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine in elderly diabetes mellitus and a systematic review of its clinical application. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1339148. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1339148
16. Tang G, Li S, Zhang C, Chen H, Wang N, and Feng Y. Clinical efficacies, underlying mechanisms and molecular targets of Chinese medicines for diabetic nephropathy treatment and management. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2021) 11:2749–67. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.12.020
17. Zheng R-L, Wang J, Liu S-Y, Sun Z-P, Zhao L-Y, and Chen G-T. Screening and extraction process optimization for potential α-glucosidase inhibitors from quinoa seeds. Food Med Homol. (2024) 1:9420004. doi: 10.26599/FMH.2024.9420004
18. Chen Y, Qi L, Zhong F, Li Y, Ke W, and Ma Y. Integrated metabolomics and ligand fishing approaches to screen the hypoglycemic ingredients from four coptis medicines. J Pharm Biomed Anal. (2021) 192:113655. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2020.113655
19. Li X, Geng-Ji JJ, Quan YY, Qi LM, Sun Q, Huang Q, et al. Role of potential bioactive metabolites from traditional Chinese medicine for type 2 diabetes mellitus: an overview. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:1023713. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1023713
20. Bai F, Luo H, Wang L, Zhu L, Guan Y, Zheng Y, et al. A meta-analysis of the association between diabetes mellitus and traditional Chinese medicine constitution. Evidence-Based complementary Altern medicine: eCAM. (2021) 2021:6390530. doi: 10.1155/2021/6390530
21. Dou Z, Xia Y, Zhang J, Li Y, Zhang Y, Zhao L, et al. Syndrome differentiation and treatment regularity in traditional Chinese medicine for type 2 diabetes: A text mining analysis. Front Endocrinol. (2021) 12:728032. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.728032
22. Guo J, Chen H, Song J, Wang J, Zhao L, and Tong X. Syndrome differentiation of diabetes by the traditional Chinese medicine according to evidence-based medicine and expert consensus opinion. Evidence-Based complementary Altern medicine: eCAM. (2014) 2014:492193. doi: 10.1155/2014/492193
23. Gao Y, Su X, Xue T, and Zhang N. The beneficial effects of astragaloside iv on ameliorating diabetic kidney disease. Biomed Pharmacother. (2023) 163:114598. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114598
24. Wang MR, Yu LH, Wang TT, Wang YM, and Han MX. Effect of shenqi dihuang decoction on inflammatory factor, renal function and microcirculation in patients with early diabetic nephropathy. Zhongguo Zhong yao za zhi = Zhongguo zhongyao zazhi = China J Chin materia Med. (2018) 43:1276–81. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.2018.0050
25. Long P, Guo C, Wen T, Luo T, Yang L, Li Y, et al. Therapeutic effects of mudan granules on diabetic retinopathy: mitigating fibrogenesis caused by fbn2 deficiency and inflammation associated with tnf-α Elevation. J ethnopharmacol. (2025) 337:118963. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118963
26. Su J, Sun G, An J, Ao Y, Li J, Shen Z, et al. Efficacy and safety of the integration of traditional Chinese medicine and western medicine in the treatment of diabetes-associated cognitive decline: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol. (2023) 14:1280736. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1280736
27. Zhang Z, Leng Y, Fu X, Yang C, Xie H, Yuan H, et al. The efficacy and safety of dachaihu decoction in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:918681. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.918681
28. Ma K, Zhou L, Zhang Y, Zhao J, Yao C, Tian C, et al. Efficacy and safety of traditional Chinese medicines combined with conventional western medicines in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Endocrinol. (2023) 14:1134297. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1134297
29. Zeng B, Qi L, Wu S, Liu N, Wang J, Nie K, et al. Network pharmacology prediction and metabolomics validation of the mechanism of fructus phyllanthi against hyperlipidemia. J Visualized Experiments (JoVE). (2023) 194):e65071. doi: 10.3791/65071
30. Ren C-X, Gao M-Y, Li N, Tang C, Chu G-H, Yusuf A, et al. Identification and mechanism elucidation of medicative diet for food therapy xqcsy in nafld prevention: an integrative in silico study. Food Med Homol. (2024) 1:9420015. doi: 10.26599/FMH.2024.9420015
31. Begg CB and Mazumdar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics. (1994) 50:1088–101. doi: 10.2307/2533446
32. Peters JL, Sutton AJ, Jones DR, Abrams KR, and Rushton L. Comparison of two methods to detect publication bias in meta-analysis. Jama. (2006) 295:676–80. doi: 10.1001/jama.295.6.676
33. Ru J, Li P, Wang J, Zhou W, Li B, Huang C, et al. Tcmsp: A database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J Cheminform. (2014) 6:13. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-6-13
34. Bairoch A, Apweiler R, Wu CH, Barker WC, Boeckmann B, Ferro S, et al. The universal protein resource (Uniprot). Nucleic Acids Res. (2005) 33:D154–9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki070
35. Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Gorodkin J, and Jensen LJ. Cytoscape stringapp: network analysis and visualization of proteomics data. J Proteome Res. (2019) 18:623–32. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00702
36. Asadi S, Gholami MS, Siassi F, Qorbani M, Khamoshian K, and Sotoudeh G. Nano curcumin supplementation reduced the severity of diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized double-blind placebo- controlled clinical trial. Complementary therapies Med. (2019) 43:253–60. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2019.02.014
37. Ataabadi G, Shahinfar N, Mardani G, and Gholami M. Effect of otostegia persica extract on blood glucose in patients with type ii diabetes. J Pharm negative results. (2019) 10:52–6. doi: 10.4103/jpnr.JPNR_5_19
38. Cao WH, Huang LH, and Guo M. Clinical observation of fengbei huayu recipe in treating diabetic nephropathy. Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he za zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi jiehe zazhi = Chin J integrated traditional Western Med. (2005) 25:1022–4. doi: 10.7661/CJIM.2005.11.1022
39. Chan SW, Chu TTW, Choi SW, Benzie IFF, and Tomlinson B. Impact of short-term bilberry supplementation on glycemic control, cardiovascular disease risk factors, and antioxidant status in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes. Phytotherapy research: PTR. (2021) 35:3236–45. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7038
40. Chen HW, Wang SL, and Chen XY. Preliminary study on effects of sodium ferulate in treating diabetic nephropathy. Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he za zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi jiehe zazhi = Chin J integrated traditional Western Med. (2006) 26:803–6. doi: 10.1631/jzus.2006.B0099
41. Chen YB and Zhang H. Effect of bushenhuoxue tablet on serum lipid peroxide, blood lipid and blood sugar in type ii diabetics. Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he za zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi jiehe zazhi = Chin J integrated traditional Western Med. (1995) 15:661‐3. doi: 10.1007/BF02934247
42. Cho YY, Baek NI, Chung HG, Jeong TS, Lee KT, Jeon SM, et al. Randomized controlled trial of sajabalssuk (Artemisia princeps pampanini) to treat pre-diabetes. Eur J Integr Med. (2012) 4:e299–308. doi: 10.1016/j.eujim.2012.01.009
43. Ebrahimi F, Aryaeian N, Pahlavani N, Abbasi D, Hosseini AF, Fallah S, et al. The effect of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) supplementation on blood pressure, and renal and liver function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A double-blinded, randomized clinical trial. Avicenna J phytomedicine. (2019) 9:322–33. doi: 10.22038/AJP.2019.12785
44. Fan W, Wang H, Yang B, Xu L, and Liu G. Clinical observation on wagner 2–3 diabetic foot ulcer treated by tcm external treatment scheme for euriching pus for tissue growth. Chin J Exp Traditional Med Formulae. (2022) 28:107–14. doi: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20221495
45. Fang Z, Bi Z, Zhao J, Wang S, Wu D, Lu R, et al. The effects of danzhi jiangtang capsule on clinical indices and vascular endothelial function in patients with impaired glucose tolerance of qi–yin deficiency type. Ann Med. (2023) 55:2291185. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2291185
46. Fang Z, Zhao J, Shi G, Shu Y, Ni Y, Wang H, et al. Shenzhu tiaopi granule combined with lifestyle intervention therapy for impaired glucose tolerance: A randomized controlled trial. Complementary therapies Med. (2014) 22:842–50. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2014.08.004
47. Ge J. Observation on the effect of treating diabetes with integrated Chinese and western medicine. Chin Community doctors [zhong guo she qu yi shi]. (2015) 31:85–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-614x.2015.28.53
48. Guo DZ, Wang YH, and Chen ZQ. Effect of treatment in 39 patients with diabetic nephropathy by safflor yellow and benazepril in combination. Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he za zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi jiehe zazhi = Chin J integrated traditional Western Med. (2008) 28:360–3. doi: CNKI:SUN:ZZXJ.0.2008-04-032
49. Guo Q, Zhang H, Li M, Zhao Z, Luo Y, Luo Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of sancai powder in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial. J traditional Chin Med = Chung i tsa chih ying wen pan. (2016) 36:640–8. doi: 10.1016/s0254-6272(16)30084-x
50. Guo XY and Zhu NN. Study on the therapeutic effect and anti-inflammatory effect of jianpi yishen decoction on diabetic nephropathy by pathway based on peripheral blood jnk/nf-κb pathway. Chin J Pharm Biotechnol. (2022) 29:393–6. doi: 10.19526/j.cnki.1005-8915.20220413
51. Guo ZA, Yu CJ, Liu G, Meng FC, Li Y, and Peng SL. Treatment of stage 3b diabetic kidney disease patients with macroalbuminuria by qizhi jiangtang capsule: A multicenter randomized control clinical study. Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he za zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi jiehe zazhi = Chin J integrated traditional Western Med. (2014) 34:1047–52. doi: CNKI:SUN:ZZXJ.0.2014-09-006
52. Huang YH, Chen ST, Liu FH, Hsieh SH, Lin CH, Liou MJ, et al. The efficacy and safety of concentrated herbal extract granules, yh1, as an add-on medication in poorly controlled type 2 diabetes: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot trial. PloS One. (2019) 14:e0221199. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221199
53. Jiang L, Fu Q, Wang S, Zhao J, Chen Y, Li J, et al. Effects of shenlian formula (参 连 方) on microbiota and inflammatory cytokines in adults with type 2 diabetes: A double-blind randomized clinical trial. J Trad Chin Med / Chung i tsa chih ying wen pan. (2023) 43:760–9. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20230608.003
54. Jin SY, Chen QG, Yao Z, and Lu H. Clinical observation of shenxie zhitong capsule in treating diabetic peripheral neuropathy of stagnant blockade of collaterals. Chin J Exp Traditional Med Formulae. (2021) 27:81–7. doi: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20202430
55. Jin YH, Zhang KN, and Hong M. Clinical effect of sanhuang jiedu tongluo decoction treating type 2 diabetes mellitus with dampness heat and dampness. China modern Med [zhong guo dang dai yi yao]. (2015) 22:157–60. doi: CNKI:SUN:ZGUD.0.2015-22-053
56. Ke B, Shi L, Jun-jie Z, Chen DS, Meng J, and Qin J. Protective effects of modified linggui zhugan decoction combined with short-term very low calorie diets on cardiovascular risk factors in obese patients with impaired glucose tolerance. J traditional Chin Med = Chung i tsa chih ying wen pan. (2012) 32:193–8. doi: 10.1016/s0254-6272(13)60010-2
57. Li BY, Peng H, Xiong DL, Yi J, and Chen H. Efficacy observation of treating diabetic nephropathy by shenshuaining granule combined telmisartan tablet. Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he za zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi jiehe zazhi = Chin J integrated traditional Western Med. (2015) 35:142‐6. doi: CNKI:SUN:ZZXJ.0.2015-02-004
58. Li JP, He XL, and Li Q. Clinical study on treatment of early diabetic nephropathy by tangshenling combined with telmisartan. Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he za zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi jiehe zazhi = Chin J integrated traditional Western Med. (2006) 26:415–8. doi: CNKI:SUN:ZZXJ.0.2006-05-009
59. Li P, Chen Y, Liu J, Hong J, Deng Y, Yang F, et al. Efficacy and safety of tangshen formula on patients with type 2 diabetic kidney disease: A multicenter double-blinded randomized placebo-controlled trial. PloS One. (2015) 10:e0126027. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126027
60. Li XS, Fu XJ, and Lang XJ. Effect of extract of gingko biloba on soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in patients with early diabetic nephropathy. Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he za zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi jiehe zazhi = Chin J integrated traditional Western Med. (2007) 27:412–4. doi: CNKI:SUN:ZZXJ.0.2007-05-014
61. Li YS and Yang BH. Effects of compound fluid of cortex phellodendri on inflammatory cytokines and growth factors in external treatment of diabetic foot ulcer. Chin J New Drugs. (2014) 23:1163–6.
62. Li YS, Zheng Q, and Yang BH. Efficacy and safety in a multi-center clinical trial for analyzing compound fluid of cortex phellodendri in the external treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. Chin J New Drugs. (2016) 25:2344–8. doi: CNKI:SUN:ZXYZ.0.2016-20-012
63. Li ZQ, Chang HJ, and Sang WF. Clinical efficacy of special effect san xiao decoction on type 2 diabetes mellitus. Zhong yao cai = Zhongyaocai [Journal Chin medicinal materials]. (2013) 36:163–6. doi: 10.13863/j.issn1001-4454.2013.01.010
64. Lian F, Tian J, Chen X, Li Z, Piao C, Guo J, et al. The efficacy and safety of Chinese herbal medicine jinlida as add-on medication in type 2 diabetes patients ineffectively managed by metformin monotherapy: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. PloS One. (2015) 10:e0130550. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130550
65. Liu H, Zheng J, and Li RH. Clinical efficacy of ‘Spleen-kidney-care’ Yiqi huayu and Jiangzhuo traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of patients with diabetic nephropathy. Exp Ther Med. (2015) 10:1096–102. doi: 10.3892/etm.2015.2627
66. Liu YH, Yang L, and Liu J. Clinical observation on treatment of early diabetic nephropathy by milkvetch injection combined with captopril. Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he za zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi jiehe zazhi = Chin J integrated traditional Western Med. (2005) 25:993–5. doi: CNKI:SUN:ZZXJ.0.2005-11-011
67. Liu YN. Effect of modified xiaoke decoction combined with metformin on clinical indicators of patients with type 2 diabetes of qi - deficiency and blood-stasis pattern. World Chin Med [shi jie zhong yi yao za zhi]. (2016) 11:2271–4.
68. Liu ZQ, Li QZ, and Qin GJ. Effect of astragalus injection on platelet function and plasma endothelin in patients with early stage diabetic nephropathy. Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he za zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi jiehe zazhi = Chin J integrated traditional Western Med. (2001) 21:274–6. doi: CNKI:SUN:ZZXJ.0.2001-04-016
69. Lu T, Sheng H, Wu J, Cheng Y, Zhu J, and Chen Y. Cinnamon extract improves fasting blood glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin level in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes. Nutr Res (New York NY). (2012) 32:408–12. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2012.05.003
70. Mehrzadi S, Tavakolifar B, Huseini HF, Mosavat SH, and Heydari M. The effects of boswellia serrata gum resin on the blood glucose and lipid profile of diabetic patients: A double-blind randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Evidence-Based Integr Med. (2018) 23:2515690X18772728. doi: 10.1177/2515690X18772728
71. Mirfeizi M, Mirfeizi S, MehdizadehTourzani Z, and AsghariJafarabadi M. Controlling diabetes mellitus type 2 with herbal medicines: A triple blind, randomized clinical trial of efficacy and safety. Diabetes Technol Ther. (2015) 17:A48–A9. doi: 10.1089/dia.2015.1525
72. Moein S, Saberi P, Moein M, Mehdizadeh R, and Zarshenas M. Hypoglycemic effects of aqueous extract of salvia mirzayanii rech. F& Esfand in diabetic patients; a randomized controlled trial study. J Nephropathol. (2020) 9:e06. doi: 10.15171/jnp.2020.06
73. Nematollahi S, Pishdad GR, Zakerkish M, Namjoyan F, Ahmadi Angali K, and Borazjani F. The effect of berberine and fenugreek seed co-supplementation on inflammatory factor, lipid and glycemic profile in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A double-blind controlled randomized clinical trial. Diabetol Metab syndrome. (2022) 14:120. doi: 10.1186/s13098-022-00888-9
74. Ni Q, Zhang X, and Cui N. Clinical observation of qiyao xiaoke capsule in intervening 76 patients with type 2 pre-diabetes. Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he za zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi jiehe zazhi = Chin J integrated traditional Western Med / Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he xue hui Zhongguo Zhong yi yan jiu yuan zhu ban. (2012) 32:1628–31. doi: CNKI:SUN:ZZXJ.0.2012-12-016
75. Pang J and Zhong R. Efficacy of modified zuoguiwan combined with perindopril tert-butylamine tablets on early diabetic kidney disease patients of qi-yin deficiency with blood stasis syndrome. Chin J Exp Traditional Med Formulae. (2023) 29:105–12. doi: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2022002025
76. Park K, Kim Y, Kim J, Kang S, Park JS, Ahn CW, et al. Supplementation with korean red ginseng improves current perception threshold in Korean type 2 diabetes patients: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Diabetes Res. (2020) 2020:5295328. doi: 10.1155/2020/5295328
77. Shi R, Wang Y, An X, Ma J, Wu T, Yu X, et al. Efficacy of co-administration of liuwei dihuang pills and ginkgo biloba tablets on albuminuria in type 2 diabetes: A 24-month, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. Front Endocrinol. (2019) 10:100. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00100
78. Shi YL, Liu WJ, Zhang XF, Su WJ, Chen NN, Lu SH, et al. Effect of Chinese herbal medicine jinlida granule in treatment of patients with impaired glucose tolerance. Chin Med J. (2016) 129:2281–6. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.190676
79. Song J, Li YH, and Yang XD. Effect of combined therapy with bailing capsule and benazepril on urinary albumin excretion rate and C-reactive protein in patients with early diabetic nephropathy. Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he za zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi jiehe zazhi = Chin J integrated traditional Western Med. (2009) 29:791–3. doi: CNKI:SUN:ZZXJ.0.2009-09-005
80. Tong XL, Wu ST, Lian FM, Zhao M, Zhou SP, Chen XY, et al. The safety and effectiveness of tm81, a Chinese herbal medicine, in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2013) 15:448–54. doi: 10.1111/dom.12051
81. Vuksan V, Sung MK, Sievenpiper JL, Stavro PM, Jenkins AL, Di Buono M, et al. Korean red ginseng (Panax ginseng) improves glucose and insulin regulation in well-controlled, type 2 diabetes: results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of efficacy and safety. Nutrition metabolism Cardiovasc diseases: NMCD. (2008) 18:46–56. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2006.04.003
82. Wainstein J, Landau Z, Dayan YB, Jakubowicz D, Grothe T, Perrinjaquet-Moccetti T, et al. Purslane extract and glucose homeostasis in adults with type 2 diabetes: A double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of efficacy and safety. J medicinal Food. (2016) 19:133–40. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2015.0090
83. Wang HY and Chen YP. Clinical observation on treatment of diabetic nephropathy with compound fructus arctii mixture. Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he za zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi jiehe zazhi = Chin J integrated traditional Western Med. (2004) 24:589–92. doi: CNKI:SUN:ZZXJ.0.2004-07-003
84. Wang WJ and Deng X. Observation of the clinical efficacy of shenfuyishen capsule in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy in high altitude regions. J Xi'an Jiaotong Univ (Medical Sciences). (2015) 36:845–8. doi: 10.7652/jdyxb201506026
85. Wang X, Tian LM, Hao YJ, Wang GY, and Li CX. Clinical observation of shenluoan decoction for treating obese patients with early diabetic nephropathy. Chin Traditional Herbal Drugs. (2015) 46:245–9. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2015.02.018
86. Wang XB, Sang Y, Han Q, Guo BR, and Liu XX. Effects of tangshenkang capsule on diabetic nephropathyon diabetic nephropathy. Chin J Integr Med. (1997) 3:21–5. doi: 10.1007/BF02935430
87. Wang Y, Ji Z, Liu J, and Wang J. Curative effect of sangzhi total alkaloid tablets in the treatment of pretype 2 diabetes and its effect on serum glucose transporter 4 and nesfatin-1. Acta Med Mediterr. (2023) 39:29‐35. doi: 10.19193/0393-6384_2023_1_4
88. Wang YH, Yang F, Ma Y, Guo S, Liu LF, Huang JA, et al. Clinical efficacy of buyang huanwu decoction combined with shenqi dihuang decoction in treatment of iii- stage diabetic kidney disease and its protective effect on renal tubular injury. Chin Traditional Herbal Drugs. (2023) 54:5289–95. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2023.16.018
89. Wang YZ, Wang XX, and Wang HC. Clinical observation on treatment of diabetic nephropathy with Chinese drugs combined with benazepril. Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he za zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi jiehe zazhi = Chin J integrated traditional Western Med. (2007) 27:683–5. doi: CNKI:SUN:ZZXJ.0.2007-08-007
90. Wang Z, Wang X, Zhang Y, Zhao L, and Li H. Treatment of diabetic foot by clearing heat, detoxification, activating blood, and dredging collaterals method. Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he za zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi jiehe zazhi = Chin J integrated traditional Western Med / Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he xue hui Zhongguo Zhong yi yan jiu yuan zhu ban. (2013) 33:480–3. doi: CNKI:SUN:ZZXJ.0.2013-04-018
91. Xiong C, Li L, Bo W, Chen H, XiaoWei L, Hongbao L, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of twhf in diabetic nephropathy patients with overt proteinuria and normal egfr. J Formosan Med Assoc. (2020) 119:685–92. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2019.11.001
92. Zhao XM, Zhang Y, He XH, Chen HD, Wang ZF, Guo J, et al. Chinese herbal medicine shenzhuo formula treatment in patients with macroalbuminuria secondary to diabetic kidney disease: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. (2018) 19:200. doi: 10.1186/s13063-018-2573-z
93. Zhao Y and Zhang XL. Effect of tongxinluo capsule on plasma endothelin in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he za zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi jiehe zazhi = Chin J integrated traditional Western Med. (2005) 25:131–3. doi: CNKI:SUN:ZZXJ.0.2005-02-013
94. Zheng Y, Bai L, Zhou Y, Tong R, Zeng M, Li X, et al. Polysaccharides from Chinese herbal medicine for anti-diabetes recent advances. Int J Biol Macromolecules. (2019) 121:1240–53. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.072
95. Zhang X, Zhang Y, Zhou M, Xie Y, Dong X, Bai F, et al. Dphc from alpinia officinarum ameliorates oxidative stress and insulin resistance via activation of nrf2/are pathway in db/db mice and high glucose-treated hepg2 cells. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12:792977. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.792977
96. Cao H, Tuo L, Tuo Y, Xia Z, Fu R, Liu Y, et al. Immune and metabolic regulation mechanism of dangguiliuhuang decoction against insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis. Front Pharmacol. (2017) 8:445. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00445
97. Mao XQ, Yu F, Wang N, Wu Y, Zou F, Wu K, et al. Hypoglycemic effect of polysaccharide enriched extract of astragalus membranaceus in diet induced insulin resistant C57bl/6j mice and its potential mechanism. Phytomed: Int J phytother phytopharmacol. (2009) 16:416–25. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2008.12.011
98. Sun J, Liu Y, Yu J, Wu J, Gao W, Ran L, et al. Aps could potentially activate hepatic insulin signaling in hfd-induced ir mice. J Mol Endocrinol. (2019) 63:77–91. doi: 10.1530/jme-19-0035
99. Zhang K, Pugliese M, Pugliese A, and Passantino A. Biological active ingredients of traditional Chinese herb astragalus membranaceus on treatment of diabetes: A systematic review. Mini Rev medicinal Chem. (2015) 15:315–29. doi: 10.2174/1389557515666150227113431
100. Zhang R, Qin X, Zhang T, Li Q, Zhang J, and Zhao J. Astragalus polysaccharide improves insulin sensitivity via ampk activation in 3t3-L1 adipocytes. Molecules (Basel Switzerland). (2018) 23:2711. doi: 10.3390/molecules23102711
101. Wang Z, Wang X, Fu L, Xu S, Wang X, Liao Q, et al. Shengmai san formula alleviates high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice through gut microbiota-derived bile acid promotion of M2 macrophage polarization and thermogenesis. Phytomed: Int J phytother phytopharmacol. (2024) 133:155938. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155938
102. Zhang F, Ning J, Chen C, Li B, and Wei Y. Advances in the mechanisms of gardenia jasminoides ellis in improving diabetes and its complications. Fitoterapia. (2024) 178:106140. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2024.106140
103. Pang B, Zhao LH, Zhou Q, Zhao TY, Wang H, Gu CJ, et al. Application of berberine on treating type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Endocrinol. (2015) 2015:905749. doi: 10.1155/2015/905749
104. Li JS, Ji T, Su SL, Zhu Y, Chen XL, Shang EX, et al. Mulberry leaves ameliorate diabetes via regulating metabolic profiling and ages/rage and P38 mapk/nf-κb pathway. J ethnopharmacol. (2022) 283:114713. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114713
105. Wang M, Chang SQ, Tian YS, Zhang GQ, and Qi J. Zengye decoction ameliorates insulin resistance by promoting glucose uptake. Rejuvenation Res. (2020) 23:367–76. doi: 10.1089/rej.2019.2228
106. Cai M, Lai W, Chen H, Cao D, Zhang B, Wang F, et al. Puerarin targets hif-1α to modulate hypoxia-related sphingolipid metabolism in diabetic hepatopathy via the sptlc2/ceramide pathway. Pharm (Basel Switzerland). (2025) 18:398. doi: 10.3390/ph18030398
107. Zhang HY, Tian JX, Lian FM, Li M, Liu WK, Zhen Z, et al. Therapeutic mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine to improve metabolic diseases via the gut microbiota. Biomed pharmacother = Biomed pharmacotherapie. (2021) 133:110857. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110857
108. Tawulie D, Jin L, Shang X, Li Y, Sun L, Xie H, et al. Jiang-tang-san-huang pill alleviates type 2 diabetes mellitus through modulating the gut microbiota and bile acids metabolism. Phytomed: Int J phytother phytopharmacol. (2023) 113:154733. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154733
109. Yang Q-H, Liang Y, Xu Q, Zhang Y, Xiao L, and Si L-Y. Protective effect of tetramethylpyrazine isolated from ligusticum chuanxiong on nephropathy in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Phytomed: Int J phytother phytopharmacol. (2011) 18:1148–52. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2011.05.003
110. Ko CY, Lin RH, Lo YM, Chang WC, Huang DW, Wu JS, et al. Effect of ruellia tuberosa L. On aorta endothelial damage-associated factors in high-fat diet and streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic rats. Food Sci Nutr. (2019) 7:3742–50. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.1233
111. Cui FQ, Tang L, Gao YB, Wang YF, Meng Y, Shen C, et al. Effect of baoshenfang formula on podocyte injury via inhibiting the nox-4/ros/P38 pathway in diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Res. (2019) 2019:2981705. doi: 10.1155/2019/2981705
112. Wang JL, Xiu CK, Yang J, Wang X, Hu YH, Fang JY, et al. Effect of ginseng radix et rhizoma, notoginseng radix et rhizoma and chuanxiong rhizoma extracts on intestinal flora of vascular aging mice induced by high glucose and high lipid. Zhongguo Zhong yao za zhi = Zhongguo zhongyao zazhi = China J Chin materia Med. (2020) 45:2938–46. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200117.401
113. Xie M, Deng L, Yu Y, Xie X, and Zhang M. The effects of bushen yiqi huoxue prescription and its disassembled prescriptions on a diabetic retinopathy model in sprague dawley rats. Biomed Pharmacother. (2021) 133:110920. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110920
114. Huang S, Tan M, Guo F, Dong L, Liu Z, Yuan R, et al. Nepeta angustifolia C. Y. Wu improves renal injury in hfd/stz-induced diabetic nephropathy and inhibits oxidative stress-induced apoptosis of mesangial cells. J ethnopharmacol. (2020) 255:112771. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112771
115. Chao M, Zou D, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Wang M, Wu H, et al. Improving insulin resistance with traditional Chinese medicine in type 2 diabetic patients. Endocrine. (2009) 36:268–74. doi: 10.1007/s12020-009-9222-y
116. Chan KW, Kwong ASK, Tsui PN, Chan GCW, Choi WF, Yiu WH, et al. Add-on astragalus in type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease: A multi-center, assessor-blind, randomized controlled trial. Phytomed: Int J phytother phytopharmacol. (2024) 130:155457. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155457
117. Gao D, Li Q, Gao Z, and Wang L. Antidiabetic effects of corni fructus extract in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Yonsei Med J. (2012) 53:691–700. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2012.53.4.691
118. Jeong SY, Kang S, Kim DS, and Park S. Codonopsis lanceolata water extract increases hepatic insulin sensitivity in rats with experimentally-induced type 2 diabetes. Nutrients. (2017) 9:1200. doi: 10.3390/nu9111200
119. Mao YP, Song YM, Pan SW, Li N, Wang WX, Feng BB, et al. Effect of codonopsis radix and polygonati rhizoma on the regulation of the irs1/pi3k/akt signaling pathway in type 2 diabetic mice. Front Endocrinol. (2022) 13:1068555. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1068555
120. Liu S, Wang L, Zhang Z, Leng Y, Yang Y, Fu X, et al. The potential of astragalus polysaccharide for treating diabetes and its action mechanism. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1339406. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1339406
121. Li N, Fan Y, Jia X, Ma Z, and Lin S. Effect of astragali radix active ingredients on serum insulin and adiponectin in diabetes rats. Chin J Exp Traditional Med Formulae. (2011) 17:144–6. doi: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2011.05.066
122. Eid HM, Martineau LC, Saleem A, Muhammad A, Vallerand D, Benhaddou-Andaloussi A, et al. Stimulation of amp-activated protein kinase and enhancement of basal glucose uptake in muscle cells by quercetin and quercetin glycosides, active principles of the antidiabetic medicinal plant vaccinium vitis-idaea. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2010) 54:991–1003. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200900218
123. Jiang H, Yamashita Y, Nakamura A, Croft K, and Ashida H. Quercetin and its metabolite isorhamnetin promote glucose uptake through different signalling pathways in myotubes. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:2690. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-38711-7
124. Dai X, Ding Y, Zhang Z, Cai X, Bao L, and Li Y. Quercetin but not quercitrin ameliorates tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced insulin resistance in C2c12 skeletal muscle cells. Biol Pharm Bull. (2013) 36:788–95. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b12-00947
125. Jiang J, Zhang G, Yu M, Gu J, Zheng Y, Sun J, et al. Quercetin improves the adipose inflammatory response and insulin signaling to reduce "Real-world" Particulate matter-induced insulin resistance. Environ Sci pollut Res Int. (2022) 29:2146–57. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-15829-8
126. Li D, Jiang C, Mei G, Zhao Y, Chen L, Liu J, et al. Quercetin alleviates ferroptosis of pancreatic β Cells in type 2 diabetes. Nutrients. (2020) 12:2954. doi: 10.3390/nu12102954
127. Zhang L, Wang X, Chang L, Ren Y, Sui M, Fu Y, et al. Quercetin improves diabetic kidney disease by inhibiting ferroptosis and regulating the nrf2 in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Ren Fail. (2024) 46:2327495. doi: 10.1080/0886022x.2024.2327495
128. Tang H, Zeng Q, Tang T, Wei Y, and Pu P. Kaempferide improves glycolipid metabolism disorder by activating pparγ in high-fat-diet-fed mice. Life Sci. (2021) 270:119133. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119133
129. Ortiz-Barragán E, Estrada-Soto S, Giacoman-Martínez A, Alarcón-Aguilar FJ, Fortis-Barrera Á, Marquina-Rodríguez H, et al. Antihyperglycemic and Hypolipidemic Activities of Flavonoids Isolated from Smilax Dominguensis Mediated by Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors. Pharm (Basel Switzerland) (2024) 17: 1451. doi: 10.3390/ph17111451
130. Luo C, Yang H, Tang C, Yao G, Kong L, He H, et al. Kaempferol alleviates insulin resistance via hepatic ikk/nf-κb signal in type 2 diabetic rats. Int Immunopharmacol. (2015) 28:744–50. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2015.07.018
131. Wang T, Wu Q, and Zhao T. Preventive effects of kaempferol on high-fat diet-induced obesity complications in C57bl/6 mice. BioMed Res Int. (2020) 2020:4532482. doi: 10.1155/2020/4532482
132. Sharma D, Kumar Tekade R, and Kalia K. Kaempferol in ameliorating diabetes-induced fibrosis and renal damage: an in vitro and in vivo study in diabetic nephropathy mice model. Phytomed: Int J phytother phytopharmacol. (2020) 76:153235. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153235
133. Ward MG, Li G, Barbosa-Lorenzi VC, and Hao M. Stigmasterol prevents glucolipotoxicity induced defects in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:9536. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10209-0
134. Wang J, Huang M, Yang J, Ma X, Zheng S, Deng S, et al. Anti-diabetic activity of stigmasterol from soybean oil by targeting the glut4 glucose transporter. Food Nutr Res. (2017) 61:1364117. doi: 10.1080/16546628.2017.1364117
135. Wang J, An G, Peng X, Zhong F, Zhao K, Qi L, et al. Effects of three huanglian-derived polysaccharides on the gut microbiome and fecal metabolome of high-fat diet/streptozocin-induced type 2 diabetes mice. Int J Biol Macromolecules. (2024) 273:133060. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.133060
136. Jiang S, Tang Y, Bao Y, Su X, Li K, Guo Y, et al. Protective effect of coptis chinensis polysaccharide against renal injury by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetic rats. Natural Product Commun. (2019) 14:1934578X19860998. doi: 10.1177/1934578x19860998
137. Cui L, Liu M, Chang X, and Sun K. The inhibiting effect of the coptis chinensis polysaccharide on the type ii diabetic mice. Biomed Pharmacother. (2016) 81:111–9. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.03.038
138. Zhang Y, Wang H, Zhang L, Yuan Y, and Yu D. Codonopsis lanceolata polysaccharide clps alleviates high fat/high sucrose diet-induced insulin resistance via anti-oxidative stress. Int J Biol Macromol. (2020) 145:944–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.09.185
139. Fu CY, Ren L, Liu WJ, Sui Y, Nong QN, Xiao QH, et al. Structural characteristics of a hypoglycemic polysaccharide from fructus corni. Carbohydr Res. (2021) 506:108358. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2021.108358
140. Lawrence JM, Divers J, Isom S, Saydah S, Imperatore G, Pihoker C, et al. Trends in prevalence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents in the us, 2001-2017. Jama. (2021) 326:717–27. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.11165
141. Mayer-Davis EJ, Lawrence JM, Dabelea D, Divers J, Isom S, Dolan L, et al. Incidence trends of type 1 and type 2 diabetes among youths, 2002-2012. New Engl J Med. (2017) 376:1419–29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1610187
Keywords: diabetes, traditional Chinese medicine, meta-analysis, network pharmacology analysis, efficacy
Citation: Tang S, Lin J, Li G, Guo H, Liu C and Wu F (2025) Evaluating efficacy and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine in diabetes treatment: a meta-analysis and network pharmacology study. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1605091. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1605091
Received: 02 April 2025; Accepted: 18 September 2025;
Published: 07 October 2025.
Edited by:
Åke Sjöholm, Gävle Hospital, SwedenReviewed by:
Luming Qi, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, ChinaZeshan Ali, Bohai University, China
Copyright © 2025 Tang, Lin, Li, Guo, Liu and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fuju Wu, d3VmakBqbHUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Shuai Tang
Shuai Tang Jie Lin
Jie Lin Gangyi Li3†
Gangyi Li3† Huaijuan Guo
Huaijuan Guo Fuju Wu
Fuju Wu