- 1Department of Orthopedics, The 921st Hospital of the People’s Liberation Army, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Hunan Normal University, Changsha, China
- 2Hangzhou Dianzi University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 3The No. 924 Hospital of the Joint Logistic Support Force of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army, Guilin, China
Background: The cardiometabolic Index (CMI) serves as a metric for evaluating the functional and metabolic health of the heart. It aids healthcare professionals in assessing cardiac health, predicting the risk of cardiovascular diseases, and determining the effectiveness of various treatments. Despite its significance, there is a scarcity of studies examining the relationship between CMI and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Consequently, our objective was to clarify the relationship between CMI and OSA.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study using data from the 2015–2018 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), focusing on a cohort of adults aged 20 years and older. To assess the prevalence of OSA, we employed the Sleep Questionnaire (SLQ) included in the NHANES dataset, which identifies OSA based on symptom-based survey items. Various analytical methods were utilized to examine the relationship between CMI and OSA, including multivariate logistic regression, restricted cubic splines (RCS), threshold effect analysis, subgroup analyses, and mediation effect analyses.
Results: In this study, we included 3,912 participants, among whom 1,997 were diagnosed with OSA, resulting in a prevalence of 51%. After thoroughly accounting for relevant covariates, a positive correlation between the CMI and OSA was observed [OR (95% CI): 1.31 (1.21, 1.42), p < 0.001]. This association was further corroborated through restricted cubic spline (RCS) analyses. Additionally, threshold effect analyses indicated a significant inflection point, with the prevalence of OSA increasing significantly with CMI and then leveling off. Further subgroup analyses demonstrated a significant interaction based on smoking status (p < 0.05). Finally, mediation analyses confirmed that smoking served as a mediator in the relationship between CMI and OSA, exhibiting a mediation effect size of 0.002115.
Conclusion: In the adult population of the United States, a positive nonlinear relationship exists between the CMI and the prevalence of OSA. Smoking status partially mediates this association. Additionally, the findings from the threshold effects analysis indicate that maintaining CMI within an appropriate range can significantly decrease the likelihood of developing OSA.
1 Introduction
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a prevalent sleep disorder marked by recurring instances of partial or complete blockage of the upper airway during sleep, which leads to interruptions in sleep and episodes of intermittent hypoxia (1, 2). This condition impacts a considerable segment of the adult population, with estimates indicating that more than 25% of adults may experience mild to moderate OSA (3, 4). OSA is linked to numerous serious health issues, including an elevated risk of cardiovascular disease, hypertension, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome (5–8). The chronic nature of OSA, along with the likelihood of many cases remaining undiagnosed (9), emphasizes the necessity for early identification and intervention to reduce its detrimental effects.
In clinical research and practice, composite indices have emerged as valuable tools for capturing complex physiological phenomena through integrated metrics. These indices combine multiple biomarkers or clinical parameters into a single quantitative measure, offering a more holistic assessment than individual variables alone. Particularly in endocrinology and metabolic medicine, composite indices like HOMA-IR for insulin resistance or TyG (triglyceride glucose) index have proven instrumental in evaluating multifaceted conditions (10, 11). Their strength lies in synthesizing interrelated biological processes, enhancing predictive capacity, and simplifying clinical decision-making. However, such indices also present limitations: they may obscure the relative contribution of individual components, vary in performance across populations, and sometimes lack standardized cutoff values. Despite these challenges, when properly validated, composite indices remain powerful tools for uncovering systemic relationships in metabolic health.
The Cardiometabolic Index (CMI) serves as a critical tool for assessing both cardiac function and metabolic status (12, 13). By integrating various parameters—such as body weight, waist circumference, and biochemical markers (14), CMI provides a comprehensive evaluation of an individual’s cardiovascular risk, thus allowing healthcare providers to identify at-risk individuals and implement timely preventive strategies (15, 16). Understanding the significance of CMI is crucial not just within clinical practice but also in research settings, as it has the potential to uncover novel associations between metabolic health and sleep disorders.
Recent studies have begun to explore the complex relationship between CMI and OSA, revealing that elevated CMI may predispose individuals to OSA. Factors such as increased adiposity can exacerbate upper airway obstruction, while systemic inflammation frequently seen in metabolic dysregulation may also play a pivotal role (17–20). Conversely, the metabolic changes associated with OSA, including insulin resistance and dyslipidemia, can further heighten the risks posed by a high CMI, suggesting a bidirectional interplay between the two conditions (21–23). The interplay between CMI and OSA is complex and multifactorial, involving several biological and behavioral mechanisms that warrant further exploration. Therefore, understanding the nuanced connection between CMI and OSA is not merely an academic exercise; it has far-reaching implications for public health strategies. A clearer understanding of how CMI and OSA interact could pave the way for targeted interventions that address both metabolic health and sleep quality, ultimately aiming to reduce the prevalence and impact of OSA in individuals with elevated CMI.
This study aims to elucidate the association between CMI and OSA, contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of their interconnected roles in cardiovascular and metabolic health. We hypothesize that elevated CMI values will demonstrate a positive association with OSA prevalence. Furthermore, investigating potential threshold effects in this relationship represents a critical research objective. Additionally, we aim to examine whether specific mediating factors influence the CMI-OSA association.
2 Methods
2.1 Study population
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) is an extensive cross-sectional study carried out by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), which is a component of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in the United States. Established in the early 1960s, NHANES seeks to evaluate the health and nutritional status of the U.S. population by utilizing a combination of interviews, physical examinations, and laboratory tests. Data in the NHANES database is collected from a representative sample of civilians, covering various demographic groups across the country. The survey employs a multistage sampling design to ensure that the findings are generalizable to the broader U.S. population.
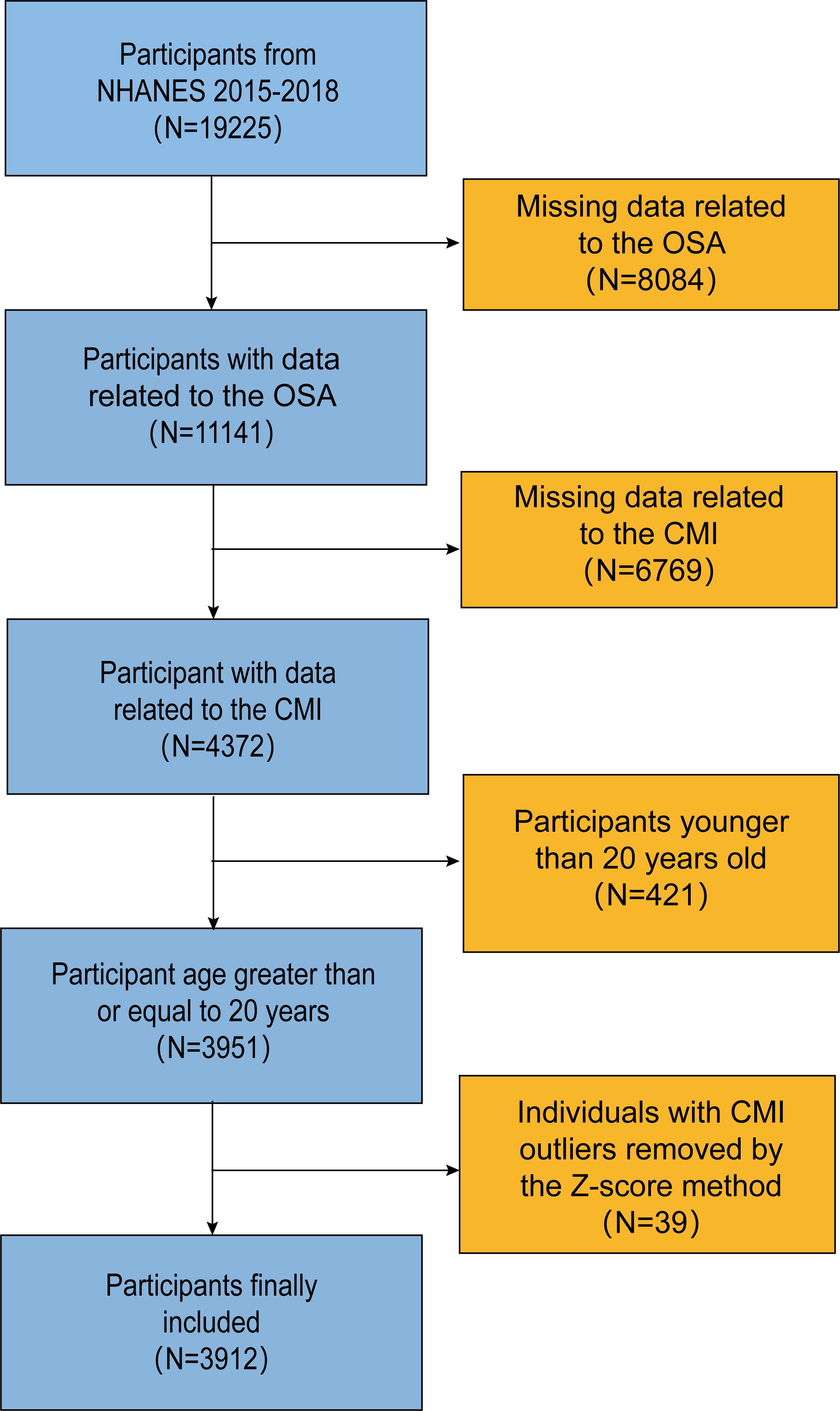
We utilized data from two cycles of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) conducted between 2015 and 2018. The initial dataset included 19,225 participants. However, after excluding cases with incomplete information on OSA, CMI, and screening out the group of adults older than 20 years, only 3,912 individuals remained after removing individuals with outlier CMI values using the Z-Score method (Figure 1).
2.2 Definition of OSA
Drawing from prior research (24), we employed the Sleep Questionnaire (SLQ) included in the NHANES dataset to evaluate the prevalence of OSA. A diagnosis of OSA is made when an individual meets any of the following criteria: (1) experiences significant daytime sleepiness despite obtaining approximately 7 or more hours of sleep on weekdays or weeknights, occurring more than 16 times per month; (2) exhibits apnea or snorting at least three nights per week; or (3) demonstrates loud snoring at least three nights per week.
2.3 Definition of CMI
The CMI is calculated as follows:
The triglyceride and HDL data were measured by Cobas 6000 Chemistry Analyzer.
2.4 Covariates
Drawing from existing literature (25–27), we incorporated several potential confounding variables as covariates in our analysis. Among these, age, poverty-to-income ratio (PIR), and total cholesterol were treated as continuous variables. Conversely, gender, race, and education level (classified as less than high school, high school, and more than high school) were considered categorical variables. Additionally, marital status (married vs. never married), smoking status (categorized based on whether the individual had smoked 100 cigarettes in their lifetime), excessive drinking status (categorized according to whether the individual consumed more than four drinks per day), as well as the prevalence of diabetes mellitus and hypertension (categorized according to whether or not they have been informed of the disease by a doctor) were also included as categorical variables.
It is important to note that due to the high correlation of variables such as BMI, height, waist circumference, high-density lipoprotein, and triglycerides with CMI, we did not consider them as associated covariates to avoid potential multicollinearity in the experimental results.
2.5 Statistical analysis
The statistical analysis for this study was conducted using R version 4.4.1. All statistical evaluations were weighted in accordance with the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) guidelines. To address the issue of missing data for additional variables (such as PIR, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, etc.) among the final cohort of 3,912 participants, we utilized the “missForest” package to perform multiple imputations, thereby minimizing the potential for multicollinearity during the analysis.
Initially, the normality of all continuous variables was assessed, revealing that they all followed a non-normal distribution. Participants were then divided into two groups according to the presence of OSA. Continuous variables were assessed using the Mann-Whitney U test, while categorical variables were analyzed with the Chi-square test. Relevant continuous variables are presented as median ± interquartile range (IQR), and categorical variables are reported as percentages (%).
In the multiple logistic regression analysis, three models were constructed: the crude model, which included no covariates; Model II, which incorporated demographic-related variables; and Model III, which included all relevant covariates. RCS regression was used to explore the nonlinear association between the CMI and OSA, while threshold effect analysis was applied to pinpoint potential inflection points in this relationship. Subgroup analyses were carried out based on factors such as age, sex, race, education level, marital status, smoking behaviors, alcohol intake, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus. Furthermore, mediation effect analysis was conducted to evaluate the mediating influence of smoking.
3 Results
3.1 Population baseline characteristics
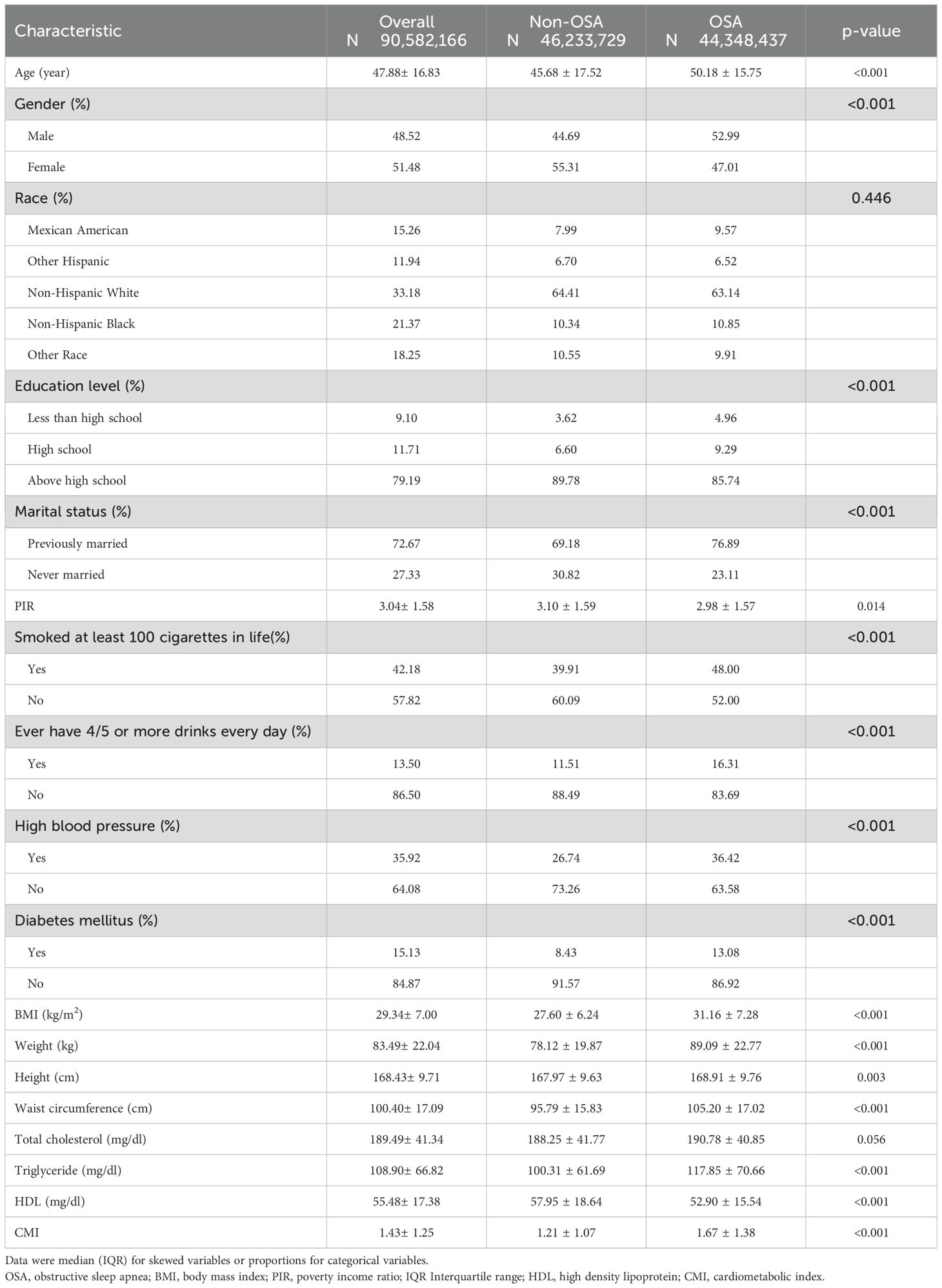
A total of 3,912 participants were included in this study, which represents an estimated population of 90,582,166 following the application of inverse weighting. Among these individuals, 1,997 were diagnosed with OSA, resulting in a prevalence rate of 51%. The participants were categorized into two groups based on their OSA status (refer to Table 1). Our analysis revealed that a higher proportion of men, married people, smokers, excessive drinkers and hypertensive people had OSA compared to the other groups in the subgroups. Furthermore, those with OSA were characterized by advanced age, increased body weight, higher BMI, greater waist circumference, elevated triglyceride levels, and a higher CMI, in addition to lower values of the PIR associated with high-density lipoprotein.
3.2 Association between CMI and OSA
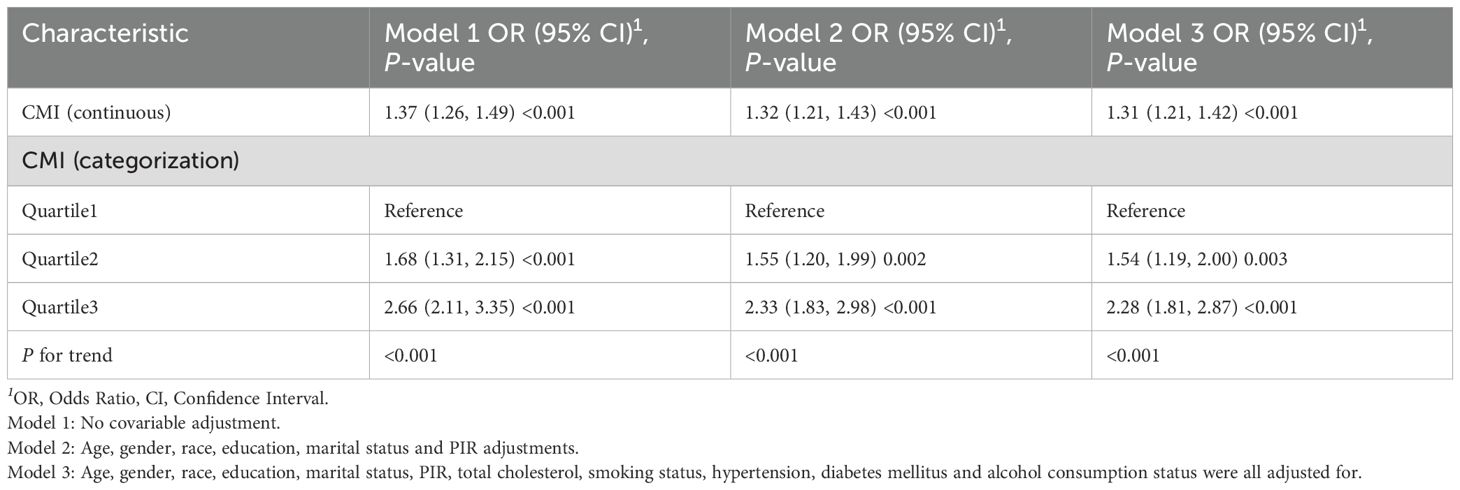
Table 2 displays the results of the multivariate logistic regression analysis that investigates the association between CMI and OSA. We developed three separate models for this analysis, and the results consistently revealed a significant positive association between CMI and OSA across all models (p < 0.001). Specifically, in the fully adjusted model (Model III), the odds ratio (OR) was found to be 1.31, indicating that for each one-unit increase in CMI, the likelihood of developing OSA increased by 31%. Furthermore, the results of the trend analysis in the fully adjusted model indicated that individuals in the highest tertile of CMI exhibited a progressively higher incidence of OSA compared to those in the lowest tertile (p for trend < 0.001).
3.3 Restricted cubic spline analysis with threshold effect analysis
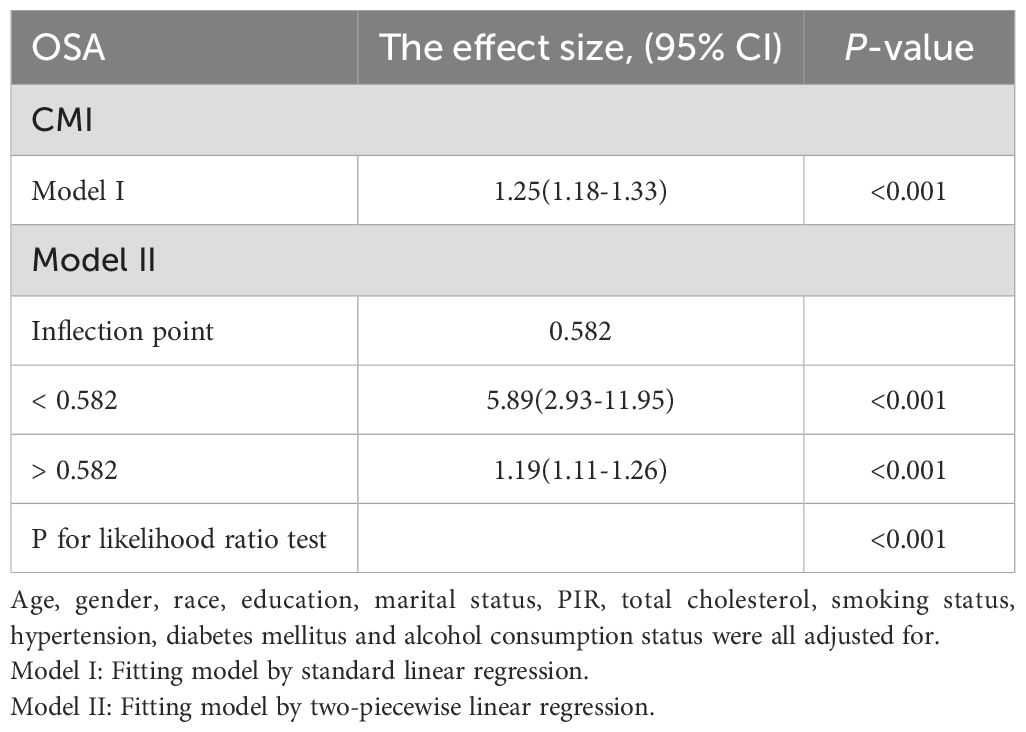
We employed restricted cubic splines to analyze the nonlinear relationship between the CMI and OSA (Figure 2). The results indicated a positive correlation between CMI and OSA in the fully adjusted model (Model III), with a statistically significant overall p-value of less than 0.001. This finding reinforces the earlier conclusions drawn from the multiple logistic regression analysis and suggests a notable nonlinear relationship between these two variables (p for nonlinear < 0.001). We observed what appeared to be a “L” shape relationship, prompting us to conduct a threshold effect analysis, which identified a significant inflection point at 0.582 (p for likelihood ratio test < 0.001). Prior to reaching this inflection point, the prevalence of OSA was found to increase by a factor of 4.89 for each one-unit rise in CMI; conversely, beyond this point, the prevalence increased by only 0.19 for each unit increment in CMI (refer to Table 3).
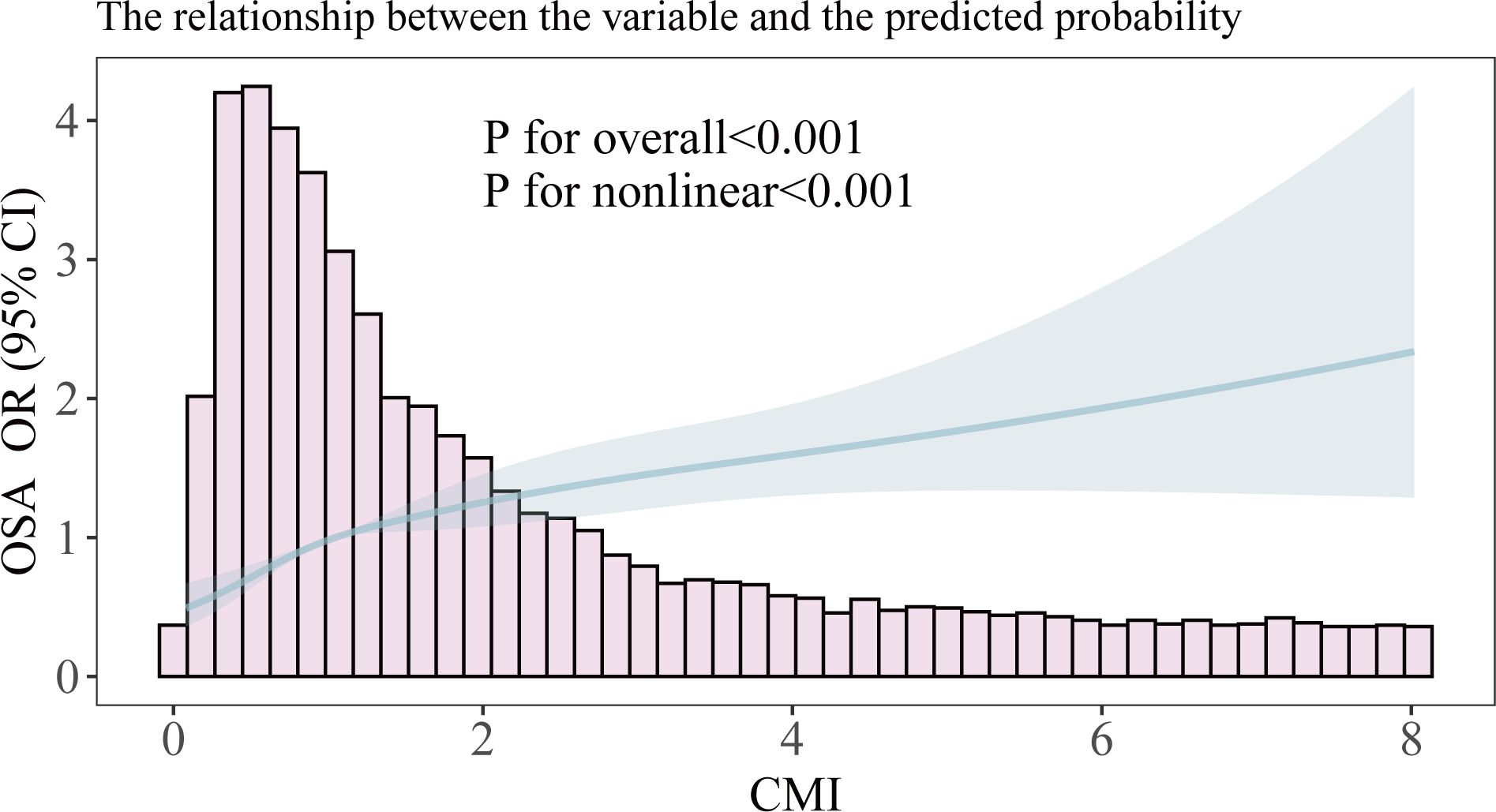
Figure 2. Smooth curve fitting of association between CMI and OSA. The solid portion and the shaded portion represent the predicted values and 95% confidence intervals, respectively. The model is model 3 after adjusting for all relevant covariates.
3.4 Subgroup analysis
To further investigate the stratified association between CMI and OSA within subgroups, we analyzed participants based on various demographic characteristics, as well as smoking status, excessive alcohol consumption, prevalence of hypertension, and prevalence of diabetes mellitus (Figure 3). The results showed that the positive correlation between CMI and OSA was broadly present across subgroups. Notably, we identified a significant interaction effect based on smoking status (p for interaction < 0.05), revealing that smokers exhibited a stronger positive association between CMI and OSA compared to non-smokers.
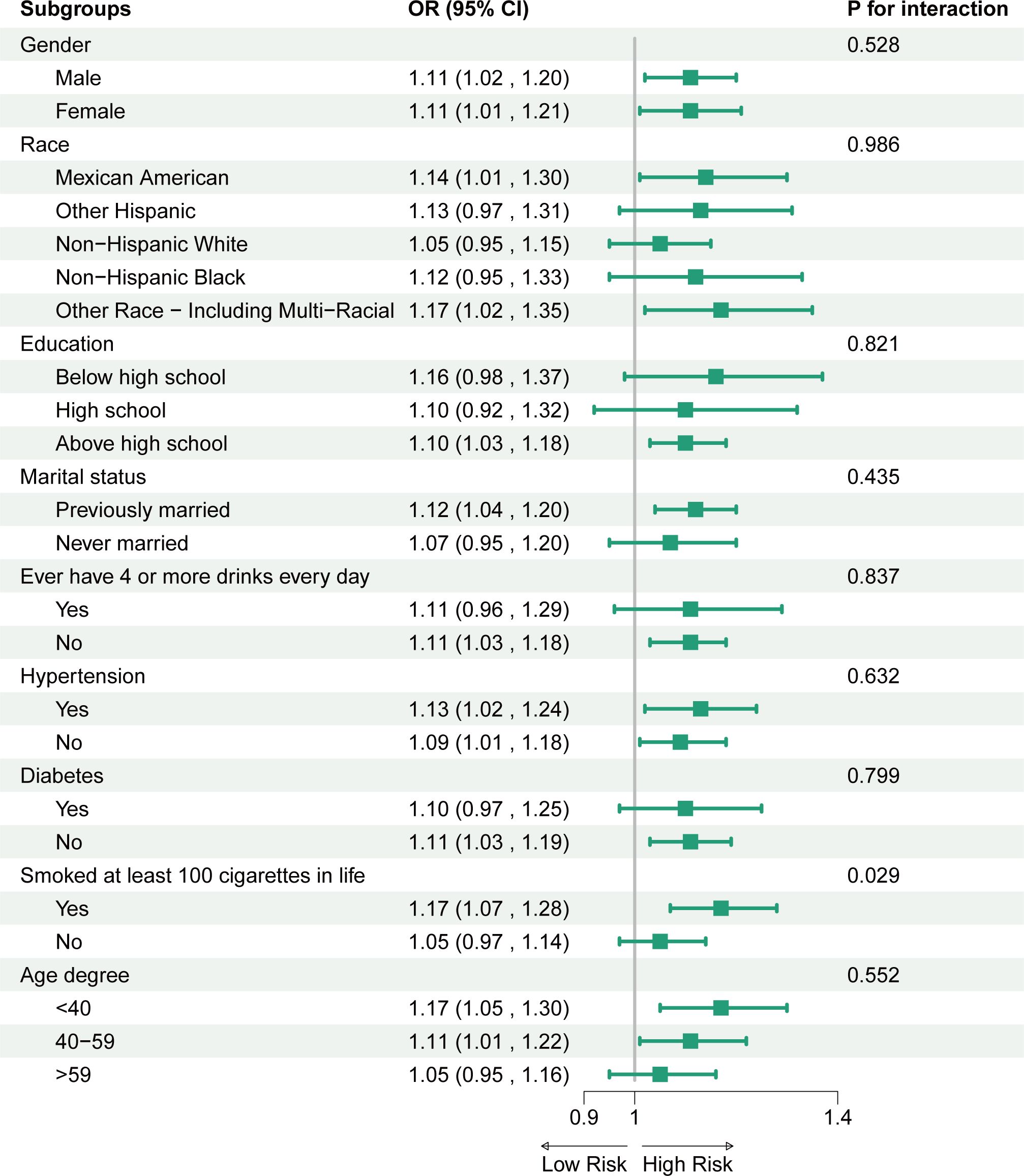
Figure 3. Association between CMI and OSA. For each stratification element we used Model 3 (fully adjusted model) for the adjustment analysis, except for the stratificationfactors themselves.
3.5 Mediation effect analysis
The results from the interaction analysis indicated that individuals who smoke have a more pronounced positive correlation between their CMI and OSA when compared to non-smokers. Consequently, we further investigated the potential mediating effect of smoking in this relationship. The mediating effect of smoking is illustrated in Figure 4, with additional data available in the Supplementary Material. The findings demonstrated that the total effect of CMI on OSA is 0.068837. After adding smoking as an intermediate medium, the direct effect of CMI on OSA is 0.066722. Smoking partially mediated the association between CMI and OSA, yielding a mediating effect size of 0.002115 (p < 0.001). This implies that smoking serves as a positive intermediary factor influencing the relationship between CMI and OSA.
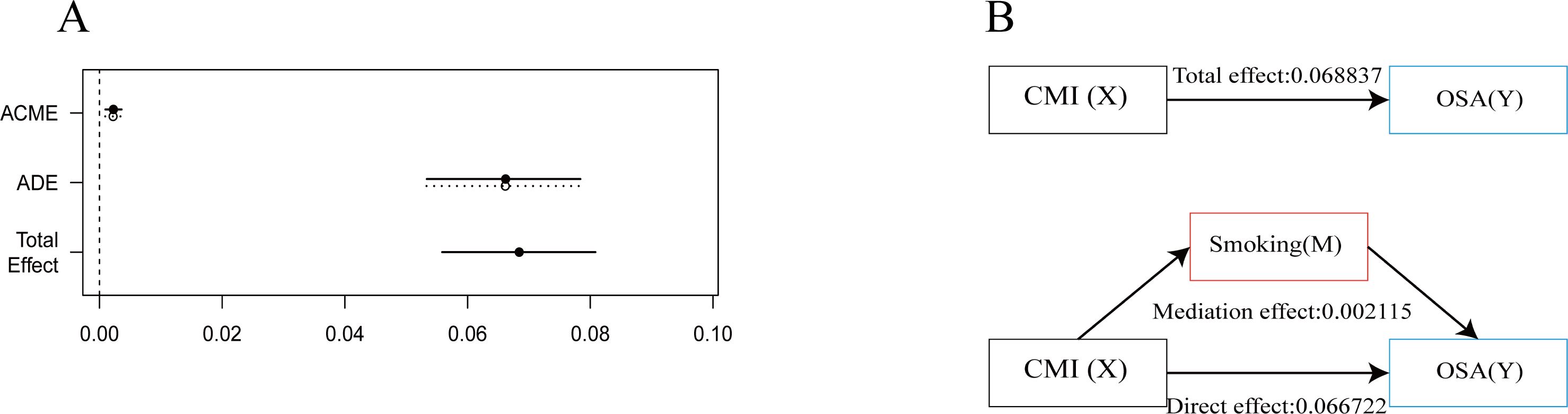
Figure 4. Analysis of intermediation effects. This figure shows the mediation model of the independent variable CMI, smoking as the mediating variable, and the dependent variable OSA. (A) Effect Values and Confidence Intervals for the CMI, OSA and smoking Mediating Effects (ACME, average causal mediation effects; ADE, Average Direct Effect). (B) Path diagram of mediation analysis of the relationship between smoking on CMI and OSA.
4 Discussion
The findings of this study reveal a significant positive nonlinear relationship between elevated CMI and the incidence of OSA in the adult population of the United States. The “L” shape relationship found through threshold effect analysis indicates that maintaining an appropriate CMI level is critical to mitigating the risk of developing OSA. Specifically, our analysis demonstrated that for each unit increase in CMI, the likelihood of OSA increases by 31% in the fully adjusted model [OR (95% CI): 1.31 (1.21, 1.42), p < 0.001]. Notably, smoking was found to mediate the association between CMI and OSA, highlighting its role as a confounding factor that exacerbates this risk.
In practical terms, these results suggest that CMI could be effectively integrated into existing risk stratification frameworks for OSA screening. Healthcare providers can utilize CMI as a quantifiable metric to identify individuals at heightened risk for OSA, allowing for timely interventions. By incorporating CMI into routine assessments, clinicians could enhance their ability to stratify patients based on risk and customize preventive strategies tailored to individuals’ profiles. For example, patients with high CMI scores could undergo more rigorous screening for OSA, enabling earlier diagnosis and targeted management, potentially including lifestyle modifications or therapeutic interventions. Overall, adopting CMI in clinical practice as part of risk stratification for OSA could significantly improve patient outcomes and empower healthcare providers to implement proactive measures against this common sleep disorder.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is increasingly acknowledged as an important public health concern due to its high prevalence and serious health consequences. Research estimates that about 25% of adult males and 10% of adult females in the United States are impacted by OSA (28, 29), with these rates continuing to rise alongside increasing obesity rates (30). This sleep disorder is marked by repeated instances of either complete or partial blockage of the upper airway during sleep, which results in intermittent hypoxia and frequent awakenings. The consequences of untreated OSA are significant, leading to various adverse health outcomes, such as cardiovascular disease, hypertension, type 2 diabetes, and an increased risk of stroke (31–36). Additionally, OSA is associated with decreased quality of life, increased healthcare utilization, and economic burdens, underscoring the urgent need for effective screening and intervention strategies.
The cardiometabolic Index (CMI) has emerged as a valuable tool for assessing cardiovascular and metabolic health. It integrates multiple physiological parameters, such as waist-to-height ratio (used to reflect abdominal obesity), and lipid levels (used to reflect lipid metabolism in the body), to provide a comprehensive evaluation of an individual’s cardiac health (37–39). Its significance lies in its potential to identify individuals at increased risk for cardiovascular complications, thereby enabling proactive management of metabolic syndrome (15, 16, 40, 41). The development of CMI reflects a growing awareness of the interactions between metabolic health and cardiovascular disease, highlighting the importance of adopting a holistic approach to patient care.
In this study, we identified a significant positive correlation between the CMI and OSA. This finding suggests that cardiac metabolic health may play an important role in the occurrence and progression of OSA. Several potential mechanisms could explain this correlation. First, CMI is derived from a combination of factors such as waist circumference, height, triglycerides, and high-density lipoprotein levels, which collectively reflect an individual’s metabolic status and fat distribution. A higher CMI is typically indicative of abdominal obesity and metabolic dysfunction (14, 42). These factors can lead to fat deposition in the upper airway tissues (18, 43), increasing airway resistance and contributing to the development of OSA. Additionally, abdominal obesity may impair diaphragm function (44), further disrupting normal nighttime respiration. Second, elevated CMI is often closely linked with the development of insulin resistance, chronic inflammation, and metabolic syndrome (15, 45–48). Insulin resistance can lead to abnormal adipocyte function and the production of pro-inflammatory mediators (49–52), which not only affect cardiac metabolic health but may also exacerbate OSA by interfering with neural control of respiration (53, 54). Researches have shown that chronic inflammation is associated with upper airway dysfunction and dysregulation of neural control, both of which can worsen OSA (20). Moreover, the deterioration of cardiovascular health may also exacerbate the symptoms of OSA by affecting the balance of the autonomic nervous system. An increase in CMI is often accompanied by elevated blood pressure and greater cardiac workload, changes that may interfere with the neural regulation of breathing (55, 56), resulting in increased frequency of nocturnal apneas. Recent studies have shown that Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors have emerged as promising candidates. Both classes of medications, initially designed for T2D and obesity management, offer pleiotropic cardiovascular benefits, including weight reduction, blood pressure lowering, and improvements in endothelial function. Clinical studies suggest that GLP-1RAs can decrease OSA severity and enhance daytime alertness by mitigating upper airway fat accumulation and enhancing respiratory control. Similarly, SGLT2 inhibitors may exert beneficial cardiovascular effects through their actions on myocardial energetics and renal function (57–59). These mechanisms provide further insight into the complex pathology of OSA and emphasize the need for consideration of cardiac metabolic health in the clinical management of this condition. Future research should explore these mechanisms in greater depth to offer new strategies for the early identification and intervention of OSA.
Additionally, we found that smoking serves as a mediating factor, exacerbating the positive correlation between CMI and OSA. This may be attributed to the fact that smoking not only induces metabolic disturbances but also compromises respiratory health, thereby elevating the risk of OSA in individuals with high CMI (60–62). These results highlight the significance of focusing on metabolic health and lifestyle factors, such as smoking cessation, in the strategies for preventing and managing OSA (63).
5 Advantages and limitations
We believe that this study, which specifically investigates the relationship between the CMI and OSA, presents a novel and significant contribution to the field. Throughout the research, we employed appropriate statistical methods and ensured continuity and logical flow by using the results from previous analyses to inform subsequent ones. The findings from the threshold effect and mediation effect analyses also offer valuable insights for clinical practice and daily life. However, since this research adopts a cross-sectional study design, the data collection is focused on a specific point in time, thereby limiting the ability to establish causal relationships among the variables. The nature of cross-sectional research prevents the identification of longitudinal trends and potential temporal relationships, which are essential for understanding the dynamics of the factors examined. Therefore, the limitations of this specific dataset hinder our ability to infer causal relationships between CMI and OSA, and to ascertain the causal role of smoking in the mediating effects between the two. Second, the constraints of covariates (key cardiovascular metabolic drugs, especially newer drugs such as GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors), may simultaneously affect CMI and OSA. Unfortunately, due to the lack of data on the use of these drugs in the NHANES database, we were unable to include them as covariates in this study. Third, in our study, the diagnosis of OSA primarily relied on self-reported symptoms evaluated through the Sleep Questionnaire within the NHANES dataset. While this approach provides valuable insights into the prevalence of OSA, it inherently lacks the rigor of objective diagnostic methods, such as polysomnography (PSG) or assessing apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) scores. The reliance on subjective reporting may result in misclassification bias, as individuals may overreport or underreport their symptoms, leading to an inaccurate assessment of OSA prevalence. Consequently, this limitation underscores the need for a multidimensional evaluation that integrates both subjective symptom assessment and objective diagnostic criteria. Future investigations should aim to incorporate objective measures alongside self-reported questionnaires to enhance the accuracy of OSA diagnosis and to better understand its implications for public health and clinical practice. In addition, potential biases from self-reported questionnaires, including recall bias and loss to follow-up, may have affected the results. Finally, it is important to note that the study sample consists exclusively of American adults, which may restrict the generalizability of the results to other populations. Variations in culture, socioeconomic status, and behavior across different demographic groups could affect the study variables, suggesting that the findings may not be relevant to individuals from outside this demographic. Future studies should further investigate longitudinal effects and related intervention strategies to improve our comprehension of the mechanisms that connect CMI to OSA and to refine the experimental findings.
6 Conclusion
Our study reveals a positive nonlinear relationship between the CMI and OSA in the adult U.S. population. Threshold analysis indicates that keeping the CMI within a specific range may significantly lower the likelihood of developing OSA. Additionally, lifestyle factors like smoking may further influence this relationship. These findings highlight the importance of a comprehensive approach to screening and intervention that considers cardiometabolic and sleep health. Future research should focus on understanding the mechanisms linking CMI and OSA to improve prevention and treatment strategies for at-risk individuals.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
YZ: Data curation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. JY: Data curation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. HT: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. JX: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere appreciation to all the participants and staff who contributed to the NHANES survey.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2025.1609585/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Gottlieb DJ and Punjabi NM. Diagnosis and management of obstructive sleep apnea: A review. Jama. (2020) 323:1389–400. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.3514
2. Javaheri S and Javaheri S. Update on persistent excessive daytime sleepiness in OSA. Chest. (2020) 158:776–86. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.02.036
3. Peppard PE, Young T, Barnet JH, Palta M, Hagen EW, and Hla KM. Increased prevalence of sleep-disordered breathing in adults. Am J Epidemiol. (2013) 177:1006–14. doi: 10.1093/aje/kws342
4. Mangione CM, Barry MJ, Nicholson WK, Cabana M, Chelmow D, Rucker Coker T, et al. Screening for obstructive sleep apnea in adults: US preventive services task force recommendation statement. Jama. (2022) 328:1945–50. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.20304
5. Brown J, Yazdi F, Jodari-Karimi M, Owen JG, and Reisin E. Obstructive sleep apnea and hypertension: updates to a critical relationship. Curr Hypertens Rep. (2022) 24:173–84. doi: 10.1007/s11906-022-01181-w
6. Mitra AK, Bhuiyan AR, and Jones EA. Association and risk factors for obstructive sleep apnea and cardiovascular diseases: A systematic review. Diseases. (2021) 9. doi: 10.3390/diseases9040088
7. Reutrakul S and Mokhlesi B. Obstructive sleep apnea and diabetes: A state of the art review. Chest. (2017) 152:1070–86. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2017.05.009
8. Giampá SQC, Lorenzi-Filho G, and Drager LF. Obstructive sleep apnea and metabolic syndrome. Obes (Silver Spring). (2023) 31:900–11. doi: 10.1002/oby.23679
9. Young T, Evans L, Finn L, and Palta M. Estimation of the clinically diagnosed proportion of sleep apnea syndrome in middle-aged men and women. Sleep. (1997) 20:705–6. doi: 10.1093/sleep/20.9.705
10. Liu C, Liang D, Xiao K, and Xie L. Association between the triglyceride-glucose index and all-cause and CVD mortality in the young population with diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2024) 23:171. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02269-0
11. Khan S, Ahmad S, Khan M, Aqil F, Khan MY, and Khan MS. Artificial intelligence derived categorizations significantly improve HOMA IR/β indicators: Combating diabetes through cross-interacting drugs. Comput Biol Med. (2024) 179:108848. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.108848
12. Zou J, Xiong H, Zhang H, Hu C, Lu S, and Zou Y. Association between the cardiometabolic index and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: insights from a general population. BMC Gastroenterol. (2022) 22:20. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02099-y
13. Lazzer S, D’Alleva M, Isola M, De Martino M, Caroli D, Bondesan A, et al. Cardiometabolic index (CMI) and visceral adiposity index (VAI) highlight a higher risk of metabolic syndrome in women with severe obesity. J Clin Med. (2023) 12. doi: 10.3390/jcm12093055
14. Wakabayashi I and Daimon T. The “cardiometabolic index” as a new marker determined by adiposity and blood lipids for discrimination of diabetes mellitus. Clin Chim Acta. (2015) 438:274–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2014.08.042
15. Xu B, Wu Q, La R, Lu L, Abdu FA, Yin G, et al. Is systemic inflammation a missing link between cardiometabolic index with mortality? Evidence from a large population-based study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2024) 23:212. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02251-w
16. Cai X, Hu J, Wen W, Wang J, Wang M, Liu S, et al. Associations of the cardiometabolic index with the risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with hypertension and obstructive sleep apnea: results of a longitudinal cohort study. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:4914791. doi: 10.1155/2022/4914791
17. Wang C, Shi M, Lin C, Wang J, Xie L, and Li Y. Association between the triglyceride glucose index and obstructive sleep apnea and its symptoms: results from the NHANES. Lipids Health Dis. (2024) 23:133. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02125-w
18. Drager LF, Togeiro SM, Polotsky VY, and Lorenzi-Filho G. Obstructive sleep apnea: a cardiometabolic risk in obesity and the metabolic syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2013) 62:569–76. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.05.045
19. Racanelli AC, Kikkers SA, Choi AMK, and Cloonan SM. Autophagy and inflammation in chronic respiratory disease. Autophagy. (2018) 14:221–32. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2017.1389823
20. Sanchez-Azofra A, Gu W, Masso-Silva JA, Sanz-Rubio D, Marin-Oto M, Cubero P, et al. Inflammation biomarkers in OSA, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease/OSA overlap syndrome. J Clin Sleep Med. (2023) 19:1447–56. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.10600
21. Lam DC, Lam KS, and Ip MS. Obstructive sleep apnoea, insulin resistance and adipocytokines. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). (2015) 82:165–77. doi: 10.1111/cen.12597
22. Barros D and García-Río F. Obstructive sleep apnea and dyslipidemia: from animal models to clinical evidence. Sleep. (2019) 42. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsy236
23. Popadic V, Brajkovic M, Klasnja S, Milic N, Rajovic N, Lisulov DP, et al. Correlation of dyslipidemia and inflammation with obstructive sleep apnea severity. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:897279. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.897279
24. Cavallino V, Rankin E, Popescu A, Gopang M, Hale L, and Meliker JR. Antimony and sleep health outcomes: NHANES 2009-2016. Sleep Health. (2022) 8:373–9. doi: 10.1016/j.sleh.2022.05.005
25. Zhou T, Chen S, Mao J, Zhu P, Yu X, and Lin R. Association between obstructive sleep apnea and visceral adiposity index and lipid accumulation product: NHANES 2015-2018. Lipids Health Dis. (2024) 23:100. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02081-5
26. Yan S, Chen S, Liu Y, Liang H, Zhang X, Zhang Q, et al. Associations of serum carotenoids with visceral adiposity index and lipid accumulation product: a cross-sectional study based on NHANES 2001-2006. Lipids Health Dis. (2023) 22:209. doi: 10.1186/s12944-023-01945-6
27. Cai S, Li S, Zhou Y, Song J, and Peng J. The association between sedentary behavior and obstructive sleep apnea: a cross-sectional study from the NHANES (2007–2008 to 2015-2020). BMC Oral Health. (2024) 24:224. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-03960-0
28. Benjafield AV, Ayas NT, Eastwood PR, Heinzer R, Ip MSM, Morrell MJ, et al. Estimation of the global prevalence and burden of obstructive sleep apnoea: a literature-based analysis. Lancet Respir Med. (2019) 7:687–98. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(19)30198-5
29. Caples SM, Gami AS, and Somers VK. Obstructive sleep apnea. Ann Intern Med. (2005) 142:187–97. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-142-3-200502010-00010
30. Senaratna CV, Perret JL, Lodge CJ, Lowe AJ, Campbell BE, Matheson MC, et al. Prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea in the general population: A systematic review. Sleep Med Rev. (2017) 34:70–81. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2016.07.002
31. Yeghiazarians Y, Jneid H, Tietjens JR, Redline S, Brown DL, El-Sherif N, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease: A scientific statement from the american heart association. Circulation. (2021) 144:e56–67. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000988
32. Salman LA, Shulman R, and Cohen JB. Obstructive sleep apnea, hypertension, and cardiovascular risk: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management. Curr Cardiol Rep. (2020) 22:6. doi: 10.1007/s11886-020-1257-y
33. Torres G, Sánchez-de-la-Torre M, and Barbé F. Relationship between OSA and hypertension. Chest. (2015) 148:824–32. doi: 10.1378/chest.15-0136
34. Muraki I, Wada H, and Tanigawa T. Sleep apnea and type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Investig. (2018) 9:991–7. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12823
35. Paschou SA, Bletsa E, Saltiki K, Kazakou P, Kantreva K, Katsaounou P, et al. Sleep apnea and cardiovascular risk in patients with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. Nutrients. (2022) 14. doi: 10.3390/nu14234989
36. Li P, Dong Z, Chen W, and Yang G. Causal relations between obstructive sleep apnea and stroke: A mendelian randomization study. Nat Sci Sleep. (2023) 15:257–66. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S398544
37. Gelber RP, Gaziano JM, Orav EJ, Manson JE, Buring JE, and Kurth T. Measures of obesity and cardiovascular risk among men and women. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2008) 52:605–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.03.066
38. Ashwell M, Gunn P, and Gibson S. Waist-to-height ratio is a better screening tool than waist circumference and BMI for adult cardiometabolic risk factors: systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev. (2012) 13:275–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-789X.2011.00952.x
39. Salazar MR, Carbajal HA, Espeche WG, Aizpurúa M, Leiva Sisnieguez CE, March CE, et al. Identifying cardiovascular disease risk and outcome: use of the plasma triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol concentration ratio versus metabolic syndrome criteria. J Intern Med. (2013) 273:595–601. doi: 10.1111/joim.12036
40. Shi WR, Wang HY, Chen S, Guo XF, Li Z, and Sun YX. Estimate of prevalent diabetes from cardiometabolic index in general Chinese population: a community-based study. Lipids Health Dis. (2018) 17:236. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0886-2
41. Shao MJ, Luo JY, Shi J, Liu F, Shan CF, Luo F, et al. Association of visceral obesity-related indices with coronary collateralization in patients with chronic total occlusion. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2021) 8:742855. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.742855
42. Gu D, Lu Y, Xu B, and Tang X. Sex-specific contribution of cardiometabolic index in predicting metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: insights from a general population. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. (2023) 16:3871–83. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S437413
43. Dixon AE, Poynter ME, Garrow OJ, Kaminsky DA, Tharp WG, and Bates JHT. Peripheral airway dysfunction in obesity and obese asthma. Chest. (2023) 163:753–62. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2022.12.030
44. Farkas GA, Gosselin LE, Zhan WZ, Schlenker EH, and Sieck GC. Histochemical and mechanical properties of diaphragm muscle in morbidly obese Zucker rats. J Appl Physiol (1985). (1994) 77:2250–9. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1994.77.5.2250
45. Song J, Li Y, Zhu J, Liang J, Xue S, and Zhu Z. Non-linear associations of cardiometabolic index with insulin resistance, impaired fasting glucose, and type 2 diabetes among US adults: a cross-sectional study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2024) 15:1341828. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1341828
46. Xu B, Wu Q, Yin G, Lu L, La R, Zhang Y, et al. Associations of cardiometabolic index with diabetic statuses and insulin resistance: the mediating role of inflammation-related indicators. BMC Public Health. (2024) 24:2736. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-20048-0
47. Wang D, Chen Y, Ding Y, Tang Y, Su X, Li S, et al. Application value of cardiometabolic index for the screening of obstructive sleep apnea with or without metabolic syndrome. Nat Sci Sleep. (2024) 16:177–91. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S449862
48. Duan S, Yang D, Xia H, Ren Z, Chen J, and Yao S. Cardiometabolic index: A new predictor for metabolic associated fatty liver disease in Chinese adults. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:1004855. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1004855
49. Kahn CR, Wang G, and Lee KY. Altered adipose tissue and adipocyte function in the pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest. (2019) 129:3990–4000. doi: 10.1172/JCI129187
50. Guilherme A, Virbasius JV, Puri V, and Czech MP. Adipocyte dysfunctions linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2008) 9:367–77. doi: 10.1038/nrm2391
51. Szukiewicz D. Molecular mechanisms for the vicious cycle between insulin resistance and the inflammatory response in obesity. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:379–94. doi: 10.3390/ijms24129818
52. Glass CK and Olefsky JM. Inflammation and lipid signaling in the etiology of insulin resistance. Cell Metab. (2012) 15:635–45. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.04.001
53. Carnevale D. Neuroimmune axis of cardiovascular control: mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2022) 19:379–94. doi: 10.1038/s41569-022-00678-w
54. van der Klaauw AA. Neuropeptides in obesity and metabolic disease. Clin Chem. (2018) 64:173–82. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2017.281568
55. Dempsey JA, Veasey SC, Morgan BJ, and O’Donnell CP. Pathophysiology of sleep apnea. Physiol Rev. (2010) 90:47–112. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00043.2008
56. Harper RM, Kumar R, Macey PM, Ogren JA, and Richardson HL. Functional neuroanatomy and sleep-disordered breathing: implications for autonomic regulation. Anat Rec (Hoboken). (2012) 295:1385–95. doi: 10.1002/ar.22514
57. Karakasis P, Sagris M, Patoulias D, Koufakis T, Theofilis P, Klisic A, et al. Mitigating increased cardiovascular risk in patients with obstructive sleep apnea using GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors: hype or hope? Biomedicines. (2024) 12. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12112503
58. Lee MMY, Petrie MC, McMurray JJV, and Sattar N. How do SGLT2 (Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2) inhibitors and GLP-1 (Glucagon-like peptide-1) receptor agonists reduce cardiovascular outcomes?: completed and ongoing mechanistic trials. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2020) 40:506–22. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.311904
59. Dragonieri S, Portacci A, Quaranta VN, Carratu P, Lazar Z, Carpagnano GE, et al. Therapeutic potential of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome management: A narrative review. Diseases. (2024) 12:157–69. doi: 10.3390/diseases12090224
60. Huttunen R, Heikkinen T, and Syrjänen J. Smoking and the outcome of infection. J Intern Med. (2011) 269:258–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2010.02332.x
61. Aghapour M, Raee P, Moghaddam SJ, Hiemstra PS, and Heijink IH. Airway epithelial barrier dysfunction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: role of cigarette smoke exposure. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2018) 58:157–69. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2017-0200TR
62. Trinder PM, Croft PR, and Lewis M. Social class, smoking and the severity of respiratory symptoms in the general population. J Epidemiol Community Health. (2000) 54:340–3. doi: 10.1136/jech.54.5.340
Keywords: CMI, OSA, NHANES, smoking, mediating effect
Citation: Zhou Y, Yu J, Tan H and Xiao J (2025) Association between cardiometabolic Index and obstructive sleep apnea and the mediating role of smoking: a cross-sectional study. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1609585. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1609585
Received: 10 April 2025; Accepted: 23 June 2025;
Published: 09 July 2025.
Edited by:
Yang Yang, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, ChinaReviewed by:
Nicoletta Cera, University of Porto, PortugalRizaldy Taslim Pinzon, Duta Wacana Christian University, Indonesia
Paschalis Karakasis, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece
Copyright © 2025 Zhou, Yu, Tan and Xiao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jun Xiao, bWFqb3J4aWFvOTIxeXlAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Haitao Tan, MTM3NTUxMzQwODBAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
‡These authors have contributed equally to this work
§ORCID: Jun Xiao, orcid.org/0009-0002-8952-6254
 Yifan Zhou
Yifan Zhou Jinghao Yu2†
Jinghao Yu2† Jun Xiao
Jun Xiao