- 1China-Japan Friendship Institute of Clinical Medical Sciences, Beijing, China
- 2Department of Interventional Medicine, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing, China
- 3Department of Pathology, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing, China
Background: To reduce the risk of local recurrence of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) after thermal ablation, in clinical practice, the ablation area is typically extended 2–3 mm beyond the original tumor margin. However, there is no definitive evidence to support the validity of this extended margin.
Objective: The objective of this study was to measure the distance from the edge of a PTC to the farthest point of tumor infiltration using digital pathology and to analyze the associated risk factors.
Methods: A total of 227 patients who underwent surgical resection for PTC were included in the study. The median age was 45 years. The slides with the maximum tumor diameter were selected as the target slides. Two authors independently assessed the characteristics of the PTCs and measured infiltration distances, with the greatest distance recorded as the infiltration distance. Risk factors associated with infiltration distance were analyzed using the rank-sum test, correlation analysis, and multiple linear regression.
Results: Of the 227 tumors, 23 tumors showed no signs of infiltration; the remaining 204 tumors had infiltration distances ranging from 0.14 to 2.26 mm, with 3 tumors having distances greater than 2 mm (2.17, 2.19 and 2.26 mm). Significant differences in infiltration distances were observed in relation to maximum tumor diameter, lymph node metastases, and tumor growth patterns (TGPs) on the basis of the rank-sum test or correlation analyses. However, multiple linear regression analyses revealed that only TGPs were risk factors for infiltration distance.
Conclusion: To minimize the risk of local recurrence of PTC following thermal ablation, extending the ablation margin by 2.5 mm is recommended, regardless of the tumor stage.
Introduction
Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) represents 80-90% of differentiated thyroid cancers, making it the predominant histological type (1). Thermal ablation (TA) techniques, such as radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and microwave ablation (MWA), have shown excellent efficacy and a lower incidence of complications in treating T1 PTC (2–4), providing an alternative for patients who decline active surveillance or surgical resection. As a malignant tumor, PTC grows and infiltrates into the surrounding normal thyroid tissue (5). However, the limited resolution of ultrasound (US) makes it difficult to detect small infiltrations around tumors. To reduce the risk of local recurrence of PTC following TA, the ablation area is typically extended by 2–3 mm beyond the original tumor margin on the basis of clinical experience (2, 6). However, there is no definitive evidence to support the validity of this extended ablation margin. In other words, insufficient extended ablation increases the risk of local recurrence, and excessive extended ablation destroys an increased amount of normal thyroid tissue. The aim of this study was to measure the distance from the edge of the PTC to the farthest point of tumor infiltration using digital pathology and analyze risk factors associated with PTC infiltration, providing a scientific basis for optimizing the extended ablation margin to minimize the risk of local recurrence.
Materials and methods
Patients
This retrospective study received approval from the Human Ethics Review Committee of China-Japan Friendship Hospital (IRB No. S2019-283-02). The medical data of all consecutive patients with PTC who underwent surgical resection between January and May 2023 at China-Japan Friendship Hospital were reviewed. All patients provided written informed consent for treatment. The need for informed consent for inclusion in the study was waived because all personal details were kept confidential.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
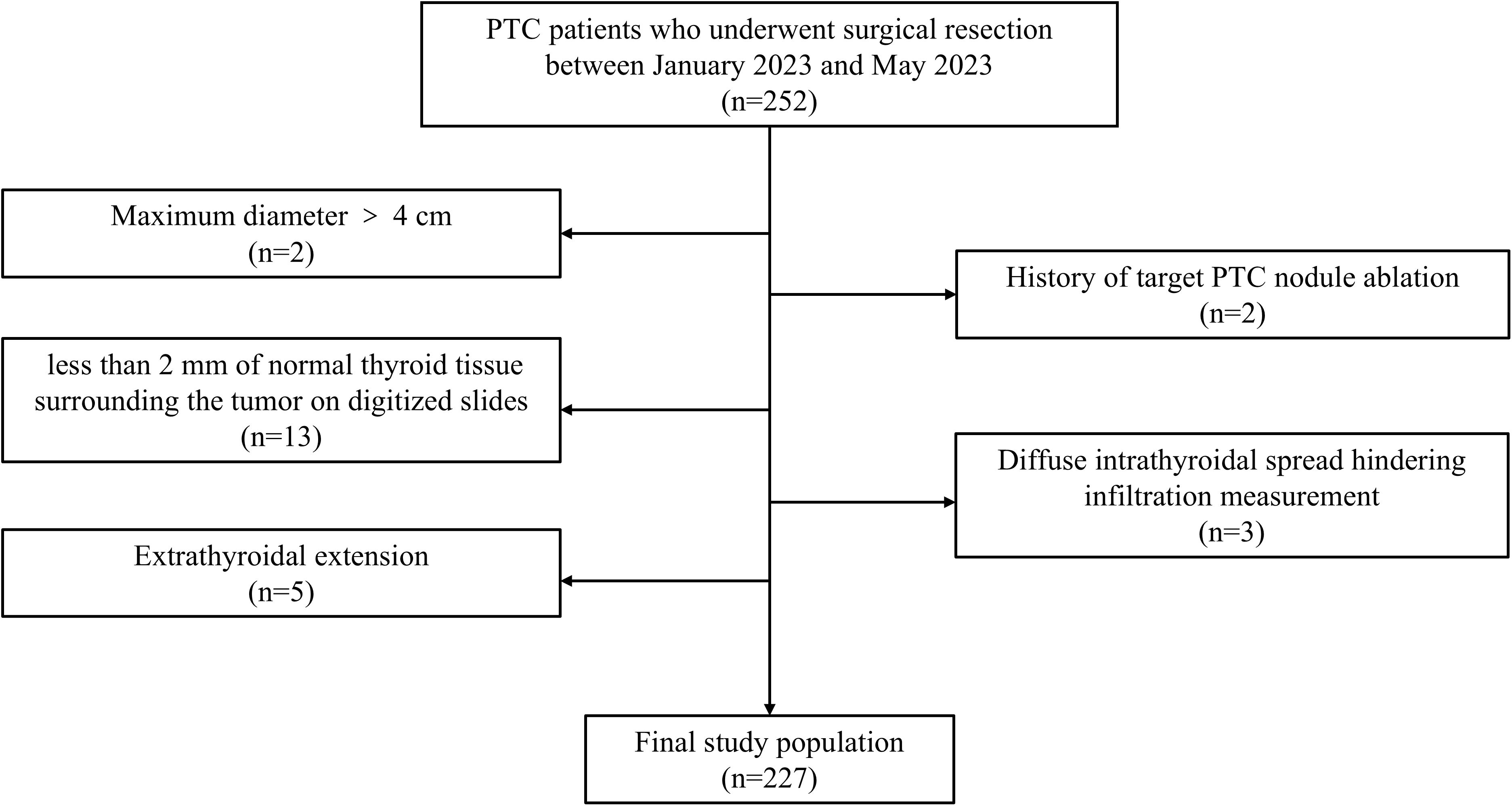
The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) underwent partial or total thyroidectomy; (2) had postoperative pathologically confirmed PTC; (3) had a maximum tumor diameter ≤ 4 cm; and (4) had no extrathyroidal extension. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) history of target PTC nodule ablation; (2) diffuse intrathyroidal spread hindering infiltration measurement; and (3) less than 2 mm of normal thyroid tissue surrounding the tumor on digitized slides. The patient selection process is shown in Figure 1, and examples of excluded cases are illustrated in Figure 2.
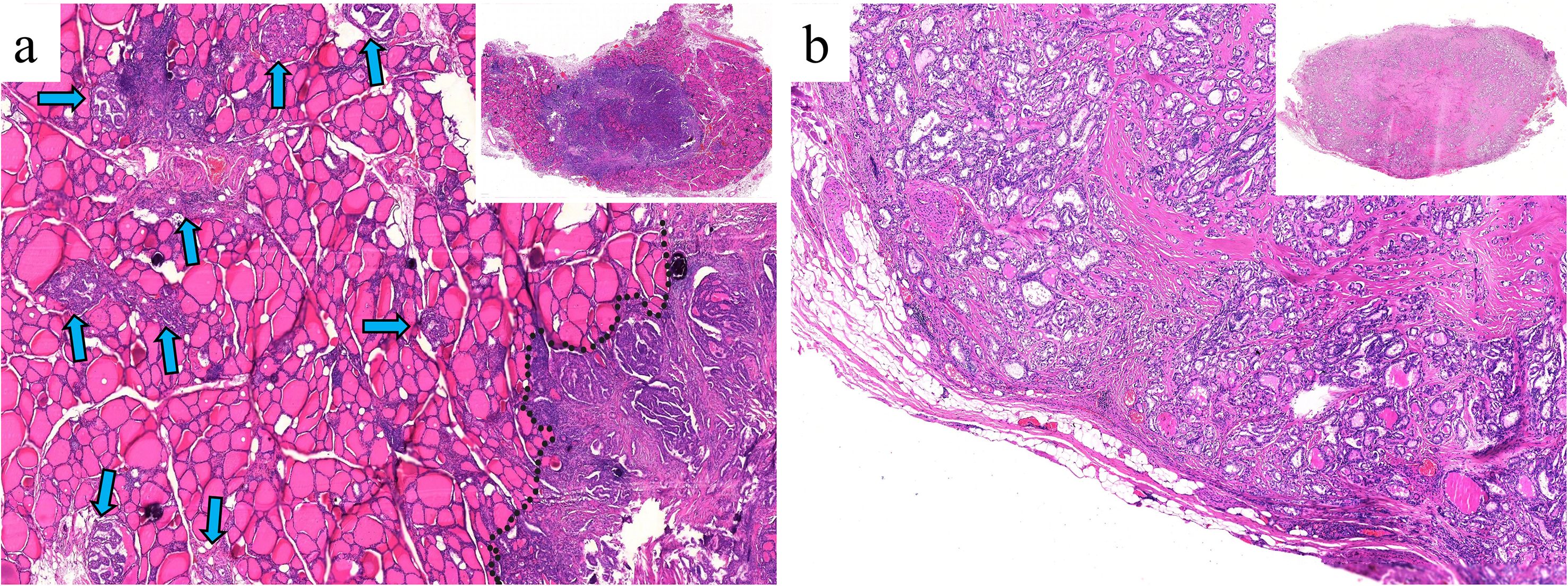
Figure 2. (a) Multifocal PTC and lymph node metastasis in a 36-year-old female patient. The largest nodule, measuring 1.2 × 1 × 0.8 cm (black dashed line), is located in the left thyroid lobe. Diffuse intrathyroidal spread is observed (blue arrows), with all spreading foci < 1 mm (H&E, × 100). (b) Multifocal PTC without lymph node metastasis in a 30-year-old male patient. The largest nodule, measuring 1.2 × 0.7 × 0.7 cm, is located in the left lobe. The target section shows almost no normal tissue surrounding the nodule (H&E, × 180). These two PTC types were excluded from this study because infiltration distances could not be measured.
Definitions
Three kinds of tumor growth patterns (TGPs) were defined: (I) well-circumscribed growth with no obvious infiltration into adjacent normal tissue, regardless of the presence or absence of fibrous pseudocapsules; (II) coexistence of encapsulated (surrounded by fibrous pseudocapsules) and infiltrative growth; and (III) infiltrative growth with irregular, stellate, or spiculated margins (7, 8). (Figure 3) On the basis of the 2022 WHO classification, PTC was categorized into classic PTC, infiltrative follicular variant, and other types (9). In this study, the “other types” category comprised only two cases: one columnar cell variant and one hobnail variant. Capsular invasion was defined as neoplastic infiltration of the thyroid fibrous capsule (10). Calcifications included psammoma bodies (spherical calcified foci with concentric laminations) and stromal calcifications (spherical without laminations or irregular with laminations) (11). Thyroid status was categorized as either normal or Hashimoto thyroiditis. The diagnosis of Hashimoto thyroiditis was based on strict criteria: (1) preoperative thyroid peroxidase antibody level > 34 IU/mL and/or antithyroglobulin antibody level > 115 IU/mL; and (2) postoperative histopathology (12).
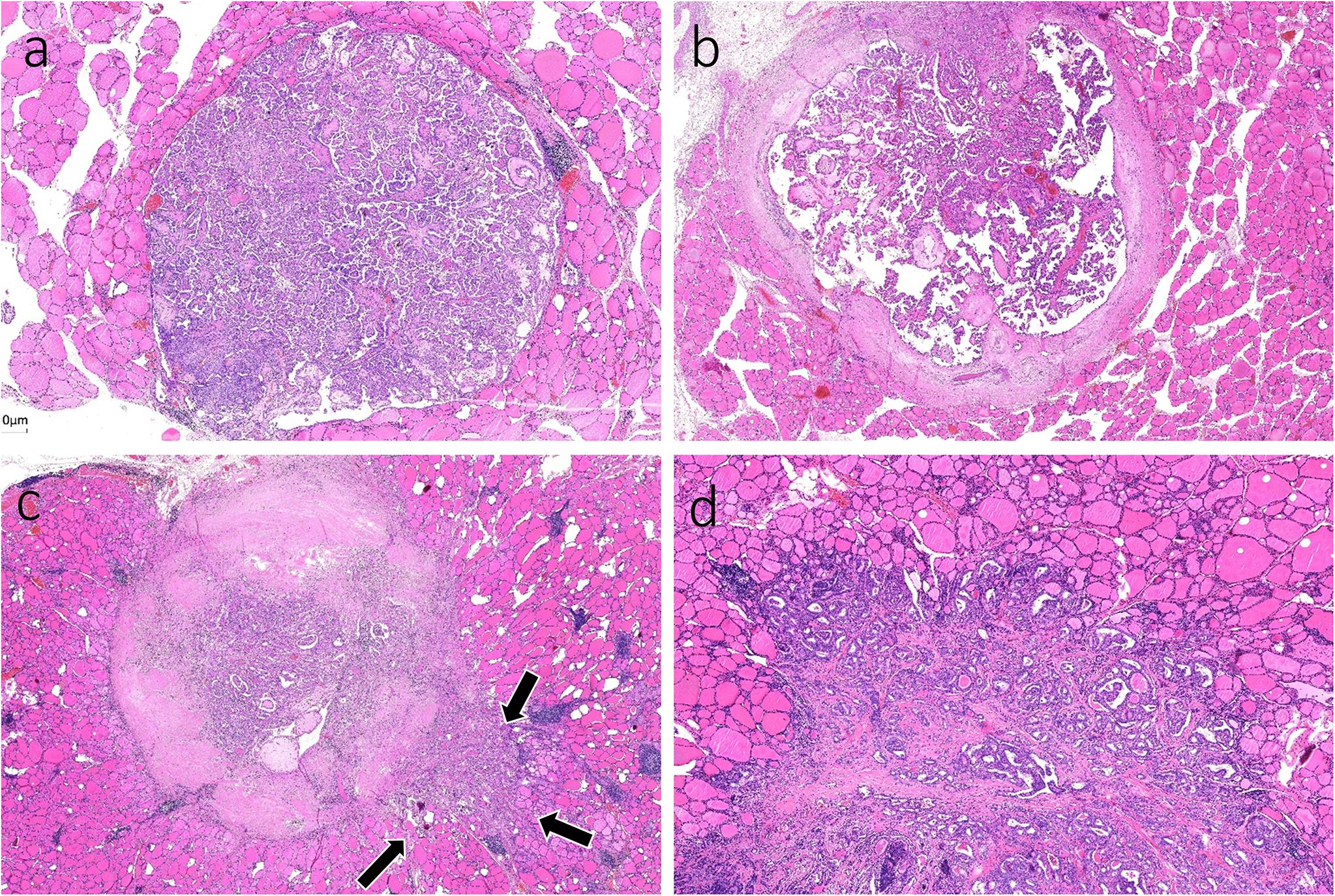
Figure 3. Tumor growth patterns (TGPs). (a) TGP I: well-circumscribed growth with no pseudocapsule and obvious infiltration into adjacent normal follicles (H&E, × 80). (b) TGP I: well-circumscribed growth completely surrounded by fibrous pseudocapsules (H&E, × 80). (c) TGP II: coexistence of encapsulated and infiltrative (black arrows) growth (H&E, × 80). (d) TGP III: infiltrative growth with irregular, stellate or spiculated margins (H&E, × 200).
Image acquisition for digital pathology
Thyroid gland specimens obtained from unilateral or bilateral lobectomies were analyzed. The head side of each sample was marked by surgeons to guide the preparation of longitudinal pathological sections. Postoperative tissues were fixed with 10% formaldehyde, cut into 4-μm sections and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). In patients with multifocal PTC, the largest nodule was identified as the dominant nodule. Slides with the maximum diameter from the unifocal nodule or the dominant nodule in multifocal cases were selected as the target slides. If the tumor required dissection due to its larger volume, all the slides with the maximum diameter were designated as target slides. All target slides were scanned and input into whole slide imaging (WSI) at × 40 magnification.
Digital image analysis
To improve accuracy, two authors (H. X. Zhao and Y. Niu) independently analyzed all digitized slides using ImageJ software. Discrepancies were resolved through joint review of the slide until consensus was achieved. The infiltration distance for TGP I tumors was determined by the vertical distance from the farthest point of tumor infiltration to the outermost boundary or fibrous pseudocapsules. Owing to the limited resolution of ultrasound, the 7.5–15 MHz probe employed in thyroid examinations can generally identify spiculation or lobulation approximately 1 mm near the tumor (13, 14). The aim of this study was to investigate infiltration distances that cannot be visualized using high-resolution ultrasound. Therefore, for TGP III tumors, the base of infiltration was established at a boundary width of 1 mm, measured as the infiltration distance from the farthest point of the tumor cells to this boundary. In TGP II tumors, infiltration distances were assessed by both methods previously described. The greatest measured distance for each tumor was considered the definitive infiltration distance. (Figure 4).
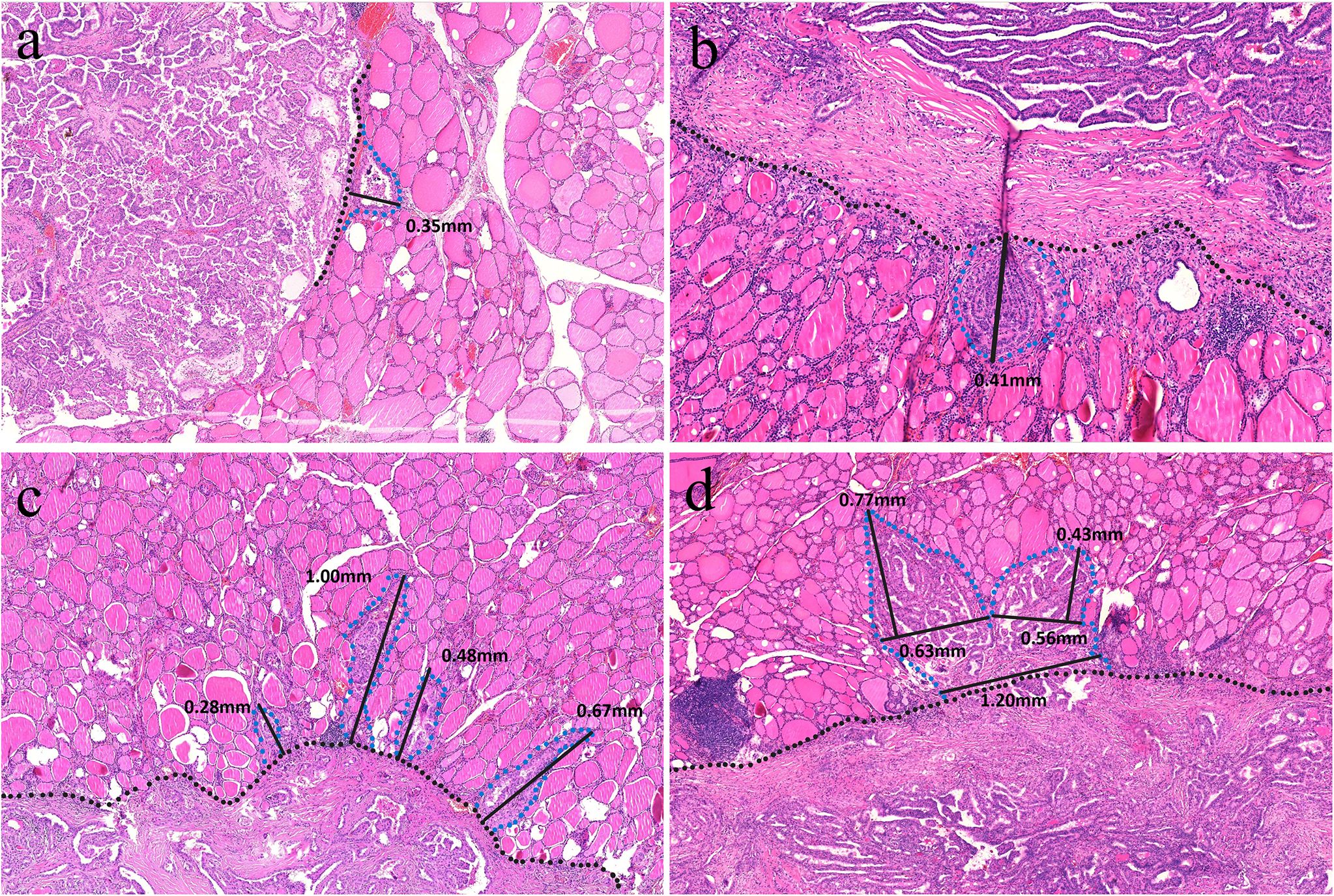
Figure 4. (a) A TGP I tumor is well circumscribed without pseudocapsules, and the vertical distance from the farthest point of the tumor to the outer boundary is 0.35 mm (H&E, × 160). (b) A TGP I tumor is well circumscribed with fibrous pseudocapsules, and the vertical distance from the farthest point of the tumor to the fibrous pseudocapsule is 0.41 mm (H&E, × 320). (c) A TGP III tumor shows infiltrative growth with spiculated margins, and the base width of each spiculated infiltration is < 1 mm. The vertical distance from the farthest point of infiltration to the boundary was measured, and the greatest distance of 1.00 mm was used (H&E, ×200). (d) A TGP III tumor shows infiltrative growth with stellate margins, and the base width of stellate infiltration is > 1 mm. A base width of < 1 mm was used as the boundary, and the vertical distance from the farthest point of infiltration to the boundary was measured, with the greatest distance of 0.77 mm (H&E, ×180).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed with SPSS (version 26.0). In terms of descriptive statistics, variables that did not follow a normal distribution are described as medians and interquartile ranges, and categorical variables are presented as numbers with percentages. To compare infiltration distances between different groups, rank-sum and grouped rank-sum tests were performed, with Bonferroni correction applied for intragroup comparisons. Rank correlation analysis was used to assess the correlation between the maximum diameter of the PTC and infiltration distance. Risk factor analysis for infiltration distances was conducted using multiple linear regression, with TGP I and classic PTC included as dummy variables. A difference in the data with P < 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance.
Results
Patient characteristics
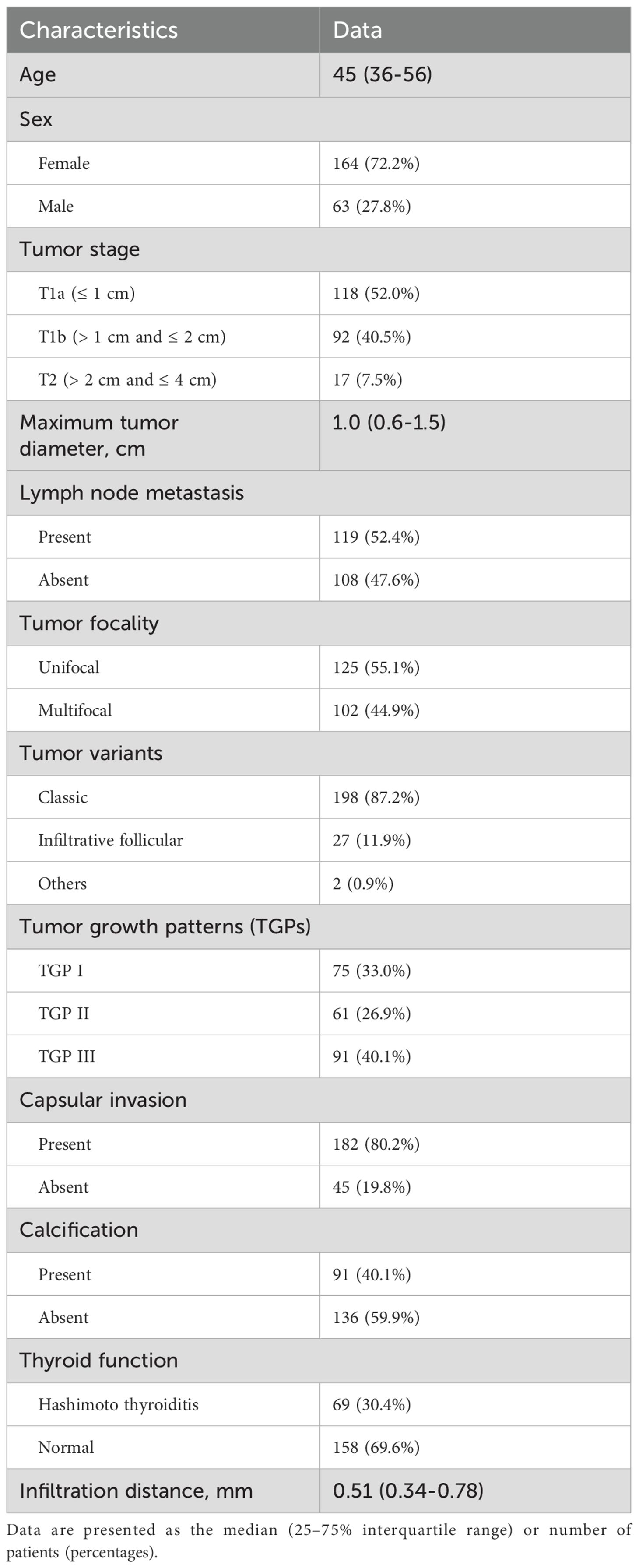
A total of 227 patients (63 males and 164 females) who underwent surgical resection for PTC were included in the present study. The median age was 45 years (25–75% IQR 36–56, age range 23–81). A total of 118 patients were in stage T1a, 92 were in stage T1b, and 17 were in stage T2. The median maximum tumor diameter was 1.0 cm (25-75% IQR 0.6-1.5, diameter range 0.3-4.0). LNMs were observed in 119 patients (52.4%), multifocal nodules in 102 (44.9%), capsular invasion in 182 (80.2%), and calcification in 91 patients (40.1%). With respect to TGP classification, 75 patients were classified as TGP I, 61 as TGP II, and 91 as TGP III. (Table 1).
Infiltration distances
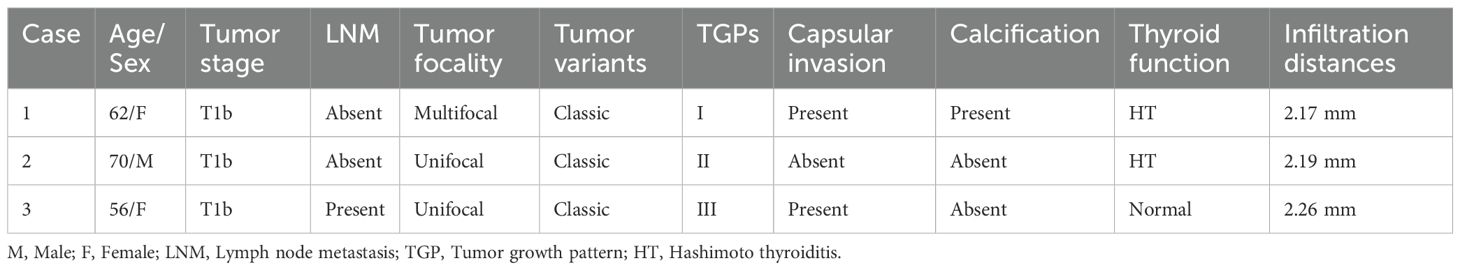
Among the 227 tumors, 23 tumors showed no signs of infiltration. The remaining 204 tumors had infiltration distances ranging from 0.14 to 2.26 mm, with 3 tumors having distances > 2 mm, measuring 2.17, 2.19 and 2.26 mm (Table 2). The tumor infiltration distances did not follow a normal distribution, with a median of 0.51 mm (25-75% IQR 0.34-0.78; range: 0–2.26 mm). In terms of tumor stage, the median infiltration distance was 0.46 mm for T1a tumors (25-75% IQR 0.34-0.75; range: 0–2 mm), 0.57 mm for T1b tumors (25-75% IQR 0.33-0.86; range: 0-2.26 mm), and 0.41 mm for T2 tumors (25-75% IQR 0.26-0.90; range: 0-1.36 mm). However, there was no significant difference among the three groups (P=0.347).
Influence factors and multiple linear regression
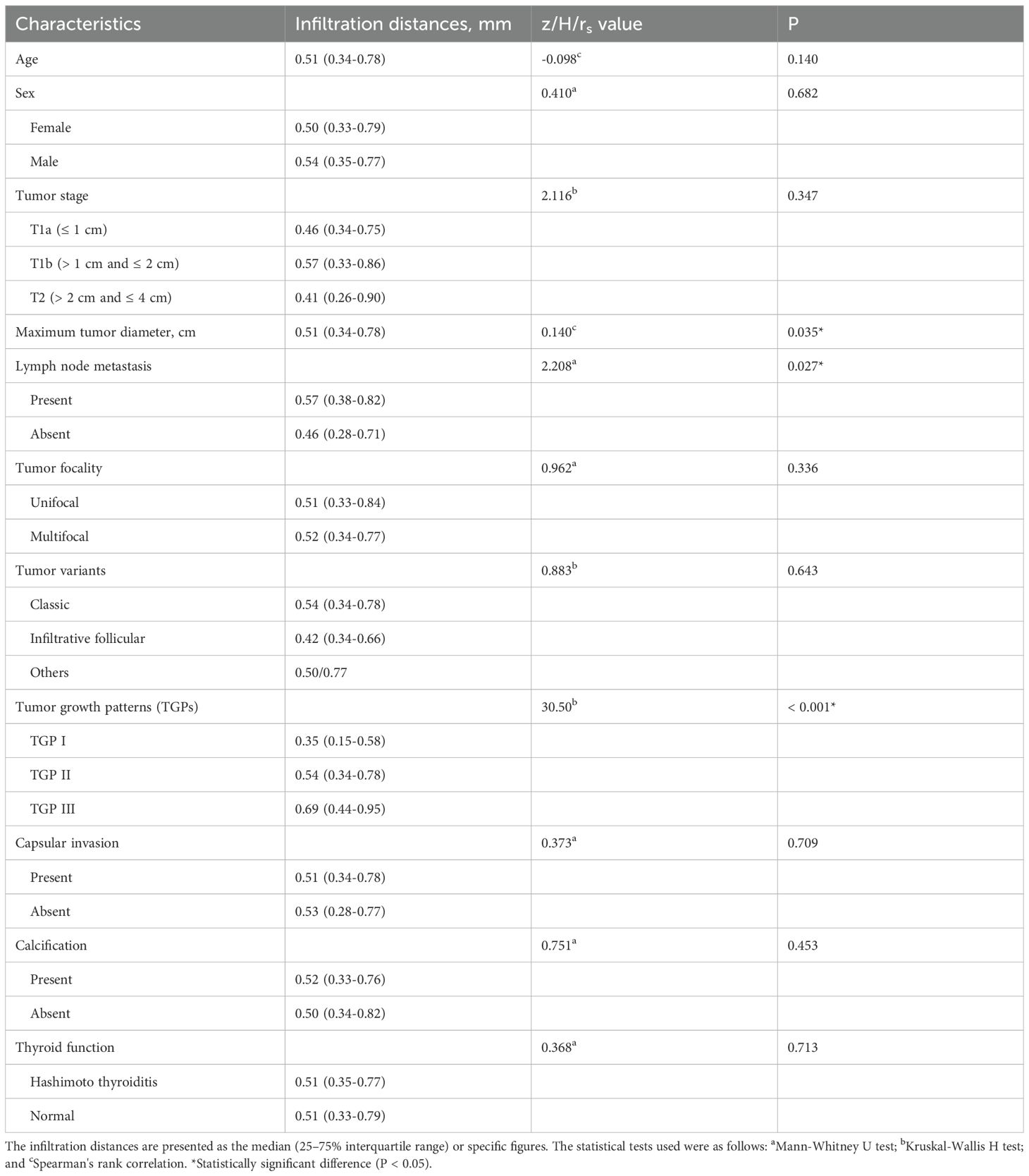
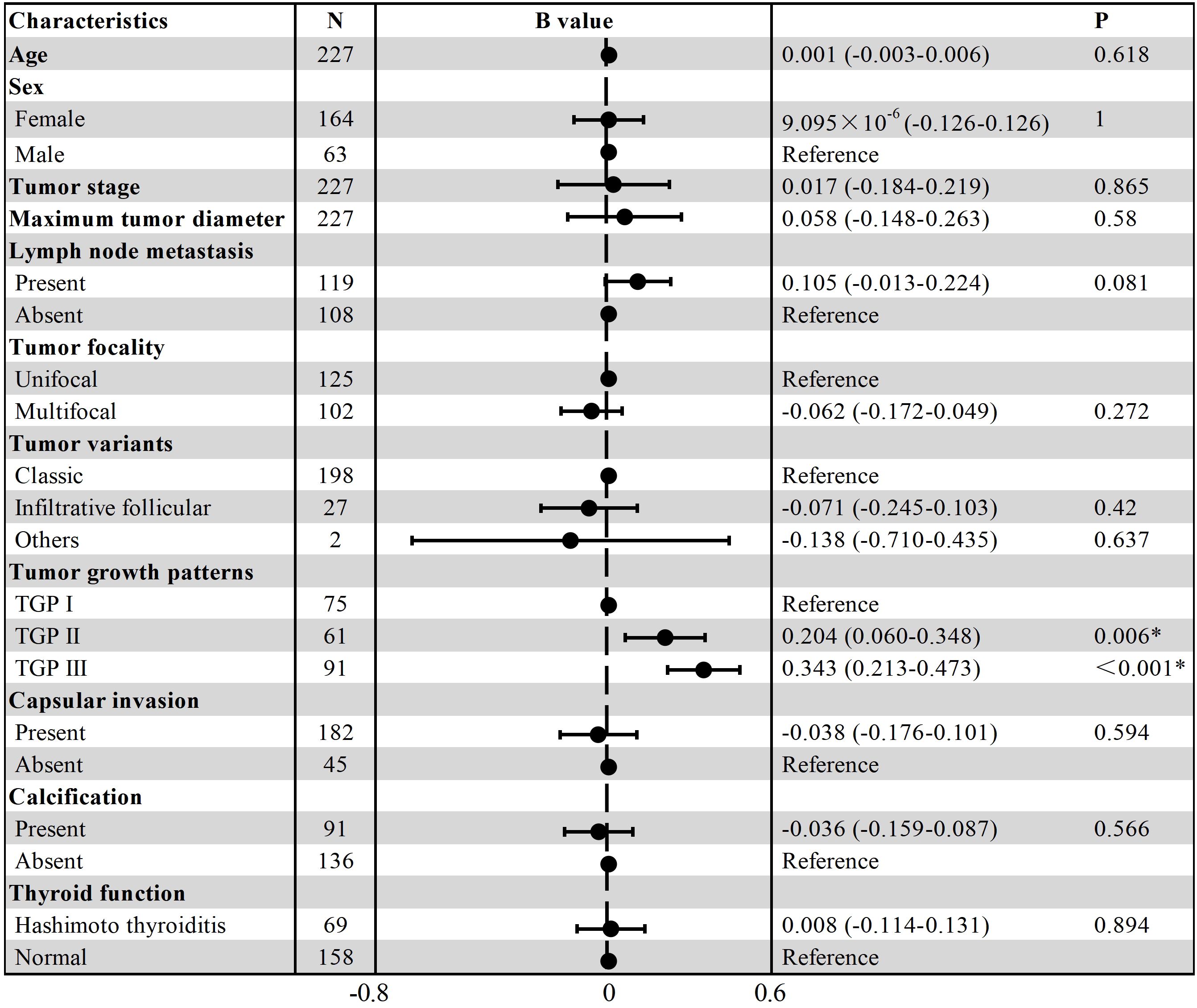
According to the univariate or correlation analysis, 3 variables (maximum tumor diameter, LNMs and TGP) were significantly associated with infiltration distance (all P < 0.05). As the maximum tumor diameter increased, the infiltration distance also increased (rs=0.140, P=0.035). Tumors with LNMs (0.57 mm, 25-75% IQR: 0.38-0.82) presented greater infiltration distances than those without (0.46 mm, 25-75% IQR: 0.28-0.71) (P=0.027). The infiltration distance of tumors in TGP III (0.69 mm, 25-75% IQR: 0.44-0.95) was significantly greater than that in TGP II (0.54 mm, 25-75% IQR: 0.34-0.78, P=0.029) and TGP I (0.35 mm, 25-75% IQR: 0.15-0.58, P < 0.001), with TGP II also having a greater infiltration distance than TGP I (P=0.004). Other variables (age, sex, tumor stage, tumor focality, tumor variants, capsular invasion, calcification, and thyroid function) were not significantly associated with infiltration distance (all P > 0.05) (Table 3).
Multiple linear regression analyses were conducted using the variables mentioned above. The results revealed that only TGPs had a statistically significant effect on infiltration distance. Compared with those with TGP I, tumors with TGP II (B=0.204, t=2.801, P=0.006) and TGP III (B=0.343, t=5.217, P < 0.001) had greater infiltration distances. The other variables did not have statistically significant differences. The results are presented as a forest plot in Figure 5.
Discussion
With advancements in diagnostic technologies such as higher-resolution ultrasound and fine needle aspiration, the detection rate of PTC has significantly increased, contributing to an increase in its incidence (15). While surgical resection remains the traditional treatment for PTC with a favorable prognosis, it can result in postoperative hypothyroidism and the need for lifelong thyroid hormone supplementation (16). Some experts recommend active surveillance for low-risk PTC patients; however, this approach may induce psychological stress and carry the risk of tumor progression and LNMs (17, 18). Thermal ablation has recently emerged as an alternative for patients who refuse surgical resection or active surveillance, demonstrating promising safety and efficacy not only for unifocal stage T1a tumors but also for multifocal or stage T2 tumors (6, 19, 20).
Malignant tumors, including PTC, commonly infiltrate surrounding normal tissues. Owing to the limited resolution of US, minor infiltration by malignant tumors outward is usually undetected. Vasiniotis et al. reported that in malignant liver tumors, biopsy-proven complete tumor ablation with margins of at least 5 mm achieves optimal local tumor control (21). However, owing to the small size of the thyroid, achieving an ablation margin of at least 5 mm is impractical. Therefore, current clinical guidelines typically recommend extending the ablation area by 2–3 mm beyond the PTC margin to minimize local recurrence (2, 6). However, this recommendation lacks robust evidence-based support, and few studies have validated its rationality and effectiveness. The aim of this study is to investigate the specific infiltration distances of PTCs using a digital pathology approach based on WSI scanning and analyze the factors influencing these distances, providing scientific evidence for optimizing the extended ablation margin.
In this study, all included tumors had measured infiltration distances within 2.5 mm. Although Spearman correlation analysis revealed a significant association between the maximum tumor diameter and infiltration distance (P=0.035), no association with tumor stage was found (P= 0.347). Moreover, multiple linear regression did not identify the maximum tumor diameter as a risk factor (P=0.580). Although some studies suggest a potential link between the maximum diameter of the PTC and tumor aggressiveness (capsular invasion, LNMs or extrathyroidal extension) (22–25), other studies indicate that tumor size is not a reliable predictor of aggressiveness, as even small PTCs can exhibit significant aggressiveness (26, 27). In the 2022 WHO Classification of Thyroid Tumors, the term “papillary thyroid microcarcinoma” (maximum diameter < 1 cm) was also removed (28). To date, no research has been published on the relationship between tumor diameter and infiltration distance, particularly when infiltration is undetectable by US. The infiltration distance may reflect tumor aggressiveness to some extent, but according to our results, it does not correlate with tumor diameter in multiple linear regression analysis. The same applies to LNMs. Although the analysis revealed greater tumor infiltration distances in patients with LNMs than in those without LNMs (P=0.027), multiple linear regression indicated that the presence of LNMs was not statistically significant (P=0.081). Therefore, the maximum tumor diameter and LNMs should not be used as references for adjusting the ablation margin.
TGP based on fibrous pseudocapsule integrity was the only factor affecting infiltration distance according to multiple linear regression (PTGP I vs. TGP II = 0.006; PTGP I vs. TGP III < 0.001). The integrity of fibrous pseudocapsules may directly influence the invasive potential of PTCs into surrounding tissues, with the median infiltration distance increasing as fibrous pseudocapsule integrity decreases (TGP I vs. TGP II vs. TGP III: 0.35 vs. 0.54 vs. 0.69 mm). An early study indicated that PTCs with a total capsule were less aggressive, whereas partially encapsulated PTCs showed no difference in aggressiveness (bloodborne metastases or tumor deaths) compared with PTCs lacking capsules (29). Giani et al. reported that classical PTC with an intact capsule is associated with an excellent prognosis; however, once the integrity of the capsule is destroyed, the prognosis significantly worsens, and they recommended redefining encapsulated classical PTC as a low-risk neoplasm (30). In the present study, although the infiltration distance of PTCs in TGP I was shorter than that in other TGP types, an intact fibrous pseudocapsule did not prevent tumor cells from infiltrating surrounding tissues. Among the 75 PTCs in TGP I, only 17 had no infiltration into adjacent thyroid tissues (17/75, 22.67%). The other PTCs showed varying degrees of outward infiltration (0.14-2.17 mm), which suggests that even when the PTC has an intact fibrous pseudocapsule, extended ablation remains necessary.
In this study, the infiltration distances and risk factors were analyzed from a histopathological perspective using digital pathology, providing evidence-based support for extending ablation distances. For patients who are appropriate candidates for thermal ablation therapy, our measurement data suggest that extending the ablation margin to 2.5 mm would be sufficient regardless of tumor stage. However, it should be emphasized that surgical resection remains the guideline-recommended standard treatment, particularly for patients with aggressive variants or LNMs. Preoperative imaging and cytological examination cannot identify these detailed pathological features. Thermal ablation, as a minimally invasive approach, has inherent limitations in identifying aggressive variants and addressing imaging-occult LNMs.
There were several limitations in the present study. First, there were inherent biases related to the single-center nature of the study. Second, the study was limited to slides with the maximum tumor diameter, preventing a comprehensive assessment of PTC infiltration in three-dimensional space. Third, the limited number of patients with other PTC variants (only two cases: one columnar cell variant and one hobnail variant) may have introduced statistical bias in assessing the impact of pathological variants on infiltration distances. Further studies with larger cohorts are needed to evaluate whether aggressive variants require larger ablation margins. Fourth, although patients with diffuse intrathyroidal spread were excluded on the basis of pathological examination, such spread may not be detectable by preoperative ultrasound, potentially leading to inappropriate patient selection for thermal ablation in clinical practice.
In conclusion, on the basis of our findings, extending the ablation margin by 2.5 mm may be appropriate to minimize the risk of local recurrence of PTC following thermal ablation, regardless of tumor stage.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Human Ethics Review Committee of China-Japan Friendship Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The human samples used in this study were acquired from a by- product of routine care or industry. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
H-xZ: Data curation, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis. YN: Data curation, Validation, Resources, Writing – original draft. Z-lZ: Data curation, Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. Y-tL: Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. M-aY: Conceptualization, Resources, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. 62176268).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Rangel-Pozzo A, Sisdelli L, Cordioli MIV, Vaisman F, Caria P, Mai S, et al. Genetic landscape of papillary thyroid carcinoma and nuclear architecture: an overview comparing pediatric and adult populations. Cancers. (2020) 12:3146. doi: 10.3390/cancers12113146, PMID: 33120984
2. Wei Y, Niu W-Q, Zhao Z-L, Wu J, Peng L-L, Li Y, et al. Microwave ablation versus surgical resection for solitary T1N0M0 papillary thyroid carcinoma. Radiology. (2022) 304:704–13. doi: 10.1148/radiol.212313, PMID: 35536133
3. Li X, Li Y, Yan L, Xiao J, Yang Z, Jing H, et al. Sonographic evolution and pathologic findings of papillary thyroid cancer after radiofrequency ablation: A five-year retrospective cohort study. Thyroid Off J Am Thyroid Assoc. (2024) 34:54–63. doi: 10.1089/thy.2023.0415, PMID: 37885207
4. Gao X, Yang Y, Wang Y, and Huang Y. Efficacy and safety of ultrasound-guided radiofrequency, microwave and laser ablation for the treatment of T1N0M0 papillary thyroid carcinoma on a large scale: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Hyperthermia. (2023) 40:2244713. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2023.2244713, PMID: 37604507
5. Wang Y, Li X, Gang Q, Huang Y, Liu M, Zhang H, et al. Pathomics and single-cell analysis of papillary thyroid carcinoma reveal the pro-metastatic influence of cancer-associated fibroblasts. BMC Cancer. (2024) 24:710. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12459-4, PMID: 38858612
6. Yan L, Li Y, Li XY, Xiao J, Tang J, and Luo Y. Clinical outcomes of ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation for solitary T1N0M0 papillary thyroid carcinoma: A retrospective study with more than 5 years of follow-up. Cancer. (2023) 129:2469–78. doi: 10.1002/cncr.34802, PMID: 37060239
7. Lim Y-S, Lee YS, Lee J-C, Son S-M, Shin D-H, Kim SS, et al. Ultrasound echogenicity of papillary thyroid cancer is affected by tumor growth patterns and tumor fibrosis. In Vivo. (2021) 35:1633–40. doi: 10.21873/invivo.12421, PMID: 33910846
8. Jung YY, Lee CH, Park SY, Park HJ, Min HS, Won JK, et al. Characteristic tumor growth patterns as novel histomorphologic predictors for lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Hum Pathol. (2013) 44:2620–7. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2013.07.025, PMID: 24139209
9. Baloch ZW, Asa SL, Barletta JA, Ghossein RA, Juhlin CC, Jung CK, et al. Overview of the 2022 WHO classification of thyroid neoplasms. Endocr Pathol. (2022) 33:27–63. doi: 10.1007/s12022-022-09707-3, PMID: 35288841
10. Basolo F, Torregrossa L, Giannini R, Miccoli M, Lupi C, Sensi E, et al. Correlation between the BRAF V600E mutation and tumor invasiveness in papillary thyroid carcinomas smaller than 20 millimeters: analysis of 1060 cases. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2010) 95:4197–205. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-0337, PMID: 20631031
11. Bai Y, Zhou G, Nakamura M, Ozaki T, Mori I, Taniguchi E, et al. Survival impact of psammoma body, stromal calcification, and bone formation in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Mod Pathol. (2009) 22:887–94. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2009.38, PMID: 19305382
12. Wang L, Chen J, Yuan X, Wang J, Sun L, Jiang J, et al. Lymph node metastasis of papillary thyroid carcinoma in the context of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. BMC Endocr Disord. (2022) 22:12. doi: 10.1186/s12902-021-00923-2, PMID: 34986823
13. Levine RA. Something old and something new: a brief history of thyroid ultrasound technology. Endocr Pract. (2004) 10:227–33. doi: 10.4158/EP.10.3.227, PMID: 15310541
14. Tessler FN and Tublin ME. Thyroid sonography: current applications and future directions. Am J Roentgenol. (1999) 173:437–43. doi: 10.2214/ajr.173.2.10430150, PMID: 10430150
15. Vaccarella S, Dal Maso L, Laversanne M, Bray F, Plummer M, and Franceschi S. The impact of diagnostic changes on the rise in thyroid cancer incidence: A population-based study in selected high-resource countries. Thyroid. (2015) 25:1127–36. doi: 10.1089/thy.2015.0116, PMID: 26133012
16. Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, Doherty GM, Mandel SJ, Nikiforov YE, et al. 2015 American thyroid association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid. (2016) 26:1–133. doi: 10.1089/thy.2015.0020, PMID: 26462967
17. Lee EK, Moon JH, Hwangbo Y, Ryu CH, Cho SW, Choi JY, et al. Progression of low-risk papillary thyroid microcarcinoma during active surveillance: interim analysis of a multicenter prospective cohort study of active surveillance on papillary thyroid microcarcinoma in korea. Thyroid. (2022) 32:1328–36. doi: 10.1089/thy.2021.0614, PMID: 36205563
18. Liu C, Zhao H, Xia Y, Cao Y, Zhang L, Zhao Y, et al. Active surveillance of highly suspicious thyroid nodules cohort in China shows a worse psychological status in younger patients. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:981495. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.981495, PMID: 36091122
19. Zhao Z-L, Wang S-R, Dong G, Liu Y, He J-F, Shi L-L, et al. Microwave ablation versus surgical resection for US-detected multifocal T1N0M0 papillary thyroid carcinoma: A 10-center study. Radiology. (2024) 311:e230459. doi: 10.1148/radiol.230459, PMID: 38563669
20. Fei Y-L, Wei Y, Zhao Z-L, Peng L-L, Li Y, Cao S-L, et al. Efficacy and safety of thermal ablation for solitary low-risk T2N0M0 papillary thyroid carcinoma. Korean J Radiol. (2024) 25:756. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2023.1279, PMID: 39109502
21. Vasiniotis Kamarinos N, Vakiani E, Gonen M, Kemeny NE, Sigel C, Saltz LB, et al. Biopsy and margins optimize outcomes after thermal ablation of colorectal liver metastases. Cancers. (2022) 14:693. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030693, PMID: 35158963
22. Zhan L, Feng H, Yu X, Li L, Song J, Tu Y, et al. Clinical and prognosis value of the number of metastatic lymph nodes in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma. BMC Surg. (2022) 22:235. doi: 10.1186/s12893-022-01635-7, PMID: 35725426
23. Ye L, Hu L, Liu W, Luo Y, Li Z, Ding Z, et al. Capsular extension at ultrasound is associated with lateral lymph node metastasis in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma: a retrospective study. BMC Cancer. (2021) 21:1250. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08875-5, PMID: 34800991
24. Mao J, Zhang Q, Zhang H, Zheng K, Wang R, and Wang G. Risk factors for lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Endocrinol. (2020) 11:265. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00265, PMID: 32477264
25. Fukushima M, Ito Y, Hirokawa M, Miya A, Shimizu K, and Miyauchi A. Prognostic impact of extrathyroid extension and clinical lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma depend on carcinoma size. World J Surg. (2010) 34:3007–14. doi: 10.1007/s00268-010-0776-x, PMID: 20824274
26. Lee JS, Lee JS, Yun HJ, Kim SM, Chang H, Lee YS, et al. Aggressive subtypes of papillary thyroid carcinoma smaller than 1 cm. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2023) 108:1370–5. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgac739, PMID: 36546348
27. Cheema Y, Repplinger D, Elson D, and Chen H. Is tumor size the best predictor of outcome for papillary thyroid cancer? Ann Surg Oncol. (2006) 13:1524–8. doi: 10.1245/s10434-006-9176-8, PMID: 17006742
28. Christofer Juhlin C, Mete O, and Baloch ZW. The 2022 WHO classification of thyroid tumors: novel concepts in nomenclature and grading. Endocr Relat Cancer. (2023) 30:e220293. doi: 10.1530/ERC-22-0293, PMID: 36445235
29. Carcangiu ML, Zampi G, Pupi A, Castagnoli A, and Rosai J. Papillary carcinoma of the thyroid. A clinicopathologic study of 241 cases treated at the University of Florence, Italy. Cancer. (1985) 55:805–28. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19850215)55:4<805::AID-CNCR2820550419>3.0.CO;2-Z, PMID: 3967175
Keywords: papillary thyroid carcinoma, thermal ablation, extended ablation margin, local recurrence, digital pathology
Citation: Zhao H-x, Niu Y, Zhao Z-l, Liu Y-t and Yu M-a (2025) Optimizing extended ablation margins in papillary thyroid carcinoma using digital pathology. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1614005. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1614005
Received: 18 April 2025; Accepted: 21 July 2025;
Published: 15 August 2025.
Edited by:
Pia Pace-Asciak, University of Toronto, CanadaCopyright © 2025 Zhao, Niu, Zhao, Liu and Yu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ming-an Yu, eW1hMzAxQDE2My5jb20=
†These authors share first authorship
 Han-xiao Zhao1,2†
Han-xiao Zhao1,2† Ming-an Yu
Ming-an Yu