- 1Clinical Biochemistry and Molecular Diagnostics Department, National Liver Institute, Menoufia University, Shebin El-Kom, Egypt
- 2Biochemistry Department, Faculty of Medicine, Umm Al-Qura University, Makkah, Saudi Arabia
- 3Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt
- 4Public Health and Community Medicine Department, Faculty of Medicine, Menoufia University, Shebin El-Kom, Egypt
- 5Faculty of Applied Health Sciences Technology, Menoufia National University, Tukh Tanbisha, Egypt
- 6Department of Hepatology, Gastroentrology and Infectious Diseases, Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University, Zagazig, Egypt
- 7Department of Pathology, National Liver Institute, Menoufia University, Shebin El-Kom, Egypt
- 8Tropical Medicine Department, Faculty of Medicine, Menoufia University, Shebin El-Kom, Egypt
- 9Medical Microbiology and Immunology, National Liver Institute, Menoufia University, Shebin El-Kom, Egypt
- 10Hepatology and Gastroenterology Department, National Liver institute, Menoufia University, Shebin El-Kom, Egypt
- 11Internal Medicine Department, Faculty of Medicine, Menoufia University, Shebin El-Kom, Egypt, Shebin El-Kom, Egypt
- 12Clinical Pathology Department, National Liver Institute, Menoufia University, Shebin El-Kom, Egypt
Introduction: Numerous risk loci have been identified to have an essential role in Metabolic associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) susceptibility and progression. The role of membrane-bound O-acyltransferase domain containing 7 (MBOAT7, rs641738) and protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 2 (PTPN2, rs2542151) genes in the risk of significant fibrosis in MASLD patients is still unclear. The aim of this study was to examine the association between MBOAT7 rs641738 and PTPN2 rs2542151 genotypes and the risk of significant fibrosis in Egyptian individuals with MASLD.
Methods: We enrolled 142 patients with varying degrees of MASLD and 142 healthy controls with no evidence of MASLD. All subjects underwent biochemical tests and genotyping of PTPN2 rs2542151 and MBOAT7 rs641738 by real-time PCR. Additionally, patients were divided according to fibrosis stages assessed by transient elastography (Fibroscan) into 103 patients with early fibrosis (F0, F1) and 39 with significant fibrosis (≥ F2).
Results and discussion: The study revealed that T allele and T/T genotype of MBOAT7 rs641738 were more frequent among MASLD patients compared to controls, with higher frequency in the significant fibrosis subgroup compared to early fibrosis or control groups. Regarding PTPN2 rs2542151, the G allele and G/G genotype were more frequent among MASLD patients compared to controls and showed higher frequency among the significant fibrosis group than controls. Multivariable regression analysis revealed that triglycerides, hepatic steatosis index, MBOAT7 rs641738 (C/T+T/T), and PTPN2 rs2542151 (G/T+G/G) were independent predictors of MASLD susceptibility. Only PTPN2 rs2542151 (G/T+G/G) was the independent predictor of significant fibrosis in MASLD patients. In conclusion, PTPN2 rs2542151 and MBOAT7 rs641738 SNPs are associated with MASLD susceptibility, while only PTPN2 rs2542151 mutations are associated with fibrosis progression.
Introduction
Pathogenesis of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is complex, thus its clinical presentation is varied. Due to the rising prevalence of obesity and metabolic syndrome, which are critical factors in the development and progression of the disease, it has emerged as the most prevalent liver disease globally, with a prevalence of about 30% (1). MASLD ranges from simple steatosis into nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, steatohepatitis with fibrosis, and cirrhosis (2).
Recently, the term of Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has been replaced with MASLD, as well as the term of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) has been changed into metabolic dysfunction- associated steatohepatitis (MASH) in a worldwide agreement. A new diagnostic criteria based on the coexistence of steatosis and clinical evidence of obesity, hypertension with dysfunction in glucose, triglyceride (TG) and high density lipoprotien (HDL) metabolism has been also stated for both of them (3). However, several studies have displayed obvious over-lap between both defined patients with NAFLD and MASLD. (4–6).
The diagnosis necessitates the lack of extensive alcohol intake and other causes of hepatic fat accumulation, as well as the presence of imaging or histological evidence of hepatic steatosis. According to current guidelines, ultrasonography is the first-line imaging tool for diagnosing hepatic steatosis and is frequently performed to screen for MASLD (7). Patients also generally accept transient elastography as a painless, quick, and complication-free method of measuring liver stiffness. Currently, it’s advised as a rather reliable method for determining whether or not patients with MASLD have significant fibrosis (8). However, no well-performing tool is available for early prediction of MASLD; particularly, the levels of liver enzymes could be normal in those patients (9). Several studies investigated the risk factors and prediction risk scores for MASLD; however, their results are debated (10–12).
The fact that not all individuals with obesity develop MASLD and that disease rates vary throughout ethnic groups points to a genetic basis for MASLD (13, 14). The available data suggest that the transcription factor 4 (TCM4) gene is not highly expressed in the human liver (15). However, the available Expression Quantitative Trait Loci analysis suggests that rs641738 SNP present in the first exon of TCM4 gene leads to C>T missense mutation, and leads to reduced expression and activity of the membrane bound O-acyltransferase domain containing 7 gene (MBOAT7), and perhaps participates in the progression of liver disease (15, 16). It was reported that sSNP; rs641738 is located a few hundred base pairs downstream of the 3′-untranslated region of MBOAT7, which belongs to a family of genes that encode specific acyl donors and acceptors (17) including lysophosphatidylinositol acyltransferase 1 (LPIAT1), which has a role in controlling the amount of free arachidonic acid in cells (18). Given its role in inflammatory lipid pathways, most mechanistic work relating to rs641738 has focussed on MBOAT7 (19). Rs 641738, C>T is associated with lower hepatic expression of MBOAT7 at both the mRNA (20) and protein levels (15). However, these findings have not been consistently replicated in different ethnicities (21) and there is a lack of data from the Middle East and African countries.
Protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 2 (PTPN2), formerly known as T-cell protein tyrosine phosphatase (TCPTP) due to its initial discovery in T cells, is another candidate gene identified by GWAS. It encodes the enzyme tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 2, a member of the superfamily of protein tyrosine kinases (22). which is a dephosphorylation enzyme that can inhibit multiple inflammatory signaling pathways and regulate many biological processes as well as a variety of pathophysiological processes (23, 24). The intergenic SNP, rs2542151 is located in chromosome 18p11, 5.5 kb upstream of the PTPN2 gene, showed the strongest association with Chrons disease (25, 26). The brain, liver, lung, and gastrointestinal system all have significant levels of PTPN2 expression. Consequently, mutations in the PTPN2 gene frequently lead to the development of inflammatory disorders such as Crohn’s disease, hepatitis, diabetes, and atherosclerosis (27, 28). Additionally, it was reported that SNPs in PTPN2 rs2542151 in patients with MASLD was associated with higher severity of fatty liver disease and a higher prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) (29).
However, the MBOAT7 and PTPN2 genes has been explored in several studies (15, 30–34), the relationship between the both genes and the risk of significant fibrosis in MASLD is still debatable due to a lack of evidence in different ethnicities especially in the Middle East and African countries. Therefore, we hypothesized to examine the association between MBOAT7 rs641738 and PTPN2 rs2542151 genotypes and the risk of significant fibrosis in Egyptian patients with MASLD.
Subjects and methods
This case-control study included 142 patients with MASLD, who were recruited from the outpatient clinic of the National Liver Institute, Menoufia University, Egypt, and the endocrinology unit of the Internal Medicine Department, Faculty of Medicine, Menoufia University, Egypt. Exclusion criteria included age <18; patients with hepatic decompensation; other causes of chronic liver disease; autoimmune diseases; thyroid abnormalities; malignancy; sepsis; and patients consuming alcohol or receiving steatogenic drugs. In addition, 142 volunteers with no evidence of MASLD and matching age and sex were included as controls.
All subjects underwent full history-taking and physical examination. Waist circumference (WC) was measured at the top of the iliac crests using a non-stretchable tape. Body mass index (BMI) was calculated by devision of Weight in Kg by height squared.
Sample collection and laboratory investigations
Eight mL of venous blood was withdrawn in the morning after an overnight fast. Two ml of blood was preserved on EDTA, to be used later for extraction of DNA. For CBC assay, one ml was evacuated into EDTA tube, CBC was assessed by the Sysmex XT-1800i automated hematology analyzer (Sysmex, Japan). Another 1 ml was used for INR assessment by The Sysmex CS-1600 Automated Hemostasis Testing (Sysmex Corporation, Kobe, Japan) and it was preserved on citrate. The remaining four ml was evacuated in a plain tube, centrifuged, and the resulting sera was divided into two aliquots: one for the assay of liver function tests as well as fasting blood sugar, lipid profiles, and creatinine using the Cobas e501 Auto analyzer (Roche-Germany), and the other for the insulin assay by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method (Shanghai Sunred Biological Technology Co., Ltd. Catalogue No. 201-12-1720).
Homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) index for insulin resistance: calculated as [fasting insulin (µU/mL)×fasting glucose (mg/dL)/405] (35).
Hepatic steatosis index: calculated as [8 × ALT/AST + BMI + 2, if DM; +2, if female], with values < 30 ruling out and values > 36 ruling in steatosis (36).
Conventional ultrasonography (US) examination: performed for all subjects using the US system (iU22, Philips Medical Systems, Bothell, WA, USA) for the diagnosis of MASLD. Increased echogenicity in liver tissue relative to renal tissue is indicative of steatosis (37)].
Liver fibrosis assessment in MASLD patients
Liver stiffness measurement (LSM) was performed using transient elastography (Fibroscan, Echosens, France) through a right intercostal space with the patient in supine position, avoiding deep inspiration during breath hold, with the right arm extended. LSM above 7.1 kilopascal was defined for significant fibrosis (F ≥ 2) according to the manufacturer’s guidelines and previous studies (8). Patients were divided according to fibrosis stages into 103 patients with early fibrosis (F0, F1) and 39 with significant fibrosis (≥ F2).
Gene polymorphism by real-time PCR
DNA was extracted from all samples using a spin column method according to the manufacturer’s instructions by Gene JET TM whole blood Genomic DNA Purification Mini Kit (Thermo Scientific, EU/Lithuania). Nanodrop spectrophotometer (UV spectrophotometer Q3000, Quawell Technology, Inc., USA) was used for determination of DNA concentrations.
PTPN2 rs2542151 and MBOAT7 rs641738 SNPs were analyzed utilizing the TaqMan SNP genotyping assay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Assay IDs for PTPN2 rs2542151 and MBOAT7 rs641738 were C_3043363_10 and C_8716820_10, respectively. Context Sequence [VIC/FAM] for rs2542151 and rs641738, respectively, were as follows: ACTTCGCCAATGCCTTGGTTCGGGC[G/T]CTTCCTGAGACTCTCATTTTCCTAA.
TCTGGCCTCCCGGGGGGCCAGCCAC[C/T]CCCTAGAGGAGCCCCAGGCTTCTGA.
The mixture of the PCR reaction consisted of 1 μL of genomic DNA (1–10 ng), 7.5 μL of TaqMan Genotyping Master Mixture (Applied Biosystems), 5.75 μL of nuclease-free water, and 0.75 μL of TaqMan SNP (probes). For the negative control reaction, 6 uL of DNAse-free water was added. PCR reactions for rs2542151 included enzyme activation at 95°C for 10 min, then 40 cycles were run at 92 °C for 15 seconds, and finally annealing at 60°C for 1 min. For rs641738, initial denaturation was at 95°C for 10 min, then 40 cycles were run at 95°C for 15 seconds (denaturing), followed by 60°C for 1 min (annealing/extension). PCR amplification was performed by a Rotor gene Q Real Time PCR System reaction (QIAGEN, GmbH-Germany). The results were analyzed with allelic discrimination software. If there was no nucleotide change in rs2542151 or rs641738 wildtype genotypes, G/G or C/C was assigned. If G changed to T at the rs2542151 SNP position, the T/T mutant genotype was assigned. If C changed to T at the rs641738 SNP position, the T/T mutant genotype was assigned. To ensure the accuracy and reliability of our genotyping results, we included duplicate samples in genotyping assays to verify the consistency and reproducibility of the results. The concordance rate between duplicate samples was >99%, indicating high genotyping accuracy. Additionally, we set a call rate threshold of >95% for both cases and controls, ensuring that only samples with high-quality genotyping data were included in the analysis.
Sample size
The idea of an event per variable (EPV) of 20 is appropriate for logistic regression analysis, according to Austin and Steyerberg (38). Only independent variables with significant effect sizes are used in order to retain their results (39, 40). Consequently, an EPV of 8 was relevant, and 260 participants were required. After allowing for a 10% dropout rate, 288 participants were recruited. Six participants were excluded either due to refusal to participate (controls) or not fulfilling the study criteria (patients), leaving 284 participants (142 subjects per group).
Statistical analysis
We used SPSS version 25.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA), was used for statistical analysis. The independent t and ANOVA tests were used for parametric data. Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney tests were applied for non-parametric data. Pearson’s chi-square (χ2) test was used for comparing between two groups. Fisher’s exact test was employed in cases where at least one of the expected cells had a value below 5. A test of homogeneity of variances was performed. The Tukey test post hoc analysis was used for assumed equal variance, while the Dunnett T3 test was used for assumed unequal variance. Statistical significance was determined at a P value less than 0.05. To assess the effects of alleles and haplotypes, the 95% confidence interval (CI) and odds ratio (OR) were calculated. Each SNP was assessed for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) in patients with MASLD and controls to detect any deviations from expected genotype frequencies identifying potential genotyping errors or other issues that could impact the validity of our results. For additional analysis of the association between gene polymorphisms and risk of disease, OR was done in various genetic models (dominant, recessive, co-dominant 1, co-dominant 2, and overdominant). Multivariable binary logistic regression analysis was performed to detect the most associated predictors in relation to MASLD.
Results
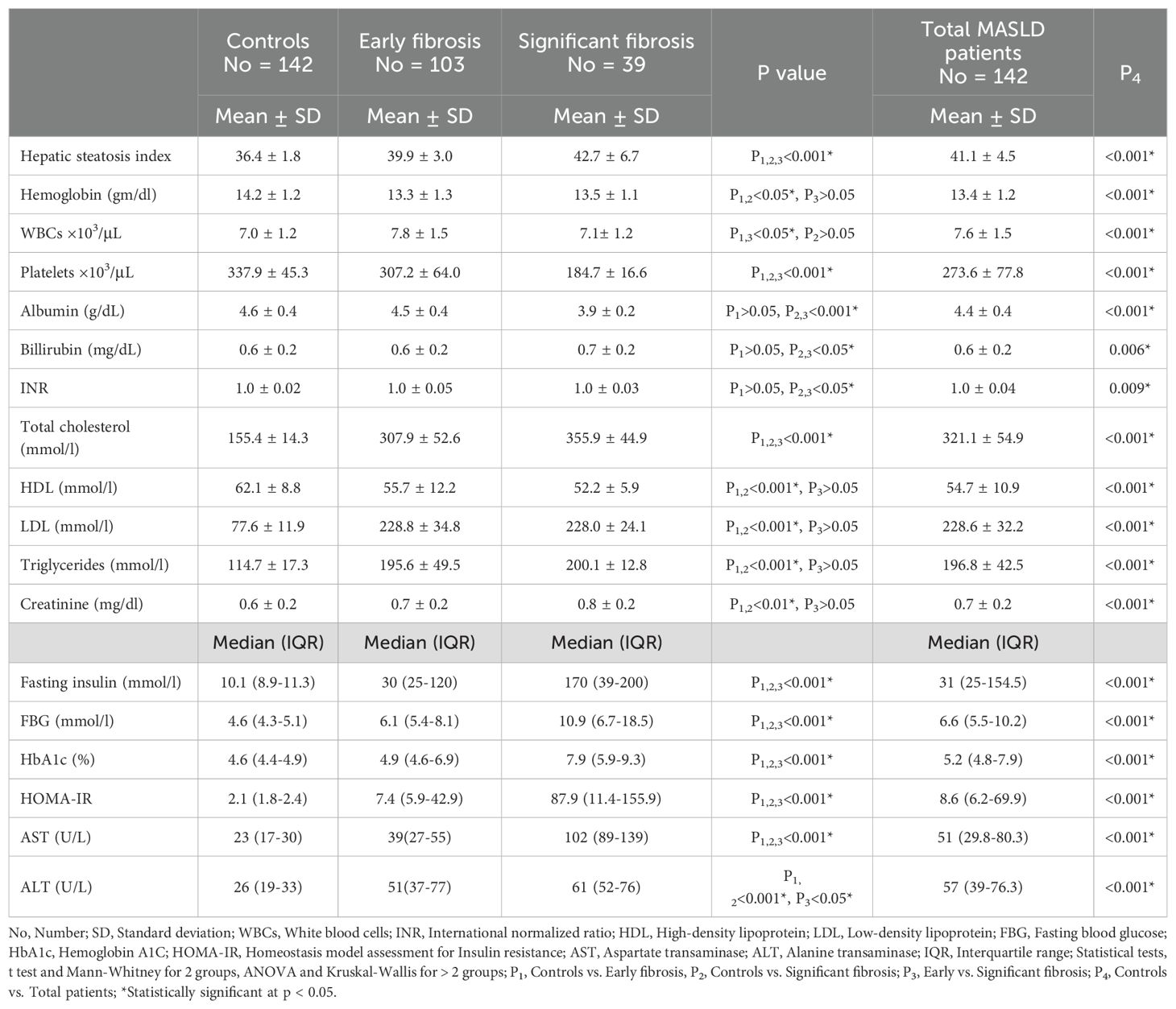
The BMI, waist circumference, diabetes mellitus, and hypertension were significantly higher in patients with MASLD compared to controls. The PTPN2 rs2542151 genotype frequencies were matched with the HWE among controls and patients with MASLD. The MBOAT7 rs641738 genotype frequencies were matched with the HWE among controls only, while it significantly differed from the HWE among patients with MASLD (Table 1). Hepatic steatosis index was significantly higher among the significant fibrosis subgroup than the early fibrosis or control groups. The laboratory characteristics of the studied groups were summarized in Table 2.
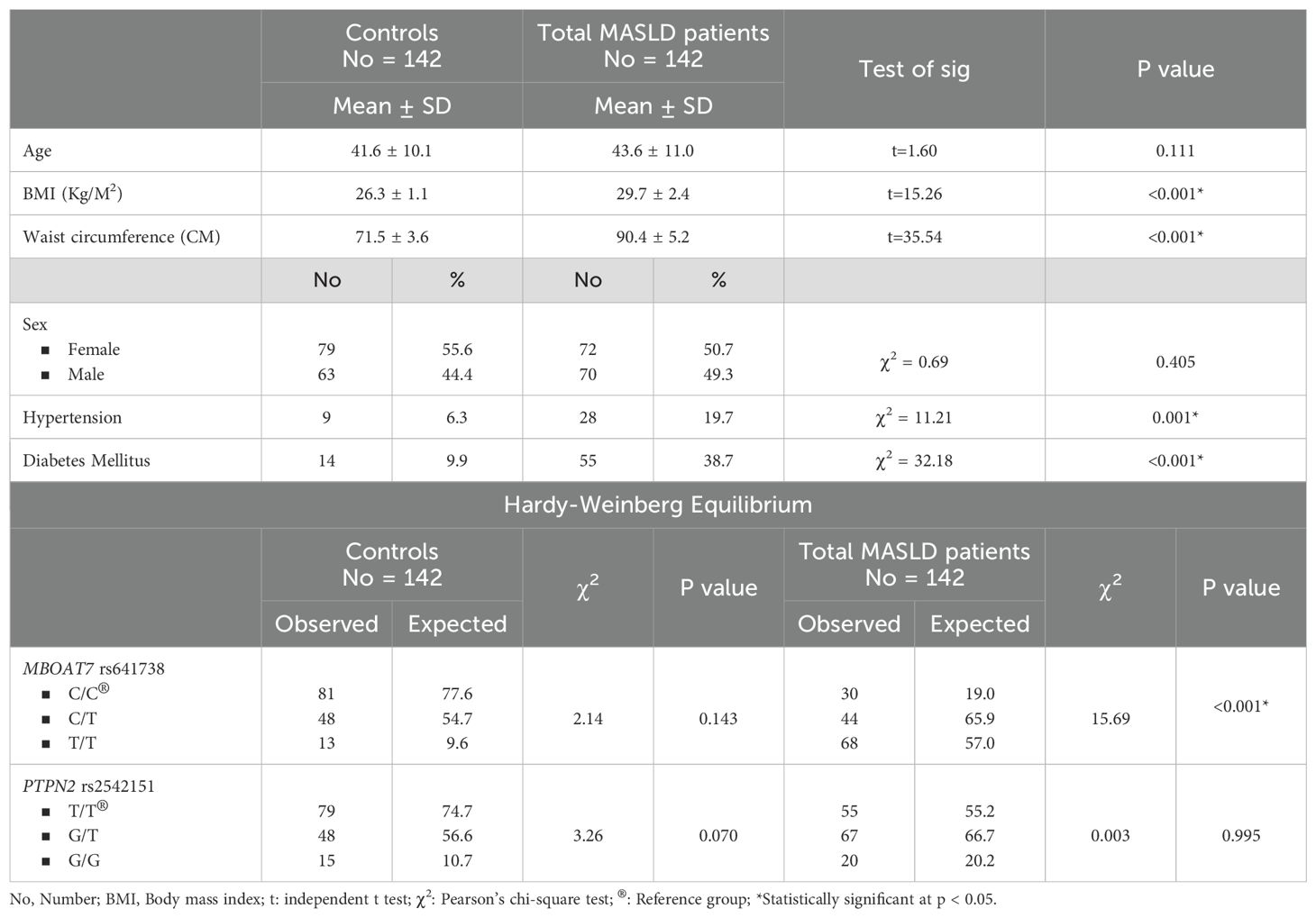
Table 1. Demographic, clinical characteristics and Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium of the studied groups(controls and total MASLD patients).
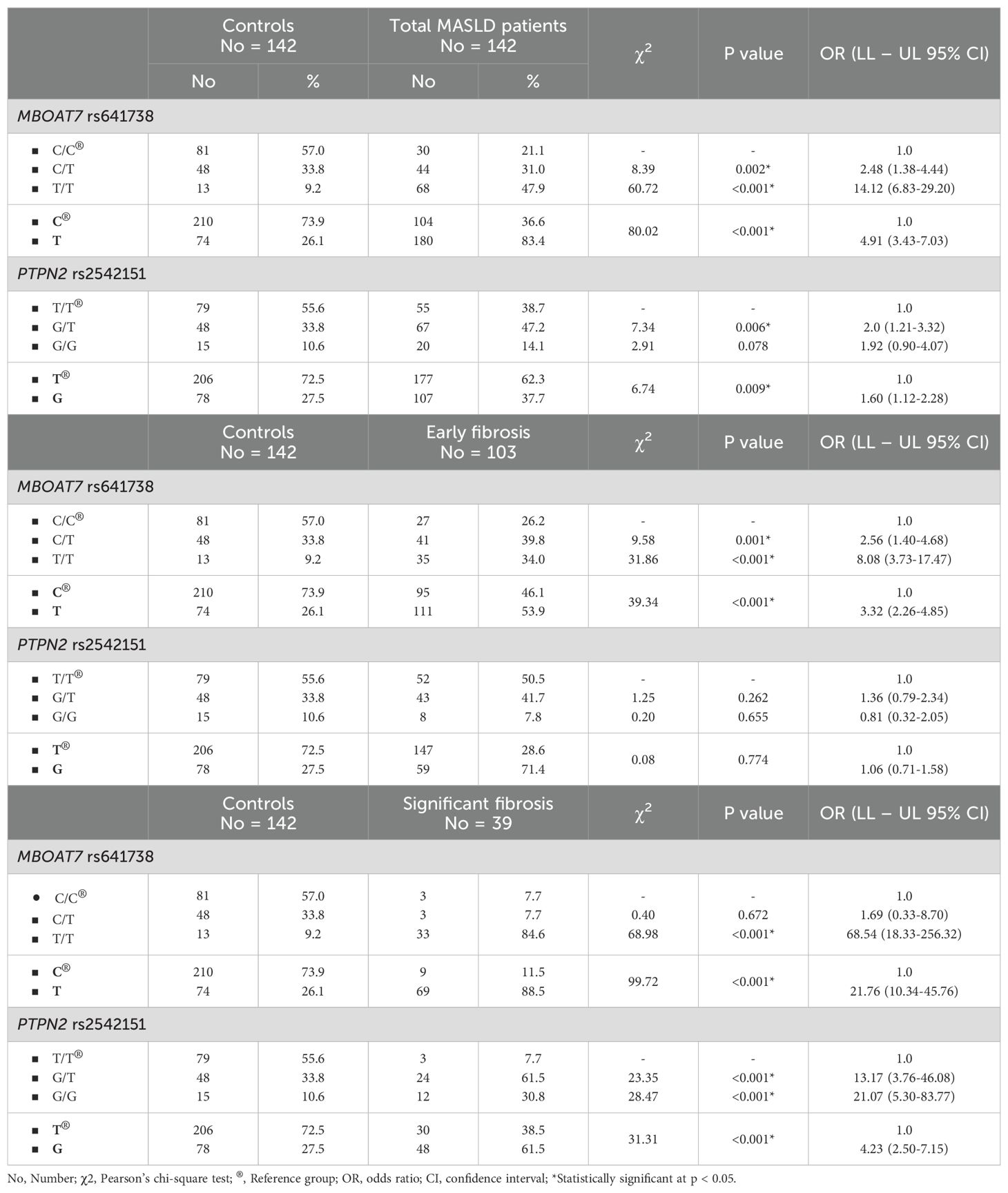
Table 3 illustrates the genotype and allele distribution of MBOAT7 rs641738 and PTPN2 rs2542151 polymorphisms among MASLD patients and controls, further stratified by fibrosis stages. Notably, the T/T genotype of MBOAT7 rs641738 was significantly more frequent in MASLD patients compared to controls (47.9% vs. 9.2%), with an OR of 14.12 (95% CI: 6.83–29.20, p < 0.001), and this association was even stronger in the significant fibrosis subgroup (OR = 68.54, 95% CI: 18.33–256.32, p < 0.001). For PTPN2 rs2542151, although the G/G genotype showed only a trend toward association with MASLD overall (OR = 1.92, 95% CI: 0.90–4.07, p = 0.078), its frequency was markedly elevated in patients with significant fibrosis (OR = 21.07, 95% CI: 5.30–83.77, p < 0.001), suggesting a specific role in fibrosis progression.
Table 4 further confirms these findings through multiple genetic models, demonstrating that the dominant model for MBOAT7 rs641738 (C/T+T/T vs. C/C) conferred an approximately fivefold increased risk of MASLD (OR = 4.96, 95% CI: 2.94–8.36, p < 0.001), with even higher risk in the recessive (OR = 9.12, 95% CI: 4.72–17.62, p < 0.001) and co-dominant models. Meanwhile, the PTPN2 rs2542151 dominant model (G/T+G/G vs. T/T) showed a significant, albeit moderate, association with MASLD susceptibility (OR = 1.98, 95% CI: 1.24–3.18, p = 0.004). Interestingly, the overdominant model revealed a protective effect of the G/T heterozygote (OR = 0.57, 95% CI: 0.35–0.92, p = 0.021), indicating a potential heterozygote advantage in disease risk.
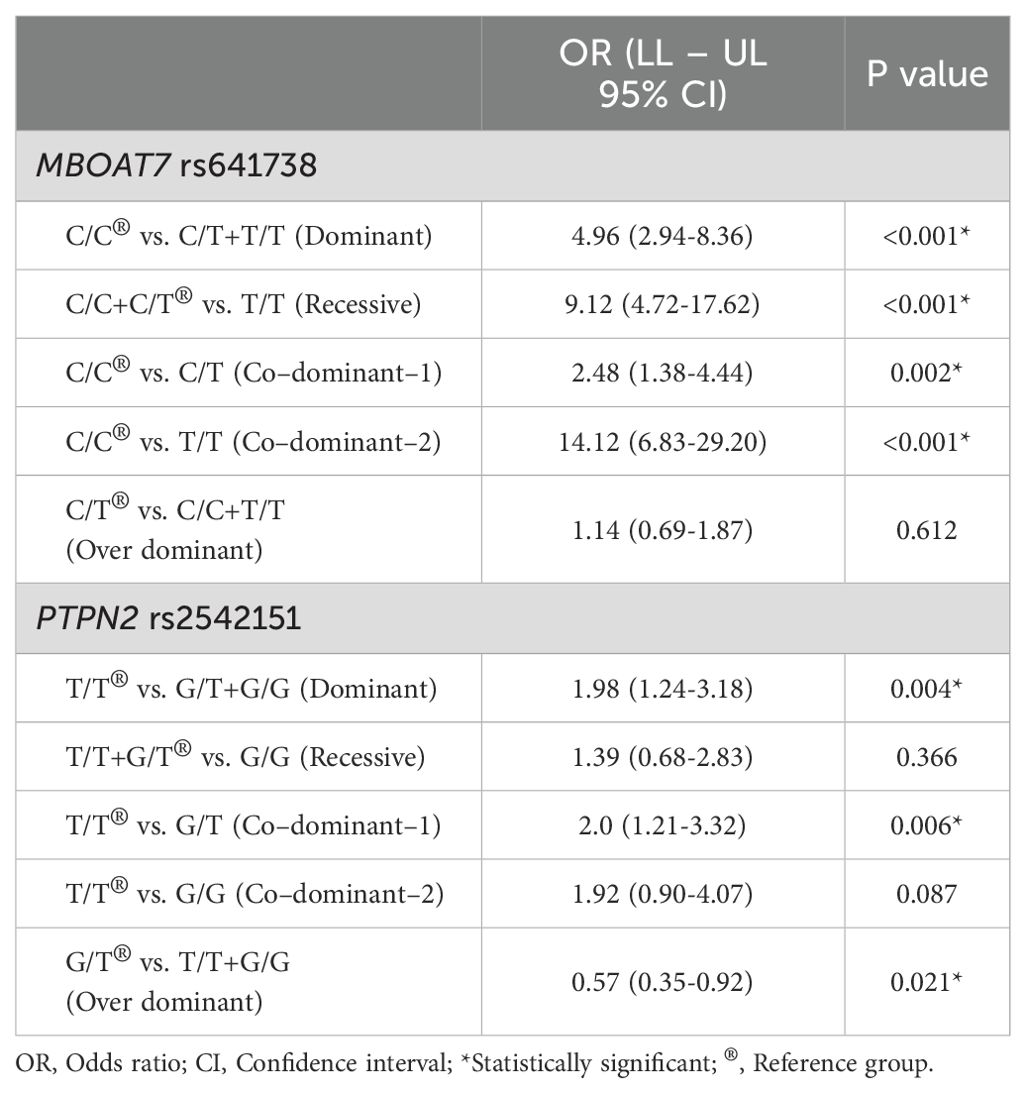
Table 4. Comparison between the control and total patients’ groups according to MBOAT7 rs641738 and PTPN2 rs2542151 gene polymorphisms in different genetic models.
The BMI, fasting insulin, FBG, HbA1c, HOMA-IR, AST, and fibroscan score were significantly higher among patients with MASLD having C/T+T/T genotypes of MBOAT7 rs641738 than those having C/C genotype. For PTPN2 rs2542151, the BMI, total cholesterol, fasting insulin, FBG, HbA1c, HOMA-IR, AST, ALT, and fibroscan score were significantly higher among patients with MASLD with G/T+T/T genotype than those with T/T genotype (Table 5).
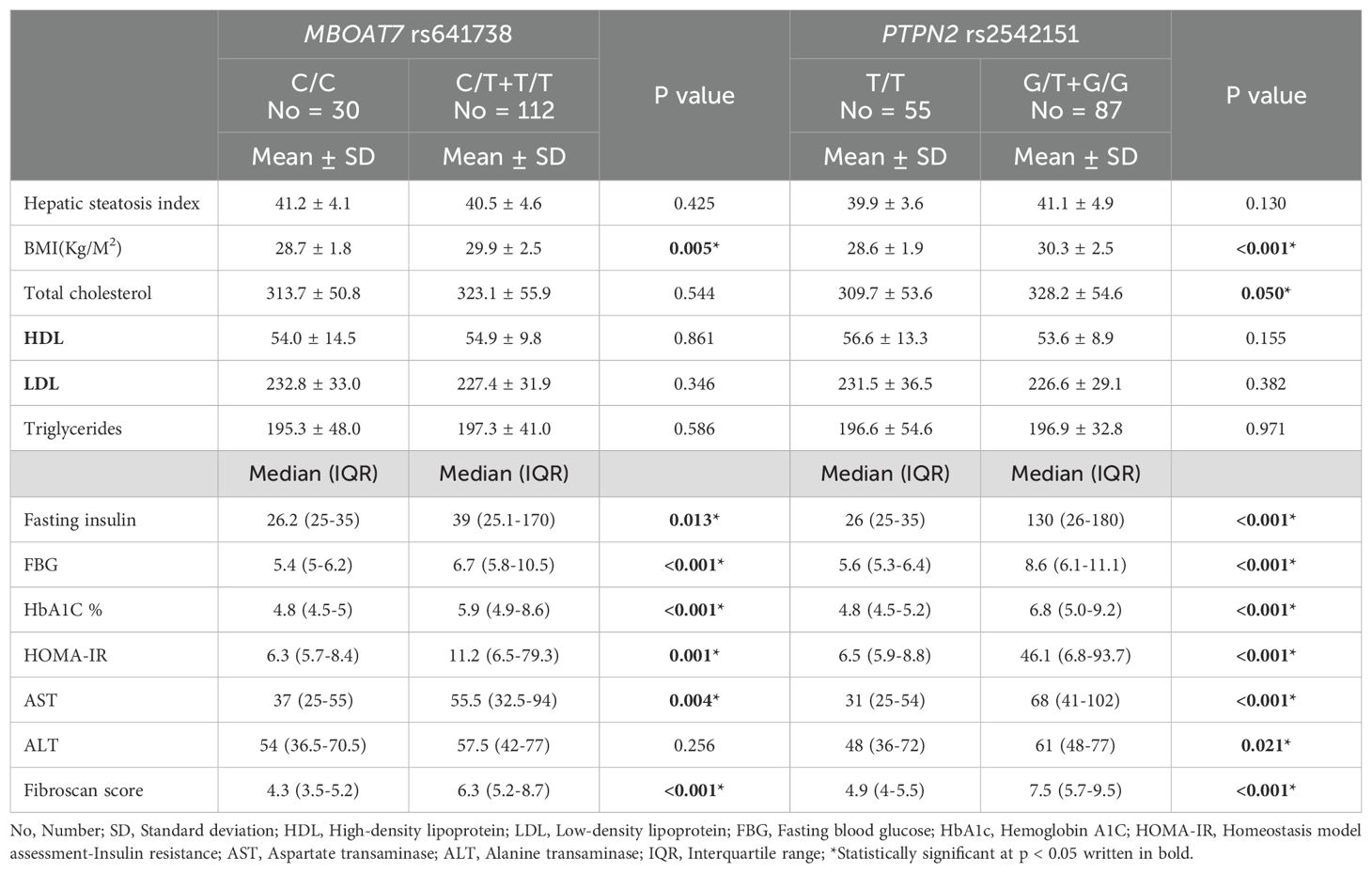
Table 5. Distribution of different parameters according to MBOAT7 rs641738 and PTPN2 rs2542151 genotypes among MASLD patients.
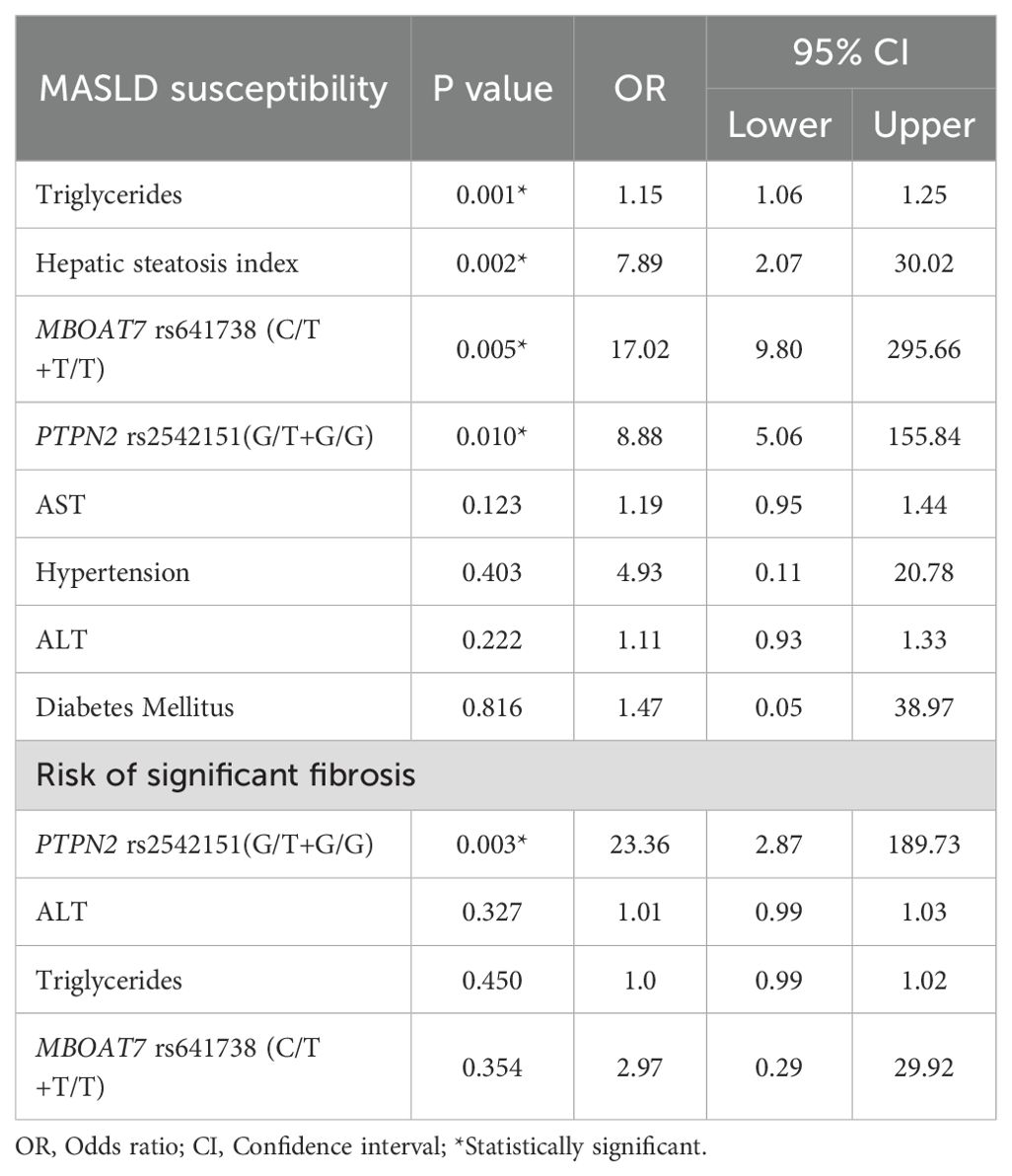
Table 6 presents multivariable logistic regression analyses adjusted for clinical variables and confirms that both MBOAT7 rs641738 (C/T+T/T) and PTPN2 rs2542151 (G/T+G/G) genotypes independently predict MASLD susceptibility with striking odds ratios of 17.02 (95% CI: 9.80–295.66, p = 0.005) and 8.88 (95% CI: 5.06–155.84, p = 0.010), respectively. In addition to genetic factors, triglycerides (OR = 1.15, 95% CI: 1.06–1.25, p = 0.001) and hepatic steatosis index (OR = 7.89, 95% CI: 2.07–30.02, p = 0.002) were significant independent clinical predictors. Importantly, regarding the prediction of significant fibrosis, PTPN2 rs2542151 (G/T+G/G) was the only independent genetic predictor with a notably high OR of 23.36 (95% CI: 2.87–189.73, p = 0.003), whereas the MBOAT7 variant and traditional biochemical markers (AST, ALT) did not maintain significance in the adjusted model. These results emphasize the robust predictive value of these polymorphisms, particularly PTPN2 rs2542151, for MASLD risk stratification and fibrosis progression in the Egyptian population studied.
Discussion
MASLD is a complicated illness where the environment and susceptibility genes combine to affect the disease’s severity (41). Population-based research in multi-ethnic cohorts have demonstrated significant inter-ethnic diversity in susceptibility to MASLD. African-Americans exhibit a diminished propensity for developing MASLD relative to Europeans, but Asians, especially Hispanics, face an elevated risk (42). The inter-ethnic disparities were not explained by type 2 diabetes, obesity, or socioeconomic variables (43). However, uncertainty surrounds the genetic components linked to MASLD pathogenesis. GWAS has identified a variety of SNPs linked to hepatic steatosis and fibrosis, some of which are less reliably replicated and seem to be affected by ethnicity (44, 45).
Dietary factors and inherited variants in genes that play important roles in antioxidant defense, such as glutathione S-transferase Mu 1 (GSTM1), glutathione S-transferase theta 1 (GSTT1), cytochrome P450 superfamily members, and sulfotransferase 1A1 (SULT1A1), have been found to interact significantly with high fruit intake (more than two fruits/day) or high consumption of grilled meat/fish (more than once per week). This increases the risk of developing MASLD and may be related to the steatosis caused by aromatic hydrocarbons, as severe MASLD is characterized by oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction (46).
Indeed, energy intake has increased generally in the Egyptian population’s nutritional pattern during the last 50 years. Nutrition shifted toward a diet with reduced consumption of fresh fruits and vegetables while increasing consumption of processed foods, fast food, red meat, vegetable oils, and soft beverages (47). According to estimates, up to 40% of the fat that Egyptian women consume is saturated fat (48), and up to 80% of them consume insufficient amounts of fresh fruit and vegetables each day. Similarly, the average prevalence of inadequate physical activity in Egypt is greater (31.0%) than the global average (27.5%), according to Guthold et al. (49), Egypt is one of the top 10 nations in the world for obesity rates (49). Also according to specific studies, the prevalence range of MASLD in Egypt is roughly 47.5%, with 56.7% having fibrosis (50), so the nature of liver disease in Egypt is changing from one of communicable to noncommunicable diseases (51, 52).
Liver fibrosis is the key prognostic factor in patients with MASLD (53). Currently, there is insufficient evidence to establish a robust connection between MBOAT7 rs641738 and PTPN2 rs2542151 gene polymorphisms and fibrosis progression in MASLD, particularly in the Middle East and African countries. Therefore, we investigated the potential role of these genotypes in the prediction of significant fibrosis in Egyptian patients with MASLD.
Our study showed that MBOAT7 rs641738 T allele and T/T genotype were more frequent among patients with MASLD than controls, with higher frequency in the significant fibrosis subgroup than the early fibrosis or control groups. In vitro and in vivo research indicates that hepatic MBOAT7 downregulation induces de novo lipogenesis, triglyceride synthesis, and hepatic lipid accumulation (54). It can promote liver inflammation and fibrosis by altering lipid composition and triggering the release of cytokines and fibrogenic mediators (55). Recent studies indicated that the MBOAT7 risk mutation was linked to hepatic fibrosis regardless of inflammation, indicating that hepatocyte signaling in fibrogenic mesenchymal cells can induce fibrosis (56, 57). Notably, MBOAT7 has been shown to be one of the single nucleotide polymorphisms that are strongly linked to the onset of MASLD and the advancement of the disease. Understanding the biology of these genetic variations has led to new discoveries in the fields of lipid droplet remodeling, hepatic very low-density lipoprotein secretion, and lipogenesis (41).
Several studies revealed that MBOAT7 rs641738 is implicated in several hepatic diseases, involving alcohol-related cirrhosis and liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B and C, as well as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (18, 33, 58, 59). However, other studies didn’t reveal any association with liver disease progression or HCC development (60–64).
In patients with MASLD, Mancina et al. initially reported, irrespective of obesity, a link between the rs641738 variants and elevated hepatic fat content, liver damage, and an increased risk of increased necroinflammation and fibrosis in individuals of European origin (15). This may be because of the association of this variant with necro-inflammation, but with no hepatocellular ballooning. Predominantly, MBOAT7 variant was found to be independently associated with fibrosis’ development, which represents the major determinant for the diagnosis of patients with MASLD (65, 66) suggesting that a common etiology for these conditions is related to alteration of hepatic lipid metabolism. (15).
Subsequently, conflicting findings about the association between MASLD and the rs641738 variant have been published. Xia et al.’s meta-analysis showed no relation of MBOAT7 rs641738 with the risk of MASLD (67). A different meta-analysis reported that the rs641738 C>T variant is a risk factor for the presence and severity of MASLD in Caucasians (21). The discrepancy among different ethnic groups implies that genetic and environmental factors interact to determine the susceptibility and severity of MASLD and liver fibrosis. Furthermore, the T allele exhibits significant variability among populations, with an allelic frequency of 0.37 in the global population. In fact, the frequency of this minor allele in the 1000 Genomes project varies from 0.44 for European to 0.32 for African and 0.22 for Asian ancestry (68). A systematic review concluded that the published evidence supports the association between MBOAT7 rs641738 C>T and increased MASLD susceptibility and severity as well as risk of advanced fibrosis in subjects with MASLD from Caucasian, Hispanic, and African American ethnicities, with contradictory findings in most studies on Asian populations (69).
More recently, this genetic variant was not found to be significantly associated with MASLD in the Indian population (70) or Korean subjects with lean MASLD (71), while in Chinese patients, it was associated with increased MASLD occurrence but not related to fibrosis in two studies (72, 73), additionally,it was found to promote inflammation and fibrosis in another study (74), however it was not related to the risk of MASLD in a different study (75). As previously mentioned, studies reported an association between MBOAT7 rs641738 and MASLD in Europeans; however, two recent studies found no association in Mexican-origin individuals (76) and Caucasian subjects from Romania (77), suggesting a potential genetic variation within ethnic sub-populations.
In the Middle East and African countries, data on the relation between MBOAT7 rs641738 and MASLD is lacking. To the far of our knowledge, this study might be the first to assess the relation between MBOAT7 SNPs and significant fibrosis in Egyptian patients with MASLD. A study involving Egyptian patients with HCV-related liver fibrosis revealed a significant correlation between the MBOAT7 T/T genotype and advanced fibrosis (78). In our study, BMI, fasting insulin, FBG, HbA1C, and HOMA-IR were significantly higher among C/T+T/T than C/C genotype. The rs641738 T allele has been associated with lower hepatic expression of MBOAT7 at both the mRNA and protein levels (68). MBOAT7 knockdown in the liver and adipose tissue of mice promoted hepatic steatosis and inflammation, hyperinsulinemia, and insulin resistance (79). We found no relation between ALT and the C/T+T/T variant. In the meta-analysis by Teo et al., the rs641738 C>T variant showed no effect on insulin resistance and a positive relation with ALT in Caucasians but not in non-Caucasian populations (21). A Mendelian randomization analysis pointed to a causal role of genetically determined steatosis in the determination of insulin resistance mediated by the degree of liver damage (80). We also found that AST and fibroscan scores were higher among C/T+T/T genotype, denoting a potential role of the T allele in fibrosis progression. However, on multivariable regression analysis, the C/T+T/T genotype was an independent predictor of MASLD susceptibility but didn’t predict significant fibrosis.
We also examined the role of PTPN2 rs2542151 genotypes in MASLD. The G allele and G/G genotype of the PTPN2 rs2542151 were more frequent among patients with MASLD compared to controls. Also, the G/T and G/G genotypes were higher among patients with significant fibrosis. Furthermore, the GT+GG genotype was the only predictor of significant fibrosis. In line with our results, Miele et al. recently demonstrated that the PTPN2 rs2542151 T>G variant is associated with the severity of fibrosis in Caucasian patients with MASLD (29).
PTPN2 is an intracellular enzyme encoded by the PTPN2 gene. It has an important role in negatively regulating various immunological pathways through the dephosphorylation of various signaling proteins. It has a significant role in the inflammatory signaling for several immune cells and intestinal epithelial cells (81). Loss of PTPN2 in intestinal epithelial cells promotes the secretion of inflammatory cytokines and dysfunction of the intestinal barrier, which are vital factors in MASLD pathogenesis. It leads to disruption of intracellular junction proteins, increased intestinal permeability, disturbance of gut microbiome, and promotes the translocation of microbes into blood circulation, which has an essential role in the development of liver steatosis and fibrosis progression (82). GWAS revealed that loss-of-function mutations in PTPN2 were associated with increased intestinal permeability, which is an early etiological event of chronic immune diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease and celiac disease (83).
We found that the rs2542151 G/T+G/G genotype was associated with significantly higher BMI, fasting insulin, FBG, HbA1C, and HOMA-IR than the T/T genotype. Consistently, Miele et al. found that the GT/GG genotype was independently associated with diabetes (29). PTPN2 has been reported to have a role in glucose metabolism. It regulates signal transduction of insulin by inactivation of its receptor through dephosphorylation mechanisms of the β-chain. In the liver, PTPN2 deficiency results in enhancement of the signaling of growth hormone, insulin resistance, increased weight and hepatic steatosis (84). Also, G/T+G/G genotype was associated with significantly higher ALT, AST, and fibroscan scores in our study, pointing to the role of the rs2542151 mutation in MASLD severity and fibrosis progression. Recently, partial PTPN2 deletion in dendritic cells was found to be associated with liver inflammation (85). In the study by Miele et al., no difference was noted in the distribution of genotypes between MASLD patients with high AST and ALT and those without high transaminases (29).
When we performed multivariable logistic regression analysis, the MBOAT7 rs641738 C/T+T/T and the PTPN2 rs2542151 G/T+G/G genotypes, as well as serum triglycerides and hepatic steatosis index, were the independent predictors of MASLD susceptibility. This confirms the possible role of these genetic variants in the pathogenesis of hepatic steatosis. High serum triglyceride level has been reported as a key factor in the development of MASLD and is an important marker for predicting MASLD even in lean patients (86). The Hepatic Steatosis Index (HSI) has shown excellent diagnostic performance in previous studies and has been suggested as a useful tool for predicting MASLD (87). The only independent predictor of significant fibrosis in our study was the PTPN2 rs2542151 G/T+G/G genotype, which strengthens a proposed pathogenetic hypothesis of PTPN2 rs2542151 as a predisposing factor of impaired gut permeability that correlates with the severity of MASLD (29). Notably, PTPN2 treatment significantly decrease serum TG, total cholesterol, and LDL levels, as well as reducing metabolic disturbances and hyperglycemia in mice (88). Additionally, taken the theatrical role of PTPN2 and CD8+ T cells in MASH pathogenesis, therapeutic targeting of PTPN2 might importantly enhance outcomes for patients with MASLD as well as MASH. (89).
The genetic differences seen among genetically distinct ethnic groups may then be a result of genomic evolution and selection (nutritional genomics). The in-depth understanding of diet-genome interactions may enable the use of novel nutritional and lifestyle strategies for the prevention and management of chronic illnesses through precision nutrition, which may be a component of customized medicine therapy (90) improving the results of MASLD and associated comorbidities (91).
Study limitations
Our study has several limitations that should be considered when interpreting the results: The cross-sectional nature of our study limits our ability to infer temporal relationships between genotypes and fibrosis progression. Longitudinal studies are needed to further explore these dynamics. The use of hospital-based volunteers as controls may introduce selection bias, potentially affecting the generalizability of our findings. Future studies could benefit from community-based recruitment strategies. The reliance on ultrasound for diagnosing the absence of MASLD in controls may not detect mild steatosis due to its limited sensitivity. More precise diagnostic methods might be necessary for accurate classification.
In conclusion, our study identified the PTPN2 rs2542151 G/T+G/G genotype as an independent predictor of significant fibrosis among Egyptian patients with MASLD. Furthermore, the MBOAT7 rs641738 C/T+T/T and PTPN2 rs2542151 G/T+G/G genotypes were significantly associated with increased risk and susceptibility to MASLD. These findings hold potential implications for genetic screening and personalized risk stratification in MASLD patients. However, validation in prospective cohorts is necessary to confirm these results and elucidate their clinical utility. Future research should prioritize larger, multi-regional studies to further investigate the role of these genetic variants in MASLD pathogenesis and progression.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/5771/ and https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/79143/.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Institutional Review Board (IRB) of National Liver Institute, Menofia University (Protocol number: 00605/2024). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
ShA: Supervision, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Methodology. HA: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. HK: Supervision, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. ZK: Software, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis. ED: Writing – original draft, Supervision. AM: Methodology, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. AS: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Methodology. HE: Writing – original draft, Methodology. MeA: Investigation, Supervision, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. MaA: Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Investigation. SZ: Writing – review & editing, Supervision. HB: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. SaA: Methodology, Investigation, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Huh Y, Cho YJ, and Nam GE. Recent epidemiology and risk factors of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Obes Metab Syndr. (2022) 31:17–27. doi: 10.7570/jomes22021
2. Mundi MS, Velapati S, Patel J, Kellogg TA, Abu Dayyeh BK, and Hurt RT. Evolution of NAFLD and its management. Nutr Clin Pract. (2020) 35:72–84. doi: 10.1002/ncp.10449
3. Rinella ME, Lazarus JV, Ratziu V, Francque SM, Sanyal AJ, Kanwal F, et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. Hepatology. (2023) 78:1966–86. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000520
4. Song SJ, Lai JC-T, Wong GL-H, Wong VW-S, and Yip TC-F. Can we use old NAFLD data under the new MASLD definition? J Hepatol. (2024) 80:e54–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.07.021
5. Portincasa P and Baffy G. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: Evolution of the final terminology. Eur J Internal Med. (2024) 124:35–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2024.04.013
6. Rinella ME and Sookoian S. From NAFLD to MASLD: updated naming and diagnosis criteria for fatty liver disease. J Lipid Res. (2024) 65:100485. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2023.100485
7. Leoni S, Tovoli F, Napoli L, Serio I, Ferri S, and Bolondi L. Current guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review with comparative analysis. World J Gastroenterol. (2018) 24:3361–73. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i30.3361
8. Zhang X, Wong GL-H, and Wong VW-S. Application of transient elastography in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Mol Hepatol. (2020) 26:128. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2019.0001n
9. Blais P, Husain N, Kramer JR, Kowalkowski M, El-Serag H, and Kanwal F. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is underrecognized in the primary care setting. Off J Am Coll Gastroenterology| ACG. (2015) 110:10–4. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2014.134
10. Canbay A, Kälsch J, Neumann U, Rau M, Hohenester S, Baba HA, et al. Non-invasive assessment of NAFLD as systemic disease—a machine learning perspective. PloS One. (2019) 14:e0214436. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0214436
11. Perveen S, Shahbaz M, Keshavjee K, and Guergachi A. A systematic machine learning based approach for the diagnosis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease risk and progression. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:2112. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20166-x
12. Wu C-C, Yeh W-C, Hsu W-D, Islam MM, Nguyen PAA, Poly TN, et al. Prediction of fatty liver disease using machine learning algorithms. Comput Methods programs biomedicine. (2019) 170:23–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.12.032
13. Chan WK. Comparison between obese and non-obese nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Mol Hepatol. (2023) 29:S58–s67. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2022.0350
14. Juanola O, Martínez-López S, Frances R, and Gómez-Hurtado I. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: metabolic, genetic, epigenetic and environmental risk factors. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2021) 18:5227. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18105227
15. Mancina RM, Dongiovanni P, Petta S, Pingitore P, Meroni M, Rametta R, et al. The MBOAT7-TMC4 variant rs641738 increases risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in individuals of European descent. Gastroenterology. (2016) 150:1219–1230.e6. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.01.032
16. Viitasalo A, Eloranta A-M, Atalay M, Romeo S, Pihlajamäki J, and Lakka TA. Association of MBOAT7 gene variant with plasma ALT levels in children: the PANIC study. Pediatr Res. (2016) 80:651–5. doi: 10.1038/pr.2016.139
17. Matsuda S, Inoue T, Lee HC, Kono N, Tanaka F, Gengyo-Ando K, et al. Member of the membrane-bound O-acyltransferase (MBOAT) family encodes a lysophospholipid acyltransferase with broad substrate specificity. Genes to Cells. (2008) 13:879–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2008.01212.x
18. Thabet K, Asimakopoulos A, Shojaei M, Romero-Gomez M, Mangia A, Irving WL, et al. MBOAT7 rs641738 increases risk of liver inflammation and transition to fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Nat Commun. (2016) 7:12757. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12757
19. Meroni M, Dongiovanni P, Longo M, Carli F, Baselli G, Rametta R, et al. Mboat7 down-regulation by hyper-insulinemia induces fat accumulation in hepatocytes. EBioMedicine. (2020) 52. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102658
20. Lonsdale J, Thomas J, Salvatore M, Phillips R, Lo E, Shad S, et al. The genotype-tissue expression (GTEx) project. Nat Genet. (2013) 45:580–5. doi: 10.1038/ng.2653
21. Teo K, Abeysekera KW, Adams L, Aigner E, Anstee QM, Banales JM, et al. rs641738C> T near MBOAT7 is associated with liver fat, ALT and fibrosis in NAFLD: A meta-analysis. J Hepatol. (2021) 74:20–30. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.08.027
22. Glas J, Wagner J, Seiderer J, Olszak T, Wetzke M, Beigel F, et al. PTPN2 gene variants are associated with susceptibility to both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis supporting a common genetic disease background. PloS One. (2012) 7:e33682. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033682
23. Bussieres-Marmen S, Hutchins AP, Schirbel A, Rebert N, Tiganis T, Fiocchi C, et al. Characterization of PTPN2 and its use as a biomarker. Methods. (2014) 65:239–46. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2013.08.020
24. Marcil V, Mack DR, Kumar V, Faure C, Carlson CS, Beaulieu P, et al. Association between the PTPN2 gene and Crohn’s disease: dissection of potential causal variants. Inflammatory bowel Dis. (2013) 19:1149–55. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0b013e318280b181
25. Espino-Paisan L, de la Calle H, Fernández-Arquero M, Figueredo M, de la Concha EG, Urcelay E, et al. A polymorphism in PTPN2 gene is associated with an earlier onset of type 1 diabetes. Immunogenetics. (2011) 63:255–8. doi: 10.1007/s00251-010-0500-x
26. Jones Richard W, McArdle Wendy L, Ring Susan M, Strachan David P, Pembrey M, Clayton DG, et al. Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature. (2007) 447:661–78. doi: 10.1038/nature05911
27. Yang C, Ming Y, Zhou K, Hao Y, Hu D, Chu B, et al. Macrophage membrane-camouflaged shRNA and doxorubicin: a pH-dependent release system for melanoma chemo-immunotherapy. Research. (2022) 2022. doi: 10.34133/2022/9768687
28. Tang XE, Cheng YQ, and Tang CK. Protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 2 as the therapeutic target of atherosclerotic diseases: past, present and future. Front Pharmacol. (2023) 14:1219690. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1219690
29. Miele L, Giorgio V, Liguori A, Petta S, Pastorino R, Arzani D, et al. Genetic susceptibility of increased intestinal permeability is associated with progressive liver disease and diabetes in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutrition Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2020) 30:2103–10. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2020.06.013
30. Long SA, Cerosaletti K, Wan JY, Ho J-C, Tatum M, Wei S, et al. An autoimmune-associated variant in PTPN2 reveals an impairment of IL-2R signaling in CD4+ T cells. Genes Immun. (2011) 12:116–25. doi: 10.1038/gene.2010.54
31. Peng H, Li J, Chen X, Zhou X, Zhu W, and Li F. Genetic variants of PTPN2 gene in chinese children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Med Sci Monit. (2015) 21:2653–8. doi: 10.12659/MSM.893607
32. Santin I, Moore F, Colli ML, Gurzov EN, Marselli L, Marchetti P, et al. PTPN2, a candidate gene for type 1 diabetes, modulates pancreatic β-cell apoptosis via regulation of the BH3-only protein Bim. Diabetes. (2011) 60:3279–88. doi: 10.2337/db11-0758
33. Thabet K, Chan HLY, Petta S, Mangia A, Berg T, Boonstra A, et al. The membrane-bound O-acyltransferase domain-containing 7 variant rs641738 increases inflammation and fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. (2017) 65:1840–50. doi: 10.1002/hep.29064
34. Zusi C, Morandi A, Maguolo A, Corradi M, Costantini S, Mosca A, et al. Association between MBOAT7 rs641738 polymorphism and non-alcoholic fatty liver in overweight or obese children. Nutrition Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2021) 31:1548–55. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2021.01.020
35. Lee SB, Kim MK, Kang S, Park K, Kim JH, Baik SJ, et al. Triglyceride glucose index is superior to the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance for predicting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Korean adults. Endocrinol Metab. (2019) 34:179–86. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2019.34.2.179
36. Eletreby R, Abdellatif Z, Gaber Y, Ramadan A, Ahmad N, Khattab H, et al. Validity of routine biochemical and ultrasound scores for prediction of hepatic fibrosis and steatosis in NAFLD. Egyptian Liver J. (2021) 11:1–10. doi: 10.1186/s43066-021-00115-6
37. Dietrich CF, Shi L, Löwe A, Dong Y, Potthoff A, Sparchez Z, et al. Conventional ultrasound for diagnosis of hepatic steatosis is better than believed. Z für Gastroenterologie. (2022) 60:1235–48. doi: 10.1055/a-1491-1771
38. Austin PC and Steyerberg EW. Events per variable (EPV) and the relative performance of different strategies for estimating the out-of-sample validity of logistic regression models. Stat Methods Med Res. (2017) 26:796–808. doi: 10.1177/0962280214558972
39. Chew BH, Ghazali SS, Ismail M, Haniff J, and Bujang MA. Age≥ 60 years was an independent risk factor for diabetes-related complications despite good control of cardiovascular risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Exp Gerontology. (2013) 48:485–91. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2013.02.017
40. Chew BH, Mastura I, Shariff-Ghazali S, Lee PY, Cheong AT, Ahmad Z, et al. Determinants of uncontrolled hypertension in adult type 2 diabetes mellitus: an analysis of the Malaysian diabetes registry 2009. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2012) 11:54. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-11-54
41. Pei Y and Goh GB-B. Genetic risk factors for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Gut Liver. (2025) 19:8. doi: 10.5009/gnl240407
42. Guerrero R, Vega GL, Grundy SM, and Browning JD. Ethnic differences in hepatic steatosis: An insulin resistance paradox?†. Hepatology. (2009) 49:791–801. doi: 10.1002/hep.22726
43. Taliento AE, Dallio M, Federico A, Prati D, and Valenti L. Novel insights into the genetic landscape of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2019) 16:2755. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16152755
44. Li Y, Van Den Berg EH, Kurilshikov A, Zhernakova DV, Gacesa R, Hu S, et al. Genome-wide studies reveal genetic risk factors for hepatic Fat Content. Genomics Proteomics Bioinf. (2024) 22:qzae031. doi: 10.1093/gpbjnl/qzae031
45. Kaplan DE, Teerlink CC, Schwantes-An T-H, Norden-Krichmar TM, Duvall SL, Morgan TR, et al. Clinical and genetic risk factors for progressive fibrosis in metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease. Hepatol Commun. (2024) 8:e0487. doi: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000487
46. Miele L, Dall’armi V, Cefalo C, Nedovic B, Arzani D, Amore R, et al. A case–control study on the effect of metabolic gene polymorphisms, nutrition, and their interaction on the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Genes Nutr. (2014) 9:383. doi: 10.1007/s12263-013-0383-1
47. Golzarand M, Mirmiran P, Jessri M, Toolabi K, Mojarrad M, and Azizi F. Dietary trends in the Middle East and North Africa: an ecological study, (1961to 2007). Public Health Nutr. (2012) 15:1835–44. doi: 10.1017/S1368980011003673
48. Mahmood A. Nutritional status and anthropometric measurements among women in Egypt, National Survey 2001–2002. Arab J Food Nutr. (2004) 11:98–107.
49. Guthold R, Stevens GA, Riley LM, and Bull FC. Worldwide trends in insufficient physical activity from 2001 to 2016: a pooled analysis of 358 population-based surveys with 1· 9 million participants. Lancet Global Health. (2018) 6:e1077–86. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(18)30357-7
50. Tomah S, Mohamed Eid E, Abouelmagd MM, Hassan AH, Eldib AH, and Hamdy O. 214-LB: Vibration-controlled transient elastography reveals alarming prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and fibrosis among young adults in Egypt. Diabetes. (2019) 68(Supplement_1):214–LB. doi: 10.2337/db19-214-LB
51. Fouad Y, Esmat G, Elwakil R, Zakaria S, Yosry A, Waked I, et al. The Egyptian clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Saudi J Gastroenterol. (2022) 28:3–20. doi: 10.4103/sjg.sjg_357_21
52. Younossi Z, Tacke F, Arrese M, Chander Sharma B, Mostafa I, Bugianesi E, et al. Global perspectives on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. (2019) 69:2672–82. doi: 10.1002/hep.30251
53. Ng CH, Lim WH, Lim GEH, Tan DJH, Syn N, Muthiah MD, et al. Mortality outcomes by fibrosis stage in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 21:931–939.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.04.014
54. Huang G, Wallace DF, Powell EE, Rahman T, Clark PJ, and Subramaniam VN. Gene variants implicated in steatotic liver disease: opportunities for diagnostics and therapeutics. Biomedicines. (2023) 11:2809. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102809
55. Meroni M, Longo M, Fracanzani AL, and Dongiovanni P. MBOAT7 down-regulation by genetic and environmental factors predisposes to MAFLD. EBioMedicine. (2020) 57. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102866
56. Thangapandi VR, Knittelfelder O, Brosch M, Patsenker E, Vvedenskaya O, Buch S, et al. Loss of hepatic Mboat7 leads to liver fibrosis. Gut. (2021) 70:940–50. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-320853
57. Moore MP, Wang X, Kennelly JP, Shi H, Ishino Y, Kano K, et al. Low MBOAT7 expression, a genetic risk for MASH, promotes a profibrotic pathway involving hepatocyte TAZ upregulation. Hepatology. (2025) 81:576–90. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000933
58. Buch S, Stickel F, Trepo E, Way M, Herrmann A, Nischalke HD, et al. A genome-wide association study confirms PNPLA3 and identifies TM6SF2 and MBOAT7 as risk loci for alcohol-related cirrhosis. Nat Genet. (2015) 47:1443–8. doi: 10.1038/ng.3417
59. Lin YC, Chang PF, Chang MH, and Ni YH. Genetic determinants of hepatic steatosis and serum cytokeratin-18 fragment levels in Taiwanese children. Liver Int. (2018) 38:1300–7. doi: 10.1111/liv.13689
60. Beaudoin JJ, Liang T, Tang Q, Banini BA, Shah VH, Sanyal AJ, et al. Role of candidate gene variants in modulating the risk and severity of alcoholic hepatitis. Alcoholism: Clin Exp Res. (2021) 45:709–19. doi: 10.1111/acer.14581
61. Ezzikouri S, Elfihry R, Chihab H, Elmessaoudi-Idrissi M, Zaidane I, Jadid FZ, et al. Effect of MBOAT7 variant on hepatitis B and C infections in Moroccan patients. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:12247. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30824-9
62. Kang Q, Xu J, Luo H, Tan N, Chen H, Cheng R, et al. Evaluation of the association of a variant in PNPLA3 and TM6SF2 with fibrosis progression in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection after eradication: a retrospective study. Gene. (2022) 820:146235. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2022.146235
63. Raksayot M, Chuaypen N, Khlaiphuengsin A, Pinjaroen N, Treeprasertsuk S, Poovorawan Y, et al. Independent and additive effects of PNPLA3 and TM6SF2 polymorphisms on the development of non-B, non-C hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol. (2019) 54:427–36. doi: 10.1007/s00535-018-01533-x
64. Goble S, Akambase J, Prieto J, Balderramo D, Ferrer JD, Mattos AZ, et al. MBOAT7 rs641738 variant is not associated with an increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in a latin american cohort. Digestive Dis Sci. (2023) 68:4212–20. doi: 10.1007/s10620-023-08104-y
65. Ekstedt M, Hagström H, Nasr P, Fredrikson M, Stål P, Kechagias S, et al. Fibrosis stage is the strongest predictor for disease-specific mortality in NAFLD after up to 33 years of follow-up. Hepatology. (2015) 61:1547–54. doi: 10.1002/hep.27368
66. Angulo P, Kleiner DE, Dam-Larsen S, Adams LA, Bjornsson ES, Charatcharoenwitthaya P, et al. Liver fibrosis, but no other histologic features, is associated with long-term outcomes of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. (2015) 149:389–397.e10. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.04.043
67. Xia Y, Huang C-X, Li G-Y, Chen K-H, Han L, Tang L, et al. Meta-analysis of the association between MBOAT7 rs641738, TM6SF2 rs58542926 and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease susceptibility. Clinics Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. (2019) 43:533–41. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2019.01.008
68. Caddeo A, Spagnuolo R, and Maurotti S. MBOAT7 in liver and extrahepatic diseases. Liver Int. (2023) 43:2351–64. doi: 10.1111/liv.15706
69. Ismaiel A and Dumitrascu DL. Genetic predisposition in metabolic-dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and cardiovascular outcomes—Systematic review. Eur J Clin Invest. (2020) 50:e13331. doi: 10.1111/eci.13331
70. Chavan SU, Rathi P, and Mandot A. Association of GCKR and MBOAT7 genetic polymorphisms with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Exp Hepatol. (2024) 10:39–46. doi: 10.5114/ceh.2024.136326
71. Park H, Yoon EL, Chung GE, Choe EK, Bae JH, Choi SH, et al. Genetic and metabolic characteristics of lean nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a Korean health examinee cohort. Gut liver. (2023) 18:316. doi: 10.5009/gnl230044
72. Xia M, Ma S, Huang Q, Zeng H, Ge J, Xu W, et al. NAFLD-related gene polymorphisms and all-cause and cause-specific mortality in an Asian population: the Shanghai Changfeng Study. Alimentary Pharmacol Ther. (2022) 55:705–21. doi: 10.1111/apt.16772
73. Mu T, Peng L, Xie X, He H, Shao Q, Wang X, et al. Single nucleotide polymorphism of genes associated with metabolic fatty liver disease. J Oncol. (2022) 2022:9282557. doi: 10.1155/2022/9282557
74. Xu X, Xu H, Liu X, Zhang S, Cao Z, Qiu L, et al. MBOAT7 rs641738 (C> T) is associated with NAFLD progression in men and decreased ASCVD risk in elder Chinese population. Front Endocrinol. (2023) 14:1199429. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1199429
75. Liao S, An K, Liu Z, He H, An Z, Su Q, et al. Genetic variants associated with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in western China. J Clin Lab Anal. (2022) 36:e24626. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24626
76. Trejo MJ, Morrill KE, Klimentidis YC, and Garcia DO. Examining genetic associations with hepatic steatosis in Mexican-origin adults. Ann Hepatol. (2023) 28:101120. doi: 10.1016/j.aohep.2023.101120
77. Ismaiel A, Spinu M, Osan S, Leucuta D-C, Popa S-L, Chis BA, et al. MBOAT7 rs641738 variant in metabolic-dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and cardiovascular risk. Med Pharm Rep. (2023) 96:41. doi: 10.15386/mpr-2504
78. Youssef SS, Abbas EAER, Aly YH, and Seif S. The correlation between single nucleotide polymorphism of MBOAT7 and PNPLA3 genes to the degree of hepatic fibrosis in HCV patients: an experience from Egypt. J Bioscience Appl Res. (2020) 6:281–94. doi: 10.21608/jbaar.2020.135612
79. Massey WJ, Varadharajan V, Banerjee R, Brown AL, Horak AJ, Hohe RC, et al. MBOAT7-driven lysophosphatidylinositol acylation in adipocytes contributes to systemic glucose homeostasis. J Lipid Res. (2023) 64:100349. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2023.100349
80. Dongiovanni P, Stender S, Pietrelli A, Mancina R, Cespiati A, Petta S, et al. Causal relationship of hepatic fat with liver damage and insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver. J Internal Med. (2018) 283:356–70. doi: 10.1111/joim.12719
81. Song J, Lan J, Tang J, and Luo N. PTPN2 in the immunity and tumor immunotherapy: a concise review. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:10025. doi: 10.3390/ijms231710025
82. Long C, Zhou X, Xia F, and Zhou B. Intestinal barrier dysfunction and gut microbiota in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: assessment, mechanisms, and therapeutic considerations. Biology. (2024) 13:243. doi: 10.3390/biology13040243
83. Sweat YY and Turner JR. PTPN2 mutations cause epithelium-intrinsic barrier loss that synergizes with mucosal immune hyperactivation. J Clin Invest. (2021) 131(17):e151414. doi: 10.1172/JCI151414
84. Wang Y-N, Liu S, Jia T, Feng Y, Xu X, and Zhang D. T cell protein tyrosine phosphatase in glucose metabolism. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:682947. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.682947
85. Hering L, Katkeviciute E, Schwarzfischer M, Busenhart P, Gottier C, Mrdjen D, et al. Protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 2 function in dendritic cells is crucial to maintain tissue tolerance. Front Immunol. (2020) 11, 1856. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01856
86. Chahal D, Sharma D, Keshavarzi S, Arisar FAQ, Patel K, Xu W, et al. Distinctive clinical and genetic features of lean vs overweight fatty liver disease using the UK Biobank. Hepatol Int. (2022) 16:325–36. doi: 10.1007/s12072-022-10304-z
87. Priego-Parra BA, Triana-Romero A, Martínez-Perez GP, Reyes-Diaz SA, Ordaz-Alvarez HR, Bernal-Reyes R, et al. Hepatic steatosis index (HSI): a valuable biomarker in subjects with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD). Ann Hepatol. (2024) 29:101391. doi: 10.1016/j.aohep.2024.101391
88. Li Y, Zhou H, Li Y, Han L, Song M, Chen F, et al. PTPN2 improved renal injury and fibrosis by suppressing STAT-induced inflammation in early diabetic nephropathy. J Cell Mol Med. (2019) 23:4179–95. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14304
89. Determann ME. The Role of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Non-Receptor Type 2 in the Development and as a Treatable Target for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis. (Doctoral dissertation). Switzerland: University of Zurich (2025).
90. Meroni M, Longo M, Rustichelli A, and Dongiovanni P. Nutrition and genetics in NAFLD: the perfect binomium. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:2986. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082986
Keywords: MASLD, genotyping, fibrosis, MBOAT7, rs641738, PTPN2, rs2542151
Citation: Abdelsattar S, Al-Amodi HS, Kamel HFM, Kasemy ZA, Darwish E, Mosbeh A, Sakr AA, Elgazzar HM, Abdelkareem M, Abozeid M, Zewain SK, Bedair HM and Abdelmageed SM (2025) Impact of genotyping (PTPN2, rs2542151) and (MBOAT7, rs641738) in prediction of fibrosis in Metabolic dysfunction- associated steatotic liver disease’ patients. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1615162. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1615162
Received: 20 April 2025; Accepted: 21 August 2025;
Published: 11 September 2025.
Edited by:
Isis Hara Trevenzoli, Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, BrazilReviewed by:
Wendong Huang, City of Hope, United StatesMehmet Emin Arayici, Dokuz Eylül University, Türkiye
Copyright © 2025 Abdelsattar, Al-Amodi, Kamel, Kasemy, Darwish, Mosbeh, Sakr, Elgazzar, Abdelkareem, Abozeid, Zewain, Bedair and Abdelmageed. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shimaa Abdelsattar, c2hpbWFhLmFiZGVsc2F0dGFyQGxpdmVyLm1lbm9maWEuZWR1LmVn
 Shimaa Abdelsattar
Shimaa Abdelsattar Hiba S. Al-Amodi2
Hiba S. Al-Amodi2 Zeinab A. Kasemy
Zeinab A. Kasemy Ehab Darwish
Ehab Darwish Ayman A. Sakr
Ayman A. Sakr Mai Abozeid
Mai Abozeid