- 1Guangxi Hospital Division of The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Nanning, China
- 2Department of Infectious Diseases and Public Health, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
- 3Faculty of Medicine, Heidelberg University, Heidelberg, Germany
- 4Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
- 5Department of Hypertension and Vascular Disease, The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
Diabetes mellitus (DM) represents a complex metabolic disorder posing urgent diagnostic and therapeutic challenges worldwide. Traditional biomarkers such as HbA1c and OGTT fail to capture the dynamic nature of metabolic remodeling underlying DM pathophysiology. Metabolomics, by offering real-time, systems-level insights into small-molecule dynamics, has emerged as a promising strategy for both early disease detection and therapeutic target discovery. Recent studies have highlighted the diagnostic and prognostic value of metabolites, including branched-chain amino acids, lipid derivatives, and bile acids. Despite its immense potential, the clinical application of metabolomics remains hindered by technical limitations, such as cross-cohort standardization and data interpretation complexity. Future advances integrating artificial intelligence and multi-omics strategies may transform metabolomics from an exploratory tool to a clinical mainstay in diabetes management. This review offers a comprehensive synthesis of recent advances in metabolomics-driven diabetes research, with a particular focus on elucidating key metabolic pathways, identifying emerging biomarkers, and exploring translational opportunities. To fully realize the clinical potential of metabolomics, further efforts toward analytical standardization, cross-cohort validation, and the integration of artificial intelligence–powered tools will be essential to bridge the gap from bench to bedside in diabetes care.
1 Introduction
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is an escalating global health crisis, currently affecting over 537 million people worldwide, with projections indicating an increase to 643 million by 2030 and 783 million by 2045, according to the International Diabetes Federation (1). As a leading cause of morbidity and mortality, DM imposes a substantial socioeconomic burden due to its diverse complications, including cardiovascular disease, nephropathy, neuropathy, and retinopathy (2). Despite notable advances in diagnostics and treatment, the global prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, underscoring the urgent need for more effective and personalized disease management strategies (3).
Despite the widespread use of traditional diagnostic markers such as hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), and fasting plasma glucose (FPG), these methods have inherent limitations in capturing the dynamic and multifactorial nature of diabetes pathogenesis. HbA1c levels, for instance, are influenced by variations in erythrocyte lifespan, potentially leading to inaccuracies in individuals with anemia or hemoglobinopathies (4). Similarly, although OGTT is the gold standard for diabetes diagnosis, it reflects only a single time point of glucose metabolism and fails to account for fluctuations in insulin sensitivity and metabolic adaptations (5). FPG remains widely used due to its accessibility, low cost, and standardized protocols (6). However, it has several inherent limitations: requiring prolonged fasting (≥8 hours), representing only a single metabolic snapshot, and exhibiting sample stability concerns (7). Furthermore, while genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified numerous genetic loci associated with diabetes susceptibility, genetic predisposition alone cannot fully explain the disease’s heterogeneity (8).
In diabetes treatment, the molecular mechanisms underlying β-cell dysfunction and tissue-specific insulin resistance remain incompletely understood, hindering the development of targeted therapies (9). Furthermore, a subset of patients demonstrates suboptimal responses to first-line treatments such as metformin, highlighting the need for personalized therapeutic strategies (10). The absence of reliable early-stage biomarkers and individualized treatment targets underscores the urgent need for innovative approaches capable of comprehensively mapping metabolic perturbations in diabetes.
Metabolomics is the large-scale study of small molecules within biological systems such as cells, biofluids, tissues, or entire organisms (11). As a rapidly evolving discipline following genomics and proteomics, metabolomics provides a comprehensive snapshot of an organism’s metabolic composition (12). Since the launch of the Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) in 2007, metabolomics has advanced significantly and has been widely applied across multiple domains, including disease diagnostics, drug discovery, nutritional science, toxicology, environmental research, and plant biology (13–17). Analytical platforms such as mass spectrometry (MS), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), and various chromatography methods (e.g., HPLC, GC) enable precise quantification of thousands of metabolites (11). Recent innovations, such as spatial and single-cell metabolomics, are further enhancing its potential in precision medicine (18, 19). Compared with other omics technologies, metabolomics offers distinct translational advantages. While genomics and transcriptomics capture static or upstream regulatory information, and proteomics is limited by protein coverage and complexity, metabolomics reflects the integrated outcomes of biological processes and environmental exposures (20). This capacity to detect real-time functional changes makes metabolomics particularly valuable for monitoring disease states, identifying therapeutic targets, and enabling individualized interventions in diabetes.
One of the most powerful applications of metabolomics in diabetes lies in its capacity to decode metabolic reprogramming, a hallmark of disease pathogenesis marked by disrupted nutrient sensing, energy metabolism, and hormonal signaling (21). At the tissue level, skeletal muscle in individuals with diabetes exhibits mitochondrial dysfunction, shifting from efficient oxidative phosphorylation to incomplete fatty acid oxidation and the accumulation of lipotoxic intermediates, such as long-chain acylcarnitine, which impair insulin signaling (22). Concurrently, inflamed and insulin-resistant adipose tissue secretes pro-inflammatory cytokines that exacerbate hepatic gluconeogenesis and contribute to systemic insulin resistance (23). These systemic perturbations ultimately lead to pancreatic β-cell dedifferentiation, wherein chronic hyperglycemia induces epigenetic silencing of key metabolic regulators (e.g., PDX1 and MAFA). This blunts glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, perpetuating a vicious cycle of metabolic deterioration. Through high-resolution metabolic profiling, metabolomics enables the detection of these maladaptive changes, offering new opportunities for early diagnosis, patient stratification, and development of targeted therapeutics tailored to specific metabolic subtypes of diabetes.
However, significant challenges remain in translating metabolomic findings into clinical practice, including the standardization of analytical protocols, cross-population validation, and the biological interpretation of complex datasets. Consequently, a comprehensive overview of the role of metabolomics in decoding the metabolic network of diabetes is urgently needed. This review therefore aims to (1) summarize recent advances in metabolomics technologies relevant to diabetes, (2) elucidate key mechanisms of metabolic reprogramming, (3) highlight promising biomarkers and patient stratification strategies, and (4) discuss translational applications and future challenges. Through this synthesis, we aim to delineate the potential of metabolomics in advancing precision medicine in diabetes management.
2 Metabolomics technologies
2.1 Analytical platforms
Metabolomics has emerged as a foundational discipline in contemporary biomedical research, offering a systems-level approach to characterize metabolic perturbations in complex diseases such as diabetes. The field employs diverse analytical platforms, each with distinct advantages and technical limitations.
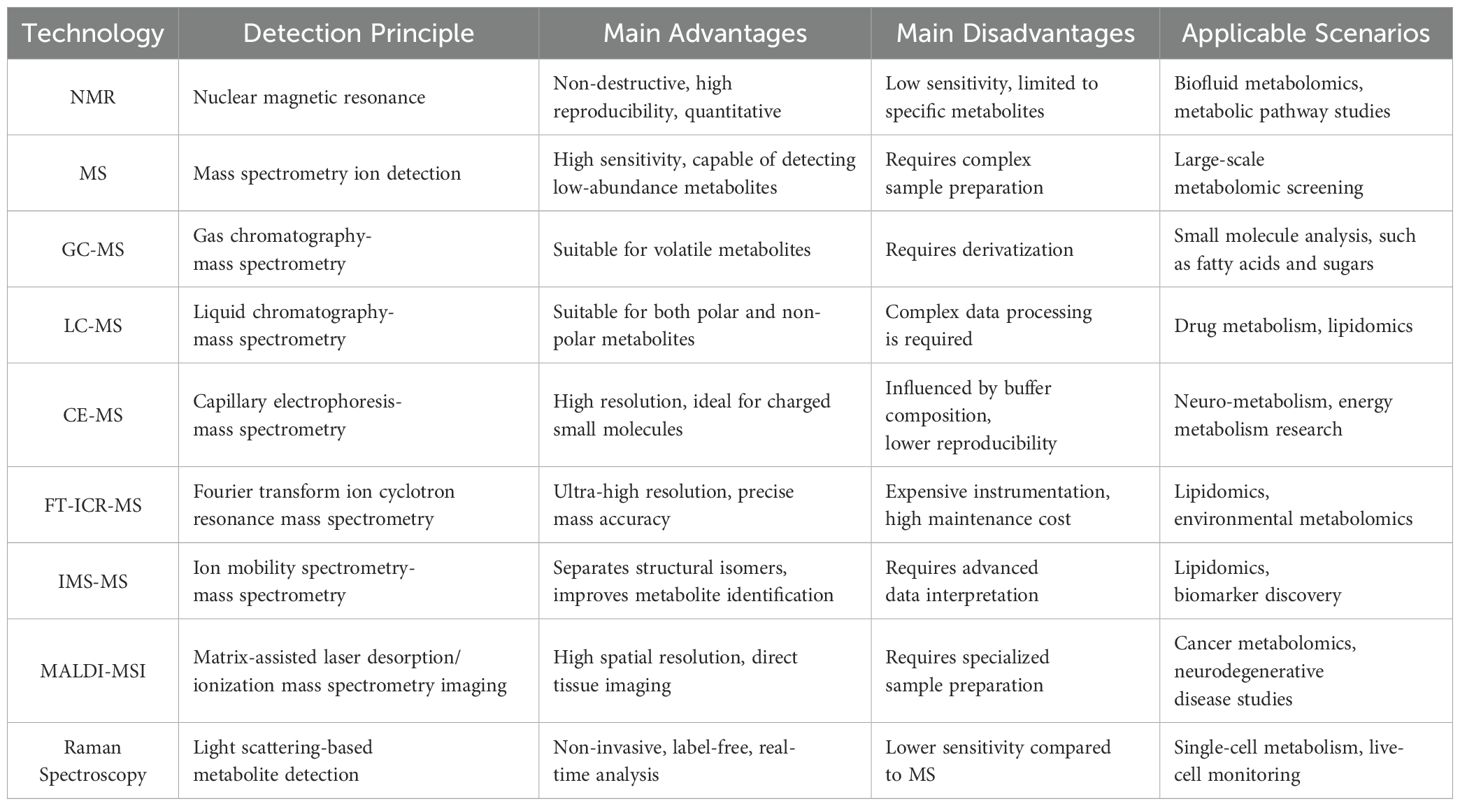
Mass spectrometry (MS) is regarded as the gold standard in metabolomic investigations, owing to its exceptional sensitivity, mass resolution, and metabolite coverage (Table 1). Current MS-based metabolomics primarily employs two complementary strategies: untargeted and targeted approaches (12). Untargeted metabolomics relies on high-resolution mass spectrometers (HRMS), including Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance (FT-ICR), time-of-flight (TOF), and Orbitrap instruments, to achieve comprehensive metabolic profiling (24, 25). These platforms offer sub-ppm mass accuracy, enabling confident metabolite identification. For example, a UHPLC-Q Exactive HF-X MS-based platform provides sub-ppm mass accuracy (± 10 ppm) and can detect over 2,000 metabolite ions in untargeted metabolomics, highlighting its superior performance in high-throughput metabolite profiling (26). In contrast, targeted metabolomics focuses on the accurate quantification of predefined metabolites or pathways, typically employing triple quadrupole (QQQ) mass spectrometers operated in multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode to enhance sensitivity and specificity (24, 27).
The coupling of MS with liquid chromatography (LC) or gas chromatography (GC) significantly improves metabolite separation and identification. LC-MS is particularly well-suited for analyzing both polar and non-polar metabolites, whereas GC-MS is primarily employed for volatile and thermally stable compounds. LC-MS demonstrates exceptional versatility in separating a wide range of compound classes across a broad polarity spectrum (28). This technique achieves a mass accuracy of 5–10 ppm in quantifying polar metabolites such as branched-chain amino acids, enabling the precise identification of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) progression biomarkers in large-scale cohort studies like the Framingham Heart Study (29). The predominant use of soft-ionization techniques in LC-MS facilitates molecular ion formation with minimal fragmentation, thereby enhancing the identification of unknown compounds (30). A key advantage of LC-MS over GC-MS is that it typically eliminates the need for chemical derivatization, as it does not require high temperatures or compound volatility. Additionally, LC-MS offers superior sensitivity across a broad molecular weight range (from <600 Da to larger molecules), including phospholipids, conjugated bile acids, glycosides, and sugars (31). GC-MS remains the gold standard for analyzing volatile and thermally stable metabolites, is capable of separating naturally volatile compounds (e.g., ketones, aldehydes) as well as non-volatile compounds rendered volatile through derivatization (e.g., sugars, amino acids) (32). This technique shows particular efficacy in fatty acid analysis and has proven invaluable for clinical research on metabolic disorders (33). However, GC–MS is limited by relatively poor reproducibility, due to potential structural alterations during derivatization (34).
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is another cornerstone technology in metabolomics, offering non-destructive, highly reproducible, and quantitative analysis of metabolites. NMR is particularly well-suited for studying complex biofluids and tissues, as it requires minimal sample preparation while offering detailed structural insights into metabolites. Additionally, NMR can be applied to in vivo tissues and living samples, enabling real-time metabolic profiling and dynamic flux analysis (35). NMR-based metabolomics has proven valuable in identifying metabolic signatures associated with diabetes progression and complications. For example, it has revealed dysregulation of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) and lipid metabolism in patients with T2DM (29). However, NMR’s relatively lower sensitivity compared to MS limits its ability to detect low-abundance metabolites. Recent advancements in high-resolution two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy may help overcome this limitation and broaden the applicability of NMR in metabolomics research (36).
In recent years, metabolomics technology has been continuously developing. In addition to traditional NMR and MS analysis methods, a variety of emerging technologies have shown unique advantages in the detection and quantification of specific metabolites. Among them, capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry (CE-MS) combines the high resolution of capillary electrophoresis with the high sensitivity of mass spectrometry (37). It is particularly suitable for the quantitative analysis of small molecule polar metabolites (such as organic acids, nucleotides, and amino acids) and has been widely used in the study of neural metabolism and energy metabolism. Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry (FT-ICR-MS) has unique advantages in the accurate identification of complex metabolites with its ultra-high resolution and extremely low mass error, especially in lipidomic and environmental metabolomics research (38). On the other hand, ion mobility spectrometry-mass spectrometry (IMS-MS) can distinguish metabolites with similar structures (such as isomers) by combining gas phase ion separation and mass spectrometry analysis, and has important value in lipidomic and biomarker screening research (39). This innovation has been particularly impactful in lipidomics, as evidenced by the successful resolution of ceramide isomers (e.g., C26:0) in clinical studies, thereby improving lipid profiling accuracy in metabolic diseases (40). Notably, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging (MALDI-MSI) is a high-spatial-resolution metabolomics imaging technique that can directly detect metabolite distribution on tissue sections (41). For example, MALDI-MSI has been used for spatial imaging of the metabolic profile of brain tissue in patients with Alzheimer’s disease, revealing changes in key metabolic pathways during disease progression (42). As reported by Prentice et al., MALDI-MSI has successfully mapped the in situ spatial distribution of hormones such as insulin, glucagon, and their protein variants in human and mouse islets with high spatial resolution. Their study revealed distinct hormone distribution patterns between the core region (β cells) and the peripheral region (α cells) of the islets, confirmed through serial section co-localization immunofluorescence and mass spectrometry imaging (43). In addition, Raman spectroscopy, as a non-invasive, label-free metabolomics detection method, has been gradually applied to in vivo single-cell metabolic monitoring and cancer diagnosis (44). Combined with surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) technology, this method can significantly improve the sensitivity of metabolite detection and show great potential in the fields of stem cell metabolism and personalized medicine (45). Nevertheless, MS-based metabolomics continues to face challenges, including data complexity, metabolite identification difficulties, and the requirement for advanced bioinformatics solutions.
The continuous development of these technologies has not only broadened the scope of metabolite detection but also improved the accuracy of metabolomics data analysis. In the future, the combined application of multiple technologies will become an important trend in metabolomics research, providing more powerful technical support for precision medicine, disease mechanism research, and biomarker discovery.
2.2 Data analysis workflow in metabolomics
Metabolomics data analysis is a complex, multi-stage process that demands a methodical and rigorous approach to convert raw spectral data into biologically interpretable results. A critical step after sample acquisition is data preprocessing, including noise reduction, peak detection, and spectral alignment (Figure 1), typically performed using specialized software such as MS-DIAL and XCMS (46). Noise reduction filters out random signal fluctuations, while peak detection and alignment standardize data across samples to ensure reproducibility. Normalization is then applied to minimize technical variability (e.g., batch effects) and improve cross-dataset comparability (47). Subsequently, an exploratory data assessment is conducted using visualization tools (e.g., histograms, boxplots) to detect outliers and validate data quality before further statistical analysis.
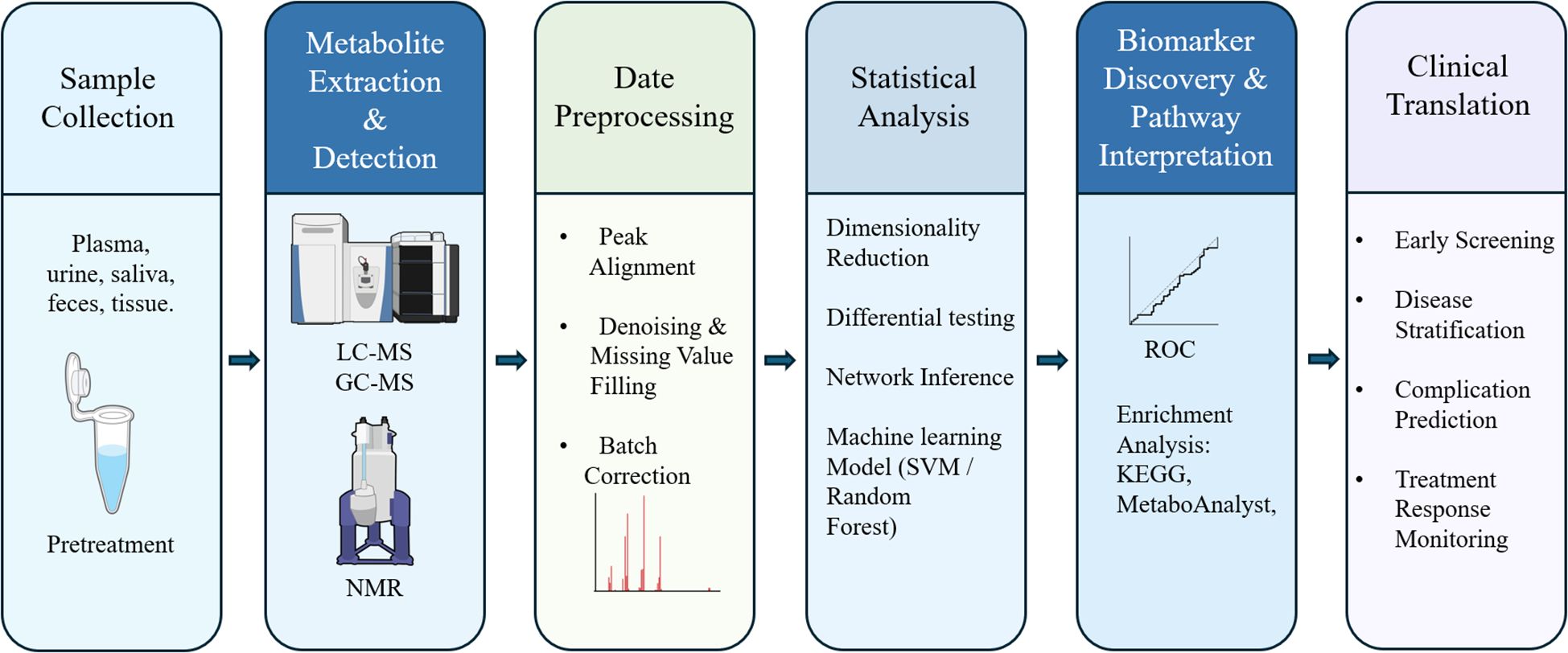
Figure 1. Integrated workflow of metabolomics application in diabetes. The six-step pipeline starts with (1) sample collection and pretreatment from various biological fluids or tissues (e.g., plasma, urine, feces); (2) metabolite extraction and detection using LC-MS, GC-MS, or NMR platforms; (3) data preprocessing, including peak alignment, denoising, and batch correction; (4) statistical analysis including dimensionality reduction, differential testing, network inference, and machine learning models (e.g., SVM, random forest); (5) biomarker discovery and pathway interpretation, guided by ROC curve analysis and enrichment tools such as KEGG and MetaboAnalyst; and (6) clinical translation, encompassing early screening, disease stratification, prediction of complications, and treatment response monitoring.
Metabolomics data analysis can be broadly classified into hypothesis-driven and hypothesis-free approaches. In hypothesis-driven analyses, parametric (e.g., Student’s t-test) or non-parametric tests (e.g., Mann–Whitney U test) are applied to compare metabolite concentrations between defined groups—such as diabetic patients versus healthy controls—depending on data distribution (48). For hypothesis-free (exploratory) analyses, multivariate statistical methods are employed to reveal hidden metabolic patterns. Principal Component Analysis (PCA), an unsupervised approach, reduces data dimensionality while highlighting major sources of metabolic variation (49). Supervised methods, including Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA) and Orthogonal Partial Least Squares (OPLS), further refine interpretations by suppressing noise and maximizing group separation (50). These are frequently integrated with PCA to isolate biologically relevant metabolic changes from confounding variation (51).
Accurate metabolite annotation and identification are critical for deriving biological insights from metabolomics data. This process entails matching experimental spectral features against curated reference databases (e.g., METLIN), which house extensive collections of standardized metabolite spectra (52). For uncharacterized or novel compounds, advanced computational pipelines such as SIRIUS coupled with CSI: FingerID enable de novo structural elucidation by analyzing mass spectral patterns and fragmentation signatures (53). This dual-strategy framework facilitates comprehensive metabolite characterization, bridging the gap between known biochemical entities and novel metabolic discoveries, thereby significantly enhancing the depth of metabolomic investigations.
To elucidate the biological relevance of identified metabolites, systematic pathway analysis is conducted to integrate metabolites into established metabolic networks. Widely utilized platforms such as MetaboAnalyst and the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) database facilitate this process (54, 55). MetaboAnalyst provides an intuitive interface for metabolite set enrichment analysis and pathway visualization, whereas KEGG offers curated, species-specific metabolic pathway references. Through this functional mapping, researchers can pinpoint dysregulated metabolic pathways associated with specific conditions, yielding mechanistic insights into disease pathogenesis and revealing potential intervention targets (56).
The integration of machine learning (ML) in metabolomics has transformed the field by facilitating high-dimensional pattern recognition and the development of predictive metabolic models. Advanced algorithms, including random forest and support vector machines (SVM), are routinely employed for feature selection and classification model construction (57). For instance, a large-scale prospective cohort study leveraging NMR-based metabolomics combined with ML approaches identified a nine-metabolite panel that significantly enhanced the prediction of T2DM progression in prediabetic individuals (58). A primary goal of metabolomics research is the discovery and validation of biomarkers. The diagnostic potential of candidate biomarkers is rigorously assessed through receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, with the area under the curve (AUC) serving as a key metric for predictive performance evaluation (59). Promising biomarkers undergo multi-stage validation, including in vivo studies using animal models or independent clinical cohorts, to verify their biological relevance and translational applicability (60, 61).
To elucidate the complexity of biological systems, integrated multi-omics approaches have emerged as a powerful strategy. The synergistic combination of metabolomics with complementary omics layers (e.g., transcriptomics, proteomics) enables systematic reconstruction of molecular interactions and regulatory networks (62). Advanced computational frameworks, including Multi-Omics Factor Analysis (MOFA) and Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis (WGCNA), provide robust solutions for data integration and biological interpretation, offering holistic insights into disease pathogenesis and potential intervention strategies (63, 64). This systems biology paradigm significantly enhances the discovery of mechanistic biomarkers and druggable targets, advancing both basic research and translational applications.
3 Metabolic reprogramming and biomarker discovery
The pathogenesis of diabetes involves complex metabolic reprogramming, characterized by eventual insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction (65). Insulin resistance, a defining feature of T2DM, is strongly associated with impaired mitochondrial function in skeletal muscle (66). β-cell dysfunction represents a fundamental pathological mechanism common to both T1DM and T2DM, characterized by progressive insulin secretory failure and consequent hyperglycemia (67, 68). Understanding the abnormalities of key metabolic pathways in the development of diabetes and making timely early diagnosis are crucial for mitigating disease progression and preventing complications (69).
3.1 Amino acid metabolites
As shown in Figure 2, branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) and lipid intermediates play a pivotal role in metabolic reprogramming. The Framingham Heart Study established a seminal association between elevated BCAAs and aromatic amino acids (e.g., tyrosine, phenylalanine) with increased T2DM risk over a 12-year follow-up period (29). This finding has been consistently validated across multi-ethnic cohorts (70, 71), solidifying BCAAs as robust predictive biomarkers for early-stage T2DM through their demonstrated role in insulin resistance and dysregulated glucose metabolism.

Figure 2. Visual summary of metabolic reprogramming in diabetes. This schematic illustrates six key metabolic subsystems that undergo characteristic shifts during the development of diabetes: amino acids, lipids, organic acids, bile acids, gut microbiota–derived metabolites, and sphingolipids. These metabolic alterations contribute to two central pathological processes: insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction. Red arrows (↑) indicate metabolites consistently upregulated in diabetes, such as BCAAs, AAAs, DAGs, and lactate, which are associated with increased disease risk. Green arrows (↓) represent downregulated, typically protective metabolites, such as HDL, butyrate, and S1P, suggesting impaired metabolic regulation. The diagram highlights metabolic crosstalk and mechanistic interdependencies, emphasizing metabolomics-based opportunities for biomarker discovery and targeted intervention in diabetes.
Aromatic amino acids (AAAs) have similarly emerged as key metabolic regulators in diabetes progression. The METSIM study identified 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl) lactate, a phenylalanine catabolite, as significantly correlated with impaired β-cell function and elevated diabetes risk (72). Notably, ethnic-specific metabolic patterns have been observed, with tyrosine demonstrating stronger diabetogenic associations in South Asian populations compared to Europeans (73), suggesting population-specific metabolic vulnerabilities may underlie disparate T2DM incidence rates.
In addition, the imbalance of the ratio of glutamate and glutamine (Gln/Glu) is one of the key metabolic abnormalities in the development of T2DM, and its mechanism involves β-cell damage, insulin resistance, and systemic metabolic disorders. Glutamate is the main excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, which mediates neuroexcitotoxicity by activating NMDA receptors (NMDARs). Long-term NMDA treatment inhibits β-cell viability, reduces ATP synthesis, and impairs glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) (74). Glutamine is one of the most abundant non-essential amino acids and is involved in regulating pancreatic β-cell function and insulin secretion. A case-cohort study showed that higher baseline plasma glutamate levels were associated with a significantly increased risk of T2DM, while higher glutamine levels were associated with a lower risk of T2DM, and higher Gln/Glu (glutamine-to-glutamate ratio) was associated with a significantly reduced risk of T2DM (75). This suggests that plasma glutamate and the Gln/Glu ratio can be used as predictive markers for T2DM risk.
3.2 Lipid metabolites
Lipid metabolism is critically involved in the pathogenesis of T2DM. Patients with T2DM often display elevated triglycerides and small, dense low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles, as well as decreased high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, even when their LDL cholesterol levels remain normal or near-normal (76). Certain lipid markers, such as diacylglycerols (DAGs), have been identified as early predictors of T2DM risk. Specifically, DAGs demonstrate a positive correlation with insulin resistance, as assessed by the Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR) (77). These findings indicate that DAGs may serve as useful biomarkers for the early detection of individuals at risk for T2DM.
A critical mediator of insulin resistance involves crosstalk between adipose tissue and hepatic metabolism, termed the “fat-liver axis” (78). Fatty acid-binding protein 4 (FABP4), an adipokine secreted by adipocytes, activates hepatic toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling, thereby promoting inflammatory responses and stimulating excessive gluconeogenesis (79). This maladaptive pathway worsens hyperglycemia and perpetuates insulin resistance. The FABP4-TLR4 signaling axis has consequently emerged as a promising therapeutic target for improving insulin sensitivity in T2DM.
Targeted metabolomics studies have further underscored the significance of acylcarnitine, key intermediates in fatty acid metabolism, as predictors of T2DM risk. Diminished mitochondrial oxidative capacity results in the accumulation of long-chain acylcarnitine, which interferes with insulin signaling pathways and impairs glucose uptake (80). These metabolites, produced during incomplete fatty acid β-oxidation, serve as sensitive biomarkers of mitochondrial dysfunction. A study has found that circulating long-chain acylcarnitine concentrations are significantly elevated in patients with T2DM (81). Elevated concentrations of specific acylcarnitine, particularly C3 and C5, correlate strongly with impaired insulin sensitivity and dysregulated glucose metabolism (66), reinforcing their potential utility in early disease detection.
3.3 Organic acids
Organic acids are key products of energy metabolism and intermediary metabolism (82). Alterations in their concentrations may indicate metabolic pathway dysregulation, particularly in early-stage diabetes. Variations in levels of organic acids, such as citric acid, lactic acid, and α-ketoglutaric acid, are strongly associated with insulin resistance, mitochondrial dysfunction, and impaired glucose metabolism, suggesting their potential as early diagnostic biomarkers for diabetes (83).
Citric acid, a central intermediate in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, has demonstrated glucose-lowering effects in animal studies, significantly reducing blood glucose and insulin resistance while enhancing insulin sensitivity (84). This implies that diminished citrate levels may signal aberrant glucose metabolism and elevated diabetes risk. A clinical trial in obese, insulin-resistant children revealed that citric acid exhibited the most pronounced metabolic changes during weight loss and correlated positively with homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) scores (85).
α-Ketoglutarate, another pivotal TCA cycle intermediate, participates in amino acid metabolism and redox homeostasis. Depleted α-ketoglutarate levels are linked to oxidative stress and disrupted energy metabolism, potentially serving as an early marker of diabetic metabolic dysfunction (86). Blood lactate is an indicator of the gap between energy expenditure and oxidative capacity, and is clinically used to indicate energy imbalance associated with strenuous exercise, hypoxia, and ischemia (87). Insufficient oxidative capacity can lead to the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes (88). Elevated fasting plasma lactate levels are observed in diabetic patients compared to non-diabetic individuals (89), with further increases noted in poorly controlled T1DM and glycogenic liver disease (90). These findings position lactate as a predictive biomarker for diabetes progression. Additionally, longitudinal lactate monitoring may aid in evaluating metabolic status and therapeutic efficacy in diabetic patients (91).
3.4 Bile acids
Bile acids (BAs) are not only key mediators of fat digestion and absorption, but also important signaling molecules that regulate glucose and lipid metabolism by activating nuclear receptors and membrane receptors (92). In T2DM and obesity, the synthesis, composition, and signal transduction of bile acids are significantly changed, directly involved in the process of insulin resistance (IR) and β-cell dysfunction. Bile acids are natural ligands of Farnesoid X Receptor (FXR). FXR can regulate the synthesis of bile acids itself and affect glucose metabolism (inhibit hepatic gluconeogenesis, promote glycogen synthesis, and enhance insulin sensitivity). Secondary bile acids are high-affinity ligands of TGR5. After activation, TGR5 stimulates intestinal L cells to secrete glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), promote insulin secretion, and improve blood sugar control (93).
3.5 Gut microbiome and its metabolic products
The gut microbiome and its metabolic products constitute another critical modulator of β-cell function. The microbial metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) disrupts β-cell physiology by attenuating intracellular calcium signaling, thereby compromising insulin exocytosis while simultaneously promoting endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptotic pathways (94). TMAO concentrations are elevated in diabetic patients since TMAO can directly reduce glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) in MIN6 cells and mouse or human pancreatic islets (95). Inhibition of TMAO production can improve β-cell GSIS, β-cell ratio, and glucose tolerance in diabetic mouse models.
In contrast, beneficial microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate exert protective effects by suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokine signaling and maintaining normal insulin secretory capacity in β-cells (96). Compared with healthy controls, patients with type 2 diabetes have reduced intestinal flora diversity, fewer butyrate-producing bacteria, and lower fecal SCFA concentrations (97). Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) from healthy donors has been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity in individuals with metabolic syndrome, accompanied by increased abundance of SCFAs-producing bacteria and favorable shifts in microbial metabolites (98). These findings highlight the complex interplay between metabolic and microbial factors in β-cell dysfunction.
3.6 Dysregulated sphingolipid metabolism
Increasing evidence indicates that abnormal sphingolipid metabolism is deeply involved in the metabolic reprogramming of diabetes (especially T2DM) by interfering with insulin signaling, inducing chronic inflammation, destroying mitochondrial function, and promoting β-cell apoptosis (99). Mechanistically, ceramide accumulation activates pro-inflammatory signaling through the CD36/NF-κB pathway, upregulating thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) expression and inducing mitochondrial oxidative stress, which collectively impair β-cell insulin secretion and viability (100). Other sphingolipid metabolites, such as sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), are significantly negatively correlated with the progression of diabetes (101). S1P has anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects, and promotes β-cell survival and insulin secretion. Low S1P can be used as a biomarker to predict the severity of diabetes and provide a new target for future precision treatment.
4 Personalized treatment strategies in diabetes
The well-established heterogeneity of diabetes pathogenesis underscores the critical need for precision medicine approaches to achieve optimal therapeutic outcomes. Contemporary advances in high-throughput metabolomics and next-generation microbiome profiling have facilitated the discovery of novel metabolic signatures and dysregulated pathways that can inform tailored therapeutic strategies. These technological innovations enable stratification of patient populations based on distinct metabolic phenotypes, thereby paving the way for truly personalized diabetes management.
4.1 Drug response stratification
Patient stratification based on pharmacological response represents a cornerstone of personalized diabetes management, particularly for metformin as first-line therapy in T2DM. Despite its clinical ubiquity, metformin demonstrates marked interpatient variability in therapeutic efficacy (102). Approximately 30% of patients failing to achieve adequate glycemic control on monotherapy (103), highlights the imperative to elucidate the biological determinants of treatment heterogeneity.
Emerging evidence implicates the gut microbiome as a key modulator of metformin pharmacodynamics. Mechanistic studies reveal that microbial processing of glutamine and related amino acids, along with purine metabolism byproducts, may condition metformin activity through microbiome-mediated metabolic reprogramming (104). Specific commensal organisms enhance therapeutic efficacy via production of guanidine derivatives (e.g., agmatine) that synergize with metformin to suppress hepatic gluconeogenesis and modulate intestinal glucose absorption. Clinically, patients possessing microbiota with enriched biosynthetic capacity for these metabolites exhibit superior glycemic responses, positioning microbiome profiling as a promising predictive biomarker for treatment stratification. Concurrently, pharmacogenomic investigations have identified functional polymorphisms in metformin transporter genes as critical determinants of interindividual variability. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in organic cation transporters (OCT1/SLC22A1, OCT2/SLC22A2, OCT3/SLC22A3) significantly impact drug pharmacokinetics through altered intestinal absorption, hepatic distribution, and renal clearance (105). Notably, the rs622342 (A>C) and rs72552763 (C>A) variants in SLC22A1 correlate with differential HbA1c reduction and plasma drug concentrations. Complementary evidence links OCT2/OCT3 regulatory SNPs (rs7757336, rs2481030) to impaired bioavailability and diminished therapeutic response, as demonstrated through integrated pharmacogenetic and pharmacokinetic analyses (106).
Therapeutic response to glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists exhibits significant interindividual variability that can be stratified using metabolomic profiling. Among emerging biomarkers, lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) - a bioactive phospholipid with pro-inflammatory properties - has been identified as a clinically relevant predictor of pharmacological response. Mechanistically, LPA contributes to insulin resistance through dual pathways: (1) activation of inflammatory cascades via LPAR1–6 receptors, and (2) direct impairment of insulin receptor substrate (IRS) phosphorylation. Elevated circulating LPA concentrations may attenuate GLP-1 efficacy by disrupting receptor-mediated insulinotropic signaling pathways (107). Beyond its glucoregulatory effects, liraglutide demonstrates significant antioxidant properties as evidenced by clinical trial data. Treatment with liraglutide results in substantial reductions in established oxidative stress markers, including thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) and malondialdehyde (MDA), particularly in patients exhibiting favorable baseline antioxidant capacity as measured by superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) activity (108). These findings suggest that pretreatment antioxidant status may serve as a predictive biomarker for liraglutide’s pleiotropic effects.
In addition, fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) analogs exhibit variable therapeutic efficacy that correlates with baseline metabolic profiles. Preclinical and early-phase clinical studies demonstrate that patients with elevated BCAAs and reduced adiponectin concentrations show attenuated responses to FGF21 therapy, likely reflecting impaired metabolic flexibility characterized by mitochondrial dysfunction and adipose tissue inflammation. These metabolic signatures may serve as stratification biomarkers for FGF21 treatment selection.
Similarly, response heterogeneity to sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors is associated with distinct pre-treatment metabolic states. Metabolomic analyses reveal that patients with lower circulating 3-hydroxyisobutyric acid (3-HIB) - a valine catabolite indicative of mitochondrial stress - achieve superior glycemic control and cardiovascular risk reduction following SGLT2 inhibition. This association positions 3-HIB as both a pathophysiological marker of metabolic inflexibility and a potential predictor of therapeutic response, with mechanistic studies suggesting its role in impairing endothelial function and promoting cardiac lipotoxicity.
4.2 Optimization of nutritional interventions
Nutritional strategies are integral to diabetes management. Time-restricted eating (TRE), for example, has been shown to reprogram hepatic lipid metabolism by aligning feeding patterns with circadian rhythms (109). TRE reduces hepatic steatosis and improves insulin sensitivity by enhancing the expression of lipid-oxidizing enzymes during fasting periods. This approach leverages metabolic rhythms to maximize therapeutic benefits. Prebiotics, such as inulin, modulate gut microbiota by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria (e.g., Bifidobacteria), which may enhance butyrate production and exert anti-inflammatory effects. Clinical trials demonstrate that inulin supplementation improves insulin sensitivity in overweight individuals, likely through these microbiota-mediated mechanisms (110).
Nutritional strategies can be further optimized based on individual metabolic responses. For instance, omega-3 can prevent and reverse insulin resistance (IR) induced by a high-fat diet, improve glucose metabolism in patients with prediabetes (such as obese children or adults with metabolic syndrome), reduce systemic inflammation, and enhance metabolic flexibility (111). Omega-3 fatty acids competitively inhibit the cyclooxygenase (COX) and lipoxygenase (LOX) pathways, reduce the production of pro-inflammatory eicosanoids (such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes), and the pro-resolution mediators derived from them (such as resolving and protecting) can actively relieve inflammation. Additionally, foods rich in polyphenols (such as coffee, green tea, red wine, olive oil, cocoa, etc.) can reduce fasting blood glucose and HbA1c, reduce insulin resistance, and inhibit inflammation and oxidative stress. In clinical trials, they have shown the potential to improve blood glucose metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and vascular function in patients with T2DM (112).
5 Technical challenges and cutting-edge breakthroughs
5.1 Existing technical bottlenecks
5.1.1 Technical limitations in sampling and pre-analytical handling
Temporal standardization of biological sampling represents a fundamental challenge in diabetes metabolomics research (113). Metabolite concentrations exhibit substantial diurnal variation and physiological state-dependent fluctuations, particularly between fasting and postprandial conditions. Li et al. demonstrated that postprandial concentrations of BCAAs (valine, leucine, isoleucine) and short-chain acylcarnitine (C3-C5) undergo significant changes, with diabetes patients showing particularly pronounced postprandial increases in specific metabolites (e.g., C16:1 acylcarnitine concentrations rising by 30% compared to fasting levels) (114). Such dynamic variations may obscure genuine metabolic signatures, potentially yielding false-positive associations or masking fasting-state pathophysiological patterns.
Pre-analytical factors such as anticoagulant type, centrifugation protocol, and storage temperature also significantly impact metabolite stability and measurement accuracy. Jobard et al. showed that EDTA versus heparin selection leads to measurable differences in amino acid concentrations, while prolonged room temperature storage degrades short-chain fatty acids and nucleotides, introducing technical bias into metabolic profiling (115).
5.1.2 Biological confounders in metabolomic profiling
In parallel, biological variables contribute additional layers of complexity to diabetes metabolomics. These include diet, physical activity, medication use, and comorbidities, each of which can significantly reshape the metabolic landscape. A systematic review by Kim demonstrated that metformin treatment alters the plasma and urine metabolomes by modulating gut microbiota and energy metabolism, while high-fat diets further exacerbate metabolic imbalances (116). These biological factors, if unaccounted for, may confound disease-specific metabolic signatures and complicate downstream analyses.
5.1.3 Pharmacologic and demographic sources of variation
Disease states (such as cancer or diabetes) themselves can also lead to significant changes in branched-chain amino acid and lipid metabolites. In the context of diabetes, pharmacological interventions can modulate metabolic pathways independently of disease mechanisms. For example, metformin therapy significantly modifies serum phosphatidylcholine profiles (notably acyl-alkyl PC species) in T2DM (117), potentially confounding the interpretation of insulin resistance-associated metabolic signatures.
Population-scale metabolomic studies must additionally account for substantial interindividual variability stemming from demographic, anthropometric (e.g., BMI effects), and lifestyle factors that collectively influence baseline metabolic set points. The inherent biological complexity of metabolites, functioning not merely as passive biomarkers but as dynamic regulators interacting with genomic, epigenetic, and proteomic networks (118), poses unique challenges for establishing clinically relevant reference ranges. This complexity is compounded by the multitude of influencing factors, including nutritional status, hydration state, and physical activity patterns, necessitating rigorous standardization protocols for meaningful metabolomic investigation in diabetes research.
5.1.4 Metabolite annotation bottlenecks
Accurately annotating unknown metabolites remains one of the most persistent and complex challenges in metabolomics research. Despite continuous advancements in analytical technology, including high-resolution mass spectrometry, only approximately 10% of detected metabolites can be identified through mass spectral library matching, leaving the remaining 90% unknown (119). These unidentified signals often correspond to low-abundance or novel metabolites that may serve as critical biomarkers, particularly in diseases such as diabetes (120). However, the absence of comprehensive reference libraries, spectral databases, and standardized annotation pipelines hinders their biological interpretation (121). For example, Tan et al. identified only 1,088 endogenous compounds using high-resolution mass spectrometry, while a significant number of lipids remain insufficiently annotated due to structural complexity and limited spectral coverage, potentially introducing bias in downstream pathway analyses (122). This issue is especially pronounced for lipid subclasses such as ceramides, which play a crucial role in driving insulin resistance via the Akt signaling pathway but are challenging to interpret due to their structural heterogeneity and inadequate mass spectrometric coverage (123).
5.1.5 Data preprocessing and quality control
Furthermore, data preprocessing remains a major technical bottleneck due to the high dimensionality and inherent variability of metabolomic datasets. Key preprocessing steps such as peak filtering, imputation of missing values, and normalization can profoundly influence analytical outcomes (124). Even when standardized acquisition protocols are employed, technical variation can obscure true biological signals. Abiotic factors, including instrumental errors, can contribute substantially to variability in untargeted metabolomics studies, necessitating rigorous quality control measures (125).
5.2 Innovative technological breakthroughs
5.2.1 Metabolic flux analysis and stable isotope tracing
Dynamic metabolic flux analysis, particularly utilizing 13C-labeled glucose tracers, has become an indispensable technique for investigating hepatic gluconeogenesis in diabetes. Unlike traditional static metabolomics, which provides only a snapshot of metabolite concentrations, this approach allows for real-time quantification of carbon flux through specific metabolic pathways, offering dynamic insights into altered hepatic metabolism. For instance, a study employed global 13C tracing and non-targeted mass spectrometry to analyze intact human liver tissue ex vivo (126). This research provided a comprehensive overview of hepatic metabolic fluxes, enhancing our understanding of liver metabolism in the context of metabolic diseases, including diabetes. Furthermore, a study utilized multi-tissue 2H/13C flux analysis to reveal compensatory upregulation of renal gluconeogenesis in hepatic PEPCK-C-knockout mice, highlighting the complexity of gluconeogenic regulation in diabetic conditions (127). 13C magnetic resonance spectroscopy (13C-MRS) has emerged as a powerful noninvasive tool for quantifying hepatic mitochondrial oxidative and anaplerotic fluxes in humans. Befroy et al. applied dynamic 13C-MRS to healthy individuals, demonstrating the feasibility of directly measuring hepatic TCA cycle and pyruvate carboxylase–mediated cataplerotic fluxes in vivo, providing a methodological framework for studying hepatic gluconeogenesis in metabolic disorders (128). Similarly, as demonstrated by Hasenour et al., the choice of isotopic tracers (e.g., 13C-propionate vs. 13C-lactate) and modeling assumptions significantly impact hepatic flux estimates, highlighting the need for rigorous experimental design in metabolic studies (129). Moreover, Kim et al. provided a detailed methodological framework for integrating 13C-based metabolic flux analysis (MFA) in metabolic studies (130). They emphasized that precise control of infusion protocols, compartmental modeling, and integration of multi-precursor data are crucial for accurately quantifying pathways such as glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis. 13C-MFA has been used to track hepatic TCA cycle fluxes and gluconeogenesis, offering insights into metabolic dysregulation in diabetes-associated conditions. Young et al. summarized how in vivo 13C and 2H tracing can capture whole-body flux alterations, including the role of lactate as a key carbon shuttle between tissues (131). However, the relative contribution of recycled lactate to diabetic hyperglycemia remains an active area of research.
5.2.2 Artificial intelligence for predictive metabolomics
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI), particularly deep learning algorithms, has profoundly expanded the analytical capacity of metabolomics in diabetes research. Unlike conventional statistical methods, AI models can efficiently process high-dimensional, nonlinear, and heterogeneous metabolomics data, thereby uncovering hidden associations between metabolic profiles and disease phenotypes. A recent study demonstrated that combining untargeted plasma metabolomics with machine learning algorithms can effectively identify metabolite signatures predictive of glycemic deterioration and progression from prediabetes to T2DM (58). This approach not only enhanced risk stratification beyond classical clinical markers but also revealed novel metabolic features with potential relevance as therapeutic targets, many of which were not captured through traditional enrichment or univariate analyses. A notable example of clinical application is the study by Huang et al., who used machine learning approaches to identify metabolic signatures of incident chronic kidney disease (CKD) in individuals with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes (132). Through targeted metabolomics and machine learning methods, the study identified sphingomyelin C18:1 and phosphatidylcholine diacyl C38:0 as candidate metabolite biomarkers of incident CKD specifically in hyperglycemic individuals. The developed prediction models outperformed the currently established clinical algorithm for CKD, demonstrating the power of machine learning in improving risk prediction for diabetes-related complications. Additionally, based on the Bagged CART integrated algorithm and metabolomics features, diabetic retinopathy subtypes (NDR/NPDR/PDR) can be effectively classified with an accuracy of 72% and a sensitivity of 91.9%, proving that artificial intelligence models can assist in the early detection and accurate classification of diabetic complications. A convolutional neural network (CNN)-based deep learning model trained on untargeted plasma metabolomics could accurately identify predictive metabolite signatures linked to glycemic control and complications in type 2 diabetes patients. The model also suggested potential drug targets and stratification markers that were not apparent through classical pathway enrichment analysis. As described by Kirtipal et al., by integrating intestinal metagenome, metabolome, and host data, machine learning algorithms can predict individual glycemic responses and reveal that microbiota metabolites (such as SCFAs) affect diabetes progression by regulating insulin sensitivity, providing a new strategy for precision nutrition (133). Based on the Bagged CART integrated algorithm and metabolomics features, diabetic retinopathy subtypes (NDR/NPDR/PDR) can be effectively classified with an accuracy of 72% and a sensitivity of 91.9%, proving that artificial intelligence models can assist in the early detection and accurate classification of diabetic complications (134).
Despite these advancements, AI-driven metabolomics models still face challenges in reproducibility and interpretability. Differences in data preprocessing and cohort characteristics can affect model stability, while the “black box” nature of deep learning algorithms limits clinical acceptance. Incorporating interpretability tools such as Shapley Additive Explanations (SHAP) and ensuring cross-cohort validation are essential steps for clinical translation (135).
6 Clinical transformation and prospects
6.1 Diagnostic reagent development
Especially in the early diagnosis and risk assessment of diabetes, metabolomics technology has shown great potential in the field of diagnostic reagent development, and its application has gradually entered the clinical transformation stage. In recent years, the development of diagnostic reagents based on metabolomics has made significant progress, among which NMR and LC-MS technologies have become mainstream tools. For instance, a study utilizing ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS) analyzed serum samples to identify metabolites associated with diabetes risk (136). This targeted metabolomics approach demonstrated the potential to detect metabolic alterations preceding diabetes onset, suggesting its utility in early diagnosis and risk assessment. Furthermore, UHPLC-MS/MS has been employed to quantify amino acids and acylcarnitine in plasma, providing insights into metabolic disturbances linked to insulin resistance and diabetes (137). Such analyses contribute to the development of diagnostic tools aimed at early intervention strategies for at-risk individuals. In addition to UHPLC-MS/MS, other advanced mass spectrometry techniques have been instrumental in diabetes research. For example, LC-MS/MS and GC-MS have significantly broadened the spectrum of detectable metabolites, even at lower concentrations (138). These technologies have enabled the identification and quantification of potential biomarkers associated with diabetes and its complications, providing new avenues for clinical diagnostics and metabolic studies.
With the advancement of technology, the platform for metabolomics detection has gradually moved from large laboratories to clinical sites. The development of microfluidic chip technology provides new possibilities for point-of-care testing (POCT) of metabolomics. Microfluidic chips can achieve rapid analysis of complex metabolites in small devices by integrating sample processing, separation, and detection functions (139). In recent years, the coupling of microfluidic chips and mass spectrometry detection has become a research hotspot, greatly improving the sensitivity and efficiency of detection. The research team has developed a metabolomics detection platform based on microfluidic chips, which can separate 16 amino acids in less than two minutes without extensive sample preparation (140). This device is not only portable, but also can monitor the metabolic status of patients in real time, providing clinicians with a rapid basis for diagnosis. In the future, with the further optimization of microfluidic technology, metabolomics detection is expected to play a greater role in family medical care and community health management.
However, the development and clinical application of metabolomics diagnostic reagents still face some challenges. First, the biomarker combination of metabolite profiles needs to be further verified for its clinical value. At present, although metabolomics has identified numerous disease-associated metabolites, their translational potential requires further validation in diverse clinical cohorts (118). Despite the growing literature on metabolomics in diabetes, a comparative understanding of cohort designs, biomarker patterns, and analytical strategies remains limited. To provide a synthesized perspective, we compiled a representative set of metabolomics studies (Table 2) that have advanced the field toward clinical translation. These studies vary in sample size, biospecimen types, and analytical platforms (e.g., LC-MS, NMR, GC-MS), yet converge on key biomarker trends such as elevated BCAAs, ceramides, and α-hydroxybutyrate in diabetic or insulin-resistant populations.
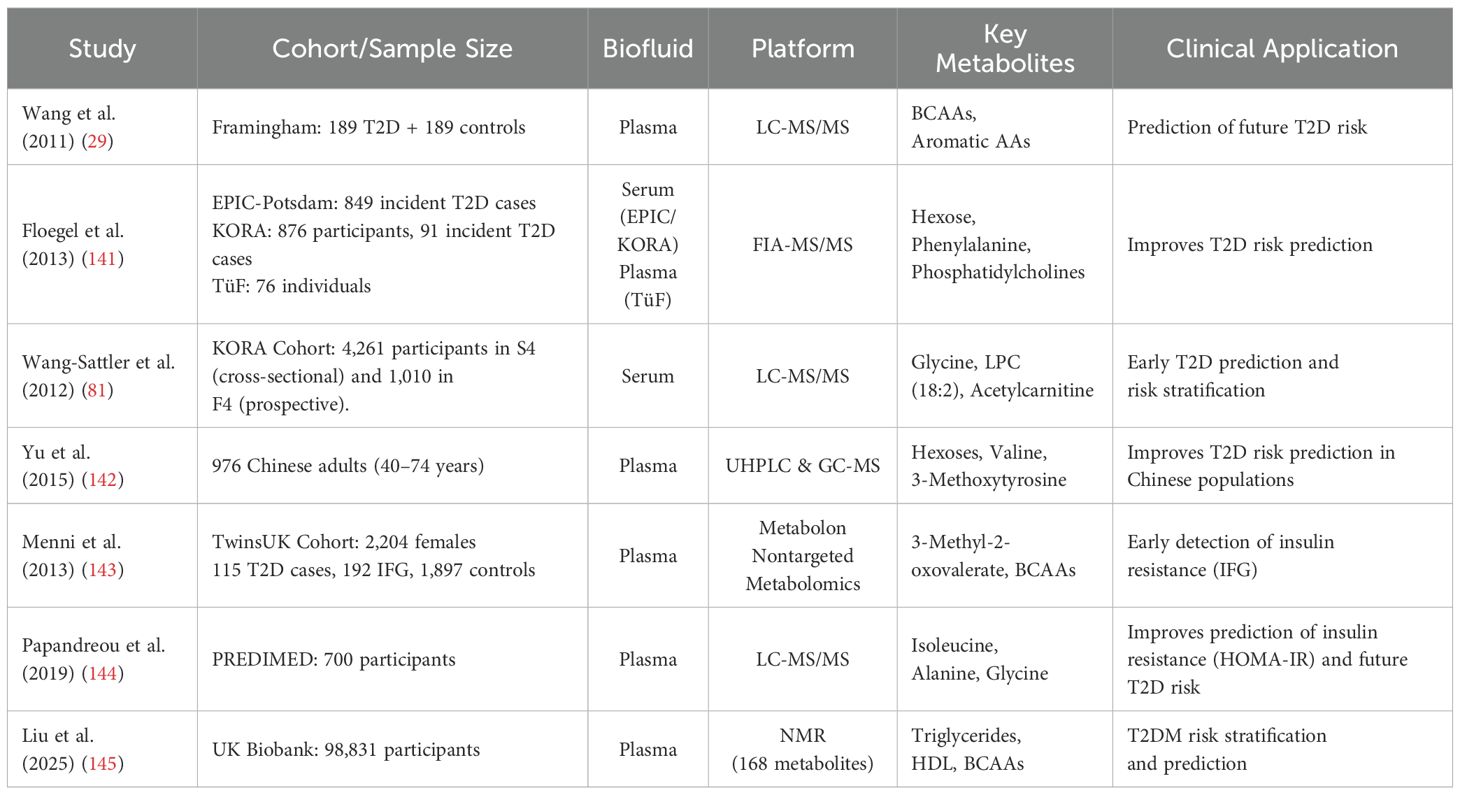
Table 2. Representative metabolomics studies highlighting key biomarkers and platforms for diabetes risk prediction.
Secondly, the technical standardization and quality control of the detection platform are the key to ensuring the reliability of the test results (146). The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has set strict requirements for the validation of biomarkers, including sensitivity, specificity, and repeatability (147). In addition, the analysis and interpretation of metabolomics data also require more intelligent tools. In recent years, machine learning-based metabolomics data analysis methods have gradually emerged, which can mine potential biomarker combinations from massive data and predict the risk and prognosis of diseases (148). A recent study developed a deep learning framework trained on plasma metabolite spectra to predict the risk of progression from prediabetes to T2DM. This model identified a panel of nine circulating metabolites that significantly improved predictive performance and provided a robust basis for early identification and intervention in high-risk individuals (58).
In the future, the development of metabolomics diagnostic reagents will move towards high precision, instant, and intelligent directions. On the one hand, with the continuous advancement of detection technology, the sensitivity and throughput of metabolomics detection will be further improved, which can more comprehensively reflect the metabolic status of patients. On the other hand, the popularization of POCT equipment will make metabolomics detection more convenient and enable rapid transformation from laboratory to the clinical site. The introduction of artificial intelligence technology will greatly improve the analysis ability of metabolomics data and provide more accurate support for diagnosis and personalized treatment. Overall, the development of metabolomics diagnostic reagents will not only promote the early diagnosis and precise treatment of diabetes but also provide new tools and methods for the clinical management of other metabolic diseases.
6.2 Therapeutic target mining
Metabolomics-driven analyses have increasingly facilitated the discovery of novel therapeutic targets in diabetes. For instance, targeted lipidomic profiling has identified ceramide species as correlates of insulin resistance, which led to the investigation of CerS6 as a driver of mitochondrial dysfunction and adipose inflammation (149). Similarly, metabolite profiling of bile acid derivatives highlighted TGR5 as a key receptor modulating GLP-1 secretion and energy expenditure (150). Metabolomics has also supported the identification of FFAR2, a short-chain fatty acid receptor, through correlation with plasma SCFA levels and metabolic phenotypes (151, 152). These findings underscore how metabolomics can inform precision pharmacology by linking endogenous metabolic shifts with actionable molecular targets.
6.3 Future development directions
The future development direction of metabolomics technology will focus on three core areas: multi-omics integration, real-time monitoring technology, and ethics and norms, to promote the application of metabolomics in precision medicine and personalized medicine.
Combining metabolomics with other omics data, such as genomics, proteomics, and transcriptomics, offers a comprehensive understanding of diabetes pathophysiology. This integrative approach is particularly powerful for dissecting the molecular basis of diabetic complications and for identifying context-specific biomarkers across tissues and comorbid conditions (153). It also facilitates the discovery of novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets. For instance, a multi-omics study integrating epigenomics, whole-genome sequencing, and metabolomics uncovered previously unrecognized pathways implicated in T2DM, underscoring the value of systems-level strategies in unraveling complex disease mechanisms (154). At the same time, AI and ML algorithms are increasingly applied to metabolomics data to predict disease progression and personalize treatment strategies. For example, integrating ML approaches with metabolomics panels has improved the prediction of T2DM, enabling early intervention (155). A recent study employed ML models on quantitative metabolomics data to accurately predict the 4-year risk of developing T2DM, demonstrating the strong potential of metabolomics-based models for early detection and prevention (156). In addition, a study in Diabetes integrated ML techniques with metabolomics to identify metabolic signatures predictive of CKD in individuals with T2DM or prediabetes, enabling early identification of high-risk individuals for timely intervention (132).
The development of real-time monitoring technology will promote metabolomics from the laboratory to clinical application, and the development of wearable devices that can monitor metabolic parameters in real time is changing diabetes management (157). As non-invasive techniques for monitoring metabolic changes gain traction, innovations such as a sweat-based wearable sensor show potential for monitoring blood sugar levels and other metabolites without the need for invasive surgery (158). In addition, integrating CGM data with other wearable technology, such as activity monitors, has been shown to improve metabolic outcomes in individuals with T2DM (157). Furthermore, advancements in wearable insulin biosensors that combine real-time glucose monitoring with automated insulin delivery are enhancing glycemic control and quality of life for diabetes patients (159). These innovations underscore the potential of wearable technology to revolutionize personalized diabetes care.
The clinical implementation of metabolomics requires careful consideration of data privacy, ethical standards, and regulatory compliance. Given the sensitivity of metabolomics data, especially when collected longitudinally, it is imperative that informed consent protocols explicitly address critical issues such as data reuse, participant re-identifiability, and the integration of data across multiple platforms. Researchers should ensure that participants are fully informed about the extent of data use, how their data will be processed, and any potential risks associated with cross-platform integration (160). In addition, researchers should consider the adoption of robust data security measures, such as encryption and de-identification, to protect the privacy of participants’ data. The use of anonymized datasets, stored in secure, open-access repositories, should be encouraged to facilitate data sharing and enhance reproducibility, while ensuring privacy and compliance with data protection laws. Furthermore, data governance should be aligned with international standards, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and similar regulations in other regions, to ensure the ethical and legal handling of metabolomics data. To facilitate ethical translation, researchers are encouraged to adopt open-access repositories with anonymized datasets and align data governance with international standards such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) (161). To further support clinical and translational applications, researchers should engage with established frameworks, such as those provided by the Metabolomics Standards Initiative (MSI), which promote the harmonization of reporting, data quality, and traceability (162). These guidelines offer valuable resources for maintaining data integrity, ensuring consistency across studies, and improving the overall credibility of metabolomics research. By adopting these ethical and regulatory practices, researchers can help ensure the responsible and impactful use of metabolomics in clinical settings.
7 Conclusion
Metabolomics has emerged as a transformative pillar in deciphering the complex metabolic landscape of diabetes, offering unprecedented access to real-time biochemical states that underlie disease onset, progression, and therapeutic response. In contrast to traditional diagnostic approaches that typically capture static or downstream manifestations of disease, metabolomics enables dynamic profiling of metabolic fluxes, revealing subtle yet clinically meaningful perturbations that precede overt hyperglycemia or complications. By detecting disease-relevant metabolites, such as branched-chain amino acids, lipid intermediates, bile acids, and gut microbiota–derived compounds, metabolomics facilitates early risk prediction, mechanistic stratification, and precision-guided interventions.
Moreover, this systems-level perspective on metabolic reprogramming has deepened our understanding of heterogeneous disease trajectories, including subtypes of insulin resistance, patterns of β-cell failure, and variations in drug responsiveness. As emphasized in this review, the integration of advanced computational tools, particularly machine learning and artificial intelligence, has greatly enhanced the analytical power of metabolomics, enabling the extraction of predictive biomarker panels and individualized treatment profiles from high-dimensional datasets. Likewise, the convergence of metabolomics with other omics layers, such as transcriptomics, genomics, and macrobiomics, marks a new era of integrated systems biology in diabetes research.
Nevertheless, the translation of metabolomic discoveries into clinical practice remains incomplete. Key bottlenecks, including the lack of standardized protocols, limited inter-laboratory harmonization, insufficient regulatory frameworks for biomarker validation, and challenges in biological interpretation, must be systematically addressed. In parallel, ethical considerations surrounding data privacy, informed consent, and the clinical implementation of AI-driven metabolic models must be carefully navigated.
Looking ahead, advances in point-of-care metabolomics platforms, wearable biosensors, and minimally invasive diagnostics may revolutionize diabetes management by enabling continuous metabolic monitoring and real-time clinical decision-making. Realizing this vision will require sustained interdisciplinary collaboration, regulatory foresight, and a strong commitment to patient-centered innovation. By meeting these imperatives, metabolomics is well-positioned to redefine diabetes diagnostics and usher in a new era of predictive, preventive, and personalized metabolic medicine.
Author contributions
ZX: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RX: Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. ZN: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The authors declare that no financial support was received for the research, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
2. Litwak L, Goh S-Y, Hussein Z, Malek R, Prusty V, and Khamseh ME. Prevalence of diabetes complications in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus and its association with baseline characteristics in the multinational A1chieve study. Diabetol Metab Syndr. (2013) 5:57. doi: 10.1186/1758-5996-5-57
3. Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, et al. and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the international diabetes federation diabetes atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2019) 157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843
4. Katwal PC, Jirjees S, Htun ZM, Aldawudi I, and Khan S. The effect of anemia and the goal of optimal hbA1c control in diabetes and non-diabetes. Cureus. (2020) 12:e8431. doi: 10.7759/cureus.8431
5. Lages M, Barros R, Moreira P, and Guarino MP. Metabolic effects of an oral glucose tolerance test compared to the mixed meal tolerance tests: A narrative review. Nutrients. (2022) 14:2032. doi: 10.3390/nu14102032
6. The International Expert Committee. International expert committee report on the role of the A1C assay in the diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes Care. (2009) 32:1327–34. doi: 10.2337/dc09-9033
7. Ortiz-Martínez M, González-González M, Martagón AJ, Hlavinka V, Willson RC, and Rito-Palomares M. Recent developments in biomarkers for diagnosis and screening of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr Diabetes Rep. (2022) 22:95–115. doi: 10.1007/s11892-022-01453-4
8. Mahajan A, Taliun D, Thurner M, Robertson NR, Torres JM, Rayner NW, et al. Fine-mapping type 2 diabetes loci to single-variant resolution using high-density imputation and islet-specific epigenome maps. Nat Genet. (2018) 50:1505–13. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0241-6
9. Alejandro EU, Gregg B, Blandino-Rosano M, Cras-Méneur C, and Bernal-Mizrachi E. Natural history of β-cell adaptation and failure in type 2 diabetes. Mol Aspects Med. (2015) 42:19–41. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2014.12.002
10. LaMoia TE and Shulman GI. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of metformin action. Endocrine Rev. (2020) 42:77. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnaa023
11. Alseekh S, Aharoni A, Brotman Y, Contrepois K, D’Auria J, Ewald J, et al. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics: A guide for annotation, quantification and best reporting practices. Nat Methods. (2021) 18:747–56. doi: 10.1038/s41592-021-01197-1
12. Jin Q and Ma RCW. Metabolomics in diabetes and diabetic complications: insights from epidemiological studies. Cells. (2021) 10:2832. doi: 10.3390/cells10112832
13. Gowda GN, Shucha Z, Haiwei Gu, Vincent A, Narasimhamurthy S, and Raftery D. Metabolomics-Based methods for early disease diagnostics. Expert Rev Mol Diagnostics. (2008) 8:617–33. doi: 10.1586/14737159.8.5.617
14. Wishart DS. Emerging applications of metabolomics in drug discovery and precision medicine. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2016) 15:473–84. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2016.32
15. Astarita G and Langridge J. An emerging role for metabolomics in nutrition science. J Nutrigenetics Nutrigenomics. (2013) 6:181–200. doi: 10.1159/000354403
16. Bedia C. Metabolomics in environmental toxicology: applications and challenges. Trends Environ Analytical Chem. (2022) 34:e00161. doi: 10.1016/j.teac.2022.e00161
17. Hong J, Yang L, Zhang D, and Shi J. Plant metabolomics: an indispensable system biology tool for plant science. Int J Mol Sci. (2016) 17:767. doi: 10.3390/ijms17060767
18. Min X, Zhao Y, Yu M, Zhang W, Jiang X, Guo K, et al. Spatially resolved metabolomics: from metabolite mapping to function visualising. Clin Transl Med. (2024) 14:e70031. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70031
19. Petrova B and Guler AT. Recent developments in single-cell metabolomics by mass spectrometry A perspective. J Proteome Res. (2024) 24:1493–518. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.4c00646
20. Araújo AM, Carvalho F, Guedes De Pinho P, and Carvalho M. Toxicometabolomics: small molecules to answer big toxicological questions. Metabolites. (2021) 11:692. doi: 10.3390/metabo11100692
21. Russo S, Kwiatkowski M, Govorukhina N, Bischoff R, and Melgert BN. Meta-inflammation and metabolic reprogramming of macrophages in diabetes and obesity: the importance of metabolites. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:746151. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.746151
22. Koves TR, Ussher JR, Noland RC, Slentz D, Mosedale M, Ilkayeva O, et al. Mitochondrial overload and incomplete fatty acid oxidation contribute to skeletal muscle insulin resistance. Cell Metab. (2008) 7:45–56. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2007.10.013
23. Sancar G and Birkenfeld AL. The role of adipose tissue dysfunction in hepatic insulin resistance and T2D. J Endocrinol. (2024) 262(3). doi: 10.1530/JOE-24-0115
24. Roberts JM, Dai DLY, Hollander Z, Ng RT, Tebbutt SJ, Wilcox PG, et al. Multiple reaction monitoring mass spectrometry to identify novel plasma protein biomarkers of treatment response in cystic fibrosis pulmonary exacerbations. J Cyst Fibros. (2018) 17:333–40. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2017.10.013
25. Mirnaghi FS and Caudy AA. Challenges of analyzing different classes of metabolites by a single analytical method. Bioanalysis. (2014) 6:3393–416. doi: 10.4155/bio.14.236
26. Yang Z, Wang D, Li Y, Zhou X, Liu T, Shi C, et al. Untargeted metabolomics analysis of the anti-diabetic effect of red ginseng extract in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats based on UHPLC-MS/MS. Biomedicine Pharmacotherapy. (2022) 146:112495. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112495
27. Khamis MM, Adamko DJ, and El-Aneed A. Mass spectrometric based approaches in urine metabolomics and biomarker discovery. Mass Spectrom Rev. (2017) 36:115–34. doi: 10.1002/mas.21455
28. Lopes AS, Cruz ECS, Sussulini A, and Klassen A. Metabolomic strategies involving mass spectrometry combined with liquid and gas chromatography. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2017) 965:77–98. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-47656-8_4
29. Wang TJ, Larson MG, Vasan RS, Cheng S, Rhee EP, McCabe E, et al. Metabolite profiles and the risk of developing diabetes. Nat Med. (2011) 17:448–53. doi: 10.1038/nm.2307
30. Iadarola P, Fumagalli M, Bardoni AM, Salvini R, and Viglio S. Recent applications of CE- and HPLC-MS in the analysis of human fluids. Electrophoresis. (2016) 37:212–30. doi: 10.1002/elps.201500272
31. Dunn WB. Current trends and future requirements for the mass spectrometric investigation of microbial, mammalian and plant metabolomes. Phys Biol. (2008) 5:11001. doi: 10.1088/1478-3975/5/1/011001
32. Trivedi DK and Iles RK. Do not just do it, do it right: urinary metabolomics–establishing clinically relevant baselines. Biomed chromatography : BMC. (2014) 28:1491–501. doi: 10.1002/bmc.3219
33. Chiu H-H and Kuo C-H. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry-based analytical strategies for fatty acid analysis in biological samples. J Food Drug Anal. (2020) 28:60–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2019.10.003
34. Lin Y, Caldwell GW, Li Y, Lang W, and Masucci J. Inter-laboratory reproducibility of an untargeted metabolomics GC–MS assay for analysis of human plasma. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:10918. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67939-x
35. Motta A, Paris D, and Melck D. Monitoring real-Time metabolism of living cells by fast two-Dimensional NMR spectroscopy. Analytical Chem. (2010) 82(6):2405–11. doi: 10.1021/ac9026934
36. Markley JL, Brüschweiler R, Edison AS, Eghbalnia HR, Powers R, Raftery D, et al. The future of NMR-based metabolomics. Curr Opin Biotechnol. (2017) 43:34–40. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2016.08.001
37. Zhang W and Ramautar R. CE-MS for metabolomics: developments and applications in the period 2018–2020. ELECTROPHORESIS. (2021) 42:381–401. doi: 10.1002/elps.202000203
38. Cochran D and Powers R. Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry applications for metabolomics. Biomedicines. (2024) 12:1786. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081786
39. Trimpin S, Inutan ED, Karki S, Elia EA, Zhang W-J, Weidner SM, et al. Fundamental studies of new ionization technologies and insights from IMS-MS. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. (2019) 30:1133–47. doi: 10.1007/s13361-019-02194-7
40. Dubland JA. Lipid analysis by ion mobility spectrometry combined with mass spectrometry: A brief update with a perspective on applications in the clinical laboratory. J Mass Spectrometry Adv Clin Lab. (2022) 23:7–13. doi: 10.1016/j.jmsacl.2021.12.005
41. Ponzoni A, Speca S, Hartle M, Gerstenberg A, Tomezyk A, Senechal V, et al. An untargeted metabolomic study using MALDI-mass spectrometry imaging reveals region-specific biomarkers associated with bowel inflammation. Metabolomics. (2024) 21:5. doi: 10.1007/s11306-024-02200-4
42. Kakuda N, Miyasaka T, Iwasaki N, Nirasawa T, Wada-Kakuda S, Takahashi-Fujigasaki J, et al. Distinct deposition of amyloid-β Species in brains with alzheimer’s disease pathology visualized with MALDI imaging mass spectrometry. Acta Neuropathol Commun. (2017) 5:73. doi: 10.1186/s40478-017-0477-x
43. Prentice BM, Hart NJ, Phillips N, Haliyur R, Judd A, Armandala R, et al. Imaging mass spectrometry enables molecular profiling of mouse and human pancreatic tissue. Diabetologia. (2019) 62:1036–47. doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-4855-8
44. Lima C, Muhamadali H, and Goodacre R. The role of raman spectroscopy within quantitative metabolomics. Annu Rev Analytical Chem. (2021) 14:323–45. doi: 10.1146/annurev-anchem-091420-092323
45. Wang J, Qi G, Qu X, Ling X, Zhang Z, and Jin Y. Molecular profiling of dental pulp stem cells during cell differentiation by surface enhanced raman spectroscopy. Anal Chem. (2020) 92:3735–41. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b05026
46. Lamichhane S, Sen P, Dickens AM, Hyötyläinen T, and Orešič M. Chapter fourteen - an overview of metabolomics data analysis: current tools and future perspectives. In: Jaumot J, Bedia C, and Tauler R, editors. Comprehensive analytical chemistry, vol. 82. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier (2018). p. 387–413. Data Analysis for Omic Sciences: Methods and Applications. doi: 10.1016/bs.coac.2018.07.001
47. Brunius C, Shi L, and Landberg R. Large-Scale Untargeted LC-MS Metabolomics Data Correction Using between-Batch Feature Alignment and Cluster-Based within-Batch Signal Intensity Drift Correction. Metabolomics. (2016) 12(11):173. doi: 10.1007/s11306-016-1124-4
48. Jeliç-Knezoviç N, Galijaševiç S, Lovriç M, Vasilj M, Selak S, and Mikuliç I. Levels of nitric oxide metabolites and myeloperoxidase in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus on metformin therapy. Exp Clin Endocrinol diabetes : Off journal German Soc Endocrinol [and] German Diabetes Assoc. (2019) 127(1):56–61. doi: 10.1055/a-0577-7776
49. Xia H, Chen J, Sekar K, Shi M, Xie T, and Hui KM. Clinical and metabolomics analysis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients with diabetes mellitus. Metabolomics. (2019) 15:156. doi: 10.1007/s11306-019-1619-x
50. Lutz U, Lutz RW, and Lutz WK. Metabolic profiling of glucuronides in human urine by LC-MS/MS and partial least-squares discriminant analysis for classification and prediction of gender. Anal Chem. (2006) 78:4564–71. doi: 10.1021/ac0522299
51. Wu X, Zhu J-C, Zhang Y, Li W-M, Rong X-L, and Feng Y-F. Lipidomics study of plasma phospholipid metabolism in early type 2 diabetes rats with ancient prescription huang-qi-san intervention by UPLC/Q-TOF-MS and correlation coefficient. Chem Biol Interact. (2016) 256:71–84. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2016.06.025
52. Domingo-Almenara X, Montenegro-Burke JR, Guijas C, Majumder EL-W, Benton HP, and Siuzdak G. Autonomous METLIN-guided in-source fragment annotation for untargeted metabolomics. Anal Chem. (2019) 91:3246–53. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b03126
53. Dührkop K, Fleischauer M, Ludwig M, Aksenov AA, Melnik AV, Meusel M, et al. SIRIUS 4: A rapid tool for turning tandem mass spectra into metabolite structure information. Nat Methods. (2019) 16:299–302. doi: 10.1038/s41592-019-0344-8
54. Liu Y, Xu X, Deng L, Cheng K, Xu J, Raftery D, et al. Novel network modelling for metabolite set analysis: A case study on CRC metabolomics. IEEE Access. (2020) 8:106425–36. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3000432
55. Wang Y, Chen W-C, Li K, Wu G, Zhang W, Ma P, et al. Tissue-based metabolomics reveals metabolic signatures and major metabolic pathways of gastric cancer with help of transcriptomic data from TCGA. Bioscience Rep. (2021) 41(10). doi: 10.1042/BSR20211476
56. Lin G, Dong L, Cheng K-K, Xu X, Wang Y, Deng L, et al. Differential correlations informed metabolite set enrichment analysis to decipher metabolic heterogeneity of disease. Anal Chem. (2023) 95:12505–13. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c02246
57. Pavel I and Ciocoiu IB. COVID-19 detection from cough recordings using bag-of-words classifiers. Sensors. (2023) 23:4996. doi: 10.3390/s23114996
58. Li J, Yu Y, Sun Y, Fu Y, Shen W, Cai L, et al. Nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomics with machine learning for predicting progression from prediabetes to diabetes. eLife. (2024) 13:RP98709. doi: 10.7554/eLife.98709
59. Xia J, Broadhurst DI, Wilson M, and Wishart DS. Translational biomarker discovery in clinical metabolomics: an introductory tutorial. Metabolomics. (2013) 9:280–99. doi: 10.1007/s11306-012-0482-9
60. Zeng J, Huang X, Zhou L, Tan Y, Hu C, Wang X, et al. Metabolomics identifies biomarker pattern for early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: from diethylnitrosamine treated rats to patients. Sci Rep. (2015) 5:16101. doi: 10.1038/srep16101
61. Xie R, Herder C, Sha S, Peng L, Brenner H, and Schöttker B. Novel type 2 diabetes prediction score based on traditional risk factors and circulating metabolites: model derivation and validation in two large cohort studies. eClinicalMedicine. (2025) 79:102971. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102971
62. Hasin Y, Seldin M, and Lusis A. Multi-omics approaches to disease. Genome Biol. (2017) 18:83. doi: 10.1186/s13059-017-1215-1
63. Argelaguet R, Velten B, Arnol D, Dietrich S, Zenz T, Marioni JC, et al. Multi-omics factor analysis - a framework for unsupervised integration of multi-omic data sets. Cold Spring Harbor, New York, USA: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (2017). doi: 10.1101/217554.
64. Kelly RS, Chawes BL, Blighe K, Virkud YV, Croteau-Chonka DC, McGeachie MJ, et al. An integrative transcriptomic and metabolomic study of lung function in children with asthma. Chest. (2018) 154:335–48. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2018.05.038
65. Ahmad E, Lim S, Lamptey R, Webb DR, and Davies MJ. Type 2 diabetes. Lancet. (2022) 400:1803–20. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01655-5
66. Newgard CB, An J, Bain JR, Muehlbauer MJ, Stevens RD, Lien LF, et al. A branched-chain amino acid-related metabolic signature that differentiates obese and lean humans and contributes to insulin resistance. Cell Metab. (2009) 9(4):311–26. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2009.02.002
67. Yang Z, Zhang Z, Li L, Jing Z, Ma Y, Lan T, et al. Bioengineered artificial extracellular vesicles presenting PD-L1 and gal-9 ameliorate new-onset type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. (2024) 73:1325–35. doi: 10.2337/db23-0987
68. Eguchi N, Vaziri ND, Dafoe DC, and Ichii H. The role of oxidative stress in pancreatic ? Cell dysfunction in diabetes. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:1509. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041509
69. Tuomilehto J, Lindström J, Eriksson JG, Valle TT, Hämäläinen H, Ilanne-Parikka P, et al. Finnish diabetes prevention study group. Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med. (2001) 344:1343–50. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200105033441801
70. Vangipurapu J, Stancáková A, Smith U, Kuusisto J, and Laakso M. Nine amino acids are associated with decreased insulin secretion and elevated glucose levels in a 7.4-Year follow-up study of 5,181 finnish men. Diabetes. (2019) 68(6):1353–8. doi: 10.2337/db18-1076
71. Lu Y, Wang Y, Ong CN, Subramaniam T, Choi HW, Yuan JM, et al. Metabolic signatures and risk of type 2 diabetes in a chinese population: an untargeted metabolomics study using both LC-MS and GC-MS. Diabetologia. (2016) 59(11):2349–59. doi: 10.1007/s00125-016-4069-2
72. Vangipurapu J, Fernandes Silva L, Kuulasmaa T, Smith U, and Laakso M. Microbiota-related metabolites and the risk of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. (2020) 43(6):1319–25. doi: 10.2337/dc19-2533
73. Tillin T, Hughes AD, Wang Q, Würtz P, Ala-Korpela M, Sattar N, et al. Diabetes risk and amino acid profiles: cross-sectional and prospective analyses of ethnicity, amino acids and diabetes in a south asian and european cohort from the SABRE (Southall and brent REvisited) study. Diabetologia. (2015) 58:968–79. doi: 10.1007/s00125-015-3517-8
74. Huang X-T, Li C, Peng X-P, Guo J, Yue S-J, Liu W, et al. An excessive increase in glutamate contributes to glucose-toxicity in β-cells via activation of pancreatic NMDA receptors in rodent diabetes. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:44120. doi: 10.1038/srep44120
75. Liu X, Zheng Y, Guasch-Ferré M, Ruiz-Canela M, Toledo E, Clish C, et al. High plasma glutamate and low glutamine-to-glutamate ratio are associated with type 2 diabetes: case-cohort study within the PREDIMED trial. Nutrition Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2019) 29:1040–9. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2019.06.005
76. Reaven GM. Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes. (1988) 37:1595–607. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.12.1595
77. Shulman GI. Ectopic fat in insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and cardiometabolic disease. N Engl J Med. (2014) 371:1131–41. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1011035
78. De Cól JP, de Lima EP, Pompeu FM, Cressoni Araújo A, de Alvares Goulart R, Bechara MD, et al. Underlying mechanisms behind the brain–gut–liver axis and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD): an update. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:3694. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073694
79. Hu X, Zhou J, Song S, Kong W, Shi Y-C, Chen L-L, et al. TLR4/AP-1-targeted anti-inflammatory intervention attenuates insulin sensitivity and liver steatosis. Mediators Inflammation. (2020) 2020:2960517. doi: 10.1155/2020/2960517
80. Guasch-Ferré M, Hruby A, Toledo E, Clish CB, Martínez-González MA, Salas-Salvadó J, et al. Metabolomics in prediabetes and diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care. (2016) 39:833–46. doi: 10.2337/dc15-2251
81. Wang-Sattler R, Yu Z, Herder C, Messias AC, Floegel A, He Y, et al. Novel biomarkers for pre-diabetes identified by metabolomics. Mol Syst Biol. (2012) 8:615. doi: 10.1038/msb.2012.43
82. Igamberdiev AU and Bykova NV. Role of organic acids in the integration of cellular redox metabolism and mediation of redox signalling in photosynthetic tissues of higher plants. Free Radical Biol Med. (2018) 122:74–85. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.01.016
83. Yuan Y, Zhu C, Wang Y, Sun J, Feng J, Ma Z, et al. α-ketoglutaric acid ameliorates hyperglycemia in diabetes by inhibiting hepatic gluconeogenesis via serpina1e signaling. Sci Adv. (2022) 8:eabn2879. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abn2879
84. Yadikar N, Ahmet A, Zhu J, Bao X, Yang X, Han H, et al. Exploring the mechanism of citric acid for treating glucose metabolism disorder induced by hyperlipidemia. J Food Biochem. (2022) 46:e14404. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.14404
85. Liu X, Zhu L, Liu J, Nie Z, and Qiu W. Effect of weight loss interventions on metabolomic signatures in obese children with insulin resistance. Amino Acids. (2024) 56:54. doi: 10.1007/s00726-024-03409-2
86. Hoang M and Joseph JW. The role of α-Ketoglutarate and the hypoxia sensing pathway in the regulation of pancreatic β-Cell function. Islets. (2020) 12:108–19. doi: 10.1080/19382014.2020.1802183
87. Jansen TC, van Bommel J, and Bakker J. Blood lactate monitoring in critically ill patients: A systematic health technology assessment *. Crit Care Med. (2009) 37:2827. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181a98899
88. Eriksson K-F and Lindgärde F. Impaired glucose tolerance in a middle-aged male urban population: A new approach for identifying high-risk cases. Diabetologia. (1990) 33:526–31. doi: 10.1007/BF00404139
89. Lanza IR, Zhang S, Ward LE, Karakelides H, Raftery D, and Nair KS. Quantitative metabolomics by 1H-NMR and LC-MS/MS confirms altered metabolic pathways in diabetes. PloS One. (2010) 5:e10538. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010538
90. Brouwers MCGJ, Ham JC, Wisse E, Misra S, Landewe S, Rosenthal M, et al. Elevated lactate levels in patients with poorly regulated type 1 diabetes and glycogenic hepatopathy: A new feature of mauriac syndrome. Diabetes Care. (2015) 38:e11–2. doi: 10.2337/dc14-2205
91. Yin R, Jing G, Tian Y, Ma M, and Zhang M. The impact of lactate on diabetic cognitive dysfunction: insights from energy metabolism to epigenetic modulation. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) - Mol Basis Dis. (2025) 1871:167749. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2025.167749
92. Rajani C and Jia W. Bile acids and their effects on diabetes. Front Med. (2018) 12:608–23. doi: 10.1007/s11684-018-0644-x
93. Alberto González-Regueiro J, Moreno-Castañeda L, Uribe M, and Carlos Chávez-Tapia N. The role of bile acids in glucose metabolism and their relation with diabetes. Ann Hepatol. (2017) 16:S15–20. doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0010.5494
94. Kong L and Li P. Gut microbiota metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide reduced pancreatic β Cell calcium transients and function. Arch Mol Biol Genet. (2024) 3:1–4. doi: 10.33696/genetics.3.014
95. Kong L, Zhao Q, Jiang X, Hu J, Jiang Q, Sheng L, et al. Trimethylamine N-oxide impairs β-cell function and glucose tolerance. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:2526. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46829-0
96. Pedersen SS, Prause M, Williams K, Barrès R, and Billestrup N. Butyrate inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammatory gene expression by suppression of NF-κB activity in pancreatic beta cells. J Biol Chem. (2022) 298(9):102312. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102312
97. Birkeland E, Gharagozlian S, Birkeland KI, Valeur J, Måge I, Rud I, et al. Prebiotic effect of inulin-type fructans on faecal microbiota and short-chain fatty acids in type 2 diabetes: A randomised controlled trial. Eur J Nutr. (2020) 59:3325–38. doi: 10.1007/s00394-020-02282-5
98. Vrieze A, Van Nood E, Holleman F, Salojärvi J, Kootte RS, Bartelsman JFWM, et al. Transfer of intestinal microbiota from lean donors increases insulin sensitivity in individuals with metabolic syndrome. Gastroenterology. (2012) 143:913–6. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.06.031
99. Boslem E, Meikle Peter J, and Biden TJ. Roles of ceramide and sphingolipids in pancreatic β-Cell function and dysfunction. Islets. (2012) 4:177–87. doi: 10.4161/isl.20102
100. Karunakaran U, Moon JS, Lee HW, and Won KC. CD36 initiated signaling mediates ceramide-induced TXNIP expression in pancreatic beta-cellsCD36. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) - Mol Basis Dis. (2015) 1852:2414–22. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.08.009
101. Sui J, He M, Wang Y, Zhao X, He Y, and Shi B. Sphingolipid metabolism in type 2 diabetes and associated cardiovascular complications. Exp Ther Med. (2019) 18(5):3603–14. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7981
102. Park J-E, Jeong G-H, Lee I-K, Yoon Y-R, Liu K-H, Gu N, et al. Pharmacometabolomic approach to predict response to metformin in early-phase type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Molecules. (2018) 23:1579. doi: 10.3390/molecules23071579
103. Damanhouri ZA, Alkreathy HM, Alharbi FA, Abualhamail H, and Ahmad MSA. Review of the impact of pharmacogenetics and metabolomics on the efficacy of metformin in type 2 diabetes. Int J Med Sci. (2023) 20:142–50. doi: 10.7150/ijms.77206
104. Elbere I, Zigmunds O, Laura A, Ivars S, Lauma J, Liga B, et al. Gut microbiome encoded purine and amino acid pathways present prospective biomarkers for predicting metformin therapy efficacy in newly diagnosed T2D patients. Gut Microbes. (2024) 16:2361491. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2361491
105. Ortega−Ayala A, De Andrés F, Llerena A, Bartolo−Montiel CM, and Molina−Guarneros JA. Impact of SLC22A1 variants rs622342 and rs72552763 on hbA1c and metformin plasmatic concentration levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biomed Rep. (2024) 21:1–10. doi: 10.3892/br.2024.1806
106. Zaharenko L, Kalnina I, Geldnere K, Konrāde I, Grinberga S, Židzik J, et al. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the intergenic region between metformin transporter OCT2 and OCT3 coding genes are associated with short-term response to metformin monotherapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Eur J Endocrinol. (2016) 175 6:531–40. doi: 10.1530/EJE-16-0347
107. Fernandes MF, Tomczewski MV, and Duncan RE. Glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion is inhibited by lysophosphatidic acid. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:4163. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084163
108. Lambadiari V, Thymis J, Kouretas D, Skaperda Z, Tekos F, Kousathana F, et al. Effects of a 12-month treatment with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors, and their combination on oxidant and antioxidant biomarkers in patients with type 2 diabetes. Antioxidants. (2021) 10:1379. doi: 10.3390/antiox10091379
109. Manoogian ENC, Chow LS, Taub PR, Laferrère B, and Panda S. Time-restricted eating for the prevention and management of metabolic diseases. Endocrine Rev. (2022) 43:405–36. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnab027
110. Chambers ES, Byrne CS, Morrison DJ, Murphy KG, Preston T, Tedford C, et al. Dietary supplementation with inulin-propionate ester or inulin improves insulin sensitivity in adults with overweight and obesity with distinct effects on the gut microbiota, plasma metabolome and systemic inflammatory responses: A randomised cross-over trial. Gut. (2019) 68:1430–8. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318424
111. Flachs P, Rossmeisl M, and Kopecky J. The effect of N-3 fatty acids on glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity. Physiol Res. (2014) 63(Suppl 1):S93–118. doi: 10.33549/physiolres
112. Cao H, Ou J, Chen L, Zhang Y, Szkudelski T, Delmas D, et al. Dietary polyphenols and type 2 diabetes: human study and clinical trial. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2019) 59:3371–9. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1492900
113. Simundic AM, Cornes M, Grankvist K, Lippi G, and Nybo M. Standardization of collection requirements for fasting samples: for the working group on preanalytical phase (WG-PA) of the european federation of clinical chemistry and laboratory medicine (EFLM). Clinica Chimica Acta. (2014) 432:33–7. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.11.008
114. Li-Gao R, de Mutsert R, Rensen PCN, van Klinken JB, Prehn C, Adamski J, et al. Postprandial metabolite profiles associated with type 2 diabetes clearly stratify individuals with impaired fasting glucose. Metabolomics. (2017) 14:13. doi: 10.1007/s11306-017-1307-7
115. Jobard E, Trédan O, Postoly D, André F, Martin A-L, Elena-Herrmann B, et al. Systematic evaluation of blood serum and plasma pre-analytics for metabolomics cohort studies. Int J Mol Sci. (2016) 17:2035. doi: 10.3390/ijms17122035
116. Kim HW. Metabolomic approaches to investigate the effect of metformin: an overview. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22(19):10275. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910275
117. Xu T, Brandmaier S, Messias AC, Herder C, Draisma HHM, Demirkan A, et al. Effects of metformin on metabolite profiles and LDL cholesterol in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. (2015) 38:1858–67. doi: 10.2337/dc15-0658
118. Rinschen MM, Ivanisevic J, Giera M, and Siuzdak G. Identification of bioactive metabolites using activity metabolomics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2019) 20:353–67. doi: 10.1038/s41580-019-0108-4
119. Čajka T, Hričko J, Rakusanova S, Brejchova K, Novakova M, Kulhavá LR, et al. Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography–hydrogen/deuterium exchange–mass spectrometry (HILIC-HDX-MS) for untargeted metabolomics. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25(5):2899. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052899
120. Yeh S, Chang W-C, Chuang H, Huang H-C, Liu R-T, and Yang KD. Differentiation of type 2 diabetes mellitus with different complications by proteomic analysis of plasma low abundance proteins. J Diabetes Metab Disord. (2016) 15:24. doi: 10.1186/s40200-016-0246-6
121. Zhang A, Qiu S, Xu H, Sun H, and Wang X. Metabolomics in diabetes. Clinica Chimica Acta. (2014) 429:106–10. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.11.037
122. Tan YM, Gao Y, Teo G, Koh H, Tai E, Khoo C, et al. Plasma metabolome and lipidome associations with type 2 diabetes and diabetic nephropathy. Metabolites. (2021) 11(4):228. doi: 10.3390/metabo11040228
123. Kirwan JP. Plasma ceramides target skeletal muscle in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. (2013) 62:352–4. doi: 10.2337/db12-1427
124. Di Guida R, Engel J, Allwood JW, Weber RJM, Jones MR, Sommer U, et al. Non-targeted UHPLC-MS metabolomic data processing methods: A comparative investigation of normalisation, missing value imputation, transformation and scaling. Metabolomics. (2016) 12:93. doi: 10.1007/s11306-016-1030-9
125. Sampson JN, Boca SM, Shu XO, Stolzenberg-Solomon RZ, Matthews CE, Hsing AW, et al. Metabolomics in epidemiology: sources of variability in metabolite measurements and implications. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers Prev. (2013) 22:631–40. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-12-1109
126. Grankvist N, Jönsson C, Hedin K, Sundqvist N, Sandström P, Björnsson B, et al. Global 13C tracing and metabolic flux analysis of intact human liver tissue ex vivo. Nat Metab. (2024) 6:1963–75. doi: 10.1038/s42255-024-01119-3
127. Rahim M, Hasenour CM, Bednarski TK, Hughey CC, Wasserman DH, and Young JD. Multitissue 2H/13C flux analysis reveals reciprocal upregulation of renal gluconeogenesis in hepatic PEPCK-C–knockout mice. JCI Insight. (2021) 6:e149278. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.149278
128. Befroy DE, Perry RJ, Jain N, Dufour S, Cline GW, Trimmer JK, et al. Direct assessment of hepatic mitochondrial oxidative and anaplerotic fluxes in humans using dynamic 13C magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Nat Med. (2014) 20:98–102. doi: 10.1038/nm.3415
129. Hasenour CM, Rahim M, and Young JD. In vivo estimates of liver metabolic flux assessed by 13C-propionate and 13C-lactate are impacted by tracer recycling and equilibrium assumptions. Cell Rep. (2020) 32(5):107986. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107986
130. Kim I-Y, Park S, Kim Y, Kim H-J, and Wolfe RR. Tracing metabolic flux in vivo: basic model structures of tracer methodology. Exp Mol Med. (2022) 54:1311–22. doi: 10.1038/s12276-022-00814-z
131. Bednarski TK, Rahim M, and Young JD. In vivo 2H/13C flux analysis in metabolism research. Curr Opin Biotechnol. (2021) 71:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2021.04.005
132. Huang J, Huth C, Covic M, Troll M, Adam J, Zukunft S, et al. Machine learning approaches reveal metabolic signatures of incident chronic kidney disease in individuals with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. (2020) 69:2756–65. doi: 10.2337/db20-0586
133. Kirtipal N, Seo Y, Son J, and Lee S. Systems biology of human microbiome for the prediction of personal glycaemic response. Diabetes Metab J. (2024) 48:821–36. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0382
134. Yagin FH and Georgian B. Development of a bagged CART model for subclassification of diabetic retinopathy using metabolomics data. J Exercise Sci Phys Activity Rev. (2024) 2:71–7. doi: 10.5281/zenodo.11544643
135. Guldogan E, Yagin FH, Ucuzal H, Alzakari SA, Alhussan AA, and Ardigò LP. Interpretable machine learning for serum-based metabolomics in breast cancer diagnostics: insights from multi-objective feature selection-driven lightGBM-SHAP models. Medicina. (2025) 61:1112. doi: 10.3390/medicina61061112
136. Hu T, An Z, Li H, Liu Y, Xia L, Qiu L, et al. UHPLC-MS/MS-based metabolomics and clinical phenotypes analysis reveal broad-scale perturbations in early pregnancy related to gestational diabetes mellitus. Dis Markers. (2022) 2022:1–13. doi: 10.1155/2022/4231031
137. Li X, Li Y, Liang Y, Hu R, Xu W, and Liu Y. Plasma targeted metabolomics analysis for amino acids and acylcarnitines in patients with prediabetes, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and diabetic vascular complications. Diabetes Metab J. (2021) 45:195–208. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2019.0209
138. Zhang F, Shan S, Fu C, Guo S, Liu C, and Wang S. Advanced mass spectrometry-based biomarker identification for metabolomics of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Molecules. (2024) 29:2530. doi: 10.3390/molecules29112530
139. Luppa PB, Müller C, Schlichtiger A, and Schlebusch H. Point-of-care testing (POCT): current techniques and future perspectives. TrAC Trends Analytical Chem. (2011) 30:887–98. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2011.01.019
140. Ribeiro da Silva M, Zaborowska I, Carillo S, and Bones JA. Rapid, simple and sensitive microfluidic chip electrophoresis mass spectrometry method for monitoring amino acids in cell culture media. J Chromatogr A. (2021) 1651:462336. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2021.462336
141. Floegel A, Stefan N, Yu Z, Mühlenbruch K, Drogan D, Joost H-G, et al. Identification of serum metabolites associated with risk of type 2 diabetes using a targeted metabolomic approach. Diabetes. (2013) 62:639–48. doi: 10.2337/db12-0495
142. Yu D, Moore SC, Matthews CE, Xiang Y-B, Zhang X, Gao Y-T, et al. Plasma metabolomic profiles in association with type 2 diabetes risk and prevalence in chinese adults. Metabolomics. (2016) 12:3. doi: 10.1007/s11306-015-0890-8
143. Menni C, Fauman E, Erte I, Perry JRB, Kastenmüller G, Shin S-Y, et al. Biomarkers for type 2 diabetes and impaired fasting glucose using a nontargeted metabolomics approach. Diabetes. (2013) 62:4270–6. doi: 10.2337/db13-0570
144. Papandreou C, Bulló M, Ruiz-Canela M, Dennis C, Deik A, Wang D, et al. Plasma metabolites predict both insulin resistance and incident type 2 diabetes: A metabolomics approach within the prevención con dieta mediterránea (PREDIMED) study. Am J Clin Nutr. (2019) 109:626–34. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqy262
145. Liu J, Shang X, Zhang X, Chen Y, Zhang B, Tang W, et al. Metabolomic network reveals novel biomarkers for type 2 diabetes mellitus in the UK biobank study. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2025) 27:3335–46. doi: 10.1111/dom.16351
146. Broadhurst D, Goodacre R, Reinke SN, Kuligowski J, Wilson ID, Lewis MR, et al. Guidelines and considerations for the use of system suitability and quality control samples in mass spectrometry assays applied in untargeted clinical metabolomic studies. Metabolomics. (2018) 14:72. doi: 10.1007/s11306-018-1367-3
147. Meesters RJ and Voswinkel S. Bioanalytical method development and validation: from the USFDA 2001 to the USFDA 2018 guidance for industry. J Appl Bioanal. (2018) 4:67–73. doi: 10.17145/jab.18.010
148. Galal A, Talal M, and Moustafa A. Applications of machine learning in metabolomics: disease modeling and classification. Front Genet. (2022) 13:1017340. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1017340
149. Wang H-N, Wang Y, Zhang S-Y, and Bai L. Emerging roles of the acid sphingomyelinase/ceramide pathway in metabolic and cardiovascular diseases: mechanistic insights and therapeutic implications. World J Cardiol. (2025) 17:102308. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i2.102308
150. Van Nierop FS, Scheltema MJ, Eggink HM, Pols TW, Sonne DP, Knop FK, et al. Clinical relevance of the bile acid receptor TGR5 in metabolism. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2017) 5:224–33. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(16)30155-3
151. Kimura I, Ozawa K, Inoue D, Imamura T, Kimura K, Maeda T, et al. The gut microbiota suppresses insulin-mediated fat accumulation via the short-chain fatty acid receptor GPR43. Nat Commun. (2013) 4:1829. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2852
152. Tolhurst G, Heffron H, Lam YS, Parker HE, Habib AM, Diakogiannaki E, et al. Short-chain fatty acids stimulate glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion via the G-protein–coupled receptor FFAR2. Diabetes. (2012) 61:364–71. doi: 10.2337/db11-1019
153. Pandey S. Metabolomics characterization of disease markers in diabetes and its associated pathologies. Metab Syndrome Related Disord. (2024) 22:499–509. doi: 10.1089/met.2024.0038
154. Yousri NA, Albagha OME, and Hunt SC. Integrated epigenome, whole genome sequence and metabolome analyses identify novel multi-omics pathways in type 2 diabetes: A middle eastern study. BMC Med. (2023) 21:347. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-03027-x
155. Arslan AK, Yagin FH, Algarni A, Karaaslan E, Al-Hashem F, and Ardigò LP. Enhancing type 2 diabetes mellitus prediction by integrating metabolomics and tree-based boosting approaches. Front Endocrinol. (2024) 15:1444282. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1444282
156. Leiherer A, Muendlein A, Mink S, Mader A, Saely CH, Festa A, et al. Machine learning approach to metabolomic data predicts type 2 diabetes mellitus incidence. IJMS. (2024) 25:5331. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105331
157. Peng P, Zhang N, Huang J, Jiao X, and Shen Y. Effectiveness of wearable activity monitors on metabolic outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocrine Pract. (2023) 29:368–78. doi: 10.1016/j.eprac.2023.02.004
158. Lyzwinski L, Elgendi M, Shokurov AV, Cuthbert TJ, Ahmadizadeh C, and Menon C. Opportunities and challenges for sweat-based monitoring of metabolic syndrome via wearable technologies. Commun Eng. (2023) 2:1–14. doi: 10.1038/s44172-023-00097-w
159. Alanzi TM, Alzahrani W, Almoraikhi M, Algannas A, Alghamdi M, Alzahrani L, et al. Adoption of wearable insulin biosensors for diabetes management: A cross-sectional study. Cureus. (2023) 15(12):e50782. doi: 10.7759/cureus.50782
160. Committee on Strategies for Responsible Sharing of Clinical TrialData, Board on Health Sciences Policy, and Institute of Medicine. Sharing clinical trial data: maximizing benefits, minimizing risk. Washington (DC: National Academies Press (US (2015).
161. Hoofnagle CJ, van der Sloot B, and Borgesius FZ. The european union general data protection regulation: what it is and what it means*. Inf Commun Technol Law. (2019) 28:65–98. doi: 10.1080/13600834.2019.1573501
Keywords: metabolomics, diabetes mellitus, metabolic reprogramming, biomarkers, clinical translation, precision medicine
Citation: Xu Z, Zhou Y, Xie R and Ning Z (2025) Metabolomics uncovers the diabetes metabolic network: from pathophysiological mechanisms to clinical applications. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1624878. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1624878
Received: 10 May 2025; Accepted: 07 August 2025;
Published: 04 September 2025.
Edited by:
Riccarda Granata, University of Turin, ItalyReviewed by:
Swarnima Pandey, University of Maryland, United StatesRahul Mittal, University of Miami, United States
Guannan Zhou, Karolinska Institutet (KI), Sweden
Copyright © 2025 Xu, Zhou, Xie and Ning. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhongxing Ning, NTkyMjIwNjkwQHFxLmNvbQ==
 Zijie Xu
Zijie Xu Yujia Zhou
Yujia Zhou Ruijie Xie
Ruijie Xie Zhongxing Ning
Zhongxing Ning