- 1Faculty of Chinese Medicine and State Key Laboratory of Quality Research in Chinese Medicines, Macau University of Science and Technology, Macao, Macao SAR, China
- 2Huizhou Health Sciences Polytechnic, Huizhou, China
- 3The Third Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan, China
- 4National Engineering Laboratory for Internet Medical Systems and Applications, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan, China
- 5Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan, China
- 6School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou, Henan, China
- 7Zunyi Medical University, Zhuhai, China
- 8Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang, China
- 9Encephalopathy Center, The Second Affiliation Hospital of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei, Anhui, China
Background: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a prevalent metabolic disorder with limited treatment options. Manual acupuncture and electroacupuncture have been investigated in numerous animal studies for their potential to improve glycemic and lipid profiles, but no comprehensive synthesis exists. This review aims to evaluate the effects of manual acupuncture and electroacupuncture on blood glucose and lipid levels in animal models of T2DM, and to explore potential mechanisms.
Methods: A systematic search was conducted in PubMed, Embase, Cochrane, Web of Science, and major Chinese databases from inception to December 2024. Only animal studies employing manual acupuncture or electroacupuncture for T2DM models were included. The methodological quality was assessed using a 10-item CAMARADES checklist. Meta-analyses were performed using STATA 17.0, and subgroup analyses explored the influence of modeling methods, intervention timing, and treatment duration.
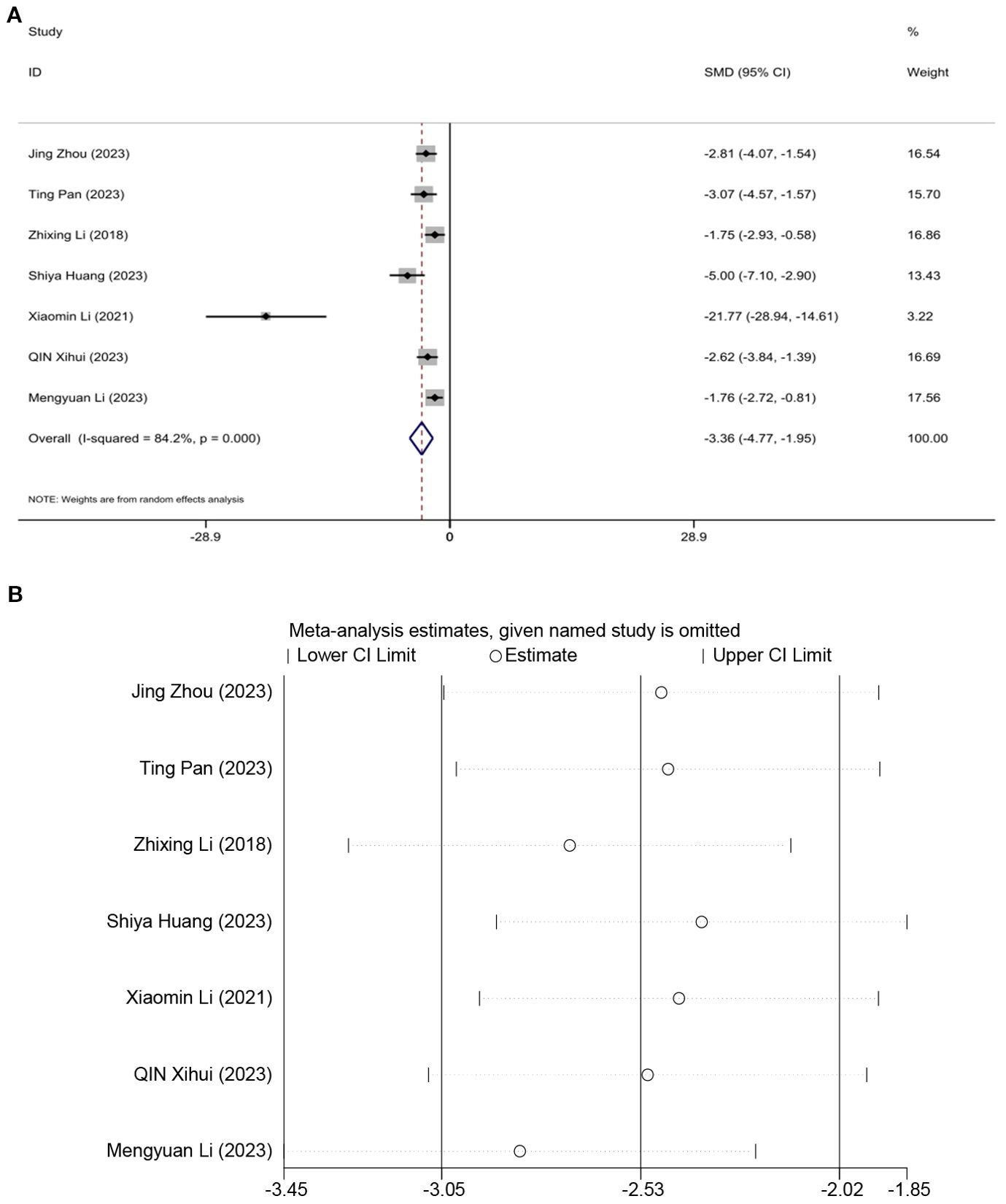
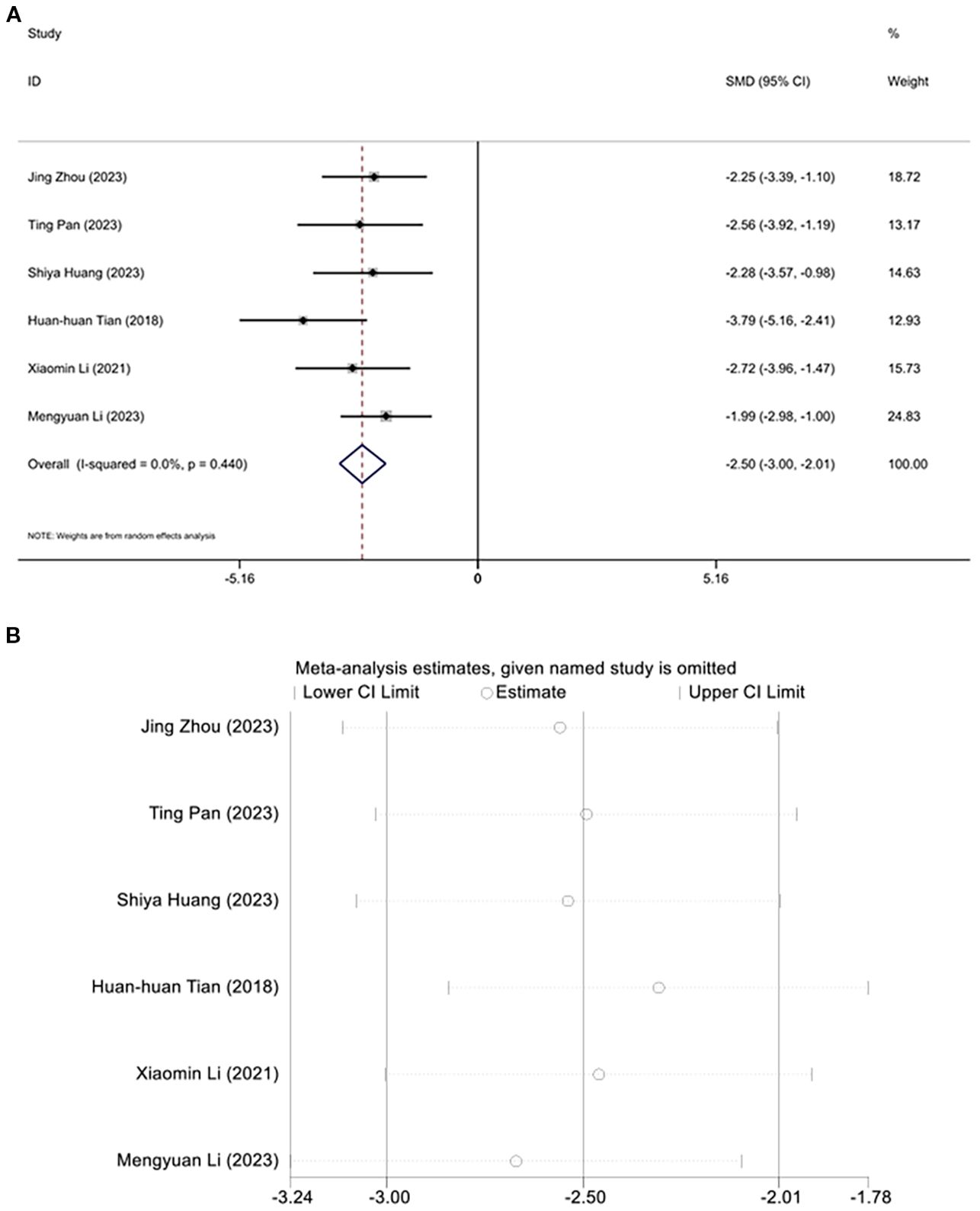
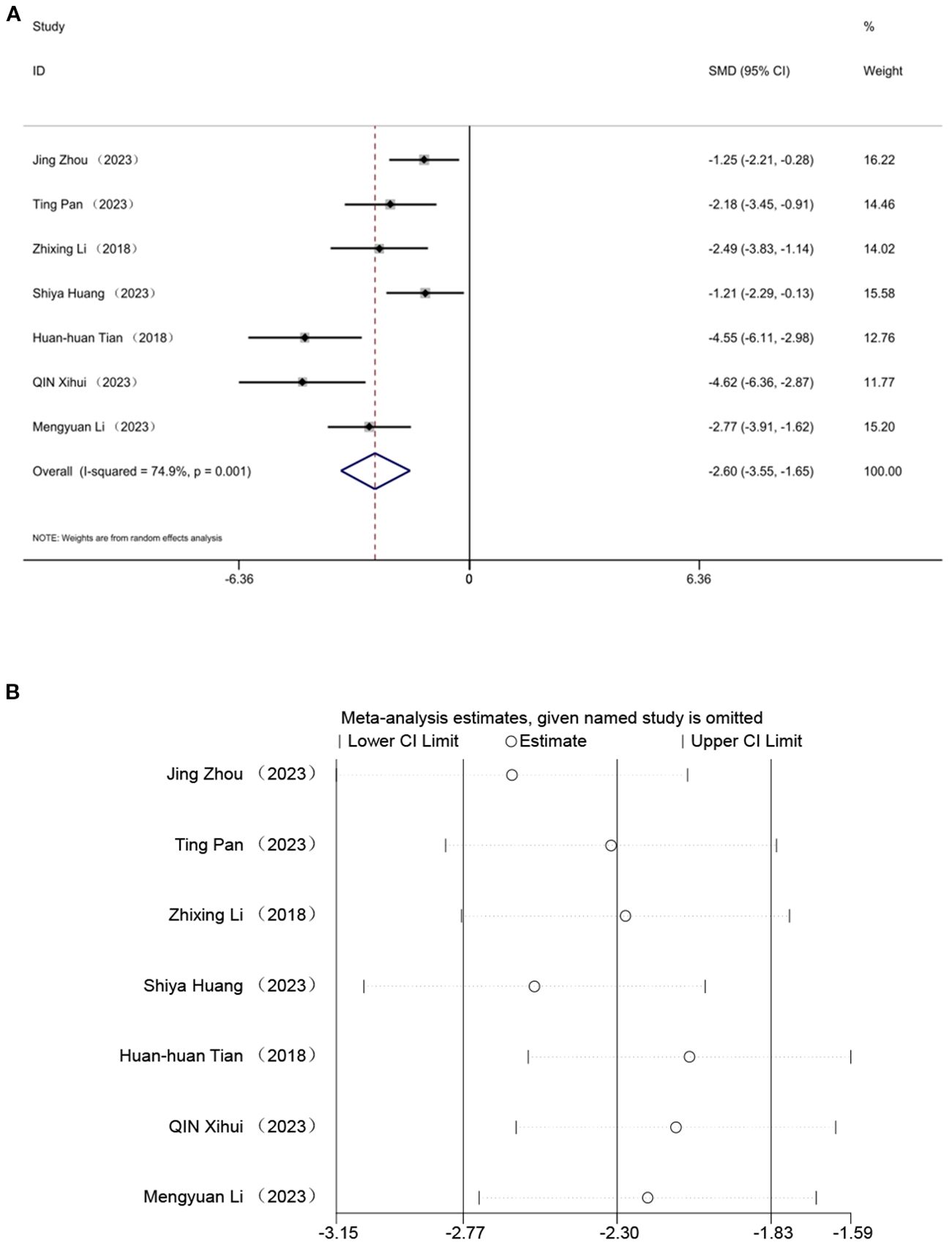
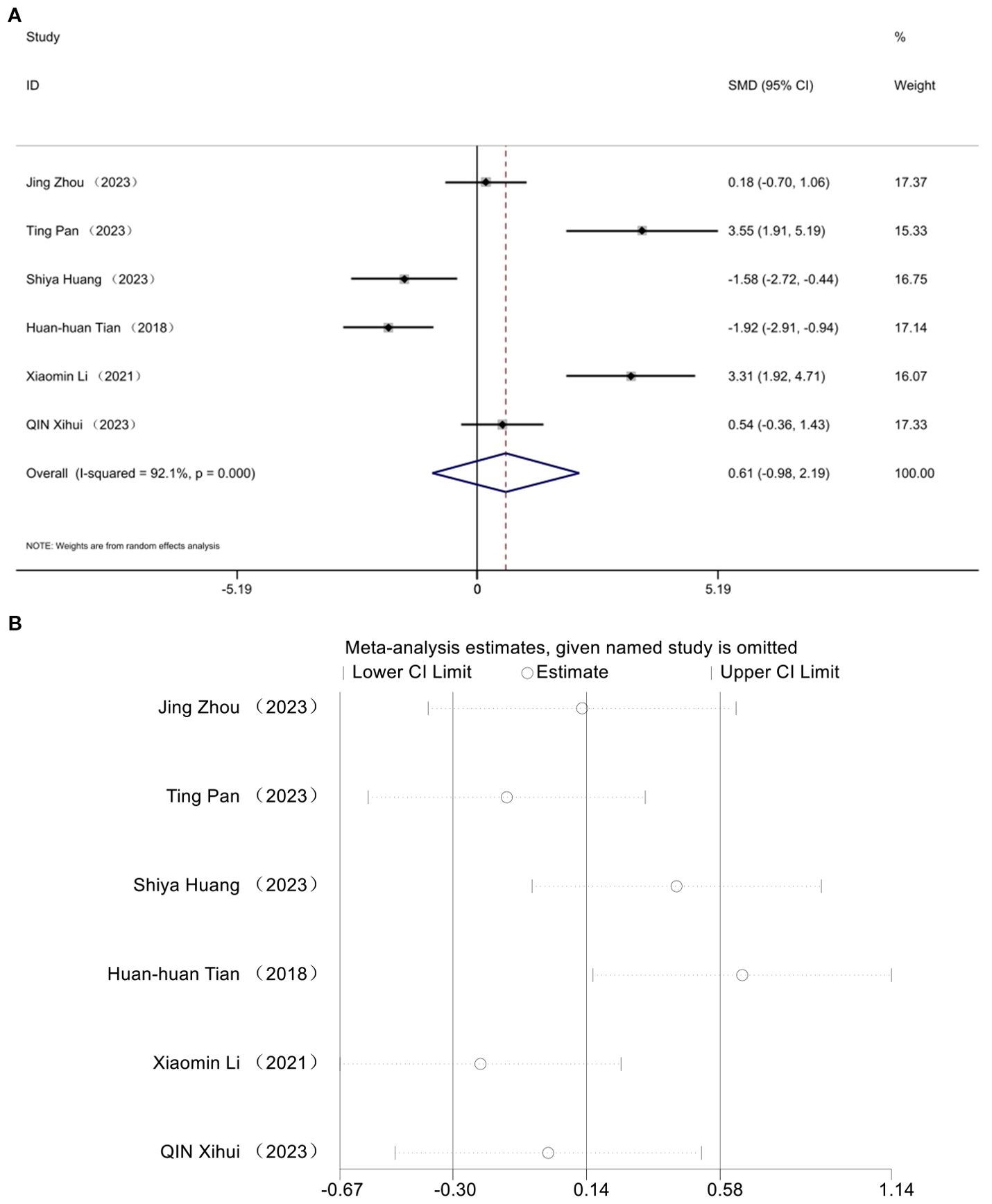
Results: A total of 14 studies with 274 animals with T2DM were included. The overall quality of the included reports was rated as moderate or higher. Meta-analysis showed that acupuncture significantly reduced blood glucose [Standardized Mean Difference(SMD)= -3.15, 95% Confidence Interval(CI) (-4.18, -2.12), I-squared (I²)= 85.1%, (P< 0.05)], body weight [SMD = -3.36, 95%CI (-4.77, -1.95), I²= 84.2%,(P<0.05)], triglycerides [SMD=-2.50, 95% CI (-3.00, -2.01), I²= 0.0%, (P< 0.05)], total cholesterol [SMD = -2.60, 95% CI (-3.55,-1.65), I²= 74.9%, (P< 0.05)], and low-density lipoprotein [SMD = -3.36, 95%CI (-5.42,-1.95), I²= 86.2%] (P< 0.05)], and no statistically significant difference was observed in high-density lipoprotein [SMD = 0.61, 95% CI (-0.98, 2.19), I² = 92.1%, (P> 0.05)] compared to the control group. These results suggest that acupuncture can effectively improve blood glucose and lipid levels in animal models of T2DM.
Conclusion: While this study is limited by the number of included studies, the results indicate that acupuncture can effectively improve blood glucose and lipid levels in animal models of T2DM.
Systematic Review Registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, identifier CRD42024520000.
1 Introduction
T2DM is an endocrine and metabolic disorder disease, which is defined as being characterized by chronic hyperglycemia resulting from pancreatic β-cell dysfunction, insulin resistance, or both (1). At present, the growing number of T2DM patients than expected, with approximately 9.36% (529 million) people of all ages suffering from T2DM in 2021 (2), it is predicted that will rise to10.9% (700 million) in 2045 (3). Diabetes not only has a high morbidity rate but also cause a series of chronic complications such as diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy and so on, which affect people’s health and lead to the primary cause of death even in diabetic patients (4). As the prevalence and treatment costs of T2DM continue to increase globally, diabetes imposes a significant economic burden, which has become one of the most serious challenges to public health worldwide (5, 6). To address this global public health issue, current treatment strategies primarily involve the commonly used drugs for the treatment of T2DM are metformin and insulin, and metformin is often used as a first-line pharmacological treatment, which have shown good clinical efficacy in controlling blood sugar and are often considered the best initial treatment for diabetes mellitus (7). Although these medications can effectively control blood glucose levels in a fast-acting manner, long-term use of them can lead to side effects such as hypoglycemia, nausea, and nerve damage (8). Therefore, there is an urgent need for research to seek more effective and alternative therapies for the prevention and treatment of T2DM, particularly with respect to both efficacy and safety, which will alleviate the burden on both families and society in the long run (9).
T2DM is a complex metabolic disorder influenced by various genetic and environmental factors, affecting multiple organs such as the heart, nerves, and blood vessels (1). The pathogenesis of T2DM is characterized by several mechanisms, including dysfunction of pancreatic β-cells, insulin resistance, and impaired insulin processing (10). Recent studies have explored acupuncture as a traditional therapeutic modality for its potential effects on diabetes management (11). Research indicates that acupuncture can improve the expression of upstream and downstream proteins and genes associated with the PI3K signaling pathway, thereby influencing critical physiological functions such as cell growth, survival, and proliferation. This regulatory effect may assist in controlling glucose metabolism levels, leading to beneficial outcomes for diabetic patients (12). Insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction are key factors in the development of diabetes. Acupuncture not only directly activates the vagus nerve to ameliorate local immune inflammatory responses in target organs but also regulates the activity of immune cells to achieve immune balance. Additionally, acupuncture may engage neuroendocrine pathways to participate in inflammation and immune regulation, further contributing to its hypoglycemic effects (13). Moreover, dysbiosis of gut microbiota has been recognized as an important pathogenic mechanism in diabetes. Studies have demonstrated that acupuncture can modulate and improve glucose and lipid metabolism as well as the structure of gut microbiota in mice, effectively regulating blood sugar levels and enhancing insulin sensitivity (14, 15). A common therapeutic strategy for both Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus is to address the absolute or relative deficiency of insulin. Evidence suggests that acupuncture can enhance the morphology and function of pancreatic β-cells by influencing the expression levels of related genes and proteins, thereby strengthening β-cell functionality. Consequently, acupuncture presents itself as a promising non-pharmacological alternative therapy for individuals with diabetes (16). In summary, acupuncture demonstrates potential in diabetes management through various mechanisms that regulate metabolism and immune responses, offering hope for improved patient outcomes.
In China, acupuncture is a key component of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and has been used as an alternative therapy to treat diseases for a long time. Since 1979, it is recognized as a complementary therapy by the World Health Organization (WHO) (17). Several systematic reviews and meta-analyses have evaluated the effects of acupuncture in patients with diabetes mellitus, generally reporting small sample sizes, methodological limitations, and insufficient evidence to make strong clinical recommendations. Our study focuses on animal models to provide preclinical evidence, which complements these human studies and can guide the design of future large-scale, high-quality clinical trials. Virtually, acupuncture has been used to treat diabetes mellitus because of its benefits in various aspects such as effectiveness, economy, convenience, and low side effect (18). Some modern medical research has confirmed that acupuncture can decrease blood sugar and improve the symptoms of diabetes because of its effects on enhancing the insulin sensitive index, ameliorating insulin resistance, and regulating blood lipids (11). In human clinical trials investigating acupuncture for diabetes, ethical constraints—such as the difficulty in designing ethical and effective sham control groups, challenges in achieving adequate blinding (which raises issues with informed consent), and the tension between standardized protocols and individualized treatment—significantly limit the methodological rigor and scope of studies. Consequently, these constraints impede the acquisition of comprehensive and unambiguous evidence regarding acupuncture’s specific efficacy. Animal studies not only allow for the minimization of external factors to attain more precise results but also facilitate the exploration of the experiment’s underlying mechanisms (19). A systematic review of animal studies can bring more precise accurate decisions in medical care (20). Therefore, we aim to a systematic review and meta-analysis of the effectiveness of acupuncture for treating diabetes in animal models by regulating lipid metabolism. whether acupuncture therapy the effects by regulating lipid metabolism for T2DM on levels of blood glucose (BG), high density lipoprotein (HDL), low-density lipoprotein (LDL), triacylglycerol (TG), Cholesterol (TC) in T2DM animals. overall, acupuncture may provide innovative therapeutic strategies to improve the clinical management of T2DM.
2 Methods and materials
This systematic review and meta-analysis were reported according to the PRISMA guidelines (21)and Cochrane Collaboration standard (22).
2.1 Search strategy
We systematically searched several major English-language electronic databases, including PubMed, EMBASE, the Cochrane Library, and Web of Science, from their inception until December 2023 with the language restricted to English. We searched for titles, abstracts, and keywords that used the following terms:((electroacupuncture[Mesh]) OR(acupuncture[Mesh])) AND ((diabetes[Mesh]) OR (diabetes mellitus[Mesh]) OR (Alloxan Diabetes[Keywords]) OR (Diabetes Mellitus, Experimental[Keywords])) Also, reference lists of the selected articles in the original search results were reviewed to obtain more relevant studies.
2.2 Inclusion/exclusion criteria
Study inclusion was based on the following criteria: subjects (rodent model of T2DM), intervention (acupuncture as the primary mode of treatment, only manual acupuncture and electroacupuncture interventions were included; other forms of acupuncture such as fire needling, warm needling, or intradermal needling were excluded to ensure methodological homogeneity), and outcome (mainly focused on assessing individual diabetes efficacy data such as animal blood glucose levels as the primary measure of acupuncture efficacy). Moreover, bodyweight and food intake data extracted from animal studies will be considered as the secondary outcomes. Studies failing to meet these specified criteria or failing to grant access to the complete text were excluded. Additionally, clinical trials not pertinent to the subject matter were omitted. Subsequently, following a comprehensive assessment of the complete text, studies diverging from the predetermined criteria concerning methodologies and reported findings were additionally eliminated.
2.3 Data extraction
Data extraction was carried out independently by two researchers, namely LLS and GZY, reviewed titles, authors, and publication dates to identify and exclude duplicate literature. They applied exclusion criteria to eliminate irrelevant studies, following this, they meticulously examined the full text to ascertain the final selection of included literature based on predetermined inclusion criteria. Finally, they proceeded to extract data from the selected literature. Extraction of data included the following variables: year of publication, first author name, type of diabetes model, specific disease or condition, sample size, type of acupuncture, and nature of specimen investigated. In addition to these parameters, average blood glucose levels within each group (e.g., disease group, intervention group) were extracted, along with corresponding measures of variability. Sham acupuncture refers to needle insertion at non-acupoints or superficial insertion without stimulation, designed to mimic the procedure without eliciting therapeutic effects. In our included studies, no sham acupuncture was applied; control groups consisted of untreated diabetic animals. These data helped to determine effect measurements and effect sizes of acupuncture’s effects on diabetes models. In cases where the data is presented entirely in graphical form, a concerted effort is made to obtain the necessary measurements. This requires contacting the study authors directly or using Get Data software to obtain the necessary values. In addition, the secondary outcomes are recorded in the form of mean ± standard deviation data. If the data is missing, we will contact the author of the article. If disputes arose, the final decision was reached through discussion and negotiation involving a third researcher.
2.4 Quality assessment
The methodological quality of the included literature was based on a 10-item checklist that had been adapted from the Collaborative Approach to Meta-Analysis and Review of Animal Data from Experimental Studies (CAMARADES) checklist (23). The checklist included the following criteria: publication in a peer-reviewed journal. Statements describing the control of temperature. Random allocation of subjects to treatment or control groups. Blinded construction of the model. Use of animals with hypertension or diabetes, if applicable. Blinded assessment of study outcomes. Utilization of anesthetic without marked intrinsic properties. Sample size calculation. Compliance with animal welfare regulations. Declaration of any potential conflicts of interest.
2.5 Statistics
In this study, we utilized STAT17.0 software for data analysis. For continuous variables, we calculated the standardized mean differences (SMD) along with their respective 95% confidence intervals (CI). Heterogeneity assessment was performed using the I² statistic. If I² was less than 50%, fixed-effects models were employed; for values exceeding 50%, random-effects models were applied. Sensitivity analysis was conducted to identify potential sources of heterogeneity. Subgroup analysis was carried out to explore heterogeneity sources, including model species, establishment of animal model, treatment duration, timing, acupuncture method, and organizational source. The publication bias of the selected study was scrutinized using Egger’s test.
3 Results
3.1 Research screening
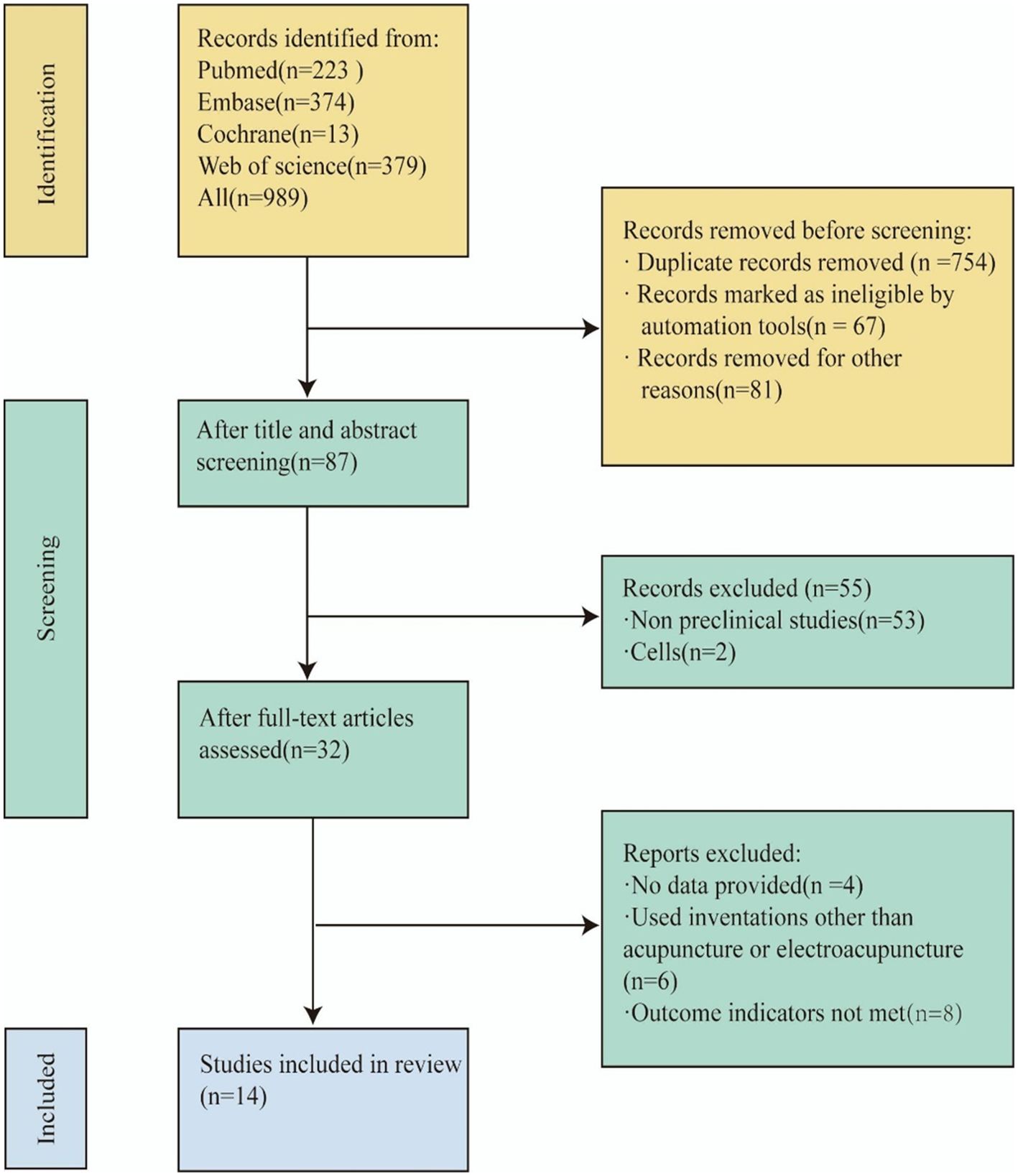
Our research endeavor commenced with the implementation of a retrieval strategy. Two independent researchers (LLS, GZY) retrieved a total of 898 articles by searching in four databases (223 from PubMed, 374 from Embase, 379 from Web of Science, and 11 from Cochrane). After reading the titles, abstracts, and authors, and eliminating duplicates and irrelevant literature, 87 articles remained. By evaluating the titles and abstracts, we excluded 53 non-preclinical studies, and 2 studies specifically related to cells. Subsequently, a comprehensive examination of the full text was conducted for 32 articles. Among these, 4 articles met the inclusion criteria but did not provide data and were thus excluded. Additionally, 6 articles used interventions other than acupuncture and electroacupuncture, and 8 articles did not meet outcome indicators, leading to their exclusion as well. Ultimately, 14 studies were selected for a comprehensive analysis (15, 24–36) The process and results of literature selection are shown in Figure 1.
3.2 Research characteristic
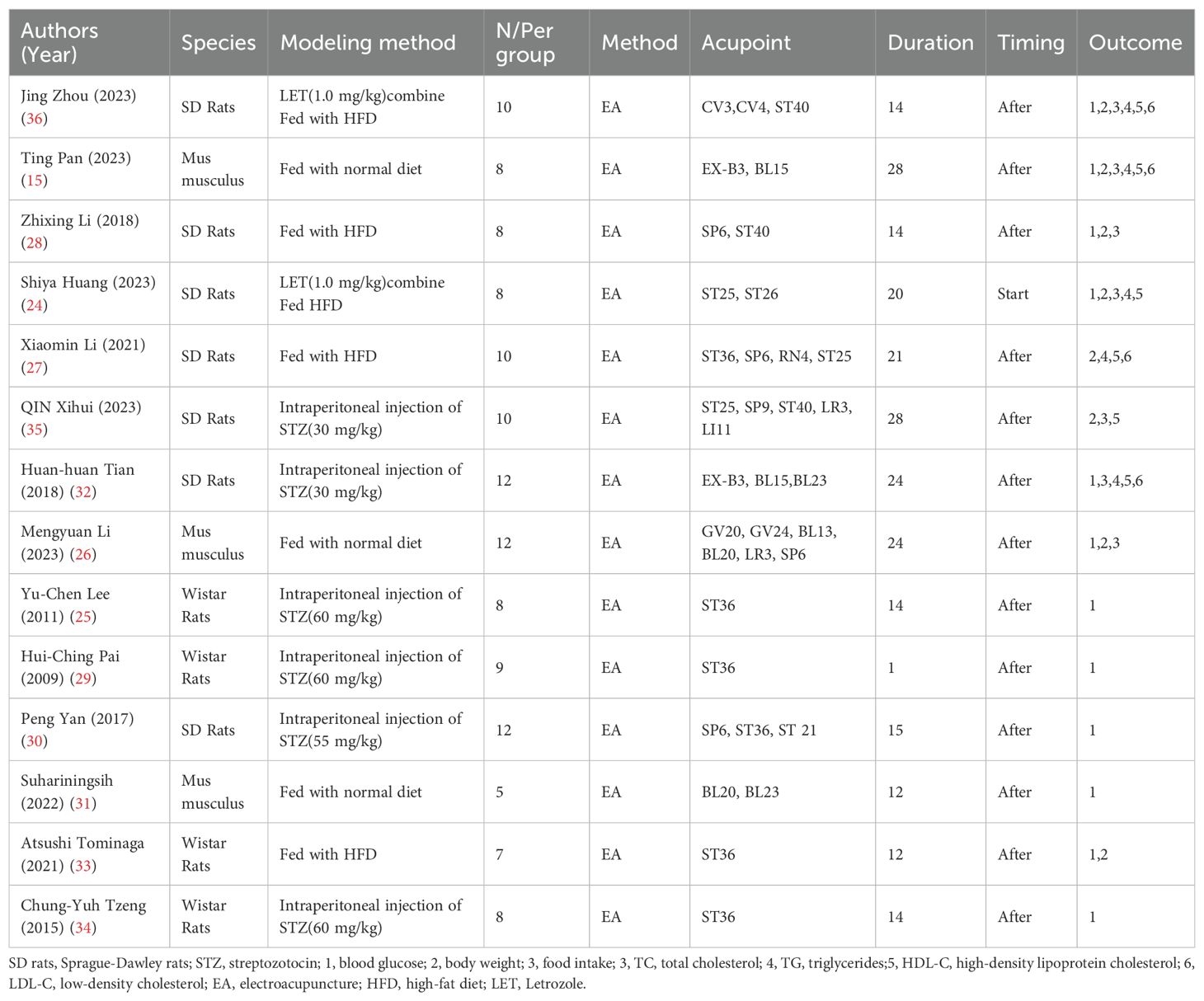
The basic characteristics of the 14 selected studies are summarized in Table 1, A total of 274 animals were included in this study. Most of these animals were Sprague–Dawley rats, accounting for 57% of the sample, followed by Wistar rats at 29%, and Mus musculus at 14% (Figure 2A). Concerning the T2DM animal models used, all included studies used induced models of diabetes, including intraperitoneal streptozotocin (STZ) injection, high-fat diet feeding, or letrozole combined with high-fat diet. no spontaneous diabetes models (genetic models such as db/db mice) were included, with the intraperitoneal injection of STZ model being the most prevalent, featured in 43% of the studies, models fed with High-Fat Diet (HFD) made up 22%, models fed with NORM represent 21% and LET accounts for 14%. Each percentage reflects the proportion of studies using these specific methods (Figure 2B). Furthermore, there are significant differences in the selection of acupuncture points. ST36 acupuncture point was the most selected (16%), followed by SP6 (11%). CV4 and ST25 each account for 8%. Several other acupoints, including BL23, CV3, ST40, and EX-B3, each account for 5%. A variety of other acupoints, such as BL20, GV24, and LI11, each account for 3% (Figure 2C). Notably, In the context of timing and duration of treatment,93% of the treatments were administered after modeling, while only 7% of the treatments were administered at the start of modeling (Figure 2D). The duration of acupuncture treatment varied, ranging from 1 to 28 days, 24-days treatment durations were the most common, representing 29% of the studies (Figure 2E). The study showed that the number of animals in each group in the included literature varied, with groups of 8 making up the largest portion (36%), groups of 10,22%, and groups of 12,21%. Groups 9, 5 and 7 each accounted for 7% of the total (Figure 2F), It shows that 50% prefer a 20-minute treatment time, 29% choose a 30-minute treatment time, and 7% each prefer a 10-minute treatment time, a 60-minute treatment time, and a 6-minute treatment time (Figure 2G). For example, both the 28 times and 15 times acupuncture sessions account for 15%, while the 12 times, 21 times, and 20 times sessions represent 7%, 14%, and 14% (Figure 2H).
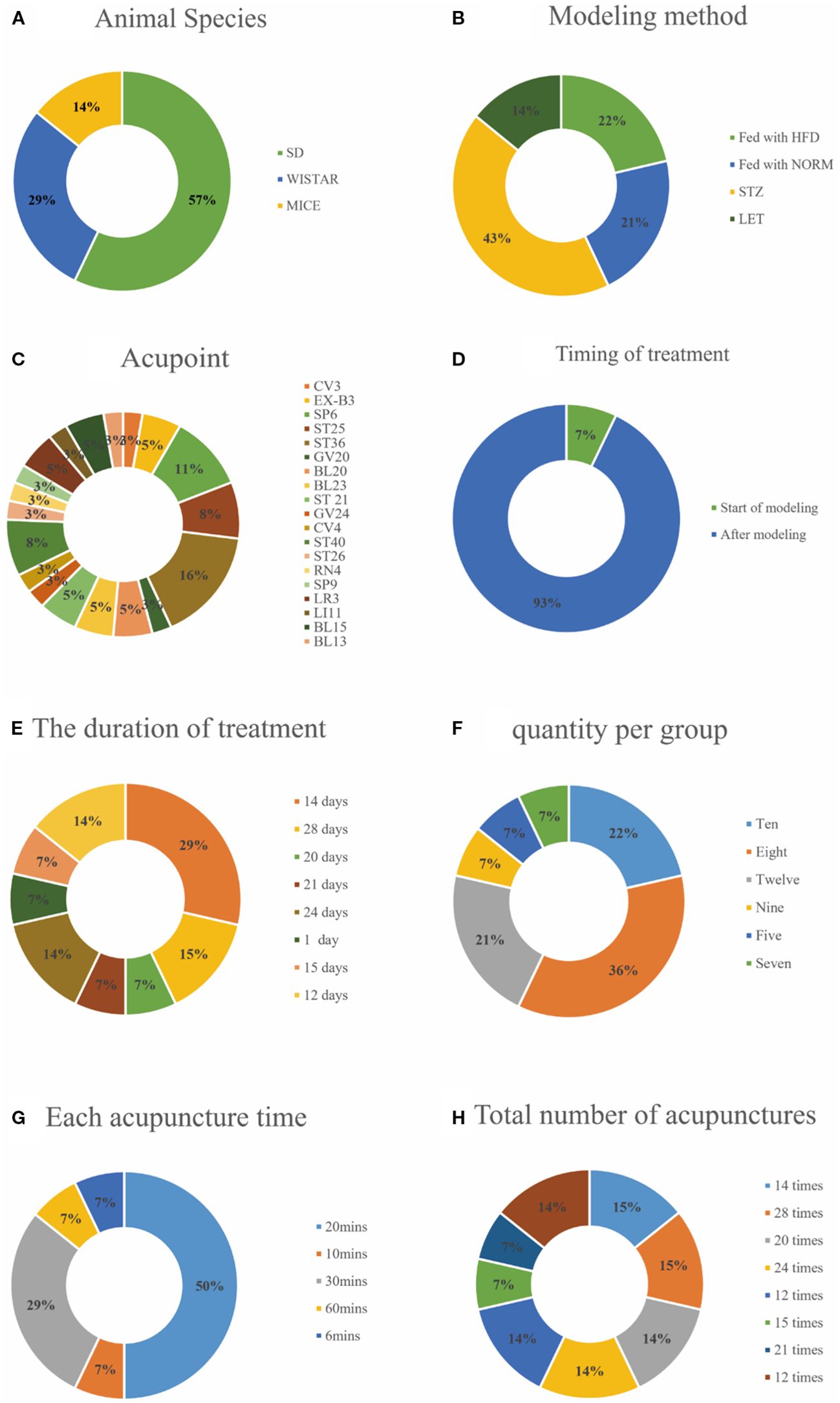
Figure 2. Included study characteristics. (A) Animal Species; (B) Modeling method; (C) Acupoint; (D) Timing of treatment; (E) The duration of treatment; (F) Quantity per group; (G) Each acupuncture time; (H) Total number of acupunctures.
3.3 Quality assessment
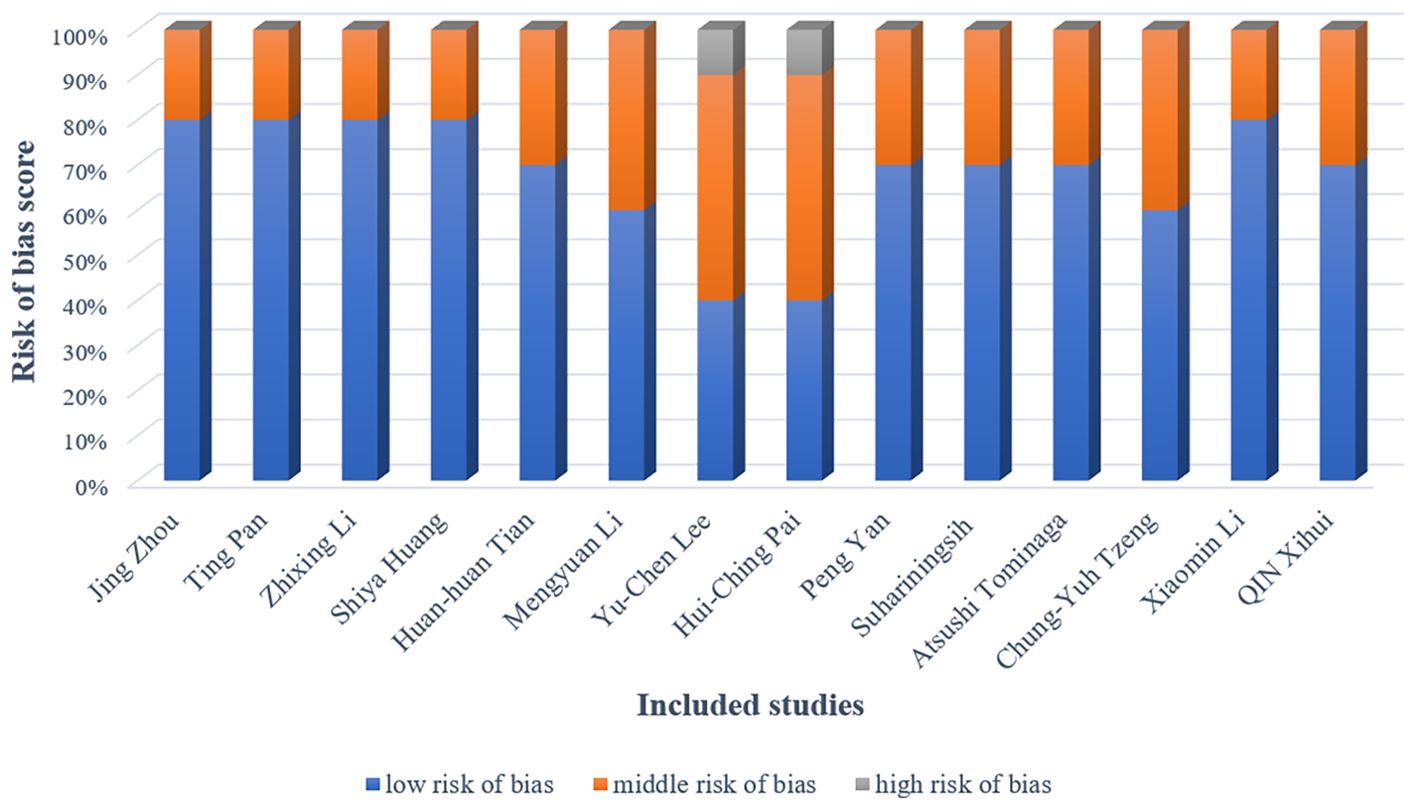
The methodological quality of included studies was rigorously evaluated using the CAMARADES checklist for bias assessment. Figure 3 provides a detailed chart of the study quality assessment; In all studies, the basic characteristics of the animals were not significantly different. The overall quality of these studies was found to be moderate or higher. However, most of the studies did not describe the details of the trials in detail, especially regarding the randomization method and blinding. Blinding of the experimenter was not possible because the test groups were acupuncture, it is worth noting that two study did not detail the random allocation method. And one study did not describe all possible prognostic factors or animal characteristics.
3.4 Blood glucose
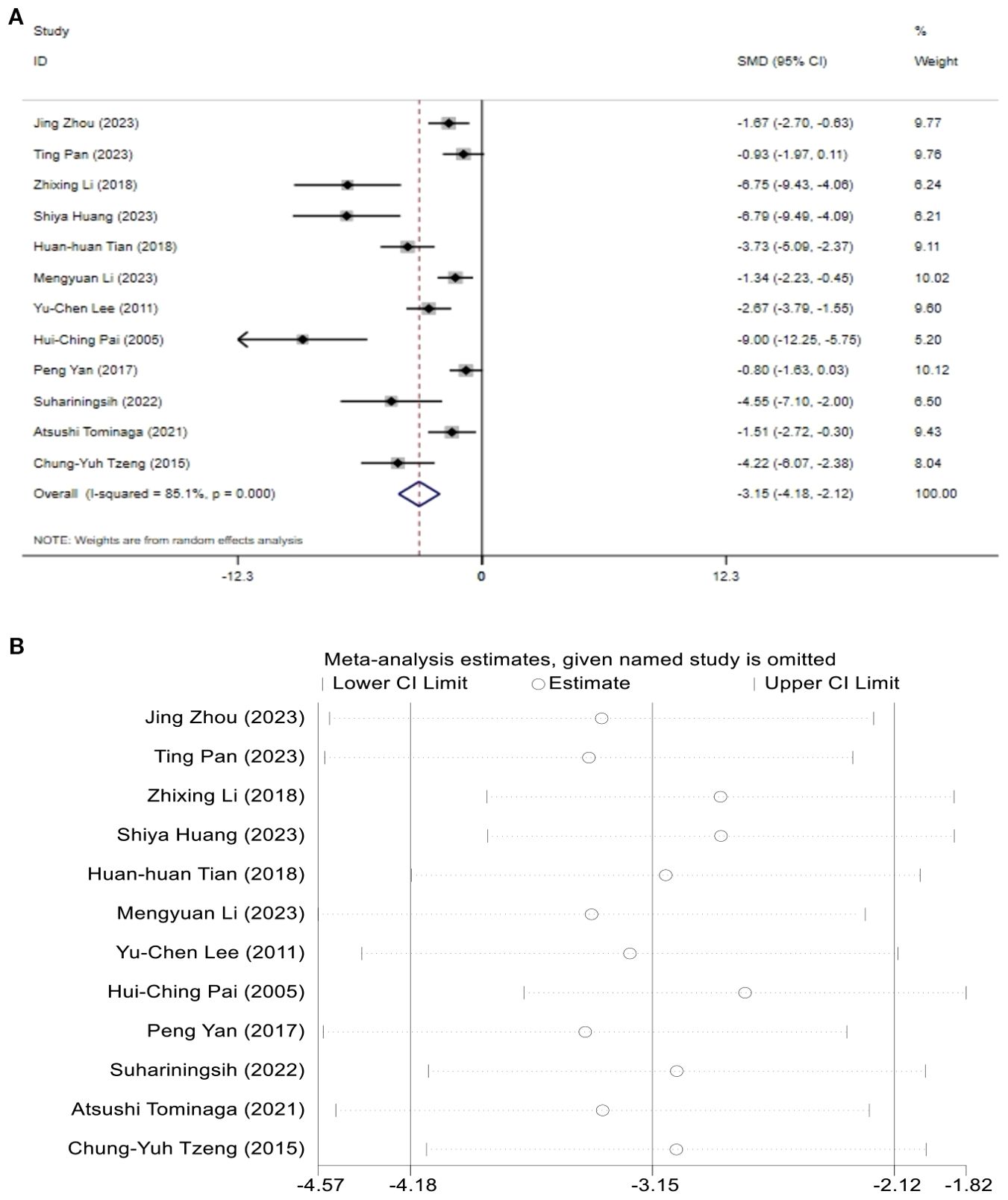
A total of 12 studies assessed the effect of BG. The results indicated that the levels of BG in the T2DM model group increased, while after acupuncture treatment, BG levels showed a significant reduction compared to the T2DM model group. [SMD = -3.15, 95% CI (-4.18, -2.12), I2 = 85.1%] (P < 0.05) (Figure 4A). Sensitivity analysis showed that the combined effect estimates of all studies were within the confidence interval of the overall effect, indicating the reliability of the study results (Figure 4B).
3.5 Body weight
Seven studies assessed the effect of BW, demonstrating that acupuncture can reduce weight. A random effects model was used, and the meta-analysis showed that acupuncture significantly reduces BW in an animal model of T2DM. [SMD = -3.36, 95%CI (-4.77, -1.95), I2 = 84.2%] (P < 0.05) (Figure 5A). Sensitivity analysis indicated that the combined effect estimates of all studies fell within the confidence interval of the overall effect, demonstrating the reliability of the study results (Figure 5B).
3.6 Triglyceide
Six studies investigated the regulation of triglyceride levels by acupuncture. Due to an I² value of less than 50, a fixed-effects model was applied for the analysis. Interestingly, following acupuncture treatment, a significant reduction in triglyceride levels was observed in the diabetic mouse model. Meta-analysis results indicated that acupuncture significantly reduced triglycerides in this animal model of T2DM. [SMD=-2.50, 95% CI (-3.00, -2.01), I2 = 0.0%], (P < 0.05) (Figure 6A), and sensitivity analysis confirmed the robustness of the Triglyceride conclusion (Figure 6B).
3.7 Total cholesterol
Seven studies evaluated the effect of TC, indicating that acupuncture can lower TC levels. A random effects model was employed, and the meta-analysis revealed a significant reduction in TC with acupuncture in an animal model of T2DM. [SMD = -2.60, 95% CI (-3.55,-1.65), I² = 74.9%](P < 0.05) (Figure 7A). Sensitivity analysis further validated the strength of the LDL-C findings (Figure 7B).
3.8 High-density lipoprotein cholesterol
The impact of HDL was documented in six studies. Analysis utilizing a random effects model revealed a notable decline in HDL levels within the diabetic mouse model [SMD = 0.61, 95% CI (-0.98, 2.19), I² = 92.1%] (P> 0.05) (Figure 8A). No statistically significant difference was observed in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels following acupuncture treatment in this T2DM animal model. Sensitivity analysis affirmed the robustness of the HDL findings (Figure 8B).
3.9 Low-density cholesterol
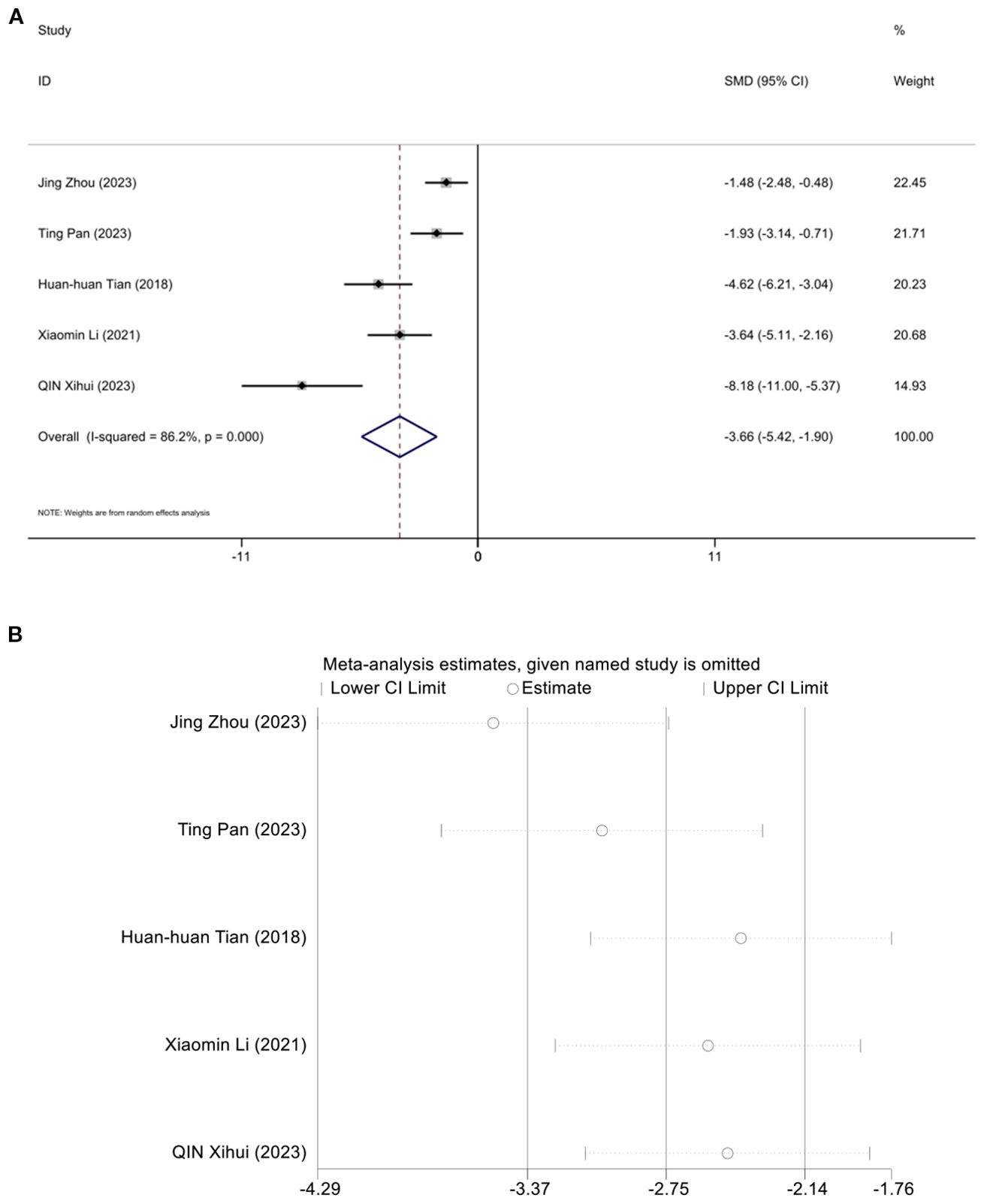
Five studies assessed the effect of LDL-C, demonstrating that acupuncture can reduce LDL-C. A random effects model was used, and the meta-analysis showed that acupuncture significantly reduces LDL-C in an animal model of T2DM. [SMD = -3.36, 95%CI (-5.42,-1.95), I2 = 86.2%] (P < 0.05) (Figure 9A). And sensitivity analysis confirmed the robustness of the LDL-C conclusion (Figure 9B).
3.10 Heterogeneity
As shown in Figure 10, investigate the sources of heterogeneity, we selected four indicators: triglycerides (Figure 10A), total cholesterol (Figure 10B), body weight (Figure 10C), and blood glucose (Figure 10D), and conducted Egger’s test. The results of Egger’s test indicated the presence of publication bias in the included studies. Subsequently, we further analyzed potential sources of heterogeneity. Subsequently, we further analyzed the potential sources of heterogeneity. Animal species, acupuncture treatment duration, and timing of acupuncture intervention may be potential sources of heterogeneity. To further elucidate these sources, we performed a subgroup analysis on blood glucose, body weight, total cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein levels.
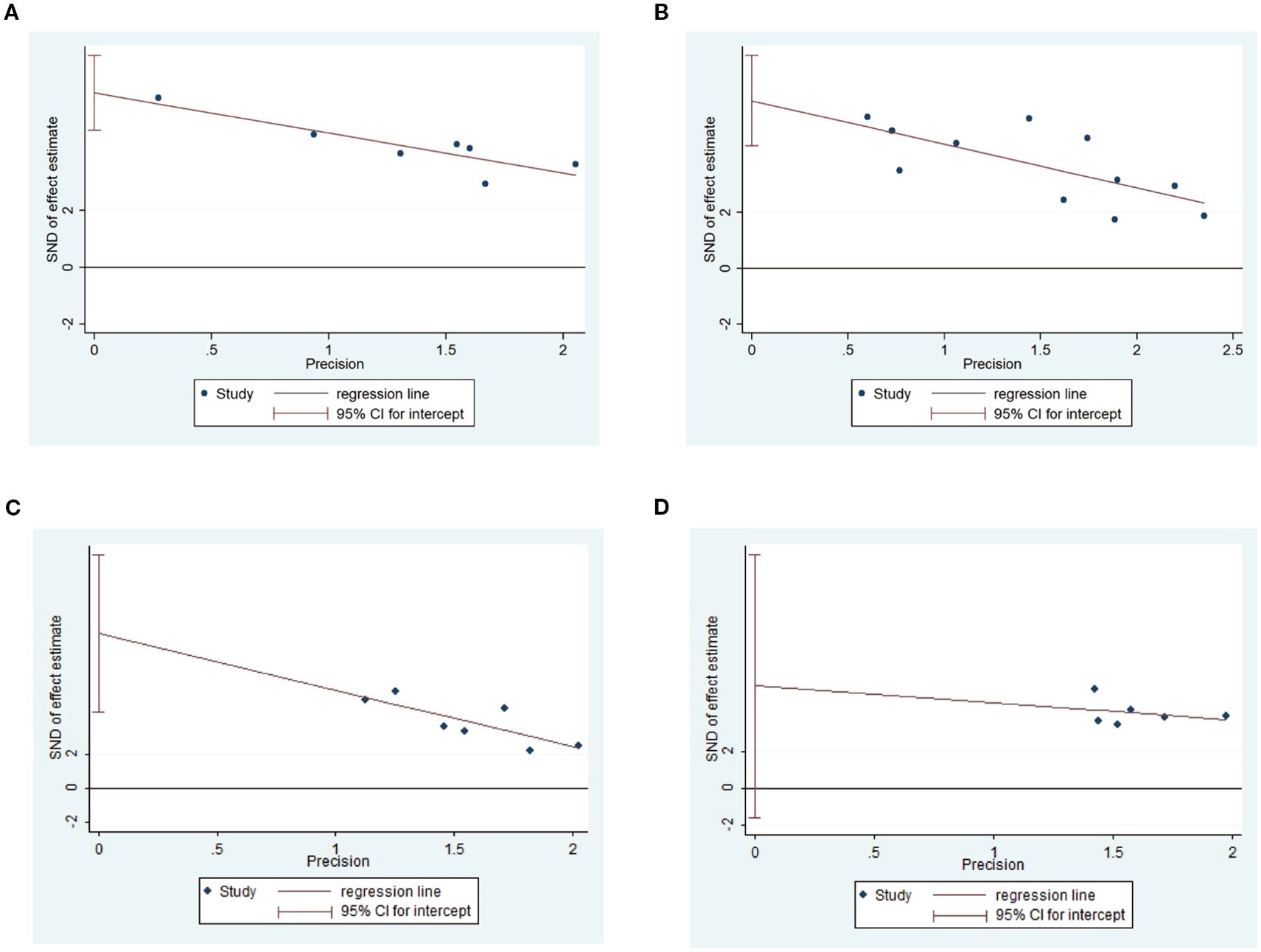
Figure 10. Egger’s test of Triglyceide (A), total cholesterol (B), body weight (C) and blood glucose (D).
3.11 subgroup analysis
3.11.1 Blood glucose
Figure 11 displays subgroup analyses of blood glucose levels stratified by model species (A), animal model establishment (B), treatment duration (C), and treatment timing (D), Subgroup meta-analysis of the model species (SD rats, Wistar rats, and mice) in the test group showed that the SD rat subgroup. [SMD = -3.02,95% CI (-4.59, -1.46); I² = 88.1% (P < 0.001)]; for the Wistar rat subgroup.[SMD = -2.71,95% CI (-5.83, 0.40); I² = 81.6% (P < 0.05)]; and for the mice subgroup.[SMD= -3.87 [95% CI (-5.99, - 1.75); I² = 85.5% (P < 0.001)] (Figure 11A). Subgroup meta- analysis of induction methods (LZ, high - fat sugar diet, STZ) showed that for LZ-induced subgroup. [SMD = -4.07, 95% CI (-9.08, 0.94), I² = 91.7% (P < 0.01)]; for high - fat sugar diet subgroup, [SMD = -2.68, 95% CI (-5.05, -0.31), I² = 87.3% (P < 0.001)]; for STZ-induced subgroup. [SMD = -3.30, 95% CI (-4.70, -1.90), I² = 86.5% (P < 0.001)] (Figure 11B). Subgroup meta-analysis of gestational age groups (<28times and ≥28times) showed that for the <28times subgroup. [SMD = -3.40, 95% CI (-4.78, -2.03); I² = 85.8% (P< 0.001)]; and for the ≥28times subgroup. [SMD = -2.85, 95% CI (-4.69, -1.00); I² = 87.7% (P< 0.001)] (Figure 11C). Subgroup meta-analysis of studies by modeling method showed that for the “After modeling” subgroup, [SMD = -2.86, 95% CI (-3.85, -1.87); I² = 83.8% (P < 0.001)]; and for the “Simultaneous” subgroup, [SMD = -6.79, 95% CI (-9.49, -4.09) (Figure 11D).
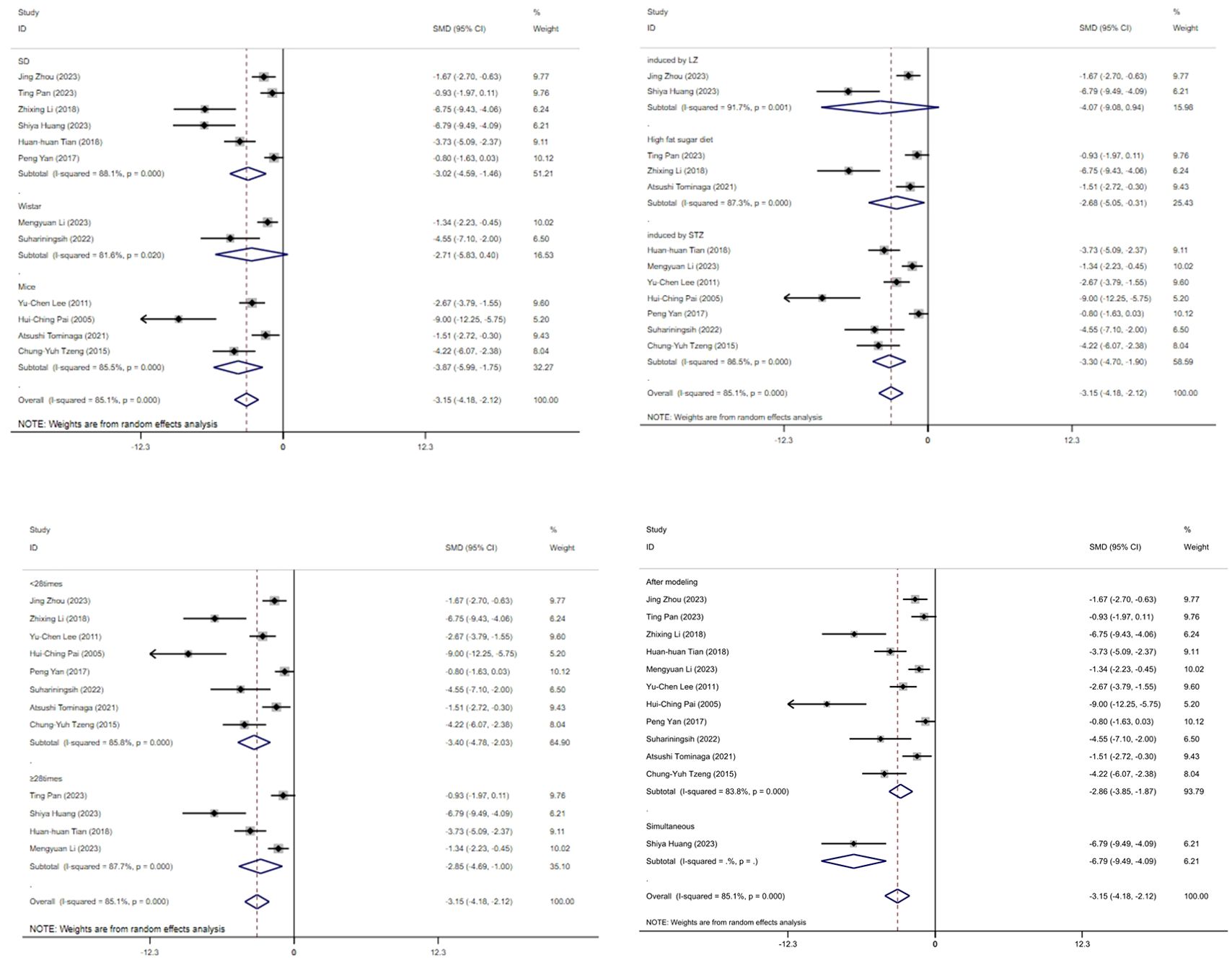
Figure 11. Subgroup analysis of blood glucose. (A) Model species; (B) Establishment of animal model; (C) The duration of treatment; (D) Timing of treatment.
3.11.2 Body weight
Figure 12 displays subgroup analyses of body weight stratified by model species (A), establishment of animal model (B), the duration of treatment (C)and timing of treatment (D). Subgroup meta-analysis of the model species (SD rats, mice) in the test group showed that for the SD rat subgroup, [SMD = -3.87, 95% CI (-5.62, -2.12); I² = 85.5% (P < 0.001)]; and for the mice subgroup, [SMD = -1.76, 95% CI (-2.72, -0.81)] (Figure 12A). Subgroup meta-analysis of induction methods (LZ, high-fat sugar diet, STZ) showed that for the LZ-induced subgroup, [SMD = -3.74, 95% CI (-5.86, -1.61); I² = 67.6% (P = 0.079)]; for the high-fat sugar diet subgroup, [SMD = -2.23, 95% CI (-3.60, -1.05); I² = 45.3% (P = 0.176)]; and for the STZ -induced subgroup, [SMD = -5.46, 95% CI (-9.20, -1.72); I² = 93.3% (P < 0.001)] (Figure 12B). Subgroup meta-analysis of time point groups (<28times, ≥28times) showed that for the <28 times subgroup, [SMD = -3.40, 95% CI (-4.78, -2.20); I² = 85.8% (P < 0.001)]; and for the ≥28times subgroup, [SMD = -4.35, 95% CI (-6.56, -1.14); I² = 88.8% (P < 0.001)] (Figure 12C). Subgroup meta - analysis of studies by modeling method showed that for the “After modeling” subgroup, [SMD = -3.07, 95% CI (-4.54, -1.60); I² = 84.5% (P < 0.001)]; and for the “Simultaneous” subgroup, [SMD = -5.00, 95% CI (-7.10, -2.90) (Figure 12D).
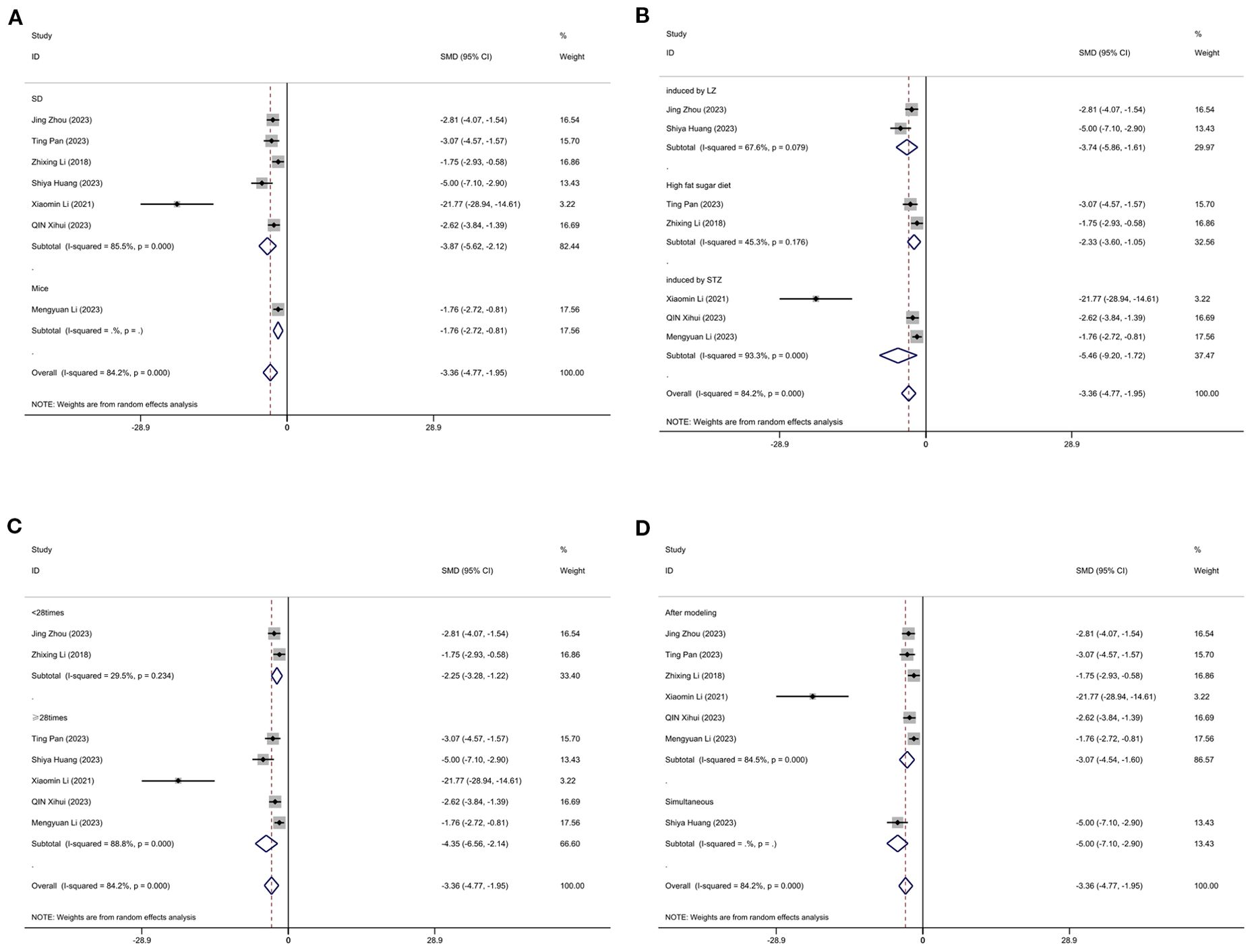
Figure 12. Subgroup analysis of body weight. (A) Model species; (B) Establishment of animal model; (C) The duration of treatment; (D) Timing of treatment.
3.11.3 Total cholesterol
Figure 13 displays subgroup analyses of total cholesterol stratified by model species (A), establishment of animal model (B), the duration of treatment (C) and timing of treatment (D). Subgroup meta-analysis of the model species (SD, mice) in the test group showed that for the SD subgroup, [SMD = -2.59, 95% CI (-3.72, -1.46); I² = 78.4% (P < 0.001)]; and for the mice subgroup, [SMD = -2.77, 95% CI (-3.91, -1.62)] (Figure 13A). Subgroup meta - analysis of establishment methods (induced by LZ, high fat sugar diet, induced by STZ) showed that for the LZ-induced subgroup, [SMD = -1.23, 95% CI (-1.95, -0.51); I² = 0% (P = 0.961)]; for the high fat sugar diet subgroup, [SMD = -2.33, 95% CI (-3.25, -1.40); I² = 0% (P = 0.749)]; and for the STZ - induced subgroup, [SMD = -3.85, 95% CI (-5.16, -2.55); I² = 57.8% (P = 0.093)] (Figure 13B). Subgroup meta - analysis of treatment duration groups (<28 times, ≥28 times) showed that for the <28 times subgroup, [SMD = -1.77, 95% CI (-2.97, -0.57); I² = 53.4% (P = 0.143)]; and for the ≥28 times subgroup, [SMD = -2.96, 95% CI (-4.21, -1.70); I² = 77.7% (P < 0.001)] (Figure 13C). Subgroup meta-analysis of studies by treatment timing showed that for the “After modeling” subgroup, [SMD = -2.86, 95% CI (-3.89, -1.82); I² = 73.8% (P < 0.01)]; and for the “Simultaneous” subgroup, [SMD = -1.21, 95% CI (-2.29, -0.13)] (Figure 13D).
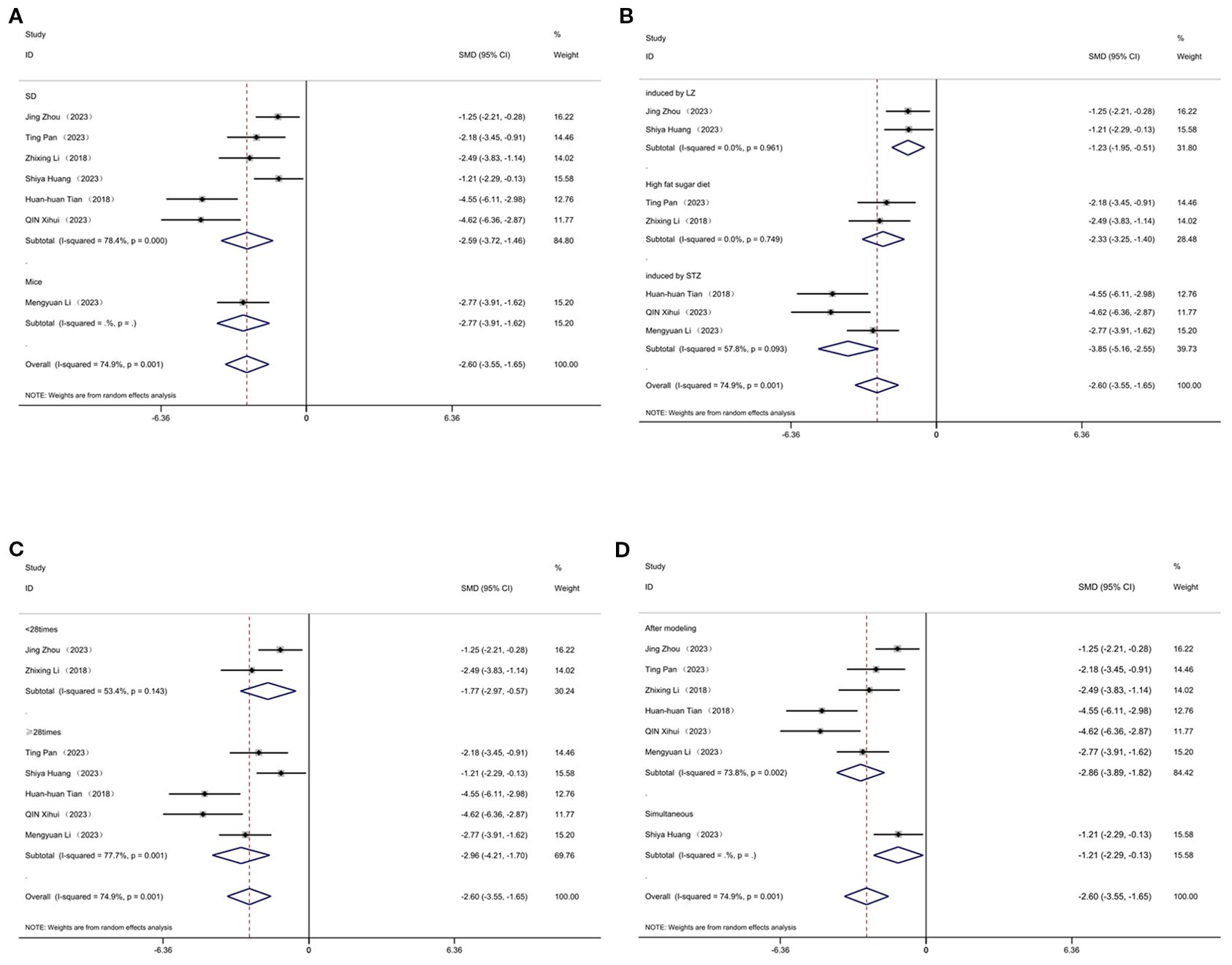
Figure 13. Subgroup analysis of cholesterol. (A) Model species; (B) Establishment of animal model; (C) The duration of treatment; (D) Timing of treatment.
3.11.4 Low-density cholesterol
Figure 14 displays subgroup analyses of blood LDL stratified by establishment of animal model (A) and the duration of treatment (B). Subgroup meta-analysis of the establishment of animal model (induced by LZ, high fat diet, induced by STZ, high fat sugar diet) showed that for the induced by LZ subgroup, [SMD = -1.48, 95% CI (-2.48, -0.48)]; for the high fat diet subgroup, [SMD = -2.73, 95% CI (-4.40, -1.05); I² = 67.6% (P = 0.079)]; and for the induced by STZ subgroup, [SMD = -6.21, 95% CI (-9.67, -2.74); I² =78.6% (P = 0.031)] (Figure 14A). Subgroup meta-analysis of the duration of treatment groups (<28times, ≥28times) showed that for the <28times subgroup, [SMD = -1.48, 95% CI (-2.48, -0.48)]; and for the ≥28times subgroup, [SMD = -4.31, 95% CI (-6.38, -2.24); I² = 84.3% (P < 0.001)] (Figure 14B).
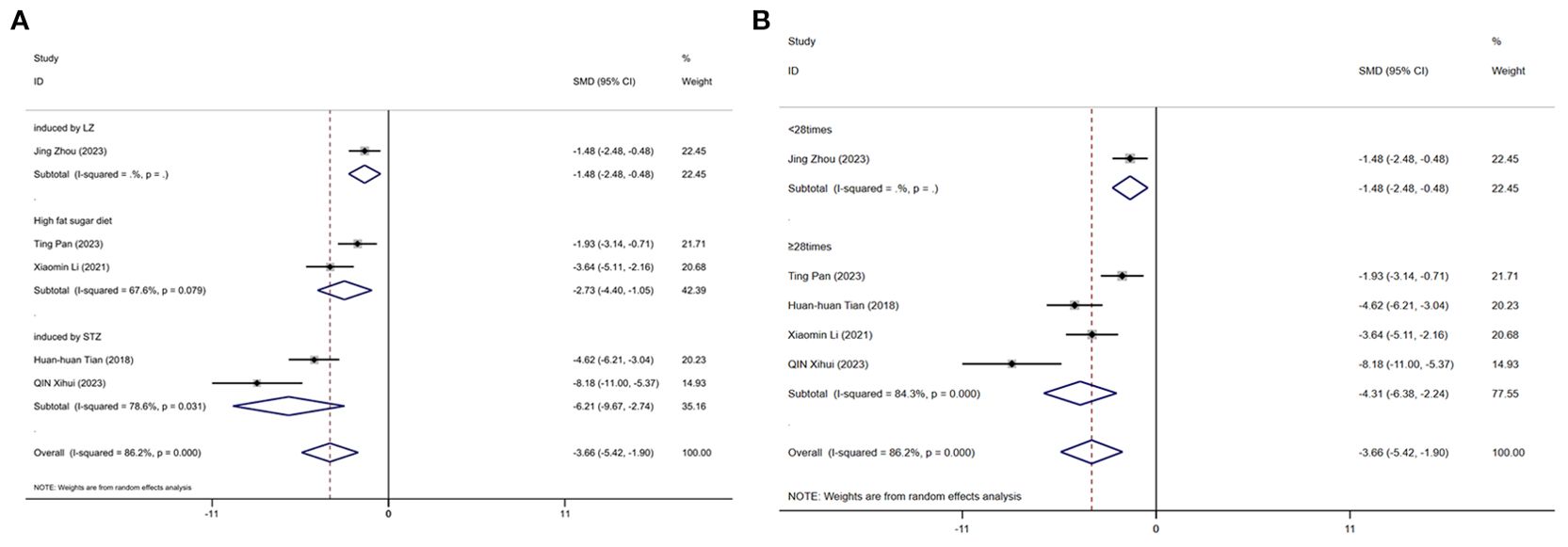
Figure 14. Subgroup analysis of blood Low-density cholesterol. (A) Establishment of animal model; (B) The duration of treatment.
4 Discussion
4.1 Principle findings
The objective of this research was to summarize and evaluate the use of acupuncture to improve blood glucose and lipid levels in the animal model of T2DM. In this study, we systematically gathered information from 14 acupuncture studies animal models of T2DM to determine, whether acupuncture can improve blood glucose and lipid levels, we found that acupuncture was closely associated with decreased BW, TC, TG and LDL, that acupuncture could significantly improve the level of blood glucose in animal with T2DM, which confirms previous reports (37). Diabetes is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by chronically elevated blood glucose levels. It disrupts glucolipid metabolism, resulting in dyslipidemia, which elevates the risk of cardiovascular disease. Glucolipid metabolism disorders cause serum levels of TC, TG and LDL-C to rise (38, 39). The meta-analysis revealed that compared to the model group, acupuncture significantly reduced blood glucose levels in diabetic animals. Both the experimental and model groups exhibited hyperglycemia prior to acupuncture treatment, but the hyperglycemic condition in the experimental group improved following acupuncture intervention; therefore, the meta-analysis showed that acupuncture intervention in T2DM animal models could effectively reduce the serum levels of TC, TG, and LDL-C and improve the lipid metabolism of T2DM animals to some extent. However, there was high heterogeneity in the analysis results, Subgroup analysis showed that intervention time, modeling methods, animal species, and duration were sources of heterogeneity.
Subgroup analyses yielded valuable insights. For body weight and cholesterol, subgroups with high-fat diet (HFD) models or combined HFD and STZ models generally exhibited larger effect sizes compared to those with letrozole-induced models, indicating that the underlying pathophysiology of the animal model can significantly influence the responsiveness to acupuncture treatment. Likewise, treatment durations shorter than 28 days seemed to result in more consistent improvements in body weight, which may be attributed to the acute-phase responsiveness of metabolic parameters in animal models. These observed trends are in line with previous research that found electroacupuncture had greater insulin-sensitizing effects in diet-induced insulin resistance models than in chemically induced β-cell injury models (40), and with Wang et al. (41) reporting that the modulation of gut microbiota by acupuncture was more prominent in HFD-fed mice, supporting our finding of model-dependent variability. Species selection did not emerge as a major factor determining the effect size. This is consistent with the understanding that the metabolic and neuroendocrine pathways targeted by acupuncture are conserved across rodent models (42). However, species-specific differences in lipid metabolism need to be taken into account in translational research.
Our findings emphasize the significance of carefully selecting appropriate animal models and optimizing treatment duration in preclinical acupuncture studies. These two parameters may also have implications for the design of clinical protocols, as the patient’s metabolic phenotype and the treatment course could potentially influence therapeutic outcomes.
4.2 Mechanistic insights into acupuncture for T2DM
4.2.1 Neural mechanisms
The autonomic nervous system regulates pancreatic islet function through sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation. Parasympathetic activity promotes insulin secretion, whereas sympathetic input generally exerts inhibitory effects. Acupuncture has been shown to modulate the pancreatic intrinsic nervous system (PINS) and associated neuropeptides, such as Substance P and CGRP, thereby improving β-cell function (43). Electroacupuncture at ST25 has also been reported to enhance TRPV1 pathway activity, leading to improved glucose metabolism (13). Moreover, transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation reduces food intake and weight gain in high-fat diet mice via an orexin-dependent pathway (K. 44), suggesting that acupuncture exerts neuromodulatory effects on energy metabolism. Collectively, acupuncture may regulate β-cell function through vagus nerve activity, PINS, and neuropeptide signaling, while auricular vagus pathways may modulate appetite and body weight, highlighting the importance of neural mechanisms in acupuncture-mediated intervention for diabetes.
4.2.2 Endocrine mechanisms
Acupuncture improves insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake by modulating the PI3K/AKT/GLUT4 signaling pathway (45, 46). This effect involves the upregulation of IRS-1, PI3K, AKT, and GLUT4 expression, while also enhancing mitochondrial function and energy metabolism through the AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α axis (47). In addition, acupuncture regulates lipid metabolism via the AMPK/ACC pathway, producing significant metabolic benefits in diabetes complicated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) (48). Furthermore, acupuncture influences the BDNF pathway, thereby ameliorating comorbid diabetes and depression (44), suggesting a dual regulatory effect on the metabolic–neuroendocrine axis. Collectively, acupuncture acts through PI3K/AKT/GLUT4 and AMPK-related pathways to enhance insulin sensitivity and energy metabolism, while also modulating BDNF signaling to improve metabolic and neuropsychiatric comorbidities.
4.2.3 Immune mechanisms
Inflammatory cytokines and immune dysregulation play pivotal roles in the pathogenesis of diabetes. SIRT1 reduces the expression of inflammatory factors such as TNF-α and IL-6 by inhibiting NF-κB signaling, thereby ameliorating insulin resistance (49). Acupuncture may exert anti-inflammatory effects via this mechanism (50). Additionally, acupuncture can regulate immune–metabolic crosstalk through miRNA modulation. For instance, acupuncture treatment protects patients with diabetes and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) via the miR-32-3p/PLA2G4A pathway (51). Furthermore, acupuncture mitigates inflammatory responses and immune-related damage in diabetic complications, such as diabetic nephropathy and cognitive impairment (52). Thus, acupuncture exerts beneficial effects on diabetes and its complications by modulating inflammation and immunity through SIRT1/NF-κB and miRNA-related pathways.
4.2.4 Gut microbiota-related mechanisms
The gut microbiota is closely linked to metabolic diseases. EA improves insulin resistance by reshaping gut microbial composition, such as increasing the abundance of Akkermansia (15). In addition, acupuncture regulates gut–brain axis function via the PI3K/Akt pathway, influencing ghrelin and peptide YY expression, thereby affecting feeding behavior and energy metabolism (46). Acupuncture also enhances gut barrier integrity by upregulating tight junction proteins, reducing inflammation, and mitigating metabolic dysregulation (53). These findings suggest that acupuncture exerts antidiabetic effects by modulating gut microbiota composition, improving intestinal barrier function, and regulating gut–brain axis signaling, ultimately restoring glucose and lipid homeostasis.
4.2.5 Autophagy-related mechanisms
Dysregulated autophagy is strongly associated with diabetes onset and progression. Acupuncture restores hepatic autophagy through the AMPK/mTOR pathway, thereby ameliorating NAFLD associated with diabetes (45). In the nervous system, acupuncture enhances mitochondrial autophagy, improving cognitive dysfunction in diabetes. Moreover, acupuncture modulates endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy processes to attenuate cognitive impairment in diabetic models (54). Collectively, acupuncture activates AMPK/mTOR and mitochondrial autophagy pathways to alleviate diabetes-related hepatic and neurological damage, underscoring the importance of autophagy in acupuncture therapy for diabetes.
4.2.6 Advances and limitations
Research on acupuncture for diabetes has gradually expanded from clinical efficacy observation to mechanistic studies at the molecular, neuroendocrine, immunological, gut microbiota, and autophagy levels. Evidence indicates that acupuncture exerts multi-target and multi-pathway regulatory effects: modulating central and autonomic neural circuits, enhancing insulin signaling, regulating immune–inflammatory responses, reshaping gut microbiota, and restoring autophagic balance. Nevertheless, current studies face limitations. Most findings are derived from animal models or small-scale clinical trials, lacking large-scale, multicenter randomized controlled trials to confirm reproducibility and clinical value. Moreover, although classical pathways such as PI3K/Akt, AMPK/mTOR, and NF-κB have been implicated, discrepancies remain due to differences in study design and acupoint selection (46, 48, 51). Individual variations in gut microbiota and immune regulation also suggest that acupuncture efficacy may have personalized characteristics, but precision-medicine–oriented research is still lacking. Furthermore, standardized treatment protocols, dose–response relationships, and long-term follow-up studies remain underdeveloped.
In conclusion, acupuncture demonstrates a unique advantage in integrative, multi-level regulation for T2DM management. Future research should focus on conducting large-scale RCTs, applying multi-omics approaches (transcriptomics, metabolomics, microbiomics), investigating individual variability to advance precision acupuncture strategies, and integrating neuroimaging and neuromodulation techniques to further elucidate central mechanisms of acupuncture.
4.3 Implications for further research
T2DM is a prevalent metabolic disorder characterized by endocrine dysregulation arising from multifactorial pathogenesis (10). Within this framework, closely intertwined insulin resistance and dyslipidemia constitute key drivers of disease progression (55). Our meta-analysis demonstrates acupuncture’s efficacy in modulating glycemic and lipidemic profiles in diabetic rodent models. These findings align with recent mechanistic evidence: Luo et al.’s (56) systematic review identified insulin signaling potentiation and AMPK-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis as core pathways underlying acupuncture’s antidiabetic effects. While our study primarily evaluates metabolic outcomes, this mechanistic coherence enhances the biological plausibility of our results (56). Nevertheless, several limitations in current experimental designs warrant acknowledgment. Firstly, most studies focus on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, with relatively few investigations addressing Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Additionally, while induced models are frequently utilized, spontaneous models are less common. The complexity of the pathogenesis of human diabetes poses challenges in replicating its symptoms and underlying mechanisms, as it is influenced by various factors. Therefore, there is a need to improve relevant animal models and conduct clinical research to explore the efficacy of acupuncture in treating diabetes. Secondly, on the clinical front, although acupuncture shows potential for managing diabetes, the underlying molecular mechanisms remain unclear. Most existing research revolves around acupuncture treatment for T2DM; however, there is a lack of direct evidence supporting the effectiveness of acupuncture in improving blood glucose levels in patients with T1DM. While many studies indicate beneficial effects of acupuncture for diabetic patients, the majority are non-randomized controlled trials with small sample sizes and limited scope. There is a notable absence of large-scale, multi-center randomized controlled trials demonstrating the efficacy and safety of acupuncture in diabetes management.
4.4 Strengths and limitations of the research
To our knowledge, our study presents the first systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy of acupuncture in treating animal models of DM, which provides scientific evidence that acupuncture can improve blood glucose and lipid levels in these models. Although there was heterogeneity among the results of the analyzed studies, exploratory meta-regression suggested that smaller sample sizes might contribute to variability in effect estimates, although statistical significance was not reached. This aligns with the general observation that underpowered studies may yield unstable results, underscoring the need for larger preclinical experiments. The study is subject to the following limitations: Firstly, the search was restricted to only English-language databases, potentially limiting the comprehensiveness of the systematic evaluation due to the restricted pool of studies. Secondly, the exclusion of non-English language studies may hinder a comprehensive understanding of acupuncture’s efficacy in T2DM treatment, potentially impacting the accuracy of the analysis results. Thirdly, the lack of description regarding blinding in animal experiments and the exclusive focus on murine species in the included literature may introduce a risk of false positive results. While our study has its scope limitations, the analysis of blood glucose and lipid metabolism allows for the first assessment of acupuncture’s efficacy in the animal model of T2DM, which carries meaningful implications. Sex information was missing in most included studies; where reported, male animals were predominantly used, potentially limiting generalizability. Future studies should follow the NIH ‘Sex as a Biological Variable’ policy to ensure balanced representation and transparent reporting. As a traditional medical treatment, corresponding measures of variability acupuncture has not yet established and internationally accepted standardized treatment protocol, which hinders its widespread application in clinical settings. This issue must be addressed in future work. It is undeniable that our research has certain limitations. There exists heterogeneity in the design of animal studies and clinical trials; although subgroup analyses were conducted, the sources of this heterogeneity remain unclear. Furthermore, not all included studies are of high quality, which may affect the assessment of acupuncture’s efficacy. The implementation of blinding in acupuncture studies also presents challenges. While factors such as sex and age play significant roles in the development of diabetes, very few experimental designs take these variables into account. Therefore, it is recommended that future experimental research standardize protocols, considering potential influencing factors such as sex, age, and disease stage. This will facilitate the exploration of different acupuncture treatment methods for diabetes and provide a solid preliminary foundation for large-scale, multi-center high-quality randomized controlled trials.
5 Conclusion
A systematic review and meta-analysis have revealed that acupuncture confers notable protective benefits for animals with T2DM. When compared to control groups, acupuncture significantly improved blood glucose, body weight, total cholesterol, triglycerides, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in animals with diabetes mellitus. Nonetheless, this study faces several limitations stemming from the inadequate number of included studies, methodological shortcomings, and insufficient sample sizes. To fully elucidate acupuncture’s effects in T2DM animals, further research involving larger samples and higher-quality methodologies is imperative. We look forward to future investigations exploring the therapeutic potential of acupuncture and trust that this review will serve as a valuable reference in advancing this area of study.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Author contributions
LL: Writing – original draft. SL: Data curation, Writing – original draft. ZG: Methodology, Writing – original draft. PF: Writing – original draft. YF: Software, Writing – original draft. CQ: Methodology, Writing – original draft. MW: Visualization, Writing – original draft. LX: Validation, Writing – review & editing. MC: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. TW: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Annual Special Research Project of the Huatuo Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Anhui Province (Fund Number: YLFW2305), Annual Key Research Project of Universities in Anhui Province (Fund Number: 2023AH050844), Annual High-Level Inheritance Talent Support Project in Anhui Province (Fund Number: Wan Chinese Medicine Development Secret (2024) No. 1), The Science and Technology Development Fund, Macau SAR (file No.0114/2022/A,0018/2024/RIA1), Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation(No:2024A1515140022), GrandC of China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grant Number GZ20252617, The Science and Technology Development Fund, Macau SAR (file No.0114/2022/A,0018/2024/RIA1).
Acknowledgments
This article was completed under the guidance of Min Chen and Tao Wang. We extend our special thanks to them for their invaluable guidance and assistance.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Schmidt AM. Highlighting diabetes mellitus: the epidemic continues. Arteriosc Thromb Vasc Biol. (2018) 38(1):e1–8. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.310221
2. Ong KL, Stafford LK, McLaughlin SA, Boyko EJ, Vollset SE, Smith AE, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of diabetes from 1990 to 2021, with projections of prevalence to 2050: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2021. Lancet. (2023) 402:203–34. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)01301-6
3. Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the international diabetes federation diabetes atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2019) 157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843
4. Nauck MA, Wefers J, and Meier JJ. Treatment of type 2 diabetes: challenges, hopes, and anticipated successes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2021) 9:525–44. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00113-3
5. Shrestha SS, Honeycutt AA, Yang W, Zhang P, Khavjou OA, Poehler DC, et al. Economic costs attributable to diabetes in each U.S. State. Diabetes Care. (2018) 41:2526–34. doi: 10.2337/dc18-1179
6. Unnikrishnan R, Anjana RM, and Mohan V. Diabetes mellitus and its complications in India. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2016) 12:357–70. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2016.53
7. Baye AM, Fanta TG, Siddiqui MK, and Dawed AY. The genetics of adverse drug outcomes in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review. Front Genet. (2021) 12:675053. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.675053
8. Arnold SV, Inzucchi SE, Echouffo-Tcheugui JB, Tang F, Lam CSP, Sperling LS, et al. Understanding contemporary use of thiazolidinediones. Circulat: Heart Failure. (2019) 12:e005855. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.118.005855
9. Chen R, Ma K, Li S, Zhou X, and Chen H. Protective effects and mechanisms of opuntia polysaccharide in animal models of diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Ethnopharmacol. (2023) 312:116490. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116490
10. Kolb H and Martin S. Environmental/lifestyle factors in the pathogenesis and prevention of type 2 diabetes. BMC Med. (2017) 15:131. doi: 10.1186/s12916-017-0901-x
11. Wu L, Chen X, Liu Y, Lan J, Wu C, Li Z, et al. Role of acupuncture in the treatment of insulin resistance: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Complement Therapies Clin Pract. (2019) 37:11–22. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2019.08.002
12. Chen H, Zhang Z-L, Wang X, and Yang Y-Q. Effect of ‘Spleen-stomach harmonizing’ Needling on insulin resistance and expression of insulin receptor substrate-1, -2, and glucose transporter-4 in insulin resistance type 2 diabetes rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu = Acupunct Res. (2017) 42:197–201.
13. Xu T, Yu Z, Liu Y, Lu M, Gong M, Li Q, et al. Hypoglycemic effect of electroacupuncture at ST25 through neural regulation of the pancreatic intrinsic nervous system. Mol Neurobiol. (2022) 59:703–16. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02609-1
14. Cao L, Zhou S, Li J, Chen K, Xue X, and Yi W. Effects of electroacupuncture on intestinal microflora and plasma metabolites in an insulin-resistant mouse model of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acupunct Med: J Br Med Acupunct Soc. (2024) 42:76–86. doi: 10.1177/09645284231207871
15. Pan T, Li X, Guo X, Wang H, Zhou X, Shang R, et al. Electroacupuncture improves insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mice by regulating intestinal flora and bile acid. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes: Targets Ther. (2023) 16:4025–42. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S421134
16. Liu Y, Xu T, Wang X, Lu M, Wang Y, Song X, et al. Neuromechanical dimorphism of hypoglycemic effect of electroacupuncture. Neuroendocrinology. (2023) 113:679–91. doi: 10.1159/000529019
17. Belivani M, Dimitroula C, Katsiki N, Apostolopoulou M, Cummings M, and Hatzitolios AI. Acupuncture in the treatment of obesity: A narrative review of the literature. Acupunct Med. (2013) 31:88–97. doi: 10.1136/acupmed-2012-010247
18. Zhang Y-h. Treatment of 35 cases with type 2 diabetes mellitus by acupuncture-moxibustion therapy. J Acupunct Tuina Sci. (2010) 8:300–1. doi: 10.1007/s11726-010-0432-x
19. Fan X-L, Yu M-L, Fu S-P, Zhuang Y, and Lu S-F. Effectiveness of acupuncture in treatment of simple obesity in animal models: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Evidence-Based Complement Altern Med. (2019) 2019:1–36. doi: 10.1155/2019/5459326
20. Xiao LY, Li Z, Du YZ, Shi HY, Yang SQ, Zhang YX, et al. Acupuncture for hypertension in animal models: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Evidence-Based Complement Altern Med. (2021) 2021:8171636. doi: 10.1155/2021/8171636
21. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ (Clinical Res ed). (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
22. Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Chandler J, Welch VA, Higgins JPT, et al. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: A new edition of the cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions” ed. Cochrane editorial unit. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2019) 10(10):ED000142. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000142
23. Hooijmans CR, IntHout J, Ritskes-Hoitinga M, and Rovers MM. Meta-analyses of animal studies: an introduction of a valuable instrument to further improve healthcare. ILAR J. (2014) 55:418–26. doi: 10.1093/ilar/ilu042
24. Huang S, Yu C, Hu M, Wen Q, Wen X, Li S, et al. Electroacupuncture ameliorates hepatic defects in a rat model of polycystic ovary syndrome induced by letrozole and a high-fat diet. Acupunct Med. (2023) 42(2):87–99. doi: 10.1177/09645284231207863
25. Lee Y-C, Li T-M, Tzeng C-Y, Chen Y-I, Ho W-J, Lin J-G, et al. Electroacupuncture at the zusanli (ST-36) acupoint induces a hypoglycemic effect by stimulating the cholinergic nerve in a rat model of streptozotocine-induced insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Evidence-Based Complement Altern Med. (2011) 2011:1–6. doi: 10.1093/ecam/neq068
26. Li M, Yao L, He M, Huang H, Zheng H, Ma S, et al. ’Adjust zang and arouse spirit’ Electroacupuncture ameliorates cognitive impairment by reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress in Db/Db Mice. Front Endocrinol. (2023) 14:1185022. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1185022
27. Li X, Wu Z, Chen Y, Cai R, and Wang Z. Effect of acupuncture on simple obesity and serum levels of prostaglandin E and leptin in sprague-dawley rats. Comput Math Methods Med. (2021) 2021:1–6. doi: 10.1155/2021/6730274
28. Li Z, Lan D, Zhang H, Zhang H, Chen X, and Sun J. Electroacupuncture mitigates skeletal muscular lipid metabolism disorder related to high-fat-diet induced insulin resistance through the AMPK/ACC signaling pathway. Evidence-Based Complement Altern Med. (2018) 2018:1–8. doi: 10.1155/2018/7925842
29. Pai H-C, Tzeng C-Y, Lee Y-C, Chang C-H, Lin J-G, Cheng J-T, et al. Increase in plasma glucose lowering action of rosiglitazone by electroacupuncture at bilateral zusanli acupoints (ST.36) in rats. J Acupunct Meridian Stud. (2009) 2:147–51. doi: 10.1016/S2005-2901(09)60047-9
30. Peng Y, Lin Y-P, He F-E, Wan Q-Q, Chen W, Liu Q, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture on gastric motility, expressions of ghrelin and GHSR mRNA in gastric antrum tissue of diabetic gastroparesis rats. J Acupunct Tuina Sci. (2017) 15:88–93. doi: 10.1007/s11726-017-0981-3
31. Suhariningsih S, Glory S, Khaleyla F, Kusumawati HN, Septriana M, Susilo Y, et al. Ameliorative and renoprotective effect of electrical stimulation on blood sugar, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine levels, and the islets of langerhans weight in diabetic mice. Vet Med Int. (2022) 2022:e7922892. doi: 10.1155/2022/7922892
32. Tian H-H, Cao B-Y, Li R, Ma Y-j, Hu X-G, Jia N, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture stimulation at different spinal segmental levels in a rat model of diabetes mellitus. Acupunct Med. (2018) 36:29–35. doi: 10.1136/acupmed-2016-011131
33. Tominaga A, Ishizaki N, Naruse Y, Kitakoji H, and Yamamura Y. Repeated application of low-frequency electroacupuncture improves high-fructose diet-induced insulin resistance in rats. Acupunct Med. (2011) 29:276–83. doi: 10.1136/acupmed-2011-010006
34. Tzeng C-Y, Lee Y-C, Ho T-Y, Chen Y-I, Hsu T-H, Lin J-G, et al. Intracellular signaling pathways associated with the glucose-lowering effect of St36 electroacupuncture in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Acupunct Med. (2015) 33:395–99. doi: 10.1136/acupmed-2014-010718
35. Xihui QIN, Pang J, Xiong G, and Feng J. Bo′s abdominal acupuncture improves disordered metabolism in obese type 2 diabetic rats through regulating fibroblast growth factor 21 and its related adipokines. J Tradit Chin Med. (2023) 43:1200–8. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20231008.002
36. Zhou J, Yin P, Zhao Q, Hu Z, Wang Y, Ma G, et al. Electroacupuncture improves follicular development and metabolism and regulates the expression of adiponectin, AMPK and ACC in an obese rat model of polycystic ovary syndrome. Acupunct Med. (2023) 41:151–62. doi: 10.1177/09645284221107690
37. Li Y, Qian Z-Y, Cheng K, Zhao L, Shen X-Y, and Deng H-P. Effect of compound laser acupuncture-moxibustion on blood glucose, fasting insulin and blood lipids levels in type 2 diabetic rats. Chin J Integr Med. (2020) 26:33–8. doi: 10.1007/s11655-019-3084-9
38. Athyros VG, Doumas M, Imprialos KP, Stavropoulos K, Georgianou E, Katsimardou A, et al. Diabetes and lipid metabolism. Hormones. (2018) 17:61–7. doi: 10.1007/s42000-018-0014-8
39. Xiao R, Wang L, Tian P, Jin X, Zhao J, Zhang H, et al. The effect of probiotic supplementation on glucolipid metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients. (2023) 15:3240. doi: 10.3390/nu15143240
40. Martinez B and Peplow PV. Treatment of insulin resistance by acupuncture: A review of human and animal studies. Acupunct Med. (2016) 34:310–19. doi: 10.1136/acupmed-2016-011074
41. Wang H, Wang Q, Liang C, Pan L, Hu H, and Fang H. Acupuncture improved hepatic steatosis in HFD-induced NAFLD rats by regulating intestinal microbiota. Front Microbiol. (2023) 14:1131092. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1131092
42. Wang M-N, Zhai M-X, Wang Y-T, Dai Q-F, Liu L, Zhao L-P, et al. Mechanism of acupuncture in treating obesity: advances and prospects. Am J Chin Med. (2024) 52:1–33. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X24500010
43. Cui J, Song W, Jin Y, Xu H, Fan K, Lin D, et al. Research progress on the mechanism of the acupuncture regulating neuro-endocrine-immune network system. Vet Sci. (2021) 8:149. doi: 10.3390/vetsci8080149
44. Zhang K, Zhai W, Ge X, Zhang X, Tian W, and Zhai X. Targeting BDNF with acupuncture: A novel integrated strategy for diabetes and depression comorbidity. Heliyon. (2023) 9(12):e22798. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22798
45. Duan H, Song S, Li R, Hu S, Zhuang S, liu S, et al. Strategy for treating MAFLD: electroacupuncture alleviates hepatic steatosis and fibrosis by enhancing AMPK mediated glycolipid metabolism and autophagy in T2DM rats. Diabetol Metab Syndr. (2024) 16:218. doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01432-7
46. Liu S, Zhuang S, Li R, and Duan H. Electroacupuncture modulates the gut-brain axis via the PI3K/Akt pathway to improve feeding behavior, body weight, glucolipid metabolism, and reduce insulin resistance in T2DM rats. Diabetol Metab Syndr. (2025) 17:122. doi: 10.1186/s13098-025-01683-y
47. Liu X-X, Zhang L-Z, Zhang H-H, Lai L-F, Wang Y-Q, Sun J, et al. Low-frequency electroacupuncture improves disordered hepatic energy metabolism in insulin-resistant zucker diabetic fatty rats via the AMPK/mTORC1/p70S6K signaling pathway. Acupunct Med. (2022) 40(4):360–8. doi: 10.1177/09645284211070301
48. Jia X, Li M, Zhang W, Guo Y, Xue F, Ma S, et al. ’Adjusting internal organs and dredging channelon’ Electroacupuncture glycolipid metabolism disorders in NAFLD mice by mediating the AMPK/ACC signaling pathway. Diabetol Metab Syndr. (2024) 16:173. doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01416-7
49. Gao T, Chen S, Han Y, Zhang D, Tan Y, He Y, et al. Ameliorating inflammation in insulin-resistant rat adipose tissue with abdominal massage regulates SIRT1/NF-κB signaling. Cell Biochem Biophys. (2022) 80:579–89. doi: 10.1007/s12013-022-01085-1
50. Yuan C-X, Wang X, Liu Y, Xu T-C, Yu Z, and Xu B. Electroacupuncture alleviates diabetic peripheral neuropathy through modulating mitochondrial biogenesis and suppressing oxidative stress. World J Diabetes. (2025) 16:93130. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i2.93130
51. Wu J and Chen X. Acupuncture therapy protects PCOS patients with diabetes by regulating miR-32-3p/PLA2G4A pathway. Am J Trans Res. (2021) 13:8819–32.
52. Shan J, Cao Z, and Yu S. Advances in understanding diabetic kidney disease progression and the mechanisms of acupuncture intervention. Int J Gen Med. (2024) 17:5593–609. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S490049
53. Wang H, Wang L, Shi X, Qi S, Hu S, Tong Z, et al. Electroacupuncture at zusanli prevents severe scalds-induced gut ischemia and paralysis by activating the cholinergic pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2015) 2015:787393. doi: 10.1155/2015/787393
54. Ge X, Wang L, Cui Q, Yan H, Wang Z, Ye S, et al. Electroacupuncture improves cognitive impairment in diabetic cognitive dysfunction rats by regulating the mitochondrial autophagy pathway. J Physiol Sci. (2022) 72:29. doi: 10.1186/s12576-022-00854-0
55. Collaboration, The Emerging Risk Factors. Diabetes mellitus, fasting blood glucose concentration, and risk of vascular disease: A collaborative meta-analysis of 102 prospective studies. Lancet. (2010) 375:2215–22. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60484-9
Keywords: acupuncture, diabetes mellitus, blood glucose, meta-analysis, animal
Citation: Lin L, Li S, Guo Z, Fang P, Feng Y, Qi C, Wang M, Xiao L, Chen M and Wang T (2025) The efficacy and potential mechanism of the acupuncture treatment for type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of data from animal models. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1627061. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1627061
Received: 16 May 2025; Accepted: 16 September 2025;
Published: 06 October 2025.
Edited by:
Åke Sjöholm, Gävle Hospita, SwedenReviewed by:
Zoran Andrija Matić, University of Pisa, ItalyYuting Cui, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, China
Copyright © 2025 Lin, Li, Guo, Fang, Feng, Qi, Wang, Xiao, Chen and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tao Wang, MzQ2MTM0NjRAcXEuY29t; Min Chen, bWNoZW5AbXVzdC5lZHUubW8=; Lu Xiao, aGJ4bDE1MjdAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors share first authorship
 Linsun Lin
Linsun Lin Shu Li3†
Shu Li3† Ziyi Guo
Ziyi Guo Peigang Fang
Peigang Fang Yanchen Feng
Yanchen Feng