- Department of Cardiology, Affiliated Hospital of Putian University, Putian, Fujian, China
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is an important risk factor for the development of heart failure (HF), both directly by impairing cardiac function and indirectly through related conditions such as hypertension, coronary heart disease, renal dysfunction, and other metabolic disorders. The prevention of T2DM-related HF is a comprehensive management process involving complex and multifactorial pathogenic mechanisms. An in-depth exploration of the pathophysiological and clinical risk factors of HF in T2DM can assist clinicians in identifying individuals at high risk of HF, enabling early intervention measures to prevent its onset. In this review, we present data on the pathophysiology and epidemiology of T2DM-mediated HF, clinical phenotypic features of cardiomyopathy, and summarize clinical risk factors predicting HF development identified in multiple studies, risk assessment tools, and clinical trial data on the efficacy of lifestyle modifications, pharmacological treatments, and bariatric surgical interventions. Finally, we discuss best practice recommendations for clinicians, highlight potential limitations and challenges, and propose possible future research directions.
1 Introduction
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disease influenced by both genetic and environmental factors, with a prevalence that continues to increase annually. The current global prevalence of diabetes among individuals aged 20–79 years is estimated at 10.5% (536.6 million) and is projected to rise to 12.2% (783.2 million) by 2045, with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), characterized by insulin resistance, accounting for more than 90% of all diabetes cases (1). The coexistence of T2DM with heart failure (HF), either with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) or reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), is common and is associated with a significantly increased risk of HF hospitalization, all-cause mortality, and cardiovascular mortality. The primary factors contributing to HF in T2DM include coronary artery disease, arterial hypertension, and the direct deleterious effects of T2DM on the myocardium (2). Notably, even in T2DM patients with optimal control of traditional risk factors such as glucose, blood pressure, smoking, and hyperlipidemia, the risk of HF remains significant (3). Furthermore, 50–70% of T2DM patients exhibit asymptomatic left ventricular diastolic or systolic dysfunction, which is challenging to detect at early stages due to limitations in diagnostic techniques (4). However, a well-defined framework of assessments and interventions aimed at preventing or delaying HF progression in T2DM is lacking.Recent American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology/Heart Failure Society of America(AHA/ACC/HFSA)Guidelines and the Universal Definition and Classification of Heart Failure categorize the HF process into four stages (5, 6). According to these guidelines, stage A HF is defined as the absence of structural or functional heart disease or abnormal serum biomarkers (5). All individuals with diabetes are considered at higher risk of developing HF and are classified as stage A HF. As myocardial damage progresses, many patients exhibit asymptomatic structural heart disease or elevated filling pressures, defined as stage B HF. This is followed by the onset of HF signs and/or symptoms, representing stage C HF, which ultimately progresses to severe disruption of daily life, classified as stage D HF (7). Data indicate that 5-year survival rates for HF stages are 97% for stage A, 96% for stage B, 75% for stage C, and 20% for stage D (8). Clearly, progression from stage B to stage C HF significantly worsens the prognosis. Therefore, early detection and intervention to delay or prevent the transition from preclinical HF to symptomatic HF are critical public health objectives.
In the effort to prevent the progression of T2DM-related HF, several comprehensive risk assessment tools have been developed to predict HF risk (9–11). The measurement of cardiovascular biomarkers and evaluation of traditional risk factors offer valuable opportunities for risk stratification and individualized HF risk prediction (12).Simultaneously, advancements in imaging techniques have significantly enhanced the sensitivity for detecting early, mild cardiac dysfunction (13, 14).This review explores the pathophysiology, clinical phenotypes, epidemiological features, and risk factors associated with the development of HF in T2DM. It further analyzes the components and efficacy of various risk scoring systems and emphasizes potential preventive strategies. Lastly, based on the currently available, albeit limited, evidence-based medical data, this review proposes both pharmacological and non-pharmacological preventive measures that may effectively reduce the risk of HF progression.
2 Pathophysiology of myocardial dysfunction in T2DM
The drivers of myocardial dysfunction in T2DM, in addition to the common coexisting conditions of hypertension and coronary artery disease, include hyperglycemia, insulin resistance/hyperinsulinemia, and impaired glucose tolerance. These factors may exert their effects years or even decades before the clinical onset of T2DM (2, 15). The deleterious effects of these mechanisms are associated with various metabolic abnormalities, such as the deposition of advanced glycosylation end products (AGEs), lipotoxicity, and microvascular dysfunction and rarefaction (16). Glucotoxicity, resulting from hyperglycemia, induces protein glycosylation, leading to an increase in AGEs. These are produced by the non-enzymatic glycosylation of lipids, lipoproteins, and amino acids (17). AGEs alter the mechanical properties of the extracellular matrix by increasing resistance to enzymatic protein hydrolysis in connective tissue and enhancing the cross-linking of collagen and laminin. This, in turn, mediates an increase in myocardial fibrosis, decreased compliance, and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (18). AGEs can also bind to the receptor for AGEs (RAGE), which promotes the expression of inflammatory genes and increases the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). This contributes further to inflammation, cardiomyocyte apoptosis, fibrosis, and disturbances in the extracellular matrix, leading to adverse cardiac remodeling and dysfunction (17, 19). Hyperglycemia also exacerbates myocardial pathophysiology through the activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) and the sympathetic nervous system, as well as coronary microvascular dysfunction secondary to end-glycosylation (20). Insulin resistance, a hallmark of T2DM, is associated with reduced myocardial glucose uptake and compensatory increased uptake of free fatty acids (FFAs) (21). Excessive FFAs in the myocardium can lead to increased lipotoxicity and oxidative stress, resulting in damage to the myocardium (22). Furthermore, normal coronary and myocardial insulin signaling promotes the activation of coronary endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and enhances nitric oxide(NO) bioavailability, both of which are critical for optimal coronary microvascular blood flow and myocardial function (17) (Figure 1). The harmful interrelationships among these pathophysiological mechanisms may reinforce one another, forming a vicious cycle that mediates myocardial injury and cardiac dysfunction in T2DM (16).
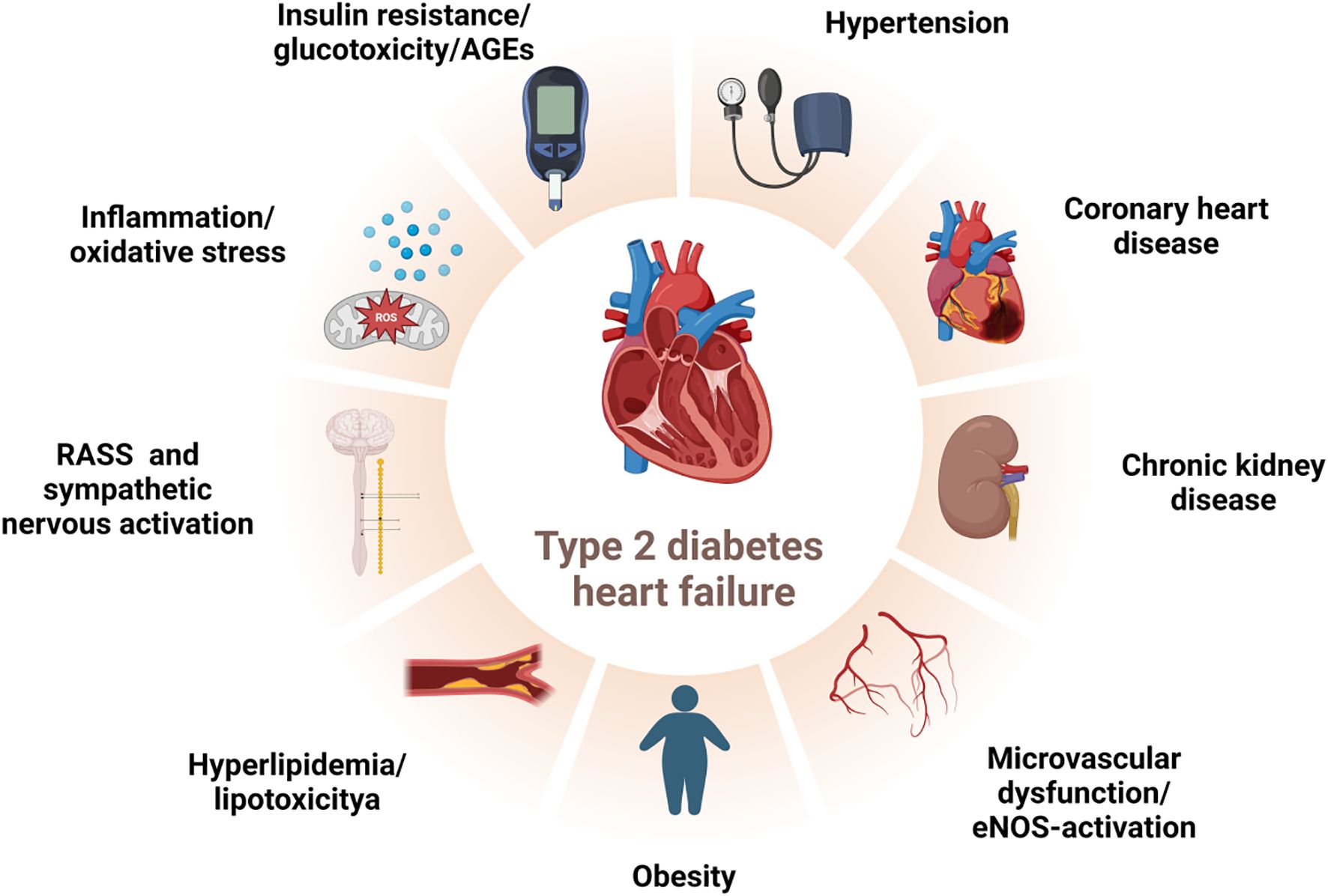
Figure 1. Risk factors for HF in T2DM. The deleterious interplay among direct/indirect hyperglycemic effects, activated neurohumoral abnormalities, and concomitant clinical conditions may reciprocally potentiate each other, forming a vicious feedback loop that culminates in myocardial injury and cardiac dysfunction in T2DM patients. T2DM:type 2 diabetes mellitus, HF: heart failure, RAAS: renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, AGEs: advanced glycosylation end products, eNOS: endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Created by BioRender.com.
3 Phenotypes of T2DM-related cardiomyopathy
In 1972, Rubler et al. reported no evidence of coronary heart disease(CHD) in the autopsy findings of four patients with diabetic glomerulosclerosis and HF. The hearts of these patients exhibited myocardial hypertrophy and fibrosis, suggesting that metabolic factors were responsible for the observed phenomenon (23). Rubler’s observations were later supported by Regan’s study in 1977. This study involved 17 patients with T2DM, in whom CHD had been ruled out by angiography, providing clear evidence of diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM). The study found elevated left ventricular end-diastolic pressure, reduced left ventricular compliance, and decreased left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) with diffuse hypokinesis (24).DCM is characterized by cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, interstitial fibrosis, and impaired coronary microvascular perfusion. In the early stages, DCM usually presents without clinical symptoms, but as the disease progresses, it leads to diastolic or systolic dysfunction. DCM is one of the primary causes of diabetes-related HF and death in patients with T2DM (25). The development of HF in T2DM is not a linear process but involves a series of evolving stages. Long-term exposure to hyperglycemia and insulin resistance (stage A HF) can eventually lead to adverse cardiac remodeling, left ventricular hypertrophy, and cardiac dysfunction (stage B HF) (26). Previous studies have shown that left ventricular diastolic dysfunction can be detected in approximately 75% of T2DM patients, even in the early stages of the disease, including those with normal blood pressure (27). The prevailing view is that left ventricular diastolic dysfunction is one of the first manifestations of DCM and is usually detected earlier than left ventricular systolic dysfunction (28). However, strain analysis and peak systolic velocity measurements have revealed subtle abnormalities in systolic function in 24% of T2DM patients without CHD or left ventricular hypertrophy (29). A recent study showed that altered systolic strain can be detected in patients with T2DM who exhibit normal diastolic function (30). This finding has led to an alternative view that diastolic dysfunction should not be regarded as the first sign of preclinical DCM (14).
Currently, two theoretical perspectives on cardiac dysfunction in DCM are debated: a single clinical phenotype and a dual clinical phenotype (31). The traditional understanding views DCM as progressing from diastolic to systolic dysfunction with structural remodeling, such as left ventricular hypertrophy. The alternative perspective suggests that diastolic and systolic dysfunction in DCM represent a single disease with two distinct phenotypes, which evolve independently into HFpEF or HFrEF (16). Abnormalities in glucose and lipid metabolism, as well as insulin resistance, coexist in obese patients with T2DM, predisposing them to the restrictive/HFpEF phenotype of DCM (diastolic insufficiency).In contrast, autoimmune-associated type 1 diabetes predisposes patients to the dilated/HFrEF phenotype (systolic insufficiency) (16).
4 Epidemiology of HF in T2DM
The global prevalence of T2DM has increased by 30% over the past decade, from 333 million people in 2005 to 435 million in 2015 (32). Contemporary data suggest that the overall prevalence of HF in the general population is 11.8%, with a range of 4.7% to 13.3% (33). In numerous clinical trials involving patients with T2DM, the prevalence of HF at baseline ranged from approximately 10% to 30% (34, 35). In the Reykjavik study, the prevalence of HF among individuals with T2DM was 12%, with a higher prevalence in those over 70 years of age—16% for men and 22% for women (34). In the Kaiser Permanente population, the incidence of HF was nearly three times higher in individuals with T2DM under 75 years of age compared to those without T2DM. In the 75–84 age group, the risk of HF was twice as high in those with T2DM as in those without (35). Several factors contribute to these disparities, with gender, race, and other factors potentially influencing the observed differences. Early Framingham studies indicated that men with diabetes were twice as likely to develop HF as non-diabetic men, while women with diabetes were five times more likely to develop HF compared to non-diabetic women (36). Subsequent observational studies have demonstrated gender differences in the association between T2DM and HF risk, with an increased risk in women. Potential explanations for these gender differences include a greater burden of cardiometabolic risk factors, such as elevated body mass index (BMI) and systolic blood pressure at the time of T2DM diagnosis in women, treatment inertia that disproportionately impacts women, and differences in hormonal profiles (37, 38). Similarly, racial differences exist in the risk of HF associated with T2DM. For example, Black individuals with T2DM have a higher risk of developing HF compared to individuals of other races. Racial disparities in HF risk are largely driven by a higher burden of adverse social determinants of health, including lower incomes and limited access to healthcare among Black individuals (39).
5 Risk factors for HF in T2DM
The increased risk of HF in T2DM is partly attributable to the direct and indirect effects of hyperglycemia(Figure 1). The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study provides evidence of subclinical myocardial injury in individuals with prediabetes and T2DM, as assessed by high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (hs-cTnT) assays. Subclinical myocardial injury increases progressively across the glycemic spectrum, from normoglycemia to prediabetes and diabetes. This is associated with an elevated risk of cardiovascular events, HF, and death, with the highest risk observed in patients with T2DM (40). Blood glucose levels, as measured by glycosylated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), serve as an independent biomarker of HF risk in patients with T2DM and even prediabetes (41–43). In T2DM patients, each 1% increase in HbA1c is associated with an 8% higher risk of HF hospitalization or HF-related death (41). In non-diabetic individuals, a 1% increase in HbA1c is associated with a 39% increased risk of HF, independent of other risk factors (43). Additionally, the duration of diabetes is an independent risk factor for HF, with each 5-year increase in the duration of diabetes corresponding to a 17% higher risk of HF (44).
Patients with T2DM often have additional comorbid risk factors for HF, which contribute to indirect myocardial injury. More than 70% of patients with T2DM have elevated blood pressure, and the coexistence of hypertension and T2DM exacerbates vascular remodeling, atherosclerosis, cardiac structural and functional abnormalities, and coronary microvascular dysfunction, all of which increase the risk of HF (45–47). Approximately 60% of individuals with T2DM also suffer from obesity, a common risk factor for both T2DM and HF (48, 49). An earlier study demonstrated that metabolic syndrome (defined by a BMI greater than 29.4 kg/m²) increased the risk of HF more than threefold over 20 years of follow-up. This increased risk persisted even after adjusting for established risk factors for HF (50). Subsequent studies have further shown that central abdominal obesity and high-fat mass are strongly associated with an elevated risk of HF in T2DM patients (51, 52). Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects approximately 40% of T2DM patients (53).Impaired renal function and albuminuria are important independent risk factors for the development of HF in individuals with T2DM (11, 54). A recent study demonstrated that the degree of elevation in the urinary albumin-creatinine ratio (uACR) was associated with a progressively higher risk of new-onset HF in T2DM. This ranged from microalbuminuria (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 2.21; 95% CI, 1.59–3.06) to macroalbuminuria (adjusted HR, 6.02; 95% CI, 4.11–8.80) (54). Conversely, slowing the progression of CKD in T2DM patients has been shown to reduce cardiovascular morbidity, particularly HF morbidity and mortality (55). The risk of CHD in individuals with T2DM is at least twice as high as in non-diabetic individuals. This is typically manifested as diffuse, multivessel coronary artery disease or, in some cases, as asymptomatic myocardial infarction, which is a significant cause of cardiac dysfunction, especially HFrEF (56–59). Notably, although some risk factors for HFpEF and HFrEF overlap (e.g., older age, diabetes mellitus, and a history of valvular disease), HFpEF is more commonly associated with women, obesity, and physical inactivity, whereas HFrEF is more commonly associated with men, smoking, and CHD (59–61).
6 Risk prediction of HF in T2DM
6.1 Clinical risk scores to predict HF risk in T2DM
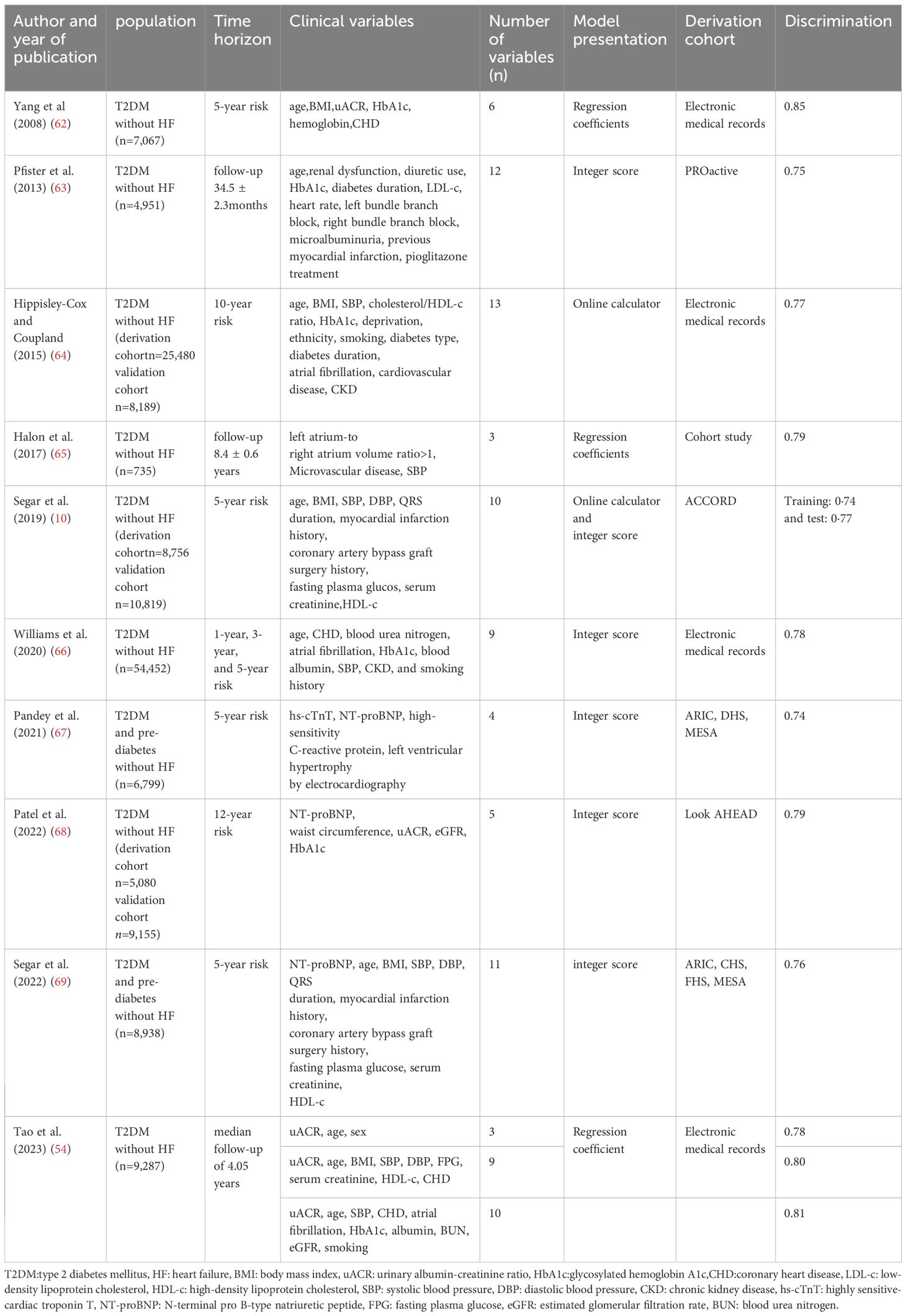
The importance of risk assessment in cardiovascular disease prevention is increasingly emphasized within the academic community. As a result, several HF risk scores based on clinical risk factors in patients with T2DM have been developed (10, 11, 62–69) (Table 1). Among these, two relatively concise and widely validated risk scores are the WATCH-DM(Weight, Age, hyperTension, Creatinine, High-density lipoprotein cholesterol[HDL-c], Diabetes control, Myocardial infarction or coronary artery bypass grafting) risk score and the Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction Risk Score for HF in Diabetes (TRS-HFDM).The WATCH-DM risk score is a machine-learning-based methodology designed to predict the 5-year risk of HF in patients with T2DM. The score includes the following variables:BMI, age, hypertension, creatinine levels, HDL-c, fasting glucose, HbA1c, QRS duration, and a history of myocardial infarction or coronary artery bypass grafting (10).The TRS-HFDM score was developed based on results from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 trial and validated in the DECLARE-TIMI 58 trial for predicting the risk of hospitalization for HF. This scoring system, which ranges from 0 to 7, incorporates five independent risk factors: history of previous HF, history of atrial fibrillation, history of CHD, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and uACR (11). Both the WATCH-DM and TRS-HFDM scores have been validated in multiple external cohorts, demonstrating adequate identification and risk stratification efficacy (69–72). However, there are some limitations to these risk scores. First, both scores rely solely on clinical risk factors and do not account for the contribution of cardiac biomarkers, such as hs-cTnT and natriuretic peptide concentrations, or some novel biomarkers, in their assessments. This is a significant consideration, as elevated hs-cTnT and natriuretic peptide concentrations are among the strongest predictors of HF in adults, and certain novel biomarkers have prognostic predictive value (73–76). Secondly, dynamic changes in these variables, including indicators related to renal function, are not included in the models. Lastly, the accuracy of these scores in predicting HF risk is limited by the presence of competing risks (77).
6.2 Value of cardiac biomarkers in predicting HF risk in T2DM
In recent years, cardiac biomarkers have been explored in various ways for the prediction and diagnosis of cardiovascular disease. These include both biomarkers already in clinical use and newly developed biomarkers still under clinical investigation (78). Numerous studies have confirmed the utility of cardiac biomarkers in guiding the prevention of HF in patients with T2DM (67, 68, 75, 79, 80). The traditional biomarker B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) is secreted from cardiomyocytes in response to myocardial wall stretch, regulated primarily at the transcriptional level. It is released as a precursor protein (pro-BNP), which is subsequently cleaved into biologically active BNP and the inactive peptide N-terminal pro-BNP (NT-proBNP) (81, 82). In the STOP-HF trial, participants older than 40 years of age and assessed to be at high risk of developing heart failure based on traditional risk factors, including T2DM, were randomly assigned to either BNP screening or usual primary care (79). In the BNP screening group, participants with BNP ≥50pg/mL (indicative of stage B HF) underwent echocardiography and received collaborative care between their primary care physician and a cardiologist. This approach resulted in a 45% reduction in the likelihood of progressing to stage C HF and left ventricular dysfunction compared to the usual primary care group.In the PONTIAC trial, patients with T2DM at high risk for HF and NT-proBNP levels ≥ 125 pg/mL benefitted from intensified neurohormonal blockade therapy and cardiovascular disease specialist care, reducing the risk of subsequent HF by 65% (83). Highly sensitive cardiac troponin (hs-cTn) has also been shown to predict the occurrence of new-onset HF in asymptomatic patients and can identify those at high risk for developing HF (80). The American Diabetes Association (ADA) published a consensus report recommending annual measurement of natriuretic peptides or hs-cTn to identify T2DM patients who may be at risk for stage B HF. Thresholds for identifying stage B HF include BNP ≥ 50 pg/mL, NT-proBNP ≥ 125 pg/mL, and hs-cTn ≥ 99th percentile of the upper reference limit of the assay (84).Several studies have evaluated the combination of biomarkers with risk scoring models or the use of multiple biomarkers to predict HF risk in patients with T2DM (67, 69). An analysis of adults with T2DM or prediabetes, without HF at baseline, in four cohort studies (Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities[ARIC], Cardiovascular Health Study[CHS], Framingham Offspring Study[FHS], and Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis[MESA])showed that NT-proBNP alone was more effective in predicting HF in subjects with low/intermediate WATCH-DM scores (<13) than in those with high WATCH-DM scores (≥13) (C-index 0.71 [95% CI 0.68–0.74] vs. 0.64 [95% CI 0.61–0.66]). HF risk identification improved when NT-proBNP levels were combined with WATCH-DM scores, showing greater improvement in low/intermediate risk patients [WATCH-DM score <13] than in those at high risk [WATCH-DM score ≥13] (C-index 0.73 [95% CI 0.71–0.75] vs. 0.71 [95% CI 0.68–0.74]) (69). A 2021 multi-cohort analysis developed a four-item scoring system based on three biomarkers—hs-cTnT (≥ 6 ng/L), NT-proBNP(≥125pg/mL),and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (≥3mg/L)—as well as electrocardiographic left ventricular hypertrophy. This model was used to predict the 5-year risk of HF in T2DM and prediabetes patients with no history of cardiovascular disease. The results indicated that the risk score was well-calibrated and discriminatory in this population (C-index 0.74, 95% CI 0.68–0.80) (67). Furthermore, soluble suppression of tumorigenicity-2 (sST2), a promising new biomarker in the field of HF, has been demonstrated to correlate with early myocardial fibrosis and predict adverse cardiovascular events in T2DM (85). However, its utility in identifying HF risk among patients with T2DM remains to be established.
6.3 Assessing HF risk by cardiac imaging techniques
In patients with T2DM, subclinical cardiac damage is a frequent concomitant condition, and echocardiography plays a pivotal role in identifying structural or functional cardiac abnormalities that may contribute to the development of HF (86–88). Three echocardiographic index abnormalities have been proposed as potential diagnostic criteria for DCM: left ventricular hypertrophy, left atrial enlargement, and the presence of diastolic dysfunction. The following specific definitions have been used to assess the prognostic impact of DCM and the subsequent development of HF: least restrictive (at least one atypical echocardiographic abnormality), intermediate restrictive (at least two atypical echocardiographic abnormalities), and most restrictive (at least two atypical echocardiographic abnormalities with elevated natriuretic peptide concentrations). The prevalence of DCM was found to range from 67% (using the least restrictive definition) to 12% (using the most restrictive definition). Regardless of the criteria used to define DCM, diabetic patients with DCM had a significantly higher risk (2–4 times higher) of developing HF compared to patients with diabetes alone (89). Given that diabetic myocardial damage often develops insidiously, the advent of two-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography has significantly improved the early recognition of left ventricular dysfunction in DCM in recent years (90, 91). Using the more sensitive left ventricular global longitudinal strain (GLS) technique, early minor abnormalities in cardiac systolic function can be detected (30). Data suggest that approximately 45% of patients with T2DM have subclinical left ventricular systolic dysfunction, and that impairment of left ventricular GLS is associated with subsequent HF (87, 92). A combined approach utilizing echocardiographic features and cardiac biomarker concentrations, which considers the presence or absence of abnormal myocardial structure (e.g., left ventricular hypertrophy or concentric remodeling), function (e.g., diastolic dysfunction or abnormal left ventricular strain), and biomarker concentrations (indicating myocardial stretching or injury), further classifies DCM and stage B HF into four subcategories (Stage B1: Elevated biomarkers with normal cardiac structure and function; Stage B2: Elevated biomarkers with atypical cardiac structural abnormalities but normal cardiac function; Stage B3: Elevated biomarkers with atypical cardiac structural and functional abnormalities; Stage B4: Elevated biomarkers, low ejection fraction, and moderate-to-severe valvular disease). This new classification suggests that the risk of developing stage C HF progressively increases from stage B1 to stage B4 (7). Additionally, the ability of other imaging methods, such as cardiac magnetic resonance and radionuclide imaging, to predict the risk of HF in diabetic patients has not been well studied (93). These cardiac imaging methods are not recommended for routine examination in asymptomatic patients.
7 Prevention of HF in T2DM
7.1 Lifestyle interventions
A meta-analysis indicated that structured aerobic, resistance, or combined exercise training, along with dietary advice, improved glycemic control and significantly reduced HbA1c in diabetic patients (94). Exercise was associated with enhanced insulin sensitivity, even when weight loss was modest (defined as ≥3% to <5% weight loss) (95). This finding suggests that the relationship between exercise and improved glycemic control may be independent of weight loss. However, the cardiac benefits of exercise in patients with T2DM may be attenuated (96, 97). In a study utilizing tissue Doppler imaging, 176 patients with T2DM were randomly assigned to exercise training or usual care. No significant differences in myocardial strain or tissue velocities were observed between the two groups after 1 year of follow-up (96). In the multicenter Look Action for Health in Diabetes(Look AHEAD)study, although the intensive lifestyle intervention resulted in modest weight loss and a significant improvement in HbA1c, it did not lead to a reduction in the primary composite outcome, which included hospitalization for cardiovascular causes, non-fatal myocardial infarction, non-fatal stroke, or angina (98). Notably, further analysis of the Look AHEAD data revealed that participants who achieved improvements in fitness and weight loss had a lower subsequent risk of HF at the 4 year follow-up.In adults with T2DM, lifestyle interventions were associated with significant reductions in fat mass and lean mass. Reductions in fat mass and waist circumference, but not lean mass, were significantly associated with a reduced risk of HF. Additionally, reductions in waist circumference were significantly associated with a reduced risk of HFpEF, but not with HFrEF (99). Therefore, exercise interventions are more likely to benefit individuals with T2DM and obesity, particularly through effective body fat reduction, reversal of central obesity, and improvements in cardiorespiratory fitness.
7.2 Pharmacological interventions
7.2.1 Traditional hypoglycemic agents
Metformin and sulfonylureas are commonly used to achieve glycemic control in diabetic patients. In addition to lowering blood glucose, metformin has been shown to have beneficial effects by stimulating insulin action, reducing inflammation, and improving myocardial energy metabolism (100–102). Despite these multiple mechanisms of cardiovascular benefit, current evidence does not support metformin’s ability to reduce HF in T2DM. A study examining the cardiovascular outcomes of the Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) Trial and the DPP Outcomes Study (DPPOS) found that metformin intervention failed to reduce the risk of HF in T2DM patients during a median follow-up of up to 21 years (103). Other studies have similarly shown that metformin treatment does not reduce the risk of developing HF (104, 105). Sulfonylureas are associated with an increased risk of adverse events in T2DM patients and a higher incidence of hypoglycemia (106–108). A recent meta-regression analysis of 18 studies evaluating the risk of cardiovascular events associated with sulfonylureas found that treatment with sulfonylureas was linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular death and events (109). In the CAROLINA trial, patients with T2DM were randomly assigned to treatment with either the sulfonylurea glimepiride or the dipeptidyl peptidase 4(DPP-4) inhibitor linagliptin. The rate of hospitalizations for HF was similar in both groups (3.1% for glimepiride and 3.7% for linagliptin) (110). Thiazolidinediones, known for their glucose-lowering effects, are also associated with fluid retention, which increases the risk of HF (111). In the PROACTIVE study, patients with T2DM and a history of macrovascular disease were randomized to receive either pioglitazone or placebo. Pioglitazone was found to increase the rate of hospitalization for HF, although this was accompanied by a reduction in cardiac ischemic events (63). In the RECORD trial, a multicenter, open-label study of T2DM patients, rosiglitazone was associated with more than a two-fold increase in the risk of HF (112). Insulin is often added to the treatment regimen when oral antidiabetic medications fail to achieve adequate glycemic control or when oral agents cannot be used. Mechanistically, insulin can contribute to fluid retention and weight gain, and it has been shown that insulin therapy in T2DM patients is associated with an increased prevalence of HF and cardiovascular disease mortality (113). However, contradictory findings exist. In the ORIGIN trial, which enrolled 12,537 patients with diabetes mellitus or prediabetes and followed them for 6 years, the results showed no increase in the risk of HF in patients treated with insulin glargine compared to those receiving standard therapy (114). Similarly, there was no difference in the incidence of HF between the two groups of T2DM patients randomized to ultra-long-acting insulin degludec and insulin glargine in the DEVOTE trial (115). In summary, although traditional oral hypoglycemic agents and injectable insulin are widely used, most do not have a preventative effect on HF, and some may even be harmful. Therefore, new oral hypoglycemic agents offer therapeutic hope for patients with T2DM at high risk for HF.
7.2.2 Novel hypoglycemic agents
7.2.2.1 Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors
SGLT2 inhibitors block glucose reabsorption in the proximal tubules of the kidney, thereby increasing glucose excretion in the urine and improving glycemic control (116). The three SGLT2 inhibitors approved for clinical use are empagliflozin, dapagliflozin, and canagliflozin (117). Recently, a large body of basic and clinical research has elucidated that the cardioprotective effects of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with T2DM and non-diabetic patients are independent of their antihyperglycemic effects (118). The EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial evaluated the non-inferiority of empagliflozin compared to placebo for major cardiovascular adverse event (MACE) in 7,020 patients with T2DM at very high cardiovascular risk. The results demonstrated that empagliflozin was superior to placebo in reducing the risk of MACE, as well as decreasing the relative risk of hospitalization for HF by 35% (119). Subsequently, the DECLARE-TIMI 58 trial assessed the cardiovascular safety and efficacy of dapagliflozin in patients with T2DM at relatively low cardiovascular risk. Although dapagliflozin did not significantly alter MACE, it was associated with a significant 17% reduction in the composite endpoint of cardiovascular death or first hospitalization for HF, primarily driven by a 27% reduction in first hospitalization for HF (120). Similarly, the CANVAS trial and the VERTIS CV trial showed a 33% and 30% reduction in the risk of hospitalization for HF, respectively, with the use of canagliflozin and ertugliflozin (121, 122). Moreover, SGLT2 inhibitors have demonstrated significant benefits in reducing the risk of major adverse clinical events in patients with CKD. In patients with T2DM and CKD, canagliflozin reduced the relative risk of renal composite adverse events (such as end-stage renal disease, doubling of serum creatinine, or death from renal causes) by 34%, cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, or stroke by 20%, and, notably, the risk of hospitalization for HF by 39% (123). The DAPA-CKD study, which enrolled adults with an eGFR of 25–75 mL/min/1.73 m² and a uACR of 200–5000 mg/g, demonstrated that dapagliflozin significantly reduced the relative risk of a composite adverse renal outcome, hospitalization for HF, or cardiovascular death, regardless of T2DM status (124). These findings strongly suggest that SGLT2 inhibitors are effective as therapeutic agents in the treatment of T2DM, cardiorenal diseases, and the prevention of HF. Studies in animal models have also revealed some of the mechanisms by which SGLT2 inhibitors improve cardiovascular outcomes, further supporting their clinical benefits. Empagliflozin has been shown to ameliorate left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in db/db mice fed a high-fat western diet by reducing spontaneous diastolic sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release (125). In the ob/ob-/- mouse model, empagliflozin induced a shift to a more catabolic state, including lower blood cholesterol and HbA1c, higher glucagon/insulin ratios, elevated ketone levels, and an increase in the L-arginine/asymmetric dimethyl arginine ratio (an indicator of endothelial function). These changes led to improvements in cardiac contractility and coronary microvascular function (126). Additionally, in a non-diabetic model, dapagliflozin alleviated myocardial hypertrophy, fibrosis, and excessive collagen synthesis, resulting in a significant improvement in left ventricular GLS (127). A variety of mechanisms underlying the cardiac benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors have been proposed, including diuresis, reduction of inflammation and oxidative stress, improved cardiac energy metabolism, and better intracellular calcium homeostasis. However, more precise mechanisms need to be further elucidated (128–131).
7.2.2.2 Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists
GLP-1 receptor agonists bind to GLP-1 receptors on pancreatic β-cells, reducing blood glucose levels by promoting insulin synthesis and secretion, inhibiting glucagon secretion, enhancing glucose utilization by peripheral tissues, decreasing hepatic glucose output, and increasing insulin sensitivity to glucose (132). Studies on the primary prevention of HF in patients with T2DM using GLP-1 receptor agonists have yielded mixed results.The LEADER study, an international multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial involving 9,340 patients with T2DM at high cardiovascular risk (81.3% of whom had a history of cardiovascular disease), compared the long-term effects of liraglutide (1.2 mg and 1.8 mg) to those of placebo over a mean follow-up of 3.8 years. This study demonstrated that the composite cardiovascular endpoint (cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke) and HF hospitalization were significantly lower in the liraglutide group compared to the placebo group (133). Subsequent cardiovascular outcome studies involving albiglutide and efpeglenatide in T2DM patients reported a 29% and 39% reduction in the risk of hospitalization for HF, respectively (134, 135). In a meta-analysis of trials evaluating cardiovascular outcomes with different GLP-1 receptor agonists, participants assigned to GLP-1 receptor agonists had a significant 11% lower risk of hospitalization for HF (136). These findings suggest a potential role for GLP-1 receptor agonists in the prevention of HF in patients with T2DM. However, two additional cardiovascular outcome studies involving liraglutide and semaglutide, respectively, demonstrated significant reductions in the risk of MACE, but did not show any effect on the risk of hospitalization for HF (133, 137). Taken together, these results raise questions about the role of GLP-1 receptor agonists in the prevention of DCM. The differences in outcomes may be attributed to variations in patient characteristics, such as obesity, with obese patients being more likely to benefit. These findings highlight the need for further high-quality randomized controlled trials to better understand the potential of GLP-1 receptor agonists in preventing HF in diverse populations of T2DM patients (138).
7.2.2.3 Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors
Intestinal insulin-based therapy has emerged as a new strategy for diabetes management, and DPP-4 plays a key role in the clearance of GLP-1 (139). DPP-4 inhibitors improve insulin sensitivity and glucose control by increasing insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells (140). The SAVOR-TIMI 53 trial enrolled 16,492 patients with T2DM who had a history of, or were at risk for, cardiovascular events. These participants were randomly assigned to receive either saxagliptin or placebo. The results showed that saxagliptin did not affect the risk of MACE but was associated with a 27% increased risk of hospitalization for HF (141). Similarly, a post hoc analysis of the EXAMINE trial revealed that alogliptin was associated with a 76% increased risk of hospitalization for HF in patients with T2DM who did not have a history of HF (142). However, the Trial Evaluating Cardiovascular Outcomes With Sitagliptin(TECOS), a randomized, double-blind study enrolling 14,671 patients with T2DM and cardiovascular disease, found that sitagliptin did not increase the risk of hospitalization for HF (143). In two additional cardiovascular outcome trials involving linagliptin, no increased risk of hospitalization for HF was observed (133, 144). In conclusion, these studies suggest that DPP-4 inhibitors may increase the risk of HF in some patients with T2DM. However, they also indicate that certain DPP-4 inhibitors may be safe. Given that other antidiabetic medications are available with favorable safety and efficacy profiles for the prevention of HF, DPP-4 inhibitors should be avoided in patients at risk for developing HF.
7.2.2.4 Renin-angiotensin system inhibitors
Approximately two-thirds of individuals with T2DM also have arterial hypertension (145). For blood pressure management in T2DM, the ADA recommends a target of less than 140/90 mmHg if the estimated 10-year risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) events is less than 15%. If the risk is 15% or more, the target should be less than 130/80 mmHg (117). Notably, intensive blood pressure lowering (systolic blood pressure less than 120 mmHg) did not provide additional benefits in reducing the risk of HF compared to a target of less than 140/90 mmHg (146). Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) are the preferred drugs for treating hypertension in T2DM, particularly in the presence of proteinuria (147). In many cases, however, patients treated with optimal doses of ACEIs or ARBs may experience aldosterone escape, leading to activation of the mineralocorticoid receptor(MR) signaling pathway. This can contribute to the development of diabetes-induced HF by promoting fibrosis and insulin resistance (148). Therefore, MR antagonists (MRAs) therapy becomes crucial. Steroidal MRAs, such as spironolactone and eplerenone, are associated with significant side effects, particularly when combined with ACEIs or ARBs, often leading to hyperkalemia (149). Non-steroidal MRAs are considered more potent and have a lower risk of hyperkalemia compared to steroidal MRAs (150). Further analysis of data from the FIGARO-DKD trial, which assessed new-onset HF (hospitalization for HF in patients without a history of HF) and total HF hospitalizations, showed that finerenone significantly reduced the incidence of new-onset HF (1.9% vs. 2.8%; HR 0.68 [95% CI, 0.50–0.93]; P=0.0162). In the overall population, finerenone was associated with an 18% reduction in cardiovascular death or first hospitalization for HF, a 29% reduction in the risk of first hospitalization for HF, and a 30% reduction in total hospitalization for HF (151). The FIGARO-DKD trial findings indicated that finerenone reduced new-onset HF and improved HF outcomes in patients with CKD and T2DM, independent of a history of HF.Effective prevention of HF hospitalization by finerenone was also observed in the FIDELIO-DKD trial, which showed a 14% reduction in risk (152). A combined analysis of the FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD trials found that the reduction in composite cardiovascular outcomes was primarily driven by a reduction in HF hospitalizations (HR 0.78; 95% CI 0.66–0.92) (153). A meta-analysis revealed that for most patients with T2DM and CKD, there were 10 additional cases of hyperkalemia per 1,000 patients over five years of non-steroidal MRA treatment, but a reduction of 16 deaths, 21 HF hospitalizations, and 14 cases of end-stage renal disease (154). This highlights the benefits of finerenone as a new-generation MRA, which outweigh its side effects.The ADA guidelines recommend adding MRAs if T2DM patients with hypertension are on three antihypertensive medications, including diuretics, and their blood pressure is not at target (117). Given that finerenone achieves equal concentrations in heart and kidney tissue—unlike the higher concentration of spironolactone and eplerenone in the kidney—and due to its higher selectivity and fewer side effects, it may be preferable to choose finerenone when adding an MRA for T2DM patients with HF or at high risk of HF (153, 155). The 2023 European Society of Cardiology (ESC) guidelines state that finerenone (Recommended for 1A) should be added to ACEIs or ARBs in patients with T2DM complicated by an eGFR > 60 mL/min/1.73 m² with a urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (uACR) ≥ 300 mg/g, or an eGFR of 25 to 60 mL/min/1.73 m² with a uACR ≥ 30 mg/g, to further reduce cardiovascular events and renal failure (156). However, research on whether to add RAAS agents to T2DM patients without hypertension or proteinuria, but at high risk of HF, is lacking.
7.3 Bariatric surgery
Metabolic surgery, which leads to long-term weight loss of 15-25%, has increasingly become a treatment for obesity and T2DM due to its positive impact on overall metabolism in these patients (157–159). Three large population studies have demonstrated a clear link between weight loss and the incidence of HF (160–162). In the SOS study, which included 2,003 patients who underwent bariatric surgery and 2,030 controls, the surgery cohort experienced the greatest weight loss (mean weight loss of 41 kg) and the lowest risk of HF at 1 year (160). Another study compared 25,804 patients who underwent gastric bypass surgery with 13,701 patients who underwent lifestyle changes, finding that the surgical cohort had a 46% reduction in the incidence of HF during a median follow-up of 4.1 years (161). Similarly, a large observational study in the United States of more than 180,000 insured individuals with obesity showed that after a median follow-up of 4 years, patients who underwent metabolic surgery had a 54% reduction in the risk of new-onset HF, with similar results observed in both patients with and without T2DM (162).A meta-analysis suggests that the cardioprotective effects of bariatric surgery are associated with the restoration of left ventricular hypertrophy and improvements in left ventricular geometry and diastolic function (163). Several studies have indicated that bariatric surgery may also have beneficial effects on subclinical myocardial dysfunction (164–168). The beneficial impact of metabolic surgery on the risk of HF in patients with T2DM may be attributed to both direct improvements in cardiac structure and function, as well as the reversal of hemodynamic changes and regenerative cell exhaustion. Additionally, metabolic surgery indirectly affects other risk factors such as hypertension, metabolic disturbances, and obesity (163, 169–172).
8 Best practices for clinicians
Based on current understanding of early screening for HF in T2DM, the following process is summarized (Figure 2): First, regular screening is recommended.The ADA guidelines suggest annual screening (84). Second, a clinical risk score can be useful as an initial step in screening. For cardiac biomarker screening, although it is reasonable to conduct it annually as recommended by the ADA, the clinical validity and cost-effectiveness of this approach for the entire T2DM population require further evaluation. Echocardiography may also be considered directly, without prior cardiac biomarker assessment, in patients with high clinical risk scores. This is because the presence of cardiac structural and functional abnormalities in these individuals can identify stage B HF, even in the absence of biomarker testing, necessitating aggressive intervention (7, 26). Third, elevated clinical risk or abnormal levels of cardiac biomarkers (e.g., BNP ≥50 pg/mL, NT-proBNP ≥125 pg/mL, or hs-cTn ≥99th percentile), in combination with echocardiogram evaluation, further subdivides stage B HF (B1-B4). This should prompt aggressive risk factor modification, lifestyle interventions, increased physical activity, weight loss, and early initiation of SGLT2 inhibitors, which should be progressively intensified as the stage B classification advances (7). Fourth, if comorbid CKD is present (uACR ≥30 mg/g or reduced eGFR), a combination of SGLT2 inhibitors and finerenone should be initiated immediately. Finally, patients at high risk should seek evaluation from a cardiologist at or after starting the recommended preventive measures, especially those with stage B3 or B4 HF.
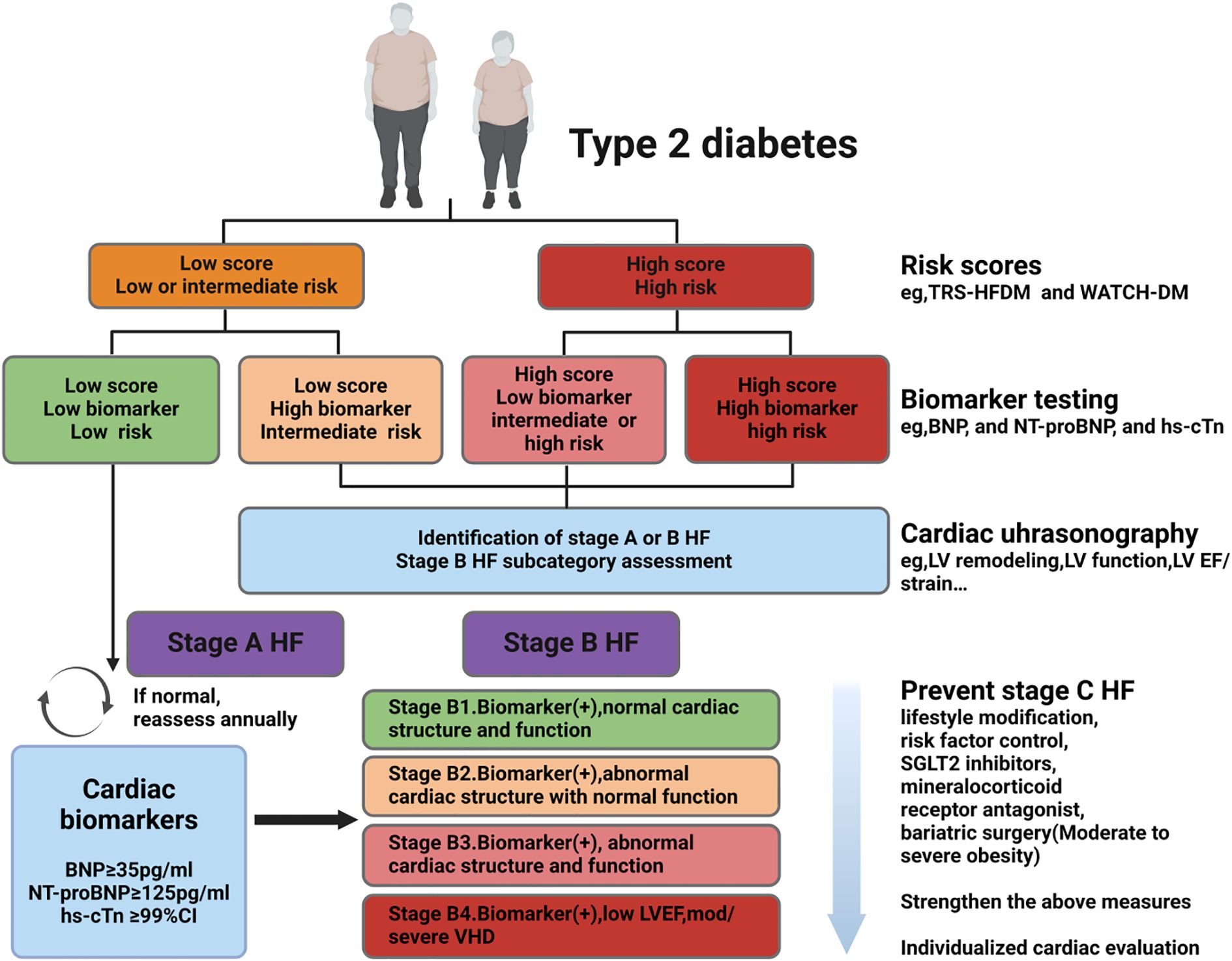
Figure 2. Early screening of HF in patients with T2DM. Screening strategy: i. Following ADA guidelines, it is recommended to screen all T2DM patients annually for Stage B HF using BNP (≥50 pg/mL) or NT-proBNP (≥125 pg/mL); clinical risk scores can be used as an initial screening tool, with high-risk patients directly undergoing echocardiography. ii. Subclassification of B1-B4 stages: Based on biomarker abnormalities and echocardiographic results, Stage B is further subdivided, necessitating intensified lifestyle interventions, weight loss, and early initiation of SGLT2 inhibitors. iii. In patients with comorbid CKD (uACR ≥30 mg/g or reduced eGFR): Immediately initiate combination therapy with SGLT2 inhibitors and finerenone. iv. Treatment intensity: Gradually escalate intervention measures with the progression of Stage B. T2DM:type 2 diabetes mellitus, HF: heart failure, hs-cTn: highly sensitive-cardiac troponin, BNP: N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide, NT-proBNP: N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide, LV: left ventricle, EF: ejection fraction, SGLT2: sodium glucose cotransporter 2,ADA: American Diabetes Association, CKD: chronic kidney disease, VHD: valvular heart disease. Created by BioRender.com.
9 Current limitations and future directions
Over the past decade, advancements in the field of HF in T2DM have primarily focused on the treatment of symptomatic HF, with limited evidence supporting the assessment and prevention of stage B HF progression to stage C HF. Specifically, tools for early risk stratification and the application of biomarkers have lacked large-scale validation, limiting the formation of clinical consensus. Existing predictive models primarily rely on clinical variables (e.g., age, gender, medical history), without fully incorporating subclinical cardiac structural changes or functional abnormalities (e.g., myocardial strain abnormalities).Additionally, the development of these models is based on regional and ethnic heterogeneity, which constrains their accuracy and generalizability. Large-scale cohort studies stratified by age, sex, and ethnicity are warranted in T2DM populations. By integrating clinical variables, novel biomarkers, and high-sensitivity indicators of cardiac dysfunction, these studies will enable the development of efficient predictive models. The discovery, clinical validation, and application of effective biomarkers are essential. Notably, as a validated surrogate marker of insulin resistance, the triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index significantly correlates with early subclinical HFpEF risk in T2DM and predicts HFpEF prognosis (173–175). This biomarker offers a novel strategy for identifying stage B HF and stratifying risk in T2DM. Emerging proteomic, metabolomic, and epigenetic technologies reveal promising biomarkers including sST2, galectin-3, and non-coding RNAs, which correlate with early myocardial fibrosis or metabolic dysregulation (176–178). However, their prognostic utility for HF progression in T2DM requires validation.Novel ultrasound techniques such as speckle-tracking echocardiography enhance diagnostic accuracy for stage B HF by detecting subtle myocardial strain abnormalities. Continued innovation in cardiac ultrasound will undoubtedly refine HF risk assessment. Moreover, recent research has achieved substantial progress in elucidating mechanisms underlying diabetes-induced myocardial damage, with key insights into mitochondrial dysfunction, apoptosis and ferroptosis regulation (179, 180). Developing precisely targeted therapeutic agents against these mechanisms holds promise for early and precise prevention of T2DM-mediated HF progression.
10 Conclusion
As a major cardiovascular complication in T2DM, HF poses significant clinical challenges.Advances in clinical risk stratification, biomarker profiling, and echocardiographic techniques for predicting HF onset, coupled with the development of novel therapeutics such as SGLT2 inhibitors, MRAs, and GLP-1 receptor agonists, hold promise for reducing the contemporary burden of HF in T2DM. Nevertheless, effective tools for screening high-risk individuals and targeted interventions to mitigate T2DM-driven pathophysiological mechanisms of HF have yet to be established.Consequently, bridging these translational gaps demands sustained advancement across developing accurate HF risk-stratification tools, identifying robust biomarkers and next-generation echocardiographic innovations, creating molecularly targeted therapeutics and ensuring their effective clinical translation.
Author contributions
XC: Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. WL: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Software. JZ: Conceptualization, Software, Writing – review & editing. MH: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition. JW: Writing – review & editing. MW: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Fujian Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no.2024J011461) to X.Chen and the Fujian Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no.2024J011466) to M.Huang.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M, Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2022) 183:109119. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119
2. Seferovic PM, Petrie MC, Filippatos GS, Anker SD, Rosano G, Bauersachs J, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and heart failure: a position statement from the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur J Heart Fail. (2018) 20:853–72. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1170
3. Rawshani A, Rawshani A, Franzen S, Sattar N, Eliasson B, Svensson AM, et al. Risk factors, mortality, and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2018) 379:633–44. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1800256
4. Natali A, Nesti L, Fabiani I, Calogero E, and Di Bello V. Impact of empagliflozin on subclinical left ventricular dysfunctions and on the mechanisms involved in myocardial disease progression in type 2 diabetes: rationale and design of the EMPA-HEART trial. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2017) 16:130. doi: 10.1186/s12933-017-0615-6
5. Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, Allen LA, Byun JJ, Colvin MM, et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA guideline for the management of heart failure: A report of the american college of cardiology/american heart association joint committee on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation. (2022) 145:e895–e1032. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001063
6. Bozkurt B, Coats AJ, Tsutsui H, Abdelhamid M, Adamopoulos S, Albert N, et al. Universal definition and classification of heart failure: A report of the heart failure society of america, heart failure association of the european society of cardiology, Japanese heart failure society and writing committee of the universal definition of heart failure. J Card Fail. (2021) 27:387–413. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2021.01.022
7. Yeung AM, Huang J, Pandey A, Hashim IA, Kerr D, Pop-Busui R, et al. Biomarkers for the diagnosis of heart failure in people with diabetes: A consensus report from diabetes technology society. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. (2023) 79:65–79. doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2023.05.002
8. Ammar KA, Jacobsen SJ, Mahoney DW, Kors JA, Redfield MM, Burnett JC Jr., et al. Prevalence and prognostic significance of heart failure stages: application of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association heart failure staging criteria in the community. Circulation. (2007) 115:1563–70. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.666818
9. Razaghizad A, Oulousian E, Randhawa VK, Ferreira JP, Brophy JM, Greene SJ, et al. Clinical prediction models for heart failure hospitalization in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Heart Assoc. (2022) 11:e024833. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.024833
10. Segar MW, Vaduganathan M, Patel KV, McGuire DK, Butler J, Fonarow GC, et al. Machine learning to predict the risk of incident heart failure hospitalization among patients with diabetes: the WATCH-DM risk score. Diabetes Care. (2019) 42:2298–306. doi: 10.2337/dc19-0587
11. Berg DD, Wiviott SD, Scirica BM, Gurmu Y, Mosenzon O, Murphy SA, et al. Heart failure risk stratification and efficacy of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation. (2019) 140:1569–77. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.042685
12. Vuori MA, Reinikainen J, Soderberg S, Bergdahl E, Jousilahti P, Tunstall-Pedoe H, et al. Diabetes status-related differences in risk factors and mediators of heart failure in the general population: results from the MORGAM/BiomarCaRE consortium. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2021) 20:195. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01378-4
13. Korosoglou G and Humpert PM. Non-invasive diagnostic imaging techniques as a window into the diabetic heart: a review of experimental and clinical data. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. (2007) 115:211–20. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-973083
14. Minciuna IA, Hilda Orasan O, Minciuna I, Lazar AL, Sitar-Taut AV, Oltean M, et al. Assessment of subclinical diabetic cardiomyopathy by speckle-tracking imaging. Eur J Clin Invest. (2021) 51:e13475. doi: 10.1111/eci.13475
15. Jia G, Whaley-Connell A, and Sowers JR. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: a hyperglycaemia- and insulin-resistance-induced heart disease. Diabetologia. (2018) 61:21–8. doi: 10.1007/s00125-017-4390-4
16. Seferovic PM and Paulus WJ. Clinical diabetic cardiomyopathy: a two-faced disease with restrictive and dilated phenotypes. Eur Heart J. (2015) 36:1718–27, 27a-27c. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv134
17. Jia G, DeMarco VG, and Sowers JR. Insulin resistance and hyperinsulinaemia in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2016) 12:144–53. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2015.216
18. Lazo M, Halushka MK, Shen L, Maruthur N, Rebholz CM, Rawlings AM, et al. Soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products and the risk for incident heart failure: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Am Heart J. (2015) 170:961–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2015.08.008
19. Skali H, Shah A, Gupta DK, Cheng S, Claggett B, Liu J, et al. Cardiac structure and function across the glycemic spectrum in elderly men and women free of prevalent heart disease: the Atherosclerosis Risk In the Community study. Circ Heart Fail. (2015) 8:448–54. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.114.001990
20. Jia G, Hill MA, and Sowers JR. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: an update of mechanisms contributing to this clinical entity. Circ Res. (2018) 122:624–38. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.311586
21. Marwick TH, Ritchie R, Shaw JE, and Kaye D. Implications of underlying mechanisms for the recognition and management of diabetic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2018) 71:339–51. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.11.019
22. Borghetti G, von Lewinski D, Eaton DM, Sourij H, Houser SR, and Wallner M. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: current and future therapies. Beyond Glycemic Control. Front Physiol. (2018) 9:1514. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01514
23. Rubler S, Dlugash J, Yuceoglu YZ, Kumral T, Branwood AW, and Grishman A. New type of cardiomyopathy associated with diabetic glomerulosclerosis. Am J Cardiol. (1972) 30:595–602. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(72)90595-4
24. Regan TJ, Lyons MM, Ahmed SS, Levinson GE, Oldewurtel HA, Ahmad MR, et al. Evidence for cardiomyopathy in familial diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. (1977) 60:884–99. doi: 10.1172/JCI108843
25. Dillmann WH. Diabetic cardiomyopathy. Circ Res. (2019) 124:1160–2. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.314665
26. Pandey A, Khan MS, Patel KV, Bhatt DL, and Verma S. Predicting and preventing heart failure in type 2 diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2023) 11:607–24. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(23)00128-6
27. Boyer JK, Thanigaraj S, Schechtman KB, and Perez JE. Prevalence of ventricular diastolic dysfunction in asymptomatic, normotensive patients with diabetes mellitus. Am J Cardiol. (2004) 93:870–5. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2003.12.026
28. Diamant M, Lamb HJ, Groeneveld Y, Endert EL, Smit JW, Bax JJ, et al. Diastolic dysfunction is associated with altered myocardial metabolism in asymptomatic normotensive patients with well-controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2003) 42:328–35. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(03)00625-9
29. Fang ZY, Schull-Meade R, Leano R, Mottram PM, Prins JB, and Marwick TH. Screening for heart disease in diabetic subjects. Am Heart J. (2005) 149:349–54. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2004.06.021
30. Ernande L, Bergerot C, Rietzschel ER, De Buyzere ML, Thibault H, Pignonblanc PG, et al. Diastolic dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: is it really the first marker of diabetic cardiomyopathy? J Am Soc Echocardiogr. (2011) 24:1268–75.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2011.07.017
31. Zhao X, Liu S, Wang X, Chen Y, Pang P, Yang Q, et al. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: Clinical phenotype and practice. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:1032268. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1032268
32. Disease GBD, Injury I, and Prevalence C. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. (2016) 388:1545–602. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6
33. van Riet EE, Hoes AW, Wagenaar KP, Limburg A, Landman MA, and Rutten FH. Epidemiology of heart failure: the prevalence of heart failure and ventricular dysfunction in older adults over time. A systematic review. Eur J Heart Fail. (2016) 18:242–52. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.483
34. Thrainsdottir IS, Aspelund T, Thorgeirsson G, Gudnason V, Hardarson T, Malmberg K, et al. The association between glucose abnormalities and heart failure in the population-based Reykjavik study. Diabetes Care. (2005) 28:612–6. doi: 10.2337/diacare.28.3.612
35. Nichols GA, Hillier TA, Erbey JR, and Brown JB. Congestive heart failure in type 2 diabetes: prevalence, incidence, and risk factors. Diabetes Care. (2001) 24:1614–9. doi: 10.2337/diacare.24.9.1614
36. Kannel WB, Hjortland M, and Castelli WP. Role of diabetes in congestive heart failure: the Framingham study. Am J Cardiol. (1974) 34:29–34. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(74)90089-7
37. Ohkuma T, Komorita Y, Peters SAE, and Woodward M. Diabetes as a risk factor for heart failure in women and men: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 47 cohorts including 12 million individuals. Diabetologia. (2019) 62:1550–60. doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-4926-x
38. Regensteiner JG, Golden S, Huebschmann AG, Barrett-Connor E, Chang AY, Chyun D, et al. Sex differences in the cardiovascular consequences of diabetes mellitus: A scientific statement from the american heart association. Circulation. (2015) 132:2424–47. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000343
39. Savage K, Williams JS, Garacci E, and Egede LE. Association between cardiovascular disease risk factors and mortality in adults with diabetes: A stratified analysis by sex, race, and ethnicity. Int J Public Health. (2022) 67:1604472. doi: 10.3389/ijph.2022.1604472
40. Selvin E, Lazo M, Chen Y, Shen L, Rubin J, McEvoy JW, et al. Diabetes mellitus, prediabetes, and incidence of subclinical myocardial damage. Circulation. (2014) 130:1374–82. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.010815
41. Dormandy JA, Charbonnel B, Eckland DJ, Erdmann E, Massi-Benedetti M, Moules IK, et al. Secondary prevention of macrovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes in the PROactive Study (PROspective pioglitAzone Clinical Trial In macroVascular Events): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. (2005) 366:1279–89. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67528-9
42. Pazin-Filho A, Kottgen A, Bertoni AG, Russell SD, Selvin E, Rosamond WD, et al. HbA 1c as a risk factor for heart failure in persons with diabetes: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Diabetologia. (2008) 51:2197–204. doi: 10.1007/s00125-008-1164-z
43. Matsushita K, Blecker S, Pazin-Filho A, Bertoni A, Chang PP, Coresh J, et al. The association of hemoglobin a1c with incident heart failure among people without diabetes: the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Diabetes. (2010) 59:2020–6. doi: 10.2337/db10-0165
44. Echouffo-Tcheugui JB, Zhang S, Florido R, Hamo C, Pankow JS, Michos ED, et al. Duration of diabetes and incident heart failure: the ARIC (Atherosclerosis risk in communities) study. JACC Heart Fail. (2021) 9:594–603. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2021.06.005
45. Sowers JR, Epstein M, and Frohlich ED. Diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease: an update. Hypertension. (2001) 37:1053–9. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.37.4.1053
46. Franjic B and Marwick TH. The diabetic, hypertensive heart: epidemiology and mechanisms of a very high-risk situation. J Hum Hypertens. (2009) 23:709–17. doi: 10.1038/jhh.2009.43
47. Taqueti VR, Solomon SD, Shah AM, Desai AS, Groarke JD, Osborne MT, et al. Coronary microvascular dysfunction and future risk of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Eur Heart J. (2018) 39:840–9. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx721
48. Cameron NA, Petito LC, McCabe M, Allen NB, O’Brien MJ, Carnethon MR, et al. Quantifying the sex-race/ethnicity-specific burden of obesity on incident diabetes mellitus in the United States, 2001 to 2016: MESA and NHANES. J Am Heart Assoc. (2021) 10:e018799. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.018799
49. Piche ME, Tchernof A, and Despres JP. Obesity phenotypes, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Circ Res. (2020) 126:1477–500. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316101
50. Ingelsson E, Arnlov J, Lind L, and Sundstrom J. Metabolic syndrome and risk for heart failure in middle-aged men. Heart. (2006) 92:1409–13. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2006.089011
51. Pandey A, Patel KV, Vaduganathan M, Sarma S, Haykowsky MJ, Berry JD, et al. Physical activity, fitness, and obesity in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. JACC Heart Fail. (2018) 6:975–82. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2018.09.006
52. Patel KV, Bahnson JL, Gaussoin SA, Johnson KC, Pi-Sunyer X, White U, et al. Association of baseline and longitudinal changes in body composition measures with risk of heart failure and myocardial infarction in type 2 diabetes: findings from the look AHEAD trial. Circulation. (2020) 142:2420–30. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.050941
53. Vijay K, Neuen BL, and Lerma EV. Heart failure in patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease: challenges and opportunities. Cardiorenal Med. (2022) 12:1–10. doi: 10.1159/000520909
54. Tao J, Sang D, Zhen L, Zhang X, Li Y, Wang G, et al. Elevated urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio increases the risk of new-onset heart failure in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2023) 22:70. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01796-6
55. Zhang RM, Persson F, McGill JB, and Rossing P. Clinical implications and guidelines for CKD in type 2 diabetes. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2023) 38:542–50. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfac285
56. Budoff MJ, Raggi P, Beller GA, Berman DS, Druz RS, Malik S, et al. Noninvasive cardiovascular risk assessment of the asymptomatic diabetic patient: the imaging council of the american college of cardiology. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. (2016) 9:176–92. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2015.11.011
57. Naito R and Miyauchi K. Coronary artery disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int Heart J. (2017) 58:475–80. doi: 10.1536/ihj.17-191
58. Tavares CA, Wajchjenberg BL, Rochitte C, and Lerario AC. Screening for asymptomatic coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch Endocrinol Metab. (2016) 60:143–51. doi: 10.1590/2359-3997000000170
59. Ho JE, Enserro D, Brouwers FP, Kizer JR, Shah SJ, Psaty BM, et al. Predicting heart failure with preserved and reduced ejection fraction: the international collaboration on heart failure subtypes. Circ Heart Fail. (2016) 9:e003116. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.115.003116
60. Ho JE, Lyass A, Lee DS, Vasan RS, Kannel WB, Larson MG, et al. Predictors of new-onset heart failure: differences in preserved versus reduced ejection fraction. Circ Heart Fail. (2013) 6:279–86. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.112.972828
61. Pandey A, LaMonte M, Klein L, Ayers C, Psaty BM, Eaton CB, et al. Relationship between physical activity, body mass index, and risk of heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2017) 69:1129–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2016.11.081
62. Yang X, Ma RC, So WY, Kong AP, Ko GT, Ho CS, et al. Development and validation of a risk score for hospitalization for heart failure in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2008) 7:9. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-7-9
63. Pfister R, Cairns R, Erdmann E, and Schneider CA. A clinical risk score for heart failure in patients with type 2 diabetes and macrovascular disease: an analysis of the PROactive study. Int J Cardiol. (2013) 162:112–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2011.05.056
64. Hippisley-Cox J and Coupland C. Development and validation of risk prediction equations to estimate future risk of heart failure in patients with diabetes: a prospective cohort study. BMJ Open. (2015) 5:e008503. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-008503
65. Halon DA, Ayman J, Rubinshtein R, Zafrir B, Azencot M, and Lewis BS. Cardiac computed tomography angiographic findings as predictors of late heart failure in an asymptomatic diabetic cohort: an 8-year prospective follow-up study. Cardiology. (2017) 138:218–27. doi: 10.1159/000478995
66. Williams BA, Geba D, Cordova JM, and Shetty SS. A risk prediction model for heart failure hospitalization in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Cardiol. (2020) 43:275–83. doi: 10.1002/clc.23298
67. Pandey A, Vaduganathan M, Patel KV, Ayers C, Ballantyne CM, Kosiborod MN, et al. Biomarker-based risk prediction of incident heart failure in pre-diabetes and diabetes. JACC Heart Fail. (2021) 9:215–23. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2020.10.013
68. Patel KV, Khan MS, Segar MW, Bahnson JL, Garcia KR, Clark JM, et al. Optimal cardiometabolic health and risk of heart failure in type 2 diabetes: an analysis from the Look AHEAD trial. Eur J Heart Fail. (2022) 24:2037–47. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.2723
69. Segar MW, Khan MS, Patel KV, Vaduganathan M, Kannan V, Willett D, et al. Incorporation of natriuretic peptides with clinical risk scores to predict heart failure among individuals with dysglycaemia. Eur J Heart Fail. (2022) 24:169–80. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.2375
70. Segar MW, Patel KV, Hellkamp AS, Vaduganathan M, Lokhnygina Y, Green JB, et al. Validation of the WATCH-DM and TRS-HF(DM) risk scores to predict the risk of incident hospitalization for heart failure among adults with type 2 diabetes: A multicohort analysis. J Am Heart Assoc. (2022) 11:e024094. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.024094
71. Verma S, Sharma A, Zinman B, Ofstad AP, Fitchett D, Brueckmann M, et al. Empagliflozin reduces the risk of mortality and hospitalization for heart failure across Thrombolysis In Myocardial Infarction Risk Score for Heart Failure in Diabetes categories: Post hoc analysis of the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2020) 22:1141–50. doi: 10.1111/dom.14015
72. Elharram M, Ferreira JP, Huynh T, Ni J, Giannetti N, Verma S, et al. Prediction of heart failure outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Validation of the Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction Risk Score for Heart Failure in Diabetes (TRS-HF(DM)) in patients in the ACCORD trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2021) 23:782–90. doi: 10.1111/dom.14283
73. Saha A, Patel KV, Ayers C, Ballantyne CM, Correa A, Defilippi C, et al. Longitudinal changes in cardiac troponin and risk of heart failure among black adults. J Card Fail. (2023) 29:6–15. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2022.05.013
74. Vaduganathan M, Sattar N, Xu J, Butler J, Mahaffey KW, Neal B, et al. Stress cardiac biomarkers, cardiovascular and renal outcomes, and response to canagliflozin. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2022) 79:432–44. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.11.027
75. Fraty M, Velho G, Gand E, Fumeron F, Ragot S, Sosner P, et al. Prognostic value of plasma MR-proADM vs NT-proBNP for heart failure in people with type 2 diabetes: the SURDIAGENE prospective study. Diabetologia. (2018) 61:2643–53. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4727-7
76. Castiglione V, Aimo A, Vergaro G, Saccaro L, Passino C, and Emdin M. Biomarkers for the diagnosis and management of heart failure. Heart Fail Rev. (2022) 27:625–43. doi: 10.1007/s10741-021-10105-w
77. Rossello X and Gonzalez-Del-Hoyo M. Survival analyses in cardiovascular research, part II: statistical methods in challenging situations. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). (2022) 75:77–85. doi: 10.1016/j.rec.2021.07.001
78. Piek A, Du W, de Boer RA, and Sillje HHW. Novel heart failure biomarkers: why do we fail to exploit their potential? Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. (2018) 55:246–63. doi: 10.1080/10408363.2018.1460576
79. Ledwidge M, Gallagher J, Conlon C, Tallon E, O’Connell E, Dawkins I, et al. Natriuretic peptide-based screening and collaborative care for heart failure: the STOP-HF randomized trial. JAMA. (2013) 310:66–74. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.7588
80. Evans JDW, Dobbin SJH, Pettit SJ, Di Angelantonio E, and Willeit P. High-sensitivity cardiac troponin and new-onset heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 67,063 patients with 4,165 incident heart failure events. JACC Heart Fail. (2018) 6:187–97. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2017.11.003
81. Levin ER, Gardner DG, and Samson WK. Natriuretic peptides. N Engl J Med. (1998) 339:321–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199807303390507
82. Cowie MR, Jourdain P, Maisel A, Dahlstrom U, Follath F, Isnard R, et al. Clinical applications of B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) testing. Eur Heart J. (2003) 24:1710–8. doi: 10.1016/s0195-668x(03)00476-7
83. Huelsmann M, Neuhold S, Resl M, Strunk G, Brath H, Francesconi C, et al. PONTIAC (NT-proBNP selected prevention of cardiac events in a population of diabetic patients without a history of cardiac disease): a prospective randomized controlled trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2013) 62:1365–72. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.05.069
84. Pop-Busui R, Januzzi JL, Bruemmer D, Butalia S, Green JB, Horton WB, et al. Heart failure: an underappreciated complication of diabetes. A consensus report of the american diabetes association. Diabetes Care. (2022) 45:1670–90. doi: 10.2337/dci22-0014
85. Sabbatinelli J, Giuliani A, Bonfigli AR, Ramini D, Matacchione G, Campolucci C, et al. Prognostic value of soluble ST2, high-sensitivity cardiac troponin, and NT-proBNP in type 2 diabetes: a 15-year retrospective study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2022) 21:180. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01616-3
86. Dandamudi S, Slusser J, Mahoney DW, Redfield MM, Rodeheffer RJ, and Chen HH. The prevalence of diabetic cardiomyopathy: a population-based study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. J Card Fail. (2014) 20:304–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2014.02.007
87. Holland DJ, Marwick TH, Haluska BA, Leano R, Hordern MD, Hare JL, et al. Subclinical LV dysfunction and 10-year outcomes in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Heart. (2015) 101:1061–6. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2014-307391
88. Lang RM, Addetia K, Narang A, and Mor-Avi V. 3-dimensional echocardiography: latest developments and future directions. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. (2018) 11:1854–78. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2018.06.024
89. Segar MW, Khan MS, Patel KV, Butler J, Tang WHW, Vaduganathan M, et al. Prevalence and prognostic implications of diabetes with cardiomyopathy in community-dwelling adults. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2021) 78:1587–98. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.08.020
90. Bogdanovic J, Asanin M, Krljanac G, Lalic NM, Jotic A, Stankovic S, et al. Impact of acute hyperglycemia on layer-specific left ventricular strain in asymptomatic diabetic patients: an analysis based on two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2019) 18:68. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0876-3
91. Mohseni-Badalabadi R, Mehrabi-Pari S, and Hosseinsabet A. Evaluation of the left atrial function by two-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography in diabetic patients with obesity. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. (2020) 36:643–52. doi: 10.1007/s10554-020-01768-x
92. Liu JH, Chen Y, Yuen M, Zhen Z, Chan CW, Lam KS, et al. Incremental prognostic value of global longitudinal strain in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2016) 15:22. doi: 10.1186/s12933-016-0333-5
93. Pan KL, Hsu YC, Chang ST, Chung CM, and Lin CL. The role of cardiac fibrosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy: from pathophysiology to clinical diagnostic tools. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:8604. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108604
94. Umpierre D, Ribeiro PA, Kramer CK, Leitao CB, Zucatti AT, Azevedo MJ, et al. Physical activity advice only or structured exercise training and association with HbA1c levels in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. (2011) 305:1790–9. doi: 10.1001/jama.2011.576
95. Swift DL, Johannsen NM, Lavie CJ, Earnest CP, Blair SN, and Church TS. Effects of clinically significant weight loss with exercise training on insulin resistance and cardiometabolic adaptations. Obes (Silver Spring). (2016) 24:812–9. doi: 10.1002/oby.21404
96. Hordern MD, Coombes JS, Cooney LM, Jeffriess L, Prins JB, and Marwick TH. Effects of exercise intervention on myocardial function in type 2 diabetes. Heart. (2009) 95:1343–9. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2009.165571
97. Jonker JT, de Mol P, de Vries ST, Widya RL, Hammer S, van Schinkel LD, et al. Exercise and type 2 diabetes mellitus: changes in tissue-specific fat distribution and cardiac function. Radiology. (2013) 269:434–42. doi: 10.1148/radiol.13121631
98. Look ARG, Wing RR, Bolin P, Brancati FL, Bray GA, Clark JM, et al. Cardiovascular effects of intensive lifestyle intervention in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2013) 369:145–54. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1212914
99. Pandey A, Patel KV, Bahnson JL, Gaussoin SA, Martin CK, Balasubramanyam A, et al. Association of intensive lifestyle intervention, fitness, and body mass index with risk of heart failure in overweight or obese adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: an analysis from the look AHEAD trial. Circulation. (2020) 141:1295–306. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.044865
100. Cameron AR, Morrison VL, Levin D, Mohan M, Forteath C, Beall C, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of metformin irrespective of diabetes status. Circ Res. (2016) 119:652–65. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308445
101. Dziubak A, Wojcicka G, Wojtak A, and Beltowski J. Metabolic effects of metformin in the failing heart. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19:2869. doi: 10.3390/ijms19102869
102. Dludla PV, Nyambuya TM, Johnson R, Silvestri S, Orlando P, Mazibuko-Mbeje SE, et al. Metformin and heart failure-related outcomes in patients with or without diabetes: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Heart Fail Rev. (2021) 26:1437–45. doi: 10.1007/s10741-020-09942-y
103. Goldberg RB, Orchard TJ, Crandall JP, Boyko EJ, Budoff M, Dabelea D, et al. Effects of long-term metformin and lifestyle interventions on cardiovascular events in the diabetes prevention program and its outcome study. Circulation. (2022) 145:1632–41. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.056756
104. Weir DL, Abrahamowicz M, Beauchamp ME, and Eurich DT. Acute vs cumulative benefits of metformin use in patients with type 2 diabetes and heart failure. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2018) 20:2653–60. doi: 10.1111/dom.13448
105. Retwinski A, Kosmalski M, Crespo-Leiro M, Maggioni A, Opolski G, Ponikowski P, et al. The influence of metformin and the presence of type 2 diabetes mellitus on mortality and hospitalisation in patients with heart failure. Kardiol Pol. (2018) 76:1336–43. doi: 10.5603/KP.a2018.0127
106. Rao AD, Kuhadiya N, Reynolds K, and Fonseca VA. Is the combination of sulfonylureas and metformin associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease or all-cause mortality?: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Diabetes Care. (2008) 31:1672–8. doi: 10.2337/dc08-0167
107. Roumie CL, Greevy RA, Grijalva CG, Hung AM, Liu X, Murff HJ, et al. Association between intensification of metformin treatment with insulin vs sulfonylureas and cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality among patients with diabetes. JAMA. (2014) 311:2288–96. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.4312
108. Sola D, Rossi L, Schianca GP, Maffioli P, Bigliocca M, Mella R, et al. Sulfonylureas and their use in clinical practice. Arch Med Sci. (2015) 11:840–8. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2015.53304
109. Azoulay L and Suissa S. Sulfonylureas and the risks of cardiovascular events and death: A methodological meta-regression analysis of the observational studies. Diabetes Care. (2017) 40:706–14. doi: 10.2337/dc16-1943
110. Rosenstock J, Kahn SE, Johansen OE, Zinman B, Espeland MA, Woerle HJ, et al. Effect of linagliptin vs glimepiride on major adverse cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: the CAROLINA randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2019) 322:1155–66. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.13772
111. Diabetes Canada Clinical Practice Guidelines Expert C, Connelly KA, Gilbert RE, and Liu P. Treatment of diabetes in people with heart failure. Can J Diabetes. (2018) 42 Suppl 1:S196–200. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjd.2017.10.026
112. Home PD, Pocock SJ, Beck-Nielsen H, Curtis PS, Gomis R, Hanefeld M, et al. Rosiglitazone evaluated for cardiovascular outcomes in oral agent combination therapy for type 2 diabetes (RECORD): a multicentre, randomised, open-label trial. Lancet. (2009) 373:2125–35. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60953-3
113. Hippisley-Cox J and Coupland C. Diabetes treatments and risk of heart failure, cardiovascular disease, and all cause mortality: cohort study in primary care. BMJ. (2016) 354:i3477. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i3477
114. Investigators OT, Gerstein HC, Bosch J, Dagenais GR, Diaz R, Jung H, et al. Basal insulin and cardiovascular and other outcomes in dysglycemia. N Engl J Med. (2012) 367:319–28. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1203858
115. Pratley RE, Husain M, Lingvay I, Pieber TR, Mark T, Saevereid HA, et al. Heart failure with insulin degludec versus glargine U100 in patients with type 2 diabetes at high risk of cardiovascular disease: DEVOTE 14. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2019) 18:156. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0960-8
116. Fathi A, Vickneson K, and Singh JS. SGLT2-inhibitors; more than just glycosuria and diuresis. Heart Fail Rev. (2021) 26:623–42. doi: 10.1007/s10741-020-10038-w
117. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice C. 10. Cardiovascular disease and risk management: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. (2022) 45:S144–S74. doi: 10.2337/dc22-S010
118. Huang K, Luo X, Liao B, Li G, and Feng J. Insights into SGLT2 inhibitor treatment of diabetic cardiomyopathy: focus on the mechanisms. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2023) 22:86. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01816-5
119. Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2015) 373:2117–28. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1504720
120. Wiviott SD, Raz I, Bonaca MP, Mosenzon O, Kato ET, Cahn A, et al. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2019) 380:347–57. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1812389
121. Fernandez−Balsells MM, Sojo-Vega L, and Ricart-Engel W. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2017) 377:2098. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1712572
122. Cannon CP, Pratley R, Dagogo-Jack S, Mancuso J, Huyck S, Masiukiewicz U, et al. Cardiovascular outcomes with ertugliflozin in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2020) 383:1425–35. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2004967
123. Perkovic V, Jardine MJ, Neal B, Bompoint S, Heerspink HJL, Charytan DM, et al. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. (2019) 380:2295–306. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1811744
124. McMurray JJV, Wheeler DC, Stefansson BV, Jongs N, Postmus D, Correa-Rotter R, et al. Effect of dapagliflozin on clinical outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease, with and without cardiovascular disease. Circulation. (2021) 143:438–48. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.051675
125. Moellmann J, Klinkhammer BM, Droste P, Kappel B, Haj-Yehia E, Maxeiner S, et al. Empagliflozin improves left ventricular diastolic function of db/db mice. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. (2020) 1866:165807. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165807
126. Adingupu DD, Gopel SO, Gronros J, Behrendt M, Sotak M, Miliotis T, et al. SGLT2 inhibition with empagliflozin improves coronary microvascular function and cardiac contractility in prediabetic ob/ob(-/-) mice. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2019) 18:16. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0820-6
127. Zhang Y, Lin X, Chu Y, Chen X, Du H, Zhang H, et al. Dapagliflozin: a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor, attenuates angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibrotic remodeling by regulating TGFbeta1/Smad signaling. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2021) 20:121. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01312-8
128. Lee TM, Chang NC, and Lin SZ. Dapagliflozin, a selective SGLT2 Inhibitor, attenuated cardiac fibrosis by regulating the macrophage polarization via STAT3 signaling in infarcted rat hearts. Free Radic Biol Med. (2017) 104:298–310. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.01.035
129. Verma S, Rawat S, Ho KL, Wagg CS, Zhang L, Teoh H, et al. Empagliflozin increases cardiac energy production in diabetes: novel translational insights into the heart failure benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors. JACC Basic Transl Sci. (2018) 3:575–87. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2018.07.006
130. Lee CC, Chen WT, Chen SY, and Lee TM. Dapagliflozin attenuates arrhythmic vulnerabilities by regulating connexin43 expression via the AMPK pathway in post-infarcted rat hearts. Biochem Pharmacol. (2021) 192:114674. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114674
131. Kadosaka T, Watanabe M, Natsui H, Koizumi T, Nakao M, Koya T, et al. Empagliflozin attenuates arrhythmogenesis in diabetic cardiomyopathy by normalizing intracellular Ca(2+) handling in ventricular cardiomyocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2023) 324:H341–H54. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00391.2022
132. Gribble FM and Reimann F. Metabolic Messengers: glucagon-like peptide 1. Nat Metab. (2021) 3:142–8. doi: 10.1038/s42255-020-00327-x
133. Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K, Kristensen P, Mann JF, Nauck MA, et al. Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2016) 375:311–22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1603827
134. Hernandez AF, Green JB, Janmohamed S, D’Agostino RB, Granger CB, Jones NP, et al. Albiglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease (Harmony Outcomes): a double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. (2018) 392:1519–29. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32261-X
135. Gerstein HC, Sattar N, Rosenstock J, Ramasundarahettige C, Pratley R, Lopes RD, et al. Cardiovascular and renal outcomes with efpeglenatide in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2021) 385:896–907. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2108269
136. Sattar N, Lee MMY, Kristensen SL, Branch KRH, Del Prato S, Khurmi NS, et al. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2021) 9:653–62. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00203-5
137. Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, Eliaschewitz FG, Jodar E, Leiter LA, et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2016) 375:1834–44. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1607141
138. Pinto LC, Rados DV, Remonti LR, Viana LV, Pulz GT, Carpena MP, et al. Patient-centered management of type 2 diabetes mellitus based on specific clinical scenarios: systematic review, meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2020) 105:dgaa534. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa534
139. Holst JJ and Deacon CF. Inhibition of the activity of dipeptidyl-peptidase IV as a treatment for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. (1998) 47:1663–70. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.47.11.1663
140. Deacon CF. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2020) 16:642–53. doi: 10.1038/s41574-020-0399-8
141. Scirica BM, Bhatt DL, Braunwald E, Steg PG, Davidson J, Hirshberg B, et al. Saxagliptin and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. (2013) 369:1317–26. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1307684
142. Zannad F, Cannon CP, Cushman WC, Bakris GL, Menon V, Perez AT, et al. Heart failure and mortality outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes taking alogliptin versus placebo in EXAMINE: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind trial. Lancet. (2015) 385:2067–76. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)62225-X
143. Green JB, Bethel MA, Armstrong PW, Buse JB, Engel SS, Garg J, et al. Effect of sitagliptin on cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2015) 373:232–42. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1501352
144. Rosenstock J, Perkovic V, Johansen OE, Cooper ME, Kahn SE, Marx N, et al. Effect of linagliptin vs placebo on major cardiovascular events in adults with type 2 diabetes and high cardiovascular and renal risk: the CARMELINA randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2019) 321:69–79. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.18269
145. Pavlou DI, Paschou SA, Anagnostis P, Spartalis M, Spartalis E, Vryonidou A, et al. Hypertension in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Targets and management. Maturitas. (2018) 112:71–7. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2018.03.013
146. Wang J, Chen Y, Xu W, Lu N, Cao J, and Yu S. Effects of intensive blood pressure lowering on mortality and cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetic patients: A meta-analysis. PloS One. (2019) 14:e0215362. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215362
147. de Boer IH, Bangalore S, Benetos A, Davis AM, Michos ED, Muntner P, et al. Diabetes and hypertension: A position statement by the american diabetes association. Diabetes Care. (2017) 40:1273–84. doi: 10.2337/dci17-0026
148. Te Riet L, van Esch JH, Roks AJ, van den Meiracker AH, and Danser AH. Hypertension: renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system alterations. Circ Res. (2015) 116:960–75. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.303587
149. Currie G, Taylor AH, Fujita T, Ohtsu H, Lindhardt M, Rossing P, et al. Effect of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists on proteinuria and progression of chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Nephrol. (2016) 17:127. doi: 10.1186/s12882-016-0337-0
150. Agarwal R, Kolkhof P, Bakris G, Bauersachs J, Haller H, Wada T, et al. Steroidal and non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in cardiorenal medicine. Eur Heart J. (2021) 42:152–61. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa736
151. Filippatos G, Anker SD, Agarwal R, Ruilope LM, Rossing P, Bakris GL, et al. Finerenone reduces risk of incident heart failure in patients with chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes: analyses from the FIGARO-DKD trial. Circulation. (2022) 145:437–47. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.057983
152. Bakris GL, Agarwal R, Anker SD, Pitt B, Ruilope LM, Rossing P, et al. Effect of finerenone on chronic kidney disease outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2020) 383:2219–29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2025845
153. Agarwal R, Filippatos G, Pitt B, Anker SD, Rossing P, Joseph A, et al. Cardiovascular and kidney outcomes with finerenone in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease: the FIDELITY pooled analysis. Eur Heart J. (2022) 43:474–84. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab777
154. Shi Q, Nong K, Vandvik PO, Guyatt GH, Schnell O, Ryden L, et al. Benefits and harms of drug treatment for type 2 diabetes: systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. (2023) 381:e074068. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2022-074068
155. Naegele M, Hernandez AF, and Ruschitzka F. Finerenone in heart failure: walking a fine line. Eur Heart J. (2016) 37:2115–7. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw155
156. Marx N, Federici M, Schutt K, Muller-Wieland D, Ajjan RA, Antunes MJ, et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the management of cardiovascular disease in patients with diabetes. Eur Heart J. (2023) 44:4043–140. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad192
157. Sjostrom L, Narbro K, Sjostrom CD, Karason K, Larsson B, Wedel H, et al. Effects of bariatric surgery on mortality in Swedish obese subjects. N Engl J Med. (2007) 357:741–52. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa066254
158. Adams TD, Gress RE, Smith SC, Halverson RC, Simper SC, Rosamond WD, et al. Long-term mortality after gastric bypass surgery. N Engl J Med. (2007) 357:753–61. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa066603
159. Schauer PR, Bhatt DL, Kirwan JP, Wolski K, Aminian A, Brethauer SA, et al. Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy for diabetes - 5-year outcomes. N Engl J Med. (2017) 376:641–51. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1600869
160. Jamaly S, Carlsson L, Peltonen M, Jacobson P, and Karason K. Surgical obesity treatment and the risk of heart failure. Eur Heart J. (2019) 40:2131–8. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz295
161. Sundstrom J, Bruze G, Ottosson J, Marcus C, Naslund I, and Neovius M. Weight loss and heart failure: A nationwide study of gastric bypass surgery versus intensive lifestyle treatment. Circulation. (2017) 135:1577–85. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.025629
162. Mentias A, Aminian A, Youssef D, Pandey A, Menon V, Cho L, et al. Long-term cardiovascular outcomes after bariatric surgery in the medicare population. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2022) 79:1429–37. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2022.01.047
163. Cuspidi C, Rescaldani M, Tadic M, Sala C, and Grassi G. Effects of bariatric surgery on cardiac structure and function: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Hypertens. (2014) 27:146–56. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpt215
164. Kaier TE, Morgan D, Grapsa J, Demir OM, Paschou SA, Sundar S, et al. Ventricular remodelling post-bariatric surgery: is the type of surgery relevant? A prospective study with 3D speckle tracking. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. (2014) 15:1256–62. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jeu116
165. Leung M, Xie M, Durmush E, Leung DY, and Wong VW. Weight loss with sleeve gastrectomy in obese type 2 diabetes mellitus: impact on cardiac function. Obes Surg. (2016) 26:321–6. doi: 10.1007/s11695-015-1748-x
166. Tuluce K, Kara C, Tuluce SY, Cetin N, Topaloglu C, Bozkaya YT, et al. Early reverse cardiac remodeling effect of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Obes Surg. (2017) 27:364–75. doi: 10.1007/s11695-016-2301-2
167. Shin SH, Lee YJ, Heo YS, Park SD, Kwon SW, Woo SI, et al. Beneficial effects of bariatric surgery on cardiac structure and function in obesity. Obes Surg. (2017) 27:620–5. doi: 10.1007/s11695-016-2330-x
168. Kurnicka K, Domienik-Karlowicz J, Lichodziejewska B, Bielecki M, Kozlowska M, Goliszek S, et al. Improvement of left ventricular diastolic function and left heart morphology in young women with morbid obesity six months after bariatric surgery. Cardiol J. (2018) 25:97–105. doi: 10.5603/CJ.a2017.0059
169. Reddy YNV, Anantha-Narayanan M, Obokata M, Koepp KE, Erwin P, Carter RE, et al. Hemodynamic effects of weight loss in obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JACC Heart Fail. (2019) 7:678–87. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2019.04.019
170. Bakbak E, Terenzi DC, Trac JZ, Teoh H, Quan A, Glazer SA, et al. Lessons from bariatric surgery: Can increased GLP-1 enhance vascular repair during cardiometabolic-based chronic disease? Rev Endocr Metab Disord. (2021) 22:1171–88. doi: 10.1007/s11154-021-09669-7
171. Schiavon CA, Bersch-Ferreira AC, Santucci EV, Oliveira JD, Torreglosa CR, Bueno PT, et al. Effects of bariatric surgery in obese patients with hypertension: the GATEWAY randomized trial (Gastric bypass to treat obese patients with steady hypertension). Circulation. (2018) 137:1132–42. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.032130
172. Sandoval DA and Patti ME. Glucose metabolism after bariatric surgery: implications for T2DM remission and hypoglycaemia. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2023) 19:164–76. doi: 10.1038/s41574-022-00757-5
173. Wang T, Xu J, Zhang H, Tao L, and Huang X. Triglyceride-glucose index for the detection of subclinical heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in patients with type 2 diabetes. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2023) 10:1086978. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1086978
174. Zhou Q, Yang J, Tang H, Guo Z, Dong W, Wang Y, et al. High triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index is associated with poor prognosis of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2023) 22:263. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-02001-4
175. Ni W, Jiang R, Xu D, Zhu J, Chen J, Lin Y, et al. Association between insulin resistance indices and outcomes in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2025) 24:32. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02595-x
176. Tunon J, Barbas C, Blanco-Colio L, Burillo E, Lorenzo O, Martin-Ventura JL, et al. Proteomics and metabolomics in biomarker discovery for cardiovascular diseases: progress and potential. Expert Rev Proteomics. (2016) 13:857–71. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2016.1217775
177. Janjusevic M, Fluca AL, Ferro F, Gagno G, D’Alessandra Y, Beltrami AP, et al. Traditional and emerging biomarkers in asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction-promising non-coding RNAs and exosomes as biomarkers in early phases of cardiac damage. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:4937. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094937
178. Zhu L, Wang Y, Zhao S, and Lu M. Detection of myocardial fibrosis: Where we stand. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 9:926378. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.926378
179. Bhagani H, Nasser SA, Dakroub A, El-Yazbi AF, Eid AA, Kobeissy F, et al. The mitochondria: A target of polyphenols in the treatment of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:4962. doi: 10.3390/ijms21144962
Keywords: type 2 diabetes mellitus, diabetic cardiomyopathy, heart failure, risk stratification, prevention
Citation: Chen X, Li W, Zheng J, Huang M, Wang J and Wu M (2025) Type 2 diabetes mediated heart failure: focus on early recognition and clinical strategies. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1630686. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1630686
Received: 18 May 2025; Accepted: 18 August 2025;
Published: 10 September 2025.
Edited by:
Giuseppe Armentaro, University of Magna Graecia, ItalyReviewed by:
Kulvinder Kochar Kaur, Kulvinder Kaur Centre For Human Reproduction, IndiaRadha Vaddavalli, The Ohio State University, United States
Haskly Mokoena, University of Limpopo, South Africa
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Li, Zheng, Huang, Wang and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jinxi Wang, OTgzNTk5ODIwQHFxLmNvbQ==; Meifang Wu, NjQ2NjkxMjA1QHFxLmNvbQ==
 Xi Chen
Xi Chen Wei Li
Wei Li Meifang Wu
Meifang Wu