- Department of Burns, Plastic Surgery and Cosmetology, Chongqing University Fuling Hospital, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China
Diabetic foot ulcers represent a significant complication of diabetes mellitus, presenting substantial challenges due to their intricate pathogenesis, which encompasses neuropathy, vasculopathy, chronic inflammation, and biofilm-associated infections. Despite considerable advancements in Western medical interventions, including surgical debridement, skin grafting, negative pressure wound therapy, and innovative dressings, these ulcers remain a leading cause of amputation and contribute to a substantial socioeconomic burden. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has emerged as a promising adjunctive therapy, offering multi-targeted mechanisms that address oxidative stress, chronic inflammation, angiogenesis, and microbial resistance associated with diabetic foot ulcers. This review aims to examine contemporary studies on the application of TCM in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers, evaluating its efficacy and elucidating its mechanisms of action, thereby providing a reference for clinical treatment decisions and guiding future research directions.
Introduction
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a chronic metabolic disorder resulting from the interplay of genetic and environmental factors, with its prevalence rising annually (1). Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) represent a significant complication of diabetes mellitus, typically arising from a series of metabolic dysfunctions induced by a hyperglycemic environment. This environment leads to neuropathy, vasculopathy, and ultimately neurological disease and peripheral vascular injury in the lower extremities, as well as deep tissue damage (2, 3). The incidence of diabetic foot ulcers is increasing each year, with approximately 20% of affected patients eventually requiring amputation (4–7). The complex pathogenesis and prolonged duration of diabetic foot ulcers have rendered them a substantial socioeconomic burden (8).
Presently, the primary strategies in Western medical treatment include glycemic control, infection management, removal of necrotic tissue, decompression, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, and restoration of blood flow (9–12).Interventions such as surgical debridement, skin grafting, negative pressure therapy, novel biological dressings, cytokine therapy, and stem cell transplantation have demonstrated promising outcomes (13–15). With the advancement of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), it has been demonstrated to possess satisfactory efficacy in the clinical management of diabetes mellitus and its associated complications (16). Research indicates that herbal medicine serves as a safe and effective adjunctive therapy to conventional treatments for diabetic foot, facilitating the healing of diabetic foot ulcers (17, 18). However, there are currently few review articles on the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers with TCM, making it difficult to quickly obtain the latest research findings in this field. Consequently, this study aims to synthesize the current research landscape regarding the use of TCM in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers, thereby providing a reference for future research directions.
Pathophysiology of diabetic foot ulcers
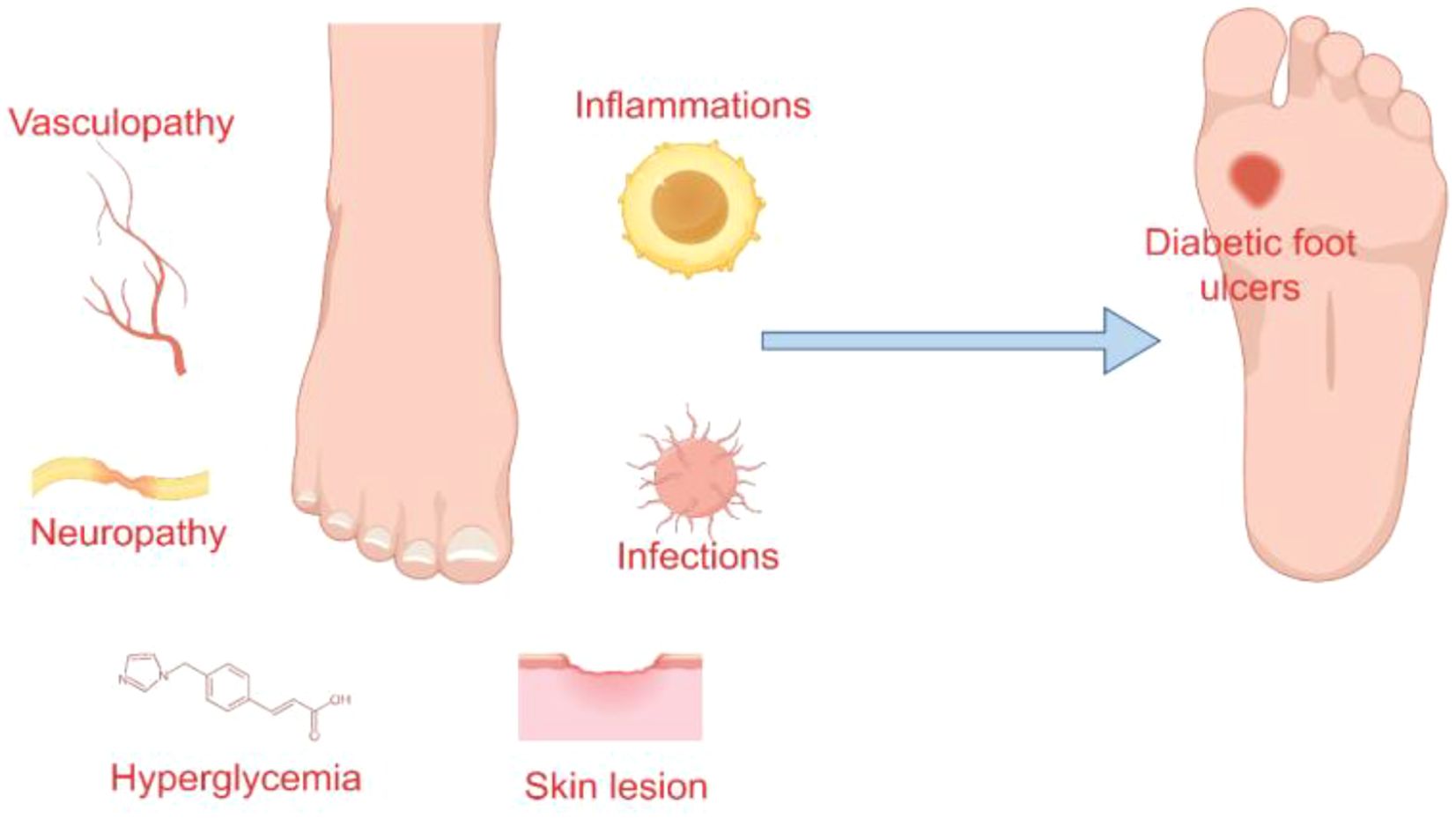
The pathogenesis of diabetic foot ulcers is predominantly linked to neuropathy, vasculopathy, and infection and inflammation (19, 20) (Figure 1). Neuropathy contributes to the formation of high-pressure areas on the plantar surface of the foot, particularly at the hammertoes and metatarsal heads, while diminished protective sensory function renders the skin more susceptible and less perceptible, ultimately leading to ulcer development (13).
Angiogenesis is a critical component of wound healing, with the functionality of vascular endothelial cells playing a pivotal role in this process (21, 22). The hyperglycemic and insulin-resistant microenvironment downregulates the expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and impairs the transport capacity of L-arginine across the endothelial cell membrane, consequently reducing nitric oxide (NO) production. Furthermore, elevated levels of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) can inactivate NO, while a decrease in tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) contributes to endothelial cell dysfunction (23–25). Such endothelial cell damage compromises vascular dilation, impairs blood flow and perfusion at the wound site, and ultimately delays wound healing (26). Moreover, angiogenesis is reliant on various proangiogenic factors, including vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF-A), fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2), and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) (27–29). Disorders in glucose metabolism can affect the function of hypoxia-inducible factor 1-α (HIF-1α), thereby inhibiting the activity of these growth factors and adversely affecting angiogenesis (30). This results in the thickening of the basement membrane, impaired vasodilation, and compromised microcirculation, thereby exacerbating ischemia, hypoxia, and peripheral nerve damage associated with diabetic foot ulcers (31–33).
Another pathological feature of diabetic foot ulcers, particularly those that are refractory to healing, is the prolonged chronic inflammatory phase. Hyperglycemia disrupts immune function, elevates levels of inflammatory cytokines, and facilitates biofilm formation (34–36). In diabetic patients, neutrophil dysfunction impairs macrophage polarization and the release of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), further intensifying the inflammatory response (37, 38). The presence of macrophages with various phenotypes is crucial for wound healing, with M2 macrophages playing a pivotal anti-inflammatory role, potentially through the promotion of vascular endothelial growth factor secretion (39, 40). The prolonged polarization of M1 macrophages extends the inflammatory response (41). Furthermore, T cells and natural killer (NK) cells intensify this inflammatory process. In individuals with diabetes, there is an increased presence of pro-inflammatory T cells in the bloodstream. Within ulcers, there is an accumulation of effector T cells, while naive T cells are markedly diminished, contributing to delayed wound healing (42, 43). NK cells enhance the inflammatory response by secreting interferon-γ, perforins, and granzymes; the interferon they release also facilitates M1 macrophage polarization and neutrophil infiltration (44, 45). The continuous infiltration of macrophages and neutrophils consequently results in impaired wound healing (46). Moreover, the hyperglycemic microenvironment present in wounds creates optimal conditions for bacterial proliferation and colonization, facilitating the formation of bacterial biofilms. These biofilms contribute to increased bacterial resistance and the likelihood of infection (47, 48). The development of bacterial biofilms triggers the release of elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines by the host, thereby extending the inflammatory phase of wound healing. Chronic inflammation is recognized as an important factor in the persistence of non-healing wounds (49–51).
Mechanisms of TCM in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers
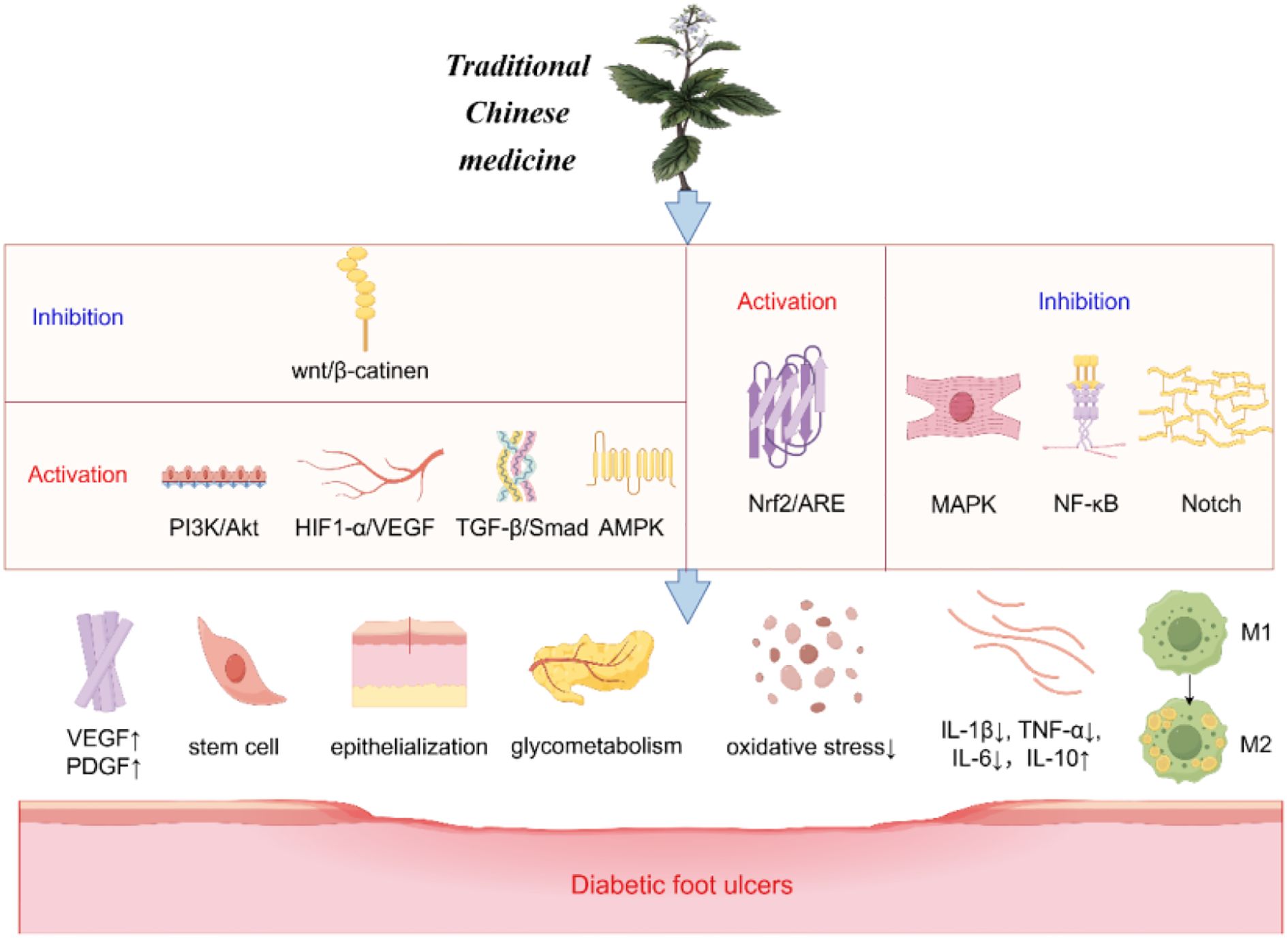
The healing process of diabetic foot ulcers encompasses several factors, including the amelioration of neurological and vascular lesions, control of oxidative stress, as well as the management of infection and inflammation (Figure 2).
Promote angiogenesis
The Wingless/Integrated (Wnt) signaling pathway promotes wound angiogenesis and epithelial remodeling, among other functions, and is associated with wound healing. Closely related to this is the classic Wnt/β-catenin pathway (52). Terpenoids derived from TCM have been shown to reduce apoptosis and promote the proliferation and differentiation of epidermal stem cells via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway (53, 54). The Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Protein Kinase B (PI3K/Akt) pathway is a well-established anti-apoptotic and proliferative signaling cascade within the body, with the mammalian target of rapamycin complexes 1 and 2 (mTORC1/2) and glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) playing significant roles in the healing process of DFUs (55, 56). Notoginsenoside Ft1 has been shown to enhance VEGF expression via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway, thereby promoting the formation of vascular and granulation tissues, controlling blood sugar, and expediting epithelialization (57). Additional pathways implicated in angiogenesis include the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β)/Smad signaling pathway, AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), and the HIF-1α/VEGF pathway, all of which facilitate angiogenesis by upregulating VEGF expression, ultimately contributing to wound healing (58–61). Nonetheless, the composition of TCM is intricate, and existing studies predominantly focus on individual components of TCM, often lacking comprehensive clinical data for validation. Future research should consider employing multi-omics approaches to explore these effects further.
Reduce oxidative stress
Wound healing is intricately linked to oxidative stress. The nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2/antioxidant response element (Nrf2/ARE) pathway facilitates the transport of antioxidants, including glutathione (GSH) and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), to mitigate reactive oxygen species (ROS) and suppress oxidative stress (62). TCM components, such as (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), flavonoids like Rutin and Luteolin, and Huangbai liniment (HB), have been shown to activate Nrf2, thereby reducing cellular damage and apoptosis induced by oxidative stress, and consequently enhancing wound healing in diabetic rat models (63–66). However, these investigations have only superficially addressed the underlying mechanisms and lack comprehensive validation through animal models or clinical trials.
Regulate inflammatory responses
The NF-κB signaling pathway plays a crucial role in mediating inflammatory responses by inducing the expression of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-6, which contribute to sustained inflammation and delayed healing of diabetic wounds (67). Both Kirenol and the natural phenolic compound salicylic acid (SA) have been demonstrated to inhibit the NF-κB pathway, thereby reducing the levels of interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-2 (IL-2), IL-8, and TNF-α, ultimately modulating inflammation (68, 69). Research by Sun et al. has further indicated that paeoniflorin (PF) can downregulate inflammatory mediators and facilitate wound healing in diabetic rat models (70). The recruitment of macrophages is linked to the Notch signaling pathway, which affects macrophage-mediated early inflammatory responses. EGCG has been shown to inhibit Notch signaling, promoting the conversion of macrophages to the M2 phenotype, thereby enhancing wound healing in diabetic mice (71, 72). Moreover, the Qizhi Jiangtang Capsule (QJC) has been reported to modulate inflammatory responses by inhibiting the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway (73). Despite these promising findings, current research on these TCMs is predominantly limited to animal studies, necessitating further clinical trials to substantiate their efficacy in humans.
Classification of traditional Chinese medicine
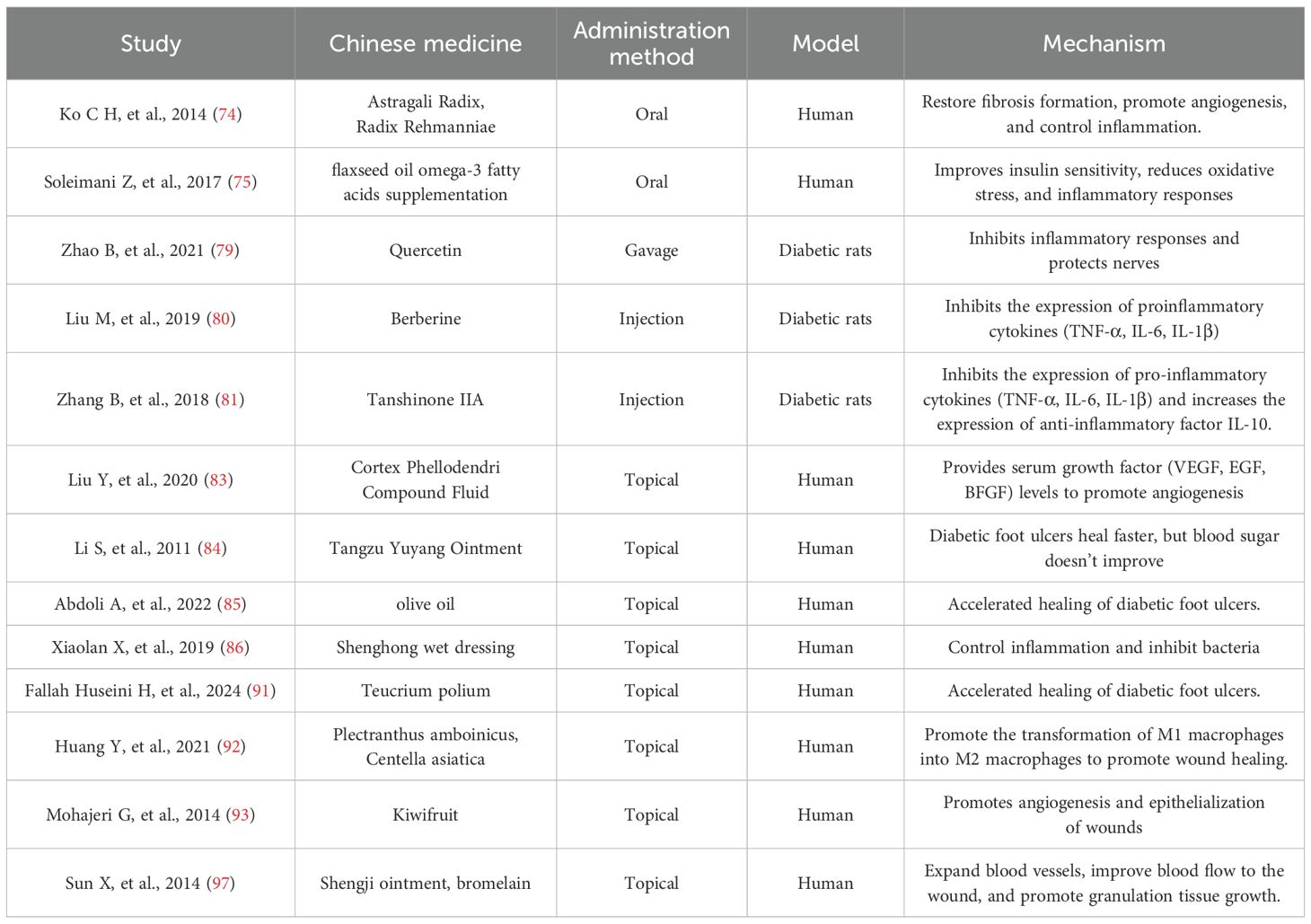
TCM can be divided into systemic and topical applications based on the method of administration. Different types of TCM promote the healing of diabetic foot ulcers through different mechanisms (Table 1).
Systematic traditional Chinese medicine
TCM, as the traditional medicine of China, has a history of several thousand years. Oral Chinese herbs have shown better efficacy for numerous diseases, including the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. Chun et al. found that a Chinese herbal formula (NF3) consisting of Astragalus and Radix et Rhizoma Dioscoreae could reduce inflammation and promote wound healing (74). Similarly, oral intake of Centella asiatica extract or omega-3 has been shown to expedite the healing process of diabetic foot ulcers (75, 76). Conversely, a study conducted by Mehrdad Mokhtari et al. revealed that while curcumin effectively lowered fasting blood glucose levels and enhanced antioxidant capacity in patients, it did not significantly accelerate wound healing (77). Numerous studies have substantiated the efficacy of herbs in inhibiting apoptosis, combating oxidative stress, reducing inflammatory factors, and protecting neural nutrients (78–82). Despite these promising findings, it is important to note that the majority of these studies remain at the preclinical stage, primarily involving animal models, and the overall quality of the literature is not consistently high. Moreover, the diabetic rat model cannot fully simulate the complex pathology of DFUs, and more clinical translational validation is needed in the future.
Traditional Chinese medicine for external application
The topical application of herbal formulations appears to be a more direct and effective method compared to herbal decoctions. The compound cypress oil solution, which includes forsythia, cypress, honeysuckle, dandelion, and centipede, has been shown to reduce inflammatory responses and enhance growth factor activity (66). In a controlled trial, this solution was found to increase growth factor concentrations and promote the healing of ulcer wounds more effectively than standard care (83). In a prospective randomized controlled trial conducted by Shufa Li et al., the healing rate of compound TANGZU YUYANG Ointment (TYO) for diabetic foot ulcers was reported to be 79.2%, demonstrating significant treatment efficacy with minimal side effects (84). Furthermore, herbal dressings derived from these formulations have also yielded promising outcomes (85, 86). The topical application of Chinese herbal medicine not only mitigates inflammation but also stimulates fibroblast proliferation, collagen synthesis, keratinocyte migration, and neovascularization, ultimately facilitating wound healing (87, 88). Topical application of TCM can also play an antibacterial role in bacterial infections that are often associated with diabetic foot ulcers, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Pneumococcus, Streptococcus, and so on (84, 89, 90). There are more trials of topical application of herbs than oral administration of herbs that have confirmed their efficacy (91–97). The beneficial effects of TCM in the local treatment of DFUs are attributed to stimulating cell proliferation, inhibiting local inflammatory responses, and promoting angiogenesis through increased vascular growth factors (VEGF, PDGF, etc.) (98).
Discussion
Diabetic foot ulcers present a complex pathogenesis and necessitate comprehensive treatment strategies. TCM, characterized by its multi-target and multi-level actions, offers various therapeutic approaches for DFUs. At present, the majority of research concerning the mechanisms underlying TCM treatment for DFUs remains at the preclinical stage. Despite notable advancements, diabetic foot rat models inadequately replicate the pathological complexity of DFUs, highlighting the need for future validation through experiments utilizing human-like skin models. Furthermore, although current research has demonstrated that TCM can facilitate wound healing via multiple pathways, most studies have concentrated on single-mechanism pathways. The application of spatial multi-omics technologies could enhance the exploration of TCM’s characteristics in treating DFUs through multi-targeted mechanisms. Moreover, existing studies on TCM treatment for DFUs are often limited by small sample sizes and suboptimal research designs, leading to evidence of generally low quality. And, there is a paucity of studies examining the effects of TCM dosage and administration methods on treatment efficacy. To address these limitations and enhance clinical application, future research should encompass multicenter, large-scale randomized controlled trials.
Conclusion
In summary, while TCM has demonstrated some efficacy in the management of DFUs, substantial progress is required to elucidate its efficacy and mechanisms of action. Additionally, exploring their integration with Western medicine may offer a more comprehensive solution to the global challenge posed by DFUs.
Author contributions
YX: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. PW: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. SC: Writing – original draft. YC: Funding acquisition, Validation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Science-Health Joint Medical Scientific Research Project of Chongqing (2022MSXM206) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2022CDJYGRH-016).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all those who contributed to this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M, Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2022) 183:109119. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119
2. Singh N, Armstrong DG, and Lipsky BA. Preventing foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. Jama. (2005) 293:217–28. doi: 10.1001/jama.293.2.217
3. Armstrong DG, Tan TW, Boulton AJM, and Bus SA. Diabetic foot ulcers: A review. Jama. (2023) 330:62–75. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.10578
4. Lipsky BA, Berendt AR, Cornia PB, Pile JC, Peters EJ, Armstrong DG, et al. 2012 infectious diseases society of america clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of diabetic foot infections. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. (2013) 103:2–7. doi: 10.7547/1030002
5. Alavi A, Sibbald RG, Mayer D, Goodman L, Botros M, Armstrong DG, et al. Diabetic foot ulcers: Part II. Management. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2014) 70:21.e1–4; quiz 45-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2013.07.048
6. Chang M and Nguyen TT. Strategy for treatment of infected diabetic foot ulcers. Acc Chem Res. (2021) 54:1080–93. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00864
7. Mauricio D, Jude E, Piaggesi A, and Frykberg R. Diabetic foot: current status and future prospects. J Diabetes Res. (2016) 2016:5691305. doi: 10.1155/2016/5691305
8. Rathnayake A, Saboo A, Malabu UH, and Falhammar H. Lower extremity amputations and long-term outcomes in diabetic foot ulcers: A systematic review. World J Diabetes. (2020) 11:391–9. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v11.i9.391
9. Reardon R, Simring D, Kim B, Mortensen J, Williams D, Leslie A, et al. The diabetic foot ulcer. Aust J Gen Pract. (2020) 49:250–5. doi: 10.31128/ajgp-11-19-5161
10. Wenhui L, Changgeng F, Lei X, Baozhong Y, Guobin L, Weijing F, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for chronic diabetic foot ulcers: An overview of systematic reviews. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2021) 176:108862. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108862
11. Fan W, Yang B, Hu X, Yang X, Shi C, Liu G, et al. Safety and efficacy of larval therapy on treating leg ulcers: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. (2020) 10:e039898. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039898
12. Schaper NC, van Netten JJ, Apelqvist J, Bus SA, Hinchliffe RJ, Lipsky BA, et al. Practical Guidelines on the prevention and management of diabetic foot disease (IWGDF 2019 update). Diabetes Metab Res Rev. (2020) 36 Suppl 1:e3266. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3266
13. Bandyk DF. The diabetic foot: Pathophysiology, evaluation, and treatment. Semin Vasc Surg. (2018) 31:43–8. doi: 10.1053/j.semvascsurg.2019.02.001
14. Shu X, Shu S, Tang S, Yang L, Liu D, Li K, et al. Efficiency of stem cell based therapy in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcer: a meta-analysis. Endocr J. (2018) 65:403–13. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ17-0424
15. Jiang P, Li Q, Luo Y, Luo F, Che Q, Lu Z, et al. Current status and progress in research on dressing management for diabetic foot ulcer. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2023) 14:1221705. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1221705
16. Yue SJ, Liu J, Feng WW, Zhang FL, Chen JX, Xin LT, et al. System pharmacology-based dissection of the synergistic mechanism of huangqi and huanglian for diabetes mellitus. Front Pharmacol. (2017) 8:694. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00694
17. Tan L, Shi Q, Liu C, Zhang J, Wang H, Zhai J, et al. Traditional chinese medicine injections in the treatment of diabetic foot: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2018) 2018:4730896. doi: 10.1155/2018/4730896
18. Chen M, Zheng H, Yin LP, and Xie CG. Is oral administration of Chinese herbal medicine effective and safe as an adjunctive therapy for managing diabetic foot ulcers? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Altern Complement Med. (2010) 16:889–98. doi: 10.1089/acm.2009.0470
19. Bus SA, Sacco ICN, Monteiro-Soares M, Raspovic A, Paton J, Rasmussen A, et al. Guidelines on the prevention of foot ulcers in persons with diabetes (IWGDF 2023 update). Diabetes Metab Res Rev. (2024) 40:e3651. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3651
20. Falanga V. Wound healing and its impairment in the diabetic foot. Lancet. (2005) 366:1736–43. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(05)67700-8
21. Pulkkinen HH, Kiema M, Lappalainen JP, Toropainen A, Beter M, Tirronen A, et al. BMP6/TAZ-Hippo signaling modulates angiogenesis and endothelial cell response to VEGF. Angiogenesis. (2021) 24:129–44. doi: 10.1007/s10456-020-09748-4
22. Liu TT, Xu HH, Liu ZJ, Zhang HP, Zhou HT, Zhu ZX, et al. Downregulated calmodulin expression contributes to endothelial cell impairment in diabetes. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2023) 44:2492–503. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01127-1
23. Xiong W, Kong X, Jiang J, Yang Z, and Jiang R. Low androgen status inhibits erectile function by inducing eNOS uncoupling in rat corpus cavernosum. Andrology. (2020) 8:1875–83. doi: 10.1111/andr.12844
24. Wan L, Bai X, Zhou Q, Chen C, Wang H, Liu T, et al. The advanced glycation end-products (AGEs)/ROS/NLRP3 inflammasome axis contributes to delayed diabetic corneal wound healing and nerve regeneration. Int J Biol Sci. (2022) 18:809–25. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.63219
25. Kulwas A, Lisewska B, Jundziłł W, Ruszkowska B, Drewniak W, Ruprecht Z, et al. Tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) and plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 (PAI-1) in diabetic foot syndrome. Adv Med Sci. (2017) 62:87–91. doi: 10.1016/j.advms.2016.07.007
26. Oh S, Son M, Park CH, Jang JT, Son KH, Byun K, et al. The reducing effects of pyrogallol-phloroglucinol-6,6-bieckol on high-fat diet-induced pyroptosis in endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells of mice aortas. Mar Drugs. (2020) 18. doi: 10.3390/md18120648
27. Rai V, Moellmer R, and Agrawal DK. Stem cells and angiogenesis: implications and limitations in enhancing chronic diabetic foot ulcer healing. Cells. (2022) 11. doi: 10.3390/cells11152287
28. Huang K, Mi B, Xiong Y, Fu Z, Zhou W, Liu W, et al. Angiogenesis during diabetic wound repair: from mechanism to therapy opportunity. Burns Trauma. (2025) 13:tkae052. doi: 10.1093/burnst/tkae052
29. Kulwas A, Drela E, Jundziłł W, Góralczyk B, Ruszkowska-Ciastek B, Roś D, et al. Circulating endothelial progenitor cells and angiogenic factors in diabetes complicated diabetic foot and without foot complications. J Diabetes Complications. (2015) 29:686–90. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.03.013
30. Li G, Li D, Wu C, Li S, Chen F, Li P, et al. Homocysteine-targeting compounds as a new treatment strategy for diabetic wounds via inhibition of the histone methyltransferase SET7/9. Exp Mol Med. (2022) 54:988–98. doi: 10.1038/s12276-022-00804-1
31. Pasupuleti VR, Arigela CS, Gan SH, Salam SKN, Krishnan KT, Rahman NA, et al. A review on oxidative stress, diabetic complications, and the roles of honey polyphenols. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2020) 2020:8878172. doi: 10.1155/2020/8878172
32. Deng L, Du C, Song P, Chen T, Rui S, Armstrong DG, et al. The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in diabetic wound healing. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2021) 2021:8852759. doi: 10.1155/2021/8852759
33. Alavi A, Sibbald RG, Mayer D, Goodman L, Botros M, Armstrong DG, et al. Diabetic foot ulcers: Part I. Pathophysiology and prevention. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2014) 70:1.e–18; quiz 9-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2013.06.055
34. Percival SL, Hill KE, Williams DW, Hooper SJ, Thomas DW, Costerton JW, et al. A review of the scientific evidence for biofilms in wounds. Wound Repair Regener. (2012) 20:647–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-475X.2012.00836.x
35. Gordon KA, Lebrun EA, Tomic-Canic M, and Kirsner RS. The role of surgical debridement in healing of diabetic foot ulcers. Skinmed. (2012) 10:24–6.
36. Smigiel KS and Parks WC. Macrophages, wound healing, and fibrosis: recent insights. Curr Rheumatol Rep. (2018) 20:17. doi: 10.1007/s11926-018-0725-5
37. Ma Y. Role of neutrophils in cardiac injury and repair following myocardial infarction. Cells. (2021) 10. doi: 10.3390/cells10071676
38. Lee MKS, Sreejit G, Nagareddy PR, and Murphy AJ. Attack of the NETs! NETosis primes IL-1β-mediated inflammation in diabetic foot ulcers. Clin Sci (Lond). (2020) 134:1399–401. doi: 10.1042/cs20200240
39. Jetten N, Verbruggen S, Gijbels MJ, Post MJ, De Winther MP, Donners MM, et al. Anti-inflammatory M2, but not pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages promote angiogenesis in vivo. Angiogenesis. (2014) 17:109–18. doi: 10.1007/s10456-013-9381-6
40. Rehak L, Giurato L, Meloni M, Panunzi A, Manti GM, Uccioli L, et al. The immune-centric revolution in the diabetic foot: monocytes and lymphocytes role in wound healing and tissue regeneration-A narrative review. J Clin Med. (2022) 11. doi: 10.3390/jcm11030889
41. Seraphim PM, Leal EC, Moura J, Gonçalves P, Gonçalves JP, Carvalho E, et al. Lack of lymphocytes impairs macrophage polarization and angiogenesis in diabetic wound healing. Life Sci. (2020) 254:117813. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117813
42. Xue X and Falcon DM. The role of immune cells and cytokines in intestinal wound healing. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20. doi: 10.3390/ijms20236097
43. Moura J, Rodrigues J, Gonçalves M, Amaral C, Lima M, Carvalho E, et al. Impaired T-cell differentiation in diabetic foot ulceration. Cell Mol Immunol. (2017) 14:758–69. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2015.116
44. Borgia F, Li Pomi F, Alessandrello C, Vaccaro M, and Gangemi S. Potential role of innate lymphoid cells in the pathogenesis and treatment of skin diseases. J Clin Med. (2023) 12. doi: 10.3390/jcm12083043
45. Zhou S, Li Q, Wu H, and Lu Q. The pathogenic role of innate lymphoid cells in autoimmune-related and inflammatory skin diseases. Cell Mol Immunol. (2020) 17:335–46. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-0399-6
46. Mohsin F, Javaid S, Tariq M, and Mustafa M. Molecular immunological mechanisms of impaired wound healing in diabetic foot ulcers (DFU), current therapeutic strategies and future directions. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 139:112713. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112713
47. Hall CW and Mah TF. Molecular mechanisms of biofilm-based antibiotic resistance and tolerance in pathogenic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. (2017) 41:276–301. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fux010
48. Sun H, Pulakat L, and Anderson DW. Challenges and new therapeutic approaches in the management of chronic wounds. Curr Drug Targets. (2020) 21:1264–75. doi: 10.2174/1389450121666200623131200
49. Louiselle AE, Niemiec SM, Zgheib C, and Liechty KW. Macrophage polarization and diabetic wound healing. Transl Res. (2021) 236:109–16. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2021.05.006
50. Larouche J, Sheoran S, Maruyama K, and Martino MM. Immune regulation of skin wound healing: mechanisms and novel therapeutic targets. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). (2018) 7:209–31. doi: 10.1089/wound.2017.0761
51. Afonso AC, Oliveira D, Saavedra MJ, Borges A, and Simões M. Biofilms in diabetic foot ulcers: impact, risk factors and control strategies. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158278
52. Zhang H, Nie X, Shi X, Zhao J, Chen Y, Yao Q, et al. Regulatory mechanisms of the wnt/β-catenin pathway in diabetic cutaneous ulcers. Front Pharmacol. (2018) 9:1114. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01114
53. Irani PS, Ranjbar H, Mehdipour-Rabori R, Torkaman M, Amirsalari S, Alazmani-Noodeh F, et al. The effect of aloe vera on the healing of diabetic foot ulcer: A randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Curr Drug Discov Technol. (2024) 21:56–63. doi: 10.2174/1570163820666230904150945
54. Zhu Y, Han S, Li X, Gao Y, Zhu J, Yang X, et al. Paeoniflorin effect of schwann cell-derived exosomes ameliorates dorsal root ganglion neurons apoptosis through IRE1α Pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2021) 2021:6079305. doi: 10.1155/2021/6079305
55. Hoxhaj G and Manning BD. The PI3K-AKT network at the interface of oncogenic signalling and cancer metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer. (2020) 20:74–88. doi: 10.1038/s41568-019-0216-7
56. Jere SW, Houreld NN, and Abrahamse H. Role of the PI3K/AKT (mTOR and GSK3β) signalling pathway and photobiomodulation in diabetic wound healing. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2019) 50:52–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2019.03.001
57. Zhang E, Gao B, Yang L, Wu X, and Wang Z. Notoginsenoside ft1 promotes fibroblast proliferation via PI3K/akt/mTOR signaling pathway and benefits wound healing in genetically diabetic mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (2016) 356:324–32. doi: 10.1124/jpet.115.229369
58. Li W, Kandhare AD, Mukherjee AA, and Bodhankar SL. Hesperidin, a plant flavonoid accelerated the cutaneous wound healing in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: Role of TGF-ß/Smads and Ang-1/Tie-2 signaling pathways. Excli J. (2018) 17:399–419. doi: 10.17179/excli2018-1036
59. Duscher D, Maan ZN, Whittam AJ, Sorkin M, Hu MS, Walmsley GG, et al. Fibroblast-specific deletion of hypoxia inducible factor-1 critically impairs murine cutaneous neovascularization and wound healing. Plast Reconstr Surg. (2015) 136:1004–13. doi: 10.1097/prs.0000000000001699
60. Hong WX, Hu MS, Esquivel M, Liang GY, Rennert RC, McArdle A, et al. The role of hypoxia-inducible factor in wound healing. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). (2014) 3:390–9. doi: 10.1089/wound.2013.0520
61. Wu LH, Lin C, Lin HY, Liu YS, Wu CY, Tsai CF, et al. Naringenin suppresses neuroinflammatory responses through inducing suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 expression. Mol Neurobiol. (2016) 53:1080–91. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-9042-9
62. Dodson M, de la Vega MR, Cholanians AB, Schmidlin CJ, Chapman E, Zhang DD, et al. Modulating NRF2 in disease: timing is everything. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. (2019) 59:555–75. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010818-021856
63. Zhang Z, Zhang X, Bi K, He Y, Yan W, Yang CS, et al. Potential protective mechanisms of green tea polyphenol EGCG against COVID-19. Trends Food Sci Technol. (2021) 114:11–24. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2021.05.023
64. Chen LY, Huang CN, Liao CK, Chang HM, Kuan YH, Tseng TJ, et al. Effects of rutin on wound healing in hyperglycemic rats. Antioxidants (Basel). (2020) 9. doi: 10.3390/antiox9111122
65. Chen LY, Cheng HL, Kuan YH, Liang TJ, Chao YY, Lin HC, et al. Therapeutic potential of luteolin on impaired wound healing in streptozotocin-induced rats. Biomedicines. (2021) 9. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9070761
66. Li X, Wang HH, Xu J, Tang LY, Li DF, Zhang Y, et al. Study on active components of Fufang Huangbai Ye for diabetic foot treatment by UPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS and network pharmacology. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. (2019) 44:2110–7. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20190328.201
67. Lawrence T. The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. (2009) 1:a001651. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a001651
68. Ren J, Yang M, Chen J, Ma S, and Wang N. Anti-inflammatory and wound healing potential of kirenol in diabetic rats through the suppression of inflammatory markers and matrix metalloproteinase expressions. BioMed Pharmacother. (2020) 129:110475. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110475
69. Ren J, Yang M, Xu F, Chen J, and Ma S. Acceleration of wound healing activity with syringic acid in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Life Sci. (2019) 233:116728. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116728
70. Sun X, Wang X, Zhao Z, Chen J, Li C, Zhao G, et al. Paeoniflorin inhibited nod-like receptor protein-3 inflammasome and NF-κB-mediated inflammatory reactions in diabetic foot ulcer by inhibiting the chemokine receptor CXCR2. Drug Dev Res. (2021) 82:404–11. doi: 10.1002/ddr.21763
71. Wang T, Xiang Z, Wang Y, Li X, Fang C, Song S, et al. (-)-epigallocatechin gallate targets notch to attenuate the inflammatory response in the immediate early stage in human macrophages. Front Immunol. (2017) 8:433. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00433
72. Huang YW, Zhu QQ, Yang XY, Xu HH, Sun B, Wang XJ, et al. Wound healing can be improved by (-)-epigallocatechin gallate through targeting Notch in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. FASEB J. (2019) 33:953–64. doi: 10.1096/fj.201800337R
73. Liu B, Yu CJ, Meng XB, Wang X, Zhao HW, Sun GB, et al. Effects of Qizhi Jiangtang capsule on dermal ulcer in type 2 diabetic rats. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. (2016) 41:118–23. doi: 10.4268/cjcmm20160123
74. Ko CH, Yi S, Ozaki R, Cochrane H, Chung H, Lau W, et al. Healing effect of a two-herb recipe (NF3) on foot ulcers in Chinese patients with diabetes: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. J Diabetes. (2014) 6:323–34. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12117
75. Soleimani Z, Hashemdokht F, Bahmani F, Taghizadeh M, Memarzadeh MR, Asemi Z, et al. Clinical and metabolic response to flaxseed oil omega-3 fatty acids supplementation in patients with diabetic foot ulcer: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Diabetes Complications. (2017) 31:1394–400. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2017.06.010
76. Paocharoen V. The efficacy and side effects of oral Centella asiatica extract for wound healing promotion in diabetic wound patients. J Med Assoc Thai. (2010) 93 Suppl 7:S166–70.
77. Mokhtari M, Razzaghi R, and Momen-Heravi M. The effects of curcumin intake on wound healing and metabolic status in patients with diabetic foot ulcer: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Phytother Res. (2021) 35:2099–107. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6957
78. Xue B, Wang L, Zhang Z, Wang R, Xia XX, Han PP, et al. Puerarin may protect against Schwann cell damage induced by glucose fluctuation. J Nat Med. (2017) 71:472–81. doi: 10.1007/s11418-016-1067-0
79. Zhao B, Zhang Q, Liang X, Xie J, and Sun Q. Quercetin reduces inflammation in a rat model of diabetic peripheral neuropathy by regulating the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signalling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. (2021) 912:174607. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174607
80. Liu M, Gao L, and Zhang N. Berberine reduces neuroglia activation and inflammation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. (2019) 33:2058738419866379. doi: 10.1177/2058738419866379
81. Zhang B, Yu Y, Aori G, Wang Q, Kong D, Yang W, et al. Tanshinone IIA attenuates diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain in experimental rats via inhibiting inflammation. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2018) 2018:2789847. doi: 10.1155/2018/2789847
82. Semis HS, Kandemir FM, Caglayan C, Kaynar O, Genc A, Arıkan SM, et al. Protective effect of naringin against oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy in rats: A behavioral and molecular study. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. (2022) 36:e23121. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23121
83. Liu Y, Li Y, Du Y, Huang T, and Zhu C. Multicenter clinical trials analyzing efficacy and safety of topical cortex phellodendri compound fluid in treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. Med Sci Monit. (2020) 26:e923424. doi: 10.12659/msm.923424
84. Li S, Zhao J, Liu J, Xiang F, Lu D, Liu B, et al. Prospective randomized controlled study of a Chinese herbal medicine compound Tangzu Yuyang Ointment for chronic diabetic foot ulcers: a preliminary report. J Ethnopharmacol. (2011) 133:543–50. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.10.040
85. Abdoli A, Shahbazi R, Zoghi G, Davoodian P, Kheirandish S, Azad M, et al. The effect of topical olive oil dressing on the healing of grade 1 and 2 diabetic foot ulcers: An assessor-blind randomized controlled trial in type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetes Metab Syndr. (2022) 16:102678. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2022.102678
86. Xiaolan X, Wujie G, Xiaoyan T, and Wenlai C. A combination of ultrasonic debridement and Shenghong wet dressing in patients with chronic ulcers of the lower limbs. J Int Med Res. (2019) 47:4656–63. doi: 10.1177/0300060519858033
87. Leu WJ, Chen JC, and Guh JH. Extract from plectranthus amboinicus inhibit maturation and release of interleukin 1β Through inhibition of NF-κB nuclear translocation and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Front Pharmacol. (2019) 10:573. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00573
88. Wan X, Gen F, Sheng Y, Ou M, Wang F, Peng T, et al. Meta-analysis of the effect of kangfuxin liquid on diabetic patients with skin ulcers. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2021) 2021:1334255. doi: 10.1155/2021/1334255
89. Morita Y, Nakashima K, Nishino K, Kotani K, Tomida J, Inoue M, et al. Berberine is a novel type efflux inhibitor which attenuates the mexXY-mediated aminoglycoside resistance in pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front Microbiol. (2016) 7:1223. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01223
90. Sun Y, Lenon GB, and Yang AWH. Phellodendri cortex: A phytochemical, pharmacological, and pharmacokinetic review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2019) 2019:7621929. doi: 10.1155/2019/7621929
91. Fallah Huseini H, Yaghoobi M, Fallahi F, Boroumand F, Ezzati MH, Tabatabaei SM, et al. Topical administration of teucrium polium on diabetic foot ulcers accelerates healing: A placebo-controlled randomized clinical study. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. (2024) 23:238–46. doi: 10.1177/15347346211048371
92. Huang YY, Lin CW, Cheng NC, Cazzell SM, Chen HH, Huang KF, et al. Effect of a novel macrophage-regulating drug on wound healing in patients with diabetic foot ulcers: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. (2021) 4:e2122607. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.22607
93. Mohajeri G, Safaee M, and Sanei MH. Effects of topical Kiwifruit on healing of neuropathic diabetic foot ulcer. J Res Med Sci. (2014) 19:520–4.
94. Najafian Y, Khorasani ZM, Najafi MN, Hamedi SS, Mahjour M, Feyzabadi Z, et al. Efficacy of aloe vera/ plantago major gel in diabetic foot ulcer: A randomized double-blind clinical trial. Curr Drug Discov Technol. (2019) 16:223–31. doi: 10.2174/1570163815666180115093007
95. Kuo YS, Chien HF, and Lu W. Plectranthus amboinicus and Centella asiatica Cream for the Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2012) 2012:418679. doi: 10.1155/2012/418679
96. Romero-Cerecero O, Zamilpa A, and Tortoriello J. Effectiveness and tolerability of a standardized extract from Ageratina pichinchensis in patients with diabetic foot ulcer: a randomized, controlled pilot study. Planta Med. (2015) 81:272–8. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1396315
97. Sun X, Jing J, Dai R, Zhu C, Sun Y, Sun J, et al. Shengji ointment combined with bromelain promotes granulation of exposed tendons in diabetic foot ulcers: A multicenter, randomized, positive-controlled clinical trial. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e39716. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39716
Keywords: diabetic foot ulcers, traditional Chinese medicine, wound, diabetes mellitus, wound healing
Citation: Xia Y, Wu P, Chen Y and Chen Z (2025) Current research progress on the use of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1637128. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1637128
Received: 28 May 2025; Accepted: 01 August 2025;
Published: 22 August 2025.
Edited by:
Fayez F. Safadi, Northeast Ohio Medical University, United StatesReviewed by:
Barbara Ciastek, University of Opole, PolandCopyright © 2025 Xia, Wu, Chen and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhiyong Chen, Y3p5MTAwMjAwOEBjcXUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors share first authorship
 Yinfeng Xia
Yinfeng Xia Ping Wu†
Ping Wu†