- The ART Center, Northwest Women’s and Children’s Hospital, Xi’an, China
Objective: The aim of this study was to explore the effectivity and safety of early rescue intracytoplasmic sperm injection (R-ICSI) in patients with poor oocyte yield and non-severe male factor.
Methods: This study was a retrospective cohort analysis which included 604 conventional ICSI cycles and 116 early R-ICSI cycles at the Northwest Women’s and Children’s Hospital from February 2014 to December 2023. All patients were during their first assisted reproductive technologies (ART) cycle with 3–5 retrieved oocytes. The male partner had normal or mildly impaired sperm parameters. We compared the reproductive outcomes of conventional ICSI and early R-ICSI cycles in such patients.
Results: We observed that there were no significant differences in the MII (86.75 versus 85.09%; p = 0.329) and two pronuclei (2PN) (71.82 versus 72.02%; p = 0.934) rates between conventional intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) and early R-ICSI groups. Following conventional ICSI, a total multi-pronuclei (MPN) rate of 1.02% was achieved, which was significantly lower than that of 6.33% after early R-ICSI (p < 0.001). There were no significant differences in the D3 good quality embryo (51.80 versus 49.67%; p = 0.499), D3 available embryo (82.28 versus 78.38%; p = 0.112) and blastocyst formation (65.15 versus 68.69%; p = 0.494) rates between the two groups. We also observed that there were no significant differences in the pregnancy (55.45 versus 50.50%; p = 0.357), clinical pregnancy (52.00 versus 46.53%; p = 0.312), ongoing pregnancy (44.91 versus 39.60%; p = 0.324) and live birth (42.73 versus 37.62%; p = 0.339) rates between the two groups.
Conclusions: Despite the higher MPN rate, comparable outcomes can be achieved following early R-ICSI when compared to conventional ICSI for couples with non-severe male factor and poor oocyte yield.
Introduction
Although the advancements in assisted reproductive technologies enable in vitro fertilization (IVF) to achieve fertilization rates ranging from 70% to 80%, unexpected total fertilization failure (TFF) still occurs in approximately 5% to 20% of conventional IVF (C-IVF) treatment cycles. When TFF occurs, no available embryos are obtained for transfer, leading to cycle cancellation. This situation is highly frustrating for patients and poses a significant challenge for clinicians. Although the causes of TFF remain incompletely understood, some studies have identified male factors, particularly sperm abnormalities, as significant contributors to this phenomenon (1, 2). However, other researches have demonstrated that sperm count, motility, and morphology are inadequate indicators of potential sperm-oocyte interaction (3, 4).
While the reliability of intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) has made it an appealing treatment option for infertile couples worldwide, including those without male factor infertility, its use in non-male factor cases remains controversial. It has been shown that ICSI significantly reduces the risk of TFF compared to C-IVF, while also decreasing cycle cancellation rates due to fertilization failure (5). Nevertheless, the arbitrary selection of sperm for injection may introduce additional risks and potential adverse outcomes (6). C-IVF preserves the natural sperm selection process during fertilization while avoiding potential mechanical oocyte damage associated with ICSI procedures. Nevertheless, multiple studies have demonstrated that patients with fewer than five oocytes are at a higher risk for TFF following C-IVF (7–9).
Multiple studies have demonstrated that ICSI had no obvious advantage in patients with normal semen parameters (10, 11). Meanwhiles, a recent study also indicated ICSI could not improve reproductive outcome compared with C-IVF in patients with non-severe male factor (12). The presented data corroborated that C-IVF should be recommended as the initial treatment option for patients with normal or near-normal semen parameters. C-IVF remains the recommended approach for most patients with a low oocyte yield and non-severe male factor infertility. Nevertheless, such patients may be at an increased risk of TFF following C-IVF.
It is crucial to balance the time-related risks associated with oocyte aging and multi-pronuclei (MPN) fertilization as both of them can lead to poor embryo quality. It’s still more challenging to perform early R-ICSI for couples who has normal semen analysis and poor oocyte yield. To salvage fertilization failure and mitigate the effects of oocyte aging, early rescue ICSI (R-ICSI) has been implemented 5–6 h post-insemination which demonstrate a promising clinical result (13). In this study, we aimed to explore the effectivity and safety of early R-ICSI in such cases.
Materials and methods
Study participants
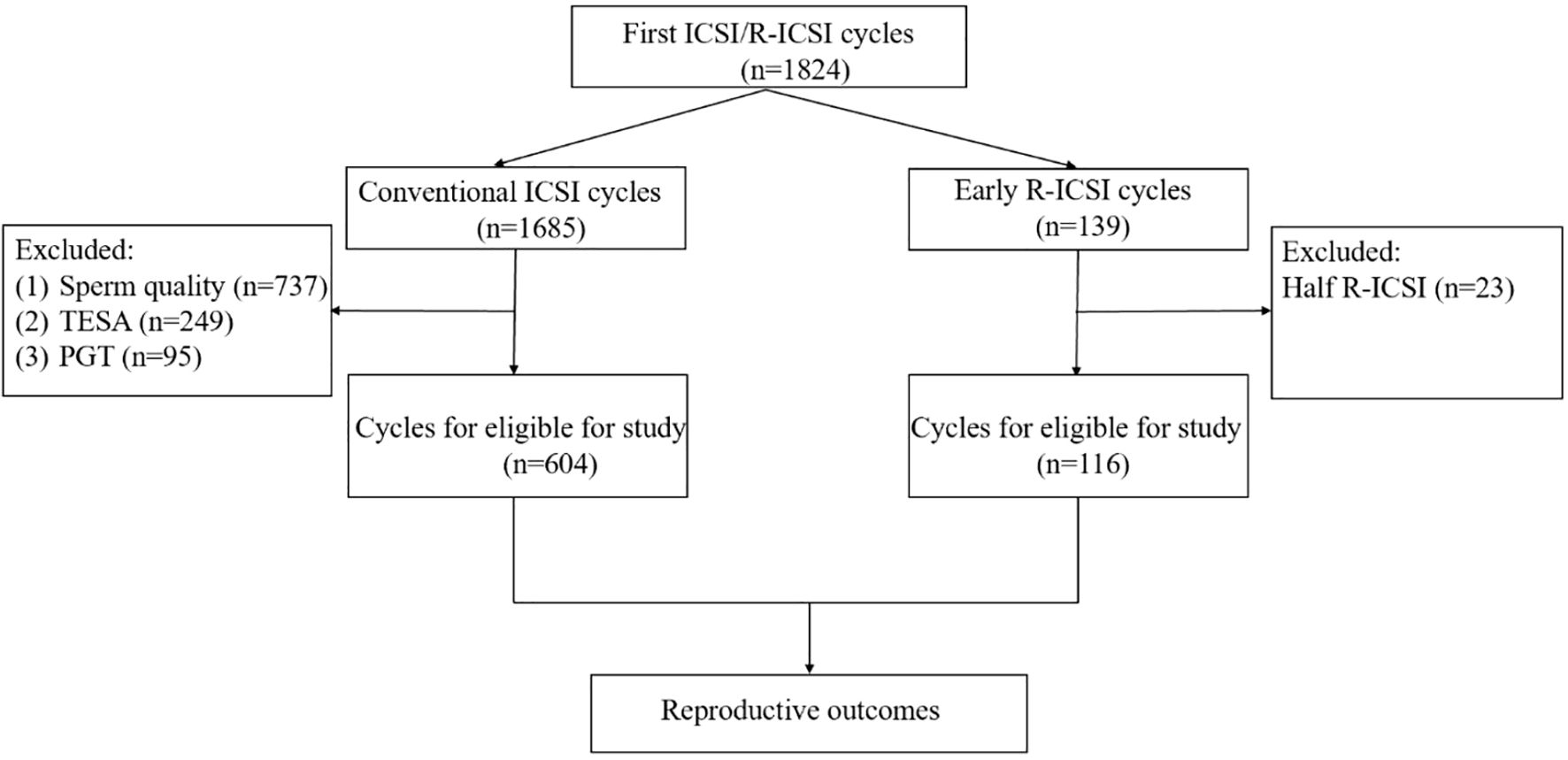
This study was a retrospective cohort analysis which included 604 conventional ICSI cycles and 116 early R-ICSI cycles at the Northwest Women’s and Children’s Hospital from February 2014 to December 2023. All patients were during their first assisted reproductive technologies (ART) cycle with 3–5 retrieved oocytes. The male partner had normal or mildly impaired sperm parameters with the processed semen sample (following density gradient purification) yielding at least 2 million progressively motile spermatozoa on the day of oocyte retrieval. TFF was defined as the absence of a second polar body in all mature oocytes. Near TFF was defined as fewer than 1/3 of mature oocytes exhibited a second polar body (second polar body rate < 33.33%). The cases of near TFF were excluded in this study. In this study, the conventional ICSI group was regarded as the control group, while early R-ICSI was considered the experimental group. The specific exclusion criteria were shown in Figure 1. All patients gave written informed consent and this study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Northwest Women’s and Children’s Hospital (No. 2023003).
Ovarian stimulation protocol
All participants in our study underwent controlled ovarian hyperstimulation. The ovarian stimulation protocols in our reproductive medicine center include the GnRH agonist long protocol, GnRH agonist short protocol, and GnRH antagonist protocol, as detailed in previous literature (13). Notably, recombinant follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) or urinary FSH and/or human menopausal gonadotropins were used with daily doses between 100 and 450 IU based on patients’ characteristics as calculated previously (13).
C-IVF and early R-ICSI
C-IVF was performed 2-2.5 h after oocyte retrieval and each oocyte was incubated with approximately 40–000 sperm. Short-term insemination was adopted and the cumulus granule cells were peeled off 4.5–5 h post-fertilization. Oocytes were analyzed for the release of the second Pb at 5–6 h after the initial insemination. If there was no second Pb (TFF), R-ICSI was performed immediately on the oocytes with only one Pb observed. Our skilled ICSI operators injected the oocytes with only one Pb by the direct penetration technique.
Fertilization check and embryo grading
Normal fertilization was confirmed 18–19 hours post-insemination through identification of two pronuclei (2PN) accompanied by second polar body extrusion. After 64–68 h of culture, the morphologic score was given for cleavage-stage embryos. The morphologic score of blastocysts were given on the fifth morning after oocyte retrieval. The detailed scoring criteria were based on our published literature (13). The D3 good quality embryos were graded I and II. The D3 available embryos were graded I, II, and III.
Luteal support and embryo transfer
Three methods of luteal support are implemented in our center. I. Vaginal progesterone gel (90 mg q.d; Crinone, Serono, Hertfordshire, UK); II. Vaginal progesterone soft capsules (0.2 g t.i.d; Utrogestan, Besins, France); III. Intramuscular progesterone (60 mg q.d; Xianju, Zhejiang, China). Patients from both groups could select one of these three luteal support methods and receive oral progesterone (10 mg t.i.d; Dydrogesterone, Abbott Biologicals B.V., Amsterdam, Netherlands) simultaneously. The luteal support was maintained until week 10 of gestation.
The mucus in the cervical os was cleaned in advance with a cotton swab soaked in warm and humid saline. Embryos were transferred under ultrasound guidance with a transfer catheter (Limerick, Ireland). Pregnancy was defined as β-HCG value more than 50 mIU/ml after 12 days of transfer. Clinical pregnancy was characterized as the presence of an intrauterine gestational sac on ultrasonography during the first trimester. Ongoing pregnancy was defined as a clinical pregnancy that continued for a minimum of 12 weeks. Live birth was defined as the delivery of a live-born infant (> 24 weeks of gestation).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis between groups in the case of continuous variables was performed with Student’s t test for data with normal distribution. Non-parametric Mann-Whitney U-test was performed for data with skewed distribution. Statistical analysis between groups in the case of categorical variables was expressed as number and percentage and Chi-square test or Fisher exact test was performed. The statistical analysis was performed with SPSS version 23 (IBM Corp.; NY, USA). A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance.
Results
General characteristics of the enrolled patients
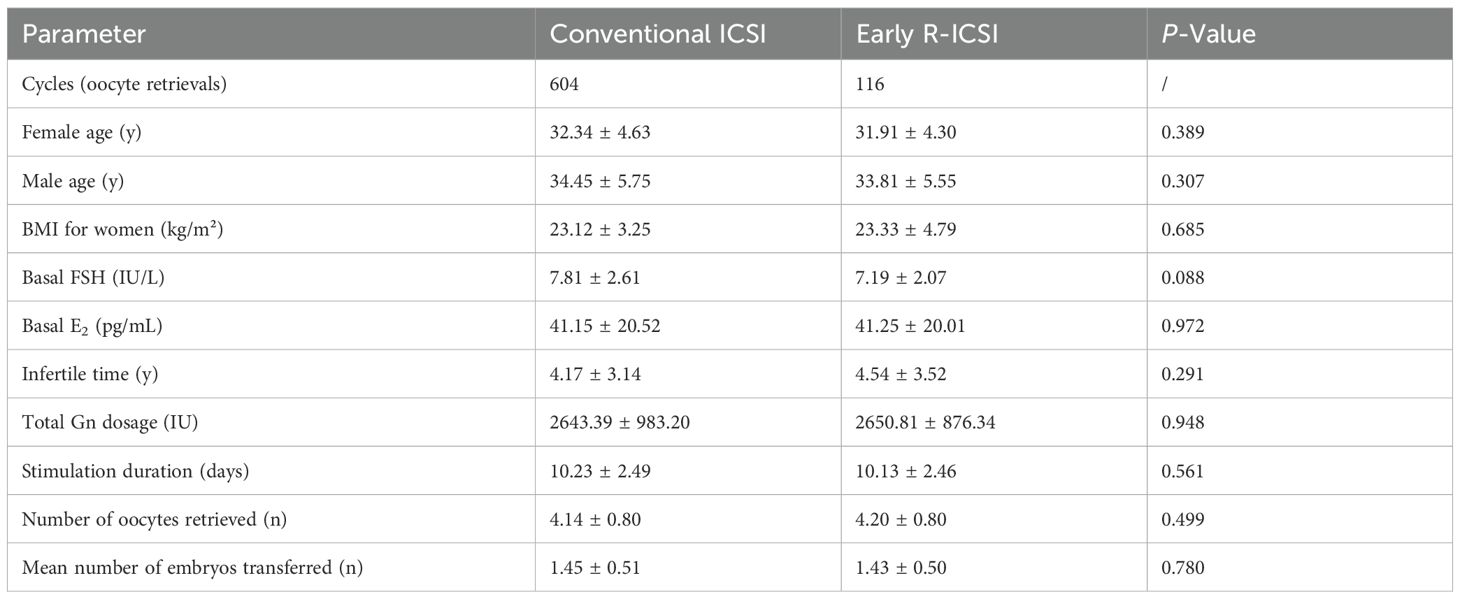
A total of 720 cycles were analyzed in this study, comprising 604 conventional ICSI cycles and 116 early R-ICSI cycles. Our data showed no significant differences in the aspects of female age, male age, BMI, basal FSH, Basal E2, infertile time, total Gn dosage, stimulation duration, the number of oocytes retrieved and the mean number of embryos transferred between conventional ICSI and early R-ICSI groups (p> 0.05) (Table 1).
Embryo development in conventional ICSI and early R-ICSI groups
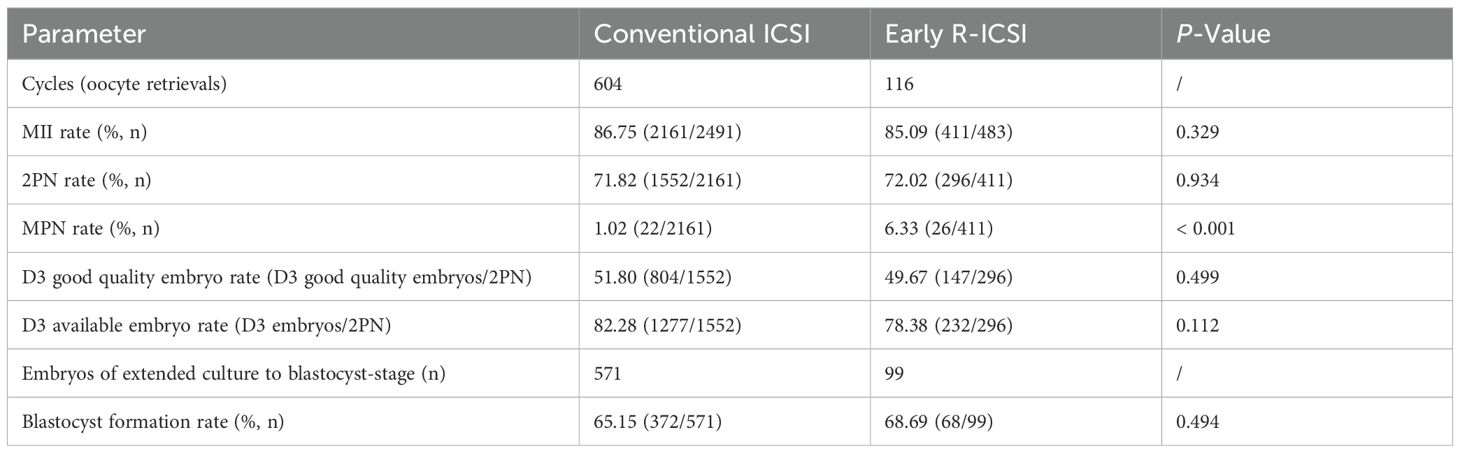
We observed that there were no significant differences in the MII (86.75 versus 85.09%; p = 0.329) and 2PN (71.82 versus 72.02%; p = 0.934) rates between conventional ICSI and early R-ICSI groups. Following conventional R-ICSI, a total ≥ 3PN rate of 1.02% was achieved, which was significantly lower than that of 6.33% after early R-ICSI (p < 0.001). There were no significant differences in the D3 good quality embryo (51.80 versus 49.67%; p = 0.499), D3 available embryo (82.28 versus 78.38%; p = 0.112) and blastocyst formation (65.15 versus 68.69%; p = 0.494) rates between the two groups (Table 2).
Clinical outcomes in conventional ICSI and early R-ICSI groups
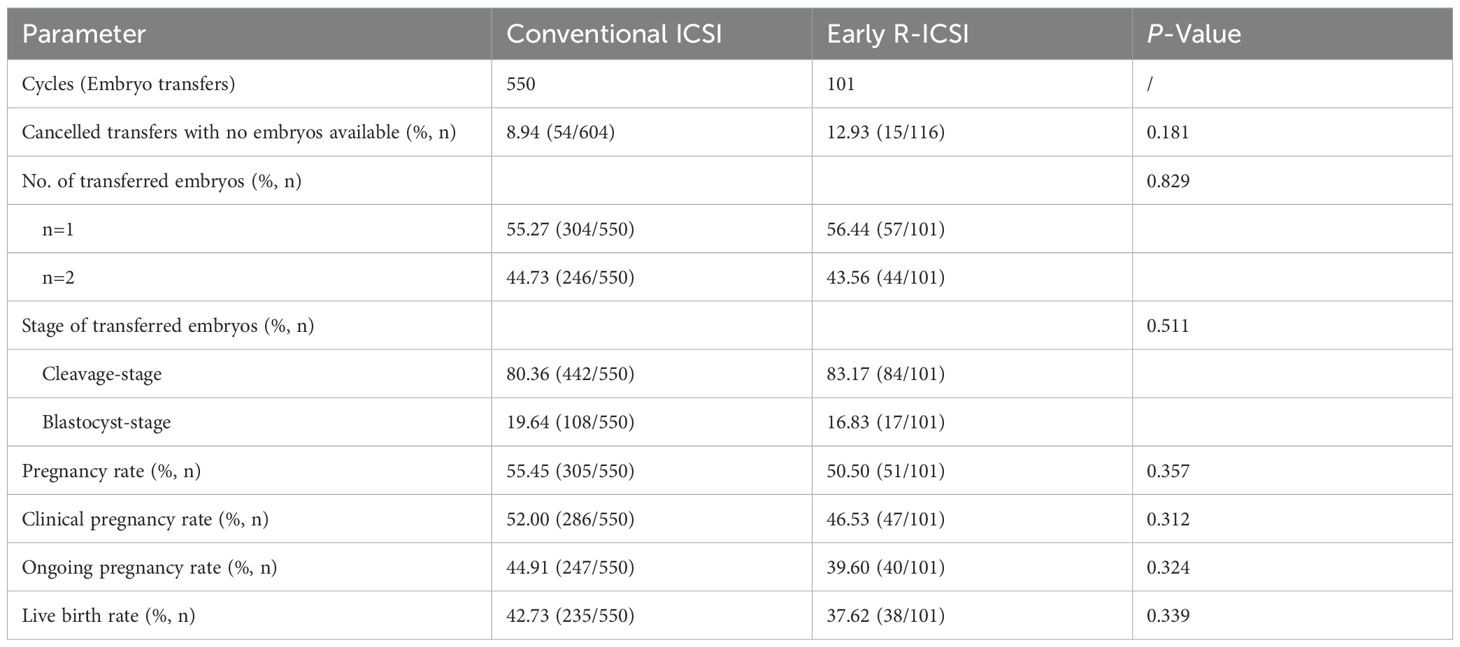
We further compared the clinical outcomes between conventional ICSI and early R-ICSI groups. Following early R-ICSI, the rate of cancelled transfers with no embryos available was 8.94%, which showed no significant difference with that of 12.93% after early R-ICSI (p> 0.05). We also observed that there were no significant differences in the pregnancy (55.45 versus 50.50%; p = 0.357), clinical pregnancy (52.00 versus 46.53%; p = 0.312), ongoing pregnancy (44.91 versus 39.60%; p = 0.324) and live birth (42.73 versus 37.62%; p = 0.339) rates between the two groups (Table 3).
Embryo development and clinical outcomes according to the oocyte retrieval rate in conventional ICSI and early R-ICSI groups
For patients with ≥ 100% oocyte retrieval rate (ORR), the MII rate was significantly lower in ICSI group compared with that of early R-ICSI group (86.62 versus 92.66%; p = 0.025). There were no significant differences in the 2PN (73.71 versus 70.12%; p = 0.339), D3 good quality embryo (56.62 versus 56.52%; p = 0.984) and D3 available embryo (86.32 versus 81.74%; p = 0.195) rates between the two groups. Our data also showed no significant differences in the pregnancy (53.49 versus 55.81%; p = 0.777), clinical pregnancy (50.00 versus 53.49%; p = 0.672), ongoing pregnancy (43.80 versus 46.51%; p = 0.740) and live birth (43.02 versus 41.86%; p = 0.887) rates between the two groups (Table 4).
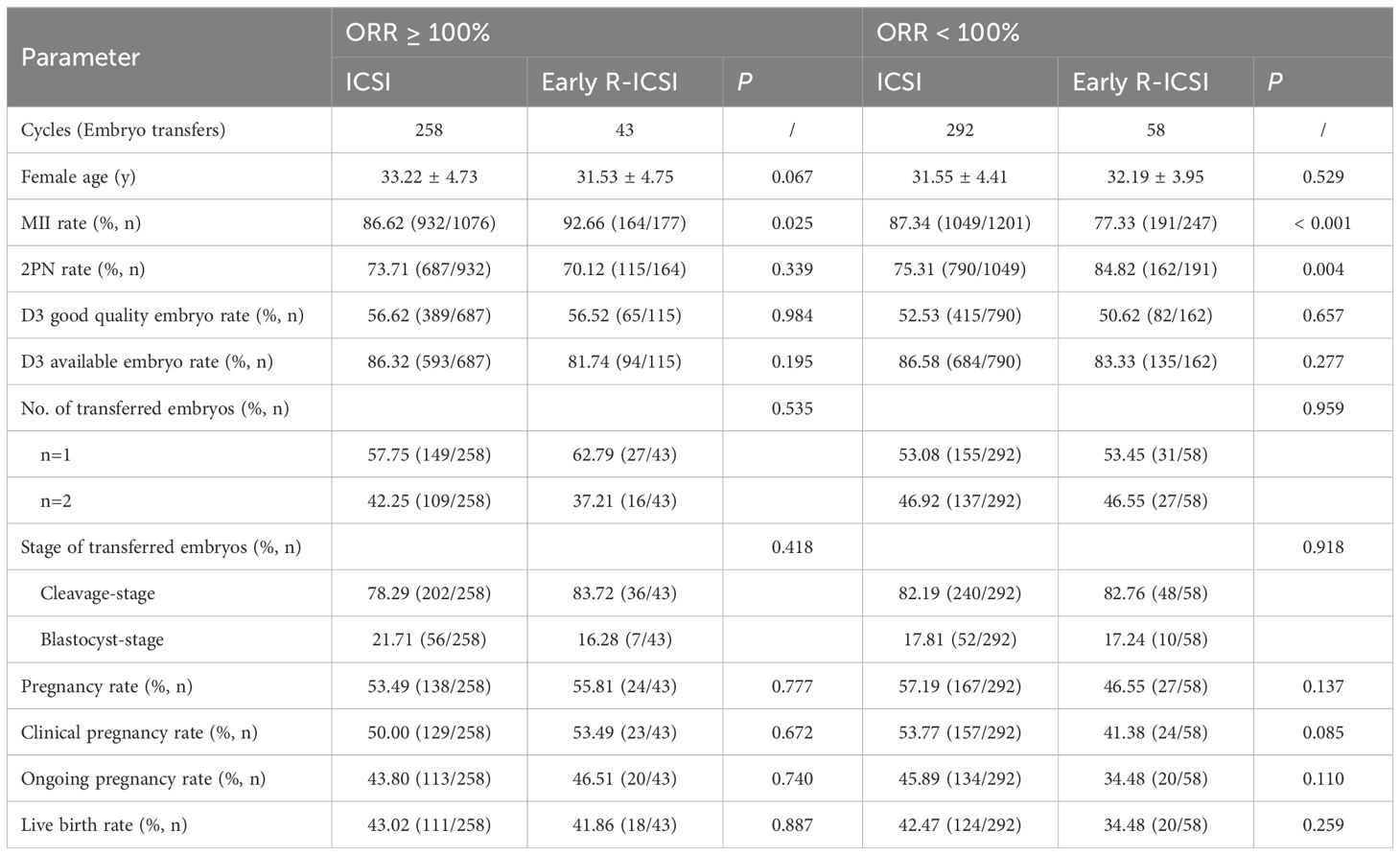
Table 4. Comparison of embryo development and clinical outcomes according to the oocyte retrieval rate (ORR) in conventional ICSI and early R-ICSI groups.
For patients with a low ORR, the MII rate was significantly higher in ICSI group compared with that of early R-ICSI group (87.34 versus 77.33%; p < 0.001). However, we observed that the 2PN rate was significantly lower in ICSI group than that of early R-ICSI group (75.31 versus 84.82%; p = 0.004). There were no significant differences in the D3 good quality embryo (52.53 versus 50.62%; p = 0.657) and D3 available embryo (86.58 versus 83.33%; p = 0.277) rates between the two groups. Our data also demonstrated there were no significant differences in the pregnancy (57.19 versus 46.55%; p = 0.137), clinical pregnancy (53.77 versus 41.38%; p = 0.085), ongoing pregnancy (45.89 versus 34.48%; p = 0.110) and live birth (42.47 versus 34.48%; p = 0.259) rates between the two groups (Table 4).
Discussion
Our results have demonstrated that comparable outcomes can be achieved following early R-ICSI when compared to conventional ICSI for couples with non-severe male factor and poor oocyte yield. Thus, we suggest that C-IVF may be the first choice of assisted reproductive technique for such patients.
When oocyte yield is limited, selecting the optimal fertilization method becomes crucial to maximize pregnancy success rates. Fang et al. showed ICSI did not improve the good-quality embryo rate or clinical pregnancy rate compared to C-IVF using semen with normal parameters in women with poor ovarian reserve (14). Isikoglu et al. concluded that low egg number is not an indication to perform ICSI in the presence of normal semen parameters (15). Meanwhiles, a recent study indicated that ICSI could not avoid the incidence of total fertilization failure and it might hamper the cumulative pregnancy rate in in poor responders (16). In non-male factor ART cycles, ICSI was not associated with improved pregnancy outcomes in older women with a low number of oocytes retrieved (17). The above data suggested that C-IVF should be the first choice of in patients with infertility with normal semen parameters and poor oocyte yield.
Nevertheless, the reproductive outcomes of such patients with fertilization failure following C-IVF have not been reported. Recently, multiple studies indicated that patients with fewer than five oocytes had a higher risk for fertilization failure following C-IVF (7–9). Tian et al. showed that semen parameters contribute to limited value in predicting TFF in unselected patients and oocyte yield is an important predictor for TFF (7). De souza et al. indicated that a decreased number of collected oocytes was the most important parameter associated with IVF failure in nonmasculine infertility (8). These results suggested that the study population had a high risk of fertilization failure in this research. However, the reproductive outcomes of such patients with fertilization failure following C-IVF have not been reported in current studies.
In cases of TFF, ICSI is routinely employed as a late remediation of unfertilized oocytes. In this research, the male partner had normal or mildly impaired sperm parameters for conventional ICSI. The primary population consists of patients with borderline semen quality or significant semen parameter fluctuations. If such patients undergo C-IVF treatment, TFF may occur, leading to cycle cancellation due to the absence of available embryos. This outcome can significantly increase both psychological and financial burdens for the patients (18). If the patients undergo ICSI treatment, it may introduce unnecessary or excessive treatment. And the application of ICSI in clinical practice should be carefully regulated as the potential long-term effects of ICSI on offspring remain a subject of ongoing debate (19). Multiple studies have shown that split insemination (combining C-IVF and ICSI for sibling oocytes) can be an effective strategy to prevent TFF while maintaining optimal embryo development potential in patients with borderline semen quality (20, 21). Nevertheless, the study population has a relatively low oocyte yield (only 3–5 oocytes retrieved), which presents significant challenges for implementing this treatment strategy.
Notably, we observed that R-ICSI could obtain similar reproductive outcomes compared conventional ICSI for patients with poor oocyte yield and no severe male factor. Thus, fertilization failure should not be a concern as early R-ICSI could achieve comparable clinical outcomes. It should be emphasized that this study was strictly limited to patients who yielded 3–5 oocytes during retrieval. The primary rationale stem is our clinical protocol against performing early R-ICSI for patients yielding only 1–2 oocytes. For such patients, long-time insemination was performed in order to minimize the MPN incidence resulting from wrong evaluation for fertilization evaluation. Historically, R-ICSI was routinely implemented for unfertilized oocytes 16–18 hours post insemination. However, the clinical outcome is always unsatisfactory which has been confirmed to be associated with oocyte aging (4). To salvage fertilization failure and mitigate the effects of oocyte aging, early R-ICSI has been implemented 5–6 h post-insemination which demonstrate a promising clinical result (13). Consistent with previous reported approach, early R-ICSI was also performed at this time point in our center.
For some patients with poor oocyte yield, a contributing factor is suboptimal oocyte retrieval rate. Only a scant number of oocytes were obtained from numerous matured follicles on the day of oocyte retrieval. It was confirmed that follicular flushing significantly increases the number of cumulus-oocyte complexes retrieved compared to single aspiration (22). Thus, Repeated flushing was performed to increase the oocyte retrieval rate. High flushing pressure might cause early rupture of the follicular wall, which results in oocytes damage as well as the outcome of embryos growth (23). Oocyte quality is widely recognized as the key factor governing embryo developmental competence in women (24).
For further analysis, the patients were allocated into subgroups according to the oocyte retrieval rate. We observed similar reproductive outcomes in conventional ICSI and early R-ICSI groups for patients with ≥ 100% predicted yield. For patients with below-anticipated oocyte retrieval, the conventional ICSI approach showed an increase rate of exceeding 10% for both clinical pregnancy and ongoing pregnancy compared to early R-ICSI intervention. Although no statistically significant differences were observed, which might be attributable to the limited R-ICSI cases in this research. And we observed that the MII rate was significantly higher in conventional ICSI group compared with that of early R-ICSI group. The way a single oocyte was affected might indicate how the whole cohort was affected, even if the other oocytes did not show the same characteristics. Low MII rates might indicate compromised cytoplasmic and nuclear maturation across the entire oocyte cohort. Complete nuclear and cytoplasmic maturation of oocytes is essential for the activation of oocytes at fertilization and the development of embryos. The preincubation of oocytes was considered to complete the final nuclear and cytoplasmic maturation of the oocyte. Ho et al. showed that the preincubation of oocytes for at least 2.5 h is beneficial to both IVF and ICSI outcomes by increasing the nuclear maturity of oocytes (25). In our center, C-IVF insemination is routinely performed at least 4 hours earlier than conventional ICSI and the oocyte preincubation period is typically limited to 2–3 hours in our protocol. Theoretically, the insemination timing should be delayed for such patients with low MII rate which might make negative effects on the embryo development and clinical outcomes. Nevertheless, we observed no significant differences in the D3 good quality embryo and available embryo rates between the conventional ICSI and early R-ICSI groups. A recent study demonstrated that the proportion of immature oocytes does not impact the outcomes of mature sibling oocytes (26). Therefore, the observed decline in success rates may not be attributable to embryo quality.
There are certain weaknesses in the current study that should be underlined. First, the primary drawback is the retrospective design and limited sample size of R-ICSI cases. Second, there may be some potential bias and confounders that cannot be excluded. Lastly, the cumulative live birth rate may be a more significant indicator and it is hard to calculate in this study. Nevertheless, few researches have explored the embryo development and clinical outcomes of early R-ICSI for such cases. Thus, the findings of the current study offer valuable insights for both clinicians and patients.
Conclusions
Despite the higher MPN rate, comparable outcomes can be achieved following early R-ICSI when compared to conventional ICSI for couples with non-severe male factor and poor oocyte yield. Given the limited data and methodological constraints, further data accumulation is needed to obtain more reliable conclusions.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Review Board of the Northwest Women’ s and Children’ s Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements. The manuscript presents research on animals that do not require ethical approval for their study.
Author contributions
ML: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. WC: Writing – original draft, Data curation. XX: Writing – review & editing, Formal Analysis, Software.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This project was supported by Shaanxi Technology Committee Industrial Public Relation Project (Project Number: 2023-YBSF-034) and Young Physicians Program of Chinese Medical Association (No. 17020470716).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Mahadevan MM and Trounson AO. The influence of seminal characteristics on the success rate of human in vitro fertilization. Fertil Steril. (1984) 42:400–5. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)48080-5
2. Jeulin C, Feneux D, Serres C, Jouannet P, Guillet-Rosso F, Belaisch-Allart J, et al. Sperm factors related to failure of human in-vitro fertilization. J Reprod Fertil. (1986) 76:735–44. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0760735
3. Aziz N, Buchan I, Taylor C, Kingsland CR, and Lewis-Jones I. The sperm deformity index: a reliable predictor of the outcome of oocyte fertilization in vitro. Fertil Steril. (1996) 66:1000–8. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)58697-x
4. Li M, Duan X, Zhang N, Ding F, Wang Y, Liu P, et al. Development and validation of a conventional in vitro total fertilization failure prediction model. J Assist Reprod Genet. (2023) 40:1915–23. doi: 10.1007/s10815-023-02851-7
5. Ola B, Afnan M, Sharif K, Papaioannou S, Hammadieh N, and Barratt CL. Should ICSI be the treatment of choice for all cases of in-vitro conception? Considerations of fertilization and embryo development, cost effectiveness and safety. Hum Reprod. (2001) 16:2485–90. doi: 10.1093/humrep/16.12.2485
6. Albertini DF. To ICSI or not to ICSI? That was the question. J Assist Reprod Genet. (2015) 32:1–2. doi: 10.1007/s10815-014-0416-8
7. Tian T, Chen L, Yang R, Long X, Li Q, Hao Y, et al. Prediction of fertilization disorders in the in vitro fertilization/intracytoplasmic sperm injection: A retrospective study of 106,728 treatment cycles. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 20:870708. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.870708
8. de Souza LK, Witusk JPD, Galgaro BC, Rodrigues LDS, and da Cunha-Filho JSL. Total fertilization failure: A single center analysis. Reprod Sci. (2024) 31:697–703. doi: 10.1007/s43032-023-01338-1
9. Jiang X, Cai J, Liu L, Liu Z, Chen J, Yang C, et al. Predicting the unexpected total fertilization failure in conventional in vitro fertilization cycles: What is the role of semen quality? Front Cell Dev Biol. (2023) 11:1133512. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1133512
10. Isikoglu M, Avci A, Kendirci Ceviren A, Aydınuraz B, and Ata B. Conventional IVF revisited: Is ICSI better for non-male factor infertility? Randomized controlled double blind study. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. (2021) 50:101990. doi: 10.1016/j.jogoh.2020.101990
11. Cutting E, Horta F, Dang V, van Rumste MM, and Mol BWJ. Intracytoplasmic sperm injection versus conventional in vitro fertilisation in couples with males presenting with normal total sperm count and motility. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2023) 8:CD001301. doi: 10.1002/14651858
12. Wang Y, Li R, Yang R, Zheng D, Zeng L, Lian Y, et al. Intracytoplasmic sperm injection versus conventional in-vitro fertilisation for couples with infertility with non-severe male factor: a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. (2024) 403:924–34. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)02416-9
13. Fang Q, Jiang X, Bai S, Xu B, Zong L, Qi M, et al. Safety of early cumulus cell removal combined with early rescue ICSI in the prevention of fertilization failure. Reprod BioMed Online. (2023) 47:103214. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2023.04.005
14. Fang C, Tang J, Huang R, Li LL, Zhang MF, and Liang XY. Comparison of IVF outcomes using conventional insemination and ICSI in ovarian cycles in which only one or two oocytes are obtained. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). (2012) 41:650–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jgyn.2012.06.004
15. Isikoglu M, Ceviren AK, Cetin T, Avci A, Aydinuraz B, Akgul OK, et al. Comparison of ICSI and conventional IVF in non-male factor patients with less than four oocytes. Arch Gynecol Obstet. (2022) 306:493–9. doi: 10.1007/s00404-022-06471-x
16. Chen J, Liu L, Liu Z, Pan L, Zhou L, Chen K, et al. Intracytoplasmic sperm injection hampers fertilization rate and pregnancy per initiated cycle in patients with extremely poor ovarian response. Arch Gynecol Obstet. (2025) 312:495–503. doi: 10.1007/s00404-025-08033-3
17. Tannus S, Son WY, Gilman A, Younes G, Shavit T, and Dahan MH. The role of intracytoplasmic sperm injection in non-male factor infertility in advanced maternal age. Hum Reprod. (2017) 32:119–24. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dew298
18. Mitchell V, Sigala J, Jumeau F, Ballot C, Peers MC, Decanter C, et al. ICSI treatment in severe asthenozoospermia. Gynecol Obstet Fertil. (2012) 40:776–9. doi: 10.1016/j.gyobfe.2012.10.003
19. Rumbold AR, Sevoyan A, Oswald TK, Fernandez RC, Davies MJ, and Moore VM. Impact of male factor infertility on offspring health and development. Fertil Steril. (2019) 111:1047–53. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2019.05.006
20. Yu CM, Fei-Liu, Zhang JH, Dai XL, Wang YF, and Chen L. Analysis of the split insemination (IVF+ICSI) treatment in patients with borderline semen in first cycle. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. (2022) 51:102491. doi: 10.1016/j.jogoh.2022.102491
21. Hershlag A, Paine T, Kvapil G, Feng H, and Napolitano B. In vitro fertilization-intracytoplasmic sperm injection split: an insemination method to prevent fertilization failure. Fertil Steril. (2002) 77:229–32. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(01)02978-8
22. Lainas GT, Lainas TG, Makris AA, Xenariou MV, Petsas GK, and Kolibianakis EM. Follicular flushing increases the number of oocytes retrieved: a randomized controlled trial. Hum Reprod. (2023) 38:1927–37. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dead169
23. Zhu LH, Ni XB, Lin F, Xu ZP, Fang JS, and Zhang NY. The impact of follicle-flushing during oocyte collection on embryo development of in-vitro fertilization. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. (2019) 17:106. doi: 10.1186/s12958-019-0540-5
24. Keefe D, Kumar M, and Kalmbach K. Oocyte competency is the key to embryo potential. Fertil Steril. (2015) 103:317–22. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2014.12.115
25. Ho JY, Chen MJ, Yi YC, Guu HF, and Ho ES. The effect of preincubation period of oocytes on nuclear maturity, fertilization rate, embryo quality, and pregnancy outcome in IVF and ICSI. J Assist Reprod Genet. (2003) 20:358–64. doi: 10.1023/a:1025476910771
Keywords: fertilization failure, rescue ICSI, ICSI, c-IVF, reproductive outcomes
Citation: Li M, Chen W and Xue X (2025) Comparison of conventional ICSI and rescue ICSI in patients without severe male factor and poor oocyte yield. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1637404. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1637404
Received: 29 May 2025; Accepted: 05 September 2025;
Published: 17 September 2025.
Edited by:
Fu-Jen Huang, Specialist Hospital, PolandCopyright © 2025 Li, Chen and Xue. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xia Xue, eHVleGlhOTEwMTFAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Mingzhao Li
Mingzhao Li Wennan Chen
Wennan Chen