- Department of Pharmacy, Hebei Medical University Third Hospital, Shijiazhuang, China
Objectives: This systematic review and meta-analysis was to evaluate and compare the efficacy and safety profiles of IDegLira versus insulin degludec in the management of type 2 diabetes (T2D).
Methods: A comprehensive search was systematically conducted across PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, and ClinicalTrials.gov from their inception until March 11, 2025. The search focused on randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared IDegLira with insulin degludec in adult patients with T2D. The primary outcomes of interest included change in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and body weight. Random-effects meta-analyses were performed using RevMan 5.4 and Stata 16.0 software.
Results: A total of six eligible RCTs, encompassing 3,393 patients (2,075 receiving IDegLira and 1,318 receiving insulin degludec), were included in the analysis. Treatment with IDegLira resulted in significant reductions in HbA1c (MD -0.79%, 95%CI: -1.03% to -0.54%), body weight (MD -1.62 kg, 95% CI: -2.13 kg to -1.11 kg), fasting plasma glucose (MD -0.45 mmol/L, 95% CI: -0.77 mmol/L to -0.14 mmol/L), self-measured plasma glucose (MD -1.00 mmol/L, 95% CI: -1.42 mmol/L to -0.59 mmol/L), and systolic blood pressure (MD -2.23 mmHg, 95% CI: -3.63 mmHg to -0.82 mmHg). In comparison to insulin degludec, IDegLira demonstrated superior blood glucose control, as evidenced by a higher proportion of patients achieving HbA1c levels below 7.0% and 6.5%, as well as those achieving these targets without weight gain and severe or blood glucose-confirmed hypoglycemic episodes. Additionally, patients treated with IDegLira required significantly lower daily insulin doses. Notably, the risk of severe or blood glucose-confirmed symptomatic hypoglycemia, adverse events, and severe adverse events was comparable between IDegLira and insulin degludec.
Conclusions: This meta-analysis provides compelling evidence that IDegLira offers superior glycemic control and more favorable effects on body weight compared to insulin degludec, while maintaining a comparable safety profile.
1 Introduction
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) poses a significant global health challenge, with its prevalence escalating annually. In 2019 alone, 463 million adults were affected, and this number is projected to surge to 700 million by 2045 (1). T2D is marked by progressive β-cell dysfunction and insulin resistance, often necessitating increasingly intensive treatment over time (2). Initially, lifestyle modifications and oral antidiabetic medications serve as the cornerstone of therapy. However, many patients eventually require insulin treatment to effectively manage their blood glucose levels (3). Basal insulin analogs, such as insulin degludec, have gained widespread acceptance due to their extended duration of action and reduced variability in glucose-lowering effects compared to earlier insulin formulations (4). Despite these benefits, insulin therapy is not without challenges. It carries risks of hypoglycemia, weight gain, and the need for careful dose titration, all of which can impact treatment adherence and long-term health outcomes (5). On the other hand, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) have emerged as a valuable addition to the antidiabetic armamentarium. These agents promote glucose-dependent insulin secretion, suppress glucagon release, slow gastric emptying, and enhance satiety, often leading to weight loss rather than gain (6). Their use, however, is primarily limited by gastrointestinal side effects, which are typically dose-dependent and tend to resolve over the course of treatment (7).
IDegLira is a once-daily, subcutaneously administered combination therapy that combines insulin degludec with the GLP-1 RA liraglutide in a fixed ratio (8). This formulation was developed to leverage the complementary mechanisms of action of these two drug classes while potentially mitigating their individual limitations. By integrating a basal insulin with a GLP-1 RA, IDegLira addresses multiple pathophysiological defects in T2D, potentially reducing the required insulin dose and associated side effects. Moreover, the convenience of a single daily injection may enhance patients’ adherence to therapy.
Several global DUAL randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have compared IDegLira with insulin degludec (9–11). However, individual studies may lack sufficient statistical power to detect differences in certain outcomes. Currently, two meta-analyses have compared IDegLira with various antidiabetic drugs to assess its initial efficacy and safety in treating T2D patients (12, 13). Nevertheless, these analyses combined different antidiabetic drugs into a single group without conducting subgroup analyses based on specific drugs. Therefore, we conducted this systematic review and meta-analysis to provide a comprehensive evaluation of the efficacy and safety of IDegLira versus insulin degludec in patients with T2D.
2 Methods
The protocol of this meta-analysis has been registered in PROSPERO (CRD420251038517). This systematic review and meta-analysis followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) guidelines for conducting a high-quality meta-analysis (14, 15).
2.1 Search strategy and selection criteria
To identify RCTs comparing the efficacy and safety of IDegLira with insulin degludec in patients with T2D, we conducted a comprehensive search across several databases. These included PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, and ClinicalTrials.gov, covering the period from their inception up until March 11, 2025. The search terms utilized encompassed a range of relevant keywords, such as diabetes mellitus, diabetes, T2DM, DM, IDegLira, Xultophy, insulin degludec and liraglutide, degludec/liraglutide, degludec plus liraglutide, degludec, and Tresiba. A detailed search strategy is outlined in Supplementary Table 1.
The specific inclusion criteria for this study were as follows: (1) The study design must be a RCT; (2) Participants should be patients with T2D; (3) The intervention is IDegLira; (4) The control group should receive insulin degludec; and (5) The study must report at least one of the following outcomes: change in HbA1c, change in body weight, patients with HbA1c <7%, patients with HbA1c <6.5%, HbA1c <7.0% without weight gain and without severe or blood glucose-confirmed hypoglycemic episodes, HbA1c <6.5% without weight gain and without severe or blood glucose-confirmed hypoglycemic episodes, change in fasting plasma glucose (FPG), change in self-measured plasma glucose (SMPG), change in systolic blood pressure, change in diastolic blood pressure, total daily insulin dose, severe or blood glucose-confirmed symptomatic hypoglycemia, as well as adverse events (AEs) and serious adverse events (SAEs).
Exclusion criteria for this study encompassed reviews, conference abstracts, case reports, meta-analyses, comments, non-English or non-Chinese language publications, RCTs with inadequate or unusable data, and studies with a treatment duration of less than 12 weeks. Two authors independently conducted a literature search based on the predefined inclusion criteria.
2.2 Data extraction and quality assessment
The extracted data encompassed a comprehensive set of items, including baseline characteristics (such as trial name, country, study arms, number of patients, age, male ratio, body weight, body-mass index, HbA1c levels, diabetes duration, and treatment duration) and the outcomes of interest (which included change in HbA1c, change in body weight, patients with HbA1c <7%, patients with HbA1c <6.5%, HbA1c <7.0% without weight gain and without severe or blood glucose-confirmed hypoglycemic episodes, HbA1c <6.5% without weight gain and without severe or blood glucose-confirmed hypoglycemic episodes, change in FPG, change in SMPG, change in systolic blood pressure, change in diastolic blood pressure, total daily insulin dose, severe or blood glucose-confirmed symptomatic hypoglycemia, as well as AEs and SAEs. Our primary outcomes were change in HbA1c and body weight. Two investigators independently extracted the data using a standardized, pre-formatted Excel template, with a third investigator serving as an arbiter in case of discrepancies. For continuous variables, the mean and standard deviation were estimated using the methodologies proposed by Hozo et al. and Wan et al. (16, 17). Because of some participants withdrew during clinical trials, almost all outcome-specific analyses included fewer participants than the total study population and the most withdrawn patients were for adverse events and/or met withdrawal criteria. All data were extracted directly from publications and authors of these included studies were not contacted for additional information.
The risk of bias within individual studies was evaluated utilizing the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool (18), which included seven domains: random sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding of participants and personnel, blinding of outcome assessment, incomplete outcome data, selective reporting, and other bias. Each domain was assessed and categorized as having a “low risk,” “high risk,” or “unclear risk” of bias.
2.3 Statistical analysis
We performed meta-analyses when at least two studies provided relevant outcome data. For continuous outcomes, we computed the mean difference (MD), while for dichotomous data, we calculated the risk ratio (RR). All effect estimates were presented alongside 95% confidence intervals (CI). The heterogeneity among studies was assessed using Cochrane’s Q statistic and the I² statistic. Pooled analyses were conducted employing a random-effects model to account for potential variability. We evaluated publication bias through a visual examination of funnel plots. To identify the sources of heterogeneity, we carried out subgroup analysis and meta-regression analysis. Furthermore, the robustness of our meta-analysis models was rigorously tested using sensitivity analyses based on the leave-one-out method. All statistical procedures were executed using RevMan 5.4 software and Stata 16.0 software.
3 Results
3.1 Search results and quality assessment
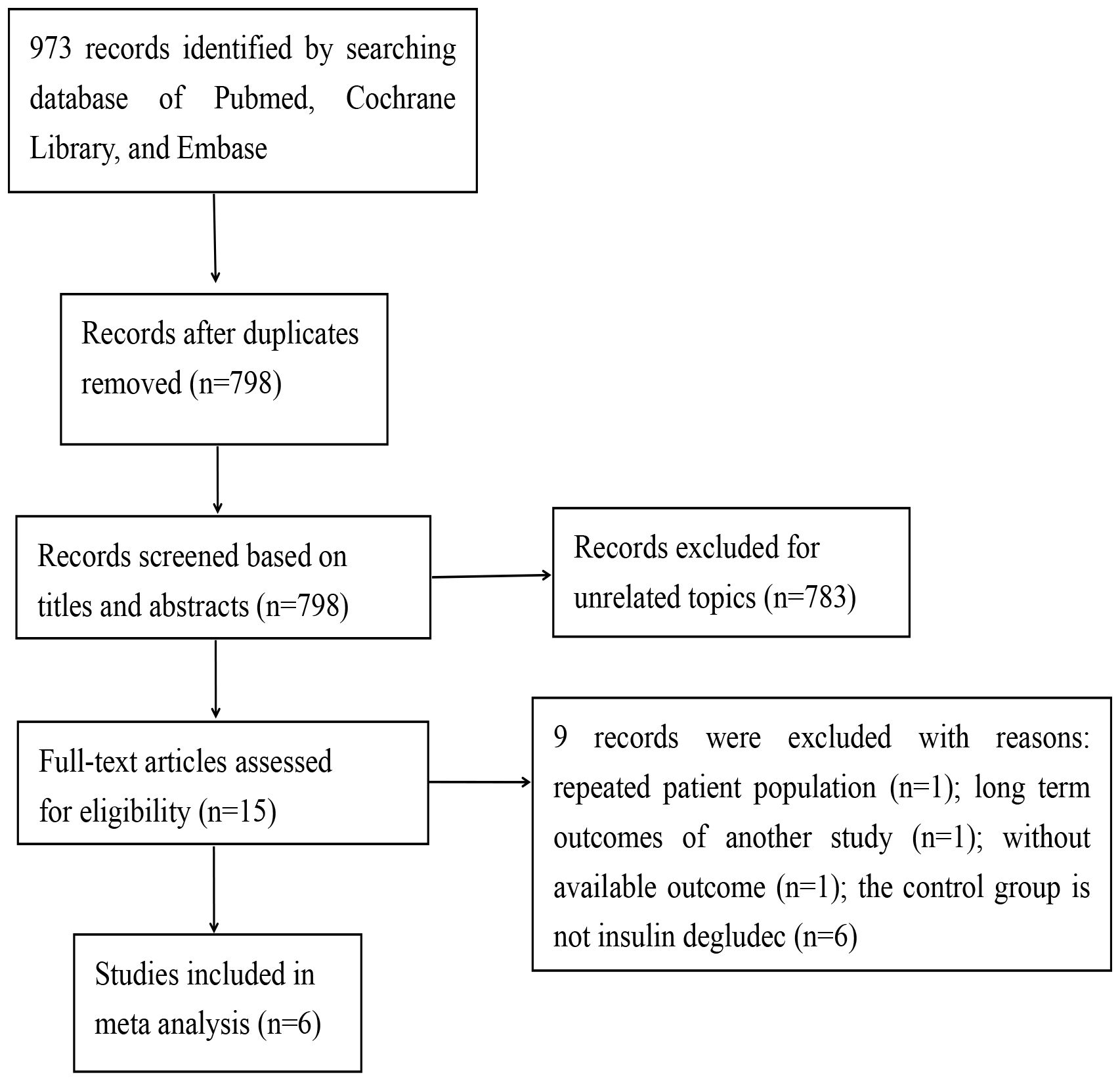
A comprehensive search across four databases yielded a total of 973 records. After eliminating duplicate entries, 798 records were retained for preliminary screening based on titles and abstracts. Of these, 783 references were excluded during this initial phase, leaving 15 studies for more in-depth evaluation. Ultimately, 6 records met the eligibility criteria and were included in this meta-analysis, while 9 records were excluded (Figure 1).
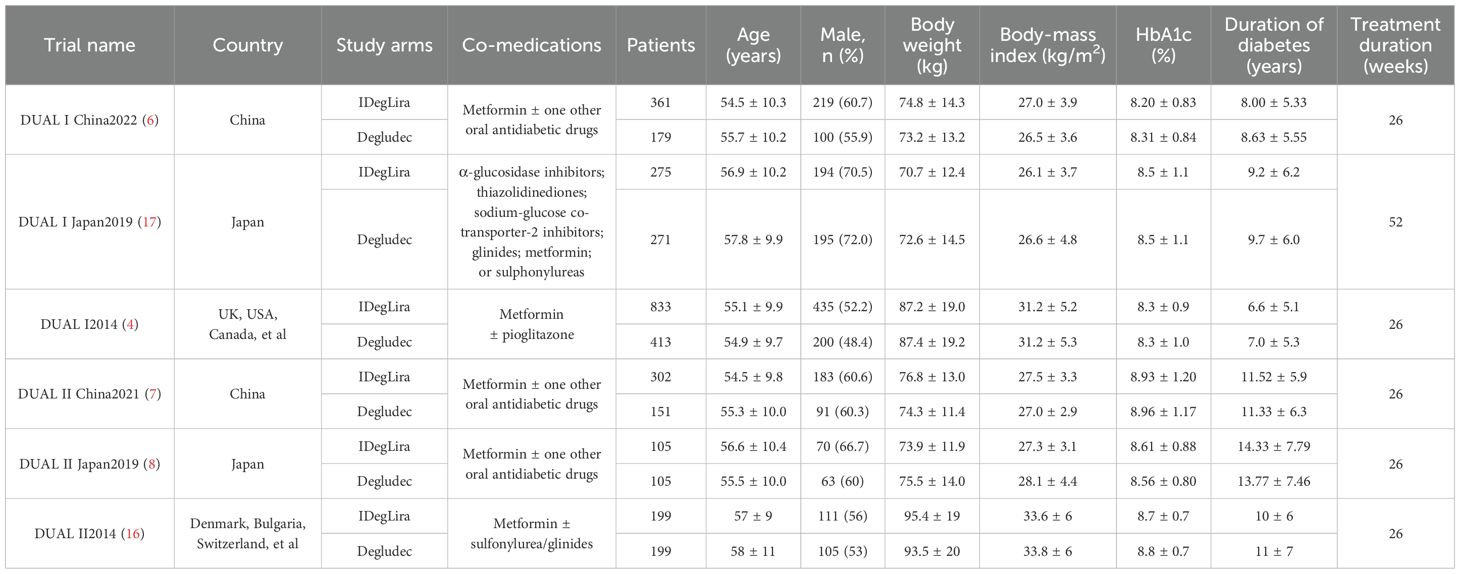
The characteristics of the trials incorporated in this analysis are summarized in Table 1. This meta-analysis encompasses 6 RCTs, involving a cumulative sample of 3,393 individuals (7, 9–11, 19, 20). Geographically, two of the included studies were conducted in China, two in Japan, and the remaining two were global or multinational in scope. The duration of these studies ranged from 26 to 52 weeks. Baseline characteristics of the participants varied across studies, with mean ages ranging from 54.5 to 58 years and initial HbA1c levels spanning from 8.2% to 8.96%. Applying the Cochrane criteria, the overall risk of bias across all studies was assessed as low. The risk of bias assessment is depicted in Figure 2.
3.2 Efficacy outcomes
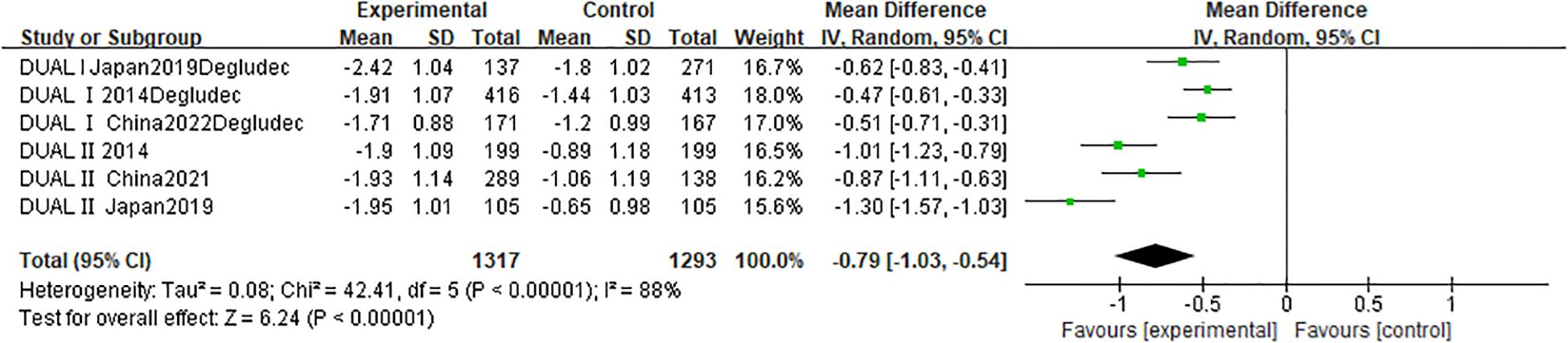
A pooled analysis of six RCTs (n = 2,610) evaluated change in HbA1c following IDegLira versus insulin degludec treatment (Figure 3). Results showed a statistically significant HbA1c reduction favoring IDegLira (MD -0.79%; 95% CI -1.03 to -0.54; p < 0.00001), though substantial heterogeneity existed (I² = 88%; p < 0.00001). Funnel plot analysis (Supplementary Figure S1) indicated no publication bias. Similarly, change in body weight (six studies; n = 2,610) was significantly reduced with IDegLira versus insulin degludec (MD -1.62 kg; 95% CI -2.13 to -1.11; p < 0.00001), with moderate heterogeneity (I² = 74%; p = 0.002) and no bias per funnel plot (Supplementary Figure S3).
IDegLira also improved glycemic targets: HbA1c <7.0% (six studies; n = 2,610): RR 1.93 (95% CI 1.45–2.56; p < 0.00001; I² = 94%) (Supplementary Figure S4); HbA1c <6.5% (six studies; n = 2,610): RR 2.51 (95% CI 1.77–3.55; p < 0.00001; I² = 91%) (Supplementary Figure S5). Funnel plots (Supplementary Figures S6, S7) showed no publication bias.
Composite outcomes further favored IDegLira: HbA1c <7.0% without weight gain and without severe or blood glucose-confirmed hypoglycemia (six studies; n = 2,636): RR 3.29 (95% CI 2.18–4.96; p < 0.00001; I² = 77%) (Supplementary Figure S8); HbA1c <6.5% without weight gain and without severe or blood glucose-confirmed hypoglycemia (six studies; n = 2,610): RR 4.15 (95% CI 2.60–6.62; p < 0.00001; I² = 70%) (Supplementary Figure S9). No publication bias was detected (Supplementary Figures S10, S11).
IDegLira reduced FPG levels (five studies; n = 1,782) more than insulin degludec (MD -0.45 mmol/L; 95% CI -0.77 to -0.14; p = 0.005; I² = 30%) (Supplementary Figure S12). Greater reductions in SMPG (four studies; n = 1,348) with IDegLira (MD -1.00 mmol/L; 95% CI -1.42 to -0.59; p < 0.00001; I² = 54%) (Supplementary Figure S13). Funnel plots (Supplementary Figures S14, S15) showed symmetry.
Significantly lower systolic blood pressure with IDegLira than with insulin degludec (MD -2.23 mmHg; 95% CI -3.63 to -0.82; p = 0.002; I² = 0%) (Supplementary Figure S16). No between-group difference was found in diastolic blood pressure (MD 0.17 mmHg; 95% CI -0.74 to 1.08; p = 0.72; I² = 0%) (Supplementary Figure S17). Daily insulin dose was lower with IDegLira than with insulin degludec (MD -6.83 U; 95% CI -11.07 to -2.60; p = 0.002; I² = 91%) (Supplementary Figure S18). No publication bias was evident (Supplementary Figures S19–S21).
3.3 Safety outcomes
Pooled safety data demonstrated comparable AE and SAE rates between groups (Supplementary Figures S22-S23). However, IDegLira was associated with significantly less severe/blood glucose-confirmed hypoglycemia (Supplementary Figure S24). Symmetrical funnel plots (Supplementary Figures S25-S27) indicated no publication bias for safety endpoints.
3.4 Meta-regression
As summarized in Table 2, baseline characteristics-including age, male, and baseline HbA1c-showed no significant association with any of these outcomes (p > 0.05). However, diabetes duration significantly contributed to heterogeneity in both change in HbA1c and patients with HbA1c <7%. Body-mass index was a significant modifier of heterogeneity for change in body. Notably, neither BMI nor diabetes duration influenced heterogeneity in the remaining outcomes (p > 0.05).
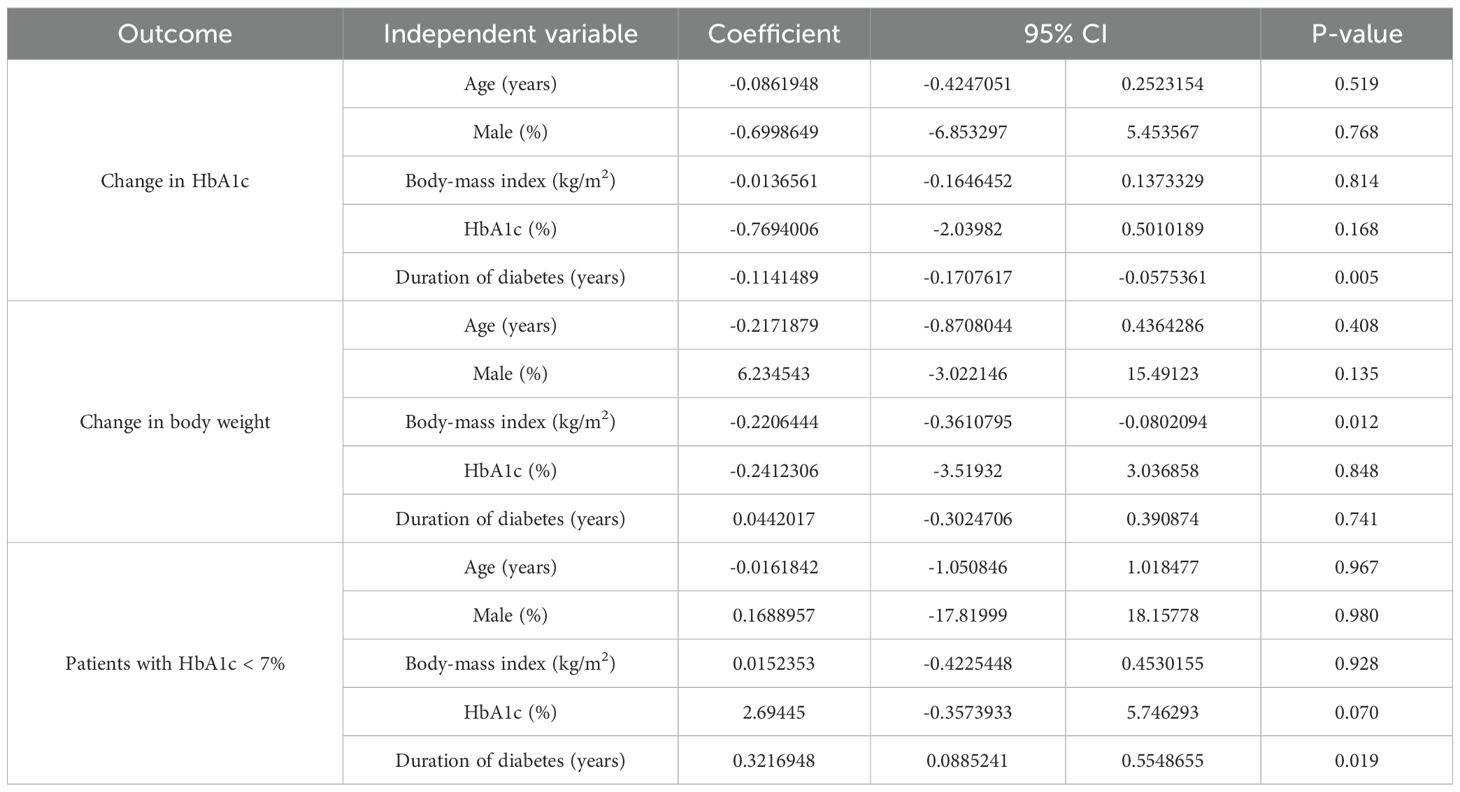
Table 2. Meta-regression on factors affecting change in HbA1c, change in body weight, and patients with HbA1c < 7%.
3.5 Subgroup analysis and sensitivity analysis
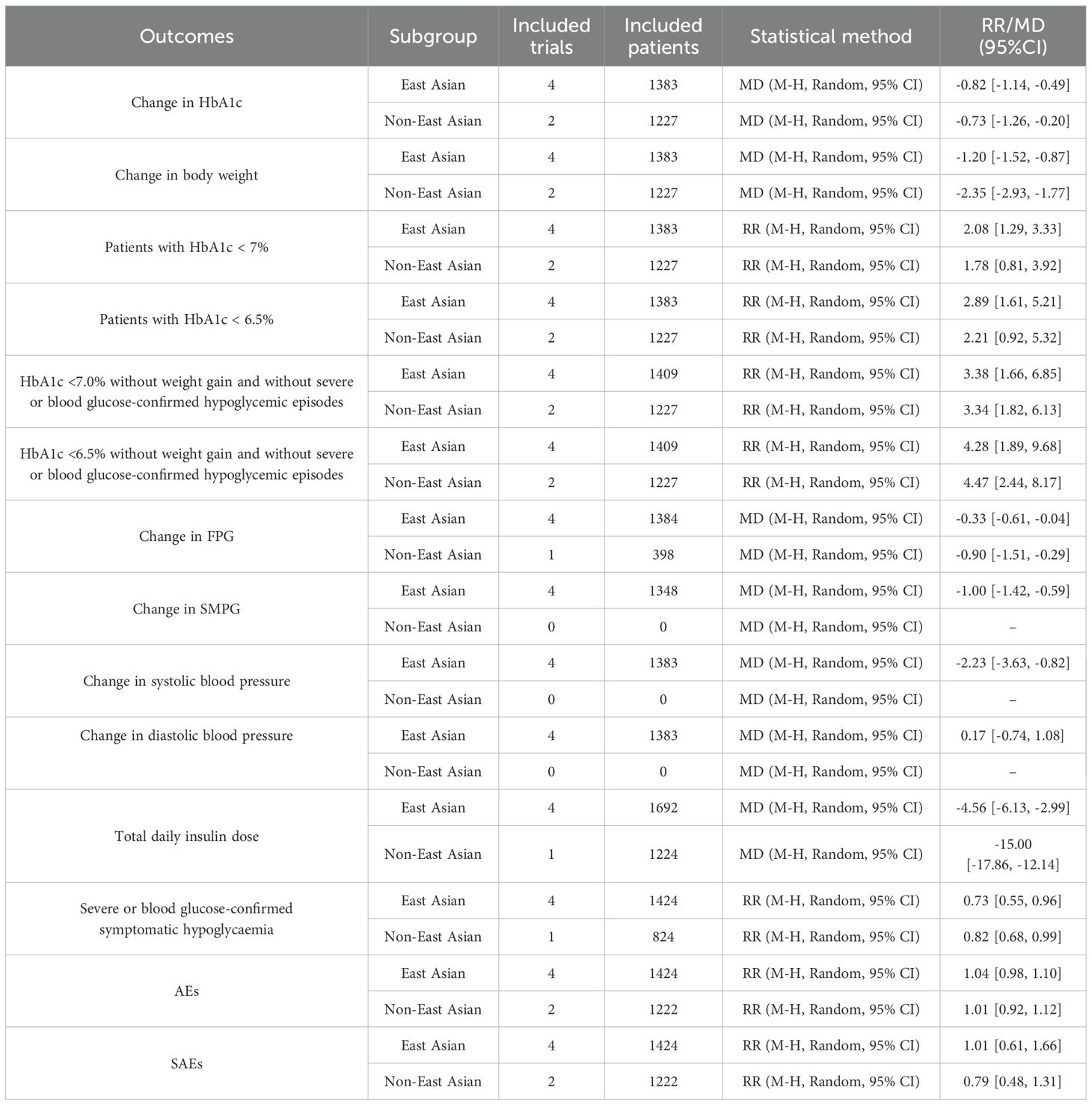
Subgroup analyses by race aligned with primary results (Table 3). Sensitivity analyses (leave-one-out method; Supplementary Figures S28–S30) confirmed robust findings for change in HbA1c, change in body weight, and patients with HbA1c <7%.
4 Discussion
This meta-analysis demonstrates IDegLira’s superiority over insulin degludec in terms of lowering blood glucose levels, controlling weight, and reducing insulin dosage. Furthermore, IDegLira showed a significantly lower incidence of severe or blood glucose-confirmed hypoglycemia, while maintaining comparable rates of other adverse events (AEs) and serious adverse events (SAEs). The robustness of these findings was confirmed through subgroup and sensitivity analyses.
Similar background glucose-lowering therapies (e.g., metformin, pioglitazone, and sulphonylureas) were permitted across all included RCTs, with metformin—recommended as first-line therapy by both the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and Chinese Diabetes Society (CDS) guidelines (21, 22)—being the most frequently used. The concurrent use of these agents may have contributed to the observed treatment effects, suggesting that the absolute benefit of the target drug in treatment-naïve populations could be lower than the pooled estimate reported here. Although randomization ensured balanced co-medication distribution between study arms, residual variations in background regimens may explain part of the heterogeneity observed in certain outcomes. Importantly, our primary analysis did not adjust for concomitant medications, which may limit the generalizability of findings to real-world settings where background therapies differ.
Clinical inertia in T2D management is often compounded by the complexity of adding medications to existing polypharmacy regimens (23). Given the established inverse relationship between regimen complexity and patient adherence (24), simplified approaches may help mitigate this inertia. IDegLira offers such simplification: despite both interventions requiring once-daily injections, it eliminates the need for separate insulin and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist administrations. Notably, its single-dose regimen shows particular promise for deprescribing in elderly patients, improving health outcomes and quality of life (25).
Balancing efficacy and cost is crucial in T2D management due to its substantial financial burden. Pharmacoeconomic analyses are therefore vital for optimizing resource allocation. In the Chinese context, Weng et al. (26) demonstrated that IDegLira is a cost-effective alternative to basal-bolus therapy or glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist monotherapy. Collectively, evidence supports IDegLira as a highly cost-effective intensification strategy for patients uncontrolled on basal insulin.
IDegLira also addresses two key barriers to insulin initiation: weight gain and hypoglycemia (5). Its liraglutide component drove significant weight reduction versus insulin degludec. Additionally, the observed trend towards lower hypoglycemia incidence aligns with global DUAL trial data (27, 28). In summary, IDegLira demonstrates greatest clinical utility as an escalation therapy for patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on oral agents who require robust HbA1c reduction without weight gain or hypoglycemia penalty, particularly when treatment adherence is a concern.
However, several limitations of our current meta-analysis should be acknowledged. Firstly, the included studies had relatively short follow-up periods, with the longest being only 52 weeks. Consequently, the long-term prognosis for patients receiving IDegLira versus insulin degludec remains uncertain and warrants continued follow-up. Secondly, we observed high heterogeneity in some of the results, which could not be fully explored through subgroup or sensitivity analyses, despite the use of random effects models. Moreover, the lack of blinding in certain studies may have influenced the reporting of specific safety outcomes, such as hypoglycemia. Finally, we do not compared IDegLira with basal insulin with premix insulin or basal bolus regimens for limited number of RCTs.
5 Conclusions
Compared with insulin degludec, treatment with IDegLira was superior to insulin degludec in terms of change in HbA1c, change in body weight, patients with HbA1c <7.0%, patients with HbA1c <6.5%, HbA1c <7.0% without weight gain and without severe or blood glucose-confirmed hypoglycemic episodes, HbA1c <6.5% without weight gain and without severe or blood glucose-confirmed hypoglycemic episodes, change in fasting plasma glucose, change in self-measured plasma glucose, and total daily insulin dose, while maintaining a comparable safety profile. This meta-analysis provided evidence of efficacy and safety differences of IDegLira and insulin degludec in T2D patients to guide the clinical practice.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
YL: Supervision, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Software, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Validation, Project administration, Resources, Visualization, Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis. XL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Software. JY: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Validation, Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Project administration. SQ: Project administration, Formal analysis, Supervision, Methodology, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Validation. XiaoW: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Supervision, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Methodology, Conceptualization, Investigation, Software, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XianW: Writing – original draft, Software, Investigation, Validation, Formal analysis, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Data curation, Methodology, Project administration.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by Medical Science Research Project of Hebei (No. 20241798).
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support from Medical Science Research Project of Hebei.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2025.1643386/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
T2D, type 2 diabetes; RCTs, randomized controlled trials; HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin; GLP, 1 RAs-glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; SMPG, self-measured plasma glucose; AEs, adverse events; SAEs, serious adverse events; MD, mean difference; RR, risk ratio; CI, confidence intervals.
References
1. Magliano DJ and Boyko EJ. IDF Diabetes Atlas 10th edition scientific committee. In: IDF DIABETES ATLAS, 10th ed. International Diabetes Federation, Brussels (2021).
2. Nolan CJ and Prentki M. Insulin resistance and insulin hypersecretion in the metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes: Time for a conceptual framework shift. Diabetes Vasc Dis Res. (2019) 16:118–27. doi: 10.1177/1479164119827611
3. Jia W, Weng J, Zhu D, Ji L, Lu J, Zhou Z, et al. Standards of medical care for type 2 diabetes in China 2019. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. (2019) 35:e3158. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3158
4. Kamrul-Hasan ABM, Borozan S, Fernandez CJ, Dutta D, Nagendra L, and Pappachan JM. Thrice-weekly insulin degludec versus once-daily insulin glargine in insulin-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). (2025) 86:1–16. doi: 10.12968/hmed.2024.0716
5. Russell-Jones D, Pouwer F, and Khunti K. Identification of barriers to insulin therapy and approaches to overcoming them. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2018) 20:488–96. doi: 10.1111/dom.13132
6. Watkins JD, Koumanov F, and Gonzalez JT. Protein- and calcium-mediated GLP-1 secretion: A narrative review. Adv Nutr. (2021) 12:2540–52. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmab078
7. Gough SC, Bode B, Woo V, Rodbard HW, Linjawi S, Poulsen P, et al. Efficacy and safety of a fixed-ratio combination of insulin degludec and liraglutide (IDegLira) compared with its components given alone: results of a phase 3, open-label, randomised, 26-week, treat-to-target trial in insulin-naive patients with type 2 diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2014) 2:885–93. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(14)70174-3
8. Aso Y, Takada Y, Tomotsune K, Chiba Y, Matsumura M, Jojima T, et al. Comparison of insulin degludec (IDeg)/insulin Aspart (IAsp) co-formulation therapy twice-daily with free combination of GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide plus insulin degludec in Tochigi: IDEAL Trial. Int J Clin Pract. (2021) 75:e13734. doi: 10.1111/ijcp.13734
9. Wang W, Agner BFR, Luo B, Liu L, Liu M, Peng Y, et al. DUAL I China: Improved glycemic control with IDegLira versus its individual components in a randomized trial with Chinese participants with type 2 diabetes uncontrolled on oral antidiabetic drugs. J Diabetes. (2022) 14:401–13. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.13286
10. Pei Y, Agner BR, Luo B, Dong X, Li D, Liu J, et al. DUAL II China: Superior HbA1c reductions and weight loss with insulin degludec/liraglutide (IDegLira) versus insulin degludec in a randomized trial of Chinese people with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on basal insulin. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2021) 23:2687–96. doi: 10.1111/dom.14522
11. Watada H, Kaneko S, Komatsu M, Agner BR, Nishida T, Ranthe M, et al. Superior HbA1c control with the fixed-ratio combination of insulin degludec and liraglutide (IDegLira) compared with a maximum dose of 50 units of insulin degludec in Japanese individuals with type 2 diabetes in a phase 3, double-blind, randomized trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2019) 21:2694–703. doi: 10.1111/dom.13859
12. Liakopoulou P, Liakos A, Vasilakou D, Athanasiadou E, Bekiari E, Kazakos K, et al. Fixed ratio combinations of glucagon like peptide 1 receptor agonists with basal insulin: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocrine. (2017) 56:485–94. doi: 10.1007/s12020-017-1293-6
13. Liu Y, Li X, Zheng Y, Wang X, and Wang X. IDegLira for type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocrine. (2024) 83:648–58. doi: 10.1007/s12020-023-03543-z
14. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, and Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ. (2009) 339:b2535. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b2535
15. Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ. (2009) 339:b2700. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b2700
16. Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, and Hozo I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol. (2005) 5:13. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-5-13
17. Wan X, Wang W, Liu J, and Tong T. Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med Res Methodol. (2014) 14:135. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-14-135
18. Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, et al. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 6.2 (updated February 2021). London, United Kingdom: Cochrane (2021). Available online at: www.training.cochrane.org/handbook (Accessed August 24, 2025).
19. Buse JB, Vilsbøll T, Thurman J, Blevins TC, Langbakke IH, Bøttcher SG, et al. Contribution of liraglutide in the fixed-ratio combination of insulin degludec and liraglutide (IDegLira). Diabetes Care. (2014) 37:2926–33. doi: 10.2337/dc14-0785
20. Kaku K, Araki E, Tanizawa Y, Agner BR, Nishida T, Ranthe M, et al. Superior efficacy with a fixed-ratio combination of insulin degludec and liraglutide (IDegLira) compared with insulin degludec and liraglutide in insulin-naïve Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes in a phase 3, open-label, randomized trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2019) 21:2674–83. doi: 10.1111/dom.13856
21. Davies MJ, Aroda VR, Collins BS, Gabbay RA, Green J, Maruthur NM, et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2022. A consensus report by the american diabetes association (ADA) and the european association for the study of diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care. (2022) 45:2753–86. doi: 10.2337/dci22-0034
22. Chinese Diabetes Society. Guideline for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in China (2020 edition). Chin J Diabetes Mellitus. (2020) 13:315–409. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115791-20210221-00095
23. Ross SA. Breaking down patient and physician barriers to optimize glycemic control in type 2 diabetes. Am J Med. (2013) 126:S38–48. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2013.06.012
24. Coleman CI, Limone B, Sobieraj DM, Lee S, Roberts MS, Kaur R, et al. Dosing frequency and medication adherence in chronic disease. J Manag Care Pharm. (2012) 18:527–39. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2012.18.7.527
25. Drummond R, Baru A, Dutkiewicz M, Basse A, and Tengmark BO. Physicians’ real-world experience with IDegLira: results of a European survey. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. (2018) 6:e000531. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2018-000531
26. Weng J, Xiao D, and Chen Y. Cost-utility of IDegLira versus alternative basal insulin intensification therapies in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus uncontrolled on basal insulin in a Chinese setting. Diabetol Metab Syndr. (2025) 17:156. doi: 10.1186/s13098-025-01722-8
27. Billings LK, Doshi A, Gouet D, Oviedo A, Rodbard HW, Tentolouris N, et al. Efficacy and safety of IDegLira versus basal-bolus insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes uncontrolled on metformin and basal insulin: the DUAL VII randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Care. (2018) 41:1009–16. doi: 10.2337/dc17-1114
28. Philis-Tsimikas A, Billings LK, Busch R, Portillo CM, Sahay R, Halladin N, et al. Superior efficacy of insulin degludec/liraglutide versus insulin glargine U100 as add-on to sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor therapy: A randomized clinical trial in people with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2019) 21:1399–408. doi: 10.1111/dom.13666
Keywords: IDegLira, insulin degludec, type 2 diabetes, randomized controlled trials, meta-analysis
Citation: Liu Y, Li X, Yang J, Qie S, Wang X, Wang X and Zheng Y (2025) IDeglira vs insulin degludec for type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1643386. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1643386
Received: 08 June 2025; Accepted: 15 August 2025;
Published: 01 September 2025.
Edited by:
Sridhar R. Gumpeny, Endocrine and Diabetes Centre, IndiaReviewed by:
Ivona Risovic, University of Banja Luka, Bosnia and HerzegovinaMassimo Quarenghi, Ente Ospedaliero Cantonale (EOC), Switzerland
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Li, Yang, Qie, Wang, Wang and Zheng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yingying Zheng, MTE2NTc1MjE4QHFxLmNvbQ==; Xianying Wang, MTMxNjA3NjIzNEBxcS5jb20=
 Yang Liu
Yang Liu Xianying Wang
Xianying Wang