- 1Department of Endocrinology, The First Hospital of Qinhuangdao, Qinhuangdao, Hebei, China
- 2Department of Endocrinology, Dongfang Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Qinhuangdao Hospital (Qinhuangdao Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine), Qinhuangdao, China
- 3Department of Respiratory, Qingdao Women and Children’s Hospital, Qingdao, Shandong, China
- 4Department of Pharmacy, The First Hospital of Qinhuangdao, Qinhuangdao, China
- 5Department of Ophthalmology, The First Hospital of Qinhuangdao, Qinhuangdao, China
Objective: This study aimed to examine the association between obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) and diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted involving 228 T2DM subjects at The First Hospital of Qinhuangdao. OSA was assessed using polysomnography. DPN was diagnosed based on clinical signs, symptoms and electromyography findings. Small fibre neuropathy was additionally assessed through corneal confocal microscopy. Among these T2DM subjects, 124 (54.4%) had DPN. The prevalence of OSA was 67.5% (mild OSA 30.7%, moderate-to-severe OSA 36.8%). DPN prevalence rates were 40.5%, 52.9% and 67.9% in subjects without OSA, with mild OSA, and with moderate-to-severe OSA respectively. Multiple logistic regression analysis revealed that moderate-to-severe OSA was independently associated with DPN in T2DM subjects (AOR=2.176, 95%CI:1.050-4.511, p=0.037). Multiple linear regression analysis demonstrated that apnea hypopnea index (AHI) was independently associated with corneal nerve fiber length (CNFL)(coefficient=-0.032, p=0.049, R2 = 0.029) and CNFT (coefficient=0.023, p<0.001, R2 = 0.171) in T2DM subjects.
Conclusion: T2DM subjects with OSA demonstrate significantly higher odds of DPN. Furthermore, OSA shows a significant correlation with small fibre damage in T2DM subjects.
Introduction
Diabetes mellitus is a global metabolic disorder characterised by chronic hyperglycaemia resulting from impaired insulin secretion, insulin action, or both. The International Diabetes Federation (IDF) Diabetes Atlas (11th edition) reports that approximately 589 million adults (20–79 years) currently live with diabetes worldwide - representing 1 in 9 adults. Projections indicate this number will rise to 853 million by 2050 (https://diabetesatlas.org/). China has experienced a dramatic increase in diabetes prevalence in recent decades, with national survey data demonstrating a diabetes prevalence rate of 12.4% in 2018 (1). Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) accounts for over 90% of diabetes cases in China (2). T2DM affects multiple major organ systems, including the cardiovascular system, nervous system, eyes, and kidneys. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN), a frequent complication of T2DM, affects approximately 67.6% of T2DM subjects in China (3, 4). Clinical manifestations of DPN include numbness, reduced pain sensation, burning sensations, and sharp pains. Without proper management, DPN may progress to serious foot complications including ulcers, and musculoskeletal damage (5). From a socioeconomic perspective, DPN contributes significantly to both direct and indirect healthcare expenditures (3).
Hyperglycaemia and diabetes duration significantly contribute to DPN development in T2DM subjects. Clinical trial evidence demonstrates that intensive glycaemic control prevents neuropathy in type 1 diabetes subjects. However, for T2DM subjects, intensive therapy shows less robust effects on clinical neuropathy outcomes, with no statistically significant benefit (6). Multiple studies indicate that beyond hyperglycaemia, additional risk factors including advanced age, visceral obesity and dyslipidaemia likely contribute to DPN pathogenesis in T2DM subjects (7, 8). Consequently, investigating these non-glycaemic risk factors is clinically crucial for developing more effective DPN prevention and management strategies in T2DM subjects.
Obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) represents a prevalent comorbidity of T2DM, capable of affecting multiple systems and inducing multi-organ damage. T2DM subjects exhibit approximately 50% greater risk of developing OSA compared to non-diabetic individuals (9). Among hospitalised T2DM subjects, OSA prevalence exceeds 60% (10). Early meta-analyses indicated a significant correlation between OSA and neuropathy in type 1 diabetes subjects, though not in T2DM subjects (11). However, variability in OSA and diabetic neuropathy definitions across included studies introduced substantial heterogeneity (12–15). Tahrani et al. demonstrated a novel independent association between OSA and DPN in T2DM subjects (15). Dhiman et al. similarly reported higher DPN prevalence among T2DM subjects with OSA versus those without (47% vs 26.1%, p=0.02) (16). Recent large-scale retrospective cohort studies have further substantiated that T2DM subjects with OSA diagnosis face elevated DPN risk compared to their non-OSA counterparts (17, 18). These studies primarily involved European and American populations. Three Chinese cross-sectional studies investigating the relationship between the apnoea-hypopnoea index (AHI) - a key OSA severity metric - and DPN yielded inconsistent results (19–21). Consequently, more extensive research on Chinese populations is warranted to elucidate the OSA-DPN association in T2DM subjects.
Electromyography assessment, a method commonly used to evaluate DPN in previous studies, primarily detects large fibre neuropathy. Diabetes mellitus also affects small fibres, with small fibre damage progressing more rapidly in T2DM subjects (22). Small fibre impairment typically precedes large fibre damage and contributes to clinically significant outcomes including painful diabetic neuropathy and foot ulceration (23). However, small fibre function has rarely been assessed in previous research (24).
This study aimed to investigate the association between OSA and DPN in subjects with T2DM This study aimed to investigate the association.
Methods
Subjects
We conducted a cross-sectional study involving inpatients with T2DM from The First Hospital of Qinhuangdao between September 2020 and December 2023. T2DM diagnosis was established according to the Chinese guidelines for T2DM management (25). The inclusion criteria included: 1) all participants had confirmed T2DM, and 2) both male and female subjects aged over 18 years. Exclusion criteria comprised: 1) type 1 diabetes, other specific diabetes types, or unclassified diabetes; 2) current diabetic ketoacidosis or hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state; 3) pregnancy; 4) active infection; 5) OSA treatment with continuous positive airway pressure, upper airway surgery, or oral appliances; and 6) neuropathy from other causes (including neurotoxic drugs, vitamin B12 deficiency, or chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy). The Ethics Committee of The First Hospital of Qinhuangdao approved the study protocol (Approval number: 2023KZ020), and all subjects provided written informed consent prior to enrolment.
Data collection
Data were extracted from the Hospital Information System including: 1) clinical data: age, sex, diabetes duration, and diagnoses of diabetes and hypertension; 2) anthropometric measurements: height (cm), weight (kg), waist circumference (WC, cm), and blood pressure. Blood pressure measurements were obtained using an Omron HEM-7122 automated electronic sphygmomanometer, with three measurements taken while subjects were seated after 10 minutes of rest; the average of these measurements was used for analysis. Hypertension was defined as systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥140 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) ≥90 mmHg, or subjects with a previous history of hypertension who are currently taking antihypertensive drugs (26). Body mass index (BMI, kg/m²) was calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in metres squared. Abdominal obesity was defined as WC ≥90 cm in males and ≥85 cm in females; 3) biochemical indicators: fasting plasma glucose (FPG), glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c), triglycerides (TG), and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C). Dyslipidaemia was defined as TG ≥1.7 mmol/L or HDL-C <1.04 mmol/L (25).
Obstructive sleep apnea
All study subjects underwent overnight polysomnography using the Alice Night One home sleep breathing monitor (Philips Respironics Inc., Murrysville, Pennsylvania, United States) during hospitalisation. The monitoring assessed nasal airflow, snoring, respiratory effort, pulse oximetry (SpO2), pulse rate, and body position. An experienced investigator blinded to participant identity conducted the measurements for one night during hospitalisation. Apnoea was defined as a ≥90% reduction in airflow lasting ≥10 seconds. Hypopnoea was defined as either a ≥30% reduction in airflow with ≥4% oxygen desaturation lasting ≥10 seconds, or a ≥50% reduction in airflow with either ≥3% oxygen desaturation or subsequent arousal lasting ≥10 seconds. The apnoea-hypopnoea index (AHI) was calculated as the number of apnoea and hypopnoea events per hour of sleep, with obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) defined as AHI ≥5 events/hour (mild: 5-<15 events/hour; moderate-to-severe: ≥15 events/hour) (27).
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy
The diagnosis of DPN was established based on clinical signs, symptoms, and electromyography findings. Subjects were evaluated for numbness and pain symptoms, along with neurological examinations comprising ankle reflexes, vibration perception (using a 128-Hz tuning fork), light touch sensation (assessed with a 10-g monofilament), thermal discrimination (cold/hot), and pinprick sensation during hospital admission.
The posterior tibial nerve, common peroneal nerve, sural nerve, and superficial peroneal nerve in both lower limbs were examined using a Nicolet Viking IV electromyography system (American) to assess latency, amplitude, and conduction velocity. All measurements were conducted by a qualified medical professional.
DPN was diagnosed when participants met any of the following criteria: (1) presence of ≥1 clinical sign and ≥1 symptom, (2) ≥2 characteristic symptoms, or (3) confirmed abnormal nerve conduction (2). Further details regarding the DPN diagnostic procedure are provided in the Supplementary Material.
Corneal confocal microscopy
All subjects underwent additional examination using laser-scanning in vivo confocal microscopy (IVCM) with a 670 nm wavelength laser (HRT3; Heidelberg, Germany). The examinations were conducted in morning sessions. The confocal system provided real-time 800× magnification of scanned structures, with each image demonstrating 1 µm lateral resolution within a 400 µm × 400 µm field of view. Scanning focused on the epithelial subbasal nerve plexus in the corneal pupillary region at depths ranging from 30 to 90 µm. Approximately 50–100 images were acquired per subject and stored securely. Six high-quality subepithelial corneal nerve fiber images were successfully captured for each eye, meeting predefined quality criteria: adequate grayscale contrast between nerve fibers and background, clearly defined nerve fiber boundaries (without blurring or halos), and minimal artefacts (such as tear film reflections, bubbles, or epithelial debris) covering less than 5% of the imaging field. A single experienced ophthalmic technician performed all procedures. Image analysis was conducted using ACCMetrics software (University of Manchester, UK). The final analysis involved averaging the values obtained from the six images. The following parameters were quantified: (1) Corneal nerve fibre length (CNFL): defined as the total length of all nerve fibres and their branches (expressed in mm/mm² of corneal tissue); (2) Corneal nerve fibre density (CNFD): calculated as the number of main nerve trunks per mm² of corneal tissue; (3) Corneal nerve branch density (CNBD): enumerated as the branches originating from main nerve trunks per mm² of corneal tissue; (4) Corneal nerve fibre tortuosity (CNFT): graded on a 0–4 scale where 0 represents predominantly straight fibres; 1 denotes slightly curved fibres; 2 indicates moderately curved fibres with frequent minor directional changes; 3 corresponds to markedly curved fibres with substantial directional alterations; and 4 designates severely tortuous fibres exhibiting abrupt and frequent directional changes (28).
Statistical analyses
Analyses were performed using STATA version 16.0 (STATA Corporation, TX, USA). Categorical data were compared using the χ² test. Quantitative data were expressed as mean with standard deviation. Continuous variables with skewed distributions, such as duration of diabetes and TG, were ln-transformed to reduce skewness and are expressed as medians with interquartile ranges. Comparisons were conducted between groups using analysis of variance (ANOVA), with Bonferroni post-hoc correction. Multiple logistic regression was used to model the relationship between OSA and DPN. Pearson’s correlation coefficient was used to measure the strength of association between variables. Multiple linear regression analyses examined relationships between corneal confocal microscopy parameters and other variables. Variance inflation factor (VIF) values greater than 10 were considered to indicate significant multicollinearity. p<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
This study included 228 T2DM subjects (133 males, 95 females) with a mean age of 54.2 ± 12.1 years and mean diabetes duration of 7.2 ± 6.8 years. Among these subjects, 124 (54.4%) had DPN. OSA prevalence was 67.5% (mild OSA 30.7%, moderate-to-severe OSA 36.8%). The DPN frequency was significantly higher in subjects with OSA compared to those without (61.0% vs 40.5%; χ²=8.466, p=0.004).
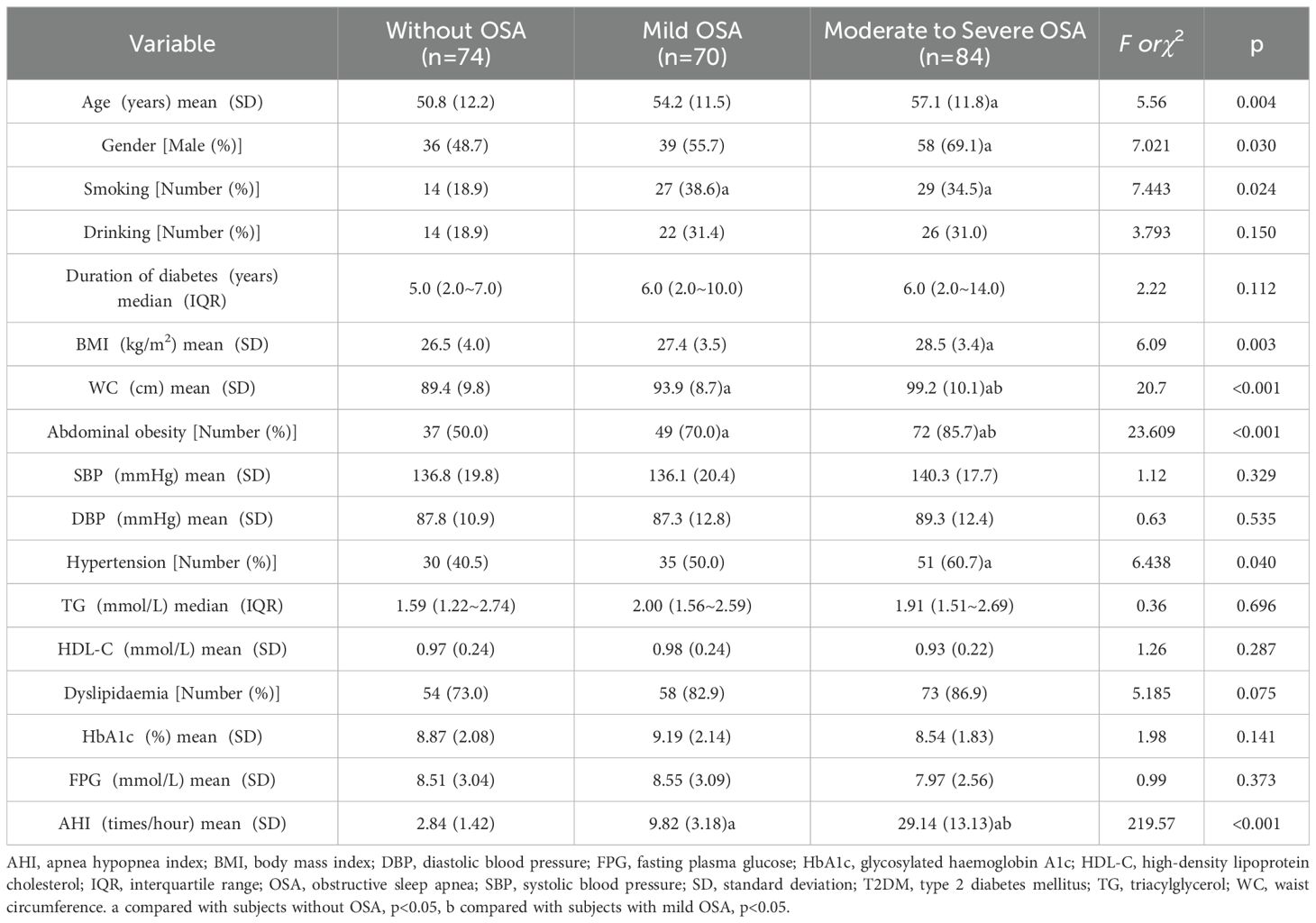
The patient characteristics stratified by OSA status are presented in Table 1. Compared to non-OSA subjects, those with moderate-to-severe OSA demonstrated significantly higher age levels and male predominance (p<0.05). Both mild and moderate-to-severe OSA groups exhibited increased smoking frequencies relative to the non-OSA group (p<0.05). Waist circumference measurements and abdominal obesity prevalence showed a positive correlation with OSA severity (p<0.05). Hypertension occurrence was significantly elevated in the moderate-to-severe OSA cohort compared to OSA-negative subjects (p<0.05). No intergroup differences were observed in TG, HDL-C, HbA1c or FPG levels (p>0.05).
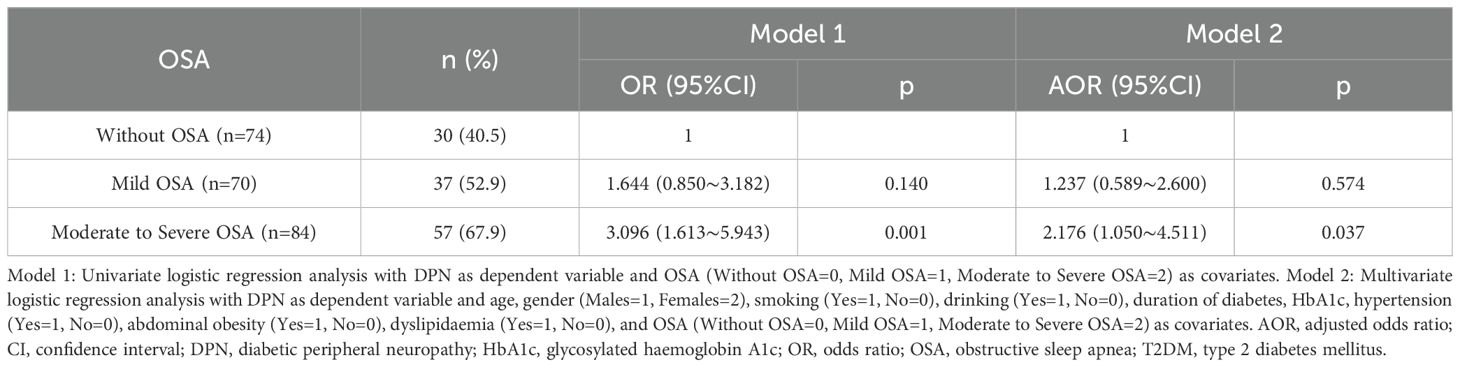
The frequencies of vibration perception impairment were higher in subjects with moderate to severe OSA than in those without OSA (p<0.05; Table 2). The DPN frequencies were 40.5% in subjects without OSA, 52.9% in those with mild OSA, and 67.9% in those with moderate to severe OSA. Subjects with moderate to severe OSA were more likely to have DPN (OR=3.096, 95% CI: 1.613-5.943, p=0.001) compared to subjects without OSA. In multiple logistic regression analysis with DPN as the dependent variable, covariates were age, gender (male=1, female=2), smoking (yes=1, no=0), drinking (yes=1, no=0), diabetes duration, HbA1c, hypertension (yes=1, no=0), abdominal obesity (yes=1, no=0), dyslipidaemia (yes=1, no=0), and OSA (without=0, mild=1, moderate to severe=2). Age (AOR=1.075, 95% CI: 1.045-1.107, p<0.001), diabetes duration (AOR=1.288, 95% CI: 1.038-1.598, p=0.021), and moderate to severe OSA (AOR=2.176, 95% CI: 1.050-4.511, p=0.037) were independent risk factors for DPN in T2DM subjects (Table 3).
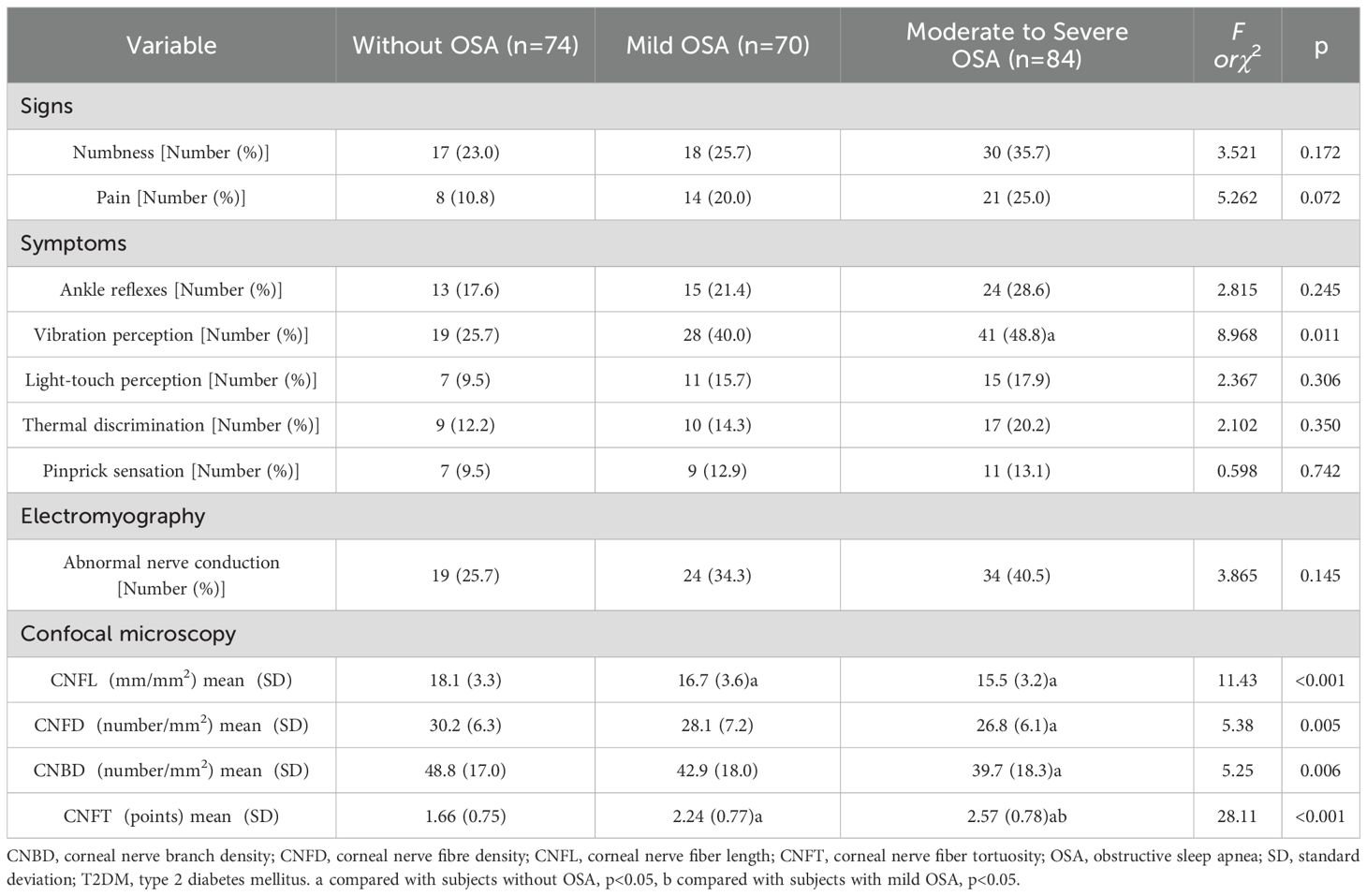
Table 2. The signs, symptoms, and the results of electromyography and corneal confocal microscopy in subjects with T2DM by the status of OSA.
Subjects with moderate to severe OSA had lower CNFL, CNFD and CNBD levels than those without OSA (p<0.05). CNFL levels were lower in subjects with mild OSA than in those without OSA (p<0.05). CNFT levels were higher in subjects with mild OSA and moderate to severe OSA than in those without OSA (p<0.05). CNFT levels were higher in subjects with moderate to severe OSA than in those with mild OSA (p<0.05) (Table 2). AHI was negatively correlated with CNFL (r=-0.216, p=0.001), CNFD (r=-0.202, p=0.002) and CNBD (r=-0.151, p=0.023), and positively correlated with CNFT (r=0.449, p<0.001). Corneal confocal microscopy parameters were also associated with age and diabetes duration (p<0.05) (Table 4). In multiple linear regression analysis with corneal confocal microscopy parameters as dependent variables, and age, gender (male=1, female=2), smoking (yes=1, no=0), drinking (yes=1, no=0), diabetes duration, BMI, WC, SBP, DBP, TG, HDL-C, HbA1c, and AHI as covariates, AHI was independently related to CNFL (coefficient=-0.032, p=0.049, R2 = 0.029) and CNFT (coefficient=0.023, p<0.001, R2 = 0.171) in T2DM subjects. All VIF values were lower than 10 (Table 5).
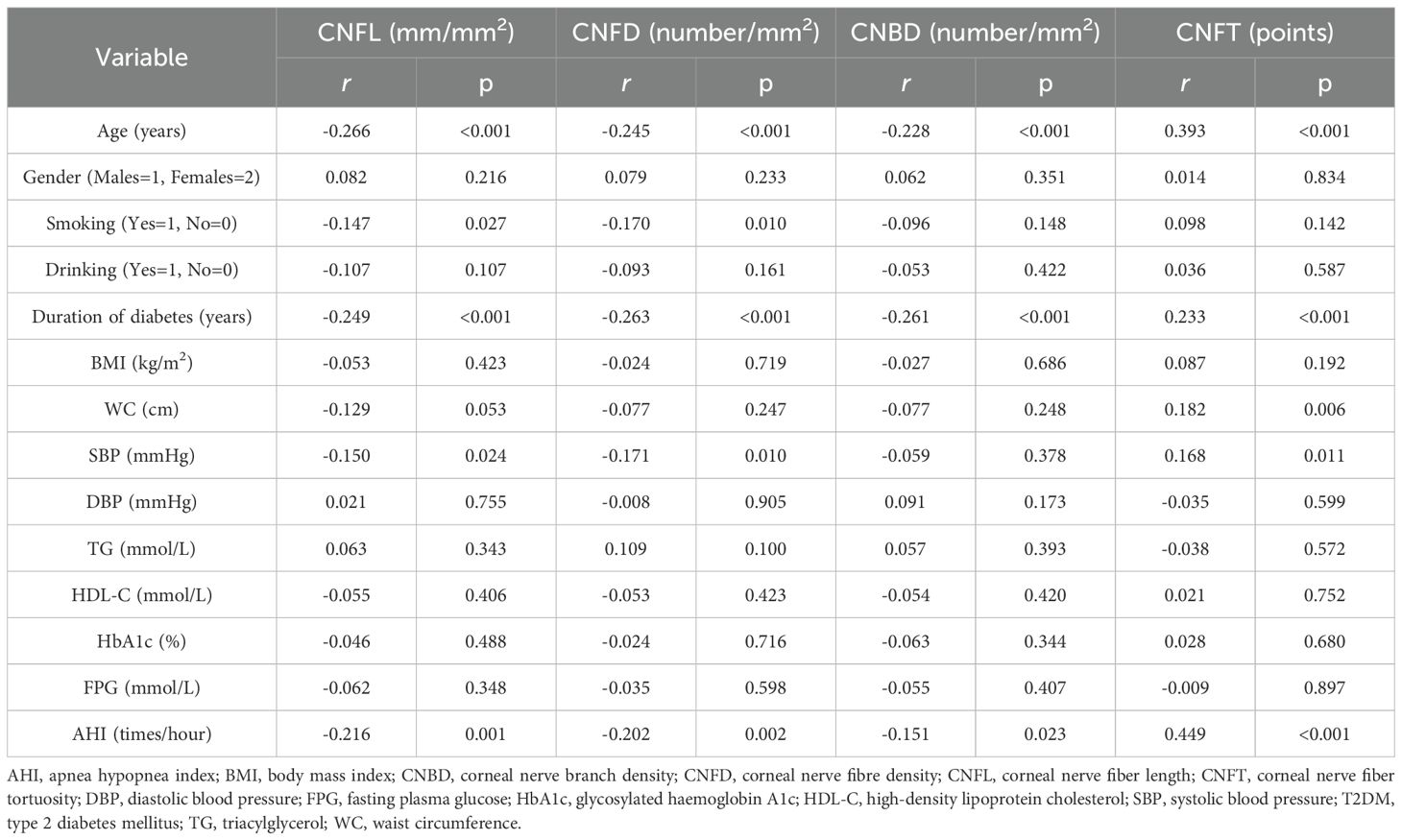
Table 4. Simple correlations between the parameters of corneal confocal microscopy, and other variables in subjects with T2DM.
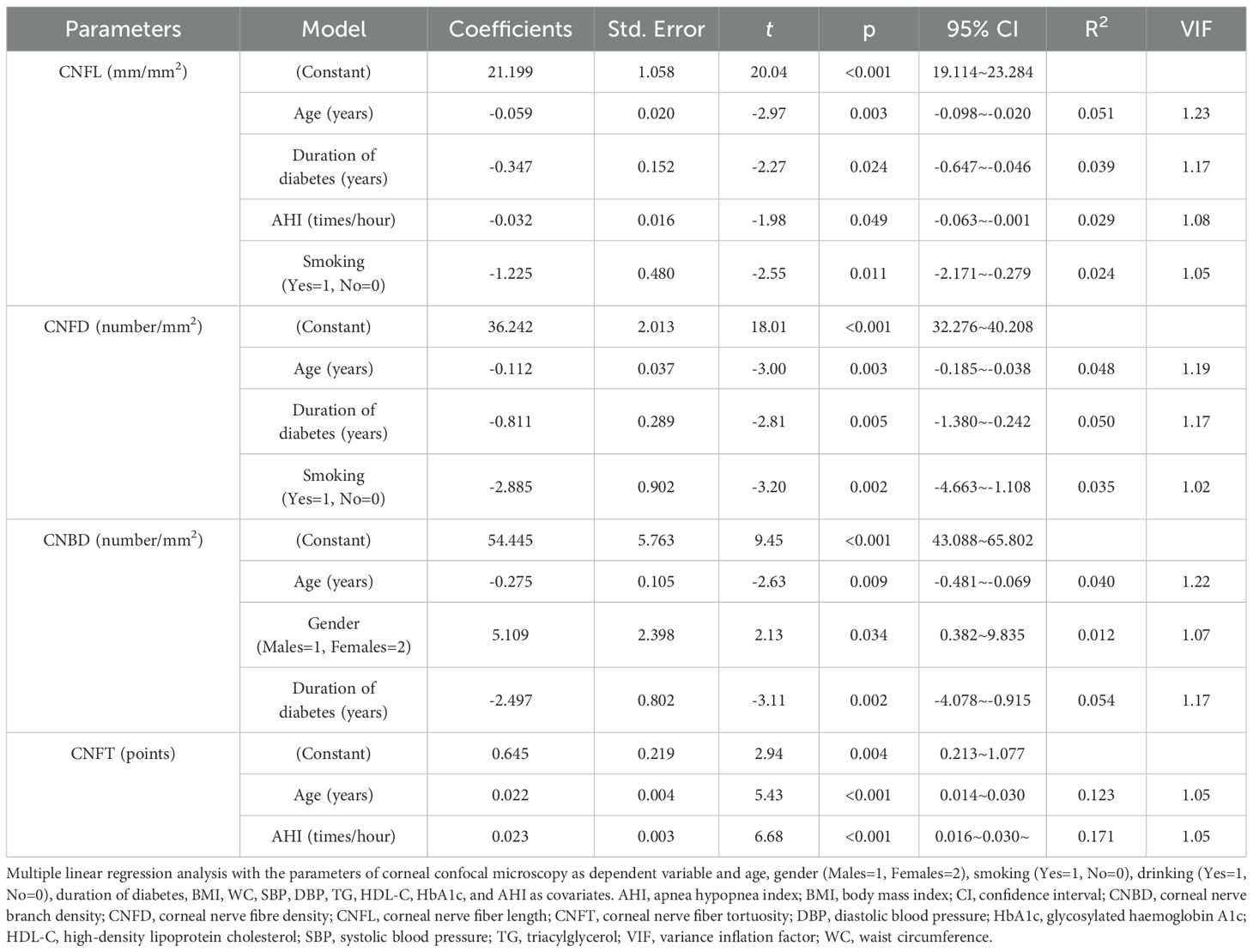
Table 5. Multiple linear regression analyses for the parameters of corneal confocal microscopy (stepwise method).
Discussion
Our study demonstrated that DPN was a common complication among inpatients with T2DM. The prevalence of DPN increased with OSA severity, with the most pronounced effects observed in moderate to severe OSA. Within the moderate to severe OSA group, approximately two-thirds of subjects exhibited DPN. These subjects were older and had a longer duration of diabetes compared to those without OSA. To account for confounding factors, multiple logistic regression analysis was performed, confirming that moderate to severe OSA was independently associated with DPN in subjects with T2DM.
In 2012, a UK study investigated the association between OSA and DPN in subjects with T2DM. OSA was defined using the apnoea-hypopnoea index (AHI), while DPN was assessed using the Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument (MNSI). The study population comprised White Caucasians and South Asians. The relationship between OSA and DPN was observed regardless of ethnicity; however, ethnic differences were noted in the strength of this association. Specifically, the prevalence of DPN was significantly higher in White Caucasians with OSA (66%) than in those without (22%; p<0.001), whereas among South Asians, the difference was less pronounced (48% vs. 29%, respectively; p=0.049) (15). These findings highlight the need for further research into the relationship between OSA and DPN across different ethnic groups. Three Chinese studies have examined the OSA-DPN association. All used AHI to define OSA and nerve conduction velocity to assess DPN (19–21). Two studies showed results consistent with our findings (19, 21). However, Du et al. reported no significant AHI-DPN association (20). This discrepancy may stem from elevated glucose levels in Du et al.’s study, where mean HbA1c reached 9.64% versus approximately 8.5% in other studies. This pronounced hyperglycaemia likely dominated DPN pathogenesis, potentially masking OSA’s independent effect.
Small fiber neuropathy (SFN) is a specific type of DPN that affects small-diameter sensory and/or autonomic axons. It manifests as autonomic neuropathy and paraesthesia, characterised by pain, numbness, coldness, and burning sensations (29). Abnormal thermal (cold/hot) discrimination and impaired pinprick sensation are also common symptoms of SFN (2). In our study, pain and thermal discrimination abnormalities were more frequently observed in subjects with moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA), though this difference was not statistically significant.
Intraepidermal nerve fibre density (IENFD) is considered an accurate and reproducible measure of SFN and the gold standard for SFN (30). Altaf QA et al. reported that AHI was associated with lower IENFD in subjects with T2DM (24). However, IENFD requires skin punch biopsy, an invasive procedure. Corneal confocal microscopy represents a reliable and non-invasive alternative to IENFD (31). In this study, small fibre function was evaluated by corneal confocal microscopy. Corneal confocal microscopy is a useful diagnostic tool for SFN in T2DM (32). Corneal confocal microscopy correlates with peripheral nerve structure and function in T2DM (33). Previous studies have reported comparable diagnostic efficacy between corneal confocal microscopy and IENFD in diabetic neuropathy, providing additional support for the clinical value of corneal confocal microscopy as a surrogate marker for DPN (31, 34). Meta-analysis has provided robust evidence that corneal confocal microscopy can detect small nerve fibre loss in DPN (35). Our results showed that AHI was independently related to CNFL and CNFT, particularly CNFT. Using multivariate regression models, we found that AHI accounted for 17.1% of the total variance in CNFT. Among the four parameters of corneal confocal microscopy, CNFT shows the closest association with the severity of painful diabetic neuropathy and autonomic neuropathy, suggesting that CNFT serves as an effective morphological marker for SFN (36, 37). This indicates that OSA may play a significant role in SFN development in subjects with T2DM. CNFL also represents a valuable biomarker for DPN, with the advantage of strong measurement repeatability (38). Rapid reduction in CNFL may help identify subjects at highest risk of DPN development and progression (39). A lower level of CNFL indicates a higher future risk of DPN in T2DM subjects with OSA and the necessity of early intervention for these subjects. Meanwhile, CNFL may serve as a monitoring indicator for the therapeutic efficacy of continuous positive airway pressure intervention.
OSA, characterised by recurrent upper airway obstruction during sleep, induces chronic intermittent hypoxia which may contribute to the development or progression of DPN through several key mechanisms. Oxidative-nitrosative stress: Subjects with DPN exhibit higher serum levels of nitrotyrosine and lipid peroxides, indicating that oxidative-nitrosative stress contributes to DPN pathogenesis (40). This stress acts through mechanisms including reduced nerve perfusion, impaired vascular reactivity, and effects on various peripheral nervous system cells, and is linked to pain abnormalities and small sensory nerve degeneration. Inhibition of such stress improves experimental diabetic neuropathy (41). Nocturnal hypoxemia correlates with serum nitrotyrosine levels, suggesting this stress as a potential mechanistic link between OSA and DPN (15). Inflammation: Low-grade intraneural inflammation may represent a major facet of diabetic neuropathy (42). Intermittent hypoxia activates pro-inflammatory pathways, including Toll-like receptor (TLR)4/nuclear factor κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) and nucleotide-binding domain (NOD)-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) signalling pathways, leading to elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (such as IL-6 and IL-1β) (43). These pathways promote neuroinflammation, further compromising nerve integrity in diabetes (44, 45). Endothelial dysfunction: Endothelial impairment is sufficient to cause neuropathy (46). Endothelial dysfunction occurs early in the pathophysiology of diabetes and represents a strong, independent predictor of DPN, including small fibre neuropathy (47, 48). Meta-analysis has demonstrated that OSA, particularly moderate-severe OSA, appears to impair endothelial function, while continuous positive airway pressure treatment for OSA exerts positive effects on endothelial function (49, 50).
Although the relationship between OSA and DPN still requires further confirmation through rigorous randomised controlled trials (RCTs), research on their correlation may provide a new intervention direction for DPN prevention and treatment in T2DM subjects. Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) represents the standard treatment for OSA. Meta-analysis of RCTs indicates that CPAP therapy appears to significantly improve HbA1c in subjects with T2DM and OSA. These trials primarily focused on glycaemic control and had relatively short treatment durations (51). Comprehensive RCTs are required to evaluate the observed beneficial association between CPAP and DPN in T2DM subjects (52).
There are several limitations to our study. First, due to insufficient information, we were unable to conduct Neuropathy Disability Score (NDS) and Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument (MNSI) assessments to evaluate DPN severity. Second, while inflammatory factors contribute to DPN, their absence in our analysis represents an additional limitation. Third, the study lacked a priori sample size calculation, and the sample size was relatively small, with only 30 subjects having severe OSA, necessitating the combination of moderate and severe cases for analysis. Future studies with larger sample sizes are required to validate these findings. Fourth, as a cross-sectional study, it cannot establish causality; prospective cohort studies are needed to determine the relationship between OSA and DPN.
In summary, OSA was common among inpatients with T2DM. Subjects with T2DM and OSA showed higher odds of DPN. OSA was also correlated with small fibre damage in T2DM subjects. Further studies are required to determine whether OSA intervention can improve DPN in T2DM.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the ethics committee of the First Hospital of Qinhuangdao. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin.
Author contributions
NL: Writing – original draft, Data curation. GC: Data curation, Writing – original draft. YQ: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. DA: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. FY: Writing – review & editing, Methodology. YH: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. XL: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. QL: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. CM: Writing – review & editing, Methodology. RW: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the Qinhuangdao Key R&D Projects (No.202301A120).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2025.1643826/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Wang L, Peng W, Zhao Z, Zhang M, Shi Z, Song Z, et al. Prevalence and treatment of diabetes in China, 2013-2018. JAMA. (2021) 326:2498–506. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.22208
2. Chinese Diabetes Society. Guideline for the prevention and treatment of diabetes mellitus in China (2024 edition). Chin J Diabetes. (2025) 17:16–139. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115791-20241203-00705
3. Savelieff MG, Elafros MA, Viswanathan V, Jensen TS, Bennett DL, and Feldman EL. The global and regional burden of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Nat Rev Neurol. (2025) 21:17–31. doi: 10.1038/s41582-024-01041-y
4. Wang W, Ji Q, Ran X, Li C, Kuang H, Yu X, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A population-based cross-sectional study in China. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. (2023) 39:e3702. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3702
5. ElSayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, Bannuru RR, Brown FM, Bruemmer D, et al. 12. Retinopathy, neuropathy, and foot care: standards of care in diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care. (2023) 46:S203–15. doi: 10.2337/dc23-S012
6. Callaghan BC, Little AA, Feldman EL, and Hughes RA. Enhanced glucose control for preventing and treating diabetic neuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2012) 2012:CD007543. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007543.pub2
7. Chen T, Xiao S, Chen Z, Yang Y, Yang B, and Liu N. Risk factors for peripheral artery disease and diabetic peripheral neuropathy among patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2024) 207:111079. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2023.111079
8. Wu RL, Chen N, Chen Y, Wu X, Ko CY, and Chen XY. Visceral adiposity as an independent risk factor for diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Study. J Diabetes Res. (2024) 2024:9912907. doi: 10.1155/2024/9912907
9. Subramanian A, Adderley NJ, Tracy A, Taverner T, Hanif W, Toulis KA, et al. Risk of Incident Obstructive sleep apnea among patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. (2019) 42:954–63. doi: 10.2337/dc18-2004
10. Ding S, Zhang P, Wang L, Wang D, Sun K, Ma Y, et al. Prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes in Beijing, China. J Diabetes Investig. (2022) 13:1889–96. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13868
11. Gu X, Luo X, Wang X, Tang J, Yang W, and Cai Z. The correlation between obstructive sleep apnea and diabetic neuropathy: A meta-analysis. Prim Care Diabetes. (2018) 12:460–6. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2018.03.005
12. Ficker JH, Dertinger SH, Siegfried W, König HJ, Pentz M, Sailer D, et al. Obstructive sleep apnoea and diabetes mellitus: the role of cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy. Eur Respir J. (1998) 11:14–9. doi: 10.1183/09031936.98.11010014
13. Laaban JP, Daenen S, Léger D, Pascal S, Bayon V, Slama G, et al. Prevalence and predictive factors of sleep apnoea syndrome in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Metab. (2009) 35:372–7. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2009.03.007
14. Nomura K, Ikeda H, Mori K, Hamamoto Y, Honjo S, Kawasaki Y, et al. Less variation of R-R interval of electrocardiogram in nonobese type 2 diabetes with nocturnal intermittent hypoxia. Endocr J. (2013) 60:225–30. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.ej11-0327
15. Tahrani AA, Ali A, Raymond NT, Begum S, Dubb K, Mughal S, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea and diabetic neuropathy: a novel association in patients with type 2 diabetes. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2012) 186:434–41. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201112-2135OC
16. Dhiman P, Singh P, Arora S, Kashyap A, Jain P, Singh M, et al. A comprehensive analysis of clinical, biochemical, and polysomnographic characteristics in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with and without obstructive sleep apnea. Cureus. (2024) 16:e59734. doi: 10.7759/cureus.59734
17. Riley DR, Henney A, Anson M, Hernadez G, Zhao SS, Alam U, et al. The cumulative impact of type 2 diabetes and obstructive sleep apnoea on cardiovascular, liver, diabetes-related and cancer outcomes. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2025) 27:663–74. doi: 10.1111/dom.16059
18. Adderley NJ, Subramanian A, Toulis K, Gokhale K, Taverner T, Hanif W, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea, a risk factor for cardiovascular and microvascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: findings from a population-based cohort study. Diabetes Care. (2020) 43:1868–77. doi: 10.2337/dc19-2116
19. Xue P, Covassin N, Ran X, Zhou J, Zhang X, Yan D, et al. Association of parameters of nocturnal hypoxemia with diabetic microvascular complications: A cross-sectional study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2020) 170:108484. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108484
20. Du C, He C, Dong L, Zheng S, Wang W, Zheng C, et al. Associations of apnea hypopnea index and educational attainments with microvascular complications in patients with T2DM. Endocrine. (2020) 67:363–73. doi: 10.1007/s12020-020-02192-w
21. Tan CX, Gao Y, Wang C, Li Y, Feng XB, Cheng YF, et al. Clinical characteristics of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. (2017) 48:441–5.
22. Løseth S, Stålberg EV, Lindal S, Olsen E, Jorde R, and Mellgren SI. Small and large fiber neuropathy in those with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a 5-year follow-up study. J Peripher Nerv Syst. (2016) 21:15–21. doi: 10.1111/jns.12154
23. Tavee J and Zhou L. Small fiber neuropathy: A burning problem. Cleve Clin J Med. (2009) 76:297–305. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.76a.08070
24. Altaf QA, Ali A, Piya MK, Raymond NT, and Tahrani AA. The relationship between obstructive sleep apnea and intra-epidermal nerve fiber density, PARP activation and foot ulceration in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Complications. (2016) 30:1315–20. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2016.05.025
25. Chinese Diabetes Society. Guideline for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in China (2020 edition). Chin J Endocrinol Metab. (2021) 37:311–98. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn311282-20210304-00142
26. Joint Committee for Guideline Revision. 2018 Chinese guidelines for prevention and treatment of hypertension-A report of the revision committee of chinese guidelines for prevention and treatment of hypertension. J Geriatr Cardiol. (2019) 16(3):182–241. doi: 10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2019.03.014.
27. Sleep Medicine Professional Committee of Chinese Medical Doctor Association. Multidisciplinary diagnosis and treatment guidelines for adult obstructive sleep apnoea. . Chin Med J. (2018) 98:1902–14. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2018.24.003
28. Oliveira-Soto L and Efron N. Morphology of corneal nerves using confocal microscopy. Cornea. (2001) 20:374–84. doi: 10.1097/00003226-200105000-00008
29. Themistocleous AC, Ramirez JD, Serra J, and Bennett DL. The clinical approach to small fibre neuropathy and painful channelopathy. Pract Neurol. (2014) 14:368–79. doi: 10.1136/practneurol-2013-000758
30. Lauria G, Hsieh ST, Johansson O, Kennedy WR, Leger JM, Mellgren SI, et al. European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on the use of skin biopsy in the diagnosis of small fiber neuropathy. Report of a joint task force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society. Eur J Neurol. (2010) 903-12:e44–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.03023.x
31. Chen X, Graham J, Dabbah MA, Petropoulos IN, Ponirakis G, Asghar O, et al. Small nerve fiber quantification in the diagnosis of diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy: comparing corneal confocal microscopy with intraepidermal nerve fiber density. Diabetes Care. (2015) 38:1138–44. doi: 10.2337/dc14-2422
32. Jin Y, Wang W, Chen W, Guo S, Li C, Zhu D, et al. Corneal confocal microscopy: A useful tool for diagnosis of small fiber neuropathy in type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Investig. (2021) 12:2183–9. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13616
33. Yan A, Issar T, Tummanapalli SS, Markoulli M, Kwai NCG, Poynten AM, et al. Relationship between corneal confocal microscopy and markers of peripheral nerve structure and function in Type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Med. (2020) 37:326–34. doi: 10.1111/dme.13952
34. Alam U, Jeziorska M, Petropoulos IN, Asghar O, Fadavi H, Ponirakis G, et al. Diagnostic utility of corneal confocal microscopy and intra-epidermal nerve fibre density in diabetic neuropathy. PloS One. (2017) 12:e0180175. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180175
35. Gad H, Petropoulos IN, Khan A, Ponirakis G, MacDonald R, Alam U, et al. Corneal confocal microscopy for the diagnosis of diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Diabetes Investig. (2022) 13:134–47. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13643
36. Wang H, Fan D, Zhang S, and Wang X. Early diagnosis of painful diabetic neuropathy by corneal confocal microscopy. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. (2014) 94:2602–6.
37. Wang H, Fan D, Wang W, Zhang S, and Wang X. Early diagnosis of diabetic autonomic neuropathy by corneal confocal microscopy. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. (2015) 95:2851–6.
38. Efron N, Edwards K, Roper N, Pritchard N, Sampson GP, Shahidi AM, et al. Repeatability of measuring corneal subbasal nerve fiber length in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Eye Contact Lens. (2010) 36:245–8. doi: 10.1097/ICL.0b013e3181eea915
39. Lewis EJH, Lovblom LE, Ferdousi M, Halpern EM, Jeziorska M, Pacaud D, et al. Rapid corneal nerve fiber loss: A marker of diabetic neuropathy onset and progression. Diabetes Care. (2020) 43:1829–35. doi: 10.2337/dc19-0951
40. Obrosova IG, Drel VR, Pacher P, Ilnytska O, Wang ZQ, Stevens MJ, et al. Oxidative-nitrosative stress and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) activation in experimental diabetic neuropathy: the relation is revisited. Diabetes. (2005) 54:3435–41. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.54.12.3435
41. Singh P, Bansal S, Kuhad A, Kumar A, and Chopra K. Naringenin ameliorates diabetic neuropathic pain by modulation of oxidative-nitrosative stress, cytokines and MMP-9 levels. Food Funct. (2020) 11:4548–60. doi: 10.1039/c9fo00881k
42. Baum P, Toyka KV, Blüher M, Kosacka J, and Nowicki M. Inflammatory mechanisms in the pathophysiology of diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DN)-new aspects. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:10835. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910835
43. Fitzpatrick SF, King AD, O’Donnell C, Roche HM, and Ryan S. Mechanisms of intermittent hypoxia-mediated macrophage activation - potential therapeutic targets for obstructive sleep apnoea. J Sleep Res. (2021) 30:e13202. doi: 10.1111/jsr.13202
44. Hernandez-Reyes M and Oo TT. From receptor to response: dissecting the TLR4 pathway in diabetic neuropathy. Inflammopharmacology. (2025) 33:2523–35. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01774-2
45. Khanna S, Kumar S, Sharma P, Daksh R, Nandakumar K, and Shenoy RR. Flavonoids regulating NLRP3 inflammasome: a promising approach in alleviating diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Inflammopharmacology. (2025) 33:2231–62. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01729-7
46. Chapouly C, Yao Q, Vandierdonck S, Larrieu-Lahargue F, Mariani JN, Gadeau AP, et al. Impaired Hedgehog signalling-induced endothelial dysfunction is sufficient to induce neuropathy: implication in diabetes. Cardiovasc Res. (2016) 109:217–27. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvv263
47. Roustit M, Loader J, Deusenbery C, Baltzis D, and Veves A. Endothelial dysfunction as a link between cardiovascular risk factors and peripheral neuropathy in diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2016) 101:3401–8. doi: 10.1210/jc.2016-2030
48. Ando A, Miyamoto M, Saito N, Kotani K, Kamiya H, Ishibashi S, et al. Small fibre neuropathy is associated with impaired vascular endothelial function in patients with type 2 diabetes. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2021) 12:653277. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.653277
49. Wang J, Yu W, Gao M, Zhang F, Gu C, Yu Y, et al. Impact of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome on endothelial function, arterial stiffening, and serum inflammatory markers: an updated meta-analysis and metaregression of 18 studies. J Am Heart Assoc. (2015) 4:e002454. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.115.002454
50. Cammaroto G, Costa F, Ruiz MVG, Andò G, Vicini C, Montevecchi F, et al. Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome and endothelial function: potential impact of different treatment strategies-meta-analysis of prospective studies. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. (2019) 276:2331–8. doi: 10.1007/s00405-019-05486-6
51. Herth J, Sievi NA, Schmidt F, and Kohler M. Effects of continuous positive airway pressure therapy on glucose metabolism in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Respir Rev. (2023) 32:230083. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0083-2023
Keywords: obstructive sleep apnea, diabetic peripheral neuropathy, diabetes mellitus, type 2, apnea-hypopnea index, corneal nerve fiber
Citation: Lu N, Cheng G, Qian Y, An D, Yin F, Hou Y, Liu X, Lu Q, Ma C and Wang R (2025) The association between obstructive sleep apnoea and diabetic peripheral neuropathy in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1643826. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1643826
Received: 09 June 2025; Accepted: 18 August 2025;
Published: 29 August 2025.
Edited by:
Ding Zou, University of Gothenburg, SwedenReviewed by:
Ou Qiong, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital, ChinaSerap Gökce Eskin, Adnan Menderes University, Türkiye
Theodoros Panou, Democritus University of Thrace, Greece
Copyright © 2025 Lu, Cheng, Qian, An, Yin, Hou, Liu, Lu, Ma and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rui Wang, d2FuZ3J1aXFoZDc2QDE2My5jb20=
†These authors share first authorship
 Na Lu1†
Na Lu1† Fuzai Yin
Fuzai Yin Chunming Ma
Chunming Ma Rui Wang
Rui Wang