- 1Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang, Jiangxi, China
- 2The Second Clinical Medical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
- 3Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun, Jilin, China
- 4The Affiliated Hospital of Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun, Jilin, China
Primary osteoporosis (POP) is a systemic metabolic bone disorder marked by diminished bone density and deterioration of bone microstructure, presenting a considerable challenge to global public health due to its widespread occurrence and heightened fracture risk. Although conventional western pharmaceutical treatments are efficacious, they are often associated with adverse events. Conversely, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) exhibits distinct potential owing to its multi-targeted and multi-pathway regulatory benefits. This systematic review elucidates the molecular mechanisms of flavonoids, polyphenols, saponins, polysaccharides, coumarins, and alkaloids in the prevention and treatment of POP. The study elucidates the mechanisms of action by modulating critical signaling pathways, including the Wnt/β-catenin, RANKL/OPG pathways and so on, thereby facilitating osteoblast differentiation, suppressing osteoclast activity, and ameliorating oxidative stress, inflammation, and dysbiosis of the intestinal microbiota, ultimately restoring the balance of the bone microenvironment. This research aims to advance the development of innovative POP medications based on TCM principles and to provide scientific validation for individualized therapy.
1 Introduction
Primary osteoporosis (POP) is a systemic metabolic bone disorder characterized by diminished bone mass, deterioration of bone microarchitecture, and heightened bone fragility. It is predominantly observed in postmenopausal women and older males. Clinically designated as the “silent killer”, hip fracture resulting from osteoporosis (OP) frequently represent “the final fractures an individual endure in their lifetime”. Globally, one-third of women and one-fifth of men over the age of 50 will experience a fracture attributable to OP (1). A 2021 meta-analysis found that the global prevalence of OP is 18.3%, with women accounting for 23.1% and men for 11.7% in the general population across various pooled sample sizes (2). The causes are multifaceted, encompassing estrogen insufficiency, aging, and additional variables (3). The treatments are varied, encompassing contemporary pharmacological medicines, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), physical therapies, and additional modalities.
Current pharmacological interventions primarily consist of bisphosphonates (4), receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand(RANKL) inhibitors (5), sclerostin inhibitors (6), and active vitamin D, along with its analogs (7). TCM predominantly encompasses herbal medicine, acupuncture, and various other comprehensive intervention measures (8–10). Moreover, consistent physical activity has been shown to influence the management of OP positively (11). Despite the beneficial effects of these methods on the treatment of POP, certain limitations persist. For instance, although bisphosphonates commonly used in clinical can inhibit bone resorption, there are adverse reactions such as osteonecrosis, atypical femoral fractures, and esophageal cancer (12). Teriparatide can enhance osteoblast activity, thereby stimulating bone production, however, it may result in undesirable effects, including limb pain, muscle spasms, fractures, and elevated calcium levels (13). Although, Chinese herbal formula exhibits multi-target synergistic benefits, their complicated ingredients frequently result in an ambiguous pharmacodynamic material foundation, and the isolation and study of single compounds may inadequately reveal their holistic therapeutic effects and underlying mechanisms of action (14, 15).
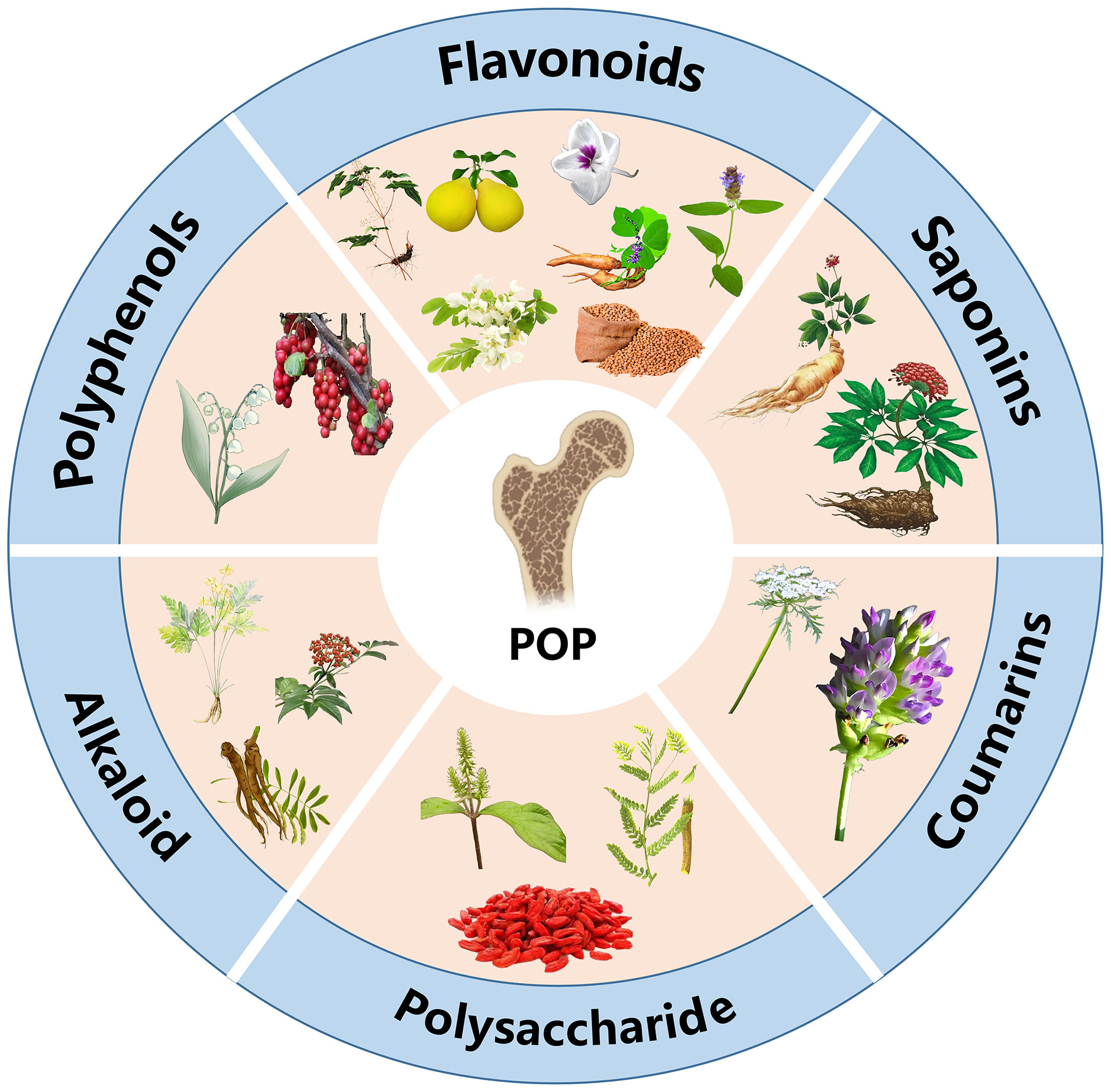
Consequently, identifying safer and more efficacious treatments is pivotal to the management of POP. The active constituents of TCM modulate bone metabolism via multifaceted, multi-target pathways, and certain chemicals can be used in combination with other drugs to enhance their effectiveness or alleviate their adverse effects. Panax ginseng saponins, flavonoids, and polysaccharides have shown potential efficacy in synergistically enhancing bone mass in arthritic rats and were well tolerated (16). The active constituents of Chinese medicines compensate for the shortcomings inherent in the intricate composition of traditional compound formulae and the ambiguity surrounding their mechanisms. As one of the key characteristics of TCM therapy, the active constituents in herbs offer diverse therapeutic options for patients and support the health of those with OP. This review delineates the role and application of active constituents in TCM therapy for the treatment of POP, utilizing databases such as China National Knowledge Infrastructure and PubMed to provide a comprehensive overview of diverse treatment options available to patients (Figure 1). The objective is to provide novel insights into the prevention and treatment of OP through TCM and its active constituents.
2 Pathogenesis of POP
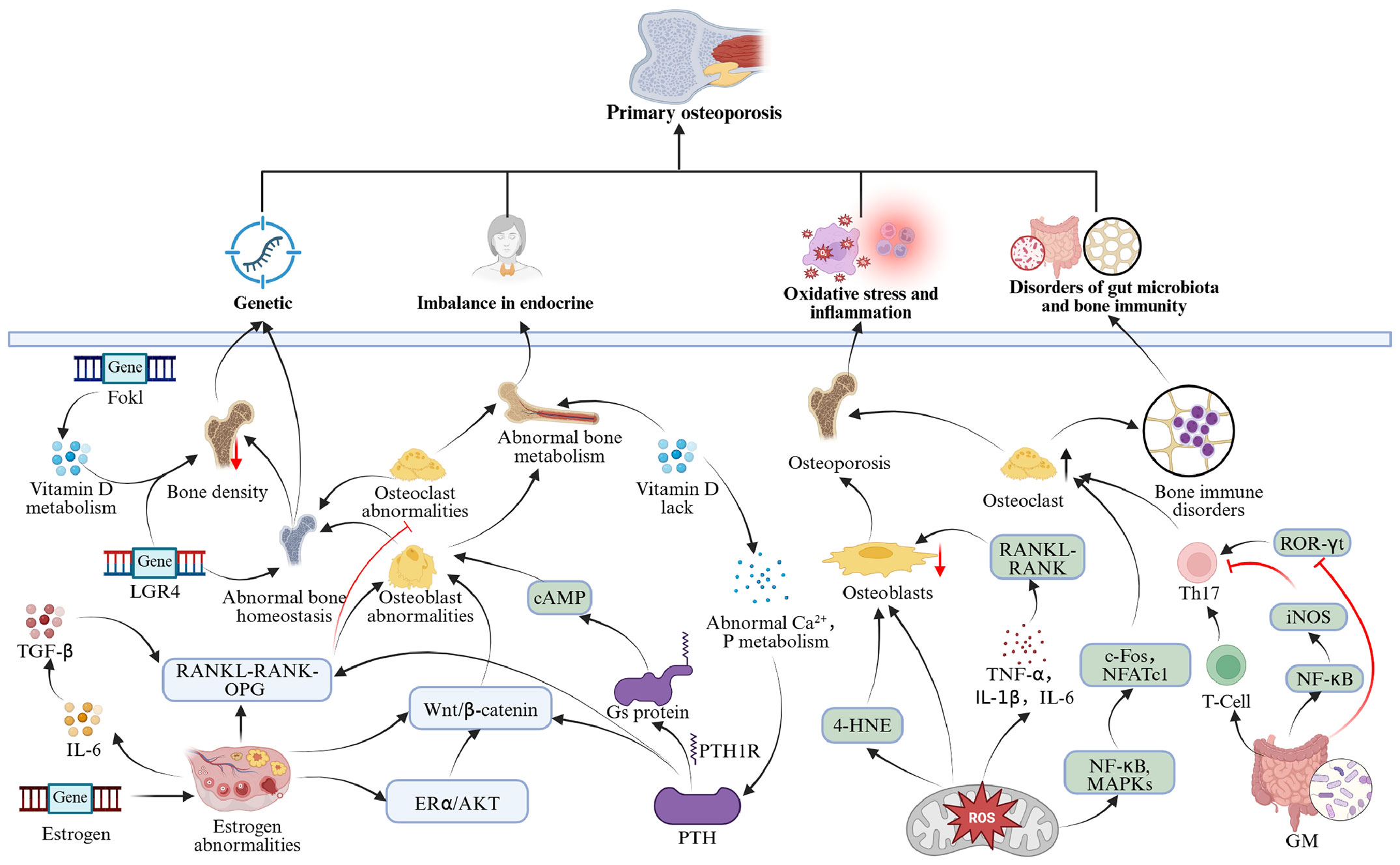
POP arises from the interplay of genetic, endocrine, microenvironmental, and gut microbiota variables, characterized by a complex pathophysiology involving multi-system and multi-pathway interactions (Figure 2).
2.1 Hereditary influences
Genetic factors significantly contribute to the etiology of OP. Genome-wide association studies and candidate gene analyses have discovered several significant gene variants strongly linked to diminished bone mineral density (BMD) and increased fracture risk. The genetic influence on OP differs by phenotype. Specifically, hereditary predisposition to osteoporotic fractures is around 25%, wrist fractures range from 25% to 54%, and hip fractures can reach up to 48% (17). Genome-wide association studies systematically revealed the molecular network of OP susceptibility genes, mainly involving the following pathways: vitamin D metabolism pathways (VDR, DBP), estrogen signaling (ESR1, ESR2, CYP19A1), the Wnt/β-catenin pathway (LRP5, SOST, WNT10B), and the RANKL-RANK-OPG system (TNFRSF11A, TNFRSF11B) (18). Polymorphisms in the vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene are among the most well-investigated genetic determinants. Research involving 174 postmenopausal women (aged 43–71) revealed the following distribution of the FokI genotype: FF (33.3%), Ff (50.6%), and ff (16.1%). The ff genotype exhibited a significantly reduced lumbar spine BMD compared to those with the FF genotype, and the prevalence of the ff genotype was markedly greater in the OP cohort than in the normal bone mass cohort, indicating that FokI polymorphism may affect bone metabolism by modulating VDR protein function (19). Studies have identified several single nucleotide polymorphisms linked to OP, including rs1061947 (COL1A1), rs10793442 (ZNF239), and rs11614913 (miR-196a), which are associated with fracture risk, while rs5854 (MMP1) and rs2910164 (miR-146a) correlate significantly with low BMD. And, rs10098470 (TPD52), rs11540149 (VDR), rs1042673 (SOX9), rs1054204 (SPARC), and rs1712 (FBXO5) have been identified as prevalent genetic markers for fractures and low BMD (20). Family studies have corroborated that the rs11029986 allele of the LGR4 gene is associated with hip BMD, whereas the rs12796247 and rs2219783 polymorphisms affect lumbar spine BMD (21). Key genetic variables associated with POP, particularly in its early stages, include the core genes LRP5, COL1A1, COL1A2, WNT1, and PLS3 (22). A study in the Volga-Ural region of Russia has demonstrated that hypomethylation of the RUNX2 gene’s promoter region is associated with POP, specifically at the CpG1 locus. The CpG1 locus may serve as a potential biomarker, with a more pronounced epigenetic profile observed in male individuals (23). Moreover, miR-422a may facilitate the lipogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) by downregulating MeCP2, potentially resulting in increased bone marrow adiposity and decreased bone production (24). These genetic factors interact through various pathways to establish the molecular foundation of OP, collectively regulating the balance between osteogenesis and resorption and influencing bone homeostasis.
2.2 Endocrine regulatory dysregulation
An imbalance in the endocrine system is a fundamental factor contributing to the start and progression of OP, predominantly characterized by estrogen insufficiency, abnormalities in parathyroid hormone (PTH), and disorders in vitamin D metabolism.
Estrogen irregularities: Estrogen is integral to bone metabolism via its receptors (ERα and ERβ), sustaining metabolic equilibrium in bone, and is a fundamental pathway in POP (25). Postmenopausal estrogen insufficiency results in an altered RANKL/OPG ratio, increased osteoclast activation, and expedited bone resorption. Estrogen specifically facilitates the production of OPG and suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation (26). Moreover, estrogen diminishes the secretion of bone resorption factors such as IL-6 and RANKL while augmenting the activity of bone formation factors like TGF-β (27). At the molecular level, estrogen activates the ERα/Akt signaling pathway, which subsequently enhances the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, thereby stimulating osteoblast proliferation and differentiation (28, 29).
Elevated PTH: PTH is crucial for regulating calcium metabolism, and older individuals with OP frequently exhibit increased PTH levels. This may result from age-related renal impairment, which diminishes the production of 1,25(OH)2D3, thereby reducing intestinal calcium absorption, lowering serum calcium levels, and subsequently inducing elevated PTH secretion, which promotes bone resorption (30). PTH interacts with the PTH1 receptor (PTH1R) to initiate the G protein-coupled signaling cascade, consequently modulating two principal pathways: protein kinase A (PKA) and protein kinase C. Upon binding to PTH1R, PTH activates the Gs protein, which stimulates adenylate cyclase to produce cAMP, thereby activating PKA and controlling the differentiation, proliferation, and death of osteoblasts. PTH can activate phospholipase C via Gq protein, producing IP3 and DAG, the latter of which activates protein kinase C, thus affecting the expression of genes associated with bone metabolism (31, 32).
Disorders in vitamin D metabolism: Inadequate levels of active vitamin D can result in disturbances in calcium and phosphorus metabolism, hence impacting bone mineralization (33). Vitamin D deficiency diminishes intestinal calcium absorption, resulting in decreased blood calcium levels that trigger increased PTH secretion (34). Elevated PTH enhances osteoclast activation by upregulating RANKL expression and concurrently inhibits the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in osteoblasts, culminating in augmented bone resorption and diminished bone formation (35). Clinical studies indicate a significant correlation between vitamin D deficiency and elevated levels of bone metabolism markers, such as PINP, B-CTX, and N-MID (36).
2.3 Oxidative stress and inflammatory response
Oxidative stress and chronic inflammation are significant contributors to OP. The excessive accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) disturbs the osteogenic-osteoclastic equilibrium, resulting in heightened osteoclast formation and suppressed osteoblast activity (37). In osteoblasts, oxidative stress impedes the nuclear translocation of nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), which contributes to increased osteoclast formation (38). The inactivation of Nrf2 leads to the accumulation of ROS in osteoblasts, inducing ferroptosis, characterized by abnormal mitochondrial morphology and elevated lipid peroxidation products (e.g., 4-HNE), which subsequently impedes osteogenic differentiation and results in bone loss (23). Furthermore, ROS activate the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways, enhancing the expression of essential osteoclast transcription factors (including c-Fos and NFATc1), therefore facilitating bone resorption (39).
In a chronic low-grade inflammatory condition, pro-inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 are consistently elevated, promoting osteoclast development through the activation of the RANKL-RANK signaling pathway. Clinical studies indicate that systemic immune inflammation indices are markedly elevated in patients with OP, and when these indices surpass 613.03, the risk of OP significantly escalates (40). Furthermore, monocytes derived from female OP patients can autonomously differentiate into osteoclasts in vitro without external stimulation (41), while macrophages and monocytes further facilitate osteoclastogenesis by secreting IL-1 and TNF-α (42).
2.4 Gut microbiota and bone immune dysfunction
The gut microbiota modulates bone metabolism via the “gut-bone axis,” employing mechanisms that include immune modulation and metabolite-mediated signaling pathways (43). Research indicates that gut microbiota can affect the equilibrium of Th17 and Treg cells by modulating the differentiation and functionality of immune cells. Th17 cells secrete pro-inflammatory mediators, including IL-17, RANKL, and TNF-α, which directly facilitate osteoclast differentiation and activation while concurrently inhibiting osteoblast activity; conversely, Treg cells produce anti-inflammatory mediators, such as IL-10 and TGF-β, which not only suppress osteoclast formation but also enhance the expression of osteoblast-related factors (44). The disruption of this equilibrium results in bone remodeling disorders, and the overactivation of Th17 cells markedly increases bone resorption via the RANKL/RANK pathway (45). Furthermore, gut microbiota can affect bone remodeling by modulating immune cell function through metabolic byproducts such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) (46). Butyrate can diminish the expression of iNOS, TNF-α, and IL-6 by reducing NFκB transcriptional activity while simultaneously boosting IL-10 expression and suppressing the development of Th17 cells (47, 48). Propionate inhibits histone deacetylase, reducing ROR-γt expression, thereby inhibiting Th17 cell differentiation (49). SUN et al. discovered that the administration of Jiangu granules could modulate intestinal flora homeostasis, enhance the secretion of short-chain fatty acids, adjust the Treg/Th17 cell ratio, and modify the expression of cytokines associated with bone immunomodulation in ovariectomized rats, thereby inhibiting osteoclast differentiation and effectively preventing bone loss (50). Blautia, Parabacteroides, and Ruminococcaceae exhibited notable disparities between osteoporotic and healthy persons, influencing bone health (51). In conclusion, the imbalance of intestinal flora and bone immunological diseases is significantly linked to OP, offering a theoretical foundation for targeting intestinal flora as an intervention strategy.
3 Mechanisms and applications of active constituents in the prevention and treatment of POP
3.1 Flavonoids
3.1.1 Icariin
Icariin is the primary bioactive component of Epimedium brevicornu Maxim, a plant belonging to the Berberidaceae family (Figure 3A). In TCM, it is extensively utilized for the management of OP owing to its capabilities in warming and tonifying kidney yang, as well as fortifying tendons and bones. Icariin is the predominant flavonoid glycoside in Epimedium brevicornu Maxim, demonstrating functions that enhance cardiovascular function, bolster immune system efficacy, and regulate the endocrine system, and it exhibits antitumor, antiviral, antihypoxia and reperfusion injury properties (52). Contemporary research demonstrates that icariin treats OP primarily by modulating the levels and functions of osteoclasts and osteoblasts, regulating the differentiation of BMSCs, thereby promoting bone formation, inhibiting bone resorption, and restoring bone mass homeostasis, thus treating OP (53). Regarding the inhibition of bone resorption, icariin can influence the differentiation and function of osteoclasts through various mechanisms. Zhiwei Li et al. discovered that icariin inhibits the formation of the osteoclast cytoskeletal filamentous actin (F-actin) ring in a dose-dependent manner by upregulating the expression of the negative regulatory factor guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit α13 (Gα13), thereby obstructing the downstream PKB/GSK-3β/NFATc1 signaling pathway and consequently inhibiting osteoclast formation (54). Additionally, Yuhao Si et al. demonstrated that icariin activates the Cullin 3/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, which inhibits osteoclast differentiation, significantly reduces oxidative stress levels, decreases the number of TRAP-positive osteoclasts in the bone tissue of ovariectomized (OVX) rats, lowers bone tissue ROS levels, and increases BMD (55). Regarding the promotion of bone formation, icariin enhances bone metabolism by regulating the bone marrow microenvironment and stem cell differentiation. Long Bai et al. discovered that icariin stimulates the autophagy process, mitigates the inflammatory aging phenotype of senescent macrophages, and diminishes the release of the senescence-associated secretory phenotype, thereby enhancing the bone immune microenvironment and restoring the osteogenic potential of aged BMSCs, ultimately alleviating OP (52). Shaozi Lin et al. also found that icariin inhibits the Hippo-YAP/TAZ signaling pathway, reduces YAP/TAZ phosphorylation, and suppresses the adipogenic regulator PPARγ, thereby promoting the osteogenic differentiation of ADSCs and inhibiting adipogenic differentiation (56). Therefore, icariin regulates the “bone formation-bone resorption” balance in a bidirectional manner, inhibiting osteoclast-mediated bone resorption while promoting osteogenic differentiation and improving the bone microenvironment, thereby restoring bone mass homeostasis.

Figure 3. Chemical structural formula of several flavonoids: (A) Icariin. (B) Puerarin. (C) Naringin. (D) Luteolin. (E) Kaempferol. (F) Isoflavone. (G) Quercetin.
3.1.2 Puerarin
Puerarin is an isoflavone compound isolated from the dried rhizomes of wild kudzu [Pueraria montana (Lour.) Merr.] (Figure 3B). It possesses anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and estrogen-like pharmacological effects and can positively influence bone metabolism by modulating multiple signaling pathways (57). Research indicates that puerarin modulates osteoclast differentiation by obstructing the TRAF6/ROS-dependent MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway. This is achieved through the downregulation of NOX1 expression, reduction of ROS production, and upregulation of HO-1 levels, which collectively inhibit the activation of the MAPK and NF-κB pathways, leading to the downregulation of osteoclast-specific genes such as NFATc1, MMP9, and CTSK (58). Furthermore, it facilitates osteoblast differentiation through the activation of the ERK1/2 and p38-MAPK pathways, markedly enhancing BMD, bone volume fraction (BV/TV), and trabecular number (Tb.N) in OVX rats (59). Additionally, puerarin suppresses the activation of the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway, efficiently mitigating bone loss and microstructural damage in postmenopausal osteoporosis(PMOP) rats (60). A meta-analysis established that puerarin exhibits a significant bone-sparing effect on ovariectomy-induced PMOP, demonstrating efficacy comparable to estrogen and enhanced safety (61). These results offer a robust theoretical foundation for the prospective application of puerarin as a therapeutic agent for POP.
3.1.3 Naringin
Naringin is a natural flavonoid compound (Figure 3C) and one of the active constituents of the TCM Drynariae Rhizoma. It possesses multiple pharmacological effects, including promoting bone growth, anti-inflammatory activity, and promoting microvascular regeneration (62). The mechanism of action of naringin in regulating POP has been widely studied, and the existing evidence shows that it can regulate POP activity through multiple pathways. Yubo Cui et al. found that naringin promotes osteoblast differentiation by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, inhibiting bone resorption and thereby improving OP in OVX mice (63). Hui Wang et al. found that naringin binds to ESR1 and HSP90AA1, activates the Wnt/β-catenin and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways, induces GSK-3β phosphorylation, promotes β-catenin nuclear translocation, thereby reversing the inhibitory effects of oxidative stress on osteoblast differentiation (64). Naringin may influence OPG mRNA expression in a time- and dose-dependent manner, facilitating the secretion of OPG protein, upregulating OPG expression, and increasing the OPG/RANKL ratio, which inhibits osteoclast differentiation and activation, thereby diminishing bone resorption, concurrently, it synergistically enhances OPG secretion with vitamin D3, further substantiating its stimulatory effect on bone formation (65). Wang Wang et al. demonstrated that naringin inhibits the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway, enhances the proliferation and osteoblast differentiation of BMSCs, and diminishes osteoclast activity, thereby rectifying the imbalance between bone formation and resorption in PMOP rats, modulating bone metabolism, and mitigating OP (66). Furthermore, naringin decreases VEC apoptosis by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress (downregulating GRP78, CHOP, and caspase-12) and mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis pathways while also regulating the ET/NO balance to facilitate bone vascularization (67). So, naringin regulates osteoblasts to treat OP by modulating signaling pathways, including the Wnt/β-catenin, JAK2/STAT3, PI3K/Akt, and estrogen receptor signaling pathways, as well as mitochondrial apoptosis pathways, thereby regulating osteoblast function and treating OP.
3.1.4 Luteolin
Luteolin is a naturally occurring flavonoid compound (Figure 3D) found in medicinal plants such as Dendranthema morifolium, Lonicera japonica Thunb, Prunella vulgaris L., and Eclipta prostrata L. Luteolin is frequently utilized in TCM for “tonifying the kidneys and strengthening bones.” As an active constituent of various medicinal plants, luteolin exhibits substantial therapeutic effects in the prevention and treatment of OP through multifaceted regulatory mechanisms. Research indicates that luteolin not only enhances the osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs by activating the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway (68), mitigates osteoclast pyroptosis and improves bone microstructure, (69) but also inhibits the RANKL signaling pathway to downregulate transcription factors such as NFATc1, thereby synergistically diminishing levels of inflammatory factors like TNF-α and IL-6 (70). Luteolin significantly improves osteoblast function via estrogen receptors and the Wnt/β-catenin pathway (71). Furthermore, in an OVX animal model, it exhibited efficacy akin to estrogen replacement therapy without associated carcinogenic risks (70), underscoring its potential as a safe and effective anti-OP agent.
3.1.5 Kaempferol
Kaempferol is a flavonoid active compound extracted from various plants, exhibiting anti-inflammatory, antitumor, antioxidant, and anti-allergic properties (Figure 3E). Kaempferol can prevent and treat OP through various signaling pathways (72). Research indicates that kaempferol enhances BMD in OVX rats and increases the bone mineralization capacity and ALP activity of BMSCs. The underlying mechanism may involve the downregulation of miR-10a-3p, which alleviates its post-transcriptional inhibition of CXCL12, consequently upregulating CXCL12 expression, promoting BMSC osteogenic differentiation, and ameliorating ovariectomy-induced OP in rats (73). YAP is a key transcriptional cofactor in the Hippo signaling pathway, which promotes osteoblast differentiation (74). The NF-κB signaling pathway activation is associated with inflammation, promoting osteoclast differentiation and inhibiting osteogenesis (75). Wencheng Liu et al. found that kaempferol alleviates the inhibition of YAP via the Hippo pathway, promotes YAP nuclear translocation, thereby upregulating the expression of osteogenesis-related genes, and inhibits RANKL-mediated osteoclast differentiation. Additionally, YAP inhibits the phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of NF-κB-p65 by binding to its subunits, reducing the release of inflammatory factors, thereby weakening osteoclast differentiation signals (76).
3.1.6 Soy isoflavones
Soy isoflavones is a natural phytoestrogen belonging to the flavonoid compound family and is widely present in leguminous plants, where it is an important secondary metabolite formed during growth (Figure 3F). Studies have shown that the primary active metabolite of soy isoflavone, equol, binds to ERβ receptors, upregulates the OPG/RANKL pathway, and promotes osteoblast proliferation while inhibiting apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner, thereby exerting a protective effect against PMOP (77). Bing et al. further confirmed that the soy isoflavone metabolite equol can promote osteoblast secretion of OPG through ERβ, significantly increase the OPG/RANKL ratio, and effectively inhibit the activation of the RANKL/RANK signaling pathway, thereby suppressing osteoclast activation (78). Additionally, soy isoflavones can promote the differentiation of BMSCs into osteoblasts by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway (79). Animal experiments have confirmed that a dose of 60 mg/kg of soy isoflavone can bidirectionally regulate the activity of osteoblasts and osteoclasts, with its effects on improving BMD and bone microstructure comparable to those of estrogen therapy (80). These findings provide robust experimental evidence supporting soy isoflavone as a safer alternative to estrogen therapy.
3.1.7 Quercetin
Quercetin (Figure 3G) is a flavonol substance exhibiting numerous biological actions, predominantly located in the stem bark, flowers, leaves, buds, seeds, and fruits of various plants, frequently as glycosides. Quercetin exhibits anti-osteoporotic effects through various synergistic mechanisms, including the promotion of bone formation, inhibition of bone resorption, anti-inflammatory properties, and antioxidative stress, thereby providing a theoretical foundation for the development of innovative OP therapeutic strategies (81). Quercetin enhances BMD, improves bone microstructure and biomechanical properties, inhibits bone resorption, promotes bone formation, enhances muscle morphology and locomotion, and decreases fracture risk in denuded mice by modulating the GPRC6A/AMPK/MTOR-mediated glycolipid metabolism pathway (82). Ruibing Feng et al. discovered that quercetin can modulate intestinal microbiota, enhance the synthesis of SCFAs, suppress inflammation, and diminish the risk of OP. SCFAs modulate the “gut flora - SCFAs - inflammation” axis to ameliorate OP and suppress inflammatory responses, hence safeguarding bone integrity in ovariectomized rats (83). A study utilizing in vitro cellular experiments and in vivo animal models revealed that quercetin enhances iron and vitamin B2/HO-1 signaling pathways by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway, which mitigates iron overload-induced apoptosis and oxidative stress, thereby restoring osteoblast function and alleviating OP (84).
3.2 Polyphenolic
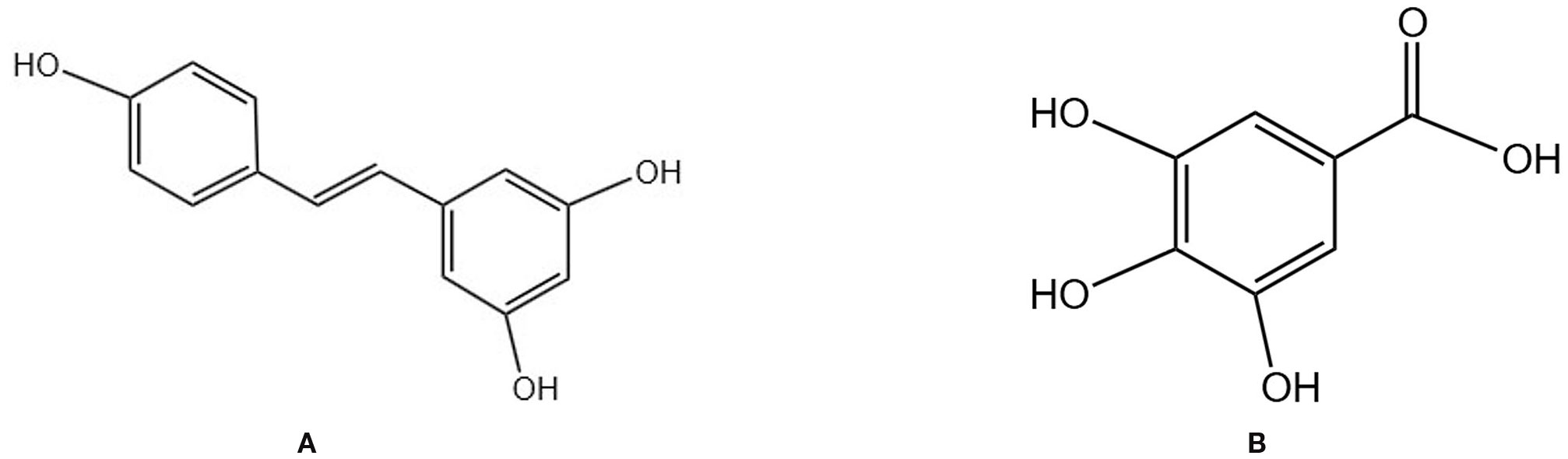
3.2.1 Resveratrol
Resveratrol is a natural plant-derived polyphenolic compound (Figure 4A) with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-aging, and phytohormonal activities. Resveratrol is found in various TCM plants, including Mori Fructus and Giant knotweed rhizome (85). It operates through multiple mechanisms, such as modulating gut microbiota, enhancing intestinal barrier integrity, and facilitating epigenetic regulation (86). A 24-month randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial indicated that long-term resveratrol supplementation (75 mg bid) significantly enhanced BMD in the lumbar spine and femoral neck of postmenopausal women, decreased bone resorption, and may correlate with phytoestrogen effects, improved systemic vascular function, and synergistic interactions with vitamin D/calcium (87). A preclinical study further demonstrated that resveratrol can markedly enhance BMD and microstructure in animal models of POP by modulating bone metabolism signals, exhibiting antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, and displaying estrogen-like activity. The dosage range is specified as 5–200 mg/kg/day, with more significant effects observed at doses of 40–80 mg/kg/day (88). An animal study corroborated that resveratrol markedly enhanced BMD in OVX rats, with the underlying mechanism involving the upregulation of the Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway, which promotes osteogenesis and inhibits osteoclast activity, thus rectifying bone metabolic imbalance (89).
3.2.2 Gallic acid
Gallic acid is a natural polyphenol (Figure 4B) primarily derived from TCMs, such as Galla Chinensis, and exhibits anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It demonstrates clear anti-bone loss effects both in vitro and in vivo. Peng Zhang et al. found that GA improves BMD, BV/TV, trabecular thickness, and trabecular number in OVX mice while reducing trabecular spacing. It also reduced fat accumulation and osteoclast numbers in bone tissue of OVX mice by inhibiting the Akt, ERK, and JNK signaling pathways and downregulating the NFATc1/c-Fos/CTSK axis, thereby suppressing osteoclast generation (90).
3.3 Saponins
3.3.1 Ginsenosides
Ginsenosides are the primary active constituents of Ginseng Radix et Rhizoma (Figure 5A), which are essentially non-toxic to normal human cells. Ginsenosides can elevate the expression of critical markers, including Runx2 and ALP, in osteoblasts, thereby promoting mineralization while simultaneously diminishing osteoclast generation and activity. This results in a reduction of TRAP (+) multinucleated cells and RANKL levels, an increase in OPG expression, and antioxidant effects through enhanced glutathione levels and decreased production of ROS and nitric oxide (91). Research indicates that ginsenosides with distinct structures influence biological processes via specific molecular mechanisms. Fei Xi et al. observed an increase in bone mass and enhancement of bone metabolic markers in OVX rats administered ginsenoside Rg3, potentially linked to the modulation of the RANKL/RANK/TRAF6 signaling pathway, which regulates bone metabolism and osteoclast activity in PMOP (92). Shanfu Wang et al. discovered through animal and cellular experiments that ginsenoside Rc elevates the levels of TGF-β, BMP2, and p-Smad2/3 proteins in OVX rats, activates the TGF-β/Smad pathway and concurrently enhances the mRNA and protein expression of Col1a1 and Col1a2, as well as increases alkaline phosphatase activity, indicating promotion of collagen synthesis and bone matrix formation, thus ameliorating OP symptoms in OVX rats (93). Ginsenoside Rg2 inhibits the phosphorylation of the MAPK pathway, downregulates the expression of c-Fos and NFATc1, and consequently diminishes the transcription of osteoclast-specific markers (Acp5, Oscar), establishing a regulatory axis of “MAPK-c-Fos/NFATc1-osteoclast markers,” thereby significantly impeding RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation (94). Ginsenoside Rh2 may modulate the OPG/RANKL signaling pathway to inhibit osteoclast differentiation and activity, while enhancing Runx2 expression, thereby facilitating osteoblast development and bone formation. This results in increased bone mass and density in aged rats, as well as improved bone microstructure and strength (95). Clinical studies have corroborated that ginsenoside extract administered at a dosage of 3 g/day for 12 weeks significantly elevated serum osteocalcin levels and decreased the DPD/OC ratio in postmenopausal women, demonstrating favorable safety (96). These mechanisms collectively form the molecular foundation for the multifaceted enhancement of bone metabolism by ginsenosides, which is achieved through their antioxidant properties, promotion of osteogenic differentiation, and inhibition of osteoclast activity.
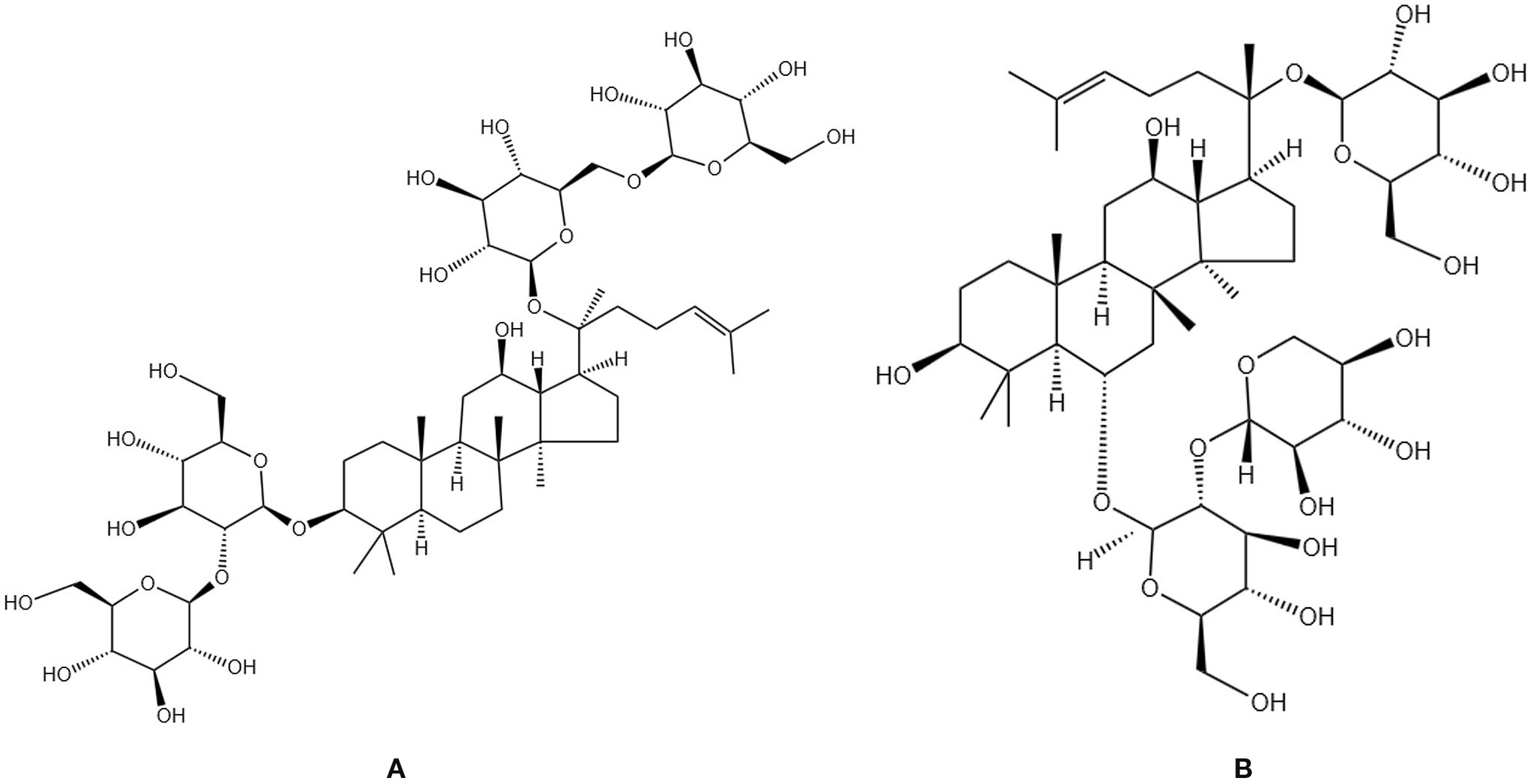
Figure 5. Chemical structural formula of several saponins: (A) Ginsenoside Rb 1. (B) Notoginsenoside R1.
3.3.2 Notoginsenosides
Notoginsenosides are the primary active constituents of the traditional Chinese medicinal herb Notoginseng Radix (Figure 5B), derived from the dried roots and rhizomes of the Araliaceae family plant Panax notoginseng. Notoginsenosides R1 can augment BMD and osteoblast activity, as well as facilitate fracture healing (97). Cellular experiments have demonstrated that notoginsenosides R1 mitigates oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial damage by inhibiting the JNK signaling pathway, decreases cell apoptosis, and fosters osteogenic differentiation (98). Ting Wang et al. discovered that notoginsenosides R1 enhances bone formation by activating ERα/β receptors, stimulating ERE-mediated transcription, upregulating osteogenic gene expression, modulating the OPG/RANKL ratio, inhibiting bone resorption, thus facilitating bone formation, while also diminishing reproductive toxicity (99). Yi Liu et al. found that notoginsenosides R1 may promote the proliferation, differentiation, and mineralization of pre-osteoblasts MC3T3-E1 by activating the p38 MAPK or Wnt signaling pathways, regulating transcription factors such as Runx2 and Osterix and significantly enhancing bone formation (100).In OVX rat experiments, total ginsenosides from Panax notoginseng can improve bone tissue damage by upregulating CTRP6 expression, inhibiting RhoA/Rock pathway activation, and alleviating inflammatory responses and oxidative stress (101). These findings systematically elucidate the multifaceted mechanisms by which notoginsenosides improve bone metabolism through “antioxidant-promoting osteogenesis-inhibiting osteoclasts”.
3.4 Polysaccharides
3.4.1 Lycium barbarum polysaccharide
Lycium barbarum polysaccharide is the main active ingredient, exhibiting antioxidant, anti-ageing, immune-modulating, and anti-OP effects (102). Studies have shown that lycium barbarum polysaccharide not only activates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway to upregulate the expression of β-catenin and Wnt10b proteins (103), promoting the differentiation of BMSCs into osteoblasts but also by regulating gut microbiota structure (promoting Lactobacillus proliferation) to increase short-chain fatty acid (acetic acid, propionic acid, butyric acid) production (104), thereby promoting bone matrix mineralization through the BMP-2/RUNX2 pathway (105). In an OVX rat model, lycium barbarum polysaccharide improves bone remodeling metabolism by upregulating serum TGF-β1 and NOS levels while alleviating oxidative stress-induced damage to osteoblasts by enhancing SOD and GSH-Px activity (106). These findings systematically reveal that lycium barbarum polysaccharide improve bone metabolism through a triple action mechanism of “directly promoting bone formation, indirectly regulating the microbiota, and synergistically exerting antioxidant effects”.
3.4.2 Astragalus polysaccharide
Astragalus polysaccharide is the primary macromolecular active component of the Astragali Radix, exhibiting various biological functions, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and osteogenic effects (107). Extensive studies have confirmed that astragalus polysaccharide can prevent and treat OP by promoting osteogenesis and inhibiting osteoclast activity. In animal models, astragalus polysaccharide significantly improved OP in OVX rats by regulating the FoxO3a/Wnt2/β-catenin signaling pathway, with mechanisms including inhibiting FoxO3a mRNA expression while activating the transcription of Wnt2, LRP5, and β-catenin, thereby increasing BMD, optimizing bone biomechanical properties, and reducing fracture risk (108). At the cellular level, astragalus polysaccharide promotes the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human BMSCs in a concentration-dependent manner (optimal concentration: 200 μg/ml),a mechanism potentially involving the inhibition of miR-760 expression and the relief of its transcriptional repression on ANKFY1 (109). Additionally, astragalus polysaccharide can effectively alleviate iron overload-induced functional impairment in BMSCs by inhibiting mitochondrial ROS accumulation, maintaining cell proliferation capacity, suppressing apoptosis and senescence, and preserving pluripotency gene expression (110). Furthermore, astragalus polysaccharide can also promote osteogenesis-related gene expression by activating the BMP-2/Smads signaling pathway through upregulating the expression of BMP-2, p-Smad1, and p-Smad5, thereby improving bone microstructure and bone metabolic indicators in OVX rats (111).
3.4.3 Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharide
Radix Achyranthis Bidentatae, a TCM used to tonify the liver and kidneys and strengthen the tendons and bones, contains the active component achyranthes bidentata polysaccharide (ABP), which exhibits multi-target regulatory effects in the prevention and treatment of OP. Yang Hao et al. found that it can activate the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, promote the expression of genes and proteins such as β-catenin, Runx2, and Osterix, significantly improve bone metabolism in osteoporotic fracture rats, increase BMD, and alleviate bone tissue pathological damage (112). Dezhi Song et al. found that bone marrow mononuclear cells and bone marrow macrophages, 10 μM ABP can inhibit RANKL-induced MAPK phosphorylation and c-Fos expression, thereby blocking the activation of the NFATc1 signaling pathway, and achieving a full-cycle inhibition of osteoclast differentiation, fusion, and bone resorption (113). Additionally, the soluble polysaccharide ABPB and its purified component ABPB-3, from A,chyranthes bidentata exhibit anti-osanti-osteoporotics by improving bone microstructure and increasing bone matrix synthesis (114). The mechanism of ABP also involves regulating the OPG/RANKL/RANK system by upregulating OPG and downregulating RANKL expression to inhibit osteoclast activity while increasing bone formation markers (OC, BAP) levels and reducing bone resorption markers (TPACP5b, NTX, CTX) levels, thereby improving bone metabolism and enhancing bone biomechanical properties in elderly osteoporotic rats (115). These findings collectively reveal the multidimensional pharmacological effects of ABP in preventing and treating OP through a bidirectional regulatory mechanism of “promoting bone formation and inhibiting bone resorption”.
3.5 Coumarin derivatives
3.5.1 Osthole
Osthole is a coumarin compound from Cnidii Fructus (Figure 6A). It promotes osteoblast differentiation and bone formation while inhibiting bone resorption (116). Studies have shown that osthole significantly increases bone mass in aged mice while inhibiting osteoclast formation and promoting OPG expression. This mechanism may involve activating the β-catenin-OPG signaling pathway to enhance OPG expression. OPG, as a decoy receptor for RANKL, inhibits the binding of RANKL to RANK, thereby suppressing osteoclast differentiation and activity and reducing bone resorption (117). Sheng Zheng et al. also found that osthole activates the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, inducing osteogenic-angiogenic coupling in BMSCs, upregulating the mRNA and protein expression of osteogenic markers (ALP, OCN) and angiogenic factors (VEGFA, CD31), accelerating the healing of tibial fractures in OVX rats, and finding that the optimal dose of osthole was 10 μM (118). Studies have shown that osthole activates key signaling pathways, such as the Wnt/β-catenin and BMP-2/p38 pathways, and upregulates the expression of autophagy-related genes (Beclin1, LC3) in BMMSCs, thereby inducing autophagy. This process promotes the expression of osteogenic-related genes by regulating the activity of transcription factors (such as Runx2 and Osterix) while inhibiting adipogenic differentiation, thereby significantly enhancing the osteogenic differentiation capacity of BMSCs. In an estrogen-deficient OP model, this mechanism was confirmed to effectively increase bone mass and improve bone metabolic indicators (119). Zhong-Rong Zhang et al. found that osthole, on the one hand, upregulates the expression of the transcription factor osterix through the cAMP/CREB signaling pathway, thereby promoting the expression of osteogenesis-related genes such as alkaline phosphatase and osteocalcin; on the other hand, it activates the BMP signaling pathway, producing a synergistic effect with the cAMP/CREB pathway. This dual pathway activation mechanism significantly promotes osteoblast differentiation in vitro and exhibits therapeutic effects, including accelerating fracture healing and enhancing bone strength in vivo (120).In terms of metabolomics, Zhenxing Si et al. analyzed and found that osthole can inhibit bone resorption and promote bone formation through 13 metabolic pathways, including linoleic acid metabolism, starch and sucrose metabolism, and arachidonic acid metabolism, thereby effectively improving OP induced by ovariectomy in rats (121).
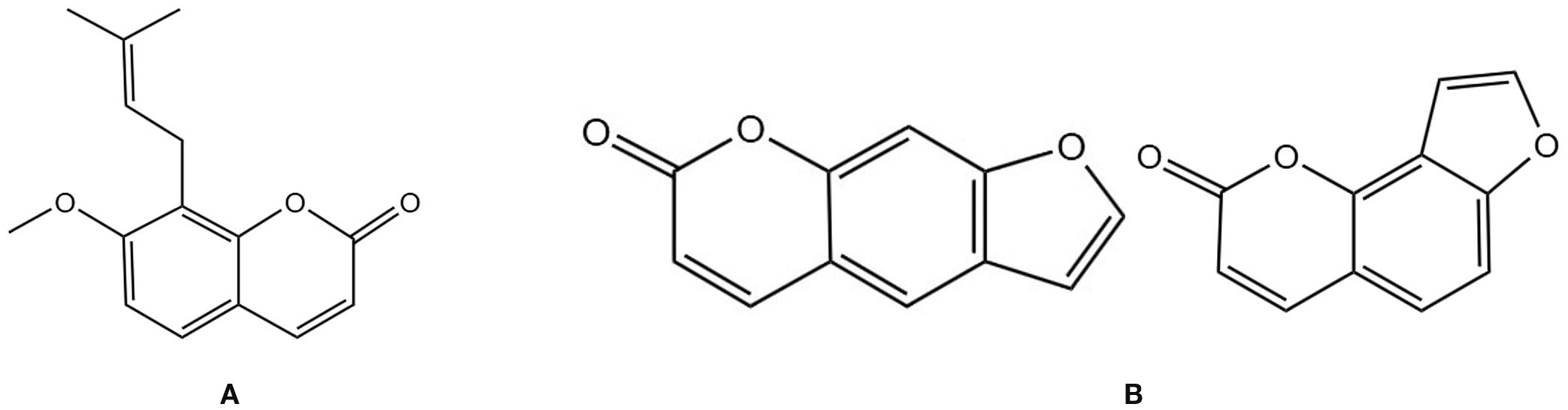
Figure 6. Chemical structural formula of several coumarins: (A) Osthole. (B) Psoralen and Isopsoralen.
3.5.2 Psoralen and isopsoralen
Isopsoralen belongs to the furanocoumarin class of extracts from Psoraleae Fructus and is one of the plant estrogens. It is one of the main active constituents of Psoralea corylifolia, a TCM used to tonify the kidneys (Figure 6B). It can participate in bone metabolism by regulating the Wnt, Runx2/MMP13, PI3K/AKT, Axin2/PPAR-γ, and WNT/β-catenin signaling pathways, thereby improving OP (122). Studies have shown that psoralen and isopsoralen may regulate the balance of bone remodeling by inhibiting osteoclast activity (reducing TRACP and CTX1) and promoting osteoblast function (increasing ALP), thereby improving bone microstructure and strength in male and female mice with OP induced by sex hormone deficiency (123). Jian Wang et al. found that psoralen can inhibit the expression of PPAR-γ, reducing the differentiation of BMSCs into adipocytes while also alleviating the inhibition of the WNT/β-catenin pathway by PPAR-γ, thereby promoting osteogenic differentiation. Additionally, it can reduce ROS levels, mitigate oxidative stress-induced damage to bone cells, inhibit caspase-3/9-mediated apoptosis, and maintain a balance in bone remodeling, thereby improving OP symptoms in ovariectomized rats (124). Jian Wang et al. also found that isopsoralen can regulate the balance of BMSCs differentiation into osteoblasts by inhibiting PPAR-γ expression and upregulating RUNX2 expression, reducing bone marrow adipogenesis, improving bone mass and microarchitecture in OVX mice without the adverse effects of estrogen replacement therapy, providing a potential option for the prevention and treatment of PMOP (125).
3.6 Alkaloids
3.6.1 Berberine
Berberine is an isoquinoline alkaloid (Figure 7A) and a major active component of various TCMs. It is widely found in herbs such as Coptis chinensis Franch. and Phellodendri Chinensis Cortex and possesses multiple pharmacological effects, including antidiabetic, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activities. In recent years, its multi-mechanistic regulatory role in the prevention and treatment of OP has garnered significant attention. In animal models, berberine activates the cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway to upregulate osteogenic genes, promoting the differentiation of BMSCs into osteocytes. It also downregulates adipogenic genes, inhibiting the differentiation of BMSCs into adipocytes and suppressing osteoclast differentiation. This leads to an increase in trabecular bone volume fraction, number, and thickness in elderly osteoporotic mice while reducing trabecular separation (126). It can also mitigate oxidative stress by inhibiting the RANK/RANKL/OPG pathway, thereby reducing osteoclast activation and alleviating bone mass loss in OVX rats (127). Additionally, berberine can exert bone-protective effects by regulating the “gut-bone axis,” such as enriching butyrate-producing gut microbiota, repairing intestinal barrier integrity, and inhibiting IL-17A-mediated inflammatory responses, thereby alleviating estrogen deficiency-induced periodontal bone resorption (128). These findings suggest that berberine modulates OP through a multidimensional mechanism involving “bone metabolism regulation-oxidative stress inhibition-gut microenvironment improvement”.
Figure 7. Chemical structural formula of several alkaloid: (A) Berbine. (B) Evodiamine. (C) Matrine and Oxymatrine.
3.6.2 Evodiamine
Evodiamine is an alkaloid extracted from the TCM Medcinal Evodia Fruit (Figure 7B), exhibiting various bioactivities, including antitumor and anti-inflammatory effects (129). Due to its lipophilic chemical structure and low water solubility, its derivative 3-amino-10-hydroxy evodiamine can inhibit the phosphorylation of NF-κB and MAPK, thereby suppressing the activation of the downstream transcription factor NFATc1 and reducing the expression of genes such as NFATc1, TRAP, CTSK, and DC-STAMP. This inhibits osteoclast differentiation, fusion, and bone resorption functions. This protects bone microarchitecture in OVX mice by reducing bone resorption, promoting osteogenic activity, and maintaining bone mass and structural integrity (130). Haiming Jin also found that evodiamine can inhibit NF-κB-mediated transcription of osteoclast-related genes (such as c-Fos and NFATc1) and inhibit RANKL-induced Ca2+ oscillations, thereby blocking NFATc1 activation and its downstream target gene expression, ultimately preventing osteoclast differentiation and maturation, and demonstrating good bone protective effects in OVX mice (131).
3.6.3 Matrine and oxymatrine
Matrine is an alkaloid isolated from the TCM Sophorae Flavescentis Radix (Figure 7C). Sophorae Flavescentis Radix is the dried root of the leguminous plant Sophora flavescens (132), which possesses broad pharmacological activities, including anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, and antiviral effects (133). Xiao Chen et al. found that matrine can inhibit RANKL-induced NF-κB, MAPK, and AKT signaling pathways, downregulating NFATc1 and its target genes (MMP-9, TRAP, etc.), thereby inhibiting osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption, improving BV/TV, BMD, and trabecular number in OVX mice, and reducing IL-6, TNF-α, and TRAcp5b levels, effectively preventing bone loss in OVX mice (134). Studies have shown that oxymatrine can increase cortical bone thickness and bone cell numbers in castrated rats, reduce osteoporotic cavities, and exhibit anti-osteoporotic effects comparable to testosterone. The mechanism may involve inhibiting the NF-κB pathway to reduce the release of inflammatory factors and enhancing antioxidant capacity through the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, thereby regulating the RANKL/OPG balance and inhibiting bone resorption. It may avoid the side effects of testosterone therapy (such as prostate hyperplasia and cardiovascular risks) (135). Further experimental studies are currently needed to investigate the pharmacokinetic characteristics of oxymatrine, providing more data to support its safe and effective use in patients.
4 Discussion
This study systematically reviewed the latest research progress in the prevention and treatment of OP using TCM, focusing on the molecular mechanisms by which various active constituents of TCM (including flavonoids, polyphenols, saponins, polysaccharides, coumarins, and alkaloids) regulate bone metabolism through multi-target, multi-pathway synergistic regulation. It has been elaborated on how these active constituents regulate key signaling pathways such as the Wnt/β-catenin, RANKL/OPG pathways while simultaneously intervening in osteoblast differentiation and osteoclast activity, thereby restoring bone metabolic balance. The study particularly emphasizes the unique advantages of TCM constituents in improving the bone microenvironment (such as regulating gut microbiota, inhibiting oxidative stress, and reducing inflammatory responses), as well as their safety profile compared to traditional therapy. By integrating extensive preclinical and clinical research evidence, this study aims to provide a scientific basis for the development of novel anti- OP drugs based on TCM theory and to offer theoretical guidance for the formulation of personalized treatment regimens.
There are also certain limitations at present. (1) Currently, research endorsing the treatment of OP with active compounds from TCM predominantly emphasizes cellular and animal studies, with limited clinical trials in humans. Consequently, it is imperative to enhance the transition from basic to clinical research by employing organoid or 3D bone tissue models to forecast the impact of TCM on the human organism. Additionally, the alterations in biomarkers in patients post-TCM intervention can be examined through metabolomics and proteomics to elucidate its systemic regulatory effects. (2) The bioavailability and formulation optimization of these active substances remain to be addressed, the active constituents of TCM include diverse functions, and when integrated with nanomaterials, they can markedly enhance their bioavailability and bioactivity (136). Numerous studies exist regarding nano-delivery systems and enhanced TCM formulations, including extracellular nanovesicles derived from Herba Epimedium, which can augment the bioavailability and bioactivity of TCM through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway, thereby facilitating the osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs with improved safety (137). And nano-aggregates may demonstrate antipyretic properties by augmenting the solubility of insoluble constituents in Baihu Tang, hence improving cellular absorption and targeted administration (138).Consequently, medication delivery by nanoparticles may emerge as a significant avenue for future research. (3) TCM often employs compound formulas for disease treatment, which are complex and involve multi-component synergistic mechanisms that have not yet been fully elucidated. Consequently, it can be integrated with contemporary analytical techniques, artificial intelligence-assisted design, multi-histology verification, and standardized clinical research to establish a closed-loop of “basic research - mechanism analysis - clinical validation,” or to disassemble the prescription. Alternatively, we can examine the impact of each medicine on OP and subsequently integrate them to confirm the synergistic effect. (4) Due to the variability in each patient’s treatment plan and medication dosage, conducting large-scale western clinical controlled trials is a challenging task. Consequently, we can uphold the principles of TCM diagnosis and treatment by randomly categorizing patients based on the stratification of evidence types, and establishing a structured electronic medical record system to document the information pertaining to the four diagnostic methods of TCM and medication specifics. Subsequently, we can integrate artificial intelligence to analyze medication patterns and standardize the diagnosis and treatment protocols. (5) There is a lack of comprehensive research on the integration of TCM active ingredients with pharmacological techniques, particularly regarding the combination of TCM active ingredients with first-line anti-OP medications. Consequently, subsequent research may concentrate on evaluating combinations of TCM active ingredients for their potential synergistic effects in the prevention and treatment of OP, as well as forecasting the interaction targets and possible effects of TCM active ingredients with western pharmaceuticals, and validating these findings through in vitro and in vivo experiments.
According to current literature reports, research on TCM treatment for POP is still in the exploratory stage. It is anticipated that future studies will employ new methods and technologies to conduct in-depth investigations, uncover the complex network mechanisms of TCM, and strengthen the integration of basic experimental research with clinical studies, thereby providing a more robust scientific foundation for the clinical application of TCM and the development of new drugs. Future research could also integrate systems pharmacology and artificial intelligence technologies to explore the “component-target-pathway” network of active constituents in TCM, providing a theoretical foundation for the development of novel anti-OP drugs.
The clinical application of active substances in TCM warrants further exploration in the future. In recent years, the integration of active constituents from TCM with exogenous carriers has demonstrated considerable benefits in the prevention and treatment of OP. For example, enteric capsules created by amalgamating epimedium glycosides with snail enzymes markedly enhanced intestinal hydrolysis and absorption efficiency in osteoporotic rats, resulting in a 50% improvement in the total oral bioavailability of epimedium glycosides (139).
In conclusion, investigating the intricate mechanisms of TCM via multidisciplinary technology to enhance clinical efficacy will yield innovative concepts for the advancement of contemporary anti-OP TCM characterized by a “clear mechanism, well-defined ingredients, and stable efficacy”.
Author contributions
CS: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. LZ: Writing – review & editing, Supervision. CZ: Writing – original draft, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in theabsence of any commercial or financial relationships that could beconstrued as a potential confict of interest.
The handling editor QW declared a shared affliation with a author at the time of review.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Zhang ZL and Yue H. Interpretation of key points in the diagnosis and treatment guidelines for primary osteoporosis (2022 edition). J Internal Intensive Med. (2024) 30:289–93. doi: 10.11768/nkjwzzzz20240401
2. Salari N, Ghasemi H, Mohammadi L, Behzadi MH, Rabieenia E, Shohaimi S, et al. The global prevalence of osteoporosis in the world: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. (2021) 16:609. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02772-0
3. Amarnath SS, Kumar V, and Das SL. Classification of osteoporosis. Indian J Orthop. (2023) 57:49–54. doi: 10.1007/s43465-023-01058-3
4. Maraka S and Kennel KA. Bisphosphonates for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. BMJ. (2015) 351:h3783. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h3783
5. Yasuda H. RANKL, a necessary chance for clinical application to osteoporosis and cancer-related bone diseases. World J Orthop. (2013) 4:207–17. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v4.i4.207
6. Makinen VN, Solling AS, McClung M, and Langdahl BL. Romosozumab for the treatment of osteoporosis - a systematic review. J Endocrinol Invest. (2025) 48:547–72. doi: 10.1007/s40618-024-02469-1
7. Hou YC, Wu CC, Liao MT, Shyu JF, Hung CF, Yen TH, et al. Role of nutritional vitamin D in osteoporosis treatment. Clin Chim Acta. (2018) 484:179–91. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2018.05.035
8. Zhao J, Zeng L, Wu M, Huang H, Liang G, Yang W, et al. Efficacy of Chinese patent medicine for primary osteoporosis: A network meta-analysis. Complement Ther Clin Pract. (2021) 44:101419. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2021.101419
9. Ma T, Zhang T, Zhang L, Zhao H, Liu K, Kuang J, et al. Efficacy of acupuncture for primary osteoporosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Orthop Surg Res. (2025) 20:127. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-05513-9
10. Huang R, Li X, Xu S, Li D, Yan P, Liu B, et al. Acupoint injection treatment for primary osteoporosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ann Palliat Med. (2019) 8:586–95. doi: 10.21037/apm.2019.11.23
11. Li Y, Zhang D, Fu S, Liu M, and Liu H. Design and application of personalized exercise prescription for primary osteoporosis. Med (Baltimore). (2023) 102:e32857. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032857
12. Turgeon RD and Yeung SS. Fracture risk and zoledronic acid in men with osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. (2013) 368:872–3. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1214992
13. Wen MT, Li JC, Lu BW, Shao HR, Ling PX, Liu F, et al. Indications and adverse events of teriparatide: based on FDA adverse event reporting system (FAERS). Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1391356. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1391356
14. Pan S, Zhou J, Zhou S, Huang Z, and Meng J. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling for Moutan Cortex/Moutan Cortex charcoal and the contributions of the chemical component using support vector regression with particle swarm optimization. RSC Adv. (2020) 10:24454–62. doi: 10.1039/d0ra04111d
15. Zhang W, Huai Y, Miao Z, Qian A, and Wang Y. Systems pharmacology for investigation of the mechanisms of action of traditional chinese medicine in drug discovery. Front Pharmacol. (2019) 10:743. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00743
16. Zhu Z, Bai Z, Cui Y, Li X, and Zhu X. The potential therapeutic effects of Panax notoginseng in osteoporosis: A comprehensive review. Phytomedicine. (2025) 142:156703. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156703
17. Raisz LG. Physiology and pathophysiology of bone remodeling. Clin Chem. (1999) 45:1353–8. doi: 10.1093/clinchem/45.8.1353
18. Zheng HF, Spector TD, and Richards JB. Insights into the genetics of osteoporosis from recent genome-wide association studies. Expert Rev Mol Med. (2011) 13:e28. doi: 10.1017/S1462399411001980
19. Choi YM, Jun JK, Choe J, Hwang D, Park SH, Ku SY, et al. Association of the vitamin D receptor start codon polymorphism (FokI) with bone mineral density in postmenopausal Korean women. J Hum Genet. (2000) 45:280–3. doi: 10.1007/s100380070016
20. Yalaev B, Deev R, Tyurin A, Salakhov R, Smirnov K, Eremkina A, et al. MicroRNA binding site variants-new potential markers of primary osteoporosis in men and women. Front Genet. (2024) 15:1470310. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1470310
21. Yu WJ, Zhang Z, Fu WZ, He JW, Wang C, and Zhang ZL. Association between LGR4 polymorphisms and peak bone mineral density and body composition. J Bone Miner Metab. (2020) 38:658–69. doi: 10.1007/s00774-020-01106-0
22. Mancini M, Chapurlat R, Isidor B, Desjonqueres M, Couture G, Guggenbuhl P, et al. Early-onset osteoporosis: molecular analysis in large cohort and focus on the PLS3 gene. Calcif Tissue Int. (2024) 115:591–8. doi: 10.1007/s00223-024-01288-z
23. Deng X, Lin B, Wang F, Xu P, and Wang N. Mangiferin attenuates osteoporosis by inhibiting osteoblastic ferroptosis through Keap1/Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway. Phytomedicine. (2024) 124:155282. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155282
24. Giuliani A, Sabbatinelli J, Amatori S, Graciotti L, Silvestrini A, Matacchione G, et al. MiR-422a promotes adipogenesis via MeCP2 downregulation in human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2023) 80:75. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04719-6
25. Khalid AB and Krum SA. Estrogen receptors alpha and beta in bone. Bone. (2016) 87:130–5. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2016.03.016
26. Hsu SH, Chen LR, and Chen KH. Primary osteoporosis induced by androgen and estrogen deficiency: the molecular and cellular perspective on pathophysiological mechanisms and treatments. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:12139. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212139
27. Khosla S, Oursler MJ, and Monroe DG. Estrogen and the skeleton. Trends Endocrinol Metab. (2012) 23:576–81. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2012.03.008
28. Bhukhai K, Suksen K, Bhummaphan N, Janjorn K, Thongon N, Tantikanlayaporn D, et al. A phytoestrogen diarylheptanoid mediates estrogen receptor/Akt/glycogen synthase kinase 3beta protein-dependent activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. (2012) 287:36168–78. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.344747
29. Amjadi-Moheb F and Akhavan-Niaki H. Wnt signaling pathway in osteoporosis: Epigenetic regulation, interaction with other signaling pathways, and therapeutic promises. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234:14641–50. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28207
30. Cheng TY, Zhou L, Gu Q, Wang J, and Pang XF. Analysis on the relationship between osteoporosis and biochemical marks of bone metabolism in aged people with high risk of osteoporosis. Shanghai J Prev Med. (2016) 28:871–4. doi: 10.19428/j.cnki.sjpm.2016.12.010
31. Chen T, Wang Y, Hao Z, Hu Y, and Li J. Parathyroid hormone and its related peptides in bone metabolism. Biochem Pharmacol. (2021) 192:114669. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114669
32. Zhu J, Siclari VA, Liu F, Spatz JM, Chandra A, Divieti Pajevic P, et al. Amphiregulin-EGFR signaling mediates the migration of bone marrow mesenchymal progenitors toward PTH-stimulated osteoblasts and osteocytes. PloS One. (2012) 7:e50099. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050099
33. Charoenngam N, Shirvani A, and Holick MF. Vitamin D for skeletal and non-skeletal health: What we should know. J Clin Orthop Trauma. (2019) 10:1082–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2019.07.004
34. Qiu MX, Liu T, Wang ZY, Wang ZL, and Xu GX. Relationship between vitamin D and cardiovascular disease. Hainan Med J. (2020) 31:1313–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6350.2020.10.026
35. Qiu DD and Jiang S. Advances in mechanisms of parathyroid hormone metabolic abnormality in chronic kidney disease. J Nephrol Dialy Transplant. (2017) 26:174–8. doi: 10.3969/cndt.j.issn.1006-298X.2017.02.016
36. Peng KJ, Yu SF, Peng RB, Huang YP, and Li J. Changes of bone metabolism indexes, vitamin D and K levels in elderly patients with osteoporosis and their correlation. Chin J Clin Healthc. (2022) 25:496–9. doi: 10.3969/J.issn.1672-6790.2022.04.014
37. Kimball JS, Johnson JP, and Carlson DA. Oxidative stress and osteoporosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. (2021) 103:1451–61. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.20.00989
38. Wang YF, Chang YY, Zhang XM, Gao MT, Zhang QL, Li X, et al. Salidroside protects against osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats by inhibiting oxidative stress and promoting osteogenesis via Nrf2 activation. Phytomedicine. (2022) 99:154020. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154020
39. Iantomasi T, Romagnoli C, Palmini G, Donati S, Falsetti I, Miglietta F, et al. Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoporosis: molecular mechanisms involved and the relationship with microRNAs. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:3772. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043772
40. Wang KT, Li ZW, Jin J, and Wang JW. Study on the correlation between systemicImmune-inflammation index and osteoporosis. Chin J Trad Med Traum Orthop. (2024) 32:46–9. doi: 10.20085/j.cnki.issn1005-0205.240509
41. Salamanna F, Giardino R, and Fini M. Spontaneous osteoclastogenesis: Hypothesis for gender-unrelated osteoporosis screening and diagnosis. Med Hypotheses. (2017) 109:70–2. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2017.09.028
42. Salamanna F, Maglio M, Borsari V, Landini MP, and Fini M. Blood factors as biomarkers in osteoporosis: points from the COVID-19 era. Trends Endocrinol Metab. (2021) 32:672–9. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2021.05.005
43. Kau AL, Ahern PP, Griffin NW, Goodman AL, and Gordon JI. Human nutrition, the gut microbiome and the immune system. Nature. (2011) 474:327–36. doi: 10.1038/nature10213
44. Guo M, Liu H, Yu Y, Zhu X, Xie H, Wei C, et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG ameliorates osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats by regulating the Th17/Treg balance and gut microbiota structure. Gut Microbes. (2023) 15:2190304. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2190304
45. Li H, Xie XW, Li N, LI JG, Li DP, Ding JX, et al. Relationship between intestinal flora and bone and joint diseases and regulation of traditional chinese medicine:A review. Chin J Exp Traditional Med Formulae. (2022) 28:268–75. doi: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20220792
46. Li L, Rao S, Cheng Y, Zhuo X, Deng C, Xu N, et al. Microbial osteoporosis: The interplay between the gut microbiota and bones via host metabolism and immunity. Microbiologyopen. (2019) 8:e00810. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.810
47. Recharla N, Geesala R, and Shi XZ. Gut microbial metabolite butyrate and its therapeutic role in inflammatory bowel disease: A literature review. Nutrients. (2023) 15:2275. doi: 10.3390/nu15102275
48. Jiang RS, Zhang L, Guan QF, Zhang J, Wu YF, and Liu MJ. Advances in the role of short-chain fatty acids in type 2 diabetes. Chin Gen Practice. (2024) 27:3031–7. doi: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0533
49. Park J, Kim M, Kang SG, Jannasch AH, Cooper B, Patterson J, et al. Short-chain fatty acids induce both effector and regulatory T cells by suppression of histone deacetylases and regulation of the mTOR-S6K pathway. Mucosal Immunol. (2015) 8:80–93. doi: 10.1038/mi.2014.44
50. Sun P, Zhang C, Huang Y, Yang J, Zhou F, Zeng J, et al. Jiangu granule ameliorated OVX rats bone loss by modulating gut microbiota-SCFAs-Treg/Th17 axis. BioMed Pharmacother. (2022) 150:112975. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112975
51. Wang J, Wang Y, Gao W, Wang B, Zhao H, Zeng Y, et al. Diversity analysis of gut microbiota in osteoporosis and osteopenia patients. PeerJ. (2017) 5:e3450. doi: 10.7717/peerj.3450
52. Bai L, Liu Y, Zhang X, Chen P, Hang R, Xiao Y, et al. Osteoporosis remission via an anti-inflammaging effect by icariin activated autophagy. Biomaterials. (2023) 297:122125. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2023.122125
53. Bao ZM, Jiang L, Li WY, Zhang ZX, Liu DZ, and Yuan L. Research progress of icariin in the treatment of osteoporosis. China J Pharm Econom. (2025) 20:111–5. doi: 10.12010/j.issn.1673-5846.2025.02.023
54. Li ZW, Ren YR, Li MW, Liu QK, Yu XJ, Jiang YQ, et al. Icariin inhibits osteoclast formation by promoting the expression of negative regulator Gα13. L Orthopaedics. (2022) 13:155–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674⁃8573.2022.02.012
55. Si Y, Li Y, Gu K, Yin H, and Ma Y. Icariin ameliorates osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats by targeting Cullin 3/Nrf2/OH pathway for osteoclast inhibition. BioMed Pharmacother. (2024) 173:116422. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116422
56. Lin S, Meng Z, Wang M, Ye Z, Long M, Zhang Y, et al. Icariin modulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation in ADSCs via the Hippo-YAP/TAZ pathway: a novel therapeutic strategy for osteoporosis. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1510561. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1510561
57. Kulczynski B, Gramza-Michalowska A, Suliburska J, and Sidor A. Puerarin-an isoflavone with beneficial effects on bone health. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). (2021) 26:1653–67. doi: 10.52586/5058
58. Xiao L, Zhong M, Huang Y, Zhu J, Tang W, Li D, et al. Puerarin alleviates osteoporosis in the ovariectomy-induced mice by suppressing osteoclastogenesis via inhibition of TRAF6/ROS-dependent MAPK/NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Aging (Albany NY). (2020) 12:21706–29. doi: 10.18632/aging.103976
59. Yang X, Yang Y, Zhou S, Gong X, Dai Q, Zhang P, et al. Puerarin stimulates osteogenic differentiation and bone formation through the ERK1/2 and p38-MAPK signaling pathways. Curr Mol Med. (2018) 17:488–96. doi: 10.2174/1566524018666171219101142
60. Zhao X, Zhou J, Liu Y, Wang J, Liu Y, Wang B, et al. Puerarin alleviates osteoporosis in rats by targeting the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Biomol Biomed. (2024) 24:1651–61. doi: 10.17305/bb.2024.10500
61. Yang X, Zheng H, Liu Y, Hao D, He B, and Kong L. Puerarin for OVX-induced postmenopausal osteoporosis in murine model: systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. (2020) 15:37–42. doi: 10.2174/1574888X14666190703143946
62. Jiang H, Zhang M, Lin X, Zheng X, Qi H, Chen J, et al. Biological activities and solubilization methodologies of naringin. Foods. (2023) 12:2327. doi: 10.3390/foods12122327
63. Cui Y, Yang Z, Yu G, Hu J, Li D, Fu X, et al. Naringin promotes osteoblast differentiation and ameliorates osteoporosis in ovariectomized mice. Sci Rep. (2025) 15:12651. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-97217-7
64. Wang H, Liang J, Wang Y, Zheng J, Liu Y, Zhao Y, et al. Exploring the effects of naringin on oxidative stress-impaired osteogenic differentiation via the Wnt/beta-catenin and PI3K/Akt pathways. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:14047. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64952-2
65. Xu T, Wang L, Tao Y, Ji Y, Deng F, and Wu XH. The function of naringin in inducing secretion of osteoprotegerin and inhibiting formation of osteoclasts. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2016) 2016:8981650. doi: 10.1155/2016/8981650
66. Wang W, Mao J, Chen Y, Zuo J, Chen L, Li Y, et al. Naringin promotes osteogenesis and ameliorates osteoporosis development by targeting JAK2/STAT3 signalling. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. (2022) 49:113–21. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.13591
67. Shangguan WJ, Zhang YH, Li ZC, Tang LM, Shao J, and Li H. Naringin inhibits vascular endothelial cell apoptosis via endoplasmic reticulum stress− and mitochondrial−mediated pathways and promotes intraosseous angiogenesis in ovariectomized rats. Int J Mol Med. (2017) 40:1741–9. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3160
68. Liang G, Zhao J, Dou Y, Yang Y, Zhao D, Zhou Z, et al. Mechanism and experimental verification of luteolin for the treatment of osteoporosis based on network pharmacology. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:866641. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.866641
69. Chai S, Yang Y, Wei L, Cao Y, Ma J, Zheng X, et al. Luteolin rescues postmenopausal osteoporosis elicited by OVX through alleviating osteoblast pyroptosis via activating PI3K-AKT signaling. Phytomedicine. (2024) 128:155516. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155516
70. Kim TH, Jung JW, Ha BG, Hong JM, Park EK, Kim HJ, et al. The effects of luteolin on osteoclast differentiation, function in vitro and ovariectomy-induced bone loss. J Nutr Biochem. (2011) 22:8–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2009.11.002
71. Calabrese EJ, Agathokleous E, Kapoor R, Dhawan G, and Calabrese V. Luteolin and hormesis. Mech Ageing Dev. (2021) 199:111559. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2021.111559
72. Yang QP, Chen F, Cui W, Zhang C, Wu RQ, Song ZH, et al. Signaling pathways related to kaempferol active monomers in the treatment of osteoporosis. Chin J Tissue Eng Res. (2024) 28:4242–9. doi: 10.12307/2024.338
73. Liu H, Yi X, Tu S, Cheng C, and Luo J. Kaempferol promotes BMSC osteogenic differentiation and improves osteoporosis by downregulating miR-10a-3p and upregulating CXCL12. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2021) 520:111074. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2020.111074
74. Kwon Y. YAP/TAZ as molecular targets in skeletal muscle atrophy and osteoporosis. Aging Dis. (2024) 16:299–320. doi: 10.14336/AD.2024.0306
75. Toya M, Kushioka J, Shen H, Utsunomiya T, Hirata H, Tsubosaka M, et al. Sex differences of NF-kappaB-targeted therapy for mitigating osteoporosis associated with chronic inflammation of bone. Bone Joint Res. (2024) 13:28–39. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.131.BJR-2023-0040.R3
76. Liu W, Liu R, Yang Y, Cheng L, Feng X, and Li Q. The targeting of YAP by kaempferol regulates bone homeostasis and improves osteoporosis in rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. (2025). doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04120-z
77. Ni X, Wu B, Li S, Zhu W, Xu Z, Zhang G, et al. Equol exerts a protective effect on postmenopausal osteoporosis by upregulating OPG/RANKL pathway. Phytomedicine. (2023) 108:154509. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154509
78. Wu B, Zhang Y, Chen ML, Wu Y, Ni XM, Zhou Y, et al. Equol improves osteoporosis in ovarietomized rats. J Third Mil Med Univ. (2015) 37:256–60. doi: 10.16016/j.1000-5404.201409076
79. Du J, Shan Z, Ma P, Wang S, and Fan Z. Allogeneic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for periodontal regeneration. J Dent Res. (2014) 93:183–8. doi: 10.1177/0022034513513026
80. Kim DW, Yoo KY, Lee YB, Lee KH, Sohn HS, Lee SJ, et al. Soy isoflavones mitigate long-term femoral and lumbar vertebral bone loss in middle-aged ovariectomized mice. J Med Food. (2009) 12:536–41. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2008.1027
81. Feng Y, Dang X, Zheng P, Liu Y, Liu D, Che Z, et al. Quercetin in osteoporosis treatment: A comprehensive review of its mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Curr Osteoporos Rep. (2024) 22:353–65. doi: 10.1007/s11914-024-00868-0
82. Sun J, Pan Y, Li X, Wang L, Liu M, Tu P, et al. Quercetin attenuates osteoporosis in orchiectomy mice by regulating glucose and lipid metabolism via the GPRC6A/AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:849544. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.849544
83. Feng R, Wang Q, Yu T, Hu H, Wu G, Duan X, et al. Quercetin ameliorates bone loss in OVX rats by modulating the intestinal flora-SCFAs-inflammatory signaling axis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 136:112341. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112341
84. Xiao J, Zhang G, Chen B, He Q, Mai J, Chen W, et al. Quercetin protects against iron overload-induced osteoporosis through activating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Life Sci. (2023) 322:121326. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.121326
85. Inchingolo AD, Inchingolo AM, Malcangi G, Avantario P, Azzollini D, Buongiorno S, et al. Effects of resveratrol, curcumin and quercetin supplementation on bone metabolism-A systematic review. Nutrients. (2022) 14:3519. doi: 10.3390/nu14173519
86. Meyer C, Brockmueller A, Ruiz de Porras V, and Shakibaei M. Microbiota and resveratrol: how are they linked to osteoporosis? Cells. (2024) 13:1145. doi: 10.3390/cells13131145
87. Wong RH, Thaung Zaw JJ, Xian CJ, and Howe PR. Regular supplementation with resveratrol improves bone mineral density in postmenopausal women: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Bone Miner Res. (2020) 35:2121–31. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.4115
88. An R, Luo Q, Li L, Cui D, and Jin J. The effects of resveratrol in animal models of primary osteoporosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. (2024) 19:137. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04595-1
89. Yu QY, Su XG, Bao QY, and Chen XY. Effect of resveratrol on the Wnt/B Catenin pathway in ovariectomizedosteoporosis rats. Chin J Clin Pharmacol Ther. (2017) 22:645–9.
90. Zhang P, Ye J, Dai J, Wang Y, Chen G, Hu J, et al. Gallic acid inhibits osteoclastogenesis and prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:963237. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.963237
91. Ko SY. Therapeutic potential of ginsenosides on bone metabolism: A review of osteoporosis, periodontal disease and osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:5828. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115828
92. Fei X, Yin J, Zhang L, Fan W, Li XP, and Tang GP. Effect of ginsenoside Rg3 regulating RANKL/RANK/TRAF6 signaling path way on bone metabolism and osteoblast in postmenopausal osteoporosis rats. Lab Med Clin. (2025) 22:24–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9455.2025.01.005
93. Wang S, Xu B, Yin H, Hua Z, Shao Y, and Wang J. Ginsenoside Rc alleviates osteoporosis by the TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). (2024) 70:95–101. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2024.70.3.14
94. Cheng B, Li J, Du J, Lv X, Weng L, and Ling C. Ginsenoside Rb1 inhibits osteoclastogenesis by modulating NF-kappaB and MAPKs pathways. Food Chem Toxicol. (2012) 50:1610–5. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2012.02.019
95. Zhu HJ, Chen YP, and Yao JL. Protective effect of ginsenoside Rh2 on bone loss in aged rats mediated by OPG/RANKL sipnaling pathway. Chin J 0steoporos. (2020) 26:1446–50. doi: 10.3969/i.issn.1006-7108.2020.10.009
96. Jung SJ, Oh MR, Lee DY, Lee YS, Kim GS, Park SH, et al. Effect of ginseng extracts on the improvement of osteopathic and arthritis symptoms in women with osteopenia: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Nutrients. (2021) 13:3352. doi: 10.3390/nu13103352
97. Wen C, Liao X, Ye X, and Lai W. Pharmacokinetics and biological activities of notoginsenoside R1: A systematical review. Am J Chin Med. (2025) 53:205–49. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X25500090
98. Li X, Lin H, Zhang X, Jaspers RT, Yu Q, Ji Y, et al. Notoginsenoside R1 attenuates oxidative stress-induced osteoblast dysfunction through JNK signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. (2021) 25:11278–89. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17054
99. Wang T, Wan D, Shao L, Dai J, and Jiang C. Notoginsenoside R1 stimulates osteogenic function in primary osteoblasts via estrogen receptor signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2015) 466:232–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.09.014
100. Liu Y, Lin Z, Guo J, Xu G, Li Y, Xu T, et al. Notoginsenoside R1 significantly promotes in vitro osteoblastogenesis. Int J Mol Med. (2016) 38:537–44. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2652
101. Cai M, Xu LL, and Zhang YP. Protective effect mechanism of Panax notoginseng saponins on regulating CTRP6/RhoA/Rock in rats with osteoporosis. Inf TCM. (2023) 40:37–43. doi: 10.19656/j.cnki.1002-2406.20230806
102. Guo M, Wu LTY, and Li G. Research progress on the pharmacological effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide. West China J Pharm Sci. (2013) 28:633–5. doi: 10.13375/j.cnki.wcjps.2013.06.021
103. Wang Y, Miao Y B, Wang Y, Zhang C, and Miao ZH. Effects of LBP on wnt signaling pathway in SD rat mesenchymal stem. J Ningxia Med Univers. (2017) 39:525–9. doi: 10.16050/j.cnki.issn1674-6309.2017.05.009
104. Zhuo JL, ZX LI, Yang N, Gao MB, Qian CH, and Han T. Effects of lycium barbarum polvsaccharides on intestinal flora and short-chain fatty acids in patients with postmenopausal osteoporosis. Chin J Microcirculation. (2023) 33:27–34. doi: 10.3969/i.issn.1005-1740.2023.04.005
105. Li ZX, Zhuo JL, Yang N, Gao MB, Qu ZH, and Han T. Effect of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 271:132415. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.132415
106. Ren XJ, Su CH, Chen YG, Yi ZG, Dong P, Liu WZ, et al. Effects of lycium barbarum polysaccharides on TGF-β1 and NOS levels in the serum of osteoporotic rats. Gansu Med J. (2020) 39:196–7. doi: 10.15975/j.cnki.gsyy.2020.03.002
107. Zheng Y, Ren W, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Liu D, and Liu Y. A review of the pharmacological action of astragalus polysaccharide. Front Pharmacol. (2020) 11:349. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00349
108. Ou L, Wei P, Li M, and Gao F. Inhibitory effect of Astragalus polysaccharide on osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats by regulating FoxO3a/Wnt signaling pathway. Acta Cir Bras. (2019) 34:e201900502. doi: 10.1590/s0102-865020190050000002
109. Hu X, Yang L, Du Y, Meng X, Shi Y, and Zeng J. Astragalus polysaccharide promotes osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells by facilitating ANKFY1 expression through miR-760 inhibition. Bone Joint Res. (2023) 12:476–85. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.128.BJR-2022-0248.R2
110. Yang F, Yan G, Li Y, Han Z, Zhang L, Chen S, et al. Astragalus polysaccharide attenuated iron overload-induced dysfunction of mesenchymal stem cells via suppressing mitochondrial ROS. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2016) 39:1369–79. doi: 10.1159/000447841
111. Zhang XY, Chen H, Ma JZ, Ma ZR, and Wang YH. Effect of astragalus polysaccharide treatment on bone mineral density, bone mass, and bone metabolism in ovariectomized osteoporotic rats. Chin J 0steoporos. (2021) 27:21–5. doi: 10.3969/i.issn.1006-7108.2021.01.004
112. Yang H and Zeng FH. Study on achyranthes bidentata polysaccharides improving bone metabolismIn osteoporotic fracture rats by regulating wnt/B-catenin pathway. Acta Chin Med. (2021) 36:2188–94. doi: 10.16368/j.issn.1674-8999.2021.10.457
113. Song D, Cao Z, Huang S, Tickner J, Li N, Qiu H, et al. Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharide suppresses osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption via inhibiting RANKL signaling. J Cell Biochem. (2018) 119:4826–35. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26682
114. Zhang S, Zhang Q, Zhang D, Wang C, and Yan C. Anti-osteoporosis activity of a novel Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharide via stimulating bone formation. Carbohydr Polym. (2018) 184:288–98. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.12.070
115. Lang XQ, Gao Y, Zhou Y, Chen MH, and Xu CY. Influence of achyranthan on bone metabolism and biomechanical characteristics of elderly rats model of osteoporosis. Chin J Gen Practice. (2019) 17:547–50. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000730
116. Li Y. Research progress on the chemical composition and pharmacological effects of cnidium monnieri. Electronic J Gen Stomatol. (2019) 6:22–3. doi: 10.16269/j.cnki.cn11-9337/r.2019.26.013
117. Jin ZX, Liao XY, Da WW, Zhao YJ, Li XF, and Tang DZ. Osthole enhances the bone mass of senile osteoporosis and stimulates the expression of osteoprotegerin by activating beta-catenin signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2021) 12:154. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02228-6
118. Zheng S, Hu G, Zheng J, Li Y, and Li J. Osthole accelerates osteoporotic fracture healing by inducing the osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling of BMSCs via the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Phytother Res. (2024) 38:4022–35. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8267
119. Zheng X, Yu Y, Shao B, Gan N, Chen L, and Yang D. Osthole improves therapy for osteoporosis through increasing autophagy of mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Anim. (2019) 68:453–63. doi: 10.1538/expanim.18-0178
120. Zhang ZR, Leung WN, Li G, Kong SK, Lu X, Wong YM, et al. Osthole Enhances Osteogenesis in Osteoblasts by Elevating Transcription Factor Osterix via cAMP/CREB Signaling In Vitro and In Vivo. Nutrients. (2017) 9:588. doi: 10.3390/nu9060588
121. Si Z, Zhou S, Shen Z, and Luan F. High-throughput metabolomics discovers metabolic biomarkers and pathways to evaluating the efficacy and exploring potential mechanisms of osthole against osteoporosis based on UPLC/Q-TOF-MS coupled with multivariate data analysis. Front Pharmacol. (2020) 11:741. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00741
122. Liu YX, Meng MX, Zhou Q, Xu HD, Zhang B, and LI W. Research progress of the effect of isopsoralen on bone metabolism. Chin J Osteoporos. (2022) 28:1674–7. doi: 10.3969/i.issn.1006-7108.2022.11.022
123. Yuan X, Bi Y, Yan Z, Pu W, Li Y, and Zhou K. Psoralen and isopsoralen ameliorate sex hormone deficiency-induced osteoporosis in female and male mice. BioMed Res Int. (2016) 2016:6869452. doi: 10.1155/2016/6869452
124. Wang J, Wang G, Gong L, Sun G, Shi B, Bao H, et al. Isopsoralen regulates PPAR−gamma/WNT to inhibit oxidative stress in osteoporosis. Mol Med Rep. (2018) 17:1125–31. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7954
125. Wang J, Chen TY, Wang G, and Ge RTL. The effects of isopsoralen on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells of mice with ovariectomized osteoporosis and the relevant mechanisms. Chin J Osteoporos. (2016) 22:980–4. doi: 10.3969/i.issn.10067108.2016.08.009
126. Chen QC, Pu YL, Bi J, and Zhang Y. Protective effects of berberine on senile osteoporosis in mice. J Bone Miner Metab. (2021) 39:748–56. doi: 10.1007/s00774-021-01225-2
127. He XF, Zhang L, Zhang CH, Zhao CR, Li H, Zhang LF, et al. Berberine alleviates oxidative stress in rats with osteoporosis through receptor activator of NF-kB/receptor activator of NF-kB ligand/osteoprotegerin (RANK/RANKL/OPG) pathway. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. (2017) 17:295–301. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2017.2596
128. Jia X, Jia L, Mo L, Yuan S, Zheng X, He J, et al. Berberine ameliorates periodontal bone loss by regulating gut microbiota. J Dent Res. (2019) 98:107–16. doi: 10.1177/0022034518797275
129. Sun Q, Xie L, Song J, and Li X. Evodiamine: A review of its pharmacology, toxicity, pharmacokinetics and preparation researches. J Ethnopharmacol. (2020) 262:113164. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113164
130. Liu C, Shen H, Li H, Wang N, He S, Ye G, et al. An evodiamine derivative inhibits osteoclast differentiation and protects against OVX-induced bone loss in mice. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. (2024) 51:e13926. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.13926
131. Jin H, Yao L, Chen K, Liu Y, Wang Q, Wang Z, et al. Evodiamine inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss in mice. J Cell Mol Med. (2019) 23:522–34. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13955
132. Zhang H, Chen L, Sun X, Yang Q, Wan L, and Guo C. Matrine: A promising natural product with various pharmacological activities. Front Pharmacol. (2020) 11:588. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00588
133. Lin Y, He F, Wu L, Xu Y, and Du Q. Matrine exerts pharmacological effects through multiple signaling pathways: A comprehensive review. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2022) 16:533–69. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S349678
134. Chen X, Zhi X, Pan P, Cui J, Cao L, Weng W, et al. Matrine prevents bone loss in ovariectomized mice by inhibiting RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis. FASEB J. (2017) 31:4855–65. doi: 10.1096/fj.201700316R
135. Shaban AM, Ali EA, Tayel SG, Rizk SK, and El Agamy DF. The antiosteoporotic effect of oxymatrine compared to testosterone in orchiectomized rats. J Orthop Surg Res. (2025) 20:25. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05344-0
136. Shang Q, Liu W, Leslie F, Yang J, Guo M, Sun M, et al. Nano-formulated delivery of active ingredients from traditional Chinese herbal medicines for cancer immunotherapy. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2024) 14:1525–41. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.12.008
137. Han R, Gao C, Tang R, Gui X, Chen W, Fu J, et al. A comprehensive study on Herba Epimedium-derived extracellular nanovesicles as a prospective therapy for alveolar bone regeneration in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Nanoscale. (2025) 17:12270–89. doi: 10.1039/d5nr00508f
138. Lu S, Su H, Sun S, Guo Y, Liu T, Ping Y, et al. Isolation and characterization of nanometre aggregates from a Bai-Hu-Tang decoction and their antipyretic effect. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:12209. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30690-5
Keywords: primary osteoporosis, traditional Chinese medicine, active constituents, mechanism, signaling pathways
Citation: Song C, Zeng L and Zhao C (2025) The role of active constituents of in traditional Chinese medicine for primary osteoporosis: a mechanistic review. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1647984. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1647984
Received: 16 June 2025; Accepted: 01 August 2025;
Published: 16 September 2025.
Edited by:
Q Wang, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, ChinaReviewed by:
Hao Pan, Hangzhou Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, ChinaYu Sheng, Beihua University, China
Copyright © 2025 Song, Zeng and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Changwei Zhao, emN3XzE5ODAxMTAxQDE2My5jb20=; Lingfeng Zeng, emVuZ2xmNjc3OEAxNjMuY29t
 Chaoqun Song1
Chaoqun Song1 Changwei Zhao
Changwei Zhao